User login
Is It Time for Universal Suicide Screening?
US suicide rates have reached alarming levels, with data from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showing a 37% increase from 2000 to 2022. Nearly 49,000 people died by suicide in 2022 alone, translating to one death every 11 minutes.
The increase in suicide rates has prompted calls for expansion of universal suicide screening, in which all individuals in medical or mental health care settings are screened for suicide risk, regardless of the purpose for their visit. But the psychiatric field is split on the issue, with some experts citing false positives and a lack of mental health care resources for those deemed at risk.
In 2022, when the US Preventative Services Task Force released its recommendations on suicide prevention, first in children and adolescents, and then in adults, the authors said there was insufficient evidence to support universal suicide screening.
Proponents of the practice pushed back on that finding, arguing that universal suicide screening could help identify those at high risk who might otherwise go undiagnosed, leading to earlier, potentially lifesaving, intervention.
So, what is the case for — and against — universal screening?
Sounding an Alert
The introduction of universal screening was driven by a confluence of factors that began with a 1999 report by then-US Surgeon General David Satcher, MD. This was followed by a report in 2016 from the Joint Commission on Detecting and Treating Suicidal Ideation that called for healthcare organizations to improve detection and treatment of suicidal ideation in all healthcare care settings.
Data from the alert showed that a significant number of people who died by suicide had a healthcare visit before their death. Half had seen a clinician a month before their death; nearly 30% had a medical visit just the week before — all with no detection of increased suicide risk.
It was that sort of finding that led Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas to become the first US hospital to implement universal suicide screening. Since the program launched in 2015, the system has screened more than 4.3 million patients in its emergency department, inpatient units, and 20 primary care clinics.
“Since the program began, we’ve completed between 40,000 to 50,000 screenings per month,” said Kimberly Roaten, PhD, associate chief quality and safety officer for behavioral health at Parkland Health.
Clinicians at Parkland use the five-item Ask Suicide-Screening Questions to assess suicidal intent, a commonly used tool that was originally developed for use in pediatric emergency rooms (ERs). The tool, which takes about 20 seconds to administer, has since been validated in both children and adults.
Based on a patient’s response, a clinical decision support system integrated into the electronic health record classifies suicide risk as none, moderate, or high.
Patients identified as moderate risk are offered a more in-depth assessment with a mental health clinician, though participation is not mandatory, said Dr. Roaten. Those at high risk receive a more thorough evaluation.
The proportion of ER patients at Parkland who screen positive for any suicidal intent has consistently remained at about 7%, and at 2% in the primary care clinics, she said.
To better understand what the program may have had on suicide prevention, Dr. Roaten is leading a National Institute of Mental Health–funded study to link a decade of mortality data from the state of Texas to patient data from Parkland Health. Investigators will analyze information about patients identified at risk for suicide, those patients’ characteristics, and who dies by suicide.
Universal Screening Expands
Other health systems have adopted universal suicide screening including the Indian Health Service and the US Veterans Health Administration. Universal suicide screening is also in place in a growing number of primary care practices and hospitals throughout the United States and will be mandatory for patients aged 12 years and older in all acute care hospitals in California beginning in 2025.
There is also a push for universal screening to be coordinated through local, state, and federal government, nonprofit, and private sectors. The National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention is charged with advancing the White House’s 2024 National Strategy for Suicide Prevention, a 10-year plan to address gaps in suicide prevention in the United States.
Sarah Brummett, JD, director of the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention’s executive committee, said that universal suicide screening is part of the 2024 strategy. “We know there are barriers to universal screening, and so it’s important to recognize what they are so we can address them,” said Ms. Brummett.
Barriers may include adequate staffing, or a system in place to triage patients who screen positive.
At Parkland, cost and workload have been minimal, Dr. Roaten said. “We built a model that only dedicates our highest-value resources to the most at-risk patients.”
She also noted that relief may be on the horizon for health systems where cost is an obstacle to universal screening and subsequent intervention. “There are efforts at the federal level to increase funding for suicide assessment and crisis response,” she said.
Pushback on Universal Screening
Universal suicide screening has its detractors, including critics who say expansion is unlikely to reduce suicide rates.
“The issue with suicidal ideation is that it is very dynamic. Suicidal ideation changes very quickly — sometimes within hours,” said Craig Bryan, PsyD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio.
Universal screening can also lead to false positives, where a patient who screens positive for suicidal ideation has no actual intention of attempting suicide, potentially creating unnecessary concern and burden on health care resources, Dr. Bryan noted.
“What do you do with everyone who screens positive?” Dr. Bryan said. “I’ve spoken with leaders of many health systems in the United States, and there is pushback against universal screening because they don’t have enough mental health resources to handle all of the referrals.”
Suicide screening also doesn’t predict who will die by suicide, Dr. Bryan added. It only identifies those willing to disclose suicidal thoughts. There is a significant number of people without mental illness who may never seek medical care, so “the warning signs we’re teaching people to recognize — depression, anxiety, and substance abuse — might not be evident in these individuals,” he said.
“Life sideswipes them suddenly, and they go from 0 to 60 ... and they may have access to a highly lethal method [of suicide] which weaponizes that moment of despair,” said Dr. Bryan. No amount of screening could possibly predict those types of suicides, he added.
Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, agrees with Dr. Bryan and noted there isn’t a strong correlation between suicidal ideation and death by suicide.
“Suicidal thoughts are very common, but suicide is a rare event,” he said.
He cited a study that showed that two thirds of individuals who died by suicide had denied experiencing suicidal thoughts when asked, and half of them died within 2 days of this denial. Other research suggests that as many as 98% of people who express suicidal ideation do not die by suicide, Dr. Nestadt said.
A Public Health Issue
If universal screening is not the answer to predicting and preventing suicide, what is? One way would be to approach suicide as a public health issue, Dr. Nestadt said.
“How did we reduce the rate of motor vehicle deaths? We didn’t test each driver’s reaction time behind the wheel,” he said. “Instead, we passed seatbelt and airbag legislation, implemented federal speed limits, and as a result, the number of motor vehicle fatalities decreased.”
Dr. Nestadt is an advocate for stronger gun safety legislation, which has proven effective in reducing suicide rates. A study published this year showed that states with child access prevention laws, negligent storage laws, and mandatory waiting periods for gun purchases reported fewer suicide deaths than those without that legislation.
Other measures might be applied in cases of extreme individual suicide risk, including extreme risk protection orders, also known as “red flag” laws, he added. This type of legislation provides a pathway for law enforcement to temporarily remove firearms from individuals who pose a risk to themselves or others.
“These have been shown to be very effective in saving lives,” Dr. Nestadt said.
Dr. Nestadt and others are also using machine learning models to predict suicide risk. Those identified as high-risk may be flagged on their electronic medical record. Ideally, when the algorithm becomes more accurate at predicting suicide, anyone treating this patient can then decide if action is needed, said Dr. Nestadt.
In his work with suicidal military personnel, Dr. Bryan and his colleagues established a brief form of cognitive behavioral therapy (BCBT) to help participants challenge cognitive distortions and build coping strategies to deal with feel with intense feelings of distress. Data show that BCBT reduced suicide attempts among active-duty soldiers by 60% compared with standard mental health treatment. It has since been shown to work in civilians as well.
Dr. Bryan is also researching fluctuations in the wish to live versus the wish to die relative to one another and mapping the trajectory of risk states along the way.
The goal is that these and other suicide prevention strategies currently under study by his team and others will help stem the rise in suicide deaths.
“Overall, we need to train mental health providers to implement suicide prevention therapies and establish suicide risk programs,” Dr. Bryan said. “But until we build one of these suicide prevention interventions to scale, we’re putting the cart before the horse.”
Dr. Roaten, Ms. Brummett, Dr. Bryan, and Dr. Nestadt reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
US suicide rates have reached alarming levels, with data from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showing a 37% increase from 2000 to 2022. Nearly 49,000 people died by suicide in 2022 alone, translating to one death every 11 minutes.
The increase in suicide rates has prompted calls for expansion of universal suicide screening, in which all individuals in medical or mental health care settings are screened for suicide risk, regardless of the purpose for their visit. But the psychiatric field is split on the issue, with some experts citing false positives and a lack of mental health care resources for those deemed at risk.
In 2022, when the US Preventative Services Task Force released its recommendations on suicide prevention, first in children and adolescents, and then in adults, the authors said there was insufficient evidence to support universal suicide screening.
Proponents of the practice pushed back on that finding, arguing that universal suicide screening could help identify those at high risk who might otherwise go undiagnosed, leading to earlier, potentially lifesaving, intervention.
So, what is the case for — and against — universal screening?
Sounding an Alert
The introduction of universal screening was driven by a confluence of factors that began with a 1999 report by then-US Surgeon General David Satcher, MD. This was followed by a report in 2016 from the Joint Commission on Detecting and Treating Suicidal Ideation that called for healthcare organizations to improve detection and treatment of suicidal ideation in all healthcare care settings.
Data from the alert showed that a significant number of people who died by suicide had a healthcare visit before their death. Half had seen a clinician a month before their death; nearly 30% had a medical visit just the week before — all with no detection of increased suicide risk.
It was that sort of finding that led Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas to become the first US hospital to implement universal suicide screening. Since the program launched in 2015, the system has screened more than 4.3 million patients in its emergency department, inpatient units, and 20 primary care clinics.
“Since the program began, we’ve completed between 40,000 to 50,000 screenings per month,” said Kimberly Roaten, PhD, associate chief quality and safety officer for behavioral health at Parkland Health.
Clinicians at Parkland use the five-item Ask Suicide-Screening Questions to assess suicidal intent, a commonly used tool that was originally developed for use in pediatric emergency rooms (ERs). The tool, which takes about 20 seconds to administer, has since been validated in both children and adults.
Based on a patient’s response, a clinical decision support system integrated into the electronic health record classifies suicide risk as none, moderate, or high.
Patients identified as moderate risk are offered a more in-depth assessment with a mental health clinician, though participation is not mandatory, said Dr. Roaten. Those at high risk receive a more thorough evaluation.
The proportion of ER patients at Parkland who screen positive for any suicidal intent has consistently remained at about 7%, and at 2% in the primary care clinics, she said.
To better understand what the program may have had on suicide prevention, Dr. Roaten is leading a National Institute of Mental Health–funded study to link a decade of mortality data from the state of Texas to patient data from Parkland Health. Investigators will analyze information about patients identified at risk for suicide, those patients’ characteristics, and who dies by suicide.
Universal Screening Expands
Other health systems have adopted universal suicide screening including the Indian Health Service and the US Veterans Health Administration. Universal suicide screening is also in place in a growing number of primary care practices and hospitals throughout the United States and will be mandatory for patients aged 12 years and older in all acute care hospitals in California beginning in 2025.
There is also a push for universal screening to be coordinated through local, state, and federal government, nonprofit, and private sectors. The National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention is charged with advancing the White House’s 2024 National Strategy for Suicide Prevention, a 10-year plan to address gaps in suicide prevention in the United States.
Sarah Brummett, JD, director of the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention’s executive committee, said that universal suicide screening is part of the 2024 strategy. “We know there are barriers to universal screening, and so it’s important to recognize what they are so we can address them,” said Ms. Brummett.
Barriers may include adequate staffing, or a system in place to triage patients who screen positive.
At Parkland, cost and workload have been minimal, Dr. Roaten said. “We built a model that only dedicates our highest-value resources to the most at-risk patients.”
She also noted that relief may be on the horizon for health systems where cost is an obstacle to universal screening and subsequent intervention. “There are efforts at the federal level to increase funding for suicide assessment and crisis response,” she said.
Pushback on Universal Screening
Universal suicide screening has its detractors, including critics who say expansion is unlikely to reduce suicide rates.
“The issue with suicidal ideation is that it is very dynamic. Suicidal ideation changes very quickly — sometimes within hours,” said Craig Bryan, PsyD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio.
Universal screening can also lead to false positives, where a patient who screens positive for suicidal ideation has no actual intention of attempting suicide, potentially creating unnecessary concern and burden on health care resources, Dr. Bryan noted.
“What do you do with everyone who screens positive?” Dr. Bryan said. “I’ve spoken with leaders of many health systems in the United States, and there is pushback against universal screening because they don’t have enough mental health resources to handle all of the referrals.”
Suicide screening also doesn’t predict who will die by suicide, Dr. Bryan added. It only identifies those willing to disclose suicidal thoughts. There is a significant number of people without mental illness who may never seek medical care, so “the warning signs we’re teaching people to recognize — depression, anxiety, and substance abuse — might not be evident in these individuals,” he said.
“Life sideswipes them suddenly, and they go from 0 to 60 ... and they may have access to a highly lethal method [of suicide] which weaponizes that moment of despair,” said Dr. Bryan. No amount of screening could possibly predict those types of suicides, he added.
Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, agrees with Dr. Bryan and noted there isn’t a strong correlation between suicidal ideation and death by suicide.
“Suicidal thoughts are very common, but suicide is a rare event,” he said.
He cited a study that showed that two thirds of individuals who died by suicide had denied experiencing suicidal thoughts when asked, and half of them died within 2 days of this denial. Other research suggests that as many as 98% of people who express suicidal ideation do not die by suicide, Dr. Nestadt said.
A Public Health Issue
If universal screening is not the answer to predicting and preventing suicide, what is? One way would be to approach suicide as a public health issue, Dr. Nestadt said.
“How did we reduce the rate of motor vehicle deaths? We didn’t test each driver’s reaction time behind the wheel,” he said. “Instead, we passed seatbelt and airbag legislation, implemented federal speed limits, and as a result, the number of motor vehicle fatalities decreased.”
Dr. Nestadt is an advocate for stronger gun safety legislation, which has proven effective in reducing suicide rates. A study published this year showed that states with child access prevention laws, negligent storage laws, and mandatory waiting periods for gun purchases reported fewer suicide deaths than those without that legislation.
Other measures might be applied in cases of extreme individual suicide risk, including extreme risk protection orders, also known as “red flag” laws, he added. This type of legislation provides a pathway for law enforcement to temporarily remove firearms from individuals who pose a risk to themselves or others.
“These have been shown to be very effective in saving lives,” Dr. Nestadt said.
Dr. Nestadt and others are also using machine learning models to predict suicide risk. Those identified as high-risk may be flagged on their electronic medical record. Ideally, when the algorithm becomes more accurate at predicting suicide, anyone treating this patient can then decide if action is needed, said Dr. Nestadt.
In his work with suicidal military personnel, Dr. Bryan and his colleagues established a brief form of cognitive behavioral therapy (BCBT) to help participants challenge cognitive distortions and build coping strategies to deal with feel with intense feelings of distress. Data show that BCBT reduced suicide attempts among active-duty soldiers by 60% compared with standard mental health treatment. It has since been shown to work in civilians as well.
Dr. Bryan is also researching fluctuations in the wish to live versus the wish to die relative to one another and mapping the trajectory of risk states along the way.
The goal is that these and other suicide prevention strategies currently under study by his team and others will help stem the rise in suicide deaths.
“Overall, we need to train mental health providers to implement suicide prevention therapies and establish suicide risk programs,” Dr. Bryan said. “But until we build one of these suicide prevention interventions to scale, we’re putting the cart before the horse.”
Dr. Roaten, Ms. Brummett, Dr. Bryan, and Dr. Nestadt reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
US suicide rates have reached alarming levels, with data from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) showing a 37% increase from 2000 to 2022. Nearly 49,000 people died by suicide in 2022 alone, translating to one death every 11 minutes.
The increase in suicide rates has prompted calls for expansion of universal suicide screening, in which all individuals in medical or mental health care settings are screened for suicide risk, regardless of the purpose for their visit. But the psychiatric field is split on the issue, with some experts citing false positives and a lack of mental health care resources for those deemed at risk.
In 2022, when the US Preventative Services Task Force released its recommendations on suicide prevention, first in children and adolescents, and then in adults, the authors said there was insufficient evidence to support universal suicide screening.
Proponents of the practice pushed back on that finding, arguing that universal suicide screening could help identify those at high risk who might otherwise go undiagnosed, leading to earlier, potentially lifesaving, intervention.
So, what is the case for — and against — universal screening?
Sounding an Alert
The introduction of universal screening was driven by a confluence of factors that began with a 1999 report by then-US Surgeon General David Satcher, MD. This was followed by a report in 2016 from the Joint Commission on Detecting and Treating Suicidal Ideation that called for healthcare organizations to improve detection and treatment of suicidal ideation in all healthcare care settings.
Data from the alert showed that a significant number of people who died by suicide had a healthcare visit before their death. Half had seen a clinician a month before their death; nearly 30% had a medical visit just the week before — all with no detection of increased suicide risk.
It was that sort of finding that led Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas to become the first US hospital to implement universal suicide screening. Since the program launched in 2015, the system has screened more than 4.3 million patients in its emergency department, inpatient units, and 20 primary care clinics.
“Since the program began, we’ve completed between 40,000 to 50,000 screenings per month,” said Kimberly Roaten, PhD, associate chief quality and safety officer for behavioral health at Parkland Health.
Clinicians at Parkland use the five-item Ask Suicide-Screening Questions to assess suicidal intent, a commonly used tool that was originally developed for use in pediatric emergency rooms (ERs). The tool, which takes about 20 seconds to administer, has since been validated in both children and adults.
Based on a patient’s response, a clinical decision support system integrated into the electronic health record classifies suicide risk as none, moderate, or high.
Patients identified as moderate risk are offered a more in-depth assessment with a mental health clinician, though participation is not mandatory, said Dr. Roaten. Those at high risk receive a more thorough evaluation.
The proportion of ER patients at Parkland who screen positive for any suicidal intent has consistently remained at about 7%, and at 2% in the primary care clinics, she said.
To better understand what the program may have had on suicide prevention, Dr. Roaten is leading a National Institute of Mental Health–funded study to link a decade of mortality data from the state of Texas to patient data from Parkland Health. Investigators will analyze information about patients identified at risk for suicide, those patients’ characteristics, and who dies by suicide.
Universal Screening Expands
Other health systems have adopted universal suicide screening including the Indian Health Service and the US Veterans Health Administration. Universal suicide screening is also in place in a growing number of primary care practices and hospitals throughout the United States and will be mandatory for patients aged 12 years and older in all acute care hospitals in California beginning in 2025.
There is also a push for universal screening to be coordinated through local, state, and federal government, nonprofit, and private sectors. The National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention is charged with advancing the White House’s 2024 National Strategy for Suicide Prevention, a 10-year plan to address gaps in suicide prevention in the United States.
Sarah Brummett, JD, director of the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention’s executive committee, said that universal suicide screening is part of the 2024 strategy. “We know there are barriers to universal screening, and so it’s important to recognize what they are so we can address them,” said Ms. Brummett.
Barriers may include adequate staffing, or a system in place to triage patients who screen positive.
At Parkland, cost and workload have been minimal, Dr. Roaten said. “We built a model that only dedicates our highest-value resources to the most at-risk patients.”
She also noted that relief may be on the horizon for health systems where cost is an obstacle to universal screening and subsequent intervention. “There are efforts at the federal level to increase funding for suicide assessment and crisis response,” she said.
Pushback on Universal Screening
Universal suicide screening has its detractors, including critics who say expansion is unlikely to reduce suicide rates.
“The issue with suicidal ideation is that it is very dynamic. Suicidal ideation changes very quickly — sometimes within hours,” said Craig Bryan, PsyD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral health at Ohio State University in Columbus, Ohio.
Universal screening can also lead to false positives, where a patient who screens positive for suicidal ideation has no actual intention of attempting suicide, potentially creating unnecessary concern and burden on health care resources, Dr. Bryan noted.
“What do you do with everyone who screens positive?” Dr. Bryan said. “I’ve spoken with leaders of many health systems in the United States, and there is pushback against universal screening because they don’t have enough mental health resources to handle all of the referrals.”
Suicide screening also doesn’t predict who will die by suicide, Dr. Bryan added. It only identifies those willing to disclose suicidal thoughts. There is a significant number of people without mental illness who may never seek medical care, so “the warning signs we’re teaching people to recognize — depression, anxiety, and substance abuse — might not be evident in these individuals,” he said.
“Life sideswipes them suddenly, and they go from 0 to 60 ... and they may have access to a highly lethal method [of suicide] which weaponizes that moment of despair,” said Dr. Bryan. No amount of screening could possibly predict those types of suicides, he added.
Paul Nestadt, MD, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, agrees with Dr. Bryan and noted there isn’t a strong correlation between suicidal ideation and death by suicide.
“Suicidal thoughts are very common, but suicide is a rare event,” he said.
He cited a study that showed that two thirds of individuals who died by suicide had denied experiencing suicidal thoughts when asked, and half of them died within 2 days of this denial. Other research suggests that as many as 98% of people who express suicidal ideation do not die by suicide, Dr. Nestadt said.
A Public Health Issue
If universal screening is not the answer to predicting and preventing suicide, what is? One way would be to approach suicide as a public health issue, Dr. Nestadt said.
“How did we reduce the rate of motor vehicle deaths? We didn’t test each driver’s reaction time behind the wheel,” he said. “Instead, we passed seatbelt and airbag legislation, implemented federal speed limits, and as a result, the number of motor vehicle fatalities decreased.”
Dr. Nestadt is an advocate for stronger gun safety legislation, which has proven effective in reducing suicide rates. A study published this year showed that states with child access prevention laws, negligent storage laws, and mandatory waiting periods for gun purchases reported fewer suicide deaths than those without that legislation.
Other measures might be applied in cases of extreme individual suicide risk, including extreme risk protection orders, also known as “red flag” laws, he added. This type of legislation provides a pathway for law enforcement to temporarily remove firearms from individuals who pose a risk to themselves or others.
“These have been shown to be very effective in saving lives,” Dr. Nestadt said.
Dr. Nestadt and others are also using machine learning models to predict suicide risk. Those identified as high-risk may be flagged on their electronic medical record. Ideally, when the algorithm becomes more accurate at predicting suicide, anyone treating this patient can then decide if action is needed, said Dr. Nestadt.
In his work with suicidal military personnel, Dr. Bryan and his colleagues established a brief form of cognitive behavioral therapy (BCBT) to help participants challenge cognitive distortions and build coping strategies to deal with feel with intense feelings of distress. Data show that BCBT reduced suicide attempts among active-duty soldiers by 60% compared with standard mental health treatment. It has since been shown to work in civilians as well.
Dr. Bryan is also researching fluctuations in the wish to live versus the wish to die relative to one another and mapping the trajectory of risk states along the way.
The goal is that these and other suicide prevention strategies currently under study by his team and others will help stem the rise in suicide deaths.
“Overall, we need to train mental health providers to implement suicide prevention therapies and establish suicide risk programs,” Dr. Bryan said. “But until we build one of these suicide prevention interventions to scale, we’re putting the cart before the horse.”
Dr. Roaten, Ms. Brummett, Dr. Bryan, and Dr. Nestadt reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moving Beyond Traditional Methods for Treatment of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
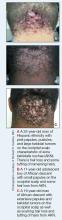
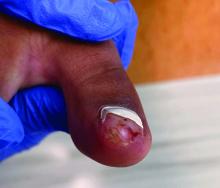
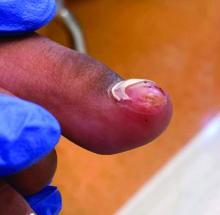
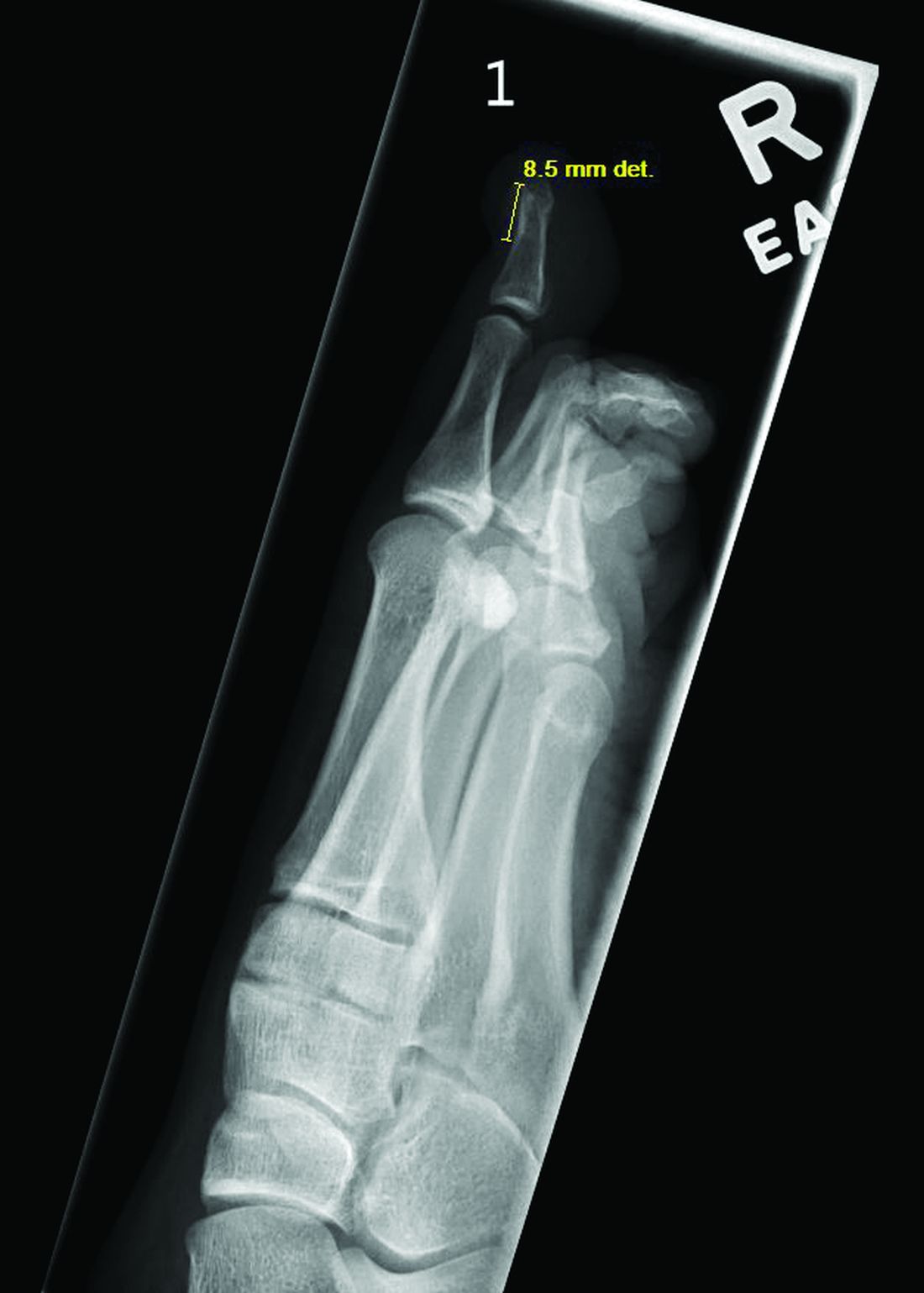
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.16
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace, which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.21
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
SGLT2 Inhibitor Reduces Risk for Neurodegenerative Diseases in T2D
MADRID — Patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) show significant reductions in the risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Parkinson’s disease, compared with those treated with other antidiabetic drugs, results from a large population-based cohort show.
“This was the largest nationwide population-based longitudinal cohort study to investigate the association between the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and the incidence of all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease,” said first author Hae Kyung Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is known to increase the risk for neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Kim. Key factors attributed to the risk include shared pathophysiological mechanisms such as central nervous system insulin resistance and reduced cerebral glucose metabolism.
While research is lacking on the role of antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, the researcher noted that “SGLT2 inhibitors, which have shown significant cardiorenal benefits and enhanced energy metabolism through ketogenesis, offer promise.”
To further investigate, Dr. Kim and her colleagues conducted the retrospective study, evaluating data on more than 1.3 million enrollees in Korea’s National Health Insurance Service Database who were aged 40 years or older, diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, and had initiated antidiabetic drugs between September 2014 and December 2019.
In the propensity score analysis, 358,862 patients were matched 1:1, in groups of 179,431 participants each, based on whether they were treated with SGLT2is or other oral antidiabetic drugs. Patients with a history of neurodegenerative disease, cancer, or use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists were excluded.
The patients had a mean age of 57.8 years, 57.9% were men, and 6837 had incident dementia or Parkinson’s disease events reported.
With a mean follow-up of 2.88 years, after adjustment for key variables, those treated with SGLT2is had a 19% reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.81), a 31% reduced risk for vascular dementia (aHR, 0.69), and a 20% reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease (aHR, 0.80) compared with the non-SGLT2i group.
Furthermore, those receiving SGLT2i treatment had a 21% reduced risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 0.79) and a 22% reduced risk for all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease compared with the oral antidiabetic drug group (aHR, 0.78) with a 6-month drug use lag period.
The association was observed regardless of SGLT2i exposure duration. Subgroup analyses indicated that the reductions in neurodegenerative disorders among those receiving SGLT2is were not associated with factors including age, sex, body mass index, blood pressure, glucose, lipid profiles, kidney function, health behaviors, comorbidities, diabetic complications, or other medication use.
Dr. Kim speculated that mechanisms underlying the reduced dementia risk could include SGLT2i effects of mitigating the common severe risk factors of type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases, including hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, and improving hyperperfusion in the heart and cerebral vascular insufficiency.
Commenting on the study to this news organization, Erik H. Serné, MD, of the VU University Medical Centre, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, who comoderated the session, noted that “people with type 2 diabetes have a 50%-100% increased risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.”
“The increasing prevalence of both conditions poses significant public health challenges, highlighting the need for effective prevention strategies and interventions.”
Currently, treatments for dementia are limited, with most primarily addressing symptoms and not the underlying cause of the neurodegenerative disease, he said.
He noted that, in addition to the effects mentioned by Dr. Kim, SGLT2is are also speculated to provide potential neuroprotective effects through improved glycemic control and insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, enhanced mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, and reduced beta-amyloid and tau pathology.
“These mechanisms collectively may reduce the risk of cognitive decline, particularly in diabetic patients, and warrant further investigation in clinical trials to solidify the neuroprotective role of SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Serné.
In addition to their benefits in type 2 diabetes, SGLT2is “now offer hope in the prevention of dementia, a disease that has very limited therapeutic options thus far. The current data [presented by Dr. Kim] seem to corroborate this,” he added.
Dr. Kim and Dr. Serné had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID — Patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) show significant reductions in the risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Parkinson’s disease, compared with those treated with other antidiabetic drugs, results from a large population-based cohort show.
“This was the largest nationwide population-based longitudinal cohort study to investigate the association between the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and the incidence of all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease,” said first author Hae Kyung Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is known to increase the risk for neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Kim. Key factors attributed to the risk include shared pathophysiological mechanisms such as central nervous system insulin resistance and reduced cerebral glucose metabolism.
While research is lacking on the role of antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, the researcher noted that “SGLT2 inhibitors, which have shown significant cardiorenal benefits and enhanced energy metabolism through ketogenesis, offer promise.”
To further investigate, Dr. Kim and her colleagues conducted the retrospective study, evaluating data on more than 1.3 million enrollees in Korea’s National Health Insurance Service Database who were aged 40 years or older, diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, and had initiated antidiabetic drugs between September 2014 and December 2019.
In the propensity score analysis, 358,862 patients were matched 1:1, in groups of 179,431 participants each, based on whether they were treated with SGLT2is or other oral antidiabetic drugs. Patients with a history of neurodegenerative disease, cancer, or use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists were excluded.
The patients had a mean age of 57.8 years, 57.9% were men, and 6837 had incident dementia or Parkinson’s disease events reported.
With a mean follow-up of 2.88 years, after adjustment for key variables, those treated with SGLT2is had a 19% reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.81), a 31% reduced risk for vascular dementia (aHR, 0.69), and a 20% reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease (aHR, 0.80) compared with the non-SGLT2i group.
Furthermore, those receiving SGLT2i treatment had a 21% reduced risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 0.79) and a 22% reduced risk for all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease compared with the oral antidiabetic drug group (aHR, 0.78) with a 6-month drug use lag period.
The association was observed regardless of SGLT2i exposure duration. Subgroup analyses indicated that the reductions in neurodegenerative disorders among those receiving SGLT2is were not associated with factors including age, sex, body mass index, blood pressure, glucose, lipid profiles, kidney function, health behaviors, comorbidities, diabetic complications, or other medication use.
Dr. Kim speculated that mechanisms underlying the reduced dementia risk could include SGLT2i effects of mitigating the common severe risk factors of type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases, including hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, and improving hyperperfusion in the heart and cerebral vascular insufficiency.
Commenting on the study to this news organization, Erik H. Serné, MD, of the VU University Medical Centre, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, who comoderated the session, noted that “people with type 2 diabetes have a 50%-100% increased risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.”
“The increasing prevalence of both conditions poses significant public health challenges, highlighting the need for effective prevention strategies and interventions.”
Currently, treatments for dementia are limited, with most primarily addressing symptoms and not the underlying cause of the neurodegenerative disease, he said.
He noted that, in addition to the effects mentioned by Dr. Kim, SGLT2is are also speculated to provide potential neuroprotective effects through improved glycemic control and insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, enhanced mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, and reduced beta-amyloid and tau pathology.
“These mechanisms collectively may reduce the risk of cognitive decline, particularly in diabetic patients, and warrant further investigation in clinical trials to solidify the neuroprotective role of SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Serné.
In addition to their benefits in type 2 diabetes, SGLT2is “now offer hope in the prevention of dementia, a disease that has very limited therapeutic options thus far. The current data [presented by Dr. Kim] seem to corroborate this,” he added.
Dr. Kim and Dr. Serné had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MADRID — Patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) show significant reductions in the risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Parkinson’s disease, compared with those treated with other antidiabetic drugs, results from a large population-based cohort show.
“This was the largest nationwide population-based longitudinal cohort study to investigate the association between the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and the incidence of all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease,” said first author Hae Kyung Kim, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is known to increase the risk for neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, said Dr. Kim. Key factors attributed to the risk include shared pathophysiological mechanisms such as central nervous system insulin resistance and reduced cerebral glucose metabolism.
While research is lacking on the role of antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, the researcher noted that “SGLT2 inhibitors, which have shown significant cardiorenal benefits and enhanced energy metabolism through ketogenesis, offer promise.”
To further investigate, Dr. Kim and her colleagues conducted the retrospective study, evaluating data on more than 1.3 million enrollees in Korea’s National Health Insurance Service Database who were aged 40 years or older, diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, and had initiated antidiabetic drugs between September 2014 and December 2019.
In the propensity score analysis, 358,862 patients were matched 1:1, in groups of 179,431 participants each, based on whether they were treated with SGLT2is or other oral antidiabetic drugs. Patients with a history of neurodegenerative disease, cancer, or use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists were excluded.
The patients had a mean age of 57.8 years, 57.9% were men, and 6837 had incident dementia or Parkinson’s disease events reported.
With a mean follow-up of 2.88 years, after adjustment for key variables, those treated with SGLT2is had a 19% reduced risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.81), a 31% reduced risk for vascular dementia (aHR, 0.69), and a 20% reduced risk for Parkinson’s disease (aHR, 0.80) compared with the non-SGLT2i group.
Furthermore, those receiving SGLT2i treatment had a 21% reduced risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 0.79) and a 22% reduced risk for all-cause dementia and Parkinson’s disease compared with the oral antidiabetic drug group (aHR, 0.78) with a 6-month drug use lag period.
The association was observed regardless of SGLT2i exposure duration. Subgroup analyses indicated that the reductions in neurodegenerative disorders among those receiving SGLT2is were not associated with factors including age, sex, body mass index, blood pressure, glucose, lipid profiles, kidney function, health behaviors, comorbidities, diabetic complications, or other medication use.
Dr. Kim speculated that mechanisms underlying the reduced dementia risk could include SGLT2i effects of mitigating the common severe risk factors of type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases, including hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease, and improving hyperperfusion in the heart and cerebral vascular insufficiency.
Commenting on the study to this news organization, Erik H. Serné, MD, of the VU University Medical Centre, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, who comoderated the session, noted that “people with type 2 diabetes have a 50%-100% increased risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.”
“The increasing prevalence of both conditions poses significant public health challenges, highlighting the need for effective prevention strategies and interventions.”
Currently, treatments for dementia are limited, with most primarily addressing symptoms and not the underlying cause of the neurodegenerative disease, he said.
He noted that, in addition to the effects mentioned by Dr. Kim, SGLT2is are also speculated to provide potential neuroprotective effects through improved glycemic control and insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress, enhanced mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, and reduced beta-amyloid and tau pathology.
“These mechanisms collectively may reduce the risk of cognitive decline, particularly in diabetic patients, and warrant further investigation in clinical trials to solidify the neuroprotective role of SGLT2 inhibitors,” said Dr. Serné.
In addition to their benefits in type 2 diabetes, SGLT2is “now offer hope in the prevention of dementia, a disease that has very limited therapeutic options thus far. The current data [presented by Dr. Kim] seem to corroborate this,” he added.
Dr. Kim and Dr. Serné had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2024
NSAIDs Offer No Relief for Pain From IUD Placement
Research on pain management during placement of intrauterine devices (IUD) is lacking, but most studies so far indicate that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not effective, according to a poster presented at Pain Week 2024 in Las Vegas.
Roughly 79% of the 14 studies included in the systematic review found NSAIDs — one of the most common drugs clinicians advise patients to take before placement — did not diminish discomfort.
“We’re challenging the current practice of using just NSAIDs as a first-line of treatment,” said Kevin Rowland, PhD, professor and chair of biomedical sciences at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine in Houston, who helped conduct the meta-analysis. “We need additional measures.”
Some studies found the drugs offered virtually no improvement for patients, while the biggest drop in pain shown in one study was about 40%. The range of pain levels women reported while using NSAIDs was between 1.8 and 7.3 on the visual analog scale (VAS), with an average score of 4.25.
The review included 10 types of NSAIDs and dosages administered to patients before the procedure. One intramuscular NSAID was included while the remaining were oral. All studies were peer-reviewed, used the VAS pain scale, and were not limited to any specific population.
The findings highlight a longstanding but unresolved problem in reproductive health: An overall lack of effective pain management strategies for gynecologic procedures.
“We went into this having a pretty good idea of what we were going to find because [the lack of NSAID efficacy] has been shown before, it’s been talked about before, and we’re just not listening as a medical community,” said Isabella D. Martingano, an MD candidate at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine, who led the review.
The research also points to a lack of robust studies on pain during IUD placement, said Emma Lakey, a coauthor and medical student at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine.
“We were only able to review 14 studies, which was enough to go off of, but considering we were looking for trials about pain control for a procedure that helps prevent pregnancy, that’s just not enough research,” Ms. Lakey said.
Discomfort associated with IUD placement ranges from mild to severe, can last for over a week, and includes cramping, bleeding, lightheadedness, nausea, and fainting. Some research suggests that providers may underestimate the level of pain the procedures cause.
“Unfortunately, the pain associated with IUD insertion and removal has been underplayed for a long time and many practitioners in the field likely haven’t counseled patients fully on what the procedure will feel like,” said Jennifer Chin, MD, an ob.gyn. and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington in Seattle.
NSAIDs are not mentioned in the recently expanded guidelines on IUD placement from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC recommends lidocaine paracervical blocks, gels, sprays, and creams, plus counseling women about pain ahead of the procedures.
IUDs are one of the most effective forms of birth control, with a failure rate below 1%.
Yet hearing about painful placement keeps many women from seeking out an IUD or replacing an existing device, Dr. Rowland said. The review adds to the body of evidence that current strategies are not working and that more research is needed, he said.
According to Dr. Chin, making IUDs more accessible means taking a more personalized approach to pain management while understanding that what may be a painless procedure for one patient may be excruciating for another.
Dr. Chin offers a range of options for her patients, including NSAIDs, lorazepam for anxiety, paracervical blocks, lidocaine jelly and spray, intravenous sedation, and general anesthesia. She also talks to her patients through the procedure and provides guided imagery and meditation.
“We should always make sure we’re prioritizing the patients and providing evidence-based, compassionate, and individualized care,” said Dr. Chin. “Each patient comes to us in a particular context and with a specific set of experiences and history that will make a difference in how we’re best able to take care of them.”
The authors reported no disclosures and no sources of funding. Dr. Chin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Research on pain management during placement of intrauterine devices (IUD) is lacking, but most studies so far indicate that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not effective, according to a poster presented at Pain Week 2024 in Las Vegas.
Roughly 79% of the 14 studies included in the systematic review found NSAIDs — one of the most common drugs clinicians advise patients to take before placement — did not diminish discomfort.
“We’re challenging the current practice of using just NSAIDs as a first-line of treatment,” said Kevin Rowland, PhD, professor and chair of biomedical sciences at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine in Houston, who helped conduct the meta-analysis. “We need additional measures.”
Some studies found the drugs offered virtually no improvement for patients, while the biggest drop in pain shown in one study was about 40%. The range of pain levels women reported while using NSAIDs was between 1.8 and 7.3 on the visual analog scale (VAS), with an average score of 4.25.
The review included 10 types of NSAIDs and dosages administered to patients before the procedure. One intramuscular NSAID was included while the remaining were oral. All studies were peer-reviewed, used the VAS pain scale, and were not limited to any specific population.
The findings highlight a longstanding but unresolved problem in reproductive health: An overall lack of effective pain management strategies for gynecologic procedures.
“We went into this having a pretty good idea of what we were going to find because [the lack of NSAID efficacy] has been shown before, it’s been talked about before, and we’re just not listening as a medical community,” said Isabella D. Martingano, an MD candidate at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine, who led the review.
The research also points to a lack of robust studies on pain during IUD placement, said Emma Lakey, a coauthor and medical student at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine.
“We were only able to review 14 studies, which was enough to go off of, but considering we were looking for trials about pain control for a procedure that helps prevent pregnancy, that’s just not enough research,” Ms. Lakey said.
Discomfort associated with IUD placement ranges from mild to severe, can last for over a week, and includes cramping, bleeding, lightheadedness, nausea, and fainting. Some research suggests that providers may underestimate the level of pain the procedures cause.
“Unfortunately, the pain associated with IUD insertion and removal has been underplayed for a long time and many practitioners in the field likely haven’t counseled patients fully on what the procedure will feel like,” said Jennifer Chin, MD, an ob.gyn. and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington in Seattle.
NSAIDs are not mentioned in the recently expanded guidelines on IUD placement from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC recommends lidocaine paracervical blocks, gels, sprays, and creams, plus counseling women about pain ahead of the procedures.
IUDs are one of the most effective forms of birth control, with a failure rate below 1%.
Yet hearing about painful placement keeps many women from seeking out an IUD or replacing an existing device, Dr. Rowland said. The review adds to the body of evidence that current strategies are not working and that more research is needed, he said.
According to Dr. Chin, making IUDs more accessible means taking a more personalized approach to pain management while understanding that what may be a painless procedure for one patient may be excruciating for another.
Dr. Chin offers a range of options for her patients, including NSAIDs, lorazepam for anxiety, paracervical blocks, lidocaine jelly and spray, intravenous sedation, and general anesthesia. She also talks to her patients through the procedure and provides guided imagery and meditation.
“We should always make sure we’re prioritizing the patients and providing evidence-based, compassionate, and individualized care,” said Dr. Chin. “Each patient comes to us in a particular context and with a specific set of experiences and history that will make a difference in how we’re best able to take care of them.”
The authors reported no disclosures and no sources of funding. Dr. Chin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Research on pain management during placement of intrauterine devices (IUD) is lacking, but most studies so far indicate that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are not effective, according to a poster presented at Pain Week 2024 in Las Vegas.
Roughly 79% of the 14 studies included in the systematic review found NSAIDs — one of the most common drugs clinicians advise patients to take before placement — did not diminish discomfort.
“We’re challenging the current practice of using just NSAIDs as a first-line of treatment,” said Kevin Rowland, PhD, professor and chair of biomedical sciences at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine in Houston, who helped conduct the meta-analysis. “We need additional measures.”
Some studies found the drugs offered virtually no improvement for patients, while the biggest drop in pain shown in one study was about 40%. The range of pain levels women reported while using NSAIDs was between 1.8 and 7.3 on the visual analog scale (VAS), with an average score of 4.25.
The review included 10 types of NSAIDs and dosages administered to patients before the procedure. One intramuscular NSAID was included while the remaining were oral. All studies were peer-reviewed, used the VAS pain scale, and were not limited to any specific population.
The findings highlight a longstanding but unresolved problem in reproductive health: An overall lack of effective pain management strategies for gynecologic procedures.
“We went into this having a pretty good idea of what we were going to find because [the lack of NSAID efficacy] has been shown before, it’s been talked about before, and we’re just not listening as a medical community,” said Isabella D. Martingano, an MD candidate at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine, who led the review.
The research also points to a lack of robust studies on pain during IUD placement, said Emma Lakey, a coauthor and medical student at Tilman J. Fertitta Family College of Medicine.
“We were only able to review 14 studies, which was enough to go off of, but considering we were looking for trials about pain control for a procedure that helps prevent pregnancy, that’s just not enough research,” Ms. Lakey said.
Discomfort associated with IUD placement ranges from mild to severe, can last for over a week, and includes cramping, bleeding, lightheadedness, nausea, and fainting. Some research suggests that providers may underestimate the level of pain the procedures cause.
“Unfortunately, the pain associated with IUD insertion and removal has been underplayed for a long time and many practitioners in the field likely haven’t counseled patients fully on what the procedure will feel like,” said Jennifer Chin, MD, an ob.gyn. and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington in Seattle.
NSAIDs are not mentioned in the recently expanded guidelines on IUD placement from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC recommends lidocaine paracervical blocks, gels, sprays, and creams, plus counseling women about pain ahead of the procedures.
IUDs are one of the most effective forms of birth control, with a failure rate below 1%.
Yet hearing about painful placement keeps many women from seeking out an IUD or replacing an existing device, Dr. Rowland said. The review adds to the body of evidence that current strategies are not working and that more research is needed, he said.
According to Dr. Chin, making IUDs more accessible means taking a more personalized approach to pain management while understanding that what may be a painless procedure for one patient may be excruciating for another.
Dr. Chin offers a range of options for her patients, including NSAIDs, lorazepam for anxiety, paracervical blocks, lidocaine jelly and spray, intravenous sedation, and general anesthesia. She also talks to her patients through the procedure and provides guided imagery and meditation.
“We should always make sure we’re prioritizing the patients and providing evidence-based, compassionate, and individualized care,” said Dr. Chin. “Each patient comes to us in a particular context and with a specific set of experiences and history that will make a difference in how we’re best able to take care of them.”
The authors reported no disclosures and no sources of funding. Dr. Chin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-Term Exposure to Road Traffic Noise and Air Pollution Linked to Infertility
TOPLINE:
Long-term exposure to particulate matter < 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5) is linked to a higher risk for infertility in men. Exposure to road traffic noise is associated with a higher risk for infertility in women aged > 35 years and possibly in men aged > 37 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- This nationwide prospective cohort study evaluated the association between long-term exposure to road traffic noise and PM2.5 and infertility in 526,056 men (mean age, 33.6 years) and 377,850 women (mean age, 32.7 years) who were cohabiting or married, had fewer than two children, and lived in Denmark between 2000 and 2017.
- Residential exposure to road traffic noise (most exposed facade of the home) and PM2.5 was estimated using validated models and linked to data from national registers.
- Diagnoses of infertility were identified in men and women from the Danish National Patient Register over a mean follow-up of 4.3 years and 4.2 years, respectively.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 2.9 µg/m3 increase in the 5-year average exposure to PM2.5 was associated with a 24% increase in the risk for infertility in men aged 30-45 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.24).
- No significant association was found between exposure to PM2.5 and infertility in women.
- Each 10.2 dB increase in the 5-year average exposure to road traffic noise was associated with a 14% increase in infertility (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10-1.18) in women aged 35-45 years.
- Exposure to noise was associated with a reduced risk for infertility in men aged 30.0-36.9 years (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.91-0.96) and an increased risk in those aged 37-45 years (aHR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11).
IN PRACTICE:
“As many Western countries are facing declining birth rates and increasing maternal age at the birth of a first child, knowledge on environmental pollutants affecting fertility is crucial,” the authors of the study wrote. “It suggests that political implementation of air pollution and noise mitigations may be important tools for improving birth rates in the Western world,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Mette Sorensen, of the Danish Cancer Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on register data meant information on lifestyle factors such as alcohol use, body mass index, and smoking was unavailable. The lack of data on exposure to noise and PM2.5 at work and during leisure activities may affect the size and statistical precision of risk estimates.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term exposure to particulate matter < 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5) is linked to a higher risk for infertility in men. Exposure to road traffic noise is associated with a higher risk for infertility in women aged > 35 years and possibly in men aged > 37 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- This nationwide prospective cohort study evaluated the association between long-term exposure to road traffic noise and PM2.5 and infertility in 526,056 men (mean age, 33.6 years) and 377,850 women (mean age, 32.7 years) who were cohabiting or married, had fewer than two children, and lived in Denmark between 2000 and 2017.
- Residential exposure to road traffic noise (most exposed facade of the home) and PM2.5 was estimated using validated models and linked to data from national registers.
- Diagnoses of infertility were identified in men and women from the Danish National Patient Register over a mean follow-up of 4.3 years and 4.2 years, respectively.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 2.9 µg/m3 increase in the 5-year average exposure to PM2.5 was associated with a 24% increase in the risk for infertility in men aged 30-45 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.24).
- No significant association was found between exposure to PM2.5 and infertility in women.
- Each 10.2 dB increase in the 5-year average exposure to road traffic noise was associated with a 14% increase in infertility (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10-1.18) in women aged 35-45 years.
- Exposure to noise was associated with a reduced risk for infertility in men aged 30.0-36.9 years (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.91-0.96) and an increased risk in those aged 37-45 years (aHR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11).
IN PRACTICE:
“As many Western countries are facing declining birth rates and increasing maternal age at the birth of a first child, knowledge on environmental pollutants affecting fertility is crucial,” the authors of the study wrote. “It suggests that political implementation of air pollution and noise mitigations may be important tools for improving birth rates in the Western world,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Mette Sorensen, of the Danish Cancer Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on register data meant information on lifestyle factors such as alcohol use, body mass index, and smoking was unavailable. The lack of data on exposure to noise and PM2.5 at work and during leisure activities may affect the size and statistical precision of risk estimates.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Long-term exposure to particulate matter < 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5) is linked to a higher risk for infertility in men. Exposure to road traffic noise is associated with a higher risk for infertility in women aged > 35 years and possibly in men aged > 37 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- This nationwide prospective cohort study evaluated the association between long-term exposure to road traffic noise and PM2.5 and infertility in 526,056 men (mean age, 33.6 years) and 377,850 women (mean age, 32.7 years) who were cohabiting or married, had fewer than two children, and lived in Denmark between 2000 and 2017.
- Residential exposure to road traffic noise (most exposed facade of the home) and PM2.5 was estimated using validated models and linked to data from national registers.
- Diagnoses of infertility were identified in men and women from the Danish National Patient Register over a mean follow-up of 4.3 years and 4.2 years, respectively.
TAKEAWAY:
- Each 2.9 µg/m3 increase in the 5-year average exposure to PM2.5 was associated with a 24% increase in the risk for infertility in men aged 30-45 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.24).
- No significant association was found between exposure to PM2.5 and infertility in women.
- Each 10.2 dB increase in the 5-year average exposure to road traffic noise was associated with a 14% increase in infertility (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.10-1.18) in women aged 35-45 years.
- Exposure to noise was associated with a reduced risk for infertility in men aged 30.0-36.9 years (aHR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.91-0.96) and an increased risk in those aged 37-45 years (aHR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.02-1.11).
IN PRACTICE:
“As many Western countries are facing declining birth rates and increasing maternal age at the birth of a first child, knowledge on environmental pollutants affecting fertility is crucial,” the authors of the study wrote. “It suggests that political implementation of air pollution and noise mitigations may be important tools for improving birth rates in the Western world,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Mette Sorensen, of the Danish Cancer Institute in Copenhagen, Denmark, was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on register data meant information on lifestyle factors such as alcohol use, body mass index, and smoking was unavailable. The lack of data on exposure to noise and PM2.5 at work and during leisure activities may affect the size and statistical precision of risk estimates.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any external funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Laughter: Comic Relief for Dry Eyes?
TOPLINE:
Laughter exercise practiced four times a day was noninferior to 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid in alleviating the symptoms of dry eye disease and improved tear film stability and the function of the meibomian gland, researchers found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of laughter exercise in patients with symptomatic dry eye disease by conducting a two-arm clinical trial at the largest ophthalmic center in southern China.
- They included 299 patients aged 18-45 years (74% women) with symptomatic dry eye disease who were randomly assigned to receive either laughter exercise or eye drops with 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid four times daily for 8 weeks.
- All the participants were required to have an ocular surface disease index score, a measure of symptoms related to dry eye disease, between 18 and 80 points and a fluorescein tear film breakup time of no more than 8 seconds.
- Participants in the laughter exercise group watched an instructional video and were requested to repeat the phrases “Hee hee hee, hah hah hah, cheese cheese cheese, cheek cheek cheek, hah hah hah hah hah hah” 30 times per 5-minute session.
- The primary outcome was the mean change in the ocular surface disease index score from baseline to 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 8 weeks, the ocular surface disease index score reduced by 10.50 points (95% CI, −13.1 to −7.82) in the laughter exercise group and by 8.83 points (95% CI, −11.7 to −6.02) in the group prescribed eye drops.
- At 12 weeks, patients in the laughter exercise group showed a significantly greater reduction in the ocular surface disease index score than those in the group prescribed eye drops (mean between-group difference, −4.08 points; P = .024).
- Laughter exercise also led to a more significant improvement in the noninvasive tear breakup time than the use of eye drops (mean between-group difference, 2.30 sec; P < .001).
- No adverse events were reported in either of the groups during the study period.
IN PRACTICE:
“As a safe, environmentally friendly, and low-cost intervention, laughter exercise could serve as a first-line, home-based treatment for people with symptomatic dry eye disease and limited corneal staining,” the authors of the study reported.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jing Li from the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology at the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center in Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, and was published online on September 11, 2024, in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a double-blinded design. The laughter exercise required a greater time investment than the application of eye drops, which may affect adherence in the long run.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and High-level Hospital Construction Project. The authors declared receiving support from the funding agencies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Laughter exercise practiced four times a day was noninferior to 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid in alleviating the symptoms of dry eye disease and improved tear film stability and the function of the meibomian gland, researchers found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of laughter exercise in patients with symptomatic dry eye disease by conducting a two-arm clinical trial at the largest ophthalmic center in southern China.
- They included 299 patients aged 18-45 years (74% women) with symptomatic dry eye disease who were randomly assigned to receive either laughter exercise or eye drops with 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid four times daily for 8 weeks.
- All the participants were required to have an ocular surface disease index score, a measure of symptoms related to dry eye disease, between 18 and 80 points and a fluorescein tear film breakup time of no more than 8 seconds.
- Participants in the laughter exercise group watched an instructional video and were requested to repeat the phrases “Hee hee hee, hah hah hah, cheese cheese cheese, cheek cheek cheek, hah hah hah hah hah hah” 30 times per 5-minute session.
- The primary outcome was the mean change in the ocular surface disease index score from baseline to 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 8 weeks, the ocular surface disease index score reduced by 10.50 points (95% CI, −13.1 to −7.82) in the laughter exercise group and by 8.83 points (95% CI, −11.7 to −6.02) in the group prescribed eye drops.
- At 12 weeks, patients in the laughter exercise group showed a significantly greater reduction in the ocular surface disease index score than those in the group prescribed eye drops (mean between-group difference, −4.08 points; P = .024).
- Laughter exercise also led to a more significant improvement in the noninvasive tear breakup time than the use of eye drops (mean between-group difference, 2.30 sec; P < .001).
- No adverse events were reported in either of the groups during the study period.
IN PRACTICE:
“As a safe, environmentally friendly, and low-cost intervention, laughter exercise could serve as a first-line, home-based treatment for people with symptomatic dry eye disease and limited corneal staining,” the authors of the study reported.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jing Li from the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology at the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center in Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, and was published online on September 11, 2024, in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a double-blinded design. The laughter exercise required a greater time investment than the application of eye drops, which may affect adherence in the long run.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and High-level Hospital Construction Project. The authors declared receiving support from the funding agencies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Laughter exercise practiced four times a day was noninferior to 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid in alleviating the symptoms of dry eye disease and improved tear film stability and the function of the meibomian gland, researchers found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of laughter exercise in patients with symptomatic dry eye disease by conducting a two-arm clinical trial at the largest ophthalmic center in southern China.
- They included 299 patients aged 18-45 years (74% women) with symptomatic dry eye disease who were randomly assigned to receive either laughter exercise or eye drops with 0.1% sodium hyaluronic acid four times daily for 8 weeks.
- All the participants were required to have an ocular surface disease index score, a measure of symptoms related to dry eye disease, between 18 and 80 points and a fluorescein tear film breakup time of no more than 8 seconds.
- Participants in the laughter exercise group watched an instructional video and were requested to repeat the phrases “Hee hee hee, hah hah hah, cheese cheese cheese, cheek cheek cheek, hah hah hah hah hah hah” 30 times per 5-minute session.
- The primary outcome was the mean change in the ocular surface disease index score from baseline to 8 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 8 weeks, the ocular surface disease index score reduced by 10.50 points (95% CI, −13.1 to −7.82) in the laughter exercise group and by 8.83 points (95% CI, −11.7 to −6.02) in the group prescribed eye drops.
- At 12 weeks, patients in the laughter exercise group showed a significantly greater reduction in the ocular surface disease index score than those in the group prescribed eye drops (mean between-group difference, −4.08 points; P = .024).
- Laughter exercise also led to a more significant improvement in the noninvasive tear breakup time than the use of eye drops (mean between-group difference, 2.30 sec; P < .001).
- No adverse events were reported in either of the groups during the study period.
IN PRACTICE:
“As a safe, environmentally friendly, and low-cost intervention, laughter exercise could serve as a first-line, home-based treatment for people with symptomatic dry eye disease and limited corneal staining,” the authors of the study reported.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jing Li from the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology at the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center in Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, and was published online on September 11, 2024, in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked a double-blinded design. The laughter exercise required a greater time investment than the application of eye drops, which may affect adherence in the long run.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and High-level Hospital Construction Project. The authors declared receiving support from the funding agencies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mom’s Potato Salad
Outside of caffeine, I have very few addictions. One of them is “Midnight Diner.”
“Midnight Diner” is a quirky, sometimes funny, sometimes bittersweet, Japanese series on Netflix. It’s about a small diner in Tokyo, open only in the wee hours of the morning, its enigmatic owner/cook, and the eclectic patrons that come and go. Each is seeking a dish that means something to them.
One episode (spoiler alert, in case you’re planning to watch it) deals with the regulars realizing a fellow who frequently comes in and orders potato salad is secretly Japan’s most famous porn actor, Erect Oki. This revelation garners him the respect, awe, and envy of the other male patrons, though Mr. Oki would rather be left to his potato salad.
The jokes are there ... but as things develop, we learn he has the potato salad because it reminds him of his mother’s potato salad — and that he’s been cut off from his family for more than 20 years because of his career path. The potato salad is all he has left.
While preparing for a shoot, he learns his mother has Alzheimer’s disease, and immediately returns home. As they sit talking on the patio of a care center, she tells him about her son, who lives in Tokyo, and loves her potato salad. The show doesn’t make it clear if she ever remembers who he is.
In the darkening hallways of her mind, she asks his sister for help in making potato salad for her visitor. It’s too salty, though whether this is from the ingredients or his tears is also never stated.
The episode is a poignant reminder of how Alzheimer’s disease is a worldwide human problem. Not American. Not western. Not restricted by race, or ethnicity, or continent. It effects us all as a species, as families, and as individuals. No matter what our jobs or backgrounds are.
For those of us on this side of the desk, it’s a reminder that Yes, we have all kinds of new toys, but from a practical viewpoint it’s hard to say that we’ve made any major advances. I’m sure my drug reps will disagree with me, and I’m not saying any of the treatments of the last 28 years are worthless, but even now we’re still far from a cure, or even something that stops progression.
That’s not from lack of trying, either.
For all the jokes about his job, Mr. Oki is no different from any other children trying to hold onto their parents as the disease slowly takes them away.
I hope we have real answers, soon.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Outside of caffeine, I have very few addictions. One of them is “Midnight Diner.”
“Midnight Diner” is a quirky, sometimes funny, sometimes bittersweet, Japanese series on Netflix. It’s about a small diner in Tokyo, open only in the wee hours of the morning, its enigmatic owner/cook, and the eclectic patrons that come and go. Each is seeking a dish that means something to them.
One episode (spoiler alert, in case you’re planning to watch it) deals with the regulars realizing a fellow who frequently comes in and orders potato salad is secretly Japan’s most famous porn actor, Erect Oki. This revelation garners him the respect, awe, and envy of the other male patrons, though Mr. Oki would rather be left to his potato salad.
The jokes are there ... but as things develop, we learn he has the potato salad because it reminds him of his mother’s potato salad — and that he’s been cut off from his family for more than 20 years because of his career path. The potato salad is all he has left.
While preparing for a shoot, he learns his mother has Alzheimer’s disease, and immediately returns home. As they sit talking on the patio of a care center, she tells him about her son, who lives in Tokyo, and loves her potato salad. The show doesn’t make it clear if she ever remembers who he is.
In the darkening hallways of her mind, she asks his sister for help in making potato salad for her visitor. It’s too salty, though whether this is from the ingredients or his tears is also never stated.
The episode is a poignant reminder of how Alzheimer’s disease is a worldwide human problem. Not American. Not western. Not restricted by race, or ethnicity, or continent. It effects us all as a species, as families, and as individuals. No matter what our jobs or backgrounds are.
For those of us on this side of the desk, it’s a reminder that Yes, we have all kinds of new toys, but from a practical viewpoint it’s hard to say that we’ve made any major advances. I’m sure my drug reps will disagree with me, and I’m not saying any of the treatments of the last 28 years are worthless, but even now we’re still far from a cure, or even something that stops progression.
That’s not from lack of trying, either.
For all the jokes about his job, Mr. Oki is no different from any other children trying to hold onto their parents as the disease slowly takes them away.
I hope we have real answers, soon.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Outside of caffeine, I have very few addictions. One of them is “Midnight Diner.”
“Midnight Diner” is a quirky, sometimes funny, sometimes bittersweet, Japanese series on Netflix. It’s about a small diner in Tokyo, open only in the wee hours of the morning, its enigmatic owner/cook, and the eclectic patrons that come and go. Each is seeking a dish that means something to them.
One episode (spoiler alert, in case you’re planning to watch it) deals with the regulars realizing a fellow who frequently comes in and orders potato salad is secretly Japan’s most famous porn actor, Erect Oki. This revelation garners him the respect, awe, and envy of the other male patrons, though Mr. Oki would rather be left to his potato salad.
The jokes are there ... but as things develop, we learn he has the potato salad because it reminds him of his mother’s potato salad — and that he’s been cut off from his family for more than 20 years because of his career path. The potato salad is all he has left.
While preparing for a shoot, he learns his mother has Alzheimer’s disease, and immediately returns home. As they sit talking on the patio of a care center, she tells him about her son, who lives in Tokyo, and loves her potato salad. The show doesn’t make it clear if she ever remembers who he is.
In the darkening hallways of her mind, she asks his sister for help in making potato salad for her visitor. It’s too salty, though whether this is from the ingredients or his tears is also never stated.
The episode is a poignant reminder of how Alzheimer’s disease is a worldwide human problem. Not American. Not western. Not restricted by race, or ethnicity, or continent. It effects us all as a species, as families, and as individuals. No matter what our jobs or backgrounds are.
For those of us on this side of the desk, it’s a reminder that Yes, we have all kinds of new toys, but from a practical viewpoint it’s hard to say that we’ve made any major advances. I’m sure my drug reps will disagree with me, and I’m not saying any of the treatments of the last 28 years are worthless, but even now we’re still far from a cure, or even something that stops progression.
That’s not from lack of trying, either.
For all the jokes about his job, Mr. Oki is no different from any other children trying to hold onto their parents as the disease slowly takes them away.
I hope we have real answers, soon.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Playing the ‘Doctor’ Card: A Lesson in Three Hypotheticals
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
FDA Approves IL-13 inhibitor for Atopic Dermatitis
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The that is not well controlled, despite treatment with topical prescription therapies.
The recommended initial starting dose of lebrikizumab consists of 500 mg (two 250 mg injections) at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks until week 16 or later when adequate clinical response is achieved. Then, maintenance dosing is recommended with one monthly injection (250 mg every 4 weeks). Children aged 12-17 years must weigh at least 88 pounds (40 kg) to be eligible for lebrikizumab treatment.
According to a press release from Lilly, which has been developing lebrikizumab, approval was based on results from the ADvocate 1, ADvocate 2, and ADhere studies, which included over 1000 adults and children aged 12 and older with moderate to severe AD. The primary endpoint for these studies was evaluated at 16 weeks and measured clear or almost clear skin (IGA score of 0 or 1).
According to Lilly, 38% of people in ADvocate 1 and 2 who took lebrikizumab achieved clear or almost-clear skin at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those in the placebo arm, and 10% experienced these results as early as 4 weeks. Of those treated with lebrikizumab who experienced clear or almost-clear skin at week 16, 77% maintained those results at 1 year on the once-monthly dose. In addition, on average, 43% of those on lebrikizumab experienced relief of itch at 16 weeks, compared with 12% of those on placebo, according to the press release.
The most common side effects of lebrikizumab observed in the clinical trials include eye and eyelid inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching; injection-site reactions; and herpes zoster (shingles).
Lebrikizumab was approved in Japan in January 2024, and by the European Commission in 2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 14-Year-Old Female Presents With a Growth Under Her Toenail
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
BY XOCHITL LONGSTAFF, BS; ANGELINA LABIB, MD; AND DAWN EICHENFIELD, MD, PHD
Diagnosis: Subungual bony exostosis
The patient was referred to orthopedics for further evaluation and ultimately underwent excisional surgery. At her most recent follow-up visit with orthopedic surgery, her new nail was observed to be growing well.
Subungual exostosis, also known as Dupuytren’s exostosis, is a benign osteocartilaginous tumor that classically presents as a bony growth at the dorsal aspect of the distal phalanx of the great toe, near the nail bed. The pathogenesis remains unclear, but suggested etiologies include prior trauma, infection, and hereditary abnormalities.1
Clinically, lesions can be painful and may be associated with skin ulceration. The location at the dorsal distal great toe is a key distinguishing feature. Physical exam reveals a firm, fixed nodule with a hyperkeratotic smooth surface.2
Radiographic evaluation, particularly with a lateral view, is often diagnostic. The classic radiographic finding in subungual exostosis is an osseous structure connected to the distal phalanx, with a hazy periphery representing a fibrocartilage cap.
Treatment involves complete marginal excision. The complications from surgical excision are minimal, with the most common being recurrence.3 However, the recurrence rate is also generally low, around 4%.1
Ms. Longstaff is currently completing a research year as a Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at University of California San Diego (UCSD) Rady Children’s Hospital prior to finishing her final year at the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Labib is the Post-Doctoral Pediatric Clinical Research Fellow at UCSD Rady Children’s Hospital. Dr. Eichenfield is a dermatologist at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego and assistant clinical professor at UCSD.
References
1. Alabdullrahman LW et al. Osteochondroma. In: StatPearls [Internet]. 2024 Feb 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544296/#.
2. DaCambra MP et al. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Apr;472(4):1251-9. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4.
3. Womack ME et al. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2022 Mar 22;6(3):e21.00239. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00239.
A 14-year-old healthy female presents with a painful nodule under her great toenail. The nodule had been present for 2 months and there was no preceding trauma. Three days prior to presentation, her nail cracked and bled after bumping her toe. The toe is painful to palpation. Given the associated pain, the patient visited urgent care and was prescribed cephalexin and acetaminophen.
Physical examination reveals a skin-colored subungual nodule with hypertrophic tissue originating from the nail bed of the right great toe, but no thickening of the nail plate (Figures 1-3).