User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
‘Inflammasomes’ may play a role in obesity-related CRC
Protein complexes referred to as inflammasomes, part of the innate immune system that helps regulate inflammation, appear to be an important contributor to the development of obesity-related colon cancer, if not other cancers, according to new research.
“Population-based studies have shown that individuals who are prone to develop chronic inflammatory diseases are at increased risk of cancer, and inflammasomes play an important role in cancer development showing tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressive actions depending on the type of tumor, the specific inflammasome involved, and downstream effector molecules,” Victoria Catalan, PhD, Navarre Institute of Health Research, Pamplona, Spain, explained in an interview.
“So inflammasomes are not only implicated in obesity-associated colon cancer but their role may be more relevant in patients with obesity,” she added.
The new research was presented during the recent European Congress on Obesity, held virtually because of the pandemic. The meeting was presented by the European Association for the Study of Obesity.
Tissue samples
Tissue samples were obtained from 38 individuals who were lean and 61 individuals who were obese, and further divided into those with or without colon cancer.
A new finding from the study was that both obesity and colon cancer increase gene expression levels of the proteins NLRP3, NLRP6, ASC, and NOD2 in visceral adipose tissue (VAT), “suggesting that obesity-associated visceral adipose tissue inflammation creates a microenvironment favorable for colon cancer development,” Dr. Catalan elaborated.
Investigators also found upregulated levels of IL-1-beta in VAT from individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer, an observation that strengthens the hypothesis that inflammasome-dependent production of these cytokines may influence colon tumorigenesis, she added.
Dr. Catalan noted that her team has previously shown that blocking the expression of NLRP3 reduces VAT inflammation and significantly attenuates fibrosis that contributes to the development of obesity-associated comorbidities including type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
“Whether obesity has an impact on colon cancer through the enhancement of inflammation or via a direct mechanism is largely unclear, and the role of inflammasomes in cancer development is still controversial,” Dr. Catalan cautioned.
Nevertheless, the study showed that tissue samples from patients with colon cancer were associated with reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18. Dr. Catalan explained that NLRP6 is an important factor in the intestinal injury response which regulates aspects of healing inflammation. The same protein is also linked to epithelial integrity and the loss of NLRP6, and IL-18 – its main effector in the intestine – has been associated with increased mortality in colorectal cancer.
“Thus, reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18 in the colon from patients with colon cancer suggests an impaired regulation in the inflammatory cascade and a decrease in the integrity of the intestinal barrier,” Dr. Catalan suggested. The same experiment revealed that gene expression levels of adiponectin, an anti-inflammatory protein produced by adipose tissue, were similarly reduced in VAT in individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer.
Low levels of adiponectin have, in turn, been linked to a higher risk of colorectal cancer, Dr. Catalan noted. But it has also been recently shown that normal levels of adiponectin inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth. “It is very important to take into account that inflammasomes have contrasting roles in tumorigenesis, demonstrating both detrimental and beneficial effects,” Dr. Catalan observed.
The researchers speculated that NLRP3 agonists may enhance immune function and help reverse the immunosuppressive microenvironment promoted by VAT inflammation. For instance, activation of IL-18 signaling by inflammasomes regulates intestinal tissue repair following the development of colon cancer by triggering the process of re-epithelialization. Development of NLRP3 antagonists that can block the signaling pathway of IL-1-beta is currently an important area of research.
Similarly, the recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (Kineret, Amgen), the neutralizing IL-1-beta antibody canakinumab (Ilaris, Novartis), and the soluble decoy IL-1-beta receptor rilonacept (Arcalyst, Regeneron) are all being evaluated as a strategy to block IL-1-beta signaling, Dr. Catalan pointed out.
Various NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors are also being developed. “Pharmacological inhibitors of the NLRP3 pathway could offer a [viable] treatment option in a wide array of chronic and autoinflammatory diseases for which no adequate therapies currently exist,” Dr. Catalan speculated.
“Strategies to restore the functions of immunosurveillance of inflammasome components could represent an interesting target to identify and treat patients with obesity at increased risk for developing colon cancer,” the researchers said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Protein complexes referred to as inflammasomes, part of the innate immune system that helps regulate inflammation, appear to be an important contributor to the development of obesity-related colon cancer, if not other cancers, according to new research.
“Population-based studies have shown that individuals who are prone to develop chronic inflammatory diseases are at increased risk of cancer, and inflammasomes play an important role in cancer development showing tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressive actions depending on the type of tumor, the specific inflammasome involved, and downstream effector molecules,” Victoria Catalan, PhD, Navarre Institute of Health Research, Pamplona, Spain, explained in an interview.
“So inflammasomes are not only implicated in obesity-associated colon cancer but their role may be more relevant in patients with obesity,” she added.
The new research was presented during the recent European Congress on Obesity, held virtually because of the pandemic. The meeting was presented by the European Association for the Study of Obesity.
Tissue samples
Tissue samples were obtained from 38 individuals who were lean and 61 individuals who were obese, and further divided into those with or without colon cancer.
A new finding from the study was that both obesity and colon cancer increase gene expression levels of the proteins NLRP3, NLRP6, ASC, and NOD2 in visceral adipose tissue (VAT), “suggesting that obesity-associated visceral adipose tissue inflammation creates a microenvironment favorable for colon cancer development,” Dr. Catalan elaborated.
Investigators also found upregulated levels of IL-1-beta in VAT from individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer, an observation that strengthens the hypothesis that inflammasome-dependent production of these cytokines may influence colon tumorigenesis, she added.
Dr. Catalan noted that her team has previously shown that blocking the expression of NLRP3 reduces VAT inflammation and significantly attenuates fibrosis that contributes to the development of obesity-associated comorbidities including type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
“Whether obesity has an impact on colon cancer through the enhancement of inflammation or via a direct mechanism is largely unclear, and the role of inflammasomes in cancer development is still controversial,” Dr. Catalan cautioned.
Nevertheless, the study showed that tissue samples from patients with colon cancer were associated with reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18. Dr. Catalan explained that NLRP6 is an important factor in the intestinal injury response which regulates aspects of healing inflammation. The same protein is also linked to epithelial integrity and the loss of NLRP6, and IL-18 – its main effector in the intestine – has been associated with increased mortality in colorectal cancer.
“Thus, reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18 in the colon from patients with colon cancer suggests an impaired regulation in the inflammatory cascade and a decrease in the integrity of the intestinal barrier,” Dr. Catalan suggested. The same experiment revealed that gene expression levels of adiponectin, an anti-inflammatory protein produced by adipose tissue, were similarly reduced in VAT in individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer.
Low levels of adiponectin have, in turn, been linked to a higher risk of colorectal cancer, Dr. Catalan noted. But it has also been recently shown that normal levels of adiponectin inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth. “It is very important to take into account that inflammasomes have contrasting roles in tumorigenesis, demonstrating both detrimental and beneficial effects,” Dr. Catalan observed.
The researchers speculated that NLRP3 agonists may enhance immune function and help reverse the immunosuppressive microenvironment promoted by VAT inflammation. For instance, activation of IL-18 signaling by inflammasomes regulates intestinal tissue repair following the development of colon cancer by triggering the process of re-epithelialization. Development of NLRP3 antagonists that can block the signaling pathway of IL-1-beta is currently an important area of research.
Similarly, the recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (Kineret, Amgen), the neutralizing IL-1-beta antibody canakinumab (Ilaris, Novartis), and the soluble decoy IL-1-beta receptor rilonacept (Arcalyst, Regeneron) are all being evaluated as a strategy to block IL-1-beta signaling, Dr. Catalan pointed out.
Various NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors are also being developed. “Pharmacological inhibitors of the NLRP3 pathway could offer a [viable] treatment option in a wide array of chronic and autoinflammatory diseases for which no adequate therapies currently exist,” Dr. Catalan speculated.
“Strategies to restore the functions of immunosurveillance of inflammasome components could represent an interesting target to identify and treat patients with obesity at increased risk for developing colon cancer,” the researchers said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Protein complexes referred to as inflammasomes, part of the innate immune system that helps regulate inflammation, appear to be an important contributor to the development of obesity-related colon cancer, if not other cancers, according to new research.
“Population-based studies have shown that individuals who are prone to develop chronic inflammatory diseases are at increased risk of cancer, and inflammasomes play an important role in cancer development showing tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressive actions depending on the type of tumor, the specific inflammasome involved, and downstream effector molecules,” Victoria Catalan, PhD, Navarre Institute of Health Research, Pamplona, Spain, explained in an interview.
“So inflammasomes are not only implicated in obesity-associated colon cancer but their role may be more relevant in patients with obesity,” she added.
The new research was presented during the recent European Congress on Obesity, held virtually because of the pandemic. The meeting was presented by the European Association for the Study of Obesity.
Tissue samples
Tissue samples were obtained from 38 individuals who were lean and 61 individuals who were obese, and further divided into those with or without colon cancer.
A new finding from the study was that both obesity and colon cancer increase gene expression levels of the proteins NLRP3, NLRP6, ASC, and NOD2 in visceral adipose tissue (VAT), “suggesting that obesity-associated visceral adipose tissue inflammation creates a microenvironment favorable for colon cancer development,” Dr. Catalan elaborated.
Investigators also found upregulated levels of IL-1-beta in VAT from individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer, an observation that strengthens the hypothesis that inflammasome-dependent production of these cytokines may influence colon tumorigenesis, she added.
Dr. Catalan noted that her team has previously shown that blocking the expression of NLRP3 reduces VAT inflammation and significantly attenuates fibrosis that contributes to the development of obesity-associated comorbidities including type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
“Whether obesity has an impact on colon cancer through the enhancement of inflammation or via a direct mechanism is largely unclear, and the role of inflammasomes in cancer development is still controversial,” Dr. Catalan cautioned.
Nevertheless, the study showed that tissue samples from patients with colon cancer were associated with reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18. Dr. Catalan explained that NLRP6 is an important factor in the intestinal injury response which regulates aspects of healing inflammation. The same protein is also linked to epithelial integrity and the loss of NLRP6, and IL-18 – its main effector in the intestine – has been associated with increased mortality in colorectal cancer.
“Thus, reduced expression of NLRP6 and IL-18 in the colon from patients with colon cancer suggests an impaired regulation in the inflammatory cascade and a decrease in the integrity of the intestinal barrier,” Dr. Catalan suggested. The same experiment revealed that gene expression levels of adiponectin, an anti-inflammatory protein produced by adipose tissue, were similarly reduced in VAT in individuals who were obese as well as those with colon cancer.
Low levels of adiponectin have, in turn, been linked to a higher risk of colorectal cancer, Dr. Catalan noted. But it has also been recently shown that normal levels of adiponectin inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth. “It is very important to take into account that inflammasomes have contrasting roles in tumorigenesis, demonstrating both detrimental and beneficial effects,” Dr. Catalan observed.
The researchers speculated that NLRP3 agonists may enhance immune function and help reverse the immunosuppressive microenvironment promoted by VAT inflammation. For instance, activation of IL-18 signaling by inflammasomes regulates intestinal tissue repair following the development of colon cancer by triggering the process of re-epithelialization. Development of NLRP3 antagonists that can block the signaling pathway of IL-1-beta is currently an important area of research.
Similarly, the recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (Kineret, Amgen), the neutralizing IL-1-beta antibody canakinumab (Ilaris, Novartis), and the soluble decoy IL-1-beta receptor rilonacept (Arcalyst, Regeneron) are all being evaluated as a strategy to block IL-1-beta signaling, Dr. Catalan pointed out.
Various NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors are also being developed. “Pharmacological inhibitors of the NLRP3 pathway could offer a [viable] treatment option in a wide array of chronic and autoinflammatory diseases for which no adequate therapies currently exist,” Dr. Catalan speculated.
“Strategies to restore the functions of immunosurveillance of inflammasome components could represent an interesting target to identify and treat patients with obesity at increased risk for developing colon cancer,” the researchers said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Worse outcomes for patients with COPD and COVID-19
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ID doctors have the most paperwork, administrative demands
Infectious disease physicians are among the doctors carrying the largest burdens in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Perhaps not surprisingly, they were the specialists least likely to feel they were fairly compensated in the Medscape Infectious Diseases Physician Compensation Report 2021.
Only 44% said the pay was fair (down from 51% the prior year) compared with those at the high end – 79% in oncology, 69% in psychiatry, and 68% in plastic surgery who answered that way.
Income, which averaged $245,000, varied little from the previous year overall, according to the survey, but nearly one-third of ID physicians saw a decline in pay.
Again this year, ID physicians ranked near the bottom on the compensation spectrum. Pediatricians were lowest paid at $221,000. Plastic surgeons topped the chart at $526,000, followed by orthopedists at $511,000.
At the same time, the ID specialty is facing increasing shortages, a gap made even more visible in the pandemic. Medscape reported last year that nearly 80% of U.S. counties have no infectious disease specialists.
Thomas File Jr., MD, last year’s president of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, emphasized that COVID-19 is not the only threat that ID specialists have had to deal with or will have. He cited the threats that Zika and SARS posed in past years.
“COVID-19 illustrates the need for more trained ID specialists, because we know we’re going to be seeing more outbreaks in the future,” he said in an interview at the onset of the pandemic in March 2020.
Longer hours in pandemic
ID physicians’ hours generally increased during the pandemic, and they remain inflated by 8 hours per week (60 compared with 52 prepandemic) as the nation struggles to manage continuing COVID-19 infections. Physicians in critical care and public health and preventive medicine are seeing heavier workloads as well, by an average of 6-7 hours per week.
At the same time, ID physicians spent the most time of physicians in all specialties on paperwork and administrative tasks. Those tasks, which include electronic health record entry and clinical reading, took ID doctors 24.2 hours a week, more the twice the hours spent by those in anesthesiology (10.1), ophthalmology (10.3), and radiology (11.6).
The 24.2 hours was a substantial increase from the last report, when ID physicians said they spent 18.5 hours on the tasks.
The survey asked about the most challenging part of the job. ID physicians reported “long hours” as number one followed by “having so many rules and regulations.”
Only 4% said the danger or risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients was the most challenging part.
The top two aspects of their work they deemed most rewarding were “being very good at what I do” (chosen by 33%) and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (31%).
Patient volume up 17%
ID physicians reported seeing 78 patients per week in this report compared with 66 prepandemic, a 17% increase. Conversely, pediatricians saw an 18% drop in patient visits, followed by dermatologists, orthopedists and otolaryngologists (all down about 15%).
Despite the challenges and dissatisfaction with pay, the great majority of ID physicians said they would choose both medicine (83%) and their specialty (89%, up from 85% last year) again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infectious disease physicians are among the doctors carrying the largest burdens in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Perhaps not surprisingly, they were the specialists least likely to feel they were fairly compensated in the Medscape Infectious Diseases Physician Compensation Report 2021.
Only 44% said the pay was fair (down from 51% the prior year) compared with those at the high end – 79% in oncology, 69% in psychiatry, and 68% in plastic surgery who answered that way.
Income, which averaged $245,000, varied little from the previous year overall, according to the survey, but nearly one-third of ID physicians saw a decline in pay.
Again this year, ID physicians ranked near the bottom on the compensation spectrum. Pediatricians were lowest paid at $221,000. Plastic surgeons topped the chart at $526,000, followed by orthopedists at $511,000.
At the same time, the ID specialty is facing increasing shortages, a gap made even more visible in the pandemic. Medscape reported last year that nearly 80% of U.S. counties have no infectious disease specialists.
Thomas File Jr., MD, last year’s president of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, emphasized that COVID-19 is not the only threat that ID specialists have had to deal with or will have. He cited the threats that Zika and SARS posed in past years.
“COVID-19 illustrates the need for more trained ID specialists, because we know we’re going to be seeing more outbreaks in the future,” he said in an interview at the onset of the pandemic in March 2020.
Longer hours in pandemic
ID physicians’ hours generally increased during the pandemic, and they remain inflated by 8 hours per week (60 compared with 52 prepandemic) as the nation struggles to manage continuing COVID-19 infections. Physicians in critical care and public health and preventive medicine are seeing heavier workloads as well, by an average of 6-7 hours per week.
At the same time, ID physicians spent the most time of physicians in all specialties on paperwork and administrative tasks. Those tasks, which include electronic health record entry and clinical reading, took ID doctors 24.2 hours a week, more the twice the hours spent by those in anesthesiology (10.1), ophthalmology (10.3), and radiology (11.6).
The 24.2 hours was a substantial increase from the last report, when ID physicians said they spent 18.5 hours on the tasks.
The survey asked about the most challenging part of the job. ID physicians reported “long hours” as number one followed by “having so many rules and regulations.”
Only 4% said the danger or risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients was the most challenging part.
The top two aspects of their work they deemed most rewarding were “being very good at what I do” (chosen by 33%) and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (31%).
Patient volume up 17%
ID physicians reported seeing 78 patients per week in this report compared with 66 prepandemic, a 17% increase. Conversely, pediatricians saw an 18% drop in patient visits, followed by dermatologists, orthopedists and otolaryngologists (all down about 15%).
Despite the challenges and dissatisfaction with pay, the great majority of ID physicians said they would choose both medicine (83%) and their specialty (89%, up from 85% last year) again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infectious disease physicians are among the doctors carrying the largest burdens in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Perhaps not surprisingly, they were the specialists least likely to feel they were fairly compensated in the Medscape Infectious Diseases Physician Compensation Report 2021.
Only 44% said the pay was fair (down from 51% the prior year) compared with those at the high end – 79% in oncology, 69% in psychiatry, and 68% in plastic surgery who answered that way.
Income, which averaged $245,000, varied little from the previous year overall, according to the survey, but nearly one-third of ID physicians saw a decline in pay.
Again this year, ID physicians ranked near the bottom on the compensation spectrum. Pediatricians were lowest paid at $221,000. Plastic surgeons topped the chart at $526,000, followed by orthopedists at $511,000.
At the same time, the ID specialty is facing increasing shortages, a gap made even more visible in the pandemic. Medscape reported last year that nearly 80% of U.S. counties have no infectious disease specialists.
Thomas File Jr., MD, last year’s president of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, emphasized that COVID-19 is not the only threat that ID specialists have had to deal with or will have. He cited the threats that Zika and SARS posed in past years.
“COVID-19 illustrates the need for more trained ID specialists, because we know we’re going to be seeing more outbreaks in the future,” he said in an interview at the onset of the pandemic in March 2020.
Longer hours in pandemic
ID physicians’ hours generally increased during the pandemic, and they remain inflated by 8 hours per week (60 compared with 52 prepandemic) as the nation struggles to manage continuing COVID-19 infections. Physicians in critical care and public health and preventive medicine are seeing heavier workloads as well, by an average of 6-7 hours per week.
At the same time, ID physicians spent the most time of physicians in all specialties on paperwork and administrative tasks. Those tasks, which include electronic health record entry and clinical reading, took ID doctors 24.2 hours a week, more the twice the hours spent by those in anesthesiology (10.1), ophthalmology (10.3), and radiology (11.6).
The 24.2 hours was a substantial increase from the last report, when ID physicians said they spent 18.5 hours on the tasks.
The survey asked about the most challenging part of the job. ID physicians reported “long hours” as number one followed by “having so many rules and regulations.”
Only 4% said the danger or risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients was the most challenging part.
The top two aspects of their work they deemed most rewarding were “being very good at what I do” (chosen by 33%) and “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (31%).
Patient volume up 17%
ID physicians reported seeing 78 patients per week in this report compared with 66 prepandemic, a 17% increase. Conversely, pediatricians saw an 18% drop in patient visits, followed by dermatologists, orthopedists and otolaryngologists (all down about 15%).
Despite the challenges and dissatisfaction with pay, the great majority of ID physicians said they would choose both medicine (83%) and their specialty (89%, up from 85% last year) again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA/ACC guidance on ethics, professionalism in cardiovascular care
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have issued a new report on medical ethics and professionalism in cardiovascular medicine.
The report addresses a variety of topics including diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; racial, ethnic and gender inequities; conflicts of interest; clinician well-being; data privacy; social justice; and modern health care delivery systems.
The 54-page report is based on the proceedings of the joint 2020 Consensus Conference on Professionalism and Ethics, held Oct. 19 and 20, 2020. It was published online May 11 in Circulation and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology .
The 2020 consensus conference on professionalism and ethics came at a time even more fraught than the eras of the three previous meetings on the same topics, held in 1989, 1997, and 2004, the writing group notes.
“We have seen the COVID-19 pandemic challenge the physical and economic health of the entire country, coupled with a series of national tragedies that have awakened the call for social justice,” conference cochair C. Michael Valentine, MD, said in a news release.
“There is no better time than now to review, evaluate, and take a fresh perspective on medical ethics and professionalism,” said Dr. Valentine, professor of medicine at the Heart and Vascular Center, University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“We hope this report will provide cardiovascular professionals and health systems with the recommendations and tools they need to address conflicts of interest; racial, ethnic, and gender inequities; and improve diversity, inclusion, and wellness among our workforce,” Dr. Valentine added. “The majority of our members are now employed and must be engaged as the leaders for change in cardiovascular care.”
Road map to improve diversity, achieve allyship
The writing committee was made up of a diverse group of cardiologists, internists, and associated health care professionals and laypeople and was organized into five task forces, each addressing a specific topic: conflicts of interest; diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging; clinician well-being; patient autonomy, privacy, and social justice in health care; and modern health care delivery.
The report serves as a road map to achieve equity, inclusion, and belonging among cardiovascular professionals and calls for ongoing assessment of the professional culture and climate, focused on improving diversity and achieving effective allyship, the writing group says.
The report proposes continuous training to address individual, structural, and systemic racism, sexism, homophobia, classism, and ableism.
It offers recommendations for championing equity in patient care that include an annual review of practice records to look for differences in patient treatment by race, ethnicity, zip code, and primary language.
The report calls for a foundation of training in allyship and antiracism as part of medical school course requirements and experiences: A required course on social justice, race, and racism as part of the first-year curriculum; school programs and professional organizations supporting students, trainees, and members in allyship and antiracism action; and facilitating immersion and partnership with surrounding communities.
“As much as 80% of a person’s health is determined by the social and economic conditions of their environment,” consensus cochair Ivor Benjamin, MD, said in the release.
“To achieve social justice and mitigate health disparities, we must go to the margins and shift our discussions to be inclusive of populations such as rural and marginalized groups from the perspective of health equity lens for all,” said Dr. Benjamin, professor of medicine, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
The report also highlights the need for psychosocial support of the cardiovascular community and recommends that health care organizations prioritize regular assessment of clinicians’ well-being and engagement.
It also recommends addressing the well-being of trainees in postgraduate training programs and calls for an ombudsman program that allows for confidential reporting of mistreatment and access to support.
The report also highlights additional opportunities to:
- improve the efficiency of health information technology, such as electronic health records, and reduce the administrative burden
- identify and assist clinicians who experience mental health conditions, , or
- emphasize patient autonomy using shared decision-making and patient-centered care that is supportive of the individual patient’s values
- increase privacy protections for patient data used in research
- maintain integrity as new ways of delivering care, such as telemedicine, team-based care approaches, and physician-owned specialty centers emerge
- perform routine audits of electronic health records to promote optimal patient care, as well as ethical medical practice
- expand and make mandatory the reporting of intellectual or associational interests in addition to relationships with industry
The report’s details and recommendations will be presented and discussed Saturday, May 15, at 8:00 AM ET, during ACC.21. The session is titled Diversity and Equity: The Means to Expand Inclusion and Belonging.
The AHA will present a live webinar and six-episode podcast series (available on demand) to highlight the report’s details, dialogue, and actionable steps for cardiovascular and health care professionals, researchers, and educators.
This research had no commercial funding. The list of 40 volunteer committee members and coauthors, including their disclosures, are listed in the original report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 in children: Weekly cases drop to 6-month low
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
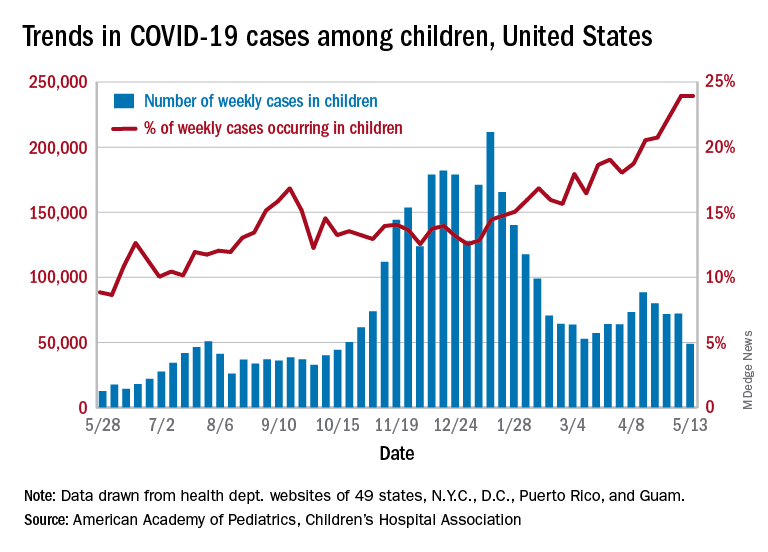
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Dr. Fauci: Extraordinary challenges, scientific triumphs with COVID-19
“Vaccines have been the bright light of this extraordinary challenge that we’ve gone through,” said Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
In an address for the opening ceremony of the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, Dr. Fauci emphasized the role of basic and clinical research and government support for science in helping turn the tide of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“A few weeks ago, I wrote an editorial in Science, because there was some misunderstanding about how and why we were able to go from a realization of a new pathogen in January of 2020, to getting doses of vaccines in the arms of individuals – a highly efficacious vaccine – 11 months later. Truly, an unprecedented accomplishment,” he said.
“But as I said in the editorial, the speed and efficiency with which these highly efficacious vaccines were developed, and their potential for saving millions of lives, are due to an extraordinary multidisciplinary effort, involving basic, preclinical, and clinical science that had been underway – out of the spotlight – for decades and decades before the unfolding of the COVID-19 pandemic, a fact that very few people really appreciate: namely, the importance of investment in biomedical research.”
The general addresses the troops
Perhaps no other audience is so well suited to receive Dr. Fauci’s speech as those who are currently attending (virtually) the ATS conference, including researchers who scrutinize the virus from every angle to describe its workings and identify its vulnerabilities, epidemiologists who study viral transmission and look for ways to thwart it, public health workers who fan out to communities across the country to push vaccine acceptance, and clinicians who specialize in critical care and pulmonary medicine, many of whom staff the respiratory floors and intensive care units where the most severely ill patients are treated.
Speaking about the lessons learned and challenges remaining from the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci briefly reviewed the epidemiology, virology and transmission, diagnostics, and clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 infections and the therapeutics and vaccines for COVID-19.
Epidemiology
The pandemic began in December 2019 with recognition of a novel type of pneumonia in the Wuhan District of Central China, Dr. Fauci noted.
“Very quickly thereafter, in the first week of January 2020, the Chinese identified a new strain of coronavirus as [the] source of the outbreak. Fast forward to where we are right now: We have experienced and are experiencing the most devastating pandemic of a respiratory illness in the last 102 years, with already approximately 160 million individuals having been infected – and this is clearly a gross undercounting – and also 3.3 million deaths, again, very likely an undercounting,” he said.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of May 9, 2021, there were approximately 32.5 million cases of COVID-19 and 578,520 deaths in the United States. Those cases and deaths occurred largely in three surges in the United States, in early spring, early summer, and late fall of 2020.
Virology and transmission
SARS-CoV-2 is a beta-coronavirus in the same subgenus as SARS-CoV-1 and some bat coronaviruses, Dr. Fauci explained. The viral genome is large, about 30,000 kilobases, and it has four structural proteins, most importantly the S or “spike” protein that allows the virus to attach to and fuse with cell membranes by binding to the ACE2 receptor on tissues in the upper and lower respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, and other organ systems.
The virus is transmitted mainly through exposure to respiratory droplets within 6 feet of an infected person, or sometimes through droplets or particles that remain in the air over time and various distances.
Contact with contaminated surfaces, once feared as a means of transmission, is now understood to be less common.
The virus has been detected in stool, blood, semen, and ocular secretions, although the role of transmission through these sources is still unknown.
“Some very interesting characteristics of this virus, really quite unique compared to other viruses, certainly other respiratory viruses, is [that] about a third to 40% of people who are infected never develop any symptoms,” Dr. Fauci said. “Importantly, and very problematic to what we do to contain it – particularly with regard to identification, isolation, and contract tracing – between 50% and 60% of the transmissions occur either from someone who will never develop symptoms, or someone in the presymptomatic phase of disease.”
The fundamentals of preventing acquisition and transmission are as familiar to most Americans now as the Pledge of Allegiance: universal mask wearing, physical distancing, avoiding crowds and congregate settings, preference for outdoor over indoor settings, and frequent hand washing, he noted.
Diagnostics
Tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection fall into three basic categories: molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that are highly specific and highly sensitive for actual infections, antigen tests that detect the viral protein rather than the nucleic acids, and antibody tests to detect serum proteins made in response to viral infection.
Antigen testing is used largely for broader surveillance of groups of individuals to detect viral penetrance within that group, Dr. Fauci noted.
Clinical course
The clinical course of COVID-19 has some interesting characteristics but is not substantially different from a flu-like syndrome, Dr. Fauci said.
Symptoms and signs common to both types of infections include fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, dyspnea, and myalgias, but the loss of smell and/or taste preceding the onset of respiratory symptoms is a unique feature of COVID-19.
Dr. Fauci cited data on more than 44,000 individuals with confirmed COVID-19 in China that showed that a large majority (81%) of cases were mild or moderate in nature, but 14% of patients experienced severe disease, and 5% were critically ill. The case-fatality rate in this study was 2.3%.
People at increased risk for severe disease include older adults and those of any age with certain comorbidities.
Manifestations of severe COVID-19 infections in adults can include neurological disorders, hyperinflammation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cardiac dysfunction, hypercoagulability, and acute kidney injury.
In children, COVID-19 has been associated with a multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) similar to Kawasaki disease.
In a substantial number of cases, the effects of COVID-19 can linger for 6 months or longer, Dr. Fauci said, pointing to a study from the University of Washington in Seattle.
Investigators there found that approximately 30% of patients enrolled at their center reported persistent symptoms for as long as 9 months after the initial illness, with fatigue as the most commonly reported symptom. One-third of outpatients with mild disease also reported persistent symptoms.
Therapeutics
Therapeutics that are either approved by the Food and Drug Administration, have emergency use authorization, or are in clinical trials for early or moderate disease include remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead Sciences), monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, antiviral agents, hyperimmune globulin, anticoagulants, and immunomodulators.
Options for moderate to severe to advanced disease include dexamethasone, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly and Company) plus remdesivir, and immunomodulators such as infliximab (Remicade, Janssen Biotech), and biosimilars.
Vaccines
Finally, Dr. Fauci reviewed the current state of vaccines, including the three with emergency use authorization from the FDA as of this writing: two nucleic acid, messenger RNA-based (mRNA) vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, and an adenoviral vector-based vaccine from Johnson & Johnson.
Other vaccines in development or in use elsewhere in the world include recombinant protein and adjuvant approaches by GlaxoSmithKline and Sanofi (in a phase 2 clinical trial launched in February 2021) and by Novavax.
The three vaccines in use in the United States were highly efficacious in both clinical trials, with efficacy of about 95% for the mRNA vaccines and 67% for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The real-world performance of these vaccines has been even more impressive, however.
For example, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had 72% efficacy at preventing moderate to severe COVID 19 in the United States, 68% in Brazil, and 64% in South Africa, and 85% efficacy against severe disease across all regions studied, Dr. Fauci said.
He cited a study of 22,234 employees of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who were vaccinated under a program started on Dec. 15, 2020. The COVID-19 infection rate among these vaccinated employees was 0.05%.
Dr. Fauci recounted the experience in Israel, where the highly transmissible B.1.1.7 strain of SARS-CoV-2 is predominant. A chart of the progress shows clearly that as the vaccine doses delivered steadily increased, the number of COVID-19 cases began a precipitous decline.
Horse race
Fittingly for a speech presented on the day that the Preakness Stakes – the second leg in thoroughbred racing’s Triple Crown – was run, Dr. Fauci closed with a cartoon showing two racehorses, labeled “SARS-CoV-2” and “Vaccines,” nearly neck-and-neck, but with vaccines having a slight lead.
“We are in a race against the virus. The vaccines, and the virus: If we vaccinate the overwhelming proportion of our population, we will without a doubt be able to crush the outbreak in the same way as we have done with other viral-borne diseases like measles, smallpox, and polio.
“So, the message is: Get vaccinated,” he concluded.
“Vaccines have been the bright light of this extraordinary challenge that we’ve gone through,” said Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
In an address for the opening ceremony of the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, Dr. Fauci emphasized the role of basic and clinical research and government support for science in helping turn the tide of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“A few weeks ago, I wrote an editorial in Science, because there was some misunderstanding about how and why we were able to go from a realization of a new pathogen in January of 2020, to getting doses of vaccines in the arms of individuals – a highly efficacious vaccine – 11 months later. Truly, an unprecedented accomplishment,” he said.
“But as I said in the editorial, the speed and efficiency with which these highly efficacious vaccines were developed, and their potential for saving millions of lives, are due to an extraordinary multidisciplinary effort, involving basic, preclinical, and clinical science that had been underway – out of the spotlight – for decades and decades before the unfolding of the COVID-19 pandemic, a fact that very few people really appreciate: namely, the importance of investment in biomedical research.”
The general addresses the troops
Perhaps no other audience is so well suited to receive Dr. Fauci’s speech as those who are currently attending (virtually) the ATS conference, including researchers who scrutinize the virus from every angle to describe its workings and identify its vulnerabilities, epidemiologists who study viral transmission and look for ways to thwart it, public health workers who fan out to communities across the country to push vaccine acceptance, and clinicians who specialize in critical care and pulmonary medicine, many of whom staff the respiratory floors and intensive care units where the most severely ill patients are treated.
Speaking about the lessons learned and challenges remaining from the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci briefly reviewed the epidemiology, virology and transmission, diagnostics, and clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 infections and the therapeutics and vaccines for COVID-19.
Epidemiology
The pandemic began in December 2019 with recognition of a novel type of pneumonia in the Wuhan District of Central China, Dr. Fauci noted.
“Very quickly thereafter, in the first week of January 2020, the Chinese identified a new strain of coronavirus as [the] source of the outbreak. Fast forward to where we are right now: We have experienced and are experiencing the most devastating pandemic of a respiratory illness in the last 102 years, with already approximately 160 million individuals having been infected – and this is clearly a gross undercounting – and also 3.3 million deaths, again, very likely an undercounting,” he said.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of May 9, 2021, there were approximately 32.5 million cases of COVID-19 and 578,520 deaths in the United States. Those cases and deaths occurred largely in three surges in the United States, in early spring, early summer, and late fall of 2020.
Virology and transmission
SARS-CoV-2 is a beta-coronavirus in the same subgenus as SARS-CoV-1 and some bat coronaviruses, Dr. Fauci explained. The viral genome is large, about 30,000 kilobases, and it has four structural proteins, most importantly the S or “spike” protein that allows the virus to attach to and fuse with cell membranes by binding to the ACE2 receptor on tissues in the upper and lower respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, and other organ systems.
The virus is transmitted mainly through exposure to respiratory droplets within 6 feet of an infected person, or sometimes through droplets or particles that remain in the air over time and various distances.
Contact with contaminated surfaces, once feared as a means of transmission, is now understood to be less common.
The virus has been detected in stool, blood, semen, and ocular secretions, although the role of transmission through these sources is still unknown.
“Some very interesting characteristics of this virus, really quite unique compared to other viruses, certainly other respiratory viruses, is [that] about a third to 40% of people who are infected never develop any symptoms,” Dr. Fauci said. “Importantly, and very problematic to what we do to contain it – particularly with regard to identification, isolation, and contract tracing – between 50% and 60% of the transmissions occur either from someone who will never develop symptoms, or someone in the presymptomatic phase of disease.”
The fundamentals of preventing acquisition and transmission are as familiar to most Americans now as the Pledge of Allegiance: universal mask wearing, physical distancing, avoiding crowds and congregate settings, preference for outdoor over indoor settings, and frequent hand washing, he noted.
Diagnostics
Tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection fall into three basic categories: molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that are highly specific and highly sensitive for actual infections, antigen tests that detect the viral protein rather than the nucleic acids, and antibody tests to detect serum proteins made in response to viral infection.
Antigen testing is used largely for broader surveillance of groups of individuals to detect viral penetrance within that group, Dr. Fauci noted.
Clinical course
The clinical course of COVID-19 has some interesting characteristics but is not substantially different from a flu-like syndrome, Dr. Fauci said.
Symptoms and signs common to both types of infections include fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, dyspnea, and myalgias, but the loss of smell and/or taste preceding the onset of respiratory symptoms is a unique feature of COVID-19.
Dr. Fauci cited data on more than 44,000 individuals with confirmed COVID-19 in China that showed that a large majority (81%) of cases were mild or moderate in nature, but 14% of patients experienced severe disease, and 5% were critically ill. The case-fatality rate in this study was 2.3%.
People at increased risk for severe disease include older adults and those of any age with certain comorbidities.
Manifestations of severe COVID-19 infections in adults can include neurological disorders, hyperinflammation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cardiac dysfunction, hypercoagulability, and acute kidney injury.
In children, COVID-19 has been associated with a multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) similar to Kawasaki disease.
In a substantial number of cases, the effects of COVID-19 can linger for 6 months or longer, Dr. Fauci said, pointing to a study from the University of Washington in Seattle.
Investigators there found that approximately 30% of patients enrolled at their center reported persistent symptoms for as long as 9 months after the initial illness, with fatigue as the most commonly reported symptom. One-third of outpatients with mild disease also reported persistent symptoms.
Therapeutics
Therapeutics that are either approved by the Food and Drug Administration, have emergency use authorization, or are in clinical trials for early or moderate disease include remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead Sciences), monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, antiviral agents, hyperimmune globulin, anticoagulants, and immunomodulators.
Options for moderate to severe to advanced disease include dexamethasone, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly and Company) plus remdesivir, and immunomodulators such as infliximab (Remicade, Janssen Biotech), and biosimilars.
Vaccines
Finally, Dr. Fauci reviewed the current state of vaccines, including the three with emergency use authorization from the FDA as of this writing: two nucleic acid, messenger RNA-based (mRNA) vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, and an adenoviral vector-based vaccine from Johnson & Johnson.
Other vaccines in development or in use elsewhere in the world include recombinant protein and adjuvant approaches by GlaxoSmithKline and Sanofi (in a phase 2 clinical trial launched in February 2021) and by Novavax.
The three vaccines in use in the United States were highly efficacious in both clinical trials, with efficacy of about 95% for the mRNA vaccines and 67% for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The real-world performance of these vaccines has been even more impressive, however.
For example, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had 72% efficacy at preventing moderate to severe COVID 19 in the United States, 68% in Brazil, and 64% in South Africa, and 85% efficacy against severe disease across all regions studied, Dr. Fauci said.
He cited a study of 22,234 employees of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who were vaccinated under a program started on Dec. 15, 2020. The COVID-19 infection rate among these vaccinated employees was 0.05%.
Dr. Fauci recounted the experience in Israel, where the highly transmissible B.1.1.7 strain of SARS-CoV-2 is predominant. A chart of the progress shows clearly that as the vaccine doses delivered steadily increased, the number of COVID-19 cases began a precipitous decline.
Horse race
Fittingly for a speech presented on the day that the Preakness Stakes – the second leg in thoroughbred racing’s Triple Crown – was run, Dr. Fauci closed with a cartoon showing two racehorses, labeled “SARS-CoV-2” and “Vaccines,” nearly neck-and-neck, but with vaccines having a slight lead.
“We are in a race against the virus. The vaccines, and the virus: If we vaccinate the overwhelming proportion of our population, we will without a doubt be able to crush the outbreak in the same way as we have done with other viral-borne diseases like measles, smallpox, and polio.
“So, the message is: Get vaccinated,” he concluded.
“Vaccines have been the bright light of this extraordinary challenge that we’ve gone through,” said Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
In an address for the opening ceremony of the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, Dr. Fauci emphasized the role of basic and clinical research and government support for science in helping turn the tide of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“A few weeks ago, I wrote an editorial in Science, because there was some misunderstanding about how and why we were able to go from a realization of a new pathogen in January of 2020, to getting doses of vaccines in the arms of individuals – a highly efficacious vaccine – 11 months later. Truly, an unprecedented accomplishment,” he said.
“But as I said in the editorial, the speed and efficiency with which these highly efficacious vaccines were developed, and their potential for saving millions of lives, are due to an extraordinary multidisciplinary effort, involving basic, preclinical, and clinical science that had been underway – out of the spotlight – for decades and decades before the unfolding of the COVID-19 pandemic, a fact that very few people really appreciate: namely, the importance of investment in biomedical research.”
The general addresses the troops
Perhaps no other audience is so well suited to receive Dr. Fauci’s speech as those who are currently attending (virtually) the ATS conference, including researchers who scrutinize the virus from every angle to describe its workings and identify its vulnerabilities, epidemiologists who study viral transmission and look for ways to thwart it, public health workers who fan out to communities across the country to push vaccine acceptance, and clinicians who specialize in critical care and pulmonary medicine, many of whom staff the respiratory floors and intensive care units where the most severely ill patients are treated.
Speaking about the lessons learned and challenges remaining from the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci briefly reviewed the epidemiology, virology and transmission, diagnostics, and clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 infections and the therapeutics and vaccines for COVID-19.
Epidemiology
The pandemic began in December 2019 with recognition of a novel type of pneumonia in the Wuhan District of Central China, Dr. Fauci noted.
“Very quickly thereafter, in the first week of January 2020, the Chinese identified a new strain of coronavirus as [the] source of the outbreak. Fast forward to where we are right now: We have experienced and are experiencing the most devastating pandemic of a respiratory illness in the last 102 years, with already approximately 160 million individuals having been infected – and this is clearly a gross undercounting – and also 3.3 million deaths, again, very likely an undercounting,” he said.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of May 9, 2021, there were approximately 32.5 million cases of COVID-19 and 578,520 deaths in the United States. Those cases and deaths occurred largely in three surges in the United States, in early spring, early summer, and late fall of 2020.
Virology and transmission
SARS-CoV-2 is a beta-coronavirus in the same subgenus as SARS-CoV-1 and some bat coronaviruses, Dr. Fauci explained. The viral genome is large, about 30,000 kilobases, and it has four structural proteins, most importantly the S or “spike” protein that allows the virus to attach to and fuse with cell membranes by binding to the ACE2 receptor on tissues in the upper and lower respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, and other organ systems.
The virus is transmitted mainly through exposure to respiratory droplets within 6 feet of an infected person, or sometimes through droplets or particles that remain in the air over time and various distances.
Contact with contaminated surfaces, once feared as a means of transmission, is now understood to be less common.
The virus has been detected in stool, blood, semen, and ocular secretions, although the role of transmission through these sources is still unknown.
“Some very interesting characteristics of this virus, really quite unique compared to other viruses, certainly other respiratory viruses, is [that] about a third to 40% of people who are infected never develop any symptoms,” Dr. Fauci said. “Importantly, and very problematic to what we do to contain it – particularly with regard to identification, isolation, and contract tracing – between 50% and 60% of the transmissions occur either from someone who will never develop symptoms, or someone in the presymptomatic phase of disease.”
The fundamentals of preventing acquisition and transmission are as familiar to most Americans now as the Pledge of Allegiance: universal mask wearing, physical distancing, avoiding crowds and congregate settings, preference for outdoor over indoor settings, and frequent hand washing, he noted.
Diagnostics
Tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection fall into three basic categories: molecular tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that are highly specific and highly sensitive for actual infections, antigen tests that detect the viral protein rather than the nucleic acids, and antibody tests to detect serum proteins made in response to viral infection.
Antigen testing is used largely for broader surveillance of groups of individuals to detect viral penetrance within that group, Dr. Fauci noted.
Clinical course
The clinical course of COVID-19 has some interesting characteristics but is not substantially different from a flu-like syndrome, Dr. Fauci said.
Symptoms and signs common to both types of infections include fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, dyspnea, and myalgias, but the loss of smell and/or taste preceding the onset of respiratory symptoms is a unique feature of COVID-19.
Dr. Fauci cited data on more than 44,000 individuals with confirmed COVID-19 in China that showed that a large majority (81%) of cases were mild or moderate in nature, but 14% of patients experienced severe disease, and 5% were critically ill. The case-fatality rate in this study was 2.3%.
People at increased risk for severe disease include older adults and those of any age with certain comorbidities.
Manifestations of severe COVID-19 infections in adults can include neurological disorders, hyperinflammation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, cardiac dysfunction, hypercoagulability, and acute kidney injury.
In children, COVID-19 has been associated with a multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) similar to Kawasaki disease.
In a substantial number of cases, the effects of COVID-19 can linger for 6 months or longer, Dr. Fauci said, pointing to a study from the University of Washington in Seattle.
Investigators there found that approximately 30% of patients enrolled at their center reported persistent symptoms for as long as 9 months after the initial illness, with fatigue as the most commonly reported symptom. One-third of outpatients with mild disease also reported persistent symptoms.
Therapeutics
Therapeutics that are either approved by the Food and Drug Administration, have emergency use authorization, or are in clinical trials for early or moderate disease include remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead Sciences), monoclonal antibodies, convalescent plasma, antiviral agents, hyperimmune globulin, anticoagulants, and immunomodulators.
Options for moderate to severe to advanced disease include dexamethasone, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly and Company) plus remdesivir, and immunomodulators such as infliximab (Remicade, Janssen Biotech), and biosimilars.
Vaccines
Finally, Dr. Fauci reviewed the current state of vaccines, including the three with emergency use authorization from the FDA as of this writing: two nucleic acid, messenger RNA-based (mRNA) vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, and an adenoviral vector-based vaccine from Johnson & Johnson.
Other vaccines in development or in use elsewhere in the world include recombinant protein and adjuvant approaches by GlaxoSmithKline and Sanofi (in a phase 2 clinical trial launched in February 2021) and by Novavax.
The three vaccines in use in the United States were highly efficacious in both clinical trials, with efficacy of about 95% for the mRNA vaccines and 67% for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The real-world performance of these vaccines has been even more impressive, however.
For example, the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had 72% efficacy at preventing moderate to severe COVID 19 in the United States, 68% in Brazil, and 64% in South Africa, and 85% efficacy against severe disease across all regions studied, Dr. Fauci said.
He cited a study of 22,234 employees of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who were vaccinated under a program started on Dec. 15, 2020. The COVID-19 infection rate among these vaccinated employees was 0.05%.
Dr. Fauci recounted the experience in Israel, where the highly transmissible B.1.1.7 strain of SARS-CoV-2 is predominant. A chart of the progress shows clearly that as the vaccine doses delivered steadily increased, the number of COVID-19 cases began a precipitous decline.
Horse race
Fittingly for a speech presented on the day that the Preakness Stakes – the second leg in thoroughbred racing’s Triple Crown – was run, Dr. Fauci closed with a cartoon showing two racehorses, labeled “SARS-CoV-2” and “Vaccines,” nearly neck-and-neck, but with vaccines having a slight lead.
“We are in a race against the virus. The vaccines, and the virus: If we vaccinate the overwhelming proportion of our population, we will without a doubt be able to crush the outbreak in the same way as we have done with other viral-borne diseases like measles, smallpox, and polio.
“So, the message is: Get vaccinated,” he concluded.
Internists’ patient visits rebound to near pre-COVID norms: Pay down slightly from previous year
Internists are seeing only 3% fewer patients than they did before the COVID-19 pandemic (72 per week on average now vs. 74 before the pandemic). Comparatively, for pediatricians, patient volume remains down 18%. Dermatologists, otolaryngologists, and orthopedists report that visits are down by about 15%.
The number of hours worked also rebounded for internists. In fact, some report working slightly more hours now than they did before the pandemic (52 hours a week, up from 50).
Pay for internists continues to hover near the bottom of the scale among specialties. In this year’s Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2021, internists averaged $248,000, down from $251,000 last year. Pediatricians were the lowest paid, at $221,000, followed by family physicians, at $236,000. Plastic surgeons made the most, at $526,000, followed by orthopedists, at $511,000.
It helped to be self-employed. These internists made $276,000 on average, compared with $238,000 for their employed counterparts.
Half say pay is fair
Internists are also near the bottom among specialists who feel they are fairly compensated. As in last year’s survey, just more than half of internists (52%) said they felt that they were fairly paid this year. By comparison, 79% of oncologists reported they were fairly compensated, which is on the high end regarding satisfaction, but only 44% of infectious diseases specialists felt that way.
Some indicators in the survey responses may help explain the dissatisfaction.
Internists are near the top in time spent on paperwork. On average, they spent 19.7 hours on paperwork and administration this year, up slightly from 18.5 last year. Infectious disease physicians spent the most time on those tasks (24.2 hours a week), and anesthesiologists spent the fewest, at 10.1 hours per week.
Administrative work was among many frustrations internists reported. The following are the top five most challenging aspects of the job, according to the respondents:
- Having so many rules and regulations (24%)
- Having to work long hours (16%)
- Dealing with difficult patients (16%)
- Working with electronic health records systems (11%)
- Danger/risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients (10%)
Conversely, the most rewarding aspects were “gratitude/relationships with patients” (31%); “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (26%); and “being very good at what I do” (20%).
More than one-third lost income
More than one-third of internists (36%) reported that they lost some income during the past year.
Among those who lost income, 81% said they expect income to return to prepandemic levels within 3 years. Half of that group expected the rebound would come within the next year.
Slightly more than one-third of internists said they would participate in the merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS), and 12% said they would participate in advanced alternative payment models. The rest either said they would participate in neither, or they hadn’t decided.
“The stakes for the Quality Payment Program – the program that incorporates MIPS – are high, with a 9% penalty applied to all Medicare reimbursement for failure to participate,” says Elizabeth Woodcock, MBA, CPC, president of the physician practice consulting firm Woodcock and Associates, in Atlanta, Georgia.
“With margins already slim,” she told this news organization, “most physicians can’t afford this massive penalty.”
If they could choose again, most internists (76%) said they would choose medicine, which was almost the same number as physicians overall who would pick medicine again. Oncologists (88%) and ophthalmologists (87%) were the specialists most likely to choose medicine again. Those in physical medicine and rehabilitation were least likely to choose medicine again, at 67%.
But asked about their specialty, internists’ enthusiasm decreased. Only 68% said that they would make that same choice again.
That was up considerably, however, from the 2015 survey: For that year, only 25% said they would choose internal medicine again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internists are seeing only 3% fewer patients than they did before the COVID-19 pandemic (72 per week on average now vs. 74 before the pandemic). Comparatively, for pediatricians, patient volume remains down 18%. Dermatologists, otolaryngologists, and orthopedists report that visits are down by about 15%.
The number of hours worked also rebounded for internists. In fact, some report working slightly more hours now than they did before the pandemic (52 hours a week, up from 50).
Pay for internists continues to hover near the bottom of the scale among specialties. In this year’s Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2021, internists averaged $248,000, down from $251,000 last year. Pediatricians were the lowest paid, at $221,000, followed by family physicians, at $236,000. Plastic surgeons made the most, at $526,000, followed by orthopedists, at $511,000.
It helped to be self-employed. These internists made $276,000 on average, compared with $238,000 for their employed counterparts.
Half say pay is fair
Internists are also near the bottom among specialists who feel they are fairly compensated. As in last year’s survey, just more than half of internists (52%) said they felt that they were fairly paid this year. By comparison, 79% of oncologists reported they were fairly compensated, which is on the high end regarding satisfaction, but only 44% of infectious diseases specialists felt that way.
Some indicators in the survey responses may help explain the dissatisfaction.
Internists are near the top in time spent on paperwork. On average, they spent 19.7 hours on paperwork and administration this year, up slightly from 18.5 last year. Infectious disease physicians spent the most time on those tasks (24.2 hours a week), and anesthesiologists spent the fewest, at 10.1 hours per week.
Administrative work was among many frustrations internists reported. The following are the top five most challenging aspects of the job, according to the respondents:
- Having so many rules and regulations (24%)
- Having to work long hours (16%)
- Dealing with difficult patients (16%)
- Working with electronic health records systems (11%)
- Danger/risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients (10%)
Conversely, the most rewarding aspects were “gratitude/relationships with patients” (31%); “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (26%); and “being very good at what I do” (20%).
More than one-third lost income
More than one-third of internists (36%) reported that they lost some income during the past year.
Among those who lost income, 81% said they expect income to return to prepandemic levels within 3 years. Half of that group expected the rebound would come within the next year.
Slightly more than one-third of internists said they would participate in the merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS), and 12% said they would participate in advanced alternative payment models. The rest either said they would participate in neither, or they hadn’t decided.
“The stakes for the Quality Payment Program – the program that incorporates MIPS – are high, with a 9% penalty applied to all Medicare reimbursement for failure to participate,” says Elizabeth Woodcock, MBA, CPC, president of the physician practice consulting firm Woodcock and Associates, in Atlanta, Georgia.
“With margins already slim,” she told this news organization, “most physicians can’t afford this massive penalty.”
If they could choose again, most internists (76%) said they would choose medicine, which was almost the same number as physicians overall who would pick medicine again. Oncologists (88%) and ophthalmologists (87%) were the specialists most likely to choose medicine again. Those in physical medicine and rehabilitation were least likely to choose medicine again, at 67%.
But asked about their specialty, internists’ enthusiasm decreased. Only 68% said that they would make that same choice again.
That was up considerably, however, from the 2015 survey: For that year, only 25% said they would choose internal medicine again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Internists are seeing only 3% fewer patients than they did before the COVID-19 pandemic (72 per week on average now vs. 74 before the pandemic). Comparatively, for pediatricians, patient volume remains down 18%. Dermatologists, otolaryngologists, and orthopedists report that visits are down by about 15%.
The number of hours worked also rebounded for internists. In fact, some report working slightly more hours now than they did before the pandemic (52 hours a week, up from 50).
Pay for internists continues to hover near the bottom of the scale among specialties. In this year’s Medscape Internist Compensation Report 2021, internists averaged $248,000, down from $251,000 last year. Pediatricians were the lowest paid, at $221,000, followed by family physicians, at $236,000. Plastic surgeons made the most, at $526,000, followed by orthopedists, at $511,000.
It helped to be self-employed. These internists made $276,000 on average, compared with $238,000 for their employed counterparts.
Half say pay is fair
Internists are also near the bottom among specialists who feel they are fairly compensated. As in last year’s survey, just more than half of internists (52%) said they felt that they were fairly paid this year. By comparison, 79% of oncologists reported they were fairly compensated, which is on the high end regarding satisfaction, but only 44% of infectious diseases specialists felt that way.
Some indicators in the survey responses may help explain the dissatisfaction.
Internists are near the top in time spent on paperwork. On average, they spent 19.7 hours on paperwork and administration this year, up slightly from 18.5 last year. Infectious disease physicians spent the most time on those tasks (24.2 hours a week), and anesthesiologists spent the fewest, at 10.1 hours per week.
Administrative work was among many frustrations internists reported. The following are the top five most challenging aspects of the job, according to the respondents:
- Having so many rules and regulations (24%)
- Having to work long hours (16%)
- Dealing with difficult patients (16%)
- Working with electronic health records systems (11%)
- Danger/risk associated with treating COVID-19 patients (10%)
Conversely, the most rewarding aspects were “gratitude/relationships with patients” (31%); “knowing that I’m making the world a better place” (26%); and “being very good at what I do” (20%).
More than one-third lost income
More than one-third of internists (36%) reported that they lost some income during the past year.
Among those who lost income, 81% said they expect income to return to prepandemic levels within 3 years. Half of that group expected the rebound would come within the next year.
Slightly more than one-third of internists said they would participate in the merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS), and 12% said they would participate in advanced alternative payment models. The rest either said they would participate in neither, or they hadn’t decided.
“The stakes for the Quality Payment Program – the program that incorporates MIPS – are high, with a 9% penalty applied to all Medicare reimbursement for failure to participate,” says Elizabeth Woodcock, MBA, CPC, president of the physician practice consulting firm Woodcock and Associates, in Atlanta, Georgia.
“With margins already slim,” she told this news organization, “most physicians can’t afford this massive penalty.”
If they could choose again, most internists (76%) said they would choose medicine, which was almost the same number as physicians overall who would pick medicine again. Oncologists (88%) and ophthalmologists (87%) were the specialists most likely to choose medicine again. Those in physical medicine and rehabilitation were least likely to choose medicine again, at 67%.
But asked about their specialty, internists’ enthusiasm decreased. Only 68% said that they would make that same choice again.
That was up considerably, however, from the 2015 survey: For that year, only 25% said they would choose internal medicine again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FIDELIO-DKD: Finerenone cuts new-onset AFib in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
Finerenone treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease was linked to a significant drop in the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation as a prespecified, exploratory endpoint of the FIDELIO-DKD pivotal trial that randomized more than 5,700 patients.
Treatment with finerenone linked with a 29% relative reduction compared with placebo in incident cases of atrial fibrillation (AFib), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The absolute reduction was modest, a 1.3% reduction from the 4.5% incidence rate on placebo to a 3.2% rate on finerenone during a median 2.6 years of follow-up. Concurrently with the report, the results appeared online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.079).
The analyses Dr. Filippatos presented also showed that whether or not patients had a history of AFib, there was no impact on either the primary benefit from finerenone treatment seen in FIDELIO-DKD, which was a significant 18% relative risk reduction compared with placebo in the combined rate of kidney failure, a 40% or greater decline from baseline in estimated glomerular filtration rate, or renal death.
Likewise, prior AFib status had no effect on the study’s key secondary endpoint, a significant 14% relative risk reduction in the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure.
The primary results from FIDELIO-DKD (Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease) appeared in a 2020 report (N Engl J Med. 2020 Dec 3;383[23];2219-29).
‘Side benefits can be very helpful’
“It’s important to know of finerenone’s benefits beyond the primary outcome of a trial because side benefits can be very helpful,” said Anne B. Curtis, MD, an electrophysiologist and professor and chair of medicine at the University of Buffalo (N.Y.) School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences. “It’s not a huge benefit, but this could be an added benefit for selected patients,” she said during a press briefing. “Background studies had shown favorable remodeling of the heart [by finerenone] that could affect AFib.”
Possible mitigating effects by finerenone on inflammation and fibrosis might also mediate the drug’s apparent effect on AFib, said Dr. Filippatos, professor of cardiology and director of the Heart Failure and Cardio-Oncology Clinic at Attikon University Hospital and the University of Athens.
He noted that additional data addressing a possible AFib effect of finerenone will emerge soon from the FIGARO-DKD trial, which enrolled patients similar to those in FIDELIO-DKD but with more moderate stages of kidney disease, and from the FINEARTS-HF trial, which is examining the effect of finerenone in patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of at least 40%.
“Heart failure and AFib go together tightly. It’s worth studying this specifically, so we can see whether there is an impact of finerenone on patients with heart failure who may not necessarily have kidney disease or diabetes,” Dr. Curtis said.
Hypothesis-generating findings
The new findings reported by Dr. Filippatos “should be considered hypothesis generating. Until we have more information, upstream therapies, including mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists [MRAs, the umbrella drug class that includes finerenone], should be used in appropriate patient populations based on defined benefits with the hope they will also reduce the development of AFib and atrial flutter over time,” Gerald V. Naccarelli, MD, and coauthors wrote in an editorial that accompanied the report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 May 17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.04.080).
The FIDELIO-DKD trial randomized 5,734 patients at 913 sites in 48 countries, including 461 patients with a history of AFib. The observed link of finerenone treatment with a reduced incidence of AFib appeared consistent regardless of patients’ age, sex, race, their kidney characteristics at baseline, baseline levels of systolic blood pressure, serum potassium, body mass index, A1c, or use of glucose-lowering medications.
Finerenone belongs to a new class of MRAs that have a nonsteroidal structure, in contrast with the MRAs spironolactone and eplerenone. This means that finerenone does not produce steroidal-associated adverse effects linked with certain other MRAs, such as gynecomastia, and may also differ in other actions.
FIDELIO-DKD was sponsored by Bayer, the company developing finerenone. Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from or participated in the direction of trials on behalf of Bayer, as well as for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Curtis is an adviser to and receives honoraria from St. Jude Medical, and receives honoraria from Medtronic. Dr. Naccarelli has been a consultant to Acesion, ARCA, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Milestone, Omeicos, and Sanofi. His coauthors had no disclosures.
FROM ACC 2021
Dapagliflozin misses as treatment for COVID-19 but leaves intriguing signal for benefit
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
In patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection, the sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin showed a trend for benefit relative to placebo on multiple outcomes, including the primary outcome of time to organ failure or death, according to results from the randomized DARE-19 trial.
Because of the failure to reach statistical significance, these results have no immediate relevance, but the trends support interest in further testing SGLT2 inhibitors in acute diseases posing a high risk for organ failure, according to Mikhail Kosiborod, MD.
In a trial that did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Kosiborod acknowledged that positive interpretations are speculative, but he does believe that there is one immediate take-home message.
“Our results do not support discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors in the setting of COVID-19 as long as patients are monitored,” said Dr. Kosiborod, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo.
At many institutions, it has been common to discontinue SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted with COVID-19. One reason was the concern that drugs in this class could exacerbate organ damage, particularly if they were to induced ketoacidosis. However, only 2 (0.003%) of 613 patients treated with dapagliflozin developed ketoacidosis, and the signal for organ protection overall, although not significant, was consistent.
“Numerically, fewer patients treated with dapagliflozin experienced organ failure and death, and this was consistent across systems, including the kidney,” Dr. Kosiborod said in presenting the study at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
Overall, the study suggests that, in the context of COVID-19, dapagliflozin did not show harm and might have potential benefit, he added.
DARE-19 was rapidly conceived, designed, and implemented during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on prior evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors “favorably affect a number of pathophysiologic pathways disrupted during acute illness” and that drugs in this class have provided organ protection in the context of heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and other cardiometabolic conditions, the study was designed to test the hypothesis that this mechanism might improve outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Kosiborod said.
The entry criteria included confirmed or suspected COVID-19 with an onset of 4 days of fewer and one additional risk factor, such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, hypertension, or type 2 diabetes. Patients with significant renal impairment or a history of diabetic ketoacidosis were excluded.
On top of standard treatments for COVID-19, patients were randomized to 10 mg dapagliflozin or placebo once daily. There were two primary endpoints. That of prevention was time to criteria for respiratory, cardiovascular, or renal organ failure or death. The second primary outcome, for recovery, was a hierarchical composite for four endpoints: death, organ failure, status at 30 days if hospitalized, and time to discharge if this occurred before day 30.
Of the 1,250 patients randomized at 95 sites in seven countries, 617 in the dapagliflozin group and 620 patients in the placebo group completed the study. Baseline characteristics, which included a mean of age of 62 years; types of comorbidities; and types of treatments were similar.
Results for two primary endpoints
The curves for the primary outcome of prevention had already separated by day 3 and continued to widen over the 30 days in which outcomes were compared. At the end of 30 days, 11.2% of the dapagliflozin group and 13.8% of the placebo group had an event. By hazard ratio, dapagliflozin was linked to 20% nonsignificant relative protection from events (hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.10).
The trend (P = .168) for the primary endpoint for prevention was reflected in the individual components. For dapagliflozin related to placebo, there were generally similar or greater reductions in new or worsening organ failure (HR, 0.80), cardiac decompensation (HR, 0.81), respiratory decompensation (HR, 0.85), and kidney decompensation (HR, 0.65). None were statistically significant, but the confidence intervals were tight with the upper end never exceeding 1.20.
Moreover, the relative risk reduction for all-cause mortality moved in the same direction (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.52-1.16).
In the hierarchical composite endpoint of recovery, there was no significant difference in the time to discharge, but again many recovery metrics numerically favored dapagliflozin with an overall difference producing a statistical trend (P = .14) similar to organ failure events and death.
In safety analyses, dapagliflozin consistently outperformed placebo across a broad array of safety measure, including any severe adverse event (65% vs. 82%), any adverse event with an outcome of death (32% vs. 48%), discontinuation caused by an adverse event (44% vs. 55%), and acute kidney injury (21% vs. 34%).
Data could fuel related studies
According to Ana Barac, MD, PhD, director of the cardio-oncology program in the Medstar Heart and Vascular Institute, Washington, these data are “thought provoking.” Although this was a negative trial, she said that it generates an “exciting hypothesis” about the potential of SGLT2 inhibitors to provide organ protection. She called for studies to pursue this path of research.
More immediately, Dr. Barac agreed that these data argue against stopping SGLT2 inhibitors in patients admitted to a hospital for COVID-19 infection.
“These data show that these drugs are not going to lead to harm, but they might lead to benefit,” she said.
For James Januzzi, MD, a cardiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, DARE-19 was perhaps most impressive because of its rigorous design and execution in the midst of a pandemic.
Over the past year, “the medical literature was flooded with grossly underpowered, poorly designed, single-center studies” yielding results that have been hard to interpret, Dr. Januzzi said. Despite the fact that this study failed to confirm its hypothesis, he said the investigators deserve praise for the quality of the work.
Dr. Januzzi also believes the study is not without clinically relevant findings, particularly the fact that dapagliflozin was associated with a lower rate of adverse events than placebo. This, at least, provides reassurance about the safety of this drug in the setting of COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Kosiborod reported financial relationships with more than 10 pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, which provided funding for DARE-19. Dr. Barac reported financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb and CTI BioPharma. Dr. Januzzi reported financial relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche.
FROM ACC 2021
FDA approves new treatment option for rare anemia
A rare, life-threatening anemia now has a new treatment option. The Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of pegcetacoplan (Empaveli) injection to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Pegcetacoplan is the first PNH treatment that binds to complement protein C3, according to the FDA announcement. Complement protein C3 is a key component of host immunity and defense.
Special concern
Because of the risk of severe side effects, the drug is available only through a restricted program under a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS). Serious infections can occur in patients taking pegcetacoplan that can become life-threatening or fatal if not treated early. According to the FDA, REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication, and only a few drugs require a REMS.
The most common other side effects are injection site reactions, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Pegcetacoplan was approved based upon a study of 80 patients with PNH and anemia who had been taking eculizumab, a previously approved treatment. During 16 weeks of treatment, patients in the pegcetacoplan group had an average increase in their hemoglobin of 2.4 g/dL, while patients in the eculizumab group had an average decrease in their hemoglobin of 1.5 g/dL.
About the disease
PNH is caused by gene mutations that affect red blood cells, causing them to be defective and susceptible to destruction by a patient’s own immune system. Red blood cells in people with these mutations are defective and can be destroyed by the immune system, causing anemia.
Other symptoms include blood clots and destruction of bone marrow. The disease affects 1-1.5 people per million, with diagnosis typically occurring around ages 35-40, and a median survival of only 10 years after diagnosis, according to the FDA.
A rare, life-threatening anemia now has a new treatment option. The Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of pegcetacoplan (Empaveli) injection to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Pegcetacoplan is the first PNH treatment that binds to complement protein C3, according to the FDA announcement. Complement protein C3 is a key component of host immunity and defense.
Special concern
Because of the risk of severe side effects, the drug is available only through a restricted program under a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS). Serious infections can occur in patients taking pegcetacoplan that can become life-threatening or fatal if not treated early. According to the FDA, REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication, and only a few drugs require a REMS.
The most common other side effects are injection site reactions, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Pegcetacoplan was approved based upon a study of 80 patients with PNH and anemia who had been taking eculizumab, a previously approved treatment. During 16 weeks of treatment, patients in the pegcetacoplan group had an average increase in their hemoglobin of 2.4 g/dL, while patients in the eculizumab group had an average decrease in their hemoglobin of 1.5 g/dL.
About the disease
PNH is caused by gene mutations that affect red blood cells, causing them to be defective and susceptible to destruction by a patient’s own immune system. Red blood cells in people with these mutations are defective and can be destroyed by the immune system, causing anemia.
Other symptoms include blood clots and destruction of bone marrow. The disease affects 1-1.5 people per million, with diagnosis typically occurring around ages 35-40, and a median survival of only 10 years after diagnosis, according to the FDA.
A rare, life-threatening anemia now has a new treatment option. The Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of pegcetacoplan (Empaveli) injection to treat adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Pegcetacoplan is the first PNH treatment that binds to complement protein C3, according to the FDA announcement. Complement protein C3 is a key component of host immunity and defense.
Special concern
Because of the risk of severe side effects, the drug is available only through a restricted program under a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS). Serious infections can occur in patients taking pegcetacoplan that can become life-threatening or fatal if not treated early. According to the FDA, REMS are designed to reinforce medication use behaviors and actions that support the safe use of that medication, and only a few drugs require a REMS.
The most common other side effects are injection site reactions, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
Pegcetacoplan was approved based upon a study of 80 patients with PNH and anemia who had been taking eculizumab, a previously approved treatment. During 16 weeks of treatment, patients in the pegcetacoplan group had an average increase in their hemoglobin of 2.4 g/dL, while patients in the eculizumab group had an average decrease in their hemoglobin of 1.5 g/dL.
About the disease
PNH is caused by gene mutations that affect red blood cells, causing them to be defective and susceptible to destruction by a patient’s own immune system. Red blood cells in people with these mutations are defective and can be destroyed by the immune system, causing anemia.
Other symptoms include blood clots and destruction of bone marrow. The disease affects 1-1.5 people per million, with diagnosis typically occurring around ages 35-40, and a median survival of only 10 years after diagnosis, according to the FDA.