User login
Medicare payments could get tougher for docs
More than 40 value-based payment models – from direct contracting to bundled payments – have been introduced into the Medicare program in the past 10 years, with the goal of improving care while lowering costs. Hopes were high that they would be successful.
Physicians could suffer a huge blow to their income.
Many of the value-based care models simply did not work as expected, said Seema Verma, head of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, at a recent HLTH Conference. “They are not producing the types of savings the taxpayers deserve,” Ms. Verma said.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPac) concluded that, while dozens of payment models were tested, most failed to generate net savings for Medicare. Even the most successful of the models produced only modest savings. MedPac elaborated: “The track record raises the question of whether changes to particular models or CMMI’s [Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation’s] broader strategies might be warranted.”
What will happen now, as government officials admit that their value-based programs haven’t worked? The value-based programs could become more stringent. Here’s what physicians will have to contend with.
More risk. Experts agree that risk – financial risk – will be a component of future programs. Two-sided risk is likely to be the norm. This means that both parties – the provider and the insurer – are at financial risk for the patients covered by the program.
For example, a plan with 50,000 beneficiary patients would estimate the cost of caring for those patients on the basis of multiple variables. If the actual cost is lower than anticipated, both parties share in the savings. However, both share in the loss if the cost of caring for their patient population exceeds expectations.
This may compel physicians to enhance efficiency and potentially limit the services provided to patients. Typically, however, the strategy is to make efforts to prevent services like ED visits and admissions by focusing on health maintenance.
In contrast to most current value-based models, which feature little to no downside risk for physicians, double-sided risk means physicians could lose money. The loss may incorporate a cap – 5%, for example – but programs may differ. Experts concur that double-sided risk will be a hallmark of future programs.
Better data. The majority of health care services are rendered via fee-for-service: Patients receive services and physicians are paid, yet little or no information about outcomes is exchanged between insurers and physicians.
Penny Noyes, president of Health Business Navigators and contract negotiator for physicians, is not a fan of the current crop of value-based programs and feels that data transparency is positive. Sound metrics can lead to improvement, she said, adding: “It’s not money that drives physicians to make decisions; it’s what’s in the best interest of their patients and their patients’ long-term care.”
Value-based programs can work but only if applicable data are developed and given to physicians so that they can better understand their current performance and how to improve.
Mandated participation. Participation in value-based programs has been voluntary, but that may have skewed the results, which were better than what typical practice would have shown. Acknowledging this may lead CMS to call for mandated participation as a component of future programs. Physicians may be brought into programs, if only to determine whether the models really work. To date, participation in the programs has been voluntary, but that may change in the future.
Innovation. The private insurance market may end up as a key player. Over the past 6 months, health insurers have either consolidated partnerships with telemedicine companies to provide no-cost care to beneficiaries or have launched their own initiatives.
Others are focused on bringing together patients and providers operating outside of the traditional health care system, such as Aetna’s merger with CVS which now offers retail-based acute care (MinuteClinic) and chronic care (HealthHUB). Still other payers are gambling with physician practice ownership, as in the case of United Healthcare’s OptumHealth, which now boasts around 50,000 physicians throughout the country.
New practice models are emerging in private practices as well. Physicians are embracing remote care, proactively managing care transitions, and seeking out more methods to keep patients healthy and at home.
Not much was expected from value-based plans
Many are not surprised that the value-based models did not produce impressive results. Ms. Noyes doubted that positive outcomes will be achieved for physicians in comparison with what could have been attained under fee-for-service arrangements with lower administrative costs.
While the Affordable Care Act attempted to encourage alternative reimbursement, it limits the maximum medical loss ratio (MLR) a payer could achieve. For many plans, that maximum was 85%. Simply put, at least $0.85 of each premium collected had to be paid in claims; the remaining $0.15 went to margin, claims, and other administrative costs. A payer with an 82% MLR then would have to rebate the 3% difference to enrollees.
But that’s not what occurred, according to Ms. Noyes. Because value-based payments to providers are considered a claims expense, an MLR ratio of 82% allowed the payer to distribute the 3% difference to providers as value-based payments. Ms. Noyes said: “That may sound good for the provider, but the result was essentially a freeze on the provider’s fee-for-service reimbursement with the prospect of getting value-based payments like ‘shared savings.’
“When the providers tried to increase their base fee-for-service rates just to match inflation, payers often advised that any future raises had to be earned through value-based programs,” Ms. Noyes added. The value-based formulas confuse providers because payments are often made for periods as far back as 18 months, and providers do not have data systems to reconcile their payer report cards retrospectively. The result is that providers tended to accept whatever amount the payer distributed.
Executives at Lumeris, a company that helps health systems participate successfully in value-based care, see potential in a newer approach to alternative payments, such as CMS’ Direct Contracting initiative. This voluntary payment model offers options tailored to several types of organizations that aim to reduce costs while preserving or enhancing the quality of care for Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries.
Jeff Smith, chief commercial officer for population health at Lumeris, explained that the Direct Contracting initiative can provide physicians with a more attractive option than prior value-based models because it adjusts for the complexity and fragility of patients with complex and chronic conditions. By allowing providers to participate in the savings generated, the initiative stands in stark contrast to what Mr. Smith described as the “shared savings to nothingness” experienced by providers in earlier-stage alternative payment models.
Physicians engaged with value-based programs like Direct Contracting are investing in nurses to aid with initiatives regarding health promotion and transitions of care. When a patient is discharged, for example, the nurse contacts the patient to discuss medications, schedule follow-up appointments, and so forth – tasks typically left to the patient (or caregiver) to navigate in the traditional system.
The initiative recognizes the importance of managing high-risk patients, those whom physicians identify as having an extraordinary number of ED visits and admissions. These patients, as well as so-called “rising-risk” patients, are targeted by nurses who proactively communicate with patients (and caregivers) to address patient’s needs, including social determinants of health.
Physicians who have a large load of patients in value-based programs are hiring social workers, pharmacists, and behavioral health experts to help. Of course, these personnel are costly, but that’s what the value-based programs aim to reimburse.
Still, the road ahead to value based is rocky and may not gain momentum for some time. Johns Hopkins University’s Doug Hough, PhD, an economist, recounts a government research study that sought to assess the university’s health system participation in a value-based payment program. While there were positive impacts on the program’s target population, Hough and his team discovered that the returns achieved by the optional model didn’t justify the health system’s financial support for it. The increasingly indebted health system ultimately decided to drop the optional program.
Dr. Hough indicated that the health system – Johns Hopkins Medicine – likely would have continued its support for the program had the government at least allowed it to break even. Although the payment program under study was a 3-year project, the bigger challenge, declared Dr. Hough, is that “we can’t turn an aircraft carrier that quickly.”
“Three years won’t show whether value-based care is really working,” Dr. Hough said.
Robert Zipper, MD, a hospitalist and senior policy advisor for Sound Physicians, a company that works to improve outcomes in acute care, agreed with Dr. Hough that performance tends to improve with time. Yet, Dr. Zipper doesn’t see much change in the near term, because “after all, there is nothing to replace them [the programs].”
The problem gets even stickier for private payers because patients may be on an insurance panel for as little as a year or 2. Thanks to this rapid churn of beneficiaries, even the best-designed value-based program will have little time to prove its worth.
Dr. Zipper is among the many who don’t expect significant changes in the near term, asserting that “President Biden will want to get a few policy wins first, and health care is not the easiest place to start.”
But it’s likely that payers and others will want to see more emphasis on value-based programs despite these programs’ possible value to patients, physicians, and health systems alike.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 40 value-based payment models – from direct contracting to bundled payments – have been introduced into the Medicare program in the past 10 years, with the goal of improving care while lowering costs. Hopes were high that they would be successful.
Physicians could suffer a huge blow to their income.
Many of the value-based care models simply did not work as expected, said Seema Verma, head of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, at a recent HLTH Conference. “They are not producing the types of savings the taxpayers deserve,” Ms. Verma said.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPac) concluded that, while dozens of payment models were tested, most failed to generate net savings for Medicare. Even the most successful of the models produced only modest savings. MedPac elaborated: “The track record raises the question of whether changes to particular models or CMMI’s [Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation’s] broader strategies might be warranted.”
What will happen now, as government officials admit that their value-based programs haven’t worked? The value-based programs could become more stringent. Here’s what physicians will have to contend with.
More risk. Experts agree that risk – financial risk – will be a component of future programs. Two-sided risk is likely to be the norm. This means that both parties – the provider and the insurer – are at financial risk for the patients covered by the program.
For example, a plan with 50,000 beneficiary patients would estimate the cost of caring for those patients on the basis of multiple variables. If the actual cost is lower than anticipated, both parties share in the savings. However, both share in the loss if the cost of caring for their patient population exceeds expectations.
This may compel physicians to enhance efficiency and potentially limit the services provided to patients. Typically, however, the strategy is to make efforts to prevent services like ED visits and admissions by focusing on health maintenance.
In contrast to most current value-based models, which feature little to no downside risk for physicians, double-sided risk means physicians could lose money. The loss may incorporate a cap – 5%, for example – but programs may differ. Experts concur that double-sided risk will be a hallmark of future programs.
Better data. The majority of health care services are rendered via fee-for-service: Patients receive services and physicians are paid, yet little or no information about outcomes is exchanged between insurers and physicians.
Penny Noyes, president of Health Business Navigators and contract negotiator for physicians, is not a fan of the current crop of value-based programs and feels that data transparency is positive. Sound metrics can lead to improvement, she said, adding: “It’s not money that drives physicians to make decisions; it’s what’s in the best interest of their patients and their patients’ long-term care.”
Value-based programs can work but only if applicable data are developed and given to physicians so that they can better understand their current performance and how to improve.
Mandated participation. Participation in value-based programs has been voluntary, but that may have skewed the results, which were better than what typical practice would have shown. Acknowledging this may lead CMS to call for mandated participation as a component of future programs. Physicians may be brought into programs, if only to determine whether the models really work. To date, participation in the programs has been voluntary, but that may change in the future.
Innovation. The private insurance market may end up as a key player. Over the past 6 months, health insurers have either consolidated partnerships with telemedicine companies to provide no-cost care to beneficiaries or have launched their own initiatives.
Others are focused on bringing together patients and providers operating outside of the traditional health care system, such as Aetna’s merger with CVS which now offers retail-based acute care (MinuteClinic) and chronic care (HealthHUB). Still other payers are gambling with physician practice ownership, as in the case of United Healthcare’s OptumHealth, which now boasts around 50,000 physicians throughout the country.
New practice models are emerging in private practices as well. Physicians are embracing remote care, proactively managing care transitions, and seeking out more methods to keep patients healthy and at home.
Not much was expected from value-based plans
Many are not surprised that the value-based models did not produce impressive results. Ms. Noyes doubted that positive outcomes will be achieved for physicians in comparison with what could have been attained under fee-for-service arrangements with lower administrative costs.
While the Affordable Care Act attempted to encourage alternative reimbursement, it limits the maximum medical loss ratio (MLR) a payer could achieve. For many plans, that maximum was 85%. Simply put, at least $0.85 of each premium collected had to be paid in claims; the remaining $0.15 went to margin, claims, and other administrative costs. A payer with an 82% MLR then would have to rebate the 3% difference to enrollees.
But that’s not what occurred, according to Ms. Noyes. Because value-based payments to providers are considered a claims expense, an MLR ratio of 82% allowed the payer to distribute the 3% difference to providers as value-based payments. Ms. Noyes said: “That may sound good for the provider, but the result was essentially a freeze on the provider’s fee-for-service reimbursement with the prospect of getting value-based payments like ‘shared savings.’
“When the providers tried to increase their base fee-for-service rates just to match inflation, payers often advised that any future raises had to be earned through value-based programs,” Ms. Noyes added. The value-based formulas confuse providers because payments are often made for periods as far back as 18 months, and providers do not have data systems to reconcile their payer report cards retrospectively. The result is that providers tended to accept whatever amount the payer distributed.
Executives at Lumeris, a company that helps health systems participate successfully in value-based care, see potential in a newer approach to alternative payments, such as CMS’ Direct Contracting initiative. This voluntary payment model offers options tailored to several types of organizations that aim to reduce costs while preserving or enhancing the quality of care for Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries.
Jeff Smith, chief commercial officer for population health at Lumeris, explained that the Direct Contracting initiative can provide physicians with a more attractive option than prior value-based models because it adjusts for the complexity and fragility of patients with complex and chronic conditions. By allowing providers to participate in the savings generated, the initiative stands in stark contrast to what Mr. Smith described as the “shared savings to nothingness” experienced by providers in earlier-stage alternative payment models.
Physicians engaged with value-based programs like Direct Contracting are investing in nurses to aid with initiatives regarding health promotion and transitions of care. When a patient is discharged, for example, the nurse contacts the patient to discuss medications, schedule follow-up appointments, and so forth – tasks typically left to the patient (or caregiver) to navigate in the traditional system.
The initiative recognizes the importance of managing high-risk patients, those whom physicians identify as having an extraordinary number of ED visits and admissions. These patients, as well as so-called “rising-risk” patients, are targeted by nurses who proactively communicate with patients (and caregivers) to address patient’s needs, including social determinants of health.
Physicians who have a large load of patients in value-based programs are hiring social workers, pharmacists, and behavioral health experts to help. Of course, these personnel are costly, but that’s what the value-based programs aim to reimburse.
Still, the road ahead to value based is rocky and may not gain momentum for some time. Johns Hopkins University’s Doug Hough, PhD, an economist, recounts a government research study that sought to assess the university’s health system participation in a value-based payment program. While there were positive impacts on the program’s target population, Hough and his team discovered that the returns achieved by the optional model didn’t justify the health system’s financial support for it. The increasingly indebted health system ultimately decided to drop the optional program.
Dr. Hough indicated that the health system – Johns Hopkins Medicine – likely would have continued its support for the program had the government at least allowed it to break even. Although the payment program under study was a 3-year project, the bigger challenge, declared Dr. Hough, is that “we can’t turn an aircraft carrier that quickly.”
“Three years won’t show whether value-based care is really working,” Dr. Hough said.
Robert Zipper, MD, a hospitalist and senior policy advisor for Sound Physicians, a company that works to improve outcomes in acute care, agreed with Dr. Hough that performance tends to improve with time. Yet, Dr. Zipper doesn’t see much change in the near term, because “after all, there is nothing to replace them [the programs].”
The problem gets even stickier for private payers because patients may be on an insurance panel for as little as a year or 2. Thanks to this rapid churn of beneficiaries, even the best-designed value-based program will have little time to prove its worth.
Dr. Zipper is among the many who don’t expect significant changes in the near term, asserting that “President Biden will want to get a few policy wins first, and health care is not the easiest place to start.”
But it’s likely that payers and others will want to see more emphasis on value-based programs despite these programs’ possible value to patients, physicians, and health systems alike.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 40 value-based payment models – from direct contracting to bundled payments – have been introduced into the Medicare program in the past 10 years, with the goal of improving care while lowering costs. Hopes were high that they would be successful.
Physicians could suffer a huge blow to their income.
Many of the value-based care models simply did not work as expected, said Seema Verma, head of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, at a recent HLTH Conference. “They are not producing the types of savings the taxpayers deserve,” Ms. Verma said.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPac) concluded that, while dozens of payment models were tested, most failed to generate net savings for Medicare. Even the most successful of the models produced only modest savings. MedPac elaborated: “The track record raises the question of whether changes to particular models or CMMI’s [Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation’s] broader strategies might be warranted.”
What will happen now, as government officials admit that their value-based programs haven’t worked? The value-based programs could become more stringent. Here’s what physicians will have to contend with.
More risk. Experts agree that risk – financial risk – will be a component of future programs. Two-sided risk is likely to be the norm. This means that both parties – the provider and the insurer – are at financial risk for the patients covered by the program.
For example, a plan with 50,000 beneficiary patients would estimate the cost of caring for those patients on the basis of multiple variables. If the actual cost is lower than anticipated, both parties share in the savings. However, both share in the loss if the cost of caring for their patient population exceeds expectations.
This may compel physicians to enhance efficiency and potentially limit the services provided to patients. Typically, however, the strategy is to make efforts to prevent services like ED visits and admissions by focusing on health maintenance.
In contrast to most current value-based models, which feature little to no downside risk for physicians, double-sided risk means physicians could lose money. The loss may incorporate a cap – 5%, for example – but programs may differ. Experts concur that double-sided risk will be a hallmark of future programs.
Better data. The majority of health care services are rendered via fee-for-service: Patients receive services and physicians are paid, yet little or no information about outcomes is exchanged between insurers and physicians.
Penny Noyes, president of Health Business Navigators and contract negotiator for physicians, is not a fan of the current crop of value-based programs and feels that data transparency is positive. Sound metrics can lead to improvement, she said, adding: “It’s not money that drives physicians to make decisions; it’s what’s in the best interest of their patients and their patients’ long-term care.”
Value-based programs can work but only if applicable data are developed and given to physicians so that they can better understand their current performance and how to improve.
Mandated participation. Participation in value-based programs has been voluntary, but that may have skewed the results, which were better than what typical practice would have shown. Acknowledging this may lead CMS to call for mandated participation as a component of future programs. Physicians may be brought into programs, if only to determine whether the models really work. To date, participation in the programs has been voluntary, but that may change in the future.
Innovation. The private insurance market may end up as a key player. Over the past 6 months, health insurers have either consolidated partnerships with telemedicine companies to provide no-cost care to beneficiaries or have launched their own initiatives.
Others are focused on bringing together patients and providers operating outside of the traditional health care system, such as Aetna’s merger with CVS which now offers retail-based acute care (MinuteClinic) and chronic care (HealthHUB). Still other payers are gambling with physician practice ownership, as in the case of United Healthcare’s OptumHealth, which now boasts around 50,000 physicians throughout the country.
New practice models are emerging in private practices as well. Physicians are embracing remote care, proactively managing care transitions, and seeking out more methods to keep patients healthy and at home.
Not much was expected from value-based plans
Many are not surprised that the value-based models did not produce impressive results. Ms. Noyes doubted that positive outcomes will be achieved for physicians in comparison with what could have been attained under fee-for-service arrangements with lower administrative costs.
While the Affordable Care Act attempted to encourage alternative reimbursement, it limits the maximum medical loss ratio (MLR) a payer could achieve. For many plans, that maximum was 85%. Simply put, at least $0.85 of each premium collected had to be paid in claims; the remaining $0.15 went to margin, claims, and other administrative costs. A payer with an 82% MLR then would have to rebate the 3% difference to enrollees.
But that’s not what occurred, according to Ms. Noyes. Because value-based payments to providers are considered a claims expense, an MLR ratio of 82% allowed the payer to distribute the 3% difference to providers as value-based payments. Ms. Noyes said: “That may sound good for the provider, but the result was essentially a freeze on the provider’s fee-for-service reimbursement with the prospect of getting value-based payments like ‘shared savings.’
“When the providers tried to increase their base fee-for-service rates just to match inflation, payers often advised that any future raises had to be earned through value-based programs,” Ms. Noyes added. The value-based formulas confuse providers because payments are often made for periods as far back as 18 months, and providers do not have data systems to reconcile their payer report cards retrospectively. The result is that providers tended to accept whatever amount the payer distributed.
Executives at Lumeris, a company that helps health systems participate successfully in value-based care, see potential in a newer approach to alternative payments, such as CMS’ Direct Contracting initiative. This voluntary payment model offers options tailored to several types of organizations that aim to reduce costs while preserving or enhancing the quality of care for Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries.
Jeff Smith, chief commercial officer for population health at Lumeris, explained that the Direct Contracting initiative can provide physicians with a more attractive option than prior value-based models because it adjusts for the complexity and fragility of patients with complex and chronic conditions. By allowing providers to participate in the savings generated, the initiative stands in stark contrast to what Mr. Smith described as the “shared savings to nothingness” experienced by providers in earlier-stage alternative payment models.
Physicians engaged with value-based programs like Direct Contracting are investing in nurses to aid with initiatives regarding health promotion and transitions of care. When a patient is discharged, for example, the nurse contacts the patient to discuss medications, schedule follow-up appointments, and so forth – tasks typically left to the patient (or caregiver) to navigate in the traditional system.
The initiative recognizes the importance of managing high-risk patients, those whom physicians identify as having an extraordinary number of ED visits and admissions. These patients, as well as so-called “rising-risk” patients, are targeted by nurses who proactively communicate with patients (and caregivers) to address patient’s needs, including social determinants of health.
Physicians who have a large load of patients in value-based programs are hiring social workers, pharmacists, and behavioral health experts to help. Of course, these personnel are costly, but that’s what the value-based programs aim to reimburse.
Still, the road ahead to value based is rocky and may not gain momentum for some time. Johns Hopkins University’s Doug Hough, PhD, an economist, recounts a government research study that sought to assess the university’s health system participation in a value-based payment program. While there were positive impacts on the program’s target population, Hough and his team discovered that the returns achieved by the optional model didn’t justify the health system’s financial support for it. The increasingly indebted health system ultimately decided to drop the optional program.
Dr. Hough indicated that the health system – Johns Hopkins Medicine – likely would have continued its support for the program had the government at least allowed it to break even. Although the payment program under study was a 3-year project, the bigger challenge, declared Dr. Hough, is that “we can’t turn an aircraft carrier that quickly.”
“Three years won’t show whether value-based care is really working,” Dr. Hough said.
Robert Zipper, MD, a hospitalist and senior policy advisor for Sound Physicians, a company that works to improve outcomes in acute care, agreed with Dr. Hough that performance tends to improve with time. Yet, Dr. Zipper doesn’t see much change in the near term, because “after all, there is nothing to replace them [the programs].”
The problem gets even stickier for private payers because patients may be on an insurance panel for as little as a year or 2. Thanks to this rapid churn of beneficiaries, even the best-designed value-based program will have little time to prove its worth.
Dr. Zipper is among the many who don’t expect significant changes in the near term, asserting that “President Biden will want to get a few policy wins first, and health care is not the easiest place to start.”
But it’s likely that payers and others will want to see more emphasis on value-based programs despite these programs’ possible value to patients, physicians, and health systems alike.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Should all skin cancer patients be taking nicotinamide?
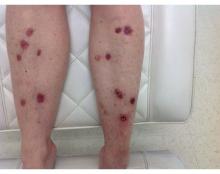
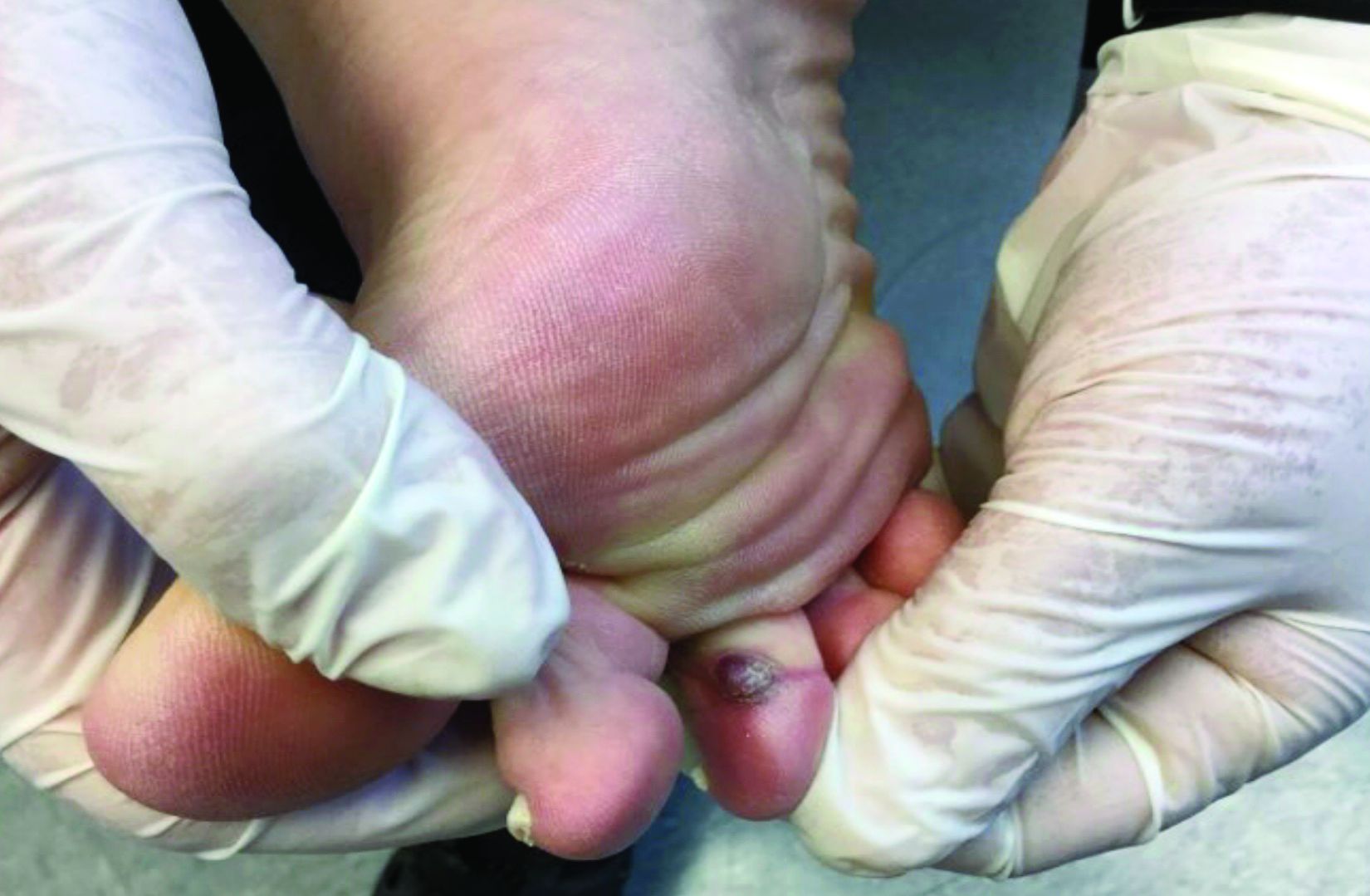
In 2014, I began taking care of a patient (see photo) who had developed over 25 basal cell carcinomas on her lower legs, which were surgically removed. She has been clear of any skin cancers in the last 2 years since starting supplementation.
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is a water soluble form of vitamin B3 that has been shown to enhance the repair of UV-induced DNA damage. Nicotinamide is found naturally in meat, fish, nuts, grains, and legumes, and is a key component of the glycolysis pathway, by generating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide for adenosine triphosphate production. Nicotinamide deficiency causes photosensitive dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia. It has been studied for its anti-inflammatory benefits as an adjunct treatment for rosacea, bullous diseases, acne, and melasma.
Nonmelanoma skin cancers are known to be caused primarily by UV radiation. The supplementation of nicotinamide orally twice daily has been shown to reduce the rate of actinic keratoses and new nonmelanoma skin cancers compared with placebo after 1 year in patients who previously had skin cancer. In the phase 3 study published in 2015, a randomized, controlled trial of 386 patients who had at least two nonmelanoma skin cancers within the previous 5-year period, oral nicotinamide 500 mg given twice daily for a 12-month period significantly reduced the number of new nonmelanoma skin cancers by 23% versus those on placebo.
The recommended dose for nicotinamide, which is available over the counter as Vitamin B3, is 500 mg twice a day. Nicotinamide should not be confused with niacin (nicotinic acid), which has been used to treat high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. There are no significant side effects from long-term use; however nicotinamide should not be used in patients with end-stage kidney disease or chronic kidney disease. (Niacin, however, can cause elevation of liver enzymes, headache, flushing, and increased blood pressure.) Nicotinamide crosses the placenta and should not be used in pregnancy as it has not been studied in pregnant populations.
We should counsel patients that this is not an oral sunscreen, and that sun avoidance, sunscreen, and yearly skin cancer checks are still the mainstay of skin cancer prevention. However, given the safety profile of nicotinamide and the protective effects, should all of our skin cancer patients be taking nicotinamide daily? In my practice they are, all of whom swear by it and have had significant reductions of both actinic keratoses and nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Dr. Talakoub and Dr. Wesley are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
In 2014, I began taking care of a patient (see photo) who had developed over 25 basal cell carcinomas on her lower legs, which were surgically removed. She has been clear of any skin cancers in the last 2 years since starting supplementation.
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is a water soluble form of vitamin B3 that has been shown to enhance the repair of UV-induced DNA damage. Nicotinamide is found naturally in meat, fish, nuts, grains, and legumes, and is a key component of the glycolysis pathway, by generating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide for adenosine triphosphate production. Nicotinamide deficiency causes photosensitive dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia. It has been studied for its anti-inflammatory benefits as an adjunct treatment for rosacea, bullous diseases, acne, and melasma.
Nonmelanoma skin cancers are known to be caused primarily by UV radiation. The supplementation of nicotinamide orally twice daily has been shown to reduce the rate of actinic keratoses and new nonmelanoma skin cancers compared with placebo after 1 year in patients who previously had skin cancer. In the phase 3 study published in 2015, a randomized, controlled trial of 386 patients who had at least two nonmelanoma skin cancers within the previous 5-year period, oral nicotinamide 500 mg given twice daily for a 12-month period significantly reduced the number of new nonmelanoma skin cancers by 23% versus those on placebo.
The recommended dose for nicotinamide, which is available over the counter as Vitamin B3, is 500 mg twice a day. Nicotinamide should not be confused with niacin (nicotinic acid), which has been used to treat high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. There are no significant side effects from long-term use; however nicotinamide should not be used in patients with end-stage kidney disease or chronic kidney disease. (Niacin, however, can cause elevation of liver enzymes, headache, flushing, and increased blood pressure.) Nicotinamide crosses the placenta and should not be used in pregnancy as it has not been studied in pregnant populations.
We should counsel patients that this is not an oral sunscreen, and that sun avoidance, sunscreen, and yearly skin cancer checks are still the mainstay of skin cancer prevention. However, given the safety profile of nicotinamide and the protective effects, should all of our skin cancer patients be taking nicotinamide daily? In my practice they are, all of whom swear by it and have had significant reductions of both actinic keratoses and nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Dr. Talakoub and Dr. Wesley are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
In 2014, I began taking care of a patient (see photo) who had developed over 25 basal cell carcinomas on her lower legs, which were surgically removed. She has been clear of any skin cancers in the last 2 years since starting supplementation.
Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide, is a water soluble form of vitamin B3 that has been shown to enhance the repair of UV-induced DNA damage. Nicotinamide is found naturally in meat, fish, nuts, grains, and legumes, and is a key component of the glycolysis pathway, by generating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide for adenosine triphosphate production. Nicotinamide deficiency causes photosensitive dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia. It has been studied for its anti-inflammatory benefits as an adjunct treatment for rosacea, bullous diseases, acne, and melasma.
Nonmelanoma skin cancers are known to be caused primarily by UV radiation. The supplementation of nicotinamide orally twice daily has been shown to reduce the rate of actinic keratoses and new nonmelanoma skin cancers compared with placebo after 1 year in patients who previously had skin cancer. In the phase 3 study published in 2015, a randomized, controlled trial of 386 patients who had at least two nonmelanoma skin cancers within the previous 5-year period, oral nicotinamide 500 mg given twice daily for a 12-month period significantly reduced the number of new nonmelanoma skin cancers by 23% versus those on placebo.
The recommended dose for nicotinamide, which is available over the counter as Vitamin B3, is 500 mg twice a day. Nicotinamide should not be confused with niacin (nicotinic acid), which has been used to treat high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. There are no significant side effects from long-term use; however nicotinamide should not be used in patients with end-stage kidney disease or chronic kidney disease. (Niacin, however, can cause elevation of liver enzymes, headache, flushing, and increased blood pressure.) Nicotinamide crosses the placenta and should not be used in pregnancy as it has not been studied in pregnant populations.
We should counsel patients that this is not an oral sunscreen, and that sun avoidance, sunscreen, and yearly skin cancer checks are still the mainstay of skin cancer prevention. However, given the safety profile of nicotinamide and the protective effects, should all of our skin cancer patients be taking nicotinamide daily? In my practice they are, all of whom swear by it and have had significant reductions of both actinic keratoses and nonmelanoma skin cancers.
Dr. Talakoub and Dr. Wesley are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. Write to them at [email protected]. They had no relevant disclosures.
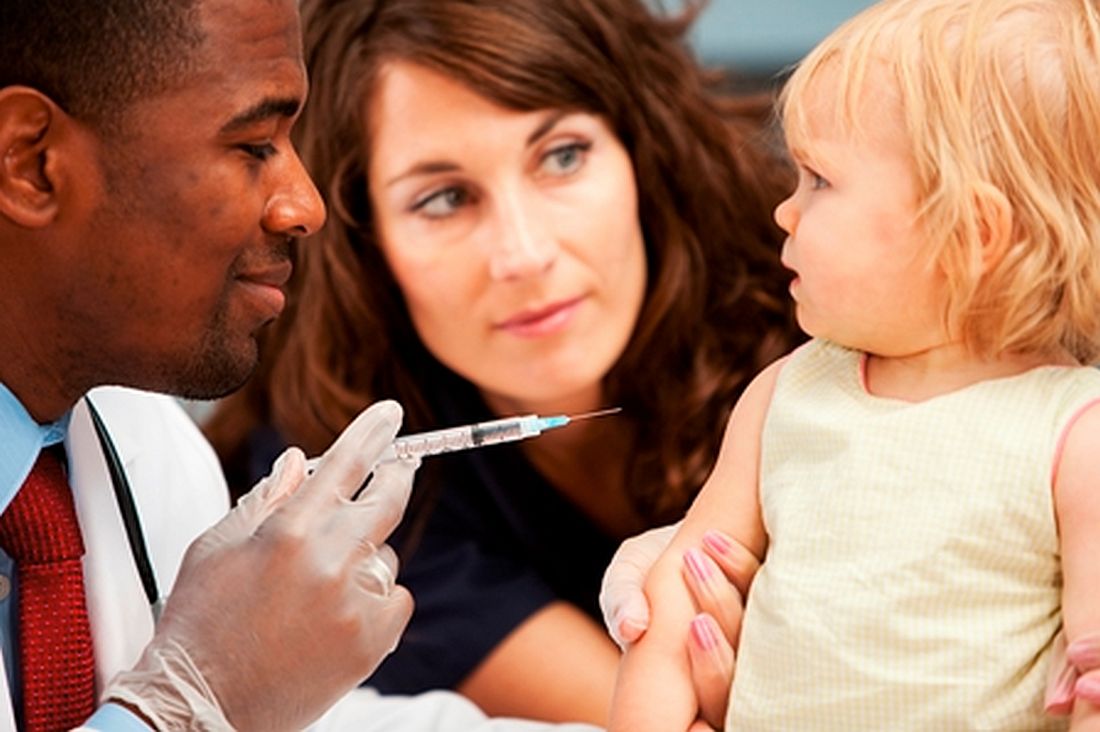
A shot in the arm
As the COVID-19 vaccine candidates have begun to roll off the production lines into the distribution networks by the millions, media coverage almost universally includes a still photo or video of someone receiving an injection. Ever observant, a retired lawyer friend of mine who learned to give shots when he was in the Army and again more recently while taking a wilderness survival course emailed me his concerns about what he felt were examples of poor injection technique. Included in his commentary was an Internet link in which a physician, who I suspect may have been a pediatrician, demonstrated what the physician considered proper intramuscular injection technique, which included a single-handed aspiration prior to giving the injection allowing the free hand to stabilize the patient’s – in this case a child’s – arm during the entire process.
I replied to my friend that I too was often troubled by what I considered to be poor injection technique. But, I said the physician in the link touting his improved technique was misguided. My understanding has been that unless the injection site is in the gluteus, there is no need aspirate prior to an intramuscular vaccine injection because the risk of intravascular injection is so small. I then confirmed this by reviewing the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Recommendations and Guidelines of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which was updated in June 2019. Included in those recommendations was the observation that the vaccine administrator does not need to wear gloves unless he or she has open lesions or is at risk from contacting the recipient’s body fluids.
Like many of the technical skills one learns in training, giving intramuscular injections is probably an example of the “see one, do one, teach one” mantra. But in the case of giving shots, I don’t recall any teaching. Do you? It was more “see a dozen and get on with it.” Or maybe you trained in an environment in which nurses gave all the injections. I hope not.
When it comes to giving immunizations to children, the art is in entering into that encounter with a calm, matter-of-fact attitude and body language, hiding the needle, firmly restraining the child, and moving quickly and smoothly. Aspirating and glove donning merely add to the drama and waste time. But how did I learn that art? No one taught me. Like many clinical skills, I watched scores of nurses and physicians, mentally logging in their tricks and mistakes that would help me craft my style.
I always felt and still feel that providing immunizations was per hour spent, the most valuable investment of my time. Doing the injecting myself was both the most efficient way to provide the service, and also emphasized the importance that I placed on the immunization. In the process of my 40-plus–year career, that included several hundred thousand patient encounters in which I gave innumerable injections. And, I egotistically assumed that I was good at it because many infants never cried, and a few children said, “That didn’t hurt.” I suspect you can make the same claim.
Injecting millions of adults with a COVID-19 vaccine, on the other hand, is a piece of cake because restraining the recipient shouldn’t factor into the scenario. However, I wonder who is going to administer all those millions of injections and who is going to train them? How many of the trainers are aware of the CDC-ACIP guidelines? Or, are they going to fall back on old techniques that lack evidence support?
From the efficiency standpoint, it probably doesn’t make much difference. The injection takes but a few seconds. Filling out the paperwork and waiting for the recipient to figure out how to expose his or her deltoid can take fifty times that long.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
As the COVID-19 vaccine candidates have begun to roll off the production lines into the distribution networks by the millions, media coverage almost universally includes a still photo or video of someone receiving an injection. Ever observant, a retired lawyer friend of mine who learned to give shots when he was in the Army and again more recently while taking a wilderness survival course emailed me his concerns about what he felt were examples of poor injection technique. Included in his commentary was an Internet link in which a physician, who I suspect may have been a pediatrician, demonstrated what the physician considered proper intramuscular injection technique, which included a single-handed aspiration prior to giving the injection allowing the free hand to stabilize the patient’s – in this case a child’s – arm during the entire process.
I replied to my friend that I too was often troubled by what I considered to be poor injection technique. But, I said the physician in the link touting his improved technique was misguided. My understanding has been that unless the injection site is in the gluteus, there is no need aspirate prior to an intramuscular vaccine injection because the risk of intravascular injection is so small. I then confirmed this by reviewing the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Recommendations and Guidelines of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which was updated in June 2019. Included in those recommendations was the observation that the vaccine administrator does not need to wear gloves unless he or she has open lesions or is at risk from contacting the recipient’s body fluids.
Like many of the technical skills one learns in training, giving intramuscular injections is probably an example of the “see one, do one, teach one” mantra. But in the case of giving shots, I don’t recall any teaching. Do you? It was more “see a dozen and get on with it.” Or maybe you trained in an environment in which nurses gave all the injections. I hope not.
When it comes to giving immunizations to children, the art is in entering into that encounter with a calm, matter-of-fact attitude and body language, hiding the needle, firmly restraining the child, and moving quickly and smoothly. Aspirating and glove donning merely add to the drama and waste time. But how did I learn that art? No one taught me. Like many clinical skills, I watched scores of nurses and physicians, mentally logging in their tricks and mistakes that would help me craft my style.
I always felt and still feel that providing immunizations was per hour spent, the most valuable investment of my time. Doing the injecting myself was both the most efficient way to provide the service, and also emphasized the importance that I placed on the immunization. In the process of my 40-plus–year career, that included several hundred thousand patient encounters in which I gave innumerable injections. And, I egotistically assumed that I was good at it because many infants never cried, and a few children said, “That didn’t hurt.” I suspect you can make the same claim.
Injecting millions of adults with a COVID-19 vaccine, on the other hand, is a piece of cake because restraining the recipient shouldn’t factor into the scenario. However, I wonder who is going to administer all those millions of injections and who is going to train them? How many of the trainers are aware of the CDC-ACIP guidelines? Or, are they going to fall back on old techniques that lack evidence support?
From the efficiency standpoint, it probably doesn’t make much difference. The injection takes but a few seconds. Filling out the paperwork and waiting for the recipient to figure out how to expose his or her deltoid can take fifty times that long.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
As the COVID-19 vaccine candidates have begun to roll off the production lines into the distribution networks by the millions, media coverage almost universally includes a still photo or video of someone receiving an injection. Ever observant, a retired lawyer friend of mine who learned to give shots when he was in the Army and again more recently while taking a wilderness survival course emailed me his concerns about what he felt were examples of poor injection technique. Included in his commentary was an Internet link in which a physician, who I suspect may have been a pediatrician, demonstrated what the physician considered proper intramuscular injection technique, which included a single-handed aspiration prior to giving the injection allowing the free hand to stabilize the patient’s – in this case a child’s – arm during the entire process.
I replied to my friend that I too was often troubled by what I considered to be poor injection technique. But, I said the physician in the link touting his improved technique was misguided. My understanding has been that unless the injection site is in the gluteus, there is no need aspirate prior to an intramuscular vaccine injection because the risk of intravascular injection is so small. I then confirmed this by reviewing the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Recommendations and Guidelines of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which was updated in June 2019. Included in those recommendations was the observation that the vaccine administrator does not need to wear gloves unless he or she has open lesions or is at risk from contacting the recipient’s body fluids.
Like many of the technical skills one learns in training, giving intramuscular injections is probably an example of the “see one, do one, teach one” mantra. But in the case of giving shots, I don’t recall any teaching. Do you? It was more “see a dozen and get on with it.” Or maybe you trained in an environment in which nurses gave all the injections. I hope not.
When it comes to giving immunizations to children, the art is in entering into that encounter with a calm, matter-of-fact attitude and body language, hiding the needle, firmly restraining the child, and moving quickly and smoothly. Aspirating and glove donning merely add to the drama and waste time. But how did I learn that art? No one taught me. Like many clinical skills, I watched scores of nurses and physicians, mentally logging in their tricks and mistakes that would help me craft my style.
I always felt and still feel that providing immunizations was per hour spent, the most valuable investment of my time. Doing the injecting myself was both the most efficient way to provide the service, and also emphasized the importance that I placed on the immunization. In the process of my 40-plus–year career, that included several hundred thousand patient encounters in which I gave innumerable injections. And, I egotistically assumed that I was good at it because many infants never cried, and a few children said, “That didn’t hurt.” I suspect you can make the same claim.
Injecting millions of adults with a COVID-19 vaccine, on the other hand, is a piece of cake because restraining the recipient shouldn’t factor into the scenario. However, I wonder who is going to administer all those millions of injections and who is going to train them? How many of the trainers are aware of the CDC-ACIP guidelines? Or, are they going to fall back on old techniques that lack evidence support?
From the efficiency standpoint, it probably doesn’t make much difference. The injection takes but a few seconds. Filling out the paperwork and waiting for the recipient to figure out how to expose his or her deltoid can take fifty times that long.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Understanding messenger RNA and other SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.
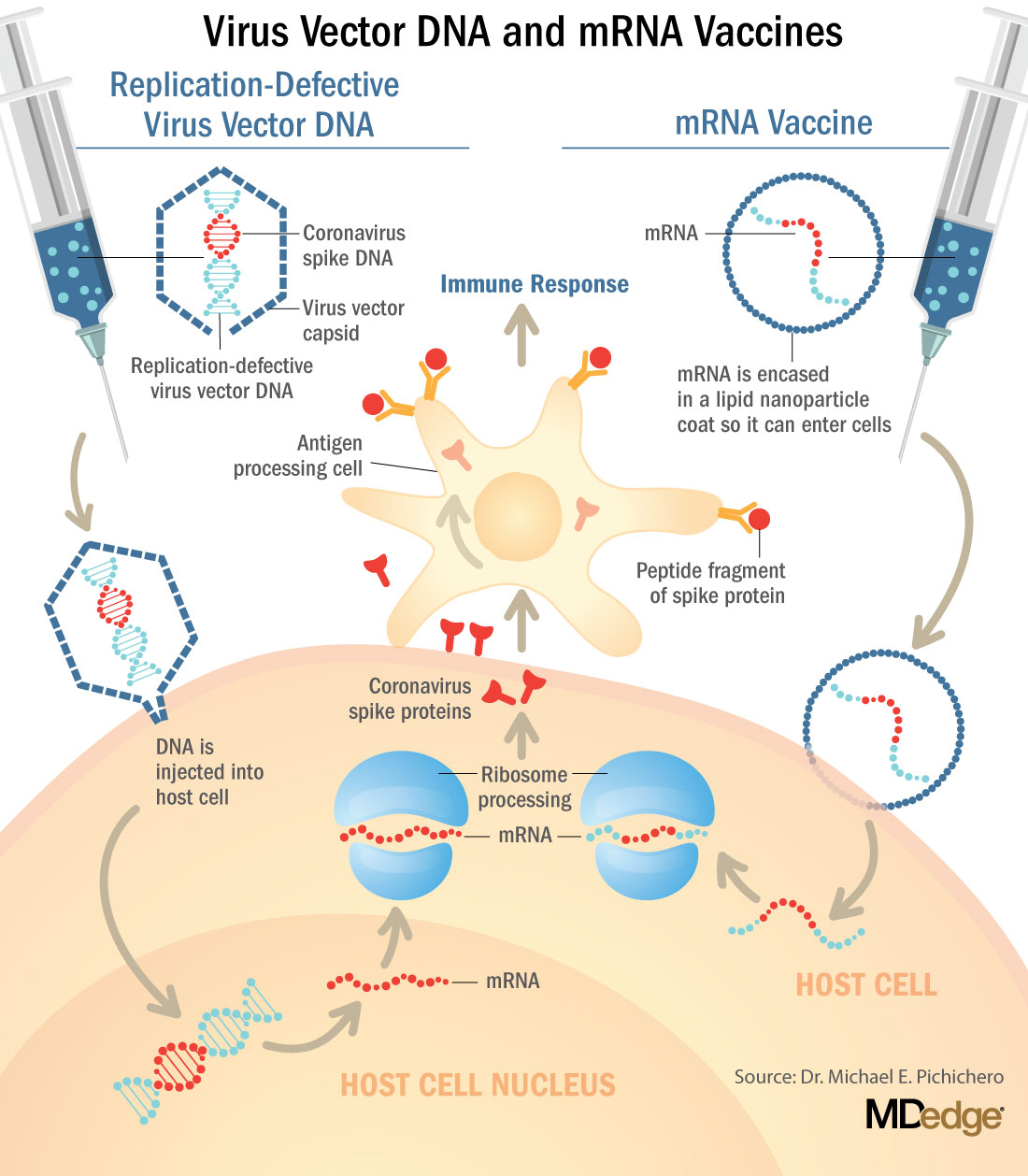
These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.

These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.

These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.
Raising psychiatry up ‘from depths of the asylums’
New biography captures Dr. Anthony Clare’s complexity
In “Psychiatrist in the Chair,” authors Brendan Kelly and Muiris Houston tell the story of a fellow Irishman, Anthony Clare, MD, who brought intelligence and eloquence to psychiatry. They tell a well-measured, well-referenced story of Anthony Clare’s personal and professional life. They capture his eloquence, wit, charm, and success in psychiatry as well as alluding to Dr. Clare’s self-reported “some kind of Irish darkness.”
In 1983, I was a young Scottish psychiatrist entering a fusty profession. Suddenly, there was Dr. Anthony Clare on the BBC! In “In the Psychiatrist’s Chair,” Dr. Clare interviewed celebrities. In addition to describing his Irish darkness, Brendan Kelly, MD, PhD and Muiris Houston, MD, FRCGP, both of whom are affiliated with Trinity College Dublin, note that Dr. Clare said: “I’m better at destroying systems than I am at putting them together – I do rather look for people to interview who will not live up to the prediction; there’s an element of destructiveness that’s still in me.”
I still listen to his talks on YouTube. His delicate probing questioning of B.F. Skinner, PhD, is one of my favorites, as he expertly and in an ever-so-friendly manner, teases out Dr. Skinner’s views of his upbringing and tags them to his behavorialism. It is this skill as an interviewer that captured us; can psychiatrists really be this clever? Yes, we can. All of the young and hopeful psychiatrists could see a future.
Dr. Clare raised psychiatry up from the depths of the asylums. He showed that a psychiatrist can be kind, charming, and sophisticated – handsome and helpful, not the ghouls of old movies. He did what needed to be done to psychiatry at that time: He set us on a footing that was not scary to the public. His vision for psychiatry was to improve services to those in need, reduce stigma, and show the public that there is a continuum between health and illness. He also took on the push for diagnoses, which he felt separated the normal from the abnormal, us from them.
He wrote his seminal work 10 years after graduating from the University College of Dublin. “Psychiatry in Dissent: Controversial Issues in Thought and Practice” was published in 1976, and is still considered one of the most influential texts in psychiatry. Dr. Clare “legitimized psychiatry not only in the eyes of the public but in the eyes of psychiatrists too,” the authors wrote. He did not support psychoanalysis and eschewed the rigor attached to the learning of new psychotherapies. He took renowned experts to task, but in ever such an elegant way. He successfully took on Hans Eysenck, PhD, I think because Dr. Eysenck insulted the intelligence of the Irish. He had a measured response to the anti-psychiatrists Thomas Szasz, MD, and R.D. Laing, MD, incorporating their ideas into his view of psychiatry. Dr. Clare was a social psychiatrist who highlighted the role of poverty and lack of access to mental health services. He stated that psychiatry was a “shambles, a mess and at a very primitive level.”
I enjoyed learning about his fight to make the membership exam for entrance into the Royal College of Psychiatry worthy of its name. Dr. Clare helped found the Association of Psychiatrists in Training (APIT) and wrote eloquently about the difference between training and indoctrination, which he described as having people fit a predetermined paradigm of how psychiatry should be constructed and practiced, versus education, which he defined as forming the mind. He highlighted the lack of good training facilities, and teaching staff in many parts of the United Kingdom. When Dr. Clare studied candidates in Edinburgh, he found that 70% had no child, forensic, or intellectual disability training. By the time I did my training there, I was able to get experience in all three subspecialties. He opposed the granting of automatic membership to current consultants, many of whom he considered to be “dunderheads.” . I can attest to that!
In the later phase of his life, Dr. Clare likened his self-punishing regime at the height of his hyperproductive fame to an addiction – a fix, with its risk/reward, pain/pleasure kick. He identified fear as being an unacknowledged presence in most of his life. There are vague hints from Dr. Clare’s friends and colleagues that something drove him back to Ireland from a successful life in London. Although his wife was described as being fully supportive of him, her words on his tombstone indicate something: What they indicate you can decide. She called him “a loving husband, father and grandfather, orator, physician, writer and broadcaster.” No mention was made of his being one of the greatest psychiatrists of his generation.
In 2000, he wrote “On Men: Masculinity in Crisis,” about men and the patriarchy, and highlighted the concept of “performance-based self-worth” in men. He stated: “What is the point of an awful lot of what I do. I’m in my 50s. I think one should be spending a good deal of your time doing things you want to do ... and what is that? I want to see much more of my family and friends. I want to continue making a contribution, but how can I best do that? ... I am contaminated by patriarchy; there is no man who isn’t. There is hope for men only if they ‘acknowledge the end of patriarchal power and participate in the discussion of how the post-patriarchal age is to be negotiated”. He opined whether it is still the case that, if men do not reevaluate their roles, they will soon be entirely irrelevant as social beings. The value of men is less in income generation but more in cultivating involvement, awareness, consistency, and caring, he stated.
As always with famous and talented people, we are interested not only in their professional gifts to us but in their personal journeys, and the authors, Dr. Kelly and Dr. Houston have given us this rich profile of one of my lifelong heroes, Anthony Clare. Anthony Clare makes you feel good about being a psychiatrist, and that is such an important gift.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest.
New biography captures Dr. Anthony Clare’s complexity
New biography captures Dr. Anthony Clare’s complexity
In “Psychiatrist in the Chair,” authors Brendan Kelly and Muiris Houston tell the story of a fellow Irishman, Anthony Clare, MD, who brought intelligence and eloquence to psychiatry. They tell a well-measured, well-referenced story of Anthony Clare’s personal and professional life. They capture his eloquence, wit, charm, and success in psychiatry as well as alluding to Dr. Clare’s self-reported “some kind of Irish darkness.”
In 1983, I was a young Scottish psychiatrist entering a fusty profession. Suddenly, there was Dr. Anthony Clare on the BBC! In “In the Psychiatrist’s Chair,” Dr. Clare interviewed celebrities. In addition to describing his Irish darkness, Brendan Kelly, MD, PhD and Muiris Houston, MD, FRCGP, both of whom are affiliated with Trinity College Dublin, note that Dr. Clare said: “I’m better at destroying systems than I am at putting them together – I do rather look for people to interview who will not live up to the prediction; there’s an element of destructiveness that’s still in me.”
I still listen to his talks on YouTube. His delicate probing questioning of B.F. Skinner, PhD, is one of my favorites, as he expertly and in an ever-so-friendly manner, teases out Dr. Skinner’s views of his upbringing and tags them to his behavorialism. It is this skill as an interviewer that captured us; can psychiatrists really be this clever? Yes, we can. All of the young and hopeful psychiatrists could see a future.
Dr. Clare raised psychiatry up from the depths of the asylums. He showed that a psychiatrist can be kind, charming, and sophisticated – handsome and helpful, not the ghouls of old movies. He did what needed to be done to psychiatry at that time: He set us on a footing that was not scary to the public. His vision for psychiatry was to improve services to those in need, reduce stigma, and show the public that there is a continuum between health and illness. He also took on the push for diagnoses, which he felt separated the normal from the abnormal, us from them.
He wrote his seminal work 10 years after graduating from the University College of Dublin. “Psychiatry in Dissent: Controversial Issues in Thought and Practice” was published in 1976, and is still considered one of the most influential texts in psychiatry. Dr. Clare “legitimized psychiatry not only in the eyes of the public but in the eyes of psychiatrists too,” the authors wrote. He did not support psychoanalysis and eschewed the rigor attached to the learning of new psychotherapies. He took renowned experts to task, but in ever such an elegant way. He successfully took on Hans Eysenck, PhD, I think because Dr. Eysenck insulted the intelligence of the Irish. He had a measured response to the anti-psychiatrists Thomas Szasz, MD, and R.D. Laing, MD, incorporating their ideas into his view of psychiatry. Dr. Clare was a social psychiatrist who highlighted the role of poverty and lack of access to mental health services. He stated that psychiatry was a “shambles, a mess and at a very primitive level.”
I enjoyed learning about his fight to make the membership exam for entrance into the Royal College of Psychiatry worthy of its name. Dr. Clare helped found the Association of Psychiatrists in Training (APIT) and wrote eloquently about the difference between training and indoctrination, which he described as having people fit a predetermined paradigm of how psychiatry should be constructed and practiced, versus education, which he defined as forming the mind. He highlighted the lack of good training facilities, and teaching staff in many parts of the United Kingdom. When Dr. Clare studied candidates in Edinburgh, he found that 70% had no child, forensic, or intellectual disability training. By the time I did my training there, I was able to get experience in all three subspecialties. He opposed the granting of automatic membership to current consultants, many of whom he considered to be “dunderheads.” . I can attest to that!
In the later phase of his life, Dr. Clare likened his self-punishing regime at the height of his hyperproductive fame to an addiction – a fix, with its risk/reward, pain/pleasure kick. He identified fear as being an unacknowledged presence in most of his life. There are vague hints from Dr. Clare’s friends and colleagues that something drove him back to Ireland from a successful life in London. Although his wife was described as being fully supportive of him, her words on his tombstone indicate something: What they indicate you can decide. She called him “a loving husband, father and grandfather, orator, physician, writer and broadcaster.” No mention was made of his being one of the greatest psychiatrists of his generation.
In 2000, he wrote “On Men: Masculinity in Crisis,” about men and the patriarchy, and highlighted the concept of “performance-based self-worth” in men. He stated: “What is the point of an awful lot of what I do. I’m in my 50s. I think one should be spending a good deal of your time doing things you want to do ... and what is that? I want to see much more of my family and friends. I want to continue making a contribution, but how can I best do that? ... I am contaminated by patriarchy; there is no man who isn’t. There is hope for men only if they ‘acknowledge the end of patriarchal power and participate in the discussion of how the post-patriarchal age is to be negotiated”. He opined whether it is still the case that, if men do not reevaluate their roles, they will soon be entirely irrelevant as social beings. The value of men is less in income generation but more in cultivating involvement, awareness, consistency, and caring, he stated.
As always with famous and talented people, we are interested not only in their professional gifts to us but in their personal journeys, and the authors, Dr. Kelly and Dr. Houston have given us this rich profile of one of my lifelong heroes, Anthony Clare. Anthony Clare makes you feel good about being a psychiatrist, and that is such an important gift.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest.
In “Psychiatrist in the Chair,” authors Brendan Kelly and Muiris Houston tell the story of a fellow Irishman, Anthony Clare, MD, who brought intelligence and eloquence to psychiatry. They tell a well-measured, well-referenced story of Anthony Clare’s personal and professional life. They capture his eloquence, wit, charm, and success in psychiatry as well as alluding to Dr. Clare’s self-reported “some kind of Irish darkness.”
In 1983, I was a young Scottish psychiatrist entering a fusty profession. Suddenly, there was Dr. Anthony Clare on the BBC! In “In the Psychiatrist’s Chair,” Dr. Clare interviewed celebrities. In addition to describing his Irish darkness, Brendan Kelly, MD, PhD and Muiris Houston, MD, FRCGP, both of whom are affiliated with Trinity College Dublin, note that Dr. Clare said: “I’m better at destroying systems than I am at putting them together – I do rather look for people to interview who will not live up to the prediction; there’s an element of destructiveness that’s still in me.”
I still listen to his talks on YouTube. His delicate probing questioning of B.F. Skinner, PhD, is one of my favorites, as he expertly and in an ever-so-friendly manner, teases out Dr. Skinner’s views of his upbringing and tags them to his behavorialism. It is this skill as an interviewer that captured us; can psychiatrists really be this clever? Yes, we can. All of the young and hopeful psychiatrists could see a future.
Dr. Clare raised psychiatry up from the depths of the asylums. He showed that a psychiatrist can be kind, charming, and sophisticated – handsome and helpful, not the ghouls of old movies. He did what needed to be done to psychiatry at that time: He set us on a footing that was not scary to the public. His vision for psychiatry was to improve services to those in need, reduce stigma, and show the public that there is a continuum between health and illness. He also took on the push for diagnoses, which he felt separated the normal from the abnormal, us from them.
He wrote his seminal work 10 years after graduating from the University College of Dublin. “Psychiatry in Dissent: Controversial Issues in Thought and Practice” was published in 1976, and is still considered one of the most influential texts in psychiatry. Dr. Clare “legitimized psychiatry not only in the eyes of the public but in the eyes of psychiatrists too,” the authors wrote. He did not support psychoanalysis and eschewed the rigor attached to the learning of new psychotherapies. He took renowned experts to task, but in ever such an elegant way. He successfully took on Hans Eysenck, PhD, I think because Dr. Eysenck insulted the intelligence of the Irish. He had a measured response to the anti-psychiatrists Thomas Szasz, MD, and R.D. Laing, MD, incorporating their ideas into his view of psychiatry. Dr. Clare was a social psychiatrist who highlighted the role of poverty and lack of access to mental health services. He stated that psychiatry was a “shambles, a mess and at a very primitive level.”
I enjoyed learning about his fight to make the membership exam for entrance into the Royal College of Psychiatry worthy of its name. Dr. Clare helped found the Association of Psychiatrists in Training (APIT) and wrote eloquently about the difference between training and indoctrination, which he described as having people fit a predetermined paradigm of how psychiatry should be constructed and practiced, versus education, which he defined as forming the mind. He highlighted the lack of good training facilities, and teaching staff in many parts of the United Kingdom. When Dr. Clare studied candidates in Edinburgh, he found that 70% had no child, forensic, or intellectual disability training. By the time I did my training there, I was able to get experience in all three subspecialties. He opposed the granting of automatic membership to current consultants, many of whom he considered to be “dunderheads.” . I can attest to that!
In the later phase of his life, Dr. Clare likened his self-punishing regime at the height of his hyperproductive fame to an addiction – a fix, with its risk/reward, pain/pleasure kick. He identified fear as being an unacknowledged presence in most of his life. There are vague hints from Dr. Clare’s friends and colleagues that something drove him back to Ireland from a successful life in London. Although his wife was described as being fully supportive of him, her words on his tombstone indicate something: What they indicate you can decide. She called him “a loving husband, father and grandfather, orator, physician, writer and broadcaster.” No mention was made of his being one of the greatest psychiatrists of his generation.
In 2000, he wrote “On Men: Masculinity in Crisis,” about men and the patriarchy, and highlighted the concept of “performance-based self-worth” in men. He stated: “What is the point of an awful lot of what I do. I’m in my 50s. I think one should be spending a good deal of your time doing things you want to do ... and what is that? I want to see much more of my family and friends. I want to continue making a contribution, but how can I best do that? ... I am contaminated by patriarchy; there is no man who isn’t. There is hope for men only if they ‘acknowledge the end of patriarchal power and participate in the discussion of how the post-patriarchal age is to be negotiated”. He opined whether it is still the case that, if men do not reevaluate their roles, they will soon be entirely irrelevant as social beings. The value of men is less in income generation but more in cultivating involvement, awareness, consistency, and caring, he stated.
As always with famous and talented people, we are interested not only in their professional gifts to us but in their personal journeys, and the authors, Dr. Kelly and Dr. Houston have given us this rich profile of one of my lifelong heroes, Anthony Clare. Anthony Clare makes you feel good about being a psychiatrist, and that is such an important gift.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest.
BTK Inhibitors: Researchers Eye Next-Generation Treatment Options for MS
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Circadian rhythms: Does the time of day you use a skin care product matter?
The majority of human cells, including skin and hair cells, keep their own time; that is, they manifest autonomous clocks and the genes that regulate their functioning.1 During the day, one primary function of the skin is protection; at night, repairing any damage (particularly DNA impairment) incurred during the day prevails.2-4 These activities are driven through circadian rhythms using clock genes that exist in all cutaneous cells.2 Important cutaneous functions such as blood flow, transepidermal water loss, and capacitance are affected by circadian rhythms.5 Hydration and inflammation are also among the several functions pertaining to epidermal homeostasis affected by circadian rhythms.6 In addition, some collagens and extracellular matrix proteases are diurnally regulated, and approximately 10% of the transcriptome, including the extracellular matrix, is thought to be controlled by circadian rhythms.7
Cutaneous cell migration and proliferation, wound healing, and tissue vulnerability to harm from UV exposure, oxidative stress, and protease activity, for example, are affected by circadian rhythms, Sherratt et al. noted in suggesting that chronotherapy presents promise for enhancing skin therapy.7 Indeed, recent research has led to the understanding that cutaneous aging, cellular repair, optimal timing for drug delivery to the skin, and skin cancer development are all affected by the chronobiological functioning of the skin.8
We have known for several years that certain types of products should be used at different times of the day. For instance, antioxidants should be used in the morning to protect skin from sun exposure and retinols should be used in the evening because of its induction of light sensitivity. The remainder of this column focuses on research in the last 2 decades that reinforces the notion of circadian rhythms working in the skin, and may alter how we view the timing of skin care. Next month’s column, part two on the circadian rhythms of the skin, will address recent clinical trials and the implications for timing treatments for certain cutaneous conditions.
Emerging data on the circadian rhythms of the skin
In 2001, Le Fur et al. studied the cutaneous circadian rhythms in the facial and forearm skin of eight healthy White women during a 48-hour period. They were able to detect such rhythms in facial sebum excretion, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) in the face and forearm, pH in the face, forearm skin temperature, and forearm capacitance using cosinor or analysis of variance methods. The investigators also observed 8- and 12-hour rhythms in TEWL in both areas, and 12 hours for forearm skin temperature. They verified that such rhythms could be measured and that they vary between skin sites. In addition, they were the first to show that ultradian and/or component rhythms can also be found in TEWL, sebum excretion, and skin temperature.9
A year later, Kawara et al. showed that mRNA of the circadian clock genes Per1, Clock, and bmal1/mop3 are expressed in normal human-cultured keratinocytes and that low-dose UVB down-regulates these genes and changes their express in keratinocyte cell cultures. They concluded that UV targeting of keratinocytes could alter circadian rhythms.10
In 2011, Spörl and colleagues characterized an in vitro functional cell autonomous circadian clock in adult human low calcium temperature keratinocytes, demonstrating that the molecular composition of the keratinocyte clock was comparable with peripheral tissue clocks. Notably, they observed that temperature acts as a robust time cue for epidermal traits, such as cholesterol homeostasis and differentiation.11
The next year, Sandu et al. investigated the kinetics of clock gene expression in epidermal and dermal cells collected from the same donor and compared their characteristics. They were able to reveal the presence of functional circadian machinery in primary cultures of fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and melanocytes, with oscillators identified in all skin cell types and thought to be involved in spurring cutaneous rhythmic functions as they exhibited discrete periods and phase relationships between clock genes.12
Three years later, Sandu et al. characterized the circadian clocks in rat skin and dermal fibroblasts. They found that skin has a self-sustaining circadian clock that experiences age-dependent alterations, and that dermal fibroblasts manifest circadian rhythms that can be modulated by endogenous (e.g., melatonin) and exogenous (e.g., temperature) influences.13
In 2019, Park et al. demonstrated that the diurnal expression of the gene TIMP3, which is thought to evince a circadian rhythm in synchronized human keratinocytes, experiences disruptions in such rhythms by UVB exposure. The inflammation that results can be blocked, they argued, by recovering the circadian expression of TIMP3 using synthetic TIMP3 peptides or bioactive natural ingredients, such as green tea extracts.6
Conclusion
Circadian rhythms and the biological clocks by which most cells, including skin and hair cells, regulate themselves represent a ripe and fascinating area of research. Applying evidence in this realm to skin care has been occurring over time and is likely to enhance our practice even more as we continue to elucidate the behavior of cutaneous cells based on the solar day. Based on this information, my recommendations are to use antioxidants and protective products in the morning, and use DNA repair enzymes, retinoids, and other repair products at night.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dong K et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010326.
2. Dong K et al. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Dec;41(6):558-62.
3. Lyons AB et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Sep;12(9):42-5.
4. Wu G et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 27;115(48):12313-8.
5. Vaughn AR et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):152-7.
6. Park S et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040862.
7. Sherratt MJ et al. Matrix Biol. 2019 Nov;84:97-110.
8. Luber AJ et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Feb;13(2):130-4.
9. Le Fur I et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Sep;117(3):718-24.
10. Kawara S et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Dec;119(6):1220-3.
11. Spörl F et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Feb;131(2):338-48.
12. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(19):3329-39.
13. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2237-48.
The majority of human cells, including skin and hair cells, keep their own time; that is, they manifest autonomous clocks and the genes that regulate their functioning.1 During the day, one primary function of the skin is protection; at night, repairing any damage (particularly DNA impairment) incurred during the day prevails.2-4 These activities are driven through circadian rhythms using clock genes that exist in all cutaneous cells.2 Important cutaneous functions such as blood flow, transepidermal water loss, and capacitance are affected by circadian rhythms.5 Hydration and inflammation are also among the several functions pertaining to epidermal homeostasis affected by circadian rhythms.6 In addition, some collagens and extracellular matrix proteases are diurnally regulated, and approximately 10% of the transcriptome, including the extracellular matrix, is thought to be controlled by circadian rhythms.7
Cutaneous cell migration and proliferation, wound healing, and tissue vulnerability to harm from UV exposure, oxidative stress, and protease activity, for example, are affected by circadian rhythms, Sherratt et al. noted in suggesting that chronotherapy presents promise for enhancing skin therapy.7 Indeed, recent research has led to the understanding that cutaneous aging, cellular repair, optimal timing for drug delivery to the skin, and skin cancer development are all affected by the chronobiological functioning of the skin.8
We have known for several years that certain types of products should be used at different times of the day. For instance, antioxidants should be used in the morning to protect skin from sun exposure and retinols should be used in the evening because of its induction of light sensitivity. The remainder of this column focuses on research in the last 2 decades that reinforces the notion of circadian rhythms working in the skin, and may alter how we view the timing of skin care. Next month’s column, part two on the circadian rhythms of the skin, will address recent clinical trials and the implications for timing treatments for certain cutaneous conditions.
Emerging data on the circadian rhythms of the skin
In 2001, Le Fur et al. studied the cutaneous circadian rhythms in the facial and forearm skin of eight healthy White women during a 48-hour period. They were able to detect such rhythms in facial sebum excretion, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) in the face and forearm, pH in the face, forearm skin temperature, and forearm capacitance using cosinor or analysis of variance methods. The investigators also observed 8- and 12-hour rhythms in TEWL in both areas, and 12 hours for forearm skin temperature. They verified that such rhythms could be measured and that they vary between skin sites. In addition, they were the first to show that ultradian and/or component rhythms can also be found in TEWL, sebum excretion, and skin temperature.9
A year later, Kawara et al. showed that mRNA of the circadian clock genes Per1, Clock, and bmal1/mop3 are expressed in normal human-cultured keratinocytes and that low-dose UVB down-regulates these genes and changes their express in keratinocyte cell cultures. They concluded that UV targeting of keratinocytes could alter circadian rhythms.10
In 2011, Spörl and colleagues characterized an in vitro functional cell autonomous circadian clock in adult human low calcium temperature keratinocytes, demonstrating that the molecular composition of the keratinocyte clock was comparable with peripheral tissue clocks. Notably, they observed that temperature acts as a robust time cue for epidermal traits, such as cholesterol homeostasis and differentiation.11
The next year, Sandu et al. investigated the kinetics of clock gene expression in epidermal and dermal cells collected from the same donor and compared their characteristics. They were able to reveal the presence of functional circadian machinery in primary cultures of fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and melanocytes, with oscillators identified in all skin cell types and thought to be involved in spurring cutaneous rhythmic functions as they exhibited discrete periods and phase relationships between clock genes.12
Three years later, Sandu et al. characterized the circadian clocks in rat skin and dermal fibroblasts. They found that skin has a self-sustaining circadian clock that experiences age-dependent alterations, and that dermal fibroblasts manifest circadian rhythms that can be modulated by endogenous (e.g., melatonin) and exogenous (e.g., temperature) influences.13
In 2019, Park et al. demonstrated that the diurnal expression of the gene TIMP3, which is thought to evince a circadian rhythm in synchronized human keratinocytes, experiences disruptions in such rhythms by UVB exposure. The inflammation that results can be blocked, they argued, by recovering the circadian expression of TIMP3 using synthetic TIMP3 peptides or bioactive natural ingredients, such as green tea extracts.6
Conclusion
Circadian rhythms and the biological clocks by which most cells, including skin and hair cells, regulate themselves represent a ripe and fascinating area of research. Applying evidence in this realm to skin care has been occurring over time and is likely to enhance our practice even more as we continue to elucidate the behavior of cutaneous cells based on the solar day. Based on this information, my recommendations are to use antioxidants and protective products in the morning, and use DNA repair enzymes, retinoids, and other repair products at night.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dong K et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010326.
2. Dong K et al. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Dec;41(6):558-62.
3. Lyons AB et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Sep;12(9):42-5.
4. Wu G et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 27;115(48):12313-8.
5. Vaughn AR et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):152-7.
6. Park S et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040862.
7. Sherratt MJ et al. Matrix Biol. 2019 Nov;84:97-110.
8. Luber AJ et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Feb;13(2):130-4.
9. Le Fur I et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Sep;117(3):718-24.
10. Kawara S et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Dec;119(6):1220-3.
11. Spörl F et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Feb;131(2):338-48.
12. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(19):3329-39.
13. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2237-48.
The majority of human cells, including skin and hair cells, keep their own time; that is, they manifest autonomous clocks and the genes that regulate their functioning.1 During the day, one primary function of the skin is protection; at night, repairing any damage (particularly DNA impairment) incurred during the day prevails.2-4 These activities are driven through circadian rhythms using clock genes that exist in all cutaneous cells.2 Important cutaneous functions such as blood flow, transepidermal water loss, and capacitance are affected by circadian rhythms.5 Hydration and inflammation are also among the several functions pertaining to epidermal homeostasis affected by circadian rhythms.6 In addition, some collagens and extracellular matrix proteases are diurnally regulated, and approximately 10% of the transcriptome, including the extracellular matrix, is thought to be controlled by circadian rhythms.7
Cutaneous cell migration and proliferation, wound healing, and tissue vulnerability to harm from UV exposure, oxidative stress, and protease activity, for example, are affected by circadian rhythms, Sherratt et al. noted in suggesting that chronotherapy presents promise for enhancing skin therapy.7 Indeed, recent research has led to the understanding that cutaneous aging, cellular repair, optimal timing for drug delivery to the skin, and skin cancer development are all affected by the chronobiological functioning of the skin.8
We have known for several years that certain types of products should be used at different times of the day. For instance, antioxidants should be used in the morning to protect skin from sun exposure and retinols should be used in the evening because of its induction of light sensitivity. The remainder of this column focuses on research in the last 2 decades that reinforces the notion of circadian rhythms working in the skin, and may alter how we view the timing of skin care. Next month’s column, part two on the circadian rhythms of the skin, will address recent clinical trials and the implications for timing treatments for certain cutaneous conditions.
Emerging data on the circadian rhythms of the skin
In 2001, Le Fur et al. studied the cutaneous circadian rhythms in the facial and forearm skin of eight healthy White women during a 48-hour period. They were able to detect such rhythms in facial sebum excretion, transepidermal water loss (TEWL) in the face and forearm, pH in the face, forearm skin temperature, and forearm capacitance using cosinor or analysis of variance methods. The investigators also observed 8- and 12-hour rhythms in TEWL in both areas, and 12 hours for forearm skin temperature. They verified that such rhythms could be measured and that they vary between skin sites. In addition, they were the first to show that ultradian and/or component rhythms can also be found in TEWL, sebum excretion, and skin temperature.9
A year later, Kawara et al. showed that mRNA of the circadian clock genes Per1, Clock, and bmal1/mop3 are expressed in normal human-cultured keratinocytes and that low-dose UVB down-regulates these genes and changes their express in keratinocyte cell cultures. They concluded that UV targeting of keratinocytes could alter circadian rhythms.10
In 2011, Spörl and colleagues characterized an in vitro functional cell autonomous circadian clock in adult human low calcium temperature keratinocytes, demonstrating that the molecular composition of the keratinocyte clock was comparable with peripheral tissue clocks. Notably, they observed that temperature acts as a robust time cue for epidermal traits, such as cholesterol homeostasis and differentiation.11
The next year, Sandu et al. investigated the kinetics of clock gene expression in epidermal and dermal cells collected from the same donor and compared their characteristics. They were able to reveal the presence of functional circadian machinery in primary cultures of fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and melanocytes, with oscillators identified in all skin cell types and thought to be involved in spurring cutaneous rhythmic functions as they exhibited discrete periods and phase relationships between clock genes.12
Three years later, Sandu et al. characterized the circadian clocks in rat skin and dermal fibroblasts. They found that skin has a self-sustaining circadian clock that experiences age-dependent alterations, and that dermal fibroblasts manifest circadian rhythms that can be modulated by endogenous (e.g., melatonin) and exogenous (e.g., temperature) influences.13
In 2019, Park et al. demonstrated that the diurnal expression of the gene TIMP3, which is thought to evince a circadian rhythm in synchronized human keratinocytes, experiences disruptions in such rhythms by UVB exposure. The inflammation that results can be blocked, they argued, by recovering the circadian expression of TIMP3 using synthetic TIMP3 peptides or bioactive natural ingredients, such as green tea extracts.6
Conclusion
Circadian rhythms and the biological clocks by which most cells, including skin and hair cells, regulate themselves represent a ripe and fascinating area of research. Applying evidence in this realm to skin care has been occurring over time and is likely to enhance our practice even more as we continue to elucidate the behavior of cutaneous cells based on the solar day. Based on this information, my recommendations are to use antioxidants and protective products in the morning, and use DNA repair enzymes, retinoids, and other repair products at night.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur who practices in Miami. She founded the Cosmetic Dermatology Center at the University of Miami in 1997. Dr. Baumann has written two textbooks and a New York Times Best Sellers book for consumers. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Revance, Evolus, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a company that independently tests skin care products and makes recommendations to physicians on which skin care technologies are best. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Dong K et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010326.
2. Dong K et al. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Dec;41(6):558-62.
3. Lyons AB et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019 Sep;12(9):42-5.
4. Wu G et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 27;115(48):12313-8.
5. Vaughn AR et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):152-7.
6. Park S et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040862.
7. Sherratt MJ et al. Matrix Biol. 2019 Nov;84:97-110.
8. Luber AJ et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Feb;13(2):130-4.
9. Le Fur I et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Sep;117(3):718-24.
10. Kawara S et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Dec;119(6):1220-3.
11. Spörl F et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2011 Feb;131(2):338-48.
12. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(19):3329-39.
13. Sandu C et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2237-48.
Advocate for legislation to improve, protect LGBTQ lives
In January in many states, the start of a new year also means the start of a new legislative session. For LGBTQ youth and their families, these sessions can create a significant amount of anxiety, as legislators in several states introduce legislation to curtail the rights of this population. In some cases, legislators have attempted to criminalize the provision of gender-affirming medical care to the trans and gender-diverse adolescents that many of us provide care to on a daily basis. As pediatricians,
2020 started on a positive note for LGBTQ children and adolescents, with Virginia becoming the 20th state to ban conversion therapy for minors. Legislation was introduced in several other states to prohibit this practice, including Kentucky, Missouri, and Ohio, and but they ultimately died in committee or were never referred. While there is not yet a nationwide ban on conversion therapy, legislation was introduced in the last three U.S. Congress sessions to ban this harmful practice. In June 2020, the Supreme Court decision in Bostock vs. Clayton County stated that employers could not fire an employee solely because of that person’s sexual orientation and/or gender identity.
However, 19 separate bills were introduced in 2020 alone in states across the United States that would prohibit gender-affirming care for adolescents under age 18.1 Many of these bills also would make the provision of gender-affirming medical care codified as felony child abuse, with loss of licensure, fines and/or jail time a possibility for physicians who prescribe hormones or puberty blockers for gender-affirming care to minors. Fortunately, these bills either died in committee or never had a hearing. However, legislation has been prefiled in several states for their 2021 session to again attempt to prohibit minors from obtaining gender-affirming medical care and/or criminalizing the provision of this care by physicians. Other bills were filed or have been prefiled again to allow various medical and mental health providers to refuse to treat LGBTQ patients because of their personal religious beliefs and/or forcing these same providers to tell a parent if a minor reveals to that provider that they are LGBTQ.
Even if this legislation does not pass or get a hearing, the fact that the bills were introduced can have a profound impact on LGBTQ patients and their families. After a bill was introduced in Texas in their 2017 legislative session that would require trans and gender-diverse (TGD) people to use the bathroom based on their sex assigned at birth, the Trevor Project reported that it had an increase of 34% in crisis calls from trans youth who were in distress.2 This was similar, but slightly less, than was reported by the Trevor Project in September 2015 when in the run-up to a vote on Houston’s Equal Rights Ordinance, advertising was run equating trans women as predators who could be lying in wait in bathrooms. On the converse, when LGBTQ youth feel supported in the media, courts, and legislatures, this can have a positive impact on their mental health. A 2017 study found that, in states who enacted same-sex marriage laws prior to the 2015 Supreme Court decision in Obergefell, compared with those who did not, there was a 7% relative reduction in the proportion of high school students who attempted suicide.3
The American Academy of Pediatrics published its policy statement in September 2018 outlining suggestions for pediatricians to provide support to TGD youth.4 In this position statement, recommendation No. 7 states “that pediatricians have a role in advocating for policies and laws that protect youth who identify as TGD from discrimination and violence.” Therefore, it is incumbent upon us to use our voices to support our LGBTQ youth. In 2020, several pediatricians from the South Dakota chapter of the AAP provided testimony – and organized public rallies – against legislation in that state which would have made gender-affirming care to minors under age 16 punishable by a fine and/or up to 10 years in prison.5
So what can you do? First, get to know your local and state legislators. While it was difficult to meet them in person for much of 2020, you can always call their district and/or Capitol offices, email them, or fill out their constituent contact form typically found on their website. Let them know that you oppose bills which introduce discrimination against your LGBTQ patients or threaten to criminalize the care that you provide to these patients.
Second, work with your state medical association or state AAP chapter to encourage them to oppose these harmful laws and support laws that improve the lives of LGBTQ patients. Third, you can write op-eds to your local newspaper, expressing your support for your patients and outlining the detrimental effects that anti-LGBTQ laws have on your patients. Lastly, you can be active on Twitter, Facebook, or other social media platforms sharing stories of how harmful or helpful certain pieces of legislation can be for your patients.
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Cooper at [email protected].
References
1. “Leglislation affecting LGBT rights across country.” www.aclu.org.
2. “Bathroom Bills Fuel Spike In Calls From Trans Youth To Suicide Hotline.” www.outsmartmagazine.com. 2017 Aug.
3. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.4529.
4. Pediatrics. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2162.
5. Wyckoff AS. “State bills seek to place limits on transgender care, ‘punish’ physicians.” AAP News. 2020 Feb 18.
In January in many states, the start of a new year also means the start of a new legislative session. For LGBTQ youth and their families, these sessions can create a significant amount of anxiety, as legislators in several states introduce legislation to curtail the rights of this population. In some cases, legislators have attempted to criminalize the provision of gender-affirming medical care to the trans and gender-diverse adolescents that many of us provide care to on a daily basis. As pediatricians,
2020 started on a positive note for LGBTQ children and adolescents, with Virginia becoming the 20th state to ban conversion therapy for minors. Legislation was introduced in several other states to prohibit this practice, including Kentucky, Missouri, and Ohio, and but they ultimately died in committee or were never referred. While there is not yet a nationwide ban on conversion therapy, legislation was introduced in the last three U.S. Congress sessions to ban this harmful practice. In June 2020, the Supreme Court decision in Bostock vs. Clayton County stated that employers could not fire an employee solely because of that person’s sexual orientation and/or gender identity.
However, 19 separate bills were introduced in 2020 alone in states across the United States that would prohibit gender-affirming care for adolescents under age 18.1 Many of these bills also would make the provision of gender-affirming medical care codified as felony child abuse, with loss of licensure, fines and/or jail time a possibility for physicians who prescribe hormones or puberty blockers for gender-affirming care to minors. Fortunately, these bills either died in committee or never had a hearing. However, legislation has been prefiled in several states for their 2021 session to again attempt to prohibit minors from obtaining gender-affirming medical care and/or criminalizing the provision of this care by physicians. Other bills were filed or have been prefiled again to allow various medical and mental health providers to refuse to treat LGBTQ patients because of their personal religious beliefs and/or forcing these same providers to tell a parent if a minor reveals to that provider that they are LGBTQ.
Even if this legislation does not pass or get a hearing, the fact that the bills were introduced can have a profound impact on LGBTQ patients and their families. After a bill was introduced in Texas in their 2017 legislative session that would require trans and gender-diverse (TGD) people to use the bathroom based on their sex assigned at birth, the Trevor Project reported that it had an increase of 34% in crisis calls from trans youth who were in distress.2 This was similar, but slightly less, than was reported by the Trevor Project in September 2015 when in the run-up to a vote on Houston’s Equal Rights Ordinance, advertising was run equating trans women as predators who could be lying in wait in bathrooms. On the converse, when LGBTQ youth feel supported in the media, courts, and legislatures, this can have a positive impact on their mental health. A 2017 study found that, in states who enacted same-sex marriage laws prior to the 2015 Supreme Court decision in Obergefell, compared with those who did not, there was a 7% relative reduction in the proportion of high school students who attempted suicide.3
The American Academy of Pediatrics published its policy statement in September 2018 outlining suggestions for pediatricians to provide support to TGD youth.4 In this position statement, recommendation No. 7 states “that pediatricians have a role in advocating for policies and laws that protect youth who identify as TGD from discrimination and violence.” Therefore, it is incumbent upon us to use our voices to support our LGBTQ youth. In 2020, several pediatricians from the South Dakota chapter of the AAP provided testimony – and organized public rallies – against legislation in that state which would have made gender-affirming care to minors under age 16 punishable by a fine and/or up to 10 years in prison.5
So what can you do? First, get to know your local and state legislators. While it was difficult to meet them in person for much of 2020, you can always call their district and/or Capitol offices, email them, or fill out their constituent contact form typically found on their website. Let them know that you oppose bills which introduce discrimination against your LGBTQ patients or threaten to criminalize the care that you provide to these patients.
Second, work with your state medical association or state AAP chapter to encourage them to oppose these harmful laws and support laws that improve the lives of LGBTQ patients. Third, you can write op-eds to your local newspaper, expressing your support for your patients and outlining the detrimental effects that anti-LGBTQ laws have on your patients. Lastly, you can be active on Twitter, Facebook, or other social media platforms sharing stories of how harmful or helpful certain pieces of legislation can be for your patients.
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Cooper at [email protected].
References
1. “Leglislation affecting LGBT rights across country.” www.aclu.org.
2. “Bathroom Bills Fuel Spike In Calls From Trans Youth To Suicide Hotline.” www.outsmartmagazine.com. 2017 Aug.
3. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.4529.
4. Pediatrics. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2162.
5. Wyckoff AS. “State bills seek to place limits on transgender care, ‘punish’ physicians.” AAP News. 2020 Feb 18.
In January in many states, the start of a new year also means the start of a new legislative session. For LGBTQ youth and their families, these sessions can create a significant amount of anxiety, as legislators in several states introduce legislation to curtail the rights of this population. In some cases, legislators have attempted to criminalize the provision of gender-affirming medical care to the trans and gender-diverse adolescents that many of us provide care to on a daily basis. As pediatricians,
2020 started on a positive note for LGBTQ children and adolescents, with Virginia becoming the 20th state to ban conversion therapy for minors. Legislation was introduced in several other states to prohibit this practice, including Kentucky, Missouri, and Ohio, and but they ultimately died in committee or were never referred. While there is not yet a nationwide ban on conversion therapy, legislation was introduced in the last three U.S. Congress sessions to ban this harmful practice. In June 2020, the Supreme Court decision in Bostock vs. Clayton County stated that employers could not fire an employee solely because of that person’s sexual orientation and/or gender identity.
However, 19 separate bills were introduced in 2020 alone in states across the United States that would prohibit gender-affirming care for adolescents under age 18.1 Many of these bills also would make the provision of gender-affirming medical care codified as felony child abuse, with loss of licensure, fines and/or jail time a possibility for physicians who prescribe hormones or puberty blockers for gender-affirming care to minors. Fortunately, these bills either died in committee or never had a hearing. However, legislation has been prefiled in several states for their 2021 session to again attempt to prohibit minors from obtaining gender-affirming medical care and/or criminalizing the provision of this care by physicians. Other bills were filed or have been prefiled again to allow various medical and mental health providers to refuse to treat LGBTQ patients because of their personal religious beliefs and/or forcing these same providers to tell a parent if a minor reveals to that provider that they are LGBTQ.
Even if this legislation does not pass or get a hearing, the fact that the bills were introduced can have a profound impact on LGBTQ patients and their families. After a bill was introduced in Texas in their 2017 legislative session that would require trans and gender-diverse (TGD) people to use the bathroom based on their sex assigned at birth, the Trevor Project reported that it had an increase of 34% in crisis calls from trans youth who were in distress.2 This was similar, but slightly less, than was reported by the Trevor Project in September 2015 when in the run-up to a vote on Houston’s Equal Rights Ordinance, advertising was run equating trans women as predators who could be lying in wait in bathrooms. On the converse, when LGBTQ youth feel supported in the media, courts, and legislatures, this can have a positive impact on their mental health. A 2017 study found that, in states who enacted same-sex marriage laws prior to the 2015 Supreme Court decision in Obergefell, compared with those who did not, there was a 7% relative reduction in the proportion of high school students who attempted suicide.3
The American Academy of Pediatrics published its policy statement in September 2018 outlining suggestions for pediatricians to provide support to TGD youth.4 In this position statement, recommendation No. 7 states “that pediatricians have a role in advocating for policies and laws that protect youth who identify as TGD from discrimination and violence.” Therefore, it is incumbent upon us to use our voices to support our LGBTQ youth. In 2020, several pediatricians from the South Dakota chapter of the AAP provided testimony – and organized public rallies – against legislation in that state which would have made gender-affirming care to minors under age 16 punishable by a fine and/or up to 10 years in prison.5
So what can you do? First, get to know your local and state legislators. While it was difficult to meet them in person for much of 2020, you can always call their district and/or Capitol offices, email them, or fill out their constituent contact form typically found on their website. Let them know that you oppose bills which introduce discrimination against your LGBTQ patients or threaten to criminalize the care that you provide to these patients.
Second, work with your state medical association or state AAP chapter to encourage them to oppose these harmful laws and support laws that improve the lives of LGBTQ patients. Third, you can write op-eds to your local newspaper, expressing your support for your patients and outlining the detrimental effects that anti-LGBTQ laws have on your patients. Lastly, you can be active on Twitter, Facebook, or other social media platforms sharing stories of how harmful or helpful certain pieces of legislation can be for your patients.
Dr. Cooper is assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine specialist at Children’s Medical Center Dallas. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Cooper at [email protected].
References
1. “Leglislation affecting LGBT rights across country.” www.aclu.org.
2. “Bathroom Bills Fuel Spike In Calls From Trans Youth To Suicide Hotline.” www.outsmartmagazine.com. 2017 Aug.
3. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Apr 1. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.4529.
4. Pediatrics. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-2162.
5. Wyckoff AS. “State bills seek to place limits on transgender care, ‘punish’ physicians.” AAP News. 2020 Feb 18.
Can a health care worker refuse the COVID-19 vaccine?
As hospitals across the country develop their plans to vaccinate their health care employees against COVID-19, a key question has come to the fore: What if an employee – whether nurse, physician, or other health care worker – refuses to receive the vaccine? Can hospitals require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19? And what consequences could an employee face for refusing the vaccine?
My answer needs to be based, in part, on the law related to previous vaccines – influenza, for example – because at the time of this writing (early December 2020), no vaccine for COVID-19 has been approved, although approval of at least one vaccine is expected within a week. So there have been no offers of vaccine and refusals yet, nor are there any cases to date involving an employee who refused a COVID-19 vaccine. As of December 2020, there are no state or federal laws that either require an employee to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or that protect an employee who refuses vaccination against COVID-19. It will take a while after the vaccine is approved and distributed before refusals, reactions, policies, cases, and laws begin to emerge.
If we look at the law related to health care workers refusing to be vaccinated against the closest relative to COVID-19 – influenza – then the answer would be yes, employers can require employees to be vaccinated.
An employer can fire an employee who refuses influenza vaccination. If an employee who refused and was fired sues the employer for wrongful termination, the employee has more or less chance of success depending on the reason for refusal. Some courts and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission have held that a refusal on religious grounds is protected by the U.S. Constitution, as in this recent case. The Constitution protects freedom to practice one’s religion. Specific religions may have a range of tenets that support refusal to be vaccinated.
A refusal on medical grounds has been successful if the medical grounds fall under the protections of the Americans with Disabilities Act but may fail when the medical grounds for the claim are not covered by the ADA.
Refusal for secular, nonmedical reasons, such as a health care worker’s policy of treating their body as their temple, has not gone over well with employers or courts. However, in at least one case, a nurse who refused vaccination on secular, nonmedical grounds won her case against her employer, on appeal. The appeals court found that the hospital violated her First Amendment rights.
Employees who refuse vaccination for religious or medical reasons still will need to take measures to protect patients and other employees from infection. An employer such as a hospital can, rather than fire the employee, offer the employee an accommodation, such as requiring that the employee wear a mask or quarantine. There are no cases that have upheld an employee’s right to refuse to wear a mask or quarantine.
The situation with the COVID-19 vaccine is different from the situation surrounding influenza vaccines. There are plenty of data on effectiveness and side effects of influenza vaccines, but there is very little evidence of short- or long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccines currently being tested and/or considered for approval. One could argue that the process of vaccine development is the same for all virus vaccines. However, public confidence in the vaccine vetting process is not what it once was. It has been widely publicized that the COVID-19 vaccine trials have been rushed. As of December 2020, only 60% of the general population say they would take the vaccine, although researchers say confidence is increasing.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has designated health care workers as first in line to get the vaccine, but some health care workers may not want to be the first to try it. A CDC survey found that 63% of health care workers polled in recent months said they would get a COVID-19 vaccine.
Unions have entered the conversation. A coalition of unions that represent health care workers said, “we need a transparent, evidence-based federal vaccine strategy based on principles of equity, safety, and priority, as well as robust efforts to address a high degree of skepticism about safety of an authorized vaccine.” The organization declined to promote a vaccine until more is known.
As of publication date, the EEOC guidance for employers responding to COVID-19 does not address vaccines.
The CDC’s Interim Guidance for Businesses and Employers Responding to Coronavirus Disease 2019, May 2020, updated Dec. 4, 2020, does not address vaccines. The CDC’s page on COVID-19 vaccination for health care workers does not address a health care worker’s refusal. The site does assure health care workers that the vaccine development process is sound: “The current vaccine safety system is strong and robust, with the capacity to effectively monitor COVID-19 vaccine safety. Existing data systems have validated analytic methods that can rapidly detect statistical signals for possible vaccine safety problems. These systems are being scaled up to fully meet the needs of the nation. Additional systems and data sources are also being developed to further enhance safety monitoring capabilities. CDC is committed to ensuring that COVID-19 vaccines are safe.”
In the coming months, government officials and vaccine manufacturers will be working to reassure the public of the safety of the vaccine and the rigor of the vaccine development process. In November 2020, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Director Anthony Fauci, MD, told Kaiser Health News: “The company looks at the data. I look at the data. Then the company puts the data to the FDA. The FDA will make the decision to do an emergency-use authorization or a license application approval. And they have career scientists who are really independent. They’re not beholden to anybody. Then there’s another independent group, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee. The FDA commissioner has vowed publicly that he will go according to the opinion of the career scientists and the advisory board.” President-elect Joe Biden said he would get a vaccine when Dr. Fauci thinks it is safe.
An employee who, after researching the vaccine and the process, still wants to refuse when offered the vaccine is not likely to be fired for that reason right away, as long as the employee takes other precautions, such as wearing a mask. If the employer does fire the employee and the employee sues the employer, it is impossible to predict how a court would decide the case.
Related legal questions may arise in the coming months. For example:
- Is an employer exempt from paying workers’ compensation to an employee who refuses to be vaccinated and then contracts the virus while on the job?
- Can a prospective employer require COVID-19 vaccination as a precondition of employment?
- Is it within a patient’s rights to receive an answer to the question: Has my health care worker been vaccinated against COVID-19?
- If a hospital allows employees to refuse vaccination and keep working, and an outbreak occurs, and it is suggested through contact tracing that unvaccinated workers infected patients, will a court hold the hospital liable for patients’ damages?
Answers to these questions are yet to be determined.
Carolyn Buppert (www.buppert.com) is an attorney and former nurse practitioner who focuses on the legal issues affecting nurse practitioners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As hospitals across the country develop their plans to vaccinate their health care employees against COVID-19, a key question has come to the fore: What if an employee – whether nurse, physician, or other health care worker – refuses to receive the vaccine? Can hospitals require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19? And what consequences could an employee face for refusing the vaccine?
My answer needs to be based, in part, on the law related to previous vaccines – influenza, for example – because at the time of this writing (early December 2020), no vaccine for COVID-19 has been approved, although approval of at least one vaccine is expected within a week. So there have been no offers of vaccine and refusals yet, nor are there any cases to date involving an employee who refused a COVID-19 vaccine. As of December 2020, there are no state or federal laws that either require an employee to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or that protect an employee who refuses vaccination against COVID-19. It will take a while after the vaccine is approved and distributed before refusals, reactions, policies, cases, and laws begin to emerge.
If we look at the law related to health care workers refusing to be vaccinated against the closest relative to COVID-19 – influenza – then the answer would be yes, employers can require employees to be vaccinated.
An employer can fire an employee who refuses influenza vaccination. If an employee who refused and was fired sues the employer for wrongful termination, the employee has more or less chance of success depending on the reason for refusal. Some courts and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission have held that a refusal on religious grounds is protected by the U.S. Constitution, as in this recent case. The Constitution protects freedom to practice one’s religion. Specific religions may have a range of tenets that support refusal to be vaccinated.
A refusal on medical grounds has been successful if the medical grounds fall under the protections of the Americans with Disabilities Act but may fail when the medical grounds for the claim are not covered by the ADA.
Refusal for secular, nonmedical reasons, such as a health care worker’s policy of treating their body as their temple, has not gone over well with employers or courts. However, in at least one case, a nurse who refused vaccination on secular, nonmedical grounds won her case against her employer, on appeal. The appeals court found that the hospital violated her First Amendment rights.
Employees who refuse vaccination for religious or medical reasons still will need to take measures to protect patients and other employees from infection. An employer such as a hospital can, rather than fire the employee, offer the employee an accommodation, such as requiring that the employee wear a mask or quarantine. There are no cases that have upheld an employee’s right to refuse to wear a mask or quarantine.
The situation with the COVID-19 vaccine is different from the situation surrounding influenza vaccines. There are plenty of data on effectiveness and side effects of influenza vaccines, but there is very little evidence of short- or long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccines currently being tested and/or considered for approval. One could argue that the process of vaccine development is the same for all virus vaccines. However, public confidence in the vaccine vetting process is not what it once was. It has been widely publicized that the COVID-19 vaccine trials have been rushed. As of December 2020, only 60% of the general population say they would take the vaccine, although researchers say confidence is increasing.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has designated health care workers as first in line to get the vaccine, but some health care workers may not want to be the first to try it. A CDC survey found that 63% of health care workers polled in recent months said they would get a COVID-19 vaccine.
Unions have entered the conversation. A coalition of unions that represent health care workers said, “we need a transparent, evidence-based federal vaccine strategy based on principles of equity, safety, and priority, as well as robust efforts to address a high degree of skepticism about safety of an authorized vaccine.” The organization declined to promote a vaccine until more is known.
As of publication date, the EEOC guidance for employers responding to COVID-19 does not address vaccines.
The CDC’s Interim Guidance for Businesses and Employers Responding to Coronavirus Disease 2019, May 2020, updated Dec. 4, 2020, does not address vaccines. The CDC’s page on COVID-19 vaccination for health care workers does not address a health care worker’s refusal. The site does assure health care workers that the vaccine development process is sound: “The current vaccine safety system is strong and robust, with the capacity to effectively monitor COVID-19 vaccine safety. Existing data systems have validated analytic methods that can rapidly detect statistical signals for possible vaccine safety problems. These systems are being scaled up to fully meet the needs of the nation. Additional systems and data sources are also being developed to further enhance safety monitoring capabilities. CDC is committed to ensuring that COVID-19 vaccines are safe.”
In the coming months, government officials and vaccine manufacturers will be working to reassure the public of the safety of the vaccine and the rigor of the vaccine development process. In November 2020, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Director Anthony Fauci, MD, told Kaiser Health News: “The company looks at the data. I look at the data. Then the company puts the data to the FDA. The FDA will make the decision to do an emergency-use authorization or a license application approval. And they have career scientists who are really independent. They’re not beholden to anybody. Then there’s another independent group, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee. The FDA commissioner has vowed publicly that he will go according to the opinion of the career scientists and the advisory board.” President-elect Joe Biden said he would get a vaccine when Dr. Fauci thinks it is safe.
An employee who, after researching the vaccine and the process, still wants to refuse when offered the vaccine is not likely to be fired for that reason right away, as long as the employee takes other precautions, such as wearing a mask. If the employer does fire the employee and the employee sues the employer, it is impossible to predict how a court would decide the case.
Related legal questions may arise in the coming months. For example:
- Is an employer exempt from paying workers’ compensation to an employee who refuses to be vaccinated and then contracts the virus while on the job?
- Can a prospective employer require COVID-19 vaccination as a precondition of employment?
- Is it within a patient’s rights to receive an answer to the question: Has my health care worker been vaccinated against COVID-19?
- If a hospital allows employees to refuse vaccination and keep working, and an outbreak occurs, and it is suggested through contact tracing that unvaccinated workers infected patients, will a court hold the hospital liable for patients’ damages?
Answers to these questions are yet to be determined.
Carolyn Buppert (www.buppert.com) is an attorney and former nurse practitioner who focuses on the legal issues affecting nurse practitioners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As hospitals across the country develop their plans to vaccinate their health care employees against COVID-19, a key question has come to the fore: What if an employee – whether nurse, physician, or other health care worker – refuses to receive the vaccine? Can hospitals require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID-19? And what consequences could an employee face for refusing the vaccine?
My answer needs to be based, in part, on the law related to previous vaccines – influenza, for example – because at the time of this writing (early December 2020), no vaccine for COVID-19 has been approved, although approval of at least one vaccine is expected within a week. So there have been no offers of vaccine and refusals yet, nor are there any cases to date involving an employee who refused a COVID-19 vaccine. As of December 2020, there are no state or federal laws that either require an employee to be vaccinated against COVID-19 or that protect an employee who refuses vaccination against COVID-19. It will take a while after the vaccine is approved and distributed before refusals, reactions, policies, cases, and laws begin to emerge.
If we look at the law related to health care workers refusing to be vaccinated against the closest relative to COVID-19 – influenza – then the answer would be yes, employers can require employees to be vaccinated.
An employer can fire an employee who refuses influenza vaccination. If an employee who refused and was fired sues the employer for wrongful termination, the employee has more or less chance of success depending on the reason for refusal. Some courts and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission have held that a refusal on religious grounds is protected by the U.S. Constitution, as in this recent case. The Constitution protects freedom to practice one’s religion. Specific religions may have a range of tenets that support refusal to be vaccinated.
A refusal on medical grounds has been successful if the medical grounds fall under the protections of the Americans with Disabilities Act but may fail when the medical grounds for the claim are not covered by the ADA.
Refusal for secular, nonmedical reasons, such as a health care worker’s policy of treating their body as their temple, has not gone over well with employers or courts. However, in at least one case, a nurse who refused vaccination on secular, nonmedical grounds won her case against her employer, on appeal. The appeals court found that the hospital violated her First Amendment rights.
Employees who refuse vaccination for religious or medical reasons still will need to take measures to protect patients and other employees from infection. An employer such as a hospital can, rather than fire the employee, offer the employee an accommodation, such as requiring that the employee wear a mask or quarantine. There are no cases that have upheld an employee’s right to refuse to wear a mask or quarantine.
The situation with the COVID-19 vaccine is different from the situation surrounding influenza vaccines. There are plenty of data on effectiveness and side effects of influenza vaccines, but there is very little evidence of short- or long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccines currently being tested and/or considered for approval. One could argue that the process of vaccine development is the same for all virus vaccines. However, public confidence in the vaccine vetting process is not what it once was. It has been widely publicized that the COVID-19 vaccine trials have been rushed. As of December 2020, only 60% of the general population say they would take the vaccine, although researchers say confidence is increasing.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has designated health care workers as first in line to get the vaccine, but some health care workers may not want to be the first to try it. A CDC survey found that 63% of health care workers polled in recent months said they would get a COVID-19 vaccine.
Unions have entered the conversation. A coalition of unions that represent health care workers said, “we need a transparent, evidence-based federal vaccine strategy based on principles of equity, safety, and priority, as well as robust efforts to address a high degree of skepticism about safety of an authorized vaccine.” The organization declined to promote a vaccine until more is known.
As of publication date, the EEOC guidance for employers responding to COVID-19 does not address vaccines.
The CDC’s Interim Guidance for Businesses and Employers Responding to Coronavirus Disease 2019, May 2020, updated Dec. 4, 2020, does not address vaccines. The CDC’s page on COVID-19 vaccination for health care workers does not address a health care worker’s refusal. The site does assure health care workers that the vaccine development process is sound: “The current vaccine safety system is strong and robust, with the capacity to effectively monitor COVID-19 vaccine safety. Existing data systems have validated analytic methods that can rapidly detect statistical signals for possible vaccine safety problems. These systems are being scaled up to fully meet the needs of the nation. Additional systems and data sources are also being developed to further enhance safety monitoring capabilities. CDC is committed to ensuring that COVID-19 vaccines are safe.”
In the coming months, government officials and vaccine manufacturers will be working to reassure the public of the safety of the vaccine and the rigor of the vaccine development process. In November 2020, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Director Anthony Fauci, MD, told Kaiser Health News: “The company looks at the data. I look at the data. Then the company puts the data to the FDA. The FDA will make the decision to do an emergency-use authorization or a license application approval. And they have career scientists who are really independent. They’re not beholden to anybody. Then there’s another independent group, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee. The FDA commissioner has vowed publicly that he will go according to the opinion of the career scientists and the advisory board.” President-elect Joe Biden said he would get a vaccine when Dr. Fauci thinks it is safe.
An employee who, after researching the vaccine and the process, still wants to refuse when offered the vaccine is not likely to be fired for that reason right away, as long as the employee takes other precautions, such as wearing a mask. If the employer does fire the employee and the employee sues the employer, it is impossible to predict how a court would decide the case.
Related legal questions may arise in the coming months. For example:
- Is an employer exempt from paying workers’ compensation to an employee who refuses to be vaccinated and then contracts the virus while on the job?
- Can a prospective employer require COVID-19 vaccination as a precondition of employment?
- Is it within a patient’s rights to receive an answer to the question: Has my health care worker been vaccinated against COVID-19?
- If a hospital allows employees to refuse vaccination and keep working, and an outbreak occurs, and it is suggested through contact tracing that unvaccinated workers infected patients, will a court hold the hospital liable for patients’ damages?
Answers to these questions are yet to be determined.
Carolyn Buppert (www.buppert.com) is an attorney and former nurse practitioner who focuses on the legal issues affecting nurse practitioners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A 70-year-old presented with a 3-week history of asymptomatic violaceous papules on his feet
and named the condition multiple benign pigmented hemorrhagic sarcoma. The disease emerged again at the onset of the AIDS epidemic among homosexual men. There are five variants: HIV/AIDS–related KS, classic KS, African cutaneous KS, African lymphadenopathic KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS (from immunosuppressive therapy or malignancies such as lymphoma).
KS is caused by human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8). Patients with KS have an increased risk of developing other malignancies such as lymphomas, leukemia, and myeloma. This patient exhibited classic KS.
The various forms of KS may appear different clinically. The lesions may appear as erythematous macules, small violaceous papules, large plaques, or ulcerated nodules. In classic KS, violaceous to bluish-black macules evolve to papules or plaques. Lesions are generally asymptomatic. The most common locations are the toes and soles, although other areas may be affected. Any mucocutaneous surface can be involved. The most common areas of internal involvement are the gastrointestinal system and lymphatics.
Histology reveals angular vessels lined by atypical cells. An associated inflammatory infiltrate containing plasma cells may be present in the upper dermis and perivascular areas. Nodules and plaques reveal a spindle cell neoplasm pattern. Lesions will stain positive for HHV-8.
In patients with HIV/AIDS–related KS, highly active antiretroviral therapy is the most important and beneficial treatment. Since the introduction of HAART, the incidence of KS has greatly decreased. However, there are a proportion of HIV/AIDS–associated Kaposi’s sarcoma patients with well-controlled HIV and undetectable viral loads who require further treatment.
Lesions may spontaneously resolve on their own. Other treatment methods include: cryotherapy, topical alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid), intralesional interferon-alpha or vinblastine, superficial radiotherapy, liposomal doxorubicin, daunorubicin or paclitaxel. Small lesions that are asymptomatic may be monitored.
This patient had no internal involvement and responded well to cryotherapy.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
and named the condition multiple benign pigmented hemorrhagic sarcoma. The disease emerged again at the onset of the AIDS epidemic among homosexual men. There are five variants: HIV/AIDS–related KS, classic KS, African cutaneous KS, African lymphadenopathic KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS (from immunosuppressive therapy or malignancies such as lymphoma).
KS is caused by human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8). Patients with KS have an increased risk of developing other malignancies such as lymphomas, leukemia, and myeloma. This patient exhibited classic KS.
The various forms of KS may appear different clinically. The lesions may appear as erythematous macules, small violaceous papules, large plaques, or ulcerated nodules. In classic KS, violaceous to bluish-black macules evolve to papules or plaques. Lesions are generally asymptomatic. The most common locations are the toes and soles, although other areas may be affected. Any mucocutaneous surface can be involved. The most common areas of internal involvement are the gastrointestinal system and lymphatics.
Histology reveals angular vessels lined by atypical cells. An associated inflammatory infiltrate containing plasma cells may be present in the upper dermis and perivascular areas. Nodules and plaques reveal a spindle cell neoplasm pattern. Lesions will stain positive for HHV-8.
In patients with HIV/AIDS–related KS, highly active antiretroviral therapy is the most important and beneficial treatment. Since the introduction of HAART, the incidence of KS has greatly decreased. However, there are a proportion of HIV/AIDS–associated Kaposi’s sarcoma patients with well-controlled HIV and undetectable viral loads who require further treatment.
Lesions may spontaneously resolve on their own. Other treatment methods include: cryotherapy, topical alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid), intralesional interferon-alpha or vinblastine, superficial radiotherapy, liposomal doxorubicin, daunorubicin or paclitaxel. Small lesions that are asymptomatic may be monitored.
This patient had no internal involvement and responded well to cryotherapy.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
and named the condition multiple benign pigmented hemorrhagic sarcoma. The disease emerged again at the onset of the AIDS epidemic among homosexual men. There are five variants: HIV/AIDS–related KS, classic KS, African cutaneous KS, African lymphadenopathic KS, and immunosuppression-associated KS (from immunosuppressive therapy or malignancies such as lymphoma).
KS is caused by human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8). Patients with KS have an increased risk of developing other malignancies such as lymphomas, leukemia, and myeloma. This patient exhibited classic KS.
The various forms of KS may appear different clinically. The lesions may appear as erythematous macules, small violaceous papules, large plaques, or ulcerated nodules. In classic KS, violaceous to bluish-black macules evolve to papules or plaques. Lesions are generally asymptomatic. The most common locations are the toes and soles, although other areas may be affected. Any mucocutaneous surface can be involved. The most common areas of internal involvement are the gastrointestinal system and lymphatics.
Histology reveals angular vessels lined by atypical cells. An associated inflammatory infiltrate containing plasma cells may be present in the upper dermis and perivascular areas. Nodules and plaques reveal a spindle cell neoplasm pattern. Lesions will stain positive for HHV-8.
In patients with HIV/AIDS–related KS, highly active antiretroviral therapy is the most important and beneficial treatment. Since the introduction of HAART, the incidence of KS has greatly decreased. However, there are a proportion of HIV/AIDS–associated Kaposi’s sarcoma patients with well-controlled HIV and undetectable viral loads who require further treatment.
Lesions may spontaneously resolve on their own. Other treatment methods include: cryotherapy, topical alitretinoin (9-cis-retinoic acid), intralesional interferon-alpha or vinblastine, superficial radiotherapy, liposomal doxorubicin, daunorubicin or paclitaxel. Small lesions that are asymptomatic may be monitored.
This patient had no internal involvement and responded well to cryotherapy.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].