User login
Pandemic tied to misdiagnosis of rare pneumonia
Psittacosis, a rare disease, has been underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed during the COVID-19 pandemic, likely because the symptoms of the disease are similar to COVID-19 symptoms, researchers suggest on the basis of data from 32 individuals.
Diagnosis of and screening for COVID-19 continues to increase; however, cases of atypical pneumonia caused by uncommon pathogens, which presents with similar symptoms, may be missed, wrote Qiaoqiao Yin, MS, of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China, and colleagues.
“The clinical manifestations of human psittacosis can present as rapidly progressing severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and multiple organ failure,” but human cases have not been well studied, they say.
In a study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 32 adults diagnosed with Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia during the COVID-19 pandemic between April 2020 and June 2021 in China. The median age of the patients was 63 years, 20 were men, and 20 had underlying diseases.
A total of 17 patients presented with fever, cough, and expectoration of yellow-white sputum. At the time of hospital admission, three patients had myalgia, two had headache, and two had hypertension. The patients were originally suspected of having COVID-19.
all of which could be observed in COVID-19 patients as well, the researchers wrote.
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) testing were used to rule out COVID-19. The researchers then used metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) to identify the disease-causing pathogens. They collected 18 bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples, 9 peripheral blood samples, and 5 sputum samples. The mNGS identified C. psittaci as the suspected pathogen within 48 hours. Suspected C. psittaci infections were confirmed by endpoint PCR for the BALF and sputum samples and six of nine blood samples, “indicating a lower sensitivity of PCR compared to mNGS for blood samples,” the researchers say. No other potential pathogens were identified.
Psittacosis is common in birds but is rare in humans. C. psittaci is responsible for 1%-8% of cases involving community-acquired pneumonia in China, the researchers note. Although poultry is a source of infection, 25 of the patients in the study did not report a history of exposure to poultry or pigeons at the time of their initial hospital admission. Many patients may be unaware of exposures to poultry, which further complicates the C. psittaci diagnosis, they note.
All patients were treated with doxycycline-based regimens and showed improvement.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of a definitive diagnostic tool for C. psittaci and the lack of convalescent serum samples to confirm cases, the researchers note. In addition, molecular detections for PCR are unavailable in most hospitals in China, they say. The results represent the largest known collection of suspected C. psittaci pneumonia cases and highlight the need for clinician vigilance and awareness of this rare condition, especially in light of the potential for misdiagnosis during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, they conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psittacosis, a rare disease, has been underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed during the COVID-19 pandemic, likely because the symptoms of the disease are similar to COVID-19 symptoms, researchers suggest on the basis of data from 32 individuals.
Diagnosis of and screening for COVID-19 continues to increase; however, cases of atypical pneumonia caused by uncommon pathogens, which presents with similar symptoms, may be missed, wrote Qiaoqiao Yin, MS, of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China, and colleagues.
“The clinical manifestations of human psittacosis can present as rapidly progressing severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and multiple organ failure,” but human cases have not been well studied, they say.
In a study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 32 adults diagnosed with Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia during the COVID-19 pandemic between April 2020 and June 2021 in China. The median age of the patients was 63 years, 20 were men, and 20 had underlying diseases.
A total of 17 patients presented with fever, cough, and expectoration of yellow-white sputum. At the time of hospital admission, three patients had myalgia, two had headache, and two had hypertension. The patients were originally suspected of having COVID-19.
all of which could be observed in COVID-19 patients as well, the researchers wrote.
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) testing were used to rule out COVID-19. The researchers then used metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) to identify the disease-causing pathogens. They collected 18 bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples, 9 peripheral blood samples, and 5 sputum samples. The mNGS identified C. psittaci as the suspected pathogen within 48 hours. Suspected C. psittaci infections were confirmed by endpoint PCR for the BALF and sputum samples and six of nine blood samples, “indicating a lower sensitivity of PCR compared to mNGS for blood samples,” the researchers say. No other potential pathogens were identified.
Psittacosis is common in birds but is rare in humans. C. psittaci is responsible for 1%-8% of cases involving community-acquired pneumonia in China, the researchers note. Although poultry is a source of infection, 25 of the patients in the study did not report a history of exposure to poultry or pigeons at the time of their initial hospital admission. Many patients may be unaware of exposures to poultry, which further complicates the C. psittaci diagnosis, they note.
All patients were treated with doxycycline-based regimens and showed improvement.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of a definitive diagnostic tool for C. psittaci and the lack of convalescent serum samples to confirm cases, the researchers note. In addition, molecular detections for PCR are unavailable in most hospitals in China, they say. The results represent the largest known collection of suspected C. psittaci pneumonia cases and highlight the need for clinician vigilance and awareness of this rare condition, especially in light of the potential for misdiagnosis during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, they conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psittacosis, a rare disease, has been underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed during the COVID-19 pandemic, likely because the symptoms of the disease are similar to COVID-19 symptoms, researchers suggest on the basis of data from 32 individuals.
Diagnosis of and screening for COVID-19 continues to increase; however, cases of atypical pneumonia caused by uncommon pathogens, which presents with similar symptoms, may be missed, wrote Qiaoqiao Yin, MS, of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China, and colleagues.
“The clinical manifestations of human psittacosis can present as rapidly progressing severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and multiple organ failure,” but human cases have not been well studied, they say.
In a study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from 32 adults diagnosed with Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia during the COVID-19 pandemic between April 2020 and June 2021 in China. The median age of the patients was 63 years, 20 were men, and 20 had underlying diseases.
A total of 17 patients presented with fever, cough, and expectoration of yellow-white sputum. At the time of hospital admission, three patients had myalgia, two had headache, and two had hypertension. The patients were originally suspected of having COVID-19.
all of which could be observed in COVID-19 patients as well, the researchers wrote.
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) testing were used to rule out COVID-19. The researchers then used metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) to identify the disease-causing pathogens. They collected 18 bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples, 9 peripheral blood samples, and 5 sputum samples. The mNGS identified C. psittaci as the suspected pathogen within 48 hours. Suspected C. psittaci infections were confirmed by endpoint PCR for the BALF and sputum samples and six of nine blood samples, “indicating a lower sensitivity of PCR compared to mNGS for blood samples,” the researchers say. No other potential pathogens were identified.
Psittacosis is common in birds but is rare in humans. C. psittaci is responsible for 1%-8% of cases involving community-acquired pneumonia in China, the researchers note. Although poultry is a source of infection, 25 of the patients in the study did not report a history of exposure to poultry or pigeons at the time of their initial hospital admission. Many patients may be unaware of exposures to poultry, which further complicates the C. psittaci diagnosis, they note.
All patients were treated with doxycycline-based regimens and showed improvement.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of a definitive diagnostic tool for C. psittaci and the lack of convalescent serum samples to confirm cases, the researchers note. In addition, molecular detections for PCR are unavailable in most hospitals in China, they say. The results represent the largest known collection of suspected C. psittaci pneumonia cases and highlight the need for clinician vigilance and awareness of this rare condition, especially in light of the potential for misdiagnosis during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, they conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
FDA approves belimumab for children with lupus nephritis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved belimumab (Benlysta) for treating active lupus nephritis (LN) in children aged 5-17 years. The drug can now be used to treat adult and pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and LN. The decision expands therapeutic options for the estimated 1.5 million Americans currently living with lupus.
“This approval marks a significant step forward in providing treatment options to these children at risk of incurring kidney damage early on in life,” Stevan W. Gibson, president and CEO of the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a press release issued by the manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline. LN is a condition that sometimes develops in people with lupus. In LN, the autoimmune cells produced by the disease attack the kidney. Roughly 40% of people with SLE experience LN.
Damage to the kidneys causes the body to have difficulty processing waste and toxins. This can create a host of problems, including end-stage kidney disease, which may be treated only with dialysis or kidney transplant. These situations significantly increase mortality among people with lupus, especially children.
Prior to the approval, the only treatment pathway for children with active LN included immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. While they may be effective, use of these classes of drugs may come with many side effects, including susceptibility to other diseases and infections. Belimumab, by contrast, is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor. It inhibits the survival of B cells, which are thought to play a role in the disease’s pathophysiology.
Belimumab was first approved to treat patients with SLE in 2011. It was approved for children with SLE 8 years later. The drug’s indications were expanded to include adults with LN in 2020.
Organizations within the lupus research community have communicated their support of the FDA’s decision. “Our community has much to celebrate with the approval of the first and much-needed treatment for children with lupus nephritis,” Lupus Research Alliance President and CEO Kenneth M. Farber said in a release from the organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Peristomal Pyoderma Gangrenosum at an Ileostomy Site
To the Editor:
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum (PPG) is a rare entity first described in 1984.1 Lesions usually begin as pustules that coalesce into an erythematous skin ulceration that contains purulent material. The lesion appears on the skin that surrounds an abdominal stoma. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum typically is associated with Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis, cancer, blood dyscrasia, diabetes mellitus, and hepatitis.2 We describe a case of PPG following an ileostomy in a patient with colon cancer and a related history of Crohn disease.
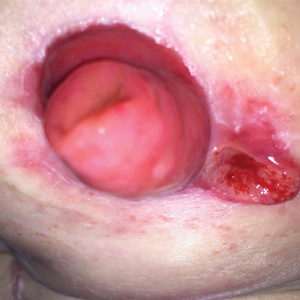
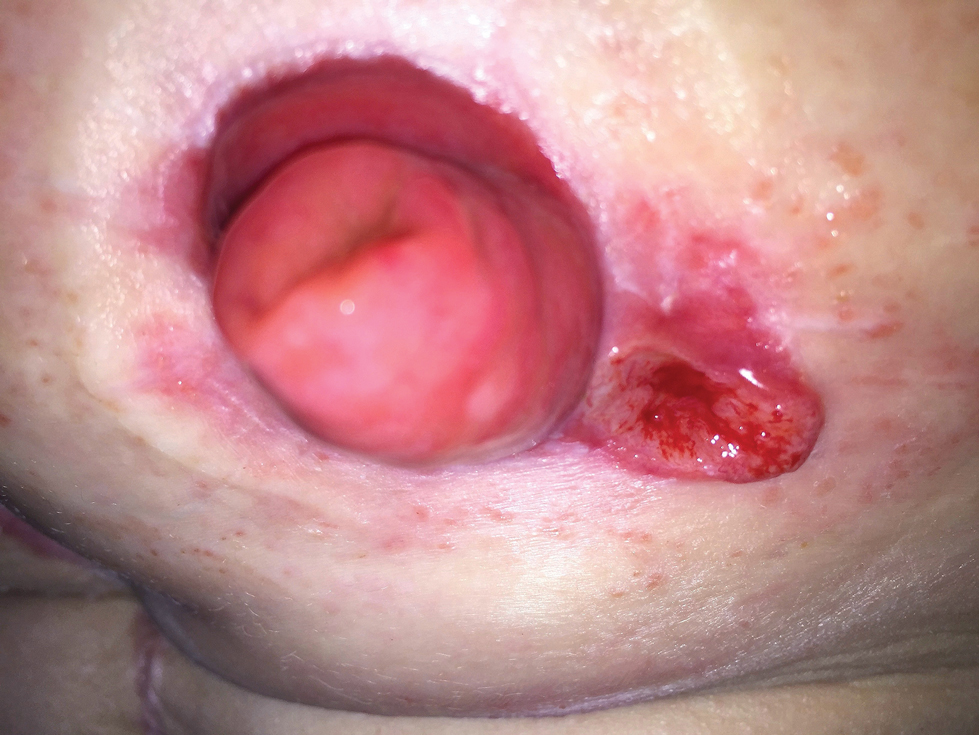
A 32-year-old woman presented to a dermatology office with a spontaneously painful, 3.2-cm ulceration that was extremely tender to palpation, located immediately adjacent to the site of an ileostomy (Figure). The patient had a history of refractory constipation that failed to respond to standard conservative measures 4 years prior. She underwent a colonoscopy, which revealed a 6.5-cm, irregularly shaped, exophytic mass in the rectosigmoid portion of the colon. Histopathologic examination of several biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, and additional evaluation determined the cancer to be stage IIB. She had a medical history of pancolonic Crohn disease since high school that was treated with periodic infusions of infliximab at the standard dose of 5 mg/kg. Colon cancer treatment consisted of preoperative radiotherapy, complete colectomy with ileoanal anastomosis, and creation of a J-pouch and formation of a temporary ileostomy, along with postoperative capecitabine chemotherapy.
The ileostomy eventually was reversed, and the patient did well for 3 years. When the patient developed severe abdominal pain, the J-pouch was examined and found to be remarkably involved with Crohn disease. However, during the colonoscopy, the J-pouch was inadvertently punctured, leading to the formation of a large pelvic abscess. The latter necessitated diversion of stool, and the patient had the original ileostomy recreated.
Prior to presentation to dermatology, various consultants suspected the ulceration was possibly a deep fungal infection, cutaneous Crohn disease, a factitious ulceration, or acute allergic contact dermatitis related to some element of ostomy care. However, dermatologic consultation suggested that the troublesome lesion was classic PPG and recommended administration of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α–blocking agent and concomitant intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide.
The patient was treated with subcutaneous adalimumab 40 mg once weekly, and received near weekly subcutaneous injections of triamcinolone acetonide 10 mg/mL. After 2 months, the discomfort subsided, and the ulceration gradually resolved into a depressed scar. Eighteen months later, the scar was barely perceptible as a minimally erythematous depression. Adalimumab ultimately was discontinued, as the residual J-pouch was removed, and the biologic drug was associated with extensive alopecia areata–like hair loss. There has been no recurrence of PPG in the 40 months since clinical resolution.
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum is an uncommon subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum, which is characterized by chronic, persistent, or recurrent painful ulceration(s) close to an abdominal stoma. In total, fewer than 100 cases of PPG have been reported thus far in the readily available medical literature.3 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is the most frequently diagnosed systemic condition associated with PPG, though other associated conditions include diverticular disease, abdominal malignancy, and neurologic dysfunction. Approximately 2% to 4.3% of all patients who have stoma creation surgery related to underlying IBD develop PPG. It is estimated that the yearly incidence rate of PPG in all abdominal stomas is quite low (approximately 0.6%).4
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum can occur at any age, but it tends to predominate in young to middle-aged adults, with a slight female predilection. The etiology and pathogenesis of PPG are largely unknown, though studies have shown that an abnormal immune response may be critical to its development. Risk factors for PPG are not well defined but potentially include autoimmune disorders, a high body mass index, and females or African Americans with IBD.4 Because PPG does not have characteristic histopathologic features, it is a diagnosis of exclusion that is based on the clinical examination and histologic findings that rule out other potential disorders.
There are 4 types of PPG based on the clinical and histopathologic characteristics: ulcerative, pustular, bullous, and vegetative. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum tends to be either ulcerative or vegetative, with ulcerative being by far the predominant type. The onset of PPG is quite variable, occurring a few weeks to several years after stoma formation.5 Ulcer size can range from less than 3 cm to 30 cm.4 Lesions begin as deep painful nodules or as superficial hemorrhagic pustules, either idiopathic or following ostensibly minimal trauma. Subsequently, they become necrotic and form an ulceration. The ulcers can be single or multiple lesions, typically with erythematous raised borders and purulent discharge. The ulcers are extremely painful and rapidly progressive. After the ulcers heal, they often leave a characteristic weblike atrophic scar that can break down further following any form of irritation or trauma.5
A prompt diagnosis of PPG is important. A diagnosis of PPG should be considered when dealing with a noninfectious ulcer surrounding a stoma in patients with IBD or other autoimmune conditions.6 Because PPG is a rare skin disorder, it is likely to be missed and lead to unnecessary diagnostic workup and a delay in proper therapy. In our patient, a diagnosis of PPG was overlooked for other infectious and autoimmune causes. The diagnostic evaluation of a patient with PPG is based on 3 principles: (1) ruling out other causes of a peristomal ulcer, such as an abscess, contact dermatitis, or wound infection; (2) determining whether there is an underlying intestinal bowel disease in the stoma; and (3) identifying associated systemic disorders such as vasculitis, erythema nodosum, or similar processes.4 The differential diagnosis depends on the type and stage of PPG and can include malignancy, vasculitis, extraintestinal IBD, infectious disease, and insect bites. A review of the history of the ulcer is helpful in ruling out other diseases, and a colonoscopy or ileoscopy can identify if patients have an underlying active IBD. Swabs for smear and both bacterial and fungal cultures should be taken from the exudate and directly from the ulcer base. Biopsy of the ulcer also helps to exclude alternative diagnoses.6
The primary goals of treating PPG include to reduce pain and the risk for secondary infection, increase pouch adherence, and decrease purulent exudate.7 Although there is not one well-defined optimal therapeutic intervention, there are a variety of effective approaches that may be considered and used. In mild cases, management methods such as dressings, topical agents, or intralesional steroids may be capable of controlling the disease. Daily wound care is important. Moisture-retentive dressings can control pain, induce collagen formation, promote angiogenesis, and prevent contamination. Cleaning the wound with sterile saline and applying an anti-infective agent also may be effective. Application of ultrapotent topical steroids and tacrolimus ointment 0.3% can be used in patients without concomitant secondary infection. In patients who are in remission, human platelet-derived growth factor may be used. Intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide or cyclosporine solution also can be helpful. Cyclosporin A was used as a systemic monotherapy to treat a 48-year-old man and 50-year-old woman with the idiopathic form of PPG. After 3 months of treatment, PPG had completely resolved and there were no major side effects.8 Other potential topical therapies that control inflammation and promote wound healing include benzoyl peroxide, chlormethine (topical alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard that has anti-inflammatory properties), nicotine, and 5-aminosalicylic acid. If an ulcer becomes infected, empiric antibiotic therapy should be given immediately and adjusted based on culture and sensitivity results.4
Systemic therapy should be considered in patients who do not respond to topical or local interventions, have a rapid and severe course, or have an active underlying bowel disease. Oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/d) has proved to be one of the most successful drugs used to treat PPG. Treatment should be continued until complete lesion healing, and low-dose maintenance therapy should be administered in recurrent cases. Intravenous corticosteroid therapy—hydrocortisone 100 mg 4 times daily or pulse therapy with intravenous methylprednisolone 1 g/d)—can be used for up to 5 days and may be effective. Oral minocycline 100 mg twice daily may be helpful as an adjunctive therapy to corticosteroids. When corticosteroids fail, oral cyclosporine 3 to 5 mg/kg/d often is prescribed. Studies have shown that patients demonstrate clinical improvement within 3 weeks of cyclosporine initiation, and it has been shown further to be more effective than either azathioprine or methotrexate.4,8
Infliximab, a chimeric antibody that binds both circulating and tissue-bound TNF-α, has been shown to effectively treat PPG. A clinical trial conducted by Brooklyn et al9 found that 46% of patients (6/13) treated with infliximab responded compared with only 6% in a placebo control group (1/17). Although infliximab may result in sepsis, the benefits far outweigh the risks, especially for patients with steroid-refractory PPG.4 Adalimumab is a human monoclonal IgG1 antibody to TNF-α that neutralizes its function by blocking the interaction between the molecule and its receptor. Many clinical studies have shown that adalimumab induces and maintains a clinical response in patients with active Crohn disease. The biologic proved to be effective in our patient, but it is associated with potential side effects that should be monitored including injection-site reactions, pruritus, leukopenia, urticaria, and rare instances of alopecia.10 Etanercept is another potentially effective biologic agent.7 Plasma exchange, immunoglobulin infusion, and interferon-alfa therapy also can be used in refractory PPG cases, though data on these treatments are very limited.4
Unlike routine pyoderma gangrenosum—for which surgical intervention is contraindicated—surgical intervention may be appropriate for the peristomal variant. Surgical treatment options include stoma revision and/or relocation; however, both of these procedures are accompanied by failure rates ranging from 40% to 100%.5 Removal of a diseased intestinal segment, especially one with active IBD, may result in healing of the skin lesion. In our patient, removal of the residual and diseased J-pouch was part of the management plan. However,it generally is recommended that any surgical intervention be accompanied by medical therapy including oral metronidazole 500 mg/d and concomitant administration of an immunosuppressant.1,3
Because PPG tends to recur, long-term maintenance therapy should always be considered. Pain reduction, anemia correction, proper nutrition, and management of associated and underlying diseases should be performed. Meticulous care of the stoma and prevention of leaks also should be emphasized. Overall, if PPG is detected and diagnosed early as well as treated appropriately and aggressively, the patient likely will have a good prognosis.4
- Sheldon DG, Sawchuk LL, Kozarek RA, et al. Twenty cases of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: diagnostic implications and management. Arch Surg. 2000;135:564-569.
- Hughes AP, Jackson JM, Callen JP. Clinical features and treatment of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum. JAMA. 2000;284:1546-1548.
- Afifi L, Sanchez IM, Wallace MM, et al. Diagnosis and management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1195-1204.
- Wu XR, Shen B. Diagnosis and management of parastomal pyoderma gangrenosum. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2013;1:1-8.
- Javed A, Pal S, Ahuja V, et al. Management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: two different approaches for the same clinical problem. Trop Gastroenterol. 2011;32:153-156.
- Toh JW, Whiteley I. Devastating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges in diagnosis and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:A19-A20.
- DeMartyn LE, Faller NA, Miller L. Treating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum with topical crushed prednisone: a report of three cases. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60:50-54.
- V’lckova-Laskoska MT, Laskoski DS, Caca-Biljanovska NG, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with cyclosporin A.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;455:541-555.
- Brooklyn TN, Dunnill MGS, Shetty A, at al. Infliximab for the treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Gut. 2006;55:505-509.
- Alkhouri N, Hupertz V, Mahajan L. Adalimumab treatment for peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:803-806.
To the Editor:
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum (PPG) is a rare entity first described in 1984.1 Lesions usually begin as pustules that coalesce into an erythematous skin ulceration that contains purulent material. The lesion appears on the skin that surrounds an abdominal stoma. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum typically is associated with Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis, cancer, blood dyscrasia, diabetes mellitus, and hepatitis.2 We describe a case of PPG following an ileostomy in a patient with colon cancer and a related history of Crohn disease.
A 32-year-old woman presented to a dermatology office with a spontaneously painful, 3.2-cm ulceration that was extremely tender to palpation, located immediately adjacent to the site of an ileostomy (Figure). The patient had a history of refractory constipation that failed to respond to standard conservative measures 4 years prior. She underwent a colonoscopy, which revealed a 6.5-cm, irregularly shaped, exophytic mass in the rectosigmoid portion of the colon. Histopathologic examination of several biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, and additional evaluation determined the cancer to be stage IIB. She had a medical history of pancolonic Crohn disease since high school that was treated with periodic infusions of infliximab at the standard dose of 5 mg/kg. Colon cancer treatment consisted of preoperative radiotherapy, complete colectomy with ileoanal anastomosis, and creation of a J-pouch and formation of a temporary ileostomy, along with postoperative capecitabine chemotherapy.

The ileostomy eventually was reversed, and the patient did well for 3 years. When the patient developed severe abdominal pain, the J-pouch was examined and found to be remarkably involved with Crohn disease. However, during the colonoscopy, the J-pouch was inadvertently punctured, leading to the formation of a large pelvic abscess. The latter necessitated diversion of stool, and the patient had the original ileostomy recreated.
Prior to presentation to dermatology, various consultants suspected the ulceration was possibly a deep fungal infection, cutaneous Crohn disease, a factitious ulceration, or acute allergic contact dermatitis related to some element of ostomy care. However, dermatologic consultation suggested that the troublesome lesion was classic PPG and recommended administration of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α–blocking agent and concomitant intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide.
The patient was treated with subcutaneous adalimumab 40 mg once weekly, and received near weekly subcutaneous injections of triamcinolone acetonide 10 mg/mL. After 2 months, the discomfort subsided, and the ulceration gradually resolved into a depressed scar. Eighteen months later, the scar was barely perceptible as a minimally erythematous depression. Adalimumab ultimately was discontinued, as the residual J-pouch was removed, and the biologic drug was associated with extensive alopecia areata–like hair loss. There has been no recurrence of PPG in the 40 months since clinical resolution.
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum is an uncommon subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum, which is characterized by chronic, persistent, or recurrent painful ulceration(s) close to an abdominal stoma. In total, fewer than 100 cases of PPG have been reported thus far in the readily available medical literature.3 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is the most frequently diagnosed systemic condition associated with PPG, though other associated conditions include diverticular disease, abdominal malignancy, and neurologic dysfunction. Approximately 2% to 4.3% of all patients who have stoma creation surgery related to underlying IBD develop PPG. It is estimated that the yearly incidence rate of PPG in all abdominal stomas is quite low (approximately 0.6%).4
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum can occur at any age, but it tends to predominate in young to middle-aged adults, with a slight female predilection. The etiology and pathogenesis of PPG are largely unknown, though studies have shown that an abnormal immune response may be critical to its development. Risk factors for PPG are not well defined but potentially include autoimmune disorders, a high body mass index, and females or African Americans with IBD.4 Because PPG does not have characteristic histopathologic features, it is a diagnosis of exclusion that is based on the clinical examination and histologic findings that rule out other potential disorders.
There are 4 types of PPG based on the clinical and histopathologic characteristics: ulcerative, pustular, bullous, and vegetative. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum tends to be either ulcerative or vegetative, with ulcerative being by far the predominant type. The onset of PPG is quite variable, occurring a few weeks to several years after stoma formation.5 Ulcer size can range from less than 3 cm to 30 cm.4 Lesions begin as deep painful nodules or as superficial hemorrhagic pustules, either idiopathic or following ostensibly minimal trauma. Subsequently, they become necrotic and form an ulceration. The ulcers can be single or multiple lesions, typically with erythematous raised borders and purulent discharge. The ulcers are extremely painful and rapidly progressive. After the ulcers heal, they often leave a characteristic weblike atrophic scar that can break down further following any form of irritation or trauma.5
A prompt diagnosis of PPG is important. A diagnosis of PPG should be considered when dealing with a noninfectious ulcer surrounding a stoma in patients with IBD or other autoimmune conditions.6 Because PPG is a rare skin disorder, it is likely to be missed and lead to unnecessary diagnostic workup and a delay in proper therapy. In our patient, a diagnosis of PPG was overlooked for other infectious and autoimmune causes. The diagnostic evaluation of a patient with PPG is based on 3 principles: (1) ruling out other causes of a peristomal ulcer, such as an abscess, contact dermatitis, or wound infection; (2) determining whether there is an underlying intestinal bowel disease in the stoma; and (3) identifying associated systemic disorders such as vasculitis, erythema nodosum, or similar processes.4 The differential diagnosis depends on the type and stage of PPG and can include malignancy, vasculitis, extraintestinal IBD, infectious disease, and insect bites. A review of the history of the ulcer is helpful in ruling out other diseases, and a colonoscopy or ileoscopy can identify if patients have an underlying active IBD. Swabs for smear and both bacterial and fungal cultures should be taken from the exudate and directly from the ulcer base. Biopsy of the ulcer also helps to exclude alternative diagnoses.6
The primary goals of treating PPG include to reduce pain and the risk for secondary infection, increase pouch adherence, and decrease purulent exudate.7 Although there is not one well-defined optimal therapeutic intervention, there are a variety of effective approaches that may be considered and used. In mild cases, management methods such as dressings, topical agents, or intralesional steroids may be capable of controlling the disease. Daily wound care is important. Moisture-retentive dressings can control pain, induce collagen formation, promote angiogenesis, and prevent contamination. Cleaning the wound with sterile saline and applying an anti-infective agent also may be effective. Application of ultrapotent topical steroids and tacrolimus ointment 0.3% can be used in patients without concomitant secondary infection. In patients who are in remission, human platelet-derived growth factor may be used. Intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide or cyclosporine solution also can be helpful. Cyclosporin A was used as a systemic monotherapy to treat a 48-year-old man and 50-year-old woman with the idiopathic form of PPG. After 3 months of treatment, PPG had completely resolved and there were no major side effects.8 Other potential topical therapies that control inflammation and promote wound healing include benzoyl peroxide, chlormethine (topical alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard that has anti-inflammatory properties), nicotine, and 5-aminosalicylic acid. If an ulcer becomes infected, empiric antibiotic therapy should be given immediately and adjusted based on culture and sensitivity results.4
Systemic therapy should be considered in patients who do not respond to topical or local interventions, have a rapid and severe course, or have an active underlying bowel disease. Oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/d) has proved to be one of the most successful drugs used to treat PPG. Treatment should be continued until complete lesion healing, and low-dose maintenance therapy should be administered in recurrent cases. Intravenous corticosteroid therapy—hydrocortisone 100 mg 4 times daily or pulse therapy with intravenous methylprednisolone 1 g/d)—can be used for up to 5 days and may be effective. Oral minocycline 100 mg twice daily may be helpful as an adjunctive therapy to corticosteroids. When corticosteroids fail, oral cyclosporine 3 to 5 mg/kg/d often is prescribed. Studies have shown that patients demonstrate clinical improvement within 3 weeks of cyclosporine initiation, and it has been shown further to be more effective than either azathioprine or methotrexate.4,8
Infliximab, a chimeric antibody that binds both circulating and tissue-bound TNF-α, has been shown to effectively treat PPG. A clinical trial conducted by Brooklyn et al9 found that 46% of patients (6/13) treated with infliximab responded compared with only 6% in a placebo control group (1/17). Although infliximab may result in sepsis, the benefits far outweigh the risks, especially for patients with steroid-refractory PPG.4 Adalimumab is a human monoclonal IgG1 antibody to TNF-α that neutralizes its function by blocking the interaction between the molecule and its receptor. Many clinical studies have shown that adalimumab induces and maintains a clinical response in patients with active Crohn disease. The biologic proved to be effective in our patient, but it is associated with potential side effects that should be monitored including injection-site reactions, pruritus, leukopenia, urticaria, and rare instances of alopecia.10 Etanercept is another potentially effective biologic agent.7 Plasma exchange, immunoglobulin infusion, and interferon-alfa therapy also can be used in refractory PPG cases, though data on these treatments are very limited.4
Unlike routine pyoderma gangrenosum—for which surgical intervention is contraindicated—surgical intervention may be appropriate for the peristomal variant. Surgical treatment options include stoma revision and/or relocation; however, both of these procedures are accompanied by failure rates ranging from 40% to 100%.5 Removal of a diseased intestinal segment, especially one with active IBD, may result in healing of the skin lesion. In our patient, removal of the residual and diseased J-pouch was part of the management plan. However,it generally is recommended that any surgical intervention be accompanied by medical therapy including oral metronidazole 500 mg/d and concomitant administration of an immunosuppressant.1,3
Because PPG tends to recur, long-term maintenance therapy should always be considered. Pain reduction, anemia correction, proper nutrition, and management of associated and underlying diseases should be performed. Meticulous care of the stoma and prevention of leaks also should be emphasized. Overall, if PPG is detected and diagnosed early as well as treated appropriately and aggressively, the patient likely will have a good prognosis.4
To the Editor:
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum (PPG) is a rare entity first described in 1984.1 Lesions usually begin as pustules that coalesce into an erythematous skin ulceration that contains purulent material. The lesion appears on the skin that surrounds an abdominal stoma. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum typically is associated with Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis, cancer, blood dyscrasia, diabetes mellitus, and hepatitis.2 We describe a case of PPG following an ileostomy in a patient with colon cancer and a related history of Crohn disease.
A 32-year-old woman presented to a dermatology office with a spontaneously painful, 3.2-cm ulceration that was extremely tender to palpation, located immediately adjacent to the site of an ileostomy (Figure). The patient had a history of refractory constipation that failed to respond to standard conservative measures 4 years prior. She underwent a colonoscopy, which revealed a 6.5-cm, irregularly shaped, exophytic mass in the rectosigmoid portion of the colon. Histopathologic examination of several biopsies confirmed the diagnosis of moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma, and additional evaluation determined the cancer to be stage IIB. She had a medical history of pancolonic Crohn disease since high school that was treated with periodic infusions of infliximab at the standard dose of 5 mg/kg. Colon cancer treatment consisted of preoperative radiotherapy, complete colectomy with ileoanal anastomosis, and creation of a J-pouch and formation of a temporary ileostomy, along with postoperative capecitabine chemotherapy.

The ileostomy eventually was reversed, and the patient did well for 3 years. When the patient developed severe abdominal pain, the J-pouch was examined and found to be remarkably involved with Crohn disease. However, during the colonoscopy, the J-pouch was inadvertently punctured, leading to the formation of a large pelvic abscess. The latter necessitated diversion of stool, and the patient had the original ileostomy recreated.
Prior to presentation to dermatology, various consultants suspected the ulceration was possibly a deep fungal infection, cutaneous Crohn disease, a factitious ulceration, or acute allergic contact dermatitis related to some element of ostomy care. However, dermatologic consultation suggested that the troublesome lesion was classic PPG and recommended administration of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α–blocking agent and concomitant intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide.
The patient was treated with subcutaneous adalimumab 40 mg once weekly, and received near weekly subcutaneous injections of triamcinolone acetonide 10 mg/mL. After 2 months, the discomfort subsided, and the ulceration gradually resolved into a depressed scar. Eighteen months later, the scar was barely perceptible as a minimally erythematous depression. Adalimumab ultimately was discontinued, as the residual J-pouch was removed, and the biologic drug was associated with extensive alopecia areata–like hair loss. There has been no recurrence of PPG in the 40 months since clinical resolution.
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum is an uncommon subtype of pyoderma gangrenosum, which is characterized by chronic, persistent, or recurrent painful ulceration(s) close to an abdominal stoma. In total, fewer than 100 cases of PPG have been reported thus far in the readily available medical literature.3 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is the most frequently diagnosed systemic condition associated with PPG, though other associated conditions include diverticular disease, abdominal malignancy, and neurologic dysfunction. Approximately 2% to 4.3% of all patients who have stoma creation surgery related to underlying IBD develop PPG. It is estimated that the yearly incidence rate of PPG in all abdominal stomas is quite low (approximately 0.6%).4
Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum can occur at any age, but it tends to predominate in young to middle-aged adults, with a slight female predilection. The etiology and pathogenesis of PPG are largely unknown, though studies have shown that an abnormal immune response may be critical to its development. Risk factors for PPG are not well defined but potentially include autoimmune disorders, a high body mass index, and females or African Americans with IBD.4 Because PPG does not have characteristic histopathologic features, it is a diagnosis of exclusion that is based on the clinical examination and histologic findings that rule out other potential disorders.
There are 4 types of PPG based on the clinical and histopathologic characteristics: ulcerative, pustular, bullous, and vegetative. Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum tends to be either ulcerative or vegetative, with ulcerative being by far the predominant type. The onset of PPG is quite variable, occurring a few weeks to several years after stoma formation.5 Ulcer size can range from less than 3 cm to 30 cm.4 Lesions begin as deep painful nodules or as superficial hemorrhagic pustules, either idiopathic or following ostensibly minimal trauma. Subsequently, they become necrotic and form an ulceration. The ulcers can be single or multiple lesions, typically with erythematous raised borders and purulent discharge. The ulcers are extremely painful and rapidly progressive. After the ulcers heal, they often leave a characteristic weblike atrophic scar that can break down further following any form of irritation or trauma.5
A prompt diagnosis of PPG is important. A diagnosis of PPG should be considered when dealing with a noninfectious ulcer surrounding a stoma in patients with IBD or other autoimmune conditions.6 Because PPG is a rare skin disorder, it is likely to be missed and lead to unnecessary diagnostic workup and a delay in proper therapy. In our patient, a diagnosis of PPG was overlooked for other infectious and autoimmune causes. The diagnostic evaluation of a patient with PPG is based on 3 principles: (1) ruling out other causes of a peristomal ulcer, such as an abscess, contact dermatitis, or wound infection; (2) determining whether there is an underlying intestinal bowel disease in the stoma; and (3) identifying associated systemic disorders such as vasculitis, erythema nodosum, or similar processes.4 The differential diagnosis depends on the type and stage of PPG and can include malignancy, vasculitis, extraintestinal IBD, infectious disease, and insect bites. A review of the history of the ulcer is helpful in ruling out other diseases, and a colonoscopy or ileoscopy can identify if patients have an underlying active IBD. Swabs for smear and both bacterial and fungal cultures should be taken from the exudate and directly from the ulcer base. Biopsy of the ulcer also helps to exclude alternative diagnoses.6
The primary goals of treating PPG include to reduce pain and the risk for secondary infection, increase pouch adherence, and decrease purulent exudate.7 Although there is not one well-defined optimal therapeutic intervention, there are a variety of effective approaches that may be considered and used. In mild cases, management methods such as dressings, topical agents, or intralesional steroids may be capable of controlling the disease. Daily wound care is important. Moisture-retentive dressings can control pain, induce collagen formation, promote angiogenesis, and prevent contamination. Cleaning the wound with sterile saline and applying an anti-infective agent also may be effective. Application of ultrapotent topical steroids and tacrolimus ointment 0.3% can be used in patients without concomitant secondary infection. In patients who are in remission, human platelet-derived growth factor may be used. Intralesional injections of dilute triamcinolone acetonide or cyclosporine solution also can be helpful. Cyclosporin A was used as a systemic monotherapy to treat a 48-year-old man and 50-year-old woman with the idiopathic form of PPG. After 3 months of treatment, PPG had completely resolved and there were no major side effects.8 Other potential topical therapies that control inflammation and promote wound healing include benzoyl peroxide, chlormethine (topical alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard that has anti-inflammatory properties), nicotine, and 5-aminosalicylic acid. If an ulcer becomes infected, empiric antibiotic therapy should be given immediately and adjusted based on culture and sensitivity results.4
Systemic therapy should be considered in patients who do not respond to topical or local interventions, have a rapid and severe course, or have an active underlying bowel disease. Oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/d) has proved to be one of the most successful drugs used to treat PPG. Treatment should be continued until complete lesion healing, and low-dose maintenance therapy should be administered in recurrent cases. Intravenous corticosteroid therapy—hydrocortisone 100 mg 4 times daily or pulse therapy with intravenous methylprednisolone 1 g/d)—can be used for up to 5 days and may be effective. Oral minocycline 100 mg twice daily may be helpful as an adjunctive therapy to corticosteroids. When corticosteroids fail, oral cyclosporine 3 to 5 mg/kg/d often is prescribed. Studies have shown that patients demonstrate clinical improvement within 3 weeks of cyclosporine initiation, and it has been shown further to be more effective than either azathioprine or methotrexate.4,8
Infliximab, a chimeric antibody that binds both circulating and tissue-bound TNF-α, has been shown to effectively treat PPG. A clinical trial conducted by Brooklyn et al9 found that 46% of patients (6/13) treated with infliximab responded compared with only 6% in a placebo control group (1/17). Although infliximab may result in sepsis, the benefits far outweigh the risks, especially for patients with steroid-refractory PPG.4 Adalimumab is a human monoclonal IgG1 antibody to TNF-α that neutralizes its function by blocking the interaction between the molecule and its receptor. Many clinical studies have shown that adalimumab induces and maintains a clinical response in patients with active Crohn disease. The biologic proved to be effective in our patient, but it is associated with potential side effects that should be monitored including injection-site reactions, pruritus, leukopenia, urticaria, and rare instances of alopecia.10 Etanercept is another potentially effective biologic agent.7 Plasma exchange, immunoglobulin infusion, and interferon-alfa therapy also can be used in refractory PPG cases, though data on these treatments are very limited.4
Unlike routine pyoderma gangrenosum—for which surgical intervention is contraindicated—surgical intervention may be appropriate for the peristomal variant. Surgical treatment options include stoma revision and/or relocation; however, both of these procedures are accompanied by failure rates ranging from 40% to 100%.5 Removal of a diseased intestinal segment, especially one with active IBD, may result in healing of the skin lesion. In our patient, removal of the residual and diseased J-pouch was part of the management plan. However,it generally is recommended that any surgical intervention be accompanied by medical therapy including oral metronidazole 500 mg/d and concomitant administration of an immunosuppressant.1,3
Because PPG tends to recur, long-term maintenance therapy should always be considered. Pain reduction, anemia correction, proper nutrition, and management of associated and underlying diseases should be performed. Meticulous care of the stoma and prevention of leaks also should be emphasized. Overall, if PPG is detected and diagnosed early as well as treated appropriately and aggressively, the patient likely will have a good prognosis.4
- Sheldon DG, Sawchuk LL, Kozarek RA, et al. Twenty cases of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: diagnostic implications and management. Arch Surg. 2000;135:564-569.
- Hughes AP, Jackson JM, Callen JP. Clinical features and treatment of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum. JAMA. 2000;284:1546-1548.
- Afifi L, Sanchez IM, Wallace MM, et al. Diagnosis and management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1195-1204.
- Wu XR, Shen B. Diagnosis and management of parastomal pyoderma gangrenosum. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2013;1:1-8.
- Javed A, Pal S, Ahuja V, et al. Management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: two different approaches for the same clinical problem. Trop Gastroenterol. 2011;32:153-156.
- Toh JW, Whiteley I. Devastating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges in diagnosis and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:A19-A20.
- DeMartyn LE, Faller NA, Miller L. Treating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum with topical crushed prednisone: a report of three cases. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60:50-54.
- V’lckova-Laskoska MT, Laskoski DS, Caca-Biljanovska NG, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with cyclosporin A.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;455:541-555.
- Brooklyn TN, Dunnill MGS, Shetty A, at al. Infliximab for the treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Gut. 2006;55:505-509.
- Alkhouri N, Hupertz V, Mahajan L. Adalimumab treatment for peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:803-806.
- Sheldon DG, Sawchuk LL, Kozarek RA, et al. Twenty cases of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: diagnostic implications and management. Arch Surg. 2000;135:564-569.
- Hughes AP, Jackson JM, Callen JP. Clinical features and treatment of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum. JAMA. 2000;284:1546-1548.
- Afifi L, Sanchez IM, Wallace MM, et al. Diagnosis and management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1195-1204.
- Wu XR, Shen B. Diagnosis and management of parastomal pyoderma gangrenosum. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2013;1:1-8.
- Javed A, Pal S, Ahuja V, et al. Management of peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: two different approaches for the same clinical problem. Trop Gastroenterol. 2011;32:153-156.
- Toh JW, Whiteley I. Devastating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges in diagnosis and management. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:A19-A20.
- DeMartyn LE, Faller NA, Miller L. Treating peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum with topical crushed prednisone: a report of three cases. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2014;60:50-54.
- V’lckova-Laskoska MT, Laskoski DS, Caca-Biljanovska NG, et al. Pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with cyclosporin A.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;455:541-555.
- Brooklyn TN, Dunnill MGS, Shetty A, at al. Infliximab for the treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Gut. 2006;55:505-509.
- Alkhouri N, Hupertz V, Mahajan L. Adalimumab treatment for peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:803-806.
Practice Points
- A pyoderma gangrenosum subtype occurs in close proximity to an abdominal stoma.
- Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum is a diagnosis of exclusion.
- Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum typically responds best to tumor necrosis factor α blockers and corticosteroid therapy (intralesional and systemic).
Topical gene therapy for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa shows promise
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
INDIANAPOLIS – An investigational compared with placebo, according to results from a small phase 3 study.
DEB is a serious, ultra-rare genetic blistering disease caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, encoding for type VII collagen and leading to skin fragility and wounds. No approved therapies are currently available. In the study, treatment was generally well tolerated.
“B-VEC is the first treatment that has not only been shown to be effective, but the first to directly target the defect through topical application,” the study’s principal investigator, Shireen V. Guide, MD, said in an interview during a poster session at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. “It delivers type VII collagen gene therapy to these patients, which allows healing in areas that they may have had open since birth. It’s been life-changing for them.”
B-VEC is a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1)-based topical, redosable gene therapy being developed by Krystal Biotech that is designed to restore functional COL7 protein by delivering the COL7A1 gene. For the phase 3, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study known GEM-3, Dr. Guide, who practices dermatology in Rancho Santa Margarita, Calif., and her colleagues, including Peter Marinkovich, MD, from Stanford (Calif.) University, and Mercedes Gonzalez, MD, from the University of Miami, enrolled 31 patients aged 6 months and older with genetically confirmed DEB. Each patient had one wound treated randomized 1:1 to treatment with B-VEC once a week or placebo for 6 months. The mean age of the 31 study participants was 17 years, 65% were male, 65% were White, and 19% were Asian.
The primary endpoint was complete wound healing (defined as 100% wound closure from exact wound area at baseline, specified as skin re-epithelialization without drainage) at 6 months. Additional endpoints included complete wound healing at 3 months and change in pain associated with wound dressing changes.
At 3 months, 70% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing, compared with 20% of wounds treated with placebo (P < .005). At 6 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC met the endpoint of complete wound healing compared with 22% of those treated with placebo (P < .005).
Of the total wounds that closed at 3 months, 67% of wounds treated with B-VEC were also closed at 6 months, compared with 33% of those treated with placebo (P = .02). In other findings, a trend toward decreased pain was observed in wounds treated with B-VEC vs. those treated with placebo.
B-VEC was well tolerated with no treatment-related serious adverse events or discontinuations. Three patients experienced a total of five serious adverse events during the study: anemia (two events), and cellulitis, diarrhea, and positive blood culture (one event each). None were considered related to the study drug.
Dr. Guide, who is on staff at Children’s Health of Orange County, Orange, Calif., characterized B-VEC as “very novel because it’s very practical.”
To date, all treatments for DEB “have been extremely labor intensive, including skin grafting and hospitalizations. It’s a topical application that can be done in the office and potentially applied at home in the future. It’s also durable. Not only are the [treated] areas closing, but they are staying closed.”
Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was asked to comment on the study, said that topical application of B-VEC “allows the side effect profile to be very favorable. The results are remarkable in the amount of wound healing and reduction in pain.”
The tolerability of this medication “is crucial,” she added. “EB patients have a lot of pain from their wounds and so any treatment needs to be as painless as possible for it to be usable. I’m very excited about the next phase of studies for this medication and hopeful that it heralds new treatments for our EB patients.”
In June 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had submitted a biologics license application to the Food and Drug Administration for approval of B-VEC for the treatment of DEB, and that it anticipates submitting an application for marketing authorization with the European Medical Agency (EMA) in the second half of 2022.
Dr. Guide disclosed that she has served as an investigator for Krystal Biotech, Innovaderm Research, Arcutis, Premier Research, Paidion, and Castle Biosciences. Dr. Marathe disclosed that she has served as an adviser for Verrica, and that Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is a site for the next phase studies for B-VEC.
*This story was updated on July 25.
AT SPD 2022
Focal Palmoplantar Keratoderma and Gingival Keratosis Caused by a KRT16 Mutation
To the Editor:
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis (FPGK)(Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] 148730) is a rare autosomal-dominant syndrome featuring focal, pressure-related, painful palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival hyperkeratosis presenting as leukokeratosis. Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis was first defined by Gorlin1 in 1976. Since then, only a few cases have been reported, but no causative mutations have been identified.2
Focal pressure-related palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) and oral hyperkeratosis also are seen in pachyonychia congenita (PC)(OMIM 167200, 615726, 615728, 167210), a rare autosomal-dominant disorder of keratinization characterized by PPK and nail dystrophy. Patients with PC often present with plantar pain; more variable features include oral leukokeratosis, follicular hyperkeratosis, pilosebaceous and epidermal inclusion cysts, hoarseness, hyperhidrosis, and natal teeth. Pachyonychia congenita is caused by mutation in keratin genes KRT6A, KRT6B, KRT16, or KRT17.
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis as well as PC are distinct from other forms of PPK with gingival involvement such as
Despite the common features of FPGK and PC, they are considered distinct disorders due to absence of nail changes in FPGK and no prior evidence of a common genetic cause. We present a patient with familial FPGK found by whole exome sequencing to be caused by a mutation in KRT16.
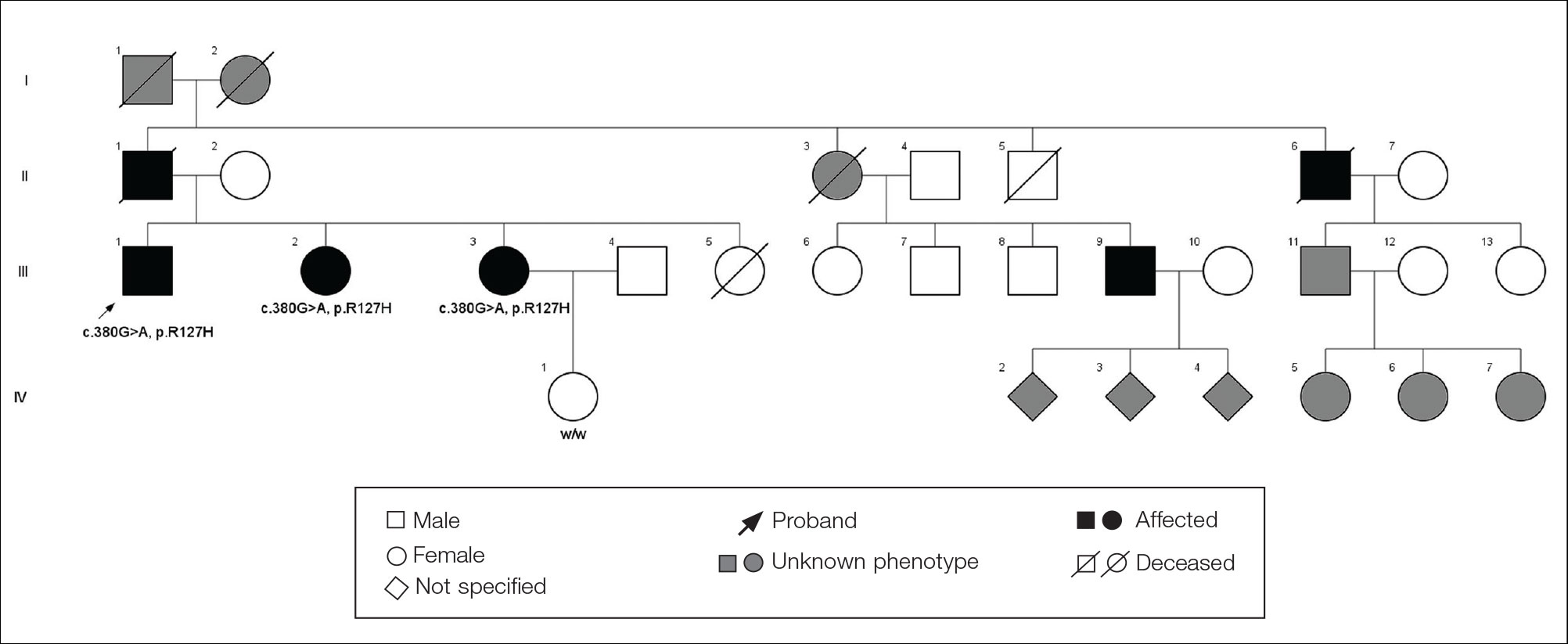
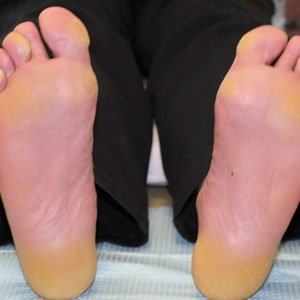
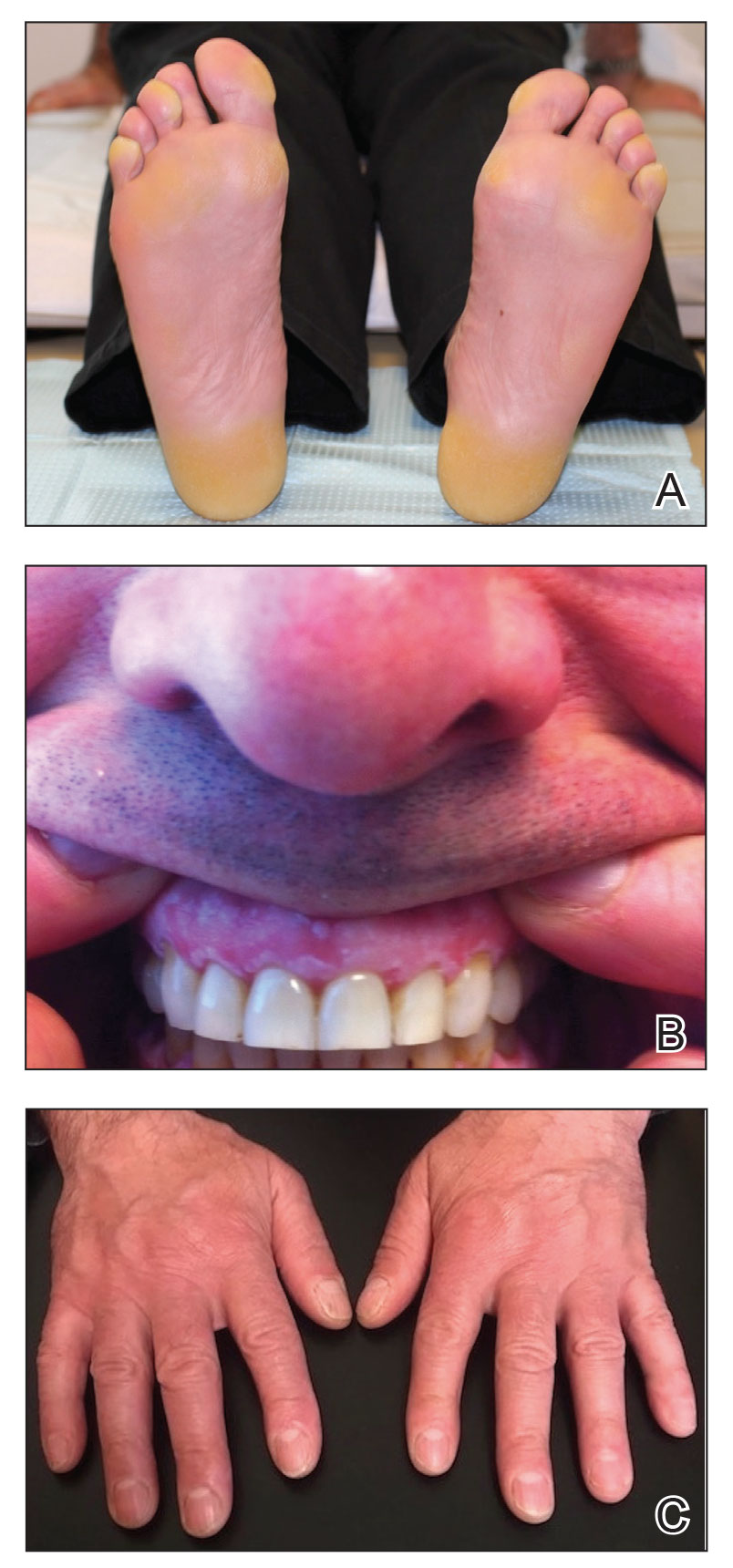
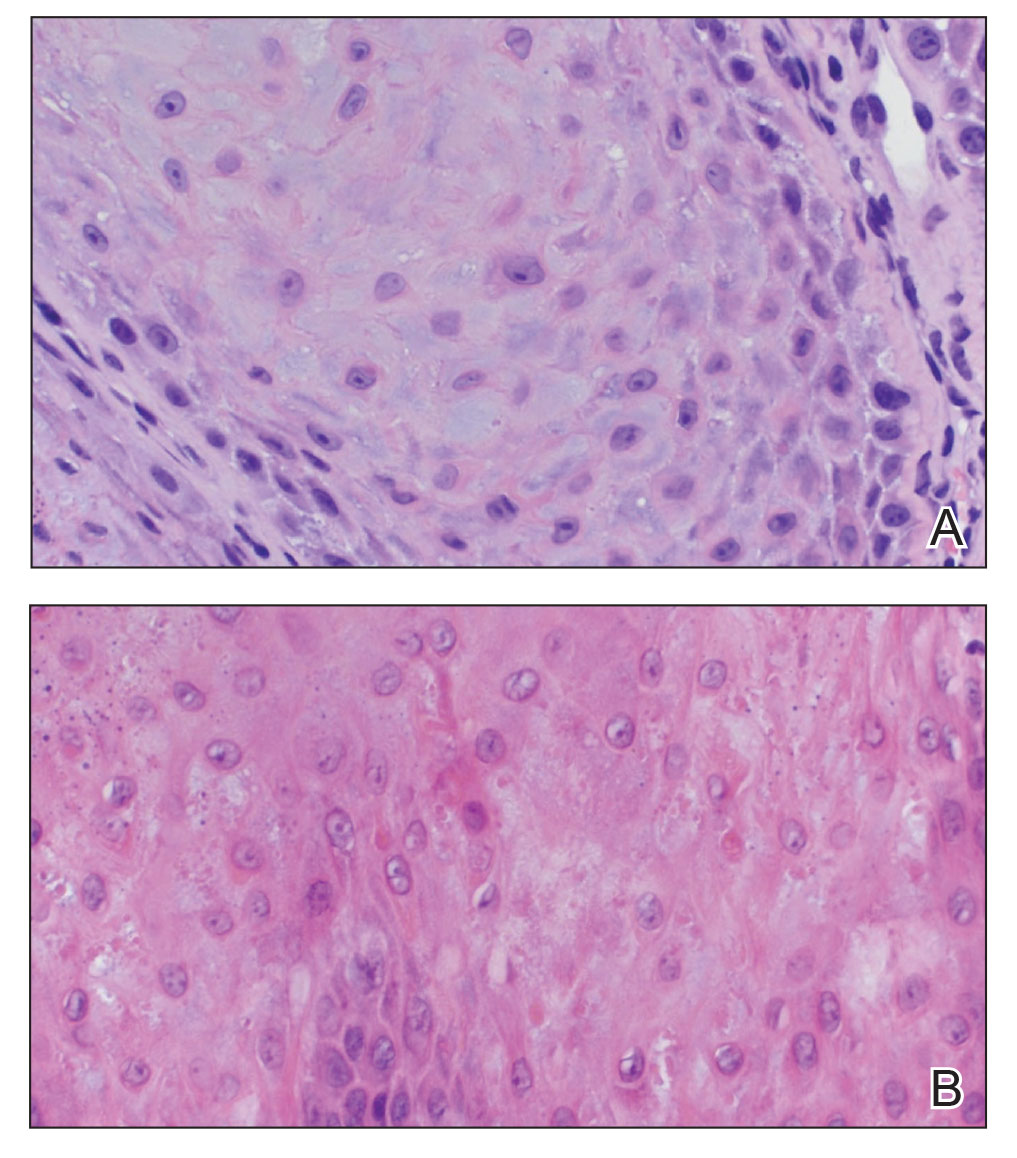
The proband was a 57-year-old man born to unrelated parents (Figure 1). He had no skin problems at birth, and his development was normal. He had painful focal keratoderma since childhood that were most prominent at pressure points on the soles and toes (Figure 2A), in addition to gingival hyperkeratosis and oral leukokeratosis (Figure 2B). He had no associated abnormalities of the skin, hair, or teeth and no nail findings (Figure 2C). He reported that his father and 2 of his 3 sisters were affected with similar symptoms. A punch biopsy of the right fifth toe was consistent with verrucous epidermal hyperplasia with perinuclear keratinization in the spinous layer (Figure 3A). A gingival biopsy showed perinuclear eosinophilic globules and basophilic stranding in the cytoplasm (Figure 3B). His older sister had more severe and painful focal keratoderma of the soles, punctate keratoderma of the palms, gingival hyperkeratosis, and leukokeratosis of the tongue.
Whole exome sequencing of the proband revealed a heterozygous missense mutation in KRT16 (c.380G>A, p.R127H, rs57424749). Sanger sequencing confirmed this mutation and showed that it was heterozygous in both of his affected sisters and absent in his unaffected niece (Figure 1). The patient was treated with topical and systemic retinoids, keratolytics, and mechanical removal to moderate effect, with noted improvement in the appearance and associated pain of the plantar keratoderma.
Phenotypic heterogeneity is common in PC, though PC due to KRT6A mutations demonstrates more severe nail disease with oral lesions, cysts, and follicular hyperkeratosis, while PC caused by KRT16 mutations generally presents with more extensive and painful PPK.4KRT16 mutations affecting p.R127 are frequent causes of PC, and genotype-phenotype correlations have been observed. Individuals with p.R127P mutations exhibit more severe disease with earlier age of onset, more extensive nail involvement and oral leukokeratosis, and greater impact on daily quality of life than in individuals with p.R127C mutations.5 Cases of PC with KRT16 p.R127S and p.R127G mutations also have been observed. The KRT16 c.380G>A, p.R127H mutation we documented has been reported in one kindred with PC who presented with PPK, oral leukokeratosis, toenail thickening, and pilosebaceous and follicular hyperkeratosis.6
Although patients with FPGK lack the thickening of fingernails and/or toenails considered a defining feature of PC, the disorders otherwise are phenotypically similar, suggesting the possibility of common pathogenesis. One linkage study of familial FPGK excluded genetic intervals containing type I and type II keratins but was limited to a single small kindred.2 This study and our data together suggest that, similar to PC, there are multiple genes in which mutations cause FPGK.
Murine Krt16 knockouts show distinct phenotypes depending on the mouse strain in which they are propagated, ranging from perinatal lethality to differences in the severity of oral and PPK lesions.7 These observations provide evidence that additional genetic variants contribute to Krt16 phenotypes in mice and suggest the same could be true for humans.
We propose that some cases of FPGK are due to mutations in KRT16 and thus share a genetic pathogenesis with PC, underscoring the utility of whole exome sequencing in providing genetic diagnoses for disorders that are genetically and clinically heterogeneous. Further biologic investigation of phenotypes caused by KRT16 mutation may reveal respective contributions of additional genetic variation and environmental effects to the variable clinical presentations.
- Gorlin RJ. Focal palmoplantar and marginal gingival hyperkeratosis—a syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12:239-242.
- Kolde G, Hennies HC, Bethke G, et al. Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis: a distinct palmoplantar ectodermal dysplasia with epidermolytic alterations but lack of mutations in known keratins. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):403-409.
- Duchatelet S, Hovnanian A. Olmsted syndrome: clinical, molecular and therapeutic aspects. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:33.
- Spaunhurst KM, Hogendorf AM, Smith FJ, et al. Pachyonychia congenita patients with mutations in KRT6A have more extensive disease compared with patients who have mutations in KRT16. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:875-878.
- Fu T, Leachman SA, Wilson NJ, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations among pachyonychia congenita patients with K16 mutations. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:1025-1028.
- Wilson NJ, O’Toole EA, Milstone LM, et al. The molecular genetic analysis of the expanding pachyonychia congenita case collection. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:343-355.
- Zieman A, Coulombe PA. The keratin 16 null phenotype is modestly impacted by genetic strain background in mice. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:672-674.
To the Editor:
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis (FPGK)(Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] 148730) is a rare autosomal-dominant syndrome featuring focal, pressure-related, painful palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival hyperkeratosis presenting as leukokeratosis. Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis was first defined by Gorlin1 in 1976. Since then, only a few cases have been reported, but no causative mutations have been identified.2
Focal pressure-related palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) and oral hyperkeratosis also are seen in pachyonychia congenita (PC)(OMIM 167200, 615726, 615728, 167210), a rare autosomal-dominant disorder of keratinization characterized by PPK and nail dystrophy. Patients with PC often present with plantar pain; more variable features include oral leukokeratosis, follicular hyperkeratosis, pilosebaceous and epidermal inclusion cysts, hoarseness, hyperhidrosis, and natal teeth. Pachyonychia congenita is caused by mutation in keratin genes KRT6A, KRT6B, KRT16, or KRT17.
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis as well as PC are distinct from other forms of PPK with gingival involvement such as
Despite the common features of FPGK and PC, they are considered distinct disorders due to absence of nail changes in FPGK and no prior evidence of a common genetic cause. We present a patient with familial FPGK found by whole exome sequencing to be caused by a mutation in KRT16.

The proband was a 57-year-old man born to unrelated parents (Figure 1). He had no skin problems at birth, and his development was normal. He had painful focal keratoderma since childhood that were most prominent at pressure points on the soles and toes (Figure 2A), in addition to gingival hyperkeratosis and oral leukokeratosis (Figure 2B). He had no associated abnormalities of the skin, hair, or teeth and no nail findings (Figure 2C). He reported that his father and 2 of his 3 sisters were affected with similar symptoms. A punch biopsy of the right fifth toe was consistent with verrucous epidermal hyperplasia with perinuclear keratinization in the spinous layer (Figure 3A). A gingival biopsy showed perinuclear eosinophilic globules and basophilic stranding in the cytoplasm (Figure 3B). His older sister had more severe and painful focal keratoderma of the soles, punctate keratoderma of the palms, gingival hyperkeratosis, and leukokeratosis of the tongue.

Whole exome sequencing of the proband revealed a heterozygous missense mutation in KRT16 (c.380G>A, p.R127H, rs57424749). Sanger sequencing confirmed this mutation and showed that it was heterozygous in both of his affected sisters and absent in his unaffected niece (Figure 1). The patient was treated with topical and systemic retinoids, keratolytics, and mechanical removal to moderate effect, with noted improvement in the appearance and associated pain of the plantar keratoderma.

Phenotypic heterogeneity is common in PC, though PC due to KRT6A mutations demonstrates more severe nail disease with oral lesions, cysts, and follicular hyperkeratosis, while PC caused by KRT16 mutations generally presents with more extensive and painful PPK.4KRT16 mutations affecting p.R127 are frequent causes of PC, and genotype-phenotype correlations have been observed. Individuals with p.R127P mutations exhibit more severe disease with earlier age of onset, more extensive nail involvement and oral leukokeratosis, and greater impact on daily quality of life than in individuals with p.R127C mutations.5 Cases of PC with KRT16 p.R127S and p.R127G mutations also have been observed. The KRT16 c.380G>A, p.R127H mutation we documented has been reported in one kindred with PC who presented with PPK, oral leukokeratosis, toenail thickening, and pilosebaceous and follicular hyperkeratosis.6
Although patients with FPGK lack the thickening of fingernails and/or toenails considered a defining feature of PC, the disorders otherwise are phenotypically similar, suggesting the possibility of common pathogenesis. One linkage study of familial FPGK excluded genetic intervals containing type I and type II keratins but was limited to a single small kindred.2 This study and our data together suggest that, similar to PC, there are multiple genes in which mutations cause FPGK.
Murine Krt16 knockouts show distinct phenotypes depending on the mouse strain in which they are propagated, ranging from perinatal lethality to differences in the severity of oral and PPK lesions.7 These observations provide evidence that additional genetic variants contribute to Krt16 phenotypes in mice and suggest the same could be true for humans.
We propose that some cases of FPGK are due to mutations in KRT16 and thus share a genetic pathogenesis with PC, underscoring the utility of whole exome sequencing in providing genetic diagnoses for disorders that are genetically and clinically heterogeneous. Further biologic investigation of phenotypes caused by KRT16 mutation may reveal respective contributions of additional genetic variation and environmental effects to the variable clinical presentations.
To the Editor:
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis (FPGK)(Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man [OMIM] 148730) is a rare autosomal-dominant syndrome featuring focal, pressure-related, painful palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival hyperkeratosis presenting as leukokeratosis. Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis was first defined by Gorlin1 in 1976. Since then, only a few cases have been reported, but no causative mutations have been identified.2
Focal pressure-related palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) and oral hyperkeratosis also are seen in pachyonychia congenita (PC)(OMIM 167200, 615726, 615728, 167210), a rare autosomal-dominant disorder of keratinization characterized by PPK and nail dystrophy. Patients with PC often present with plantar pain; more variable features include oral leukokeratosis, follicular hyperkeratosis, pilosebaceous and epidermal inclusion cysts, hoarseness, hyperhidrosis, and natal teeth. Pachyonychia congenita is caused by mutation in keratin genes KRT6A, KRT6B, KRT16, or KRT17.
Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis as well as PC are distinct from other forms of PPK with gingival involvement such as
Despite the common features of FPGK and PC, they are considered distinct disorders due to absence of nail changes in FPGK and no prior evidence of a common genetic cause. We present a patient with familial FPGK found by whole exome sequencing to be caused by a mutation in KRT16.

The proband was a 57-year-old man born to unrelated parents (Figure 1). He had no skin problems at birth, and his development was normal. He had painful focal keratoderma since childhood that were most prominent at pressure points on the soles and toes (Figure 2A), in addition to gingival hyperkeratosis and oral leukokeratosis (Figure 2B). He had no associated abnormalities of the skin, hair, or teeth and no nail findings (Figure 2C). He reported that his father and 2 of his 3 sisters were affected with similar symptoms. A punch biopsy of the right fifth toe was consistent with verrucous epidermal hyperplasia with perinuclear keratinization in the spinous layer (Figure 3A). A gingival biopsy showed perinuclear eosinophilic globules and basophilic stranding in the cytoplasm (Figure 3B). His older sister had more severe and painful focal keratoderma of the soles, punctate keratoderma of the palms, gingival hyperkeratosis, and leukokeratosis of the tongue.

Whole exome sequencing of the proband revealed a heterozygous missense mutation in KRT16 (c.380G>A, p.R127H, rs57424749). Sanger sequencing confirmed this mutation and showed that it was heterozygous in both of his affected sisters and absent in his unaffected niece (Figure 1). The patient was treated with topical and systemic retinoids, keratolytics, and mechanical removal to moderate effect, with noted improvement in the appearance and associated pain of the plantar keratoderma.

Phenotypic heterogeneity is common in PC, though PC due to KRT6A mutations demonstrates more severe nail disease with oral lesions, cysts, and follicular hyperkeratosis, while PC caused by KRT16 mutations generally presents with more extensive and painful PPK.4KRT16 mutations affecting p.R127 are frequent causes of PC, and genotype-phenotype correlations have been observed. Individuals with p.R127P mutations exhibit more severe disease with earlier age of onset, more extensive nail involvement and oral leukokeratosis, and greater impact on daily quality of life than in individuals with p.R127C mutations.5 Cases of PC with KRT16 p.R127S and p.R127G mutations also have been observed. The KRT16 c.380G>A, p.R127H mutation we documented has been reported in one kindred with PC who presented with PPK, oral leukokeratosis, toenail thickening, and pilosebaceous and follicular hyperkeratosis.6
Although patients with FPGK lack the thickening of fingernails and/or toenails considered a defining feature of PC, the disorders otherwise are phenotypically similar, suggesting the possibility of common pathogenesis. One linkage study of familial FPGK excluded genetic intervals containing type I and type II keratins but was limited to a single small kindred.2 This study and our data together suggest that, similar to PC, there are multiple genes in which mutations cause FPGK.
Murine Krt16 knockouts show distinct phenotypes depending on the mouse strain in which they are propagated, ranging from perinatal lethality to differences in the severity of oral and PPK lesions.7 These observations provide evidence that additional genetic variants contribute to Krt16 phenotypes in mice and suggest the same could be true for humans.
We propose that some cases of FPGK are due to mutations in KRT16 and thus share a genetic pathogenesis with PC, underscoring the utility of whole exome sequencing in providing genetic diagnoses for disorders that are genetically and clinically heterogeneous. Further biologic investigation of phenotypes caused by KRT16 mutation may reveal respective contributions of additional genetic variation and environmental effects to the variable clinical presentations.
- Gorlin RJ. Focal palmoplantar and marginal gingival hyperkeratosis—a syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12:239-242.
- Kolde G, Hennies HC, Bethke G, et al. Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis: a distinct palmoplantar ectodermal dysplasia with epidermolytic alterations but lack of mutations in known keratins. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):403-409.
- Duchatelet S, Hovnanian A. Olmsted syndrome: clinical, molecular and therapeutic aspects. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:33.
- Spaunhurst KM, Hogendorf AM, Smith FJ, et al. Pachyonychia congenita patients with mutations in KRT6A have more extensive disease compared with patients who have mutations in KRT16. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:875-878.
- Fu T, Leachman SA, Wilson NJ, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations among pachyonychia congenita patients with K16 mutations. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:1025-1028.
- Wilson NJ, O’Toole EA, Milstone LM, et al. The molecular genetic analysis of the expanding pachyonychia congenita case collection. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:343-355.
- Zieman A, Coulombe PA. The keratin 16 null phenotype is modestly impacted by genetic strain background in mice. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:672-674.
- Gorlin RJ. Focal palmoplantar and marginal gingival hyperkeratosis—a syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1976;12:239-242.
- Kolde G, Hennies HC, Bethke G, et al. Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis: a distinct palmoplantar ectodermal dysplasia with epidermolytic alterations but lack of mutations in known keratins. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 pt 1):403-409.
- Duchatelet S, Hovnanian A. Olmsted syndrome: clinical, molecular and therapeutic aspects. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10:33.
- Spaunhurst KM, Hogendorf AM, Smith FJ, et al. Pachyonychia congenita patients with mutations in KRT6A have more extensive disease compared with patients who have mutations in KRT16. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:875-878.
- Fu T, Leachman SA, Wilson NJ, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations among pachyonychia congenita patients with K16 mutations. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:1025-1028.
- Wilson NJ, O’Toole EA, Milstone LM, et al. The molecular genetic analysis of the expanding pachyonychia congenita case collection. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:343-355.
- Zieman A, Coulombe PA. The keratin 16 null phenotype is modestly impacted by genetic strain background in mice. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:672-674.
Practice Points
- Focal palmoplantar keratoderma and gingival keratosis (FPGK) is a rare autosomal-dominant syndrome featuring focal, pressure-related, painful palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) and gingival hyperkeratosis presenting as leukokeratosis.
- Focal pressure-related PPK and oral hyperkeratosis also are seen in pachyonychia congenita (PC), which is caused by mutations in keratin genes and is distinguished from FPGK by characteristic nail changes.
- A shared causative gene suggests that FPGK should be considered part of the PC spectrum.
Topical gel for epidermolysis bullosa shows ongoing benefit
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLASGOW, Scotland – the phase 3 safety and efficacy study of the treatment.
Over 200 patients from the trial, including 105 who began treatment with a control gel, continued taking oleogel-S10 after 90 days. The current interim analysis at 12 months indicates there was a 55% reduction in the proportion of the body affected, compared with baseline.
Moreover, reductions in skin activity scores seen in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained during the open-label extension. About 6% of patients experienced adverse events that led to withdrawal from the study.
The results show that oleogel-S10 was associated with “accelerated wound healing,” said study presenter Tracey Cunningham, MD, chief medical officer, Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC, Dublin, which is developing the topical agent. “There were no new safety signals with this longer exposure to oleogel-S10, and patients had sustained improvement in wound burden,” she added.
The research was presented at the British Association of Dermatologists (BAD) 2022 Annual Meeting on July 6.
In April, European Medicines Agency recommended approval of oleogel-S10 for the treatment of partial-thickness skin wounds associated with dystrophic and junctional EB for patients aged 6 months and older.
However, just a month earlier, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration declined to approve the topical agent for use in EB, even after it extended its review by 3 months to include additional analyses of data previously submitted by the company.
In the post-presentation discussion, Dr. Cunningham said that the FDA had “not been satisfied at this point with the information that we have given them,” adding, “We don’t agree with the decision, and we will be appealing.”
Raman K. Madan, MD, a dermatologist at Northwell Health, Huntington, New York, who was not involved in the study, said that the reductions in wound healing seen in the study are “meaningful” and that the numbers represent a “big breakthrough.”
He told this news organization that there are “very few products on the market” for EB and that having an option for patients “would be amazing.”
“The big issue here would be cost and coverage for patients,” he said. If approved, “hopefully” it will be affordable, he added.
Dr. Madan noted that from his perspective, the majority of the reactions to the topical gel were “mild,” and there are “a lot of confounding factors” underlying the number of serious adverse events. “These patients with epidermolysis are prone to some of these issues regardless of treatment,” he said.
During her presentation, Dr. Cunningham noted that EB is a rare, debilitating condition that is characterized by varying degrees of skin fragility, blisters, and impaired wound healing that in turn lead to serious complications that affect quality of life.
While wound management is a “fundamental priority” for patients living with EB, she said, there is a “high, unmet” clinical need.
To those ends, EASE was the largest randomized controlled phase 3 efficacy and safety study in EB. In the study, 252 patients were allocated to receive oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing.
The double-blind phase of the trial met its primary endpoint: A higher proportion of patients who were given oleogel-S10 achieved first complete closure of the EB target wound by day 45, compared with patients who were given control gel, at 41.3% versus 28.9%. This equated to a relative risk of wound closure by day 45 of 1.44, or an odds ratio of 1.84 (P = .013).
However, as reported at the time by this news organization, the difference in time to wound healing by day 90 between the two patient groups was not statistically significant (P = .302), with 50.5% of oleogel-S10 patients achieving wound closure, versus 43.9% of those in the control group.
Dr. Cunningham discussed the open-label extension, which involved 205 patients from the double-blind phase (mean age, of 16.3 years) treated with oleogel-S10 or control gel plus standard-of-care nonadhesive wound dressing for 24 months.
In presenting the results of the first 12 months of the open-label extension, she said that oleogel-S10 led to “consistent” reductions in the body surface area percentage (BSAP) affected by EB. The overall reduction from baseline was 55% after receiving treatment for 15 months.
Between day 90 and month 12 of the open-label extension, the absolute BSAP was reduced from 7.4% to 5.4% for patients who had received oleogel-S10 from the start of the study. For those who started in the control group and then switched to the oleogel-S10 arm during the open-label extension, the reduction was from 8.3% to 6.4%.
Dr. Cunningham pointed out that a 1% reduction in BSAP equates approximately to the palmar surface of the hand.
Scores on the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI) Skin activity subscale indicated that the reductions achieved in the double-blind phase of the trial were maintained.
Among patients who received oleogel-S10 from the start of the trial, EBDASI Skin scores were reduced from 19.6 at baseline to 13.5 at 12 months’ follow-up in the open-label extension. The reduction was from 19.6 to 13.5 for those who began the trial taking control gel.
Dr. Cunningham showed that adverse events of any grade were seen in 72.0% of patients who began taking oleogel-S10 at the start of the trial and in 69.5% of those who began the trial taking control gel.
Serious adverse events were recorded in 23.0% and 20.0% of patients, respectively, while 6.0% of those who initially received oleogel-S10 and 6.7% of those initially assigned to control gel experienced adverse events that led to study withdrawal during the open-label phase.
The most frequently reported adverse events in the open-label extension were wound complications, seen in 39.5% of patients; anemia, seen in 14.1%; wound infection, seen in 9.3%; pyrexia, seen in 8.3%; and pruritus, seen in 5.9%. No more details regarding adverse events were provided.
The study was funded by Amryt Pharmaceuticals DAC. Dr. Cunningham is an employee of Amryt Pharmaceuticals. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Quality of life benefit exaggerated in some cancer studies
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
First-ever Huntington staging system may jump-start drug development for early-stage disease
Researchers liken the Huntington’s disease Integrated Staging System (HD-ISS) to the system currently used to stage cancer. It groups patients according to their underlying biological, clinical, and functional characteristics.
It also includes criteria to biologically define Huntington’s disease stages across the entire disease spectrum, from birth to death, which is something that has not been done before. For now, the HD-ISS is only intended for research, but it could one day be modified for use in the clinic, investigators wrote.
“This systematization is of critical importance to select the most appropriate target population for clinical trials and studies,” said co-investigator Cristina Sampaio, MD, chief medical officer at the CHDI Foundation, Princeton, N.J.
“By providing a methodology to precisely define cases early in the neurodegenerative process, the HD-ISS will be instrumental in conducting trials in the very early disease stages,” Dr. Sampaio added.
The position paper was published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
New approach needed
There is no approved therapy to slow Huntington’s disease progression. Clinical trials currently enroll patients with demonstrable symptoms, which limits the ability to test therapeutics that could delay or prevent neurodegeneration.
Huntington’s disease is rare, occurring in about 2.7 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. It is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene involving a DNA segment known as a CAG trinucleotide repeat.
Currently, Huntington’s disease is diagnosed on the basis of clinical signs that emerge late in the disease course, an approach developed before the discovery of the HTT gene and the development of the genetic test for the CAG mutation.
The disease phase prior to diagnosis has been described as presymptomatic, premanifest, or prodromal. However, the three terms have varying definitions that make it difficult to compare study results across trials.
Because drug development had focused on the overt motor sign phase of the disease, there was no real need for an evidence-based staging system that classified disease phases from birth, the investigators noted.
“Now, the research community and regulators recognize that it is critical to conduct trials early in the disease when no signs or overt symptoms are measurable,” Dr. Sampaio said.
Defining disease stages
Work on the staging system was done through the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, an international project begun in 2018 among biotech and pharma companies, academic institutions, and nonprofit research and advocacy organizations.
Overall, more than 50 clinicians and researchers were involved in developing the HD-ISS.
Using modeling data from four large observational studies that included patients with Huntington’s disease and control groups, researchers identified four different stages of Huntington’s disease:
- Stage 0: Begins at birth with identification of HTT gene mutations but no detectable pathologic changes.
- Stage 1: Begins when biomarker changes are detected via MRI by a volume decrease in six brain areas.
- Stage 2: Begins when clinical signs of Huntington’s disease are present, as determined through motor and cognitive assessments.
- Stage 3: Begins when functional decline is evident, with worsening on the Independence Scale and the Total Functional Capacity of the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale.
Applying the HD-ISS to clinical trials requires the collection of information routinely recorded in Huntington’s disease research, as well as some additional data, but researchers say its application is straightforward.
The HD-ISS uses a numerical staging system similar to that used in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s guidance for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and integrates the prodromal, presymptomatic, or premanifest phase of the disease. This distinguishes it from earlier classification systems.
The HD-ISS can be adapted if new Huntington’s disease biomarkers are identified.
“As research results are generated, this will further validate the HD-ISS and potentially lead to the development of a derivative, and possibly simplified, system for clinical practice,” Dr. Sampaio said.
The new system goes further than a more recent proposal from the Movement Disorder Society task force, which addresses earlier stages in Huntington’s disease but doesn’t consider objective biomarker data.
Question of timing
Commenting on the findings, Erin Furr-Stimming, MD, neurologist and director of the Huntington’s Disease Society of America Center of Excellence with McGovern Medical School, UTHealth, Houston, said targeting early-stage disease will be key.
“Similar to more common neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, there is a period of at least a decade when changes are occurring in the nervous system, prior to the manifestation of clinical symptoms and signs significant enough to warrant a clinical diagnosis,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
She noted that multiple trials of disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease have failed for a multitude of reasons, “but one consistent question that is relevant to all these diseases is that of timing: Should we intervene and test these therapies earlier?
“The premanifest or prodromal period may be the ideal time to intervene with a disease-modifying therapy, prior to onset of any neurodegeneration,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
The CHDI Foundation provided financial support to the Critical Path Institute for the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, including all working group efforts. Dr. Sampio is an employee of and receives salary from CHDI Management. She has also received consultancy honorariums (unrelated to HD) from Pfizer, Kyowa Kirin, vTv Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuraly, Neuroderm, Green Valley Pharmaceuticals, and Pinteon Pharmaceuticals. A full list of disclosures for the other researchers is in the original article. Dr. Furr-Stimming reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers liken the Huntington’s disease Integrated Staging System (HD-ISS) to the system currently used to stage cancer. It groups patients according to their underlying biological, clinical, and functional characteristics.
It also includes criteria to biologically define Huntington’s disease stages across the entire disease spectrum, from birth to death, which is something that has not been done before. For now, the HD-ISS is only intended for research, but it could one day be modified for use in the clinic, investigators wrote.
“This systematization is of critical importance to select the most appropriate target population for clinical trials and studies,” said co-investigator Cristina Sampaio, MD, chief medical officer at the CHDI Foundation, Princeton, N.J.
“By providing a methodology to precisely define cases early in the neurodegenerative process, the HD-ISS will be instrumental in conducting trials in the very early disease stages,” Dr. Sampaio added.
The position paper was published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
New approach needed
There is no approved therapy to slow Huntington’s disease progression. Clinical trials currently enroll patients with demonstrable symptoms, which limits the ability to test therapeutics that could delay or prevent neurodegeneration.
Huntington’s disease is rare, occurring in about 2.7 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. It is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene involving a DNA segment known as a CAG trinucleotide repeat.
Currently, Huntington’s disease is diagnosed on the basis of clinical signs that emerge late in the disease course, an approach developed before the discovery of the HTT gene and the development of the genetic test for the CAG mutation.
The disease phase prior to diagnosis has been described as presymptomatic, premanifest, or prodromal. However, the three terms have varying definitions that make it difficult to compare study results across trials.
Because drug development had focused on the overt motor sign phase of the disease, there was no real need for an evidence-based staging system that classified disease phases from birth, the investigators noted.
“Now, the research community and regulators recognize that it is critical to conduct trials early in the disease when no signs or overt symptoms are measurable,” Dr. Sampaio said.
Defining disease stages
Work on the staging system was done through the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, an international project begun in 2018 among biotech and pharma companies, academic institutions, and nonprofit research and advocacy organizations.
Overall, more than 50 clinicians and researchers were involved in developing the HD-ISS.
Using modeling data from four large observational studies that included patients with Huntington’s disease and control groups, researchers identified four different stages of Huntington’s disease:
- Stage 0: Begins at birth with identification of HTT gene mutations but no detectable pathologic changes.
- Stage 1: Begins when biomarker changes are detected via MRI by a volume decrease in six brain areas.
- Stage 2: Begins when clinical signs of Huntington’s disease are present, as determined through motor and cognitive assessments.
- Stage 3: Begins when functional decline is evident, with worsening on the Independence Scale and the Total Functional Capacity of the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale.
Applying the HD-ISS to clinical trials requires the collection of information routinely recorded in Huntington’s disease research, as well as some additional data, but researchers say its application is straightforward.
The HD-ISS uses a numerical staging system similar to that used in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s guidance for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and integrates the prodromal, presymptomatic, or premanifest phase of the disease. This distinguishes it from earlier classification systems.
The HD-ISS can be adapted if new Huntington’s disease biomarkers are identified.
“As research results are generated, this will further validate the HD-ISS and potentially lead to the development of a derivative, and possibly simplified, system for clinical practice,” Dr. Sampaio said.
The new system goes further than a more recent proposal from the Movement Disorder Society task force, which addresses earlier stages in Huntington’s disease but doesn’t consider objective biomarker data.
Question of timing
Commenting on the findings, Erin Furr-Stimming, MD, neurologist and director of the Huntington’s Disease Society of America Center of Excellence with McGovern Medical School, UTHealth, Houston, said targeting early-stage disease will be key.
“Similar to more common neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, there is a period of at least a decade when changes are occurring in the nervous system, prior to the manifestation of clinical symptoms and signs significant enough to warrant a clinical diagnosis,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
She noted that multiple trials of disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease have failed for a multitude of reasons, “but one consistent question that is relevant to all these diseases is that of timing: Should we intervene and test these therapies earlier?
“The premanifest or prodromal period may be the ideal time to intervene with a disease-modifying therapy, prior to onset of any neurodegeneration,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
The CHDI Foundation provided financial support to the Critical Path Institute for the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, including all working group efforts. Dr. Sampio is an employee of and receives salary from CHDI Management. She has also received consultancy honorariums (unrelated to HD) from Pfizer, Kyowa Kirin, vTv Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuraly, Neuroderm, Green Valley Pharmaceuticals, and Pinteon Pharmaceuticals. A full list of disclosures for the other researchers is in the original article. Dr. Furr-Stimming reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers liken the Huntington’s disease Integrated Staging System (HD-ISS) to the system currently used to stage cancer. It groups patients according to their underlying biological, clinical, and functional characteristics.
It also includes criteria to biologically define Huntington’s disease stages across the entire disease spectrum, from birth to death, which is something that has not been done before. For now, the HD-ISS is only intended for research, but it could one day be modified for use in the clinic, investigators wrote.
“This systematization is of critical importance to select the most appropriate target population for clinical trials and studies,” said co-investigator Cristina Sampaio, MD, chief medical officer at the CHDI Foundation, Princeton, N.J.
“By providing a methodology to precisely define cases early in the neurodegenerative process, the HD-ISS will be instrumental in conducting trials in the very early disease stages,” Dr. Sampaio added.
The position paper was published in the July issue of the Lancet Neurology.
New approach needed
There is no approved therapy to slow Huntington’s disease progression. Clinical trials currently enroll patients with demonstrable symptoms, which limits the ability to test therapeutics that could delay or prevent neurodegeneration.
Huntington’s disease is rare, occurring in about 2.7 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. It is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene involving a DNA segment known as a CAG trinucleotide repeat.
Currently, Huntington’s disease is diagnosed on the basis of clinical signs that emerge late in the disease course, an approach developed before the discovery of the HTT gene and the development of the genetic test for the CAG mutation.
The disease phase prior to diagnosis has been described as presymptomatic, premanifest, or prodromal. However, the three terms have varying definitions that make it difficult to compare study results across trials.
Because drug development had focused on the overt motor sign phase of the disease, there was no real need for an evidence-based staging system that classified disease phases from birth, the investigators noted.
“Now, the research community and regulators recognize that it is critical to conduct trials early in the disease when no signs or overt symptoms are measurable,” Dr. Sampaio said.
Defining disease stages
Work on the staging system was done through the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, an international project begun in 2018 among biotech and pharma companies, academic institutions, and nonprofit research and advocacy organizations.
Overall, more than 50 clinicians and researchers were involved in developing the HD-ISS.
Using modeling data from four large observational studies that included patients with Huntington’s disease and control groups, researchers identified four different stages of Huntington’s disease:
- Stage 0: Begins at birth with identification of HTT gene mutations but no detectable pathologic changes.
- Stage 1: Begins when biomarker changes are detected via MRI by a volume decrease in six brain areas.
- Stage 2: Begins when clinical signs of Huntington’s disease are present, as determined through motor and cognitive assessments.
- Stage 3: Begins when functional decline is evident, with worsening on the Independence Scale and the Total Functional Capacity of the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale.
Applying the HD-ISS to clinical trials requires the collection of information routinely recorded in Huntington’s disease research, as well as some additional data, but researchers say its application is straightforward.
The HD-ISS uses a numerical staging system similar to that used in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s guidance for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and integrates the prodromal, presymptomatic, or premanifest phase of the disease. This distinguishes it from earlier classification systems.
The HD-ISS can be adapted if new Huntington’s disease biomarkers are identified.
“As research results are generated, this will further validate the HD-ISS and potentially lead to the development of a derivative, and possibly simplified, system for clinical practice,” Dr. Sampaio said.
The new system goes further than a more recent proposal from the Movement Disorder Society task force, which addresses earlier stages in Huntington’s disease but doesn’t consider objective biomarker data.
Question of timing
Commenting on the findings, Erin Furr-Stimming, MD, neurologist and director of the Huntington’s Disease Society of America Center of Excellence with McGovern Medical School, UTHealth, Houston, said targeting early-stage disease will be key.
“Similar to more common neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, there is a period of at least a decade when changes are occurring in the nervous system, prior to the manifestation of clinical symptoms and signs significant enough to warrant a clinical diagnosis,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
She noted that multiple trials of disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease have failed for a multitude of reasons, “but one consistent question that is relevant to all these diseases is that of timing: Should we intervene and test these therapies earlier?
“The premanifest or prodromal period may be the ideal time to intervene with a disease-modifying therapy, prior to onset of any neurodegeneration,” Dr. Furr-Stimming said.
The CHDI Foundation provided financial support to the Critical Path Institute for the Huntington’s Disease Regulatory Science Consortium, including all working group efforts. Dr. Sampio is an employee of and receives salary from CHDI Management. She has also received consultancy honorariums (unrelated to HD) from Pfizer, Kyowa Kirin, vTv Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, Neuraly, Neuroderm, Green Valley Pharmaceuticals, and Pinteon Pharmaceuticals. A full list of disclosures for the other researchers is in the original article. Dr. Furr-Stimming reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET NEUROLOGY
Acute hepatitis cases in children show declining trend; adenovirus, COVID-19 remain key leads
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022
FDA unveils 5-year plan for ALS and other neurodegenerative diseases
The agency’s Action Plan for Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases including Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) aims to advance the development of safe and effective medical products and facilitate patient access to novel treatments.
“The effects of rare neurodegenerative diseases are devastating, with very few effective therapeutic options available to patients. We recognize the urgent need for new treatments that can both improve and extend the lives of people diagnosed with these diseases,” FDA Commissioner Robert M. Califf, MD, said in a news release.
“To face that challenge and to accelerate drug development, we need innovative approaches to better understand these diseases while also building on current scientific and research capabilities,” Dr. Califf acknowledged.
“This action plan, especially including the use of public-private partnerships and direct involvement of patients, will ensure the FDA is working toward meeting the task set forth by Congress to enhance the quality of life for those suffering by facilitating access to new therapies,” Dr. Califf added.
Blueprint to ‘aggressively’ move forward
The action plan represents a “blueprint” for how the agency will “aggressively” move forward to address challenges in drug development for rare neurodegenerative diseases to improve patient health, the FDA said.
The plan was created in accordance with provisions in the Accelerating Access to Critical Therapies for ALS Act (ACT for ALS) that President Biden signed into law in late 2021.
Targeted activities include establishing the FDA Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases Task Force and the public-private partnership for rare neurodegenerative diseases, developing disease-specific science strategies over the next 5 years, and leveraging ongoing FDA regulatory science efforts.
The ALS Science Strategy is part of the plan focused specifically on ALS. It provides a “forward-leaning” framework for FDA activities, which include efforts to improve characterization of disease pathogenesis and natural history, boost clinical trial infrastructure and agility to enable early selection of promising therapeutic candidates for further development, optimize clinical trial design, improve access to the trials, streamline clinical trial operations, and reduce the time and cost of drug development.
The FDA says patient engagement, public workshops, research projects, coordination across FDA centers and offices, and collaboration with the National Institutes of Health will be key to the success of implementation of the ALS Science Strategy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency’s Action Plan for Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases including Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) aims to advance the development of safe and effective medical products and facilitate patient access to novel treatments.
“The effects of rare neurodegenerative diseases are devastating, with very few effective therapeutic options available to patients. We recognize the urgent need for new treatments that can both improve and extend the lives of people diagnosed with these diseases,” FDA Commissioner Robert M. Califf, MD, said in a news release.
“To face that challenge and to accelerate drug development, we need innovative approaches to better understand these diseases while also building on current scientific and research capabilities,” Dr. Califf acknowledged.
“This action plan, especially including the use of public-private partnerships and direct involvement of patients, will ensure the FDA is working toward meeting the task set forth by Congress to enhance the quality of life for those suffering by facilitating access to new therapies,” Dr. Califf added.
Blueprint to ‘aggressively’ move forward
The action plan represents a “blueprint” for how the agency will “aggressively” move forward to address challenges in drug development for rare neurodegenerative diseases to improve patient health, the FDA said.
The plan was created in accordance with provisions in the Accelerating Access to Critical Therapies for ALS Act (ACT for ALS) that President Biden signed into law in late 2021.
Targeted activities include establishing the FDA Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases Task Force and the public-private partnership for rare neurodegenerative diseases, developing disease-specific science strategies over the next 5 years, and leveraging ongoing FDA regulatory science efforts.
The ALS Science Strategy is part of the plan focused specifically on ALS. It provides a “forward-leaning” framework for FDA activities, which include efforts to improve characterization of disease pathogenesis and natural history, boost clinical trial infrastructure and agility to enable early selection of promising therapeutic candidates for further development, optimize clinical trial design, improve access to the trials, streamline clinical trial operations, and reduce the time and cost of drug development.
The FDA says patient engagement, public workshops, research projects, coordination across FDA centers and offices, and collaboration with the National Institutes of Health will be key to the success of implementation of the ALS Science Strategy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency’s Action Plan for Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases including Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) aims to advance the development of safe and effective medical products and facilitate patient access to novel treatments.
“The effects of rare neurodegenerative diseases are devastating, with very few effective therapeutic options available to patients. We recognize the urgent need for new treatments that can both improve and extend the lives of people diagnosed with these diseases,” FDA Commissioner Robert M. Califf, MD, said in a news release.
“To face that challenge and to accelerate drug development, we need innovative approaches to better understand these diseases while also building on current scientific and research capabilities,” Dr. Califf acknowledged.
“This action plan, especially including the use of public-private partnerships and direct involvement of patients, will ensure the FDA is working toward meeting the task set forth by Congress to enhance the quality of life for those suffering by facilitating access to new therapies,” Dr. Califf added.
Blueprint to ‘aggressively’ move forward
The action plan represents a “blueprint” for how the agency will “aggressively” move forward to address challenges in drug development for rare neurodegenerative diseases to improve patient health, the FDA said.
The plan was created in accordance with provisions in the Accelerating Access to Critical Therapies for ALS Act (ACT for ALS) that President Biden signed into law in late 2021.
Targeted activities include establishing the FDA Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases Task Force and the public-private partnership for rare neurodegenerative diseases, developing disease-specific science strategies over the next 5 years, and leveraging ongoing FDA regulatory science efforts.
The ALS Science Strategy is part of the plan focused specifically on ALS. It provides a “forward-leaning” framework for FDA activities, which include efforts to improve characterization of disease pathogenesis and natural history, boost clinical trial infrastructure and agility to enable early selection of promising therapeutic candidates for further development, optimize clinical trial design, improve access to the trials, streamline clinical trial operations, and reduce the time and cost of drug development.
The FDA says patient engagement, public workshops, research projects, coordination across FDA centers and offices, and collaboration with the National Institutes of Health will be key to the success of implementation of the ALS Science Strategy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.