User login
Evolocumab safe, well-tolerated in HIV+ patients
Evolocumab proved effective, well tolerated, and safe for the treatment of refractory dyslipidemia in persons living with HIV in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind BEIJERINCK study.
At 24 weeks, nearly three-quarters of patients randomized to evolocumab (Repatha) achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol while on maximally tolerated background lipid lowering with a statin and/or other drugs. This was accompanied by significant reductions in other atherogenic lipids, Franck Boccara, MD, PhD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Evolocumab thus shows the potential to help fill a major unmet need for more effective treatment of dyslipidemia in HIV-positive patients, who number an estimated 38 million worldwide, including 1.1 million in the United States. Access to highly active antiretroviral therapies has transformed HIV infection into a chronic manageable disease, but this major advance has been accompanied by a rate of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that’s nearly twice that of the general population, observed Dr. Boccara, a cardiologist at Sorbonne University, Paris.
The BEIJERINCK study included 464 HIV-infected patients in the United States and 14 other countries on five continents. Participants had a mean baseline LDL cholesterol of 133 mg/dL and triglycerides of about 190 mg/dL while on maximally tolerated lipid-lowering therapy. They had been diagnosed with HIV an average of 18 years earlier. One-third of them had known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. More than one-quarter of participants were cigarette smokers. Patients were randomized 2:1 to 24 weeks of double-blind subcutaneous evolocumab at 420 mg once monthly or placebo, then an additional 24 weeks of open-label evolocumab for all.
The primary endpoint was change in LDL from baseline to week 24: a 56.2% reduction in the evolocumab group and a 0.7% increase with placebo. About 73% of patients on evolocumab achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol, as did less than 1% of controls. Likewise, 73% of the evolocumab group got their LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL, compared with 7.9% with placebo.
The evolocumab group also experienced favorable placebo-subtracted differences from baseline of 23% in triglycerides, 27% in lipoprotein(a), and 22% in very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
As was the case in the earlier, much larger landmark clinical trials, evolocumab was well tolerated in BEIJERINCK, with a side effect profile similar to placebo. Notably, there was no increase in liver abnormalities in evolocumab-treated patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy, and no one developed evolocumab neutralizing antibodies.
Dr. Boccara reported receiving a research grant from Amgen, the study sponsor, as well as lecture fees from several other pharmaceutical companies.
Simultaneous with the presentation at ACC 2020, the primary results of the BEIJERINCK study were published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.025).
Evolocumab proved effective, well tolerated, and safe for the treatment of refractory dyslipidemia in persons living with HIV in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind BEIJERINCK study.
At 24 weeks, nearly three-quarters of patients randomized to evolocumab (Repatha) achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol while on maximally tolerated background lipid lowering with a statin and/or other drugs. This was accompanied by significant reductions in other atherogenic lipids, Franck Boccara, MD, PhD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Evolocumab thus shows the potential to help fill a major unmet need for more effective treatment of dyslipidemia in HIV-positive patients, who number an estimated 38 million worldwide, including 1.1 million in the United States. Access to highly active antiretroviral therapies has transformed HIV infection into a chronic manageable disease, but this major advance has been accompanied by a rate of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that’s nearly twice that of the general population, observed Dr. Boccara, a cardiologist at Sorbonne University, Paris.
The BEIJERINCK study included 464 HIV-infected patients in the United States and 14 other countries on five continents. Participants had a mean baseline LDL cholesterol of 133 mg/dL and triglycerides of about 190 mg/dL while on maximally tolerated lipid-lowering therapy. They had been diagnosed with HIV an average of 18 years earlier. One-third of them had known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. More than one-quarter of participants were cigarette smokers. Patients were randomized 2:1 to 24 weeks of double-blind subcutaneous evolocumab at 420 mg once monthly or placebo, then an additional 24 weeks of open-label evolocumab for all.
The primary endpoint was change in LDL from baseline to week 24: a 56.2% reduction in the evolocumab group and a 0.7% increase with placebo. About 73% of patients on evolocumab achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol, as did less than 1% of controls. Likewise, 73% of the evolocumab group got their LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL, compared with 7.9% with placebo.
The evolocumab group also experienced favorable placebo-subtracted differences from baseline of 23% in triglycerides, 27% in lipoprotein(a), and 22% in very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
As was the case in the earlier, much larger landmark clinical trials, evolocumab was well tolerated in BEIJERINCK, with a side effect profile similar to placebo. Notably, there was no increase in liver abnormalities in evolocumab-treated patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy, and no one developed evolocumab neutralizing antibodies.
Dr. Boccara reported receiving a research grant from Amgen, the study sponsor, as well as lecture fees from several other pharmaceutical companies.
Simultaneous with the presentation at ACC 2020, the primary results of the BEIJERINCK study were published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.025).
Evolocumab proved effective, well tolerated, and safe for the treatment of refractory dyslipidemia in persons living with HIV in the phase 3, randomized, double-blind BEIJERINCK study.
At 24 weeks, nearly three-quarters of patients randomized to evolocumab (Repatha) achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol while on maximally tolerated background lipid lowering with a statin and/or other drugs. This was accompanied by significant reductions in other atherogenic lipids, Franck Boccara, MD, PhD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Evolocumab thus shows the potential to help fill a major unmet need for more effective treatment of dyslipidemia in HIV-positive patients, who number an estimated 38 million worldwide, including 1.1 million in the United States. Access to highly active antiretroviral therapies has transformed HIV infection into a chronic manageable disease, but this major advance has been accompanied by a rate of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that’s nearly twice that of the general population, observed Dr. Boccara, a cardiologist at Sorbonne University, Paris.
The BEIJERINCK study included 464 HIV-infected patients in the United States and 14 other countries on five continents. Participants had a mean baseline LDL cholesterol of 133 mg/dL and triglycerides of about 190 mg/dL while on maximally tolerated lipid-lowering therapy. They had been diagnosed with HIV an average of 18 years earlier. One-third of them had known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. More than one-quarter of participants were cigarette smokers. Patients were randomized 2:1 to 24 weeks of double-blind subcutaneous evolocumab at 420 mg once monthly or placebo, then an additional 24 weeks of open-label evolocumab for all.
The primary endpoint was change in LDL from baseline to week 24: a 56.2% reduction in the evolocumab group and a 0.7% increase with placebo. About 73% of patients on evolocumab achieved at least a 50% reduction in LDL cholesterol, as did less than 1% of controls. Likewise, 73% of the evolocumab group got their LDL cholesterol below 70 mg/dL, compared with 7.9% with placebo.
The evolocumab group also experienced favorable placebo-subtracted differences from baseline of 23% in triglycerides, 27% in lipoprotein(a), and 22% in very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
As was the case in the earlier, much larger landmark clinical trials, evolocumab was well tolerated in BEIJERINCK, with a side effect profile similar to placebo. Notably, there was no increase in liver abnormalities in evolocumab-treated patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy, and no one developed evolocumab neutralizing antibodies.
Dr. Boccara reported receiving a research grant from Amgen, the study sponsor, as well as lecture fees from several other pharmaceutical companies.
Simultaneous with the presentation at ACC 2020, the primary results of the BEIJERINCK study were published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 19. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.025).
FROM ACC 2020
How to expand the APP role in a crisis
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
An opportunity to better appreciate the value of PAs, NPs
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.
Advanced practice providers – physician assistants and nurse practitioners – at the 733-bed Emory University Hospital in Atlanta are playing an expanded role in the admission of patients into the hospital, particularly those suspected of having COVID-19.
Before the pandemic crisis, evaluation visits by the APP would have been reviewed on the same day by the supervising physician through an in-person encounter with the patient. The new protocol is not outside of scope-of-practice regulations for APPs in Georgia or of the hospital’s bylaws. But it offers a way to help limit the overall exposure of hospital staff to patients suspected of COVID-19 infection, and the total amount of time providers spend in such patients’ room. Just one provider now needs to meet the patient during the admissions process, while the attending physician can fulfill a requirement for seeing the patient within 24 hours during rounds the following day. Emergency encounters would still be done as needed.
These protocols point toward future conversations about the limits to APPs’ scope of practice, and whether more expansive approaches could be widely adopted once the current crisis is over, say advocates for the APPs’ role.
“Our APPs are primarily doing the admissions to the hospital of COVID patients and of non-COVID patients, as we’ve always done. But with COVID-infected or -suspected patients, we’re trying to minimize exposure for our providers,” explained Susan Ortiz, a certified PA, lead APP at Emory University Hospital. “In this way, we can also see more patients more efficiently.” Ms. Ortiz said she finds in talking to other APP leads in the Emory system that “each facility has its own culture and way of doing things. But for the most part, they’re all trying to do something to limit providers’ time in patients’ rooms.”
In response to the rapidly moving crisis, tactics to limit personnel in COVID patients’ rooms to the “absolutely essential” include gathering much of the needed history and other information requested from the patient by telephone, Ms. Ortiz said. This can be done either over the patient’s own cell phone or a phone placed in the room by hospital staff. Family members may be called to supplement this information, with the patient’s consent.
Once vital sign monitoring equipment is hooked up, it is possible to monitor the patient’s vital signs remotely without making frequent trips into the room. That way, in-person vital sign monitoring doesn’t need to happen routinely – at least not as often. One observation by clinicians on Ms. Ortiz’s team: listening for lung sounds with a stethoscope has not been shown to alter treatment for these patients. Once a chest X-ray shows structural changes in a patient’s lung, all lung exams are going to sound bad.
The admitting provider still needs to meet the patient in person for part of the admission visit and physical exam, but the amount of time spent in close personal contact with the patient can be much shorter, Ms. Ortiz said. For patients who are admitted, if there is a question about difficulty swallowing, they will see a speech pathologist, and if evidence of malnutrition, a nutritionist. “But we have to be extremely thoughtful about when people go into the room. So we are not ordering these ancillary services as routinely as we do during non-COVID times,” she said.
Appropriate levels of fear
Emory’s hospitalists are communicating daily about a rapidly changing situation. “We get a note by email every day, and we have a Dropbox account for downloading more information,” Ms. Ortiz said. A joint on-call system is used to provide backup coverage of APPs at the seven Emory hospitals. When replacement shifts need filling in a hurry, practitioners are able to obtain emergency credentials at any of the other hospitals. “It’s a voluntary process to sign up to be on-call,” Ms. Ortiz said. So far, that has been sufficient.
All staff have their own level of “appropriate fear” of this infection, Ms. Ortiz noted. “We have an extremely supportive group here to back up those of us who, for good reason, don’t want to be admitting the COVID patients.” Ms. Ortiz opted out of doing COVID admissions because her husband’s health places him at particular risk. “But with the cross-coverage we have, sometimes I’ll provide assistance when needed if a patient is suspected of being infected.” APPs are critical to Emory’s hospital medicine group – not ancillaries. “Everyone here feels that way. So we want to give them a lot of support. We’re all pitching in, doing it together,” she said.
“We said when we started with this, a couple of weeks before the surge started, that you could volunteer to see COVID patients,” said Emory hospitalist Jessica Nave, MD. “As we came to realize that the demand would be greater, we said you would need to opt out of seeing these patients, rather than opt in, and have a reason for doing so.” An example is pregnant staff, of which there seems to be a lot at Emory right now, Dr. Nave said, or those who are immunocompromised for other reasons. Those who don’t opt out are seeing the majority of the COVID patients, depending on actual need.
Dr. Nave is married to another hospitalist at Emory. “We can’t isolate from each other or our children. He and I have a regimented protocol for how we handle the risk, which includes taking off our shoes and clothes in the garage, showering and wiping down every place we might have touched. But those steps are not guarantees.” Other staff at Emory are isolating from their families for weeks at a time. Emory has a conference hotel offering discounted rates to staff. Nine physicians at Emory have been tested for the infection based on presenting symptoms, but at press time none had tested positive.
Streamlining code blue
Another area in which Emory has revised its policies in response to COVID-19 is for in-hospital cardiac arrest code response. Codes are inherently unpredictable, and crowd control has always been an issue for them, Dr. Nave said. “Historically, you could have 15 or more people show up when a code was called. Now, more than ever, we need to limit the number of people involved, for the same reason, avoiding unnecessary patient contact.”
The hospital’s Resuscitation Committee took the lead on developing a new policy, approved by the its Critical Care Committee and COVID Task Force, to limit the number of professionals in the room when running a code to an essential six: two doing chest compression, two managing airways, a code leader, and a critical care nurse. Outside the patient’s door, wearing the same personal protective equipment (PPE), are a pharmacist, recorder, and runner. “If you’re not one of those nine, you don’t need to be involved and should leave the area,” Dr. Nave said.
Staff have been instructed that they need to don appropriate PPE, including gown, mask, and eye wear, before entering the room for a code – even if that delays the start of intervention. “We’ve also made a code kit for each unit with quickly accessible gowns and masks. It should be used only for code blues.”
Increasing flexibility for the team
PAs and NPs in other locations are also exploring opportunities for gearing up to play larger roles in hospital care in the current crisis situation. The American Association of Physician Assistants has urged all U.S. governors to issue executive orders to waive state-specific licensing requirements for physician supervision or collaboration during the crisis, in order to increase flexibility of health care teams to deploy APPs.
AAPA believes the supervisory requirement is the biggest current barrier to mobilizing PAs and NPs. That includes those who have been furloughed from outpatient or other settings but are limited in their ability to contribute to the COVID crisis by the need to sign a supervision agreement with a physician at a new hospital.
The crisis is creating an opportunity to better appreciate the value PAs and NPs bring to health care, said Tracy Cardin, ACNP-BC, SFHM, vice president for advanced practice providers at Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash. The company recently sent a memo to the leadership of hospital sites at which it has contracts, requesting suspension of the hospitals’ requirements for a daily physician supervisory visit for APPs – which can be a hurdle when trying to leverage all hands on deck in the crisis.
NPs and PAs are stepping up and volunteering for COVID patients, Ms. Cardin said. Some have even taken leaves from their jobs to go to New York to help out at the epicenter of the U.S. crisis. “They want to make a difference. We’ve been deploying nonhospital medicine APPs from surgery, primary care, and elsewhere, embedding them on the hospital medicine team.”
Before the crisis, APPs at Sound Physicians weren’t always able to practice at the top of their licenses, depending on the hospital setting, added Alicia Scheffer, CNP, the company’s Great Lakes regional director for APPs. “Then COVID-19 showed up and really expedited conversations about how to maximize caseloads using APPs and about the fear of failing patients due to lack of capacity.”
In several locales, Sound Physicians is using quarantined providers to do telephone triage, or staffing ICUs with APPs backed up by telemedicine. “In APP-led ICUs, where the nurses are leading, they are intubating patients, placing central lines, things we weren’t allowed to do before,” Ms. Scheffer said.
A spirit of improvisation
There is a lot of tension at Emory University Hospital these days, reflecting the fears and uncertainties about the crisis, Dr. Nave said. “But there’s also a strangely powerful camaraderie like I’ve never seen before. When you walk onto the COVID units, you feel immediately bonded to the nurses, the techs, the phlebotomists. And you feel like you could talk about anything.”
Changes such as those made at Emory, have been talked about for a while, for example when hospitalists are having a busy night, she said. “But because this is a big cultural change, some physicians resisted it. We trust our APPs. But if the doctor’s name is on a patient chart, they want to see the patient – just for their own comfort level.”
Ms. Ortiz thinks the experience with the COVID crisis could help to advance the conversation about the appropriate role for APPs and their scope of practice in hospital medicine, once the current crisis has passed. “People were used to always doing things a certain way. This experience, hopefully, will get us to the point where attending physicians have more comfort with the APP’s ability to act autonomously,” she said.
“We’ve also talked about piloting telemedicine examinations using Zoom,” Dr. Nave added. “It’s making us think a lot of remote cross-coverage could be done that way. We’ve talked about using the hospital’s iPads with patients. This crisis really makes you think you want to innovate, in a spirit of improvisation,” she said. “Now is the time to try some of these things.”
Editors note: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals are seeing unprecedented volumes of patients requiring hospital medicine groups to stretch their current resources and recruit providers from outside their groups to bolster their inpatient services. The Society of Hospital Medicine has put together the following stepwise guide for onboarding traditional outpatient and subspecialty-based providers to work on general medicine wards: COVID-19 nonhospitalist onboarding resources.
MRSA decolonization reduces postdischarge infections
Background: MRSA carriers are at higher risk of infection and rehospitalization after hospital discharge. Education regarding hygiene, environmental cleaning, and decolonization of MRSA carriers have been used as possible preventive strategies. Decolonization has been effective in reducing surgical-site infections, recurrent skin infections, and infections in ICU. However, there is sparsity of data on the efficacy of routine decolonization of MRSA carriers after hospital discharge.
Study design: Multicenter, randomized, unblinded controlled trial.
Setting: A total of 17 hospitals and seven nursing homes in Southern California.
Synopsis: The study included 2,121 inpatients hospitalized within the previous 30 days and found to be MRSA carriers. Patients were randomized to education only (1,063) or decolonization plus education (1,058), with both groups followed for 12 months after discharge. Decolonization consisted of 4% rinse-off chlorhexidine for daily bathing or showering, 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthwash twice daily, and 2% nasal mupirocin twice daily. The primary outcome was MRSA infection as defined by the CDC. Secondary outcomes included MRSA infection based on clinical judgment, infection from any cause, and infection-related hospitalization. Per protocol analysis showed that MRSA infection occurred in 9.2% in the education group and 6.3% in the decolonization plus education group, with 30% reduction in the risk of infection (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.99; number needed to treat to prevent one infection, 30). The decolonization group also had a lower hazard of clinically judged infection from any cause (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.70-0.99) and infection-related hospitalization (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.93).
Limitations of the study include unblinded intervention, missing of milder infections that might not have required hospitalization, and frequent insufficient documentation in charts for events to be deemed infection according to the CDC criteria.
Bottom line: Decolonization of MRSA carriers post discharge may lower MRSA-related infections and infections more than hygiene education alone.
Citation: Huang SS et al. Decolonization to reduce postdischarge infection risk among MRSA carriers. N Eng J Med. 2019;380:638-50.
Dr. Vedamurthy is a hospitalist at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Background: MRSA carriers are at higher risk of infection and rehospitalization after hospital discharge. Education regarding hygiene, environmental cleaning, and decolonization of MRSA carriers have been used as possible preventive strategies. Decolonization has been effective in reducing surgical-site infections, recurrent skin infections, and infections in ICU. However, there is sparsity of data on the efficacy of routine decolonization of MRSA carriers after hospital discharge.
Study design: Multicenter, randomized, unblinded controlled trial.
Setting: A total of 17 hospitals and seven nursing homes in Southern California.
Synopsis: The study included 2,121 inpatients hospitalized within the previous 30 days and found to be MRSA carriers. Patients were randomized to education only (1,063) or decolonization plus education (1,058), with both groups followed for 12 months after discharge. Decolonization consisted of 4% rinse-off chlorhexidine for daily bathing or showering, 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthwash twice daily, and 2% nasal mupirocin twice daily. The primary outcome was MRSA infection as defined by the CDC. Secondary outcomes included MRSA infection based on clinical judgment, infection from any cause, and infection-related hospitalization. Per protocol analysis showed that MRSA infection occurred in 9.2% in the education group and 6.3% in the decolonization plus education group, with 30% reduction in the risk of infection (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.99; number needed to treat to prevent one infection, 30). The decolonization group also had a lower hazard of clinically judged infection from any cause (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.70-0.99) and infection-related hospitalization (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.93).
Limitations of the study include unblinded intervention, missing of milder infections that might not have required hospitalization, and frequent insufficient documentation in charts for events to be deemed infection according to the CDC criteria.
Bottom line: Decolonization of MRSA carriers post discharge may lower MRSA-related infections and infections more than hygiene education alone.
Citation: Huang SS et al. Decolonization to reduce postdischarge infection risk among MRSA carriers. N Eng J Med. 2019;380:638-50.
Dr. Vedamurthy is a hospitalist at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Background: MRSA carriers are at higher risk of infection and rehospitalization after hospital discharge. Education regarding hygiene, environmental cleaning, and decolonization of MRSA carriers have been used as possible preventive strategies. Decolonization has been effective in reducing surgical-site infections, recurrent skin infections, and infections in ICU. However, there is sparsity of data on the efficacy of routine decolonization of MRSA carriers after hospital discharge.
Study design: Multicenter, randomized, unblinded controlled trial.
Setting: A total of 17 hospitals and seven nursing homes in Southern California.
Synopsis: The study included 2,121 inpatients hospitalized within the previous 30 days and found to be MRSA carriers. Patients were randomized to education only (1,063) or decolonization plus education (1,058), with both groups followed for 12 months after discharge. Decolonization consisted of 4% rinse-off chlorhexidine for daily bathing or showering, 0.12% chlorhexidine mouthwash twice daily, and 2% nasal mupirocin twice daily. The primary outcome was MRSA infection as defined by the CDC. Secondary outcomes included MRSA infection based on clinical judgment, infection from any cause, and infection-related hospitalization. Per protocol analysis showed that MRSA infection occurred in 9.2% in the education group and 6.3% in the decolonization plus education group, with 30% reduction in the risk of infection (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.99; number needed to treat to prevent one infection, 30). The decolonization group also had a lower hazard of clinically judged infection from any cause (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.70-0.99) and infection-related hospitalization (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.93).
Limitations of the study include unblinded intervention, missing of milder infections that might not have required hospitalization, and frequent insufficient documentation in charts for events to be deemed infection according to the CDC criteria.
Bottom line: Decolonization of MRSA carriers post discharge may lower MRSA-related infections and infections more than hygiene education alone.
Citation: Huang SS et al. Decolonization to reduce postdischarge infection risk among MRSA carriers. N Eng J Med. 2019;380:638-50.
Dr. Vedamurthy is a hospitalist at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Plan now to address the COVID-19 mental health fallout
COVID-19 affects the physical, psychological, and social health of people around the world. In the United States, newly reported cases are rising at alarming rates.
As of early May, more than 1.3 million people were confirmed to be COVID-19 infected in the United States and more than 4 million cases were reported globally.1
According to new internal projections from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, by June 1, the number of daily deaths could reach about 3,000. By the end of June, a draft CDC report projects that the United States will see 200,000 new cases each day.2
COVID-19 undeniably harms mental health. It gravely instills uncertainty and anxiety, sometimes compounded by the grief of losing loved ones and not being able to mourn those losses in traditional ways. The pandemic also has led to occupational and/or financial losses. Physical distancing and shelter-in-place practices make it even harder to cope with those stresses, although those practices mitigate the dangers. The fears tied to those practices are thought to be keeping some patients with health problems from seeking needed care from hospital EDs.3 In light of the mental health crisis emerging because of the profound impact of this pandemic on all aspects of life, clinicians should start working with public health and political leaders to develop plans to address these issues now.
Known impact of previous outbreaks
Previous disease outbreaks evidence a similar pattern of heightened anxiety as the patterns seen with COVID-19. For example, during the 2009 swine flu outbreak, 36 surveys of more than 3,000 participants in the United Kingdom found that 9.6%-32.9% of the participants were “very” or “fairly” worried about the possibility of contracting swine flu.4 The 1995 Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo produced stigmatization tied to the illness. That outbreak provided many lessons for physicians.5
The metaphors ascribed to different diseases affect communities’ responses to it. The SARS virus has been particularly insidious and has been thought of as a “plague.”6 Epidemics of all kinds cause fears, not only of contracting the disease and dying, but also of social exclusion.7 The emotional responses to COVID-19 can precipitate anxiety, depression, insomnia, and somatic symptoms.
Repeated exposure to news media about the disease adds to theses stresss.10 Constant news consumption can result in panicky hoarding of resources, such as masks; gloves; first-aid kits; alcohol hand rubs; and daily necessities such as food, water, and toilet paper.
Who is most affected by outbreaks?
Those most affected after a disease outbreak are patients, their families, and medical personnel. In one study, researchers who conducted an online survey of 1,210 respondents in 194 cities in China during the early phase of the outbreak found that the psychological effects were worst among women, students, and vulnerable populations.11
Meanwhile, a 2003 cross-sectional survey of 1,115 ethnic Chinese adults in Hong Kong who responded to the SARS outbreak found that the respondents most likely to heed precautionary measures against the infection were “older, female, more educated people as well as those with a positive contact history and SARS-like symptoms.”12
Negative mental health consequences of a disease outbreak might persist long after the infection has dissipated. An increased association has been found between people with mental illness and posttraumatic stress following many disasters.13,14,15
Political and health care leaders should develop plans aimed at helping people copewith pandemics.16 Such strategies should include prioritizing treatment of the physical and mental health needs of patients infected with COVID-19 and of the general population. Screening for anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts ought to be implemented, and specialized psychiatric care teams should be assigned.17 We know that psychiatrists and other physicians turned to telemedicine to provide support, psychotherapy, and medical attention to patients soon after physical distancing measures were put into place. Those kinds of quick responses are important for our patients.
Fear of contagious diseases often creates social divisions. Governments should offer accurate information to reduce the detrimental effect of rumors and false propaganda.18 “Social distancing” is a misleading term; these practices should be referred to as “physical distancing.” We should encourage patients to maintain interpersonal contacts – albeit at a distance – to reach out to those in need, and to support one another during these troubled times.19
References
1. World Health Organization. Situation Report–107. 2020 May 6.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Situation Update. 2020 Apr 30.
3. O’Brien M. “Are Americans in medical crisis avoiding the ER due to coronavirus?” PBS Newshour. 2020 May 6.
4. Rubin G et al. Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jul;14(340):183-266.
5. Hall R et al. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008 Sep-Oct;30(5):466-52.
6. Verghese A. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:932-3.
7. Interagency Standing Committee. Briefing note on addressing health and psychosocial aspects of COVID-19 Outbreak – Version 11. 2020 Feb.
8. Sim K et al. J Psychosom Res. 2010;68:195-202.
9. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020;74:281-2.
10. Garfin DR et al. Health Psychol. 2020 May;39(5):355-7.
11. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 6. doi: 10.3390/ijerph1751729.
12. Leung GM et al. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003 Nov;57(1):857-63.
13. Xiang Y et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:1741-4.
14. Alvarez J, Hunt M. J Trauma Stress. 2005 Oct 18(5);18:497-505.
15. Cukor J et al. Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):210-7.
16. Horton R. Lancet. 2020 Feb;395(10222):400.
17. Xiang Y-T et al. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 4;7:228-9.
18. World Health Organization. “Rational use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for coronavirus (COVID-19).” Interim Guidance. 2020 Mar.
19. Brooks S et al. Lancet 2020 Mar 14;395:912-20.
Dr. Doppalapudi is affiliated with Griffin Memorial Hospital in Norman, Okla. Dr. Lippmann is emeritus professor of psychiatry and also in family medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Doppalapudi and Dr. Lippmann disclosed no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 affects the physical, psychological, and social health of people around the world. In the United States, newly reported cases are rising at alarming rates.
As of early May, more than 1.3 million people were confirmed to be COVID-19 infected in the United States and more than 4 million cases were reported globally.1
According to new internal projections from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, by June 1, the number of daily deaths could reach about 3,000. By the end of June, a draft CDC report projects that the United States will see 200,000 new cases each day.2
COVID-19 undeniably harms mental health. It gravely instills uncertainty and anxiety, sometimes compounded by the grief of losing loved ones and not being able to mourn those losses in traditional ways. The pandemic also has led to occupational and/or financial losses. Physical distancing and shelter-in-place practices make it even harder to cope with those stresses, although those practices mitigate the dangers. The fears tied to those practices are thought to be keeping some patients with health problems from seeking needed care from hospital EDs.3 In light of the mental health crisis emerging because of the profound impact of this pandemic on all aspects of life, clinicians should start working with public health and political leaders to develop plans to address these issues now.
Known impact of previous outbreaks
Previous disease outbreaks evidence a similar pattern of heightened anxiety as the patterns seen with COVID-19. For example, during the 2009 swine flu outbreak, 36 surveys of more than 3,000 participants in the United Kingdom found that 9.6%-32.9% of the participants were “very” or “fairly” worried about the possibility of contracting swine flu.4 The 1995 Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo produced stigmatization tied to the illness. That outbreak provided many lessons for physicians.5
The metaphors ascribed to different diseases affect communities’ responses to it. The SARS virus has been particularly insidious and has been thought of as a “plague.”6 Epidemics of all kinds cause fears, not only of contracting the disease and dying, but also of social exclusion.7 The emotional responses to COVID-19 can precipitate anxiety, depression, insomnia, and somatic symptoms.
Repeated exposure to news media about the disease adds to theses stresss.10 Constant news consumption can result in panicky hoarding of resources, such as masks; gloves; first-aid kits; alcohol hand rubs; and daily necessities such as food, water, and toilet paper.
Who is most affected by outbreaks?
Those most affected after a disease outbreak are patients, their families, and medical personnel. In one study, researchers who conducted an online survey of 1,210 respondents in 194 cities in China during the early phase of the outbreak found that the psychological effects were worst among women, students, and vulnerable populations.11
Meanwhile, a 2003 cross-sectional survey of 1,115 ethnic Chinese adults in Hong Kong who responded to the SARS outbreak found that the respondents most likely to heed precautionary measures against the infection were “older, female, more educated people as well as those with a positive contact history and SARS-like symptoms.”12
Negative mental health consequences of a disease outbreak might persist long after the infection has dissipated. An increased association has been found between people with mental illness and posttraumatic stress following many disasters.13,14,15
Political and health care leaders should develop plans aimed at helping people copewith pandemics.16 Such strategies should include prioritizing treatment of the physical and mental health needs of patients infected with COVID-19 and of the general population. Screening for anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts ought to be implemented, and specialized psychiatric care teams should be assigned.17 We know that psychiatrists and other physicians turned to telemedicine to provide support, psychotherapy, and medical attention to patients soon after physical distancing measures were put into place. Those kinds of quick responses are important for our patients.
Fear of contagious diseases often creates social divisions. Governments should offer accurate information to reduce the detrimental effect of rumors and false propaganda.18 “Social distancing” is a misleading term; these practices should be referred to as “physical distancing.” We should encourage patients to maintain interpersonal contacts – albeit at a distance – to reach out to those in need, and to support one another during these troubled times.19
References
1. World Health Organization. Situation Report–107. 2020 May 6.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Situation Update. 2020 Apr 30.
3. O’Brien M. “Are Americans in medical crisis avoiding the ER due to coronavirus?” PBS Newshour. 2020 May 6.
4. Rubin G et al. Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jul;14(340):183-266.
5. Hall R et al. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008 Sep-Oct;30(5):466-52.
6. Verghese A. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:932-3.
7. Interagency Standing Committee. Briefing note on addressing health and psychosocial aspects of COVID-19 Outbreak – Version 11. 2020 Feb.
8. Sim K et al. J Psychosom Res. 2010;68:195-202.
9. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020;74:281-2.
10. Garfin DR et al. Health Psychol. 2020 May;39(5):355-7.
11. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 6. doi: 10.3390/ijerph1751729.
12. Leung GM et al. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003 Nov;57(1):857-63.
13. Xiang Y et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:1741-4.
14. Alvarez J, Hunt M. J Trauma Stress. 2005 Oct 18(5);18:497-505.
15. Cukor J et al. Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):210-7.
16. Horton R. Lancet. 2020 Feb;395(10222):400.
17. Xiang Y-T et al. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 4;7:228-9.
18. World Health Organization. “Rational use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for coronavirus (COVID-19).” Interim Guidance. 2020 Mar.
19. Brooks S et al. Lancet 2020 Mar 14;395:912-20.
Dr. Doppalapudi is affiliated with Griffin Memorial Hospital in Norman, Okla. Dr. Lippmann is emeritus professor of psychiatry and also in family medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Doppalapudi and Dr. Lippmann disclosed no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 affects the physical, psychological, and social health of people around the world. In the United States, newly reported cases are rising at alarming rates.
As of early May, more than 1.3 million people were confirmed to be COVID-19 infected in the United States and more than 4 million cases were reported globally.1
According to new internal projections from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, by June 1, the number of daily deaths could reach about 3,000. By the end of June, a draft CDC report projects that the United States will see 200,000 new cases each day.2
COVID-19 undeniably harms mental health. It gravely instills uncertainty and anxiety, sometimes compounded by the grief of losing loved ones and not being able to mourn those losses in traditional ways. The pandemic also has led to occupational and/or financial losses. Physical distancing and shelter-in-place practices make it even harder to cope with those stresses, although those practices mitigate the dangers. The fears tied to those practices are thought to be keeping some patients with health problems from seeking needed care from hospital EDs.3 In light of the mental health crisis emerging because of the profound impact of this pandemic on all aspects of life, clinicians should start working with public health and political leaders to develop plans to address these issues now.
Known impact of previous outbreaks
Previous disease outbreaks evidence a similar pattern of heightened anxiety as the patterns seen with COVID-19. For example, during the 2009 swine flu outbreak, 36 surveys of more than 3,000 participants in the United Kingdom found that 9.6%-32.9% of the participants were “very” or “fairly” worried about the possibility of contracting swine flu.4 The 1995 Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo produced stigmatization tied to the illness. That outbreak provided many lessons for physicians.5
The metaphors ascribed to different diseases affect communities’ responses to it. The SARS virus has been particularly insidious and has been thought of as a “plague.”6 Epidemics of all kinds cause fears, not only of contracting the disease and dying, but also of social exclusion.7 The emotional responses to COVID-19 can precipitate anxiety, depression, insomnia, and somatic symptoms.
Repeated exposure to news media about the disease adds to theses stresss.10 Constant news consumption can result in panicky hoarding of resources, such as masks; gloves; first-aid kits; alcohol hand rubs; and daily necessities such as food, water, and toilet paper.
Who is most affected by outbreaks?
Those most affected after a disease outbreak are patients, their families, and medical personnel. In one study, researchers who conducted an online survey of 1,210 respondents in 194 cities in China during the early phase of the outbreak found that the psychological effects were worst among women, students, and vulnerable populations.11
Meanwhile, a 2003 cross-sectional survey of 1,115 ethnic Chinese adults in Hong Kong who responded to the SARS outbreak found that the respondents most likely to heed precautionary measures against the infection were “older, female, more educated people as well as those with a positive contact history and SARS-like symptoms.”12
Negative mental health consequences of a disease outbreak might persist long after the infection has dissipated. An increased association has been found between people with mental illness and posttraumatic stress following many disasters.13,14,15
Political and health care leaders should develop plans aimed at helping people copewith pandemics.16 Such strategies should include prioritizing treatment of the physical and mental health needs of patients infected with COVID-19 and of the general population. Screening for anxiety, depression, and suicidal thoughts ought to be implemented, and specialized psychiatric care teams should be assigned.17 We know that psychiatrists and other physicians turned to telemedicine to provide support, psychotherapy, and medical attention to patients soon after physical distancing measures were put into place. Those kinds of quick responses are important for our patients.
Fear of contagious diseases often creates social divisions. Governments should offer accurate information to reduce the detrimental effect of rumors and false propaganda.18 “Social distancing” is a misleading term; these practices should be referred to as “physical distancing.” We should encourage patients to maintain interpersonal contacts – albeit at a distance – to reach out to those in need, and to support one another during these troubled times.19
References
1. World Health Organization. Situation Report–107. 2020 May 6.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Situation Update. 2020 Apr 30.
3. O’Brien M. “Are Americans in medical crisis avoiding the ER due to coronavirus?” PBS Newshour. 2020 May 6.
4. Rubin G et al. Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jul;14(340):183-266.
5. Hall R et al. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008 Sep-Oct;30(5):466-52.
6. Verghese A. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:932-3.
7. Interagency Standing Committee. Briefing note on addressing health and psychosocial aspects of COVID-19 Outbreak – Version 11. 2020 Feb.
8. Sim K et al. J Psychosom Res. 2010;68:195-202.
9. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020;74:281-2.
10. Garfin DR et al. Health Psychol. 2020 May;39(5):355-7.
11. Wang C et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 6. doi: 10.3390/ijerph1751729.
12. Leung GM et al. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003 Nov;57(1):857-63.
13. Xiang Y et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16:1741-4.
14. Alvarez J, Hunt M. J Trauma Stress. 2005 Oct 18(5);18:497-505.
15. Cukor J et al. Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):210-7.
16. Horton R. Lancet. 2020 Feb;395(10222):400.
17. Xiang Y-T et al. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 4;7:228-9.
18. World Health Organization. “Rational use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for coronavirus (COVID-19).” Interim Guidance. 2020 Mar.
19. Brooks S et al. Lancet 2020 Mar 14;395:912-20.
Dr. Doppalapudi is affiliated with Griffin Memorial Hospital in Norman, Okla. Dr. Lippmann is emeritus professor of psychiatry and also in family medicine at the University of Louisville (Ky.) Dr. Doppalapudi and Dr. Lippmann disclosed no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 in pregnancy: Supplement oxygen if saturation dips below 94%
Oxygen supplementation for pregnant women with COVID-19 should begin when saturations fall below 94%, according to physicians in the divisions of maternal-fetal medicine and surgical critical care at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston.
That’s a bit higher than the 92% cut point for nonpregnant women, but necessary due to the increased oxygen demand and oxygen partial pressure in pregnancy. The goal is a saturation of 94%-96%, said Luis Pacheco, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine and critical care specialist at the university, and associates.
so Dr. Pacheco and associates addressed the issue in a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Women on respiratory support should lie prone if under 20 weeks’ gestation to help with posterior lung recruitment and oxygenation.
If conventional oxygen therapy isn’t enough, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) at 60 L/min and 100% oxygen should be the next step, not positive-pressure ventilation. Positive pressure, another option, kicks off aerosols that increase the risk of viral transmission to medical staff. “This makes high-flow nasal cannula the first-line option for patients not responding to conventional oxygen therapy but who are not yet candidates for endotracheal intubation,” the team said. If women do well, the fraction of inspired oxygen should be weaned before the nasal cannula flow is decreased.
However, if they continue to struggle with dyspnea, tachypnea, and oxygen saturation after 30-60 minutes on HFNC, it’s time for mechanical ventilation, and fast. “Delays in recognizing early failure of high-flow nasal cannula ... may result in life-threatening hypoxemia at the time of induction and intubation (especially in pregnant patients with difficult airway anatomy),” the authors said.
For birth, Dr. Pacheco and associates recommended controlled delivery, likely cesarean, if respiration continues to deteriorate despite intubation, especially after 28 weeks’ gestation, instead of waiting for fetal distress and an ICU delivery. A single course of steroids is reasonable to help fetal lung development beforehand, if indicated.
As for fluid strategy during respiratory support, pregnant women are at higher risk for pulmonary edema with lung inflammation, so the authors cautioned against giving maintenance fluids, and said “if daily positive fluid balances are present, combined with worsening respiratory status, the use of furosemide (10-20 mg intravenously every 12 hours) may be indicated.”
For women stable on conventional oxygen therapy or HFNC, they suggested daily nonstress tests starting at 25 weeks’ gestation instead of continuous monitoring, to minimize the COVID-19 transmission risk for staff.
The team cautioned against nebulized treatments and sputum-inducing agents when possible as this may aerosolize the virus.
There was no external funding for the report, and the authors didn’t have any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pacheco LD et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003929.
Oxygen supplementation for pregnant women with COVID-19 should begin when saturations fall below 94%, according to physicians in the divisions of maternal-fetal medicine and surgical critical care at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston.
That’s a bit higher than the 92% cut point for nonpregnant women, but necessary due to the increased oxygen demand and oxygen partial pressure in pregnancy. The goal is a saturation of 94%-96%, said Luis Pacheco, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine and critical care specialist at the university, and associates.
so Dr. Pacheco and associates addressed the issue in a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Women on respiratory support should lie prone if under 20 weeks’ gestation to help with posterior lung recruitment and oxygenation.
If conventional oxygen therapy isn’t enough, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) at 60 L/min and 100% oxygen should be the next step, not positive-pressure ventilation. Positive pressure, another option, kicks off aerosols that increase the risk of viral transmission to medical staff. “This makes high-flow nasal cannula the first-line option for patients not responding to conventional oxygen therapy but who are not yet candidates for endotracheal intubation,” the team said. If women do well, the fraction of inspired oxygen should be weaned before the nasal cannula flow is decreased.
However, if they continue to struggle with dyspnea, tachypnea, and oxygen saturation after 30-60 minutes on HFNC, it’s time for mechanical ventilation, and fast. “Delays in recognizing early failure of high-flow nasal cannula ... may result in life-threatening hypoxemia at the time of induction and intubation (especially in pregnant patients with difficult airway anatomy),” the authors said.
For birth, Dr. Pacheco and associates recommended controlled delivery, likely cesarean, if respiration continues to deteriorate despite intubation, especially after 28 weeks’ gestation, instead of waiting for fetal distress and an ICU delivery. A single course of steroids is reasonable to help fetal lung development beforehand, if indicated.
As for fluid strategy during respiratory support, pregnant women are at higher risk for pulmonary edema with lung inflammation, so the authors cautioned against giving maintenance fluids, and said “if daily positive fluid balances are present, combined with worsening respiratory status, the use of furosemide (10-20 mg intravenously every 12 hours) may be indicated.”
For women stable on conventional oxygen therapy or HFNC, they suggested daily nonstress tests starting at 25 weeks’ gestation instead of continuous monitoring, to minimize the COVID-19 transmission risk for staff.
The team cautioned against nebulized treatments and sputum-inducing agents when possible as this may aerosolize the virus.
There was no external funding for the report, and the authors didn’t have any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pacheco LD et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003929.
Oxygen supplementation for pregnant women with COVID-19 should begin when saturations fall below 94%, according to physicians in the divisions of maternal-fetal medicine and surgical critical care at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston.
That’s a bit higher than the 92% cut point for nonpregnant women, but necessary due to the increased oxygen demand and oxygen partial pressure in pregnancy. The goal is a saturation of 94%-96%, said Luis Pacheco, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine and critical care specialist at the university, and associates.
so Dr. Pacheco and associates addressed the issue in a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Women on respiratory support should lie prone if under 20 weeks’ gestation to help with posterior lung recruitment and oxygenation.
If conventional oxygen therapy isn’t enough, high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) at 60 L/min and 100% oxygen should be the next step, not positive-pressure ventilation. Positive pressure, another option, kicks off aerosols that increase the risk of viral transmission to medical staff. “This makes high-flow nasal cannula the first-line option for patients not responding to conventional oxygen therapy but who are not yet candidates for endotracheal intubation,” the team said. If women do well, the fraction of inspired oxygen should be weaned before the nasal cannula flow is decreased.
However, if they continue to struggle with dyspnea, tachypnea, and oxygen saturation after 30-60 minutes on HFNC, it’s time for mechanical ventilation, and fast. “Delays in recognizing early failure of high-flow nasal cannula ... may result in life-threatening hypoxemia at the time of induction and intubation (especially in pregnant patients with difficult airway anatomy),” the authors said.
For birth, Dr. Pacheco and associates recommended controlled delivery, likely cesarean, if respiration continues to deteriorate despite intubation, especially after 28 weeks’ gestation, instead of waiting for fetal distress and an ICU delivery. A single course of steroids is reasonable to help fetal lung development beforehand, if indicated.
As for fluid strategy during respiratory support, pregnant women are at higher risk for pulmonary edema with lung inflammation, so the authors cautioned against giving maintenance fluids, and said “if daily positive fluid balances are present, combined with worsening respiratory status, the use of furosemide (10-20 mg intravenously every 12 hours) may be indicated.”
For women stable on conventional oxygen therapy or HFNC, they suggested daily nonstress tests starting at 25 weeks’ gestation instead of continuous monitoring, to minimize the COVID-19 transmission risk for staff.
The team cautioned against nebulized treatments and sputum-inducing agents when possible as this may aerosolize the virus.
There was no external funding for the report, and the authors didn’t have any relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Pacheco LD et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003929.
OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
With life in the balance, a pediatric palliative care program expands its work to adults
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
In late March of 2020, when it became clear that hospitals in the greater New York City area would face a capacity crisis in caring for seriously ill patients with COVID-19, members of the leadership team at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore (CHAM) in the Bronx, N.Y., convened to draft a response plan.
The recommendations put into action that day included moving the hospital’s emergency department from the lower level to the fourth floor, increasing the age limit for patients seen in the ED from 21 years of age to 30 and freeing up an entire hospital floor and a half to accommodate the anticipated surge of patients with COVID-19 admitted to Montefiore’s interconnected adult hospital, according to Sarah E. Norris, MD.
“We made multiple moves all at once,” said Dr. Norris, director of pediatric palliative care at CHAM. “It struck everyone as logical that palliative care had to be expanded, because all of the news we had received as the surge came to New York from around the world was full of death and uncertainty, and would require thoughtful conversations about end-of-life wishes at critical times and how to really respect the person and understand their values.”
When Dr. Norris left the leadership team meeting, she returned to her office, put her face in her hands, and sobbed as she began to process the gravity of what was ahead. “I cried because I knew that so many families were going to suffer a heartbreak, no matter how much we could do,” she said.
Stitching the QUILT
Over the next few days, Dr. Norris began recruiting colleagues from the large Montefiore Health System – most of whom she did not know – who met criteria for work deployment to expand CHAM’s palliative care program of clinician to 27 clinicians consisting of pediatricians, nurse practitioners, and psychologists, to meet the projected needs of COVID-19 patients and their families.
Some candidates for the effort, known as the Quality in Life Team (QUILT), were 65 years of age or older, considered at high risk for developing COVID-19-related complications themselves. Others were immunocompromised or had medical conditions that would not allow them to have direct contact with COVID-19 patients. “There were also clinicians in other parts of our health system whose practice hours were going to be severely reduced,” said Dr. Norris, who is board-certified in general pediatrics and in hospice and palliative care medicine.
Once she assembled QUILT, members participated in a 1-day rapid training webinar covering the basics of palliative care and grief, and readied themselves for one of three roles: physicians to provide face-to-face palliative care in CHAM; supportive callers to provide support to patients with COVID-19 and their families between 12:00-8:00 p.m. each day; and bereavement callers to reach out to families who lost loved ones to COVID-19 and provide grief counseling for 3 weeks.
“This allows families to have at least two contacts a day from the hospital: one from the medical team that’s giving them technical, medical information, and another from members of the QUILT team,” Dr. Norris said. “We provide support for the worry, anxiety, and fear that we know creeps in when you’re separated from your family member, especially during a pandemic when you watch TV and there’s a death count rising.”
During her early meetings with QUILT members via Zoom or on the phone, Dr. Norris encouraged them to stretch their skill sets and mindsets as they shifted from caring for children and adolescents to mostly adults. “Pediatricians are all about family; that’s why we get into this,” she said. “We’re used to treating your kids, but then, suddenly, the parent becomes our patient, like in COVID-19, or the grandparent becomes our patient. We treat you all the same; you’re part of our family. There has been no adult who has died ‘within our house’ that has died alone. There has either been a staff member at their bedside, or when possible, a family member. We are witnessing life until the last breath here.”
‘They have no loved ones with them’
One day, members of CHAM’s medical team contacted Dr. Norris about a patient with COVID-19 who’d been cared for by Montefiore clinicians all of his young life. The boy’s mother, who did not speak English, was at his bedside in the ICU, and the clinicians asked Dr. Norris to speak with her by cell phone while they prepared him for intubation.
“We were looking at each other through a glass window wall in our ICU,” Dr. Norris recalled. “I talked to her the entire time the team worked to put him on the breathing machine, through an interpreter. I asked her to tell me about her son and about her family, and she did. We developed a warm relationship. After that, every day I would see her son through the glass window wall. Every couple of days, I would have the privilege of talking to his mother by phone. At one point, she asked me, ‘Dr. Norris, do you think his lungs will heal?’ I had to tell her no. Almost selfishly, I was relieved we were on the phone, because she cried, and so did I. When he died, she was able to be by his side.”
Frederick J. Kaskel, MD, PhD, joined QUILT as a supportive caller after being asked to go home during his on-call shift on St. Patrick’s Day at CHAM, where he serves as chief emeritus of nephrology. “I was told that I was deemed to be at high risk because of my age,” the 75-year-old said. “The next day, a junior person took over for me, and 2 days later she got sick with COVID-19. She’s fine but she was home for 3 weeks sick as a dog. It was scary.”
In his role as a supportive caller, Dr. Kaskel found himself engaged in his share of detective work, trying to find phone numbers of next of kin for patients hospitalized with COVID-19. “When they come into the ER, they may not have been with a loved one or a family member; they may have been brought in by an EMT,” he said. “Some of them speak little English and others have little documentation with them. It takes a lot of work to get phone numbers.”
Once Dr. Kaskel reaches a loved one by phone, he introduces himself as a member of the QUILT team. “I tell them I’m not calling to update the medical status but just to talk to them about their loved one,” he said. “Then I usually ask, ‘So, how are you doing with this? The stress is enormous, the uncertainties.’ Then they open up and express their fears. I’ve had a lot of people say, ‘we have no money, and I don’t know how we’re going to pay rent for the apartment. We have to line up for food.’ I also ask what they do to alleviate stress. One guy said, ‘I drink a lot, but I’m careful.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel, who is also a past president of the American Society of Pediatric Nephrology, applies that same personable approach in daily conversations with adult patients hospitalized at CHAM with COVID-19, the majority of whom are African Americans in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. “Invariably, they ask, ‘Has my loved one been updated as to my status?’ ” he said. “The second thing they often say is, ‘I’m worried about infecting other people, but I also worry if I’m going to get through this. I’m really afraid I’m going to die.’ I say, ‘You have a wonderful team keeping track of you. They’re seeing you all the time and making changes to your medicines.’ ”
When patients express their fear of dying from the virus, Dr. Kaskel asks them how they’re coping with that fear. Most tell him that they pray.
“If they don’t answer, I ask if they have any hobbies, like ‘Are you watching TV? Are you reading? Do you have your cell phone?’ ” he said. “Then they open up and say things like, ‘I’m listening to music on the cell phone,’ or ‘I’m FaceTiming with my loved ones.’ The use of FaceTime is crucial, because they are in a hospital, critically ill, potentially dying alone with strangers. This really hit me on the first day [of this work]. They have no loved ones with them. They have strangers: the CHAM nurses, the medical residents, the social workers, and the doctors.”
No hospital cheeseburgers
QUILT began its work on April 6, and at one time provided palliative care services for a peak of 92 mostly adult patients with COVID-19. The supportive callers made 249 individual connections with patients and family members by phone from April 6-13, 162 connections from April 13-19, and 130 connections from April 20-26, according to Dr. Norris. As of April 28, the CHAM inpatient census of patients aged 18 years and over with COVID-19 was 42, “and we’re making 130 connections by phone to patients and family members each day,” she said.
QUILT bereavement callers are following 30 families, providing 3 weeks of acute grief counseling from the date of death. “A sad truth is that, here in New York, our entire funeral, burial, cremation system is overwhelmed in volume,” Dr. Norris said. “Only half of the patients we’re following 3 weeks out have been able to have their family member buried or cremated; many are still waiting. What strikes me here is that pediatricians are often partners in care. With time, we’re partners in care in heartbreak, and in the occasional victory. We mourn patients who have died. We’ve had colleagues who died from COVID-19 right here at our hospital. But we stand together like a family.”
Dr. Norris recalled an older woman who came into CHAM’s ICU on a ventilator, critically ill from COVID-19. She called her husband at home every day with updates. “I got to know her husband, and I got to know her through him,” Dr. Norris said. “We talked every single day and she was able to graduate off of the breathing tube and out of the ICU, which was amazing.” The woman was moved to a floor in the adult hospital, but Dr. Norris continues to visit her and to provide her husband with updates, “because I’m devoted to them,” she said.
Recently, physicians in the adult hospital consulted with Dr. Norris about the woman. “They were trying to figure out what to do with her next,” she said. “Could she go home, or did she need rehab? They said, ‘We called you, Dr. Norris, because her husband thinks he can take her home.’ We know that COVID-19 really weakens people, so I went over to see her myself. I thought, ‘No single person could take care of an adult so weak at home.’ So, I called her husband and said, ‘I’m here with your wife, and I have to tell you; if she were my mother, I couldn’t take her home today. I need you to trust me.’ He said, ‘OK. We trust you and know that you have her best interest at heart.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel relayed the story of an older patient who was slowly recovering from COVID-19. During a phone call, he asked the man if there was anything he wanted at that moment.
“He said, ‘I’d love to see my wife and my children and my grandkids. I know I’m going to see them again, but right now, doc, if you could get me a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato and ketchup and French fries from outside of the hospital, I’d be the happiest man in the world.’
I said, ‘What’s the matter with the cheeseburger made at the hospital?’
He said, ‘No! They can’t make the cheeseburger I want.’
I promised him I’d relay that message to the social worker responsible for the patient. I told her please, if you buy this for him, I’ll pay you back.”
Self-care and the next chapter
Twice each week, QUILT members gather in front of their computer monitors for mandatory Zoom meetings facilitated by two psychologists to share challenges, best practices, and to discuss the difficult work they’re doing. “We meet, because you cannot help someone if you cannot help yourself,” Dr. Norris said. “We have been encouraged each and every meeting to practice self-compassion, and to recognize that things happen during a pandemic – some will be the best you can do.”
She described organizing and serving on QUILT as a grounding experience with important lessons for the delivery of health care after the pandemic subsides and the team members return to their respective practices. “I think we’ve all gained a greater sense of humility, and we understand that the badge I wear every day does not protect me from becoming a patient, or from having my own family fall ill,” she said. “Here, we think about it very simply: ‘I’m going to treat you like you’re part of my own family.’ ”
Dr. Kaskel said that serving on QUILT as a supportive caller is an experience he won’t soon forget.
“The human bond is so accessible if you accept it,” he said. “If someone is an introvert that might not be able to draw out a stranger on the phone, then [he or she] shouldn’t do this [work]. But the fact that you can make a bond with someone that you’re not even seeing in person and know that both sides of this phone call are getting good vibes, that’s a remarkable feeling that I never really knew before, because I’ve never really had to do that before. It brings up feelings like I had after 9/11 – a unified approach to surviving this as people, as a community, the idea that ‘we will get through this,’ even though it’s totally different than anything before. The idea that there’s still hope. Those are things you can’t put a price on.”
An article about how CHAM transformed to provide care to adult COVID-19 patients was published online May 4, 2020, in the Journal of Pediatrics: doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.04.060.
Operation Quack Hack: FDA moves to stop fraudulent COVID-19 products
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.
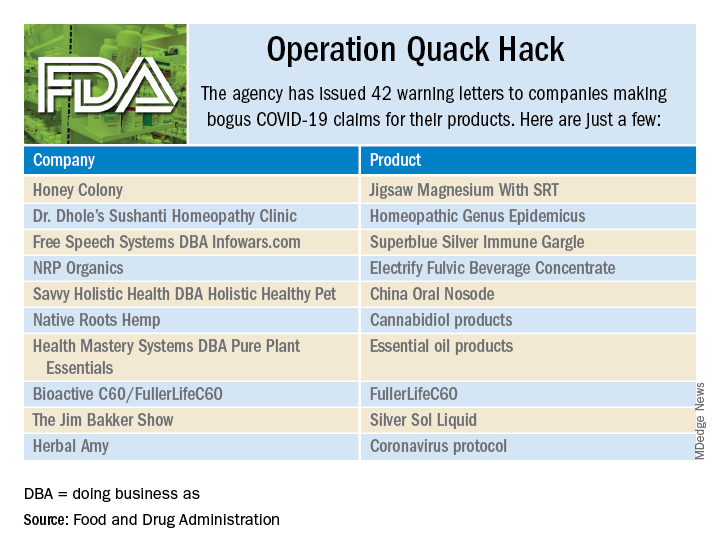
As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.

As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
No form of human misery can be allowed to go unexploited, and the pandemic, it seems, is no exception.

As part of Operation Quack Hack, the Food and Drug Administration has stepped up its investigation and enforcement efforts against companies and individuals that are “taking advantage of widespread fear among consumers during the COVID-19 pandemic” by selling fake products and treatments for coronavirus.
As of May 7, 2020, the agency had issued 42 warning letters to companies that were “selling unapproved products that fraudulently claim to mitigate, prevent, treat, diagnose or cure COVID-19,” the FDA announced in a written statement. Of those 42 products, 29 are no longer being sold with any sort of COVID-19 claim.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, Operation Quack Hack has uncovered hundreds of such products – drugs, testing kits, and personal protective equipment – being sold online, and complaints were sent to domain-name registrars and Internet marketplaces that have, in most cases, removed the postings, the FDA said.
“We will continue to monitor the online ecosystem for fraudulent products peddled by bad actors seeking to profit from this global pandemic. We encourage anyone aware of suspected fraudulent medical products for COVID-19 to report them to the FDA,” the statement said.
U.S. ‘deaths of despair’ from COVID-19 could top 75,000, experts warn
The number of “deaths of despair” could be even higher if the country fails to take bold action to address the mental health toll of unemployment, isolation, and uncertainty, according to the report from the Well Being Trust (WBT) and the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care.
“If nothing happens and nothing improves – ie, the worst-case scenario – we could be looking at an additional 150,000 people who died who didn’t have to,” Benjamin Miller, PsyD, WBT chief strategy officer, told Medscape Medical News.
“We can prevent these deaths. We know how and have a bevy of evidence-based solutions. We lack the resources to really stand this up in a way that can most positively impact communities,” Miller added.
Slow recovery, quick recovery scenarios
For the analysis, Miller and colleagues combined information on the number of deaths from suicide, alcohol, and drugs from 2018 as a baseline (n = 181,686). They projected levels of unemployment from 2020 to 2029 and then used economic modeling to estimate the additional annual number of deaths.
Across nine different scenarios, the number of additional deaths of despair range from 27,644 (quick recovery, smallest impact of unemployment on suicide, alcohol-, and drug-related deaths) to 154,037 (slow recovery, greatest impact of unemployment on these deaths), with 75,000 being the most likely.
The report offers several policy solutions to prevent a surge in “avoidable” deaths. They include finding ways to ameliorate the effects of unemployment and provide meaningful work to those who are out of work. Making access to care easier and fully integrating mental health and addiction care into primary and clinical care as well as community settings are also essential.
These solutions should also serve to prevent drug and alcohol misuse and suicide in normal times, the researchers say.
Miller believes it’s time for the federal government to fully support a framework of excellence in mental health and well-being and to invest in mental health now.
“In the short term, we need at least $48 billion to keep the lights on in the current system,” he said.
“This is because 92.6% of mental health organizations have had to reduce their operations in some capacity, 61.8% have had to completely close at least one program, and 31.0% have had to turn away patients. This scenario is not optimal for people who will need a system to help them right now during a crisis,” he added.
In the long term, $150 billion is needed for a “massive structural redesign” of the US mental health system, Miller said.
“This means bringing mental health fully into all facets of our healthcare system, of our community. It will take robust investment in creating new mechanisms for care ― those that are team-based, create a new type of workforce to deliver that care, and one that is seamless across clinical and community settings,” said Miller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of “deaths of despair” could be even higher if the country fails to take bold action to address the mental health toll of unemployment, isolation, and uncertainty, according to the report from the Well Being Trust (WBT) and the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care.
“If nothing happens and nothing improves – ie, the worst-case scenario – we could be looking at an additional 150,000 people who died who didn’t have to,” Benjamin Miller, PsyD, WBT chief strategy officer, told Medscape Medical News.
“We can prevent these deaths. We know how and have a bevy of evidence-based solutions. We lack the resources to really stand this up in a way that can most positively impact communities,” Miller added.
Slow recovery, quick recovery scenarios
For the analysis, Miller and colleagues combined information on the number of deaths from suicide, alcohol, and drugs from 2018 as a baseline (n = 181,686). They projected levels of unemployment from 2020 to 2029 and then used economic modeling to estimate the additional annual number of deaths.
Across nine different scenarios, the number of additional deaths of despair range from 27,644 (quick recovery, smallest impact of unemployment on suicide, alcohol-, and drug-related deaths) to 154,037 (slow recovery, greatest impact of unemployment on these deaths), with 75,000 being the most likely.
The report offers several policy solutions to prevent a surge in “avoidable” deaths. They include finding ways to ameliorate the effects of unemployment and provide meaningful work to those who are out of work. Making access to care easier and fully integrating mental health and addiction care into primary and clinical care as well as community settings are also essential.
These solutions should also serve to prevent drug and alcohol misuse and suicide in normal times, the researchers say.
Miller believes it’s time for the federal government to fully support a framework of excellence in mental health and well-being and to invest in mental health now.
“In the short term, we need at least $48 billion to keep the lights on in the current system,” he said.
“This is because 92.6% of mental health organizations have had to reduce their operations in some capacity, 61.8% have had to completely close at least one program, and 31.0% have had to turn away patients. This scenario is not optimal for people who will need a system to help them right now during a crisis,” he added.
In the long term, $150 billion is needed for a “massive structural redesign” of the US mental health system, Miller said.
“This means bringing mental health fully into all facets of our healthcare system, of our community. It will take robust investment in creating new mechanisms for care ― those that are team-based, create a new type of workforce to deliver that care, and one that is seamless across clinical and community settings,” said Miller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of “deaths of despair” could be even higher if the country fails to take bold action to address the mental health toll of unemployment, isolation, and uncertainty, according to the report from the Well Being Trust (WBT) and the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care.
“If nothing happens and nothing improves – ie, the worst-case scenario – we could be looking at an additional 150,000 people who died who didn’t have to,” Benjamin Miller, PsyD, WBT chief strategy officer, told Medscape Medical News.
“We can prevent these deaths. We know how and have a bevy of evidence-based solutions. We lack the resources to really stand this up in a way that can most positively impact communities,” Miller added.
Slow recovery, quick recovery scenarios
For the analysis, Miller and colleagues combined information on the number of deaths from suicide, alcohol, and drugs from 2018 as a baseline (n = 181,686). They projected levels of unemployment from 2020 to 2029 and then used economic modeling to estimate the additional annual number of deaths.
Across nine different scenarios, the number of additional deaths of despair range from 27,644 (quick recovery, smallest impact of unemployment on suicide, alcohol-, and drug-related deaths) to 154,037 (slow recovery, greatest impact of unemployment on these deaths), with 75,000 being the most likely.
The report offers several policy solutions to prevent a surge in “avoidable” deaths. They include finding ways to ameliorate the effects of unemployment and provide meaningful work to those who are out of work. Making access to care easier and fully integrating mental health and addiction care into primary and clinical care as well as community settings are also essential.
These solutions should also serve to prevent drug and alcohol misuse and suicide in normal times, the researchers say.
Miller believes it’s time for the federal government to fully support a framework of excellence in mental health and well-being and to invest in mental health now.
“In the short term, we need at least $48 billion to keep the lights on in the current system,” he said.
“This is because 92.6% of mental health organizations have had to reduce their operations in some capacity, 61.8% have had to completely close at least one program, and 31.0% have had to turn away patients. This scenario is not optimal for people who will need a system to help them right now during a crisis,” he added.
In the long term, $150 billion is needed for a “massive structural redesign” of the US mental health system, Miller said.
“This means bringing mental health fully into all facets of our healthcare system, of our community. It will take robust investment in creating new mechanisms for care ― those that are team-based, create a new type of workforce to deliver that care, and one that is seamless across clinical and community settings,” said Miller.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fewer than 20% of eligible children received the recommended two doses of flu vaccine
A second booster dose of the influenza vaccine in vaccine-naive children may significantly reduce their likelihood of getting the disease, new research suggests.
Writing for JAMA Pediatrics, researchers reported on a case-control study of 7,533 children presenting to outpatient clinics – all in the U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network – with acute respiratory tract illnesses from 2014 to 2018. The study looked at the effectiveness of vaccination against laboratory-confirmed influenza.
Current U.S. guidelines recommend that children aged 6 months to 8 years receive two doses of the influenza vaccine initially – a priming dose and a booster dose – while those aged 9 years or older are considered to be ‘immunologically primed’ and therefore only require one annual dose.
The study found that 60% of the children had received two doses of the influenza vaccine during their first vaccination season, and 68% were first vaccinated before the current influenza season. Of those who had been vaccinated, 89% had received their first influenza vaccine dose when they were younger than 2 years.
Among the 2,140 children who were unvaccinated before the current influenza season, the 436 children who received two doses of the influenza vaccine had 43% lower odds of influenza compared with the 466 children who received one dose. The overall vaccine effectiveness among this vaccine-naive group aged under 2 years was 38%; for those who received two doses it was 53%, and for those who received one dose it was 23%.
“The higher risk of infection resulting from underdeveloped immune and respiratory tract systems provides a reason to identify vaccination strategies focusing on this vulnerable population of younger children,” wrote Jessie R. Chung, MPH, of the Influenza Division of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors. “Promoting efforts to improve influenza vaccine coverage—particularly with 2 doses in the first vaccination season – may reduce the burden of influenza illness among young children, who are particularly vulnerable to complications and death from influenza infection.”
Overall 52% of children were unvaccinated for the current influenza season and 9% were partially vaccinated. Of those who were fully vaccinated for the current season, 83% had received one dose in the current season, and 17% had received two doses.
The authors found that full vaccination against any influenza was associated with a 22% lower odds of influenza compared with partial vaccination (95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.01), with partial vaccination defined as anything less than two doses of vaccine in the current season – at least 4 weeks apart – or two or more doses before the current season and one or more doses in the current season. However, even children who were only partially vaccinated still showed statistically significant vaccine effectiveness, except for those who received one dose of vaccine in the current season and were aged under 2 years.
“Compared with older children, young children, even if healthy, are at an elevated risk of influenza infection and influenza-associated complications, such as hospitalization,” the authors wrote. “One recent simulation study reported that even small improvements in either vaccine coverage or VE [vaccine effectiveness], and ideally both, may avert substantial amounts of influenza-associated illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations.”
The study also noted that children who had received only a single previous vaccine dose rarely received two doses in the current season.
In an accompanying editorial, Claire Abraham, MD, and Melissa S. Stockwell, MD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, wrote that modeling suggested that in the 2017-2018 influenza season, vaccination prevented 1.3 million cases of infection, 895,000 medical visits, 10,500 hospitalizations and 111 deaths in children aged under 5 years.
“This study highlights the importance of administering 2 doses of the influenza vaccine to children younger than 9 years for whom 2 doses are needed, and especially to vaccine naive children younger than 2 years,” they wrote.
But despite many studies showing the impact and importance of influenza vaccination, uptake of this vaccine remained lower than for other pediatric vaccines.
“This present study reemphasizes the need for further research exploring why families who are seemingly willing to vaccinate their children against influenza, as indicated by their receiving the first needed dose of influenza vaccine, find barriers to receiving all of the needed doses, placing their children at higher risk for contracting a potentially devastating virus.”
The U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network is funded by the CDC, and this project also received support from the National Institutes of Health. Eight authors declared grants from the CDC during the conduct of the study, and five declared grants and other funding from private industry outside the study.
SOURCE: Chung J et al. JAMA Pediatrics 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0372.
A second booster dose of the influenza vaccine in vaccine-naive children may significantly reduce their likelihood of getting the disease, new research suggests.
Writing for JAMA Pediatrics, researchers reported on a case-control study of 7,533 children presenting to outpatient clinics – all in the U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network – with acute respiratory tract illnesses from 2014 to 2018. The study looked at the effectiveness of vaccination against laboratory-confirmed influenza.
Current U.S. guidelines recommend that children aged 6 months to 8 years receive two doses of the influenza vaccine initially – a priming dose and a booster dose – while those aged 9 years or older are considered to be ‘immunologically primed’ and therefore only require one annual dose.
The study found that 60% of the children had received two doses of the influenza vaccine during their first vaccination season, and 68% were first vaccinated before the current influenza season. Of those who had been vaccinated, 89% had received their first influenza vaccine dose when they were younger than 2 years.
Among the 2,140 children who were unvaccinated before the current influenza season, the 436 children who received two doses of the influenza vaccine had 43% lower odds of influenza compared with the 466 children who received one dose. The overall vaccine effectiveness among this vaccine-naive group aged under 2 years was 38%; for those who received two doses it was 53%, and for those who received one dose it was 23%.
“The higher risk of infection resulting from underdeveloped immune and respiratory tract systems provides a reason to identify vaccination strategies focusing on this vulnerable population of younger children,” wrote Jessie R. Chung, MPH, of the Influenza Division of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors. “Promoting efforts to improve influenza vaccine coverage—particularly with 2 doses in the first vaccination season – may reduce the burden of influenza illness among young children, who are particularly vulnerable to complications and death from influenza infection.”
Overall 52% of children were unvaccinated for the current influenza season and 9% were partially vaccinated. Of those who were fully vaccinated for the current season, 83% had received one dose in the current season, and 17% had received two doses.
The authors found that full vaccination against any influenza was associated with a 22% lower odds of influenza compared with partial vaccination (95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.01), with partial vaccination defined as anything less than two doses of vaccine in the current season – at least 4 weeks apart – or two or more doses before the current season and one or more doses in the current season. However, even children who were only partially vaccinated still showed statistically significant vaccine effectiveness, except for those who received one dose of vaccine in the current season and were aged under 2 years.
“Compared with older children, young children, even if healthy, are at an elevated risk of influenza infection and influenza-associated complications, such as hospitalization,” the authors wrote. “One recent simulation study reported that even small improvements in either vaccine coverage or VE [vaccine effectiveness], and ideally both, may avert substantial amounts of influenza-associated illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations.”
The study also noted that children who had received only a single previous vaccine dose rarely received two doses in the current season.
In an accompanying editorial, Claire Abraham, MD, and Melissa S. Stockwell, MD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, wrote that modeling suggested that in the 2017-2018 influenza season, vaccination prevented 1.3 million cases of infection, 895,000 medical visits, 10,500 hospitalizations and 111 deaths in children aged under 5 years.
“This study highlights the importance of administering 2 doses of the influenza vaccine to children younger than 9 years for whom 2 doses are needed, and especially to vaccine naive children younger than 2 years,” they wrote.
But despite many studies showing the impact and importance of influenza vaccination, uptake of this vaccine remained lower than for other pediatric vaccines.
“This present study reemphasizes the need for further research exploring why families who are seemingly willing to vaccinate their children against influenza, as indicated by their receiving the first needed dose of influenza vaccine, find barriers to receiving all of the needed doses, placing their children at higher risk for contracting a potentially devastating virus.”
The U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network is funded by the CDC, and this project also received support from the National Institutes of Health. Eight authors declared grants from the CDC during the conduct of the study, and five declared grants and other funding from private industry outside the study.
SOURCE: Chung J et al. JAMA Pediatrics 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0372.
A second booster dose of the influenza vaccine in vaccine-naive children may significantly reduce their likelihood of getting the disease, new research suggests.
Writing for JAMA Pediatrics, researchers reported on a case-control study of 7,533 children presenting to outpatient clinics – all in the U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network – with acute respiratory tract illnesses from 2014 to 2018. The study looked at the effectiveness of vaccination against laboratory-confirmed influenza.
Current U.S. guidelines recommend that children aged 6 months to 8 years receive two doses of the influenza vaccine initially – a priming dose and a booster dose – while those aged 9 years or older are considered to be ‘immunologically primed’ and therefore only require one annual dose.
The study found that 60% of the children had received two doses of the influenza vaccine during their first vaccination season, and 68% were first vaccinated before the current influenza season. Of those who had been vaccinated, 89% had received their first influenza vaccine dose when they were younger than 2 years.
Among the 2,140 children who were unvaccinated before the current influenza season, the 436 children who received two doses of the influenza vaccine had 43% lower odds of influenza compared with the 466 children who received one dose. The overall vaccine effectiveness among this vaccine-naive group aged under 2 years was 38%; for those who received two doses it was 53%, and for those who received one dose it was 23%.
“The higher risk of infection resulting from underdeveloped immune and respiratory tract systems provides a reason to identify vaccination strategies focusing on this vulnerable population of younger children,” wrote Jessie R. Chung, MPH, of the Influenza Division of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and coauthors. “Promoting efforts to improve influenza vaccine coverage—particularly with 2 doses in the first vaccination season – may reduce the burden of influenza illness among young children, who are particularly vulnerable to complications and death from influenza infection.”
Overall 52% of children were unvaccinated for the current influenza season and 9% were partially vaccinated. Of those who were fully vaccinated for the current season, 83% had received one dose in the current season, and 17% had received two doses.
The authors found that full vaccination against any influenza was associated with a 22% lower odds of influenza compared with partial vaccination (95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.01), with partial vaccination defined as anything less than two doses of vaccine in the current season – at least 4 weeks apart – or two or more doses before the current season and one or more doses in the current season. However, even children who were only partially vaccinated still showed statistically significant vaccine effectiveness, except for those who received one dose of vaccine in the current season and were aged under 2 years.
“Compared with older children, young children, even if healthy, are at an elevated risk of influenza infection and influenza-associated complications, such as hospitalization,” the authors wrote. “One recent simulation study reported that even small improvements in either vaccine coverage or VE [vaccine effectiveness], and ideally both, may avert substantial amounts of influenza-associated illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations.”
The study also noted that children who had received only a single previous vaccine dose rarely received two doses in the current season.
In an accompanying editorial, Claire Abraham, MD, and Melissa S. Stockwell, MD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, wrote that modeling suggested that in the 2017-2018 influenza season, vaccination prevented 1.3 million cases of infection, 895,000 medical visits, 10,500 hospitalizations and 111 deaths in children aged under 5 years.
“This study highlights the importance of administering 2 doses of the influenza vaccine to children younger than 9 years for whom 2 doses are needed, and especially to vaccine naive children younger than 2 years,” they wrote.
But despite many studies showing the impact and importance of influenza vaccination, uptake of this vaccine remained lower than for other pediatric vaccines.
“This present study reemphasizes the need for further research exploring why families who are seemingly willing to vaccinate their children against influenza, as indicated by their receiving the first needed dose of influenza vaccine, find barriers to receiving all of the needed doses, placing their children at higher risk for contracting a potentially devastating virus.”
The U.S. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network is funded by the CDC, and this project also received support from the National Institutes of Health. Eight authors declared grants from the CDC during the conduct of the study, and five declared grants and other funding from private industry outside the study.
SOURCE: Chung J et al. JAMA Pediatrics 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.0372.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Novel inflammatory syndrome in children possibly linked to COVID-19
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.
according to reports from National Health Service England, The Lancet, and the New York City health department.
Fifteen children in New York City hospitals have presented with the condition, provisionally called pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome, between April 17 and May 1, according to a health alert from New York City health department deputy commissioner Demetre C. Daskalakis, MD, MPH, on May 4. On May 5, the New York state department of health released a health advisory that 64 suspected cases had been reported in children in New York state hospitals, including New York City.
The New York City reports follow a case study published April 7 in Hospital Pediatrics about the presentation. There also was a statement from the U.K.’s Paediatric Intensive Care Society (PICS) on April 27 that noted “blood parameters consistent with severe COVID-19 in children” as well as abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac inflammation.
“Whilst it is too early to say with confidence, features appear to include high CRP [C-reactive protein], high [erythrocyte sedimentation rate] and high ferritin,” the PICS release stated. The cardiac inflammation consists of “myocarditis with raised troponin and [prohormone brain natriuretic peptide],” according to the PICS statement. “Some have an appearance of their coronary arteries in keeping with Kawasaki disease.”
The initial 15 New York City patients reportedly all had “subjective or measured fever, and more than half reported rash, abdominal pain, vomiting, or diarrhea,” but fewer than half had respiratory symptoms.
The case study described a 6-month-old infant who was admitted and diagnosed with classic Kawasaki disease, who also tested positive for COVID-19 with fever and mild respiratory symptoms, reported Veena G. Jones, MD, a pediatric hospitalist in Palo Alto, Calif., and associates.
While many of the U.K. children presenting with the symptoms had a positive polymerase chain reaction tests for infection from SARS-CoV-2, some also had a negative test. Polymerase chain reaction testing in New York City was positive for 4 children and negative for 11 children, but 6 of the those who tested negative had positive serology tests, potentially pointing to postinfection sequelae.
At press time, more cases were reported from the United Kingdom in The Lancet. In London, eight children with hyperinflammatory shock, showing features similar to atypical Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome, or toxic shock syndrome, presented within 10 days to Evelina London Children’s Hospital Paediatric ICU, Shelley Riphagen, MBChB, and colleagues revealed.
Clinically, their presentations were similar, with persistent fever, rash, conjunctivitis, peripheral edema, extremity pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms. They all developed warm vasoplegic shock that did not respond to volume resuscitation; noradrenaline and milrinone were administered for hemodynamic support. Seven of the children needed mechanical ventilation for cardiovascular stabilization, although most of them had no significant respiratory involvement.
Of note was development of small pleural, pericardial, and ascitic effusion – “suggestive of a diffuse inflammatory process,” Dr. Riphagen and associates wrote. None of the children initially was positive for SARS-CoV-2; laboratory evidence of infection or inflammation included “elevated concentrations of CRP, procalcitonin, ferritin, triglycerides or d-dimers.”
“A common echocardiographic finding was echobright coronary vessels,” they wrote. “One child developed arrhythmia with refractory shock, requiring extracorporeal life support, and died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.”
As the article went to press, the doctors in that same ICU had seen more than 20 children with similar clinical presentations, Dr. Riphagen and associates reported, and the first 10 tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibody, including the 8 described above.
“Most of the children appear to have antibodies to the novel coronavirus, even when they do not have virus detectable in their nose,” said Audrey John, MD, PhD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, where clinicians have seen several cases similar to those described by NHS England and the New York City health department. “This suggests that these symptoms are ‘postinfectious,’ likely due to an abnormal immune response that happens after viral infection.”
She noted at the time of her interview, however, that fewer than 100 U.S. pediatric cases appear to have been reported.
“While our understanding is evolving, given the scope of the COVID-19 pandemic, this suggests that this kind of severe disease in children is very rare indeed,” Dr. John said. “Because this syndrome is so newly described, we have to continue to be cautious in attributing this syndrome to COVID-19, as there are many other diseases that look quite similar.”
She advised clinicians to be “wary of attributing fever/rash/shock to this syndrome, as the differential is broad, and we do not want to fail to recognize and treat true toxic shock or tick-borne disease.”
Dawn Nolt, MD, MPH, an associate professor of pediatrics in infectious diseases at Oregon Health & Science University’s Doernbecher Children’s Hospital, Portland, also underscored the need to avoid drawing conclusions too quickly.
“At this time, there is no causality established between SARS-COV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes other than a temporal association,” said Dr. Nolt, whose hospital has not yet seen any of these cases. “If there is a link, then the symptoms may be from a ‘direct hit’ of the virus on tissues, or from an overly exuberant immune response.”
None of the initial 15 New York City children died, although 5 needed mechanical ventilation and over half needed blood pressure support. The one child in London died from a large cerebrovascular infarct.
If the cases are connected to COVID-19, one explanation for the presentation may be related to the leading hypothesis “that SARS-CoV-2 may stimulate the immune system in such a way to promote vasculitis,” Dr. Nolt said in an interview.
“It is unusual that this particular constellation was not reported from the known pediatric cases out of China, where the COVID-19 pandemic originated,” Dr. Nolt said. “If there is a link between SARS-CoV-2 and these inflammatory syndromes, this may have resulted from genetic/host differences, changes in the SARS-CoV-2 virus, or other factors yet to be determined.”
The New York City bulletin recommended that clinicians immediately refer children presenting with the described symptoms to a specialist in pediatric infectious disease, rheumatology, or critical care.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of patients meeting full or partial criteria for Kawasaki disease is critical to preventing end-organ damage and other long-term complications,” the bulletin stated. It recommended aspirin and intravenous immunoglobulin for those who met Kawasaki criteria.
Dr. John said that children with the presentation appear to be responding well to intravenous immunoglobulin and/or steroids. She further emphasized that virtually all pediatric patients recover from COVID-19.
“Physicians should advise families to bring their children and teens back in for evaluation if they develop new fever, rash, or abdominal pain and diarrhea,” Dr. John said. “Families should not be afraid to seek care when their kids are sick. Our pediatric hospitals and EDs are open for business and working hard to protect staff and patients.”
A Kawasaki syndrome diagnosis requires at least 5 days of a fever at 101-104° F or higher along with four of the following five symptoms: rash over the torso; redness and swelling on palms and soles of the feet with later skin peeling; bloodshot, light-sensitive eyes; swollen lymph glands in the neck; and irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat, sometimes with “strawberry” tongue, according to the American Heart Association.
A press release from the AHA noted that Kawasaki disease is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in developed countries, but the condition remains rare.
Kawasaki disease’s etiology is unknown, but “some evidence suggests an infectious trigger, with winter-spring seasonality of the disease,” wrote the case study authors, noting that past research has linked Kawasaki disease with previous or concurrent infections of rhinovirus/enterovirus, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza, adenovirus, and the four common human coronavirus strains.
“We have to remember that our experience with this pandemic is less than 12 months,” Dr. Nolt said. “We are still accumulating information, and any additional manifestations, particularly severe ones, adds to our ability to more quickly detect and treat children.”
Dr. Nolt and Dr. John had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Jones VG et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123; Riphagen S et al. Lancet. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1.