User login
Most oncology trainees encounter discrimination, don’t report it, survey finds
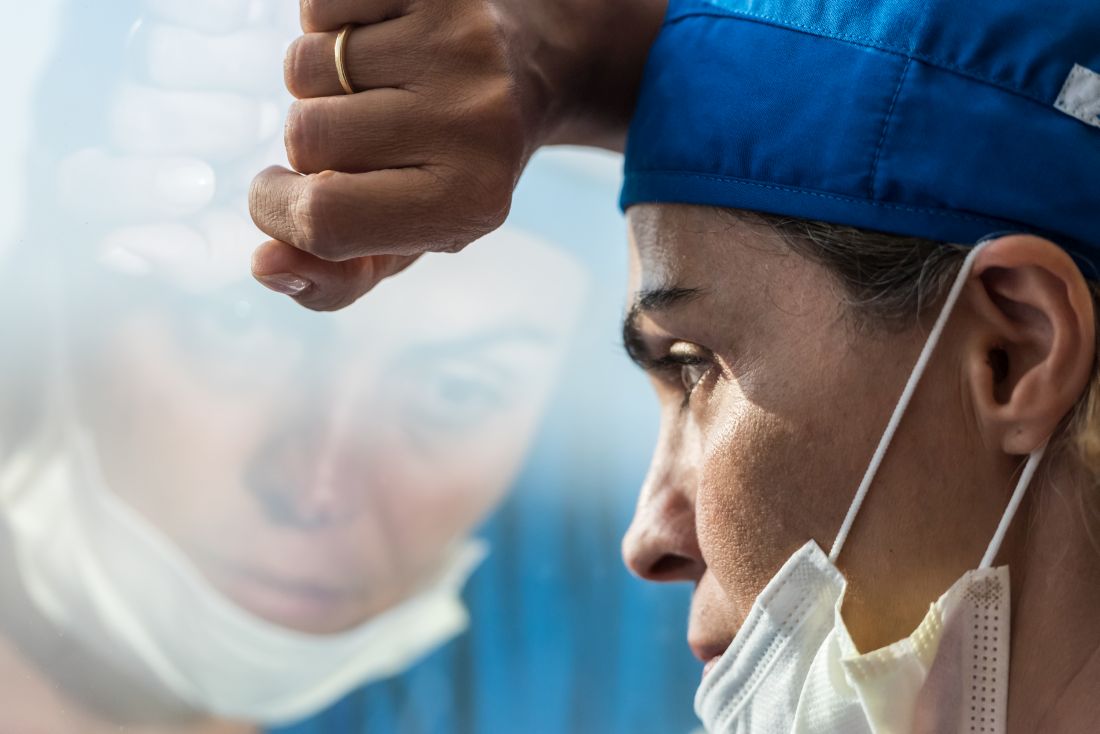
On day 1 of her fellowship, Francesca C. Duncan, MD, was blindsided by her first patient.
The patient, a White man who was accompanied by his wife, sat in the exam room with his sunglasses on.
“I remember him saying, ‘I need to take off my sunglasses so you don’t look so Black,’” said Dr. Duncan, a pulmonologist and intensivist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, who has a specialty in lung cancer disparities.
The patient proceeded to grill her about her experience and training. He asked where she attended college and mocked her degree from a historically Black university. His wife sat there, silent.
Dr. Duncan was shocked by the fact that she still had to defend her credentials.
“I just kind of felt like at that point in my training, my title would have earned me more respect,” said Dr. Duncan, now an assistant professor after recently completing a 3-year fellowship in pulmonary and critical care medicine. “I thought at some point [the racism and discrimination] would stop, but after all that training, all that late-night studying, I still had to prove myself.”
Unfortunately, Dr. Duncan’s experience in fellowship is not unique.
A recent survey of hematology and oncology fellows revealed that medical trainees routinely encounter discrimination during their training.
The 17 fellows who were anonymously interviewed in the survey all recalled experiencing or witnessing discriminatory behaviors during their fellowship, mostly from patients. These encounters rarely come to light. Only one respondent officially reported an incident.
The findings, published online November 8 in JAMA Network Open, underscore the need for graduate medical education programs to improve learning environments and support for trainees, lead author Rahma M. Warsame, MD, and colleagues say .
Discrimination at work
Initially, Dr. Warsame and co–principal investigator Katharine Price, MD, were tasked with developing strategies to mitigate instances of racism and bias that fellows encountered during training, but both felt it was critical to understand the experiences of their trainees first.
Out of 34 fellows and recent graduates of the hematology and oncology fellowship program of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., 20 consented to participate in the study. Of those, 17 were interviewed between July and November 2018. Among the 17 interviewees, six were Asian, two were Black, three were Hispanic, two were multiracial, and four were White.
The majority of these offenses were committed by patients, not faculty or other employees. The researchers largely interpreted most of the incidents as microaggressions.
From the interviews, the researchers identified six central themes. Among them: foreign fellows and U.S.-born trainees being perceived or made to feel like outsiders; inappropriate comments being made toward female employees about their looks, credentials, or marital status; lack of action after reporting incidents or concerns that reporting such incidents would be futile; and strategies fellows used to cope after negative interactions.
One interviewee said, “I was fired by a patient because I have an accent.” Another said that when she is interviewing for jobs, she is always asked if she has children: “Maybe they’re asking in an innocuous manner, but I always feel like people worry. Is this person going to take maternity leave and be less available for work?”
For Dr. Warsame, “the idea that American citizens were frequently made to feel like they do not belong was surprising.”
Not surprising to Dr. Warsame, however, was the importance of fostering diversity and inclusion during fellowship years. Fellows often noted that greater diversity within the program helped create a more inclusive environment.
“[What’s] important to reinforce is the value of creating platforms for honest discussion and intentionally seeking fellows’ voices and perspectives, which in turn makes them feel like they belong,” Dr. Warsame said.
Still, the researchers found that fellows often did not report incidents of discrimination or bias. Only six trainees were aware of policies for reporting patient misconduct or discrimination, and only one ever reported an incident.
Where’s the support?
For Dr. Duncan, her encounter 3 years ago with the patient with sunglasses wasn’t her first experience of discrimination on the job — or her last.
Although hurtful in the moment, she had the wherewithal to report the incident to her attending physician, who was equally shocked. Initially unsure of how to handle it, the attending ultimately stepped up and provided “immense support,” Dr. Duncan said
The issue was brought to the attention of the program director, who took swift action. The patient was documented as “disruptive,” informed of that status in writing, and was banned from receiving treatment from trainees at the center, although Dr. Duncan noted he still received the medical care he needed.
Often, however, fellows who report incidents of discrimination and racism receive little support. According to Dr. Warsame and colleagues, most trainees don’t bother reporting these experiences because they believe that doing so would be futile.
“Concerns about reporting included jeopardizing future employability, risk of retaliation, and challenges reporting experiences that could be perceived as subjective and difficult to prove,” the authors write.
For instance, one interviewee said: “I’m afraid to report these things because there’s gonna be repercussions. There’s no way it’s gonna be anonymous.... I just have to toughen up and, you know, get used [to it].”
Dr. Warsame added, “A major challenge for trainees was that they often felt unheard, and at the time, there was no formal debrief regarding discrimination issues when they arose.”
These instances of bias have implications for trainee well-being. In a 2019 study, discrimination that physicians and students experienced during training had adverse effects on their emotional health. Responses from 50 trainees and physicians revealed a wide range of discriminatory experiences, including patients rejecting care and spewing racist, sexist, or homophobic epithets. Many physicians were uncertain about how to respond effectively and appropriately.
Since that study was published and after having completed her own fellowship, Dr. Duncan said she has seen some change for the better.
“There is a lot more awareness around this, and programs are trying to do better in recognizing and responding to incidents,” she said. She noted that it’s important to ensure that those who are directly affected by discriminatory behaviors aren’t left to do all of the “heavy lifting” of addressing and resolving the issues.
The weight of discriminatory incidents, from microaggressions to overt racism, is cumulative and can adversely affect a person’s career. “It’s exhausting -- we need support,” she said.
The Mayo Clinic is working to ensure that trainees receive support. “The study has prompted communication workshops and faculty development to better equip trainees with strategies to address [and report] patients who behave or display disrespectful or discriminatory behavior,” Dr. Warsame said.
She and her colleagues noted that the anonymous hotline used for the survey cultivated a safe environment for candid discussions and that such an approach is “feasible and effective to explore sensitive topics and scalable to various geographic locations and different medical specialties.”
“We recognize that our program must seek this feedback regularly and ensure we keep a finger on the pulse of our trainees,” Dr. Warsame added.
Dr. Warsame and Dr. Duncan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Duncan noted that her views and comments are her own and do not necessarily reflect those of her institution.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On day 1 of her fellowship, Francesca C. Duncan, MD, was blindsided by her first patient.
The patient, a White man who was accompanied by his wife, sat in the exam room with his sunglasses on.
“I remember him saying, ‘I need to take off my sunglasses so you don’t look so Black,’” said Dr. Duncan, a pulmonologist and intensivist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, who has a specialty in lung cancer disparities.
The patient proceeded to grill her about her experience and training. He asked where she attended college and mocked her degree from a historically Black university. His wife sat there, silent.
Dr. Duncan was shocked by the fact that she still had to defend her credentials.
“I just kind of felt like at that point in my training, my title would have earned me more respect,” said Dr. Duncan, now an assistant professor after recently completing a 3-year fellowship in pulmonary and critical care medicine. “I thought at some point [the racism and discrimination] would stop, but after all that training, all that late-night studying, I still had to prove myself.”
Unfortunately, Dr. Duncan’s experience in fellowship is not unique.
A recent survey of hematology and oncology fellows revealed that medical trainees routinely encounter discrimination during their training.
The 17 fellows who were anonymously interviewed in the survey all recalled experiencing or witnessing discriminatory behaviors during their fellowship, mostly from patients. These encounters rarely come to light. Only one respondent officially reported an incident.
The findings, published online November 8 in JAMA Network Open, underscore the need for graduate medical education programs to improve learning environments and support for trainees, lead author Rahma M. Warsame, MD, and colleagues say .
Discrimination at work
Initially, Dr. Warsame and co–principal investigator Katharine Price, MD, were tasked with developing strategies to mitigate instances of racism and bias that fellows encountered during training, but both felt it was critical to understand the experiences of their trainees first.
Out of 34 fellows and recent graduates of the hematology and oncology fellowship program of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., 20 consented to participate in the study. Of those, 17 were interviewed between July and November 2018. Among the 17 interviewees, six were Asian, two were Black, three were Hispanic, two were multiracial, and four were White.
The majority of these offenses were committed by patients, not faculty or other employees. The researchers largely interpreted most of the incidents as microaggressions.
From the interviews, the researchers identified six central themes. Among them: foreign fellows and U.S.-born trainees being perceived or made to feel like outsiders; inappropriate comments being made toward female employees about their looks, credentials, or marital status; lack of action after reporting incidents or concerns that reporting such incidents would be futile; and strategies fellows used to cope after negative interactions.
One interviewee said, “I was fired by a patient because I have an accent.” Another said that when she is interviewing for jobs, she is always asked if she has children: “Maybe they’re asking in an innocuous manner, but I always feel like people worry. Is this person going to take maternity leave and be less available for work?”
For Dr. Warsame, “the idea that American citizens were frequently made to feel like they do not belong was surprising.”
Not surprising to Dr. Warsame, however, was the importance of fostering diversity and inclusion during fellowship years. Fellows often noted that greater diversity within the program helped create a more inclusive environment.
“[What’s] important to reinforce is the value of creating platforms for honest discussion and intentionally seeking fellows’ voices and perspectives, which in turn makes them feel like they belong,” Dr. Warsame said.
Still, the researchers found that fellows often did not report incidents of discrimination or bias. Only six trainees were aware of policies for reporting patient misconduct or discrimination, and only one ever reported an incident.
Where’s the support?
For Dr. Duncan, her encounter 3 years ago with the patient with sunglasses wasn’t her first experience of discrimination on the job — or her last.
Although hurtful in the moment, she had the wherewithal to report the incident to her attending physician, who was equally shocked. Initially unsure of how to handle it, the attending ultimately stepped up and provided “immense support,” Dr. Duncan said
The issue was brought to the attention of the program director, who took swift action. The patient was documented as “disruptive,” informed of that status in writing, and was banned from receiving treatment from trainees at the center, although Dr. Duncan noted he still received the medical care he needed.
Often, however, fellows who report incidents of discrimination and racism receive little support. According to Dr. Warsame and colleagues, most trainees don’t bother reporting these experiences because they believe that doing so would be futile.
“Concerns about reporting included jeopardizing future employability, risk of retaliation, and challenges reporting experiences that could be perceived as subjective and difficult to prove,” the authors write.
For instance, one interviewee said: “I’m afraid to report these things because there’s gonna be repercussions. There’s no way it’s gonna be anonymous.... I just have to toughen up and, you know, get used [to it].”
Dr. Warsame added, “A major challenge for trainees was that they often felt unheard, and at the time, there was no formal debrief regarding discrimination issues when they arose.”
These instances of bias have implications for trainee well-being. In a 2019 study, discrimination that physicians and students experienced during training had adverse effects on their emotional health. Responses from 50 trainees and physicians revealed a wide range of discriminatory experiences, including patients rejecting care and spewing racist, sexist, or homophobic epithets. Many physicians were uncertain about how to respond effectively and appropriately.
Since that study was published and after having completed her own fellowship, Dr. Duncan said she has seen some change for the better.
“There is a lot more awareness around this, and programs are trying to do better in recognizing and responding to incidents,” she said. She noted that it’s important to ensure that those who are directly affected by discriminatory behaviors aren’t left to do all of the “heavy lifting” of addressing and resolving the issues.
The weight of discriminatory incidents, from microaggressions to overt racism, is cumulative and can adversely affect a person’s career. “It’s exhausting -- we need support,” she said.
The Mayo Clinic is working to ensure that trainees receive support. “The study has prompted communication workshops and faculty development to better equip trainees with strategies to address [and report] patients who behave or display disrespectful or discriminatory behavior,” Dr. Warsame said.
She and her colleagues noted that the anonymous hotline used for the survey cultivated a safe environment for candid discussions and that such an approach is “feasible and effective to explore sensitive topics and scalable to various geographic locations and different medical specialties.”
“We recognize that our program must seek this feedback regularly and ensure we keep a finger on the pulse of our trainees,” Dr. Warsame added.
Dr. Warsame and Dr. Duncan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Duncan noted that her views and comments are her own and do not necessarily reflect those of her institution.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On day 1 of her fellowship, Francesca C. Duncan, MD, was blindsided by her first patient.
The patient, a White man who was accompanied by his wife, sat in the exam room with his sunglasses on.
“I remember him saying, ‘I need to take off my sunglasses so you don’t look so Black,’” said Dr. Duncan, a pulmonologist and intensivist at Indiana University, Indianapolis, who has a specialty in lung cancer disparities.
The patient proceeded to grill her about her experience and training. He asked where she attended college and mocked her degree from a historically Black university. His wife sat there, silent.
Dr. Duncan was shocked by the fact that she still had to defend her credentials.
“I just kind of felt like at that point in my training, my title would have earned me more respect,” said Dr. Duncan, now an assistant professor after recently completing a 3-year fellowship in pulmonary and critical care medicine. “I thought at some point [the racism and discrimination] would stop, but after all that training, all that late-night studying, I still had to prove myself.”
Unfortunately, Dr. Duncan’s experience in fellowship is not unique.
A recent survey of hematology and oncology fellows revealed that medical trainees routinely encounter discrimination during their training.
The 17 fellows who were anonymously interviewed in the survey all recalled experiencing or witnessing discriminatory behaviors during their fellowship, mostly from patients. These encounters rarely come to light. Only one respondent officially reported an incident.
The findings, published online November 8 in JAMA Network Open, underscore the need for graduate medical education programs to improve learning environments and support for trainees, lead author Rahma M. Warsame, MD, and colleagues say .
Discrimination at work
Initially, Dr. Warsame and co–principal investigator Katharine Price, MD, were tasked with developing strategies to mitigate instances of racism and bias that fellows encountered during training, but both felt it was critical to understand the experiences of their trainees first.
Out of 34 fellows and recent graduates of the hematology and oncology fellowship program of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., 20 consented to participate in the study. Of those, 17 were interviewed between July and November 2018. Among the 17 interviewees, six were Asian, two were Black, three were Hispanic, two were multiracial, and four were White.
The majority of these offenses were committed by patients, not faculty or other employees. The researchers largely interpreted most of the incidents as microaggressions.
From the interviews, the researchers identified six central themes. Among them: foreign fellows and U.S.-born trainees being perceived or made to feel like outsiders; inappropriate comments being made toward female employees about their looks, credentials, or marital status; lack of action after reporting incidents or concerns that reporting such incidents would be futile; and strategies fellows used to cope after negative interactions.
One interviewee said, “I was fired by a patient because I have an accent.” Another said that when she is interviewing for jobs, she is always asked if she has children: “Maybe they’re asking in an innocuous manner, but I always feel like people worry. Is this person going to take maternity leave and be less available for work?”
For Dr. Warsame, “the idea that American citizens were frequently made to feel like they do not belong was surprising.”
Not surprising to Dr. Warsame, however, was the importance of fostering diversity and inclusion during fellowship years. Fellows often noted that greater diversity within the program helped create a more inclusive environment.
“[What’s] important to reinforce is the value of creating platforms for honest discussion and intentionally seeking fellows’ voices and perspectives, which in turn makes them feel like they belong,” Dr. Warsame said.
Still, the researchers found that fellows often did not report incidents of discrimination or bias. Only six trainees were aware of policies for reporting patient misconduct or discrimination, and only one ever reported an incident.
Where’s the support?
For Dr. Duncan, her encounter 3 years ago with the patient with sunglasses wasn’t her first experience of discrimination on the job — or her last.
Although hurtful in the moment, she had the wherewithal to report the incident to her attending physician, who was equally shocked. Initially unsure of how to handle it, the attending ultimately stepped up and provided “immense support,” Dr. Duncan said
The issue was brought to the attention of the program director, who took swift action. The patient was documented as “disruptive,” informed of that status in writing, and was banned from receiving treatment from trainees at the center, although Dr. Duncan noted he still received the medical care he needed.
Often, however, fellows who report incidents of discrimination and racism receive little support. According to Dr. Warsame and colleagues, most trainees don’t bother reporting these experiences because they believe that doing so would be futile.
“Concerns about reporting included jeopardizing future employability, risk of retaliation, and challenges reporting experiences that could be perceived as subjective and difficult to prove,” the authors write.
For instance, one interviewee said: “I’m afraid to report these things because there’s gonna be repercussions. There’s no way it’s gonna be anonymous.... I just have to toughen up and, you know, get used [to it].”
Dr. Warsame added, “A major challenge for trainees was that they often felt unheard, and at the time, there was no formal debrief regarding discrimination issues when they arose.”
These instances of bias have implications for trainee well-being. In a 2019 study, discrimination that physicians and students experienced during training had adverse effects on their emotional health. Responses from 50 trainees and physicians revealed a wide range of discriminatory experiences, including patients rejecting care and spewing racist, sexist, or homophobic epithets. Many physicians were uncertain about how to respond effectively and appropriately.
Since that study was published and after having completed her own fellowship, Dr. Duncan said she has seen some change for the better.
“There is a lot more awareness around this, and programs are trying to do better in recognizing and responding to incidents,” she said. She noted that it’s important to ensure that those who are directly affected by discriminatory behaviors aren’t left to do all of the “heavy lifting” of addressing and resolving the issues.
The weight of discriminatory incidents, from microaggressions to overt racism, is cumulative and can adversely affect a person’s career. “It’s exhausting -- we need support,” she said.
The Mayo Clinic is working to ensure that trainees receive support. “The study has prompted communication workshops and faculty development to better equip trainees with strategies to address [and report] patients who behave or display disrespectful or discriminatory behavior,” Dr. Warsame said.
She and her colleagues noted that the anonymous hotline used for the survey cultivated a safe environment for candid discussions and that such an approach is “feasible and effective to explore sensitive topics and scalable to various geographic locations and different medical specialties.”
“We recognize that our program must seek this feedback regularly and ensure we keep a finger on the pulse of our trainees,” Dr. Warsame added.
Dr. Warsame and Dr. Duncan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Duncan noted that her views and comments are her own and do not necessarily reflect those of her institution.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic stresses harder on physician moms than physician dads: Study
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 has been difficult for parents trying to balance careers, home life, and keeping their loved ones safe. A new study indicates that, not only are physicians not immune to these stressors, but the long-term effects could be devastating for health care overall.
In a study published Nov. 11, 2021, in JAMA Network Open , researchers found that stresses to work/life balance and family life caused by the pandemic have differed among men and women physicians.
Physicians and other health care workers have been at the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic, and their work lives have been the focus of a lot of attention in the media and by researchers. Their family lives, not so much. But physicians have families, and the pandemic has upended almost everything about their lives, particularly where work life and home life intersect. School and day care closures, working from home, working extra hours, or working less – all of these changes have consequences on family life and the mental health of parents who are also physicians.
Findings from a Medscape survey published in early 2021 indicate that more female physicians than male physicians were either “conflicted” or “very conflicted” as parents because of work demands (42% vs. 23%) nearly 6 months into the pandemic.
In the current study, researchers from the University of Michigan, Harvard University, and the Medical University of South Carolina teamed up to investigate gender differences in how work/family factors affected the mental health of early-career physician parents in the United States during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results suggest that the pandemic has increased gender disparity and added disproportionately to the burden of female physicians.
Managing the household falls mostly on moms
Participants were physicians enrolled in the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal study that regularly surveys medical interns in the United States to assess stress and mood. When researchers compared survey results from before the onset of the pandemic (2018) with later results (2020), they found a striking gender difference in how the pandemic has changed family and work duties for physicians.
The authors of the study pointed out that previous research had found that female physicians take on a greater share of household and childcare duties than male physicians. The current study found that their share had increased with the pandemic. Physician moms are now 30 times more likely to be in charge of these tasks than physician dads.
In families in which both parents were physicians, none of the men said they took the primary role in managing the extra demands caused by the pandemic. In addition, women were twice as likely as men to work primarily from home and to work reduced hours.
The extra stress seems to be taking a toll on women physicians. In the 2020 survey, physician mothers had higher scores for anxiety and depression symptoms, compared with men. Notably, the 2018 survey did not show a significant difference in depression scores between men and women. Nor were there significant differences in depression and anxiety scores between women and men who were not parents or in reports of work/family conflict before and after the pandemic.
In general, the results indicate that the pandemic has only widened the gender gap between women and men physicians when it comes to managing family life and dealing with the stresses of maintaining a suitable work-life balance.
‘Long-term repercussions’ for gender equity in medicine
Although these are serious problems for women physicians and their families, the effects go beyond the home and beyond individuals. Even before the pandemic, women in medicine struggled for parity in career advancement and opportunities as well as in pay, and this new setback could make those challenges even greater.
“Even short-term adjustments can have serious long-term repercussions as they may lead to lower earnings and negatively impact opportunities for promotion, further exacerbating gender inequalities in compensation and advancement,” the study’s authors wrote.
The potential damage extends to the entire profession and the health care system itself. The profession is already struggling to retain young female physicians, and this situation is likely to make that problem worse and have long-term consequences. Citing data showing that female physicians spend more time with patients and that their patients may have better outcomes, the authors wrote that the consequences of losing more early-career female physicians “could be devastating to the U.S. health care system, particularly in the context of a global pandemic and an impending physician shortage.”
The sample size was small (276 U.S. physicians), and the study relied on self-reported data. The findings suggest that more research on this topic is needed, especially research that includes other demographic factors, such as sexual orientation and ethnicity. The authors recommend that institutional and public policymakers take into account the effects of the pandemic on physician mothers to ensure that recent gains in gender equity for women physicians do not fall victim to COVID-19.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What does it mean to be a trustworthy male ally?
“If you want to be trusted, be trustworthy” – Stephen Covey
A few years ago, while working in my office, a female colleague stopped by for a casual chat. During the course of the conversation, she noticed that I did not have any diplomas or certificates hanging on my office walls. Instead, there were clusters of pictures drawn by my children, family photos, and a white board with my “to-do” list. The only wall art was a print of Banksy’s “The Thinker Monkey,” which depicts a monkey with its fist to its chin similar to Rodin’s famous sculpture, “Le Penseur.”
When asked why I didn’t hang any diplomas or awards, I replied that I preferred to keep my office atmosphere light and fun, and to focus on future goals rather than past accomplishments. I could see her jaw tense. Her frustration appeared deep, but it was for reasons beyond just my self-righteous tone. She said, “You know, I appreciate your focus on future goals, but it’s a pretty privileged position to not have to worry about sharing your accomplishments publicly.”
What followed was a discussion that was generative, enlightening, uncomfortable, and necessary. I had never considered what I chose to hang (or not hang) on my office walls as a privilege, and that was exactly the point. She described numerous episodes when her accomplishments were overlooked or (worse) attributed to a male colleague because she was a woman. I began to understand that graceful self-promotion is not optional for many women in medicine, it is a necessary skill.
This is just one example of how my privilege as a male in medicine contributed to my ignorance of the gender inequities that my female coworkers have faced throughout their careers. My colleague showed a lot of grace by taking the time to help me navigate my male privilege in a constructive manner. I decided to learn more about gender inequities, and eventually determined that I was woefully inadequate as a male ally, not by refusal but by ignorance. I wanted to start earning my colleague’s trust that I would be an ally that she could count on.
Trustworthiness
I wanted to be a trustworthy ally, but what does that entail? Perhaps we can learn from medical education. Trust is a complex construct that is increasingly used as a framework for assessing medical students and residents, such as with entrustable professional activities (EPAs).1,2 Multiple studies have examined the characteristics that make a learner “trustworthy” when determining how much supervision is required.3-8 Ten Cate and Chen performed an interpretivist, narrative review to synthesize the medical education literature on learner trustworthiness in the past 15 years,9 developing five major themes that contribute to trustworthiness: Humility, Capability, Agency, Reliability, and Integrity. Let’s examine each of these through the lens of male allyship.
Humility
Humility involves knowing one’s limits, asking for help, and being receptive to feedback.9 The first thing men need to do is to put their egos in check and recognize that women do not need rescuing; they need partnership. Systemic inequities have led to men holding the majority of leadership positions and significant sociopolitical capital, and correcting these inequities is more feasible when those in leadership and positions of power contribute. Women don’t need knights in shining armor, they need collaborative activism.
Humility also means a willingness to admit fallibility and to ask for help. Men often don’t know what they don’t know (see my foibles in the opening). As David G. Smith, PhD, and W. Brad Johnson, PhD, write in their book, “Good Guys,” “There are no perfect allies. As you work to become a better ally for the women around you, you will undoubtedly make a mistake.”10 Men must accept feedback on their shortcomings as allies without feeling as though they are losing their sociopolitical standing. Allyship for women does not mean there is a devaluing of men. We must escape a “zero-sum” mindset. Mistakes are where growth happens, but only if we approach our missteps with humility.
Capability
Capability entails having the necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes to be a strong ally. Allyship is not intuitive for most men for several reasons. Many men do not experience the same biases or systemic inequities that women do, and therefore perceive them less frequently. I want to acknowledge that men can be victims of other systemic biases such as those against one’s race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, religion, or any number of factors. Men who face inequities for these other reasons may be more cognizant of the biases women face. Even so, allyship is a skill that few men have been explicitly taught. Even if taught, few standard or organized mechanisms for feedback on allyship capability exist. How, then, can men become capable allies?
Just like in medical education, men must become self-directed learners who seek to build capability and receive feedback on their performance as allies. Men should seek allyship training through local women-in-medicine programs or organizations, or through the increasing number of national education options such as the recent ADVANCE PHM Gender Equity Symposium. As with learning any skill, men should go to the literature, seeking knowledge from experts in the field. I recommend starting with “Good Guys: How Men Can Be Better Allies for Women in the Workplace10 or “Athena Rising: How and Why Men Should Mentor Women.”11 Both books, by Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson, are great entry points into the gender allyship literature. Seek out other resources from local experts on gender equity and allyship. Both aforementioned books were recommended to me by a friend and gender equity expert; without her guidance I would not have known where to start.
Agency
Agency involves being proactive and engaged rather than passive or apathetic. Men must be enthusiastic allies who seek out opportunities to mentor and sponsor women rather than waiting for others to ask. Agency requires being curious and passionate about improving. Most men in medicine are not openly and explicitly misogynistic or sexist, but many are only passive when it comes to gender equity and allyship. Trustworthy allyship entails turning passive support into active change. Not sure how to start? A good first step is to ask female colleagues questions such as, “What can I do to be a better ally for you in the workplace?” or “What are some things at work that are most challenging to you, but I might not notice because I’m a man?” Curiosity is the springboard toward agency.
Reliability
Reliability means being conscientious, accountable, and doing what we say we will do. Nothing undermines trustworthiness faster than making a commitment and not following through. Allyship cannot be a show or an attempt to get public plaudits. It is a longitudinal commitment to supporting women through individual mentorship and sponsorship, and to work toward institutional and systems change.
Reliability also means taking an equitable approach to what Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson call “office housework.” They define this as “administrative work that is necessary but undervalued, unlikely to lead to promotion, and disproportionately assigned to women.”10 In medicine, these tasks include organizing meetings, taking notes, planning social events, and remembering to celebrate colleagues’ achievements and milestones. Men should take on more of these tasks and advocate for change when the distribution of office housework in their workplace is inequitably directed toward women.
Integrity
Integrity involves honesty, professionalism, and benevolence. It is about making the morally correct choice even if there is potential risk. When men see gender inequity, they have an obligation to speak up. Whether it is overtly misogynistic behavior, subtle sexism, use of gendered language, inequitable distribution of office housework, lack of inclusivity and recognition for women, or another form of inequity, men must act with integrity and make it clear that they are partnering with women for change. Integrity means being an ally even when women are not present, and advocating that women be “at the table” for important conversations.
Beyond the individual
Allyship cannot end with individual actions; systems changes that build trustworthy institutions are necessary. Organizational leaders must approach gender conversations with humility to critically examine inequities and agency to implement meaningful changes. Workplace cultures and institutional policies should be reviewed with an eye toward system-level integrity and reliability for promoting and supporting women. Ongoing faculty and staff development programs must provide men with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes (capability) to be strong allies. We have a long history of male-dominated institutions that are unfair or (worse) unsafe for women. Many systems are designed in a way that disadvantages women. These systems must be redesigned through an equity lens to start building trust with women in medicine.
Becoming trustworthy is a process
Even the best male allies have room to improve their trustworthiness. Many men (myself included) have a LOT of room to improve, but they should not get discouraged by the amount of ground to be gained. Steady, deliberate improvement in men’s humility, capability, agency, reliability, and integrity can build the foundation of trust with female colleagues. Trust takes time. It takes effort. It takes vulnerability. It is an ongoing, developmental process that requires deliberate practice, frequent reflection, and feedback from our female colleagues.
Dr. Kinnear is associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati Medical Center. He is associate program director for the Med-Peds and Internal Medicine residency programs.
References
1. Ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013 Mar;5(1):157-8. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00380.1.
2. Ten Cate O. Entrustment decisions: Bringing the patient into the assessment equation. Acad Med. 2017 Jun;92(6):736-8. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001623.
3. Kennedy TJT et al. Point-of-care assessment of medical trainee competence for independent clinical work. Acad Med. 2008 Oct;83(10 Suppl):S89-92. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318183c8b7.
4. Choo KJ et al. How do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? A qualitative analysis. J Hosp Med. 2014 Mar;9(3):169-75. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2150.
5. Hauer KE et al. How clinical supervisors develop trust in their trainees: A qualitative study. Med Educ. 2015 Aug;49(8):783-95. doi: 10.1111/medu.12745.
6. Sterkenburg A et al. When do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? Acad Med. 2010 Sep;85(9):1408-17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181eab0ec.
7. Sheu L et al. How supervisor experience influences trust, supervision, and trainee learning: A qualitative study. Acad Med. 2017 Sep;92(9):1320-7. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001560.
8. Pingree EW et al. Encouraging entrustment: A qualitative study of resident behaviors that promote entrustment. Acad Med. 2020 Nov;95(11):1718-25. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003487.
9. Ten Cate O, Chen HC. The ingredients of a rich entrustment decision. Med Teach. 2020 Dec;42(12):1413-20. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1817348.
10. Smith DG, Johnson WB. Good guys: How men can be better allies for women in the workplace: Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation 2020.
11. Johnson WB, Smith D. Athena rising: How and why men should mentor women: Routledge 2016.
“If you want to be trusted, be trustworthy” – Stephen Covey
A few years ago, while working in my office, a female colleague stopped by for a casual chat. During the course of the conversation, she noticed that I did not have any diplomas or certificates hanging on my office walls. Instead, there were clusters of pictures drawn by my children, family photos, and a white board with my “to-do” list. The only wall art was a print of Banksy’s “The Thinker Monkey,” which depicts a monkey with its fist to its chin similar to Rodin’s famous sculpture, “Le Penseur.”
When asked why I didn’t hang any diplomas or awards, I replied that I preferred to keep my office atmosphere light and fun, and to focus on future goals rather than past accomplishments. I could see her jaw tense. Her frustration appeared deep, but it was for reasons beyond just my self-righteous tone. She said, “You know, I appreciate your focus on future goals, but it’s a pretty privileged position to not have to worry about sharing your accomplishments publicly.”
What followed was a discussion that was generative, enlightening, uncomfortable, and necessary. I had never considered what I chose to hang (or not hang) on my office walls as a privilege, and that was exactly the point. She described numerous episodes when her accomplishments were overlooked or (worse) attributed to a male colleague because she was a woman. I began to understand that graceful self-promotion is not optional for many women in medicine, it is a necessary skill.
This is just one example of how my privilege as a male in medicine contributed to my ignorance of the gender inequities that my female coworkers have faced throughout their careers. My colleague showed a lot of grace by taking the time to help me navigate my male privilege in a constructive manner. I decided to learn more about gender inequities, and eventually determined that I was woefully inadequate as a male ally, not by refusal but by ignorance. I wanted to start earning my colleague’s trust that I would be an ally that she could count on.
Trustworthiness
I wanted to be a trustworthy ally, but what does that entail? Perhaps we can learn from medical education. Trust is a complex construct that is increasingly used as a framework for assessing medical students and residents, such as with entrustable professional activities (EPAs).1,2 Multiple studies have examined the characteristics that make a learner “trustworthy” when determining how much supervision is required.3-8 Ten Cate and Chen performed an interpretivist, narrative review to synthesize the medical education literature on learner trustworthiness in the past 15 years,9 developing five major themes that contribute to trustworthiness: Humility, Capability, Agency, Reliability, and Integrity. Let’s examine each of these through the lens of male allyship.
Humility
Humility involves knowing one’s limits, asking for help, and being receptive to feedback.9 The first thing men need to do is to put their egos in check and recognize that women do not need rescuing; they need partnership. Systemic inequities have led to men holding the majority of leadership positions and significant sociopolitical capital, and correcting these inequities is more feasible when those in leadership and positions of power contribute. Women don’t need knights in shining armor, they need collaborative activism.
Humility also means a willingness to admit fallibility and to ask for help. Men often don’t know what they don’t know (see my foibles in the opening). As David G. Smith, PhD, and W. Brad Johnson, PhD, write in their book, “Good Guys,” “There are no perfect allies. As you work to become a better ally for the women around you, you will undoubtedly make a mistake.”10 Men must accept feedback on their shortcomings as allies without feeling as though they are losing their sociopolitical standing. Allyship for women does not mean there is a devaluing of men. We must escape a “zero-sum” mindset. Mistakes are where growth happens, but only if we approach our missteps with humility.
Capability
Capability entails having the necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes to be a strong ally. Allyship is not intuitive for most men for several reasons. Many men do not experience the same biases or systemic inequities that women do, and therefore perceive them less frequently. I want to acknowledge that men can be victims of other systemic biases such as those against one’s race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, religion, or any number of factors. Men who face inequities for these other reasons may be more cognizant of the biases women face. Even so, allyship is a skill that few men have been explicitly taught. Even if taught, few standard or organized mechanisms for feedback on allyship capability exist. How, then, can men become capable allies?
Just like in medical education, men must become self-directed learners who seek to build capability and receive feedback on their performance as allies. Men should seek allyship training through local women-in-medicine programs or organizations, or through the increasing number of national education options such as the recent ADVANCE PHM Gender Equity Symposium. As with learning any skill, men should go to the literature, seeking knowledge from experts in the field. I recommend starting with “Good Guys: How Men Can Be Better Allies for Women in the Workplace10 or “Athena Rising: How and Why Men Should Mentor Women.”11 Both books, by Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson, are great entry points into the gender allyship literature. Seek out other resources from local experts on gender equity and allyship. Both aforementioned books were recommended to me by a friend and gender equity expert; without her guidance I would not have known where to start.
Agency
Agency involves being proactive and engaged rather than passive or apathetic. Men must be enthusiastic allies who seek out opportunities to mentor and sponsor women rather than waiting for others to ask. Agency requires being curious and passionate about improving. Most men in medicine are not openly and explicitly misogynistic or sexist, but many are only passive when it comes to gender equity and allyship. Trustworthy allyship entails turning passive support into active change. Not sure how to start? A good first step is to ask female colleagues questions such as, “What can I do to be a better ally for you in the workplace?” or “What are some things at work that are most challenging to you, but I might not notice because I’m a man?” Curiosity is the springboard toward agency.
Reliability
Reliability means being conscientious, accountable, and doing what we say we will do. Nothing undermines trustworthiness faster than making a commitment and not following through. Allyship cannot be a show or an attempt to get public plaudits. It is a longitudinal commitment to supporting women through individual mentorship and sponsorship, and to work toward institutional and systems change.
Reliability also means taking an equitable approach to what Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson call “office housework.” They define this as “administrative work that is necessary but undervalued, unlikely to lead to promotion, and disproportionately assigned to women.”10 In medicine, these tasks include organizing meetings, taking notes, planning social events, and remembering to celebrate colleagues’ achievements and milestones. Men should take on more of these tasks and advocate for change when the distribution of office housework in their workplace is inequitably directed toward women.
Integrity
Integrity involves honesty, professionalism, and benevolence. It is about making the morally correct choice even if there is potential risk. When men see gender inequity, they have an obligation to speak up. Whether it is overtly misogynistic behavior, subtle sexism, use of gendered language, inequitable distribution of office housework, lack of inclusivity and recognition for women, or another form of inequity, men must act with integrity and make it clear that they are partnering with women for change. Integrity means being an ally even when women are not present, and advocating that women be “at the table” for important conversations.
Beyond the individual
Allyship cannot end with individual actions; systems changes that build trustworthy institutions are necessary. Organizational leaders must approach gender conversations with humility to critically examine inequities and agency to implement meaningful changes. Workplace cultures and institutional policies should be reviewed with an eye toward system-level integrity and reliability for promoting and supporting women. Ongoing faculty and staff development programs must provide men with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes (capability) to be strong allies. We have a long history of male-dominated institutions that are unfair or (worse) unsafe for women. Many systems are designed in a way that disadvantages women. These systems must be redesigned through an equity lens to start building trust with women in medicine.
Becoming trustworthy is a process
Even the best male allies have room to improve their trustworthiness. Many men (myself included) have a LOT of room to improve, but they should not get discouraged by the amount of ground to be gained. Steady, deliberate improvement in men’s humility, capability, agency, reliability, and integrity can build the foundation of trust with female colleagues. Trust takes time. It takes effort. It takes vulnerability. It is an ongoing, developmental process that requires deliberate practice, frequent reflection, and feedback from our female colleagues.
Dr. Kinnear is associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati Medical Center. He is associate program director for the Med-Peds and Internal Medicine residency programs.
References
1. Ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013 Mar;5(1):157-8. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00380.1.
2. Ten Cate O. Entrustment decisions: Bringing the patient into the assessment equation. Acad Med. 2017 Jun;92(6):736-8. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001623.
3. Kennedy TJT et al. Point-of-care assessment of medical trainee competence for independent clinical work. Acad Med. 2008 Oct;83(10 Suppl):S89-92. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318183c8b7.
4. Choo KJ et al. How do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? A qualitative analysis. J Hosp Med. 2014 Mar;9(3):169-75. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2150.
5. Hauer KE et al. How clinical supervisors develop trust in their trainees: A qualitative study. Med Educ. 2015 Aug;49(8):783-95. doi: 10.1111/medu.12745.
6. Sterkenburg A et al. When do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? Acad Med. 2010 Sep;85(9):1408-17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181eab0ec.
7. Sheu L et al. How supervisor experience influences trust, supervision, and trainee learning: A qualitative study. Acad Med. 2017 Sep;92(9):1320-7. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001560.
8. Pingree EW et al. Encouraging entrustment: A qualitative study of resident behaviors that promote entrustment. Acad Med. 2020 Nov;95(11):1718-25. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003487.
9. Ten Cate O, Chen HC. The ingredients of a rich entrustment decision. Med Teach. 2020 Dec;42(12):1413-20. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1817348.
10. Smith DG, Johnson WB. Good guys: How men can be better allies for women in the workplace: Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation 2020.
11. Johnson WB, Smith D. Athena rising: How and why men should mentor women: Routledge 2016.
“If you want to be trusted, be trustworthy” – Stephen Covey
A few years ago, while working in my office, a female colleague stopped by for a casual chat. During the course of the conversation, she noticed that I did not have any diplomas or certificates hanging on my office walls. Instead, there were clusters of pictures drawn by my children, family photos, and a white board with my “to-do” list. The only wall art was a print of Banksy’s “The Thinker Monkey,” which depicts a monkey with its fist to its chin similar to Rodin’s famous sculpture, “Le Penseur.”
When asked why I didn’t hang any diplomas or awards, I replied that I preferred to keep my office atmosphere light and fun, and to focus on future goals rather than past accomplishments. I could see her jaw tense. Her frustration appeared deep, but it was for reasons beyond just my self-righteous tone. She said, “You know, I appreciate your focus on future goals, but it’s a pretty privileged position to not have to worry about sharing your accomplishments publicly.”
What followed was a discussion that was generative, enlightening, uncomfortable, and necessary. I had never considered what I chose to hang (or not hang) on my office walls as a privilege, and that was exactly the point. She described numerous episodes when her accomplishments were overlooked or (worse) attributed to a male colleague because she was a woman. I began to understand that graceful self-promotion is not optional for many women in medicine, it is a necessary skill.
This is just one example of how my privilege as a male in medicine contributed to my ignorance of the gender inequities that my female coworkers have faced throughout their careers. My colleague showed a lot of grace by taking the time to help me navigate my male privilege in a constructive manner. I decided to learn more about gender inequities, and eventually determined that I was woefully inadequate as a male ally, not by refusal but by ignorance. I wanted to start earning my colleague’s trust that I would be an ally that she could count on.
Trustworthiness
I wanted to be a trustworthy ally, but what does that entail? Perhaps we can learn from medical education. Trust is a complex construct that is increasingly used as a framework for assessing medical students and residents, such as with entrustable professional activities (EPAs).1,2 Multiple studies have examined the characteristics that make a learner “trustworthy” when determining how much supervision is required.3-8 Ten Cate and Chen performed an interpretivist, narrative review to synthesize the medical education literature on learner trustworthiness in the past 15 years,9 developing five major themes that contribute to trustworthiness: Humility, Capability, Agency, Reliability, and Integrity. Let’s examine each of these through the lens of male allyship.
Humility
Humility involves knowing one’s limits, asking for help, and being receptive to feedback.9 The first thing men need to do is to put their egos in check and recognize that women do not need rescuing; they need partnership. Systemic inequities have led to men holding the majority of leadership positions and significant sociopolitical capital, and correcting these inequities is more feasible when those in leadership and positions of power contribute. Women don’t need knights in shining armor, they need collaborative activism.
Humility also means a willingness to admit fallibility and to ask for help. Men often don’t know what they don’t know (see my foibles in the opening). As David G. Smith, PhD, and W. Brad Johnson, PhD, write in their book, “Good Guys,” “There are no perfect allies. As you work to become a better ally for the women around you, you will undoubtedly make a mistake.”10 Men must accept feedback on their shortcomings as allies without feeling as though they are losing their sociopolitical standing. Allyship for women does not mean there is a devaluing of men. We must escape a “zero-sum” mindset. Mistakes are where growth happens, but only if we approach our missteps with humility.
Capability
Capability entails having the necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes to be a strong ally. Allyship is not intuitive for most men for several reasons. Many men do not experience the same biases or systemic inequities that women do, and therefore perceive them less frequently. I want to acknowledge that men can be victims of other systemic biases such as those against one’s race, ethnicity, gender identity, sexual orientation, religion, or any number of factors. Men who face inequities for these other reasons may be more cognizant of the biases women face. Even so, allyship is a skill that few men have been explicitly taught. Even if taught, few standard or organized mechanisms for feedback on allyship capability exist. How, then, can men become capable allies?
Just like in medical education, men must become self-directed learners who seek to build capability and receive feedback on their performance as allies. Men should seek allyship training through local women-in-medicine programs or organizations, or through the increasing number of national education options such as the recent ADVANCE PHM Gender Equity Symposium. As with learning any skill, men should go to the literature, seeking knowledge from experts in the field. I recommend starting with “Good Guys: How Men Can Be Better Allies for Women in the Workplace10 or “Athena Rising: How and Why Men Should Mentor Women.”11 Both books, by Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson, are great entry points into the gender allyship literature. Seek out other resources from local experts on gender equity and allyship. Both aforementioned books were recommended to me by a friend and gender equity expert; without her guidance I would not have known where to start.
Agency
Agency involves being proactive and engaged rather than passive or apathetic. Men must be enthusiastic allies who seek out opportunities to mentor and sponsor women rather than waiting for others to ask. Agency requires being curious and passionate about improving. Most men in medicine are not openly and explicitly misogynistic or sexist, but many are only passive when it comes to gender equity and allyship. Trustworthy allyship entails turning passive support into active change. Not sure how to start? A good first step is to ask female colleagues questions such as, “What can I do to be a better ally for you in the workplace?” or “What are some things at work that are most challenging to you, but I might not notice because I’m a man?” Curiosity is the springboard toward agency.
Reliability
Reliability means being conscientious, accountable, and doing what we say we will do. Nothing undermines trustworthiness faster than making a commitment and not following through. Allyship cannot be a show or an attempt to get public plaudits. It is a longitudinal commitment to supporting women through individual mentorship and sponsorship, and to work toward institutional and systems change.
Reliability also means taking an equitable approach to what Dr. Smith and Dr. Johnson call “office housework.” They define this as “administrative work that is necessary but undervalued, unlikely to lead to promotion, and disproportionately assigned to women.”10 In medicine, these tasks include organizing meetings, taking notes, planning social events, and remembering to celebrate colleagues’ achievements and milestones. Men should take on more of these tasks and advocate for change when the distribution of office housework in their workplace is inequitably directed toward women.
Integrity
Integrity involves honesty, professionalism, and benevolence. It is about making the morally correct choice even if there is potential risk. When men see gender inequity, they have an obligation to speak up. Whether it is overtly misogynistic behavior, subtle sexism, use of gendered language, inequitable distribution of office housework, lack of inclusivity and recognition for women, or another form of inequity, men must act with integrity and make it clear that they are partnering with women for change. Integrity means being an ally even when women are not present, and advocating that women be “at the table” for important conversations.
Beyond the individual
Allyship cannot end with individual actions; systems changes that build trustworthy institutions are necessary. Organizational leaders must approach gender conversations with humility to critically examine inequities and agency to implement meaningful changes. Workplace cultures and institutional policies should be reviewed with an eye toward system-level integrity and reliability for promoting and supporting women. Ongoing faculty and staff development programs must provide men with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes (capability) to be strong allies. We have a long history of male-dominated institutions that are unfair or (worse) unsafe for women. Many systems are designed in a way that disadvantages women. These systems must be redesigned through an equity lens to start building trust with women in medicine.
Becoming trustworthy is a process
Even the best male allies have room to improve their trustworthiness. Many men (myself included) have a LOT of room to improve, but they should not get discouraged by the amount of ground to be gained. Steady, deliberate improvement in men’s humility, capability, agency, reliability, and integrity can build the foundation of trust with female colleagues. Trust takes time. It takes effort. It takes vulnerability. It is an ongoing, developmental process that requires deliberate practice, frequent reflection, and feedback from our female colleagues.
Dr. Kinnear is associate professor of internal medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Hospital Medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati Medical Center. He is associate program director for the Med-Peds and Internal Medicine residency programs.
References
1. Ten Cate O. Nuts and bolts of entrustable professional activities. J Grad Med Educ. 2013 Mar;5(1):157-8. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-12-00380.1.
2. Ten Cate O. Entrustment decisions: Bringing the patient into the assessment equation. Acad Med. 2017 Jun;92(6):736-8. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001623.
3. Kennedy TJT et al. Point-of-care assessment of medical trainee competence for independent clinical work. Acad Med. 2008 Oct;83(10 Suppl):S89-92. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e318183c8b7.
4. Choo KJ et al. How do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? A qualitative analysis. J Hosp Med. 2014 Mar;9(3):169-75. doi: 10.1002/jhm.2150.
5. Hauer KE et al. How clinical supervisors develop trust in their trainees: A qualitative study. Med Educ. 2015 Aug;49(8):783-95. doi: 10.1111/medu.12745.
6. Sterkenburg A et al. When do supervising physicians decide to entrust residents with unsupervised tasks? Acad Med. 2010 Sep;85(9):1408-17. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181eab0ec.
7. Sheu L et al. How supervisor experience influences trust, supervision, and trainee learning: A qualitative study. Acad Med. 2017 Sep;92(9):1320-7. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001560.
8. Pingree EW et al. Encouraging entrustment: A qualitative study of resident behaviors that promote entrustment. Acad Med. 2020 Nov;95(11):1718-25. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003487.
9. Ten Cate O, Chen HC. The ingredients of a rich entrustment decision. Med Teach. 2020 Dec;42(12):1413-20. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1817348.
10. Smith DG, Johnson WB. Good guys: How men can be better allies for women in the workplace: Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation 2020.
11. Johnson WB, Smith D. Athena rising: How and why men should mentor women: Routledge 2016.
The Supreme Court 2020‒2021: What will affect ObGyns?
The Supreme Court’s usual processes were disrupted this term. The COVID-19 pandemic required audio hearings rather than in-person, and it resulted in a number of emergency legal appeals. As the Court began its regular sessions on October 5, 2020, there were only 8 justices—Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg had passed away and Amy Coney Barrett had not yet been confirmed by the Senate. The Court decided many important cases this term, including dealing with the delivery of drugs to induce abortions, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) moratorium on housing evictions, yet another case on the Affordable Care Act, state laws concerning pharmacy benefit managers, and the Hologic and Minerva endometrial ablation systems patents. After considering these cases, we also will briefly look at other cases of general interest.
Abortion
Patient access to mifepristone
In May 2020, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) was the named plaintiff in a lawsuit against the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regarding the drugs mifepristone and misoprostol that are used to induce medical abortions.1 The case was filed by the American Civil Liberties Union on behalf of ACOG and others2,3 and raised the issue of patients’ access to these medications. The basic claim of the case was that during the pandemic, the FDA’s regulation of mifepristone was unconstitutional in that they imposed an undue burden on the decision of women to have an abortion.4 (Although misoprostol is a part of the medical abortion regimen, it is not subject to special regulation and was not part of the litigation.)
The FDA regulation of mifepristone, begun in 2000 but modified since then, includes 3 elements to assure safe use:
- prescribers must have special training or certification
- the drug can be dispensed to patients only in a hospital, clinic, or medical office under the supervision of a certified health care provider (known as the “in-person dispensing requirement” because retail pharmacy or mail distribution are prohibited)
- the health care provider must review a “patient agreement form” with the patient and have the patient sign the consent form in the provider’s presence.5
The pandemic made fulfilling these requirements substantially more burdensome and difficult. The question was whether the FDA was constitutionally required to modify its regulations during a pandemic to take account of the undue burden of the regulation created by the pandemic. That is, the question was not whether the FDA could have or should have chosen to make the modification, but whether it was required to do so.
In July 2020, a federal district court in Maryland held that the FDA regulation was an unconstitutional burden on the abortion rights of women during the pandemic and issued a preliminary injunction to stop the FDA from enforcing the in-person dispensing and signature rules. The district judge applied the injunction to Maryland, but also made it a nationwide injunction. (The issue of district court nationwide injunctions is considered in, “District court ‘nationwide injunctions’”).
The FDA asked the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals to stay the enforcement of the injunction, which the appeals court denied. The FDA then appealed to the Supreme Court, asking it to stay the injunction. In October 2020, the Court announced that it was holding the FDA’s request “in abeyance” to allow the district court to consider a motion by the FDA to dissolve or change the injunction. It gave the district court 40 days in which to act. That decision by the Court was in the “Shadow Docket” (see sidebar on page XX), so the exact vote of the Court in October is not clear, but 2 Justices (Alito and Thomas) dissented and would have stayed the injunction.6 Over the next 40 days, the district court did not withdraw its nationwide injunction.
Thus, on January 12, 2021, the case was again before the Supreme Court, which let the FDA’s regulations regarding mifepristone remain in place by lifting the district court’s injunction. Most of the justices supporting the stay did not write to explain their decision, although their dissent in the earlier cases may have served that purpose. (Maryland was permitting many kinds of activity that were more risky than visiting a clinic—indoor dining, with open hair salons, gyms, and casinos.)7 Chief Justice Roberts wrote a concurrence to indicate that, in his view, the issue was not whether the FDA’s regulations placed an undue burden on a right to an abortion generally, but that “My view is that courts owe significant deference” to the public health authorities (here meaning the FDA). Justices Sotomayor and Kagan dissented, saying that the issue was the undue burden on women, given the difficulties of the pandemic, particularly going to medical facilities during the COVID-19 pandemic.8
The injunction, sought by ACOG and others, was issued by the district court and was in effect for several months before it was dissolved by the Supreme Court. Following the change in presidential administrations, in April 2021 the FDA announced that it was going to “exercise enforcement discretion with respect to the in-person dispensing requirement…during the COVID-19 public health emergency.”9
Continue to: The Texas abortion case...
The Texas abortion case
The Court, on September 1, 2021, declined to block a Texas abortion statute from taking effect.10 This law precludes abortions after a fetal heartbeat is present at about 6 weeks of gestation. The Fifth Circuit declined to grant an injunction delaying implementation of the Texas law, and the Court did not reverse that decision.
Over the years, a variety of states have placed limitations on abortion, and those almost always have been enjoined by federal courts before they went into effect. However, the Texas statute, which undoubtedly is unconstitutional, was creatively constructed to avoid an early injunction.11 The statute does not allow state officials to enforce the new law, but rather it allows almost any private citizen to seek monetary damages from anyone performing an abortion or who “aids and abets” an abortion. Thus, it is difficult to tailor a lawsuit before this law is enforced. First, courts do not enjoin laws; they usually enjoin individuals from enforcing the law, and in this case it is difficult to know which individuals will be enforcing the laws and what their decisions might be. There also are some questions about the degree to which federal courts can enjoin state courts from deciding lawsuits under state law. For these procedural reasons, the majority of the Court found that those attacking the Texas law had not met their burden of showing that that they would win their case.
Even 3 of the dissenting justices said the defendants may be right that “existing doctrines preclude judicial intervention,” but that the consequences are such that the Court should delay the law until there is time for briefing and argument. The other 3 dissenting justices thought there would be ways of getting around the clever roadblock Texas had erected for the federal courts.
There has been some commentary that this case portends the abandonment of Roe v Wade and Casey,12 but that conclusion does not seem warranted by this case. The Court has accepted a Mississippi abortion law to be heard next term.13 In addition, the Texas statute is likely to be back in federal court once a private individual has filed a claim for money from an abortion provider (and likely even before that).
COVID-19 cases
The Supreme Court decided several cases related to COVID-19, including adjustments to election procedures, church services, and CDC eviction moratoria. As a general matter early in the pandemic, the Court deferred to government authorities, generally upholding government actions. Chief Justice Roberts emphasized the importance of the Court deferring to government officials in emergencies. As the pandemic progressed into 2021, however, the Court became less and less sympathetic to government actions that were not consistent, permitted by existing law, or reasonably necessary. For example, regulations of churches that were inconsistent with the regulation of similar organizations were struck down.14
Among the most interesting of the summer 2021 cases was the CDC eviction moratorium that essentially prohibited landlords nationwide from evicting tenants for nonpayment of rent. When the challenges to these CDC regulations first reached the Court, the moratorium was about to expire; in a 5-4 decision, the Court did not enjoin the CDC from continuing that policy. Justice Kavanaugh (the fifth vote) warned that “clear and specific congressional authorization…would be necessary to extend the moratorium past July 31.”15 Despite telling the Court that the moratorium would expire on July 31, just 3 days after the expiration and without any congressional authorization, the CDC reinstated what was practically the same moratorium.16 On August 26, the Court struck down the reinstated regulation, probably by a 6-3 margin. (Because this case arose in the “Shadow Docket,” the vote of some justices is not certain).17
Continue to: The Affordable Care Act...
The Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act was challenged in the Court for the third time.18 In this term’s case, several states argued that when Congress essentially eliminated the penalty/tax for not purchasing insurance coverage, there was no longer a constitutional basis for the individual mandate. With that centerpiece gone, they claimed, the whole statute should be declared unconstitutional.
Along with many other specialty groups, ACOG joined an amicus curiae brief sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA).19 An amicus brief is one not filed by the parties to the case, but by organizations or individuals who have information that may be of use to the Court in considering the case. Among other things, the filing of an amicus brief indicates the interest of the organization in the outcome of the case. In this case, the crux of the amicus was that even if the individual mandate currently is not constitutional, the Court should sever that provision and retain the rest of the ACA.
Despite some wild predictions about what the Court might do, it did not decide any substantive issue. Rather, it found that none of the parties to the case had “standing” to challenge the constitutionality of the ACA. Therefore, in effect, the Court dismissed the case without deciding the substantive legal issues.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers
The powerful Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) are a hidden part of the health care system; however, in recent years there has been increasing regulatory attention paid to them. Some states have begun regulating aspects of PBMs. In this term, the Court considered an Arkansas law that sought to protect local pharmacies from PBM pricing practices.20 The AMA filed an amicus brief in the case which made legal arguments, most of which had been made by the parties to the litigation.21
PBMs generally tell pharmacies how much they will reimburse the pharmacy for filling a prescription for a particular drug. In some instances, PBMs will set a reimbursement price that is lower than the wholesale price at which local pharmacies can purchase the drug. The Arkansas law prohibited PBMs in the state from reimbursing pharmacies for less than the wholesale cost the pharmacy paid for the drug.
The claim of the PBMs was that the Arkansas law violated the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). In part, this act preempts state law that relates to fringe benefit plans. States have the authority to regulate insurance, but ERISA limits what they can do when the insurance relates to fringe benefits. The Court held that ERISA does not preempt the Arkansas law or similar state laws in other states. Because the state law was not preempted by the state law, the Arkansas regulation was upheld. The fact that this was a unanimous decision (8-0, because Justice Barrett was not on the Court when the case was heard) suggests that states may have leeway in additional regulations of PBMs, and it would not be surprising to see more of that state regulation in the future.
Continue to: Patent uncertainty...
Patent uncertainty
Csaba Truckai invented and patented the NovaSure System ablation device with a “moisture permeable” head. He sold his company and the related patents, which eventually were purchased by Hologic. Over time, Hologic added claims to the original patent. In the meantime, Truckai went on to invent another device, the Minerva Endometrial Ablation System (MEAS), which had a “moisture impermeable” head. (Note that the “Minerva Surgical, Inc.” involved in this case is not related to the company “Minerva Industries,” which some identified as a “patent troll.”)22
Hologic sued Minerva, claiming that Truckai’s second device (MEAS) infringed on its patent for the first device (NovaSure). Truckai’s defense was that the patent on NovaSure was invalid. Hologic felt that since Truckai had obtained that patent and then sold it, it was improper for him now to claim it was invalid. There is a doctrine for that: assignor estoppel—the person who sold (assigned) the patent is prevented from later claiming it was invalid. The question in this case was whether assignor estoppel is part of the patent law of the United States. It is not in the patent statutes, so it is a court-determined part of the law.
In a 5-4 decision this Term, the Court held that assignor estoppel is recognized, but that it is narrow.23 The Court identified several exceptions to assignor estoppel, notably for this case, including the situation in which the purchaser of the patent, after the purchase, returns to the Patent and Trademark Office to expand (amend) the patent’s claims. In that case, the seller could not be estopped by the amended terms of the patent. Minerva claimed that it was attacking the expanded patent that included changes made after it sold the patent. The Court, therefore, returned the case to the Federal Circuit to apply the principles it laid out about assignor estoppel.
Biotech and other fast-moving fields frequently have new technology building on slightly earlier technology. The current patent system often leaves uncertainty about who owns which part of a valid patent. This uncertainty is a drag on innovation, and the patent system is supposed to spur innovation. Assignor estoppel is likely to create additional complexity and uncertainty in some patents, which is regrettable.
Review of the Term
In addition to the other disruptions of the Term, during the first part of the Term, Amy Coney Barrett was not yet confirmed by the Senate, so there were only 8 justices until October 27. She did not participate in those cases that were heard before she joined the Court. The consensus is that the Court heard 67 cases: 57 were formally briefed and argued along with 8 summary reversals and 2 religious cases in the Shadow Docket. In my opinion, this undercounts both the number and the importance of the Shadow Docket cases, but the following data use the 67 case convention.24
The Court was unanimous in 43% of the cases, including some of the most divisive issues. That unanimity reflects very narrow decisions. There were (by conventional count) only eight 5-4 opinions (12%), an unusually low number. Justice Kavanaugh is viewed as the “median” justice. He was in the majority in 97% of all cases. Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett were in the majority 91%, and Justice Gorsuch 90%. As for the other justices, they were in the majority (all cases) most of the time: Justice Alito, 83%; Justice Thomas, 81%; Justice Breyer, 76%; Justice Kagan, 75%; and Justice Sotomayor, 69%. In “divided cases” (when unanimous cases are removed), the percentages are: Justice Kavanaugh, 95%; Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett, 84%; Justice Gorsuch, 82%; Justice Alito, 70%; Justice Thomas, 66%; Justice Breyer, 58%; Justice Kagan, 55%; and Justice Sotomayor, 45%.
When the term began, many Court watchers expected a relatively uninteresting term, dealing with many technical legal details. In fact, it turned out to be more interesting and important than expected, even with narrow holdings in important cases. Part of the secret of the term was that a lot of the real action was in the Shadow Docket. The end of the term is sometimes the moment when a justice announces a plan to retire. Many commentators expected Justice Breyer might announce—he has been under pressure to do so, to allow President Biden to nominate and a Democratic Senate to confirm a progressive justice. However, he did not do so. It is possible that he will announce his retirement to be effective when his successor is confirmed, but that is pure speculation.
Continue to: Next Term...
Next Term
The next term began on Monday, October 4, 2021. With the considerable current activity in the Shadow Docket, there was not much of a summer break. The coming term looks extraordinary. The headline case is an abortion case from Mississippi, Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization.25 The legal question is the constitutionality of Mississippi law that prohibits most abortions after 15 weeks of gestation. The Texas abortion law will also be back before the Court. As we saw this term, big cases may produce very narrow results, but this case has the potential for being a notable abortion decision.
In a different case the Court will decide whether a state attorney general can step in to defend an abortion law when the state health secretary does not do so.26
The Court also has accepted 3 cases dealing with reimbursement for health services. One deals with whether or not the Department of Health and Human Services can set reimbursement rates without good survey data regarding costs,27 another involves the calculation of additional payments for hospitals that serve a “disproportionate number of low-income patients,”28 and the third whether state Medicaid programs can take funds from an injured beneficiary’s tort recovery to cover future Medicaid costs.29
In other cases, the Court will review a gun control law from New York. The Court’s earlier Second Amendment cases involved guns in the home used for self-defense, but this case raises the question of whether a state can practically preclude “concealed-carry licenses.”30 Many experts believe the Court will accept a case dealing with racial preferences in college admissions, perhaps the Harvard case in which the claim is discrimination against Asian Americans.31
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum.
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum. Reference Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
Reference
1. Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
The “Shadow Docket”
The ACOG mifepristone decisions do not appear on the Supreme Court’s “Court Opinions” website.1 They appear in what has become known in recent years as “The Shadow Docket,” an informal term that includes many orders of the Court and statements of individual justices regarding some cases.2 There are hundreds of orders by the Court each Term, there is nothing particularly shadowy about any of these items—they are all publicly available on the Court’s website and later in paper format. It is, however, a little harder to find and much harder to sort through than the major opinions. In some cases, it is not possible to tell what the vote was, how each justice voted, and what the reasoning of the Court was. In a few cases it is difficult to know exactly what the Court was holding or otherwise leaves some confusion about what the law actually is.3
The part of the Shadow Docket that is most intriguing for commentators, and where the ACOG cases appear, is the “Opinions Relating to Orders.”4 These are a variety of opinions, some written by the Court and many by individual justices. It also includes the action of the Court in some cases in which there was not full briefing or oral argument. The statements by justices often are to dissent from the denial of cert of decisions of the Court. These opinions have become much more common over the years. In this past term, there were approximately 60 such opinions related to about 50 cases. In part, this relates to the number of pandemic cases that could not wait for a Court decision going through the extended ordinary process. Although the Shadow Docket has been of interest to academic observers and Court watchers for years, this year it has attracted the attention of Congress.5
References
1. Opinions of the Court. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/slipopinion/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
2. Baude W. Foreword: the Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket, 9 N.Y.U. J.L. & Liberty 1 (2015).
3. Vladeck SI. The Solicitor General and the Shadow Docket, 133 Harvard Law Review. 123 (2019).
4. Opinions relating to orders. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/relatingtoorders/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
5. The Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket: Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Courts, Intellectual Property and the Internet of the H. Committee on the Judiciary, 117th Congress (2021).
- American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 472 F. Supp. 3d 183 (D. Md. 2020).
- Michael Kunzelman, Doctors Sue to Block FDA Abortion Pill Rule During Pandemic, (May 29, 2020).
- ACLU, American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists V. U.S. Food And Drug Administration, https://www.aclu.org/cases/american-college-obstetricians-and-gynecologists-v-us-food-and-drug-administration. Updated February 12, 2021. Accessed August 27, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Hellerstedt, 579 US ___ (2016), 136 S Ct 2292.
- 2016 Clinical Review at 39, 47, 49, Opp’n Mot. PI Ex. 19, ECF No. 62-11.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists v FDA (I), decided October 8, 2020.
- October 8, 2020, dissenting opinion by Justice Alito.
- January 12, 2021, dissenting opinion by Justice Sotomayor.
- Questions and answers on Mifeprex. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. Published April 13, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/questions-and-answers-mifeprex. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Jackson, decided September 1, 2021.
- Texas Senate Bill 8, relating to abortion, including abortions after detection of unborn child’s heartbeat; authorizing a private civil right of action. LegiScan website. https://legiscan.com/TX/text/SB8/id/2395961. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v Casey, 505 U. S. 833 (1992); Roe v Wade, 410 U. S. 113 (1973).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn v Cuomo, decided November 25, 2020.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided June 29, 2021.
- Temporary halt in residential evictions in communities with substantial or high levels of community transmission of COVID-19 to prevent the further spread of COVID-19. August 6, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/08/06/2021-16945/temporary-halt-in-residential-evictions-in-communities-with-substantial-or-high-transmission-of.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided August 26, 2021.
- California v Texas, decided June 17, 2021.
- Brief of Amici Curiae American Medical Association, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Aerospace Medical Association, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Cardiology, American College of Emergency Physicians, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Physicians, American College of Radiation Oncology, American College of Radiology, American Psychiatric Association, American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, American Society of Hematology, American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, Endocrine Society, GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ Equality, Renal Physicians Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology in Support of Petitioners, in California v. Texas. May 13, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/19/19-840/143469/20200513150051995_19-840%20Amici%20Brief%20AMA.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, decided December 10, 2020.
- Brief of the American Medical Association, The Arkansas Medical Society, and The Litigation Center of the American Medical Association and the State Medical Societies as Amici Curiae in Support of Petitioner in Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association. March 2, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/18/18-540/134670/20200302163622018_Rutledge%20v.%20PCMA%20Amicus%20Brief%20of%20AMA%20et%20al.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Apple quietly settles patent lawsuit, promptly gets hit with another one. TechCrunch website. Published July 30, 2010. https://techcrunch.com/2010/07/30/apple-minerva-emblaze/. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Minerva Surgical, Inc. v Hologic, Inc., decided June 29, 2021.
- Stat pack. SCOTUS Blog website. Published July 6, 2021. https://www.scotusblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Final-Stat-Pack-7.6.21.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Cameron v. EMW Women’s Surgical Center, https://www.scotusblog.com/case-files/cases/cameron-v-emw-womens-surgical-center-p-s-c/. Accessed August 28, 2021.
- American Hospital Association v Becerra, No. 20-1114.
- Becerra v Empire Health Foundation, No. 20-1312.
- Gallardo v Marstiller, No. 20-1263.
- New York State Rifle & Pistol Association Inc. v Corlett, No. 20-843.
- Students for Fair Admissions v President & Fellows of Harvard College, No. 20-1199.
The Supreme Court’s usual processes were disrupted this term. The COVID-19 pandemic required audio hearings rather than in-person, and it resulted in a number of emergency legal appeals. As the Court began its regular sessions on October 5, 2020, there were only 8 justices—Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg had passed away and Amy Coney Barrett had not yet been confirmed by the Senate. The Court decided many important cases this term, including dealing with the delivery of drugs to induce abortions, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) moratorium on housing evictions, yet another case on the Affordable Care Act, state laws concerning pharmacy benefit managers, and the Hologic and Minerva endometrial ablation systems patents. After considering these cases, we also will briefly look at other cases of general interest.
Abortion
Patient access to mifepristone
In May 2020, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) was the named plaintiff in a lawsuit against the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regarding the drugs mifepristone and misoprostol that are used to induce medical abortions.1 The case was filed by the American Civil Liberties Union on behalf of ACOG and others2,3 and raised the issue of patients’ access to these medications. The basic claim of the case was that during the pandemic, the FDA’s regulation of mifepristone was unconstitutional in that they imposed an undue burden on the decision of women to have an abortion.4 (Although misoprostol is a part of the medical abortion regimen, it is not subject to special regulation and was not part of the litigation.)
The FDA regulation of mifepristone, begun in 2000 but modified since then, includes 3 elements to assure safe use:
- prescribers must have special training or certification
- the drug can be dispensed to patients only in a hospital, clinic, or medical office under the supervision of a certified health care provider (known as the “in-person dispensing requirement” because retail pharmacy or mail distribution are prohibited)
- the health care provider must review a “patient agreement form” with the patient and have the patient sign the consent form in the provider’s presence.5
The pandemic made fulfilling these requirements substantially more burdensome and difficult. The question was whether the FDA was constitutionally required to modify its regulations during a pandemic to take account of the undue burden of the regulation created by the pandemic. That is, the question was not whether the FDA could have or should have chosen to make the modification, but whether it was required to do so.
In July 2020, a federal district court in Maryland held that the FDA regulation was an unconstitutional burden on the abortion rights of women during the pandemic and issued a preliminary injunction to stop the FDA from enforcing the in-person dispensing and signature rules. The district judge applied the injunction to Maryland, but also made it a nationwide injunction. (The issue of district court nationwide injunctions is considered in, “District court ‘nationwide injunctions’”).
The FDA asked the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals to stay the enforcement of the injunction, which the appeals court denied. The FDA then appealed to the Supreme Court, asking it to stay the injunction. In October 2020, the Court announced that it was holding the FDA’s request “in abeyance” to allow the district court to consider a motion by the FDA to dissolve or change the injunction. It gave the district court 40 days in which to act. That decision by the Court was in the “Shadow Docket” (see sidebar on page XX), so the exact vote of the Court in October is not clear, but 2 Justices (Alito and Thomas) dissented and would have stayed the injunction.6 Over the next 40 days, the district court did not withdraw its nationwide injunction.
Thus, on January 12, 2021, the case was again before the Supreme Court, which let the FDA’s regulations regarding mifepristone remain in place by lifting the district court’s injunction. Most of the justices supporting the stay did not write to explain their decision, although their dissent in the earlier cases may have served that purpose. (Maryland was permitting many kinds of activity that were more risky than visiting a clinic—indoor dining, with open hair salons, gyms, and casinos.)7 Chief Justice Roberts wrote a concurrence to indicate that, in his view, the issue was not whether the FDA’s regulations placed an undue burden on a right to an abortion generally, but that “My view is that courts owe significant deference” to the public health authorities (here meaning the FDA). Justices Sotomayor and Kagan dissented, saying that the issue was the undue burden on women, given the difficulties of the pandemic, particularly going to medical facilities during the COVID-19 pandemic.8
The injunction, sought by ACOG and others, was issued by the district court and was in effect for several months before it was dissolved by the Supreme Court. Following the change in presidential administrations, in April 2021 the FDA announced that it was going to “exercise enforcement discretion with respect to the in-person dispensing requirement…during the COVID-19 public health emergency.”9
Continue to: The Texas abortion case...
The Texas abortion case
The Court, on September 1, 2021, declined to block a Texas abortion statute from taking effect.10 This law precludes abortions after a fetal heartbeat is present at about 6 weeks of gestation. The Fifth Circuit declined to grant an injunction delaying implementation of the Texas law, and the Court did not reverse that decision.
Over the years, a variety of states have placed limitations on abortion, and those almost always have been enjoined by federal courts before they went into effect. However, the Texas statute, which undoubtedly is unconstitutional, was creatively constructed to avoid an early injunction.11 The statute does not allow state officials to enforce the new law, but rather it allows almost any private citizen to seek monetary damages from anyone performing an abortion or who “aids and abets” an abortion. Thus, it is difficult to tailor a lawsuit before this law is enforced. First, courts do not enjoin laws; they usually enjoin individuals from enforcing the law, and in this case it is difficult to know which individuals will be enforcing the laws and what their decisions might be. There also are some questions about the degree to which federal courts can enjoin state courts from deciding lawsuits under state law. For these procedural reasons, the majority of the Court found that those attacking the Texas law had not met their burden of showing that that they would win their case.
Even 3 of the dissenting justices said the defendants may be right that “existing doctrines preclude judicial intervention,” but that the consequences are such that the Court should delay the law until there is time for briefing and argument. The other 3 dissenting justices thought there would be ways of getting around the clever roadblock Texas had erected for the federal courts.
There has been some commentary that this case portends the abandonment of Roe v Wade and Casey,12 but that conclusion does not seem warranted by this case. The Court has accepted a Mississippi abortion law to be heard next term.13 In addition, the Texas statute is likely to be back in federal court once a private individual has filed a claim for money from an abortion provider (and likely even before that).
COVID-19 cases
The Supreme Court decided several cases related to COVID-19, including adjustments to election procedures, church services, and CDC eviction moratoria. As a general matter early in the pandemic, the Court deferred to government authorities, generally upholding government actions. Chief Justice Roberts emphasized the importance of the Court deferring to government officials in emergencies. As the pandemic progressed into 2021, however, the Court became less and less sympathetic to government actions that were not consistent, permitted by existing law, or reasonably necessary. For example, regulations of churches that were inconsistent with the regulation of similar organizations were struck down.14
Among the most interesting of the summer 2021 cases was the CDC eviction moratorium that essentially prohibited landlords nationwide from evicting tenants for nonpayment of rent. When the challenges to these CDC regulations first reached the Court, the moratorium was about to expire; in a 5-4 decision, the Court did not enjoin the CDC from continuing that policy. Justice Kavanaugh (the fifth vote) warned that “clear and specific congressional authorization…would be necessary to extend the moratorium past July 31.”15 Despite telling the Court that the moratorium would expire on July 31, just 3 days after the expiration and without any congressional authorization, the CDC reinstated what was practically the same moratorium.16 On August 26, the Court struck down the reinstated regulation, probably by a 6-3 margin. (Because this case arose in the “Shadow Docket,” the vote of some justices is not certain).17
Continue to: The Affordable Care Act...
The Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act was challenged in the Court for the third time.18 In this term’s case, several states argued that when Congress essentially eliminated the penalty/tax for not purchasing insurance coverage, there was no longer a constitutional basis for the individual mandate. With that centerpiece gone, they claimed, the whole statute should be declared unconstitutional.
Along with many other specialty groups, ACOG joined an amicus curiae brief sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA).19 An amicus brief is one not filed by the parties to the case, but by organizations or individuals who have information that may be of use to the Court in considering the case. Among other things, the filing of an amicus brief indicates the interest of the organization in the outcome of the case. In this case, the crux of the amicus was that even if the individual mandate currently is not constitutional, the Court should sever that provision and retain the rest of the ACA.
Despite some wild predictions about what the Court might do, it did not decide any substantive issue. Rather, it found that none of the parties to the case had “standing” to challenge the constitutionality of the ACA. Therefore, in effect, the Court dismissed the case without deciding the substantive legal issues.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers
The powerful Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) are a hidden part of the health care system; however, in recent years there has been increasing regulatory attention paid to them. Some states have begun regulating aspects of PBMs. In this term, the Court considered an Arkansas law that sought to protect local pharmacies from PBM pricing practices.20 The AMA filed an amicus brief in the case which made legal arguments, most of which had been made by the parties to the litigation.21
PBMs generally tell pharmacies how much they will reimburse the pharmacy for filling a prescription for a particular drug. In some instances, PBMs will set a reimbursement price that is lower than the wholesale price at which local pharmacies can purchase the drug. The Arkansas law prohibited PBMs in the state from reimbursing pharmacies for less than the wholesale cost the pharmacy paid for the drug.
The claim of the PBMs was that the Arkansas law violated the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). In part, this act preempts state law that relates to fringe benefit plans. States have the authority to regulate insurance, but ERISA limits what they can do when the insurance relates to fringe benefits. The Court held that ERISA does not preempt the Arkansas law or similar state laws in other states. Because the state law was not preempted by the state law, the Arkansas regulation was upheld. The fact that this was a unanimous decision (8-0, because Justice Barrett was not on the Court when the case was heard) suggests that states may have leeway in additional regulations of PBMs, and it would not be surprising to see more of that state regulation in the future.
Continue to: Patent uncertainty...
Patent uncertainty
Csaba Truckai invented and patented the NovaSure System ablation device with a “moisture permeable” head. He sold his company and the related patents, which eventually were purchased by Hologic. Over time, Hologic added claims to the original patent. In the meantime, Truckai went on to invent another device, the Minerva Endometrial Ablation System (MEAS), which had a “moisture impermeable” head. (Note that the “Minerva Surgical, Inc.” involved in this case is not related to the company “Minerva Industries,” which some identified as a “patent troll.”)22
Hologic sued Minerva, claiming that Truckai’s second device (MEAS) infringed on its patent for the first device (NovaSure). Truckai’s defense was that the patent on NovaSure was invalid. Hologic felt that since Truckai had obtained that patent and then sold it, it was improper for him now to claim it was invalid. There is a doctrine for that: assignor estoppel—the person who sold (assigned) the patent is prevented from later claiming it was invalid. The question in this case was whether assignor estoppel is part of the patent law of the United States. It is not in the patent statutes, so it is a court-determined part of the law.
In a 5-4 decision this Term, the Court held that assignor estoppel is recognized, but that it is narrow.23 The Court identified several exceptions to assignor estoppel, notably for this case, including the situation in which the purchaser of the patent, after the purchase, returns to the Patent and Trademark Office to expand (amend) the patent’s claims. In that case, the seller could not be estopped by the amended terms of the patent. Minerva claimed that it was attacking the expanded patent that included changes made after it sold the patent. The Court, therefore, returned the case to the Federal Circuit to apply the principles it laid out about assignor estoppel.
Biotech and other fast-moving fields frequently have new technology building on slightly earlier technology. The current patent system often leaves uncertainty about who owns which part of a valid patent. This uncertainty is a drag on innovation, and the patent system is supposed to spur innovation. Assignor estoppel is likely to create additional complexity and uncertainty in some patents, which is regrettable.
Review of the Term
In addition to the other disruptions of the Term, during the first part of the Term, Amy Coney Barrett was not yet confirmed by the Senate, so there were only 8 justices until October 27. She did not participate in those cases that were heard before she joined the Court. The consensus is that the Court heard 67 cases: 57 were formally briefed and argued along with 8 summary reversals and 2 religious cases in the Shadow Docket. In my opinion, this undercounts both the number and the importance of the Shadow Docket cases, but the following data use the 67 case convention.24
The Court was unanimous in 43% of the cases, including some of the most divisive issues. That unanimity reflects very narrow decisions. There were (by conventional count) only eight 5-4 opinions (12%), an unusually low number. Justice Kavanaugh is viewed as the “median” justice. He was in the majority in 97% of all cases. Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett were in the majority 91%, and Justice Gorsuch 90%. As for the other justices, they were in the majority (all cases) most of the time: Justice Alito, 83%; Justice Thomas, 81%; Justice Breyer, 76%; Justice Kagan, 75%; and Justice Sotomayor, 69%. In “divided cases” (when unanimous cases are removed), the percentages are: Justice Kavanaugh, 95%; Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett, 84%; Justice Gorsuch, 82%; Justice Alito, 70%; Justice Thomas, 66%; Justice Breyer, 58%; Justice Kagan, 55%; and Justice Sotomayor, 45%.
When the term began, many Court watchers expected a relatively uninteresting term, dealing with many technical legal details. In fact, it turned out to be more interesting and important than expected, even with narrow holdings in important cases. Part of the secret of the term was that a lot of the real action was in the Shadow Docket. The end of the term is sometimes the moment when a justice announces a plan to retire. Many commentators expected Justice Breyer might announce—he has been under pressure to do so, to allow President Biden to nominate and a Democratic Senate to confirm a progressive justice. However, he did not do so. It is possible that he will announce his retirement to be effective when his successor is confirmed, but that is pure speculation.
Continue to: Next Term...
Next Term
The next term began on Monday, October 4, 2021. With the considerable current activity in the Shadow Docket, there was not much of a summer break. The coming term looks extraordinary. The headline case is an abortion case from Mississippi, Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization.25 The legal question is the constitutionality of Mississippi law that prohibits most abortions after 15 weeks of gestation. The Texas abortion law will also be back before the Court. As we saw this term, big cases may produce very narrow results, but this case has the potential for being a notable abortion decision.
In a different case the Court will decide whether a state attorney general can step in to defend an abortion law when the state health secretary does not do so.26
The Court also has accepted 3 cases dealing with reimbursement for health services. One deals with whether or not the Department of Health and Human Services can set reimbursement rates without good survey data regarding costs,27 another involves the calculation of additional payments for hospitals that serve a “disproportionate number of low-income patients,”28 and the third whether state Medicaid programs can take funds from an injured beneficiary’s tort recovery to cover future Medicaid costs.29
In other cases, the Court will review a gun control law from New York. The Court’s earlier Second Amendment cases involved guns in the home used for self-defense, but this case raises the question of whether a state can practically preclude “concealed-carry licenses.”30 Many experts believe the Court will accept a case dealing with racial preferences in college admissions, perhaps the Harvard case in which the claim is discrimination against Asian Americans.31
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum.
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum. Reference Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
Reference
1. Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
The “Shadow Docket”
The ACOG mifepristone decisions do not appear on the Supreme Court’s “Court Opinions” website.1 They appear in what has become known in recent years as “The Shadow Docket,” an informal term that includes many orders of the Court and statements of individual justices regarding some cases.2 There are hundreds of orders by the Court each Term, there is nothing particularly shadowy about any of these items—they are all publicly available on the Court’s website and later in paper format. It is, however, a little harder to find and much harder to sort through than the major opinions. In some cases, it is not possible to tell what the vote was, how each justice voted, and what the reasoning of the Court was. In a few cases it is difficult to know exactly what the Court was holding or otherwise leaves some confusion about what the law actually is.3
The part of the Shadow Docket that is most intriguing for commentators, and where the ACOG cases appear, is the “Opinions Relating to Orders.”4 These are a variety of opinions, some written by the Court and many by individual justices. It also includes the action of the Court in some cases in which there was not full briefing or oral argument. The statements by justices often are to dissent from the denial of cert of decisions of the Court. These opinions have become much more common over the years. In this past term, there were approximately 60 such opinions related to about 50 cases. In part, this relates to the number of pandemic cases that could not wait for a Court decision going through the extended ordinary process. Although the Shadow Docket has been of interest to academic observers and Court watchers for years, this year it has attracted the attention of Congress.5
References
1. Opinions of the Court. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/slipopinion/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
2. Baude W. Foreword: the Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket, 9 N.Y.U. J.L. & Liberty 1 (2015).
3. Vladeck SI. The Solicitor General and the Shadow Docket, 133 Harvard Law Review. 123 (2019).
4. Opinions relating to orders. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/relatingtoorders/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
5. The Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket: Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Courts, Intellectual Property and the Internet of the H. Committee on the Judiciary, 117th Congress (2021).
The Supreme Court’s usual processes were disrupted this term. The COVID-19 pandemic required audio hearings rather than in-person, and it resulted in a number of emergency legal appeals. As the Court began its regular sessions on October 5, 2020, there were only 8 justices—Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg had passed away and Amy Coney Barrett had not yet been confirmed by the Senate. The Court decided many important cases this term, including dealing with the delivery of drugs to induce abortions, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) moratorium on housing evictions, yet another case on the Affordable Care Act, state laws concerning pharmacy benefit managers, and the Hologic and Minerva endometrial ablation systems patents. After considering these cases, we also will briefly look at other cases of general interest.
Abortion
Patient access to mifepristone
In May 2020, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) was the named plaintiff in a lawsuit against the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regarding the drugs mifepristone and misoprostol that are used to induce medical abortions.1 The case was filed by the American Civil Liberties Union on behalf of ACOG and others2,3 and raised the issue of patients’ access to these medications. The basic claim of the case was that during the pandemic, the FDA’s regulation of mifepristone was unconstitutional in that they imposed an undue burden on the decision of women to have an abortion.4 (Although misoprostol is a part of the medical abortion regimen, it is not subject to special regulation and was not part of the litigation.)
The FDA regulation of mifepristone, begun in 2000 but modified since then, includes 3 elements to assure safe use:
- prescribers must have special training or certification
- the drug can be dispensed to patients only in a hospital, clinic, or medical office under the supervision of a certified health care provider (known as the “in-person dispensing requirement” because retail pharmacy or mail distribution are prohibited)
- the health care provider must review a “patient agreement form” with the patient and have the patient sign the consent form in the provider’s presence.5
The pandemic made fulfilling these requirements substantially more burdensome and difficult. The question was whether the FDA was constitutionally required to modify its regulations during a pandemic to take account of the undue burden of the regulation created by the pandemic. That is, the question was not whether the FDA could have or should have chosen to make the modification, but whether it was required to do so.
In July 2020, a federal district court in Maryland held that the FDA regulation was an unconstitutional burden on the abortion rights of women during the pandemic and issued a preliminary injunction to stop the FDA from enforcing the in-person dispensing and signature rules. The district judge applied the injunction to Maryland, but also made it a nationwide injunction. (The issue of district court nationwide injunctions is considered in, “District court ‘nationwide injunctions’”).
The FDA asked the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals to stay the enforcement of the injunction, which the appeals court denied. The FDA then appealed to the Supreme Court, asking it to stay the injunction. In October 2020, the Court announced that it was holding the FDA’s request “in abeyance” to allow the district court to consider a motion by the FDA to dissolve or change the injunction. It gave the district court 40 days in which to act. That decision by the Court was in the “Shadow Docket” (see sidebar on page XX), so the exact vote of the Court in October is not clear, but 2 Justices (Alito and Thomas) dissented and would have stayed the injunction.6 Over the next 40 days, the district court did not withdraw its nationwide injunction.
Thus, on January 12, 2021, the case was again before the Supreme Court, which let the FDA’s regulations regarding mifepristone remain in place by lifting the district court’s injunction. Most of the justices supporting the stay did not write to explain their decision, although their dissent in the earlier cases may have served that purpose. (Maryland was permitting many kinds of activity that were more risky than visiting a clinic—indoor dining, with open hair salons, gyms, and casinos.)7 Chief Justice Roberts wrote a concurrence to indicate that, in his view, the issue was not whether the FDA’s regulations placed an undue burden on a right to an abortion generally, but that “My view is that courts owe significant deference” to the public health authorities (here meaning the FDA). Justices Sotomayor and Kagan dissented, saying that the issue was the undue burden on women, given the difficulties of the pandemic, particularly going to medical facilities during the COVID-19 pandemic.8
The injunction, sought by ACOG and others, was issued by the district court and was in effect for several months before it was dissolved by the Supreme Court. Following the change in presidential administrations, in April 2021 the FDA announced that it was going to “exercise enforcement discretion with respect to the in-person dispensing requirement…during the COVID-19 public health emergency.”9
Continue to: The Texas abortion case...
The Texas abortion case
The Court, on September 1, 2021, declined to block a Texas abortion statute from taking effect.10 This law precludes abortions after a fetal heartbeat is present at about 6 weeks of gestation. The Fifth Circuit declined to grant an injunction delaying implementation of the Texas law, and the Court did not reverse that decision.
Over the years, a variety of states have placed limitations on abortion, and those almost always have been enjoined by federal courts before they went into effect. However, the Texas statute, which undoubtedly is unconstitutional, was creatively constructed to avoid an early injunction.11 The statute does not allow state officials to enforce the new law, but rather it allows almost any private citizen to seek monetary damages from anyone performing an abortion or who “aids and abets” an abortion. Thus, it is difficult to tailor a lawsuit before this law is enforced. First, courts do not enjoin laws; they usually enjoin individuals from enforcing the law, and in this case it is difficult to know which individuals will be enforcing the laws and what their decisions might be. There also are some questions about the degree to which federal courts can enjoin state courts from deciding lawsuits under state law. For these procedural reasons, the majority of the Court found that those attacking the Texas law had not met their burden of showing that that they would win their case.
Even 3 of the dissenting justices said the defendants may be right that “existing doctrines preclude judicial intervention,” but that the consequences are such that the Court should delay the law until there is time for briefing and argument. The other 3 dissenting justices thought there would be ways of getting around the clever roadblock Texas had erected for the federal courts.
There has been some commentary that this case portends the abandonment of Roe v Wade and Casey,12 but that conclusion does not seem warranted by this case. The Court has accepted a Mississippi abortion law to be heard next term.13 In addition, the Texas statute is likely to be back in federal court once a private individual has filed a claim for money from an abortion provider (and likely even before that).
COVID-19 cases
The Supreme Court decided several cases related to COVID-19, including adjustments to election procedures, church services, and CDC eviction moratoria. As a general matter early in the pandemic, the Court deferred to government authorities, generally upholding government actions. Chief Justice Roberts emphasized the importance of the Court deferring to government officials in emergencies. As the pandemic progressed into 2021, however, the Court became less and less sympathetic to government actions that were not consistent, permitted by existing law, or reasonably necessary. For example, regulations of churches that were inconsistent with the regulation of similar organizations were struck down.14
Among the most interesting of the summer 2021 cases was the CDC eviction moratorium that essentially prohibited landlords nationwide from evicting tenants for nonpayment of rent. When the challenges to these CDC regulations first reached the Court, the moratorium was about to expire; in a 5-4 decision, the Court did not enjoin the CDC from continuing that policy. Justice Kavanaugh (the fifth vote) warned that “clear and specific congressional authorization…would be necessary to extend the moratorium past July 31.”15 Despite telling the Court that the moratorium would expire on July 31, just 3 days after the expiration and without any congressional authorization, the CDC reinstated what was practically the same moratorium.16 On August 26, the Court struck down the reinstated regulation, probably by a 6-3 margin. (Because this case arose in the “Shadow Docket,” the vote of some justices is not certain).17
Continue to: The Affordable Care Act...
The Affordable Care Act
The Affordable Care Act was challenged in the Court for the third time.18 In this term’s case, several states argued that when Congress essentially eliminated the penalty/tax for not purchasing insurance coverage, there was no longer a constitutional basis for the individual mandate. With that centerpiece gone, they claimed, the whole statute should be declared unconstitutional.
Along with many other specialty groups, ACOG joined an amicus curiae brief sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA).19 An amicus brief is one not filed by the parties to the case, but by organizations or individuals who have information that may be of use to the Court in considering the case. Among other things, the filing of an amicus brief indicates the interest of the organization in the outcome of the case. In this case, the crux of the amicus was that even if the individual mandate currently is not constitutional, the Court should sever that provision and retain the rest of the ACA.
Despite some wild predictions about what the Court might do, it did not decide any substantive issue. Rather, it found that none of the parties to the case had “standing” to challenge the constitutionality of the ACA. Therefore, in effect, the Court dismissed the case without deciding the substantive legal issues.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers
The powerful Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) are a hidden part of the health care system; however, in recent years there has been increasing regulatory attention paid to them. Some states have begun regulating aspects of PBMs. In this term, the Court considered an Arkansas law that sought to protect local pharmacies from PBM pricing practices.20 The AMA filed an amicus brief in the case which made legal arguments, most of which had been made by the parties to the litigation.21
PBMs generally tell pharmacies how much they will reimburse the pharmacy for filling a prescription for a particular drug. In some instances, PBMs will set a reimbursement price that is lower than the wholesale price at which local pharmacies can purchase the drug. The Arkansas law prohibited PBMs in the state from reimbursing pharmacies for less than the wholesale cost the pharmacy paid for the drug.
The claim of the PBMs was that the Arkansas law violated the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA). In part, this act preempts state law that relates to fringe benefit plans. States have the authority to regulate insurance, but ERISA limits what they can do when the insurance relates to fringe benefits. The Court held that ERISA does not preempt the Arkansas law or similar state laws in other states. Because the state law was not preempted by the state law, the Arkansas regulation was upheld. The fact that this was a unanimous decision (8-0, because Justice Barrett was not on the Court when the case was heard) suggests that states may have leeway in additional regulations of PBMs, and it would not be surprising to see more of that state regulation in the future.
Continue to: Patent uncertainty...
Patent uncertainty
Csaba Truckai invented and patented the NovaSure System ablation device with a “moisture permeable” head. He sold his company and the related patents, which eventually were purchased by Hologic. Over time, Hologic added claims to the original patent. In the meantime, Truckai went on to invent another device, the Minerva Endometrial Ablation System (MEAS), which had a “moisture impermeable” head. (Note that the “Minerva Surgical, Inc.” involved in this case is not related to the company “Minerva Industries,” which some identified as a “patent troll.”)22
Hologic sued Minerva, claiming that Truckai’s second device (MEAS) infringed on its patent for the first device (NovaSure). Truckai’s defense was that the patent on NovaSure was invalid. Hologic felt that since Truckai had obtained that patent and then sold it, it was improper for him now to claim it was invalid. There is a doctrine for that: assignor estoppel—the person who sold (assigned) the patent is prevented from later claiming it was invalid. The question in this case was whether assignor estoppel is part of the patent law of the United States. It is not in the patent statutes, so it is a court-determined part of the law.
In a 5-4 decision this Term, the Court held that assignor estoppel is recognized, but that it is narrow.23 The Court identified several exceptions to assignor estoppel, notably for this case, including the situation in which the purchaser of the patent, after the purchase, returns to the Patent and Trademark Office to expand (amend) the patent’s claims. In that case, the seller could not be estopped by the amended terms of the patent. Minerva claimed that it was attacking the expanded patent that included changes made after it sold the patent. The Court, therefore, returned the case to the Federal Circuit to apply the principles it laid out about assignor estoppel.
Biotech and other fast-moving fields frequently have new technology building on slightly earlier technology. The current patent system often leaves uncertainty about who owns which part of a valid patent. This uncertainty is a drag on innovation, and the patent system is supposed to spur innovation. Assignor estoppel is likely to create additional complexity and uncertainty in some patents, which is regrettable.
Review of the Term
In addition to the other disruptions of the Term, during the first part of the Term, Amy Coney Barrett was not yet confirmed by the Senate, so there were only 8 justices until October 27. She did not participate in those cases that were heard before she joined the Court. The consensus is that the Court heard 67 cases: 57 were formally briefed and argued along with 8 summary reversals and 2 religious cases in the Shadow Docket. In my opinion, this undercounts both the number and the importance of the Shadow Docket cases, but the following data use the 67 case convention.24
The Court was unanimous in 43% of the cases, including some of the most divisive issues. That unanimity reflects very narrow decisions. There were (by conventional count) only eight 5-4 opinions (12%), an unusually low number. Justice Kavanaugh is viewed as the “median” justice. He was in the majority in 97% of all cases. Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett were in the majority 91%, and Justice Gorsuch 90%. As for the other justices, they were in the majority (all cases) most of the time: Justice Alito, 83%; Justice Thomas, 81%; Justice Breyer, 76%; Justice Kagan, 75%; and Justice Sotomayor, 69%. In “divided cases” (when unanimous cases are removed), the percentages are: Justice Kavanaugh, 95%; Chief Justice Roberts and Justice Barrett, 84%; Justice Gorsuch, 82%; Justice Alito, 70%; Justice Thomas, 66%; Justice Breyer, 58%; Justice Kagan, 55%; and Justice Sotomayor, 45%.
When the term began, many Court watchers expected a relatively uninteresting term, dealing with many technical legal details. In fact, it turned out to be more interesting and important than expected, even with narrow holdings in important cases. Part of the secret of the term was that a lot of the real action was in the Shadow Docket. The end of the term is sometimes the moment when a justice announces a plan to retire. Many commentators expected Justice Breyer might announce—he has been under pressure to do so, to allow President Biden to nominate and a Democratic Senate to confirm a progressive justice. However, he did not do so. It is possible that he will announce his retirement to be effective when his successor is confirmed, but that is pure speculation.
Continue to: Next Term...
Next Term
The next term began on Monday, October 4, 2021. With the considerable current activity in the Shadow Docket, there was not much of a summer break. The coming term looks extraordinary. The headline case is an abortion case from Mississippi, Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization.25 The legal question is the constitutionality of Mississippi law that prohibits most abortions after 15 weeks of gestation. The Texas abortion law will also be back before the Court. As we saw this term, big cases may produce very narrow results, but this case has the potential for being a notable abortion decision.
In a different case the Court will decide whether a state attorney general can step in to defend an abortion law when the state health secretary does not do so.26
The Court also has accepted 3 cases dealing with reimbursement for health services. One deals with whether or not the Department of Health and Human Services can set reimbursement rates without good survey data regarding costs,27 another involves the calculation of additional payments for hospitals that serve a “disproportionate number of low-income patients,”28 and the third whether state Medicaid programs can take funds from an injured beneficiary’s tort recovery to cover future Medicaid costs.29
In other cases, the Court will review a gun control law from New York. The Court’s earlier Second Amendment cases involved guns in the home used for self-defense, but this case raises the question of whether a state can practically preclude “concealed-carry licenses.”30 Many experts believe the Court will accept a case dealing with racial preferences in college admissions, perhaps the Harvard case in which the claim is discrimination against Asian Americans.31
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum.
The ACOG mifepristone case was interesting, in part because the federal district court issued a nationwide injunction against the Americans with Disabilities Act, enforcing its rules anywhere in the country. The effect of these orders is for a single district judge to create the “law of the land,” at least until that is reviewed—which can take months. The advantage of the nationwide injunction is that it avoids having to repeatedly litigate the same issues in multiple courts around the country. The downside is that plaintiffs can seek out a nonrepresentative judge or circuit and receive an injunction that would be granted by few other circuits. In addition, a nationwide injunction can apply to specific circumstances that are not before the court issuing the injunction. In the mifepristone case, for example, 10 states requested to intervene in the ACOG case. The court rejected the request, but the nationwide injunction applied to those states.1
Although federal judges have had the authority to issue nationwide injunctions for years, they are becoming much more common. One reason is the ease of forum shopping noted earlier—organizations can cherry-pick district courts and circuits sympathetic to their views. Both left- and right-leaning organizations have learned this lesson, so left-leaning groups are likely to file in specific districts in the Ninth Circuit, and right-leaning groups to districts in the Fifth Circuit.
If the current trend of increasing nationwide injunctions continues, either the rules for the federal courts or congressional action may be required to reduce some of the abuses by both sides of the political spectrum. Reference Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
Reference
1. Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 467 F. Supp. 3d 282, 284 (D. Md. 2020).
The “Shadow Docket”
The ACOG mifepristone decisions do not appear on the Supreme Court’s “Court Opinions” website.1 They appear in what has become known in recent years as “The Shadow Docket,” an informal term that includes many orders of the Court and statements of individual justices regarding some cases.2 There are hundreds of orders by the Court each Term, there is nothing particularly shadowy about any of these items—they are all publicly available on the Court’s website and later in paper format. It is, however, a little harder to find and much harder to sort through than the major opinions. In some cases, it is not possible to tell what the vote was, how each justice voted, and what the reasoning of the Court was. In a few cases it is difficult to know exactly what the Court was holding or otherwise leaves some confusion about what the law actually is.3
The part of the Shadow Docket that is most intriguing for commentators, and where the ACOG cases appear, is the “Opinions Relating to Orders.”4 These are a variety of opinions, some written by the Court and many by individual justices. It also includes the action of the Court in some cases in which there was not full briefing or oral argument. The statements by justices often are to dissent from the denial of cert of decisions of the Court. These opinions have become much more common over the years. In this past term, there were approximately 60 such opinions related to about 50 cases. In part, this relates to the number of pandemic cases that could not wait for a Court decision going through the extended ordinary process. Although the Shadow Docket has been of interest to academic observers and Court watchers for years, this year it has attracted the attention of Congress.5
References
1. Opinions of the Court. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/slipopinion/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
2. Baude W. Foreword: the Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket, 9 N.Y.U. J.L. & Liberty 1 (2015).
3. Vladeck SI. The Solicitor General and the Shadow Docket, 133 Harvard Law Review. 123 (2019).
4. Opinions relating to orders. Supreme Court website. https://www.supremecourt.gov/opinions/relatingtoorders/20#list. Accessed October 10, 2021.
5. The Supreme Court’s Shadow Docket: Hearing Before the Subcommittee on Courts, Intellectual Property and the Internet of the H. Committee on the Judiciary, 117th Congress (2021).
- American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 472 F. Supp. 3d 183 (D. Md. 2020).
- Michael Kunzelman, Doctors Sue to Block FDA Abortion Pill Rule During Pandemic, (May 29, 2020).
- ACLU, American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists V. U.S. Food And Drug Administration, https://www.aclu.org/cases/american-college-obstetricians-and-gynecologists-v-us-food-and-drug-administration. Updated February 12, 2021. Accessed August 27, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Hellerstedt, 579 US ___ (2016), 136 S Ct 2292.
- 2016 Clinical Review at 39, 47, 49, Opp’n Mot. PI Ex. 19, ECF No. 62-11.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists v FDA (I), decided October 8, 2020.
- October 8, 2020, dissenting opinion by Justice Alito.
- January 12, 2021, dissenting opinion by Justice Sotomayor.
- Questions and answers on Mifeprex. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. Published April 13, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/questions-and-answers-mifeprex. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Jackson, decided September 1, 2021.
- Texas Senate Bill 8, relating to abortion, including abortions after detection of unborn child’s heartbeat; authorizing a private civil right of action. LegiScan website. https://legiscan.com/TX/text/SB8/id/2395961. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v Casey, 505 U. S. 833 (1992); Roe v Wade, 410 U. S. 113 (1973).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn v Cuomo, decided November 25, 2020.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided June 29, 2021.
- Temporary halt in residential evictions in communities with substantial or high levels of community transmission of COVID-19 to prevent the further spread of COVID-19. August 6, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/08/06/2021-16945/temporary-halt-in-residential-evictions-in-communities-with-substantial-or-high-transmission-of.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided August 26, 2021.
- California v Texas, decided June 17, 2021.
- Brief of Amici Curiae American Medical Association, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Aerospace Medical Association, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Cardiology, American College of Emergency Physicians, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Physicians, American College of Radiation Oncology, American College of Radiology, American Psychiatric Association, American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, American Society of Hematology, American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, Endocrine Society, GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ Equality, Renal Physicians Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology in Support of Petitioners, in California v. Texas. May 13, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/19/19-840/143469/20200513150051995_19-840%20Amici%20Brief%20AMA.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, decided December 10, 2020.
- Brief of the American Medical Association, The Arkansas Medical Society, and The Litigation Center of the American Medical Association and the State Medical Societies as Amici Curiae in Support of Petitioner in Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association. March 2, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/18/18-540/134670/20200302163622018_Rutledge%20v.%20PCMA%20Amicus%20Brief%20of%20AMA%20et%20al.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Apple quietly settles patent lawsuit, promptly gets hit with another one. TechCrunch website. Published July 30, 2010. https://techcrunch.com/2010/07/30/apple-minerva-emblaze/. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Minerva Surgical, Inc. v Hologic, Inc., decided June 29, 2021.
- Stat pack. SCOTUS Blog website. Published July 6, 2021. https://www.scotusblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Final-Stat-Pack-7.6.21.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Cameron v. EMW Women’s Surgical Center, https://www.scotusblog.com/case-files/cases/cameron-v-emw-womens-surgical-center-p-s-c/. Accessed August 28, 2021.
- American Hospital Association v Becerra, No. 20-1114.
- Becerra v Empire Health Foundation, No. 20-1312.
- Gallardo v Marstiller, No. 20-1263.
- New York State Rifle & Pistol Association Inc. v Corlett, No. 20-843.
- Students for Fair Admissions v President & Fellows of Harvard College, No. 20-1199.
- American College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists v. United States FDA, 472 F. Supp. 3d 183 (D. Md. 2020).
- Michael Kunzelman, Doctors Sue to Block FDA Abortion Pill Rule During Pandemic, (May 29, 2020).
- ACLU, American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists V. U.S. Food And Drug Administration, https://www.aclu.org/cases/american-college-obstetricians-and-gynecologists-v-us-food-and-drug-administration. Updated February 12, 2021. Accessed August 27, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Hellerstedt, 579 US ___ (2016), 136 S Ct 2292.
- 2016 Clinical Review at 39, 47, 49, Opp’n Mot. PI Ex. 19, ECF No. 62-11.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists v FDA (I), decided October 8, 2020.
- October 8, 2020, dissenting opinion by Justice Alito.
- January 12, 2021, dissenting opinion by Justice Sotomayor.
- Questions and answers on Mifeprex. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. Published April 13, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/questions-and-answers-mifeprex. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Whole Woman’s Health v Jackson, decided September 1, 2021.
- Texas Senate Bill 8, relating to abortion, including abortions after detection of unborn child’s heartbeat; authorizing a private civil right of action. LegiScan website. https://legiscan.com/TX/text/SB8/id/2395961. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v Casey, 505 U. S. 833 (1992); Roe v Wade, 410 U. S. 113 (1973).
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn v Cuomo, decided November 25, 2020.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided June 29, 2021.
- Temporary halt in residential evictions in communities with substantial or high levels of community transmission of COVID-19 to prevent the further spread of COVID-19. August 6, 2021. https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/08/06/2021-16945/temporary-halt-in-residential-evictions-in-communities-with-substantial-or-high-transmission-of.
- Alabama Association of Realtors v Department of Health and Human Services, decided August 26, 2021.
- California v Texas, decided June 17, 2021.
- Brief of Amici Curiae American Medical Association, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Aerospace Medical Association, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Cardiology, American College of Emergency Physicians, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American College of Physicians, American College of Radiation Oncology, American College of Radiology, American Psychiatric Association, American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, American Society of Hematology, American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, Endocrine Society, GLMA: Health Professionals Advancing LGBTQ Equality, Renal Physicians Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology in Support of Petitioners, in California v. Texas. May 13, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/19/19-840/143469/20200513150051995_19-840%20Amici%20Brief%20AMA.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, decided December 10, 2020.
- Brief of the American Medical Association, The Arkansas Medical Society, and The Litigation Center of the American Medical Association and the State Medical Societies as Amici Curiae in Support of Petitioner in Rutledge v Pharmaceutical Care Management Association. March 2, 2020. https://www.supremecourt.gov/DocketPDF/18/18-540/134670/20200302163622018_Rutledge%20v.%20PCMA%20Amicus%20Brief%20of%20AMA%20et%20al.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Apple quietly settles patent lawsuit, promptly gets hit with another one. TechCrunch website. Published July 30, 2010. https://techcrunch.com/2010/07/30/apple-minerva-emblaze/. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Minerva Surgical, Inc. v Hologic, Inc., decided June 29, 2021.
- Stat pack. SCOTUS Blog website. Published July 6, 2021. https://www.scotusblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Final-Stat-Pack-7.6.21.pdf. Accessed October 9, 2021.
- Dobbs v Jackson Women’s Health Organization, No. 19-1392.
- Cameron v. EMW Women’s Surgical Center, https://www.scotusblog.com/case-files/cases/cameron-v-emw-womens-surgical-center-p-s-c/. Accessed August 28, 2021.
- American Hospital Association v Becerra, No. 20-1114.
- Becerra v Empire Health Foundation, No. 20-1312.
- Gallardo v Marstiller, No. 20-1263.
- New York State Rifle & Pistol Association Inc. v Corlett, No. 20-843.
- Students for Fair Admissions v President & Fellows of Harvard College, No. 20-1199.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
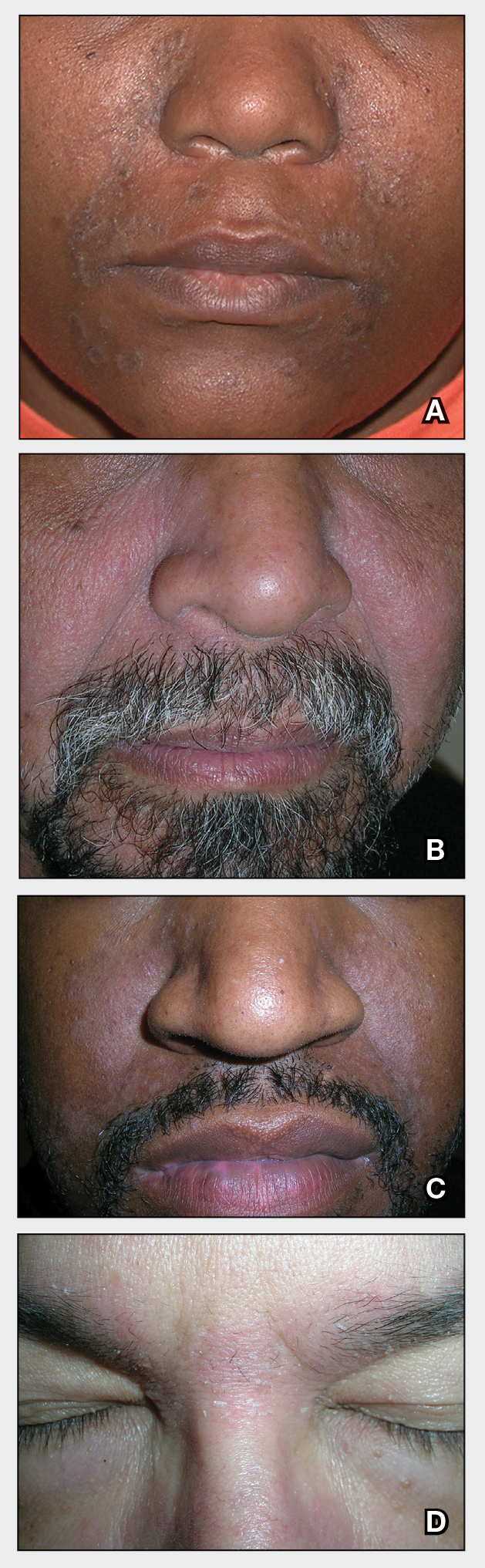
THE COMPARISON
A Seborrheic dermatitis in a woman with brown-gray greasy scale as well as petaloid papules and plaques that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
B Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, scale, and mild postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
C Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, faint scale, and postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
D Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema and scale of the eyebrows and glabellar region.
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is an inflammatory condition that is thought to be part of a response to Malassezia yeast. The scalp and face are most commonly affected, particularly the nasolabial folds, eyebrows, ears, postauricular areas, and beard area. Men also may have SD on the mid upper chest in association with chest hair. In infants, the scalp and body skin folds often are affected.
Epidemiology
Seborrheic dermatitis affects patients of all ages: infants, adolescents, and adults. It is among the most common dermatologic diagnoses reported in Black patients in the United States.1
Key clinical features in darker skin tones
- In those with darker skin tones, arcuate, polycyclic, or petaloid (flower petal–like) plaques may be present (Figure A). Also, hypopigmented patches and plaques may be prominent (Figures B and C). The classic description includes thin pink patches and plaques with white greasy scale on the face (Figure D).
- The scalp may have diffuse scale or isolated scaly plaques.
Worth noting
- In those with tightly coiled hair, there is a predisposition for dry hair and increased risk for breakage.
- Treatment plans for patients with SD often include frequent hair washing. However, in those with tightly coiled hair, the treatment plan may need to be modified due to hair texture, tendency for dryness, and washing frequency preferences. Washing the scalp at least every 1 to 2 weeks may be a preferred approach for those with tightly coiled hair at increased risk for dryness/breakage vs washing daily.2 In a sample of 201 caregivers of Black girls, Rucker Wright et al3 found that washing the hair more than once per week was not correlated with a lower prevalence of SD.
- If tightly coiled hair is temporarily straightened with heat (eg, blow-dryer, flat iron), adding a liquid-based treatment such as clobetasol solution or fluocinonide solution will cause the hair to revert to its normal curl pattern.
- It is appropriate to ask patients for their vehicle preference for medications.2 For example, if clobetasol is the treatment selected for the patient, the vehicle can reflect patient preference for a liquid, foam, cream, or ointment.
- Some antifungal/antiyeast shampoos may cause further hair dryness and breakage.
- Treatment may be delayed because patients often use various topical pomades and ointments to cover up the scale and help with pruritus.
- Diffuse scale of tinea capitis in school-aged children can be mistaken for SD, which leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Clinicians should become comfortable with scalp examinations in patients with tightly coiled hair. Patients with chief concerns related to their hair and scalp expect their clinicians to touch these areas. Avoid leaning in to examine the patient without touching the patient’s hair and scalp.2,4
Health disparity highlight
Seborrheic dermatitis is among the most common cutaneous disorders diagnosed in patients with skin of color.1,5 Delay in recognition of SD in those with darker skin tones leads to delayed treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis of the face can cause notable postinflammatory pigmentation alteration. Pigmentation changes in the skin further impact quality of life.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath C. Tips for addressing common conditions affecting pediatric and adolescent patients with skin of color [published online March 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;10.1111/pde.14525
- Rucker Wright D, Gathers R, Kapke A, et al. Hair care practices and their association with scalp and hair disorders in African American girls. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:253-262. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2010.05.037
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Gaulding JV, Gutierrez D, Bhatia BK, et al. Epidemiology of skin diseases in a diverse patient population. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018; 17:1032-1036.

THE COMPARISON
A Seborrheic dermatitis in a woman with brown-gray greasy scale as well as petaloid papules and plaques that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
B Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, scale, and mild postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
C Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, faint scale, and postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
D Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema and scale of the eyebrows and glabellar region.
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is an inflammatory condition that is thought to be part of a response to Malassezia yeast. The scalp and face are most commonly affected, particularly the nasolabial folds, eyebrows, ears, postauricular areas, and beard area. Men also may have SD on the mid upper chest in association with chest hair. In infants, the scalp and body skin folds often are affected.
Epidemiology
Seborrheic dermatitis affects patients of all ages: infants, adolescents, and adults. It is among the most common dermatologic diagnoses reported in Black patients in the United States.1
Key clinical features in darker skin tones
- In those with darker skin tones, arcuate, polycyclic, or petaloid (flower petal–like) plaques may be present (Figure A). Also, hypopigmented patches and plaques may be prominent (Figures B and C). The classic description includes thin pink patches and plaques with white greasy scale on the face (Figure D).
- The scalp may have diffuse scale or isolated scaly plaques.
Worth noting
- In those with tightly coiled hair, there is a predisposition for dry hair and increased risk for breakage.
- Treatment plans for patients with SD often include frequent hair washing. However, in those with tightly coiled hair, the treatment plan may need to be modified due to hair texture, tendency for dryness, and washing frequency preferences. Washing the scalp at least every 1 to 2 weeks may be a preferred approach for those with tightly coiled hair at increased risk for dryness/breakage vs washing daily.2 In a sample of 201 caregivers of Black girls, Rucker Wright et al3 found that washing the hair more than once per week was not correlated with a lower prevalence of SD.
- If tightly coiled hair is temporarily straightened with heat (eg, blow-dryer, flat iron), adding a liquid-based treatment such as clobetasol solution or fluocinonide solution will cause the hair to revert to its normal curl pattern.
- It is appropriate to ask patients for their vehicle preference for medications.2 For example, if clobetasol is the treatment selected for the patient, the vehicle can reflect patient preference for a liquid, foam, cream, or ointment.
- Some antifungal/antiyeast shampoos may cause further hair dryness and breakage.
- Treatment may be delayed because patients often use various topical pomades and ointments to cover up the scale and help with pruritus.
- Diffuse scale of tinea capitis in school-aged children can be mistaken for SD, which leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Clinicians should become comfortable with scalp examinations in patients with tightly coiled hair. Patients with chief concerns related to their hair and scalp expect their clinicians to touch these areas. Avoid leaning in to examine the patient without touching the patient’s hair and scalp.2,4
Health disparity highlight
Seborrheic dermatitis is among the most common cutaneous disorders diagnosed in patients with skin of color.1,5 Delay in recognition of SD in those with darker skin tones leads to delayed treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis of the face can cause notable postinflammatory pigmentation alteration. Pigmentation changes in the skin further impact quality of life.

THE COMPARISON
A Seborrheic dermatitis in a woman with brown-gray greasy scale as well as petaloid papules and plaques that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
B Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, scale, and mild postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
C Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema, faint scale, and postinflammatory hypopigmentation that are especially prominent in the nasolabial folds.
D Seborrheic dermatitis in a man with erythema and scale of the eyebrows and glabellar region.
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is an inflammatory condition that is thought to be part of a response to Malassezia yeast. The scalp and face are most commonly affected, particularly the nasolabial folds, eyebrows, ears, postauricular areas, and beard area. Men also may have SD on the mid upper chest in association with chest hair. In infants, the scalp and body skin folds often are affected.
Epidemiology
Seborrheic dermatitis affects patients of all ages: infants, adolescents, and adults. It is among the most common dermatologic diagnoses reported in Black patients in the United States.1
Key clinical features in darker skin tones
- In those with darker skin tones, arcuate, polycyclic, or petaloid (flower petal–like) plaques may be present (Figure A). Also, hypopigmented patches and plaques may be prominent (Figures B and C). The classic description includes thin pink patches and plaques with white greasy scale on the face (Figure D).
- The scalp may have diffuse scale or isolated scaly plaques.
Worth noting
- In those with tightly coiled hair, there is a predisposition for dry hair and increased risk for breakage.
- Treatment plans for patients with SD often include frequent hair washing. However, in those with tightly coiled hair, the treatment plan may need to be modified due to hair texture, tendency for dryness, and washing frequency preferences. Washing the scalp at least every 1 to 2 weeks may be a preferred approach for those with tightly coiled hair at increased risk for dryness/breakage vs washing daily.2 In a sample of 201 caregivers of Black girls, Rucker Wright et al3 found that washing the hair more than once per week was not correlated with a lower prevalence of SD.
- If tightly coiled hair is temporarily straightened with heat (eg, blow-dryer, flat iron), adding a liquid-based treatment such as clobetasol solution or fluocinonide solution will cause the hair to revert to its normal curl pattern.
- It is appropriate to ask patients for their vehicle preference for medications.2 For example, if clobetasol is the treatment selected for the patient, the vehicle can reflect patient preference for a liquid, foam, cream, or ointment.
- Some antifungal/antiyeast shampoos may cause further hair dryness and breakage.
- Treatment may be delayed because patients often use various topical pomades and ointments to cover up the scale and help with pruritus.
- Diffuse scale of tinea capitis in school-aged children can be mistaken for SD, which leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Clinicians should become comfortable with scalp examinations in patients with tightly coiled hair. Patients with chief concerns related to their hair and scalp expect their clinicians to touch these areas. Avoid leaning in to examine the patient without touching the patient’s hair and scalp.2,4
Health disparity highlight
Seborrheic dermatitis is among the most common cutaneous disorders diagnosed in patients with skin of color.1,5 Delay in recognition of SD in those with darker skin tones leads to delayed treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis of the face can cause notable postinflammatory pigmentation alteration. Pigmentation changes in the skin further impact quality of life.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath C. Tips for addressing common conditions affecting pediatric and adolescent patients with skin of color [published online March 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;10.1111/pde.14525
- Rucker Wright D, Gathers R, Kapke A, et al. Hair care practices and their association with scalp and hair disorders in African American girls. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:253-262. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2010.05.037
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Gaulding JV, Gutierrez D, Bhatia BK, et al. Epidemiology of skin diseases in a diverse patient population. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018; 17:1032-1036.
- Alexis AF, Sergay AB, Taylor SC. Common dermatologic disorders in skin of color: a comparative practice survey. Cutis. 2007;80:387-394.
- Grayson C, Heath C. Tips for addressing common conditions affecting pediatric and adolescent patients with skin of color [published online March 2, 2021]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;10.1111/pde.14525
- Rucker Wright D, Gathers R, Kapke A, et al. Hair care practices and their association with scalp and hair disorders in African American girls. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:253-262. doi:10.1016/j .jaad.2010.05.037
- Grayson C, Heath C. An approach to examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race-discordant patient-physician interactions. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:505-506. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0338
- Gaulding JV, Gutierrez D, Bhatia BK, et al. Epidemiology of skin diseases in a diverse patient population. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018; 17:1032-1036.
Detransitioners received poor evaluation when transitioning
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Filtering pulmonary function tests through race/ethnicity may add to biased care
The use of race/ethnicity in medicine to explain and interpret pulmonary function test (PFT) differences between individuals may contribute to biased medical care and research. Furthermore, it may perpetuate health disparities and structural racism, according to a study published in the journal CHEST®.
Current practices of PFT measurement and interpretation, are imperfect in their ability to accurately describe the relationship between function and health outcomes, according to Nirav R. Bhakta, MD, University of California,San Francisco, and colleagues.
The authors summarized arguments against using race-specific equations, while voicing genuine concerns about removing race from PFT interpretations, and described knowledge gaps and critical questions needing to be addressed for remediation of health disparities.
“Leaving out the perspectives of practicing pulmonologists and physiologists has global relevance for increasingly multicultural communities in which the range of values that represent normal lung function is uncertain,” Dr. Bhakta said in an interview.
A lesson in history
Tracing the history of spirometry, the authors stated that observations about vital lung capacity showing differences attributable to height, age, sex, and occupation (e.g., typesetter vs. firefighter) were then extended to include social classes and ultimately race. Whites showed greater average vital capacity for the same sex, height, and age than non-Whites.
While some investigators pointed to environmental sources (such as early life nutrition, respiratory illness, air pollution, exercise, and altitude), research into their mechanisms and magnitudes of effect was not pursued, but rather “a narrative of innate differences took hold,” Dr. Bhakta and colleagues reported.
That sort of narrative risks comparison with those used to uphold slavery and structural racism in the past. More recently, such a narrative was used to deny disability claims of Welsh versus English White miners, and was expanded to interpret algorithms designed to predict expected lung function.
Use of standing height questioned
The current practice of using normalized standard height for lung function comparisons misses racial and ethnic differences in the proportion of sitting height to standing height shown in multiple studies, the authors stated. These comparisons may ignore effects on standing height of early-life nutrition, genetics, lung-specific factors such as respiratory infections and exposures to indoor and outdoor pollution, physical activity, and high altitude. Using sitting height instead of standing height reduces lung volume differences up to 50% between White and Black populations, they noted, and socioeconomic variables, such as poverty and immigration status, accounted further for the differences seen. Population differences disappeared by as much as 90% when chest measurements used to estimate surface area or volume were more finely detailed.
The researchers warned, however, that, “because current clinical and policy algorithms rely so heavily on the comparison of an individual’s observed lung function to that which is expected for similar people without typical respiratory disease, an abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity, if not paired with education and a reform of existing algorithms and policies, is also expected to have risks on average to groups of non-White individuals.”
That could lead to potential challenges for some groups ranging from the ability to obtain employment in certain occupations, to being considered for potentially curative lung resections, or having access to home assisted ventilation and rehabilitation programs. “An abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity and taking a society’s overall average as the reference range also has the potential to lead to delayed care, denial of disability benefits, and higher life insurance premiums to White individuals.”
Evidence base is limited
“Although evidence demonstrates differences in lung function between racial/ethnic groups, the premise that dividing lung function interpretation up by racial/ethnic background is helpful in the clinical setting is not a proven one.” The authors cited some evidence that lung function interpretation without consideration of race/ethnicity has superior prognostic ability. In addition, research has shown only a weak relationship between lung function and work ability, according to the authors. More appropriate ways of assessing expected lung function for an individual in the absence of a diagnoses are under study.
Offering an alternative
As an alternative to race, Dr. Bhakta and colleagues proposed using a range of values that include individuals across many global populations while still adjusting for sex, age, and height. The resultant value would represent a diverse population average and widen the limits of normal that can be expected in otherwise-healthy people.
The approach would include PFTs with other factors for clinical decision-making, but would allow clinicians and patients to appreciate the limitations of interpretation based on comparison to reference values. However, such an approach may miss pathophysiologically reduced lung function in some individuals, in which case lifesaving therapies, such as chemotherapy, lung cancer resection, and bone marrow transplantation could be withheld. In other instances the consequence would be overtesting and diagnosis, they acknowledged.
The authors further discussed general concerns about the use of race in interpretation of PFTs, addressing limits/considerations as well as knowledge and practice gaps.
For example, one particular concern involves the fact that race does not capture acculturation and mixed ancestry. The limit/consideration is the need to discover mechanisms for differences and to suggest societal interventions, and the knowledge gap pertains to ignorance regarding mechanisms leading to differences in lung function.
For the concern that race is not a proxy for an individual’s genetics, the limit/consideration is that race captures only some genetics and the gap is the need for better genetic information. As an antidote to over reliance on lung function thresholds (without supporting data), they urged outcomes-based standards rather than comparisons with reference populations.
New thinking needed
Dr. Bhakta and colleagues pointed out that the forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratios important for diagnosis of obstructive lung disease are similar between racial/ethnic categories, underscoring the need for education about limitations of thresholds and reference values with regard to race, particularly as they are used to detect mild disease.
Ignoring race, on the other hand, can lead to unnecessary testing and treatment (with concomitant side effects), and anxiety.
“Reporting through race-based algorithms in the PFT laboratory risks portraying racial disparities as innate and immutable. By anchoring on the improved prediction of lung function from racial/ethnic-specific reference equations, we miss how the significant residual variation still leaves much uncertainty about the expected value for an individual,” the authors concluded. “Given their origin and historical and current use in society, these racial/ethnic labels are better used to identify the effects of structural racism on respiratory health in research and ensure adequate representation in research, rather than in clinical algorithms.”
One of the authors is a speaker for MGC Diagnostics. The others indicated that they had no relevant disclosures.
The use of race/ethnicity in medicine to explain and interpret pulmonary function test (PFT) differences between individuals may contribute to biased medical care and research. Furthermore, it may perpetuate health disparities and structural racism, according to a study published in the journal CHEST®.
Current practices of PFT measurement and interpretation, are imperfect in their ability to accurately describe the relationship between function and health outcomes, according to Nirav R. Bhakta, MD, University of California,San Francisco, and colleagues.
The authors summarized arguments against using race-specific equations, while voicing genuine concerns about removing race from PFT interpretations, and described knowledge gaps and critical questions needing to be addressed for remediation of health disparities.
“Leaving out the perspectives of practicing pulmonologists and physiologists has global relevance for increasingly multicultural communities in which the range of values that represent normal lung function is uncertain,” Dr. Bhakta said in an interview.
A lesson in history
Tracing the history of spirometry, the authors stated that observations about vital lung capacity showing differences attributable to height, age, sex, and occupation (e.g., typesetter vs. firefighter) were then extended to include social classes and ultimately race. Whites showed greater average vital capacity for the same sex, height, and age than non-Whites.
While some investigators pointed to environmental sources (such as early life nutrition, respiratory illness, air pollution, exercise, and altitude), research into their mechanisms and magnitudes of effect was not pursued, but rather “a narrative of innate differences took hold,” Dr. Bhakta and colleagues reported.
That sort of narrative risks comparison with those used to uphold slavery and structural racism in the past. More recently, such a narrative was used to deny disability claims of Welsh versus English White miners, and was expanded to interpret algorithms designed to predict expected lung function.
Use of standing height questioned
The current practice of using normalized standard height for lung function comparisons misses racial and ethnic differences in the proportion of sitting height to standing height shown in multiple studies, the authors stated. These comparisons may ignore effects on standing height of early-life nutrition, genetics, lung-specific factors such as respiratory infections and exposures to indoor and outdoor pollution, physical activity, and high altitude. Using sitting height instead of standing height reduces lung volume differences up to 50% between White and Black populations, they noted, and socioeconomic variables, such as poverty and immigration status, accounted further for the differences seen. Population differences disappeared by as much as 90% when chest measurements used to estimate surface area or volume were more finely detailed.
The researchers warned, however, that, “because current clinical and policy algorithms rely so heavily on the comparison of an individual’s observed lung function to that which is expected for similar people without typical respiratory disease, an abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity, if not paired with education and a reform of existing algorithms and policies, is also expected to have risks on average to groups of non-White individuals.”
That could lead to potential challenges for some groups ranging from the ability to obtain employment in certain occupations, to being considered for potentially curative lung resections, or having access to home assisted ventilation and rehabilitation programs. “An abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity and taking a society’s overall average as the reference range also has the potential to lead to delayed care, denial of disability benefits, and higher life insurance premiums to White individuals.”
Evidence base is limited
“Although evidence demonstrates differences in lung function between racial/ethnic groups, the premise that dividing lung function interpretation up by racial/ethnic background is helpful in the clinical setting is not a proven one.” The authors cited some evidence that lung function interpretation without consideration of race/ethnicity has superior prognostic ability. In addition, research has shown only a weak relationship between lung function and work ability, according to the authors. More appropriate ways of assessing expected lung function for an individual in the absence of a diagnoses are under study.
Offering an alternative
As an alternative to race, Dr. Bhakta and colleagues proposed using a range of values that include individuals across many global populations while still adjusting for sex, age, and height. The resultant value would represent a diverse population average and widen the limits of normal that can be expected in otherwise-healthy people.
The approach would include PFTs with other factors for clinical decision-making, but would allow clinicians and patients to appreciate the limitations of interpretation based on comparison to reference values. However, such an approach may miss pathophysiologically reduced lung function in some individuals, in which case lifesaving therapies, such as chemotherapy, lung cancer resection, and bone marrow transplantation could be withheld. In other instances the consequence would be overtesting and diagnosis, they acknowledged.
The authors further discussed general concerns about the use of race in interpretation of PFTs, addressing limits/considerations as well as knowledge and practice gaps.
For example, one particular concern involves the fact that race does not capture acculturation and mixed ancestry. The limit/consideration is the need to discover mechanisms for differences and to suggest societal interventions, and the knowledge gap pertains to ignorance regarding mechanisms leading to differences in lung function.
For the concern that race is not a proxy for an individual’s genetics, the limit/consideration is that race captures only some genetics and the gap is the need for better genetic information. As an antidote to over reliance on lung function thresholds (without supporting data), they urged outcomes-based standards rather than comparisons with reference populations.
New thinking needed
Dr. Bhakta and colleagues pointed out that the forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratios important for diagnosis of obstructive lung disease are similar between racial/ethnic categories, underscoring the need for education about limitations of thresholds and reference values with regard to race, particularly as they are used to detect mild disease.
Ignoring race, on the other hand, can lead to unnecessary testing and treatment (with concomitant side effects), and anxiety.
“Reporting through race-based algorithms in the PFT laboratory risks portraying racial disparities as innate and immutable. By anchoring on the improved prediction of lung function from racial/ethnic-specific reference equations, we miss how the significant residual variation still leaves much uncertainty about the expected value for an individual,” the authors concluded. “Given their origin and historical and current use in society, these racial/ethnic labels are better used to identify the effects of structural racism on respiratory health in research and ensure adequate representation in research, rather than in clinical algorithms.”
One of the authors is a speaker for MGC Diagnostics. The others indicated that they had no relevant disclosures.
The use of race/ethnicity in medicine to explain and interpret pulmonary function test (PFT) differences between individuals may contribute to biased medical care and research. Furthermore, it may perpetuate health disparities and structural racism, according to a study published in the journal CHEST®.
Current practices of PFT measurement and interpretation, are imperfect in their ability to accurately describe the relationship between function and health outcomes, according to Nirav R. Bhakta, MD, University of California,San Francisco, and colleagues.
The authors summarized arguments against using race-specific equations, while voicing genuine concerns about removing race from PFT interpretations, and described knowledge gaps and critical questions needing to be addressed for remediation of health disparities.
“Leaving out the perspectives of practicing pulmonologists and physiologists has global relevance for increasingly multicultural communities in which the range of values that represent normal lung function is uncertain,” Dr. Bhakta said in an interview.
A lesson in history
Tracing the history of spirometry, the authors stated that observations about vital lung capacity showing differences attributable to height, age, sex, and occupation (e.g., typesetter vs. firefighter) were then extended to include social classes and ultimately race. Whites showed greater average vital capacity for the same sex, height, and age than non-Whites.
While some investigators pointed to environmental sources (such as early life nutrition, respiratory illness, air pollution, exercise, and altitude), research into their mechanisms and magnitudes of effect was not pursued, but rather “a narrative of innate differences took hold,” Dr. Bhakta and colleagues reported.
That sort of narrative risks comparison with those used to uphold slavery and structural racism in the past. More recently, such a narrative was used to deny disability claims of Welsh versus English White miners, and was expanded to interpret algorithms designed to predict expected lung function.
Use of standing height questioned
The current practice of using normalized standard height for lung function comparisons misses racial and ethnic differences in the proportion of sitting height to standing height shown in multiple studies, the authors stated. These comparisons may ignore effects on standing height of early-life nutrition, genetics, lung-specific factors such as respiratory infections and exposures to indoor and outdoor pollution, physical activity, and high altitude. Using sitting height instead of standing height reduces lung volume differences up to 50% between White and Black populations, they noted, and socioeconomic variables, such as poverty and immigration status, accounted further for the differences seen. Population differences disappeared by as much as 90% when chest measurements used to estimate surface area or volume were more finely detailed.
The researchers warned, however, that, “because current clinical and policy algorithms rely so heavily on the comparison of an individual’s observed lung function to that which is expected for similar people without typical respiratory disease, an abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity, if not paired with education and a reform of existing algorithms and policies, is also expected to have risks on average to groups of non-White individuals.”
That could lead to potential challenges for some groups ranging from the ability to obtain employment in certain occupations, to being considered for potentially curative lung resections, or having access to home assisted ventilation and rehabilitation programs. “An abrupt change to not using race/ethnicity and taking a society’s overall average as the reference range also has the potential to lead to delayed care, denial of disability benefits, and higher life insurance premiums to White individuals.”
Evidence base is limited
“Although evidence demonstrates differences in lung function between racial/ethnic groups, the premise that dividing lung function interpretation up by racial/ethnic background is helpful in the clinical setting is not a proven one.” The authors cited some evidence that lung function interpretation without consideration of race/ethnicity has superior prognostic ability. In addition, research has shown only a weak relationship between lung function and work ability, according to the authors. More appropriate ways of assessing expected lung function for an individual in the absence of a diagnoses are under study.
Offering an alternative
As an alternative to race, Dr. Bhakta and colleagues proposed using a range of values that include individuals across many global populations while still adjusting for sex, age, and height. The resultant value would represent a diverse population average and widen the limits of normal that can be expected in otherwise-healthy people.
The approach would include PFTs with other factors for clinical decision-making, but would allow clinicians and patients to appreciate the limitations of interpretation based on comparison to reference values. However, such an approach may miss pathophysiologically reduced lung function in some individuals, in which case lifesaving therapies, such as chemotherapy, lung cancer resection, and bone marrow transplantation could be withheld. In other instances the consequence would be overtesting and diagnosis, they acknowledged.
The authors further discussed general concerns about the use of race in interpretation of PFTs, addressing limits/considerations as well as knowledge and practice gaps.
For example, one particular concern involves the fact that race does not capture acculturation and mixed ancestry. The limit/consideration is the need to discover mechanisms for differences and to suggest societal interventions, and the knowledge gap pertains to ignorance regarding mechanisms leading to differences in lung function.
For the concern that race is not a proxy for an individual’s genetics, the limit/consideration is that race captures only some genetics and the gap is the need for better genetic information. As an antidote to over reliance on lung function thresholds (without supporting data), they urged outcomes-based standards rather than comparisons with reference populations.
New thinking needed
Dr. Bhakta and colleagues pointed out that the forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratios important for diagnosis of obstructive lung disease are similar between racial/ethnic categories, underscoring the need for education about limitations of thresholds and reference values with regard to race, particularly as they are used to detect mild disease.
Ignoring race, on the other hand, can lead to unnecessary testing and treatment (with concomitant side effects), and anxiety.
“Reporting through race-based algorithms in the PFT laboratory risks portraying racial disparities as innate and immutable. By anchoring on the improved prediction of lung function from racial/ethnic-specific reference equations, we miss how the significant residual variation still leaves much uncertainty about the expected value for an individual,” the authors concluded. “Given their origin and historical and current use in society, these racial/ethnic labels are better used to identify the effects of structural racism on respiratory health in research and ensure adequate representation in research, rather than in clinical algorithms.”
One of the authors is a speaker for MGC Diagnostics. The others indicated that they had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST®
Time to retire race- and ethnicity-based carrier screening
The social reckoning of 2020 has led to many discussions and conversations around equity and disparities. With the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a particular spotlight on health care disparities and race-based medicine. Racism in medicine is pervasive; little has been done over the years to dismantle and unlearn practices that continue to contribute to existing gaps and disparities. Race and ethnicity are both social constructs that have long been used within medical practice and in dictating the type of care an individual receives. Without a universal definition, race, ethnicity, and ancestry have long been used interchangeably within medicine and society. Appreciating that race and ethnicity-based constructs can have other social implications in health care, with their impact on structural racism beyond health care settings, these constructs may still be part of assessments and key modifiers to understanding health differences. It is imperative that medical providers examine the use of race and ethnicity within the care that they provide.
While racial determinants of health cannot be removed from historical access, utilization, and barriers related to reproductive care, guidelines structured around historical ethnicity and race further restrict universal access to carrier screening and informed reproductive testing decisions.
Carrier screening
The goal of preconception and prenatal carrier screening is to provide individuals and reproductive partners with information to optimize pregnancy outcomes based on personal values and preferences.1 The practice of carrier screening began almost half a century ago with screening for individual conditions seen more frequently in certain populations, such as Tay-Sachs disease in those of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and sickle cell disease in those of African descent. Cystic fibrosis carrier screening was first recommended for individuals of Northern European descent in 2001 before being recommended for pan ethnic screening a decade later. Other individual conditions are also recommended for screening based on race/ethnicity (eg, Canavan disease in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, Tay-Sachs disease in individuals of Cajun or French-Canadian descent).2-4 Practice guidelines from professional societies recommend offering carrier screening for individual conditions based on condition severity, race or ethnicity, prevalence, carrier frequency, detection rates, and residual risk.1 However, this process can be problematic, as the data frequently used in updating guidelines and recommendations come primarily from studies and databases where much of the cohort is White.5,6 Failing to identify genetic associations in diverse populations limits the ability to illuminate new discoveries that inform risk management and treatment, especially for populations that are disproportionately underserved in medicine.7
Need for expanded carrier screening
The evolution of genomics and technology within the realm of carrier screening has enabled the simultaneous screening for many serious Mendelian diseases, known as expanded carrier screening (ECS). A 2016 study illustrated that, in most racial/ethnic categories, the cumulative risk of severe and profound conditions found on ECS panels outside the guideline recommendations are greater than the risk identified by guideline-based panels.8 Additionally, a 2020 study showed that self-reported ethnicity was an imperfect indicator of genetic ancestry, with 9% of those in the cohort having a >50% genetic ancestry from a lineage inconsistent with their self-reported ethnicity.9 Data over the past decade have established the clinical utility,10 clinical validity,11 analytical validity,12 and cost-effectiveness13 of pan-ethnic ECS. In 2021, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) recommended a panel of pan-ethnic conditions that should be offered to all patients due to smaller ethnicity-based panels failing to provide equitable evaluation of all racial and ethnic groups.14 The guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) fall short of recommending that ECS be offered to all individuals in lieu of screening based on self-reported ethnicity.3,4
Phasing out ethnicity-based carrier screening
This begs the question: Do race, ethnicity, or ancestry have a role in carrier screening? While each may have had a role at the inception of offering carrier screening due to high costs of technology, recent studies have shown the limitations of using self-reported ethnicity in screening. Guideline-based carrier screenings miss a significant percentage of pregnancies (13% to 94%) affected by serious conditions on expanded carrier screening panels.8 Additionally, 40% of Americans cannot identify the ethnicity of all 4 grandparents.15
Founder mutations due to ancestry patterns are still present; however, stratification of care should only be pursued when the presence or absence of these markers would alter clinical management. While the reproductive risk an individual may receive varies based on their self-reported ethnicity, the clinically indicated follow-up testing is the same: offering carrier screening for the reproductive partner or gamete donor. With increased detection rates via sequencing for most autosomal recessive conditions, if the reproductive partner or gamete donor is not identified as a carrier, no further testing is generally indicated regardless of ancestry. Genotyping platforms should not be used for partner carrier screening as they primarily target common pathogenic variants based on dominant ancestry groups and do not provide the same risk reduction.
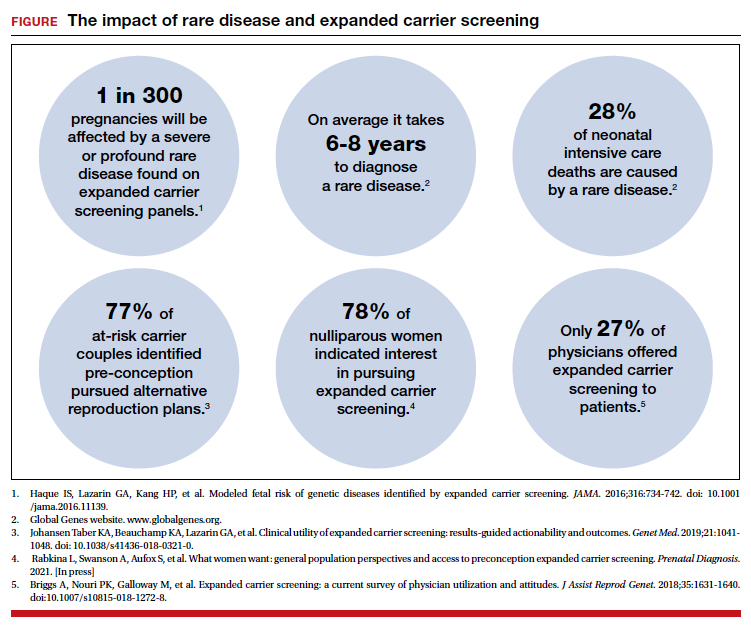
Continue to: Variant reporting...
Variant reporting
We have long known that databases and registries in the United States have an increased representation of individuals from European ancestries.5,6 However, there have been limited conversations about how the lack of representation within our databases and registries leads to inequities in guidelines and the care that we provide to patients. As a result, studies have shown higher rates of variants of uncertain significance (VUS) identified during genetic testing in non-White individuals than in Whites.16 When it comes to reporting of variants, carrier screening laboratories follow guidelines set forth by the ACMG, and most laboratories only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants.17 It is unknown how the higher rate of VUSs in the non-White population, and lack of data and representation in databases and software used to calculate predicted phenotype, impacts identification of at-risk carrier couples in these underrepresented populations. It is imperative that we increase knowledge and representation of variants across ethnicities to improve sensitivity and specificity across the population and not just for those of European descent.
Moving forward
Being aware of social- and race-based biases in carrier screening is important, but modifying structural systems to increase representation, access, and utility of carrier screening is a critical next step. Organizations like ACOG and ACMG have committed not only to understanding but also to addressing factors that have led to disparities and inequities in health care delivery and access.18,19 Actionable steps include offering a universal carrier screening program to all preconception and prenatal patients that addresses conditions with increased carrier frequency, in any population, defined as severe and moderate phenotype with established natural history.3,4 Educational materials should be provided to detail risks, benefits, and limitations of carrier screening, as well as shared decision making between patient and provider to align the patient’s wishes for the information provided by carrier screening.
A broader number of conditions offered through carrier screening will increase the likelihood of positive carrier results. The increase in carriers identified should be viewed as more accurate reproductive risk assessment in the context of equitable care, rather than justification for panels to be limited to specific ancestries. Simultaneous or tandem reproductive partner or donor testing can be considered to reduce clinical workload and time for results return.
In addition, increased representation of individuals who are from diverse ancestries in promotional and educational resources can reinforce that risk for Mendelian conditions is not specific to single ancestries or for targeted conditions. Future research should be conducted to examine the role of racial disparities related to carrier screening and greater inclusion and recruitment of diverse populations in data sets and research studies.
Learned biases toward race, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, and economic status in the context of carrier screening should be examined and challenged to increase access for all patients who may benefit from this testing. For example, the use of gendered language within carrier screening guidelines and policies and how such screening is offered to patients should be examined. Guidelines do not specify what to do when someone is adopted, for instance, or does not know their ethnicity. It is important that, as genomic testing becomes more available, individuals and groups are not left behind and existing gaps are not further widened. Assessing for genetic variation that modifies for disease or treatment will be more powerful than stratifying based on race. Carrier screening panels should be comprehensive regardless of ancestry to ensure coverage for global genetic variation and to increase access for all patients to risk assessments that promote informed reproductive decision making.
Health equity requires unlearning certain behaviors
As clinicians we all have a commitment to educate and empower one another to offer care that helps promote health equity. Equitable care requires us to look at the current gaps and figure out what programs and initiatives need to be designed to address those gaps. Carrier screening is one such area in which we can work together to improve the overall care that our patients receive, but it is imperative that we examine our practices and unlearn behaviors that contribute to existing disparities. ●
- Edwards JG, Feldman G, Goldberg J, et al. Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicine—points to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, National Society of Genetic Counselors, Perinatal Quality Foundation, and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:653-662. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000000666.
- Grody WW, Thompson BH, Gregg AR, et al. ACMG position statement on prenatal/preconception expanded carrier screening. Genet Med. 2013;15:482-483. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.47.
- Committee Opinion No. 690. Summary: carrier screening in the age of genomic medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129: 595-596. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001947.
- Committee Opinion No. 691. Carrier screening for genetic conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129:e41-e55. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000001952.
- Need AC, Goldstein DB. Next generation disparities in human genomics: concerns and remedies. Trends Genet. 2009;25:489-494. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.09.012.
- Popejoy A, Fullerton S. Genomics is failing on diversity. Nature. 2016;538;161-164. doi: 10.1038/538161a.
- Ewing A. Reimagining health equity in genetic testing. Medpage Today. June 17, 2021. https://www.medpagetoday.com /opinion/second-opinions/93173. Accessed October 27, 2021.
- Haque IS, Lazarin GA, Kang HP, et al. Modeled fetal risk of genetic diseases identified by expanded carrier screening. JAMA. 2016;316:734-742. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.11139.
- Kaseniit KE, Haque IS, Goldberg JD, et al. Genetic ancestry analysis on >93,000 individuals undergoing expanded carrier screening reveals limitations of ethnicity-based medical guidelines. Genet Med. 2020;22:1694-1702. doi: 10 .1038/s41436-020-0869-3.
- Johansen Taber KA, Beauchamp KA, Lazarin GA, et al. Clinical utility of expanded carrier screening: results-guided actionability and outcomes. Genet Med. 2019;21:1041-1048. doi: 10.1038/s41436-018-0321-0.
- Balzotti M, Meng L, Muzzey D, et al. Clinical validity of expanded carrier screening: Evaluating the gene-disease relationship in more than 200 conditions. Hum Mutat. 2020;41:1365-1371. doi: 10.1002/humu.24033.
- Hogan GJ, Vysotskaia VS, Beauchamp KA, et al. Validation of an expanded carrier screen that optimizes sensitivity via full-exon sequencing and panel-wide copy number variant identification. Clin Chem. 2018;64:1063-1073. doi: 10.1373 /clinchem.2018.286823.
- Beauchamp KA, Johansen Taber KA, Muzzey D. Clinical impact and cost-effectiveness of a 176-condition expanded carrier screen. Genet Med. 2019;21:1948-1957. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0455-8.
- Gregg AR, Aarabi M, Klugman S, et al. Screening for autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions during pregnancy and preconception: a practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. 2021;23:1793-1806. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01203-z.
- Condit C, Templeton A, Bates BR, et al. Attitudinal barriers to delivery of race-targeted pharmacogenomics among informed lay persons. Genet Med. 2003;5:385-392. doi: 10 .1097/01.gim.0000087990.30961.72.
- Caswell-Jin J, Gupta T, Hall E, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in multiple-gene sequencing results for hereditary cancer risk. Genet Med. 2018;20:234-239.
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405-424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30.
- Gregg AR. Message from ACMG President: overcoming disparities. Genet Med. 2020;22:1758.
The social reckoning of 2020 has led to many discussions and conversations around equity and disparities. With the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a particular spotlight on health care disparities and race-based medicine. Racism in medicine is pervasive; little has been done over the years to dismantle and unlearn practices that continue to contribute to existing gaps and disparities. Race and ethnicity are both social constructs that have long been used within medical practice and in dictating the type of care an individual receives. Without a universal definition, race, ethnicity, and ancestry have long been used interchangeably within medicine and society. Appreciating that race and ethnicity-based constructs can have other social implications in health care, with their impact on structural racism beyond health care settings, these constructs may still be part of assessments and key modifiers to understanding health differences. It is imperative that medical providers examine the use of race and ethnicity within the care that they provide.
While racial determinants of health cannot be removed from historical access, utilization, and barriers related to reproductive care, guidelines structured around historical ethnicity and race further restrict universal access to carrier screening and informed reproductive testing decisions.
Carrier screening
The goal of preconception and prenatal carrier screening is to provide individuals and reproductive partners with information to optimize pregnancy outcomes based on personal values and preferences.1 The practice of carrier screening began almost half a century ago with screening for individual conditions seen more frequently in certain populations, such as Tay-Sachs disease in those of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and sickle cell disease in those of African descent. Cystic fibrosis carrier screening was first recommended for individuals of Northern European descent in 2001 before being recommended for pan ethnic screening a decade later. Other individual conditions are also recommended for screening based on race/ethnicity (eg, Canavan disease in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, Tay-Sachs disease in individuals of Cajun or French-Canadian descent).2-4 Practice guidelines from professional societies recommend offering carrier screening for individual conditions based on condition severity, race or ethnicity, prevalence, carrier frequency, detection rates, and residual risk.1 However, this process can be problematic, as the data frequently used in updating guidelines and recommendations come primarily from studies and databases where much of the cohort is White.5,6 Failing to identify genetic associations in diverse populations limits the ability to illuminate new discoveries that inform risk management and treatment, especially for populations that are disproportionately underserved in medicine.7
Need for expanded carrier screening
The evolution of genomics and technology within the realm of carrier screening has enabled the simultaneous screening for many serious Mendelian diseases, known as expanded carrier screening (ECS). A 2016 study illustrated that, in most racial/ethnic categories, the cumulative risk of severe and profound conditions found on ECS panels outside the guideline recommendations are greater than the risk identified by guideline-based panels.8 Additionally, a 2020 study showed that self-reported ethnicity was an imperfect indicator of genetic ancestry, with 9% of those in the cohort having a >50% genetic ancestry from a lineage inconsistent with their self-reported ethnicity.9 Data over the past decade have established the clinical utility,10 clinical validity,11 analytical validity,12 and cost-effectiveness13 of pan-ethnic ECS. In 2021, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) recommended a panel of pan-ethnic conditions that should be offered to all patients due to smaller ethnicity-based panels failing to provide equitable evaluation of all racial and ethnic groups.14 The guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) fall short of recommending that ECS be offered to all individuals in lieu of screening based on self-reported ethnicity.3,4
Phasing out ethnicity-based carrier screening
This begs the question: Do race, ethnicity, or ancestry have a role in carrier screening? While each may have had a role at the inception of offering carrier screening due to high costs of technology, recent studies have shown the limitations of using self-reported ethnicity in screening. Guideline-based carrier screenings miss a significant percentage of pregnancies (13% to 94%) affected by serious conditions on expanded carrier screening panels.8 Additionally, 40% of Americans cannot identify the ethnicity of all 4 grandparents.15
Founder mutations due to ancestry patterns are still present; however, stratification of care should only be pursued when the presence or absence of these markers would alter clinical management. While the reproductive risk an individual may receive varies based on their self-reported ethnicity, the clinically indicated follow-up testing is the same: offering carrier screening for the reproductive partner or gamete donor. With increased detection rates via sequencing for most autosomal recessive conditions, if the reproductive partner or gamete donor is not identified as a carrier, no further testing is generally indicated regardless of ancestry. Genotyping platforms should not be used for partner carrier screening as they primarily target common pathogenic variants based on dominant ancestry groups and do not provide the same risk reduction.

Continue to: Variant reporting...
Variant reporting
We have long known that databases and registries in the United States have an increased representation of individuals from European ancestries.5,6 However, there have been limited conversations about how the lack of representation within our databases and registries leads to inequities in guidelines and the care that we provide to patients. As a result, studies have shown higher rates of variants of uncertain significance (VUS) identified during genetic testing in non-White individuals than in Whites.16 When it comes to reporting of variants, carrier screening laboratories follow guidelines set forth by the ACMG, and most laboratories only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants.17 It is unknown how the higher rate of VUSs in the non-White population, and lack of data and representation in databases and software used to calculate predicted phenotype, impacts identification of at-risk carrier couples in these underrepresented populations. It is imperative that we increase knowledge and representation of variants across ethnicities to improve sensitivity and specificity across the population and not just for those of European descent.
Moving forward
Being aware of social- and race-based biases in carrier screening is important, but modifying structural systems to increase representation, access, and utility of carrier screening is a critical next step. Organizations like ACOG and ACMG have committed not only to understanding but also to addressing factors that have led to disparities and inequities in health care delivery and access.18,19 Actionable steps include offering a universal carrier screening program to all preconception and prenatal patients that addresses conditions with increased carrier frequency, in any population, defined as severe and moderate phenotype with established natural history.3,4 Educational materials should be provided to detail risks, benefits, and limitations of carrier screening, as well as shared decision making between patient and provider to align the patient’s wishes for the information provided by carrier screening.
A broader number of conditions offered through carrier screening will increase the likelihood of positive carrier results. The increase in carriers identified should be viewed as more accurate reproductive risk assessment in the context of equitable care, rather than justification for panels to be limited to specific ancestries. Simultaneous or tandem reproductive partner or donor testing can be considered to reduce clinical workload and time for results return.
In addition, increased representation of individuals who are from diverse ancestries in promotional and educational resources can reinforce that risk for Mendelian conditions is not specific to single ancestries or for targeted conditions. Future research should be conducted to examine the role of racial disparities related to carrier screening and greater inclusion and recruitment of diverse populations in data sets and research studies.
Learned biases toward race, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, and economic status in the context of carrier screening should be examined and challenged to increase access for all patients who may benefit from this testing. For example, the use of gendered language within carrier screening guidelines and policies and how such screening is offered to patients should be examined. Guidelines do not specify what to do when someone is adopted, for instance, or does not know their ethnicity. It is important that, as genomic testing becomes more available, individuals and groups are not left behind and existing gaps are not further widened. Assessing for genetic variation that modifies for disease or treatment will be more powerful than stratifying based on race. Carrier screening panels should be comprehensive regardless of ancestry to ensure coverage for global genetic variation and to increase access for all patients to risk assessments that promote informed reproductive decision making.
Health equity requires unlearning certain behaviors
As clinicians we all have a commitment to educate and empower one another to offer care that helps promote health equity. Equitable care requires us to look at the current gaps and figure out what programs and initiatives need to be designed to address those gaps. Carrier screening is one such area in which we can work together to improve the overall care that our patients receive, but it is imperative that we examine our practices and unlearn behaviors that contribute to existing disparities. ●
The social reckoning of 2020 has led to many discussions and conversations around equity and disparities. With the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a particular spotlight on health care disparities and race-based medicine. Racism in medicine is pervasive; little has been done over the years to dismantle and unlearn practices that continue to contribute to existing gaps and disparities. Race and ethnicity are both social constructs that have long been used within medical practice and in dictating the type of care an individual receives. Without a universal definition, race, ethnicity, and ancestry have long been used interchangeably within medicine and society. Appreciating that race and ethnicity-based constructs can have other social implications in health care, with their impact on structural racism beyond health care settings, these constructs may still be part of assessments and key modifiers to understanding health differences. It is imperative that medical providers examine the use of race and ethnicity within the care that they provide.
While racial determinants of health cannot be removed from historical access, utilization, and barriers related to reproductive care, guidelines structured around historical ethnicity and race further restrict universal access to carrier screening and informed reproductive testing decisions.
Carrier screening
The goal of preconception and prenatal carrier screening is to provide individuals and reproductive partners with information to optimize pregnancy outcomes based on personal values and preferences.1 The practice of carrier screening began almost half a century ago with screening for individual conditions seen more frequently in certain populations, such as Tay-Sachs disease in those of Ashkenazi Jewish descent and sickle cell disease in those of African descent. Cystic fibrosis carrier screening was first recommended for individuals of Northern European descent in 2001 before being recommended for pan ethnic screening a decade later. Other individual conditions are also recommended for screening based on race/ethnicity (eg, Canavan disease in the Ashkenazi Jewish population, Tay-Sachs disease in individuals of Cajun or French-Canadian descent).2-4 Practice guidelines from professional societies recommend offering carrier screening for individual conditions based on condition severity, race or ethnicity, prevalence, carrier frequency, detection rates, and residual risk.1 However, this process can be problematic, as the data frequently used in updating guidelines and recommendations come primarily from studies and databases where much of the cohort is White.5,6 Failing to identify genetic associations in diverse populations limits the ability to illuminate new discoveries that inform risk management and treatment, especially for populations that are disproportionately underserved in medicine.7
Need for expanded carrier screening
The evolution of genomics and technology within the realm of carrier screening has enabled the simultaneous screening for many serious Mendelian diseases, known as expanded carrier screening (ECS). A 2016 study illustrated that, in most racial/ethnic categories, the cumulative risk of severe and profound conditions found on ECS panels outside the guideline recommendations are greater than the risk identified by guideline-based panels.8 Additionally, a 2020 study showed that self-reported ethnicity was an imperfect indicator of genetic ancestry, with 9% of those in the cohort having a >50% genetic ancestry from a lineage inconsistent with their self-reported ethnicity.9 Data over the past decade have established the clinical utility,10 clinical validity,11 analytical validity,12 and cost-effectiveness13 of pan-ethnic ECS. In 2021, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) recommended a panel of pan-ethnic conditions that should be offered to all patients due to smaller ethnicity-based panels failing to provide equitable evaluation of all racial and ethnic groups.14 The guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) fall short of recommending that ECS be offered to all individuals in lieu of screening based on self-reported ethnicity.3,4
Phasing out ethnicity-based carrier screening
This begs the question: Do race, ethnicity, or ancestry have a role in carrier screening? While each may have had a role at the inception of offering carrier screening due to high costs of technology, recent studies have shown the limitations of using self-reported ethnicity in screening. Guideline-based carrier screenings miss a significant percentage of pregnancies (13% to 94%) affected by serious conditions on expanded carrier screening panels.8 Additionally, 40% of Americans cannot identify the ethnicity of all 4 grandparents.15
Founder mutations due to ancestry patterns are still present; however, stratification of care should only be pursued when the presence or absence of these markers would alter clinical management. While the reproductive risk an individual may receive varies based on their self-reported ethnicity, the clinically indicated follow-up testing is the same: offering carrier screening for the reproductive partner or gamete donor. With increased detection rates via sequencing for most autosomal recessive conditions, if the reproductive partner or gamete donor is not identified as a carrier, no further testing is generally indicated regardless of ancestry. Genotyping platforms should not be used for partner carrier screening as they primarily target common pathogenic variants based on dominant ancestry groups and do not provide the same risk reduction.

Continue to: Variant reporting...
Variant reporting
We have long known that databases and registries in the United States have an increased representation of individuals from European ancestries.5,6 However, there have been limited conversations about how the lack of representation within our databases and registries leads to inequities in guidelines and the care that we provide to patients. As a result, studies have shown higher rates of variants of uncertain significance (VUS) identified during genetic testing in non-White individuals than in Whites.16 When it comes to reporting of variants, carrier screening laboratories follow guidelines set forth by the ACMG, and most laboratories only report likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants.17 It is unknown how the higher rate of VUSs in the non-White population, and lack of data and representation in databases and software used to calculate predicted phenotype, impacts identification of at-risk carrier couples in these underrepresented populations. It is imperative that we increase knowledge and representation of variants across ethnicities to improve sensitivity and specificity across the population and not just for those of European descent.
Moving forward
Being aware of social- and race-based biases in carrier screening is important, but modifying structural systems to increase representation, access, and utility of carrier screening is a critical next step. Organizations like ACOG and ACMG have committed not only to understanding but also to addressing factors that have led to disparities and inequities in health care delivery and access.18,19 Actionable steps include offering a universal carrier screening program to all preconception and prenatal patients that addresses conditions with increased carrier frequency, in any population, defined as severe and moderate phenotype with established natural history.3,4 Educational materials should be provided to detail risks, benefits, and limitations of carrier screening, as well as shared decision making between patient and provider to align the patient’s wishes for the information provided by carrier screening.
A broader number of conditions offered through carrier screening will increase the likelihood of positive carrier results. The increase in carriers identified should be viewed as more accurate reproductive risk assessment in the context of equitable care, rather than justification for panels to be limited to specific ancestries. Simultaneous or tandem reproductive partner or donor testing can be considered to reduce clinical workload and time for results return.
In addition, increased representation of individuals who are from diverse ancestries in promotional and educational resources can reinforce that risk for Mendelian conditions is not specific to single ancestries or for targeted conditions. Future research should be conducted to examine the role of racial disparities related to carrier screening and greater inclusion and recruitment of diverse populations in data sets and research studies.
Learned biases toward race, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, and economic status in the context of carrier screening should be examined and challenged to increase access for all patients who may benefit from this testing. For example, the use of gendered language within carrier screening guidelines and policies and how such screening is offered to patients should be examined. Guidelines do not specify what to do when someone is adopted, for instance, or does not know their ethnicity. It is important that, as genomic testing becomes more available, individuals and groups are not left behind and existing gaps are not further widened. Assessing for genetic variation that modifies for disease or treatment will be more powerful than stratifying based on race. Carrier screening panels should be comprehensive regardless of ancestry to ensure coverage for global genetic variation and to increase access for all patients to risk assessments that promote informed reproductive decision making.
Health equity requires unlearning certain behaviors
As clinicians we all have a commitment to educate and empower one another to offer care that helps promote health equity. Equitable care requires us to look at the current gaps and figure out what programs and initiatives need to be designed to address those gaps. Carrier screening is one such area in which we can work together to improve the overall care that our patients receive, but it is imperative that we examine our practices and unlearn behaviors that contribute to existing disparities. ●
- Edwards JG, Feldman G, Goldberg J, et al. Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicine—points to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, National Society of Genetic Counselors, Perinatal Quality Foundation, and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:653-662. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000000666.
- Grody WW, Thompson BH, Gregg AR, et al. ACMG position statement on prenatal/preconception expanded carrier screening. Genet Med. 2013;15:482-483. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.47.
- Committee Opinion No. 690. Summary: carrier screening in the age of genomic medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129: 595-596. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001947.
- Committee Opinion No. 691. Carrier screening for genetic conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129:e41-e55. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000001952.
- Need AC, Goldstein DB. Next generation disparities in human genomics: concerns and remedies. Trends Genet. 2009;25:489-494. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.09.012.
- Popejoy A, Fullerton S. Genomics is failing on diversity. Nature. 2016;538;161-164. doi: 10.1038/538161a.
- Ewing A. Reimagining health equity in genetic testing. Medpage Today. June 17, 2021. https://www.medpagetoday.com /opinion/second-opinions/93173. Accessed October 27, 2021.
- Haque IS, Lazarin GA, Kang HP, et al. Modeled fetal risk of genetic diseases identified by expanded carrier screening. JAMA. 2016;316:734-742. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.11139.
- Kaseniit KE, Haque IS, Goldberg JD, et al. Genetic ancestry analysis on >93,000 individuals undergoing expanded carrier screening reveals limitations of ethnicity-based medical guidelines. Genet Med. 2020;22:1694-1702. doi: 10 .1038/s41436-020-0869-3.
- Johansen Taber KA, Beauchamp KA, Lazarin GA, et al. Clinical utility of expanded carrier screening: results-guided actionability and outcomes. Genet Med. 2019;21:1041-1048. doi: 10.1038/s41436-018-0321-0.
- Balzotti M, Meng L, Muzzey D, et al. Clinical validity of expanded carrier screening: Evaluating the gene-disease relationship in more than 200 conditions. Hum Mutat. 2020;41:1365-1371. doi: 10.1002/humu.24033.
- Hogan GJ, Vysotskaia VS, Beauchamp KA, et al. Validation of an expanded carrier screen that optimizes sensitivity via full-exon sequencing and panel-wide copy number variant identification. Clin Chem. 2018;64:1063-1073. doi: 10.1373 /clinchem.2018.286823.
- Beauchamp KA, Johansen Taber KA, Muzzey D. Clinical impact and cost-effectiveness of a 176-condition expanded carrier screen. Genet Med. 2019;21:1948-1957. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0455-8.
- Gregg AR, Aarabi M, Klugman S, et al. Screening for autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions during pregnancy and preconception: a practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. 2021;23:1793-1806. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01203-z.
- Condit C, Templeton A, Bates BR, et al. Attitudinal barriers to delivery of race-targeted pharmacogenomics among informed lay persons. Genet Med. 2003;5:385-392. doi: 10 .1097/01.gim.0000087990.30961.72.
- Caswell-Jin J, Gupta T, Hall E, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in multiple-gene sequencing results for hereditary cancer risk. Genet Med. 2018;20:234-239.
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405-424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30.
- Gregg AR. Message from ACMG President: overcoming disparities. Genet Med. 2020;22:1758.
- Edwards JG, Feldman G, Goldberg J, et al. Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicine—points to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, National Society of Genetic Counselors, Perinatal Quality Foundation, and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:653-662. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000000666.
- Grody WW, Thompson BH, Gregg AR, et al. ACMG position statement on prenatal/preconception expanded carrier screening. Genet Med. 2013;15:482-483. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.47.
- Committee Opinion No. 690. Summary: carrier screening in the age of genomic medicine. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129: 595-596. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001947.
- Committee Opinion No. 691. Carrier screening for genetic conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129:e41-e55. doi: 10.1097 /AOG.0000000000001952.
- Need AC, Goldstein DB. Next generation disparities in human genomics: concerns and remedies. Trends Genet. 2009;25:489-494. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.09.012.
- Popejoy A, Fullerton S. Genomics is failing on diversity. Nature. 2016;538;161-164. doi: 10.1038/538161a.
- Ewing A. Reimagining health equity in genetic testing. Medpage Today. June 17, 2021. https://www.medpagetoday.com /opinion/second-opinions/93173. Accessed October 27, 2021.
- Haque IS, Lazarin GA, Kang HP, et al. Modeled fetal risk of genetic diseases identified by expanded carrier screening. JAMA. 2016;316:734-742. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.11139.
- Kaseniit KE, Haque IS, Goldberg JD, et al. Genetic ancestry analysis on >93,000 individuals undergoing expanded carrier screening reveals limitations of ethnicity-based medical guidelines. Genet Med. 2020;22:1694-1702. doi: 10 .1038/s41436-020-0869-3.
- Johansen Taber KA, Beauchamp KA, Lazarin GA, et al. Clinical utility of expanded carrier screening: results-guided actionability and outcomes. Genet Med. 2019;21:1041-1048. doi: 10.1038/s41436-018-0321-0.
- Balzotti M, Meng L, Muzzey D, et al. Clinical validity of expanded carrier screening: Evaluating the gene-disease relationship in more than 200 conditions. Hum Mutat. 2020;41:1365-1371. doi: 10.1002/humu.24033.
- Hogan GJ, Vysotskaia VS, Beauchamp KA, et al. Validation of an expanded carrier screen that optimizes sensitivity via full-exon sequencing and panel-wide copy number variant identification. Clin Chem. 2018;64:1063-1073. doi: 10.1373 /clinchem.2018.286823.
- Beauchamp KA, Johansen Taber KA, Muzzey D. Clinical impact and cost-effectiveness of a 176-condition expanded carrier screen. Genet Med. 2019;21:1948-1957. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0455-8.
- Gregg AR, Aarabi M, Klugman S, et al. Screening for autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions during pregnancy and preconception: a practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med. 2021;23:1793-1806. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01203-z.
- Condit C, Templeton A, Bates BR, et al. Attitudinal barriers to delivery of race-targeted pharmacogenomics among informed lay persons. Genet Med. 2003;5:385-392. doi: 10 .1097/01.gim.0000087990.30961.72.
- Caswell-Jin J, Gupta T, Hall E, et al. Racial/ethnic differences in multiple-gene sequencing results for hereditary cancer risk. Genet Med. 2018;20:234-239.
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405-424. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.30.
- Gregg AR. Message from ACMG President: overcoming disparities. Genet Med. 2020;22:1758.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual youth miss out on health care
Youth identifying as lesbian, gay, or bisexual were significantly less likely than were their peers to communicate with a physician or utilize health care in the past 12 months, according to data from a cohort study of approximately 4,000 adolescents.
Disparities in physical and mental health outcomes for individuals who identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) persist in the United States, and emerge in adolescents and young adults, wrote Sari L. Reisner, ScD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues.
“LGB adult research indicates substantial unmet medical needs, including needed care and preventive care,” for reasons including “reluctance to disclose sexual identity to clinicians, lower health insurance rates, lack of culturally appropriate preventive services, and lack of clinician LGB care competence,” they said.
However, health use trends by adolescents who identify as LGB have not been well studied, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 4,256 participants in the third wave (10th grade) of adolescents in Healthy Passages, a longitudinal, observational cohort study of diverse public school students in Birmingham, Ala.; Houston; and Los Angeles County. Data were collected in grades 5, 7, and 10.
The study population included 640 youth who identified as LGB, and 3,616 non-LGB youth. Sexual status was based on responses to questions in the grade 10 youth survey. Health care use was based on the responses to questions about routine care, such as a regular checkup, and other care, such as a sick visit. Data on delayed care were collected from parents and youth. At baseline, the average age of the study participants in fifth grade was 11 years, 48.9% were female, 44.5% were Hispanic or Latino, and 28.9% were Black.
Overall, more LGB youth reported not receiving needed medical care when they thought they needed it within the past 12 months compared with non-LGB youth (42.4% of LGB vs. 30.2% of non-LGB youth; adjusted odds ratio 1.68). The most common conditions for which LGB youth did not seek care were sexually transmitted infections, contraception, and substance use.
Overall, the main reason given for not seeking medical care was that they thought the problem would go away (approximately 26% for LGB and non-LGB). Approximately twice as many LGB youth as non-LGB youth said they avoided medical care because they did not want their parents to know (14.5% vs. 9.4%).
Significantly more LGB youth than non-LGB youth reported difficulty communicating with their physicians in the past 12 months (15.3% vs. 9.4%; aOR 1.71). The main reasons for not communicating with a clinician about a topic of concern were that the adolescent did not want parents to know (40.7% of LGB and 30.2% of non-LGB) and that they were too embarrassed to talk about the topic (37.5% of LGB and 25.9% of non-LGB).
The researchers were not surprised that “LGB youth self-reported greater difficulty communicating with a clinician about topics they wanted to discuss,” but they found no significant differences in reasons for communication difficulty based on sexual orientation.
Approximately two-thirds (65.8%) of LGB youth reported feeling “a little or not at all comfortable” talking to a health care clinician about their sexual attractions, compared with approximately one-third (37.8%) of non-LGB youth.
Only 12.5% of the LGB youth said that their clinicians knew their sexual orientation, the researchers noted. However, clinicians need to know youths’ sexual orientation to provide appropriate and comprehensive care, they said, especially in light of the known negative health consequences of LGB internalized stigma, as well as the pertinence of certain sexual behaviors to preventive care and screening.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design and inability to show causality, and by the incongruence of different dimensions of sexual orientation, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use only of English and Spanish language, and a lack of complete information on disclosure of sexual orientation to parents, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the diverse demographics, although they may not be generalizable to a wider population, they added.
However, the data show that responsive health care is needed to reduce disparities for LGB youth, they emphasized. “Care should be sensitive and respectful to sexual orientation for all youth, with clinicians taking time to ask adolescents about their sexual identity, attractions, and behaviors, particularly in sexual and reproductive health,” they concluded.
Adolescents suffer barriers similar to those of adults
“We know that significant health disparities exist for LGBTQ adults and adolescents,” Kelly Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “LGBTQ adults often have had poor experiences during health care encounters – ranging from poor interactions with inadequately trained clinicians to frank discrimination,” she said. “These experiences can prevent individuals from seeking health care in the future or disclosing important information during a medical visit, both of which can contribute to worsened health outcomes,” she emphasized.
Prior to this study, data to confirm similar patterns of decreased health care utilization in LGB youth were limited, Dr. Curran said. “Identifying and understanding barriers to health care for LGBTQ youth are essential to help address the disparities in this population,” she said.
Dr. Curran said she was not surprised by the study findings for adolescents, which reflect patterns seen in LGBTQ adults.
Overcoming barriers to encourage LGB youth to seek regular medical care involves “training health care professionals about LGBTQ health, teaching the skill of taking a nonjudgmental, inclusive history, and making health care facilities welcoming and inclusive, such as displaying a pride flag in clinic, and using forms asking for pronouns,” Dr. Curran said.
Dr. Curran said she thinks the trends in decreased health care use are similar for transgender youth. “I suspect, if anything, that transgender youth will have even further decreased health care utilization when compared to cisgender heterosexual peers and LGB peers,” she noted.
Going forward, it will be important to understand the reasons behind decreased health care use among LGB youth, such as poor experiences, discrimination, or fears about confidentiality, said Dr. Curran. “Additionally, it would be important to understand if this decreased health utilization also occurs with transgender youth,” she said.
The Healthy Passages Study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. One of the study coauthors disclosed funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality as part of the Harvard-wide Pediatric Health Services Research Fellowship Program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Youth identifying as lesbian, gay, or bisexual were significantly less likely than were their peers to communicate with a physician or utilize health care in the past 12 months, according to data from a cohort study of approximately 4,000 adolescents.
Disparities in physical and mental health outcomes for individuals who identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) persist in the United States, and emerge in adolescents and young adults, wrote Sari L. Reisner, ScD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues.
“LGB adult research indicates substantial unmet medical needs, including needed care and preventive care,” for reasons including “reluctance to disclose sexual identity to clinicians, lower health insurance rates, lack of culturally appropriate preventive services, and lack of clinician LGB care competence,” they said.
However, health use trends by adolescents who identify as LGB have not been well studied, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 4,256 participants in the third wave (10th grade) of adolescents in Healthy Passages, a longitudinal, observational cohort study of diverse public school students in Birmingham, Ala.; Houston; and Los Angeles County. Data were collected in grades 5, 7, and 10.
The study population included 640 youth who identified as LGB, and 3,616 non-LGB youth. Sexual status was based on responses to questions in the grade 10 youth survey. Health care use was based on the responses to questions about routine care, such as a regular checkup, and other care, such as a sick visit. Data on delayed care were collected from parents and youth. At baseline, the average age of the study participants in fifth grade was 11 years, 48.9% were female, 44.5% were Hispanic or Latino, and 28.9% were Black.
Overall, more LGB youth reported not receiving needed medical care when they thought they needed it within the past 12 months compared with non-LGB youth (42.4% of LGB vs. 30.2% of non-LGB youth; adjusted odds ratio 1.68). The most common conditions for which LGB youth did not seek care were sexually transmitted infections, contraception, and substance use.
Overall, the main reason given for not seeking medical care was that they thought the problem would go away (approximately 26% for LGB and non-LGB). Approximately twice as many LGB youth as non-LGB youth said they avoided medical care because they did not want their parents to know (14.5% vs. 9.4%).
Significantly more LGB youth than non-LGB youth reported difficulty communicating with their physicians in the past 12 months (15.3% vs. 9.4%; aOR 1.71). The main reasons for not communicating with a clinician about a topic of concern were that the adolescent did not want parents to know (40.7% of LGB and 30.2% of non-LGB) and that they were too embarrassed to talk about the topic (37.5% of LGB and 25.9% of non-LGB).
The researchers were not surprised that “LGB youth self-reported greater difficulty communicating with a clinician about topics they wanted to discuss,” but they found no significant differences in reasons for communication difficulty based on sexual orientation.
Approximately two-thirds (65.8%) of LGB youth reported feeling “a little or not at all comfortable” talking to a health care clinician about their sexual attractions, compared with approximately one-third (37.8%) of non-LGB youth.
Only 12.5% of the LGB youth said that their clinicians knew their sexual orientation, the researchers noted. However, clinicians need to know youths’ sexual orientation to provide appropriate and comprehensive care, they said, especially in light of the known negative health consequences of LGB internalized stigma, as well as the pertinence of certain sexual behaviors to preventive care and screening.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design and inability to show causality, and by the incongruence of different dimensions of sexual orientation, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use only of English and Spanish language, and a lack of complete information on disclosure of sexual orientation to parents, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the diverse demographics, although they may not be generalizable to a wider population, they added.
However, the data show that responsive health care is needed to reduce disparities for LGB youth, they emphasized. “Care should be sensitive and respectful to sexual orientation for all youth, with clinicians taking time to ask adolescents about their sexual identity, attractions, and behaviors, particularly in sexual and reproductive health,” they concluded.
Adolescents suffer barriers similar to those of adults
“We know that significant health disparities exist for LGBTQ adults and adolescents,” Kelly Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “LGBTQ adults often have had poor experiences during health care encounters – ranging from poor interactions with inadequately trained clinicians to frank discrimination,” she said. “These experiences can prevent individuals from seeking health care in the future or disclosing important information during a medical visit, both of which can contribute to worsened health outcomes,” she emphasized.
Prior to this study, data to confirm similar patterns of decreased health care utilization in LGB youth were limited, Dr. Curran said. “Identifying and understanding barriers to health care for LGBTQ youth are essential to help address the disparities in this population,” she said.
Dr. Curran said she was not surprised by the study findings for adolescents, which reflect patterns seen in LGBTQ adults.
Overcoming barriers to encourage LGB youth to seek regular medical care involves “training health care professionals about LGBTQ health, teaching the skill of taking a nonjudgmental, inclusive history, and making health care facilities welcoming and inclusive, such as displaying a pride flag in clinic, and using forms asking for pronouns,” Dr. Curran said.
Dr. Curran said she thinks the trends in decreased health care use are similar for transgender youth. “I suspect, if anything, that transgender youth will have even further decreased health care utilization when compared to cisgender heterosexual peers and LGB peers,” she noted.
Going forward, it will be important to understand the reasons behind decreased health care use among LGB youth, such as poor experiences, discrimination, or fears about confidentiality, said Dr. Curran. “Additionally, it would be important to understand if this decreased health utilization also occurs with transgender youth,” she said.
The Healthy Passages Study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. One of the study coauthors disclosed funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality as part of the Harvard-wide Pediatric Health Services Research Fellowship Program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
Youth identifying as lesbian, gay, or bisexual were significantly less likely than were their peers to communicate with a physician or utilize health care in the past 12 months, according to data from a cohort study of approximately 4,000 adolescents.
Disparities in physical and mental health outcomes for individuals who identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) persist in the United States, and emerge in adolescents and young adults, wrote Sari L. Reisner, ScD, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues.
“LGB adult research indicates substantial unmet medical needs, including needed care and preventive care,” for reasons including “reluctance to disclose sexual identity to clinicians, lower health insurance rates, lack of culturally appropriate preventive services, and lack of clinician LGB care competence,” they said.
However, health use trends by adolescents who identify as LGB have not been well studied, they noted.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers analyzed data from 4,256 participants in the third wave (10th grade) of adolescents in Healthy Passages, a longitudinal, observational cohort study of diverse public school students in Birmingham, Ala.; Houston; and Los Angeles County. Data were collected in grades 5, 7, and 10.
The study population included 640 youth who identified as LGB, and 3,616 non-LGB youth. Sexual status was based on responses to questions in the grade 10 youth survey. Health care use was based on the responses to questions about routine care, such as a regular checkup, and other care, such as a sick visit. Data on delayed care were collected from parents and youth. At baseline, the average age of the study participants in fifth grade was 11 years, 48.9% were female, 44.5% were Hispanic or Latino, and 28.9% were Black.
Overall, more LGB youth reported not receiving needed medical care when they thought they needed it within the past 12 months compared with non-LGB youth (42.4% of LGB vs. 30.2% of non-LGB youth; adjusted odds ratio 1.68). The most common conditions for which LGB youth did not seek care were sexually transmitted infections, contraception, and substance use.
Overall, the main reason given for not seeking medical care was that they thought the problem would go away (approximately 26% for LGB and non-LGB). Approximately twice as many LGB youth as non-LGB youth said they avoided medical care because they did not want their parents to know (14.5% vs. 9.4%).
Significantly more LGB youth than non-LGB youth reported difficulty communicating with their physicians in the past 12 months (15.3% vs. 9.4%; aOR 1.71). The main reasons for not communicating with a clinician about a topic of concern were that the adolescent did not want parents to know (40.7% of LGB and 30.2% of non-LGB) and that they were too embarrassed to talk about the topic (37.5% of LGB and 25.9% of non-LGB).
The researchers were not surprised that “LGB youth self-reported greater difficulty communicating with a clinician about topics they wanted to discuss,” but they found no significant differences in reasons for communication difficulty based on sexual orientation.
Approximately two-thirds (65.8%) of LGB youth reported feeling “a little or not at all comfortable” talking to a health care clinician about their sexual attractions, compared with approximately one-third (37.8%) of non-LGB youth.
Only 12.5% of the LGB youth said that their clinicians knew their sexual orientation, the researchers noted. However, clinicians need to know youths’ sexual orientation to provide appropriate and comprehensive care, they said, especially in light of the known negative health consequences of LGB internalized stigma, as well as the pertinence of certain sexual behaviors to preventive care and screening.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design and inability to show causality, and by the incongruence of different dimensions of sexual orientation, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use only of English and Spanish language, and a lack of complete information on disclosure of sexual orientation to parents, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the diverse demographics, although they may not be generalizable to a wider population, they added.
However, the data show that responsive health care is needed to reduce disparities for LGB youth, they emphasized. “Care should be sensitive and respectful to sexual orientation for all youth, with clinicians taking time to ask adolescents about their sexual identity, attractions, and behaviors, particularly in sexual and reproductive health,” they concluded.
Adolescents suffer barriers similar to those of adults
“We know that significant health disparities exist for LGBTQ adults and adolescents,” Kelly Curran, MD, of the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “LGBTQ adults often have had poor experiences during health care encounters – ranging from poor interactions with inadequately trained clinicians to frank discrimination,” she said. “These experiences can prevent individuals from seeking health care in the future or disclosing important information during a medical visit, both of which can contribute to worsened health outcomes,” she emphasized.
Prior to this study, data to confirm similar patterns of decreased health care utilization in LGB youth were limited, Dr. Curran said. “Identifying and understanding barriers to health care for LGBTQ youth are essential to help address the disparities in this population,” she said.
Dr. Curran said she was not surprised by the study findings for adolescents, which reflect patterns seen in LGBTQ adults.
Overcoming barriers to encourage LGB youth to seek regular medical care involves “training health care professionals about LGBTQ health, teaching the skill of taking a nonjudgmental, inclusive history, and making health care facilities welcoming and inclusive, such as displaying a pride flag in clinic, and using forms asking for pronouns,” Dr. Curran said.
Dr. Curran said she thinks the trends in decreased health care use are similar for transgender youth. “I suspect, if anything, that transgender youth will have even further decreased health care utilization when compared to cisgender heterosexual peers and LGB peers,” she noted.
Going forward, it will be important to understand the reasons behind decreased health care use among LGB youth, such as poor experiences, discrimination, or fears about confidentiality, said Dr. Curran. “Additionally, it would be important to understand if this decreased health utilization also occurs with transgender youth,” she said.
The Healthy Passages Study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. One of the study coauthors disclosed funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality as part of the Harvard-wide Pediatric Health Services Research Fellowship Program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Curran had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Chatbots can improve mental health in vulnerable populations
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.