User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Lung ultrasound works well in children with COVID-19
researchers wrote in Pediatrics.
They also noted the benefits that modality provides over other imaging techniques.
Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy, performed an observational study of eight children aged 0-17 years who were admitted to the hospital for COVID-19 between March 8 and 26, 2020. In seven of eight patients, the findings were concordant between imaging modalities; in the remaining patient, lung ultrasound (LUS) found an interstitial B-lines pattern that was not seen on radiography. In seven patients with pathologic ultrasound findings at baseline, the improvement or resolution of the subpleural consolidations or interstitial patterns was consistent with concomitant radiologic findings.
The authors cited the benefits of using point-of-care ultrasound instead of other modalities, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” they wrote. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, LUS allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].”
One limitation of the study is the small sample size; however, the researchers felt the high concordance still suggests LUS is a reasonable method for COVID-19 patients.
There was no external funding for this study and the investigators had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Denina M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1157.
researchers wrote in Pediatrics.
They also noted the benefits that modality provides over other imaging techniques.
Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy, performed an observational study of eight children aged 0-17 years who were admitted to the hospital for COVID-19 between March 8 and 26, 2020. In seven of eight patients, the findings were concordant between imaging modalities; in the remaining patient, lung ultrasound (LUS) found an interstitial B-lines pattern that was not seen on radiography. In seven patients with pathologic ultrasound findings at baseline, the improvement or resolution of the subpleural consolidations or interstitial patterns was consistent with concomitant radiologic findings.
The authors cited the benefits of using point-of-care ultrasound instead of other modalities, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” they wrote. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, LUS allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].”
One limitation of the study is the small sample size; however, the researchers felt the high concordance still suggests LUS is a reasonable method for COVID-19 patients.
There was no external funding for this study and the investigators had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Denina M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1157.
researchers wrote in Pediatrics.
They also noted the benefits that modality provides over other imaging techniques.
Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy, performed an observational study of eight children aged 0-17 years who were admitted to the hospital for COVID-19 between March 8 and 26, 2020. In seven of eight patients, the findings were concordant between imaging modalities; in the remaining patient, lung ultrasound (LUS) found an interstitial B-lines pattern that was not seen on radiography. In seven patients with pathologic ultrasound findings at baseline, the improvement or resolution of the subpleural consolidations or interstitial patterns was consistent with concomitant radiologic findings.
The authors cited the benefits of using point-of-care ultrasound instead of other modalities, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” they wrote. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, LUS allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].”
One limitation of the study is the small sample size; however, the researchers felt the high concordance still suggests LUS is a reasonable method for COVID-19 patients.
There was no external funding for this study and the investigators had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Denina M et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1157.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Assessing Spinal Muscular Atrophy Across the Patient Journey

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA

Click here to read.
Supplement Faculty
Perry Shieh, MD, PhD
Professor
Department of Neurology
David Geffen School
of Medicine at UCLA
Ronald Reagan UCLA
Medical Center
Los Angeles, CA
Sally Dunaway Young, PT, DPT
Physical Therapist
and Clinical Research
Evaluator/Manager
Stanford University School
of Medicine
Stanford, CA
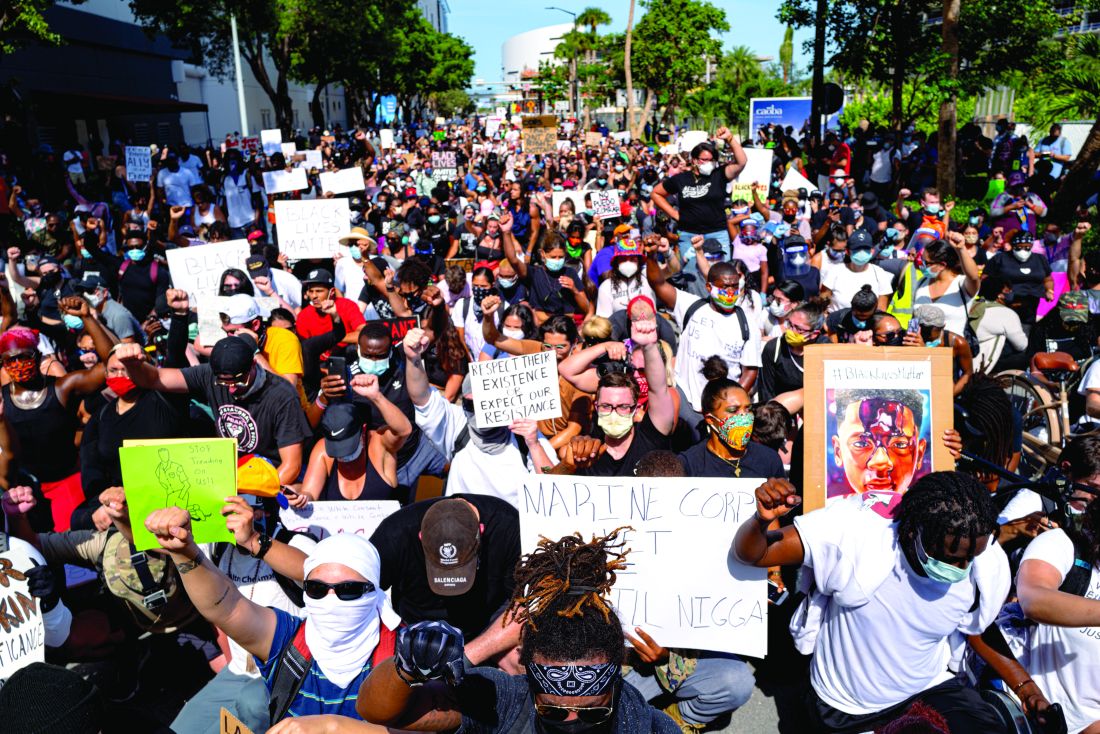
‘I can’t breathe’: Health inequity and state-sanctioned violence
One might immediately think of the deaths of Eric Garner, George Floyd, or even the fictional character Radio Raheem from Spike Lee’s critically acclaimed film, “Do the Right Thing,” when they hear the words “I can’t breathe.” These words are a cry for help. The deaths of these unarmed black men is devastating and has led to a state of rage, palpable pain, and protest across the world.
However, in this moment, I am talking about the health inequity exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Whether it be acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to severe COVID-19, or the subsequent hypercoagulable state of COVID-19 that leads to venous thromboembolism, many black people in this country are left breathless. Many black patients who had no employee-based health insurance also had no primary care physician to order a SARS-CoV2 PCR lab test for them. Many of these patients have preexisting conditions, such as asthma from living in redlined communities affected by environmental racism. Many grew up in food deserts, where no fresh-produce store was interested enough to set up shop in their neighborhoods. They have been eating fast food since early childhood, as a fast-food burger is still cheaper than a salad. The result is obesity, an epidemic that can lead to diabetes mellitus, hypertension that can lead to coronary artery disease, stroke, and end-stage renal disease.
Earlier in my career, I once had a colleague gleefully tell me that all black people drank Kool-Aid while in discussion of the effects of high-sugar diets in our patients; this colleague was sure I would agree. Not all black people drink Kool-Aid. Secondary to my fear of the backlash that can come from the discomfort of “white fragility” that Robin DiAngelo describes in her New York Times bestseller by the same name, ”White Fragility: Why It’s So Hard for White People to Talk About Racism,” I refrained from expressing my own hurt, and I did not offer explicit correction. I, instead, took a serious pause. That pause, which lasted only minutes, seemed to last 400 years. It was a brief reflection of the 400 years of systemic racism seeping into everyday life. This included the circumstances that would lead to the health inequities that result in the health disparities from which many black patients suffer. It is that same systemic racism that could create two America’s in which my colleague might not have to know the historic context in which that question could be hurtful. I retorted with modified shock and a chuckle so that I could muster up enough strength to repeat what was said and leave it open for reflection. The goal was for my colleague to realize the obvious implicit bias that lingered, despite intention. The chuckle was also to cover my pain.
Whether we know it or not, we all carry some form of implicit bias, regardless of race, class, gender, ethnicity, sexual preference, or socioeconomic status. In this case, it is the same implicit bias that causes physicians to ignore some black patients when they have said that they are in pain. A groundbreaking April 2016 article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, “Racial Bias in Pain Assessment and Treatment Recommendations, and False Beliefs about Biological Differences Between Blacks and Whites” (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516047113), revealed that racial disparities in pain assessment and treatment recommendations can be directly connected to the racial bias of the provider. It could be possible that this phenomenon has affected black patients who have walked into clinics and emergency departments and said, “I’m short of breath. I think that I might have coronavirus and need to be tested.” It may be that same implicit bias that has cut the air supply to a patient encounter. Instead of inquiring further, the patient might be met with minimum questions while their provider obtains their history and physical. Assumptions and blame on behavior and lack of personal responsibility secretly replace questions that could have been asked. Differentials between exacerbations and other etiologies are not explored. Could that patient have been sent home without a SARS-CoV2 polymerase chain reaction test? Well, what if the tests were in short supply? Sometimes they may have been sent home without a chest x-ray. In most cases, there are no funds to send them home with a pulse oximeter.
The act of assuming a person’s story that we consider to be one dimensional is always dangerous – and even more so during this pandemic. That person we can relate to – secondary to a cool pop culture moment, a TikTok song, or a negative stereotype – is not one dimensional. That assumption and that stereotype can make room for implicit bias. That same implicit bias is the knee on a neck of any marginalized patient. Implicit bias is the choke hold that slowly removes the light and life from a person who has a story, who has a family, and who has been an essential worker who can’t work from home. That person is telling us that they can’t breathe, but sometimes the only things seen are comorbidities through a misinformed or biased lens that suggest an assumed lack of personal responsibility. In a May 2020 New England Journal of Medicine perspective, “Racial health disparities and Covid-19” (doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2012910), Merlin Chowkwanyun, PhD, MPH, and Adolph L. Reed Jr., PhD, caution us against creating race-based explanations for presumed behavioral patterns.
Systemic racism has created the myth that the playing field has been leveled since the end of enslavement. It hasn’t. That black man, woman, or nonbinary person is telling you “I can’t breathe. I’m tired. I’m short of breath ... I have a cough ... I’m feeling weak these days, Doc.” However, implicit bias is still that knee that won’t let up. It has not let up. Communities with lower-income black and Hispanic patients have already seen local hospitals and frontline workers fight to save their lives while losing their own to COVID-19. We all witnessed the battle for scarce resources and PPE [personal protective equipment]. In contrast, some wealthy neighborhoods have occupants who most likely have access to a primary care physician and more testing centers.
As we reexamine ourselves and look at these cases of police brutality against unarmed black men, women, and children with the appropriate shame and outrage, let us reflect upon the privileges that we enjoy. Let us find our voice as we speak up for black lives. Let us look deeply into the history of medicine as it relates to black patients by reading “Medical Apartheid: The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on Black Americans from Colonial Times to the Present” by Harriet A. Washington. Let us examine that painful legacy, which, while having moments of good intention, still carries the stain of indifference, racism, neglect, and even experimentation without informed consent.
Why should we do these things? Because some of our black patients have also yelled or whispered, “I can’t breathe,” and we were not always listening either.
Dr. Ajala is a hospitalist and associate site director for education at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. She is a member of the executive council for SHM’s Care for Vulnerable Populations special interest group.
One might immediately think of the deaths of Eric Garner, George Floyd, or even the fictional character Radio Raheem from Spike Lee’s critically acclaimed film, “Do the Right Thing,” when they hear the words “I can’t breathe.” These words are a cry for help. The deaths of these unarmed black men is devastating and has led to a state of rage, palpable pain, and protest across the world.
However, in this moment, I am talking about the health inequity exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Whether it be acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to severe COVID-19, or the subsequent hypercoagulable state of COVID-19 that leads to venous thromboembolism, many black people in this country are left breathless. Many black patients who had no employee-based health insurance also had no primary care physician to order a SARS-CoV2 PCR lab test for them. Many of these patients have preexisting conditions, such as asthma from living in redlined communities affected by environmental racism. Many grew up in food deserts, where no fresh-produce store was interested enough to set up shop in their neighborhoods. They have been eating fast food since early childhood, as a fast-food burger is still cheaper than a salad. The result is obesity, an epidemic that can lead to diabetes mellitus, hypertension that can lead to coronary artery disease, stroke, and end-stage renal disease.
Earlier in my career, I once had a colleague gleefully tell me that all black people drank Kool-Aid while in discussion of the effects of high-sugar diets in our patients; this colleague was sure I would agree. Not all black people drink Kool-Aid. Secondary to my fear of the backlash that can come from the discomfort of “white fragility” that Robin DiAngelo describes in her New York Times bestseller by the same name, ”White Fragility: Why It’s So Hard for White People to Talk About Racism,” I refrained from expressing my own hurt, and I did not offer explicit correction. I, instead, took a serious pause. That pause, which lasted only minutes, seemed to last 400 years. It was a brief reflection of the 400 years of systemic racism seeping into everyday life. This included the circumstances that would lead to the health inequities that result in the health disparities from which many black patients suffer. It is that same systemic racism that could create two America’s in which my colleague might not have to know the historic context in which that question could be hurtful. I retorted with modified shock and a chuckle so that I could muster up enough strength to repeat what was said and leave it open for reflection. The goal was for my colleague to realize the obvious implicit bias that lingered, despite intention. The chuckle was also to cover my pain.
Whether we know it or not, we all carry some form of implicit bias, regardless of race, class, gender, ethnicity, sexual preference, or socioeconomic status. In this case, it is the same implicit bias that causes physicians to ignore some black patients when they have said that they are in pain. A groundbreaking April 2016 article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, “Racial Bias in Pain Assessment and Treatment Recommendations, and False Beliefs about Biological Differences Between Blacks and Whites” (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516047113), revealed that racial disparities in pain assessment and treatment recommendations can be directly connected to the racial bias of the provider. It could be possible that this phenomenon has affected black patients who have walked into clinics and emergency departments and said, “I’m short of breath. I think that I might have coronavirus and need to be tested.” It may be that same implicit bias that has cut the air supply to a patient encounter. Instead of inquiring further, the patient might be met with minimum questions while their provider obtains their history and physical. Assumptions and blame on behavior and lack of personal responsibility secretly replace questions that could have been asked. Differentials between exacerbations and other etiologies are not explored. Could that patient have been sent home without a SARS-CoV2 polymerase chain reaction test? Well, what if the tests were in short supply? Sometimes they may have been sent home without a chest x-ray. In most cases, there are no funds to send them home with a pulse oximeter.
The act of assuming a person’s story that we consider to be one dimensional is always dangerous – and even more so during this pandemic. That person we can relate to – secondary to a cool pop culture moment, a TikTok song, or a negative stereotype – is not one dimensional. That assumption and that stereotype can make room for implicit bias. That same implicit bias is the knee on a neck of any marginalized patient. Implicit bias is the choke hold that slowly removes the light and life from a person who has a story, who has a family, and who has been an essential worker who can’t work from home. That person is telling us that they can’t breathe, but sometimes the only things seen are comorbidities through a misinformed or biased lens that suggest an assumed lack of personal responsibility. In a May 2020 New England Journal of Medicine perspective, “Racial health disparities and Covid-19” (doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2012910), Merlin Chowkwanyun, PhD, MPH, and Adolph L. Reed Jr., PhD, caution us against creating race-based explanations for presumed behavioral patterns.
Systemic racism has created the myth that the playing field has been leveled since the end of enslavement. It hasn’t. That black man, woman, or nonbinary person is telling you “I can’t breathe. I’m tired. I’m short of breath ... I have a cough ... I’m feeling weak these days, Doc.” However, implicit bias is still that knee that won’t let up. It has not let up. Communities with lower-income black and Hispanic patients have already seen local hospitals and frontline workers fight to save their lives while losing their own to COVID-19. We all witnessed the battle for scarce resources and PPE [personal protective equipment]. In contrast, some wealthy neighborhoods have occupants who most likely have access to a primary care physician and more testing centers.
As we reexamine ourselves and look at these cases of police brutality against unarmed black men, women, and children with the appropriate shame and outrage, let us reflect upon the privileges that we enjoy. Let us find our voice as we speak up for black lives. Let us look deeply into the history of medicine as it relates to black patients by reading “Medical Apartheid: The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on Black Americans from Colonial Times to the Present” by Harriet A. Washington. Let us examine that painful legacy, which, while having moments of good intention, still carries the stain of indifference, racism, neglect, and even experimentation without informed consent.
Why should we do these things? Because some of our black patients have also yelled or whispered, “I can’t breathe,” and we were not always listening either.
Dr. Ajala is a hospitalist and associate site director for education at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. She is a member of the executive council for SHM’s Care for Vulnerable Populations special interest group.
One might immediately think of the deaths of Eric Garner, George Floyd, or even the fictional character Radio Raheem from Spike Lee’s critically acclaimed film, “Do the Right Thing,” when they hear the words “I can’t breathe.” These words are a cry for help. The deaths of these unarmed black men is devastating and has led to a state of rage, palpable pain, and protest across the world.
However, in this moment, I am talking about the health inequity exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Whether it be acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to severe COVID-19, or the subsequent hypercoagulable state of COVID-19 that leads to venous thromboembolism, many black people in this country are left breathless. Many black patients who had no employee-based health insurance also had no primary care physician to order a SARS-CoV2 PCR lab test for them. Many of these patients have preexisting conditions, such as asthma from living in redlined communities affected by environmental racism. Many grew up in food deserts, where no fresh-produce store was interested enough to set up shop in their neighborhoods. They have been eating fast food since early childhood, as a fast-food burger is still cheaper than a salad. The result is obesity, an epidemic that can lead to diabetes mellitus, hypertension that can lead to coronary artery disease, stroke, and end-stage renal disease.
Earlier in my career, I once had a colleague gleefully tell me that all black people drank Kool-Aid while in discussion of the effects of high-sugar diets in our patients; this colleague was sure I would agree. Not all black people drink Kool-Aid. Secondary to my fear of the backlash that can come from the discomfort of “white fragility” that Robin DiAngelo describes in her New York Times bestseller by the same name, ”White Fragility: Why It’s So Hard for White People to Talk About Racism,” I refrained from expressing my own hurt, and I did not offer explicit correction. I, instead, took a serious pause. That pause, which lasted only minutes, seemed to last 400 years. It was a brief reflection of the 400 years of systemic racism seeping into everyday life. This included the circumstances that would lead to the health inequities that result in the health disparities from which many black patients suffer. It is that same systemic racism that could create two America’s in which my colleague might not have to know the historic context in which that question could be hurtful. I retorted with modified shock and a chuckle so that I could muster up enough strength to repeat what was said and leave it open for reflection. The goal was for my colleague to realize the obvious implicit bias that lingered, despite intention. The chuckle was also to cover my pain.
Whether we know it or not, we all carry some form of implicit bias, regardless of race, class, gender, ethnicity, sexual preference, or socioeconomic status. In this case, it is the same implicit bias that causes physicians to ignore some black patients when they have said that they are in pain. A groundbreaking April 2016 article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, “Racial Bias in Pain Assessment and Treatment Recommendations, and False Beliefs about Biological Differences Between Blacks and Whites” (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516047113), revealed that racial disparities in pain assessment and treatment recommendations can be directly connected to the racial bias of the provider. It could be possible that this phenomenon has affected black patients who have walked into clinics and emergency departments and said, “I’m short of breath. I think that I might have coronavirus and need to be tested.” It may be that same implicit bias that has cut the air supply to a patient encounter. Instead of inquiring further, the patient might be met with minimum questions while their provider obtains their history and physical. Assumptions and blame on behavior and lack of personal responsibility secretly replace questions that could have been asked. Differentials between exacerbations and other etiologies are not explored. Could that patient have been sent home without a SARS-CoV2 polymerase chain reaction test? Well, what if the tests were in short supply? Sometimes they may have been sent home without a chest x-ray. In most cases, there are no funds to send them home with a pulse oximeter.
The act of assuming a person’s story that we consider to be one dimensional is always dangerous – and even more so during this pandemic. That person we can relate to – secondary to a cool pop culture moment, a TikTok song, or a negative stereotype – is not one dimensional. That assumption and that stereotype can make room for implicit bias. That same implicit bias is the knee on a neck of any marginalized patient. Implicit bias is the choke hold that slowly removes the light and life from a person who has a story, who has a family, and who has been an essential worker who can’t work from home. That person is telling us that they can’t breathe, but sometimes the only things seen are comorbidities through a misinformed or biased lens that suggest an assumed lack of personal responsibility. In a May 2020 New England Journal of Medicine perspective, “Racial health disparities and Covid-19” (doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2012910), Merlin Chowkwanyun, PhD, MPH, and Adolph L. Reed Jr., PhD, caution us against creating race-based explanations for presumed behavioral patterns.
Systemic racism has created the myth that the playing field has been leveled since the end of enslavement. It hasn’t. That black man, woman, or nonbinary person is telling you “I can’t breathe. I’m tired. I’m short of breath ... I have a cough ... I’m feeling weak these days, Doc.” However, implicit bias is still that knee that won’t let up. It has not let up. Communities with lower-income black and Hispanic patients have already seen local hospitals and frontline workers fight to save their lives while losing their own to COVID-19. We all witnessed the battle for scarce resources and PPE [personal protective equipment]. In contrast, some wealthy neighborhoods have occupants who most likely have access to a primary care physician and more testing centers.
As we reexamine ourselves and look at these cases of police brutality against unarmed black men, women, and children with the appropriate shame and outrage, let us reflect upon the privileges that we enjoy. Let us find our voice as we speak up for black lives. Let us look deeply into the history of medicine as it relates to black patients by reading “Medical Apartheid: The Dark History of Medical Experimentation on Black Americans from Colonial Times to the Present” by Harriet A. Washington. Let us examine that painful legacy, which, while having moments of good intention, still carries the stain of indifference, racism, neglect, and even experimentation without informed consent.
Why should we do these things? Because some of our black patients have also yelled or whispered, “I can’t breathe,” and we were not always listening either.
Dr. Ajala is a hospitalist and associate site director for education at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. She is a member of the executive council for SHM’s Care for Vulnerable Populations special interest group.
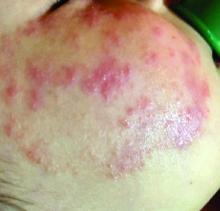
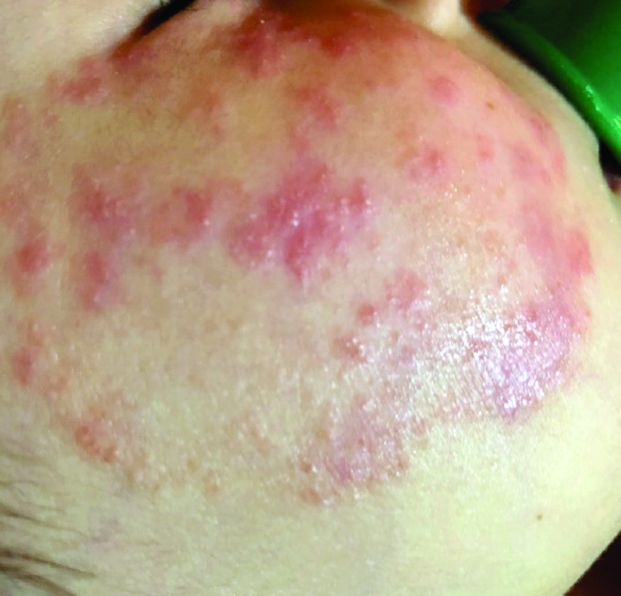
What presents as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque?
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
A 3-year-old girl with a known history of eczema presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a persistent rash for about a year on the right cheek.
The mother reported she was treating the lesions with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% as instructed previously for her eczema. Initially the rash got partially better but then started getting worse again. The area was itchy.
The child was later seen in the emergency department, where she was recommended to treat the area with a combination cream of terbinafine 1% and betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%. The mother applied this cream as instructed for 3 weeks with some improvement of the lesions on the cheek.
A few weeks later, pimples started coming back. The mother tried the medication again but this time it was not helpful and the rash continued to expand.
The mother reported having a rash on her hand months back, which she successfully treated with the combination cream provided at the emergency department. They have no pets at home.
The child has a little sister who also has mild eczema.
She goes to day care and dances ballet.
Preventing arrhythmias and QTc prolongation in COVID-19 patients on psychotropics
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Over the last few weeks, several conflicting reports about the efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 treatments have emerged, including high-profile papers that were placed in the limelight and groundbreaking retractions that were issued by the Lancet and New England Journal of Medicine, involving the potential dangers of COVID therapy with findings derived from the Surgisphere database. Hydroxychloroquine has garnered considerable media attention and was touted earlier by President Trump for its therapeutic effects.1 Naturally, there are political connotations associated with the agent, and it is unlikely that hydroxychloroquine will be supplanted in the near future as ongoing clinical trials have demonstrated mixed results amid the controversy.
As clinicians navigating unchartered territory within the hospital setting, we have to come to terms with these new challenges, tailoring treatment protocols accordingly with the best clinical practices in mind. Patients with preexisting mental health conditions and who are being treated for COVID-19 are particularly susceptible to clinical deterioration. Recent studies have indicated that psychiatric patients are more prone to feelings of isolation and/or estrangement as well as exacerbation of symptoms such as paranoia.2 Even more concerning is the medication regimen, namely, the novel combination therapies that arise when agents such as hydroxychloroquine are used in tandem with certain antipsychotics or antidepressants.
What’s at stake for COVID-19–positive mental health care patients?
Although the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine is currently being investigated,3 the antimalarial is usually prescribed in tandem with azithromycin for people with COVID-19. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has advised against that particular combination therapy because of ongoing concerns about toxicities.3,4
In another study, azithromycin was effectively substituted with doxycycline to help minimize systemic effects for patients with cardiac and/or pulmonary issues.5 Azithromycin is notorious in the literature for influencing the electrical activity of the heart with the potential for fatal arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease.5,6,7 It should be noted that both of these commonly prescribed COVID-19 medications (for example, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin) could lead to QT interval prolongation especially within the context of combination therapy. This is largely concerning for psychiatrists and various other mental health practitioners for the following reasons: (1) higher rates of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases among psychiatric patients8 and/or (2) effects of certain antipsychotics (for example, IV haloperidol, thioridazine, and ziprasidone) and antidepressants (for example, citalopram and escitalopram) on the QT interval.9
SARS-CoV-2 and clinical judgment: Evaluating patients at higher risk
Although COVID-19 medication guidelines are still being actively developed, hydroxychloroquine appears to be commonly prescribed by physicians. The medication is known myriad untoward effects, including potential behavioral dysfunction (for example, irritability, agitation, suicidal ideation)10 as well as the aforementioned issues concerning arrhythmia (for example, torsades de pointes). Health care professionals might not have much control over the choice of COVID-19 agents because of a lack of available resources or limited options, but they can exercise clinical judgment with respect to selecting the appropriate psychotropic medications.
Treatment recommendations
1. Establish a baseline EKG
A baseline 12-lead EKG is the standard of care for patients currently being screened for COVID-19. It is necessary to rule out the presence of an underlying cardiovascular disease or a rhythm irregularity. A prolonged QTc interval is generally regarded as being around greater than 450-470 msecs with variations attributable to gender;11 numerous studies have affirmed that the risk of acquiring torsades de pointes is substantial when the QTc interval exceeds 500 msecs.12
2. Medical management and risk assessment
Commonly prescribed antipsychotics such as IV haloperidol and ziprasidone are known for exerting a negative effect on the interval and should readily be substituted with other agents in patients who are being treated for COVID-19; the combination of these antipsychotics alongside some COVID-19 medication regimens (for example, hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin) might prove to be fatal. The same logic applies to COVID-19 patients previously on antidepressant therapeutics such as citalopram and escitalopram.
3. Embrace an individually tailored approach to therapeutics
While American Psychiatric Association guidelines historically supported a cessation or reduction in the offending agent under normal circumstances,12 our team is recommending that the psychotropics associated with QTc interval prolongation are discontinued altogether (or substituted with a low-risk agent) in the event that a patient presents with suspected COVID-19. However, after the patients tests negative with COVID-19, they may resume therapy as indicated under the discretion of the mental health practitioner.
References
1. Offard C. “Lancet, NEJM Retract Surgisphere Studies on COVID-19 Patients.” The Scientist Magazine. 2020 Jun 4.
2. Shigemura J et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020 Apr;74(4):281-2.
3. Keshtkar-Jahromi M and Bavari S. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 May;102(5):932-3.
4. Palca J. “NIH panel recommends against drug combination promoted by Trump for COVID-19.” NPR. 2020 Apr 21.
5. Mongelli L. “Long Island doctor tries new twist on hydroxychloroquine for elderly COVID-19 patients.” New York Post. 2020 Apr 4.
6. Hancox JC et al. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;(5):155-65.
7. Giudicessi JR and Ackerman MJ. Cleve Clin J Med. 2013 Sep;80(9):539-44.
8. Casey DE. Am J Med. 2005 Apr 1;118(Suppl 2):15S-22S.
9. Beach SR et al. Psychosomatics. 2013 Jan 1;54(1):1-3.
10. Bogaczewicz A and Sobów T. Psychiatria i Psychologia Kliniczna. 2017;17(2):111-4.
11. Chohan PS et al. Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Sep-Oct;31(5):1269-71.
12. Lieberman JA et al. APA guidance on the use of antipsychotic drugs and cardiac sudden death. NYS Office of Mental Health. 2012.
Dr. Faisal A. Islam is medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation, Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Faisal Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Mohammed Islam is affiliated with the department of psychiatry at the Interfaith Medical Center, New York. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clinical research at the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Face mask type matters when sterilizing, study finds
according to researchers. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks.
With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%.
In a research letter published online June 15 in JAMA Network Open, researchers from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, report the results of a study of the two sterilization techniques on the pressure drop and filtration efficiency of N95, KN95, and surgical face masks.
“The H2O2 treatment showed a small effect on the overall filtration efficiency of the tested masks, but the ClO2 treatment showed marked reduction in the overall filtration efficiency of the KN95s and surgical face masks. All pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range,” the researchers write.
The study did not evaluate the effect of repeated sterilizations on face masks.
Five masks of each type were sterilized with either H2O2 or ClO2. Masks were then placed in a test chamber, and a salt aerosol was nebulized to assess both upstream and downstream filtration as well as pressure drop. The researchers used a mobility particle sizer to measure particle number concentration from 16.8 nm to 514 nm. An acceptable pressure drop was defined as a drop of less than 1.38 inches of water (35 mm) for inhalation.
Although pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range for all three mask types following sterilization with either method, H2O2 sterilization yielded the least reduction in filtration efficacy in all cases. After sterilization with H2O2, filtration efficiencies were 96.6%, 97.1%, and 91.6% for the N95s, KN95s, and the surgical face masks, respectively. In contrast, filtration efficiencies after ClO2 sterilization were 95.1%, 76.2%, and 77.9%, respectively.
The researchers note that, although overall filtration efficiency was maintained with ClO2 sterilization, there was a significant drop in efficiency with respect to particles of approximately 300 nm (0.3 microns) in size. For particles of that size, mean filtration efficiency decreased to 86.2% for N95s, 40.8% for KN95s, and 47.1% for surgical face masks.
The testing described in the report is “quite affordable at $350 per mask type, so it is hard to imagine any health care provider cannot set aside a small budget to conduct such an important test,” author Evan Floyd, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
Given the high demand for effective face masks and the current risk for counterfeit products, Floyd suggested that individual facilities test all masks intended for use by healthcare workers before and after sterilization procedures.
“However, if for some reason testing is not an option, we would recommend sticking to established brands and suppliers, perhaps reach out to your state health department or a local representative of the strategic stockpile of PPE,” he noted.
The authors acknowledge that further studies using a larger sample size and a greater variety of masks, as well as studies to evaluate different sterilization techniques, are required. Further, “measuring the respirator’s filtration efficiency by aerosol size instead of only measuring the overall filtration efficiency” should also be considered. Such an approach would enable researchers to evaluate the degree to which masks protect against specific infectious agents.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to researchers. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks.
With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%.
In a research letter published online June 15 in JAMA Network Open, researchers from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, report the results of a study of the two sterilization techniques on the pressure drop and filtration efficiency of N95, KN95, and surgical face masks.
“The H2O2 treatment showed a small effect on the overall filtration efficiency of the tested masks, but the ClO2 treatment showed marked reduction in the overall filtration efficiency of the KN95s and surgical face masks. All pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range,” the researchers write.
The study did not evaluate the effect of repeated sterilizations on face masks.
Five masks of each type were sterilized with either H2O2 or ClO2. Masks were then placed in a test chamber, and a salt aerosol was nebulized to assess both upstream and downstream filtration as well as pressure drop. The researchers used a mobility particle sizer to measure particle number concentration from 16.8 nm to 514 nm. An acceptable pressure drop was defined as a drop of less than 1.38 inches of water (35 mm) for inhalation.
Although pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range for all three mask types following sterilization with either method, H2O2 sterilization yielded the least reduction in filtration efficacy in all cases. After sterilization with H2O2, filtration efficiencies were 96.6%, 97.1%, and 91.6% for the N95s, KN95s, and the surgical face masks, respectively. In contrast, filtration efficiencies after ClO2 sterilization were 95.1%, 76.2%, and 77.9%, respectively.
The researchers note that, although overall filtration efficiency was maintained with ClO2 sterilization, there was a significant drop in efficiency with respect to particles of approximately 300 nm (0.3 microns) in size. For particles of that size, mean filtration efficiency decreased to 86.2% for N95s, 40.8% for KN95s, and 47.1% for surgical face masks.
The testing described in the report is “quite affordable at $350 per mask type, so it is hard to imagine any health care provider cannot set aside a small budget to conduct such an important test,” author Evan Floyd, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
Given the high demand for effective face masks and the current risk for counterfeit products, Floyd suggested that individual facilities test all masks intended for use by healthcare workers before and after sterilization procedures.
“However, if for some reason testing is not an option, we would recommend sticking to established brands and suppliers, perhaps reach out to your state health department or a local representative of the strategic stockpile of PPE,” he noted.
The authors acknowledge that further studies using a larger sample size and a greater variety of masks, as well as studies to evaluate different sterilization techniques, are required. Further, “measuring the respirator’s filtration efficiency by aerosol size instead of only measuring the overall filtration efficiency” should also be considered. Such an approach would enable researchers to evaluate the degree to which masks protect against specific infectious agents.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to researchers. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks.
With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%.
In a research letter published online June 15 in JAMA Network Open, researchers from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, report the results of a study of the two sterilization techniques on the pressure drop and filtration efficiency of N95, KN95, and surgical face masks.
“The H2O2 treatment showed a small effect on the overall filtration efficiency of the tested masks, but the ClO2 treatment showed marked reduction in the overall filtration efficiency of the KN95s and surgical face masks. All pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range,” the researchers write.
The study did not evaluate the effect of repeated sterilizations on face masks.
Five masks of each type were sterilized with either H2O2 or ClO2. Masks were then placed in a test chamber, and a salt aerosol was nebulized to assess both upstream and downstream filtration as well as pressure drop. The researchers used a mobility particle sizer to measure particle number concentration from 16.8 nm to 514 nm. An acceptable pressure drop was defined as a drop of less than 1.38 inches of water (35 mm) for inhalation.
Although pressure drop changes were within the acceptable range for all three mask types following sterilization with either method, H2O2 sterilization yielded the least reduction in filtration efficacy in all cases. After sterilization with H2O2, filtration efficiencies were 96.6%, 97.1%, and 91.6% for the N95s, KN95s, and the surgical face masks, respectively. In contrast, filtration efficiencies after ClO2 sterilization were 95.1%, 76.2%, and 77.9%, respectively.
The researchers note that, although overall filtration efficiency was maintained with ClO2 sterilization, there was a significant drop in efficiency with respect to particles of approximately 300 nm (0.3 microns) in size. For particles of that size, mean filtration efficiency decreased to 86.2% for N95s, 40.8% for KN95s, and 47.1% for surgical face masks.
The testing described in the report is “quite affordable at $350 per mask type, so it is hard to imagine any health care provider cannot set aside a small budget to conduct such an important test,” author Evan Floyd, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
Given the high demand for effective face masks and the current risk for counterfeit products, Floyd suggested that individual facilities test all masks intended for use by healthcare workers before and after sterilization procedures.
“However, if for some reason testing is not an option, we would recommend sticking to established brands and suppliers, perhaps reach out to your state health department or a local representative of the strategic stockpile of PPE,” he noted.
The authors acknowledge that further studies using a larger sample size and a greater variety of masks, as well as studies to evaluate different sterilization techniques, are required. Further, “measuring the respirator’s filtration efficiency by aerosol size instead of only measuring the overall filtration efficiency” should also be considered. Such an approach would enable researchers to evaluate the degree to which masks protect against specific infectious agents.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap 6/17
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Comorbidities increase COVID-19 deaths by factor of 12
COVID-19 patients with an underlying condition are 6 times as likely to be hospitalized and 12 times as likely to die, compared with those who have no such condition, according to the CDC.
The most frequently reported underlying conditions were cardiovascular disease (32%), diabetes (30%), chronic lung disease (18%), and renal disease (7.6%), and there were no significant differences between males and females.
The pandemic “continues to affect all populations and result in severe outcomes including death,” noted the CDC, emphasizing “the continued need for community mitigation strategies, especially for vulnerable populations, to slow COVID-19 transmission.” Read more.
Preventive services coalition recommends routine anxiety screening for women
Women and girls aged 13 years and older with no current diagnosis of anxiety should be screened routinely for anxiety, according to a new recommendation from the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative.
The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders in women in the United States is 40%, approximately twice that of men, and anxiety can be a manifestation of underlying issues including posttraumatic stress, sexual harassment, and assault.
“The WPSI based its rationale for anxiety screening on several considerations,” the researchers noted. “Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent mental health disorders in women, and the problems created by untreated anxiety can impair function in all areas of a woman’s life.” Read more.
High-fat, high-sugar diet may promote adult acne
A diet higher in fat, sugar, and milk was associated with having acne in a cross-sectional study of approximately 24,000 adults in France.
Although acne patients may believe that eating certain foods exacerbates acne, data on the effects of nutrition on acne, including associations between acne and a high-glycemic diet, are limited and have produced conflicting results, noted investigators.
“The results of our study appear to support the hypothesis that the Western diet (rich in animal products and fatty and sugary foods) is associated with the presence of acne in adulthood,” the researchers concluded.
Population study supports migraine-dementia link
Preliminary results from a population-based cohort study support previous reports that migraine is a midlife risk factor for dementia later in life, but further determined that migraine with aura and frequent hospital contacts significantly increased dementia risk after age 60 years, according to results from a Danish registry presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
The preliminary findings revealed that the median age at diagnosis was 49 years and about 70% of the migraine population were women. “There was a 50% higher dementia rate in individuals who had any migraine diagnosis,” Dr. Islamoska said.
“To the best of our knowledge, no previous national register–based studies have investigated the risk of dementia among individuals who suffer from migraine with aura,” Dr. Sabrina Islamoska said.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Comorbidities increase COVID-19 deaths by factor of 12
COVID-19 patients with an underlying condition are 6 times as likely to be hospitalized and 12 times as likely to die, compared with those who have no such condition, according to the CDC.
The most frequently reported underlying conditions were cardiovascular disease (32%), diabetes (30%), chronic lung disease (18%), and renal disease (7.6%), and there were no significant differences between males and females.
The pandemic “continues to affect all populations and result in severe outcomes including death,” noted the CDC, emphasizing “the continued need for community mitigation strategies, especially for vulnerable populations, to slow COVID-19 transmission.” Read more.
Preventive services coalition recommends routine anxiety screening for women
Women and girls aged 13 years and older with no current diagnosis of anxiety should be screened routinely for anxiety, according to a new recommendation from the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative.
The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders in women in the United States is 40%, approximately twice that of men, and anxiety can be a manifestation of underlying issues including posttraumatic stress, sexual harassment, and assault.
“The WPSI based its rationale for anxiety screening on several considerations,” the researchers noted. “Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent mental health disorders in women, and the problems created by untreated anxiety can impair function in all areas of a woman’s life.” Read more.
High-fat, high-sugar diet may promote adult acne
A diet higher in fat, sugar, and milk was associated with having acne in a cross-sectional study of approximately 24,000 adults in France.
Although acne patients may believe that eating certain foods exacerbates acne, data on the effects of nutrition on acne, including associations between acne and a high-glycemic diet, are limited and have produced conflicting results, noted investigators.
“The results of our study appear to support the hypothesis that the Western diet (rich in animal products and fatty and sugary foods) is associated with the presence of acne in adulthood,” the researchers concluded.
Population study supports migraine-dementia link
Preliminary results from a population-based cohort study support previous reports that migraine is a midlife risk factor for dementia later in life, but further determined that migraine with aura and frequent hospital contacts significantly increased dementia risk after age 60 years, according to results from a Danish registry presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
The preliminary findings revealed that the median age at diagnosis was 49 years and about 70% of the migraine population were women. “There was a 50% higher dementia rate in individuals who had any migraine diagnosis,” Dr. Islamoska said.
“To the best of our knowledge, no previous national register–based studies have investigated the risk of dementia among individuals who suffer from migraine with aura,” Dr. Sabrina Islamoska said.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Comorbidities increase COVID-19 deaths by factor of 12
COVID-19 patients with an underlying condition are 6 times as likely to be hospitalized and 12 times as likely to die, compared with those who have no such condition, according to the CDC.
The most frequently reported underlying conditions were cardiovascular disease (32%), diabetes (30%), chronic lung disease (18%), and renal disease (7.6%), and there were no significant differences between males and females.
The pandemic “continues to affect all populations and result in severe outcomes including death,” noted the CDC, emphasizing “the continued need for community mitigation strategies, especially for vulnerable populations, to slow COVID-19 transmission.” Read more.
Preventive services coalition recommends routine anxiety screening for women
Women and girls aged 13 years and older with no current diagnosis of anxiety should be screened routinely for anxiety, according to a new recommendation from the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative.
The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders in women in the United States is 40%, approximately twice that of men, and anxiety can be a manifestation of underlying issues including posttraumatic stress, sexual harassment, and assault.
“The WPSI based its rationale for anxiety screening on several considerations,” the researchers noted. “Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent mental health disorders in women, and the problems created by untreated anxiety can impair function in all areas of a woman’s life.” Read more.
High-fat, high-sugar diet may promote adult acne
A diet higher in fat, sugar, and milk was associated with having acne in a cross-sectional study of approximately 24,000 adults in France.
Although acne patients may believe that eating certain foods exacerbates acne, data on the effects of nutrition on acne, including associations between acne and a high-glycemic diet, are limited and have produced conflicting results, noted investigators.
“The results of our study appear to support the hypothesis that the Western diet (rich in animal products and fatty and sugary foods) is associated with the presence of acne in adulthood,” the researchers concluded.
Population study supports migraine-dementia link
Preliminary results from a population-based cohort study support previous reports that migraine is a midlife risk factor for dementia later in life, but further determined that migraine with aura and frequent hospital contacts significantly increased dementia risk after age 60 years, according to results from a Danish registry presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society.
The preliminary findings revealed that the median age at diagnosis was 49 years and about 70% of the migraine population were women. “There was a 50% higher dementia rate in individuals who had any migraine diagnosis,” Dr. Islamoska said.
“To the best of our knowledge, no previous national register–based studies have investigated the risk of dementia among individuals who suffer from migraine with aura,” Dr. Sabrina Islamoska said.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Getting unstuck: Helping patients with behavior change
Kyle is a 14-year-old cisgender male who just moved to your town. At his first well-check, his single father brings him in reluctantly, stating, “We’ve never liked doctors.” Kyle has a history of asthma and obesity that have been relatively unchanged over time. He is an average student, an avid gamer, and seems somewhat shy. Privately he admits to occasional cannabis use. His father has no concerns, lamenting, “He’s always been pretty healthy for a fat kid.” Next patient?
Of course there is a lot to work with here. You might be concerned with Kyle’s asthma; his weight, sedentary nature, and body image; the criticism from his father and concerns about self-esteem; the possibility of anxiety in relation to his shyness; and the health effects of his cannabis use. In the end, recommendations for behavior change seem likely. These might take the form of tips on exercise, nutrition, substance use, study habits, parenting, social activities, or mental health support; the literature on behavior change would suggest that any success will be predicated on trust. How can we learn from someone we do not trust?1
To build trust is no easy task, and yet is perhaps the foundation on which the entire clinical relationship rests. Guidance from decades of evidence supporting the use of motivational interviewing2 suggests that the process of building rapport can be neatly summed up in an acronym as PACE. This represents Partnership, Acceptance, Compassion, and Evocation. Almost too clichéd to repeat, the most powerful change agent is the person making the change. In the setting of pediatric health care, we sometimes lean on caregivers to initiate or promote change because they are an intimate part of the patient’s microsystem, and thus moving one gear (the parents) inevitably shifts something in connected gears (the children).
So Partnership is centered on the patient, but inclusive of any important person in the patient’s sphere. In a family-based approach, this might show up as leveraging Kyle’s father’s motivation for behavior change by having the father start an exercise routine. This role models behavior change, shifts the home environment around the behavior, and builds empathy in the parent for the inherent challenges of change processes.
Acceptance can be distilled into knowing that the patient and family are doing the best they can. This does not preclude the possibility of change, but it seats this possibility in an attitude of assumed adequacy. There is nothing wrong with the patient, nothing to be fixed, just the possibility for change.
Similarly, Compassion takes a nonjudgmental viewpoint. With the stance of “this could happen to anybody,” the patient can feel responsible without feeling blamed. Noting the patient’s suffering without blame allows the clinician to be motivated not just to empathize, but to help.
And from this basis of compassionate partnership, the work of Evocation begins. What is happening in the patient’s life and relationships? What are their own goals and values? Where are the discrepancies between what the patient wants and what the patient does? For teenagers, this often brings into conflict developmentally appropriate wishes for autonomy – wanting to drive or get a car or stay out later or have more privacy – with developmentally typical challenges regarding responsibility.3 For example:
Clinician: “You want to use the car, and your parents want you to pay for the gas, but you’re out of money from buying weed. I see how you’re stuck.”
Teen: “Yeah, they really need to give me more allowance. It’s not like we’re living in the 1990s anymore!”
Clinician: “So you could ask for more allowance to get more money for gas. Any other ideas?”
Teen: “I could give up smoking pot and just be miserable all the time.”
Clinician: “Yeah, that sounds too difficult right now; if anything it sounds like you’d like to smoke more pot if you had more money.”
Teen: “Nah, I’m not that hooked on it. ... I could probably smoke a bit less each week and save some gas money.”
The PACE acronym also serves as a reminder of the patience required to grow connection where none has previously existed – pace yourself. Here are some skills-based tips to foster the spirit of motivational interviewing to help balance patience with the time frame of a pediatric check-in. The OARS skills represent the fundamental building blocks of motivational interviewing in practice. Taking the case of Kyle as an example, an Open-Ended Question makes space for the child or parent to express their views with less interviewer bias. Reflections expand this space by underscoring and, in the case of complex Reflections, adding some nuance to what the patient has to say.
Clinician: “How do you feel about your body?”
Teen: “Well, I’m fat. Nobody really wants to be fat. It sucks. But what can I do?”
Clinician: “You feel fat and kind of hopeless.”
Teen: “Yeah, I know you’re going to tell me to go on a diet and start exercising. Doesn’t work. My dad says I was born fat; I guess I’m going to stay that way.”
Clinician: “Sounds like you and your dad can get down on you for your weight. That must feel terrible.”
Teen: “Ah, it’s not that bad. I’m kind of used to it. Fat kid at home, fat kid at school.”
Affirmations are statements focusing on positive actions or attributes of the patient. They tend to build rapport by demonstrating that the clinician sees the strengths of the patient, not just the problems.
Clinician: “I’m pretty impressed that you’re able to show up here and talk about this. It can’t be easy when it sounds like your family and friends have put you down so much that you’re even putting yourself down about your body.”
Teen: “I didn’t really want to come, but then I thought, maybe this new doctor will have some new ideas. I actually want to do something about it, I just don’t know if anything will help. Plus my dad said if I showed up, we could go to McDonald’s afterward.”
Summaries are multipurpose. They demonstrate that you have been listening closely, which builds rapport. They provide a chance to put information together so that both clinician and patient can reflect on the sum of the data and notice what may be missing. And they provide a pause to consider where to go next.
Clinician: “So if I’m getting it right, you’ve been worried about your weight for a long time now. Your dad and your friends give you a hard time about it, which makes you feel down and hopeless, but somehow you stay brave and keep trying to figure it out. You feel ready to do something, you just don’t know what, and you were hoping maybe coming here could give you a place to work on your health. Does that sound about right?”
Teen: “I think that’s pretty much it. Plus the McDonald’s.”
Clinician: “Right, that’s important too – we have to consider your motivation! I wonder if we could talk about this more at our next visit – would that be alright?”
Offices with additional resources might be able to offer some of those as well, if timing seems appropriate; for example, referral to a wellness coach or social worker or nutritionist could be helpful int his case. With the spirit of PACE and the skills of OARS, you can be well on your way to fostering behavior changes that could last a lifetime! Check out the resources from the American Academy of Pediatrics with video and narrative demonstrations of motivational interviewing in pediatrics.
Dr. Rosenfeld is assistant professor in the departments of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Medical Center and the university’s Robert Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. He reported no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “Engagement and disengagement,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
2. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “The spirit of motivational interviewing,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
3. Naar S, Suarez M. “Adolescence and emerging adulthood: A brief review of development,” in “Motivational interviewing with adolescents and young adults” (New York: Guilford, 2011).
Kyle is a 14-year-old cisgender male who just moved to your town. At his first well-check, his single father brings him in reluctantly, stating, “We’ve never liked doctors.” Kyle has a history of asthma and obesity that have been relatively unchanged over time. He is an average student, an avid gamer, and seems somewhat shy. Privately he admits to occasional cannabis use. His father has no concerns, lamenting, “He’s always been pretty healthy for a fat kid.” Next patient?
Of course there is a lot to work with here. You might be concerned with Kyle’s asthma; his weight, sedentary nature, and body image; the criticism from his father and concerns about self-esteem; the possibility of anxiety in relation to his shyness; and the health effects of his cannabis use. In the end, recommendations for behavior change seem likely. These might take the form of tips on exercise, nutrition, substance use, study habits, parenting, social activities, or mental health support; the literature on behavior change would suggest that any success will be predicated on trust. How can we learn from someone we do not trust?1
To build trust is no easy task, and yet is perhaps the foundation on which the entire clinical relationship rests. Guidance from decades of evidence supporting the use of motivational interviewing2 suggests that the process of building rapport can be neatly summed up in an acronym as PACE. This represents Partnership, Acceptance, Compassion, and Evocation. Almost too clichéd to repeat, the most powerful change agent is the person making the change. In the setting of pediatric health care, we sometimes lean on caregivers to initiate or promote change because they are an intimate part of the patient’s microsystem, and thus moving one gear (the parents) inevitably shifts something in connected gears (the children).
So Partnership is centered on the patient, but inclusive of any important person in the patient’s sphere. In a family-based approach, this might show up as leveraging Kyle’s father’s motivation for behavior change by having the father start an exercise routine. This role models behavior change, shifts the home environment around the behavior, and builds empathy in the parent for the inherent challenges of change processes.
Acceptance can be distilled into knowing that the patient and family are doing the best they can. This does not preclude the possibility of change, but it seats this possibility in an attitude of assumed adequacy. There is nothing wrong with the patient, nothing to be fixed, just the possibility for change.
Similarly, Compassion takes a nonjudgmental viewpoint. With the stance of “this could happen to anybody,” the patient can feel responsible without feeling blamed. Noting the patient’s suffering without blame allows the clinician to be motivated not just to empathize, but to help.
And from this basis of compassionate partnership, the work of Evocation begins. What is happening in the patient’s life and relationships? What are their own goals and values? Where are the discrepancies between what the patient wants and what the patient does? For teenagers, this often brings into conflict developmentally appropriate wishes for autonomy – wanting to drive or get a car or stay out later or have more privacy – with developmentally typical challenges regarding responsibility.3 For example:
Clinician: “You want to use the car, and your parents want you to pay for the gas, but you’re out of money from buying weed. I see how you’re stuck.”
Teen: “Yeah, they really need to give me more allowance. It’s not like we’re living in the 1990s anymore!”
Clinician: “So you could ask for more allowance to get more money for gas. Any other ideas?”
Teen: “I could give up smoking pot and just be miserable all the time.”
Clinician: “Yeah, that sounds too difficult right now; if anything it sounds like you’d like to smoke more pot if you had more money.”
Teen: “Nah, I’m not that hooked on it. ... I could probably smoke a bit less each week and save some gas money.”
The PACE acronym also serves as a reminder of the patience required to grow connection where none has previously existed – pace yourself. Here are some skills-based tips to foster the spirit of motivational interviewing to help balance patience with the time frame of a pediatric check-in. The OARS skills represent the fundamental building blocks of motivational interviewing in practice. Taking the case of Kyle as an example, an Open-Ended Question makes space for the child or parent to express their views with less interviewer bias. Reflections expand this space by underscoring and, in the case of complex Reflections, adding some nuance to what the patient has to say.
Clinician: “How do you feel about your body?”
Teen: “Well, I’m fat. Nobody really wants to be fat. It sucks. But what can I do?”
Clinician: “You feel fat and kind of hopeless.”
Teen: “Yeah, I know you’re going to tell me to go on a diet and start exercising. Doesn’t work. My dad says I was born fat; I guess I’m going to stay that way.”
Clinician: “Sounds like you and your dad can get down on you for your weight. That must feel terrible.”
Teen: “Ah, it’s not that bad. I’m kind of used to it. Fat kid at home, fat kid at school.”
Affirmations are statements focusing on positive actions or attributes of the patient. They tend to build rapport by demonstrating that the clinician sees the strengths of the patient, not just the problems.
Clinician: “I’m pretty impressed that you’re able to show up here and talk about this. It can’t be easy when it sounds like your family and friends have put you down so much that you’re even putting yourself down about your body.”
Teen: “I didn’t really want to come, but then I thought, maybe this new doctor will have some new ideas. I actually want to do something about it, I just don’t know if anything will help. Plus my dad said if I showed up, we could go to McDonald’s afterward.”
Summaries are multipurpose. They demonstrate that you have been listening closely, which builds rapport. They provide a chance to put information together so that both clinician and patient can reflect on the sum of the data and notice what may be missing. And they provide a pause to consider where to go next.
Clinician: “So if I’m getting it right, you’ve been worried about your weight for a long time now. Your dad and your friends give you a hard time about it, which makes you feel down and hopeless, but somehow you stay brave and keep trying to figure it out. You feel ready to do something, you just don’t know what, and you were hoping maybe coming here could give you a place to work on your health. Does that sound about right?”
Teen: “I think that’s pretty much it. Plus the McDonald’s.”
Clinician: “Right, that’s important too – we have to consider your motivation! I wonder if we could talk about this more at our next visit – would that be alright?”
Offices with additional resources might be able to offer some of those as well, if timing seems appropriate; for example, referral to a wellness coach or social worker or nutritionist could be helpful int his case. With the spirit of PACE and the skills of OARS, you can be well on your way to fostering behavior changes that could last a lifetime! Check out the resources from the American Academy of Pediatrics with video and narrative demonstrations of motivational interviewing in pediatrics.
Dr. Rosenfeld is assistant professor in the departments of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Medical Center and the university’s Robert Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. He reported no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “Engagement and disengagement,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
2. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “The spirit of motivational interviewing,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
3. Naar S, Suarez M. “Adolescence and emerging adulthood: A brief review of development,” in “Motivational interviewing with adolescents and young adults” (New York: Guilford, 2011).
Kyle is a 14-year-old cisgender male who just moved to your town. At his first well-check, his single father brings him in reluctantly, stating, “We’ve never liked doctors.” Kyle has a history of asthma and obesity that have been relatively unchanged over time. He is an average student, an avid gamer, and seems somewhat shy. Privately he admits to occasional cannabis use. His father has no concerns, lamenting, “He’s always been pretty healthy for a fat kid.” Next patient?
Of course there is a lot to work with here. You might be concerned with Kyle’s asthma; his weight, sedentary nature, and body image; the criticism from his father and concerns about self-esteem; the possibility of anxiety in relation to his shyness; and the health effects of his cannabis use. In the end, recommendations for behavior change seem likely. These might take the form of tips on exercise, nutrition, substance use, study habits, parenting, social activities, or mental health support; the literature on behavior change would suggest that any success will be predicated on trust. How can we learn from someone we do not trust?1
To build trust is no easy task, and yet is perhaps the foundation on which the entire clinical relationship rests. Guidance from decades of evidence supporting the use of motivational interviewing2 suggests that the process of building rapport can be neatly summed up in an acronym as PACE. This represents Partnership, Acceptance, Compassion, and Evocation. Almost too clichéd to repeat, the most powerful change agent is the person making the change. In the setting of pediatric health care, we sometimes lean on caregivers to initiate or promote change because they are an intimate part of the patient’s microsystem, and thus moving one gear (the parents) inevitably shifts something in connected gears (the children).
So Partnership is centered on the patient, but inclusive of any important person in the patient’s sphere. In a family-based approach, this might show up as leveraging Kyle’s father’s motivation for behavior change by having the father start an exercise routine. This role models behavior change, shifts the home environment around the behavior, and builds empathy in the parent for the inherent challenges of change processes.
Acceptance can be distilled into knowing that the patient and family are doing the best they can. This does not preclude the possibility of change, but it seats this possibility in an attitude of assumed adequacy. There is nothing wrong with the patient, nothing to be fixed, just the possibility for change.
Similarly, Compassion takes a nonjudgmental viewpoint. With the stance of “this could happen to anybody,” the patient can feel responsible without feeling blamed. Noting the patient’s suffering without blame allows the clinician to be motivated not just to empathize, but to help.
And from this basis of compassionate partnership, the work of Evocation begins. What is happening in the patient’s life and relationships? What are their own goals and values? Where are the discrepancies between what the patient wants and what the patient does? For teenagers, this often brings into conflict developmentally appropriate wishes for autonomy – wanting to drive or get a car or stay out later or have more privacy – with developmentally typical challenges regarding responsibility.3 For example:
Clinician: “You want to use the car, and your parents want you to pay for the gas, but you’re out of money from buying weed. I see how you’re stuck.”
Teen: “Yeah, they really need to give me more allowance. It’s not like we’re living in the 1990s anymore!”
Clinician: “So you could ask for more allowance to get more money for gas. Any other ideas?”
Teen: “I could give up smoking pot and just be miserable all the time.”
Clinician: “Yeah, that sounds too difficult right now; if anything it sounds like you’d like to smoke more pot if you had more money.”
Teen: “Nah, I’m not that hooked on it. ... I could probably smoke a bit less each week and save some gas money.”
The PACE acronym also serves as a reminder of the patience required to grow connection where none has previously existed – pace yourself. Here are some skills-based tips to foster the spirit of motivational interviewing to help balance patience with the time frame of a pediatric check-in. The OARS skills represent the fundamental building blocks of motivational interviewing in practice. Taking the case of Kyle as an example, an Open-Ended Question makes space for the child or parent to express their views with less interviewer bias. Reflections expand this space by underscoring and, in the case of complex Reflections, adding some nuance to what the patient has to say.
Clinician: “How do you feel about your body?”
Teen: “Well, I’m fat. Nobody really wants to be fat. It sucks. But what can I do?”
Clinician: “You feel fat and kind of hopeless.”
Teen: “Yeah, I know you’re going to tell me to go on a diet and start exercising. Doesn’t work. My dad says I was born fat; I guess I’m going to stay that way.”
Clinician: “Sounds like you and your dad can get down on you for your weight. That must feel terrible.”
Teen: “Ah, it’s not that bad. I’m kind of used to it. Fat kid at home, fat kid at school.”
Affirmations are statements focusing on positive actions or attributes of the patient. They tend to build rapport by demonstrating that the clinician sees the strengths of the patient, not just the problems.
Clinician: “I’m pretty impressed that you’re able to show up here and talk about this. It can’t be easy when it sounds like your family and friends have put you down so much that you’re even putting yourself down about your body.”
Teen: “I didn’t really want to come, but then I thought, maybe this new doctor will have some new ideas. I actually want to do something about it, I just don’t know if anything will help. Plus my dad said if I showed up, we could go to McDonald’s afterward.”
Summaries are multipurpose. They demonstrate that you have been listening closely, which builds rapport. They provide a chance to put information together so that both clinician and patient can reflect on the sum of the data and notice what may be missing. And they provide a pause to consider where to go next.
Clinician: “So if I’m getting it right, you’ve been worried about your weight for a long time now. Your dad and your friends give you a hard time about it, which makes you feel down and hopeless, but somehow you stay brave and keep trying to figure it out. You feel ready to do something, you just don’t know what, and you were hoping maybe coming here could give you a place to work on your health. Does that sound about right?”
Teen: “I think that’s pretty much it. Plus the McDonald’s.”
Clinician: “Right, that’s important too – we have to consider your motivation! I wonder if we could talk about this more at our next visit – would that be alright?”
Offices with additional resources might be able to offer some of those as well, if timing seems appropriate; for example, referral to a wellness coach or social worker or nutritionist could be helpful int his case. With the spirit of PACE and the skills of OARS, you can be well on your way to fostering behavior changes that could last a lifetime! Check out the resources from the American Academy of Pediatrics with video and narrative demonstrations of motivational interviewing in pediatrics.
Dr. Rosenfeld is assistant professor in the departments of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Medical Center and the university’s Robert Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. He reported no relevant disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “Engagement and disengagement,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
2. Miller WR, Rollnick S. “The spirit of motivational interviewing,” in “Motivational interviewing: Helping people change,” 3rd ed. (New York: Guilford, 2013).
3. Naar S, Suarez M. “Adolescence and emerging adulthood: A brief review of development,” in “Motivational interviewing with adolescents and young adults” (New York: Guilford, 2011).
Hospitalist well-being during the pandemic
Navigating COVID-19 requires self-care
The global COVID-19 pandemic has escalated everyone’s stress levels, especially clinicians caring for hospitalized patients. New pressures have added to everyday stress, new studies have revised prior patient care recommendations, and the world generally seems upside down. What can a busy hospitalist do to maintain a modicum of sanity in all the craziness?
The stressors facing hospitalists
Uncertainty
Of all the burdens COVID-19 has unleashed, the biggest may be uncertainty. Not only is there unease about the virus itself, there also is legitimate concern about the future of medicine, said Elizabeth Harry, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist and senior director of clinical affairs at the University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora.
“What does it look like after an event like this, particularly in areas like academic medicine and teaching our next generation and getting funding for research? And how do we continue to produce physicians that can provide excellent care?” she asked.
There is also uncertainty in the best way to care for patients, said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“There are some models that are emerging to predict who will have a worse outcome, but they’re still not great models, so we have uncertainty for a given patient.” And, she noted, as the science continues to evolve, there exists a constant worry that “you might have inadvertently caused someone harm.”
The financial implications of the pandemic are creating uncertainty too. “When you fund a health care system with elective procedures and you can’t do those, and instead have to shift to the most essential services, a lot of places are seeing a massive deficit, which is going to affect staff morale and some physician offices are going to close,” said Elisabeth Poorman, MD, MPH, a primary care and internal medicine physician and chair of the King County Medical Society Physician Wellness Committee in Seattle.
Fear
When the pandemic began in the United States, “fear of the unknown was perhaps the scariest part, particularly as it pertained to personal protective equipment,” said Mark Rudolph, MD, SFHM, chief experience officer and vice president of patient experience and physician development at Sound Physicians in Tacoma, Wash. “For most clinicians, this is the first time that they are themselves in harm’s way while they do their jobs. And worse, they risk bringing the virus home to their families. That is the concern I hear most.”
Anxiety
Worrying about being able to provide excellent patient care is a big stressor, especially since this is the heart and soul of why most hospitalists have gone into their line of work.
“Part of providing excellent care to your patients is providing excellent supportive care to their families,” Dr. Harry said. “There’s some dissonance there in not being able to allow the family to come visit, but wanting to keep them safe, and it feels really hard to support your patients and support their families in the best way. It can feel like you’re just watching and waiting to see what will happen, and that we don’t have a lot of agency over which direction things take.”
There is concern for health care team members as well, Dr. Harry added. “Physicians care a lot about their teams and how they’re doing. I think there’s a sense of esprit de corps among folks and worry for each other there.”
Guilt
Although you may be at the hospital all day, you may feel guilty when you are not providing direct patient care. Or maybe you or someone on your team has an immunodeficiency and can’t be on the front line. Perhaps one of your team members contracted COVID-19 and you did not. Whatever the case, guilt is another emotion that is rampant among hospitalists right now, Dr. Barrett said.
Burnout
Unfortunately, burnout is a potential reality in times of high stress. “Burnout is dynamic,” said Dr. Poorman. “It’s a process by which your emotional and cognitive reserves are exhausted. The people with the highest burnout are the ones who are still trying to provide the standard of care, or above the standard of care in dysfunctional systems.”
Dr. Harry noted that burnout presents in different ways for different people, but Dr. Rudolph added that it’s crucial for hospitalist team members to watch for signs of burnout so they can intervene and/or get help for their colleagues.
Warning signs in yourself or others that burnout could be on the horizon include:
- Fatigue/exhaustion – Whether emotional or physical (or both), this can become a problem if it “just doesn’t seem to go away despite rest and time away from work,” said Dr. Rudolph.
- Behavioral changes – Any behavior that’s out of the ordinary may be a red flag, like lashing out at someone at work.
- Overwork – Working too much can be caused by an inability to let go of patient care, Dr. Barrett said.
- Not working enough – This may include avoiding tasks and having difficulty meeting deadlines.
- Maladaptive coping behaviors – Excessive consumption of alcohol or drugs is a common coping mechanism. “Even excessive consumption of news is something that people are using to numb out a little bit,” said Dr. Harry.
- Depersonalization – “This is where you start to look at patients, colleagues, or administrators as ‘them’ and you can’t connect as deeply,” Dr. Harry said. “Part of that’s protective and a normal thing to do during a big trauma like this, but it’s also incredibly distancing. Any language that people start using that feels like ‘us’ or ‘them’ is a warning sign.”
- Disengagement – Many people disengage from their work, but Dr. Poorman said physicians tend to disengage from other parts of their lives, such as exercise and family interaction.
Protecting yourself while supporting others
Like the illustration of putting the oxygen mask on yourself first so you can help others, it’s important to protect your own mental and physical health as you support your fellow physicians. Here’s what the experts suggest.
Focus on basic needs
“When you’re in the midst of a trauma, which we are, you don’t want to open all of that up and go to the depths of your thoughts about the grief of all of it because it can actually make the trauma worse,” said Dr. Harry. “There’s a lot of literature that debriefing is really helpful after the event, but if you do it during the event, it can be really dangerous.”
Instead, she said, the goal should be focusing on your basic needs and what you need to do to get through each day, like keeping you and your family in good health. “What is your purpose? Staying connected to why you do this and staying focused on the present is really important,” Dr. Harry noted.
Do your best to get a good night’s sleep, exercise as much as you can, talk to others, and see a mental health provider if your anxiety is too high, advises Dr. Barrett. “Even avoiding blue light from phones and screens within 2 hours of bedtime, parking further away from the hospital and walking, and taking the stairs are things that add up in a big way.”
Keep up your normal routine
“Right now, it’s really critical for clinicians to keep up components of their routine that feel ‘normal,’ ” Dr. Rudolph said. “Whether it’s exercise, playing board games with their kids, or spending time on a hobby, it’s critical to allow yourself these comfortable, predictable, and rewarding detours.”
Set limits
People under stress tend to find unhealthy ways to cope. Instead, try being intentional about what you are consuming by putting limits on things like your news, alcohol consumption, and the number of hours you work, said Dr. Harry.
Implement a culture of wellness
Dr. Barrett believes in creating the work culture we want to be in, one that ensures people have psychological safety, allows them to ask for help, encourages them to disconnect completely from work, and makes them feel valued and listened to. She likes the example of “the pause,” which is called by a team member right after a patient expires.
“It’s a 30-second moment of silence where we reflect on the patient, their loved ones, and every member of the health care team who helped support and treat them,” said Dr. Barrett. “At the conclusion, you say: ‘Thank you. Is there anything you need to be able to go back to the care of other patients?’ Because it’s unnatural to have this terrible thing that happened and then just act like nothing happened.”
Target resources
Be proactive and know where to find resources before you need them, advised Dr. Harry. “Most institutions have free mental health resources, either through their employee assistance programs or HR, plus there’s lots of national organizations that are offering free resources to health care providers.”
Focus on what you can control
Separating what is under your control from what is not is a struggle for everyone, Dr. Poorman said, but it’s helpful to think about the ways you can have an impact and what you’re able to control.
“There was a woman who was diagnosed with early-onset Parkinson’s that I heard giving an interview at the beginning of this pandemic,” she said. “It was the most helpful advice I got, which was: ‘Think of the next good thing you can do.’ You can’t fix everything, so what’s the next good thing you can do?”
Maintain connectivity
Make sure you are utilizing your support circle and staying connected. “That sense of connection is incredibly protective on multiple fronts for depression, for burnout, for suicide ideation, etc.,” Dr. Harry said.
“It doesn’t matter if it’s your teammates at work, your family at home, your best friend from medical school – whomever you can debrief with, vent with, and just share your thoughts and feelings with, these outlets are critical for all of us to process our emotions and diffuse stress and anxiety,” said Dr. Rudolph.
Dr. Poorman is concerned that there could be a spike in physician suicides caused by increased stress, so she also encourages talking openly about what is going on and about getting help when it’s necessary. “Many of us are afraid to seek care because we can actually have our ability to practice medicine questioned, but now is not the time for heroes. Now is the time for people who are willing to recognize their own strengths and limitations to take care of one another.”
Be compassionate toward others
Keep in mind that everyone is stressed out and offer empathy and compassion. “I think everybody’s struggling to try to figure this out and the more that we can give each other the benefit of the doubt and a little grace, the more protective that is,” said Dr. Harry.
Listening is meaningful too. “Recognizing opportunities to validate and acknowledge the feelings that are being shared with you by your colleagues is critical,” Dr. Rudolph said. “We all need to know that we’re not alone, that our thoughts and feelings are okay, and when we share a difficult story, the value of someone saying something as simple as, ‘wow, that sounds like it was really hard,’ is immense.”
Be compassionate toward yourself
Try to give yourself a break and be as compassionate with yourself as you would with others. It’s okay that you’re not getting in shape, publishing prolifically, or redesigning your house right now.
“There’s a lot of data linking lack of self-compassion to burnout,” said Dr. Harry. She says there are courses on self-compassion available that help you work on being kinder to yourself.
Get a “battle buddy”
The American Medical Association has a free “buddy system” program called PeerRx to help physicians cope during the pandemic. Dr. Rudolph said that now is a great time to use this military-developed intervention in which each team member checks in with a chosen partner at agreed-upon intervals.
For example, “You can tell that person: ‘If I don’t call my family for a week that’s a red flag for me.’ And then you hold each other accountable to those things,” Dr. Harry said.
The buddy system is another way to harness that sense of connection that is so vital to our health and well-being.
“The simple act of showing that you care … can make all the difference when you’re doing this kind of work that is both challenging and dangerous,” said Dr. Rudolph.
Navigating COVID-19 requires self-care
Navigating COVID-19 requires self-care
The global COVID-19 pandemic has escalated everyone’s stress levels, especially clinicians caring for hospitalized patients. New pressures have added to everyday stress, new studies have revised prior patient care recommendations, and the world generally seems upside down. What can a busy hospitalist do to maintain a modicum of sanity in all the craziness?
The stressors facing hospitalists
Uncertainty
Of all the burdens COVID-19 has unleashed, the biggest may be uncertainty. Not only is there unease about the virus itself, there also is legitimate concern about the future of medicine, said Elizabeth Harry, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist and senior director of clinical affairs at the University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora.
“What does it look like after an event like this, particularly in areas like academic medicine and teaching our next generation and getting funding for research? And how do we continue to produce physicians that can provide excellent care?” she asked.
There is also uncertainty in the best way to care for patients, said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“There are some models that are emerging to predict who will have a worse outcome, but they’re still not great models, so we have uncertainty for a given patient.” And, she noted, as the science continues to evolve, there exists a constant worry that “you might have inadvertently caused someone harm.”
The financial implications of the pandemic are creating uncertainty too. “When you fund a health care system with elective procedures and you can’t do those, and instead have to shift to the most essential services, a lot of places are seeing a massive deficit, which is going to affect staff morale and some physician offices are going to close,” said Elisabeth Poorman, MD, MPH, a primary care and internal medicine physician and chair of the King County Medical Society Physician Wellness Committee in Seattle.
Fear
When the pandemic began in the United States, “fear of the unknown was perhaps the scariest part, particularly as it pertained to personal protective equipment,” said Mark Rudolph, MD, SFHM, chief experience officer and vice president of patient experience and physician development at Sound Physicians in Tacoma, Wash. “For most clinicians, this is the first time that they are themselves in harm’s way while they do their jobs. And worse, they risk bringing the virus home to their families. That is the concern I hear most.”
Anxiety
Worrying about being able to provide excellent patient care is a big stressor, especially since this is the heart and soul of why most hospitalists have gone into their line of work.
“Part of providing excellent care to your patients is providing excellent supportive care to their families,” Dr. Harry said. “There’s some dissonance there in not being able to allow the family to come visit, but wanting to keep them safe, and it feels really hard to support your patients and support their families in the best way. It can feel like you’re just watching and waiting to see what will happen, and that we don’t have a lot of agency over which direction things take.”
There is concern for health care team members as well, Dr. Harry added. “Physicians care a lot about their teams and how they’re doing. I think there’s a sense of esprit de corps among folks and worry for each other there.”
Guilt
Although you may be at the hospital all day, you may feel guilty when you are not providing direct patient care. Or maybe you or someone on your team has an immunodeficiency and can’t be on the front line. Perhaps one of your team members contracted COVID-19 and you did not. Whatever the case, guilt is another emotion that is rampant among hospitalists right now, Dr. Barrett said.
Burnout
Unfortunately, burnout is a potential reality in times of high stress. “Burnout is dynamic,” said Dr. Poorman. “It’s a process by which your emotional and cognitive reserves are exhausted. The people with the highest burnout are the ones who are still trying to provide the standard of care, or above the standard of care in dysfunctional systems.”
Dr. Harry noted that burnout presents in different ways for different people, but Dr. Rudolph added that it’s crucial for hospitalist team members to watch for signs of burnout so they can intervene and/or get help for their colleagues.
Warning signs in yourself or others that burnout could be on the horizon include:
- Fatigue/exhaustion – Whether emotional or physical (or both), this can become a problem if it “just doesn’t seem to go away despite rest and time away from work,” said Dr. Rudolph.
- Behavioral changes – Any behavior that’s out of the ordinary may be a red flag, like lashing out at someone at work.
- Overwork – Working too much can be caused by an inability to let go of patient care, Dr. Barrett said.
- Not working enough – This may include avoiding tasks and having difficulty meeting deadlines.
- Maladaptive coping behaviors – Excessive consumption of alcohol or drugs is a common coping mechanism. “Even excessive consumption of news is something that people are using to numb out a little bit,” said Dr. Harry.
- Depersonalization – “This is where you start to look at patients, colleagues, or administrators as ‘them’ and you can’t connect as deeply,” Dr. Harry said. “Part of that’s protective and a normal thing to do during a big trauma like this, but it’s also incredibly distancing. Any language that people start using that feels like ‘us’ or ‘them’ is a warning sign.”
- Disengagement – Many people disengage from their work, but Dr. Poorman said physicians tend to disengage from other parts of their lives, such as exercise and family interaction.
Protecting yourself while supporting others
Like the illustration of putting the oxygen mask on yourself first so you can help others, it’s important to protect your own mental and physical health as you support your fellow physicians. Here’s what the experts suggest.
Focus on basic needs
“When you’re in the midst of a trauma, which we are, you don’t want to open all of that up and go to the depths of your thoughts about the grief of all of it because it can actually make the trauma worse,” said Dr. Harry. “There’s a lot of literature that debriefing is really helpful after the event, but if you do it during the event, it can be really dangerous.”
Instead, she said, the goal should be focusing on your basic needs and what you need to do to get through each day, like keeping you and your family in good health. “What is your purpose? Staying connected to why you do this and staying focused on the present is really important,” Dr. Harry noted.
Do your best to get a good night’s sleep, exercise as much as you can, talk to others, and see a mental health provider if your anxiety is too high, advises Dr. Barrett. “Even avoiding blue light from phones and screens within 2 hours of bedtime, parking further away from the hospital and walking, and taking the stairs are things that add up in a big way.”
Keep up your normal routine
“Right now, it’s really critical for clinicians to keep up components of their routine that feel ‘normal,’ ” Dr. Rudolph said. “Whether it’s exercise, playing board games with their kids, or spending time on a hobby, it’s critical to allow yourself these comfortable, predictable, and rewarding detours.”
Set limits
People under stress tend to find unhealthy ways to cope. Instead, try being intentional about what you are consuming by putting limits on things like your news, alcohol consumption, and the number of hours you work, said Dr. Harry.
Implement a culture of wellness
Dr. Barrett believes in creating the work culture we want to be in, one that ensures people have psychological safety, allows them to ask for help, encourages them to disconnect completely from work, and makes them feel valued and listened to. She likes the example of “the pause,” which is called by a team member right after a patient expires.
“It’s a 30-second moment of silence where we reflect on the patient, their loved ones, and every member of the health care team who helped support and treat them,” said Dr. Barrett. “At the conclusion, you say: ‘Thank you. Is there anything you need to be able to go back to the care of other patients?’ Because it’s unnatural to have this terrible thing that happened and then just act like nothing happened.”
Target resources
Be proactive and know where to find resources before you need them, advised Dr. Harry. “Most institutions have free mental health resources, either through their employee assistance programs or HR, plus there’s lots of national organizations that are offering free resources to health care providers.”
Focus on what you can control
Separating what is under your control from what is not is a struggle for everyone, Dr. Poorman said, but it’s helpful to think about the ways you can have an impact and what you’re able to control.
“There was a woman who was diagnosed with early-onset Parkinson’s that I heard giving an interview at the beginning of this pandemic,” she said. “It was the most helpful advice I got, which was: ‘Think of the next good thing you can do.’ You can’t fix everything, so what’s the next good thing you can do?”
Maintain connectivity
Make sure you are utilizing your support circle and staying connected. “That sense of connection is incredibly protective on multiple fronts for depression, for burnout, for suicide ideation, etc.,” Dr. Harry said.
“It doesn’t matter if it’s your teammates at work, your family at home, your best friend from medical school – whomever you can debrief with, vent with, and just share your thoughts and feelings with, these outlets are critical for all of us to process our emotions and diffuse stress and anxiety,” said Dr. Rudolph.
Dr. Poorman is concerned that there could be a spike in physician suicides caused by increased stress, so she also encourages talking openly about what is going on and about getting help when it’s necessary. “Many of us are afraid to seek care because we can actually have our ability to practice medicine questioned, but now is not the time for heroes. Now is the time for people who are willing to recognize their own strengths and limitations to take care of one another.”
Be compassionate toward others
Keep in mind that everyone is stressed out and offer empathy and compassion. “I think everybody’s struggling to try to figure this out and the more that we can give each other the benefit of the doubt and a little grace, the more protective that is,” said Dr. Harry.
Listening is meaningful too. “Recognizing opportunities to validate and acknowledge the feelings that are being shared with you by your colleagues is critical,” Dr. Rudolph said. “We all need to know that we’re not alone, that our thoughts and feelings are okay, and when we share a difficult story, the value of someone saying something as simple as, ‘wow, that sounds like it was really hard,’ is immense.”
Be compassionate toward yourself
Try to give yourself a break and be as compassionate with yourself as you would with others. It’s okay that you’re not getting in shape, publishing prolifically, or redesigning your house right now.
“There’s a lot of data linking lack of self-compassion to burnout,” said Dr. Harry. She says there are courses on self-compassion available that help you work on being kinder to yourself.
Get a “battle buddy”
The American Medical Association has a free “buddy system” program called PeerRx to help physicians cope during the pandemic. Dr. Rudolph said that now is a great time to use this military-developed intervention in which each team member checks in with a chosen partner at agreed-upon intervals.
For example, “You can tell that person: ‘If I don’t call my family for a week that’s a red flag for me.’ And then you hold each other accountable to those things,” Dr. Harry said.
The buddy system is another way to harness that sense of connection that is so vital to our health and well-being.
“The simple act of showing that you care … can make all the difference when you’re doing this kind of work that is both challenging and dangerous,” said Dr. Rudolph.
The global COVID-19 pandemic has escalated everyone’s stress levels, especially clinicians caring for hospitalized patients. New pressures have added to everyday stress, new studies have revised prior patient care recommendations, and the world generally seems upside down. What can a busy hospitalist do to maintain a modicum of sanity in all the craziness?
The stressors facing hospitalists
Uncertainty
Of all the burdens COVID-19 has unleashed, the biggest may be uncertainty. Not only is there unease about the virus itself, there also is legitimate concern about the future of medicine, said Elizabeth Harry, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist and senior director of clinical affairs at the University of Colorado Hospital in Aurora.
“What does it look like after an event like this, particularly in areas like academic medicine and teaching our next generation and getting funding for research? And how do we continue to produce physicians that can provide excellent care?” she asked.
There is also uncertainty in the best way to care for patients, said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, a hospitalist at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“There are some models that are emerging to predict who will have a worse outcome, but they’re still not great models, so we have uncertainty for a given patient.” And, she noted, as the science continues to evolve, there exists a constant worry that “you might have inadvertently caused someone harm.”
The financial implications of the pandemic are creating uncertainty too. “When you fund a health care system with elective procedures and you can’t do those, and instead have to shift to the most essential services, a lot of places are seeing a massive deficit, which is going to affect staff morale and some physician offices are going to close,” said Elisabeth Poorman, MD, MPH, a primary care and internal medicine physician and chair of the King County Medical Society Physician Wellness Committee in Seattle.
Fear
When the pandemic began in the United States, “fear of the unknown was perhaps the scariest part, particularly as it pertained to personal protective equipment,” said Mark Rudolph, MD, SFHM, chief experience officer and vice president of patient experience and physician development at Sound Physicians in Tacoma, Wash. “For most clinicians, this is the first time that they are themselves in harm’s way while they do their jobs. And worse, they risk bringing the virus home to their families. That is the concern I hear most.”
Anxiety
Worrying about being able to provide excellent patient care is a big stressor, especially since this is the heart and soul of why most hospitalists have gone into their line of work.
“Part of providing excellent care to your patients is providing excellent supportive care to their families,” Dr. Harry said. “There’s some dissonance there in not being able to allow the family to come visit, but wanting to keep them safe, and it feels really hard to support your patients and support their families in the best way. It can feel like you’re just watching and waiting to see what will happen, and that we don’t have a lot of agency over which direction things take.”
There is concern for health care team members as well, Dr. Harry added. “Physicians care a lot about their teams and how they’re doing. I think there’s a sense of esprit de corps among folks and worry for each other there.”
Guilt
Although you may be at the hospital all day, you may feel guilty when you are not providing direct patient care. Or maybe you or someone on your team has an immunodeficiency and can’t be on the front line. Perhaps one of your team members contracted COVID-19 and you did not. Whatever the case, guilt is another emotion that is rampant among hospitalists right now, Dr. Barrett said.
Burnout
Unfortunately, burnout is a potential reality in times of high stress. “Burnout is dynamic,” said Dr. Poorman. “It’s a process by which your emotional and cognitive reserves are exhausted. The people with the highest burnout are the ones who are still trying to provide the standard of care, or above the standard of care in dysfunctional systems.”
Dr. Harry noted that burnout presents in different ways for different people, but Dr. Rudolph added that it’s crucial for hospitalist team members to watch for signs of burnout so they can intervene and/or get help for their colleagues.
Warning signs in yourself or others that burnout could be on the horizon include:
- Fatigue/exhaustion – Whether emotional or physical (or both), this can become a problem if it “just doesn’t seem to go away despite rest and time away from work,” said Dr. Rudolph.
- Behavioral changes – Any behavior that’s out of the ordinary may be a red flag, like lashing out at someone at work.
- Overwork – Working too much can be caused by an inability to let go of patient care, Dr. Barrett said.
- Not working enough – This may include avoiding tasks and having difficulty meeting deadlines.
- Maladaptive coping behaviors – Excessive consumption of alcohol or drugs is a common coping mechanism. “Even excessive consumption of news is something that people are using to numb out a little bit,” said Dr. Harry.
- Depersonalization – “This is where you start to look at patients, colleagues, or administrators as ‘them’ and you can’t connect as deeply,” Dr. Harry said. “Part of that’s protective and a normal thing to do during a big trauma like this, but it’s also incredibly distancing. Any language that people start using that feels like ‘us’ or ‘them’ is a warning sign.”
- Disengagement – Many people disengage from their work, but Dr. Poorman said physicians tend to disengage from other parts of their lives, such as exercise and family interaction.
Protecting yourself while supporting others
Like the illustration of putting the oxygen mask on yourself first so you can help others, it’s important to protect your own mental and physical health as you support your fellow physicians. Here’s what the experts suggest.
Focus on basic needs
“When you’re in the midst of a trauma, which we are, you don’t want to open all of that up and go to the depths of your thoughts about the grief of all of it because it can actually make the trauma worse,” said Dr. Harry. “There’s a lot of literature that debriefing is really helpful after the event, but if you do it during the event, it can be really dangerous.”
Instead, she said, the goal should be focusing on your basic needs and what you need to do to get through each day, like keeping you and your family in good health. “What is your purpose? Staying connected to why you do this and staying focused on the present is really important,” Dr. Harry noted.
Do your best to get a good night’s sleep, exercise as much as you can, talk to others, and see a mental health provider if your anxiety is too high, advises Dr. Barrett. “Even avoiding blue light from phones and screens within 2 hours of bedtime, parking further away from the hospital and walking, and taking the stairs are things that add up in a big way.”
Keep up your normal routine
“Right now, it’s really critical for clinicians to keep up components of their routine that feel ‘normal,’ ” Dr. Rudolph said. “Whether it’s exercise, playing board games with their kids, or spending time on a hobby, it’s critical to allow yourself these comfortable, predictable, and rewarding detours.”
Set limits
People under stress tend to find unhealthy ways to cope. Instead, try being intentional about what you are consuming by putting limits on things like your news, alcohol consumption, and the number of hours you work, said Dr. Harry.
Implement a culture of wellness
Dr. Barrett believes in creating the work culture we want to be in, one that ensures people have psychological safety, allows them to ask for help, encourages them to disconnect completely from work, and makes them feel valued and listened to. She likes the example of “the pause,” which is called by a team member right after a patient expires.
“It’s a 30-second moment of silence where we reflect on the patient, their loved ones, and every member of the health care team who helped support and treat them,” said Dr. Barrett. “At the conclusion, you say: ‘Thank you. Is there anything you need to be able to go back to the care of other patients?’ Because it’s unnatural to have this terrible thing that happened and then just act like nothing happened.”
Target resources
Be proactive and know where to find resources before you need them, advised Dr. Harry. “Most institutions have free mental health resources, either through their employee assistance programs or HR, plus there’s lots of national organizations that are offering free resources to health care providers.”
Focus on what you can control
Separating what is under your control from what is not is a struggle for everyone, Dr. Poorman said, but it’s helpful to think about the ways you can have an impact and what you’re able to control.
“There was a woman who was diagnosed with early-onset Parkinson’s that I heard giving an interview at the beginning of this pandemic,” she said. “It was the most helpful advice I got, which was: ‘Think of the next good thing you can do.’ You can’t fix everything, so what’s the next good thing you can do?”
Maintain connectivity
Make sure you are utilizing your support circle and staying connected. “That sense of connection is incredibly protective on multiple fronts for depression, for burnout, for suicide ideation, etc.,” Dr. Harry said.
“It doesn’t matter if it’s your teammates at work, your family at home, your best friend from medical school – whomever you can debrief with, vent with, and just share your thoughts and feelings with, these outlets are critical for all of us to process our emotions and diffuse stress and anxiety,” said Dr. Rudolph.
Dr. Poorman is concerned that there could be a spike in physician suicides caused by increased stress, so she also encourages talking openly about what is going on and about getting help when it’s necessary. “Many of us are afraid to seek care because we can actually have our ability to practice medicine questioned, but now is not the time for heroes. Now is the time for people who are willing to recognize their own strengths and limitations to take care of one another.”
Be compassionate toward others
Keep in mind that everyone is stressed out and offer empathy and compassion. “I think everybody’s struggling to try to figure this out and the more that we can give each other the benefit of the doubt and a little grace, the more protective that is,” said Dr. Harry.
Listening is meaningful too. “Recognizing opportunities to validate and acknowledge the feelings that are being shared with you by your colleagues is critical,” Dr. Rudolph said. “We all need to know that we’re not alone, that our thoughts and feelings are okay, and when we share a difficult story, the value of someone saying something as simple as, ‘wow, that sounds like it was really hard,’ is immense.”
Be compassionate toward yourself
Try to give yourself a break and be as compassionate with yourself as you would with others. It’s okay that you’re not getting in shape, publishing prolifically, or redesigning your house right now.
“There’s a lot of data linking lack of self-compassion to burnout,” said Dr. Harry. She says there are courses on self-compassion available that help you work on being kinder to yourself.
Get a “battle buddy”
The American Medical Association has a free “buddy system” program called PeerRx to help physicians cope during the pandemic. Dr. Rudolph said that now is a great time to use this military-developed intervention in which each team member checks in with a chosen partner at agreed-upon intervals.
For example, “You can tell that person: ‘If I don’t call my family for a week that’s a red flag for me.’ And then you hold each other accountable to those things,” Dr. Harry said.
The buddy system is another way to harness that sense of connection that is so vital to our health and well-being.
“The simple act of showing that you care … can make all the difference when you’re doing this kind of work that is both challenging and dangerous,” said Dr. Rudolph.
Racism: Developmental perspective can inform tough conversations
Can we help our pediatric patients with the complicated problems of racism, especially if we are privileged (and even white) professionals? We may not have experienced discrimination, but we can still advise and address it. Racist discrimination, fear, trauma, or distress may produce or exacerbate conditions we are treating.
Three levels of racism impact children’s health and health care: “structural or institutional” policies that influence social determinants of health; “personally mediated” differential treatment based on assumptions about one’s abilities, motives, or intents; and the resulting “internalization” of stereotypes into one’s identity, undermining confidence, self-esteem, and mental health. We can help advocate about structural racism and ensure equity within our offices, but how best to counsel the families and children themselves?
Racism includes actions of “assigning value based on the social interpretation of how a person looks” (Ethn Dis. 2008;18[4]:496-504). “Social interpretations” develop from an early age. Newborns detect differences in appearance and may startle or cry seeing a parent’s drastic haircut or new hat. Parents generally know to use soothing words and tone, bring the difference into view gradually, smile and comfort the child, and explain the change; these are good skills for later, too. Infants notice skin color, which, unlike clothes, is a stable feature by which to recognize parents. Social interpretation of these differences is cued from the parents’ feelings and reactions. Adults naturally transmit biases from their own past unless they work to dampen them. If the parent was taught to regard “other” as negative or is generally fearful, the child mirrors this. Working to reduce racism thus requires parents (and professionals) to examine their prejudices to be able to convey positive or neutral reactions to people who are different. Parents need to show curiosity, positive affect, and comfort about people who are different, and do well to seek contact and friendships with people from other groups and include their children in these relationships. We can encourage this outreach plus ensure diversity and respectful interactions in our offices.
Children from age 3 years value fairness and are upset seeing others treated unfairly – easily understanding “not fair” or “mean.” If the person being hurt is like them in race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or sexual preference, they also fear for themselves, family, and friends. Balance is needed in discussing racism to avoid increasing fear or overpromising as risks are real and solutions difficult. Children look to adults for understanding and evidence of action to feel safer, rather than helpless. We should state that leaders are working on “making the rules more fair,” ensuring that people “won’t be allowed do it again,” and “teaching that everyone deserves respect.” Even better, parents and children can generate ideas about child actions, giving them some power as an antidote to anxiety. Age-related possibilities might include drawing a picture of people getting along, talking at show-and-tell, writing a note to officials, making a protest sign, posting thoughts on Facebook, or protesting.
With age, the culture increasingly influences a child’s attitudes. Children see lots of teasing and bullying based on differences from being overweight or wearing glasses, to skin color. It is helpful to interpret for children that bullies are insecure, or sometimes have been hurt, and they put other people down to feel better than someone else. Thinking about racist acts this way may reduce the desire for revenge and a cycle of aggression. Effective anti-bullying programs help children recognize bullying, see it as an emergency that requires their action, tell adults, and take action. This action could be surrounding the bully, standing tall, making eye contact, having a dismissive retort, or asking questions that require the bully to think, such as “What do you want to happen by doing this?” We can coach our patients and their parents on these principles as well as advising schools.
Children need to be told that those being put down or held down – especially those like them – have strengths; have made discoveries; have produced writings, art, and music; have shown military bravery, moral leadership, and resistance to discrimination, but it is not the time to show strength when confronted by a gun or police. We can use and arm parents with examples to discuss strengths and accomplishments to help buffer the child from internalization of racist stereotypes. Children need positive role models who look like them; parents can seek out diverse professionals in their children’s lives, such as dentists, doctors, teachers, clergy, mentors, or coaches. We, and parents, can ensure that dolls and books are available, and that the children’s shows, movies, and video games are watched together and include diverse people doing good or brave things. These exposures also are key to all children becoming anti-racist.
Parents can be advised to initiate discussion of racism because children, detecting adult discomfort, may avoid the topic. We can encourage families to give their point of view; otherwise children simply absorb those of peers or the press. Parents should tell their children, “I want you to be able to talk about it if someone is mean or treats you unfairly because of [the color of your skin, your religion, your sex, your disability, etc.]. You might feel helpless, or angry, which is natural. We need to talk about this so you can feel strong. Then we can plan on what we are going to do.” The “sandwich” method of “ask-give information-ask what they think” can encourage discussion and correct misperceptions.
Racist policies have succeeded partly by adult “bullies” dehumanizing the “other.” Most children can consider someone else’s point of view by 4½ years old, shaped with adult help. Parents can begin by telling babies, “That hurts, doesn’t it?” asking toddlers and older, “How would you feel if ... [someone called you a name just because of having red hair]?” or “How do you think she feels when ... [someone pushes her out of line because she wears certain clothes]?” in cases of grabbing, not sharing, hitting, bullying, etc. Older children and teens can analyze more abstract situations when asked, “What if you were the one who ... [got expelled for mumbling about the teacher]?” or “What if that were your sister?” or “How would the world be if everyone ... [got a chance to go to college]?” We can encourage parents to propose these mental exercises to build the child’s perspective-taking while conveying their opinions.
Experiences, including through media, may increase or decrease fear; the child needs to have a supportive person moderating the exposure, providing a positive interpretation, and protecting the child from overwhelm, if needed.
Experiences are insufficient for developing anti-racist attitudes; listening and talking are needed. The first step is to ask children about what they notice, think, and feel about situations reflecting racism, especially as they lack words for these complicated observations. There are television, Internet, and newspaper examples of both racism and anti-racism that can be fruitfully discussed. We can recommend watching or reading together, and asking questions such as, “Why do you think they are shouting [protesting]?” “How do you think the [victim, police] felt?” or “What do you think should be done about this?”
It is important to acknowledge the child’s confusion, fear, anxiety, sadness, or anger as normal and appropriate, not dismissing, too quickly reassuring, or changing the subject, even though it’s uncomfortable.
Physicians and nurse practitioners can make a difference by being aware of our privilege and biases, being open, modeling discussion, screening for impact, offering strategies, advocating with schools, and providing resources such as therapy or legal counsel, as for other social determinants of health.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (https://www.site.chadis.com/). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Can we help our pediatric patients with the complicated problems of racism, especially if we are privileged (and even white) professionals? We may not have experienced discrimination, but we can still advise and address it. Racist discrimination, fear, trauma, or distress may produce or exacerbate conditions we are treating.
Three levels of racism impact children’s health and health care: “structural or institutional” policies that influence social determinants of health; “personally mediated” differential treatment based on assumptions about one’s abilities, motives, or intents; and the resulting “internalization” of stereotypes into one’s identity, undermining confidence, self-esteem, and mental health. We can help advocate about structural racism and ensure equity within our offices, but how best to counsel the families and children themselves?
Racism includes actions of “assigning value based on the social interpretation of how a person looks” (Ethn Dis. 2008;18[4]:496-504). “Social interpretations” develop from an early age. Newborns detect differences in appearance and may startle or cry seeing a parent’s drastic haircut or new hat. Parents generally know to use soothing words and tone, bring the difference into view gradually, smile and comfort the child, and explain the change; these are good skills for later, too. Infants notice skin color, which, unlike clothes, is a stable feature by which to recognize parents. Social interpretation of these differences is cued from the parents’ feelings and reactions. Adults naturally transmit biases from their own past unless they work to dampen them. If the parent was taught to regard “other” as negative or is generally fearful, the child mirrors this. Working to reduce racism thus requires parents (and professionals) to examine their prejudices to be able to convey positive or neutral reactions to people who are different. Parents need to show curiosity, positive affect, and comfort about people who are different, and do well to seek contact and friendships with people from other groups and include their children in these relationships. We can encourage this outreach plus ensure diversity and respectful interactions in our offices.
Children from age 3 years value fairness and are upset seeing others treated unfairly – easily understanding “not fair” or “mean.” If the person being hurt is like them in race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or sexual preference, they also fear for themselves, family, and friends. Balance is needed in discussing racism to avoid increasing fear or overpromising as risks are real and solutions difficult. Children look to adults for understanding and evidence of action to feel safer, rather than helpless. We should state that leaders are working on “making the rules more fair,” ensuring that people “won’t be allowed do it again,” and “teaching that everyone deserves respect.” Even better, parents and children can generate ideas about child actions, giving them some power as an antidote to anxiety. Age-related possibilities might include drawing a picture of people getting along, talking at show-and-tell, writing a note to officials, making a protest sign, posting thoughts on Facebook, or protesting.
With age, the culture increasingly influences a child’s attitudes. Children see lots of teasing and bullying based on differences from being overweight or wearing glasses, to skin color. It is helpful to interpret for children that bullies are insecure, or sometimes have been hurt, and they put other people down to feel better than someone else. Thinking about racist acts this way may reduce the desire for revenge and a cycle of aggression. Effective anti-bullying programs help children recognize bullying, see it as an emergency that requires their action, tell adults, and take action. This action could be surrounding the bully, standing tall, making eye contact, having a dismissive retort, or asking questions that require the bully to think, such as “What do you want to happen by doing this?” We can coach our patients and their parents on these principles as well as advising schools.
Children need to be told that those being put down or held down – especially those like them – have strengths; have made discoveries; have produced writings, art, and music; have shown military bravery, moral leadership, and resistance to discrimination, but it is not the time to show strength when confronted by a gun or police. We can use and arm parents with examples to discuss strengths and accomplishments to help buffer the child from internalization of racist stereotypes. Children need positive role models who look like them; parents can seek out diverse professionals in their children’s lives, such as dentists, doctors, teachers, clergy, mentors, or coaches. We, and parents, can ensure that dolls and books are available, and that the children’s shows, movies, and video games are watched together and include diverse people doing good or brave things. These exposures also are key to all children becoming anti-racist.
Parents can be advised to initiate discussion of racism because children, detecting adult discomfort, may avoid the topic. We can encourage families to give their point of view; otherwise children simply absorb those of peers or the press. Parents should tell their children, “I want you to be able to talk about it if someone is mean or treats you unfairly because of [the color of your skin, your religion, your sex, your disability, etc.]. You might feel helpless, or angry, which is natural. We need to talk about this so you can feel strong. Then we can plan on what we are going to do.” The “sandwich” method of “ask-give information-ask what they think” can encourage discussion and correct misperceptions.
Racist policies have succeeded partly by adult “bullies” dehumanizing the “other.” Most children can consider someone else’s point of view by 4½ years old, shaped with adult help. Parents can begin by telling babies, “That hurts, doesn’t it?” asking toddlers and older, “How would you feel if ... [someone called you a name just because of having red hair]?” or “How do you think she feels when ... [someone pushes her out of line because she wears certain clothes]?” in cases of grabbing, not sharing, hitting, bullying, etc. Older children and teens can analyze more abstract situations when asked, “What if you were the one who ... [got expelled for mumbling about the teacher]?” or “What if that were your sister?” or “How would the world be if everyone ... [got a chance to go to college]?” We can encourage parents to propose these mental exercises to build the child’s perspective-taking while conveying their opinions.
Experiences, including through media, may increase or decrease fear; the child needs to have a supportive person moderating the exposure, providing a positive interpretation, and protecting the child from overwhelm, if needed.
Experiences are insufficient for developing anti-racist attitudes; listening and talking are needed. The first step is to ask children about what they notice, think, and feel about situations reflecting racism, especially as they lack words for these complicated observations. There are television, Internet, and newspaper examples of both racism and anti-racism that can be fruitfully discussed. We can recommend watching or reading together, and asking questions such as, “Why do you think they are shouting [protesting]?” “How do you think the [victim, police] felt?” or “What do you think should be done about this?”
It is important to acknowledge the child’s confusion, fear, anxiety, sadness, or anger as normal and appropriate, not dismissing, too quickly reassuring, or changing the subject, even though it’s uncomfortable.
Physicians and nurse practitioners can make a difference by being aware of our privilege and biases, being open, modeling discussion, screening for impact, offering strategies, advocating with schools, and providing resources such as therapy or legal counsel, as for other social determinants of health.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (https://www.site.chadis.com/). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Can we help our pediatric patients with the complicated problems of racism, especially if we are privileged (and even white) professionals? We may not have experienced discrimination, but we can still advise and address it. Racist discrimination, fear, trauma, or distress may produce or exacerbate conditions we are treating.
Three levels of racism impact children’s health and health care: “structural or institutional” policies that influence social determinants of health; “personally mediated” differential treatment based on assumptions about one’s abilities, motives, or intents; and the resulting “internalization” of stereotypes into one’s identity, undermining confidence, self-esteem, and mental health. We can help advocate about structural racism and ensure equity within our offices, but how best to counsel the families and children themselves?
Racism includes actions of “assigning value based on the social interpretation of how a person looks” (Ethn Dis. 2008;18[4]:496-504). “Social interpretations” develop from an early age. Newborns detect differences in appearance and may startle or cry seeing a parent’s drastic haircut or new hat. Parents generally know to use soothing words and tone, bring the difference into view gradually, smile and comfort the child, and explain the change; these are good skills for later, too. Infants notice skin color, which, unlike clothes, is a stable feature by which to recognize parents. Social interpretation of these differences is cued from the parents’ feelings and reactions. Adults naturally transmit biases from their own past unless they work to dampen them. If the parent was taught to regard “other” as negative or is generally fearful, the child mirrors this. Working to reduce racism thus requires parents (and professionals) to examine their prejudices to be able to convey positive or neutral reactions to people who are different. Parents need to show curiosity, positive affect, and comfort about people who are different, and do well to seek contact and friendships with people from other groups and include their children in these relationships. We can encourage this outreach plus ensure diversity and respectful interactions in our offices.
Children from age 3 years value fairness and are upset seeing others treated unfairly – easily understanding “not fair” or “mean.” If the person being hurt is like them in race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or sexual preference, they also fear for themselves, family, and friends. Balance is needed in discussing racism to avoid increasing fear or overpromising as risks are real and solutions difficult. Children look to adults for understanding and evidence of action to feel safer, rather than helpless. We should state that leaders are working on “making the rules more fair,” ensuring that people “won’t be allowed do it again,” and “teaching that everyone deserves respect.” Even better, parents and children can generate ideas about child actions, giving them some power as an antidote to anxiety. Age-related possibilities might include drawing a picture of people getting along, talking at show-and-tell, writing a note to officials, making a protest sign, posting thoughts on Facebook, or protesting.
With age, the culture increasingly influences a child’s attitudes. Children see lots of teasing and bullying based on differences from being overweight or wearing glasses, to skin color. It is helpful to interpret for children that bullies are insecure, or sometimes have been hurt, and they put other people down to feel better than someone else. Thinking about racist acts this way may reduce the desire for revenge and a cycle of aggression. Effective anti-bullying programs help children recognize bullying, see it as an emergency that requires their action, tell adults, and take action. This action could be surrounding the bully, standing tall, making eye contact, having a dismissive retort, or asking questions that require the bully to think, such as “What do you want to happen by doing this?” We can coach our patients and their parents on these principles as well as advising schools.
Children need to be told that those being put down or held down – especially those like them – have strengths; have made discoveries; have produced writings, art, and music; have shown military bravery, moral leadership, and resistance to discrimination, but it is not the time to show strength when confronted by a gun or police. We can use and arm parents with examples to discuss strengths and accomplishments to help buffer the child from internalization of racist stereotypes. Children need positive role models who look like them; parents can seek out diverse professionals in their children’s lives, such as dentists, doctors, teachers, clergy, mentors, or coaches. We, and parents, can ensure that dolls and books are available, and that the children’s shows, movies, and video games are watched together and include diverse people doing good or brave things. These exposures also are key to all children becoming anti-racist.
Parents can be advised to initiate discussion of racism because children, detecting adult discomfort, may avoid the topic. We can encourage families to give their point of view; otherwise children simply absorb those of peers or the press. Parents should tell their children, “I want you to be able to talk about it if someone is mean or treats you unfairly because of [the color of your skin, your religion, your sex, your disability, etc.]. You might feel helpless, or angry, which is natural. We need to talk about this so you can feel strong. Then we can plan on what we are going to do.” The “sandwich” method of “ask-give information-ask what they think” can encourage discussion and correct misperceptions.
Racist policies have succeeded partly by adult “bullies” dehumanizing the “other.” Most children can consider someone else’s point of view by 4½ years old, shaped with adult help. Parents can begin by telling babies, “That hurts, doesn’t it?” asking toddlers and older, “How would you feel if ... [someone called you a name just because of having red hair]?” or “How do you think she feels when ... [someone pushes her out of line because she wears certain clothes]?” in cases of grabbing, not sharing, hitting, bullying, etc. Older children and teens can analyze more abstract situations when asked, “What if you were the one who ... [got expelled for mumbling about the teacher]?” or “What if that were your sister?” or “How would the world be if everyone ... [got a chance to go to college]?” We can encourage parents to propose these mental exercises to build the child’s perspective-taking while conveying their opinions.
Experiences, including through media, may increase or decrease fear; the child needs to have a supportive person moderating the exposure, providing a positive interpretation, and protecting the child from overwhelm, if needed.
Experiences are insufficient for developing anti-racist attitudes; listening and talking are needed. The first step is to ask children about what they notice, think, and feel about situations reflecting racism, especially as they lack words for these complicated observations. There are television, Internet, and newspaper examples of both racism and anti-racism that can be fruitfully discussed. We can recommend watching or reading together, and asking questions such as, “Why do you think they are shouting [protesting]?” “How do you think the [victim, police] felt?” or “What do you think should be done about this?”
It is important to acknowledge the child’s confusion, fear, anxiety, sadness, or anger as normal and appropriate, not dismissing, too quickly reassuring, or changing the subject, even though it’s uncomfortable.
Physicians and nurse practitioners can make a difference by being aware of our privilege and biases, being open, modeling discussion, screening for impact, offering strategies, advocating with schools, and providing resources such as therapy or legal counsel, as for other social determinants of health.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS (https://www.site.chadis.com/). She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].