User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Experts publish imaging recommendations for pediatric COVID-19
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
A team of pulmonologists has synthesized the clinical and imaging characteristics of COVID-19 in children, and has devised recommendations for ordering imaging studies in suspected cases of the infection.
The review also included useful radiographic findings to help in the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other respiratory infections. Alexandra M. Foust, DO, of Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues reported the summary of findings and recommendations in Pediatric Pulmonology.
“Pediatricians face numerous challenges created by increasing reports of severe COVID-19 related findings in affected children,” said Mary Cataletto, MD, of NYU Langone Health in Mineola, N.Y. “[The current review] represents a multinational collaboration to provide up to date information and key imaging findings to guide chest physicians caring for children with pneumonia symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Clinical presentation in children
In general, pediatric patients infected with the virus show milder symptoms compared with adults, and based on the limited evidence reported to date, the most common clinical symptoms of COVID-19 in children are rhinorrhea and/or nasal congestion, fever and cough with sore throat, fatigue or dyspnea, and diarrhea.
As with other viral pneumonias in children, the laboratory parameters are usually nonspecific; however, while the complete blood count (CBC) is often normal, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia have been reported in some cases of pediatric COVID-19, the authors noted.
The current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendation for initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is obtaining a nasopharyngeal swab, followed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing, they explained.
Role of imaging in diagnosis
The researchers reported that current recommendations from the American College of Radiology (ACR) do not include chest computed tomography (CT) or chest radiography (CXR) as a upfront test to diagnose pediatric COVID-19, but they may still have a role in clinical monitoring, especially in patients with a moderate to severe disease course.
The potential benefits of utilizing radiologic evaluation, such as establishing a baseline for monitoring disease progression, must be balanced with potential drawbacks, which include radiation exposure, and reduced availability of imaging resources owing to necessary cleaning and air turnover time.
Recommendations for ordering imaging studies
Based on the most recent international guidelines for pediatric COVID-19 patient management, the authors developed an algorithm for performing imaging studies in suspected cases of COVID-19 pneumonia.
The purpose of the tool is to support clinical decision-making around the utilization of CXR and CT to evaluate pediatric COVID-19 pneumonia.
“The step by step algorithm addresses the selection, sequence and timing of imaging studies with multiple images illustrating key findings of COVID-19 pneumonia in the pediatric age group,” said Dr. Cataletto. “By synthesizing the available imaging case series and guidelines, this primer provides a useful tool for the practicing pulmonologist,” she explained.
Key recommendations: CXR
“For pediatric patients with suspected or known COVID-19 infection with moderate to severe clinical symptoms requiring hospitalization (i.e., hypoxia, moderate or severe dyspnea, signs of sepsis, shock, cardiovascular compromise, altered mentation), CXR is usually indicated to establish an imaging baseline and to assess for an alternative diagnosis,” they recommended.
“Sequential CXRs may be helpful to assess pediatric patients with COVID-19 who demonstrate worsening clinical symptoms or to assess response to supportive therapy,” they wrote.
Key recommendations: CT
“Due to the increased radiation sensitivity of pediatric patients, chest CT is not recommended as an initial diagnostic test for pediatric patients with known or suspected COVID-19 pneumonia,” they explained.
The guide also included several considerations around the differential diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia from other pediatric lung disorders, including immune-related conditions, infectious etiologies, hematological dyscrasias, and inhalation-related lung injury.
As best practice recommendations for COVID-19 continue to evolve, the availability of practical clinical decision-making tools becomes essential to ensure optimal patient care.
No funding sources or financial disclosures were reported in the manuscript.
SOURCE: Foust AM et al. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 May 28. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24870.
FROM PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY
What’s pushing cannabis use in first-episode psychosis?
The desire to feel better is a major driver for patients with first-episode psychosis (FEP) to turn to cannabis, new research shows.
An analysis of more than 1,300 individuals from six European countries showed patients with FEP were four times more likely than their healthy peers to start smoking cannabis in order to make themselves feel better.
The results also revealed that initiating cannabis use to feel better was associated with a more than tripled risk of being a daily user.
as well as offer an opportunity for psychoeducation – particularly as the reasons for starting cannabis appear to influence frequency of use, study investigator Edoardo Spinazzola, MD, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, and Neuroscience at King’s College London, said in an interview.
Patients who start smoking cannabis because their friends or family partakes may benefit from therapies that encourage more “assertiveness” and being “socially comfortable without the substance,” Dr. Spinazzola said, noting that it might also be beneficial to identify the specific cause of the psychological discomfort driving cannabis use, such as depression, and specifically treat that issue.
The results were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Answering the skeptics
Previous studies suggest that cannabis use can increase risk for psychosis up to 290%, with both frequency of use and potency playing a role, the researchers noted.
However, they added that “skeptics” argue the association could be caused by individuals with psychosis using cannabis as a form of self-medication, the comorbid effect of other psychogenic drugs, or a common genetic vulnerability between cannabis use and psychosis.
The reasons for starting cannabis use remain “largely unexplored,” so the researchers examined records from the European network of national schizophrenia networks studying Gene-Environment Interactions (EU-GEI) database, which includes patients with FEP and healthy individuals acting as controls from France, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, United Kingdom, and Brazil.
The analysis included 1,347 individuals, of whom 446 had a diagnosis of nonaffective psychosis, 89 had bipolar disorder, and 58 had psychotic depression.
Reasons to start smoking cannabis and patterns of use were determined using the modified version of the Cannabis Experiences Questionnaire.
Results showed that participants who started cannabis to feel better were significantly more likely to be younger, have fewer years of education, to be black or of mixed ethnicity, to be single, or to not be living independently than those who started it because their friends or family were using it (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In addition, 68% of the patients with FEP and 85% of the healthy controls started using cannabis because friends or family were using it. In contrast, 18% of those with FEP versus 5% of controls starting using cannabis to feel better; 13% versus 10%, respectively, started using for “other reasons.”
After taking into account gender, age, ethnicity, and study site, the patients with FEP were significantly more likely than their healthy peers to have started using cannabis to feel better (relative risk ratio, 4.67; P < .001).
Starting to smoke cannabis to feel better versus any other reason was associated with an increased frequency of use in both those with and without FEP, with an RRR of 2.9 for using the drug more than once a week (P = .001) and an RRR of 3.13 for daily use (P < .001). However, the association was stronger in the healthy controls than in those with FEP, with an RRR for daily use of 4.45 versus 3.11, respectively.
The investigators also examined whether there was a link between reasons to start smoking and an individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) for developing schizophrenia.
Multinomial regression indicated that PRS was not associated with starting cannabis to feel better or because friends were using it. However, there was an association between PRS score and starting the drug because family members were using it (RRR, 0.68; P < .05).
Complex association
Gabriella Gobbi, MD, PhD, professor in the neurobiological psychiatry unit, department of psychiatry, at McGill University, Montreal, said the data confirm “what we already know about cannabis.”
She noted that one of the “major causes” of young people starting cannabis is the social environment, while the desire to use the drug to feel better is linked to “the fact that cannabis, in a lot of cases, is used as a self-medication” in order to be calmer and as a relief from anxiety.
There is a “very complex” association between using cannabis to feel better and the self-medication seen with cigarette smoking and alcohol in patients with schizophrenia, said Dr. Gobbi, who was not involved with the research.
“When we talk about [patients using] cannabis, alcohol, and cigarettes, actually we’re talking about the same group of people,” she said.
Although “it is true they say that people look to cigarettes, tobacco, and alcohol to feel happier because they are depressed, the risk of psychosis is only for cannabis,” she added. “It is very low for alcohol and tobacco.”
As a result, Dr. Gobbi said she and her colleagues are “very worried” about the consequences for mental health of the legalization of cannabis consumption in Canada in October 2018 with the passing of the Cannabis Act.
Although there are no firm statistics yet, she has observed that since the law was passed, cannabis use has stabilized at a lower level among adolescents. “But now we have another population of people aged 34 and older that consume cannabis,” she said.
Particularly when considering the impact of higher strength cannabis on psychosis risk, Dr. Gobbi believes the increase in consumption in this age group will result in a “more elevated” risk for mental health issues.
Dr. Spinazzola and Dr. Gobbi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The desire to feel better is a major driver for patients with first-episode psychosis (FEP) to turn to cannabis, new research shows.
An analysis of more than 1,300 individuals from six European countries showed patients with FEP were four times more likely than their healthy peers to start smoking cannabis in order to make themselves feel better.
The results also revealed that initiating cannabis use to feel better was associated with a more than tripled risk of being a daily user.
as well as offer an opportunity for psychoeducation – particularly as the reasons for starting cannabis appear to influence frequency of use, study investigator Edoardo Spinazzola, MD, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, and Neuroscience at King’s College London, said in an interview.
Patients who start smoking cannabis because their friends or family partakes may benefit from therapies that encourage more “assertiveness” and being “socially comfortable without the substance,” Dr. Spinazzola said, noting that it might also be beneficial to identify the specific cause of the psychological discomfort driving cannabis use, such as depression, and specifically treat that issue.
The results were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Answering the skeptics
Previous studies suggest that cannabis use can increase risk for psychosis up to 290%, with both frequency of use and potency playing a role, the researchers noted.
However, they added that “skeptics” argue the association could be caused by individuals with psychosis using cannabis as a form of self-medication, the comorbid effect of other psychogenic drugs, or a common genetic vulnerability between cannabis use and psychosis.
The reasons for starting cannabis use remain “largely unexplored,” so the researchers examined records from the European network of national schizophrenia networks studying Gene-Environment Interactions (EU-GEI) database, which includes patients with FEP and healthy individuals acting as controls from France, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, United Kingdom, and Brazil.
The analysis included 1,347 individuals, of whom 446 had a diagnosis of nonaffective psychosis, 89 had bipolar disorder, and 58 had psychotic depression.
Reasons to start smoking cannabis and patterns of use were determined using the modified version of the Cannabis Experiences Questionnaire.
Results showed that participants who started cannabis to feel better were significantly more likely to be younger, have fewer years of education, to be black or of mixed ethnicity, to be single, or to not be living independently than those who started it because their friends or family were using it (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In addition, 68% of the patients with FEP and 85% of the healthy controls started using cannabis because friends or family were using it. In contrast, 18% of those with FEP versus 5% of controls starting using cannabis to feel better; 13% versus 10%, respectively, started using for “other reasons.”
After taking into account gender, age, ethnicity, and study site, the patients with FEP were significantly more likely than their healthy peers to have started using cannabis to feel better (relative risk ratio, 4.67; P < .001).
Starting to smoke cannabis to feel better versus any other reason was associated with an increased frequency of use in both those with and without FEP, with an RRR of 2.9 for using the drug more than once a week (P = .001) and an RRR of 3.13 for daily use (P < .001). However, the association was stronger in the healthy controls than in those with FEP, with an RRR for daily use of 4.45 versus 3.11, respectively.
The investigators also examined whether there was a link between reasons to start smoking and an individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) for developing schizophrenia.
Multinomial regression indicated that PRS was not associated with starting cannabis to feel better or because friends were using it. However, there was an association between PRS score and starting the drug because family members were using it (RRR, 0.68; P < .05).
Complex association
Gabriella Gobbi, MD, PhD, professor in the neurobiological psychiatry unit, department of psychiatry, at McGill University, Montreal, said the data confirm “what we already know about cannabis.”
She noted that one of the “major causes” of young people starting cannabis is the social environment, while the desire to use the drug to feel better is linked to “the fact that cannabis, in a lot of cases, is used as a self-medication” in order to be calmer and as a relief from anxiety.
There is a “very complex” association between using cannabis to feel better and the self-medication seen with cigarette smoking and alcohol in patients with schizophrenia, said Dr. Gobbi, who was not involved with the research.
“When we talk about [patients using] cannabis, alcohol, and cigarettes, actually we’re talking about the same group of people,” she said.
Although “it is true they say that people look to cigarettes, tobacco, and alcohol to feel happier because they are depressed, the risk of psychosis is only for cannabis,” she added. “It is very low for alcohol and tobacco.”
As a result, Dr. Gobbi said she and her colleagues are “very worried” about the consequences for mental health of the legalization of cannabis consumption in Canada in October 2018 with the passing of the Cannabis Act.
Although there are no firm statistics yet, she has observed that since the law was passed, cannabis use has stabilized at a lower level among adolescents. “But now we have another population of people aged 34 and older that consume cannabis,” she said.
Particularly when considering the impact of higher strength cannabis on psychosis risk, Dr. Gobbi believes the increase in consumption in this age group will result in a “more elevated” risk for mental health issues.
Dr. Spinazzola and Dr. Gobbi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The desire to feel better is a major driver for patients with first-episode psychosis (FEP) to turn to cannabis, new research shows.
An analysis of more than 1,300 individuals from six European countries showed patients with FEP were four times more likely than their healthy peers to start smoking cannabis in order to make themselves feel better.
The results also revealed that initiating cannabis use to feel better was associated with a more than tripled risk of being a daily user.
as well as offer an opportunity for psychoeducation – particularly as the reasons for starting cannabis appear to influence frequency of use, study investigator Edoardo Spinazzola, MD, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, and Neuroscience at King’s College London, said in an interview.
Patients who start smoking cannabis because their friends or family partakes may benefit from therapies that encourage more “assertiveness” and being “socially comfortable without the substance,” Dr. Spinazzola said, noting that it might also be beneficial to identify the specific cause of the psychological discomfort driving cannabis use, such as depression, and specifically treat that issue.
The results were scheduled to be presented at the Congress of the Schizophrenia International Research Society 2020, but the meeting was canceled because of the coronavirus pandemic.
Answering the skeptics
Previous studies suggest that cannabis use can increase risk for psychosis up to 290%, with both frequency of use and potency playing a role, the researchers noted.
However, they added that “skeptics” argue the association could be caused by individuals with psychosis using cannabis as a form of self-medication, the comorbid effect of other psychogenic drugs, or a common genetic vulnerability between cannabis use and psychosis.
The reasons for starting cannabis use remain “largely unexplored,” so the researchers examined records from the European network of national schizophrenia networks studying Gene-Environment Interactions (EU-GEI) database, which includes patients with FEP and healthy individuals acting as controls from France, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, United Kingdom, and Brazil.
The analysis included 1,347 individuals, of whom 446 had a diagnosis of nonaffective psychosis, 89 had bipolar disorder, and 58 had psychotic depression.
Reasons to start smoking cannabis and patterns of use were determined using the modified version of the Cannabis Experiences Questionnaire.
Results showed that participants who started cannabis to feel better were significantly more likely to be younger, have fewer years of education, to be black or of mixed ethnicity, to be single, or to not be living independently than those who started it because their friends or family were using it (P < .001 for all comparisons).
In addition, 68% of the patients with FEP and 85% of the healthy controls started using cannabis because friends or family were using it. In contrast, 18% of those with FEP versus 5% of controls starting using cannabis to feel better; 13% versus 10%, respectively, started using for “other reasons.”
After taking into account gender, age, ethnicity, and study site, the patients with FEP were significantly more likely than their healthy peers to have started using cannabis to feel better (relative risk ratio, 4.67; P < .001).
Starting to smoke cannabis to feel better versus any other reason was associated with an increased frequency of use in both those with and without FEP, with an RRR of 2.9 for using the drug more than once a week (P = .001) and an RRR of 3.13 for daily use (P < .001). However, the association was stronger in the healthy controls than in those with FEP, with an RRR for daily use of 4.45 versus 3.11, respectively.
The investigators also examined whether there was a link between reasons to start smoking and an individual’s polygenic risk score (PRS) for developing schizophrenia.
Multinomial regression indicated that PRS was not associated with starting cannabis to feel better or because friends were using it. However, there was an association between PRS score and starting the drug because family members were using it (RRR, 0.68; P < .05).
Complex association
Gabriella Gobbi, MD, PhD, professor in the neurobiological psychiatry unit, department of psychiatry, at McGill University, Montreal, said the data confirm “what we already know about cannabis.”
She noted that one of the “major causes” of young people starting cannabis is the social environment, while the desire to use the drug to feel better is linked to “the fact that cannabis, in a lot of cases, is used as a self-medication” in order to be calmer and as a relief from anxiety.
There is a “very complex” association between using cannabis to feel better and the self-medication seen with cigarette smoking and alcohol in patients with schizophrenia, said Dr. Gobbi, who was not involved with the research.
“When we talk about [patients using] cannabis, alcohol, and cigarettes, actually we’re talking about the same group of people,” she said.
Although “it is true they say that people look to cigarettes, tobacco, and alcohol to feel happier because they are depressed, the risk of psychosis is only for cannabis,” she added. “It is very low for alcohol and tobacco.”
As a result, Dr. Gobbi said she and her colleagues are “very worried” about the consequences for mental health of the legalization of cannabis consumption in Canada in October 2018 with the passing of the Cannabis Act.
Although there are no firm statistics yet, she has observed that since the law was passed, cannabis use has stabilized at a lower level among adolescents. “But now we have another population of people aged 34 and older that consume cannabis,” she said.
Particularly when considering the impact of higher strength cannabis on psychosis risk, Dr. Gobbi believes the increase in consumption in this age group will result in a “more elevated” risk for mental health issues.
Dr. Spinazzola and Dr. Gobbi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SIRS 2020
Hashtag medicine: #ShareTheMicNowMed highlights Black female physicians on social media
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Prominent female physicians are handing over their social media platforms today to black female physicians as part of a campaign called #ShareTheMicNowMed.
The social media event, which will play out on both Twitter and Instagram, is an offshoot of #ShareTheMicNow, held earlier this month. For that event, more than 90 women, including A-list celebrities like Ellen DeGeneres, Julia Roberts, and Senator Elizabeth Warren, swapped accounts with women of color, such as “I’m Still Here” author Austin Channing Brown, Olympic fencer Ibtihaj Muhammad, and #MeToo founder Tarana Burke.
The physician event will feature 10 teams of two, with one physician handing over her account to her black female counterpart for the day. The takeover will allow the black physician to share her thoughts about the successes and challenges she faces as a woman of color in medicine.
“It was such an honor to be contacted by Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, to participate in an event that has a goal of connecting like-minded women from various backgrounds to share a diverse perspective with a different audience,” Minnesota family medicine physician Jay-Sheree Allen, MD, told Medscape Medical News. “This event is not only incredibly important but timely.”
Only about 5% of all active physicians in 2018 identified as Black or African American, according to a report by the Association of American Medical Colleges. And of those, just over a third are female, the report found.
“I think that as we hear those small numbers we often celebrate the success of those people without looking back and understanding where all of the barriers are that are limiting talented black women from entering medicine at every stage,” another campaign participant, Chicago pediatrician Rebekah Fenton, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
Allen says that, amid continuing worldwide protests over racial injustice, prompted by the death of George Floyd while in Minneapolis police custody last month, the online event is very timely and an important way to advocate for black lives and engage in a productive conversation.
“I believe that with the #ShareTheMicNowMed movement we will start to show people how they can become allies. I always say that a candle loses nothing by lighting another candle, and sharing that stage is one of the many ways you can support the Black Lives Matters movement by amplifying black voices,” she said.
Allen went on to add that women in medicine have many of the same experiences as any other doctor but do face some unique challenges. This is especially true for female physicians of color, she noted.
To join the conversation follow the hashtag #ShareTheMicNowMed all day on Monday, June 22, 2020.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Where does dexamethasone fit in with diabetic ketoacidosis in COVID-19?
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
Corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, director of the diabetes program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, discussed the recommendations with Medscape Medical News and also spoke about the news this week that the corticosteroid dexamethasone reduced death rates in severely ill patients with COVID-19.
The full JCEM article, by lead author Nadine E. Palermo, DO, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension, also at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, covers DKA diagnosis and triage, and emphasizes that usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 to help preserve personal protective equipment and ICU beds.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” McDonnell said in an Endocrine Society statement.
What about dexamethasone for severe COVID-19 in diabetes?
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors.
But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
McDonnell told Medscape Medical News that she would need to see formal results to better understand exactly which patients were studied and which ones benefited.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” she said. “If they all had acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS],” that’s different.
“There are already some data supporting steroid use in ARDS,” she noted, but added that not all of it suggests benefit.
She pointed to one of several studies now showing that diabetes, and hyperglycemia among people without a prior diabetes diagnosis, are both strong predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
“There was a very clear relationship between hyperglycemia and outcomes. We really shouldn’t put people at risk until we have clear data,” she said.
If, once the data are reviewed and appropriate dexamethasone becomes an established treatment for severe COVID-19, hyperglycemia would be a concern among all patients, not just those with previously diagnosed diabetes, she noted.
“We know a good number of people with prediabetes develop hyperglycemia when put on steroids. They can push people over the edge. We’re not going to miss anybody, but treating steroid-induced hyperglycemia is really hard,” McDonnell explained.
She also recommended 2014 guidance from Diabetes UK and the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, which addresses management of inpatient steroid-induced DKA in patients with and without pre-existing diabetes.
Another major concern, she said, is “patients trying to get dexamethasone when they start to get sick” because this is not the right population to use this agent.
“We worry about people who do not need this drug. If they have diabetes, they put themselves at risk of hyperglycemia, which then increases the risk of severe COVID-19. And then they’re also putting themselves at risk of DKA. It would just be bad medicine,” she said.
Managing DKA in the face of COVID-19: Flexibility is key
In the JCEM article, Palermo and colleagues emphasize that the usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 in the interest of reducing transmission risk and preserving scare resources.
They provide evidence for alternative treatment strategies, such as the use of subcutaneous rather than intravenous insulin when appropriate.
“We wanted to outline when exactly you should consider nonintensive management strategies for DKA,” McDonnell further explained to Medscape Medical News.
“That would include those with mild or some with moderate DKA. ... The idea is to remind our colleagues about that because hospitals tend to operate on a protocol-driven algorithmic methodology, they can forget to step off the usual care pathway even if evidence supports that,” she said.
But on the other hand, she also said that, in some very complex or severely ill patients with COVID-19, classical intravenous insulin therapy makes the most sense even if their DKA is mild.
The outpatient setting: Prevention and preparation
The new article also addresses several concerns regarding DKA prevention in the outpatient setting.
As with other guidelines, it includes a reminder that patients with diabetes should be advised to discontinue sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors if they become ill with COVID-19, especially if they’re not eating or drinking normally, because they raise the risk for DKA.
Also, for patients with type 1 diabetes, particularly those with a history of repeated DKA, “this is the time to make sure we reach out to patients to refill their insulin prescriptions and address issues related to cost and other access difficulties,” McDonnell said.
The authors also emphasize that insulin starts and education should not be postponed during the pandemic. “Patients identified as meeting criteria to start insulin should be referred for urgent education, either in person or, whenever possible and practical, via video teleconferencing,” they urge.
McDonnell has reported receiving research funding from Novo Nordisk. The other two authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
Corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, director of the diabetes program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, discussed the recommendations with Medscape Medical News and also spoke about the news this week that the corticosteroid dexamethasone reduced death rates in severely ill patients with COVID-19.
The full JCEM article, by lead author Nadine E. Palermo, DO, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension, also at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, covers DKA diagnosis and triage, and emphasizes that usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 to help preserve personal protective equipment and ICU beds.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” McDonnell said in an Endocrine Society statement.
What about dexamethasone for severe COVID-19 in diabetes?
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors.
But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
McDonnell told Medscape Medical News that she would need to see formal results to better understand exactly which patients were studied and which ones benefited.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” she said. “If they all had acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS],” that’s different.
“There are already some data supporting steroid use in ARDS,” she noted, but added that not all of it suggests benefit.
She pointed to one of several studies now showing that diabetes, and hyperglycemia among people without a prior diabetes diagnosis, are both strong predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
“There was a very clear relationship between hyperglycemia and outcomes. We really shouldn’t put people at risk until we have clear data,” she said.
If, once the data are reviewed and appropriate dexamethasone becomes an established treatment for severe COVID-19, hyperglycemia would be a concern among all patients, not just those with previously diagnosed diabetes, she noted.
“We know a good number of people with prediabetes develop hyperglycemia when put on steroids. They can push people over the edge. We’re not going to miss anybody, but treating steroid-induced hyperglycemia is really hard,” McDonnell explained.
She also recommended 2014 guidance from Diabetes UK and the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, which addresses management of inpatient steroid-induced DKA in patients with and without pre-existing diabetes.
Another major concern, she said, is “patients trying to get dexamethasone when they start to get sick” because this is not the right population to use this agent.
“We worry about people who do not need this drug. If they have diabetes, they put themselves at risk of hyperglycemia, which then increases the risk of severe COVID-19. And then they’re also putting themselves at risk of DKA. It would just be bad medicine,” she said.
Managing DKA in the face of COVID-19: Flexibility is key
In the JCEM article, Palermo and colleagues emphasize that the usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 in the interest of reducing transmission risk and preserving scare resources.
They provide evidence for alternative treatment strategies, such as the use of subcutaneous rather than intravenous insulin when appropriate.
“We wanted to outline when exactly you should consider nonintensive management strategies for DKA,” McDonnell further explained to Medscape Medical News.
“That would include those with mild or some with moderate DKA. ... The idea is to remind our colleagues about that because hospitals tend to operate on a protocol-driven algorithmic methodology, they can forget to step off the usual care pathway even if evidence supports that,” she said.
But on the other hand, she also said that, in some very complex or severely ill patients with COVID-19, classical intravenous insulin therapy makes the most sense even if their DKA is mild.
The outpatient setting: Prevention and preparation
The new article also addresses several concerns regarding DKA prevention in the outpatient setting.
As with other guidelines, it includes a reminder that patients with diabetes should be advised to discontinue sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors if they become ill with COVID-19, especially if they’re not eating or drinking normally, because they raise the risk for DKA.
Also, for patients with type 1 diabetes, particularly those with a history of repeated DKA, “this is the time to make sure we reach out to patients to refill their insulin prescriptions and address issues related to cost and other access difficulties,” McDonnell said.
The authors also emphasize that insulin starts and education should not be postponed during the pandemic. “Patients identified as meeting criteria to start insulin should be referred for urgent education, either in person or, whenever possible and practical, via video teleconferencing,” they urge.
McDonnell has reported receiving research funding from Novo Nordisk. The other two authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new article in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) addresses unique concerns and considerations regarding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in the setting of COVID-19.
Corresponding author Marie E. McDonnell, MD, director of the diabetes program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, discussed the recommendations with Medscape Medical News and also spoke about the news this week that the corticosteroid dexamethasone reduced death rates in severely ill patients with COVID-19.
The full JCEM article, by lead author Nadine E. Palermo, DO, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Hypertension, also at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, covers DKA diagnosis and triage, and emphasizes that usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 to help preserve personal protective equipment and ICU beds.
“Hospitals and clinicians need to be able to quickly identify and manage DKA in COVID patients to save lives. This involves determining the options for management, including when less intensive subcutaneous insulin is indicated, and understanding how to guide patients on avoiding this serious complication,” McDonnell said in an Endocrine Society statement.
What about dexamethasone for severe COVID-19 in diabetes?
The new article briefly touches on the fact that upward adjustments to intensive intravenous insulin therapy for DKA may be necessary in patients with COVID-19 who are receiving concomitant corticosteroids or vasopressors.
But it was written prior to the June 16 announcement of the “RECOVERY” trial results with dexamethasone. The UK National Health Service immediately approved the drug’s use in the COVID-19 setting, despite the fact that there has been no published article on the findings yet.
McDonnell told Medscape Medical News that she would need to see formal results to better understand exactly which patients were studied and which ones benefited.
“The peer review will be critical. It looks as if it only benefits people who need respiratory support, but I want to understand that in much more detail,” she said. “If they all had acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS],” that’s different.
“There are already some data supporting steroid use in ARDS,” she noted, but added that not all of it suggests benefit.
She pointed to one of several studies now showing that diabetes, and hyperglycemia among people without a prior diabetes diagnosis, are both strong predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
“There was a very clear relationship between hyperglycemia and outcomes. We really shouldn’t put people at risk until we have clear data,” she said.
If, once the data are reviewed and appropriate dexamethasone becomes an established treatment for severe COVID-19, hyperglycemia would be a concern among all patients, not just those with previously diagnosed diabetes, she noted.
“We know a good number of people with prediabetes develop hyperglycemia when put on steroids. They can push people over the edge. We’re not going to miss anybody, but treating steroid-induced hyperglycemia is really hard,” McDonnell explained.
She also recommended 2014 guidance from Diabetes UK and the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, which addresses management of inpatient steroid-induced DKA in patients with and without pre-existing diabetes.
Another major concern, she said, is “patients trying to get dexamethasone when they start to get sick” because this is not the right population to use this agent.
“We worry about people who do not need this drug. If they have diabetes, they put themselves at risk of hyperglycemia, which then increases the risk of severe COVID-19. And then they’re also putting themselves at risk of DKA. It would just be bad medicine,” she said.
Managing DKA in the face of COVID-19: Flexibility is key
In the JCEM article, Palermo and colleagues emphasize that the usual hospital protocols for DKA management may need to be adjusted during COVID-19 in the interest of reducing transmission risk and preserving scare resources.
They provide evidence for alternative treatment strategies, such as the use of subcutaneous rather than intravenous insulin when appropriate.
“We wanted to outline when exactly you should consider nonintensive management strategies for DKA,” McDonnell further explained to Medscape Medical News.
“That would include those with mild or some with moderate DKA. ... The idea is to remind our colleagues about that because hospitals tend to operate on a protocol-driven algorithmic methodology, they can forget to step off the usual care pathway even if evidence supports that,” she said.
But on the other hand, she also said that, in some very complex or severely ill patients with COVID-19, classical intravenous insulin therapy makes the most sense even if their DKA is mild.
The outpatient setting: Prevention and preparation
The new article also addresses several concerns regarding DKA prevention in the outpatient setting.
As with other guidelines, it includes a reminder that patients with diabetes should be advised to discontinue sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors if they become ill with COVID-19, especially if they’re not eating or drinking normally, because they raise the risk for DKA.
Also, for patients with type 1 diabetes, particularly those with a history of repeated DKA, “this is the time to make sure we reach out to patients to refill their insulin prescriptions and address issues related to cost and other access difficulties,” McDonnell said.
The authors also emphasize that insulin starts and education should not be postponed during the pandemic. “Patients identified as meeting criteria to start insulin should be referred for urgent education, either in person or, whenever possible and practical, via video teleconferencing,” they urge.
McDonnell has reported receiving research funding from Novo Nordisk. The other two authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After the ICU: A ‘fraternity of people who are struggling’
By the time she was discharged from a suburban New Jersey hospital on April 10, Kathleen Ronan thought the worst was behind her. For a week before her husband rushed her to the emergency department (ED), incoherent and struggling to breathe, the novel coronavirus had ravaged her body. She tried to treat her fevers with acetaminophen and ice packs. Despite taking enough Tylenol to risk liver damage and packing herself on ice like the catch of the day, Ronan’s fever continued to rise. By the time her temperature reached 104.5° F, Ronan knew the time had come for more drastic measures.
A team of masked and gowned nurses greeted her at a triage tent outside the ED, and from there, everything becomes hazy for Ronan. She was immediately rushed to the hospital’s special COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU), where she spent 5 days. But she has few distinct memories from this time. What she does remember is the exhaustion, the pain, the loneliness, and the fear. Her family couldn’t visit, and though Ronan works as a home health nurse, her brain was so addled with fever that she couldn’t make sense of what was happening. After a week in the hospital, 5 days of which were spent in the ICU, 51-year-old Ronan was discharged.
Her years of working as a home health nurse told her that the return home wouldn’t be easy, but nothing prepared her for just how much she would struggle. The once-active Ronan, who had supplemented long days on her feet caring for others as a nurse with regular trips to the gym, now needed a walker to traverse the few steps from her bed to the toilet, an effort that left her gasping for air. Her brain couldn’t even focus on an audiobook, let alone a short magazine article.
“It just completely knocked the stuffing out of me,” Ronan said.
Ronan’s lingering symptoms aren’t unique to COVID-19 patients. In as many as 80% of patients leaving the ICU, . Although underlying illness plays a role in these symptoms, the amount of time spent in critical care is a major factor.
Nor is PICS simply a set of side effects that will go away on their own. It includes ongoing cognitive difficulties and physical weakness, both of which can lead to employment problems. Beyond that, depression and anxiety can exacerbate – and be exacerbated by – these challenges. Psychologist Jim Jackson, PsyD, assistant director of the ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, recently spoke with a former ICU patient who has struggled since her discharge 30 years ago.
“Her life essentially stopped with her critical care stay. She hasn’t been able to move forward,” he said. “She’s part of a whole fraternity of people who are struggling.”
The good news is that over the past decade, researchers have made important strides in understanding what makes PICS symptoms worse and how critical care physicians can tweak ICU protocols to reduce PICS severity. Practitioners will need to draw on this knowledge to help Ronan and the thousands of COVID-19 ICU patients like her.
Surviving the ICU
Although the new coronavirus has pushed the world’s critical care system to its limits, it was an outbreak in 1952 that inspired the creation of intensive care units. That summer, a wave of paralytic polio swept over Copenhagen, Denmark, and anesthesiologist Bjørn Ibsen, MD, PhD, used mechanical ventilation — physically operated by medical and dental students – to help 316 children breathe for weeks at a time while their small bodies worked to fight off the virus. The effort halved the mortality rate from polio that affected breathing, from 80% to 40%.
In these wards, dedicated to the very sickest, each patient was assigned his or her own nurse. Over the next decade, hospitals in the United Kingdom and the United States established their own ICUs to treat patients with a variety of conditions. Although it helped improve survival, mortality rates in critical care units remained stubbornly high, owing to the patients’ severe underlying illnesses.
“We thought we were doing a good job if the patient survived, but we had no idea what happened after discharge,” said Carla Sevin, MD, medical director of Vanderbilt’s ICU Recovery Center. Nor did their efforts to find out always bring answers. “We struggled to get people to come in for support — they were debilitated, physically burdened, and weak.”
Through further advances in life support, by the early 2000s, the average mortality rates in American ICUs had dropped to 8% to 19%. As the number of critical care survivors began to climb, clinical researchers noticed that the lives of these patients and their families were profoundly altered by their severe illness.
As Dale Needham, MD, PhD, began his pulmonology and critical care residency in Toronto, Canada, in 2005, a group of physicians there began a 5-year longitudinal study to assess long-term outcomes of patients who developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although ARDS is an acute condition, the investigators found that patients felt effects for years. Younger patients recovered better than older ones, but none of the patients› physical functioning was equivalent to that of age-matched control persons. Even 5 years later, former ICU patients only reached 76% of expected physical functioning, according to results published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study was a wake-up call.
At a meeting in Chicago in 2010, Needham, now an intensivist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland, gathered an interdisciplinary group of colleagues, including patients and caregivers, to clarify the phenomena they were seeing. What emerged from that meeting, published in 2012 in Critical Care Medicine, were the diagnostic criteria for PICS: According to the new definition, PICS is characterized by new or worsening physical and neuropsychiatric deficits that range from forgetfulness and loss of motivation to physical weakness and insomnia.
The issue, Needham says, is that although the trouble starts in the ICU, it only becomes clear once patients leave. “ICU doctors aren’t the ones dealing with this,” Needham said. “We need to build stronger bridges between critical care and other professions.” That’s where PICS comes in, a definition that exists explicitly to alert healthcare providers about the constellation of challenges many of these individuals face as they try to reenter “normal” life.
Defining the problem
As an ICU nurse at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, Annie Johnson, ACNP-BC, knew lots about helping hospitalized patients, but she says she didn’t know anything about what to do after discharge – at least not until her own mother became a patient.
On the first day of retirement in October 2014, Johnson’s mother flatlined. Quick-thinking paramedics resuscitated her, and after several days in critical care, she was discharged. Since then, her heart has remained healthy. Johnson’s sister, who spent time worrying over her mother at the hospital, also had lingering effects. Both have since struggled, plagued by nightmares, flashbacks, and insomnia.
Johnson initially believed her mom’s and sister’s neuropsychiatric, post-ICU struggles were unique to her family. It was only a year later, at a seminar she was attending, that she first heard the words “post–intensive care syndrome.” Suddenly, Johnson had a name for her family’s experiences, and she began to create support groups and resources to help other families like hers.
“I thought of all the patients I had treated over the years who had been on ventilators for days and days and days. And if this happened to my mom after 48 hours, what must they be going through?” she asked.
Once physicians formally defined PICS, the Society for Critical Care Medicine helped create programs to educate ICU staff, patients, and families about potential post-discharge challenges. Researchers also began to investigate factors affecting post-ICU functioning. Follow-up studies of patients with delirium (ranging from general confusion about time and place to extreme agitation and violence) showed they had striking cognitive deficits. Problems with short-term memory, flexible thinking, and motivation plagued patients for years after their critical illness, similar to the physical deficiencies seen after ARDS. Delirium was one of the strongest risk factors for neuropsychiatric problems.
“Delirium is basically a stress test for the brain,” said Babar Khan, MD, a critical care specialist at Indiana University’s Regenstrief Institute, in Bloomington. But whether delirium accentuates preexisting cognitive difficulties or creates them afresh isn’t yet clear.
Sophia Wang, MD, a geriatric psychiatrist at Indiana University who works with many critical care patients, says patients who had experienced delirium in the ICU showed significant defects in memory and executive functioning long after their hospital stay. She points to a 2015 study that followed 47 ICU patients for a year post discharge. Among those who experienced delirium, brain volumes, as measured by MRI, were smaller at 3 months, something associated with cognitive problems at 1 year. Many struggled at work, and unemployment was common. Depression and posttraumatic stress compounded these difficulties. Among those with acute respiratory distress, ICU patients who are young, female, and unemployed are most likely to suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder after they are discharge.
Critical care medicine may have given these patients a second chance at life, Wang says, but the life they return to often looks nothing like the one they had before their illness.
Prolonged mechanical ventilation and the heavy sedation that often accompanies it are predictors of PICS severity. Some of these links could be explained by the gravity of the illness that landed someone in critical care, but others are more likely to be iatrogenic, says Gerald Weinhouse, MD, a pulmonology and critical care physician and co-director of the Critical Illness Recovery Program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. The involvement of loved ones at the patient’s bedside, however, improved the entire family’s outcome.
When Weinhouse saw those data, he and his colleagues founded a peer support program for ICU survivors. In a study published in 2019 in Critical Care Medicine, they identified six different models for peer support for those with PICS and their families, including both online and in-person approaches. An ongoing challenge for physicians, Weinhouse says, is getting patients to engage with these programs, given that their calendars are crowded with medical appointments and that they suffer from increased physical and mental disability.
Studies such as these led critical care physicians to form the ICU Liberation Collaborative to rethink critical care medicine. At Vanderbilt, Sevin and Jackson headed up one of the world’s first post-ICU clinics, which uses an interdisciplinary team to help patients maximize their functioning. They redesigned their critical care unit in a way that allows families to spend the night and that encourages patient mobility. Both Needham and Weinhouse continue tracking patient outcomes.
Even before the novel coronavirus struck, the United States — and the world — had begun to realize that graduating from the ICU was only the start of what was often an extensive recovery.
The long road back
When COVID-19 patients began flooding intensive care wards around the world, physicians scrambled to meet their complex and desperate acute medical needs. Over the past few months, physicians have focused on keeping these patients alive. “We’ve never seen anything like it ― not even during polio — with the sheer number of patients, all with respiratory distress,” Needham said.
But he and his colleagues know this is only the beginning.
“We’re aware that survivorship issues are coming. There’s going to be a wave of sick people who survived the coronavirus but are going to need more help,” Weinhouse said.
Intensivists have been drawing on PICS research in their fight to help COVID-19 patients. Work from the past few years has shown that although sedation is required during intubation itself, not everyone needs it while on a ventilator. Titrating down sedating medication helps reduce delirium, Wang says. Such medication has been shown to contribute to later cognitive problems. Needham’s studies showing that prolonged bedrest by ICU patients causes muscular atrophy has led him to encourage patients to move as much as possible. With the help of physical therapists, many patients on ventilators can be awake, alert, and moving around the ward.
One of the biggest challenges critical-care coronavirus patients face is prolonged isolation. The constant presence of a familiar face helps orient confused and delirious patients and provides emotional support during a frightening time. But because the immediate need for infection control outweighs these benefits, few hospitals allow visitors, especially for COVID-19 patients.
To address this, some units have been using video technology to allow loved ones to call in. At Johns Hopkins, physicians have also been relying on the expertise of occupational therapists (OTs). Needham says that one OT found that rubbing the hand and back of an agitated, delirious patient helped soothe and calm him better than many medications.
Ronan, who spent 5 days in intensive care, echoes that problem. She says she found the relative lack of human contact to be one of the most challenging parts of being in a bed on a COVID-19 ward. Separated from her husband and daughter, suffering from high fever and severe illness, she lost all track of time.
Her return home was difficult, too. Although her job as a home health nurse had prepared her on some level for the challenges she would face after discharge, Ronan says the hospital provided little practical help.
“Everything is so much harder at home, even little things like going to the bathroom,” she said. “I feel like I’m trying to bail out a sinking ship with a teacup.”
Khan and other physicians, aware of the challenges Ronan and others face once home, aim to create post-ICU clinics specifically for COVID-19 patients. They want to build what Khan calls a “one-stop shop” for all the support patients need to recover. Some of that can be provided via telehealth, which may also help ease the physical burden.
Because there’s so much physicians don’t know about the coronavirus, Johnson says, such clinics are not only a chance to help the sickest COVID-19 patients, they will also help researchers learn more about the virus and improve critical care for other illnesses.
Today, nearly 2 months after discharge, Ronan is back on the job but struggles with a persistent cough — likely due to the lung damage she sustained while ill. She has constant fatigue, as well as ongoing upset stomach from all the medications she took to reduce fever and body aches. When she dons a mask for work, the tangible reminder of her hospital stay sends her into a panic attack. Physically, she’s weaker than before.
Researchers are still trying to understand everything that Ronan and other COVID-19 patients need to move on with their lives after being in the ICU. Mysteries abound, but the ground laid by Sevin, Needham, Weinhouse, and others has provided a solid foundation on which to build.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
By the time she was discharged from a suburban New Jersey hospital on April 10, Kathleen Ronan thought the worst was behind her. For a week before her husband rushed her to the emergency department (ED), incoherent and struggling to breathe, the novel coronavirus had ravaged her body. She tried to treat her fevers with acetaminophen and ice packs. Despite taking enough Tylenol to risk liver damage and packing herself on ice like the catch of the day, Ronan’s fever continued to rise. By the time her temperature reached 104.5° F, Ronan knew the time had come for more drastic measures.
A team of masked and gowned nurses greeted her at a triage tent outside the ED, and from there, everything becomes hazy for Ronan. She was immediately rushed to the hospital’s special COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU), where she spent 5 days. But she has few distinct memories from this time. What she does remember is the exhaustion, the pain, the loneliness, and the fear. Her family couldn’t visit, and though Ronan works as a home health nurse, her brain was so addled with fever that she couldn’t make sense of what was happening. After a week in the hospital, 5 days of which were spent in the ICU, 51-year-old Ronan was discharged.
Her years of working as a home health nurse told her that the return home wouldn’t be easy, but nothing prepared her for just how much she would struggle. The once-active Ronan, who had supplemented long days on her feet caring for others as a nurse with regular trips to the gym, now needed a walker to traverse the few steps from her bed to the toilet, an effort that left her gasping for air. Her brain couldn’t even focus on an audiobook, let alone a short magazine article.
“It just completely knocked the stuffing out of me,” Ronan said.
Ronan’s lingering symptoms aren’t unique to COVID-19 patients. In as many as 80% of patients leaving the ICU, . Although underlying illness plays a role in these symptoms, the amount of time spent in critical care is a major factor.
Nor is PICS simply a set of side effects that will go away on their own. It includes ongoing cognitive difficulties and physical weakness, both of which can lead to employment problems. Beyond that, depression and anxiety can exacerbate – and be exacerbated by – these challenges. Psychologist Jim Jackson, PsyD, assistant director of the ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, recently spoke with a former ICU patient who has struggled since her discharge 30 years ago.
“Her life essentially stopped with her critical care stay. She hasn’t been able to move forward,” he said. “She’s part of a whole fraternity of people who are struggling.”
The good news is that over the past decade, researchers have made important strides in understanding what makes PICS symptoms worse and how critical care physicians can tweak ICU protocols to reduce PICS severity. Practitioners will need to draw on this knowledge to help Ronan and the thousands of COVID-19 ICU patients like her.
Surviving the ICU
Although the new coronavirus has pushed the world’s critical care system to its limits, it was an outbreak in 1952 that inspired the creation of intensive care units. That summer, a wave of paralytic polio swept over Copenhagen, Denmark, and anesthesiologist Bjørn Ibsen, MD, PhD, used mechanical ventilation — physically operated by medical and dental students – to help 316 children breathe for weeks at a time while their small bodies worked to fight off the virus. The effort halved the mortality rate from polio that affected breathing, from 80% to 40%.
In these wards, dedicated to the very sickest, each patient was assigned his or her own nurse. Over the next decade, hospitals in the United Kingdom and the United States established their own ICUs to treat patients with a variety of conditions. Although it helped improve survival, mortality rates in critical care units remained stubbornly high, owing to the patients’ severe underlying illnesses.
“We thought we were doing a good job if the patient survived, but we had no idea what happened after discharge,” said Carla Sevin, MD, medical director of Vanderbilt’s ICU Recovery Center. Nor did their efforts to find out always bring answers. “We struggled to get people to come in for support — they were debilitated, physically burdened, and weak.”
Through further advances in life support, by the early 2000s, the average mortality rates in American ICUs had dropped to 8% to 19%. As the number of critical care survivors began to climb, clinical researchers noticed that the lives of these patients and their families were profoundly altered by their severe illness.
As Dale Needham, MD, PhD, began his pulmonology and critical care residency in Toronto, Canada, in 2005, a group of physicians there began a 5-year longitudinal study to assess long-term outcomes of patients who developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although ARDS is an acute condition, the investigators found that patients felt effects for years. Younger patients recovered better than older ones, but none of the patients› physical functioning was equivalent to that of age-matched control persons. Even 5 years later, former ICU patients only reached 76% of expected physical functioning, according to results published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study was a wake-up call.
At a meeting in Chicago in 2010, Needham, now an intensivist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland, gathered an interdisciplinary group of colleagues, including patients and caregivers, to clarify the phenomena they were seeing. What emerged from that meeting, published in 2012 in Critical Care Medicine, were the diagnostic criteria for PICS: According to the new definition, PICS is characterized by new or worsening physical and neuropsychiatric deficits that range from forgetfulness and loss of motivation to physical weakness and insomnia.
The issue, Needham says, is that although the trouble starts in the ICU, it only becomes clear once patients leave. “ICU doctors aren’t the ones dealing with this,” Needham said. “We need to build stronger bridges between critical care and other professions.” That’s where PICS comes in, a definition that exists explicitly to alert healthcare providers about the constellation of challenges many of these individuals face as they try to reenter “normal” life.
Defining the problem
As an ICU nurse at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, Annie Johnson, ACNP-BC, knew lots about helping hospitalized patients, but she says she didn’t know anything about what to do after discharge – at least not until her own mother became a patient.
On the first day of retirement in October 2014, Johnson’s mother flatlined. Quick-thinking paramedics resuscitated her, and after several days in critical care, she was discharged. Since then, her heart has remained healthy. Johnson’s sister, who spent time worrying over her mother at the hospital, also had lingering effects. Both have since struggled, plagued by nightmares, flashbacks, and insomnia.
Johnson initially believed her mom’s and sister’s neuropsychiatric, post-ICU struggles were unique to her family. It was only a year later, at a seminar she was attending, that she first heard the words “post–intensive care syndrome.” Suddenly, Johnson had a name for her family’s experiences, and she began to create support groups and resources to help other families like hers.
“I thought of all the patients I had treated over the years who had been on ventilators for days and days and days. And if this happened to my mom after 48 hours, what must they be going through?” she asked.
Once physicians formally defined PICS, the Society for Critical Care Medicine helped create programs to educate ICU staff, patients, and families about potential post-discharge challenges. Researchers also began to investigate factors affecting post-ICU functioning. Follow-up studies of patients with delirium (ranging from general confusion about time and place to extreme agitation and violence) showed they had striking cognitive deficits. Problems with short-term memory, flexible thinking, and motivation plagued patients for years after their critical illness, similar to the physical deficiencies seen after ARDS. Delirium was one of the strongest risk factors for neuropsychiatric problems.
“Delirium is basically a stress test for the brain,” said Babar Khan, MD, a critical care specialist at Indiana University’s Regenstrief Institute, in Bloomington. But whether delirium accentuates preexisting cognitive difficulties or creates them afresh isn’t yet clear.
Sophia Wang, MD, a geriatric psychiatrist at Indiana University who works with many critical care patients, says patients who had experienced delirium in the ICU showed significant defects in memory and executive functioning long after their hospital stay. She points to a 2015 study that followed 47 ICU patients for a year post discharge. Among those who experienced delirium, brain volumes, as measured by MRI, were smaller at 3 months, something associated with cognitive problems at 1 year. Many struggled at work, and unemployment was common. Depression and posttraumatic stress compounded these difficulties. Among those with acute respiratory distress, ICU patients who are young, female, and unemployed are most likely to suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder after they are discharge.
Critical care medicine may have given these patients a second chance at life, Wang says, but the life they return to often looks nothing like the one they had before their illness.
Prolonged mechanical ventilation and the heavy sedation that often accompanies it are predictors of PICS severity. Some of these links could be explained by the gravity of the illness that landed someone in critical care, but others are more likely to be iatrogenic, says Gerald Weinhouse, MD, a pulmonology and critical care physician and co-director of the Critical Illness Recovery Program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. The involvement of loved ones at the patient’s bedside, however, improved the entire family’s outcome.
When Weinhouse saw those data, he and his colleagues founded a peer support program for ICU survivors. In a study published in 2019 in Critical Care Medicine, they identified six different models for peer support for those with PICS and their families, including both online and in-person approaches. An ongoing challenge for physicians, Weinhouse says, is getting patients to engage with these programs, given that their calendars are crowded with medical appointments and that they suffer from increased physical and mental disability.
Studies such as these led critical care physicians to form the ICU Liberation Collaborative to rethink critical care medicine. At Vanderbilt, Sevin and Jackson headed up one of the world’s first post-ICU clinics, which uses an interdisciplinary team to help patients maximize their functioning. They redesigned their critical care unit in a way that allows families to spend the night and that encourages patient mobility. Both Needham and Weinhouse continue tracking patient outcomes.
Even before the novel coronavirus struck, the United States — and the world — had begun to realize that graduating from the ICU was only the start of what was often an extensive recovery.
The long road back
When COVID-19 patients began flooding intensive care wards around the world, physicians scrambled to meet their complex and desperate acute medical needs. Over the past few months, physicians have focused on keeping these patients alive. “We’ve never seen anything like it ― not even during polio — with the sheer number of patients, all with respiratory distress,” Needham said.
But he and his colleagues know this is only the beginning.
“We’re aware that survivorship issues are coming. There’s going to be a wave of sick people who survived the coronavirus but are going to need more help,” Weinhouse said.
Intensivists have been drawing on PICS research in their fight to help COVID-19 patients. Work from the past few years has shown that although sedation is required during intubation itself, not everyone needs it while on a ventilator. Titrating down sedating medication helps reduce delirium, Wang says. Such medication has been shown to contribute to later cognitive problems. Needham’s studies showing that prolonged bedrest by ICU patients causes muscular atrophy has led him to encourage patients to move as much as possible. With the help of physical therapists, many patients on ventilators can be awake, alert, and moving around the ward.
One of the biggest challenges critical-care coronavirus patients face is prolonged isolation. The constant presence of a familiar face helps orient confused and delirious patients and provides emotional support during a frightening time. But because the immediate need for infection control outweighs these benefits, few hospitals allow visitors, especially for COVID-19 patients.
To address this, some units have been using video technology to allow loved ones to call in. At Johns Hopkins, physicians have also been relying on the expertise of occupational therapists (OTs). Needham says that one OT found that rubbing the hand and back of an agitated, delirious patient helped soothe and calm him better than many medications.
Ronan, who spent 5 days in intensive care, echoes that problem. She says she found the relative lack of human contact to be one of the most challenging parts of being in a bed on a COVID-19 ward. Separated from her husband and daughter, suffering from high fever and severe illness, she lost all track of time.
Her return home was difficult, too. Although her job as a home health nurse had prepared her on some level for the challenges she would face after discharge, Ronan says the hospital provided little practical help.
“Everything is so much harder at home, even little things like going to the bathroom,” she said. “I feel like I’m trying to bail out a sinking ship with a teacup.”
Khan and other physicians, aware of the challenges Ronan and others face once home, aim to create post-ICU clinics specifically for COVID-19 patients. They want to build what Khan calls a “one-stop shop” for all the support patients need to recover. Some of that can be provided via telehealth, which may also help ease the physical burden.
Because there’s so much physicians don’t know about the coronavirus, Johnson says, such clinics are not only a chance to help the sickest COVID-19 patients, they will also help researchers learn more about the virus and improve critical care for other illnesses.
Today, nearly 2 months after discharge, Ronan is back on the job but struggles with a persistent cough — likely due to the lung damage she sustained while ill. She has constant fatigue, as well as ongoing upset stomach from all the medications she took to reduce fever and body aches. When she dons a mask for work, the tangible reminder of her hospital stay sends her into a panic attack. Physically, she’s weaker than before.
Researchers are still trying to understand everything that Ronan and other COVID-19 patients need to move on with their lives after being in the ICU. Mysteries abound, but the ground laid by Sevin, Needham, Weinhouse, and others has provided a solid foundation on which to build.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
By the time she was discharged from a suburban New Jersey hospital on April 10, Kathleen Ronan thought the worst was behind her. For a week before her husband rushed her to the emergency department (ED), incoherent and struggling to breathe, the novel coronavirus had ravaged her body. She tried to treat her fevers with acetaminophen and ice packs. Despite taking enough Tylenol to risk liver damage and packing herself on ice like the catch of the day, Ronan’s fever continued to rise. By the time her temperature reached 104.5° F, Ronan knew the time had come for more drastic measures.
A team of masked and gowned nurses greeted her at a triage tent outside the ED, and from there, everything becomes hazy for Ronan. She was immediately rushed to the hospital’s special COVID-19 intensive care unit (ICU), where she spent 5 days. But she has few distinct memories from this time. What she does remember is the exhaustion, the pain, the loneliness, and the fear. Her family couldn’t visit, and though Ronan works as a home health nurse, her brain was so addled with fever that she couldn’t make sense of what was happening. After a week in the hospital, 5 days of which were spent in the ICU, 51-year-old Ronan was discharged.
Her years of working as a home health nurse told her that the return home wouldn’t be easy, but nothing prepared her for just how much she would struggle. The once-active Ronan, who had supplemented long days on her feet caring for others as a nurse with regular trips to the gym, now needed a walker to traverse the few steps from her bed to the toilet, an effort that left her gasping for air. Her brain couldn’t even focus on an audiobook, let alone a short magazine article.
“It just completely knocked the stuffing out of me,” Ronan said.
Ronan’s lingering symptoms aren’t unique to COVID-19 patients. In as many as 80% of patients leaving the ICU, . Although underlying illness plays a role in these symptoms, the amount of time spent in critical care is a major factor.
Nor is PICS simply a set of side effects that will go away on their own. It includes ongoing cognitive difficulties and physical weakness, both of which can lead to employment problems. Beyond that, depression and anxiety can exacerbate – and be exacerbated by – these challenges. Psychologist Jim Jackson, PsyD, assistant director of the ICU Recovery Center at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, recently spoke with a former ICU patient who has struggled since her discharge 30 years ago.
“Her life essentially stopped with her critical care stay. She hasn’t been able to move forward,” he said. “She’s part of a whole fraternity of people who are struggling.”
The good news is that over the past decade, researchers have made important strides in understanding what makes PICS symptoms worse and how critical care physicians can tweak ICU protocols to reduce PICS severity. Practitioners will need to draw on this knowledge to help Ronan and the thousands of COVID-19 ICU patients like her.
Surviving the ICU
Although the new coronavirus has pushed the world’s critical care system to its limits, it was an outbreak in 1952 that inspired the creation of intensive care units. That summer, a wave of paralytic polio swept over Copenhagen, Denmark, and anesthesiologist Bjørn Ibsen, MD, PhD, used mechanical ventilation — physically operated by medical and dental students – to help 316 children breathe for weeks at a time while their small bodies worked to fight off the virus. The effort halved the mortality rate from polio that affected breathing, from 80% to 40%.
In these wards, dedicated to the very sickest, each patient was assigned his or her own nurse. Over the next decade, hospitals in the United Kingdom and the United States established their own ICUs to treat patients with a variety of conditions. Although it helped improve survival, mortality rates in critical care units remained stubbornly high, owing to the patients’ severe underlying illnesses.
“We thought we were doing a good job if the patient survived, but we had no idea what happened after discharge,” said Carla Sevin, MD, medical director of Vanderbilt’s ICU Recovery Center. Nor did their efforts to find out always bring answers. “We struggled to get people to come in for support — they were debilitated, physically burdened, and weak.”
Through further advances in life support, by the early 2000s, the average mortality rates in American ICUs had dropped to 8% to 19%. As the number of critical care survivors began to climb, clinical researchers noticed that the lives of these patients and their families were profoundly altered by their severe illness.
As Dale Needham, MD, PhD, began his pulmonology and critical care residency in Toronto, Canada, in 2005, a group of physicians there began a 5-year longitudinal study to assess long-term outcomes of patients who developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Although ARDS is an acute condition, the investigators found that patients felt effects for years. Younger patients recovered better than older ones, but none of the patients› physical functioning was equivalent to that of age-matched control persons. Even 5 years later, former ICU patients only reached 76% of expected physical functioning, according to results published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The study was a wake-up call.
At a meeting in Chicago in 2010, Needham, now an intensivist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland, gathered an interdisciplinary group of colleagues, including patients and caregivers, to clarify the phenomena they were seeing. What emerged from that meeting, published in 2012 in Critical Care Medicine, were the diagnostic criteria for PICS: According to the new definition, PICS is characterized by new or worsening physical and neuropsychiatric deficits that range from forgetfulness and loss of motivation to physical weakness and insomnia.
The issue, Needham says, is that although the trouble starts in the ICU, it only becomes clear once patients leave. “ICU doctors aren’t the ones dealing with this,” Needham said. “We need to build stronger bridges between critical care and other professions.” That’s where PICS comes in, a definition that exists explicitly to alert healthcare providers about the constellation of challenges many of these individuals face as they try to reenter “normal” life.
Defining the problem
As an ICU nurse at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, Annie Johnson, ACNP-BC, knew lots about helping hospitalized patients, but she says she didn’t know anything about what to do after discharge – at least not until her own mother became a patient.
On the first day of retirement in October 2014, Johnson’s mother flatlined. Quick-thinking paramedics resuscitated her, and after several days in critical care, she was discharged. Since then, her heart has remained healthy. Johnson’s sister, who spent time worrying over her mother at the hospital, also had lingering effects. Both have since struggled, plagued by nightmares, flashbacks, and insomnia.
Johnson initially believed her mom’s and sister’s neuropsychiatric, post-ICU struggles were unique to her family. It was only a year later, at a seminar she was attending, that she first heard the words “post–intensive care syndrome.” Suddenly, Johnson had a name for her family’s experiences, and she began to create support groups and resources to help other families like hers.
“I thought of all the patients I had treated over the years who had been on ventilators for days and days and days. And if this happened to my mom after 48 hours, what must they be going through?” she asked.
Once physicians formally defined PICS, the Society for Critical Care Medicine helped create programs to educate ICU staff, patients, and families about potential post-discharge challenges. Researchers also began to investigate factors affecting post-ICU functioning. Follow-up studies of patients with delirium (ranging from general confusion about time and place to extreme agitation and violence) showed they had striking cognitive deficits. Problems with short-term memory, flexible thinking, and motivation plagued patients for years after their critical illness, similar to the physical deficiencies seen after ARDS. Delirium was one of the strongest risk factors for neuropsychiatric problems.
“Delirium is basically a stress test for the brain,” said Babar Khan, MD, a critical care specialist at Indiana University’s Regenstrief Institute, in Bloomington. But whether delirium accentuates preexisting cognitive difficulties or creates them afresh isn’t yet clear.
Sophia Wang, MD, a geriatric psychiatrist at Indiana University who works with many critical care patients, says patients who had experienced delirium in the ICU showed significant defects in memory and executive functioning long after their hospital stay. She points to a 2015 study that followed 47 ICU patients for a year post discharge. Among those who experienced delirium, brain volumes, as measured by MRI, were smaller at 3 months, something associated with cognitive problems at 1 year. Many struggled at work, and unemployment was common. Depression and posttraumatic stress compounded these difficulties. Among those with acute respiratory distress, ICU patients who are young, female, and unemployed are most likely to suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder after they are discharge.
Critical care medicine may have given these patients a second chance at life, Wang says, but the life they return to often looks nothing like the one they had before their illness.
Prolonged mechanical ventilation and the heavy sedation that often accompanies it are predictors of PICS severity. Some of these links could be explained by the gravity of the illness that landed someone in critical care, but others are more likely to be iatrogenic, says Gerald Weinhouse, MD, a pulmonology and critical care physician and co-director of the Critical Illness Recovery Program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. The involvement of loved ones at the patient’s bedside, however, improved the entire family’s outcome.
When Weinhouse saw those data, he and his colleagues founded a peer support program for ICU survivors. In a study published in 2019 in Critical Care Medicine, they identified six different models for peer support for those with PICS and their families, including both online and in-person approaches. An ongoing challenge for physicians, Weinhouse says, is getting patients to engage with these programs, given that their calendars are crowded with medical appointments and that they suffer from increased physical and mental disability.
Studies such as these led critical care physicians to form the ICU Liberation Collaborative to rethink critical care medicine. At Vanderbilt, Sevin and Jackson headed up one of the world’s first post-ICU clinics, which uses an interdisciplinary team to help patients maximize their functioning. They redesigned their critical care unit in a way that allows families to spend the night and that encourages patient mobility. Both Needham and Weinhouse continue tracking patient outcomes.
Even before the novel coronavirus struck, the United States — and the world — had begun to realize that graduating from the ICU was only the start of what was often an extensive recovery.
The long road back
When COVID-19 patients began flooding intensive care wards around the world, physicians scrambled to meet their complex and desperate acute medical needs. Over the past few months, physicians have focused on keeping these patients alive. “We’ve never seen anything like it ― not even during polio — with the sheer number of patients, all with respiratory distress,” Needham said.
But he and his colleagues know this is only the beginning.
“We’re aware that survivorship issues are coming. There’s going to be a wave of sick people who survived the coronavirus but are going to need more help,” Weinhouse said.
Intensivists have been drawing on PICS research in their fight to help COVID-19 patients. Work from the past few years has shown that although sedation is required during intubation itself, not everyone needs it while on a ventilator. Titrating down sedating medication helps reduce delirium, Wang says. Such medication has been shown to contribute to later cognitive problems. Needham’s studies showing that prolonged bedrest by ICU patients causes muscular atrophy has led him to encourage patients to move as much as possible. With the help of physical therapists, many patients on ventilators can be awake, alert, and moving around the ward.
One of the biggest challenges critical-care coronavirus patients face is prolonged isolation. The constant presence of a familiar face helps orient confused and delirious patients and provides emotional support during a frightening time. But because the immediate need for infection control outweighs these benefits, few hospitals allow visitors, especially for COVID-19 patients.
To address this, some units have been using video technology to allow loved ones to call in. At Johns Hopkins, physicians have also been relying on the expertise of occupational therapists (OTs). Needham says that one OT found that rubbing the hand and back of an agitated, delirious patient helped soothe and calm him better than many medications.
Ronan, who spent 5 days in intensive care, echoes that problem. She says she found the relative lack of human contact to be one of the most challenging parts of being in a bed on a COVID-19 ward. Separated from her husband and daughter, suffering from high fever and severe illness, she lost all track of time.
Her return home was difficult, too. Although her job as a home health nurse had prepared her on some level for the challenges she would face after discharge, Ronan says the hospital provided little practical help.
“Everything is so much harder at home, even little things like going to the bathroom,” she said. “I feel like I’m trying to bail out a sinking ship with a teacup.”
Khan and other physicians, aware of the challenges Ronan and others face once home, aim to create post-ICU clinics specifically for COVID-19 patients. They want to build what Khan calls a “one-stop shop” for all the support patients need to recover. Some of that can be provided via telehealth, which may also help ease the physical burden.
Because there’s so much physicians don’t know about the coronavirus, Johnson says, such clinics are not only a chance to help the sickest COVID-19 patients, they will also help researchers learn more about the virus and improve critical care for other illnesses.
Today, nearly 2 months after discharge, Ronan is back on the job but struggles with a persistent cough — likely due to the lung damage she sustained while ill. She has constant fatigue, as well as ongoing upset stomach from all the medications she took to reduce fever and body aches. When she dons a mask for work, the tangible reminder of her hospital stay sends her into a panic attack. Physically, she’s weaker than before.
Researchers are still trying to understand everything that Ronan and other COVID-19 patients need to move on with their lives after being in the ICU. Mysteries abound, but the ground laid by Sevin, Needham, Weinhouse, and others has provided a solid foundation on which to build.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Race and race relations: Be curious, not furious
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Racism has been around for a very long time, and we still have a long way to go to eradicate it, in all of its forms. Racism can be subtle, such as not offering employment to a fully qualified candidate or lowering your level of care because of the color of a person’s skin. Also, you never know if the future will place you in the same position as that of the person you are discriminating against or excluding. Diversity through the mixture of cultures and races is what provides a richness to our communities and our country.
No matter what race we may be, we all are human and deserve to be treated and respected as such. The patient you misunderstood, feared, or dismissed could be the same person who helps you become a better physician. For instance, one of my teenage patients of Chinese descent confessed one day that she was feeling depressed, sometimes to the point of suicidal ideation. However, she was adamant that I not report this condition to her parents. From her, I learned that mental illness, such as depression, are taboo subjects in Asian cultures. This information enabled me to be more sensitive with handling this patient’s condition and treatment.
In many cities across America, people have been protesting the recent tragic death of Mr. George Floyd, an African American man killed by a white police officer. In the past few months, unfortunately, we have seen similar cases of racist acts against African Americans. Sadly, this is nothing new.
There are examples of racist acts against other racial groups as well. Since the coronavirus pandemic became global news, Asian Americans have faced a wave of intense xenophobia in the United States. Be mindful that one race suffering injustice in one country could themselves be racist against another group given the opportunity. An example of this was reported in an April 16, 2020, article in the Los Angeles Times. The events took place in Guangzhou, China. The article reported that Africans living there were harassed, targeted, and evicted from their homes in the port city following the positive COVID-19 tests of five Nigerians. Instead of imposing quarantine based on contact history, China’s response has been based on race amid the coronavirus crisis. Stories like this remind us that racism is not just black and white, but can occur by any dominant culture against the minority. To be clear, not everyone is a racist.
Fear of the unknown causes misunderstanding and weakens the relationship between a pediatrician and the patient. Instead, let us “be curious and not furious.”1 We may look different on the outside, but inside we are all human, with feelings, desires, and dreams. An example of being misunderstood is commonly observed as others stereotype African American populations. For example, an African American mother may be described as rude, loud, and disrespectful by those in your office. Such labeling fails to take the time necessary to understand the other’s perspective, and it dismisses her. Why might she be acting this way? What false assumptions are you making? How would you react if you were frequently disrespected or dismissed? How would you react if you had to worry about being physically harmed? Your visage could appear to be angry or guarded – not exactly welcoming or pleasant. It is much easier to quickly dismiss such a patient and not be sincerely interested in what she or her child’s medical needs may be. Such a disposition only results in frustrating outcomes and the destruction of trust between a patient and the provider.
Although I encounter racism daily in my work, I strive to put aside those violations as I treat my patients and interact with their parents. The decision to be inquisitive and empathetic is a conscious one, which can disarm strangers, allowing for trust to be built. It can engender a smile as well.
Teachers frequently refer parents to us when their children are having learning or behavioral difficulties in school. One challenging case for me involved a Latino boy with learning difficulties. The mother, who does not speak English, had been struggling with getting help for her son. I decided to attend a meeting for the patient’s Individualized Education Plan (IEP) at his school (an IEP is a requirement of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, or IDEA). My presence at the meeting, given that I am also fluent in Spanish, provided a bridge in communication between the parent and the teachers. Moreover, my presence persuaded the patient’s teachers to be more aggressive in designing an individualized plan to truly help my patient. Latino and African American students commonly suffer from disparities in health and education. In my own practice, I also work toward improving disparities within Latino and African American communities through medical education initiatives. There is so much we, as pediatricians, can do to advocate for these communities.
The absence of empathy leading to the killing of Mr. Floyd admittedly is not the same as what generates an inadequate IEP or the desire to avoid a “loud” parent. Even so, any lack of empathy lowers the quality of patient care. It takes conscious effort to be open to helping someone you do not innately understand. Quality pediatric care cannot happen where racism and misunderstanding exist between a patient and provider. Until we truly stop being selfish, the issue of racism will continue to resurface. One impactful way the majority population can help people of color is by not being a bystander to injustice. Inaction makes you an accomplice to the racist act. We must be brave – “be curious, not furious.” Remember that an injustice to one culture eventually becomes an injustice against us all. Being open to what is different, new, or not well known is how a culture becomes richer and even better.
Dr. Mba Wright is a primary care pediatrician practicing in Sacramento, Calif., for more than 14 years. She has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
1. “Going the Distance: Finding and Keeping Lifelong Love” (New York, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1991).
Asthma leads spending on avoidable pediatric inpatient stays
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
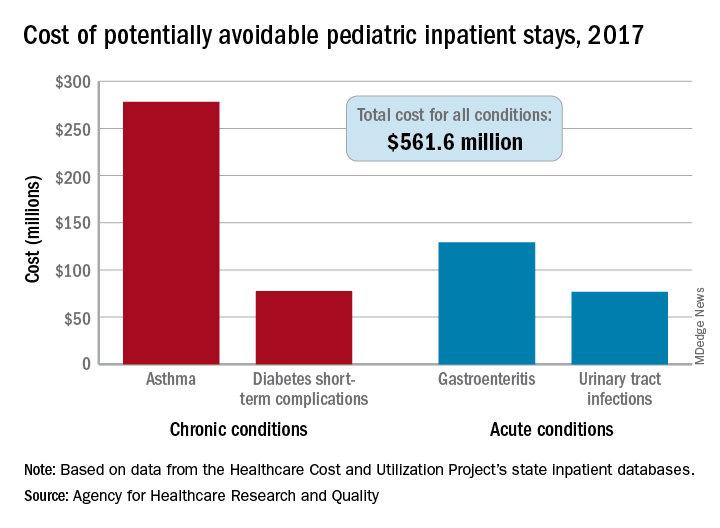
The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

The cost of potentially avoidable visits for asthma that year was $278 million, versus $284 million combined for the other three conditions “that evidence suggests may be avoidable, in part, through timely and quality primary and preventive care,” Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and H. Joanna Jiang, PhD, said in an AHRQ statistical brief.
Those three other conditions are diabetes short-term complications, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Neonatal stays were excluded from the analysis, Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Dr. Jiang of the AHRQ noted.
The state inpatient databases of the AHRQ’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project included 1.4 million inpatient stays among children aged 3 months to 17 years in 2017, of which 8% (108,300) were deemed potentially preventable. Hospital charges for the preventable stays came to $561.6 million, or 3% of the $20 billion in total costs for all nonneonatal stays, they said.
Rates of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (159 per 100,000 population), gastroenteritis (90 per 100,000), and UTIs (41 per 100,000) were highest for children aged 0-4 years and generally decreased with age, but diabetes stays increased with age, rising from 12 per 100,000 in children aged 5-9 years to 38 per 100,000 for those 15-17 years old, the researchers said.
Black children had a much higher rate of potentially avoidable stays for asthma (218 per 100,000) than did Hispanic children (74), Asian/Pacific Islander children (46), or white children (43), but children classified as other race/ethnicity were higher still: 380 per 100,000. Rates for children classified as other race/ethnicity were highest for the other three conditions as well, they reported.
Comparisons by sex for the four conditions ended up in a 2-2 tie: Girls had higher rates for diabetes (28 vs. 23) and UTIs (35 vs. 8), and boys had higher rates for asthma (96 vs. 67) and gastroenteritis (38 vs. 35), Dr. McDermott and Dr. Jiang reported.
SOURCE: McDermott KW, Jiang HJ. HCUP Statistical Brief #259. June 2020.
The evolution of “COVIDists”
Adapting to the demands placed on hospital resources by COVID-19
The challenges posed by COVID-19 have crippled health care systems around the globe. By February 2020, the first outbreak in the United States had been set off in Washington State. We quickly became the world’s epicenter of the epidemic, with over 1.8 million patients and over 110,000 deaths.1 The rapidity of spread and the severity of the disease created a tremendous strain on resources. It blindsided policymakers and hospital administrators, which left little time to react to the challenges placed on hospital operations all over the country.
The necessity of a new care model
Although health systems in the United States are adept in managing complications of common seasonal viral respiratory illnesses, COVID-19 presented an entirely different challenge with its significantly higher mortality rate. A respiratory disease turning into a multiorgan disease that causes debilitating cardiac, renal, neurological, hematological, and psychosocial complications2 was not something we had experience managing effectively. Additional challenges included a massive surge of COVID-19 patients, a limited supply of personal protective equipment (PPE), an inadequate number of intensivists for managing the anticipated ventilated patients, and most importantly, the potential of losing some of our workforce if they became infected.
Based on the experiences in China and Italy, and various predictive models, the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health quickly realized the necessity of a new model of care for COVID-19 patients. We came up with an elaborate plan to manage the disease burden and the strain on resources effectively. The measures we put in place could be broadly divided into three categories following the timeline of the disease: the preparatory phase, the execution phase, and the maintenance phase.
The preparatory phase: From “Hospitalists” to “COVIDists”
As in most hospitals around the country, hospitalists are the backbone of inpatient clinical operations at our health system. A focused group of 10 hospitalists who volunteered to take care of COVID-19 patients with a particular interest in the pandemic and experience in critical care were selected, and the term “COVIDists” was coined to refer to them.
COVIDists were trained in various treatment protocols and ongoing clinical trials. They were given refresher training in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) and Fundamental Critical Care Support (FCCS) courses and were taught in critical care/ventilator management by the intensivists through rapid indoctrination in the ICU. All of them had their N-95 mask fitting updated and were trained in the safe donning and doffing of all kinds of PPE by PPE coaches. The palliative care team trained them in conducting end-of-life/code status discussions with a focus on being unable to speak with family members at the bedside. COVIDists were also assigned as Code Blue leaders for any “COVID code blue” in the hospital.
In addition to the rapid training course, COVID-related updates were disseminated daily using three different modalities: brief huddles at the start of the day with the COVIDists; a COVID-19 newsletter summarizing daily updates, new treatments, strategies, and policies; and a WhatsApp group for instantly broadcasting information to the COVIDists (Table 1).
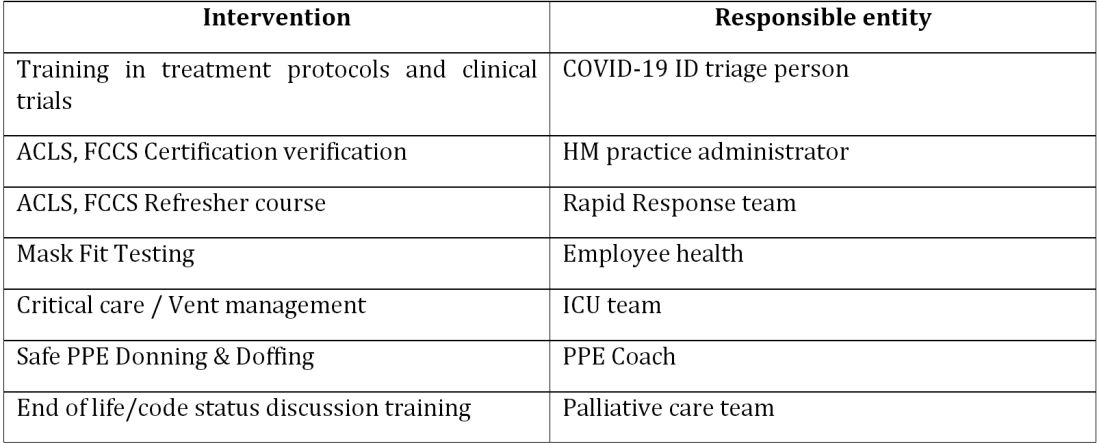
The execution phase
All the hospitalized COVID-19 patients were grouped together to COVID units, and the COVIDists were deployed to those units geographically. COVIDists were given lighter than usual patient loads to deal with the extra time needed for donning and doffing of PPE and for coordination with specialists. COVIDists were almost the only clinicians physically visiting the patients in most cases, and they became the “eyes and ears” of specialists since the specialists were advised to minimize exposure and pursue telemedicine consults. The COVIDists were also undertaking the most challenging part of the care – talking to families about end-of-life issues and the futility of aggressive care in certain patients with preexisting conditions.
Some COVIDists were deployed to the ICU to work alongside the intensivists and became an invaluable resource in ICU management when the ICU census skyrocketed during the initial phase of the outbreak. This helped in tiding the health system over during the initial crisis. Within a short time, we shifted away from an early intubation strategy, and most of the ICU patients were managed in the intermediate care units on high flow oxygen along with the awake-proning protocol. The COVIDists exclusively managed these units. They led multidisciplinary rounds two times a day with the ICU, rapid response team (RRT), the palliative care team, and the nursing team. This step drastically decreased the number of intubations, RRT activations, reduced ICU census,3 and helped with hospital capacity and patient flow (Tables 2 and 3).
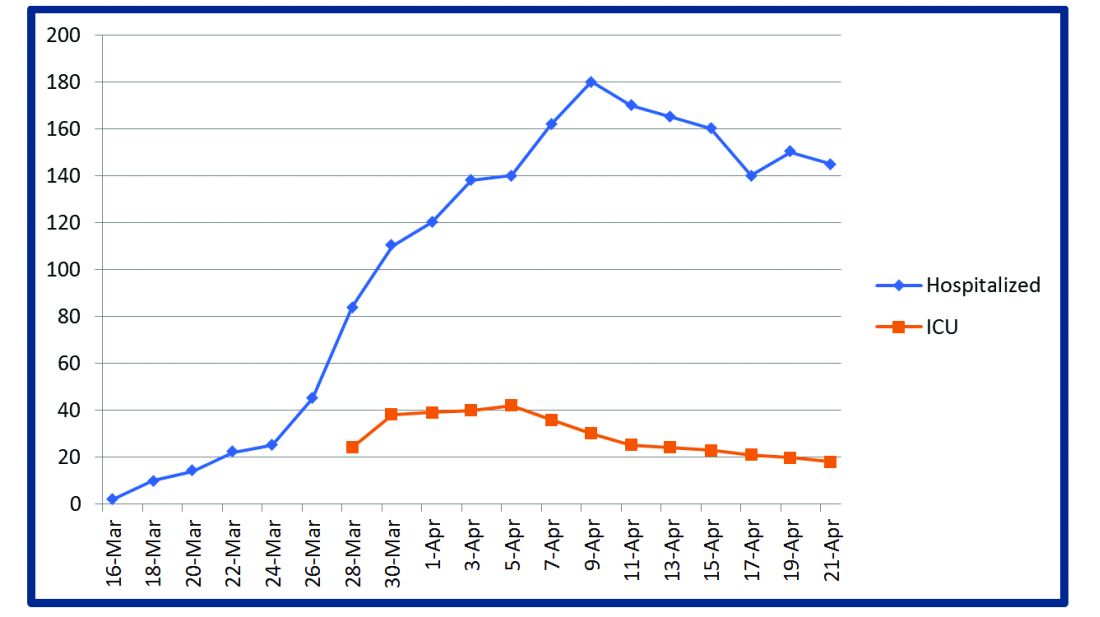
This strategy also helped build solidarity and camaraderie between all these groups, making the COVIDists feel that they were never alone and that the whole hospital supported them. We are currently evaluating clinical outcomes and attempting to identify effects on mortality, length of stay, days on the ventilator, and days in ICU.

The maintenance phase
It is already 2 months since the first devising COVIDists. There is no difference in sick callouts between COVIDists and non-COVIDists. One COVIDist and one non-COVIDist contracted the disease, but none of them required hospitalization. Although we initially thought that COVIDists would be needed for only a short period of time, the evolution of the disease is showing signs that it might be prolonged over the next several months. Hence, we are planning to continue COVIDist service for at least the next 6 months and reevaluate the need.
Hospital medicine leadership checked on COVIDists daily in regard to their physical health and, more importantly, their mental well-being. They were offered the chance to be taken off the schedule if they felt burned out, but no one wanted to come off their scheduled service before finishing their shifts. BlueCross MA recognized one of the COVIDists, Raghuveer Rakasi, MD, as a “hero on the front line.”4 In Dr. Rakasi’s words, “We took a nosedive into something without knowing its depth, and aware that we could have fatalities among ourselves. We took up new roles, faced new challenges, learned new things every day, evolving every step of the way. We had to change the way we practice medicine, finding new ways to treat patients, and protecting the workforce by limiting patient exposure, prioritizing investigations.” He added that “we have to adapt to a new normal; we should be prepared for this to come in waves. Putting aside our political views, we should stand united 6 feet apart, with a mask covering our brave faces, frequently washing our helping hands to overcome these uncertain times.”
Conclusion
The creation of a focused group of hospitalists called COVIDists and providing them with structured and rapid training (in various aspects of clinical care of COVID-19 patients, critical care/ventilator management, efficient and safe use of PPE) and daily information dissemination allowed our health system to prepare for the large volume of COVID-19 patients. It also helped in preserving the larger hospital workforce for a possible future surge.
The rapid development and implementation of the COVIDist strategy succeeded because of the intrinsic motivation of the providers to improve the outcomes of this high-risk patient population and the close collaboration of the stakeholders. Our institution remains successful in managing the pandemic in Western Massachusetts, with reserve capacity remaining even during the peak of the epidemic. A large part of this was because of creating and training a pool of COVIDists.
Dr. Medarametla is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health, and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts, Worcester. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Prabhakaran is unit medical director, geriatrics unit, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Bryson is associate program director of the Internal Medicine Residency at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Umar is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health. Dr. Natanasabapathy is division chief of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Updated Jun 10, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/cases-in-us.html.
2. Zhou F et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054-62.
3. Westafer LM et al. A transdisciplinary COVID-19 early respiratory intervention protocol: An implementation story. J Hosp Med. 2020 May 21;15(6):372-374.
4. Miller J. “Heroes on the front line: Dr. Raghuveer Rakasi.” Coverage. May 18, 2020. https://coverage.bluecrossma.com/article/heroes-front-line-dr-raghuveer-rakasi
Adapting to the demands placed on hospital resources by COVID-19
Adapting to the demands placed on hospital resources by COVID-19
The challenges posed by COVID-19 have crippled health care systems around the globe. By February 2020, the first outbreak in the United States had been set off in Washington State. We quickly became the world’s epicenter of the epidemic, with over 1.8 million patients and over 110,000 deaths.1 The rapidity of spread and the severity of the disease created a tremendous strain on resources. It blindsided policymakers and hospital administrators, which left little time to react to the challenges placed on hospital operations all over the country.
The necessity of a new care model
Although health systems in the United States are adept in managing complications of common seasonal viral respiratory illnesses, COVID-19 presented an entirely different challenge with its significantly higher mortality rate. A respiratory disease turning into a multiorgan disease that causes debilitating cardiac, renal, neurological, hematological, and psychosocial complications2 was not something we had experience managing effectively. Additional challenges included a massive surge of COVID-19 patients, a limited supply of personal protective equipment (PPE), an inadequate number of intensivists for managing the anticipated ventilated patients, and most importantly, the potential of losing some of our workforce if they became infected.
Based on the experiences in China and Italy, and various predictive models, the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health quickly realized the necessity of a new model of care for COVID-19 patients. We came up with an elaborate plan to manage the disease burden and the strain on resources effectively. The measures we put in place could be broadly divided into three categories following the timeline of the disease: the preparatory phase, the execution phase, and the maintenance phase.
The preparatory phase: From “Hospitalists” to “COVIDists”
As in most hospitals around the country, hospitalists are the backbone of inpatient clinical operations at our health system. A focused group of 10 hospitalists who volunteered to take care of COVID-19 patients with a particular interest in the pandemic and experience in critical care were selected, and the term “COVIDists” was coined to refer to them.
COVIDists were trained in various treatment protocols and ongoing clinical trials. They were given refresher training in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) and Fundamental Critical Care Support (FCCS) courses and were taught in critical care/ventilator management by the intensivists through rapid indoctrination in the ICU. All of them had their N-95 mask fitting updated and were trained in the safe donning and doffing of all kinds of PPE by PPE coaches. The palliative care team trained them in conducting end-of-life/code status discussions with a focus on being unable to speak with family members at the bedside. COVIDists were also assigned as Code Blue leaders for any “COVID code blue” in the hospital.
In addition to the rapid training course, COVID-related updates were disseminated daily using three different modalities: brief huddles at the start of the day with the COVIDists; a COVID-19 newsletter summarizing daily updates, new treatments, strategies, and policies; and a WhatsApp group for instantly broadcasting information to the COVIDists (Table 1).

The execution phase
All the hospitalized COVID-19 patients were grouped together to COVID units, and the COVIDists were deployed to those units geographically. COVIDists were given lighter than usual patient loads to deal with the extra time needed for donning and doffing of PPE and for coordination with specialists. COVIDists were almost the only clinicians physically visiting the patients in most cases, and they became the “eyes and ears” of specialists since the specialists were advised to minimize exposure and pursue telemedicine consults. The COVIDists were also undertaking the most challenging part of the care – talking to families about end-of-life issues and the futility of aggressive care in certain patients with preexisting conditions.
Some COVIDists were deployed to the ICU to work alongside the intensivists and became an invaluable resource in ICU management when the ICU census skyrocketed during the initial phase of the outbreak. This helped in tiding the health system over during the initial crisis. Within a short time, we shifted away from an early intubation strategy, and most of the ICU patients were managed in the intermediate care units on high flow oxygen along with the awake-proning protocol. The COVIDists exclusively managed these units. They led multidisciplinary rounds two times a day with the ICU, rapid response team (RRT), the palliative care team, and the nursing team. This step drastically decreased the number of intubations, RRT activations, reduced ICU census,3 and helped with hospital capacity and patient flow (Tables 2 and 3).

This strategy also helped build solidarity and camaraderie between all these groups, making the COVIDists feel that they were never alone and that the whole hospital supported them. We are currently evaluating clinical outcomes and attempting to identify effects on mortality, length of stay, days on the ventilator, and days in ICU.

The maintenance phase
It is already 2 months since the first devising COVIDists. There is no difference in sick callouts between COVIDists and non-COVIDists. One COVIDist and one non-COVIDist contracted the disease, but none of them required hospitalization. Although we initially thought that COVIDists would be needed for only a short period of time, the evolution of the disease is showing signs that it might be prolonged over the next several months. Hence, we are planning to continue COVIDist service for at least the next 6 months and reevaluate the need.
Hospital medicine leadership checked on COVIDists daily in regard to their physical health and, more importantly, their mental well-being. They were offered the chance to be taken off the schedule if they felt burned out, but no one wanted to come off their scheduled service before finishing their shifts. BlueCross MA recognized one of the COVIDists, Raghuveer Rakasi, MD, as a “hero on the front line.”4 In Dr. Rakasi’s words, “We took a nosedive into something without knowing its depth, and aware that we could have fatalities among ourselves. We took up new roles, faced new challenges, learned new things every day, evolving every step of the way. We had to change the way we practice medicine, finding new ways to treat patients, and protecting the workforce by limiting patient exposure, prioritizing investigations.” He added that “we have to adapt to a new normal; we should be prepared for this to come in waves. Putting aside our political views, we should stand united 6 feet apart, with a mask covering our brave faces, frequently washing our helping hands to overcome these uncertain times.”
Conclusion
The creation of a focused group of hospitalists called COVIDists and providing them with structured and rapid training (in various aspects of clinical care of COVID-19 patients, critical care/ventilator management, efficient and safe use of PPE) and daily information dissemination allowed our health system to prepare for the large volume of COVID-19 patients. It also helped in preserving the larger hospital workforce for a possible future surge.
The rapid development and implementation of the COVIDist strategy succeeded because of the intrinsic motivation of the providers to improve the outcomes of this high-risk patient population and the close collaboration of the stakeholders. Our institution remains successful in managing the pandemic in Western Massachusetts, with reserve capacity remaining even during the peak of the epidemic. A large part of this was because of creating and training a pool of COVIDists.
Dr. Medarametla is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health, and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts, Worcester. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Prabhakaran is unit medical director, geriatrics unit, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Bryson is associate program director of the Internal Medicine Residency at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Umar is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health. Dr. Natanasabapathy is division chief of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Updated Jun 10, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/cases-in-us.html.
2. Zhou F et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054-62.
3. Westafer LM et al. A transdisciplinary COVID-19 early respiratory intervention protocol: An implementation story. J Hosp Med. 2020 May 21;15(6):372-374.
4. Miller J. “Heroes on the front line: Dr. Raghuveer Rakasi.” Coverage. May 18, 2020. https://coverage.bluecrossma.com/article/heroes-front-line-dr-raghuveer-rakasi
The challenges posed by COVID-19 have crippled health care systems around the globe. By February 2020, the first outbreak in the United States had been set off in Washington State. We quickly became the world’s epicenter of the epidemic, with over 1.8 million patients and over 110,000 deaths.1 The rapidity of spread and the severity of the disease created a tremendous strain on resources. It blindsided policymakers and hospital administrators, which left little time to react to the challenges placed on hospital operations all over the country.
The necessity of a new care model
Although health systems in the United States are adept in managing complications of common seasonal viral respiratory illnesses, COVID-19 presented an entirely different challenge with its significantly higher mortality rate. A respiratory disease turning into a multiorgan disease that causes debilitating cardiac, renal, neurological, hematological, and psychosocial complications2 was not something we had experience managing effectively. Additional challenges included a massive surge of COVID-19 patients, a limited supply of personal protective equipment (PPE), an inadequate number of intensivists for managing the anticipated ventilated patients, and most importantly, the potential of losing some of our workforce if they became infected.
Based on the experiences in China and Italy, and various predictive models, the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health quickly realized the necessity of a new model of care for COVID-19 patients. We came up with an elaborate plan to manage the disease burden and the strain on resources effectively. The measures we put in place could be broadly divided into three categories following the timeline of the disease: the preparatory phase, the execution phase, and the maintenance phase.
The preparatory phase: From “Hospitalists” to “COVIDists”
As in most hospitals around the country, hospitalists are the backbone of inpatient clinical operations at our health system. A focused group of 10 hospitalists who volunteered to take care of COVID-19 patients with a particular interest in the pandemic and experience in critical care were selected, and the term “COVIDists” was coined to refer to them.
COVIDists were trained in various treatment protocols and ongoing clinical trials. They were given refresher training in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) and Fundamental Critical Care Support (FCCS) courses and were taught in critical care/ventilator management by the intensivists through rapid indoctrination in the ICU. All of them had their N-95 mask fitting updated and were trained in the safe donning and doffing of all kinds of PPE by PPE coaches. The palliative care team trained them in conducting end-of-life/code status discussions with a focus on being unable to speak with family members at the bedside. COVIDists were also assigned as Code Blue leaders for any “COVID code blue” in the hospital.
In addition to the rapid training course, COVID-related updates were disseminated daily using three different modalities: brief huddles at the start of the day with the COVIDists; a COVID-19 newsletter summarizing daily updates, new treatments, strategies, and policies; and a WhatsApp group for instantly broadcasting information to the COVIDists (Table 1).

The execution phase
All the hospitalized COVID-19 patients were grouped together to COVID units, and the COVIDists were deployed to those units geographically. COVIDists were given lighter than usual patient loads to deal with the extra time needed for donning and doffing of PPE and for coordination with specialists. COVIDists were almost the only clinicians physically visiting the patients in most cases, and they became the “eyes and ears” of specialists since the specialists were advised to minimize exposure and pursue telemedicine consults. The COVIDists were also undertaking the most challenging part of the care – talking to families about end-of-life issues and the futility of aggressive care in certain patients with preexisting conditions.
Some COVIDists were deployed to the ICU to work alongside the intensivists and became an invaluable resource in ICU management when the ICU census skyrocketed during the initial phase of the outbreak. This helped in tiding the health system over during the initial crisis. Within a short time, we shifted away from an early intubation strategy, and most of the ICU patients were managed in the intermediate care units on high flow oxygen along with the awake-proning protocol. The COVIDists exclusively managed these units. They led multidisciplinary rounds two times a day with the ICU, rapid response team (RRT), the palliative care team, and the nursing team. This step drastically decreased the number of intubations, RRT activations, reduced ICU census,3 and helped with hospital capacity and patient flow (Tables 2 and 3).

This strategy also helped build solidarity and camaraderie between all these groups, making the COVIDists feel that they were never alone and that the whole hospital supported them. We are currently evaluating clinical outcomes and attempting to identify effects on mortality, length of stay, days on the ventilator, and days in ICU.

The maintenance phase
It is already 2 months since the first devising COVIDists. There is no difference in sick callouts between COVIDists and non-COVIDists. One COVIDist and one non-COVIDist contracted the disease, but none of them required hospitalization. Although we initially thought that COVIDists would be needed for only a short period of time, the evolution of the disease is showing signs that it might be prolonged over the next several months. Hence, we are planning to continue COVIDist service for at least the next 6 months and reevaluate the need.
Hospital medicine leadership checked on COVIDists daily in regard to their physical health and, more importantly, their mental well-being. They were offered the chance to be taken off the schedule if they felt burned out, but no one wanted to come off their scheduled service before finishing their shifts. BlueCross MA recognized one of the COVIDists, Raghuveer Rakasi, MD, as a “hero on the front line.”4 In Dr. Rakasi’s words, “We took a nosedive into something without knowing its depth, and aware that we could have fatalities among ourselves. We took up new roles, faced new challenges, learned new things every day, evolving every step of the way. We had to change the way we practice medicine, finding new ways to treat patients, and protecting the workforce by limiting patient exposure, prioritizing investigations.” He added that “we have to adapt to a new normal; we should be prepared for this to come in waves. Putting aside our political views, we should stand united 6 feet apart, with a mask covering our brave faces, frequently washing our helping hands to overcome these uncertain times.”
Conclusion
The creation of a focused group of hospitalists called COVIDists and providing them with structured and rapid training (in various aspects of clinical care of COVID-19 patients, critical care/ventilator management, efficient and safe use of PPE) and daily information dissemination allowed our health system to prepare for the large volume of COVID-19 patients. It also helped in preserving the larger hospital workforce for a possible future surge.
The rapid development and implementation of the COVIDist strategy succeeded because of the intrinsic motivation of the providers to improve the outcomes of this high-risk patient population and the close collaboration of the stakeholders. Our institution remains successful in managing the pandemic in Western Massachusetts, with reserve capacity remaining even during the peak of the epidemic. A large part of this was because of creating and training a pool of COVIDists.
Dr. Medarametla is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health, and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts, Worcester. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Prabhakaran is unit medical director, geriatrics unit, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Bryson is associate program director of the Internal Medicine Residency at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts. Dr. Umar is medical director, clinical operations, in the division of hospital medicine at Baystate Health. Dr. Natanasabapathy is division chief of hospital medicine at Baystate Health and assistant professor at University of Massachusetts.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Updated Jun 10, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/cases-in-us.html.
2. Zhou F et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054-62.
3. Westafer LM et al. A transdisciplinary COVID-19 early respiratory intervention protocol: An implementation story. J Hosp Med. 2020 May 21;15(6):372-374.
4. Miller J. “Heroes on the front line: Dr. Raghuveer Rakasi.” Coverage. May 18, 2020. https://coverage.bluecrossma.com/article/heroes-front-line-dr-raghuveer-rakasi
Daily Recap: Lung ultrasound helps diagnose COVID-19 in kids, first treatment approved for adult-onset Still’s disease
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lung ultrasound works well in children with COVID-19
Lung ultrasound has “high concordance” with radiologic findings in children with COVID-19 and offers benefits over other imaging techniques, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” wrote Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, [lung ultrasound] allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].” The findings of the small, observational study were published in Pediatrics. Read more.
New hypertension definitions reveal preclampsia risk
Using the new clinical definitions of hypertension, pregnant women with even modest elevations in blood pressure are at increased risk for preeclampsia, according to results from a large retrospective cohort study. Elizabeth F. Sutton, PhD, of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues looked at records from 18,162 women who had given birth to a single baby. The authors found preeclampsia risk increased with increasing blood pressure elevation. Among women with normal blood pressure before 20 weeks’ gestation, 5% had preeclampsia, while 7% of those with elevated blood pressure did, as did 12% of women with stage 1 hypertension and 30% of women with stage 2 hypertension. The increase in risk of preeclampsia was because of preterm preeclampsia in the women with elevated blood pressure. Preeclampsia researcher Mark Santillan, MD, PhD, of the University of Iowa in Iowa City, said in an interview that the results “open the door to considering these new blood pressure categories as a prognosticator” for preeclampsia. “This paper furthers the field by applying these new categories to hypertensive diseases in pregnancy, which are not well studied” in comparison to nonpregnant hypertensive states. Read more.
Face mask type matters when sterilizing
When sterilizing face masks, the type of mask and the method of sterilization have a bearing on subsequent filtration efficiency, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks. With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%. Read more.
FDA approves first treatment for adult-onset Still’s disease
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indications for canakinumab (Ilaris) to include all patients with active Still’s disease older than 2 years, adding adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) to a previous approval for juvenile-onset Still’s disease, also known as systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). That makes Ilaris the first approved treatment for AOSD. The results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 36 patients with AOSD aged 22-70 years showed that the efficacy and safety data in AOSD were generally consistent with the results of a pooled analysis of sJIA patients, according to Novartis, which markets canakinumab. Read more.
Intranasal DHE shows promise in migraine
An intranasal form of dihydroergotamine (DHE) targeting the upper nasal region is safe and effective for the treatment of migraine, according to results from a phase 3 clinical trial. The new formulation could offer patients an at-home alternative to intramuscular infusions or intravenous injections currently used to deliver DHE. The STOP 301 phase 3 open-label safety and tolerability trial treated over 5,650 migraine attacks in 354 patients who self-administered INP104 for up to 52 weeks. They were provided up to three doses per week (1.45 mg in a dose of two puffs, one per nostril). A total of 66.3% of participants reported pain relief by 2 hours following a dose, and 38% had freedom from pain. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lung ultrasound works well in children with COVID-19
Lung ultrasound has “high concordance” with radiologic findings in children with COVID-19 and offers benefits over other imaging techniques, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” wrote Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, [lung ultrasound] allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].” The findings of the small, observational study were published in Pediatrics. Read more.
New hypertension definitions reveal preclampsia risk
Using the new clinical definitions of hypertension, pregnant women with even modest elevations in blood pressure are at increased risk for preeclampsia, according to results from a large retrospective cohort study. Elizabeth F. Sutton, PhD, of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues looked at records from 18,162 women who had given birth to a single baby. The authors found preeclampsia risk increased with increasing blood pressure elevation. Among women with normal blood pressure before 20 weeks’ gestation, 5% had preeclampsia, while 7% of those with elevated blood pressure did, as did 12% of women with stage 1 hypertension and 30% of women with stage 2 hypertension. The increase in risk of preeclampsia was because of preterm preeclampsia in the women with elevated blood pressure. Preeclampsia researcher Mark Santillan, MD, PhD, of the University of Iowa in Iowa City, said in an interview that the results “open the door to considering these new blood pressure categories as a prognosticator” for preeclampsia. “This paper furthers the field by applying these new categories to hypertensive diseases in pregnancy, which are not well studied” in comparison to nonpregnant hypertensive states. Read more.
Face mask type matters when sterilizing
When sterilizing face masks, the type of mask and the method of sterilization have a bearing on subsequent filtration efficiency, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks. With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%. Read more.
FDA approves first treatment for adult-onset Still’s disease
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indications for canakinumab (Ilaris) to include all patients with active Still’s disease older than 2 years, adding adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) to a previous approval for juvenile-onset Still’s disease, also known as systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). That makes Ilaris the first approved treatment for AOSD. The results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 36 patients with AOSD aged 22-70 years showed that the efficacy and safety data in AOSD were generally consistent with the results of a pooled analysis of sJIA patients, according to Novartis, which markets canakinumab. Read more.
Intranasal DHE shows promise in migraine
An intranasal form of dihydroergotamine (DHE) targeting the upper nasal region is safe and effective for the treatment of migraine, according to results from a phase 3 clinical trial. The new formulation could offer patients an at-home alternative to intramuscular infusions or intravenous injections currently used to deliver DHE. The STOP 301 phase 3 open-label safety and tolerability trial treated over 5,650 migraine attacks in 354 patients who self-administered INP104 for up to 52 weeks. They were provided up to three doses per week (1.45 mg in a dose of two puffs, one per nostril). A total of 66.3% of participants reported pain relief by 2 hours following a dose, and 38% had freedom from pain. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Lung ultrasound works well in children with COVID-19
Lung ultrasound has “high concordance” with radiologic findings in children with COVID-19 and offers benefits over other imaging techniques, such as CT. “First, it may reduce the number of radiologic examinations, lowering the radiation exposure of the patients,” wrote Marco Denina, MD, and colleagues from the pediatric infectious diseases unit at Regina Margherita Children’s Hospital in Turin, Italy. “Secondly, when performed at the bedside, [lung ultrasound] allows for the reduction of the patient’s movement within the hospital; thus, it lowers the number of health care workers and medical devices exposed to [SARS-CoV-2].” The findings of the small, observational study were published in Pediatrics. Read more.
New hypertension definitions reveal preclampsia risk
Using the new clinical definitions of hypertension, pregnant women with even modest elevations in blood pressure are at increased risk for preeclampsia, according to results from a large retrospective cohort study. Elizabeth F. Sutton, PhD, of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues looked at records from 18,162 women who had given birth to a single baby. The authors found preeclampsia risk increased with increasing blood pressure elevation. Among women with normal blood pressure before 20 weeks’ gestation, 5% had preeclampsia, while 7% of those with elevated blood pressure did, as did 12% of women with stage 1 hypertension and 30% of women with stage 2 hypertension. The increase in risk of preeclampsia was because of preterm preeclampsia in the women with elevated blood pressure. Preeclampsia researcher Mark Santillan, MD, PhD, of the University of Iowa in Iowa City, said in an interview that the results “open the door to considering these new blood pressure categories as a prognosticator” for preeclampsia. “This paper furthers the field by applying these new categories to hypertensive diseases in pregnancy, which are not well studied” in comparison to nonpregnant hypertensive states. Read more.
Face mask type matters when sterilizing
When sterilizing face masks, the type of mask and the method of sterilization have a bearing on subsequent filtration efficiency, according to new research published in JAMA Network Open. The greatest reduction in filtration efficiency after sterilization occurred with surgical face masks. With plasma vapor hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) sterilization, filtration efficiency of N95 and KN95 masks was maintained at more than 95%, but for surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 95%. With chlorine dioxide (ClO2) sterilization, on the other hand, filtration efficiency was maintained at above 95% for N95 masks, but for KN95 and surgical face masks, filtration efficiency was reduced to less than 80%. Read more.
FDA approves first treatment for adult-onset Still’s disease
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indications for canakinumab (Ilaris) to include all patients with active Still’s disease older than 2 years, adding adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) to a previous approval for juvenile-onset Still’s disease, also known as systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). That makes Ilaris the first approved treatment for AOSD. The results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 36 patients with AOSD aged 22-70 years showed that the efficacy and safety data in AOSD were generally consistent with the results of a pooled analysis of sJIA patients, according to Novartis, which markets canakinumab. Read more.
Intranasal DHE shows promise in migraine
An intranasal form of dihydroergotamine (DHE) targeting the upper nasal region is safe and effective for the treatment of migraine, according to results from a phase 3 clinical trial. The new formulation could offer patients an at-home alternative to intramuscular infusions or intravenous injections currently used to deliver DHE. The STOP 301 phase 3 open-label safety and tolerability trial treated over 5,650 migraine attacks in 354 patients who self-administered INP104 for up to 52 weeks. They were provided up to three doses per week (1.45 mg in a dose of two puffs, one per nostril). A total of 66.3% of participants reported pain relief by 2 hours following a dose, and 38% had freedom from pain. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
First-episode psychosis in the time of COVID-19
Patients may need more than weekly teletherapy
In response to COVID-19, we have seen a rapid transformation to virtually delivered mental health care, essential for the prevention and treatment of various mental health conditions during an isolating and stress-inducing pandemic. Yet teletherapy and virtual medication management alone may not adequately address the needs of some of the populations we serve.
Take Jackson, whose name and details have been changed for privacy. A year ago, Jackson, in his last year of high school, began hearing voices that others could not hear. After becoming increasingly withdrawn, his father sought out treatment for him and learned that Jackson was experiencing his first episode of psychosis.
Psychosis involves disruptions in the way one processes thoughts and feelings or behaves, and includes delusions – or unusual beliefs – and hallucinations, meaning seeing and hearing things that others cannot. “First-episode psychosis” (FEP) simply refers to the first time an individual experiences this. It typically occurs between one’s teenage years and their 20s. Whereas some individuals recover from their first episode and may not experience another, others go on to experience recurrence, and sometimes a waxing and waning illness course.
Jackson enrolled in a comprehensive mental health program that not only includes a psychiatrist, but also therapists who provide case management services, as well as a peer specialist; this is someone with lived experience navigating mental illness. The program also includes an employment and education specialist and family and group therapy sessions. His team helped him identify and work toward his personal recovery goals: graduating from high school, obtaining a job, and maintaining a strong relationship with his father.
One hundred thousand adolescents and young adults like Jackson experience FEP each year, and now, in the wake of COVID-19, they probably have more limited access to the kind of support that can be vital to recovery.
Studies have shown that untreated psychosis can detrimentally affect quality of life in several ways, including by negatively affecting interpersonal relationships, interfering with obtaining or maintaining employment, and increasing the risk for problematic substance use. The psychosocial effects of COVID-19 could compound problems that individuals navigating psychosis already face, such as stigmatization, social isolation, and unemployment. On top of this, individuals who experience additional marginalization and downstream effects of systematic discriminatory practices by virtue of their race or ethnicity, immigration status, or language bear the brunt of some of this pandemic’s worst health inequities.
Early and efficacious treatment is critically important for individuals experiencing psychosis. Evidence shows that engagement in coordinated specialty care (CSC) specifically can improve outcomes, including the likelihood of being engaged in school or work and lower rates of hospitalization. CSC is a team-based approach that utilizes the unique skills of every team member to support an individual in reaching their recovery goals, whether it’s starting or finishing college or building a new relationship.
Unlike traditional treatment goals, which often focus on “symptom reduction,” recovery-oriented care is about supporting an individual in obtaining a sense of satisfaction, meaning, and purpose in life. It also supports navigating such experiences as a job interview or a date. These key, multifaceted components must be made accessible and adapted during these times.
For individuals like Jackson, it is crucial to be able to continue accessing quality CSC, even during our current pandemic. Lisa Dixon, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, leads ONTrackNY, a statewide FEP program. She states that “effective, recovery-oriented treatment can make such a huge difference in the lives of these young people who are at a potential inflection point in their lives. Creative, collaborative clinicians can maintain connection and support.”
So how can we adapt CSC during this time? In addition to virtualized medication management and individual therapy, other components of CSC can be creatively adapted for online platforms. Group sessions can be completed virtually, from family to peer-led. Though the unemployment rate continues to rise, we can still help participants with a desire to work find employers that are offering remote work or navigate the risks of potential COVID-19 work exposures if remote options aren’t available. We can also support their developing skills to be used once other employers that pose less risk reopen.
For those in school, virtual education support can provide study skills, ways to cope with transition to an online classroom, or help with obtaining tutoring. Nutritionists can work remotely to provide support and creatively use online platforms for real-time feedback in a participant’s kitchen. Virtual case management is even more essential in the wake of COVID-19, from assistance with applying for unemployment insurance and financial aid to obtaining health insurance or determining eligibility.
For those without access to virtual platforms, individual and group telephone sessions and text check-ins can provide meaningful opportunities for continued engagement. For those who are unstably housed or have limited privacy in housing, teams must generate ideas of where to have remote sessions, such as a nearby park.
In a world now dominated by virtual care, it is critically important that individuals needing to see a clinician in person still be able to do so. Whether it is due to an acute crisis or to administer a long-acting injection medication, it is our responsibility to thoughtfully and judiciously remain available to patients, using appropriate personal protective equipment and precautions.
Jackson is one of many young people in recovery from psychosis. He is not defined by or limited by his experiences, but rather is navigating the possibilities that lie ahead of him, defining for himself who he wants to be in this world as it evolves. In the midst of COVID-19, as we seek to innovate – from how we exercise to how we throw birthday parties – let’s also be innovative in how we provide care and support for individuals experiencing psychosis.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients may need more than weekly teletherapy
Patients may need more than weekly teletherapy
In response to COVID-19, we have seen a rapid transformation to virtually delivered mental health care, essential for the prevention and treatment of various mental health conditions during an isolating and stress-inducing pandemic. Yet teletherapy and virtual medication management alone may not adequately address the needs of some of the populations we serve.
Take Jackson, whose name and details have been changed for privacy. A year ago, Jackson, in his last year of high school, began hearing voices that others could not hear. After becoming increasingly withdrawn, his father sought out treatment for him and learned that Jackson was experiencing his first episode of psychosis.
Psychosis involves disruptions in the way one processes thoughts and feelings or behaves, and includes delusions – or unusual beliefs – and hallucinations, meaning seeing and hearing things that others cannot. “First-episode psychosis” (FEP) simply refers to the first time an individual experiences this. It typically occurs between one’s teenage years and their 20s. Whereas some individuals recover from their first episode and may not experience another, others go on to experience recurrence, and sometimes a waxing and waning illness course.
Jackson enrolled in a comprehensive mental health program that not only includes a psychiatrist, but also therapists who provide case management services, as well as a peer specialist; this is someone with lived experience navigating mental illness. The program also includes an employment and education specialist and family and group therapy sessions. His team helped him identify and work toward his personal recovery goals: graduating from high school, obtaining a job, and maintaining a strong relationship with his father.
One hundred thousand adolescents and young adults like Jackson experience FEP each year, and now, in the wake of COVID-19, they probably have more limited access to the kind of support that can be vital to recovery.
Studies have shown that untreated psychosis can detrimentally affect quality of life in several ways, including by negatively affecting interpersonal relationships, interfering with obtaining or maintaining employment, and increasing the risk for problematic substance use. The psychosocial effects of COVID-19 could compound problems that individuals navigating psychosis already face, such as stigmatization, social isolation, and unemployment. On top of this, individuals who experience additional marginalization and downstream effects of systematic discriminatory practices by virtue of their race or ethnicity, immigration status, or language bear the brunt of some of this pandemic’s worst health inequities.
Early and efficacious treatment is critically important for individuals experiencing psychosis. Evidence shows that engagement in coordinated specialty care (CSC) specifically can improve outcomes, including the likelihood of being engaged in school or work and lower rates of hospitalization. CSC is a team-based approach that utilizes the unique skills of every team member to support an individual in reaching their recovery goals, whether it’s starting or finishing college or building a new relationship.
Unlike traditional treatment goals, which often focus on “symptom reduction,” recovery-oriented care is about supporting an individual in obtaining a sense of satisfaction, meaning, and purpose in life. It also supports navigating such experiences as a job interview or a date. These key, multifaceted components must be made accessible and adapted during these times.
For individuals like Jackson, it is crucial to be able to continue accessing quality CSC, even during our current pandemic. Lisa Dixon, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, leads ONTrackNY, a statewide FEP program. She states that “effective, recovery-oriented treatment can make such a huge difference in the lives of these young people who are at a potential inflection point in their lives. Creative, collaborative clinicians can maintain connection and support.”
So how can we adapt CSC during this time? In addition to virtualized medication management and individual therapy, other components of CSC can be creatively adapted for online platforms. Group sessions can be completed virtually, from family to peer-led. Though the unemployment rate continues to rise, we can still help participants with a desire to work find employers that are offering remote work or navigate the risks of potential COVID-19 work exposures if remote options aren’t available. We can also support their developing skills to be used once other employers that pose less risk reopen.
For those in school, virtual education support can provide study skills, ways to cope with transition to an online classroom, or help with obtaining tutoring. Nutritionists can work remotely to provide support and creatively use online platforms for real-time feedback in a participant’s kitchen. Virtual case management is even more essential in the wake of COVID-19, from assistance with applying for unemployment insurance and financial aid to obtaining health insurance or determining eligibility.
For those without access to virtual platforms, individual and group telephone sessions and text check-ins can provide meaningful opportunities for continued engagement. For those who are unstably housed or have limited privacy in housing, teams must generate ideas of where to have remote sessions, such as a nearby park.
In a world now dominated by virtual care, it is critically important that individuals needing to see a clinician in person still be able to do so. Whether it is due to an acute crisis or to administer a long-acting injection medication, it is our responsibility to thoughtfully and judiciously remain available to patients, using appropriate personal protective equipment and precautions.
Jackson is one of many young people in recovery from psychosis. He is not defined by or limited by his experiences, but rather is navigating the possibilities that lie ahead of him, defining for himself who he wants to be in this world as it evolves. In the midst of COVID-19, as we seek to innovate – from how we exercise to how we throw birthday parties – let’s also be innovative in how we provide care and support for individuals experiencing psychosis.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In response to COVID-19, we have seen a rapid transformation to virtually delivered mental health care, essential for the prevention and treatment of various mental health conditions during an isolating and stress-inducing pandemic. Yet teletherapy and virtual medication management alone may not adequately address the needs of some of the populations we serve.
Take Jackson, whose name and details have been changed for privacy. A year ago, Jackson, in his last year of high school, began hearing voices that others could not hear. After becoming increasingly withdrawn, his father sought out treatment for him and learned that Jackson was experiencing his first episode of psychosis.
Psychosis involves disruptions in the way one processes thoughts and feelings or behaves, and includes delusions – or unusual beliefs – and hallucinations, meaning seeing and hearing things that others cannot. “First-episode psychosis” (FEP) simply refers to the first time an individual experiences this. It typically occurs between one’s teenage years and their 20s. Whereas some individuals recover from their first episode and may not experience another, others go on to experience recurrence, and sometimes a waxing and waning illness course.
Jackson enrolled in a comprehensive mental health program that not only includes a psychiatrist, but also therapists who provide case management services, as well as a peer specialist; this is someone with lived experience navigating mental illness. The program also includes an employment and education specialist and family and group therapy sessions. His team helped him identify and work toward his personal recovery goals: graduating from high school, obtaining a job, and maintaining a strong relationship with his father.
One hundred thousand adolescents and young adults like Jackson experience FEP each year, and now, in the wake of COVID-19, they probably have more limited access to the kind of support that can be vital to recovery.
Studies have shown that untreated psychosis can detrimentally affect quality of life in several ways, including by negatively affecting interpersonal relationships, interfering with obtaining or maintaining employment, and increasing the risk for problematic substance use. The psychosocial effects of COVID-19 could compound problems that individuals navigating psychosis already face, such as stigmatization, social isolation, and unemployment. On top of this, individuals who experience additional marginalization and downstream effects of systematic discriminatory practices by virtue of their race or ethnicity, immigration status, or language bear the brunt of some of this pandemic’s worst health inequities.
Early and efficacious treatment is critically important for individuals experiencing psychosis. Evidence shows that engagement in coordinated specialty care (CSC) specifically can improve outcomes, including the likelihood of being engaged in school or work and lower rates of hospitalization. CSC is a team-based approach that utilizes the unique skills of every team member to support an individual in reaching their recovery goals, whether it’s starting or finishing college or building a new relationship.
Unlike traditional treatment goals, which often focus on “symptom reduction,” recovery-oriented care is about supporting an individual in obtaining a sense of satisfaction, meaning, and purpose in life. It also supports navigating such experiences as a job interview or a date. These key, multifaceted components must be made accessible and adapted during these times.
For individuals like Jackson, it is crucial to be able to continue accessing quality CSC, even during our current pandemic. Lisa Dixon, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, leads ONTrackNY, a statewide FEP program. She states that “effective, recovery-oriented treatment can make such a huge difference in the lives of these young people who are at a potential inflection point in their lives. Creative, collaborative clinicians can maintain connection and support.”
So how can we adapt CSC during this time? In addition to virtualized medication management and individual therapy, other components of CSC can be creatively adapted for online platforms. Group sessions can be completed virtually, from family to peer-led. Though the unemployment rate continues to rise, we can still help participants with a desire to work find employers that are offering remote work or navigate the risks of potential COVID-19 work exposures if remote options aren’t available. We can also support their developing skills to be used once other employers that pose less risk reopen.
For those in school, virtual education support can provide study skills, ways to cope with transition to an online classroom, or help with obtaining tutoring. Nutritionists can work remotely to provide support and creatively use online platforms for real-time feedback in a participant’s kitchen. Virtual case management is even more essential in the wake of COVID-19, from assistance with applying for unemployment insurance and financial aid to obtaining health insurance or determining eligibility.
For those without access to virtual platforms, individual and group telephone sessions and text check-ins can provide meaningful opportunities for continued engagement. For those who are unstably housed or have limited privacy in housing, teams must generate ideas of where to have remote sessions, such as a nearby park.
In a world now dominated by virtual care, it is critically important that individuals needing to see a clinician in person still be able to do so. Whether it is due to an acute crisis or to administer a long-acting injection medication, it is our responsibility to thoughtfully and judiciously remain available to patients, using appropriate personal protective equipment and precautions.
Jackson is one of many young people in recovery from psychosis. He is not defined by or limited by his experiences, but rather is navigating the possibilities that lie ahead of him, defining for himself who he wants to be in this world as it evolves. In the midst of COVID-19, as we seek to innovate – from how we exercise to how we throw birthday parties – let’s also be innovative in how we provide care and support for individuals experiencing psychosis.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.













