User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
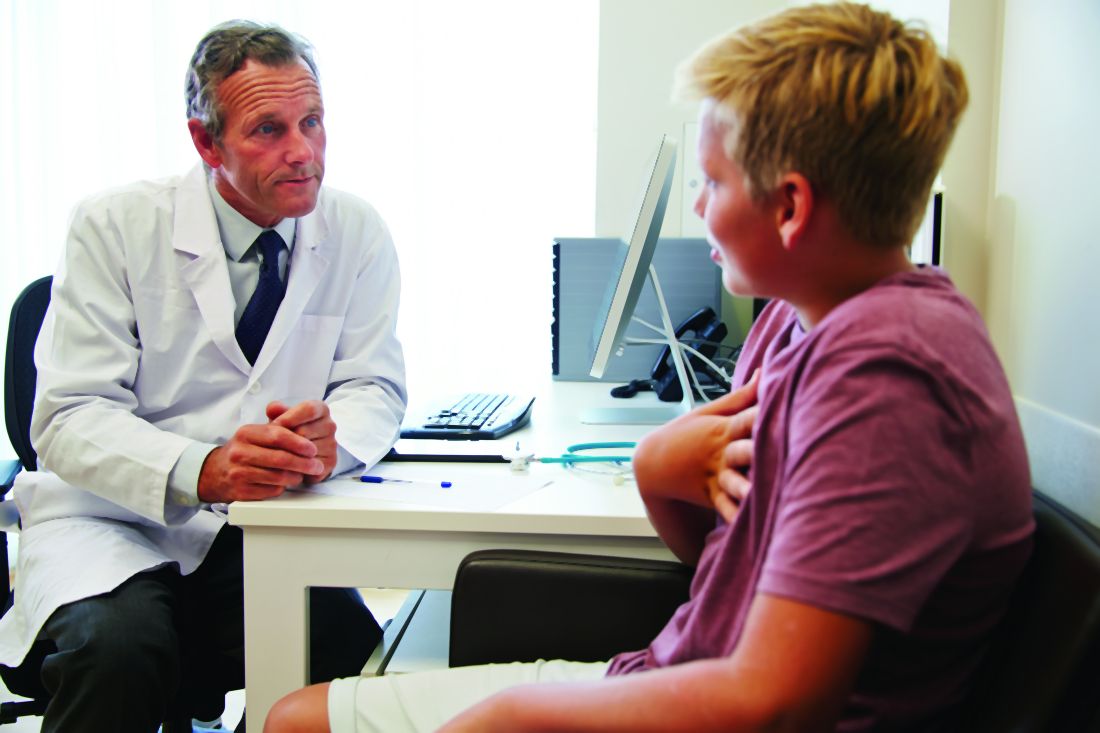
Does daily inhaler monitoring improve asthma outcomes in children?
Among children with moderate or severe persistent asthma, a randomized trial suggests.
But the intervention also may lead to more ED visits and increased hospitalization rates.
“We improved asthma symptom control but did not reduce health care use,” Ruchi S. Gupta, MD, MPH, and colleagues, wrote in a study published in Pediatrics.
The monitoring system alerted clinicians when a patient used a short-acting beta-agonist more than four times in a day. It could be that the “alerts enabled providers to detect asthma exacerbation virtually and refer for clinically appropriate care that included directing children to the ED,” the authors suggested. It also is possible that the intervention led caregivers to be more vigilant about symptoms and more empowered to seek care.
Adherence to preventive regimens
Many patients with asthma need to use preventive medications such as daily inhaled corticosteroids to control symptoms. Researchers have developed sensor-based inhaler monitoring interventions to improve treatment adherence, but the effectiveness of these interventions in improving asthma outcomes in urban and minority populations is unclear.
To assess the effectiveness of a clinically integrated, sensor-based inhaler monitoring intervention on improving asthma symptom control and related outcomes in children, Dr. Gupta, of Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, and colleagues conducted a randomized, unblinded study, known as the Improving Technology-Assisted Recording of Asthma Control in Children (iTRACC) trial. They included 252 children: 127 in the control group and 125 in the intervention group.
Patients in the intervention group received Propeller Health’s Food and Drug Administration–cleared inhaler sensors for inhaled corticosteroids and short-acting beta-agonists. Caregivers could use a mobile application and clinicians could use a Web portal to track patients’ medication use. The app featured personalized insights, educational content, encouragement, surveys, and care team services.
Researchers recruited caregivers and children from five Chicago clinics for the study, which was conducted between 2016 and 2018. They included children aged 4-17 years who had a prescription for daily inhaled corticosteroids for at least 1 year before enrollment. In addition, participants had at least 1 exacerbation requiring oral corticosteroids in the previous year. They excluded children with other respiratory conditions. They also excluded participants who did not speak English because the app was available only in English.
“Sensors monitored inhaled medication use, capturing the date, time, and number of uses, and transmitted this information via Bluetooth to a paired smartphone and the provider portal in real-time,” the authors said.
Clinicians were alerted to call participants if a patient missed inhaled corticosteroid doses for 4 continuous days or used more than 4 short-acting beta-agonist doses per day. Clinicians could help guide asthma management, schedule an appointment, refill medications, and address technical difficulties with the sensors.
The intervention and control groups had similar baseline characteristics. About one-third of the patients were female, and the mean age was 9.3 years. In the control group, 28% identified as Hispanic, and 33% identified as non-Hispanic Black. In the intervention group, 40% identified as Hispanic, and 23% identified as non-Hispanic Black. About 59% reported Medicaid insurance. The intervention and control arms completed electronic surveys at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
Average Asthma Control Test score increased from 19 to 22 in the intervention group, compared with an increase from 19 to 20 in the control group. Adjusted rates of emergency department visits and hospitalizations were greater in the intervention group (incidence rate ratios, 2.2 and 3.4, respectively). A measure of caregiver quality of life was greater in the intervention group, although the difference was not significant.
During the trial, more caregivers in the intervention group reported asthma attacks for which steroids were prescribed by a medical office (73% vs. 35%).
Some participants had to manually enter the number of daily puffs into the app because their inhalers were incompatible with the sensors. In addition, some data were missing because of incomplete or missing survey responses and sensor failure over time. “The number of intervention participants with actively transmitting sensors decreased from 102 at baseline to 56 at 12 months,” Dr. Gupta and associates noted.
Important area of research
“One interesting finding of this study is the increase in health care use in the intervention group to nearly twice as many emergency department (ED) visits and three times as many hospitalizations as the control group over 12 months,” Rachelle R. Ramsey, PhD, and Theresa W. Guilbert, MD, MS, of the University of Cincinnati, wrote in a related commentary. “Although it is plausible that, as the authors suggest, greater asthma knowledge and monitoring may have led to increased vigilance of asthma symptoms, it seems that this would have only led to an increase in ED visits but not hospitalizations.”
The mixture of objective electronic monitoring and subjective self-reported adherence may complicate interpretation of the results, they added.
“Overall, this article underscores the feasibility and importance of sensor-based electronic monitoring of adherence in pediatric asthma and encourages future research in this area,” Dr. Ramsey and Dr. Guilbert said.
The trial was supported by the UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Gupta has received grants from the National Institutes of Health, Rho, and other organizations, and has served as a medical consultant and adviser for a variety of companies. Dr. Ramsey is supported by the NIH. Dr. Guilbert reported fees from the American Board of Pediatrics, the Pediatric Pulmonary Subboard, and some pharmaceutical companies, plus grants from the NIH, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca, and royalties from UpToDate.
SOURCE: Gupta RS et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Dec 22. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1330.
Among children with moderate or severe persistent asthma, a randomized trial suggests.
But the intervention also may lead to more ED visits and increased hospitalization rates.
“We improved asthma symptom control but did not reduce health care use,” Ruchi S. Gupta, MD, MPH, and colleagues, wrote in a study published in Pediatrics.
The monitoring system alerted clinicians when a patient used a short-acting beta-agonist more than four times in a day. It could be that the “alerts enabled providers to detect asthma exacerbation virtually and refer for clinically appropriate care that included directing children to the ED,” the authors suggested. It also is possible that the intervention led caregivers to be more vigilant about symptoms and more empowered to seek care.
Adherence to preventive regimens
Many patients with asthma need to use preventive medications such as daily inhaled corticosteroids to control symptoms. Researchers have developed sensor-based inhaler monitoring interventions to improve treatment adherence, but the effectiveness of these interventions in improving asthma outcomes in urban and minority populations is unclear.
To assess the effectiveness of a clinically integrated, sensor-based inhaler monitoring intervention on improving asthma symptom control and related outcomes in children, Dr. Gupta, of Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, and colleagues conducted a randomized, unblinded study, known as the Improving Technology-Assisted Recording of Asthma Control in Children (iTRACC) trial. They included 252 children: 127 in the control group and 125 in the intervention group.
Patients in the intervention group received Propeller Health’s Food and Drug Administration–cleared inhaler sensors for inhaled corticosteroids and short-acting beta-agonists. Caregivers could use a mobile application and clinicians could use a Web portal to track patients’ medication use. The app featured personalized insights, educational content, encouragement, surveys, and care team services.
Researchers recruited caregivers and children from five Chicago clinics for the study, which was conducted between 2016 and 2018. They included children aged 4-17 years who had a prescription for daily inhaled corticosteroids for at least 1 year before enrollment. In addition, participants had at least 1 exacerbation requiring oral corticosteroids in the previous year. They excluded children with other respiratory conditions. They also excluded participants who did not speak English because the app was available only in English.
“Sensors monitored inhaled medication use, capturing the date, time, and number of uses, and transmitted this information via Bluetooth to a paired smartphone and the provider portal in real-time,” the authors said.
Clinicians were alerted to call participants if a patient missed inhaled corticosteroid doses for 4 continuous days or used more than 4 short-acting beta-agonist doses per day. Clinicians could help guide asthma management, schedule an appointment, refill medications, and address technical difficulties with the sensors.
The intervention and control groups had similar baseline characteristics. About one-third of the patients were female, and the mean age was 9.3 years. In the control group, 28% identified as Hispanic, and 33% identified as non-Hispanic Black. In the intervention group, 40% identified as Hispanic, and 23% identified as non-Hispanic Black. About 59% reported Medicaid insurance. The intervention and control arms completed electronic surveys at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
Average Asthma Control Test score increased from 19 to 22 in the intervention group, compared with an increase from 19 to 20 in the control group. Adjusted rates of emergency department visits and hospitalizations were greater in the intervention group (incidence rate ratios, 2.2 and 3.4, respectively). A measure of caregiver quality of life was greater in the intervention group, although the difference was not significant.
During the trial, more caregivers in the intervention group reported asthma attacks for which steroids were prescribed by a medical office (73% vs. 35%).
Some participants had to manually enter the number of daily puffs into the app because their inhalers were incompatible with the sensors. In addition, some data were missing because of incomplete or missing survey responses and sensor failure over time. “The number of intervention participants with actively transmitting sensors decreased from 102 at baseline to 56 at 12 months,” Dr. Gupta and associates noted.
Important area of research
“One interesting finding of this study is the increase in health care use in the intervention group to nearly twice as many emergency department (ED) visits and three times as many hospitalizations as the control group over 12 months,” Rachelle R. Ramsey, PhD, and Theresa W. Guilbert, MD, MS, of the University of Cincinnati, wrote in a related commentary. “Although it is plausible that, as the authors suggest, greater asthma knowledge and monitoring may have led to increased vigilance of asthma symptoms, it seems that this would have only led to an increase in ED visits but not hospitalizations.”
The mixture of objective electronic monitoring and subjective self-reported adherence may complicate interpretation of the results, they added.
“Overall, this article underscores the feasibility and importance of sensor-based electronic monitoring of adherence in pediatric asthma and encourages future research in this area,” Dr. Ramsey and Dr. Guilbert said.
The trial was supported by the UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Gupta has received grants from the National Institutes of Health, Rho, and other organizations, and has served as a medical consultant and adviser for a variety of companies. Dr. Ramsey is supported by the NIH. Dr. Guilbert reported fees from the American Board of Pediatrics, the Pediatric Pulmonary Subboard, and some pharmaceutical companies, plus grants from the NIH, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca, and royalties from UpToDate.
SOURCE: Gupta RS et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Dec 22. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1330.
Among children with moderate or severe persistent asthma, a randomized trial suggests.
But the intervention also may lead to more ED visits and increased hospitalization rates.
“We improved asthma symptom control but did not reduce health care use,” Ruchi S. Gupta, MD, MPH, and colleagues, wrote in a study published in Pediatrics.
The monitoring system alerted clinicians when a patient used a short-acting beta-agonist more than four times in a day. It could be that the “alerts enabled providers to detect asthma exacerbation virtually and refer for clinically appropriate care that included directing children to the ED,” the authors suggested. It also is possible that the intervention led caregivers to be more vigilant about symptoms and more empowered to seek care.
Adherence to preventive regimens
Many patients with asthma need to use preventive medications such as daily inhaled corticosteroids to control symptoms. Researchers have developed sensor-based inhaler monitoring interventions to improve treatment adherence, but the effectiveness of these interventions in improving asthma outcomes in urban and minority populations is unclear.
To assess the effectiveness of a clinically integrated, sensor-based inhaler monitoring intervention on improving asthma symptom control and related outcomes in children, Dr. Gupta, of Northwestern University and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, and colleagues conducted a randomized, unblinded study, known as the Improving Technology-Assisted Recording of Asthma Control in Children (iTRACC) trial. They included 252 children: 127 in the control group and 125 in the intervention group.
Patients in the intervention group received Propeller Health’s Food and Drug Administration–cleared inhaler sensors for inhaled corticosteroids and short-acting beta-agonists. Caregivers could use a mobile application and clinicians could use a Web portal to track patients’ medication use. The app featured personalized insights, educational content, encouragement, surveys, and care team services.
Researchers recruited caregivers and children from five Chicago clinics for the study, which was conducted between 2016 and 2018. They included children aged 4-17 years who had a prescription for daily inhaled corticosteroids for at least 1 year before enrollment. In addition, participants had at least 1 exacerbation requiring oral corticosteroids in the previous year. They excluded children with other respiratory conditions. They also excluded participants who did not speak English because the app was available only in English.
“Sensors monitored inhaled medication use, capturing the date, time, and number of uses, and transmitted this information via Bluetooth to a paired smartphone and the provider portal in real-time,” the authors said.
Clinicians were alerted to call participants if a patient missed inhaled corticosteroid doses for 4 continuous days or used more than 4 short-acting beta-agonist doses per day. Clinicians could help guide asthma management, schedule an appointment, refill medications, and address technical difficulties with the sensors.
The intervention and control groups had similar baseline characteristics. About one-third of the patients were female, and the mean age was 9.3 years. In the control group, 28% identified as Hispanic, and 33% identified as non-Hispanic Black. In the intervention group, 40% identified as Hispanic, and 23% identified as non-Hispanic Black. About 59% reported Medicaid insurance. The intervention and control arms completed electronic surveys at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
Average Asthma Control Test score increased from 19 to 22 in the intervention group, compared with an increase from 19 to 20 in the control group. Adjusted rates of emergency department visits and hospitalizations were greater in the intervention group (incidence rate ratios, 2.2 and 3.4, respectively). A measure of caregiver quality of life was greater in the intervention group, although the difference was not significant.
During the trial, more caregivers in the intervention group reported asthma attacks for which steroids were prescribed by a medical office (73% vs. 35%).
Some participants had to manually enter the number of daily puffs into the app because their inhalers were incompatible with the sensors. In addition, some data were missing because of incomplete or missing survey responses and sensor failure over time. “The number of intervention participants with actively transmitting sensors decreased from 102 at baseline to 56 at 12 months,” Dr. Gupta and associates noted.
Important area of research
“One interesting finding of this study is the increase in health care use in the intervention group to nearly twice as many emergency department (ED) visits and three times as many hospitalizations as the control group over 12 months,” Rachelle R. Ramsey, PhD, and Theresa W. Guilbert, MD, MS, of the University of Cincinnati, wrote in a related commentary. “Although it is plausible that, as the authors suggest, greater asthma knowledge and monitoring may have led to increased vigilance of asthma symptoms, it seems that this would have only led to an increase in ED visits but not hospitalizations.”
The mixture of objective electronic monitoring and subjective self-reported adherence may complicate interpretation of the results, they added.
“Overall, this article underscores the feasibility and importance of sensor-based electronic monitoring of adherence in pediatric asthma and encourages future research in this area,” Dr. Ramsey and Dr. Guilbert said.
The trial was supported by the UnitedHealth Group. Dr. Gupta has received grants from the National Institutes of Health, Rho, and other organizations, and has served as a medical consultant and adviser for a variety of companies. Dr. Ramsey is supported by the NIH. Dr. Guilbert reported fees from the American Board of Pediatrics, the Pediatric Pulmonary Subboard, and some pharmaceutical companies, plus grants from the NIH, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, Regeneron, and AstraZeneca, and royalties from UpToDate.
SOURCE: Gupta RS et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Dec 22. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1330.
FROM PEDIATRICS
HPV vaccine appears effective for treating warts, particularly in children
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the prevention of HPV-associated genital warts and neoplasia, appears to be an effective and perhaps underappreciated treatment of existing cutaneous warts, according to expert speaking at the annual Coastal Dermatology symposium, held virtually.
, but a recently published review provides strong evidence that this is a practical clinical strategy, according to Theodore Rosen, MD, professor of dermatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
“Clearly, if you have someone, particularly a youngster, and you’re having trouble getting rid of their warts and they are age 9 years or above – and they need the vaccine anyhow – that’s a win-win proposition,” Dr. Rosen said.
The current nonavalent HPV vaccine is approved for individuals from age 9 to age 45. Although the CDC recommends routine vaccination at age 11 or 12 years, it allows earlier vaccination within the label.
The recently published and updated evidence of a benefit from treatment comes from a systematic literature review. For the review, 63 articles were drawn from the PubMed and Cochrane databases. The studies yielded 4,439 patients with cutaneous warts at the time they received the HPV vaccine or who specifically received vaccine as a treatment strategy.
As has been suggested previously in the case series and in a limited number of prospective studies, the majority of warts, including cutaneous warts and anogenital warts, resolved following vaccine administration.
“Mostly these were common warts, plantar warts, and flat warts,” Dr. Rosen said, but the paper also reported successful treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, squamous cell carcinomas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Case reports and small studies associating HPV vaccine with successful resolution of warts are easy to find in the literature. For example, 60% of patients achieved a complete response and 30% a partial response to HPV vaccine in one small prospective study of 26 patients with genital warts. Following vaccination, no recurrences were observed after a median follow-up of more than 8 months.
In the review paper, most of the cases involved patients who received the quadrivalent HPV vaccine, Dr. Rosen noted. Only one received the updated nonavalent vaccine, which, in addition to protection against the 6, 11, 16, and 18 subtypes extends protection to subtypes 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58.
“You would expect the nonavalent vaccine to provide the same protection. It is the same vaccine. It just offers activity against more subtypes,” Dr. Rosen said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He reported that he personally has used the nonavalent vaccine successfully to treat a cutaneous wart.
The nonavalent vaccine can be administered in just two doses for those who receive the first dose before age 15. In others, it is given in three doses at 1- to 2-month intervals, according to Dr. Rosen. He said the efficacy for preventing genital warts and most HPV-related neoplasia exceeds 90%, although it is lower for penile and anal cancer. The protection extends for at least 10 years, but he said that he believes that it is likely to be longer.
“The HPV vaccine is really, really safe,” Dr. Rosen said. Besides injection-site reactions, the most common adverse event is syncope. For this reason, patients are advised to stay seated for 30 minutes after administration.
There is some evidence for cross-immunity for HPV subtypes not covered by the vaccine, particularly among children, Dr. Rosen commented. Citing the review article, he said that, although almost all HPV-associated warts resolve in children when treated with the vaccine, response is somewhat lower in adolescents and further reduced in adults.
In an interview, the senior author of the recent literature review, Natasha A. Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, University of California, Irvine, agreed with Dr. Rosen about the value of HPV vaccine for patients not responding to conventional therapies for HPV-related cutaneous warts.
“I think HPV vaccine is an excellent option for those patients, even older ones at 45 years of age if cost is not an issue,” she said. She did offer a caveat. In a recent statement from the International Papillomavirus Society (IPVS) on a world shortage of HPV vaccine, it was estimated that supplies might be limited for the next 3-5 years.
Given this shortage, “obtaining them currently may prove to be difficult,” she cautioned.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the prevention of HPV-associated genital warts and neoplasia, appears to be an effective and perhaps underappreciated treatment of existing cutaneous warts, according to expert speaking at the annual Coastal Dermatology symposium, held virtually.
, but a recently published review provides strong evidence that this is a practical clinical strategy, according to Theodore Rosen, MD, professor of dermatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
“Clearly, if you have someone, particularly a youngster, and you’re having trouble getting rid of their warts and they are age 9 years or above – and they need the vaccine anyhow – that’s a win-win proposition,” Dr. Rosen said.
The current nonavalent HPV vaccine is approved for individuals from age 9 to age 45. Although the CDC recommends routine vaccination at age 11 or 12 years, it allows earlier vaccination within the label.
The recently published and updated evidence of a benefit from treatment comes from a systematic literature review. For the review, 63 articles were drawn from the PubMed and Cochrane databases. The studies yielded 4,439 patients with cutaneous warts at the time they received the HPV vaccine or who specifically received vaccine as a treatment strategy.
As has been suggested previously in the case series and in a limited number of prospective studies, the majority of warts, including cutaneous warts and anogenital warts, resolved following vaccine administration.
“Mostly these were common warts, plantar warts, and flat warts,” Dr. Rosen said, but the paper also reported successful treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, squamous cell carcinomas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Case reports and small studies associating HPV vaccine with successful resolution of warts are easy to find in the literature. For example, 60% of patients achieved a complete response and 30% a partial response to HPV vaccine in one small prospective study of 26 patients with genital warts. Following vaccination, no recurrences were observed after a median follow-up of more than 8 months.
In the review paper, most of the cases involved patients who received the quadrivalent HPV vaccine, Dr. Rosen noted. Only one received the updated nonavalent vaccine, which, in addition to protection against the 6, 11, 16, and 18 subtypes extends protection to subtypes 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58.
“You would expect the nonavalent vaccine to provide the same protection. It is the same vaccine. It just offers activity against more subtypes,” Dr. Rosen said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He reported that he personally has used the nonavalent vaccine successfully to treat a cutaneous wart.
The nonavalent vaccine can be administered in just two doses for those who receive the first dose before age 15. In others, it is given in three doses at 1- to 2-month intervals, according to Dr. Rosen. He said the efficacy for preventing genital warts and most HPV-related neoplasia exceeds 90%, although it is lower for penile and anal cancer. The protection extends for at least 10 years, but he said that he believes that it is likely to be longer.
“The HPV vaccine is really, really safe,” Dr. Rosen said. Besides injection-site reactions, the most common adverse event is syncope. For this reason, patients are advised to stay seated for 30 minutes after administration.
There is some evidence for cross-immunity for HPV subtypes not covered by the vaccine, particularly among children, Dr. Rosen commented. Citing the review article, he said that, although almost all HPV-associated warts resolve in children when treated with the vaccine, response is somewhat lower in adolescents and further reduced in adults.
In an interview, the senior author of the recent literature review, Natasha A. Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, University of California, Irvine, agreed with Dr. Rosen about the value of HPV vaccine for patients not responding to conventional therapies for HPV-related cutaneous warts.
“I think HPV vaccine is an excellent option for those patients, even older ones at 45 years of age if cost is not an issue,” she said. She did offer a caveat. In a recent statement from the International Papillomavirus Society (IPVS) on a world shortage of HPV vaccine, it was estimated that supplies might be limited for the next 3-5 years.
Given this shortage, “obtaining them currently may prove to be difficult,” she cautioned.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine, recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the prevention of HPV-associated genital warts and neoplasia, appears to be an effective and perhaps underappreciated treatment of existing cutaneous warts, according to expert speaking at the annual Coastal Dermatology symposium, held virtually.
, but a recently published review provides strong evidence that this is a practical clinical strategy, according to Theodore Rosen, MD, professor of dermatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
“Clearly, if you have someone, particularly a youngster, and you’re having trouble getting rid of their warts and they are age 9 years or above – and they need the vaccine anyhow – that’s a win-win proposition,” Dr. Rosen said.
The current nonavalent HPV vaccine is approved for individuals from age 9 to age 45. Although the CDC recommends routine vaccination at age 11 or 12 years, it allows earlier vaccination within the label.
The recently published and updated evidence of a benefit from treatment comes from a systematic literature review. For the review, 63 articles were drawn from the PubMed and Cochrane databases. The studies yielded 4,439 patients with cutaneous warts at the time they received the HPV vaccine or who specifically received vaccine as a treatment strategy.
As has been suggested previously in the case series and in a limited number of prospective studies, the majority of warts, including cutaneous warts and anogenital warts, resolved following vaccine administration.
“Mostly these were common warts, plantar warts, and flat warts,” Dr. Rosen said, but the paper also reported successful treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, squamous cell carcinomas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Case reports and small studies associating HPV vaccine with successful resolution of warts are easy to find in the literature. For example, 60% of patients achieved a complete response and 30% a partial response to HPV vaccine in one small prospective study of 26 patients with genital warts. Following vaccination, no recurrences were observed after a median follow-up of more than 8 months.
In the review paper, most of the cases involved patients who received the quadrivalent HPV vaccine, Dr. Rosen noted. Only one received the updated nonavalent vaccine, which, in addition to protection against the 6, 11, 16, and 18 subtypes extends protection to subtypes 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58.
“You would expect the nonavalent vaccine to provide the same protection. It is the same vaccine. It just offers activity against more subtypes,” Dr. Rosen said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He reported that he personally has used the nonavalent vaccine successfully to treat a cutaneous wart.
The nonavalent vaccine can be administered in just two doses for those who receive the first dose before age 15. In others, it is given in three doses at 1- to 2-month intervals, according to Dr. Rosen. He said the efficacy for preventing genital warts and most HPV-related neoplasia exceeds 90%, although it is lower for penile and anal cancer. The protection extends for at least 10 years, but he said that he believes that it is likely to be longer.
“The HPV vaccine is really, really safe,” Dr. Rosen said. Besides injection-site reactions, the most common adverse event is syncope. For this reason, patients are advised to stay seated for 30 minutes after administration.
There is some evidence for cross-immunity for HPV subtypes not covered by the vaccine, particularly among children, Dr. Rosen commented. Citing the review article, he said that, although almost all HPV-associated warts resolve in children when treated with the vaccine, response is somewhat lower in adolescents and further reduced in adults.
In an interview, the senior author of the recent literature review, Natasha A. Mesinkovska, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, University of California, Irvine, agreed with Dr. Rosen about the value of HPV vaccine for patients not responding to conventional therapies for HPV-related cutaneous warts.
“I think HPV vaccine is an excellent option for those patients, even older ones at 45 years of age if cost is not an issue,” she said. She did offer a caveat. In a recent statement from the International Papillomavirus Society (IPVS) on a world shortage of HPV vaccine, it was estimated that supplies might be limited for the next 3-5 years.
Given this shortage, “obtaining them currently may prove to be difficult,” she cautioned.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
FROM COASTAL DERM
Expert picks top pediatric dermatology studies of 2020
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, presented a list of studies, some of which resulted in approvals of pediatric indications in 2020, that he believes deserve attention.
Crisaborole
Crisaborole ointment, 2% is now approved for topical treatment of children aged as young as 3 months, based on the results of the CrisADe CARE1 phase 4 study. In this open-label study of infants aged from 3 months to under 2 years with mild to moderate AD, treated with crisaborole twice a day for 28 days, the mean reduction from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 49.6% on day 15 and 57.5% on day 29. The most common side effects were erythema and application-site pain, but neither occurred in more than 4% of patients. The discontinuation rate was less than 3%.
When the indication for treatment of young children down to age 3 months (from 24 months) was granted by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2020, crisaborole, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, became the only nonsteroidal approved for treatment of AD in children aged younger than 2 years, Dr. Eichenfield pointed out.
Tacrolimus
The topical calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus (Protopic) poses no detectable risk of cancer in children treated for AD, according to a prospective, multinational study that followed nearly 8,000 children with AD who used topical tacrolimus for at least 6 weeks over 10 years. With 44,469 person-years of follow-up in a population with at least 6 weeks of exposure to tacrolimus, there were six confirmed cancers, a rate not different than background rates, and no lymphomas.
“I have always tried to educate my patients about the potential use of the topical calcineurin inhibitors while reassuring them that the data did not support significant risk,” Dr. Eichenfield said. However, a large set of data reconfirming a low risk of cancer, although not definitive, “are really nice to have.”
Ruxolitinib
For treatment of AD in children aged as young as 12 years, a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1/JAK2 inhibitor, met its primary outcomes in the phase 3 TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials. (These data are not yet published but were presented at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium in April 2020.) The primary endpoint of 75% EASI clearance (EASI-75) was achieved in approximately 62% of patients treated with the 1.5% dose of ruxolitinib twice daily. This was a highly significant advantage over vehicle in both studies (P < .0001).
The EASI-75 rates at 8 weeks for the 0.75% formulation, at 56% and 51.5% for the TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials, respectively, were lower but also superior (P < .0001) to the 24.6% and 14.4% response rates on vehicle, respectively.
Emphasizing a consistent benefit on multiple secondary endpoints, including the “really early itch decrease,” Dr. Eichenfield described the phase 3 data as “really excellent results.” The data have not yet led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib for AD, but approval seems likely. Dr. Eichenfield noted that other drugs in the same class, such as abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have also demonstrated promising efficacy in children aged 12 years or older.
Dupilumab
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, was approved in May, 2020, for the treatment of AD in children ages 6-11 years, on the basis of a recently published phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled children aged between 6 and 11 years, comparing dupilumab and topical corticosteroids and placebo plus topical corticosteroids. Severe involvement was an entry criterion.
At 16 weeks, an EASI-75 response was achieved by 67% of the group randomized to 200 mg of dupilumab administered every 2 weeks and 70% of the group randomized to 300 mg every 4 weeks versus 27% of those randomized to placebo. More patients in the dupilumab arms developed conjunctivitis (10.8% vs. 4.7%) and had injection-site reactions (8.5% vs. 3.5%), but the monoclonal antibody was otherwise well tolerated and safe.
These data suggest that younger patients with severe disease “do, if anything, better than adults,” Dr. Eichenfield said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He cautioned that avoiding live vaccines, which is recommended in patients on dupilumab, “is likely more of an issue in children.”
Ixekizumab
Ixekizumab has been approved for pediatric patients aged as young as 6 years who are eligible for systemic therapy on the basis of a phase 3 trial. For the primary endpoint of 75% clearance on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, the response rates were 89% for the IL-17 inhibitor administered every 4 weeks and 25% for placebo. The study also associated ixekizumab with a significant improvement in quality of life.
The availability of more targeted therapies for children are likely. In Europe, secukinumab, another IL-17 inhibitor, was approved for treatment in pediatric patients this past summer, Dr. Eichenfield noted. These data are not yet published, but he expects targeted therapies to join a growing list of biologics already approved in children.
For drugs with established efficacy and safety, he advised, “look at your pediatric psoriasis patients and don’t be wimpy.” In children with poorly controlled psoriasis, he concluded these drugs have been associated with improved quality of life.
In November 2019, the American Academy of Dermatology and National Psoriasis Foundation published psoriasis management guidelines for children. Not all of the most recently approved therapies are included in these guidelines, which are the first to provide specific recommendations for children, but Dr. Eichenfield also included this publication among his top picks for important contributions to the pediatric dermatology literature in 2020.
Dr. Eichenfield reported financial relationships with 20 pharmaceutical companies that manufacture dermatologic products, including those for the diseases he discussed.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, presented a list of studies, some of which resulted in approvals of pediatric indications in 2020, that he believes deserve attention.
Crisaborole
Crisaborole ointment, 2% is now approved for topical treatment of children aged as young as 3 months, based on the results of the CrisADe CARE1 phase 4 study. In this open-label study of infants aged from 3 months to under 2 years with mild to moderate AD, treated with crisaborole twice a day for 28 days, the mean reduction from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 49.6% on day 15 and 57.5% on day 29. The most common side effects were erythema and application-site pain, but neither occurred in more than 4% of patients. The discontinuation rate was less than 3%.
When the indication for treatment of young children down to age 3 months (from 24 months) was granted by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2020, crisaborole, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, became the only nonsteroidal approved for treatment of AD in children aged younger than 2 years, Dr. Eichenfield pointed out.
Tacrolimus
The topical calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus (Protopic) poses no detectable risk of cancer in children treated for AD, according to a prospective, multinational study that followed nearly 8,000 children with AD who used topical tacrolimus for at least 6 weeks over 10 years. With 44,469 person-years of follow-up in a population with at least 6 weeks of exposure to tacrolimus, there were six confirmed cancers, a rate not different than background rates, and no lymphomas.
“I have always tried to educate my patients about the potential use of the topical calcineurin inhibitors while reassuring them that the data did not support significant risk,” Dr. Eichenfield said. However, a large set of data reconfirming a low risk of cancer, although not definitive, “are really nice to have.”
Ruxolitinib
For treatment of AD in children aged as young as 12 years, a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1/JAK2 inhibitor, met its primary outcomes in the phase 3 TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials. (These data are not yet published but were presented at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium in April 2020.) The primary endpoint of 75% EASI clearance (EASI-75) was achieved in approximately 62% of patients treated with the 1.5% dose of ruxolitinib twice daily. This was a highly significant advantage over vehicle in both studies (P < .0001).
The EASI-75 rates at 8 weeks for the 0.75% formulation, at 56% and 51.5% for the TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials, respectively, were lower but also superior (P < .0001) to the 24.6% and 14.4% response rates on vehicle, respectively.
Emphasizing a consistent benefit on multiple secondary endpoints, including the “really early itch decrease,” Dr. Eichenfield described the phase 3 data as “really excellent results.” The data have not yet led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib for AD, but approval seems likely. Dr. Eichenfield noted that other drugs in the same class, such as abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have also demonstrated promising efficacy in children aged 12 years or older.
Dupilumab
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, was approved in May, 2020, for the treatment of AD in children ages 6-11 years, on the basis of a recently published phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled children aged between 6 and 11 years, comparing dupilumab and topical corticosteroids and placebo plus topical corticosteroids. Severe involvement was an entry criterion.
At 16 weeks, an EASI-75 response was achieved by 67% of the group randomized to 200 mg of dupilumab administered every 2 weeks and 70% of the group randomized to 300 mg every 4 weeks versus 27% of those randomized to placebo. More patients in the dupilumab arms developed conjunctivitis (10.8% vs. 4.7%) and had injection-site reactions (8.5% vs. 3.5%), but the monoclonal antibody was otherwise well tolerated and safe.
These data suggest that younger patients with severe disease “do, if anything, better than adults,” Dr. Eichenfield said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He cautioned that avoiding live vaccines, which is recommended in patients on dupilumab, “is likely more of an issue in children.”
Ixekizumab
Ixekizumab has been approved for pediatric patients aged as young as 6 years who are eligible for systemic therapy on the basis of a phase 3 trial. For the primary endpoint of 75% clearance on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, the response rates were 89% for the IL-17 inhibitor administered every 4 weeks and 25% for placebo. The study also associated ixekizumab with a significant improvement in quality of life.
The availability of more targeted therapies for children are likely. In Europe, secukinumab, another IL-17 inhibitor, was approved for treatment in pediatric patients this past summer, Dr. Eichenfield noted. These data are not yet published, but he expects targeted therapies to join a growing list of biologics already approved in children.
For drugs with established efficacy and safety, he advised, “look at your pediatric psoriasis patients and don’t be wimpy.” In children with poorly controlled psoriasis, he concluded these drugs have been associated with improved quality of life.
In November 2019, the American Academy of Dermatology and National Psoriasis Foundation published psoriasis management guidelines for children. Not all of the most recently approved therapies are included in these guidelines, which are the first to provide specific recommendations for children, but Dr. Eichenfield also included this publication among his top picks for important contributions to the pediatric dermatology literature in 2020.
Dr. Eichenfield reported financial relationships with 20 pharmaceutical companies that manufacture dermatologic products, including those for the diseases he discussed.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, said at the annual Coastal Dermatology Symposium, held virtually.
Dr. Eichenfield, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, at the University of California, San Diego, presented a list of studies, some of which resulted in approvals of pediatric indications in 2020, that he believes deserve attention.
Crisaborole
Crisaborole ointment, 2% is now approved for topical treatment of children aged as young as 3 months, based on the results of the CrisADe CARE1 phase 4 study. In this open-label study of infants aged from 3 months to under 2 years with mild to moderate AD, treated with crisaborole twice a day for 28 days, the mean reduction from baseline in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score was 49.6% on day 15 and 57.5% on day 29. The most common side effects were erythema and application-site pain, but neither occurred in more than 4% of patients. The discontinuation rate was less than 3%.
When the indication for treatment of young children down to age 3 months (from 24 months) was granted by the Food and Drug Administration in March 2020, crisaborole, a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, became the only nonsteroidal approved for treatment of AD in children aged younger than 2 years, Dr. Eichenfield pointed out.
Tacrolimus
The topical calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus (Protopic) poses no detectable risk of cancer in children treated for AD, according to a prospective, multinational study that followed nearly 8,000 children with AD who used topical tacrolimus for at least 6 weeks over 10 years. With 44,469 person-years of follow-up in a population with at least 6 weeks of exposure to tacrolimus, there were six confirmed cancers, a rate not different than background rates, and no lymphomas.
“I have always tried to educate my patients about the potential use of the topical calcineurin inhibitors while reassuring them that the data did not support significant risk,” Dr. Eichenfield said. However, a large set of data reconfirming a low risk of cancer, although not definitive, “are really nice to have.”
Ruxolitinib
For treatment of AD in children aged as young as 12 years, a cream formulation of ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1/JAK2 inhibitor, met its primary outcomes in the phase 3 TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials. (These data are not yet published but were presented at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium in April 2020.) The primary endpoint of 75% EASI clearance (EASI-75) was achieved in approximately 62% of patients treated with the 1.5% dose of ruxolitinib twice daily. This was a highly significant advantage over vehicle in both studies (P < .0001).
The EASI-75 rates at 8 weeks for the 0.75% formulation, at 56% and 51.5% for the TRuE AD1 and TRuE AD2 trials, respectively, were lower but also superior (P < .0001) to the 24.6% and 14.4% response rates on vehicle, respectively.
Emphasizing a consistent benefit on multiple secondary endpoints, including the “really early itch decrease,” Dr. Eichenfield described the phase 3 data as “really excellent results.” The data have not yet led to FDA approval of ruxolitinib for AD, but approval seems likely. Dr. Eichenfield noted that other drugs in the same class, such as abrocitinib and upadacitinib, have also demonstrated promising efficacy in children aged 12 years or older.
Dupilumab
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, was approved in May, 2020, for the treatment of AD in children ages 6-11 years, on the basis of a recently published phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled children aged between 6 and 11 years, comparing dupilumab and topical corticosteroids and placebo plus topical corticosteroids. Severe involvement was an entry criterion.
At 16 weeks, an EASI-75 response was achieved by 67% of the group randomized to 200 mg of dupilumab administered every 2 weeks and 70% of the group randomized to 300 mg every 4 weeks versus 27% of those randomized to placebo. More patients in the dupilumab arms developed conjunctivitis (10.8% vs. 4.7%) and had injection-site reactions (8.5% vs. 3.5%), but the monoclonal antibody was otherwise well tolerated and safe.
These data suggest that younger patients with severe disease “do, if anything, better than adults,” Dr. Eichenfield said at the meeting, jointly presented by the University of Louisville and Global Academy for Medical Education. He cautioned that avoiding live vaccines, which is recommended in patients on dupilumab, “is likely more of an issue in children.”
Ixekizumab
Ixekizumab has been approved for pediatric patients aged as young as 6 years who are eligible for systemic therapy on the basis of a phase 3 trial. For the primary endpoint of 75% clearance on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, the response rates were 89% for the IL-17 inhibitor administered every 4 weeks and 25% for placebo. The study also associated ixekizumab with a significant improvement in quality of life.
The availability of more targeted therapies for children are likely. In Europe, secukinumab, another IL-17 inhibitor, was approved for treatment in pediatric patients this past summer, Dr. Eichenfield noted. These data are not yet published, but he expects targeted therapies to join a growing list of biologics already approved in children.
For drugs with established efficacy and safety, he advised, “look at your pediatric psoriasis patients and don’t be wimpy.” In children with poorly controlled psoriasis, he concluded these drugs have been associated with improved quality of life.
In November 2019, the American Academy of Dermatology and National Psoriasis Foundation published psoriasis management guidelines for children. Not all of the most recently approved therapies are included in these guidelines, which are the first to provide specific recommendations for children, but Dr. Eichenfield also included this publication among his top picks for important contributions to the pediatric dermatology literature in 2020.
Dr. Eichenfield reported financial relationships with 20 pharmaceutical companies that manufacture dermatologic products, including those for the diseases he discussed.
This publication and Global Academy for Medical Education are owned by the same parent company.
FROM COASTAL DERM
Getting closer to a lifesaving RSV vaccine
Louis Bont, MD, PhD, provided an overview of the most recent developments in the complex respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine landscape at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
RSV imposes significant burden worldwide, with 33 million patients, 3 million hospitalizations, and at least 120,000 deaths, reported Dr. Bont of the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital, University Medical Centre, Utrecht, the Netherlands. Of those deaths, more than 50% are in infants younger than 5 months, and “about 99% of the children dying from RSV live in low- and middle-income countries.”
“There are high-risk populations, such as children with prematurity, congenital heart disease, lung disease, and Down syndrome, but about 73% of all children who are hospitalized for RSV infection were previously healthy children,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, we need to find a solution for all children to prevent RSV infection.”
As observed by Nienke Scheltema in a Lancet Global Health article, population distributions of RSV infection mortality show that, regardless of whether children have comorbidities or they are previously healthy, most children die at a very young age, Dr. Bont explained. These data suggest “that a maternal vaccine or an antibody prophylaxis approach from birth onwards or during the first RSV season is the solution for the problem.”
The path to developing an RSV vaccine has now narrowed its focus onto a structural element of RSV, the prefusion F protein. This shift started with the discovery by Jason McLellan (Science, 2013 [two papers]) that there are two variants of the RSV F-fusion protein: the very stable postfusion conformation and the prefusion active conformation, a metastable protein that exists for a “fraction of a second,” Dr. Bont said.
“The interesting thing is that epitopes that are visible at the prefusion, metastable state … induce highly neutralizing antibodies, whereas epitopes at the postfusion conformation do not,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, by stabilizing the prefusion state, we start inducing neutralizing antibodies that will protect against severe RSV infection, and this is the basic concept of all the vaccine developments currently ongoing.”
These RSV vaccine developments fall into five approach types: live-attenuated or chimeric vaccines, vector-based vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, particle-based vaccines, and subunit or protein-based vaccines.
One breakthrough, which was presented at last year’s ESPID meeting, is the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab. In addition to being nine times more potent than the broadly used antibody palivizumab, it is also more stable; whereas many antibodies have a half-life of 3 weeks, nirsevimab has a half-life of 100 days. “The idea is that a single injection at the start of the RSV season protects children in the first RSV season of their life, a dangerous episode for them.” Dr. Bont explained. The originators, AstraZeneca and Sanofi Pasteur, have “the vision that every child on this planet should receive a single injection with this antibody in the first season,” he explained.
Studies of nanoparticle-based maternal vaccines have also revealed interesting results: Although a phase 3 trial investigating such vaccines didn’t achieve its primary endpoint, “interestingly, 15% of all RSV infections were mild, and only 2% were very severe and leading to hypoxemia,” Dr. Bont noted. “But if we look at vaccine efficacy, we see the opposite – the vaccine was not very efficacious to prevent mild disease, but very efficacious to prevent severe hypoxemia; actually, this is exactly what you would like to see in a vaccine.”
Investigations into live-attenuated and vector-based vaccines have been promising as well, Dr. Bont shared. Studies of live-attenuated vaccines suggest they have a future and that we can move onto their next phase of clinical development, and a study investigating adenoviral vector-based vaccines has demonstrated safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity, though it has also shown that we should anticipate some side effects when using them.
Simple subunit vaccines for RSV are also being explored – a study of DS-Cav1, a stabilized prefusion F subunit protein candidate vaccine, has shown that it has a superior functional profile, compared with previous pre-F subunit vaccines. However, it seemed to be more efficacious against strains of RSV A than strains of RSV B, the dominant strain.
Dr. Bont also discussed exciting work by Sesterhenn et al., in which they used a computer-based program to develop their own vaccine. Using their in-depth knowledge of the RSV prefusion F protein and a computer program, Sesterhenn et al. developed a trivalent vaccine, produced it, and showed – both in vitro and in monkeys – that such vaccines can work up to the level of preclinical in vivo experiments.
“We can now make vaccines behind our computer,” Dr. Bont declared. “And the system doesn’t only work for RSV vaccines, but also for other pathogens – as long as you have an in-depth molecular knowledge of the target epitope,” he added.
Joanne Wildenbeest, MD, PhD, at the Utrecht University, the Netherlands commented: “Lower respiratory tract infections due to RSV are among the leading causes of death worldwide in children under the age of 5, especially young infants. The recent advances in the development of a vaccine and passive immunization are important steps towards the goal to reduce childhood mortality due to RSV worldwide. Since RSV-related mortality is mainly seen in developing countries it is important that, once a vaccine has been approved, it will also be made easily available to these countries.”
Dr. Bont reported the following disclosures: ReSViNET (a nonprofit foundation); investigator-initiated studies with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, AbbVie, MedImmune, and MeMed; participation with Pfizer, Regeneron, and Janssen; and consultancy with GlaxoSmithKline, Ablynx, Novavax, and Janssen.
Louis Bont, MD, PhD, provided an overview of the most recent developments in the complex respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine landscape at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
RSV imposes significant burden worldwide, with 33 million patients, 3 million hospitalizations, and at least 120,000 deaths, reported Dr. Bont of the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital, University Medical Centre, Utrecht, the Netherlands. Of those deaths, more than 50% are in infants younger than 5 months, and “about 99% of the children dying from RSV live in low- and middle-income countries.”
“There are high-risk populations, such as children with prematurity, congenital heart disease, lung disease, and Down syndrome, but about 73% of all children who are hospitalized for RSV infection were previously healthy children,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, we need to find a solution for all children to prevent RSV infection.”
As observed by Nienke Scheltema in a Lancet Global Health article, population distributions of RSV infection mortality show that, regardless of whether children have comorbidities or they are previously healthy, most children die at a very young age, Dr. Bont explained. These data suggest “that a maternal vaccine or an antibody prophylaxis approach from birth onwards or during the first RSV season is the solution for the problem.”
The path to developing an RSV vaccine has now narrowed its focus onto a structural element of RSV, the prefusion F protein. This shift started with the discovery by Jason McLellan (Science, 2013 [two papers]) that there are two variants of the RSV F-fusion protein: the very stable postfusion conformation and the prefusion active conformation, a metastable protein that exists for a “fraction of a second,” Dr. Bont said.
“The interesting thing is that epitopes that are visible at the prefusion, metastable state … induce highly neutralizing antibodies, whereas epitopes at the postfusion conformation do not,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, by stabilizing the prefusion state, we start inducing neutralizing antibodies that will protect against severe RSV infection, and this is the basic concept of all the vaccine developments currently ongoing.”
These RSV vaccine developments fall into five approach types: live-attenuated or chimeric vaccines, vector-based vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, particle-based vaccines, and subunit or protein-based vaccines.
One breakthrough, which was presented at last year’s ESPID meeting, is the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab. In addition to being nine times more potent than the broadly used antibody palivizumab, it is also more stable; whereas many antibodies have a half-life of 3 weeks, nirsevimab has a half-life of 100 days. “The idea is that a single injection at the start of the RSV season protects children in the first RSV season of their life, a dangerous episode for them.” Dr. Bont explained. The originators, AstraZeneca and Sanofi Pasteur, have “the vision that every child on this planet should receive a single injection with this antibody in the first season,” he explained.
Studies of nanoparticle-based maternal vaccines have also revealed interesting results: Although a phase 3 trial investigating such vaccines didn’t achieve its primary endpoint, “interestingly, 15% of all RSV infections were mild, and only 2% were very severe and leading to hypoxemia,” Dr. Bont noted. “But if we look at vaccine efficacy, we see the opposite – the vaccine was not very efficacious to prevent mild disease, but very efficacious to prevent severe hypoxemia; actually, this is exactly what you would like to see in a vaccine.”
Investigations into live-attenuated and vector-based vaccines have been promising as well, Dr. Bont shared. Studies of live-attenuated vaccines suggest they have a future and that we can move onto their next phase of clinical development, and a study investigating adenoviral vector-based vaccines has demonstrated safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity, though it has also shown that we should anticipate some side effects when using them.
Simple subunit vaccines for RSV are also being explored – a study of DS-Cav1, a stabilized prefusion F subunit protein candidate vaccine, has shown that it has a superior functional profile, compared with previous pre-F subunit vaccines. However, it seemed to be more efficacious against strains of RSV A than strains of RSV B, the dominant strain.
Dr. Bont also discussed exciting work by Sesterhenn et al., in which they used a computer-based program to develop their own vaccine. Using their in-depth knowledge of the RSV prefusion F protein and a computer program, Sesterhenn et al. developed a trivalent vaccine, produced it, and showed – both in vitro and in monkeys – that such vaccines can work up to the level of preclinical in vivo experiments.
“We can now make vaccines behind our computer,” Dr. Bont declared. “And the system doesn’t only work for RSV vaccines, but also for other pathogens – as long as you have an in-depth molecular knowledge of the target epitope,” he added.
Joanne Wildenbeest, MD, PhD, at the Utrecht University, the Netherlands commented: “Lower respiratory tract infections due to RSV are among the leading causes of death worldwide in children under the age of 5, especially young infants. The recent advances in the development of a vaccine and passive immunization are important steps towards the goal to reduce childhood mortality due to RSV worldwide. Since RSV-related mortality is mainly seen in developing countries it is important that, once a vaccine has been approved, it will also be made easily available to these countries.”
Dr. Bont reported the following disclosures: ReSViNET (a nonprofit foundation); investigator-initiated studies with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, AbbVie, MedImmune, and MeMed; participation with Pfizer, Regeneron, and Janssen; and consultancy with GlaxoSmithKline, Ablynx, Novavax, and Janssen.
Louis Bont, MD, PhD, provided an overview of the most recent developments in the complex respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine landscape at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
RSV imposes significant burden worldwide, with 33 million patients, 3 million hospitalizations, and at least 120,000 deaths, reported Dr. Bont of the Wilhelmina Children’s Hospital, University Medical Centre, Utrecht, the Netherlands. Of those deaths, more than 50% are in infants younger than 5 months, and “about 99% of the children dying from RSV live in low- and middle-income countries.”
“There are high-risk populations, such as children with prematurity, congenital heart disease, lung disease, and Down syndrome, but about 73% of all children who are hospitalized for RSV infection were previously healthy children,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, we need to find a solution for all children to prevent RSV infection.”
As observed by Nienke Scheltema in a Lancet Global Health article, population distributions of RSV infection mortality show that, regardless of whether children have comorbidities or they are previously healthy, most children die at a very young age, Dr. Bont explained. These data suggest “that a maternal vaccine or an antibody prophylaxis approach from birth onwards or during the first RSV season is the solution for the problem.”
The path to developing an RSV vaccine has now narrowed its focus onto a structural element of RSV, the prefusion F protein. This shift started with the discovery by Jason McLellan (Science, 2013 [two papers]) that there are two variants of the RSV F-fusion protein: the very stable postfusion conformation and the prefusion active conformation, a metastable protein that exists for a “fraction of a second,” Dr. Bont said.
“The interesting thing is that epitopes that are visible at the prefusion, metastable state … induce highly neutralizing antibodies, whereas epitopes at the postfusion conformation do not,” Dr. Bont explained. “So, by stabilizing the prefusion state, we start inducing neutralizing antibodies that will protect against severe RSV infection, and this is the basic concept of all the vaccine developments currently ongoing.”
These RSV vaccine developments fall into five approach types: live-attenuated or chimeric vaccines, vector-based vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, particle-based vaccines, and subunit or protein-based vaccines.
One breakthrough, which was presented at last year’s ESPID meeting, is the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab. In addition to being nine times more potent than the broadly used antibody palivizumab, it is also more stable; whereas many antibodies have a half-life of 3 weeks, nirsevimab has a half-life of 100 days. “The idea is that a single injection at the start of the RSV season protects children in the first RSV season of their life, a dangerous episode for them.” Dr. Bont explained. The originators, AstraZeneca and Sanofi Pasteur, have “the vision that every child on this planet should receive a single injection with this antibody in the first season,” he explained.
Studies of nanoparticle-based maternal vaccines have also revealed interesting results: Although a phase 3 trial investigating such vaccines didn’t achieve its primary endpoint, “interestingly, 15% of all RSV infections were mild, and only 2% were very severe and leading to hypoxemia,” Dr. Bont noted. “But if we look at vaccine efficacy, we see the opposite – the vaccine was not very efficacious to prevent mild disease, but very efficacious to prevent severe hypoxemia; actually, this is exactly what you would like to see in a vaccine.”
Investigations into live-attenuated and vector-based vaccines have been promising as well, Dr. Bont shared. Studies of live-attenuated vaccines suggest they have a future and that we can move onto their next phase of clinical development, and a study investigating adenoviral vector-based vaccines has demonstrated safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity, though it has also shown that we should anticipate some side effects when using them.
Simple subunit vaccines for RSV are also being explored – a study of DS-Cav1, a stabilized prefusion F subunit protein candidate vaccine, has shown that it has a superior functional profile, compared with previous pre-F subunit vaccines. However, it seemed to be more efficacious against strains of RSV A than strains of RSV B, the dominant strain.
Dr. Bont also discussed exciting work by Sesterhenn et al., in which they used a computer-based program to develop their own vaccine. Using their in-depth knowledge of the RSV prefusion F protein and a computer program, Sesterhenn et al. developed a trivalent vaccine, produced it, and showed – both in vitro and in monkeys – that such vaccines can work up to the level of preclinical in vivo experiments.
“We can now make vaccines behind our computer,” Dr. Bont declared. “And the system doesn’t only work for RSV vaccines, but also for other pathogens – as long as you have an in-depth molecular knowledge of the target epitope,” he added.
Joanne Wildenbeest, MD, PhD, at the Utrecht University, the Netherlands commented: “Lower respiratory tract infections due to RSV are among the leading causes of death worldwide in children under the age of 5, especially young infants. The recent advances in the development of a vaccine and passive immunization are important steps towards the goal to reduce childhood mortality due to RSV worldwide. Since RSV-related mortality is mainly seen in developing countries it is important that, once a vaccine has been approved, it will also be made easily available to these countries.”
Dr. Bont reported the following disclosures: ReSViNET (a nonprofit foundation); investigator-initiated studies with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, AbbVie, MedImmune, and MeMed; participation with Pfizer, Regeneron, and Janssen; and consultancy with GlaxoSmithKline, Ablynx, Novavax, and Janssen.
FROM ESPID 2020
Analysis characterizes common wound microbes in epidermolysis bullosa
– in a retrospective analysis of over 700 wound cultures from 158 patients across the United States and Canada.
The findings from the EB Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database speak to the value of surveillance cultures with routine testing for microbial resistance – including mupirocin resistance – and to the importance of antibiotic stewardship not only for oral antibiotics but for topicals as well, according to Laura E. Levin, MD, and Kimberly D. Morel, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, the lead and senior authors, respectively, of the paper recently published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Almost all of the 158 patients with at least one wound culture recorded in the database from the period of 2001-2018 had one or more positive culture results. Of 152 patients with positive cultures, 131 (86%) were positive for SA and 56 (37%) and 34 (22%) were positive for PA and GAS, respectively. Other bacteria isolated included Corynebacterium spp and Proteus spp. Nearly half (47%) of patients with SA-positive cultures had methicillin-resistant SA, and 68% had methicillin-susceptible SA. (Some patients grew both MSSA and MRSA at different points in time.)
Mupirocin-susceptibility testing was performed at only some of the 13 participating centers. Of 15 patients whose cultures had recorded SA mupirocin-susceptibility testing, 11 had cultures positive for mupirocin-susceptible SA and 6 (40%) had mupirocin-resistant SA isolates (2 patients grew both). Of these six patients, half had isolates that were also methicillin-resistant.
Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, has been a cornerstone of decolonization regimens for MSSA and MRSA, but resistance has been demonstrated in other research as well and is not specific to EB, wrote Dr. Levin, Dr. Morel, and coauthors.
“Pediatric dermatologists often rely on topical antimicrobials in the treatment of patients’ open wounds to both prevent and treat infection, depending on the clinical scenario,” and surveillance cultures with routine testing for mupirocin resistance can help guide antibiotic choice and management strategies, Dr. Levin said in an interview.
More broadly, she added, “it’s helpful to know what bacteria are routinely colonizing wounds, not causing infection, versus those that are more likely to be associated with infection, chronic wounds, or the risk of developing skin cancer ... [to know] which wounds need to be treated more aggressively.”
A subset of patients with EB have been known to be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma, and research is implicating certain bacteria “as contributing to wound inflammation,” Dr. Morel said in an interview.
SCC was reported in 23 out of 717 patients in the database – but fewer than half of the patients with SCC had recorded wound cultures. The small numbers precluded the identification of microbes that may confer significant risk.
Correlating particular microbes with clinical features also will take more research. About half (57%) of the patients with recorded wound cultures had wounds with purulent exudate or other features of clinical infection. However, the presence or absence of clinical signs of infection was not temporally correlated with culture results in the database.
The 158 patients with recorded wound cultures had a mean age of 12.8 years and represented a range of EB subtypes.
PA was present in the wounds of patients as young as 1 month old, the authors noted. Investigators are “looking to further study PA and characterize clinical features ... to understand more about this microbe and its impact on patients with EB,” Dr. Morel said.
In the meantime, the analysis reaffirms the importance of antibiotic stewardship. Mupirocin is labeled to be used three times a day for a short period of time, but “tends to be prescribed and used less judiciously than intended,” Dr. Morel said. “It’s important [not to overuse it]. We have seen that patients’ culture results become sensitive to mupirocin again in the future when they avoid it for a period of time.”
The work was supported by the EB Research Partnership and EB Medical Research Foundation, as well as an NIH/NCATS grant. No investigator disclosures were listed.
SOURCE: Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/pde.14444.
– in a retrospective analysis of over 700 wound cultures from 158 patients across the United States and Canada.
The findings from the EB Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database speak to the value of surveillance cultures with routine testing for microbial resistance – including mupirocin resistance – and to the importance of antibiotic stewardship not only for oral antibiotics but for topicals as well, according to Laura E. Levin, MD, and Kimberly D. Morel, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, the lead and senior authors, respectively, of the paper recently published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Almost all of the 158 patients with at least one wound culture recorded in the database from the period of 2001-2018 had one or more positive culture results. Of 152 patients with positive cultures, 131 (86%) were positive for SA and 56 (37%) and 34 (22%) were positive for PA and GAS, respectively. Other bacteria isolated included Corynebacterium spp and Proteus spp. Nearly half (47%) of patients with SA-positive cultures had methicillin-resistant SA, and 68% had methicillin-susceptible SA. (Some patients grew both MSSA and MRSA at different points in time.)
Mupirocin-susceptibility testing was performed at only some of the 13 participating centers. Of 15 patients whose cultures had recorded SA mupirocin-susceptibility testing, 11 had cultures positive for mupirocin-susceptible SA and 6 (40%) had mupirocin-resistant SA isolates (2 patients grew both). Of these six patients, half had isolates that were also methicillin-resistant.
Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, has been a cornerstone of decolonization regimens for MSSA and MRSA, but resistance has been demonstrated in other research as well and is not specific to EB, wrote Dr. Levin, Dr. Morel, and coauthors.
“Pediatric dermatologists often rely on topical antimicrobials in the treatment of patients’ open wounds to both prevent and treat infection, depending on the clinical scenario,” and surveillance cultures with routine testing for mupirocin resistance can help guide antibiotic choice and management strategies, Dr. Levin said in an interview.
More broadly, she added, “it’s helpful to know what bacteria are routinely colonizing wounds, not causing infection, versus those that are more likely to be associated with infection, chronic wounds, or the risk of developing skin cancer ... [to know] which wounds need to be treated more aggressively.”
A subset of patients with EB have been known to be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma, and research is implicating certain bacteria “as contributing to wound inflammation,” Dr. Morel said in an interview.
SCC was reported in 23 out of 717 patients in the database – but fewer than half of the patients with SCC had recorded wound cultures. The small numbers precluded the identification of microbes that may confer significant risk.
Correlating particular microbes with clinical features also will take more research. About half (57%) of the patients with recorded wound cultures had wounds with purulent exudate or other features of clinical infection. However, the presence or absence of clinical signs of infection was not temporally correlated with culture results in the database.
The 158 patients with recorded wound cultures had a mean age of 12.8 years and represented a range of EB subtypes.
PA was present in the wounds of patients as young as 1 month old, the authors noted. Investigators are “looking to further study PA and characterize clinical features ... to understand more about this microbe and its impact on patients with EB,” Dr. Morel said.
In the meantime, the analysis reaffirms the importance of antibiotic stewardship. Mupirocin is labeled to be used three times a day for a short period of time, but “tends to be prescribed and used less judiciously than intended,” Dr. Morel said. “It’s important [not to overuse it]. We have seen that patients’ culture results become sensitive to mupirocin again in the future when they avoid it for a period of time.”
The work was supported by the EB Research Partnership and EB Medical Research Foundation, as well as an NIH/NCATS grant. No investigator disclosures were listed.
SOURCE: Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/pde.14444.
– in a retrospective analysis of over 700 wound cultures from 158 patients across the United States and Canada.
The findings from the EB Clinical Characterization and Outcomes Database speak to the value of surveillance cultures with routine testing for microbial resistance – including mupirocin resistance – and to the importance of antibiotic stewardship not only for oral antibiotics but for topicals as well, according to Laura E. Levin, MD, and Kimberly D. Morel, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, the lead and senior authors, respectively, of the paper recently published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Almost all of the 158 patients with at least one wound culture recorded in the database from the period of 2001-2018 had one or more positive culture results. Of 152 patients with positive cultures, 131 (86%) were positive for SA and 56 (37%) and 34 (22%) were positive for PA and GAS, respectively. Other bacteria isolated included Corynebacterium spp and Proteus spp. Nearly half (47%) of patients with SA-positive cultures had methicillin-resistant SA, and 68% had methicillin-susceptible SA. (Some patients grew both MSSA and MRSA at different points in time.)
Mupirocin-susceptibility testing was performed at only some of the 13 participating centers. Of 15 patients whose cultures had recorded SA mupirocin-susceptibility testing, 11 had cultures positive for mupirocin-susceptible SA and 6 (40%) had mupirocin-resistant SA isolates (2 patients grew both). Of these six patients, half had isolates that were also methicillin-resistant.
Mupirocin, a topical antibiotic, has been a cornerstone of decolonization regimens for MSSA and MRSA, but resistance has been demonstrated in other research as well and is not specific to EB, wrote Dr. Levin, Dr. Morel, and coauthors.
“Pediatric dermatologists often rely on topical antimicrobials in the treatment of patients’ open wounds to both prevent and treat infection, depending on the clinical scenario,” and surveillance cultures with routine testing for mupirocin resistance can help guide antibiotic choice and management strategies, Dr. Levin said in an interview.
More broadly, she added, “it’s helpful to know what bacteria are routinely colonizing wounds, not causing infection, versus those that are more likely to be associated with infection, chronic wounds, or the risk of developing skin cancer ... [to know] which wounds need to be treated more aggressively.”
A subset of patients with EB have been known to be at risk for squamous cell carcinoma, and research is implicating certain bacteria “as contributing to wound inflammation,” Dr. Morel said in an interview.
SCC was reported in 23 out of 717 patients in the database – but fewer than half of the patients with SCC had recorded wound cultures. The small numbers precluded the identification of microbes that may confer significant risk.
Correlating particular microbes with clinical features also will take more research. About half (57%) of the patients with recorded wound cultures had wounds with purulent exudate or other features of clinical infection. However, the presence or absence of clinical signs of infection was not temporally correlated with culture results in the database.
The 158 patients with recorded wound cultures had a mean age of 12.8 years and represented a range of EB subtypes.
PA was present in the wounds of patients as young as 1 month old, the authors noted. Investigators are “looking to further study PA and characterize clinical features ... to understand more about this microbe and its impact on patients with EB,” Dr. Morel said.
In the meantime, the analysis reaffirms the importance of antibiotic stewardship. Mupirocin is labeled to be used three times a day for a short period of time, but “tends to be prescribed and used less judiciously than intended,” Dr. Morel said. “It’s important [not to overuse it]. We have seen that patients’ culture results become sensitive to mupirocin again in the future when they avoid it for a period of time.”
The work was supported by the EB Research Partnership and EB Medical Research Foundation, as well as an NIH/NCATS grant. No investigator disclosures were listed.
SOURCE: Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/pde.14444.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Disparities in child abuse evaluation arise from implicit bias
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
according to research discussed by Tiffani J. Johnson, MD, an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the University of California, Davis.
“These disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting are bidirectional,” she said. “We also recognize that abuse is more likely to be unrecognized in White children.”
Dr. Johnson presented data on the health disparities in child abuse reporting in a session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year. Health care disparities, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, refers to differences in the quality of care between minority and nonminority populations that are not caused by clinical appropriateness, access, need, or patient preference, she explained. Instead, they result from discrimination, bias, stereotyping, and uncertainty.
Disparities lead to harm in all children
For example, a 2018 systematic review found that Black and other non-White children were significantly more likely than White children to be evaluated with a skeletal survey. In one of the studies included, at a large urban academic center, Black and Latinx children with accidental fractures were 8.75 times more likely to undergo a skeletal survey than White children and 4.3 times more likely to be reported to child protective services.
“And let me emphasize that these are children who were ultimately found to have accidental fractures,” Dr. Johnson said.
Meanwhile, in an analysis of known cases of head trauma, researchers found that abuse was missed in 37% of White children, compared with 19% of non-White children.
“These only represent the tip of the iceberg as a true number of cases of abuse may never really be detected because some cases are still unknown,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. And the harm of these disparities runs in both directions.
“Failing to diagnose abuse in White children clearly puts them at increased risk for return visits and return evaluations for repeated abuse by the perpetrators,” she said. But harm also can result from overreporting and investigation, including psychological trauma and a waste of limited resources. Overinvestigation also can erode family-physician relationships and perpetuate distrust of medical care in communities of color.
Yet at the same time, it’s clear that Black children, adolescents, and young adults are not protected from harm in society more generally, when at home, where they learn, or where they play, Dr. Johnson said, referencing the deaths of Breonna Taylor and Tamir Rice as examples.
“And now we’re seeing increased evidence that children are not protected in the health care center when we think about the many disparities that have been identified in the care and outcomes of children, including the disproportionality in terms of child abuse evaluation and referrals,” Dr. Johnson said.
Racism is a root cause of that harm to Black children, she said, as the systemic structure of opportunities unfairly disadvantages some individuals and communities while unfairly advantaging others, thereby “sapping the strength of the whole society through the waste of human resources.”
Tonya Chaffee, MD, MPH, a clinical professor of health sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, who attended the session, said she particularly appreciated “seeing data on which racial/ethnic populations have child abuse reports made and the disparities that exist that are similar to what we are noticing in our own institution.”
Role of individual-level implicit bias and racism
While institutional and structural racism play a substantial role in health care disparities, Dr. Johnson focused primarily on the impact of personal racism when it comes to child abuse evaluations, through overt discrimination, explicit bias, implicit bias, and stigmatization. The most challenging of these to identify and acknowledge is often implicit bias, a tendency to believe, even unconsciously, that some people or ideas are better than others, which results in unfair treatment.
For example, a 2016 study found that half of medical students and residents held at least one biological belief about differences between Black and White individuals that was actually false, such as Black people having more pain tolerance or stronger bones than White people, which then affected treatment recommendations.
“Implicit bias refers to our attitudes that lie below the surface, but they can still influence our behaviors,” Dr. Johnson explained. She encouraged providers to take the implicit bias test online to learn about their own unrecognized implicit biases. These biases have a hand in influencing decisions particularly in fast-paced environments where cognitive load is high – such as EDs, where many child abuse evaluations occur.
For example, in one study Dr. Johnson led, the researchers measured implicit bias in participants before and after an ED shift to assess how cognitive load affected bias. They found that participants who care for more than 10 patients, the average score for implicit bias increased.
Similarly, “when the ED was more overcrowded, there was also increased bias at the end of the shift, compared to the beginning of the shift,” Dr. Johnson said. She asked clinicians to take into consideration that at the start of the shift, they may feel well rested and freshly caffeinated, able to suppress or overcome the biases that they know they have.
“But our biases [are] more likely to come into play with every subsequent decision that we make throughout the day when we’re engaged in clinical encounters,” such as who does and does not receive a skeletal survey or get referred to child protective services, she said.
In another study where she hypothesized that resident physicians would have less bias on the child race implicit bias test than on the adult race one, Dr. Johnson reported that 85% of 91 residents working in an ED had an implicit pro-White/anti-Black bias in the test on adult race, but an even higher bias score – 91% – with child race.
Research has found that even children’s names can conjure implicit bias when it comes to stereotypically “White-sounding” names versus stereotypically “Black-sounding names.”
The implicit bias among clinicians extends beyond care of different children. Research has also identified association between higher implicit bias scores and less interpersonal treatment, less supportive communication, less patient-centered communication, poorer patient ratings of satisfaction, and greater patient-reported difficulty with following recommendations, Dr. Johnson said.
“I want you to think about that because I know that when we’re engaging with parents and making decisions about whether or not we’re going to do a skeletal survey or report someone for it, there is a lot of subjectivity that comes into play with how you’re interacting with families,” Dr. Johnson said. Those verbal and nonverbal cues may be triggering to parents, which then affects your interaction with them. Further, research shows that these biases may impact treatment decisions as well.
Personal-mediated racism also shows up in the use of stigmatizing language, Dr. Johnson said.
“When providers read stigmatizing language in the patient’s medical records, it was associated with them having more negative attitudes about that patient,” which then influenced their clinical decision-making, she said. “So when providers got primed with stigmatizing language, they subsequently had less aggressive pain management for those patients.”
Clinical implications for patient care
Dr. Johnson encouraged attendees to be careful about the language and tone they use in communicating with other health care providers and during documentation in medical records. Disparities in child abuse evaluation and reporting tend to be greater in EDs with more subjective conditions, whereas disparities are lower in departments with more established protocols.
She recommended several changes to practice that can reduce the impact of implicit bias. Universal screening for child abuse can increase how many injuries are found, but usually at the cost of increased resources and radiation. Another option is use of validated clinical decision support rules to identify who is at high or low risk for maltreatment, something Dr. Johnson is working on in her research.
But it’s also important for individual providers to confront their personal biases. Evidence-based strategies for reducing bias include perspective taking, focusing on common identities with patients, using counter-stereotypical imaging, seeking increased opportunity for cross-cultural contact, and mindfulness meditation.
“When you interact with people of different backgrounds, it helps to reduce the impact of stereotypes in society about those individuals,” Dr. Johnson told attendees. It’s also important to recognize how diversity in your clinical team can reduce bias.
“We need to work with our institutions to confront racial biases in child abuse reporting and develop quality improvement projects to ensure reporting is done objectively,” Dr. Chaffee said in an interview after attending the session. “This will require training and likely policy changes, including how reports are made to child welfare and/or the police moving forward.”
FROM AAP 2020
Light-based technologies emerging as promising acne treatments
such as Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD.
“I love treating acne, because it can have a huge impact on our patients’ lives,” Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Acne is the most common disease in dermatology, affecting about 80% of our patients. Eleven percent of these patients have difficult-to-treat acne, and it is also the No. 1 cause of depression and suicide among teenagers and young adults. And, even though there’s no strong evidence that optical treatments work better than conventional acne treatments, people still spend a lot on those treatments: more than 220 million in 2019.”
Early results from a pilot study suggest that use of a novel laser system known as Accure in patients with mild to moderate acne resulted in an 80% reduction in acne lesions at 12 weeks. The laser prototype, which uses a 1,726 nm wavelength and is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, features a built-in thermal camera in the handpiece that allows the user to monitor the skin’s temperature during treatment.
In initial pilot studies of the device, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues observed consistent damage of the sebaceous glands, with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures. “But because the contrast of absorption of lipids and water is not very high, we needed to create a laser with features that we have never seen before,” she said. “One of them is a robust cooling system. The second prototype features a built-in thermal camera within the handpiece that allows us to see the temperature while we’re treating the patient. It also has built-in software that would shut down the laser if the temperature is too high. “This is the first laser with some safety features that will give the user direct feedback while treating the patient,” she said, noting that its “unique cooling system and real-time monitoring ... makes it different from any of the lasers we see on the market right now.”
Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues (Emil Tanghetti, MD, in San Diego, Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York, and Joel L. Cohen, MD, in Colorado) are conducting a clinical trial of the device, to evaluate whether Accure can selectively target sebaceous glands. As of Oct. 23, 2020, the study enrolled more than 50 patients, who are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment, she said.
To date, 16 patients have completed the study, and the researchers have observed an average lesion reduction of 80% at 12 weeks post treatment, after four treatment sessions. This amounted to more than 12,000 trigger pulls of the device, with no unexpected adverse events. Average visual analogue scale pain scores immediately after treatment have been 1.09 out of 10.
Histologic assessment of skin samples collected from the study participants have revealed selective damage of the sebaceous glands with a normal epidermis and surrounding dermis. “Because this laser is near infrared, it is not absorbed by melanin, making it possible for a safe treatment in darker skin tones,” Dr. Sakamoto said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“We have shown that it is possible to create a selective laser for acne treatment at 1,726 nm. We have proven it mathematically as well as with histological samples,” she said. “Now we are moving on to a larger clinical trial for the FDA clearance.”
Another strategy being developed for acne treatment is to make nonselective lasers selective by adding gold microparticles into the hair follicle and sebaceous glands, to allow the lasers to be absorbed. In a study that used a free electron laser, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues demonstrated that these microparticles can stay within the sebaceous glands for selective damage of the sebaceous glands. In a subsequent pilot clinical trial they showed that the addition of the gold microparticles followed by a diode laser treatment made it possible to reduce both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
More recently, an open-label European study of acne treatment with light absorbing gold microparticles and optical pulses demonstrated that the treatment led to an 80%-90% reduction of inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks, with a reduction of Investigator’s Global Assessment scale from 2 to 4.
The Food and Drug Administration cleared the treatment, Sebacia Microparticles, for the treatment of mild to moderate acne in September of 2018, but according to Dr. Sakamoto, “the company has struggled, as they were only commercializing the device in California and Washington, DC.”
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is also being studied as an acne treatment. “PDT uses a photosensitizer that needs to be activated by a light source,” she noted. “The combination of red light and aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ester ALA has been shown to damage the sebaceous glands”.
In a recent randomized controlled trial that compared PDT to adapalene gel plus oral doxycycline, PDT showed superiority. “Because PDT induces apoptosis of the sebaceous glands, it causes a lot of pain and side effects after treatment,” Dr. Sakamoto said. “However, it can clear 80%-90% of acne in 80%-90% of patients. But because of the side effects, PDT should be limited to those patients who cannot take conventional treatments.”
Dr. Sakamoto reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
such as Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD.
“I love treating acne, because it can have a huge impact on our patients’ lives,” Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Acne is the most common disease in dermatology, affecting about 80% of our patients. Eleven percent of these patients have difficult-to-treat acne, and it is also the No. 1 cause of depression and suicide among teenagers and young adults. And, even though there’s no strong evidence that optical treatments work better than conventional acne treatments, people still spend a lot on those treatments: more than 220 million in 2019.”
Early results from a pilot study suggest that use of a novel laser system known as Accure in patients with mild to moderate acne resulted in an 80% reduction in acne lesions at 12 weeks. The laser prototype, which uses a 1,726 nm wavelength and is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, features a built-in thermal camera in the handpiece that allows the user to monitor the skin’s temperature during treatment.
In initial pilot studies of the device, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues observed consistent damage of the sebaceous glands, with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures. “But because the contrast of absorption of lipids and water is not very high, we needed to create a laser with features that we have never seen before,” she said. “One of them is a robust cooling system. The second prototype features a built-in thermal camera within the handpiece that allows us to see the temperature while we’re treating the patient. It also has built-in software that would shut down the laser if the temperature is too high. “This is the first laser with some safety features that will give the user direct feedback while treating the patient,” she said, noting that its “unique cooling system and real-time monitoring ... makes it different from any of the lasers we see on the market right now.”
Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues (Emil Tanghetti, MD, in San Diego, Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York, and Joel L. Cohen, MD, in Colorado) are conducting a clinical trial of the device, to evaluate whether Accure can selectively target sebaceous glands. As of Oct. 23, 2020, the study enrolled more than 50 patients, who are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment, she said.
To date, 16 patients have completed the study, and the researchers have observed an average lesion reduction of 80% at 12 weeks post treatment, after four treatment sessions. This amounted to more than 12,000 trigger pulls of the device, with no unexpected adverse events. Average visual analogue scale pain scores immediately after treatment have been 1.09 out of 10.
Histologic assessment of skin samples collected from the study participants have revealed selective damage of the sebaceous glands with a normal epidermis and surrounding dermis. “Because this laser is near infrared, it is not absorbed by melanin, making it possible for a safe treatment in darker skin tones,” Dr. Sakamoto said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“We have shown that it is possible to create a selective laser for acne treatment at 1,726 nm. We have proven it mathematically as well as with histological samples,” she said. “Now we are moving on to a larger clinical trial for the FDA clearance.”
Another strategy being developed for acne treatment is to make nonselective lasers selective by adding gold microparticles into the hair follicle and sebaceous glands, to allow the lasers to be absorbed. In a study that used a free electron laser, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues demonstrated that these microparticles can stay within the sebaceous glands for selective damage of the sebaceous glands. In a subsequent pilot clinical trial they showed that the addition of the gold microparticles followed by a diode laser treatment made it possible to reduce both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
More recently, an open-label European study of acne treatment with light absorbing gold microparticles and optical pulses demonstrated that the treatment led to an 80%-90% reduction of inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks, with a reduction of Investigator’s Global Assessment scale from 2 to 4.
The Food and Drug Administration cleared the treatment, Sebacia Microparticles, for the treatment of mild to moderate acne in September of 2018, but according to Dr. Sakamoto, “the company has struggled, as they were only commercializing the device in California and Washington, DC.”
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is also being studied as an acne treatment. “PDT uses a photosensitizer that needs to be activated by a light source,” she noted. “The combination of red light and aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ester ALA has been shown to damage the sebaceous glands”.
In a recent randomized controlled trial that compared PDT to adapalene gel plus oral doxycycline, PDT showed superiority. “Because PDT induces apoptosis of the sebaceous glands, it causes a lot of pain and side effects after treatment,” Dr. Sakamoto said. “However, it can clear 80%-90% of acne in 80%-90% of patients. But because of the side effects, PDT should be limited to those patients who cannot take conventional treatments.”
Dr. Sakamoto reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
such as Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD.
“I love treating acne, because it can have a huge impact on our patients’ lives,” Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “Acne is the most common disease in dermatology, affecting about 80% of our patients. Eleven percent of these patients have difficult-to-treat acne, and it is also the No. 1 cause of depression and suicide among teenagers and young adults. And, even though there’s no strong evidence that optical treatments work better than conventional acne treatments, people still spend a lot on those treatments: more than 220 million in 2019.”
Early results from a pilot study suggest that use of a novel laser system known as Accure in patients with mild to moderate acne resulted in an 80% reduction in acne lesions at 12 weeks. The laser prototype, which uses a 1,726 nm wavelength and is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, features a built-in thermal camera in the handpiece that allows the user to monitor the skin’s temperature during treatment.
In initial pilot studies of the device, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues observed consistent damage of the sebaceous glands, with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures. “But because the contrast of absorption of lipids and water is not very high, we needed to create a laser with features that we have never seen before,” she said. “One of them is a robust cooling system. The second prototype features a built-in thermal camera within the handpiece that allows us to see the temperature while we’re treating the patient. It also has built-in software that would shut down the laser if the temperature is too high. “This is the first laser with some safety features that will give the user direct feedback while treating the patient,” she said, noting that its “unique cooling system and real-time monitoring ... makes it different from any of the lasers we see on the market right now.”
Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues (Emil Tanghetti, MD, in San Diego, Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York, and Joel L. Cohen, MD, in Colorado) are conducting a clinical trial of the device, to evaluate whether Accure can selectively target sebaceous glands. As of Oct. 23, 2020, the study enrolled more than 50 patients, who are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment, she said.
To date, 16 patients have completed the study, and the researchers have observed an average lesion reduction of 80% at 12 weeks post treatment, after four treatment sessions. This amounted to more than 12,000 trigger pulls of the device, with no unexpected adverse events. Average visual analogue scale pain scores immediately after treatment have been 1.09 out of 10.
Histologic assessment of skin samples collected from the study participants have revealed selective damage of the sebaceous glands with a normal epidermis and surrounding dermis. “Because this laser is near infrared, it is not absorbed by melanin, making it possible for a safe treatment in darker skin tones,” Dr. Sakamoto said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“We have shown that it is possible to create a selective laser for acne treatment at 1,726 nm. We have proven it mathematically as well as with histological samples,” she said. “Now we are moving on to a larger clinical trial for the FDA clearance.”
Another strategy being developed for acne treatment is to make nonselective lasers selective by adding gold microparticles into the hair follicle and sebaceous glands, to allow the lasers to be absorbed. In a study that used a free electron laser, Dr. Sakamoto and colleagues demonstrated that these microparticles can stay within the sebaceous glands for selective damage of the sebaceous glands. In a subsequent pilot clinical trial they showed that the addition of the gold microparticles followed by a diode laser treatment made it possible to reduce both inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
More recently, an open-label European study of acne treatment with light absorbing gold microparticles and optical pulses demonstrated that the treatment led to an 80%-90% reduction of inflammatory lesions at 12 weeks, with a reduction of Investigator’s Global Assessment scale from 2 to 4.
The Food and Drug Administration cleared the treatment, Sebacia Microparticles, for the treatment of mild to moderate acne in September of 2018, but according to Dr. Sakamoto, “the company has struggled, as they were only commercializing the device in California and Washington, DC.”
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is also being studied as an acne treatment. “PDT uses a photosensitizer that needs to be activated by a light source,” she noted. “The combination of red light and aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or methyl ester ALA has been shown to damage the sebaceous glands”.
In a recent randomized controlled trial that compared PDT to adapalene gel plus oral doxycycline, PDT showed superiority. “Because PDT induces apoptosis of the sebaceous glands, it causes a lot of pain and side effects after treatment,” Dr. Sakamoto said. “However, it can clear 80%-90% of acne in 80%-90% of patients. But because of the side effects, PDT should be limited to those patients who cannot take conventional treatments.”
Dr. Sakamoto reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
More severe AD correlates with worse sleep health and attention problems in children
, results from a national survey demonstrated.
“We think it’s important for dermatologists and pediatricians to be monitoring children with AD for sleep and attention dysregulation,” Nina Y. Zhou said during a late-breaking research session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “It’s also important to highlight sleep hygiene habits to improve sleep health overall.”
In an effort to determine the impact of AD severity on these symptoms in young children with AD and characterize sleep health and attention regulation behaviors, Ms. Zhou, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues drew from a national survey distributed via panel company OP4G and the National Eczema Association that was conducted with parents of 60 children with AD aged 1-5 years. Questionnaires included the Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Early Childhood Sleep Health Measures to assess sleep health, the Peak Pruritus NRS to measure itch severity, and the Multidimensional Assessment Profile of Attention Regulation (MAPS-AR) to measure attention dysregulation related to inattention and hyperactivity. The researchers performed linear regression to determine the predictors of sleep health and attention dysregulation.
The mean age of 60 children was 3 years, 55% were male, 32% were black, 42% had severe disease, 42% had moderate disease, and 16% had mild disease. Children with more extensive AD were significantly more likely to report worse sleep disturbance. The proportion of children who reported sleep disturbance on at least 5 nights per week was 67% among those with severe AD, 24% among those with moderate AD, and 0% among those with mild AD.
In addition, 72% of parents of children with severe AD reported trouble paying attention at least 3 times per week “no matter what was going on,” compared with 24% of those with moderate AD and none of those with mild AD.
Parents of children with more severe AD reported more itch-related burden and significantly decreased quality of life for their children. For example, 76% of parents with children who had severe AD reported “because of itch, their child was frustrated,” compared to 44% of those with moderate AD and 10% with mild AD.
In fully adjusted linear regression analysis, the strongest predictors of sleep disturbance were AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 0.79, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 3.89, P = .03). AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 1.22, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 7.79, P less than .01) also predicted more attention dysregulation.
Household income appeared to differ significantly based on AD severity groups. “If you have mild AD, you are more likely to come from a higher income household,” Ms. Zhou said.
She concluded her presentation by calling for future studies with larger samples sizes to establish causality and directional effects between AD severity, itch, sleep, race, and attention.
The study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Ms. Zhou reported having no financial disclosures.
, results from a national survey demonstrated.
“We think it’s important for dermatologists and pediatricians to be monitoring children with AD for sleep and attention dysregulation,” Nina Y. Zhou said during a late-breaking research session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “It’s also important to highlight sleep hygiene habits to improve sleep health overall.”
In an effort to determine the impact of AD severity on these symptoms in young children with AD and characterize sleep health and attention regulation behaviors, Ms. Zhou, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues drew from a national survey distributed via panel company OP4G and the National Eczema Association that was conducted with parents of 60 children with AD aged 1-5 years. Questionnaires included the Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Early Childhood Sleep Health Measures to assess sleep health, the Peak Pruritus NRS to measure itch severity, and the Multidimensional Assessment Profile of Attention Regulation (MAPS-AR) to measure attention dysregulation related to inattention and hyperactivity. The researchers performed linear regression to determine the predictors of sleep health and attention dysregulation.
The mean age of 60 children was 3 years, 55% were male, 32% were black, 42% had severe disease, 42% had moderate disease, and 16% had mild disease. Children with more extensive AD were significantly more likely to report worse sleep disturbance. The proportion of children who reported sleep disturbance on at least 5 nights per week was 67% among those with severe AD, 24% among those with moderate AD, and 0% among those with mild AD.
In addition, 72% of parents of children with severe AD reported trouble paying attention at least 3 times per week “no matter what was going on,” compared with 24% of those with moderate AD and none of those with mild AD.
Parents of children with more severe AD reported more itch-related burden and significantly decreased quality of life for their children. For example, 76% of parents with children who had severe AD reported “because of itch, their child was frustrated,” compared to 44% of those with moderate AD and 10% with mild AD.
In fully adjusted linear regression analysis, the strongest predictors of sleep disturbance were AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 0.79, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 3.89, P = .03). AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 1.22, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 7.79, P less than .01) also predicted more attention dysregulation.
Household income appeared to differ significantly based on AD severity groups. “If you have mild AD, you are more likely to come from a higher income household,” Ms. Zhou said.
She concluded her presentation by calling for future studies with larger samples sizes to establish causality and directional effects between AD severity, itch, sleep, race, and attention.
The study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Ms. Zhou reported having no financial disclosures.
, results from a national survey demonstrated.
“We think it’s important for dermatologists and pediatricians to be monitoring children with AD for sleep and attention dysregulation,” Nina Y. Zhou said during a late-breaking research session at the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis virtual symposium. “It’s also important to highlight sleep hygiene habits to improve sleep health overall.”
In an effort to determine the impact of AD severity on these symptoms in young children with AD and characterize sleep health and attention regulation behaviors, Ms. Zhou, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues drew from a national survey distributed via panel company OP4G and the National Eczema Association that was conducted with parents of 60 children with AD aged 1-5 years. Questionnaires included the Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) Early Childhood Sleep Health Measures to assess sleep health, the Peak Pruritus NRS to measure itch severity, and the Multidimensional Assessment Profile of Attention Regulation (MAPS-AR) to measure attention dysregulation related to inattention and hyperactivity. The researchers performed linear regression to determine the predictors of sleep health and attention dysregulation.
The mean age of 60 children was 3 years, 55% were male, 32% were black, 42% had severe disease, 42% had moderate disease, and 16% had mild disease. Children with more extensive AD were significantly more likely to report worse sleep disturbance. The proportion of children who reported sleep disturbance on at least 5 nights per week was 67% among those with severe AD, 24% among those with moderate AD, and 0% among those with mild AD.
In addition, 72% of parents of children with severe AD reported trouble paying attention at least 3 times per week “no matter what was going on,” compared with 24% of those with moderate AD and none of those with mild AD.
Parents of children with more severe AD reported more itch-related burden and significantly decreased quality of life for their children. For example, 76% of parents with children who had severe AD reported “because of itch, their child was frustrated,” compared to 44% of those with moderate AD and 10% with mild AD.
In fully adjusted linear regression analysis, the strongest predictors of sleep disturbance were AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 0.79, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 3.89, P = .03). AD severity (unstandardized beta value = 1.22, P less than .01) and being Black (unstandardized beta value = 7.79, P less than .01) also predicted more attention dysregulation.
Household income appeared to differ significantly based on AD severity groups. “If you have mild AD, you are more likely to come from a higher income household,” Ms. Zhou said.
She concluded her presentation by calling for future studies with larger samples sizes to establish causality and directional effects between AD severity, itch, sleep, race, and attention.
The study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Ms. Zhou reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM REVOLUTIONIZING AD 2020
COVID-19 mortality rates declined, but vary by hospital
Mortality rates for inpatients with COVID-19 dropped significantly during the first 6 months of the pandemic, but outcomes depend on the hospital where patients receive care, new data show.
“[T]he characteristic that is most associated with poor or worsening hospital outcomes is high or increasing community case rates,” write David A. Asch, MD, MBA, executive director of the Center for Health Care Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The relationship between COVID-19 mortality rates and local disease prevalence suggests that “hospitals do worse when they are burdened with cases and is consistent with imperatives to flatten the curve,” the authors continue. “As case rates of COVID-19 increase across the nation, hospital mortality outcomes may worsen.”
The researchers published their study online December 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The quick and substantial improvement in survival “is a tribute in part to new science — for example, the science that revealed the benefits of dexamethasone,” Asch told Medscape Medical News. “But it’s also a tribute to the doctors and nurses in the hospitals who developed experience. It’s a cliché to refer to them as heroes, but that is what they are. The science and the heroic experience continues on, and so I’m optimistic that we’ll see even more improvement over time.”
However, the data also indicate that “with lots of disease in the community, hospitals may have a harder time keeping patients alive,” Asch said. “And of course the reason this is bad news is that community level case rates are rising all over, and in some cases at rapid rates. With that rise, we might be giving back some of our past gains in survival — just as the vaccine is beginning to be distributed.”
Examining mortality trends
The researchers analyzed administrative claims data from a large national health insurer. They included data from 38,517 adults who were admitted with COVID-19 to 955 US hospitals between January 1 and June 30 of this year. The investigators estimated hospitals’ risk-standardized rate of 30-day in-hospital mortality or referral to hospice, adjusted for patient-level characteristics.
Overall, 3179 patients (8.25%) died, and 1433 patients (3.7%) were referred to hospice. Risk-standardized mortality or hospice referral rates for individual hospitals ranged from 5.7% to 24.7%. The average rate was 9.1% in the best-performing quintile, compared with 15.7% in the worst-performing quintile.
In a subset of 398 hospitals that had at least 10 patients admitted for COVID-19 during early (January 1 through April 30) and later periods (between May 1 and June 30), rates in all but one hospital improved, and 94% improved by at least 25%. The average risk-standardized event rate declined from 16.6% to 9.3%.
“That rate of relative improvement is striking and encouraging, but perhaps not surprising,” Asch and coauthors write. “Early efforts at treating patients with COVID-19 were based on experience with previously known causes of severe respiratory illness. Later efforts could draw on experiences specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
For instance, doctors tried different inpatient management approaches, such as early vs late assisted ventilation, differences in oxygen flow, prone or supine positioning, and anticoagulation. “Those efforts varied in how systematically they were evaluated, but our results suggest that valuable experience was gained,” the authors note.
In addition, variation between hospitals could reflect differences in quality or different admission thresholds, they continue.
The study provides “a reason for optimism that our healthcare system has improved in our ability to care for persons with COVID-19,” write Leon Boudourakis, MD, MHS, and Amit Uppal, MD, in a related commentary. Boudourakis and Uppal are both affiliated with NYC Health + Hospitals in New York City and with SUNY Downstate and New York University School of Medicine, respectively.
Similar improvements in mortality rates have been reported in the United Kingdom and in a New York City hospital system, the editorialists note. The lower mortality rates may represent clinical, healthcare system, and epidemiologic trends.
“Since the first wave of serious COVID-19 cases, physicians have learned a great deal about the best ways to treat this serious infection,” they say. “Steroids may decrease mortality in patients with respiratory failure. Remdesivir may shorten hospitalizations of patients with serious illness. Anticoagulation and prone positioning may help certain patients. Using noninvasive ventilation and high-flow oxygen therapy may spare subsets of patients from the harms of intubation, such as ventilator-induced lung injury.»
Overwhelmed hospitals
“Hospitals do not perform as well when they are overwhelmed,” which may be a reason for the correlation between community prevalence and mortality rates, Boudourakis and Uppal suggested. “In particular, patients with a precarious respiratory status require expert, meticulous therapy to avoid intubation; those who undergo intubation or have kidney failure require nuanced and timely expert care with ventilatory adjustments and kidney replacement therapy, which are difficult to perform optimally when hospital capacity is strained.”
Although the death rate has fallen to about 9% for hospitalized patients, “9% is still high,” Asch said.
“Our results show that hospitals can’t do it on their own,” Asch said. “They need all of us to keep the community spread of the disease down. The right answer now is the right answer since the beginning of the pandemic: Keep your distance, wash your hands, and wear a mask.”
Asch, Boudourakis, and Uppal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A study coauthor reported personal fees and grants from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mortality rates for inpatients with COVID-19 dropped significantly during the first 6 months of the pandemic, but outcomes depend on the hospital where patients receive care, new data show.
“[T]he characteristic that is most associated with poor or worsening hospital outcomes is high or increasing community case rates,” write David A. Asch, MD, MBA, executive director of the Center for Health Care Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The relationship between COVID-19 mortality rates and local disease prevalence suggests that “hospitals do worse when they are burdened with cases and is consistent with imperatives to flatten the curve,” the authors continue. “As case rates of COVID-19 increase across the nation, hospital mortality outcomes may worsen.”
The researchers published their study online December 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The quick and substantial improvement in survival “is a tribute in part to new science — for example, the science that revealed the benefits of dexamethasone,” Asch told Medscape Medical News. “But it’s also a tribute to the doctors and nurses in the hospitals who developed experience. It’s a cliché to refer to them as heroes, but that is what they are. The science and the heroic experience continues on, and so I’m optimistic that we’ll see even more improvement over time.”
However, the data also indicate that “with lots of disease in the community, hospitals may have a harder time keeping patients alive,” Asch said. “And of course the reason this is bad news is that community level case rates are rising all over, and in some cases at rapid rates. With that rise, we might be giving back some of our past gains in survival — just as the vaccine is beginning to be distributed.”
Examining mortality trends
The researchers analyzed administrative claims data from a large national health insurer. They included data from 38,517 adults who were admitted with COVID-19 to 955 US hospitals between January 1 and June 30 of this year. The investigators estimated hospitals’ risk-standardized rate of 30-day in-hospital mortality or referral to hospice, adjusted for patient-level characteristics.
Overall, 3179 patients (8.25%) died, and 1433 patients (3.7%) were referred to hospice. Risk-standardized mortality or hospice referral rates for individual hospitals ranged from 5.7% to 24.7%. The average rate was 9.1% in the best-performing quintile, compared with 15.7% in the worst-performing quintile.
In a subset of 398 hospitals that had at least 10 patients admitted for COVID-19 during early (January 1 through April 30) and later periods (between May 1 and June 30), rates in all but one hospital improved, and 94% improved by at least 25%. The average risk-standardized event rate declined from 16.6% to 9.3%.
“That rate of relative improvement is striking and encouraging, but perhaps not surprising,” Asch and coauthors write. “Early efforts at treating patients with COVID-19 were based on experience with previously known causes of severe respiratory illness. Later efforts could draw on experiences specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
For instance, doctors tried different inpatient management approaches, such as early vs late assisted ventilation, differences in oxygen flow, prone or supine positioning, and anticoagulation. “Those efforts varied in how systematically they were evaluated, but our results suggest that valuable experience was gained,” the authors note.
In addition, variation between hospitals could reflect differences in quality or different admission thresholds, they continue.
The study provides “a reason for optimism that our healthcare system has improved in our ability to care for persons with COVID-19,” write Leon Boudourakis, MD, MHS, and Amit Uppal, MD, in a related commentary. Boudourakis and Uppal are both affiliated with NYC Health + Hospitals in New York City and with SUNY Downstate and New York University School of Medicine, respectively.
Similar improvements in mortality rates have been reported in the United Kingdom and in a New York City hospital system, the editorialists note. The lower mortality rates may represent clinical, healthcare system, and epidemiologic trends.
“Since the first wave of serious COVID-19 cases, physicians have learned a great deal about the best ways to treat this serious infection,” they say. “Steroids may decrease mortality in patients with respiratory failure. Remdesivir may shorten hospitalizations of patients with serious illness. Anticoagulation and prone positioning may help certain patients. Using noninvasive ventilation and high-flow oxygen therapy may spare subsets of patients from the harms of intubation, such as ventilator-induced lung injury.»
Overwhelmed hospitals
“Hospitals do not perform as well when they are overwhelmed,” which may be a reason for the correlation between community prevalence and mortality rates, Boudourakis and Uppal suggested. “In particular, patients with a precarious respiratory status require expert, meticulous therapy to avoid intubation; those who undergo intubation or have kidney failure require nuanced and timely expert care with ventilatory adjustments and kidney replacement therapy, which are difficult to perform optimally when hospital capacity is strained.”
Although the death rate has fallen to about 9% for hospitalized patients, “9% is still high,” Asch said.
“Our results show that hospitals can’t do it on their own,” Asch said. “They need all of us to keep the community spread of the disease down. The right answer now is the right answer since the beginning of the pandemic: Keep your distance, wash your hands, and wear a mask.”
Asch, Boudourakis, and Uppal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A study coauthor reported personal fees and grants from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mortality rates for inpatients with COVID-19 dropped significantly during the first 6 months of the pandemic, but outcomes depend on the hospital where patients receive care, new data show.
“[T]he characteristic that is most associated with poor or worsening hospital outcomes is high or increasing community case rates,” write David A. Asch, MD, MBA, executive director of the Center for Health Care Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and colleagues.
The relationship between COVID-19 mortality rates and local disease prevalence suggests that “hospitals do worse when they are burdened with cases and is consistent with imperatives to flatten the curve,” the authors continue. “As case rates of COVID-19 increase across the nation, hospital mortality outcomes may worsen.”
The researchers published their study online December 22 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The quick and substantial improvement in survival “is a tribute in part to new science — for example, the science that revealed the benefits of dexamethasone,” Asch told Medscape Medical News. “But it’s also a tribute to the doctors and nurses in the hospitals who developed experience. It’s a cliché to refer to them as heroes, but that is what they are. The science and the heroic experience continues on, and so I’m optimistic that we’ll see even more improvement over time.”
However, the data also indicate that “with lots of disease in the community, hospitals may have a harder time keeping patients alive,” Asch said. “And of course the reason this is bad news is that community level case rates are rising all over, and in some cases at rapid rates. With that rise, we might be giving back some of our past gains in survival — just as the vaccine is beginning to be distributed.”
Examining mortality trends
The researchers analyzed administrative claims data from a large national health insurer. They included data from 38,517 adults who were admitted with COVID-19 to 955 US hospitals between January 1 and June 30 of this year. The investigators estimated hospitals’ risk-standardized rate of 30-day in-hospital mortality or referral to hospice, adjusted for patient-level characteristics.
Overall, 3179 patients (8.25%) died, and 1433 patients (3.7%) were referred to hospice. Risk-standardized mortality or hospice referral rates for individual hospitals ranged from 5.7% to 24.7%. The average rate was 9.1% in the best-performing quintile, compared with 15.7% in the worst-performing quintile.
In a subset of 398 hospitals that had at least 10 patients admitted for COVID-19 during early (January 1 through April 30) and later periods (between May 1 and June 30), rates in all but one hospital improved, and 94% improved by at least 25%. The average risk-standardized event rate declined from 16.6% to 9.3%.
“That rate of relative improvement is striking and encouraging, but perhaps not surprising,” Asch and coauthors write. “Early efforts at treating patients with COVID-19 were based on experience with previously known causes of severe respiratory illness. Later efforts could draw on experiences specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
For instance, doctors tried different inpatient management approaches, such as early vs late assisted ventilation, differences in oxygen flow, prone or supine positioning, and anticoagulation. “Those efforts varied in how systematically they were evaluated, but our results suggest that valuable experience was gained,” the authors note.
In addition, variation between hospitals could reflect differences in quality or different admission thresholds, they continue.
The study provides “a reason for optimism that our healthcare system has improved in our ability to care for persons with COVID-19,” write Leon Boudourakis, MD, MHS, and Amit Uppal, MD, in a related commentary. Boudourakis and Uppal are both affiliated with NYC Health + Hospitals in New York City and with SUNY Downstate and New York University School of Medicine, respectively.
Similar improvements in mortality rates have been reported in the United Kingdom and in a New York City hospital system, the editorialists note. The lower mortality rates may represent clinical, healthcare system, and epidemiologic trends.
“Since the first wave of serious COVID-19 cases, physicians have learned a great deal about the best ways to treat this serious infection,” they say. “Steroids may decrease mortality in patients with respiratory failure. Remdesivir may shorten hospitalizations of patients with serious illness. Anticoagulation and prone positioning may help certain patients. Using noninvasive ventilation and high-flow oxygen therapy may spare subsets of patients from the harms of intubation, such as ventilator-induced lung injury.»
Overwhelmed hospitals
“Hospitals do not perform as well when they are overwhelmed,” which may be a reason for the correlation between community prevalence and mortality rates, Boudourakis and Uppal suggested. “In particular, patients with a precarious respiratory status require expert, meticulous therapy to avoid intubation; those who undergo intubation or have kidney failure require nuanced and timely expert care with ventilatory adjustments and kidney replacement therapy, which are difficult to perform optimally when hospital capacity is strained.”
Although the death rate has fallen to about 9% for hospitalized patients, “9% is still high,” Asch said.
“Our results show that hospitals can’t do it on their own,” Asch said. “They need all of us to keep the community spread of the disease down. The right answer now is the right answer since the beginning of the pandemic: Keep your distance, wash your hands, and wear a mask.”
Asch, Boudourakis, and Uppal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A study coauthor reported personal fees and grants from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LGBTQ+ youth issues include fertility counseling and foster care
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
Caring for LGBTQ+ pediatric patients often requires physicians to consider issues – such as preservation of fertility for transgender youth and resource allocation to sexual-minority youth in the foster-care system – that they may not think about as frequently with their other patients.
“It’s important to engage transgender and gender-diverse youth and families in fertility counseling early in their gender affirmation process,” but it does not happen as often as it should, said Jason Rafferty, MD (he/him/his), a clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and human behavior at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Rafferty discussed two studies at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics, held virtually this year: one on fertility outcomes among a small transgender sample and another finding that sexual-minority youth are 2.5 times more likely to be involved in the foster-care system.
“We need to recognize and address disparities in health that place sexual-minority youth at increased risk for child welfare involvement,” he told attendees.
Fertility preservation and counseling for transgender patients
Evidence suggests gender-affirming hormone treatment affects gonadal structures and functions in ways that may decrease fertility potential, Dr. Rafferty said. “Yet, there’s very little [research] into the reversibility or thresholds above which fertility potential is affected.”
The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) recommends that doctors discuss the possible adverse health effects of feminizing or masculinizing treatments and the patient’s reproductive options before starting hormone therapy, although the extent to which this therapy may impair fertility isn’t known.
The first study Dr. Rafferty discussed was an assessment of semen cryopreservation outcomes among youth asserting a female identity. The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review on a convenience sample of 11 transgender and gender-diverse adolescents and young adults who had been referred for fertility preservation between January 2015 and September 2018 at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Children’s Hospital and the UPMC Magee-Womens Hospital in Pittsburgh.
Of the 11, 1 did not provide a sample, and another discarded their sample after 4 months. The seven patients without prior gender-affirming hormone treatment (average age 19 at time of fertility consultation) were all able to produce a semen sample, which showed normal parameters, except for some abnormal morphology. The significance of that one abnormal finding was unclear without a control group, Dr. Rafferty said. All seven began gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapy, and four also began estradiol therapy, although Dr. Rafferty questioned why GnRH agonist therapy was started at such late ages.
Regardless, he said, the takeaway from this first group was the efficiency and effectiveness of getting a semen sample before beginning gender-affirming hormone therapy. The second group offered a different takeaway.
“What I think is probably the most unique aspect of this study is this second group of two individuals who had previously received hormones or blockers,” Dr. Rafferty told attendees. The first patient was 13 years of age at gender dysphoria onset and 18 years at the time of their fertility consultation. They had been on GnRH agonists for 6 months before semen collection. Their first sample, at 3 months after discontinuing hormones, was low-quality, but they did produce a viable sample 2 months later.
The other patient, who underwent fertility consultation at age 19, had taken estrogen and spironolactone for 26 months before semen collection and were not able to produce sperm 4 months after stopping the treatment. They did not try again because they underwent an orchiectomy.
Despite the small sample size and lack of confounding data, such as smoking and stress, the study remains the first to show successful sampling after gender-affirming hormone therapy in a teen, Dr. Rafferty said. It also shows that sampling after beginning hormone therapy may require discontinuation for several months before a successful sample is possible, thereby supporting WPATH’s recommendation for early fertility counseling.
“However, the standard of providing fertility counseling before intervention does not always occur,” Dr. Rafferty said, citing research that found low percentages of teens had received fertility counseling or discussed negative effects of therapy on fertility prior to starting it. These low numbers may result from changes in youths’ interest in fertility throughout development, but they could also relate to youths’ reluctance to discuss family planning while they feel uncomfortable in their bodies.
“My experience, and there is some empirical evidence for this, is that many transgender and gender-diverse youth feel more comfortable conceptualizing and pursuing intimate partner relationships and family planning after they start gender affirmation interventions,” Dr. Rafferty said. The stress associated with gender dysphoria can further complicate fertility discussions, and providers have to consider whether it’s more stressful to hold off on gender-affirming hormone therapy until the patient gets a successful semen sample or to start therapy and then discontinue for several months to get a sample later.
While decisions about fertility services should be fully up to the patient, in reality, multiple barriers – such as high cost, low insurance coverage, a dearth of specialists who can do the procedures, and inaccurate assumptions about transgender people’s interest in family planning – complicate the decision,.
“Systemically denying a marginalized population the ability to reproduce, or at least the ability to make a free choice about reproduction and family planning, is a reproductive justice issue that’s not getting the attention it deserves,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Clair Kronk, BSc, a session attendee from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital and Medical Center, said in an interview that she appreciated the session even while she lamented the lack of adequate evidence on transgender and gender-diverse care.
“I do feel like there are a lot of provider-based questions with no sufficient guidelines right now when it comes to transgender care,” Ms. Kronk said. “Despite being nearly a century old, treatment of trans patients is somehow still a ‘Wild West’ of medical care, which is sad to see.” She is grateful to see attention finally reaching this population.
“It is imperative that medical institutions focus on real, advanceable diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives which center marginalized groups,” she said. “Centering minoritized and marginalized peoples in improving care is the only way lasting change will happen.”
Sexual-minority youth in foster care
The second study Dr. Rafferty discussed was the first nationally representative systemic assessment of the prevalence of sexual-minority youth in foster care, child welfare, and out-of-home placement. Anecdotal evidence and community samples already suggest that a disproportionately higher number of sexual-minority youth enter foster care, he said, possibly resulting in part from family conflict about sexual orientation. In addition, LGBTQ+ youth already experience higher rates of psychological and physical abuse at home – a top reason for entry into child welfare – and this population has high rates of running away, particularly around the time of coming out.
Past research has found that sexual-minority youth experience higher rates of maltreatment and discrimination than do their peers from foster parents, siblings, and agency staff, which translates to fewer support services and lower levels of reunification or adoption.
In the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health involving 14,154 respondents, 6.3% reported any same-sex attraction, and 2.1% were involved in the foster-care system. The researchers determined that 4.3% of sexual-minority youth were involved in foster care, compared with just 1.9% of heterosexual youth (P = .002) – a 2.5 times greater rate – with a stronger effect among those with exclusively same-sex attraction.
In the second part of the study, the researchers looked at 1,014 youths in the foster-care system, of whom 80% had experienced an out-of-home placement. The 16% of youth in foster care reporting same sex attraction did not have a higher rate of out-of-home placement than did heterosexual youth within the system. However, there were twice as many sexual-minority youth in child welfare and four times as many in out-of-home placement, compared with their heterosexual peers, possibly suggesting that sexual-minority youth are less likely to exit the system, Dr. Rafferty said.
“Many studies have shown that family acceptance is a critical factor in building resiliency, while rejection is tied to poor physical and emotional outcomes,” he said. “It would follow that we’re identifying a critical at-risk group of sexual-minority youth lacking in fundamental and essential family support.”
This population “experiences the intersection of multiple forces of marginalization, including out-of-home placement, socioeconomic stress, sexual minority status, and likely, race,” Dr. Rafferty said.
Ms. Kronk commented during the session that fertility services and collection are extremely expensive, often forcing trans people into the absurd situation of having to choose between paying for hormone therapy or paying for fertility treatment.
“This makes a really strong argument for resource allocation based on risk” and has ramifications for the higher proportions of sexual-minority youth facing transition without adequate support services, Dr. Rafferty said.
It also suggests the need for providers to help patients feel comfortable and safe talking about their needs, Ms. Kronk said.
“Unfortunately, LGBTQIA+ health care is not taught very comprehensively in the United States [and most other countries],” she said. “Oftentimes, this leads to awkward situations where patients are more knowledgeable than their providers. Listening, learning, supporting, and being open to change are what every provider should take to heart.”
Dr. Rafferty and Ms. Kronk had no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2020