User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program pits pharmacists against physicians
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Biden administration’s new test-to-treat program is simple on the surface: if you feel like you may have COVID-19, go to a pharmacy, get tested, and, if positive, get treated with an antiviral medication on the spot.
One large physicians’ group is concerned that the program leaves doctors on the margins, and may put patients at risk if there are adverse effects from the medications. Pharmacists groups, on the other hand, say the program is too restrictive, according to an article by the research group Advisory Board.
Recently, the White House announced that more than 1,000 pharmacy clinics across the United States had registered to participate in the initiative, according to CNN. Ordering of the drugs is underway in many of these clinics, a White House official told the network.
Besides retail clinics in chain pharmacies, the antivirals will also be available in community health centers, long-term-care facilities, and Veterans Health Administration clinics, according to a statement from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The two antiviral pills authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration include Pfizer’s Paxlovid, for people 12 and older, and Merck’s molnupiravir, for adults. Either drug has to be taken within 5 days after symptoms appear to be effective in preventing serious illness.
The need for speed is a major reason why the government chose to work with retail clinics that are more accessible than most primary care offices. However, the American Medical Association (AMA), the National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) have publicly criticized the administration’s approach.
The pharmacists’ groups are concerned that the program is limited only to pharmacies with clinics on site, thus restricting the number of pharmacies qualified to participate. Fourteen pharmacy groups, including the NCPA and the APhA, have also sent a letter to the Biden administration urging it to remove barriers to pharmacies ordering the medications.
The groups also want permission as “clinically trained medication experts” to prescribe the drugs and ensure their safe use.
The AMA on March 4 took issue with the prescribing component, saying that “the pharmacy-based clinic component of the test-to-treat plan flouts patient safety and risks significant negative health outcomes.”
In the AMA’s view, prescribing Paxlovid without a patient’s physician being present poses a risk for adverse drug interactions, as neither the nurse practitioners in retail clinics nor the pharmacists who dispense the drug have full knowledge of a patient›s medical history.
The next day, the AMA released another statement, saying it was reassured by comments from administration officials “that patients who have access to a regular source of care should contact their physician shortly after testing positive for COVID-19 to assess their treatment options.”
“Traditional doctor-only approach”
Having patients call their doctors after testing positive for COVID in a pharmacy “strikes me as unnecessary in the vast majority of cases, and it will delay treatment,” Robert Wachter, MD, professor and chair of the department of medicine at the University of California San Francisco, said in an interview. “In this case, it seems like the AMA is taking a very traditional doctor-only approach. And the world has changed. It’s much more of a team sport than an individual sport, the way it was years ago.”
Dr. Wachter said he has the utmost respect for pharmacists’ ability to screen prescriptions for adverse drug interactions. “We’re required to do medication reconciliation when patients see us,” he says. “And in many hospitals, we delegate that to pharmacists. They’re at least as good at it if not better than physicians are.”
While it’s essential to know what other medications a patient is taking, he noted, pharmacies have computer records of all the prescriptions they’ve filled for patients. In addition, pharmacies have access to complete medication histories through Surescripts, the company that enables electronic prescribing transactions between prescribers and pharmacies.
Drug interactions “not trivial”
Preeti Malani, MD, the chief health officer and a professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, told this news organization that the potential interactions between Paxlovid and some other medications are “not trivial.”
However, she said, “The really dangerous drugs are the ones for people who have had organ transplants and the like. Those aren’t individuals who are going to shop at a pharmacy.”
Besides the antirejection drugs, Dr. Wachter said, there can be serious interactions with cholesterol-lowering medications. If a person is taking Lipitor, for instance, “Someone would have to make the decision on whether it’s ok for me to stop it for a while, or to lower the dose. But I trust the pharmacist to do that as well as anybody.”
Except for these potential drug interactions with Paxlovid, the antiviral medications are “quite safe,” he said, adding that being able to treat people who test positive for COVID-19 right away is a big advantage of the test-to-treat program, considering how difficult it is for many people to get access to a doctor. That delay could mean that the antivirals are not prescribed and taken until they are no longer effective.
Both Dr. Wachter and Dr. Malani said that the widespread distribution of pharmacies and their extended hours are other big pluses, especially for people who can’t easily leave work or travel far to visit a physician.
Dr. Malani cautioned that there are still kinks to work out in the test-to-treat program. It will be a while before the retail clinics all have the antiviral drugs, and many pharmacies don’t have clinics on site.
Still, she said people can still go to their physicians to be tested, and presumably those doctors can also write antiviral prescriptions. But it’s not clear where the antivirals will be available in the near term.
“Right now, we’re playing catch-up,” Dr. Malani said. “But pharmacies are an important piece of the puzzle.”
Looking at the big picture, she said, “We know that neither vaccination nor natural infection provides long lasting immunity, and so there will be a role for antivirals in order to make this a manageable illness. And when you’re talking about millions of cases, as we were having a few months ago, the health system can’t field all those patients. So we do need a system where I can go to a pharmacy and get a test and treatment.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharma should stop doing business in Russia, says ethicist
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should pharmaceutical companies continue to do business in Russia, running ongoing clinical trials, starting new ones, or continuing to sell their products there?
Some argue that medicine and science must not get enmeshed in politics, staying above the fray to protect their independence and credibility. Other defenders of business-as-usual say the pharmaceutical industry deals in health and aids the vulnerable. Humanitarianism requires continued interaction with Russia.
I think both arguments fail.
We are fighting a war with Russia. It is a war of economic strangulation, social isolation, and pushing Russia as hard as we can to become a pariah state so that internal pressure on Putin will cause him to rethink his cruel, unjustified invasion or the Russian people to replace him. This pressure must be harsh and it must happen quickly. Why?
Having failed to rapidly defeat the Ukrainian army in the war’s first weeks, Russian commanders are now resorting to the horrible barbarism they used in previous wars in Chechnya and Syria: flattening cities, attacking civilians, killing children with massive and indiscriminate firepower.
To mention one recent horror among many, Russian shelling destroyed a maternity hospital in Mariupol. Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelensky, in bemoaning the Russians for their continuing series of war crimes called on the world to act.
“Mariupol. Direct Strike of Russian troops at the maternity hospital,” he wrote in a Twitter post. “People, children are under the wreckage. Atrocity! How much longer will the world be an accomplice ignoring terror?”
The Russian government’s response: “It is not the first time we have seen pathetic outcries concerning the so-called atrocities,” said Minister of Foreign Affairs Sergei Lavrov, claiming the hospital was being used as a base by an “ultra-radical” Ukrainian battalion.
Health and its preservation are key parts of the aim of medicine and science. There is no way that medicine and science can ignore what war does to health, what attacks on hospitals do to the sick and those who serve them there, the psychological toll that intentional terrorism takes on civilians and their defenders, and what the destruction of infrastructure means for the long-term well-being of Ukrainians.
There can be no collusion with war criminals. There can be no denial of the inextricable link between medicine, science, and politics. Medicine and science are controlled by political forces; their use for good or evil is driven by political considerations, and each doctor, scientist, and scientific society must take a stand when politics corrodes the underlying aims of research and healing.
How far does noncooperation with Russia go? Very, very far. All research, both ongoing and new, must cease immediately. Whatever can be done to minimize harm to existing subjects in a short period of time ought to be done, but that is it.
Similarly, no sale of medicines or therapies ought to be occurring, be they life-saving or consumer products. Putin will see to it that such shipments go to the military or are sold on the black market for revenue, and there is nothing pharma companies can do to stop that.
The Russian people need to be pinched not only by the loss of cheeseburgers and boutique coffee but by products they use to maintain their well-being. War is cruel that way, but if you tolerate a government that is bombing and shelling a peaceful neighbor to oblivion, then pharma must ensure that efforts to make Putin and his kleptocratic goons feel the wrath of their fellow citizens.
Given the realities of nuclear Armageddon, the civilized world must fight obvious barbarity as best it can with sanctions, financial assaults, property seizures, and forgoing commerce, including important raw materials and health products. War, even in a fiscal form, is not without terrible costs; but achieving a rapid, just resolution against tyranny permits no exceptions for pharma or any other business if it is a war that must be fought.
Dr. Caplan is director of the division of medical ethics at New York University. He has consulted with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
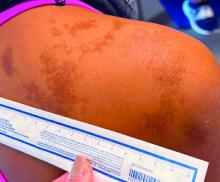
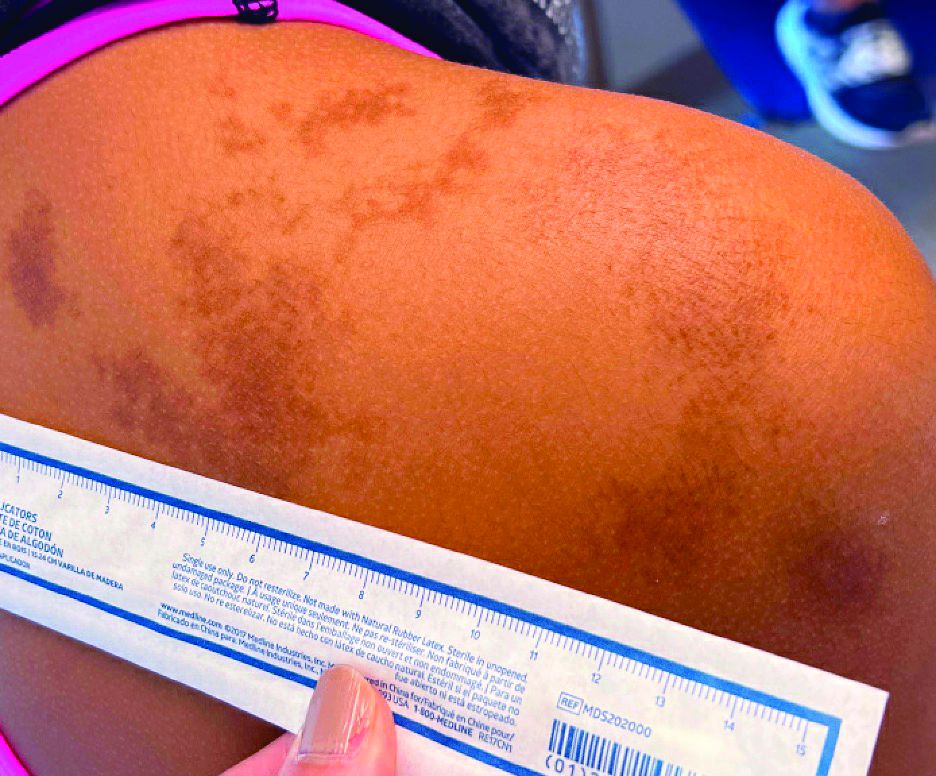
An 11-year-old female presented with skin discoloration on her back
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
Becker’s nevus
The history and physical exam are most consistent with Becker’s nevus, also known as Becker’s melanosis. This is a benign cutaneous hamartoma, usually found in males, characterized by a large, irregularly shaped brown patch, often with hypertrichosis.1 Becker’s nevus can be congenital but is more commonly noticed in late childhood or early adolescence, with thickening, increased pigmentation, and hair growth. Becker’s nevus is considered an overgrowth of epidermal pigment cells and hair follicles and is thought to be attributable to postzygotic mutations (with ACTB mutations most reported).1 It is often located unilaterally on the upper trunk but is occasionally present elsewhere on the body. Acne may occasionally develop within the nevus, which is believed to be triggered by puberty-associated androgens.1 The lesion tends to persist indefinitely but has no propensity for malignant transformation.
Becker’s nevus is generally an isolated skin lesion without other anomalies. However, in rare instances, it may be associated with ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or hypoplastic defects of the muscle, skin, or skeleton, which is known as Becker’s nevus syndrome.2 Treatment is not medically warranted for an isolated Becker’s nevus but may be pursued for cosmetic reasons. Although treatment is generally discouraged because of variable success, laser hair removal and laser therapy may be pursued to address the hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, respectively.
What is on the differential?
A café-au-lait macule (CALM) is a light- to dark-brown, oval lesion that commonly presents at birth or in early childhood. CALMs vary widely in size from less than 1.5 cm to more than 20 cm in diameter. They are asymptomatic and grow in proportion to the individual over time.3 Becker’s nevus can be distinguished from CALMs by the development of hypertrichosis, typical location and course, and other skin changes within the nevus.
Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is characterized by asymptomatic, darkened macules or patches that are brown to blue-gray in color. It is one of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin of color, and can take months to years to resolve. PIH is caused by increased melanin production in response to a cutaneous inflammatory process, such as a drug reaction, allergy, mechanical or thermal injury, infection, phototoxicity, or an underlying skin condition.3 Our patient’s history with the lack of an inciting inflammatory process is more consistent with Becker’s nevus.
Erythema ab igne is a cutaneous reaction to heat that presents as a hyperpigmented patch with a reticular or mottled configuration and superficial venular telangiectasia. The lesion is initially erythematous and progresses to a pale pink to purplish dark-brown color.4 Causes include long-term use of a heating pad, laptop, electric blanket, or a hot water bottle. The absence of prolonged heat exposure in our patient’s history does not favor erythema ab igne.
Pigmentary mosaicism is characterized by a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation that follows the lines of ectodermal embryologic development, known as the lines of Blaschko.5 This condition is also known as linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis because of its streaky or swirl-like pattern. Pigmentary mosaicism can be present at birth or appear within the first few weeks of life. It is caused by genetic heterogeneity in neuroectodermal cells, which results in skin with areas of varying colors. Pigmentary mosaicism is unlikely in this case as our patient’s lesion does not follow the lines of Blaschko.
Ms. Laborada is a pediatric dermatology research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is the vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital. Ms. Laborada and Dr. Eichenfield have no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Atzmony L et al. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47(8):681-5.
2. Danarti R et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(6):965-9.
3. Paller A and Mancini AJ. “Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A textbook of skin disorders of childhood and adolescence” 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2011.
4. Patel DP. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153(7):685.
5. Kromann AB et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):39.
Which companies aren’t exiting Russia? Big pharma
Even as the war in Ukraine has prompted an exodus of international companies — from fast-food chains and oil producers to luxury retailers — from Russia,
Airlines, automakers, banks, and technology giants — at least 320 companies by one count — are among the businesses curtailing operations or making high-profile exits from Russia as its invasion of Ukraine intensifies. McDonald’s, Starbucks, and Coca-Cola announced a pause in sales recently.
But drugmakers, medical device manufacturers, and health care companies, which are exempted from U.S. and European sanctions, said Russians need access to medicines and medical equipment and contend that international humanitarian law requires they keep supply chains open.
“As a health care company, we have an important purpose, which is why at this time we continue to serve people in all countries in which we operate who depend on us for essential products, some life-sustaining,” said Scott Stoffel, divisional vice president for Illinois-based Abbott Laboratories, which manufactures and sells medicines in Russia for oncology, women’s health, pancreatic insufficiency, and liver health.
Johnson & Johnson — which has corporate offices in Moscow, Novosibirsk, St. Petersburg, and Yekaterinburg — said in a statement, “We remain committed to providing essential health products to those in need in Ukraine, Russia, and the region, in compliance with current sanctions and while adapting to the rapidly changing situation on the ground.”
The reluctance of drugmakers to pause operations in Russia is being met with a growing chorus of criticism.
Pharmaceutical companies that say they must continue to manufacture drugs in Russia for humanitarian reasons are “being misguided at best, cynical in the medium case, and outright deplorably misleading and deceptive,” said Jeffrey Sonnenfeld, DBA, a professor at the Yale School of Management who is tracking which companies have curtailed operations in Russia. He noted that banks and technology companies also provide essential services.
“Russians are put in a tragic position of unearned suffering. If we continue to make life palatable for them, then we are continuing to support the regime,” Dr. Sonnenfeld said. “These drug companies will be seen as complicit with the most vicious operation on the planet. Instead of protecting life, they are going to be seen as destroying life. The goal here is to show that Putin is not in control of all sectors of the economy.”
U.S. pharmaceutical and medical companies have operated in Russia for decades, and many ramped up operations after Russia invaded and annexed Crimea in 2014, navigating the fraught relationship between the United States and Russia amid sanctions. In 2010, Vladimir Putin, then Russian prime minister, announced an ambitious national plan for the Russian pharmaceutical industry that would be a pillar in his efforts to reestablish his country as an influential superpower and wean the country off Western pharmaceutical imports. Under the plan, called “Pharma-2020” and “Pharma-2030,” the government required Western pharmaceutical companies eager to sell to Russia’s growing middle class to locate production inside the country.
Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and Abbott are among the drugmakers that manufacture pharmaceutical drugs at facilities in St. Petersburg and elsewhere in the country and typically sell those drugs as branded generics or under Russian brands.
Pfizer’s CEO, Albert Bourla, said on CBS that the giant drugmaker is not going to make further investments in Russia, but that it will not cut ties with Russia, as multinational companies in other industries are doing.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants in Kaluga, a major manufacturing center for Volkswagen and Volvo southwest of Moscow, have been funded through a partnership between Rusnano, a state-owned venture that promotes the development of high-tech enterprises, and U.S. venture capital firms.
Russia also has sought to position itself as an attractive research market, offering an inexpensive and lax regulatory environment for clinical drug trials. Last year, Pfizer conducted in Russia clinical trials of Paxlovid, its experimental antiviral pill to treat covid-19. Before the invasion began in late February, 3,072 trials were underway in Russia and 503 were underway in Ukraine, according to BioWorld, a reporting hub focused on drug development that features data from Cortellis.
AstraZeneca is the top sponsor of clinical trials in Russia, with 49 trials, followed by a subsidiary of Merck, with 48 trials.
So far, drugmakers’ response to the Ukraine invasion has largely centered on public pledges to donate essential medicines and vaccines to Ukrainian patients and refugees. They’ve also made general comments about the need to keep open the supply of medicines flowing within Russia.
Abbott has pledged $2 million to support humanitarian efforts in Ukraine, and Pfizer, based in New York, said it has supplied $1 million in humanitarian grants. Swiss drug maker Novartis said it was expanding humanitarian efforts in Ukraine and working to “ensure the continued supply of our medicines in Ukraine.”
But no major pharmaceutical or medical device maker has announced plans to shutter manufacturing plants or halt sales inside Russia.
In an open letter, hundreds of leaders of mainly smaller biotechnology companies have called on industry members to cease business activities in Russia, including “investment in Russian companies and new investment within the borders of Russia,” and to halt trade and collaboration with Russian companies, except for supplying food and medicines. How many of the signatories have business operations in Russia was unclear.
Ulrich Neumann, director for market access at Janssen, a Johnson & Johnson company, was among those who signed the letter, but whether he was speaking for the company was unclear. In its own statement posted on social media, the company said it’s “committed to providing access to our essential medical products in the countries where we operate, in compliance with current international sanctions.”
GlaxoSmithKline, headquartered in the United Kingdom, said in a statement that it’s stopping all advertising in Russia and will not enter into contracts that “directly support the Russian administration or military.” But the company said that as a “supplier of needed medicines, vaccines and everyday health products, we have a responsibility to do all we can to make them available. For this reason, we will continue to supply our products to the people of Russia, while we can.”
Nell Minow, vice chair of ValueEdge Advisors, an investment consulting firm, noted that drug companies have been treated differently than other industries during previous global conflicts. For example, some corporate ethicists advised against pharmaceutical companies’ total divestment from South Africa’s apartheid regime to ensure essential medicines flowed to the country.
“There is a difference between a hamburger and a pill,” Mr. Minow said. Companies should strongly condemn Russia’s actions, she said, but unless the United States enters directly into a war with Russia, companies that make essential medicines and health care products should continue to operate. Before U.S. involvement in World War II, she added, there were “some American companies that did business with Germany until the last minute.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation. KHN senior correspondent Arthur Allen contributed to this article.
Even as the war in Ukraine has prompted an exodus of international companies — from fast-food chains and oil producers to luxury retailers — from Russia,
Airlines, automakers, banks, and technology giants — at least 320 companies by one count — are among the businesses curtailing operations or making high-profile exits from Russia as its invasion of Ukraine intensifies. McDonald’s, Starbucks, and Coca-Cola announced a pause in sales recently.
But drugmakers, medical device manufacturers, and health care companies, which are exempted from U.S. and European sanctions, said Russians need access to medicines and medical equipment and contend that international humanitarian law requires they keep supply chains open.
“As a health care company, we have an important purpose, which is why at this time we continue to serve people in all countries in which we operate who depend on us for essential products, some life-sustaining,” said Scott Stoffel, divisional vice president for Illinois-based Abbott Laboratories, which manufactures and sells medicines in Russia for oncology, women’s health, pancreatic insufficiency, and liver health.
Johnson & Johnson — which has corporate offices in Moscow, Novosibirsk, St. Petersburg, and Yekaterinburg — said in a statement, “We remain committed to providing essential health products to those in need in Ukraine, Russia, and the region, in compliance with current sanctions and while adapting to the rapidly changing situation on the ground.”
The reluctance of drugmakers to pause operations in Russia is being met with a growing chorus of criticism.
Pharmaceutical companies that say they must continue to manufacture drugs in Russia for humanitarian reasons are “being misguided at best, cynical in the medium case, and outright deplorably misleading and deceptive,” said Jeffrey Sonnenfeld, DBA, a professor at the Yale School of Management who is tracking which companies have curtailed operations in Russia. He noted that banks and technology companies also provide essential services.
“Russians are put in a tragic position of unearned suffering. If we continue to make life palatable for them, then we are continuing to support the regime,” Dr. Sonnenfeld said. “These drug companies will be seen as complicit with the most vicious operation on the planet. Instead of protecting life, they are going to be seen as destroying life. The goal here is to show that Putin is not in control of all sectors of the economy.”
U.S. pharmaceutical and medical companies have operated in Russia for decades, and many ramped up operations after Russia invaded and annexed Crimea in 2014, navigating the fraught relationship between the United States and Russia amid sanctions. In 2010, Vladimir Putin, then Russian prime minister, announced an ambitious national plan for the Russian pharmaceutical industry that would be a pillar in his efforts to reestablish his country as an influential superpower and wean the country off Western pharmaceutical imports. Under the plan, called “Pharma-2020” and “Pharma-2030,” the government required Western pharmaceutical companies eager to sell to Russia’s growing middle class to locate production inside the country.
Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and Abbott are among the drugmakers that manufacture pharmaceutical drugs at facilities in St. Petersburg and elsewhere in the country and typically sell those drugs as branded generics or under Russian brands.
Pfizer’s CEO, Albert Bourla, said on CBS that the giant drugmaker is not going to make further investments in Russia, but that it will not cut ties with Russia, as multinational companies in other industries are doing.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants in Kaluga, a major manufacturing center for Volkswagen and Volvo southwest of Moscow, have been funded through a partnership between Rusnano, a state-owned venture that promotes the development of high-tech enterprises, and U.S. venture capital firms.
Russia also has sought to position itself as an attractive research market, offering an inexpensive and lax regulatory environment for clinical drug trials. Last year, Pfizer conducted in Russia clinical trials of Paxlovid, its experimental antiviral pill to treat covid-19. Before the invasion began in late February, 3,072 trials were underway in Russia and 503 were underway in Ukraine, according to BioWorld, a reporting hub focused on drug development that features data from Cortellis.
AstraZeneca is the top sponsor of clinical trials in Russia, with 49 trials, followed by a subsidiary of Merck, with 48 trials.
So far, drugmakers’ response to the Ukraine invasion has largely centered on public pledges to donate essential medicines and vaccines to Ukrainian patients and refugees. They’ve also made general comments about the need to keep open the supply of medicines flowing within Russia.
Abbott has pledged $2 million to support humanitarian efforts in Ukraine, and Pfizer, based in New York, said it has supplied $1 million in humanitarian grants. Swiss drug maker Novartis said it was expanding humanitarian efforts in Ukraine and working to “ensure the continued supply of our medicines in Ukraine.”
But no major pharmaceutical or medical device maker has announced plans to shutter manufacturing plants or halt sales inside Russia.
In an open letter, hundreds of leaders of mainly smaller biotechnology companies have called on industry members to cease business activities in Russia, including “investment in Russian companies and new investment within the borders of Russia,” and to halt trade and collaboration with Russian companies, except for supplying food and medicines. How many of the signatories have business operations in Russia was unclear.
Ulrich Neumann, director for market access at Janssen, a Johnson & Johnson company, was among those who signed the letter, but whether he was speaking for the company was unclear. In its own statement posted on social media, the company said it’s “committed to providing access to our essential medical products in the countries where we operate, in compliance with current international sanctions.”
GlaxoSmithKline, headquartered in the United Kingdom, said in a statement that it’s stopping all advertising in Russia and will not enter into contracts that “directly support the Russian administration or military.” But the company said that as a “supplier of needed medicines, vaccines and everyday health products, we have a responsibility to do all we can to make them available. For this reason, we will continue to supply our products to the people of Russia, while we can.”
Nell Minow, vice chair of ValueEdge Advisors, an investment consulting firm, noted that drug companies have been treated differently than other industries during previous global conflicts. For example, some corporate ethicists advised against pharmaceutical companies’ total divestment from South Africa’s apartheid regime to ensure essential medicines flowed to the country.
“There is a difference between a hamburger and a pill,” Mr. Minow said. Companies should strongly condemn Russia’s actions, she said, but unless the United States enters directly into a war with Russia, companies that make essential medicines and health care products should continue to operate. Before U.S. involvement in World War II, she added, there were “some American companies that did business with Germany until the last minute.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation. KHN senior correspondent Arthur Allen contributed to this article.
Even as the war in Ukraine has prompted an exodus of international companies — from fast-food chains and oil producers to luxury retailers — from Russia,
Airlines, automakers, banks, and technology giants — at least 320 companies by one count — are among the businesses curtailing operations or making high-profile exits from Russia as its invasion of Ukraine intensifies. McDonald’s, Starbucks, and Coca-Cola announced a pause in sales recently.
But drugmakers, medical device manufacturers, and health care companies, which are exempted from U.S. and European sanctions, said Russians need access to medicines and medical equipment and contend that international humanitarian law requires they keep supply chains open.
“As a health care company, we have an important purpose, which is why at this time we continue to serve people in all countries in which we operate who depend on us for essential products, some life-sustaining,” said Scott Stoffel, divisional vice president for Illinois-based Abbott Laboratories, which manufactures and sells medicines in Russia for oncology, women’s health, pancreatic insufficiency, and liver health.
Johnson & Johnson — which has corporate offices in Moscow, Novosibirsk, St. Petersburg, and Yekaterinburg — said in a statement, “We remain committed to providing essential health products to those in need in Ukraine, Russia, and the region, in compliance with current sanctions and while adapting to the rapidly changing situation on the ground.”
The reluctance of drugmakers to pause operations in Russia is being met with a growing chorus of criticism.
Pharmaceutical companies that say they must continue to manufacture drugs in Russia for humanitarian reasons are “being misguided at best, cynical in the medium case, and outright deplorably misleading and deceptive,” said Jeffrey Sonnenfeld, DBA, a professor at the Yale School of Management who is tracking which companies have curtailed operations in Russia. He noted that banks and technology companies also provide essential services.
“Russians are put in a tragic position of unearned suffering. If we continue to make life palatable for them, then we are continuing to support the regime,” Dr. Sonnenfeld said. “These drug companies will be seen as complicit with the most vicious operation on the planet. Instead of protecting life, they are going to be seen as destroying life. The goal here is to show that Putin is not in control of all sectors of the economy.”
U.S. pharmaceutical and medical companies have operated in Russia for decades, and many ramped up operations after Russia invaded and annexed Crimea in 2014, navigating the fraught relationship between the United States and Russia amid sanctions. In 2010, Vladimir Putin, then Russian prime minister, announced an ambitious national plan for the Russian pharmaceutical industry that would be a pillar in his efforts to reestablish his country as an influential superpower and wean the country off Western pharmaceutical imports. Under the plan, called “Pharma-2020” and “Pharma-2030,” the government required Western pharmaceutical companies eager to sell to Russia’s growing middle class to locate production inside the country.
Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and Abbott are among the drugmakers that manufacture pharmaceutical drugs at facilities in St. Petersburg and elsewhere in the country and typically sell those drugs as branded generics or under Russian brands.
Pfizer’s CEO, Albert Bourla, said on CBS that the giant drugmaker is not going to make further investments in Russia, but that it will not cut ties with Russia, as multinational companies in other industries are doing.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants in Kaluga, a major manufacturing center for Volkswagen and Volvo southwest of Moscow, have been funded through a partnership between Rusnano, a state-owned venture that promotes the development of high-tech enterprises, and U.S. venture capital firms.
Russia also has sought to position itself as an attractive research market, offering an inexpensive and lax regulatory environment for clinical drug trials. Last year, Pfizer conducted in Russia clinical trials of Paxlovid, its experimental antiviral pill to treat covid-19. Before the invasion began in late February, 3,072 trials were underway in Russia and 503 were underway in Ukraine, according to BioWorld, a reporting hub focused on drug development that features data from Cortellis.
AstraZeneca is the top sponsor of clinical trials in Russia, with 49 trials, followed by a subsidiary of Merck, with 48 trials.
So far, drugmakers’ response to the Ukraine invasion has largely centered on public pledges to donate essential medicines and vaccines to Ukrainian patients and refugees. They’ve also made general comments about the need to keep open the supply of medicines flowing within Russia.
Abbott has pledged $2 million to support humanitarian efforts in Ukraine, and Pfizer, based in New York, said it has supplied $1 million in humanitarian grants. Swiss drug maker Novartis said it was expanding humanitarian efforts in Ukraine and working to “ensure the continued supply of our medicines in Ukraine.”
But no major pharmaceutical or medical device maker has announced plans to shutter manufacturing plants or halt sales inside Russia.
In an open letter, hundreds of leaders of mainly smaller biotechnology companies have called on industry members to cease business activities in Russia, including “investment in Russian companies and new investment within the borders of Russia,” and to halt trade and collaboration with Russian companies, except for supplying food and medicines. How many of the signatories have business operations in Russia was unclear.
Ulrich Neumann, director for market access at Janssen, a Johnson & Johnson company, was among those who signed the letter, but whether he was speaking for the company was unclear. In its own statement posted on social media, the company said it’s “committed to providing access to our essential medical products in the countries where we operate, in compliance with current international sanctions.”
GlaxoSmithKline, headquartered in the United Kingdom, said in a statement that it’s stopping all advertising in Russia and will not enter into contracts that “directly support the Russian administration or military.” But the company said that as a “supplier of needed medicines, vaccines and everyday health products, we have a responsibility to do all we can to make them available. For this reason, we will continue to supply our products to the people of Russia, while we can.”
Nell Minow, vice chair of ValueEdge Advisors, an investment consulting firm, noted that drug companies have been treated differently than other industries during previous global conflicts. For example, some corporate ethicists advised against pharmaceutical companies’ total divestment from South Africa’s apartheid regime to ensure essential medicines flowed to the country.
“There is a difference between a hamburger and a pill,” Mr. Minow said. Companies should strongly condemn Russia’s actions, she said, but unless the United States enters directly into a war with Russia, companies that make essential medicines and health care products should continue to operate. Before U.S. involvement in World War II, she added, there were “some American companies that did business with Germany until the last minute.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation. KHN senior correspondent Arthur Allen contributed to this article.
Can a tool help overcome barriers to diabetes medication cost?
The resource, “Having Healthcare Cost Conversations to Improve Patient Outcomes: A Practical Guide,” was jointly developed by the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and Beyond Type 1, the nonprofit patient advocacy organization.
Indeed, the guide appeared as President Biden discussed his proposal to cap insulin costs at $35 per insulin vial during the State of the Union address, during which he introduced a young boy with type 1 diabetes in the guest box, as reported by this news organization. On March 3, Civica, a nonprofit coalition of health systems and philanthropies, announced it plans to manufacture generic insulin at a deeply discounted price, as reported by this news organization.
“Just to see diabetes front and center at the State of the Union followed by these announcements is certainly reflective of our own advocacy effort to make sure that people have affordable options for insulin, diabetes medications, services,” Kate Thomas, ADCES chief advocacy and external affairs officer, said in an interview. She added that ADCES has also pushed for legislation in Congress that would expand access to diabetes self-management training under the Medicare program.
The guide includes advice about overcoming barriers to discussing treatment costs with patients, suggested questions to ask patients about specific costs, and determinants of health and conversational approaches. Links are provided to resources for obtaining affordable insulin, other diabetes medications, and continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump equipment.
“We know that, especially during primary care visits, there is limited time along with numbers of issues to talk about, so I think our challenge is how do we prioritize these conversations with something that can lead to action, not just saying you should do this but how do you actually do it,” Ms. Thomas said.
The introduction summarizes results from a 2021 Beyond Type 1 survey confirming prior findings reported by this news organization that cost is a frequent barrier for many individuals living with diabetes. “Especially right now where we are in terms of the impact of the pandemic and with peoples’ job statuses changing, I think it’s worthwhile to raise this in patient encounters,” Ms. Thomas said.
Overcoming conversational barriers
The first of three tables in the guide provides a list of “barriers to having a cost conversation” in the first column and “suggested solutions” in the second. For example, for the barrier, “You have insufficient time and/or knowledge about cost,” the suggestion is, “request and share available faculty and resources, including benefits coordinators, social workers, and community-based organizations. Work with the pharmacists and other members of the diabetes care team to identify resources that lower cost of medications.”
And for another barrier, “patients are often embarrassed or ashamed to initiate discussions of affordability,” the suggested solution is: “Normalize the issue of cost of care barriers for patients.”
A second table offers specific questions to ask patients about costs of medications and care, determinants of health, and financial barriers. These include: “What are some challenges you’ve had to accessing your medications or taking them as prescribed? What are some out-of-pocket health care costs you need help with? What challenges do you have accessing healthy food for you and your family?”
A link to a screening tool for social determinants of health is also included.
Language suggestions include talking about “cost of care” rather than “money,” asking patients if they’ve understood everything correctly by repeating back what they’ve said, and asking for confirmation and discussing follow-up.
Overall, the tool is designed to be a “broad conversation starter,” and not just about medications, Ms. Thomas said. “This is for all audiences and it’s meant to be something that the provider can tailor depending on who they’re speaking to. ... It’s about medications, but also the entire cost of care, including services and devices, transportation to appointments, access to food. ... Diabetes care isn’t just taking medication. It’s so many more factors.”
Ms. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The resource, “Having Healthcare Cost Conversations to Improve Patient Outcomes: A Practical Guide,” was jointly developed by the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and Beyond Type 1, the nonprofit patient advocacy organization.
Indeed, the guide appeared as President Biden discussed his proposal to cap insulin costs at $35 per insulin vial during the State of the Union address, during which he introduced a young boy with type 1 diabetes in the guest box, as reported by this news organization. On March 3, Civica, a nonprofit coalition of health systems and philanthropies, announced it plans to manufacture generic insulin at a deeply discounted price, as reported by this news organization.
“Just to see diabetes front and center at the State of the Union followed by these announcements is certainly reflective of our own advocacy effort to make sure that people have affordable options for insulin, diabetes medications, services,” Kate Thomas, ADCES chief advocacy and external affairs officer, said in an interview. She added that ADCES has also pushed for legislation in Congress that would expand access to diabetes self-management training under the Medicare program.
The guide includes advice about overcoming barriers to discussing treatment costs with patients, suggested questions to ask patients about specific costs, and determinants of health and conversational approaches. Links are provided to resources for obtaining affordable insulin, other diabetes medications, and continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump equipment.
“We know that, especially during primary care visits, there is limited time along with numbers of issues to talk about, so I think our challenge is how do we prioritize these conversations with something that can lead to action, not just saying you should do this but how do you actually do it,” Ms. Thomas said.
The introduction summarizes results from a 2021 Beyond Type 1 survey confirming prior findings reported by this news organization that cost is a frequent barrier for many individuals living with diabetes. “Especially right now where we are in terms of the impact of the pandemic and with peoples’ job statuses changing, I think it’s worthwhile to raise this in patient encounters,” Ms. Thomas said.
Overcoming conversational barriers
The first of three tables in the guide provides a list of “barriers to having a cost conversation” in the first column and “suggested solutions” in the second. For example, for the barrier, “You have insufficient time and/or knowledge about cost,” the suggestion is, “request and share available faculty and resources, including benefits coordinators, social workers, and community-based organizations. Work with the pharmacists and other members of the diabetes care team to identify resources that lower cost of medications.”
And for another barrier, “patients are often embarrassed or ashamed to initiate discussions of affordability,” the suggested solution is: “Normalize the issue of cost of care barriers for patients.”
A second table offers specific questions to ask patients about costs of medications and care, determinants of health, and financial barriers. These include: “What are some challenges you’ve had to accessing your medications or taking them as prescribed? What are some out-of-pocket health care costs you need help with? What challenges do you have accessing healthy food for you and your family?”
A link to a screening tool for social determinants of health is also included.
Language suggestions include talking about “cost of care” rather than “money,” asking patients if they’ve understood everything correctly by repeating back what they’ve said, and asking for confirmation and discussing follow-up.
Overall, the tool is designed to be a “broad conversation starter,” and not just about medications, Ms. Thomas said. “This is for all audiences and it’s meant to be something that the provider can tailor depending on who they’re speaking to. ... It’s about medications, but also the entire cost of care, including services and devices, transportation to appointments, access to food. ... Diabetes care isn’t just taking medication. It’s so many more factors.”
Ms. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The resource, “Having Healthcare Cost Conversations to Improve Patient Outcomes: A Practical Guide,” was jointly developed by the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists and Beyond Type 1, the nonprofit patient advocacy organization.
Indeed, the guide appeared as President Biden discussed his proposal to cap insulin costs at $35 per insulin vial during the State of the Union address, during which he introduced a young boy with type 1 diabetes in the guest box, as reported by this news organization. On March 3, Civica, a nonprofit coalition of health systems and philanthropies, announced it plans to manufacture generic insulin at a deeply discounted price, as reported by this news organization.
“Just to see diabetes front and center at the State of the Union followed by these announcements is certainly reflective of our own advocacy effort to make sure that people have affordable options for insulin, diabetes medications, services,” Kate Thomas, ADCES chief advocacy and external affairs officer, said in an interview. She added that ADCES has also pushed for legislation in Congress that would expand access to diabetes self-management training under the Medicare program.
The guide includes advice about overcoming barriers to discussing treatment costs with patients, suggested questions to ask patients about specific costs, and determinants of health and conversational approaches. Links are provided to resources for obtaining affordable insulin, other diabetes medications, and continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump equipment.
“We know that, especially during primary care visits, there is limited time along with numbers of issues to talk about, so I think our challenge is how do we prioritize these conversations with something that can lead to action, not just saying you should do this but how do you actually do it,” Ms. Thomas said.
The introduction summarizes results from a 2021 Beyond Type 1 survey confirming prior findings reported by this news organization that cost is a frequent barrier for many individuals living with diabetes. “Especially right now where we are in terms of the impact of the pandemic and with peoples’ job statuses changing, I think it’s worthwhile to raise this in patient encounters,” Ms. Thomas said.
Overcoming conversational barriers
The first of three tables in the guide provides a list of “barriers to having a cost conversation” in the first column and “suggested solutions” in the second. For example, for the barrier, “You have insufficient time and/or knowledge about cost,” the suggestion is, “request and share available faculty and resources, including benefits coordinators, social workers, and community-based organizations. Work with the pharmacists and other members of the diabetes care team to identify resources that lower cost of medications.”
And for another barrier, “patients are often embarrassed or ashamed to initiate discussions of affordability,” the suggested solution is: “Normalize the issue of cost of care barriers for patients.”
A second table offers specific questions to ask patients about costs of medications and care, determinants of health, and financial barriers. These include: “What are some challenges you’ve had to accessing your medications or taking them as prescribed? What are some out-of-pocket health care costs you need help with? What challenges do you have accessing healthy food for you and your family?”
A link to a screening tool for social determinants of health is also included.
Language suggestions include talking about “cost of care” rather than “money,” asking patients if they’ve understood everything correctly by repeating back what they’ve said, and asking for confirmation and discussing follow-up.
Overall, the tool is designed to be a “broad conversation starter,” and not just about medications, Ms. Thomas said. “This is for all audiences and it’s meant to be something that the provider can tailor depending on who they’re speaking to. ... It’s about medications, but also the entire cost of care, including services and devices, transportation to appointments, access to food. ... Diabetes care isn’t just taking medication. It’s so many more factors.”
Ms. Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 often more severe with congenital heart defects
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adults with a congenital heart defect (CHD) are at increased risk for serious illness and death when hospitalized with COVID-19, making vaccination and other preventive measures even important in this population, say researchers with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We found that hospitalized patients with heart defects are up to twice as likely to have critical outcomes of COVID-19 illness (admission to the intensive care unit, use of a ventilator to help with breathing, or death) compared to hospitalized COVID-19 patients without heart defects,” Karrie Downing, MPH, epidemiologist, with the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, said in an interview.
“Additionally, we learned that people with hearts defects who were older or who also had other conditions like heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity were the most likely to have critical COVID-19 illness, but children and adults with heart defects without these other conditions were still at increased risk,” Ms. Downing said.
The message for health care providers is clear: “Encourage your patients with heart defects to get vaccinated and discuss with your patients the need for other preventive measures to avoid infection that may progress to severe COVID-19 illness,” Ms. Downing added.
The study was published online March 7, 2022, in Circulation.
The researchers analyzed data on 235,638 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between March 2020 and January 2021, including 421 (0.2%) with CHD. Most CHD patients were older than 30 years (73%) and 61% were men, with 55% non-Hispanic white, 19% Hispanic and 16% non-Hispanic Black.
Overall, 68% of CHD patients had at least one comorbidity, as did 59% of patients without CHD.
Rates of ICU admission were higher in the CHD group (54% vs. 43%), as were rates of invasive mechanical ventilation (24% vs. 15%) and in-hospital death (11% vs. 7%).
After accounting for patient characteristics, ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death were more prevalent among COVID-19 patients with rather than without CHD, with adjusted prevalence ratios of 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0, respectively.
When stratified by high-risk characteristics, prevalence estimates for ICU admission, invasive mechanical ventilation and death remained higher among patients with COVID-19 and CHD across nearly all strata, including younger age groups and those without heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, Down syndrome, diabetes, or obesity, the researchers reported.
Ms. Downing said more work is needed to identify why the clinical course of COVID-19 disease results in admission to the ICU, the need for a ventilator, or death for some hospitalized patients with CHD and not for others.
“There could be a number of social, environmental, economic, medical, and genetic factors playing a role. But staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and following preventive measures for COVID-19 are effective ways to reduce the risk of severe illness from COVID-19,” Ms. Downing said.
The study had no specific funding. The authors reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Half of U.S. adults exposed to harmful lead levels as children: Study
published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In addition, the researchers found, 90% of children born in the United States between 1951 and 1980 had blood-lead levels higher than the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention threshold. On average, early childhood exposure to lead resulted in a 2.6-point drop in IQ per person.
“Most of what we think of as the Lost Generation and the Greatest Generation and Baby Boomers had a moderate amount of lead exposure,” Matt Hauer, PhD, one of the coauthors and an assistant professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a statement.
“Generation X was exposed to very high amounts of lead, and now Millennials and the generation following them have been exposed to very low amounts of lead,” he said.
The findings were “infuriating” because scientists have long known that lead exposure is harmful, Michael McFarland, PhD, coauthor and an associate professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, told The Associated Press.
The research team analyzed blood-lead levels, census data, and the use of leaded gasoline to understand how widespread early childhood lead exposure was in the United States between 1940 and 2015. They looked mostly at exposure caused by leaded gasoline, which was the dominant form of exposure between the 1940s and 1980s.
They estimated that half of the U.S. adult population in 2015 had been exposed to lead levels that surpassed 5 micrograms per deciliter, which was the CDC threshold at the time. More than 54 million had been exposed to levels above 15 micrograms per deciliter, and 4.5 million were exposed to 30 micrograms per deciliter – or six times the threshold.
They found that estimated lead-linked deficits were greatest for the 21 million people born between 1966 and 1970, who had an average 5.9-point drop in IQ per person.
The United States has put in place tougher regulations to protect Americans from lead poisoning in recent decades, particularly from gasoline. The study team found that blood-lead levels were considerably lower than 5 micrograms per deciliter among those born since 2001.
At the same time, the public health effects of childhood exposure for older generations will last for years to come.
“Childhood lead exposure is not just here and now. It’s going to impact your lifelong health,” Abheet Solomon, a senior program manager at the United Nations Children’s Fund, told the AP.
Childhood lead exposure is known to affect the development of mental skills, and it raises the risk of hypertension, kidney damage, and heart disease. It has been linked to harm in pregnant women and developing children.
“The more tragic part is that we keep making the same … mistakes again,” Bruce Lanphear, MD, a health sciences professor at Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, B.C., told the AP.
Dr. Lanphear’s research on lead exposure has found loss of mental skills and IQ as well.
“First it was lead, then it was air pollution. Now it’s PFAS chemicals and phthalates (chemicals used to make plastics more durable),” he said. “And we can’t stop long enough to ask ourselves should we be regulating chemicals differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In addition, the researchers found, 90% of children born in the United States between 1951 and 1980 had blood-lead levels higher than the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention threshold. On average, early childhood exposure to lead resulted in a 2.6-point drop in IQ per person.
“Most of what we think of as the Lost Generation and the Greatest Generation and Baby Boomers had a moderate amount of lead exposure,” Matt Hauer, PhD, one of the coauthors and an assistant professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a statement.
“Generation X was exposed to very high amounts of lead, and now Millennials and the generation following them have been exposed to very low amounts of lead,” he said.
The findings were “infuriating” because scientists have long known that lead exposure is harmful, Michael McFarland, PhD, coauthor and an associate professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, told The Associated Press.
The research team analyzed blood-lead levels, census data, and the use of leaded gasoline to understand how widespread early childhood lead exposure was in the United States between 1940 and 2015. They looked mostly at exposure caused by leaded gasoline, which was the dominant form of exposure between the 1940s and 1980s.
They estimated that half of the U.S. adult population in 2015 had been exposed to lead levels that surpassed 5 micrograms per deciliter, which was the CDC threshold at the time. More than 54 million had been exposed to levels above 15 micrograms per deciliter, and 4.5 million were exposed to 30 micrograms per deciliter – or six times the threshold.
They found that estimated lead-linked deficits were greatest for the 21 million people born between 1966 and 1970, who had an average 5.9-point drop in IQ per person.
The United States has put in place tougher regulations to protect Americans from lead poisoning in recent decades, particularly from gasoline. The study team found that blood-lead levels were considerably lower than 5 micrograms per deciliter among those born since 2001.
At the same time, the public health effects of childhood exposure for older generations will last for years to come.
“Childhood lead exposure is not just here and now. It’s going to impact your lifelong health,” Abheet Solomon, a senior program manager at the United Nations Children’s Fund, told the AP.
Childhood lead exposure is known to affect the development of mental skills, and it raises the risk of hypertension, kidney damage, and heart disease. It has been linked to harm in pregnant women and developing children.
“The more tragic part is that we keep making the same … mistakes again,” Bruce Lanphear, MD, a health sciences professor at Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, B.C., told the AP.
Dr. Lanphear’s research on lead exposure has found loss of mental skills and IQ as well.
“First it was lead, then it was air pollution. Now it’s PFAS chemicals and phthalates (chemicals used to make plastics more durable),” he said. “And we can’t stop long enough to ask ourselves should we be regulating chemicals differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In addition, the researchers found, 90% of children born in the United States between 1951 and 1980 had blood-lead levels higher than the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention threshold. On average, early childhood exposure to lead resulted in a 2.6-point drop in IQ per person.
“Most of what we think of as the Lost Generation and the Greatest Generation and Baby Boomers had a moderate amount of lead exposure,” Matt Hauer, PhD, one of the coauthors and an assistant professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, said in a statement.
“Generation X was exposed to very high amounts of lead, and now Millennials and the generation following them have been exposed to very low amounts of lead,” he said.
The findings were “infuriating” because scientists have long known that lead exposure is harmful, Michael McFarland, PhD, coauthor and an associate professor of sociology at Florida State University, Tallahassee, told The Associated Press.
The research team analyzed blood-lead levels, census data, and the use of leaded gasoline to understand how widespread early childhood lead exposure was in the United States between 1940 and 2015. They looked mostly at exposure caused by leaded gasoline, which was the dominant form of exposure between the 1940s and 1980s.
They estimated that half of the U.S. adult population in 2015 had been exposed to lead levels that surpassed 5 micrograms per deciliter, which was the CDC threshold at the time. More than 54 million had been exposed to levels above 15 micrograms per deciliter, and 4.5 million were exposed to 30 micrograms per deciliter – or six times the threshold.
They found that estimated lead-linked deficits were greatest for the 21 million people born between 1966 and 1970, who had an average 5.9-point drop in IQ per person.
The United States has put in place tougher regulations to protect Americans from lead poisoning in recent decades, particularly from gasoline. The study team found that blood-lead levels were considerably lower than 5 micrograms per deciliter among those born since 2001.
At the same time, the public health effects of childhood exposure for older generations will last for years to come.
“Childhood lead exposure is not just here and now. It’s going to impact your lifelong health,” Abheet Solomon, a senior program manager at the United Nations Children’s Fund, told the AP.
Childhood lead exposure is known to affect the development of mental skills, and it raises the risk of hypertension, kidney damage, and heart disease. It has been linked to harm in pregnant women and developing children.
“The more tragic part is that we keep making the same … mistakes again,” Bruce Lanphear, MD, a health sciences professor at Simon Fraser University in Vancouver, B.C., told the AP.
Dr. Lanphear’s research on lead exposure has found loss of mental skills and IQ as well.
“First it was lead, then it was air pollution. Now it’s PFAS chemicals and phthalates (chemicals used to make plastics more durable),” he said. “And we can’t stop long enough to ask ourselves should we be regulating chemicals differently.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Raise a glass to speed up the brain’s aging process
Drink a day could age your brain
There are many things we can do daily to improve our health: Exercise, read a book, eat an apple (supposedly). Not drink a glass of red wine. Wait, not drink? That’s right. We were told that a glass of red wine each night was doing something good for our hearts, but it’s doing something bad to our brains: Aging them prematurely.
According to a recent study in Nature Communications, drinking half a pint of beer a day could age the brain of a 50-year-old by 6 months. A pint of beer equaled 2 years of aging and a pint and a half aged participants’ brains by 3.5 years.
Compared with people who didn’t drink, those who averaged about two pints of beer or two glasses of wine daily had brains aged 10 years older!
The researchers’ analysis included MRI scans of about 37,000 middle-aged men in the United Kingdom, along with their medical information and drinking habits, Everyday Health reported. They determined volume reductions in two parts of the brain potentially impacted by daily consumption of alcohol: White matter, which controls the senses and communication, and gray matter, which controls cognitive functions such as movement, emotions, and memories.
Normal brain aging is bad enough: Stuff like forgetting why we walked into the kitchen or having a word we want to use on the tips of our tongues. Who knew that happy hour could be speeding up the process?
Bartender, make that mimosa a virgin.
A big dose of meta-cine
The metaverse is big news in the tech world. For those who are less technologically inclined or haven’t thrown a few hundred dollars at a clunky virtual reality headset, the metaverse is a vaguely defined artificial reality world, brought to you by Facebo-, excuse us, Meta, where you hang out with people using a virtual avatar and do various activities, all from the comfort of your own home.
That’s not the most helpful definition, if we’re being honest, and that’s partially because the metaverse, as it’s being pushed by companies such as Meta, is very new and kind of a Wild West. No one really knows what it’ll be used for, but that’s not going to stop big business from pushing to secure their own corners of a new and exciting market, and that brings us to CVS, which is looking to become the first pharmacy in the metaverse.
Specifically, the company is looking to provide the entirety of its health care services – nonemergency medical care, wellness programs, nutrition advice, and counseling – to the metaverse. That makes sense. Telemedicine has become big during the pandemic, and bringing that care to the metaverse could work. Probably overcomplicated, since the sort of person who couldn’t figure out a video call to a doctor probably won’t be spending much time in the metaverse, but hey, if they can make it work, more power to them.
Where things get a bit silly is the online store. CVS looking to sell not only NFTs (because of course it is), but also downloadable virtual goods, including “prescription drugs, health, wellness, beauty, and personal care products,” according to the company’s claim to the U.S. Patent Trade Office. What exactly is a downloadable virtual prescription drug? Excellent question. We’re picturing holographic meatloaf, but the true answer is bound to be sillier than anything SpongeBob and friends could conjure.
Please don’t eat the winner
Hello friends. LOTME Sports welcomes you to the University of Toledo’s Glass Bowl for the wackiest virtual sporting event since Usain Bolt raced against a cheetah.
Hi, I’m Jim Nantz, and we’re here to witness the brainchild of Toledo physics professor Scott Lee, PhD, who posed an unusual question to his students: Is Usain Bolt faster than a 900-pound dinosaur?
Before we get started, though, I’ve got a quick question for my partner in today’s broadcast, Hall of Fame quarterback Peyton Manning: Why is someone who practices physics called a physicist when someone who practices medicine is known as a physician?
Jim, I’m prepared to talk about how Dr. Lee’s students used the concepts of 1D kinematics – displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration – to determine if a Jamaican sprinter could beat Dilophosaurus wetherilli in a hypothetical race. Heck, it took me 2 days to be able to pronounce Dilophosaurus wetherilli. Don’t get me started on etymology.
Fair enough, my friend. What else can you tell us?
In his article in The Physics Teacher, Dr. Lee noted that recent musculoskeletal models of vertebrate animals have shown that a dinosaur like Dilophosaurus could run about as fast as Usain Bolt when he set the world record of 9.58 seconds for 100 meters in 2009. You might remember Dilophosaurus from “Jurassic Park.” It was the one that attacked the guy who played Newman on “Seinfeld.”
Fascinating stuff, Peyton, but it looks like the race is about to start. And they’re off! Newton’s second law, which says that acceleration is determined by a combination of mass and force, gives the smaller Bolt an early advantage. The dinosaur takes longer to reach maximum running velocity and crosses the line 2 seconds behind the world’s fastest human. Amazing!
Be sure to tune in again next week, when tennis legend Serena Williams takes the court against a hungry velociraptor.
Turning back the egg timer
The idea of getting older can be scary. Wouldn’t it be nice if we could reverse the aging process? Nice, sure, but not possible. Well, it may just be possible for women undergoing assisted reproductive treatment.
It’s generally known that oocytes accumulate DNA damage over time as well, hindering fertility, but a lab in Jerusalem has found a way to reverse the age of eggs.
If you’re wondering how on Earth that was possible, here’s how. Scientists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem said that they found a previously unknown aging mechanism, which they were able to reverse using antiviral medications, they reported in Aging Cell.
The experiment started on mice eggs, but soon real human eggs were donated. After the procedure, the treated eggs appeared younger, with less of the DNA damage that comes from age. Sperm has not yet been used to test fertility so it is unclear if this will result in something game changing, but the investigators have high hopes.
“Many women are trying to get pregnant aged 40 or over, and we think this could actually increase their level of fertility,” senior investigator Michael Klutstein, PhD, told the Times of Israel. “Within 10 years, we hope to use antiviral drugs to increase fertility among older women.”
We’re counting on you, science! Do your thing!
Drink a day could age your brain
There are many things we can do daily to improve our health: Exercise, read a book, eat an apple (supposedly). Not drink a glass of red wine. Wait, not drink? That’s right. We were told that a glass of red wine each night was doing something good for our hearts, but it’s doing something bad to our brains: Aging them prematurely.
According to a recent study in Nature Communications, drinking half a pint of beer a day could age the brain of a 50-year-old by 6 months. A pint of beer equaled 2 years of aging and a pint and a half aged participants’ brains by 3.5 years.
Compared with people who didn’t drink, those who averaged about two pints of beer or two glasses of wine daily had brains aged 10 years older!
The researchers’ analysis included MRI scans of about 37,000 middle-aged men in the United Kingdom, along with their medical information and drinking habits, Everyday Health reported. They determined volume reductions in two parts of the brain potentially impacted by daily consumption of alcohol: White matter, which controls the senses and communication, and gray matter, which controls cognitive functions such as movement, emotions, and memories.
Normal brain aging is bad enough: Stuff like forgetting why we walked into the kitchen or having a word we want to use on the tips of our tongues. Who knew that happy hour could be speeding up the process?
Bartender, make that mimosa a virgin.
A big dose of meta-cine
The metaverse is big news in the tech world. For those who are less technologically inclined or haven’t thrown a few hundred dollars at a clunky virtual reality headset, the metaverse is a vaguely defined artificial reality world, brought to you by Facebo-, excuse us, Meta, where you hang out with people using a virtual avatar and do various activities, all from the comfort of your own home.
That’s not the most helpful definition, if we’re being honest, and that’s partially because the metaverse, as it’s being pushed by companies such as Meta, is very new and kind of a Wild West. No one really knows what it’ll be used for, but that’s not going to stop big business from pushing to secure their own corners of a new and exciting market, and that brings us to CVS, which is looking to become the first pharmacy in the metaverse.
Specifically, the company is looking to provide the entirety of its health care services – nonemergency medical care, wellness programs, nutrition advice, and counseling – to the metaverse. That makes sense. Telemedicine has become big during the pandemic, and bringing that care to the metaverse could work. Probably overcomplicated, since the sort of person who couldn’t figure out a video call to a doctor probably won’t be spending much time in the metaverse, but hey, if they can make it work, more power to them.
Where things get a bit silly is the online store. CVS looking to sell not only NFTs (because of course it is), but also downloadable virtual goods, including “prescription drugs, health, wellness, beauty, and personal care products,” according to the company’s claim to the U.S. Patent Trade Office. What exactly is a downloadable virtual prescription drug? Excellent question. We’re picturing holographic meatloaf, but the true answer is bound to be sillier than anything SpongeBob and friends could conjure.
Please don’t eat the winner
Hello friends. LOTME Sports welcomes you to the University of Toledo’s Glass Bowl for the wackiest virtual sporting event since Usain Bolt raced against a cheetah.
Hi, I’m Jim Nantz, and we’re here to witness the brainchild of Toledo physics professor Scott Lee, PhD, who posed an unusual question to his students: Is Usain Bolt faster than a 900-pound dinosaur?
Before we get started, though, I’ve got a quick question for my partner in today’s broadcast, Hall of Fame quarterback Peyton Manning: Why is someone who practices physics called a physicist when someone who practices medicine is known as a physician?
Jim, I’m prepared to talk about how Dr. Lee’s students used the concepts of 1D kinematics – displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration – to determine if a Jamaican sprinter could beat Dilophosaurus wetherilli in a hypothetical race. Heck, it took me 2 days to be able to pronounce Dilophosaurus wetherilli. Don’t get me started on etymology.
Fair enough, my friend. What else can you tell us?
In his article in The Physics Teacher, Dr. Lee noted that recent musculoskeletal models of vertebrate animals have shown that a dinosaur like Dilophosaurus could run about as fast as Usain Bolt when he set the world record of 9.58 seconds for 100 meters in 2009. You might remember Dilophosaurus from “Jurassic Park.” It was the one that attacked the guy who played Newman on “Seinfeld.”
Fascinating stuff, Peyton, but it looks like the race is about to start. And they’re off! Newton’s second law, which says that acceleration is determined by a combination of mass and force, gives the smaller Bolt an early advantage. The dinosaur takes longer to reach maximum running velocity and crosses the line 2 seconds behind the world’s fastest human. Amazing!
Be sure to tune in again next week, when tennis legend Serena Williams takes the court against a hungry velociraptor.
Turning back the egg timer
The idea of getting older can be scary. Wouldn’t it be nice if we could reverse the aging process? Nice, sure, but not possible. Well, it may just be possible for women undergoing assisted reproductive treatment.
It’s generally known that oocytes accumulate DNA damage over time as well, hindering fertility, but a lab in Jerusalem has found a way to reverse the age of eggs.
If you’re wondering how on Earth that was possible, here’s how. Scientists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem said that they found a previously unknown aging mechanism, which they were able to reverse using antiviral medications, they reported in Aging Cell.
The experiment started on mice eggs, but soon real human eggs were donated. After the procedure, the treated eggs appeared younger, with less of the DNA damage that comes from age. Sperm has not yet been used to test fertility so it is unclear if this will result in something game changing, but the investigators have high hopes.
“Many women are trying to get pregnant aged 40 or over, and we think this could actually increase their level of fertility,” senior investigator Michael Klutstein, PhD, told the Times of Israel. “Within 10 years, we hope to use antiviral drugs to increase fertility among older women.”
We’re counting on you, science! Do your thing!
Drink a day could age your brain
There are many things we can do daily to improve our health: Exercise, read a book, eat an apple (supposedly). Not drink a glass of red wine. Wait, not drink? That’s right. We were told that a glass of red wine each night was doing something good for our hearts, but it’s doing something bad to our brains: Aging them prematurely.
According to a recent study in Nature Communications, drinking half a pint of beer a day could age the brain of a 50-year-old by 6 months. A pint of beer equaled 2 years of aging and a pint and a half aged participants’ brains by 3.5 years.
Compared with people who didn’t drink, those who averaged about two pints of beer or two glasses of wine daily had brains aged 10 years older!
The researchers’ analysis included MRI scans of about 37,000 middle-aged men in the United Kingdom, along with their medical information and drinking habits, Everyday Health reported. They determined volume reductions in two parts of the brain potentially impacted by daily consumption of alcohol: White matter, which controls the senses and communication, and gray matter, which controls cognitive functions such as movement, emotions, and memories.
Normal brain aging is bad enough: Stuff like forgetting why we walked into the kitchen or having a word we want to use on the tips of our tongues. Who knew that happy hour could be speeding up the process?
Bartender, make that mimosa a virgin.
A big dose of meta-cine
The metaverse is big news in the tech world. For those who are less technologically inclined or haven’t thrown a few hundred dollars at a clunky virtual reality headset, the metaverse is a vaguely defined artificial reality world, brought to you by Facebo-, excuse us, Meta, where you hang out with people using a virtual avatar and do various activities, all from the comfort of your own home.
That’s not the most helpful definition, if we’re being honest, and that’s partially because the metaverse, as it’s being pushed by companies such as Meta, is very new and kind of a Wild West. No one really knows what it’ll be used for, but that’s not going to stop big business from pushing to secure their own corners of a new and exciting market, and that brings us to CVS, which is looking to become the first pharmacy in the metaverse.
Specifically, the company is looking to provide the entirety of its health care services – nonemergency medical care, wellness programs, nutrition advice, and counseling – to the metaverse. That makes sense. Telemedicine has become big during the pandemic, and bringing that care to the metaverse could work. Probably overcomplicated, since the sort of person who couldn’t figure out a video call to a doctor probably won’t be spending much time in the metaverse, but hey, if they can make it work, more power to them.
Where things get a bit silly is the online store. CVS looking to sell not only NFTs (because of course it is), but also downloadable virtual goods, including “prescription drugs, health, wellness, beauty, and personal care products,” according to the company’s claim to the U.S. Patent Trade Office. What exactly is a downloadable virtual prescription drug? Excellent question. We’re picturing holographic meatloaf, but the true answer is bound to be sillier than anything SpongeBob and friends could conjure.
Please don’t eat the winner
Hello friends. LOTME Sports welcomes you to the University of Toledo’s Glass Bowl for the wackiest virtual sporting event since Usain Bolt raced against a cheetah.
Hi, I’m Jim Nantz, and we’re here to witness the brainchild of Toledo physics professor Scott Lee, PhD, who posed an unusual question to his students: Is Usain Bolt faster than a 900-pound dinosaur?
Before we get started, though, I’ve got a quick question for my partner in today’s broadcast, Hall of Fame quarterback Peyton Manning: Why is someone who practices physics called a physicist when someone who practices medicine is known as a physician?
Jim, I’m prepared to talk about how Dr. Lee’s students used the concepts of 1D kinematics – displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration – to determine if a Jamaican sprinter could beat Dilophosaurus wetherilli in a hypothetical race. Heck, it took me 2 days to be able to pronounce Dilophosaurus wetherilli. Don’t get me started on etymology.
Fair enough, my friend. What else can you tell us?
In his article in The Physics Teacher, Dr. Lee noted that recent musculoskeletal models of vertebrate animals have shown that a dinosaur like Dilophosaurus could run about as fast as Usain Bolt when he set the world record of 9.58 seconds for 100 meters in 2009. You might remember Dilophosaurus from “Jurassic Park.” It was the one that attacked the guy who played Newman on “Seinfeld.”
Fascinating stuff, Peyton, but it looks like the race is about to start. And they’re off! Newton’s second law, which says that acceleration is determined by a combination of mass and force, gives the smaller Bolt an early advantage. The dinosaur takes longer to reach maximum running velocity and crosses the line 2 seconds behind the world’s fastest human. Amazing!
Be sure to tune in again next week, when tennis legend Serena Williams takes the court against a hungry velociraptor.
Turning back the egg timer
The idea of getting older can be scary. Wouldn’t it be nice if we could reverse the aging process? Nice, sure, but not possible. Well, it may just be possible for women undergoing assisted reproductive treatment.
It’s generally known that oocytes accumulate DNA damage over time as well, hindering fertility, but a lab in Jerusalem has found a way to reverse the age of eggs.
If you’re wondering how on Earth that was possible, here’s how. Scientists from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem said that they found a previously unknown aging mechanism, which they were able to reverse using antiviral medications, they reported in Aging Cell.
The experiment started on mice eggs, but soon real human eggs were donated. After the procedure, the treated eggs appeared younger, with less of the DNA damage that comes from age. Sperm has not yet been used to test fertility so it is unclear if this will result in something game changing, but the investigators have high hopes.
“Many women are trying to get pregnant aged 40 or over, and we think this could actually increase their level of fertility,” senior investigator Michael Klutstein, PhD, told the Times of Israel. “Within 10 years, we hope to use antiviral drugs to increase fertility among older women.”
We’re counting on you, science! Do your thing!
Commentary - TB treatment can be shortened for most children: Study
In spring 2022 the World Health Organization did release the new guidelines (module 5) for the shorter (4 month) regimen for 3-month- to 16-year-olds with nonsevere pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) limited to one lobe that is also smear-negative and at least presumed to be due to drug-susceptible M. tuberculosis. This regimen is NOT for children with clinically significant airway obstruction, cavitary disease, miliary TB, complex pleural effusion, or peripheral lymph node involvement. The newly recommended regimen consists of 8 weeks as an “intensive phase” (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, per local guidance) followed by 8 weeks of a “continuation phase” (isoniazid and rifampin only). Of note, the Turkova study had shown nearly identical adverse event and adherence rates – 8% and 94% – for both the short- and traditional-length regimens. The onerous multidrug treatment of uncomplicated TB in most children has become less onerous.
Caveat: The newly recommended 4-month schedule (March 2022) of traditional TB drugs is not to be confused with rifapentine-moxifloxacin–based 4-month regimen recommended by the WHO in June 2021 (CDC added guidance February 2022). This rifapentine-based regimen had been okayed for patients 12 years or older weighing at least 40 kg and also with drug-susceptible pulmonary TB, but no extrapulmonary involvement.
The new shorter regimen shows the value of trials in non-U.S. countries. The careful work in Africa and India has borne fruit that makes things easier for families, providers, and public health organizations.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.
In spring 2022 the World Health Organization did release the new guidelines (module 5) for the shorter (4 month) regimen for 3-month- to 16-year-olds with nonsevere pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) limited to one lobe that is also smear-negative and at least presumed to be due to drug-susceptible M. tuberculosis. This regimen is NOT for children with clinically significant airway obstruction, cavitary disease, miliary TB, complex pleural effusion, or peripheral lymph node involvement. The newly recommended regimen consists of 8 weeks as an “intensive phase” (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, per local guidance) followed by 8 weeks of a “continuation phase” (isoniazid and rifampin only). Of note, the Turkova study had shown nearly identical adverse event and adherence rates – 8% and 94% – for both the short- and traditional-length regimens. The onerous multidrug treatment of uncomplicated TB in most children has become less onerous.
Caveat: The newly recommended 4-month schedule (March 2022) of traditional TB drugs is not to be confused with rifapentine-moxifloxacin–based 4-month regimen recommended by the WHO in June 2021 (CDC added guidance February 2022). This rifapentine-based regimen had been okayed for patients 12 years or older weighing at least 40 kg and also with drug-susceptible pulmonary TB, but no extrapulmonary involvement.
The new shorter regimen shows the value of trials in non-U.S. countries. The careful work in Africa and India has borne fruit that makes things easier for families, providers, and public health organizations.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.
In spring 2022 the World Health Organization did release the new guidelines (module 5) for the shorter (4 month) regimen for 3-month- to 16-year-olds with nonsevere pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) limited to one lobe that is also smear-negative and at least presumed to be due to drug-susceptible M. tuberculosis. This regimen is NOT for children with clinically significant airway obstruction, cavitary disease, miliary TB, complex pleural effusion, or peripheral lymph node involvement. The newly recommended regimen consists of 8 weeks as an “intensive phase” (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, per local guidance) followed by 8 weeks of a “continuation phase” (isoniazid and rifampin only). Of note, the Turkova study had shown nearly identical adverse event and adherence rates – 8% and 94% – for both the short- and traditional-length regimens. The onerous multidrug treatment of uncomplicated TB in most children has become less onerous.
Caveat: The newly recommended 4-month schedule (March 2022) of traditional TB drugs is not to be confused with rifapentine-moxifloxacin–based 4-month regimen recommended by the WHO in June 2021 (CDC added guidance February 2022). This rifapentine-based regimen had been okayed for patients 12 years or older weighing at least 40 kg and also with drug-susceptible pulmonary TB, but no extrapulmonary involvement.
The new shorter regimen shows the value of trials in non-U.S. countries. The careful work in Africa and India has borne fruit that makes things easier for families, providers, and public health organizations.
Christopher J. Harrison, MD, is professor, University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, department of medicine, infectious diseases section, Kansas City. He has no financial conflicts of interest.
‘Baby-friendly’ steps help women meet prenatal breastfeeding goals
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
A first-ever study of the effect of evidence-based maternity care practices on prenatal breastfeeding intentions in women from low-income U.S. households shows that the use of “baby-friendly steps” during birth hospitalization made it possible for almost half to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month.
Analyses of national data from a longitudinal study of 1,080 women enrolled in the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) revealed that 47% were able to meet their prenatal intention to breastfeed without formula or other milk for at least 30 days.
The odds of meeting prenatal breastfeeding intentions more than quadrupled when babies received only breast milk (risk ratio, 4.4; 95% confidence interval, 3.4-5.7), the study showed. Breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth was also associated with greater likelihood of breastfeeding success (RR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.0-1.6).
The study, led by Heather C. Hamner, PhD, MS, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, , Atlanta, was reported online in Pediatrics.
“This study confirms the relationship between experiencing maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding and meeting one’s breastfeeding intentions, and adds evidence specifically among low-income women, who are known to be at higher risk of not breastfeeding,” the study authors wrote.
Women from low-income households often face additional barriers to meeting their breastfeeding goals, including lack of access to professional lactation services, Dr. Hamner said in an interview. “We want physicians to know how important maternity care practices supportive of breastfeeding are to helping all women achieve their breastfeeding goals. Physicians can be champions for implementation of evidence-based maternity care practices in the hospitals and practices in which they work.”
Dr. Hamner emphasized that physicians need to discuss the importance of breastfeeding with patients and their families, brief them on what to expect in the maternity care setting, and ensure women are connected to lactation resources. The American Academy of Pediatrics is working to increase physician capacity to support breastfeeding through the Physician Engagement and Training Focused on Breastfeeding project.
For the study, Dr. Hamner and colleagues analyzed data from the longitudinal WIC Infant and Toddler Feeding Practices Study-2 (ITFPS-2), which assessed the impact of 6 steps from a 10-step maternity care protocol known as The Ten Steps To Successful Breastfeeding. These steps are part of the worldwide Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative (BFHI), which has been shown to improve rates of breastfeeding initiation, duration, and exclusivity.
After adjusting for sociodemographic and other factors, the study authors estimated risk ratios for associations between each of six maternity care practices assessed in ITFPS-2 and the success of women who reported an intention to breastfeed exclusively for 1 month. The six steps included initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth (step 4), showing moms how to breastfeed and maintain lactation (step 5), giving no food or drink other than breast milk unless medically indicated (step 6), rooming-in (step 7), breastfeeding on demand (step 8), and giving no pacifiers (step 9).
The analyses showed that only steps 4 and 6 – initiating breastfeeding at birth and giving only breast milk – remained significantly associated with meeting breastfeeding intentions. The results also revealed a dose-response relationship between the number of baby steps experienced during birth hospitalization and the likelihood of meeting breastfeeding goals, a finding in keeping with previous studies. In women who experienced all six steps, for example, 76% were breastfeeding exclusively at 1 month, compared with 16% of those who experienced zero to two steps.
Although the dose-response relationship did not appear to differ significantly by race or ethnicity, it was driven primarily by a hospital policy of providing infant formula or other supplementation, the study authors found. Notably, 44% of women reported that their infant had been fed something other than breast milk while in the hospital, and about 60% said they stopped breastfeeding earlier than intended.
“This finding reiterates the importance of limiting in-hospital formula or other supplementation of breastfed infants to only those with medical necessity,” Dr. Hamner and colleagues said.
Despite improvements in maternity care practices that promote breastfeeding, including an increase in the number of births occurring in U.S. hospitals with a baby-friendly designation, many women continue to experience significant barriers to breastfeeding, the investigators pointed out. Currently, there are 592 baby-friendly hospitals in the United States, representing 28.29% of annual births.
“I think more hospitals becoming baby friendly would really help,” Mary Franklin, DNP, CNM, assistant professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. More needs to be done to support women during birth hospitalization and after they return home, so they can continue to breastfeed for “longer than the initial 6 weeks,” added Dr. Franklin, who is also director of the nurse midwifery and women’s health NP program.
The AAP recommends exclusive breastfeeding for about 6 months followed by complementary food introduction and continued breastfeeding through 12 months or beyond.
Like Dr. Hamner, Dr. Franklin emphasized that physicians have an important role to play in the initiation, duration, and exclusivity of breastfeeding. This includes promoting enrichment of the pregnancy experience with prenatal education and increased support from health care providers and peers. At delivery, obstetricians can delay cord clamping to facilitate early breastfeeding. They can also support the elimination of the central nursery in hospitals so that mother and baby stay together from birth. In addition, prescriptions can be written for breast pumps, which are covered by Medicaid.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Hamner and coauthors disclosed having no potential financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Franklin also disclosed having no financial conflicts of interest.
FROM PEDIATRICS