User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Physician pleads guilty to 52 counts in opioid scheme
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Comment & Controversy
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Addressing OR sustainability: How we can decrease waste and emissions
In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
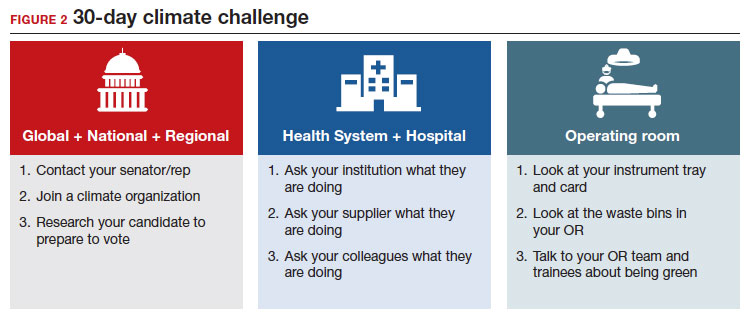
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●

In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●

- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
Toxic chemicals we consume without knowing it
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians and clinicians should be required to get flu shots: Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Doxy PEP does not lower risk of STIs in cisgender women
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis (Doxy PEP) in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and transgender women do not appear to extend to cisgender women, who have disproportionately high rates of infection in many regions.
“This was the first trial to evaluate doxycycline PEP for cisgender women,” said first author Jenell Stewart, DO, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, in discussing the findings at a press conference at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
“Unfortunately, our primary outcome was not statistically significant – we did not see a reduction in STIs among cisgender women, which is in stark contrast to [reported effects] among cisgender men and transgender women,” she said.
The findings are from a study of 449 nonpregnant cisgender women (mean age, 24 years) in Kenya who had been taking daily oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for a median of about 7 months.
The women were randomly assigned to receive either Doxy PEP 200 mg, to be taken within 72 hours of sex (n = 224), or standard care, which included quarterly screening and treatment of STIs (n = 225).
Of the women, 36.7% reported transactional sex at enrollment; their baseline prevalence of STIs was 17.9%, including 14.1% with chlamydia, 3.8% gonorrhea, and 0.4% syphilis. There were no differences between the study groups.
In surveys, 78% of the women reported adherence to the use of Doxy PEP; they took the prophylaxis at least as many days as they had sex.
Nevertheless, there was no significant difference in the incidence of STIs, reported over 1 year, at quarterly visits that included genital STI testing, between groups, with 50 patients in the Doxy PEP group and 59 in the standard screening group developing STIs (relative risk, 0.88; P = .51).
Of the infections, 85 were chlamydia, including 35 in the Doxy PEP group and 50 with standard of care, while 31 were gonorrhea, including 19 in the Doxy PEP group and 12 with standard of care; 8 had both infections, and there was 1 syphilis infection.
The results were consistent across subanalyses of patients grouped according to STI, who became pregnant (n = 80), or sorted by other factors including age, contraceptive use, transactional sex, and STI at baseline.
None of the women developed HIV, and there were no serious events associated with the Doxy PEP treatment.
Cisgender women bear ‘highest burden’ of STIs
The findings are disappointing in light of the higher rates of STIs among cisgender women, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that women also disproportionately bear the long-term consequences of STIs.
“For example, each year, untreated sexually transmitted diseases cause infertility in at least 20,000 women in the United States, and a pregnant woman is highly likely to pass syphilis unto her unborn baby if left untested or untreated,” the CDC reports.
The STI rates are particularly high for women taking HIV PrEP in regions like East Africa, where rates of STIs among cisgender women in many cases are higher than rates for men taking PrEP in high income countries, Dr. Stewart said.
Previous studies of Doxy PEP in men and transgender women taking HIV PrEP, including new research presented at CROI, have shown highly encouraging reductions in STIs, at rates of up to approximately 80% for chlamydia and syphilis.
Adherence, anatomy, resistance
The key theories for the lack of a prevention of infections in cisgender women surround the issues of resistances, as well as anatomy and adherence, said Dr. Stewart.
In terms of bacterial resistances, while initial testing in a limited number of samples the study found no evidence of markers of resistance for chlamydia, all of the gonorrhea samples did show tetracycline-resistant N gonorrhea at baseline and follow-up in both groups.
Regarding anatomic differences, doxycycline may not prevent STIs in endocervical tissue among cisgender women, Dr. Stewart noted. Women are known to be at higher risk of infection because the lining of the vagina is thinner than the skin of the penis, allowing for easier penetration of bacteria and viruses.
The study was designed to optimize adherence to Doxy PEP. Measures included monitoring with weekly text message surveys, in which the women reported a high rate of adherence.
The overall retention rate in the study was high; as many as 97% of the quarterly follow-up visits were completed, including 95% in the Doxy PEP group and 98% of the standard care group. The response rate for the weekly surveys was 81%.
Of note, women reported the use of the treatment to be “imperfect,” suggesting social problems, such as biases toward the use of the prophylaxis.
The results underscore the need for ongoing efforts to make sure no groups of patients are left behind as interventions advance, Dr. Stewart said.
“The burden of STIs on cisgender women is large and growing,” she concluded. “STI prevention interventions are needed.”
Commenting on the study, Renee A. Heffron, PhD, MPH, said the findings “are somewhat surprising because results from trials in other populations have been positive.
“But cisgender women are exposed through the cervix, and this tissue is different from rectal or urethral tissue,” Dr. Heffron, a professor at the department of medicine and director of the Center for AIDS Research at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, told this news organization.
Further findings from the research should help shed light on key issues of adherence and drug concentration levels in cervical tissue, she added.
“For cisgender women, these data are the first and the beginning of understanding whether this is a viable strategy,” Dr. Heffron said.
“We have more to learn to better understand the results from the trial main outcomes, and if there are tweaks to this strategy that would improve efficacy.”
The authors and Dr. Heffron have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CROI 2023
Ninety-four women allege a Utah doctor sexually assaulted them. Here’s why a judge threw out their case
This article was produced for ProPublica’s Local Reporting Network in partnership with The Salt Lake Tribune.
At 19 years old and about to be married, Stephanie Mateer went to an ob.gyn. within walking distance of her student housing near Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah.
She wanted to start using birth control, and she was looking for guidance about having sex for the first time on her 2008 wedding night.
Ms. Mateer was shocked, she said, when David Broadbent, MD, reached under her gown to grab and squeeze her breasts, started a vaginal exam without warning, then followed it with an extremely painful examination of her rectum.
She felt disgusted and violated, but doubt also crept in. She told herself she must have misinterpreted his actions, or that she should have known that he would do a rectal exam. Raised as a member of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, she said she was taught to defer to men in leadership.
“I viewed him as being a man in authority,” Ms. Mateer said. “He’s a doctor.”
It was years, she said, before she learned that her experience was in a sharp contrast to the conduct called for in professional standards, including that doctors use only their fingertips during a breast exam and communicate clearly what they are doing in advance, to gain the consent of their patients. Eventually, she gave her experience another name: sexual assault.
Utah judges, however, have called it health care.
And that legal distinction means Utahns like Ms. Mateer who decide to sue a health care provider for alleged sexual abuse are treated more harshly by the court system than plaintiffs who say they were harmed in other settings.
The chance to go to civil court for damages is an important option for survivors, experts say. While a criminal conviction can provide a sense of justice, winning a lawsuit can help victims pay for the therapy and additional support they need to heal after trauma.
Ms. Mateer laid out her allegations in a lawsuit that she and 93 other women filed against Dr. Broadbent last year. But they quickly learned they would be treated differently than other sexual assault survivors.
Filing their case, which alleged the Utah County doctor sexually assaulted them over the span of his 47-year career, was an empowering moment, Ms. Mateer said. But a judge threw out the lawsuit without even considering the merits, determining that because their alleged assailant is a doctor, the case must be governed by medical malpractice rules rather than those that apply to cases of sexual assault.
Under Utah’s rules of medical malpractice, claims made by victims who allege a health care worker sexually assaulted them are literally worth less than lawsuits brought by someone who was assaulted in other settings – even if a jury rules in their favor, a judge is required to limit how much money they receive. And they must meet a shorter filing deadline.
“It’s just crazy that a doctor can sexually assault women and then be protected by the white coat,” Ms. Mateer said. “It’s just a really scary precedent to be calling sexual assault ‘health care.’ ”
Because of the judge’s ruling that leaves them with a shorter window in which to file, some of Dr. Broadbent’s accusers stand to lose their chance to sue. Others were already past that deadline but had hoped to take advantage of an exception that allows plaintiffs to sue if they can prove that the person who harmed them had covered up the wrongdoing and if they discovered they had been hurt within the previous year.
As a group, the women are appealing the ruling to the Utah Supreme Court, which has agreed to hear the case. This decision will set a precedent for future sexual assault victims in Utah.
Dr. Broadbent’s attorney, Chris Nelson, declined an interview request but wrote in an email: “We believe that the allegations against Dr. Broadbent are without merit and will present our case in court. Given that this is an active legal matter, we will not be sharing any details outside the courtroom.”
States have varying legal definitions of medical malpractice, but it’s generally described as treatment that falls short of accepted standards of care. That includes mistakes, such as a surgeon leaving a piece of gauze inside a patient.
The Utah Supreme Court has ruled that a teenage boy was receiving health care when he was allowed to climb a steep, snow-dusted rock outcrop as part of wilderness therapy. When he broke his leg, he could only sue for medical malpractice, so the case faced shorter filing deadlines and lower monetary caps. Similarly, the court has ruled that a boy harmed by another child while in foster care was also bound by medical malpractice law.
Despite these state Supreme Court rulings, Utah legislators have so far not moved to narrow the wording of the malpractice act.
The lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent – and the questions it raises about the broadness of Utah’s medical malpractice laws – comes during a national reckoning with how sexual assault survivors are treated by the law. Legislators in several states have been rewriting laws to give sexual assault victims more time to sue their attackers, in response to the growing cultural understanding of the impact of trauma and the barriers to reporting. Even in Utah, those who were sexually abused as children now have no deadline to file suits against their abusers.
That isn’t true for sexual abuse in a medical setting, where cases must be filed within 2 years of the assault.
These higher hurdles should not exist in Utah, said state Sen. Mike K. McKell, a Utah County Republican who works as a personal injury attorney. He is trying to change state law to ensure that sexual assault lawsuits do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act, a law designed to cover negligence and poor care, not necessarily deliberate actions like an assault.
“Sexual assault, to me, is not medical care. Period,” he said. “It’s sad that we need to clarify that sexual assault is not medical care. But trying to tie sexual assault to a medical malpractice [filing deadline] – it’s just wrong.”
‘Your husband is a lucky man’
Ms. Mateer had gone to Dr. Broadbent in 2008 for a premarital exam, a uniquely Utah visit often scheduled by young women who are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Leaders of the faith, which is predominant in Utah, focus on chastity when speaking to young, unmarried people about sex, and public schools have typically focused on abstinence-based sex education. So for some, these visits are the first place they learn about sexual health.
Young women who get premarital exams are typically given a birth control prescription, but the appointments can include care that’s less common for healthy women in other states – such as doctors giving them vaginal dilators to stretch their tissues before their wedding nights.
That’s what Ms. Mateer was expecting when she visited Dr. Broadbent’s office. The ob.gyn. had been practicing for decades in his Provo clinic nestled between student housing apartments across the street from Brigham Young University, which is owned by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
So Ms. Mateer was “just totally taken aback,” she said, by the painful examination and by Dr. Broadbent snapping off his gloves after the exam and saying, “Your husband is a lucky man.”
She repeated that remark in her legal filing, along with the doctor’s advice for her: If she bled during intercourse, “just do what the Boy Scouts do and apply pressure.”
“The whole thing was like I’m some object for my husband to enjoy and let him do whatever he wants,” Ms. Mateer said. “It was just very violating and not a great way to start my sexual relationship with my new husband, with these ideas in mind.”
Ms. Mateer thought back to that visit over the years, particularly when she went to other ob.gyns. for health care. Her subsequent doctors, she said, never performed a rectal exam and always explained to her what they were doing and how it would feel, and asked for her consent.
She thought about Dr. Broadbent again in 2017, as the #MeToo movement gained momentum, and looked him up online. Ms. Mateer found reviews from other women who described Dr. Broadbent doing rough examinations without warning that left them feeling the same way she had years before.
Then in December 2021, she spoke out on “Mormon Stories,” a podcast where people who have left or have questioned their Latter-day Saint faith share their life stories. In the episode, she described the painful way he examined her, how it left her feeling traumatized, and her discovery of the reviews that echoed her experience.
“He’s on University Avenue, in Provo, giving these exams to who knows how many naive Mormon 18-year-old, 19-year-old girls who are getting married. … They are naive and they don’t know what to expect,” she said on the podcast. “His name is Dr. David Broadbent.”
After the podcast aired, Ms. Mateer was flooded with messages from women who heard the episode and reached out to tell her that Dr. Broadbent had harmed them, too.
Ms. Mateer and three other women decided to sue the ob.gyn., and in the following weeks and months, 90 additional women joined the lawsuit they filed in Provo. Many of the women allege Dr. Broadbent inappropriately touched their breasts, vaginas and rectums, hurting them, without warning or explanation. Some said he used his bare hand – instead of using a speculum or gloves – during exams. One alleged that she saw he had an erection while he was touching her.
Dr. Broadbent’s actions were not medically necessary, the women allege, and were instead “performed for no other reason than his own sexual gratification.”
The lawsuit also named as defendants two hospitals where Dr. Broadbent had delivered babies and where some of the women allege they were assaulted. The suit accused hospital administrators of knowing about Dr. Broadbent’s inappropriate behavior and doing nothing about it.
After he was sued, the ob.gyn. quickly lost his privileges at the hospitals where he worked. Dr. Broadbent, now 75, has also voluntarily put his medical license in Utah on hold while police investigate 29 reports of sexual assault made against him.
Prosecutors are still considering whether to criminally prosecute Dr. Broadbent. Provo police forwarded more than a dozen reports to the Utah County attorney’s office in November, which are still being reviewed by a local prosecutor.
A spokesperson for Intermountain Health, the nonprofit health system that owns Utah Valley Hospital, where some of the women in the suit were treated, did not respond to specific questions. The spokesperson emphasized in an email that Dr. Broadbent was an “independent physician” who was not employed by Utah Valley Hospital, adding that most of the alleged incidents took place at Dr. Broadbent’s medical office.
A representative for MountainStar Healthcare, another hospital chain named as a defendant, denied knowledge of any allegations of inappropriate conduct reported to its hospital and also emphasized that Dr. Broadbent worked independently, not as an employee.
“Our position since this lawsuit was filed has been that we were inappropriately named in this suit,” said Brittany Glas, the communications director for MountainStar.
Debating whether sexual abuse is health care
For the women who sued Dr. Broadbent, their case boiled down to a key question: Were the sexual assaults they say they experienced part of their health care? There was a lot hanging on the answer.
If their case was considered medical malpractice, they would be limited in how much money they could receive in damages for their pain and suffering. If a jury awarded them millions of dollars, a judge would be required by law to cut that down to $450,000. There’s no cap on these monetary awards for victims sexually assaulted in other settings.
They would also be required to go before a panel, which includes a doctor, a lawyer and a community member, that decides whether their claims have merit. This step, aimed at resolving disputes out of court, does not block anyone from suing afterward. But it does add cost and delay, and for sexual assault victims who’ve gone through this step, it has been another time they were required to describe their experiences and hope they were believed.
The shorter, 2-year filing deadline for medical malpractice cases can also be a particular challenge for those who have been sexually abused because research shows that it’s common to delay reporting such assaults.
Nationwide, these kinds of malpractice reforms were adopted in the 1970s amid concerns – largely driven by insurance companies – that the cost of health care was rising because of frivolous lawsuits and “runaway juries” doling out multimillion-dollar payouts.
Restricting the size of malpractice awards and imposing other limits, many argued, were effective ways to balance compensating injured patients with protecting everyone’s access to health care.
State laws are generally silent on whether sexual assault lawsuits should be covered by malpractice laws, leaving courts to grapple with that question and leading to different conclusions across the country. The Tribune and ProPublica identified at least six cases in which state appellate judges sharply distinguished between assault and health care in considering whether malpractice laws should apply to sexual assault–related cases.
An appellate court in Wisconsin, for example, ruled in 1993 that a physician having an erection and groping a patient was a purposeful harm, not medical malpractice.
Florida’s law is similar to Utah’s, defining allegations “arising” out of medical care as malpractice. While an earlier ruling did treat sexual assault in a health care setting as medical malpractice, appellate rulings in the last decade have moved away from that interpretation. In 2005, an appellate court affirmed a lower-court ruling that when a dentist “stopped providing dental treatment to the victim and began sexually assaulting her, his professional services ended.”
Similarly, a federal judge in Iowa in 1995 weighed in on the meaning of “arising” out of health care: “Rape is not patient care activity,” he wrote.
But Utah’s malpractice law is so broad that judges have been interpreting it as covering any act performed by a health care provider during medical care. The law was passed in 1976 and is popular with doctors and other health care providers, who have lobbied to keep it in place – and who use it to get lawsuits dismissed.
One precedent-setting case in Utah shows the law’s power to safeguard health care providers and was an important test of how Utah defines medical malpractice. Jacob Scott sued WinGate Wilderness Therapy after the teen broke his leg in 2015 when a hiking guide from the center allowed him to climb up and down a steep outcrop in Utah’s red rock desert.
His parents are both lawyers, and after they found that Utah had a 4-year deadline for filing a personal injury lawsuit, court records said, they decided to prioritize “getting Jacob better” for the first 2 years after the accident. But when Mr. Scott’s suit was filed, WinGate argued it was too late – based on the shorter, 2-year deadline for medical malpractice claims.
Mr. Scott’s attorneys scoffed. “Interacting with nature,” his attorneys argued, “is not health care even under the broadest interpretation of … the Utah Health Care Malpractice Act.”
A judge disagreed and threw out Mr. Scott’s case. The Utah Supreme Court unanimously upheld that ruling in 2021.
“We agree with WinGate,” the justices wrote, “that it was acting as a ‘health care provider’ and providing ‘health care’ when Jacob was hiking and rock climbing.”
Last summer, the women who had sued Dr. Broadbent and the two hospitals watched online as lawyers debated whether the abuse they allegedly suffered was health care.
At the hearing, attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued that the women should have pursued a medical malpractice case, which required them to first notify Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals that they wanted to sue. They also argued to Judge Robert Lunnen that the case couldn’t move forward because the women hadn’t gone before a prelitigation panel.
Attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued, one after the other, that the painful and traumatic exams the women described arose out of health care treatments.
“Accepting the allegations of the complaint as true – as we must for purposes of this proceeding – we have to assume that [Broadbent] did something that was medically unnecessary, medically inappropriate,” argued David Jordan, a lawyer for Intermountain Health.
“But it doesn’t change the fact that it’s an act performed to a patient, during the patient’s treatment,” he said. “Because that’s what the patient is doing in the doctor’s office. They’re there for treatment.”
The attorney team for the women pushed back. Terry Rooney argued that if Dr. Broadbent’s actions fell under medical malpractice laws, many women would be knocked out of the case because of the age of their claims, and those who remained would be limited in the amount of money in damages they could receive.
“That’s really what this is about,” he argued. “And so it’s troubling – quite frankly it’s shocking to me – that we’re debating heavily the question of whether sexual abuse is health care.”
The judge mulled the issue for months. Judge Lunnen wrote in a September ruling that if the allegations were true, Dr. Broadbent’s treatment of his patients was “insensitive, disrespectful and degrading.”
But Utah law is clear, he said. Malpractice law covers any act or treatment performed by any health care provider during the patient’s medical care. The women had all been seeking health care, Judge Lunnen wrote, and Dr. Broadbent was providing that when the alleged assaults happened.
Their lawsuit was dismissed.
‘I felt defeated’
Brooke, another plaintiff who alleges Dr. Broadbent groped her, remembers feeling sick on the June day she watched the attorneys arguing. She asked to be identified by only her first name for this story.
She alleges Dr. Broadbent violated her in December 2008 while she was hospitalized after experiencing complications with her first pregnancy.
The nearest hospital to her rural town didn’t have a special unit to take care of premature babies, and her doctors feared she might need to deliver her son 6 weeks early. So Brooke had been rushed by ambulance over a mountain pass in a snowstorm to Utah Valley Hospital.
Brooke and her husband were terrified, she said, when they arrived at the Provo hospital. Dr. Broadbent happened to be the doctor on call. With Brooke’s husband and brother-in-law in the room, Dr. Broadbent examined her late that evening, she said, listening to her chest with a stethoscope.
The doctor then suddenly grabbed her breasts, she recalled – his movements causing her hospital gown to fall to expose her chest. She recounted this experience in her lawsuit, saying it was nothing like the breast exams she has had since.
“It was really traumatizing,” she said. “I was mortified. My husband and brother-in-law – we just didn’t say anything about it because it was so uncomfortable.”
Brooke voiced concerns to the nurse manager, and she was assigned a new doctor.
She gave birth to a healthy baby a little more than a month later, at the hospital near her home.
Hearing the judge’s ruling 14 years later, Brooke felt the decision revealed how Utah’s laws are broken.
“I was frustrated,” she said, “and I felt defeated. … I thought justice is not on our side with this.”
If the Utah Supreme Court rules that these alleged sexual assaults should legally be considered health care, the women will likely refile their claims as a medical malpractice lawsuit, said their attorney, Adam Sorensen. But it would be a challenge to keep all 94 women in the case, he said, due to the shorter filing window. Only two women in the lawsuit allege that they were harmed within the last 2 years.
The legal team for the women would have to convince a judge that their claims should still be allowed because they only recently discovered they were harmed. But based on previous rulings, Mr. Sorensen believes the women will have a better chance to win that argument if the civil suit remained a sexual assault case.
Regardless of what happens in their legal case, the decision by Brooke and the other women to come forward could help change state law for victims who come after them.
Recently, Mr. McKell, the state senator, introduced legislation to clarify that civil lawsuits alleging sexual assault by a health care worker do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act.
“I don’t think it’s a close call. Sexual assault is not medical care,” he said. “I know we’ve got some bizarre rulings that have come down through our courts in Utah.”
Both an association of Utah trial lawyers and the Utah Medical Association, which lobbies on behalf of the state’s physicians, support this reform.
“We support the fact that sexual assault should not be part of health care medical malpractice,” said Michelle McOmber, the CEO for the Utah Medical Association. “Sexual assault should be sexual assault, regardless of where it happens or who’s doing it. Sexual assault should be in that category, which is separate from actual health care. Because it’s not health care.”
MountainStar doesn’t have a position on the bill, Ms. Glas said. “If the laws were to change via new legislation and/or interpretation by the courts, we would abide by and comply with those new laws.”
But lawmakers are running out of time. With only a short time left in Utah’s legislative session, state senate and house leaders have so far prioritized passing new laws banning gender-affirming health care for transgender youths and creating a controversial school voucher program that will provide taxpayer funds for students to attend private school.
Utah lawmakers were also expected to consider a dramatic change for other sexual assault victims: a bill that would remove filing deadlines for civil lawsuits brought by people abused as adults. But that bill stalled before it could be debated.
Brooke had been eager to share her story, she said, in hopes it would help the first four women who’d come forward bolster their lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent. She later joined the case as a plaintiff. She read in their lawsuit about one woman who complained about him to the same hospital 7 years before she did, and about another woman who said Dr. Broadbent similarly molested her 2 days after Brooke had expressed her own concern.
“That bothered me so much,” she said. “It didn’t have to happen to all these women.”
Brooke doubts she’ll get vindication in a courtroom. Justice for her, she suspects, won’t come in the form of a legal ruling or a settlement against the doctor she says hurt her years ago.
Instead, she said, “maybe justice looks like changing the laws for future women.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive the biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
This article was produced for ProPublica’s Local Reporting Network in partnership with The Salt Lake Tribune.
At 19 years old and about to be married, Stephanie Mateer went to an ob.gyn. within walking distance of her student housing near Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah.
She wanted to start using birth control, and she was looking for guidance about having sex for the first time on her 2008 wedding night.
Ms. Mateer was shocked, she said, when David Broadbent, MD, reached under her gown to grab and squeeze her breasts, started a vaginal exam without warning, then followed it with an extremely painful examination of her rectum.
She felt disgusted and violated, but doubt also crept in. She told herself she must have misinterpreted his actions, or that she should have known that he would do a rectal exam. Raised as a member of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, she said she was taught to defer to men in leadership.
“I viewed him as being a man in authority,” Ms. Mateer said. “He’s a doctor.”
It was years, she said, before she learned that her experience was in a sharp contrast to the conduct called for in professional standards, including that doctors use only their fingertips during a breast exam and communicate clearly what they are doing in advance, to gain the consent of their patients. Eventually, she gave her experience another name: sexual assault.
Utah judges, however, have called it health care.
And that legal distinction means Utahns like Ms. Mateer who decide to sue a health care provider for alleged sexual abuse are treated more harshly by the court system than plaintiffs who say they were harmed in other settings.
The chance to go to civil court for damages is an important option for survivors, experts say. While a criminal conviction can provide a sense of justice, winning a lawsuit can help victims pay for the therapy and additional support they need to heal after trauma.
Ms. Mateer laid out her allegations in a lawsuit that she and 93 other women filed against Dr. Broadbent last year. But they quickly learned they would be treated differently than other sexual assault survivors.
Filing their case, which alleged the Utah County doctor sexually assaulted them over the span of his 47-year career, was an empowering moment, Ms. Mateer said. But a judge threw out the lawsuit without even considering the merits, determining that because their alleged assailant is a doctor, the case must be governed by medical malpractice rules rather than those that apply to cases of sexual assault.
Under Utah’s rules of medical malpractice, claims made by victims who allege a health care worker sexually assaulted them are literally worth less than lawsuits brought by someone who was assaulted in other settings – even if a jury rules in their favor, a judge is required to limit how much money they receive. And they must meet a shorter filing deadline.
“It’s just crazy that a doctor can sexually assault women and then be protected by the white coat,” Ms. Mateer said. “It’s just a really scary precedent to be calling sexual assault ‘health care.’ ”
Because of the judge’s ruling that leaves them with a shorter window in which to file, some of Dr. Broadbent’s accusers stand to lose their chance to sue. Others were already past that deadline but had hoped to take advantage of an exception that allows plaintiffs to sue if they can prove that the person who harmed them had covered up the wrongdoing and if they discovered they had been hurt within the previous year.
As a group, the women are appealing the ruling to the Utah Supreme Court, which has agreed to hear the case. This decision will set a precedent for future sexual assault victims in Utah.
Dr. Broadbent’s attorney, Chris Nelson, declined an interview request but wrote in an email: “We believe that the allegations against Dr. Broadbent are without merit and will present our case in court. Given that this is an active legal matter, we will not be sharing any details outside the courtroom.”
States have varying legal definitions of medical malpractice, but it’s generally described as treatment that falls short of accepted standards of care. That includes mistakes, such as a surgeon leaving a piece of gauze inside a patient.
The Utah Supreme Court has ruled that a teenage boy was receiving health care when he was allowed to climb a steep, snow-dusted rock outcrop as part of wilderness therapy. When he broke his leg, he could only sue for medical malpractice, so the case faced shorter filing deadlines and lower monetary caps. Similarly, the court has ruled that a boy harmed by another child while in foster care was also bound by medical malpractice law.
Despite these state Supreme Court rulings, Utah legislators have so far not moved to narrow the wording of the malpractice act.
The lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent – and the questions it raises about the broadness of Utah’s medical malpractice laws – comes during a national reckoning with how sexual assault survivors are treated by the law. Legislators in several states have been rewriting laws to give sexual assault victims more time to sue their attackers, in response to the growing cultural understanding of the impact of trauma and the barriers to reporting. Even in Utah, those who were sexually abused as children now have no deadline to file suits against their abusers.
That isn’t true for sexual abuse in a medical setting, where cases must be filed within 2 years of the assault.
These higher hurdles should not exist in Utah, said state Sen. Mike K. McKell, a Utah County Republican who works as a personal injury attorney. He is trying to change state law to ensure that sexual assault lawsuits do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act, a law designed to cover negligence and poor care, not necessarily deliberate actions like an assault.
“Sexual assault, to me, is not medical care. Period,” he said. “It’s sad that we need to clarify that sexual assault is not medical care. But trying to tie sexual assault to a medical malpractice [filing deadline] – it’s just wrong.”
‘Your husband is a lucky man’
Ms. Mateer had gone to Dr. Broadbent in 2008 for a premarital exam, a uniquely Utah visit often scheduled by young women who are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Leaders of the faith, which is predominant in Utah, focus on chastity when speaking to young, unmarried people about sex, and public schools have typically focused on abstinence-based sex education. So for some, these visits are the first place they learn about sexual health.
Young women who get premarital exams are typically given a birth control prescription, but the appointments can include care that’s less common for healthy women in other states – such as doctors giving them vaginal dilators to stretch their tissues before their wedding nights.
That’s what Ms. Mateer was expecting when she visited Dr. Broadbent’s office. The ob.gyn. had been practicing for decades in his Provo clinic nestled between student housing apartments across the street from Brigham Young University, which is owned by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
So Ms. Mateer was “just totally taken aback,” she said, by the painful examination and by Dr. Broadbent snapping off his gloves after the exam and saying, “Your husband is a lucky man.”
She repeated that remark in her legal filing, along with the doctor’s advice for her: If she bled during intercourse, “just do what the Boy Scouts do and apply pressure.”
“The whole thing was like I’m some object for my husband to enjoy and let him do whatever he wants,” Ms. Mateer said. “It was just very violating and not a great way to start my sexual relationship with my new husband, with these ideas in mind.”
Ms. Mateer thought back to that visit over the years, particularly when she went to other ob.gyns. for health care. Her subsequent doctors, she said, never performed a rectal exam and always explained to her what they were doing and how it would feel, and asked for her consent.
She thought about Dr. Broadbent again in 2017, as the #MeToo movement gained momentum, and looked him up online. Ms. Mateer found reviews from other women who described Dr. Broadbent doing rough examinations without warning that left them feeling the same way she had years before.
Then in December 2021, she spoke out on “Mormon Stories,” a podcast where people who have left or have questioned their Latter-day Saint faith share their life stories. In the episode, she described the painful way he examined her, how it left her feeling traumatized, and her discovery of the reviews that echoed her experience.
“He’s on University Avenue, in Provo, giving these exams to who knows how many naive Mormon 18-year-old, 19-year-old girls who are getting married. … They are naive and they don’t know what to expect,” she said on the podcast. “His name is Dr. David Broadbent.”
After the podcast aired, Ms. Mateer was flooded with messages from women who heard the episode and reached out to tell her that Dr. Broadbent had harmed them, too.
Ms. Mateer and three other women decided to sue the ob.gyn., and in the following weeks and months, 90 additional women joined the lawsuit they filed in Provo. Many of the women allege Dr. Broadbent inappropriately touched their breasts, vaginas and rectums, hurting them, without warning or explanation. Some said he used his bare hand – instead of using a speculum or gloves – during exams. One alleged that she saw he had an erection while he was touching her.
Dr. Broadbent’s actions were not medically necessary, the women allege, and were instead “performed for no other reason than his own sexual gratification.”
The lawsuit also named as defendants two hospitals where Dr. Broadbent had delivered babies and where some of the women allege they were assaulted. The suit accused hospital administrators of knowing about Dr. Broadbent’s inappropriate behavior and doing nothing about it.
After he was sued, the ob.gyn. quickly lost his privileges at the hospitals where he worked. Dr. Broadbent, now 75, has also voluntarily put his medical license in Utah on hold while police investigate 29 reports of sexual assault made against him.
Prosecutors are still considering whether to criminally prosecute Dr. Broadbent. Provo police forwarded more than a dozen reports to the Utah County attorney’s office in November, which are still being reviewed by a local prosecutor.
A spokesperson for Intermountain Health, the nonprofit health system that owns Utah Valley Hospital, where some of the women in the suit were treated, did not respond to specific questions. The spokesperson emphasized in an email that Dr. Broadbent was an “independent physician” who was not employed by Utah Valley Hospital, adding that most of the alleged incidents took place at Dr. Broadbent’s medical office.
A representative for MountainStar Healthcare, another hospital chain named as a defendant, denied knowledge of any allegations of inappropriate conduct reported to its hospital and also emphasized that Dr. Broadbent worked independently, not as an employee.
“Our position since this lawsuit was filed has been that we were inappropriately named in this suit,” said Brittany Glas, the communications director for MountainStar.
Debating whether sexual abuse is health care
For the women who sued Dr. Broadbent, their case boiled down to a key question: Were the sexual assaults they say they experienced part of their health care? There was a lot hanging on the answer.
If their case was considered medical malpractice, they would be limited in how much money they could receive in damages for their pain and suffering. If a jury awarded them millions of dollars, a judge would be required by law to cut that down to $450,000. There’s no cap on these monetary awards for victims sexually assaulted in other settings.
They would also be required to go before a panel, which includes a doctor, a lawyer and a community member, that decides whether their claims have merit. This step, aimed at resolving disputes out of court, does not block anyone from suing afterward. But it does add cost and delay, and for sexual assault victims who’ve gone through this step, it has been another time they were required to describe their experiences and hope they were believed.
The shorter, 2-year filing deadline for medical malpractice cases can also be a particular challenge for those who have been sexually abused because research shows that it’s common to delay reporting such assaults.
Nationwide, these kinds of malpractice reforms were adopted in the 1970s amid concerns – largely driven by insurance companies – that the cost of health care was rising because of frivolous lawsuits and “runaway juries” doling out multimillion-dollar payouts.
Restricting the size of malpractice awards and imposing other limits, many argued, were effective ways to balance compensating injured patients with protecting everyone’s access to health care.
State laws are generally silent on whether sexual assault lawsuits should be covered by malpractice laws, leaving courts to grapple with that question and leading to different conclusions across the country. The Tribune and ProPublica identified at least six cases in which state appellate judges sharply distinguished between assault and health care in considering whether malpractice laws should apply to sexual assault–related cases.
An appellate court in Wisconsin, for example, ruled in 1993 that a physician having an erection and groping a patient was a purposeful harm, not medical malpractice.
Florida’s law is similar to Utah’s, defining allegations “arising” out of medical care as malpractice. While an earlier ruling did treat sexual assault in a health care setting as medical malpractice, appellate rulings in the last decade have moved away from that interpretation. In 2005, an appellate court affirmed a lower-court ruling that when a dentist “stopped providing dental treatment to the victim and began sexually assaulting her, his professional services ended.”
Similarly, a federal judge in Iowa in 1995 weighed in on the meaning of “arising” out of health care: “Rape is not patient care activity,” he wrote.
But Utah’s malpractice law is so broad that judges have been interpreting it as covering any act performed by a health care provider during medical care. The law was passed in 1976 and is popular with doctors and other health care providers, who have lobbied to keep it in place – and who use it to get lawsuits dismissed.
One precedent-setting case in Utah shows the law’s power to safeguard health care providers and was an important test of how Utah defines medical malpractice. Jacob Scott sued WinGate Wilderness Therapy after the teen broke his leg in 2015 when a hiking guide from the center allowed him to climb up and down a steep outcrop in Utah’s red rock desert.
His parents are both lawyers, and after they found that Utah had a 4-year deadline for filing a personal injury lawsuit, court records said, they decided to prioritize “getting Jacob better” for the first 2 years after the accident. But when Mr. Scott’s suit was filed, WinGate argued it was too late – based on the shorter, 2-year deadline for medical malpractice claims.
Mr. Scott’s attorneys scoffed. “Interacting with nature,” his attorneys argued, “is not health care even under the broadest interpretation of … the Utah Health Care Malpractice Act.”
A judge disagreed and threw out Mr. Scott’s case. The Utah Supreme Court unanimously upheld that ruling in 2021.
“We agree with WinGate,” the justices wrote, “that it was acting as a ‘health care provider’ and providing ‘health care’ when Jacob was hiking and rock climbing.”
Last summer, the women who had sued Dr. Broadbent and the two hospitals watched online as lawyers debated whether the abuse they allegedly suffered was health care.
At the hearing, attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued that the women should have pursued a medical malpractice case, which required them to first notify Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals that they wanted to sue. They also argued to Judge Robert Lunnen that the case couldn’t move forward because the women hadn’t gone before a prelitigation panel.
Attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued, one after the other, that the painful and traumatic exams the women described arose out of health care treatments.
“Accepting the allegations of the complaint as true – as we must for purposes of this proceeding – we have to assume that [Broadbent] did something that was medically unnecessary, medically inappropriate,” argued David Jordan, a lawyer for Intermountain Health.
“But it doesn’t change the fact that it’s an act performed to a patient, during the patient’s treatment,” he said. “Because that’s what the patient is doing in the doctor’s office. They’re there for treatment.”
The attorney team for the women pushed back. Terry Rooney argued that if Dr. Broadbent’s actions fell under medical malpractice laws, many women would be knocked out of the case because of the age of their claims, and those who remained would be limited in the amount of money in damages they could receive.
“That’s really what this is about,” he argued. “And so it’s troubling – quite frankly it’s shocking to me – that we’re debating heavily the question of whether sexual abuse is health care.”
The judge mulled the issue for months. Judge Lunnen wrote in a September ruling that if the allegations were true, Dr. Broadbent’s treatment of his patients was “insensitive, disrespectful and degrading.”
But Utah law is clear, he said. Malpractice law covers any act or treatment performed by any health care provider during the patient’s medical care. The women had all been seeking health care, Judge Lunnen wrote, and Dr. Broadbent was providing that when the alleged assaults happened.
Their lawsuit was dismissed.
‘I felt defeated’
Brooke, another plaintiff who alleges Dr. Broadbent groped her, remembers feeling sick on the June day she watched the attorneys arguing. She asked to be identified by only her first name for this story.
She alleges Dr. Broadbent violated her in December 2008 while she was hospitalized after experiencing complications with her first pregnancy.
The nearest hospital to her rural town didn’t have a special unit to take care of premature babies, and her doctors feared she might need to deliver her son 6 weeks early. So Brooke had been rushed by ambulance over a mountain pass in a snowstorm to Utah Valley Hospital.
Brooke and her husband were terrified, she said, when they arrived at the Provo hospital. Dr. Broadbent happened to be the doctor on call. With Brooke’s husband and brother-in-law in the room, Dr. Broadbent examined her late that evening, she said, listening to her chest with a stethoscope.
The doctor then suddenly grabbed her breasts, she recalled – his movements causing her hospital gown to fall to expose her chest. She recounted this experience in her lawsuit, saying it was nothing like the breast exams she has had since.
“It was really traumatizing,” she said. “I was mortified. My husband and brother-in-law – we just didn’t say anything about it because it was so uncomfortable.”
Brooke voiced concerns to the nurse manager, and she was assigned a new doctor.
She gave birth to a healthy baby a little more than a month later, at the hospital near her home.
Hearing the judge’s ruling 14 years later, Brooke felt the decision revealed how Utah’s laws are broken.
“I was frustrated,” she said, “and I felt defeated. … I thought justice is not on our side with this.”
If the Utah Supreme Court rules that these alleged sexual assaults should legally be considered health care, the women will likely refile their claims as a medical malpractice lawsuit, said their attorney, Adam Sorensen. But it would be a challenge to keep all 94 women in the case, he said, due to the shorter filing window. Only two women in the lawsuit allege that they were harmed within the last 2 years.
The legal team for the women would have to convince a judge that their claims should still be allowed because they only recently discovered they were harmed. But based on previous rulings, Mr. Sorensen believes the women will have a better chance to win that argument if the civil suit remained a sexual assault case.
Regardless of what happens in their legal case, the decision by Brooke and the other women to come forward could help change state law for victims who come after them.
Recently, Mr. McKell, the state senator, introduced legislation to clarify that civil lawsuits alleging sexual assault by a health care worker do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act.
“I don’t think it’s a close call. Sexual assault is not medical care,” he said. “I know we’ve got some bizarre rulings that have come down through our courts in Utah.”
Both an association of Utah trial lawyers and the Utah Medical Association, which lobbies on behalf of the state’s physicians, support this reform.
“We support the fact that sexual assault should not be part of health care medical malpractice,” said Michelle McOmber, the CEO for the Utah Medical Association. “Sexual assault should be sexual assault, regardless of where it happens or who’s doing it. Sexual assault should be in that category, which is separate from actual health care. Because it’s not health care.”
MountainStar doesn’t have a position on the bill, Ms. Glas said. “If the laws were to change via new legislation and/or interpretation by the courts, we would abide by and comply with those new laws.”
But lawmakers are running out of time. With only a short time left in Utah’s legislative session, state senate and house leaders have so far prioritized passing new laws banning gender-affirming health care for transgender youths and creating a controversial school voucher program that will provide taxpayer funds for students to attend private school.
Utah lawmakers were also expected to consider a dramatic change for other sexual assault victims: a bill that would remove filing deadlines for civil lawsuits brought by people abused as adults. But that bill stalled before it could be debated.
Brooke had been eager to share her story, she said, in hopes it would help the first four women who’d come forward bolster their lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent. She later joined the case as a plaintiff. She read in their lawsuit about one woman who complained about him to the same hospital 7 years before she did, and about another woman who said Dr. Broadbent similarly molested her 2 days after Brooke had expressed her own concern.
“That bothered me so much,” she said. “It didn’t have to happen to all these women.”
Brooke doubts she’ll get vindication in a courtroom. Justice for her, she suspects, won’t come in the form of a legal ruling or a settlement against the doctor she says hurt her years ago.
Instead, she said, “maybe justice looks like changing the laws for future women.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive the biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
This article was produced for ProPublica’s Local Reporting Network in partnership with The Salt Lake Tribune.
At 19 years old and about to be married, Stephanie Mateer went to an ob.gyn. within walking distance of her student housing near Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah.
She wanted to start using birth control, and she was looking for guidance about having sex for the first time on her 2008 wedding night.
Ms. Mateer was shocked, she said, when David Broadbent, MD, reached under her gown to grab and squeeze her breasts, started a vaginal exam without warning, then followed it with an extremely painful examination of her rectum.
She felt disgusted and violated, but doubt also crept in. She told herself she must have misinterpreted his actions, or that she should have known that he would do a rectal exam. Raised as a member of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, she said she was taught to defer to men in leadership.
“I viewed him as being a man in authority,” Ms. Mateer said. “He’s a doctor.”
It was years, she said, before she learned that her experience was in a sharp contrast to the conduct called for in professional standards, including that doctors use only their fingertips during a breast exam and communicate clearly what they are doing in advance, to gain the consent of their patients. Eventually, she gave her experience another name: sexual assault.
Utah judges, however, have called it health care.
And that legal distinction means Utahns like Ms. Mateer who decide to sue a health care provider for alleged sexual abuse are treated more harshly by the court system than plaintiffs who say they were harmed in other settings.
The chance to go to civil court for damages is an important option for survivors, experts say. While a criminal conviction can provide a sense of justice, winning a lawsuit can help victims pay for the therapy and additional support they need to heal after trauma.
Ms. Mateer laid out her allegations in a lawsuit that she and 93 other women filed against Dr. Broadbent last year. But they quickly learned they would be treated differently than other sexual assault survivors.
Filing their case, which alleged the Utah County doctor sexually assaulted them over the span of his 47-year career, was an empowering moment, Ms. Mateer said. But a judge threw out the lawsuit without even considering the merits, determining that because their alleged assailant is a doctor, the case must be governed by medical malpractice rules rather than those that apply to cases of sexual assault.
Under Utah’s rules of medical malpractice, claims made by victims who allege a health care worker sexually assaulted them are literally worth less than lawsuits brought by someone who was assaulted in other settings – even if a jury rules in their favor, a judge is required to limit how much money they receive. And they must meet a shorter filing deadline.
“It’s just crazy that a doctor can sexually assault women and then be protected by the white coat,” Ms. Mateer said. “It’s just a really scary precedent to be calling sexual assault ‘health care.’ ”
Because of the judge’s ruling that leaves them with a shorter window in which to file, some of Dr. Broadbent’s accusers stand to lose their chance to sue. Others were already past that deadline but had hoped to take advantage of an exception that allows plaintiffs to sue if they can prove that the person who harmed them had covered up the wrongdoing and if they discovered they had been hurt within the previous year.
As a group, the women are appealing the ruling to the Utah Supreme Court, which has agreed to hear the case. This decision will set a precedent for future sexual assault victims in Utah.
Dr. Broadbent’s attorney, Chris Nelson, declined an interview request but wrote in an email: “We believe that the allegations against Dr. Broadbent are without merit and will present our case in court. Given that this is an active legal matter, we will not be sharing any details outside the courtroom.”
States have varying legal definitions of medical malpractice, but it’s generally described as treatment that falls short of accepted standards of care. That includes mistakes, such as a surgeon leaving a piece of gauze inside a patient.
The Utah Supreme Court has ruled that a teenage boy was receiving health care when he was allowed to climb a steep, snow-dusted rock outcrop as part of wilderness therapy. When he broke his leg, he could only sue for medical malpractice, so the case faced shorter filing deadlines and lower monetary caps. Similarly, the court has ruled that a boy harmed by another child while in foster care was also bound by medical malpractice law.
Despite these state Supreme Court rulings, Utah legislators have so far not moved to narrow the wording of the malpractice act.
The lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent – and the questions it raises about the broadness of Utah’s medical malpractice laws – comes during a national reckoning with how sexual assault survivors are treated by the law. Legislators in several states have been rewriting laws to give sexual assault victims more time to sue their attackers, in response to the growing cultural understanding of the impact of trauma and the barriers to reporting. Even in Utah, those who were sexually abused as children now have no deadline to file suits against their abusers.
That isn’t true for sexual abuse in a medical setting, where cases must be filed within 2 years of the assault.
These higher hurdles should not exist in Utah, said state Sen. Mike K. McKell, a Utah County Republican who works as a personal injury attorney. He is trying to change state law to ensure that sexual assault lawsuits do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act, a law designed to cover negligence and poor care, not necessarily deliberate actions like an assault.
“Sexual assault, to me, is not medical care. Period,” he said. “It’s sad that we need to clarify that sexual assault is not medical care. But trying to tie sexual assault to a medical malpractice [filing deadline] – it’s just wrong.”
‘Your husband is a lucky man’
Ms. Mateer had gone to Dr. Broadbent in 2008 for a premarital exam, a uniquely Utah visit often scheduled by young women who are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Leaders of the faith, which is predominant in Utah, focus on chastity when speaking to young, unmarried people about sex, and public schools have typically focused on abstinence-based sex education. So for some, these visits are the first place they learn about sexual health.
Young women who get premarital exams are typically given a birth control prescription, but the appointments can include care that’s less common for healthy women in other states – such as doctors giving them vaginal dilators to stretch their tissues before their wedding nights.
That’s what Ms. Mateer was expecting when she visited Dr. Broadbent’s office. The ob.gyn. had been practicing for decades in his Provo clinic nestled between student housing apartments across the street from Brigham Young University, which is owned by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
So Ms. Mateer was “just totally taken aback,” she said, by the painful examination and by Dr. Broadbent snapping off his gloves after the exam and saying, “Your husband is a lucky man.”
She repeated that remark in her legal filing, along with the doctor’s advice for her: If she bled during intercourse, “just do what the Boy Scouts do and apply pressure.”
“The whole thing was like I’m some object for my husband to enjoy and let him do whatever he wants,” Ms. Mateer said. “It was just very violating and not a great way to start my sexual relationship with my new husband, with these ideas in mind.”
Ms. Mateer thought back to that visit over the years, particularly when she went to other ob.gyns. for health care. Her subsequent doctors, she said, never performed a rectal exam and always explained to her what they were doing and how it would feel, and asked for her consent.
She thought about Dr. Broadbent again in 2017, as the #MeToo movement gained momentum, and looked him up online. Ms. Mateer found reviews from other women who described Dr. Broadbent doing rough examinations without warning that left them feeling the same way she had years before.
Then in December 2021, she spoke out on “Mormon Stories,” a podcast where people who have left or have questioned their Latter-day Saint faith share their life stories. In the episode, she described the painful way he examined her, how it left her feeling traumatized, and her discovery of the reviews that echoed her experience.
“He’s on University Avenue, in Provo, giving these exams to who knows how many naive Mormon 18-year-old, 19-year-old girls who are getting married. … They are naive and they don’t know what to expect,” she said on the podcast. “His name is Dr. David Broadbent.”
After the podcast aired, Ms. Mateer was flooded with messages from women who heard the episode and reached out to tell her that Dr. Broadbent had harmed them, too.
Ms. Mateer and three other women decided to sue the ob.gyn., and in the following weeks and months, 90 additional women joined the lawsuit they filed in Provo. Many of the women allege Dr. Broadbent inappropriately touched their breasts, vaginas and rectums, hurting them, without warning or explanation. Some said he used his bare hand – instead of using a speculum or gloves – during exams. One alleged that she saw he had an erection while he was touching her.
Dr. Broadbent’s actions were not medically necessary, the women allege, and were instead “performed for no other reason than his own sexual gratification.”
The lawsuit also named as defendants two hospitals where Dr. Broadbent had delivered babies and where some of the women allege they were assaulted. The suit accused hospital administrators of knowing about Dr. Broadbent’s inappropriate behavior and doing nothing about it.
After he was sued, the ob.gyn. quickly lost his privileges at the hospitals where he worked. Dr. Broadbent, now 75, has also voluntarily put his medical license in Utah on hold while police investigate 29 reports of sexual assault made against him.
Prosecutors are still considering whether to criminally prosecute Dr. Broadbent. Provo police forwarded more than a dozen reports to the Utah County attorney’s office in November, which are still being reviewed by a local prosecutor.
A spokesperson for Intermountain Health, the nonprofit health system that owns Utah Valley Hospital, where some of the women in the suit were treated, did not respond to specific questions. The spokesperson emphasized in an email that Dr. Broadbent was an “independent physician” who was not employed by Utah Valley Hospital, adding that most of the alleged incidents took place at Dr. Broadbent’s medical office.
A representative for MountainStar Healthcare, another hospital chain named as a defendant, denied knowledge of any allegations of inappropriate conduct reported to its hospital and also emphasized that Dr. Broadbent worked independently, not as an employee.
“Our position since this lawsuit was filed has been that we were inappropriately named in this suit,” said Brittany Glas, the communications director for MountainStar.
Debating whether sexual abuse is health care
For the women who sued Dr. Broadbent, their case boiled down to a key question: Were the sexual assaults they say they experienced part of their health care? There was a lot hanging on the answer.
If their case was considered medical malpractice, they would be limited in how much money they could receive in damages for their pain and suffering. If a jury awarded them millions of dollars, a judge would be required by law to cut that down to $450,000. There’s no cap on these monetary awards for victims sexually assaulted in other settings.
They would also be required to go before a panel, which includes a doctor, a lawyer and a community member, that decides whether their claims have merit. This step, aimed at resolving disputes out of court, does not block anyone from suing afterward. But it does add cost and delay, and for sexual assault victims who’ve gone through this step, it has been another time they were required to describe their experiences and hope they were believed.
The shorter, 2-year filing deadline for medical malpractice cases can also be a particular challenge for those who have been sexually abused because research shows that it’s common to delay reporting such assaults.
Nationwide, these kinds of malpractice reforms were adopted in the 1970s amid concerns – largely driven by insurance companies – that the cost of health care was rising because of frivolous lawsuits and “runaway juries” doling out multimillion-dollar payouts.
Restricting the size of malpractice awards and imposing other limits, many argued, were effective ways to balance compensating injured patients with protecting everyone’s access to health care.
State laws are generally silent on whether sexual assault lawsuits should be covered by malpractice laws, leaving courts to grapple with that question and leading to different conclusions across the country. The Tribune and ProPublica identified at least six cases in which state appellate judges sharply distinguished between assault and health care in considering whether malpractice laws should apply to sexual assault–related cases.
An appellate court in Wisconsin, for example, ruled in 1993 that a physician having an erection and groping a patient was a purposeful harm, not medical malpractice.
Florida’s law is similar to Utah’s, defining allegations “arising” out of medical care as malpractice. While an earlier ruling did treat sexual assault in a health care setting as medical malpractice, appellate rulings in the last decade have moved away from that interpretation. In 2005, an appellate court affirmed a lower-court ruling that when a dentist “stopped providing dental treatment to the victim and began sexually assaulting her, his professional services ended.”
Similarly, a federal judge in Iowa in 1995 weighed in on the meaning of “arising” out of health care: “Rape is not patient care activity,” he wrote.
But Utah’s malpractice law is so broad that judges have been interpreting it as covering any act performed by a health care provider during medical care. The law was passed in 1976 and is popular with doctors and other health care providers, who have lobbied to keep it in place – and who use it to get lawsuits dismissed.
One precedent-setting case in Utah shows the law’s power to safeguard health care providers and was an important test of how Utah defines medical malpractice. Jacob Scott sued WinGate Wilderness Therapy after the teen broke his leg in 2015 when a hiking guide from the center allowed him to climb up and down a steep outcrop in Utah’s red rock desert.
His parents are both lawyers, and after they found that Utah had a 4-year deadline for filing a personal injury lawsuit, court records said, they decided to prioritize “getting Jacob better” for the first 2 years after the accident. But when Mr. Scott’s suit was filed, WinGate argued it was too late – based on the shorter, 2-year deadline for medical malpractice claims.
Mr. Scott’s attorneys scoffed. “Interacting with nature,” his attorneys argued, “is not health care even under the broadest interpretation of … the Utah Health Care Malpractice Act.”
A judge disagreed and threw out Mr. Scott’s case. The Utah Supreme Court unanimously upheld that ruling in 2021.
“We agree with WinGate,” the justices wrote, “that it was acting as a ‘health care provider’ and providing ‘health care’ when Jacob was hiking and rock climbing.”
Last summer, the women who had sued Dr. Broadbent and the two hospitals watched online as lawyers debated whether the abuse they allegedly suffered was health care.
At the hearing, attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued that the women should have pursued a medical malpractice case, which required them to first notify Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals that they wanted to sue. They also argued to Judge Robert Lunnen that the case couldn’t move forward because the women hadn’t gone before a prelitigation panel.
Attorneys for Dr. Broadbent and the hospitals argued, one after the other, that the painful and traumatic exams the women described arose out of health care treatments.
“Accepting the allegations of the complaint as true – as we must for purposes of this proceeding – we have to assume that [Broadbent] did something that was medically unnecessary, medically inappropriate,” argued David Jordan, a lawyer for Intermountain Health.
“But it doesn’t change the fact that it’s an act performed to a patient, during the patient’s treatment,” he said. “Because that’s what the patient is doing in the doctor’s office. They’re there for treatment.”
The attorney team for the women pushed back. Terry Rooney argued that if Dr. Broadbent’s actions fell under medical malpractice laws, many women would be knocked out of the case because of the age of their claims, and those who remained would be limited in the amount of money in damages they could receive.
“That’s really what this is about,” he argued. “And so it’s troubling – quite frankly it’s shocking to me – that we’re debating heavily the question of whether sexual abuse is health care.”
The judge mulled the issue for months. Judge Lunnen wrote in a September ruling that if the allegations were true, Dr. Broadbent’s treatment of his patients was “insensitive, disrespectful and degrading.”
But Utah law is clear, he said. Malpractice law covers any act or treatment performed by any health care provider during the patient’s medical care. The women had all been seeking health care, Judge Lunnen wrote, and Dr. Broadbent was providing that when the alleged assaults happened.
Their lawsuit was dismissed.
‘I felt defeated’
Brooke, another plaintiff who alleges Dr. Broadbent groped her, remembers feeling sick on the June day she watched the attorneys arguing. She asked to be identified by only her first name for this story.
She alleges Dr. Broadbent violated her in December 2008 while she was hospitalized after experiencing complications with her first pregnancy.
The nearest hospital to her rural town didn’t have a special unit to take care of premature babies, and her doctors feared she might need to deliver her son 6 weeks early. So Brooke had been rushed by ambulance over a mountain pass in a snowstorm to Utah Valley Hospital.
Brooke and her husband were terrified, she said, when they arrived at the Provo hospital. Dr. Broadbent happened to be the doctor on call. With Brooke’s husband and brother-in-law in the room, Dr. Broadbent examined her late that evening, she said, listening to her chest with a stethoscope.
The doctor then suddenly grabbed her breasts, she recalled – his movements causing her hospital gown to fall to expose her chest. She recounted this experience in her lawsuit, saying it was nothing like the breast exams she has had since.
“It was really traumatizing,” she said. “I was mortified. My husband and brother-in-law – we just didn’t say anything about it because it was so uncomfortable.”
Brooke voiced concerns to the nurse manager, and she was assigned a new doctor.
She gave birth to a healthy baby a little more than a month later, at the hospital near her home.
Hearing the judge’s ruling 14 years later, Brooke felt the decision revealed how Utah’s laws are broken.
“I was frustrated,” she said, “and I felt defeated. … I thought justice is not on our side with this.”
If the Utah Supreme Court rules that these alleged sexual assaults should legally be considered health care, the women will likely refile their claims as a medical malpractice lawsuit, said their attorney, Adam Sorensen. But it would be a challenge to keep all 94 women in the case, he said, due to the shorter filing window. Only two women in the lawsuit allege that they were harmed within the last 2 years.
The legal team for the women would have to convince a judge that their claims should still be allowed because they only recently discovered they were harmed. But based on previous rulings, Mr. Sorensen believes the women will have a better chance to win that argument if the civil suit remained a sexual assault case.
Regardless of what happens in their legal case, the decision by Brooke and the other women to come forward could help change state law for victims who come after them.
Recently, Mr. McKell, the state senator, introduced legislation to clarify that civil lawsuits alleging sexual assault by a health care worker do not fall under Utah’s Health Care Malpractice Act.
“I don’t think it’s a close call. Sexual assault is not medical care,” he said. “I know we’ve got some bizarre rulings that have come down through our courts in Utah.”
Both an association of Utah trial lawyers and the Utah Medical Association, which lobbies on behalf of the state’s physicians, support this reform.
“We support the fact that sexual assault should not be part of health care medical malpractice,” said Michelle McOmber, the CEO for the Utah Medical Association. “Sexual assault should be sexual assault, regardless of where it happens or who’s doing it. Sexual assault should be in that category, which is separate from actual health care. Because it’s not health care.”
MountainStar doesn’t have a position on the bill, Ms. Glas said. “If the laws were to change via new legislation and/or interpretation by the courts, we would abide by and comply with those new laws.”
But lawmakers are running out of time. With only a short time left in Utah’s legislative session, state senate and house leaders have so far prioritized passing new laws banning gender-affirming health care for transgender youths and creating a controversial school voucher program that will provide taxpayer funds for students to attend private school.
Utah lawmakers were also expected to consider a dramatic change for other sexual assault victims: a bill that would remove filing deadlines for civil lawsuits brought by people abused as adults. But that bill stalled before it could be debated.
Brooke had been eager to share her story, she said, in hopes it would help the first four women who’d come forward bolster their lawsuit against Dr. Broadbent. She later joined the case as a plaintiff. She read in their lawsuit about one woman who complained about him to the same hospital 7 years before she did, and about another woman who said Dr. Broadbent similarly molested her 2 days after Brooke had expressed her own concern.
“That bothered me so much,” she said. “It didn’t have to happen to all these women.”
Brooke doubts she’ll get vindication in a courtroom. Justice for her, she suspects, won’t come in the form of a legal ruling or a settlement against the doctor she says hurt her years ago.
Instead, she said, “maybe justice looks like changing the laws for future women.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive the biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
No advantage for full-term aspirin in preventing preterm preeclampsia
Stopping aspirin at 24-28 weeks of gestation has no disadvantage, compared with continuing aspirin full term, for preventing preterm preeclampsia in women at high risk of preeclampsia who have a normal fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 to placental growth factor (sFlt-1:PlGF) ratio, a randomized controlled trial has found.
The findings were published online in JAMA.
Editorialists advise careful consideration
However, in an accompanying editorial, Ukachi N. Emeruwa, MD, MPH, with the division of maternal fetal medicine, department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues noted that the questions surrounding continuing or discontinuing aspirin in this high-risk population need further consideration.
They added that the results from this study – conducted in nine maternity hospitals across Spain – are hard to translate for the U.S. population.
In this study, Manel Mendoza, PhD, with the maternal fetal medicine unit, department of obstetrics, at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, and colleagues compared the two approaches because of the potential to mitigate peripartum bleeding by discontinuing aspirin before full term (37 weeks’ gestation) and by an accurate selection of women in the first trimester at higher risk of preeclampsia.
Aspirin cuts preterm preeclampsia by 62% in women at high risk
While aspirin might be associated with an increased risk of peripartum bleeding, aspirin has been proven to reduce the incidence of preterm preeclampsia by 62% in pregnant women at high risk of preeclampsia.
In the multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial, pregnant women who had a high risk of preeclampsia during the first-trimester screening and an sFlt-1:PlGF ratio of 38 or less at 24-28 weeks’ gestation were recruited between Aug. 20, 2019, and Sept. 15, 2021. Of those, 936 were analyzed (473 in the intervention group [stopping aspirin] and 473 in the control group [continuing]).
Screening for risk of preterm preeclampsia included analyzing maternal factors, uterine artery pulsatility index, mean arterial pressure, serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, and placental growth factor. Follow-up was until delivery for all participants.
Incidence of preterm preeclampsia was 1.48% in the intervention group (discontinuing aspirin) and 1.73% in the control group (continuing aspirin until 36 weeks of gestation; absolute difference, –0.25%; 95% confidence interval, –1.86% to 1.36%), which indicates noninferiority for stopping aspirin. The bar for noninferiority was less than a 1.9% difference in preterm preeclampsia incidences between groups.
Researchers did find a higher incidence of minor antepartum bleeding in the group that continued aspirin (7.61% in the low-dose aspirin discontinuation group vs. 12.31% in the low-dose aspirin continuation group; absolute difference, –4.70; 95% CI, –8.53 to –0.87).
Differences in U.S. guidelines
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues noted the study challenges a growing body of evidence favoring increasingly widespread use of low-dose aspirin in pregnancy.
They called the study “well designed and provocative,” but wrote that the findings are hard to interpret for a U.S. population. Some key differences in the U.S. preeclampsia prevention guidelines, compared with the practices of the study’s authors, included the reliance on clinical maternal factors in the United States for screening for low-dose aspirin prophylaxis as opposed to molecular biomarkers; a different aspirin dose prescribed in the United States (81 mg daily), compared with international societies (150 mg daily); and a lack of a recommendation in the United States to stop prophylactic low-dose aspirin at 36 weeks.
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues also questioned the scope of the outcome measure used.
They wrote that limiting outcomes to preterm preeclampsia dims the effects of all types of preeclampsia on perinatal and maternal outcomes and that early-onset preeclampsia at less than 34 weeks “occurs in just 0.38% of pregnancies, while 3%-5% are affected by late-onset preeclampsia.”
‘Late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact’
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues wrote: “Though the odds of adverse perinatal and maternal outcomes are higher with preterm preeclampsia, due to its overall higher incidence, late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact on perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality.”
The study can inform future U.S. approaches, the editorialists wrote, and build on work already being done in the United States.
The study investigators used biophysical and molecular markers to more accurately assess risk for starting low-dose aspirin prophylaxis in the first trimester and applied a growing body of data showing the high negative predictive value of second-trimester biomarkers.
The editorialists noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations would have captured “less than 50% of the at-risk population” that Dr. Mendoza’s team found eligible for low-dose aspirin.
Those factors, the editorialists wrote, point to the potential to improve guidelines for personalized preeclampsia management in pregnancy.
They concluded: “U.S. practitioners and professional societies should reconsider current risk assessment strategies, which are largely based on maternal factors, and evaluate whether incorporation of molecular biomarkers would improve maternal and fetal/neonatal outcomes.”
The study authors acknowledged that 92% of participants in the study were White, thus limiting generalizability.
The authors and editorialists reported no relevant financial relationships.
Stopping aspirin at 24-28 weeks of gestation has no disadvantage, compared with continuing aspirin full term, for preventing preterm preeclampsia in women at high risk of preeclampsia who have a normal fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 to placental growth factor (sFlt-1:PlGF) ratio, a randomized controlled trial has found.
The findings were published online in JAMA.
Editorialists advise careful consideration
However, in an accompanying editorial, Ukachi N. Emeruwa, MD, MPH, with the division of maternal fetal medicine, department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues noted that the questions surrounding continuing or discontinuing aspirin in this high-risk population need further consideration.
They added that the results from this study – conducted in nine maternity hospitals across Spain – are hard to translate for the U.S. population.
In this study, Manel Mendoza, PhD, with the maternal fetal medicine unit, department of obstetrics, at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, and colleagues compared the two approaches because of the potential to mitigate peripartum bleeding by discontinuing aspirin before full term (37 weeks’ gestation) and by an accurate selection of women in the first trimester at higher risk of preeclampsia.
Aspirin cuts preterm preeclampsia by 62% in women at high risk
While aspirin might be associated with an increased risk of peripartum bleeding, aspirin has been proven to reduce the incidence of preterm preeclampsia by 62% in pregnant women at high risk of preeclampsia.
In the multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial, pregnant women who had a high risk of preeclampsia during the first-trimester screening and an sFlt-1:PlGF ratio of 38 or less at 24-28 weeks’ gestation were recruited between Aug. 20, 2019, and Sept. 15, 2021. Of those, 936 were analyzed (473 in the intervention group [stopping aspirin] and 473 in the control group [continuing]).
Screening for risk of preterm preeclampsia included analyzing maternal factors, uterine artery pulsatility index, mean arterial pressure, serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, and placental growth factor. Follow-up was until delivery for all participants.
Incidence of preterm preeclampsia was 1.48% in the intervention group (discontinuing aspirin) and 1.73% in the control group (continuing aspirin until 36 weeks of gestation; absolute difference, –0.25%; 95% confidence interval, –1.86% to 1.36%), which indicates noninferiority for stopping aspirin. The bar for noninferiority was less than a 1.9% difference in preterm preeclampsia incidences between groups.
Researchers did find a higher incidence of minor antepartum bleeding in the group that continued aspirin (7.61% in the low-dose aspirin discontinuation group vs. 12.31% in the low-dose aspirin continuation group; absolute difference, –4.70; 95% CI, –8.53 to –0.87).
Differences in U.S. guidelines
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues noted the study challenges a growing body of evidence favoring increasingly widespread use of low-dose aspirin in pregnancy.
They called the study “well designed and provocative,” but wrote that the findings are hard to interpret for a U.S. population. Some key differences in the U.S. preeclampsia prevention guidelines, compared with the practices of the study’s authors, included the reliance on clinical maternal factors in the United States for screening for low-dose aspirin prophylaxis as opposed to molecular biomarkers; a different aspirin dose prescribed in the United States (81 mg daily), compared with international societies (150 mg daily); and a lack of a recommendation in the United States to stop prophylactic low-dose aspirin at 36 weeks.
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues also questioned the scope of the outcome measure used.
They wrote that limiting outcomes to preterm preeclampsia dims the effects of all types of preeclampsia on perinatal and maternal outcomes and that early-onset preeclampsia at less than 34 weeks “occurs in just 0.38% of pregnancies, while 3%-5% are affected by late-onset preeclampsia.”
‘Late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact’
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues wrote: “Though the odds of adverse perinatal and maternal outcomes are higher with preterm preeclampsia, due to its overall higher incidence, late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact on perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality.”
The study can inform future U.S. approaches, the editorialists wrote, and build on work already being done in the United States.
The study investigators used biophysical and molecular markers to more accurately assess risk for starting low-dose aspirin prophylaxis in the first trimester and applied a growing body of data showing the high negative predictive value of second-trimester biomarkers.
The editorialists noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations would have captured “less than 50% of the at-risk population” that Dr. Mendoza’s team found eligible for low-dose aspirin.
Those factors, the editorialists wrote, point to the potential to improve guidelines for personalized preeclampsia management in pregnancy.
They concluded: “U.S. practitioners and professional societies should reconsider current risk assessment strategies, which are largely based on maternal factors, and evaluate whether incorporation of molecular biomarkers would improve maternal and fetal/neonatal outcomes.”
The study authors acknowledged that 92% of participants in the study were White, thus limiting generalizability.
The authors and editorialists reported no relevant financial relationships.
Stopping aspirin at 24-28 weeks of gestation has no disadvantage, compared with continuing aspirin full term, for preventing preterm preeclampsia in women at high risk of preeclampsia who have a normal fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 to placental growth factor (sFlt-1:PlGF) ratio, a randomized controlled trial has found.
The findings were published online in JAMA.
Editorialists advise careful consideration
However, in an accompanying editorial, Ukachi N. Emeruwa, MD, MPH, with the division of maternal fetal medicine, department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues noted that the questions surrounding continuing or discontinuing aspirin in this high-risk population need further consideration.
They added that the results from this study – conducted in nine maternity hospitals across Spain – are hard to translate for the U.S. population.
In this study, Manel Mendoza, PhD, with the maternal fetal medicine unit, department of obstetrics, at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, and colleagues compared the two approaches because of the potential to mitigate peripartum bleeding by discontinuing aspirin before full term (37 weeks’ gestation) and by an accurate selection of women in the first trimester at higher risk of preeclampsia.
Aspirin cuts preterm preeclampsia by 62% in women at high risk
While aspirin might be associated with an increased risk of peripartum bleeding, aspirin has been proven to reduce the incidence of preterm preeclampsia by 62% in pregnant women at high risk of preeclampsia.
In the multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase 3, noninferiority trial, pregnant women who had a high risk of preeclampsia during the first-trimester screening and an sFlt-1:PlGF ratio of 38 or less at 24-28 weeks’ gestation were recruited between Aug. 20, 2019, and Sept. 15, 2021. Of those, 936 were analyzed (473 in the intervention group [stopping aspirin] and 473 in the control group [continuing]).
Screening for risk of preterm preeclampsia included analyzing maternal factors, uterine artery pulsatility index, mean arterial pressure, serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, and placental growth factor. Follow-up was until delivery for all participants.
Incidence of preterm preeclampsia was 1.48% in the intervention group (discontinuing aspirin) and 1.73% in the control group (continuing aspirin until 36 weeks of gestation; absolute difference, –0.25%; 95% confidence interval, –1.86% to 1.36%), which indicates noninferiority for stopping aspirin. The bar for noninferiority was less than a 1.9% difference in preterm preeclampsia incidences between groups.
Researchers did find a higher incidence of minor antepartum bleeding in the group that continued aspirin (7.61% in the low-dose aspirin discontinuation group vs. 12.31% in the low-dose aspirin continuation group; absolute difference, –4.70; 95% CI, –8.53 to –0.87).
Differences in U.S. guidelines
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues noted the study challenges a growing body of evidence favoring increasingly widespread use of low-dose aspirin in pregnancy.
They called the study “well designed and provocative,” but wrote that the findings are hard to interpret for a U.S. population. Some key differences in the U.S. preeclampsia prevention guidelines, compared with the practices of the study’s authors, included the reliance on clinical maternal factors in the United States for screening for low-dose aspirin prophylaxis as opposed to molecular biomarkers; a different aspirin dose prescribed in the United States (81 mg daily), compared with international societies (150 mg daily); and a lack of a recommendation in the United States to stop prophylactic low-dose aspirin at 36 weeks.
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues also questioned the scope of the outcome measure used.
They wrote that limiting outcomes to preterm preeclampsia dims the effects of all types of preeclampsia on perinatal and maternal outcomes and that early-onset preeclampsia at less than 34 weeks “occurs in just 0.38% of pregnancies, while 3%-5% are affected by late-onset preeclampsia.”
‘Late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact’
Dr. Emeruwa and colleagues wrote: “Though the odds of adverse perinatal and maternal outcomes are higher with preterm preeclampsia, due to its overall higher incidence, late-onset preeclampsia has a higher overall impact on perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality.”
The study can inform future U.S. approaches, the editorialists wrote, and build on work already being done in the United States.
The study investigators used biophysical and molecular markers to more accurately assess risk for starting low-dose aspirin prophylaxis in the first trimester and applied a growing body of data showing the high negative predictive value of second-trimester biomarkers.
The editorialists noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations would have captured “less than 50% of the at-risk population” that Dr. Mendoza’s team found eligible for low-dose aspirin.
Those factors, the editorialists wrote, point to the potential to improve guidelines for personalized preeclampsia management in pregnancy.
They concluded: “U.S. practitioners and professional societies should reconsider current risk assessment strategies, which are largely based on maternal factors, and evaluate whether incorporation of molecular biomarkers would improve maternal and fetal/neonatal outcomes.”
The study authors acknowledged that 92% of participants in the study were White, thus limiting generalizability.
The authors and editorialists reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA
How spirituality guides these three doctors
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zero tolerance for patient bias: Too harsh? Clinicians respond
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.


