User login
Patients with Epilepsy with Chromosome 15 Duplications Face Increased Risk of Sudden Death
In order to determine how common sudden unexpected death from epilepsy (SUDEP) is in people with an extra isodicentric 15 chromosome (idic15), researchers studied approximately 709 families registered with the Dup15Q Alliance. Their case-control study found 19 deaths among patients with idic15, 17 of whom had epilepsy. Nine of these deaths were caused by probable or definite SUDEP; 2 others had what investigators considered possible SUDEP. Researchers concluded that SUDEP is common among children and young adults with duplications of the idic15 chromosome and that the risk of death is most likely to occur in patients with the most severe neurologic dysfunction.
Friedman D, Thaler A, Thaler J et al. Mortality in isodicentric chromosome 15 syndrome: the role of SUDEP. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;61:1-5.
In order to determine how common sudden unexpected death from epilepsy (SUDEP) is in people with an extra isodicentric 15 chromosome (idic15), researchers studied approximately 709 families registered with the Dup15Q Alliance. Their case-control study found 19 deaths among patients with idic15, 17 of whom had epilepsy. Nine of these deaths were caused by probable or definite SUDEP; 2 others had what investigators considered possible SUDEP. Researchers concluded that SUDEP is common among children and young adults with duplications of the idic15 chromosome and that the risk of death is most likely to occur in patients with the most severe neurologic dysfunction.
Friedman D, Thaler A, Thaler J et al. Mortality in isodicentric chromosome 15 syndrome: the role of SUDEP. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;61:1-5.
In order to determine how common sudden unexpected death from epilepsy (SUDEP) is in people with an extra isodicentric 15 chromosome (idic15), researchers studied approximately 709 families registered with the Dup15Q Alliance. Their case-control study found 19 deaths among patients with idic15, 17 of whom had epilepsy. Nine of these deaths were caused by probable or definite SUDEP; 2 others had what investigators considered possible SUDEP. Researchers concluded that SUDEP is common among children and young adults with duplications of the idic15 chromosome and that the risk of death is most likely to occur in patients with the most severe neurologic dysfunction.
Friedman D, Thaler A, Thaler J et al. Mortality in isodicentric chromosome 15 syndrome: the role of SUDEP. Epilepsy Behav. 2016;61:1-5.
Adult Epilepsy Surgeries Have “Flatlined”
Contrary to conventional wisdom, the epilepsy surgery rate among adults in North America has remained stagnant according to a recent analysis of data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Part B National Summary Data File and the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. A review of 6200 surgeries performed from 2000 to 2013 revealed that temporal lobectomy, the most common operation, was done in 59% of patients, but surgical rates for temporal and extra-temporal surgery did not change significantly during the study period. The researchers concluded that the findings in this study contrasted with previously published reports that suggested a dramatic decline in temporal lobectomy rates at high volume epilepsy centers in recent years. However, investigators did find that surgical adverse effects were higher when statistics from low and high volume centers were combined.
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Knowlton RC, Chang EF. Rate and complications of adult epilepsy surgery in North America: Analysis of multiple databases. Epilepsy Res. 2016;124:55-62.
Contrary to conventional wisdom, the epilepsy surgery rate among adults in North America has remained stagnant according to a recent analysis of data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Part B National Summary Data File and the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. A review of 6200 surgeries performed from 2000 to 2013 revealed that temporal lobectomy, the most common operation, was done in 59% of patients, but surgical rates for temporal and extra-temporal surgery did not change significantly during the study period. The researchers concluded that the findings in this study contrasted with previously published reports that suggested a dramatic decline in temporal lobectomy rates at high volume epilepsy centers in recent years. However, investigators did find that surgical adverse effects were higher when statistics from low and high volume centers were combined.
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Knowlton RC, Chang EF. Rate and complications of adult epilepsy surgery in North America: Analysis of multiple databases. Epilepsy Res. 2016;124:55-62.
Contrary to conventional wisdom, the epilepsy surgery rate among adults in North America has remained stagnant according to a recent analysis of data from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Part B National Summary Data File and the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. A review of 6200 surgeries performed from 2000 to 2013 revealed that temporal lobectomy, the most common operation, was done in 59% of patients, but surgical rates for temporal and extra-temporal surgery did not change significantly during the study period. The researchers concluded that the findings in this study contrasted with previously published reports that suggested a dramatic decline in temporal lobectomy rates at high volume epilepsy centers in recent years. However, investigators did find that surgical adverse effects were higher when statistics from low and high volume centers were combined.
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Knowlton RC, Chang EF. Rate and complications of adult epilepsy surgery in North America: Analysis of multiple databases. Epilepsy Res. 2016;124:55-62.
AGA Governing Board welcomes new members at DDW® 2016
The new AGA Institute Governing Board began its term immediately following Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2016. In addition to Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF, of Columbia University, who began his term as the 111th president of AGA Institute, the other 2016-2017 board members include:
• Sheila E. Crowe, MD, AGAF, President-Elect
• David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, Vice President
• Francis M. Giardiello, MD, AGAF, Secretary/Treasurer
• Michael Camilleri, MD, AGAF, Past President
Additionally, the Councillors of the 2016-2017 board include:
• Marcia R. Cruz-Correa, MD, PhD, AGAF, At-Large Councillor
• Gregory J. Gores, MD, AGAF, Basic Research Councillor
• John M. Inadomi, MD, AGAF, Clinical Research Councillor
• Rajeev Jain, MD, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Lawrence R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Deborah D. Proctor, MD, AGAF, Education & Training Councillor
• Robert S. Sandler, MD, MPH, AGAF, AGA Research Foundation Chair
AGA also thanks the outgoing board members for their service, including John Allen, MD, MBA; Martin Brotman, MD; Byron Cryer, MD; and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSed. AGA congratulates both the incoming and outgoing board members, and thanks them for their commitment to advancing the science and practice of gastroenterology.
The new AGA Institute Governing Board began its term immediately following Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2016. In addition to Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF, of Columbia University, who began his term as the 111th president of AGA Institute, the other 2016-2017 board members include:
• Sheila E. Crowe, MD, AGAF, President-Elect
• David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, Vice President
• Francis M. Giardiello, MD, AGAF, Secretary/Treasurer
• Michael Camilleri, MD, AGAF, Past President
Additionally, the Councillors of the 2016-2017 board include:
• Marcia R. Cruz-Correa, MD, PhD, AGAF, At-Large Councillor
• Gregory J. Gores, MD, AGAF, Basic Research Councillor
• John M. Inadomi, MD, AGAF, Clinical Research Councillor
• Rajeev Jain, MD, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Lawrence R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Deborah D. Proctor, MD, AGAF, Education & Training Councillor
• Robert S. Sandler, MD, MPH, AGAF, AGA Research Foundation Chair
AGA also thanks the outgoing board members for their service, including John Allen, MD, MBA; Martin Brotman, MD; Byron Cryer, MD; and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSed. AGA congratulates both the incoming and outgoing board members, and thanks them for their commitment to advancing the science and practice of gastroenterology.
The new AGA Institute Governing Board began its term immediately following Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2016. In addition to Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF, of Columbia University, who began his term as the 111th president of AGA Institute, the other 2016-2017 board members include:
• Sheila E. Crowe, MD, AGAF, President-Elect
• David A. Lieberman, MD, AGAF, Vice President
• Francis M. Giardiello, MD, AGAF, Secretary/Treasurer
• Michael Camilleri, MD, AGAF, Past President
Additionally, the Councillors of the 2016-2017 board include:
• Marcia R. Cruz-Correa, MD, PhD, AGAF, At-Large Councillor
• Gregory J. Gores, MD, AGAF, Basic Research Councillor
• John M. Inadomi, MD, AGAF, Clinical Research Councillor
• Rajeev Jain, MD, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Lawrence R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF, Practice Councillor
• Deborah D. Proctor, MD, AGAF, Education & Training Councillor
• Robert S. Sandler, MD, MPH, AGAF, AGA Research Foundation Chair
AGA also thanks the outgoing board members for their service, including John Allen, MD, MBA; Martin Brotman, MD; Byron Cryer, MD; and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSed. AGA congratulates both the incoming and outgoing board members, and thanks them for their commitment to advancing the science and practice of gastroenterology.
AGA joins campaign for sustainable Rx pricing
This June AGA announced it has joined the Campaign for Sustainable Rx Pricing (CSRxP), a broad-based campaign that works to curb rising drug costs.
“Gastroenterologists have a unique view of rising drug prices because the patients they treat are subjected to some of the most expensive medications on the market,” said CSRxP Executive Director John Rother, noting pricey hepatitis C medications, injectables, and other specialty drugs that often force patients to delay or forgo treatment because of cost. “AGA’s voice is a welcome addition to our diverse campaign as we call on policy makers to increase transparency, competition, and value in the prescription drug market.”
“Given that some of the most expensive drugs on the market are drugs that treat GI and hepatology diseases, I believe it is important that AGA be part of the dialogue addressing drug costs. These treatments have been revolutionary and lifesaving, but we need to ensure that all patients have access to the right treatments and are not prevented from receiving the proper therapy because of cost. AGA looks forward to working with the coalition and policy makers on finding common-sense solutions to address the growing problem of drug prices,” said Dr. Timothy C. Wang, AGAF, AGA Institute president.
Prices for specialty drugs, which require special handling, administration, or monitoring, are one of the largest drivers of increased health care costs, even for those who do not use medication. Today, prescription drug expenditures are nearly 20% of health care costs and prescription spending is growing faster than any other part of the health care dollar, according to data from IMS and Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Additionally, IMS found that spending on specialty medicines has increased by $54 billion over the past 5 years, accounting for 73% of all medicine spending growth.
This June AGA announced it has joined the Campaign for Sustainable Rx Pricing (CSRxP), a broad-based campaign that works to curb rising drug costs.
“Gastroenterologists have a unique view of rising drug prices because the patients they treat are subjected to some of the most expensive medications on the market,” said CSRxP Executive Director John Rother, noting pricey hepatitis C medications, injectables, and other specialty drugs that often force patients to delay or forgo treatment because of cost. “AGA’s voice is a welcome addition to our diverse campaign as we call on policy makers to increase transparency, competition, and value in the prescription drug market.”
“Given that some of the most expensive drugs on the market are drugs that treat GI and hepatology diseases, I believe it is important that AGA be part of the dialogue addressing drug costs. These treatments have been revolutionary and lifesaving, but we need to ensure that all patients have access to the right treatments and are not prevented from receiving the proper therapy because of cost. AGA looks forward to working with the coalition and policy makers on finding common-sense solutions to address the growing problem of drug prices,” said Dr. Timothy C. Wang, AGAF, AGA Institute president.
Prices for specialty drugs, which require special handling, administration, or monitoring, are one of the largest drivers of increased health care costs, even for those who do not use medication. Today, prescription drug expenditures are nearly 20% of health care costs and prescription spending is growing faster than any other part of the health care dollar, according to data from IMS and Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Additionally, IMS found that spending on specialty medicines has increased by $54 billion over the past 5 years, accounting for 73% of all medicine spending growth.
This June AGA announced it has joined the Campaign for Sustainable Rx Pricing (CSRxP), a broad-based campaign that works to curb rising drug costs.
“Gastroenterologists have a unique view of rising drug prices because the patients they treat are subjected to some of the most expensive medications on the market,” said CSRxP Executive Director John Rother, noting pricey hepatitis C medications, injectables, and other specialty drugs that often force patients to delay or forgo treatment because of cost. “AGA’s voice is a welcome addition to our diverse campaign as we call on policy makers to increase transparency, competition, and value in the prescription drug market.”
“Given that some of the most expensive drugs on the market are drugs that treat GI and hepatology diseases, I believe it is important that AGA be part of the dialogue addressing drug costs. These treatments have been revolutionary and lifesaving, but we need to ensure that all patients have access to the right treatments and are not prevented from receiving the proper therapy because of cost. AGA looks forward to working with the coalition and policy makers on finding common-sense solutions to address the growing problem of drug prices,” said Dr. Timothy C. Wang, AGAF, AGA Institute president.
Prices for specialty drugs, which require special handling, administration, or monitoring, are one of the largest drivers of increased health care costs, even for those who do not use medication. Today, prescription drug expenditures are nearly 20% of health care costs and prescription spending is growing faster than any other part of the health care dollar, according to data from IMS and Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Additionally, IMS found that spending on specialty medicines has increased by $54 billion over the past 5 years, accounting for 73% of all medicine spending growth.
Now accepting applications for 2017 AGA Fellows
AGA recognizes members whose accomplishments demonstrate personal commitment to the GI field with the distinction of AGA fellowship. Apply today to the program to gain recognition as a distinguished AGA Fellow. AGA fellowships honor superior professional achievement in clinical, private, or academic practice, and in basic or clinical research.
AGA Fellows will be acknowledged in several ways, including a certificate commemorating their accomplishment and the privilege of using the prestigious designation “AGAF” in professional activities. AGA Fellows are also honored at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) and on the AGA website. View the full list of benefits and criteria today.
Learn more and complete the online application by visiting http://www.gastro.org/about/aga-fellows-program. The deadline for submissions is Monday, Aug. 22, 2016.
AGA recognizes members whose accomplishments demonstrate personal commitment to the GI field with the distinction of AGA fellowship. Apply today to the program to gain recognition as a distinguished AGA Fellow. AGA fellowships honor superior professional achievement in clinical, private, or academic practice, and in basic or clinical research.
AGA Fellows will be acknowledged in several ways, including a certificate commemorating their accomplishment and the privilege of using the prestigious designation “AGAF” in professional activities. AGA Fellows are also honored at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) and on the AGA website. View the full list of benefits and criteria today.
Learn more and complete the online application by visiting http://www.gastro.org/about/aga-fellows-program. The deadline for submissions is Monday, Aug. 22, 2016.
AGA recognizes members whose accomplishments demonstrate personal commitment to the GI field with the distinction of AGA fellowship. Apply today to the program to gain recognition as a distinguished AGA Fellow. AGA fellowships honor superior professional achievement in clinical, private, or academic practice, and in basic or clinical research.
AGA Fellows will be acknowledged in several ways, including a certificate commemorating their accomplishment and the privilege of using the prestigious designation “AGAF” in professional activities. AGA Fellows are also honored at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) and on the AGA website. View the full list of benefits and criteria today.
Learn more and complete the online application by visiting http://www.gastro.org/about/aga-fellows-program. The deadline for submissions is Monday, Aug. 22, 2016.
Take networking into your own hands
The AGA Community forum has spurred engagement and collaborations on many different professional levels since its launch in early May. Recently trending topics included viral hepatitis, fecal immunochemical testing, reimbursement, practice guidelines, women in GI, and fecal transplants.
It’s easy to incorporate your new networking tool in your day-to-day practice using the AGA Community mobile app. The app gives you around-the-clock handheld access to AGA members and the discussion topics and resources that matter to you.
Learn more by downloading the app, available in AGA App Central or search your mobile app store for AGA Community. You can also join the conversations through your web browser, http://community.gastro.org.
The AGA Community forum has spurred engagement and collaborations on many different professional levels since its launch in early May. Recently trending topics included viral hepatitis, fecal immunochemical testing, reimbursement, practice guidelines, women in GI, and fecal transplants.
It’s easy to incorporate your new networking tool in your day-to-day practice using the AGA Community mobile app. The app gives you around-the-clock handheld access to AGA members and the discussion topics and resources that matter to you.
Learn more by downloading the app, available in AGA App Central or search your mobile app store for AGA Community. You can also join the conversations through your web browser, http://community.gastro.org.
The AGA Community forum has spurred engagement and collaborations on many different professional levels since its launch in early May. Recently trending topics included viral hepatitis, fecal immunochemical testing, reimbursement, practice guidelines, women in GI, and fecal transplants.
It’s easy to incorporate your new networking tool in your day-to-day practice using the AGA Community mobile app. The app gives you around-the-clock handheld access to AGA members and the discussion topics and resources that matter to you.
Learn more by downloading the app, available in AGA App Central or search your mobile app store for AGA Community. You can also join the conversations through your web browser, http://community.gastro.org.
Make the Diagnosis - June 2016
Diagnosis: Agminated blue nevus
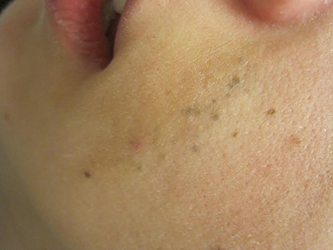
Agminated blue nevi are aggregated clusters of nevi that appear blue due to their deep dermal location and the subsequent scattering of short wavelengths of light (Tyndall effect). The clusters are typically contained within a 10 cm area. The intervening background skin is usually without hyperpigmentation or skin discoloration, although speckled pigmentation can occur. Generally, all forms of agminated nevi likely result from a loss of heterozygosity (LOH) mutation in the somatic line of an embryo, inducing a localized predilection for the development of nevi.
The differential diagnosis for agminated blue nevi includes segmental melanocytic nevi, melanoma, and other agminated melanocytic nevi: benign melanocytic nevi, atypical or dysplastic nevi, and speckled lentiginous nevi (nevus spilus). The distribution of the nevi can help narrow the differential, as segmental melanocytic nevi are less clustered and spread over a larger area than agminated blue nevi. Congenital nevi are present at birth or within a few months and often have unique features, including perifollicular pigmentary changes, hypertrichosis, and focal hypopigmentation. Acquired nevi (blue nevi, benign melanocytic nevi, and atypical or dysplastic nevi) usually descend over time from the dermal-epidermal junction to the dermis and typically become a lighter color. Lastly, the presence or absence of background pigmentation can help distinguish between agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus. Nevus spilus is a subtype of congenital melanocytic nevi with a similar aggregated appearance but has a characteristic background hyperpigmentation between the discrete nevi.
Agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus can be differentiated in the clinic by using a Wood’s lamp or performing a biopsy, which is not indicated unless atypia is present. If a non-speckled background hyperpigmentation is present on Wood’s lamp illumination, the diagnosis of nevus spilus may be more appropriate, as agminated blue nevi typically show no background pigmentation. A biopsy of the skin would allow for distinguishing between nevus spilus and agminated nevi based on the pigment within the surrounding skin. The presence of melanocytic hyperplasia within the skin surrounding the discrete nevi would support the diagnosis of nevus spilus.
The main concern with any melanocytic proliferation is the potential for transformation into a melanoma. In general, agminated nevi carry an increased melanoma risk. Specifically, congenital melanocytic nevi result in a <1-5% risk of melanoma depending on the lesion size. The risk of melanoma associated with agminated blue nevi is currently unknown, but it should be noted that individual blue nevi rarely become malignant. Since more than 50% of cutaneous melanomas develop without a preceding nevus, removal of nevi to reduce melanoma risk is not typically indicated, except in the case of a large congenital melanocytic nevi (>20cm). However, long-term surveillance is crucial for agminated blue nevi, especially if the individual has dysplastic nevus syndrome. If the involved nevi develop any features of atypia, a biopsy should be performed to assess for the development of a melanoma.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Damon McClain of Three Rivers Dermatology in Coraopolis, Pa., and Mark Ash, a medical student at East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.
Dr. Bilu Martin is in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit your case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References:
- Ashfaq A. Marghoob, Robin Blum, Robert Nossa, Klaus J. Busam, Dana Sachs, Allan Halpern. Agminated Atypical (Dysplastic) Nevi Case Report and Review of the Literature. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(7):917-920.
- Belinda Tan, Noah Craft, Lindy P. Fox, Lowell A. Goldsmith, Michael D. Tharp. Visual Dx. Blue Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16. Camila Roos Mariano da Rocha, Thaís Corsetti Grazziotin, Maria Carolina Widholzer Rey, Laura Luzzatto, Renan Rangel Bonamigo. Congenital agminated melanocytic nevus - Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 Suppl 1):170-2.
- Chris G. Adigun, Jeffrey D. Bernhard, Sarah Stein, Karen Wiss, Sheila Galbraith, Craig N. Burkhart, Dean Morrell, Lynn Garfunkel, Nancy Esterly. Visual Dx. Agminated Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16.
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Acquired melanocytic nevi (moles). In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Congenital melanocytic nevi. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Maria A. Pizzichetta, H. Peter Soyer, Cesare Massone, Lorenzo Cerroni. Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Agminated Blue Nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1209-1226.
Diagnosis: Agminated blue nevus
Agminated blue nevi are aggregated clusters of nevi that appear blue due to their deep dermal location and the subsequent scattering of short wavelengths of light (Tyndall effect). The clusters are typically contained within a 10 cm area. The intervening background skin is usually without hyperpigmentation or skin discoloration, although speckled pigmentation can occur. Generally, all forms of agminated nevi likely result from a loss of heterozygosity (LOH) mutation in the somatic line of an embryo, inducing a localized predilection for the development of nevi.
The differential diagnosis for agminated blue nevi includes segmental melanocytic nevi, melanoma, and other agminated melanocytic nevi: benign melanocytic nevi, atypical or dysplastic nevi, and speckled lentiginous nevi (nevus spilus). The distribution of the nevi can help narrow the differential, as segmental melanocytic nevi are less clustered and spread over a larger area than agminated blue nevi. Congenital nevi are present at birth or within a few months and often have unique features, including perifollicular pigmentary changes, hypertrichosis, and focal hypopigmentation. Acquired nevi (blue nevi, benign melanocytic nevi, and atypical or dysplastic nevi) usually descend over time from the dermal-epidermal junction to the dermis and typically become a lighter color. Lastly, the presence or absence of background pigmentation can help distinguish between agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus. Nevus spilus is a subtype of congenital melanocytic nevi with a similar aggregated appearance but has a characteristic background hyperpigmentation between the discrete nevi.
Agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus can be differentiated in the clinic by using a Wood’s lamp or performing a biopsy, which is not indicated unless atypia is present. If a non-speckled background hyperpigmentation is present on Wood’s lamp illumination, the diagnosis of nevus spilus may be more appropriate, as agminated blue nevi typically show no background pigmentation. A biopsy of the skin would allow for distinguishing between nevus spilus and agminated nevi based on the pigment within the surrounding skin. The presence of melanocytic hyperplasia within the skin surrounding the discrete nevi would support the diagnosis of nevus spilus.
The main concern with any melanocytic proliferation is the potential for transformation into a melanoma. In general, agminated nevi carry an increased melanoma risk. Specifically, congenital melanocytic nevi result in a <1-5% risk of melanoma depending on the lesion size. The risk of melanoma associated with agminated blue nevi is currently unknown, but it should be noted that individual blue nevi rarely become malignant. Since more than 50% of cutaneous melanomas develop without a preceding nevus, removal of nevi to reduce melanoma risk is not typically indicated, except in the case of a large congenital melanocytic nevi (>20cm). However, long-term surveillance is crucial for agminated blue nevi, especially if the individual has dysplastic nevus syndrome. If the involved nevi develop any features of atypia, a biopsy should be performed to assess for the development of a melanoma.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Damon McClain of Three Rivers Dermatology in Coraopolis, Pa., and Mark Ash, a medical student at East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.
Dr. Bilu Martin is in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit your case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References:
- Ashfaq A. Marghoob, Robin Blum, Robert Nossa, Klaus J. Busam, Dana Sachs, Allan Halpern. Agminated Atypical (Dysplastic) Nevi Case Report and Review of the Literature. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(7):917-920.
- Belinda Tan, Noah Craft, Lindy P. Fox, Lowell A. Goldsmith, Michael D. Tharp. Visual Dx. Blue Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16. Camila Roos Mariano da Rocha, Thaís Corsetti Grazziotin, Maria Carolina Widholzer Rey, Laura Luzzatto, Renan Rangel Bonamigo. Congenital agminated melanocytic nevus - Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 Suppl 1):170-2.
- Chris G. Adigun, Jeffrey D. Bernhard, Sarah Stein, Karen Wiss, Sheila Galbraith, Craig N. Burkhart, Dean Morrell, Lynn Garfunkel, Nancy Esterly. Visual Dx. Agminated Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16.
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Acquired melanocytic nevi (moles). In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Congenital melanocytic nevi. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Maria A. Pizzichetta, H. Peter Soyer, Cesare Massone, Lorenzo Cerroni. Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Agminated Blue Nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1209-1226.
Diagnosis: Agminated blue nevus
Agminated blue nevi are aggregated clusters of nevi that appear blue due to their deep dermal location and the subsequent scattering of short wavelengths of light (Tyndall effect). The clusters are typically contained within a 10 cm area. The intervening background skin is usually without hyperpigmentation or skin discoloration, although speckled pigmentation can occur. Generally, all forms of agminated nevi likely result from a loss of heterozygosity (LOH) mutation in the somatic line of an embryo, inducing a localized predilection for the development of nevi.
The differential diagnosis for agminated blue nevi includes segmental melanocytic nevi, melanoma, and other agminated melanocytic nevi: benign melanocytic nevi, atypical or dysplastic nevi, and speckled lentiginous nevi (nevus spilus). The distribution of the nevi can help narrow the differential, as segmental melanocytic nevi are less clustered and spread over a larger area than agminated blue nevi. Congenital nevi are present at birth or within a few months and often have unique features, including perifollicular pigmentary changes, hypertrichosis, and focal hypopigmentation. Acquired nevi (blue nevi, benign melanocytic nevi, and atypical or dysplastic nevi) usually descend over time from the dermal-epidermal junction to the dermis and typically become a lighter color. Lastly, the presence or absence of background pigmentation can help distinguish between agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus. Nevus spilus is a subtype of congenital melanocytic nevi with a similar aggregated appearance but has a characteristic background hyperpigmentation between the discrete nevi.
Agminated blue nevi and nevus spilus can be differentiated in the clinic by using a Wood’s lamp or performing a biopsy, which is not indicated unless atypia is present. If a non-speckled background hyperpigmentation is present on Wood’s lamp illumination, the diagnosis of nevus spilus may be more appropriate, as agminated blue nevi typically show no background pigmentation. A biopsy of the skin would allow for distinguishing between nevus spilus and agminated nevi based on the pigment within the surrounding skin. The presence of melanocytic hyperplasia within the skin surrounding the discrete nevi would support the diagnosis of nevus spilus.
The main concern with any melanocytic proliferation is the potential for transformation into a melanoma. In general, agminated nevi carry an increased melanoma risk. Specifically, congenital melanocytic nevi result in a <1-5% risk of melanoma depending on the lesion size. The risk of melanoma associated with agminated blue nevi is currently unknown, but it should be noted that individual blue nevi rarely become malignant. Since more than 50% of cutaneous melanomas develop without a preceding nevus, removal of nevi to reduce melanoma risk is not typically indicated, except in the case of a large congenital melanocytic nevi (>20cm). However, long-term surveillance is crucial for agminated blue nevi, especially if the individual has dysplastic nevus syndrome. If the involved nevi develop any features of atypia, a biopsy should be performed to assess for the development of a melanoma.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Damon McClain of Three Rivers Dermatology in Coraopolis, Pa., and Mark Ash, a medical student at East Carolina University, Greenville, N.C.
Dr. Bilu Martin is in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at edermatologynews.com. To submit your case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References:
- Ashfaq A. Marghoob, Robin Blum, Robert Nossa, Klaus J. Busam, Dana Sachs, Allan Halpern. Agminated Atypical (Dysplastic) Nevi Case Report and Review of the Literature. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(7):917-920.
- Belinda Tan, Noah Craft, Lindy P. Fox, Lowell A. Goldsmith, Michael D. Tharp. Visual Dx. Blue Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16. Camila Roos Mariano da Rocha, Thaís Corsetti Grazziotin, Maria Carolina Widholzer Rey, Laura Luzzatto, Renan Rangel Bonamigo. Congenital agminated melanocytic nevus - Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(6 Suppl 1):170-2.
- Chris G. Adigun, Jeffrey D. Bernhard, Sarah Stein, Karen Wiss, Sheila Galbraith, Craig N. Burkhart, Dean Morrell, Lynn Garfunkel, Nancy Esterly. Visual Dx. Agminated Nevus. Accessed 2/11/16.
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Acquired melanocytic nevi (moles). In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Julie V Schaffer and Jean L Bolognia. Congenital melanocytic nevi. In: UpToDate, Post TW (Ed), UpToDate, Waltham, MA. (Accessed on February 11, 2016.)
- Maria A. Pizzichetta, H. Peter Soyer, Cesare Massone, Lorenzo Cerroni. Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Agminated Blue Nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(9):1209-1226.
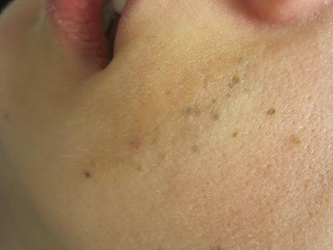
A 23-year-old healthy female presented with a several-year history of asymptomatic dark spots on her left cheek. The lesions seemed to be darkening. Incidentally, she was in a four-wheeler accident in middle school and suffered facial trauma, which resulted in the replacement of two superior left front teeth, but she denied significant cutaneous injury at that time. On physical examination, there were several clustered 1-mm blue-gray macules in linear formation with a subtle underlying tan patch on her left cheek.
Case Study: Seizure Freedom and Side Effects
Nikesh Ardeshna, MD
Dr. Ardeshna is the Medical Director of Adult Epilepsy Services at Royal Oak Hospital, Beaumont Health System, in Royal Oak, Michigan.
The patient is a 74-year-old male diagnosed with primary generalized epilepsy since age 35. The patient’s last grand mal seizure was 15 years ago. He was referred to an epileptologist for establishment of care, as his current neurologist was retiring. The patient was accompanied by his family. The patient indicated that he was seizure free. His antiepileptic regimen included levetiracetam (Keppra) 2000 mg twice daily, primidone (Mysoline) 500 mg twice daily, phenytoin (Dilantin) 300 mg twice daily, and topiramate (Topamax) 300 mg twice daily. When taking the inital history, the epileptologist noticed the patient’s attention and concentration waxed and waned. Instructions had to be repeated and items re-explained. His rate of processing was slow and there were pauses in his speech. On mental status testing, registration was three out of three items; recall after delay was one out of three. The physical examination revealed a wide based gait. Swelling of the gums was noted (the patient mentioned that his dentist told him that his gums bleed easily). The patient showed the epileptologist the report of his recent bone scan, demonstrating significant osteopenia, and asked if a cause for that could be determined. Though the patient did not admit it, his family indicated that the patient’s short-term memory was essentially “non-existent” and his walking also had become quite unstable. All of these observations have been happening for the last few years.
Questions:
1. Was the patient seizure free?
Possibly yes, possibly no. Based on the examination: the patient has pauses in his speech and slowed processing. The differential diagnosis includes seizures. Some of the patient’s presentation may be due to the side effects of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It is also possible that the patient’s presentation was due to a combination of seizures and side effects of AEDs.
2. What are some of the side effects of AEDs the patient is taking?
Cognitive slowing, memory loss, slowed processing, word-finding difficulties, mood changes, osteopenia, gait instability, dizziness, and gingival hyperplasia.
3. Based on the patient’s age, medical conditions, and exam what if any changes should be considered to the antiepileptic regimen?
a. Simplify the regimen, if possible to 3 or fewer AEDs. Polytherapy can lead to more side effects.
b. Based on the patient’s complaining of bleeding gums, and family indicating he walks unsteady, consideration could be given to tapering phenytoin and increasing one of the other AEDs, or substituting the phenytoin for another AED. The overall goal would be to simplify the patient’s AED regimen, and/or use newer agents with comparatively lesser likelihood of side effects that are less likely to interact with other AEDs or medications.
Nikesh Ardeshna, MD
Dr. Ardeshna is the Medical Director of Adult Epilepsy Services at Royal Oak Hospital, Beaumont Health System, in Royal Oak, Michigan.
The patient is a 74-year-old male diagnosed with primary generalized epilepsy since age 35. The patient’s last grand mal seizure was 15 years ago. He was referred to an epileptologist for establishment of care, as his current neurologist was retiring. The patient was accompanied by his family. The patient indicated that he was seizure free. His antiepileptic regimen included levetiracetam (Keppra) 2000 mg twice daily, primidone (Mysoline) 500 mg twice daily, phenytoin (Dilantin) 300 mg twice daily, and topiramate (Topamax) 300 mg twice daily. When taking the inital history, the epileptologist noticed the patient’s attention and concentration waxed and waned. Instructions had to be repeated and items re-explained. His rate of processing was slow and there were pauses in his speech. On mental status testing, registration was three out of three items; recall after delay was one out of three. The physical examination revealed a wide based gait. Swelling of the gums was noted (the patient mentioned that his dentist told him that his gums bleed easily). The patient showed the epileptologist the report of his recent bone scan, demonstrating significant osteopenia, and asked if a cause for that could be determined. Though the patient did not admit it, his family indicated that the patient’s short-term memory was essentially “non-existent” and his walking also had become quite unstable. All of these observations have been happening for the last few years.
Questions:
1. Was the patient seizure free?
Possibly yes, possibly no. Based on the examination: the patient has pauses in his speech and slowed processing. The differential diagnosis includes seizures. Some of the patient’s presentation may be due to the side effects of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It is also possible that the patient’s presentation was due to a combination of seizures and side effects of AEDs.
2. What are some of the side effects of AEDs the patient is taking?
Cognitive slowing, memory loss, slowed processing, word-finding difficulties, mood changes, osteopenia, gait instability, dizziness, and gingival hyperplasia.
3. Based on the patient’s age, medical conditions, and exam what if any changes should be considered to the antiepileptic regimen?
a. Simplify the regimen, if possible to 3 or fewer AEDs. Polytherapy can lead to more side effects.
b. Based on the patient’s complaining of bleeding gums, and family indicating he walks unsteady, consideration could be given to tapering phenytoin and increasing one of the other AEDs, or substituting the phenytoin for another AED. The overall goal would be to simplify the patient’s AED regimen, and/or use newer agents with comparatively lesser likelihood of side effects that are less likely to interact with other AEDs or medications.
Nikesh Ardeshna, MD
Dr. Ardeshna is the Medical Director of Adult Epilepsy Services at Royal Oak Hospital, Beaumont Health System, in Royal Oak, Michigan.
The patient is a 74-year-old male diagnosed with primary generalized epilepsy since age 35. The patient’s last grand mal seizure was 15 years ago. He was referred to an epileptologist for establishment of care, as his current neurologist was retiring. The patient was accompanied by his family. The patient indicated that he was seizure free. His antiepileptic regimen included levetiracetam (Keppra) 2000 mg twice daily, primidone (Mysoline) 500 mg twice daily, phenytoin (Dilantin) 300 mg twice daily, and topiramate (Topamax) 300 mg twice daily. When taking the inital history, the epileptologist noticed the patient’s attention and concentration waxed and waned. Instructions had to be repeated and items re-explained. His rate of processing was slow and there were pauses in his speech. On mental status testing, registration was three out of three items; recall after delay was one out of three. The physical examination revealed a wide based gait. Swelling of the gums was noted (the patient mentioned that his dentist told him that his gums bleed easily). The patient showed the epileptologist the report of his recent bone scan, demonstrating significant osteopenia, and asked if a cause for that could be determined. Though the patient did not admit it, his family indicated that the patient’s short-term memory was essentially “non-existent” and his walking also had become quite unstable. All of these observations have been happening for the last few years.
Questions:
1. Was the patient seizure free?
Possibly yes, possibly no. Based on the examination: the patient has pauses in his speech and slowed processing. The differential diagnosis includes seizures. Some of the patient’s presentation may be due to the side effects of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It is also possible that the patient’s presentation was due to a combination of seizures and side effects of AEDs.
2. What are some of the side effects of AEDs the patient is taking?
Cognitive slowing, memory loss, slowed processing, word-finding difficulties, mood changes, osteopenia, gait instability, dizziness, and gingival hyperplasia.
3. Based on the patient’s age, medical conditions, and exam what if any changes should be considered to the antiepileptic regimen?
a. Simplify the regimen, if possible to 3 or fewer AEDs. Polytherapy can lead to more side effects.
b. Based on the patient’s complaining of bleeding gums, and family indicating he walks unsteady, consideration could be given to tapering phenytoin and increasing one of the other AEDs, or substituting the phenytoin for another AED. The overall goal would be to simplify the patient’s AED regimen, and/or use newer agents with comparatively lesser likelihood of side effects that are less likely to interact with other AEDs or medications.
SLEEP TIGHT: CPAP may be vasculoprotective in stroke/TIA
DENVER – Long-term continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack resulted in improved cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors, better neurologic function, and a reduction in the recurrent vascular event rate, compared with usual care in the SLEEP TIGHT study.
“Up to 25% of patients will have a stroke, cardiovascular event, or death within 90 days after a minor stroke or TIA [transient ischemic attack] despite current preventive strategies. And, importantly, patients with a TIA or stroke have a high prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea – on the order of 60%-80%,” explained Dr. H. Klar Yaggi at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
SLEEP TIGHT’s findings support the hypothesis that diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent minor stroke or TIA will address a major unmet need for better methods of reducing the high vascular risk present in this population, said Dr. Yaggi of Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
SLEEP TIGHT was a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored phase II, 12-month, multicenter, single-blind, randomized, proof-of-concept study. It included 252 patients, 80% of whom had a recent minor stroke, the rest a TIA. These were patients with high levels of cardiovascular risk factors: two-thirds had hypertension, half were hyperlipidemic, 40% had diabetes, 15% had a prior MI, 10% had atrial fibrillation, and the group’s mean body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Polysomnography revealed that 76% of subjects had sleep apnea as defined by an apnea-hypopnea index of at least 5 events per hour. In fact, they averaged about 23 events per hour, putting them in the moderate-severity range. As is common among stroke/TIA patients with sleep apnea, they experienced less daytime sleepiness than is typical in a sleep clinic population, with a mean baseline Epworth Sleepiness Scale score of 7.
Participants were randomized to one of three groups: a usual care control group, a CPAP arm, or an enhanced CPAP arm. The enhanced intervention protocol was designed to boost CPAP adherence; it included targeted education, a customized cognitive intervention, and additional CPAP support beyond the standard CPAP protocols used in sleep medicine clinics. Patients with sleep apnea in the two intervention arms were then placed on CPAP.
At 1 year of follow-up, the stroke rate was 8.7 per 100 patient-years in the usual care group, compared with 5.5 per 100 person-years in the combined intervention arms. The composite cardiovascular event rate, composed of all-cause mortality, acute MI, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or urgent coronary revascularization, was 13.1 per 100 person-years with usual care and 11.0 in the CPAP intervention arms. While these results are encouraging, SLEEP TIGHT wasn’t powered to show significant differences in these hard events.
Outcomes across the board didn’t differ significantly between the CPAP and enhanced CPAP groups. And since the mean number of hours of CPAP use per night was also similar in the two groups – 3.9 hours with standard CPAP and 4.3 hours with enhanced CPAP – it’s likely that the phase III trial will rely upon the much simpler standard CPAP intervention, according to Dr. Yaggi.
He deemed CPAP adherence in this stroke/TIA population to be similar to the rates typically seen in routine sleep medicine practice. Roughly 40% of the stroke/TIA patients were rated as having good adherence, 30% made some use of the therapy, and 30% had no or poor adherence.
Nonetheless, patients in the two intervention arms did significantly better than the usual care group in terms of 1-year changes in insulin resistance and glycosylated hemoglobin. They also had lower 24-hour mean systolic blood pressure and were more likely to convert to a favorable pattern of nocturnal blood pressure dipping. However, no differences between the intervention and usual care groups were seen in levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, the two markers of systemic inflammation analyzed. Nor did the CPAP intervention provide any benefit in terms of heart rate variability and other measures of autonomic function.
Fifty-eight percent of patients in the intervention arms ended up with a desirable National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 0-1, compared with 38% of the usual care group. In addition, daytime sleepiness as reflected in Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores was reduced at last follow-up to a significantly greater extent in the CPAP groups, Dr. Yaggi noted.
Greater CPAP use was associated with a favorable trend for improvement in the modified Rankin score, a measure of functional ability: a 0.3-point reduction with no or poor CPAP use, a 0.4-point decrease with some use, and a 0.9-point reduction with good use.
The encouraging results will be helpful in designing a planned much larger, event-driven, definitive phase III trial, Dr. Yaggi said.
Dr. Yaggi reported having no financial conflicts regarding this National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute-sponsored study.
DENVER – Long-term continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack resulted in improved cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors, better neurologic function, and a reduction in the recurrent vascular event rate, compared with usual care in the SLEEP TIGHT study.
“Up to 25% of patients will have a stroke, cardiovascular event, or death within 90 days after a minor stroke or TIA [transient ischemic attack] despite current preventive strategies. And, importantly, patients with a TIA or stroke have a high prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea – on the order of 60%-80%,” explained Dr. H. Klar Yaggi at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
SLEEP TIGHT’s findings support the hypothesis that diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent minor stroke or TIA will address a major unmet need for better methods of reducing the high vascular risk present in this population, said Dr. Yaggi of Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
SLEEP TIGHT was a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored phase II, 12-month, multicenter, single-blind, randomized, proof-of-concept study. It included 252 patients, 80% of whom had a recent minor stroke, the rest a TIA. These were patients with high levels of cardiovascular risk factors: two-thirds had hypertension, half were hyperlipidemic, 40% had diabetes, 15% had a prior MI, 10% had atrial fibrillation, and the group’s mean body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Polysomnography revealed that 76% of subjects had sleep apnea as defined by an apnea-hypopnea index of at least 5 events per hour. In fact, they averaged about 23 events per hour, putting them in the moderate-severity range. As is common among stroke/TIA patients with sleep apnea, they experienced less daytime sleepiness than is typical in a sleep clinic population, with a mean baseline Epworth Sleepiness Scale score of 7.
Participants were randomized to one of three groups: a usual care control group, a CPAP arm, or an enhanced CPAP arm. The enhanced intervention protocol was designed to boost CPAP adherence; it included targeted education, a customized cognitive intervention, and additional CPAP support beyond the standard CPAP protocols used in sleep medicine clinics. Patients with sleep apnea in the two intervention arms were then placed on CPAP.
At 1 year of follow-up, the stroke rate was 8.7 per 100 patient-years in the usual care group, compared with 5.5 per 100 person-years in the combined intervention arms. The composite cardiovascular event rate, composed of all-cause mortality, acute MI, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or urgent coronary revascularization, was 13.1 per 100 person-years with usual care and 11.0 in the CPAP intervention arms. While these results are encouraging, SLEEP TIGHT wasn’t powered to show significant differences in these hard events.
Outcomes across the board didn’t differ significantly between the CPAP and enhanced CPAP groups. And since the mean number of hours of CPAP use per night was also similar in the two groups – 3.9 hours with standard CPAP and 4.3 hours with enhanced CPAP – it’s likely that the phase III trial will rely upon the much simpler standard CPAP intervention, according to Dr. Yaggi.
He deemed CPAP adherence in this stroke/TIA population to be similar to the rates typically seen in routine sleep medicine practice. Roughly 40% of the stroke/TIA patients were rated as having good adherence, 30% made some use of the therapy, and 30% had no or poor adherence.
Nonetheless, patients in the two intervention arms did significantly better than the usual care group in terms of 1-year changes in insulin resistance and glycosylated hemoglobin. They also had lower 24-hour mean systolic blood pressure and were more likely to convert to a favorable pattern of nocturnal blood pressure dipping. However, no differences between the intervention and usual care groups were seen in levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, the two markers of systemic inflammation analyzed. Nor did the CPAP intervention provide any benefit in terms of heart rate variability and other measures of autonomic function.
Fifty-eight percent of patients in the intervention arms ended up with a desirable National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 0-1, compared with 38% of the usual care group. In addition, daytime sleepiness as reflected in Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores was reduced at last follow-up to a significantly greater extent in the CPAP groups, Dr. Yaggi noted.
Greater CPAP use was associated with a favorable trend for improvement in the modified Rankin score, a measure of functional ability: a 0.3-point reduction with no or poor CPAP use, a 0.4-point decrease with some use, and a 0.9-point reduction with good use.
The encouraging results will be helpful in designing a planned much larger, event-driven, definitive phase III trial, Dr. Yaggi said.
Dr. Yaggi reported having no financial conflicts regarding this National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute-sponsored study.
DENVER – Long-term continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent mild stroke or transient ischemic attack resulted in improved cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors, better neurologic function, and a reduction in the recurrent vascular event rate, compared with usual care in the SLEEP TIGHT study.
“Up to 25% of patients will have a stroke, cardiovascular event, or death within 90 days after a minor stroke or TIA [transient ischemic attack] despite current preventive strategies. And, importantly, patients with a TIA or stroke have a high prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea – on the order of 60%-80%,” explained Dr. H. Klar Yaggi at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
SLEEP TIGHT’s findings support the hypothesis that diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea in patients with a recent minor stroke or TIA will address a major unmet need for better methods of reducing the high vascular risk present in this population, said Dr. Yaggi of Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
SLEEP TIGHT was a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored phase II, 12-month, multicenter, single-blind, randomized, proof-of-concept study. It included 252 patients, 80% of whom had a recent minor stroke, the rest a TIA. These were patients with high levels of cardiovascular risk factors: two-thirds had hypertension, half were hyperlipidemic, 40% had diabetes, 15% had a prior MI, 10% had atrial fibrillation, and the group’s mean body mass index was 30 kg/m2. Polysomnography revealed that 76% of subjects had sleep apnea as defined by an apnea-hypopnea index of at least 5 events per hour. In fact, they averaged about 23 events per hour, putting them in the moderate-severity range. As is common among stroke/TIA patients with sleep apnea, they experienced less daytime sleepiness than is typical in a sleep clinic population, with a mean baseline Epworth Sleepiness Scale score of 7.
Participants were randomized to one of three groups: a usual care control group, a CPAP arm, or an enhanced CPAP arm. The enhanced intervention protocol was designed to boost CPAP adherence; it included targeted education, a customized cognitive intervention, and additional CPAP support beyond the standard CPAP protocols used in sleep medicine clinics. Patients with sleep apnea in the two intervention arms were then placed on CPAP.
At 1 year of follow-up, the stroke rate was 8.7 per 100 patient-years in the usual care group, compared with 5.5 per 100 person-years in the combined intervention arms. The composite cardiovascular event rate, composed of all-cause mortality, acute MI, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or urgent coronary revascularization, was 13.1 per 100 person-years with usual care and 11.0 in the CPAP intervention arms. While these results are encouraging, SLEEP TIGHT wasn’t powered to show significant differences in these hard events.
Outcomes across the board didn’t differ significantly between the CPAP and enhanced CPAP groups. And since the mean number of hours of CPAP use per night was also similar in the two groups – 3.9 hours with standard CPAP and 4.3 hours with enhanced CPAP – it’s likely that the phase III trial will rely upon the much simpler standard CPAP intervention, according to Dr. Yaggi.
He deemed CPAP adherence in this stroke/TIA population to be similar to the rates typically seen in routine sleep medicine practice. Roughly 40% of the stroke/TIA patients were rated as having good adherence, 30% made some use of the therapy, and 30% had no or poor adherence.
Nonetheless, patients in the two intervention arms did significantly better than the usual care group in terms of 1-year changes in insulin resistance and glycosylated hemoglobin. They also had lower 24-hour mean systolic blood pressure and were more likely to convert to a favorable pattern of nocturnal blood pressure dipping. However, no differences between the intervention and usual care groups were seen in levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, the two markers of systemic inflammation analyzed. Nor did the CPAP intervention provide any benefit in terms of heart rate variability and other measures of autonomic function.
Fifty-eight percent of patients in the intervention arms ended up with a desirable National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 0-1, compared with 38% of the usual care group. In addition, daytime sleepiness as reflected in Epworth Sleepiness Scale scores was reduced at last follow-up to a significantly greater extent in the CPAP groups, Dr. Yaggi noted.
Greater CPAP use was associated with a favorable trend for improvement in the modified Rankin score, a measure of functional ability: a 0.3-point reduction with no or poor CPAP use, a 0.4-point decrease with some use, and a 0.9-point reduction with good use.
The encouraging results will be helpful in designing a planned much larger, event-driven, definitive phase III trial, Dr. Yaggi said.
Dr. Yaggi reported having no financial conflicts regarding this National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute-sponsored study.
AT SLEEP 2016
Key clinical point: CPAP treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in patients with a recent TIA or mild stroke appears to reduce their risk of further vascular events.
Major finding: At 1 year of follow-up, the stroke rate in patients randomized to CPAP, including the large subgroup with poor or no adherence, was 5.5 events per 100 person-years, compared with 8.7 in usual care controls.
Data source: SLEEP TIGHT was a 12-month, multicenter, prospective, randomized, single-blind, phase II trial including 252 patients.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding this National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–sponsored trial.