User login
Use of bilateral internal mammary arteries in CABG stagnates
HOUSTON – Over the past 5 years there has been no growth in bilateral internal mammary artery use among Medicare beneficiaries, and the frequency of bilateral internal mammary artery use during coronary artery bypass grafting remained low, according to a large observational analysis.
“Despite a growing evidence base supporting bilateral internal mammary artery use with regard to long-term survival and freedom from repeat revascularization, rates of bilateral internal mammary artery [BIMA] use remain low, with no evidence of growth,” Alexander Iribarne, MD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. “Therefore, there is significant opportunity for adoption of bilateral internal mammary artery grafting in the United States.”
The most recent report of CABG trends in the United States published from the STS database showed that in 2009, fewer than 5% of patients who underwent CABG received a BIMA (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012 Feb;143[2]:273-81). In an effort to characterize the adoption rate and regional variation of BIMA use in the United States, Dr. Iribarne, director of cardiac surgical research in the section of cardiac surgery at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and his associates examined records from nearly 150 million Medicare beneficiaries from 2009-2014. “This work is unique in that we not only looked at trends in rates of usage but also how this varied by geographic location,” he said.
“I was surprised to find that despite the growing literature supporting BIMA use, there was no growth in rates of usage over the 5-year study period, with rates remaining low,” Dr. Iribarne said. “I was also surprised to see that there was significant regional variation in use that appeared to correlate, in part, with overall CABG volume, although the moderate correlation coefficient indicates that additional factors beyond CABG volume are involved.”
A key limitation of the study, he said, was that its patients were aged 65 and older. Dr. Iribarne disclosed that he receives grant funding from the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Graham Foundation and the Dartmouth SYNERGY Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
HOUSTON – Over the past 5 years there has been no growth in bilateral internal mammary artery use among Medicare beneficiaries, and the frequency of bilateral internal mammary artery use during coronary artery bypass grafting remained low, according to a large observational analysis.
“Despite a growing evidence base supporting bilateral internal mammary artery use with regard to long-term survival and freedom from repeat revascularization, rates of bilateral internal mammary artery [BIMA] use remain low, with no evidence of growth,” Alexander Iribarne, MD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. “Therefore, there is significant opportunity for adoption of bilateral internal mammary artery grafting in the United States.”
The most recent report of CABG trends in the United States published from the STS database showed that in 2009, fewer than 5% of patients who underwent CABG received a BIMA (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012 Feb;143[2]:273-81). In an effort to characterize the adoption rate and regional variation of BIMA use in the United States, Dr. Iribarne, director of cardiac surgical research in the section of cardiac surgery at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and his associates examined records from nearly 150 million Medicare beneficiaries from 2009-2014. “This work is unique in that we not only looked at trends in rates of usage but also how this varied by geographic location,” he said.
“I was surprised to find that despite the growing literature supporting BIMA use, there was no growth in rates of usage over the 5-year study period, with rates remaining low,” Dr. Iribarne said. “I was also surprised to see that there was significant regional variation in use that appeared to correlate, in part, with overall CABG volume, although the moderate correlation coefficient indicates that additional factors beyond CABG volume are involved.”
A key limitation of the study, he said, was that its patients were aged 65 and older. Dr. Iribarne disclosed that he receives grant funding from the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Graham Foundation and the Dartmouth SYNERGY Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
HOUSTON – Over the past 5 years there has been no growth in bilateral internal mammary artery use among Medicare beneficiaries, and the frequency of bilateral internal mammary artery use during coronary artery bypass grafting remained low, according to a large observational analysis.
“Despite a growing evidence base supporting bilateral internal mammary artery use with regard to long-term survival and freedom from repeat revascularization, rates of bilateral internal mammary artery [BIMA] use remain low, with no evidence of growth,” Alexander Iribarne, MD, said during an interview at the annual meeting of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. “Therefore, there is significant opportunity for adoption of bilateral internal mammary artery grafting in the United States.”
The most recent report of CABG trends in the United States published from the STS database showed that in 2009, fewer than 5% of patients who underwent CABG received a BIMA (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012 Feb;143[2]:273-81). In an effort to characterize the adoption rate and regional variation of BIMA use in the United States, Dr. Iribarne, director of cardiac surgical research in the section of cardiac surgery at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and his associates examined records from nearly 150 million Medicare beneficiaries from 2009-2014. “This work is unique in that we not only looked at trends in rates of usage but also how this varied by geographic location,” he said.
“I was surprised to find that despite the growing literature supporting BIMA use, there was no growth in rates of usage over the 5-year study period, with rates remaining low,” Dr. Iribarne said. “I was also surprised to see that there was significant regional variation in use that appeared to correlate, in part, with overall CABG volume, although the moderate correlation coefficient indicates that additional factors beyond CABG volume are involved.”
A key limitation of the study, he said, was that its patients were aged 65 and older. Dr. Iribarne disclosed that he receives grant funding from the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Graham Foundation and the Dartmouth SYNERGY Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
AT THE STS ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The absolute national rate of BIMA use fell from 0.216 claims per 1,000 beneficiaries in 2009 to 0.143 in 2014 (P less than .001).
Data source: An analysis of medical records from nearly 150 million Medicare beneficiaries during 2009-2014.
Disclosures: Dr. Iribarne disclosed that he receives grant funding from the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Graham Foundation and the Dartmouth SYNERGY Clinical and Translational Science Institute.
AGA statement on U.S. travel ban
In early February, AGA released the following statement on the U.S. travel ban:
Science and illness ignore borders and political divides. That is why AGA is concerned that the recent U.S. executive order on immigration could limit scientific exchange, delay patient care, and impair medical training.
AGA is committed to diversity, which includes race, ethnicity, and national origin. Diversity within training programs and laboratories in the United States built today’s practice of gastroenterology. Scientists from around the world publish in our journals, work in our laboratories, train in our programs, and present data at Digestive Disease Week.® This exchange leads to better patient care, and very sick patients travel to the U.S. from around the world for the best digestive health care.
In light of these concerns, AGA adds our support to a growing number of medical institutions urging the administration to consider the devastating impact of the executive order on the health of the nation that will result from turning away patients, health professionals, and researchers. The recent immigration policy is clearly detrimental to America’s leadership role in advancing health care and to the standing of the U.S. within the international community.
“Know that the policies of AGA’s home country in no way reflect our position as an organization, and we continue to welcome and support physicians and investigators from all nations,” said AGA Institute President Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF. “We understand the impact that the recent ban has had on many, and apologize for any hurt or disruption it may have caused in your lives or careers.”
To better advocate on behalf of international members and patients, Dr. Wang invites members to the AGA Community, either publicly or anonymously, to share your stories about how a travel ban could affect your patients, practice, academic center, training program, or lab.
For more updates, please visit gastro.org.
In early February, AGA released the following statement on the U.S. travel ban:
Science and illness ignore borders and political divides. That is why AGA is concerned that the recent U.S. executive order on immigration could limit scientific exchange, delay patient care, and impair medical training.
AGA is committed to diversity, which includes race, ethnicity, and national origin. Diversity within training programs and laboratories in the United States built today’s practice of gastroenterology. Scientists from around the world publish in our journals, work in our laboratories, train in our programs, and present data at Digestive Disease Week.® This exchange leads to better patient care, and very sick patients travel to the U.S. from around the world for the best digestive health care.
In light of these concerns, AGA adds our support to a growing number of medical institutions urging the administration to consider the devastating impact of the executive order on the health of the nation that will result from turning away patients, health professionals, and researchers. The recent immigration policy is clearly detrimental to America’s leadership role in advancing health care and to the standing of the U.S. within the international community.
“Know that the policies of AGA’s home country in no way reflect our position as an organization, and we continue to welcome and support physicians and investigators from all nations,” said AGA Institute President Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF. “We understand the impact that the recent ban has had on many, and apologize for any hurt or disruption it may have caused in your lives or careers.”
To better advocate on behalf of international members and patients, Dr. Wang invites members to the AGA Community, either publicly or anonymously, to share your stories about how a travel ban could affect your patients, practice, academic center, training program, or lab.
For more updates, please visit gastro.org.
In early February, AGA released the following statement on the U.S. travel ban:
Science and illness ignore borders and political divides. That is why AGA is concerned that the recent U.S. executive order on immigration could limit scientific exchange, delay patient care, and impair medical training.
AGA is committed to diversity, which includes race, ethnicity, and national origin. Diversity within training programs and laboratories in the United States built today’s practice of gastroenterology. Scientists from around the world publish in our journals, work in our laboratories, train in our programs, and present data at Digestive Disease Week.® This exchange leads to better patient care, and very sick patients travel to the U.S. from around the world for the best digestive health care.
In light of these concerns, AGA adds our support to a growing number of medical institutions urging the administration to consider the devastating impact of the executive order on the health of the nation that will result from turning away patients, health professionals, and researchers. The recent immigration policy is clearly detrimental to America’s leadership role in advancing health care and to the standing of the U.S. within the international community.
“Know that the policies of AGA’s home country in no way reflect our position as an organization, and we continue to welcome and support physicians and investigators from all nations,” said AGA Institute President Timothy Wang, MD, AGAF. “We understand the impact that the recent ban has had on many, and apologize for any hurt or disruption it may have caused in your lives or careers.”
To better advocate on behalf of international members and patients, Dr. Wang invites members to the AGA Community, either publicly or anonymously, to share your stories about how a travel ban could affect your patients, practice, academic center, training program, or lab.
For more updates, please visit gastro.org.
Report of potential interaction between PPIs, clopidogrel
The January 2009 issue of GI & Hepatology News (GIHN) featured an article on the potential drug interaction between proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and clopidogrel.
In the study of interest, researchers retrospectively reviewed 16,000 patients prescribed clopidogrel after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and found that those patients also on a PPI were 1.5 times as likely to suffer from a myocardial infarction, stroke, or be hospitalized for angina as those not on a PPI. A second study mentioned in the GIHN article, a post hoc analysis of the CREDO trial, found a higher rate of ischemic events in patients on a PPI, but this increase was seen whether the patient was on clopidogrel or not. The conflicting data presented a management challenge for cardiologists and gastroenterologists alike.
Multiple subsequent studies, including a large randomized trial, COGENT (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1909-17), comparing omeprazole with placebo in patients on clopidogrel, found no significant interaction. A consensus document published in December 2010 acknowledged the potential risks from pharmacodynamic studies but suggested that the clinical data were unclear.
This story speaks to the power of research to change practice, the importance of effectively communicating research findings to the public, and the fact that the practice of medicine is often an exercise in balancing conflicting data on behalf of our patients.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.; a faculty member at the Duke Clinical Research Institute; and an Associate Editor of GI & Hepatology News.
The January 2009 issue of GI & Hepatology News (GIHN) featured an article on the potential drug interaction between proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and clopidogrel.
In the study of interest, researchers retrospectively reviewed 16,000 patients prescribed clopidogrel after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and found that those patients also on a PPI were 1.5 times as likely to suffer from a myocardial infarction, stroke, or be hospitalized for angina as those not on a PPI. A second study mentioned in the GIHN article, a post hoc analysis of the CREDO trial, found a higher rate of ischemic events in patients on a PPI, but this increase was seen whether the patient was on clopidogrel or not. The conflicting data presented a management challenge for cardiologists and gastroenterologists alike.
Multiple subsequent studies, including a large randomized trial, COGENT (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1909-17), comparing omeprazole with placebo in patients on clopidogrel, found no significant interaction. A consensus document published in December 2010 acknowledged the potential risks from pharmacodynamic studies but suggested that the clinical data were unclear.
This story speaks to the power of research to change practice, the importance of effectively communicating research findings to the public, and the fact that the practice of medicine is often an exercise in balancing conflicting data on behalf of our patients.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.; a faculty member at the Duke Clinical Research Institute; and an Associate Editor of GI & Hepatology News.
The January 2009 issue of GI & Hepatology News (GIHN) featured an article on the potential drug interaction between proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and clopidogrel.
In the study of interest, researchers retrospectively reviewed 16,000 patients prescribed clopidogrel after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and found that those patients also on a PPI were 1.5 times as likely to suffer from a myocardial infarction, stroke, or be hospitalized for angina as those not on a PPI. A second study mentioned in the GIHN article, a post hoc analysis of the CREDO trial, found a higher rate of ischemic events in patients on a PPI, but this increase was seen whether the patient was on clopidogrel or not. The conflicting data presented a management challenge for cardiologists and gastroenterologists alike.
Multiple subsequent studies, including a large randomized trial, COGENT (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1909-17), comparing omeprazole with placebo in patients on clopidogrel, found no significant interaction. A consensus document published in December 2010 acknowledged the potential risks from pharmacodynamic studies but suggested that the clinical data were unclear.
This story speaks to the power of research to change practice, the importance of effectively communicating research findings to the public, and the fact that the practice of medicine is often an exercise in balancing conflicting data on behalf of our patients.
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, is associate professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C.; a faculty member at the Duke Clinical Research Institute; and an Associate Editor of GI & Hepatology News.
Federal Health Care Leadership Starting to Take Shape
After a prolonged period under intense investigation, the VA seems to be one of the few parts of the federal government not under intense scrutiny these days. VA Secretary David J. Shulkin, MD, became the first appointee of the Trump administration to receive a unanimous vote in the Senate. Given Dr. Shulkin’s experience as VA Under Secretary of Health, he is not expected to need much time to get up to speed on VA operations.
Little turmoil is expected in Defense Health either. Defense Secretary James Mattis was one of the first Trump administration confirmations with a 99-1 vote. A new Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs has not been named, but David J. Smith, MD, is currently performing the duties of that position and VADM Raquel C. Bono is continuing as the Director of the Defense Health Agency.
Positions in other agencies are less settled. Tom Price was confirmed on a party-line vote (53-47) as Secretary of Health and Human Services on February 10th following a bruising confirmation process. At HHS, many of the senior level positions are filled with acting directors, who have limited authority, including a director for Indian Health Service. No name has been officially put forward for the FDA Commissioner position, though former deputy commissioner Scott Gottlieb is rumored to be a leading candidate. One exception is Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, who remains in place as does much of the PHS senior leadership.
At IHS, the lack of a permanent director is particularly concerning, as the agency confronts chronic understaffing and now a federal hiring freeze. “Any freeze in hiring for Indian initiatives, whether temporary or permanent, threatens to make the challenges facing Indian Country worse,” Sen. Jon Tester, (D-Mont), said in a statement.
“Today’s confirmation of Dr. David Shulkin places the first non-veteran to lead the very lifeline to veterans’ health care and benefits—particularly within VA spinal cord injury/disease centers,” said Al Kovach, Jr., president of the Paralyzed Veterans of America. “But it also places a doctor who is intimately familiar with the value and challenges of the VA health care system as it stands at the crossroad of private health care for veterans and veteran-centric care with Congressional oversight… We look forward to working with Dr. Shulkin on the future of veterans’ health care, and ensuring the voices of the most catastrophically injured veterans are heard above the political din.”
After a prolonged period under intense investigation, the VA seems to be one of the few parts of the federal government not under intense scrutiny these days. VA Secretary David J. Shulkin, MD, became the first appointee of the Trump administration to receive a unanimous vote in the Senate. Given Dr. Shulkin’s experience as VA Under Secretary of Health, he is not expected to need much time to get up to speed on VA operations.
Little turmoil is expected in Defense Health either. Defense Secretary James Mattis was one of the first Trump administration confirmations with a 99-1 vote. A new Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs has not been named, but David J. Smith, MD, is currently performing the duties of that position and VADM Raquel C. Bono is continuing as the Director of the Defense Health Agency.
Positions in other agencies are less settled. Tom Price was confirmed on a party-line vote (53-47) as Secretary of Health and Human Services on February 10th following a bruising confirmation process. At HHS, many of the senior level positions are filled with acting directors, who have limited authority, including a director for Indian Health Service. No name has been officially put forward for the FDA Commissioner position, though former deputy commissioner Scott Gottlieb is rumored to be a leading candidate. One exception is Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, who remains in place as does much of the PHS senior leadership.
At IHS, the lack of a permanent director is particularly concerning, as the agency confronts chronic understaffing and now a federal hiring freeze. “Any freeze in hiring for Indian initiatives, whether temporary or permanent, threatens to make the challenges facing Indian Country worse,” Sen. Jon Tester, (D-Mont), said in a statement.
“Today’s confirmation of Dr. David Shulkin places the first non-veteran to lead the very lifeline to veterans’ health care and benefits—particularly within VA spinal cord injury/disease centers,” said Al Kovach, Jr., president of the Paralyzed Veterans of America. “But it also places a doctor who is intimately familiar with the value and challenges of the VA health care system as it stands at the crossroad of private health care for veterans and veteran-centric care with Congressional oversight… We look forward to working with Dr. Shulkin on the future of veterans’ health care, and ensuring the voices of the most catastrophically injured veterans are heard above the political din.”
After a prolonged period under intense investigation, the VA seems to be one of the few parts of the federal government not under intense scrutiny these days. VA Secretary David J. Shulkin, MD, became the first appointee of the Trump administration to receive a unanimous vote in the Senate. Given Dr. Shulkin’s experience as VA Under Secretary of Health, he is not expected to need much time to get up to speed on VA operations.
Little turmoil is expected in Defense Health either. Defense Secretary James Mattis was one of the first Trump administration confirmations with a 99-1 vote. A new Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs has not been named, but David J. Smith, MD, is currently performing the duties of that position and VADM Raquel C. Bono is continuing as the Director of the Defense Health Agency.
Positions in other agencies are less settled. Tom Price was confirmed on a party-line vote (53-47) as Secretary of Health and Human Services on February 10th following a bruising confirmation process. At HHS, many of the senior level positions are filled with acting directors, who have limited authority, including a director for Indian Health Service. No name has been officially put forward for the FDA Commissioner position, though former deputy commissioner Scott Gottlieb is rumored to be a leading candidate. One exception is Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, who remains in place as does much of the PHS senior leadership.
At IHS, the lack of a permanent director is particularly concerning, as the agency confronts chronic understaffing and now a federal hiring freeze. “Any freeze in hiring for Indian initiatives, whether temporary or permanent, threatens to make the challenges facing Indian Country worse,” Sen. Jon Tester, (D-Mont), said in a statement.
“Today’s confirmation of Dr. David Shulkin places the first non-veteran to lead the very lifeline to veterans’ health care and benefits—particularly within VA spinal cord injury/disease centers,” said Al Kovach, Jr., president of the Paralyzed Veterans of America. “But it also places a doctor who is intimately familiar with the value and challenges of the VA health care system as it stands at the crossroad of private health care for veterans and veteran-centric care with Congressional oversight… We look forward to working with Dr. Shulkin on the future of veterans’ health care, and ensuring the voices of the most catastrophically injured veterans are heard above the political din.”
Pediatric Nail Diseases: Clinical Pearls
Our dermatology department recently sponsored a pediatric dermatology lecture series for the pediatric residency program. Within this series, Antonella Tosti, MD, a professor at the University of Miami Health System, Florida, and a renowned expert in nail disorders and allergic contact dermatitis, presented her clinical expertise on the presentation and management of common pediatric nail diseases. This article highlights pearls from her unique and enlightening lecture.
Pearl: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a recognized trigger for onychomadesis
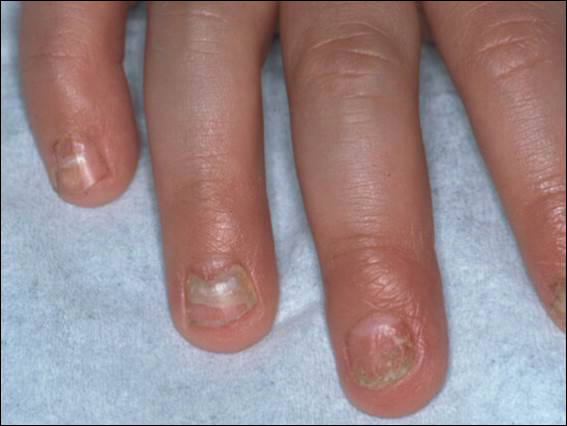
An arrest in nail matrix activity is responsible for onychomadesis, or shedding of the nail. Its presentation in children can be further divided based upon the degree of involvement. If a few nails are affected, trauma should be implicated. In contrast, if all nails are involved, a systemic etiology should be suspected. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) has been recognized as a trigger for onychomadesis in school-aged children. Onychomadesis presents with characteristic proximal nail detachment (Figure 1). The association of HFMD with onychomadesis and Beau lines was first reported in 2000. Five patients who resided within close proximity and shared a physician-diagnosed case of HFMD presented with representative nail findings 4 weeks after illness.1 Hypotheses for these changes include viral-induced nail pathology, inflammation from cutaneous lesions of HFMD, and systemic effects from the disease.2 Given the prevalence of HFMD and benign outcome, clinicians should be cognizant of this unique cutaneous manifestation.
Pearl: Management of pediatric melanonychia can take a wait-and-see approach
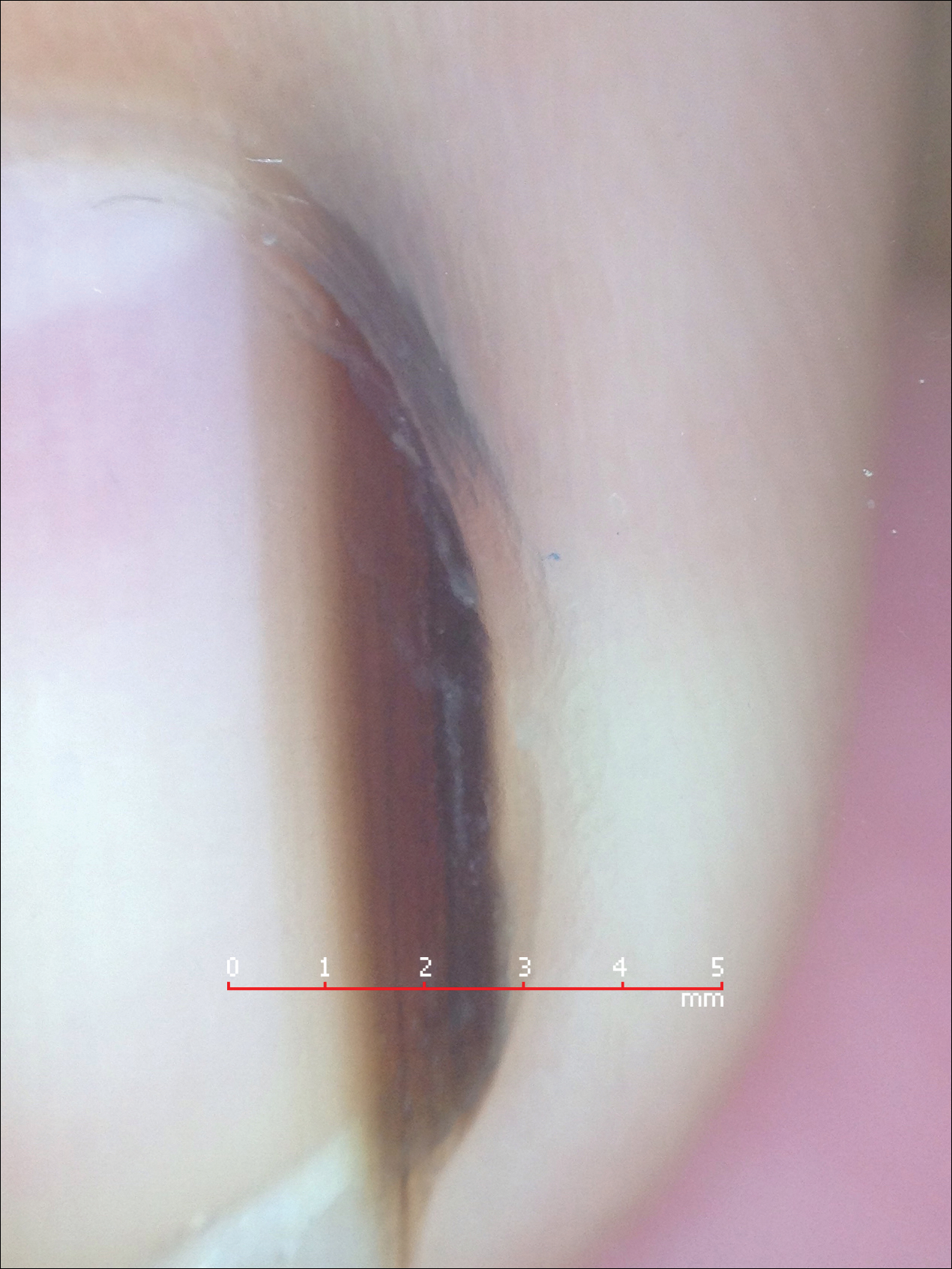
Melanonychia is the presence of a longitudinal brown-black band extending from the proximal nail fold. The cause of melanonychia can be due to either activation or hyperplasia. Activation is the less common etiology in children; however, if present, activation can be due to Laugier-Hunziker syndrome or trauma such as onychotillomania. Melanonychia in children usually is the result of hyperplasia of melanocytes and can manifest as a lentigo, nevus, or more rarely melanoma. Nail matrix nevi are typically exhibited on the fingernails, particularly the thumb, and frequently are junctional nevi (Figure 2). Spontaneous fading of nevi is expected with time due to decreased melanin production. Therapeutic options for melanonychia include regular clinical monitoring, biopsy, or excision. Dr. Tosti explained that one must be wary when pursuing a biopsy, as it can result in a false-negative finding due to missed pathology. If clinically indicated, a shave biopsy of the nail matrix can be performed to best analyze the lesion. She noted that if more than 3 mm of the matrix is removed, a resultant scar will ensue. Conservative management is recommended given the indolent clinical behavior of the majority of cases of melanonychia in children.3
Pearl: Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds can be treated with tape
Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds is relatively common in children and normally improves with age. Koilonychia may also occur simultaneously and can be viewed as a physiologic process in this age group. The etiology of the underlying disorder is due to anomalous periungual soft-tissue changes of the bilateral halluces; the resulting overgrowth can partially cover the nail plate. Although usually a self-limiting condition, the changes can cause inflammation and discomfort due to an ingrown nail.4 Dr. Tosti advised that by simply taping and retracting the bilateral overgrowth, the condition can be more readily resolved. This simple treatment can be demonstrated in the office and subsequently performed at home.
Pearl: Onychomycosis is uncommon in children
Onychomycosis occurs in less than 1% of children.5 Several factors are responsible for this decreased prevalence. More rapid nail growth and smaller nail surface area decreases the ability of the fungi to penetrate the nail plate.6 Furthermore, children have a diminished rate of tinea pedis, leading to less neighboring infection. When onychomycosis does affect this patient population, it commonly presents as distal subungual onychomycosis and favors the fingernails over the toenails. Treatment options usually parallel those of the adult population; however, all medications for children are considered off-label use by the US Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tosti explained that oral granules of terbinafine can be sprinkled on food to help with pediatric ingestion. Topical therapies should also be considered; children usually respond better than their adult counterparts due to their thinner nails, which grant enhanced drug delivery and penetration.6
Pearl: Acute paronychia can be due to nail-biting and sucking
Acute paronychia is inflammation of the proximal nail fold. In children, it frequently is a result of mixed flora induced by nail-biting and sucking. Management involves culturing the affected lesions and is effectively treated with warm soaks alone. Dr. Tosti highlighted that Candida in the subungual space is a common colonizer and is typically self-limiting in nature if isolated. Candida can be cultured more readily in premature infants, immunosuppressed patients, and those with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis can exhibit periungual inflammation involving several digits. The differential can include nail psoriasis, as both can demonstrate dystrophic changes. The differential for localized paronychia includes herpetic whitlow and can manifest as vesicles under the proximal nail fold.
Final Thoughts
These clinical pearls are shared to help deliver utmost care to our pediatric patients presenting with nail pathology. For example, a child exhibiting melanonychia can cause alarm due to the possibility of underlying melanoma; given the rarity of neoplasia in these patients, a conservative approach is favored to help avoid unnecessary biopsies and subsequent scarring. Similarly, it is important to be aware of the common colonizers of the subungual area, particularly Candida, to avoid unessential medications with potential side effects. The examples demonstrated help shed light on the management of pediatric nail diseases.
Acknowledgment
This article is possible thanks to the help of Antonella Tosti, MD (Miami, Florida), who contributed her time and expertise at the University of Miami Pediatric Grand Rounds to expand the foundation and knowledge of pediatric nail diseases.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand-foot-mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Yuksel S, Evrengul H, Ozhan B, et al. Onychomadesis-a late complication of hand-foot-mouth disease [published online May 2, 2016]. J Pediatr. 2016;174:274.
- Cooper C, Arva NC, Lee C, et al. A clinical, histopathologic, and outcome study of melanonychia striata in childhood. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:773-779.
- Piraccini BM, Parente GL, Varotti E, et al. Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds of the hallux: clinical features and follow-up of seven cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:348-351.
- Totri CR, Feldstein S, Admani S, et al. Epidemiologic analysis of onychomycosis in the San Diego pediatric population [published online October 4, 2016]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:46-49.
- Feldstein S, Totri C, Friedlander SF. Antifungal therapy for onychomycosis in children. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:333-339.
Our dermatology department recently sponsored a pediatric dermatology lecture series for the pediatric residency program. Within this series, Antonella Tosti, MD, a professor at the University of Miami Health System, Florida, and a renowned expert in nail disorders and allergic contact dermatitis, presented her clinical expertise on the presentation and management of common pediatric nail diseases. This article highlights pearls from her unique and enlightening lecture.
Pearl: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a recognized trigger for onychomadesis
An arrest in nail matrix activity is responsible for onychomadesis, or shedding of the nail. Its presentation in children can be further divided based upon the degree of involvement. If a few nails are affected, trauma should be implicated. In contrast, if all nails are involved, a systemic etiology should be suspected. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) has been recognized as a trigger for onychomadesis in school-aged children. Onychomadesis presents with characteristic proximal nail detachment (Figure 1). The association of HFMD with onychomadesis and Beau lines was first reported in 2000. Five patients who resided within close proximity and shared a physician-diagnosed case of HFMD presented with representative nail findings 4 weeks after illness.1 Hypotheses for these changes include viral-induced nail pathology, inflammation from cutaneous lesions of HFMD, and systemic effects from the disease.2 Given the prevalence of HFMD and benign outcome, clinicians should be cognizant of this unique cutaneous manifestation.

Pearl: Management of pediatric melanonychia can take a wait-and-see approach
Melanonychia is the presence of a longitudinal brown-black band extending from the proximal nail fold. The cause of melanonychia can be due to either activation or hyperplasia. Activation is the less common etiology in children; however, if present, activation can be due to Laugier-Hunziker syndrome or trauma such as onychotillomania. Melanonychia in children usually is the result of hyperplasia of melanocytes and can manifest as a lentigo, nevus, or more rarely melanoma. Nail matrix nevi are typically exhibited on the fingernails, particularly the thumb, and frequently are junctional nevi (Figure 2). Spontaneous fading of nevi is expected with time due to decreased melanin production. Therapeutic options for melanonychia include regular clinical monitoring, biopsy, or excision. Dr. Tosti explained that one must be wary when pursuing a biopsy, as it can result in a false-negative finding due to missed pathology. If clinically indicated, a shave biopsy of the nail matrix can be performed to best analyze the lesion. She noted that if more than 3 mm of the matrix is removed, a resultant scar will ensue. Conservative management is recommended given the indolent clinical behavior of the majority of cases of melanonychia in children.3

Pearl: Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds can be treated with tape
Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds is relatively common in children and normally improves with age. Koilonychia may also occur simultaneously and can be viewed as a physiologic process in this age group. The etiology of the underlying disorder is due to anomalous periungual soft-tissue changes of the bilateral halluces; the resulting overgrowth can partially cover the nail plate. Although usually a self-limiting condition, the changes can cause inflammation and discomfort due to an ingrown nail.4 Dr. Tosti advised that by simply taping and retracting the bilateral overgrowth, the condition can be more readily resolved. This simple treatment can be demonstrated in the office and subsequently performed at home.
Pearl: Onychomycosis is uncommon in children
Onychomycosis occurs in less than 1% of children.5 Several factors are responsible for this decreased prevalence. More rapid nail growth and smaller nail surface area decreases the ability of the fungi to penetrate the nail plate.6 Furthermore, children have a diminished rate of tinea pedis, leading to less neighboring infection. When onychomycosis does affect this patient population, it commonly presents as distal subungual onychomycosis and favors the fingernails over the toenails. Treatment options usually parallel those of the adult population; however, all medications for children are considered off-label use by the US Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tosti explained that oral granules of terbinafine can be sprinkled on food to help with pediatric ingestion. Topical therapies should also be considered; children usually respond better than their adult counterparts due to their thinner nails, which grant enhanced drug delivery and penetration.6
Pearl: Acute paronychia can be due to nail-biting and sucking
Acute paronychia is inflammation of the proximal nail fold. In children, it frequently is a result of mixed flora induced by nail-biting and sucking. Management involves culturing the affected lesions and is effectively treated with warm soaks alone. Dr. Tosti highlighted that Candida in the subungual space is a common colonizer and is typically self-limiting in nature if isolated. Candida can be cultured more readily in premature infants, immunosuppressed patients, and those with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis can exhibit periungual inflammation involving several digits. The differential can include nail psoriasis, as both can demonstrate dystrophic changes. The differential for localized paronychia includes herpetic whitlow and can manifest as vesicles under the proximal nail fold.
Final Thoughts
These clinical pearls are shared to help deliver utmost care to our pediatric patients presenting with nail pathology. For example, a child exhibiting melanonychia can cause alarm due to the possibility of underlying melanoma; given the rarity of neoplasia in these patients, a conservative approach is favored to help avoid unnecessary biopsies and subsequent scarring. Similarly, it is important to be aware of the common colonizers of the subungual area, particularly Candida, to avoid unessential medications with potential side effects. The examples demonstrated help shed light on the management of pediatric nail diseases.
Acknowledgment
This article is possible thanks to the help of Antonella Tosti, MD (Miami, Florida), who contributed her time and expertise at the University of Miami Pediatric Grand Rounds to expand the foundation and knowledge of pediatric nail diseases.
Our dermatology department recently sponsored a pediatric dermatology lecture series for the pediatric residency program. Within this series, Antonella Tosti, MD, a professor at the University of Miami Health System, Florida, and a renowned expert in nail disorders and allergic contact dermatitis, presented her clinical expertise on the presentation and management of common pediatric nail diseases. This article highlights pearls from her unique and enlightening lecture.
Pearl: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is a recognized trigger for onychomadesis
An arrest in nail matrix activity is responsible for onychomadesis, or shedding of the nail. Its presentation in children can be further divided based upon the degree of involvement. If a few nails are affected, trauma should be implicated. In contrast, if all nails are involved, a systemic etiology should be suspected. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) has been recognized as a trigger for onychomadesis in school-aged children. Onychomadesis presents with characteristic proximal nail detachment (Figure 1). The association of HFMD with onychomadesis and Beau lines was first reported in 2000. Five patients who resided within close proximity and shared a physician-diagnosed case of HFMD presented with representative nail findings 4 weeks after illness.1 Hypotheses for these changes include viral-induced nail pathology, inflammation from cutaneous lesions of HFMD, and systemic effects from the disease.2 Given the prevalence of HFMD and benign outcome, clinicians should be cognizant of this unique cutaneous manifestation.

Pearl: Management of pediatric melanonychia can take a wait-and-see approach
Melanonychia is the presence of a longitudinal brown-black band extending from the proximal nail fold. The cause of melanonychia can be due to either activation or hyperplasia. Activation is the less common etiology in children; however, if present, activation can be due to Laugier-Hunziker syndrome or trauma such as onychotillomania. Melanonychia in children usually is the result of hyperplasia of melanocytes and can manifest as a lentigo, nevus, or more rarely melanoma. Nail matrix nevi are typically exhibited on the fingernails, particularly the thumb, and frequently are junctional nevi (Figure 2). Spontaneous fading of nevi is expected with time due to decreased melanin production. Therapeutic options for melanonychia include regular clinical monitoring, biopsy, or excision. Dr. Tosti explained that one must be wary when pursuing a biopsy, as it can result in a false-negative finding due to missed pathology. If clinically indicated, a shave biopsy of the nail matrix can be performed to best analyze the lesion. She noted that if more than 3 mm of the matrix is removed, a resultant scar will ensue. Conservative management is recommended given the indolent clinical behavior of the majority of cases of melanonychia in children.3

Pearl: Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds can be treated with tape
Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds is relatively common in children and normally improves with age. Koilonychia may also occur simultaneously and can be viewed as a physiologic process in this age group. The etiology of the underlying disorder is due to anomalous periungual soft-tissue changes of the bilateral halluces; the resulting overgrowth can partially cover the nail plate. Although usually a self-limiting condition, the changes can cause inflammation and discomfort due to an ingrown nail.4 Dr. Tosti advised that by simply taping and retracting the bilateral overgrowth, the condition can be more readily resolved. This simple treatment can be demonstrated in the office and subsequently performed at home.
Pearl: Onychomycosis is uncommon in children
Onychomycosis occurs in less than 1% of children.5 Several factors are responsible for this decreased prevalence. More rapid nail growth and smaller nail surface area decreases the ability of the fungi to penetrate the nail plate.6 Furthermore, children have a diminished rate of tinea pedis, leading to less neighboring infection. When onychomycosis does affect this patient population, it commonly presents as distal subungual onychomycosis and favors the fingernails over the toenails. Treatment options usually parallel those of the adult population; however, all medications for children are considered off-label use by the US Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tosti explained that oral granules of terbinafine can be sprinkled on food to help with pediatric ingestion. Topical therapies should also be considered; children usually respond better than their adult counterparts due to their thinner nails, which grant enhanced drug delivery and penetration.6
Pearl: Acute paronychia can be due to nail-biting and sucking
Acute paronychia is inflammation of the proximal nail fold. In children, it frequently is a result of mixed flora induced by nail-biting and sucking. Management involves culturing the affected lesions and is effectively treated with warm soaks alone. Dr. Tosti highlighted that Candida in the subungual space is a common colonizer and is typically self-limiting in nature if isolated. Candida can be cultured more readily in premature infants, immunosuppressed patients, and those with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis can exhibit periungual inflammation involving several digits. The differential can include nail psoriasis, as both can demonstrate dystrophic changes. The differential for localized paronychia includes herpetic whitlow and can manifest as vesicles under the proximal nail fold.
Final Thoughts
These clinical pearls are shared to help deliver utmost care to our pediatric patients presenting with nail pathology. For example, a child exhibiting melanonychia can cause alarm due to the possibility of underlying melanoma; given the rarity of neoplasia in these patients, a conservative approach is favored to help avoid unnecessary biopsies and subsequent scarring. Similarly, it is important to be aware of the common colonizers of the subungual area, particularly Candida, to avoid unessential medications with potential side effects. The examples demonstrated help shed light on the management of pediatric nail diseases.
Acknowledgment
This article is possible thanks to the help of Antonella Tosti, MD (Miami, Florida), who contributed her time and expertise at the University of Miami Pediatric Grand Rounds to expand the foundation and knowledge of pediatric nail diseases.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand-foot-mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Yuksel S, Evrengul H, Ozhan B, et al. Onychomadesis-a late complication of hand-foot-mouth disease [published online May 2, 2016]. J Pediatr. 2016;174:274.
- Cooper C, Arva NC, Lee C, et al. A clinical, histopathologic, and outcome study of melanonychia striata in childhood. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:773-779.
- Piraccini BM, Parente GL, Varotti E, et al. Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds of the hallux: clinical features and follow-up of seven cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:348-351.
- Totri CR, Feldstein S, Admani S, et al. Epidemiologic analysis of onychomycosis in the San Diego pediatric population [published online October 4, 2016]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:46-49.
- Feldstein S, Totri C, Friedlander SF. Antifungal therapy for onychomycosis in children. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:333-339.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand-foot-mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Yuksel S, Evrengul H, Ozhan B, et al. Onychomadesis-a late complication of hand-foot-mouth disease [published online May 2, 2016]. J Pediatr. 2016;174:274.
- Cooper C, Arva NC, Lee C, et al. A clinical, histopathologic, and outcome study of melanonychia striata in childhood. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:773-779.
- Piraccini BM, Parente GL, Varotti E, et al. Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral nail folds of the hallux: clinical features and follow-up of seven cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:348-351.
- Totri CR, Feldstein S, Admani S, et al. Epidemiologic analysis of onychomycosis in the San Diego pediatric population [published online October 4, 2016]. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:46-49.
- Feldstein S, Totri C, Friedlander SF. Antifungal therapy for onychomycosis in children. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:333-339.
Minimizing Postdisaster Fatalities
Environmental disasters can overpower local medical resources. Fortunately, such crises are rare in the U.S. This situation, however, has not always been the case. For example, in 1812, an earthquake along the New Madrid fault of the Mississippi Valley caused the Mississippi River to flow backward for 3 days.1 Today, in urbanized America, an earthquake of that magnitude would be devastating and severely overwhelm medical systems. All nations, including highly modernized nations, would need help in such disasters.2 A response system that is nimble, well-trained, scalable, and rapidly deployable can mitigate disaster sequelae. This article focuses on key aspects of effective rapid response, including speed, appropriate triage, quick-response strike teams, and disaster dynamics.
Why Speed Matters Most
Response time arguably is the most important factor in increasing survival in a disaster. In a 1996 study of earthquake disasters worldwide, Schultz and colleagues found a lower survival rate for victims who received medical care outside a 24-hour window.1 Studies of earthquakes in China have suggested that unless aid is rendered within 2 to 6 hours, fewer than half the victims will survive.3 Regarding a 1980 earthquake in Italy, de Bruycker and colleagues emphasized the importance of engaging in rescue activities within the first 48 hours.4 Safar reviewed mass disasters and reported that 25% to 50% of the injured and dead could have been saved if first aid had been provided immediately.5 In 1992 and 1994, Pretto and colleagues wrote that in earthquakes in Armenia and Costa Rica, many deaths could have been prevented had the victims received medical attention within the first 6 hours.6,7 The question is: How can responses to such crises be improved? Confederate Army Lt. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest’s dictum “[Get] there first with the most men” holds true in disaster medicine as well: get there fast with the right people, training, equipment, and supplies.8
Deaths in disasters can be described in a 3-phase distribution: immediate, early, and delayed. Stringent building codes and public warnings and evacuations reduce immediate deaths, but victims also die of catastrophic injury soon after an event. Early deaths are preventable with use of rapid interventions, such as tourniquets and airway adjuncts, but these must be administered within minutes or hours. Delayed deaths occur days or weeks after injury secondary to infection or organ system failure—which emphasizes the value of early wound care.
Emergency Supplies
What items are most needed? As each disaster is different, it would be presumptuous to provide a one-size-fits-all list, but some common supplies have been suggested. In 2010, Ginzberg and colleagues reported that during the first 24 hours of the Haiti earthquake of 1996, the overwhelming need was for IV hydration, narcotic analgesics, and casting supplies for the splinting of fractures.9 During the next 24 hours, IV stabilization was key, along with monitoring by Foley and suprapubic catheters. In the third 24-hour period, providers began to see sepsis-related deaths. In response to this challenge, teams began aggressive treatment with open surgical debridement of wounds, amputation of severely injured limbs, and administration of broad-spectrum IV antibiotics. Regional anesthesia with conscious sedation was mandatory because supplemental oxygen and ventilators were unavailable. By day 4, wound debridement, amputations, and fasciotomies were being provided by newly arrived anesthesiologists and orthopedic surgeons. Ginzberg and colleagues emphasized that rapid response was key in maximizing survival and by day 4, there was a greater need for surgical teams and broad-spectrum antibiotics (eg, piperacillin, tazobactam) to combat sepsis.
Pereira and colleagues reported that in a catastrophe caused by a tropical storm and landslides in Brazil, the most common injuries involved the extremities; the majority of wounds required only cleaning, debridement, and suture; and the most commonly performed operations were for orthopedic injuries.10 Incidentally, population baseline morbidity and mortality continue during disasters, and rescue personnel invariably sustain injuries, which contribute to the total medical burden. These additional injuries must be anticipated, and plans to manage them must be included in any disaster contingency planning.
Triage
Speed and correct triage are essential building blocks of disaster response. When resources are limited, triage is crucial in providing the right treatment to the right patient. There are numerous triage methods, some more rapid and straightforward; others more effective and cumbersome.11 In 2012, Sasser and colleagues wrote that the purpose of triage is to ensure injured patients are transported to a trauma center or the hospital best equipped to manage their specific injuries in an appropriate and timely manner.12 Their report focused on prehospital emergent care, not mass-casualty or disaster situations.
Triage is sometimes performed inconsistently. In a 2013 study, Kleber and colleagues found that 24% of providers overtriage and 16% undertriage.13 In the U.S., simple triage and rapid treatment (START) is commonly used to sort traumatized patients. All these methods take a “worst gets first treatment” approach. Depending on the magnitude of an event, however, providers may take a reverse-triage approach, in which they better use resources for the least injured patients and provide palliative care to the gravely ill.
During pandemic disasters, trauma triage protocols are ineffective. Instead, these events demand assessments that are sensitive to infectious diseases. Timely, didactic, hands-on training must be conducted before the fact so responders can adapt to react appropriately to a given disaster.14
Accurate, timely triage in mass-casualty incidents was conceptually demonstrated by Mekel and colleagues who reviewed the medical management of bombing victims in metropolitan Haifa, Israel during the period 2000 to 2006.15 Providers initiated a predetermined triage system in which patients are assigned to the appropriate echelon of care. Of 342 injured patients, 9.5% had severe injuries, 2.4% had moderate-severe injuries, and 88.9% had mild injuries. Correct and timely triage directed trauma victims to the appropriate medical care. Such action prevents the highest level facility from becoming overcrowded with less severely injured patients and ensures that the more critically injured receive a level of care comparable to that given under nondisaster circumstances.
The handheld ultrasound device, which can be used to correctly diagnose fractures, is an efficient triage resource for prehospital teams. In a 2008 study, McManus and colleagues suggested that ultrasound (vs traditional radiography) could be used to identify fractures in an emergency room.16 A handheld ultrasound device could be used outside the hospital, in the field, potentially reducing the number of referrals to overwhelmed orthopedic hospitals.
In 2007, Dean and colleagues reported on using ultrasound to rapidly triage disease during an earthquake in Guatemala.17 In that disaster, 23% of injuries presented within the first 24 hours, and a handheld ultrasound device was used to assess orthopedic injuries—ruling in 12% and ruling out 42%. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a tool that small medical teams can use to speed triage, enhance patient care, and relieve overcrowded medical centers of the unrelenting pressure.
On-Site vs Hospital
Complicating disaster response is self-triage. Victims with injuries of all severity levels go to the nearest hospital and overwhelm it. In 1991, Waeckerle reported that within the first 30 minutes of a disaster, a wave of victims arrives, usually with minor injuries, and impedes care for the more severely wounded.18 Correct triage instead would have directed these patients to a hospital other than the overwhelmed level I trauma center.15 This is not to say that patients with mild or moderate injuries are unimportant—just that their care may take scarce space and resources from the more severely injured.
Mallonee and colleagues reported that of the 759 people injured in the 1996 Oklahoma City bombing, 167 (22%) were fatalities, 83 (11%) were hospitalized, and 509 (67%) were treated on an outpatient basis.19 Most of the injuries could have been managed by quick-response medical teams operating in the affected area, outside the hospitals. This action would have reduced operational pressure on hospitals and improved severely injured patients’ access to care.
Specialized Teams
In 2008, Barillo and colleagues suggested that having standardized medic bags would allow a small detachment of medical professionals to provide care nimbly—and doing so would represent a leap forward in access to care.20
Because of their unique ability to understand the culture and coordinate military assets with local authorities, DoD international health specialists are crucial interfaces for any population, foreign or domestic. Seyedin and colleagues and Merin and colleagues suggested that in both the Bam earthquake in 2003 and the Nepal earthquake in 2015, understanding the culture played a vital role in health care delivery and in adhering to cultural norms in deciding when to perform surgery, making end-of-life decisions, communicating with family, establishing trust with local and regional leaders, and other matters.21,22
Strike teams are small groups of variably trained health care providers who are dispatched to underserved, outlying, or overwhelmed areas to deliver precached basic medical care and triage significant injuries to medical centers. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a strike team tool. During a local emergency, it is understood or assumed that response is inundated and that people are going untreated.
Crucially, strike teams must be trained, prepared, and readily dispatched ahead of larger response elements. Though quickly deployable, disaster medical assistance teams (DMATs) and National Guard Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and High-Yield Explosive Enhanced Response Force Package units, take time to mobilize. Therefore, strike teams should consist of community citizens or local National Guard assets, the latter being particularly suited to rapid response given their training, effective command and control, and intrinsic logistics.
The efficacy of strike teams was demonstrated during the 2011 earthquake in Japan.23 Disaster medical assistance teams were invaluable in triaging and treating patients during the first 3 days. A team left 34 minutes after the event to render aid to people caught in a roof collapse. During triage, 17% of the injuries were classified urgent, 22% intermediate, and 61% minor. On day 7, a DMAT was dispatched to assist with emergency medicine and primary care; 3% of the injuries were severe and required urgent care, 50% required intermediate care, and 47% required minor care.
The value of strike teams is 3-fold: It provides rapid, professional care at a crucial place and critical time; it correctly triages patients and thus allow hospitals to maintain resources for the more severely injured; and augments overwhelmed providers at crucial sites. The roles of strike teams were echoed in 2006 by Campos-Outcalt, who reported that DMATs deployed to austere locations had the flexibility to augment existing medical staff and to rapidly deploy, self-sustain, and treat patients until a situation was resolved.24 This nimble strike team mentality could become a rapid and flexible model to save more lives, relieve significant suffering, and offload pressure from local hospitals by treating the less critically injured.
After a disaster, space is at a premium, and nonmedical residents who make up 40% to 70% of the shelter population require resources as well.25 Family members and the lightly injured may be conscripted to augment the overwhelmed medical staff. In 1988, Halbert and colleagues described how Afghan volunteers with minimal medical experience were given training and supplies and served as advanced emergency medics, delivering medical care and performing well under austere conditions.26,27 Strike teams thus may provide on-scene training in addition to medical care.
In 2012, Kirsch and colleaguesfound that Haiti earthquake victims who received treatment and remained in camps showed no improvement in income, employment, or food access 1 year after the disaster compared with victims who remained outside the camps and in their own neighborhoods.28 This finding underscores the need for accurate and timely triage by strike teams outside hospitals and quick treatment and return of patients to their homes.
Conceptually, strike teams need not be confined to medical response. Team members also might be specialists in epidemiology, disease surveillance, public health, culinary water protection, municipal security, and civil engineering. Noji reported that malnutrition, diarrheal diseases, measles, acute respiratory infections, and malaria consistently accounted for 60% to 95% of reported deaths among refugees and displaced populations.29 In 2005, Spiegel found that the potential for epidemics of communicable diseases was increased by overcrowding and poor sanitation in both natural disasters and complex emergencies.30 In 2007, Watson and colleagues suggested that communicable diseases may account for two-thirds of the deaths in conflict areas, and malnutrition significantly increases the risk of these diseases.31 Effective disaster care may be better accomplished through decentralized strike team interventions, which avoid the pitfalls of displacement and overcrowding.
Conclusion
Crises of all magnitudes can be greatly eased by well-trained, quick-response, all-hazards medical detachments—small teams that can be rapidly mobilized and deployed to establish casualty collection points, provide accurate triage, and render emergency care. These highly mobile teams can bridge the gap between the occurrence of a disaster and the arrival of substantial assistance from state, federal, and nongovernmental organizations—a most vulnerable time. These competent, flexible teams then can be absorbed by the larger force when it arrives for sustained disaster operations. Predisaster planning must take into account the possibility of long-term care for casualties and the displaced. Careful attention should be given to the potential for epidemics—immunizations should be administered quickly to achieve herd immunity—and a program that will provide food, water, shelter, sanitation, and security should be established.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sarah M. Paulsen and members of the Utah Air National Guard and Morrocan military for their friendship and help in preparing the manuscript.
1. Schultz CH, Koenig KL, Noji EK. A medical disaster response to reduce immediate mortality after an earthquake. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(7):438-444.
2. Merin O, Blumberg N, Raveh D, Bar A, Nishizawa M, Cohen-Marom O. Global responsibility in mass casualty events: the Israeli experience in Japan. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(1):61-64.
3. Sheng ZY. Medical support in the Tangshan earthquake: a review of the management of mass casualties and certain major injuries. J Trauma. 1987;27(10):1130-1135.
4. de Bruycker M, Greco D, Annino I, et al. The 1980 earthquake in southern Italy: rescue of trapped victims and mortality. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(6):1021-1025.
5. Safar P. Resuscitation potentials in mass disasters. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1986;2:34-47.
6. Pretto EA, Ricci E, Klain M, et al. Disaster reanimatology potentials: a structured interview study in Armenia III. Results, conclusions and recommendations. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1992;7:327-338.
7. Pretto EA, Angus DC, Abrams JI, et al. An analysis of prehospital mortality in an earthquake. Disaster Reanimatology Study Group. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1994;9(2):107-124.
8. Keyes R. The Quote Verifier: Who Said What, Where, and When. New York, NY: St. Martin’s Griffin; 2006.
9. Ginzberg E, O’Neill WW, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, de Marchena E, Pust D, Green BA. Rapid medical relief—Project Medishare and the Haitian earthquake. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(10):e31.
10. Pereira BM, Morales W, Cardoso RG, Fiorelli R, Fraga GP, Briggs SM. Lessons learned from a landslide catastrophe in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(4):253-258.
11. Cross KP, Cicero MX. Head-to-head comparison of disaster triage methods in pediatric, adult, and geriatric patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;61(6):668-676.e7.
12. Sasser SM, Hunt RC, Faul M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Guidelines for field triage of injured patients: recommendations of the National Expert Panel on Field Triage, 2011. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2012;61(RR-1):1-20.
13. Kleber C, Cwojdzinski D, Strehl M, Poloczek S, Haas NP. Results of in-hospital triage in 17 mass casualty trainings: underestimation of life-threatening injuries and need for re-triage. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(1):5-11.
14. Talmor D, Jones AE, Rubinson L, Howell MD, Shapiro NI. Simple triage scoring system predicting death and the need for critical care resources for use during epidemics. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5):1251-1256.
15. Mekel M, Bumenfeld A, Feigenberg Z, et al. Terrorist suicide bombings: lessons learned in metropolitan Haifa from September 2000 to January 2006. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(4):233-248.
16. McManus JG, Morton MJ, Crystal CS, et al. Use of ultrasound to assess acute fracture reduction in emergency care settings. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(4):241-247.
17. Dean AJ, Ku BS, Zeserson EM. The utility of handheld ultrasound in an austere medical setting in Guatemala after a natural disaster. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(5):249-256.
18. Waeckerle JF. Disaster planning and response. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(12):815-821.
19. Mallonee S, Shariat S, Stennies G, Waxweiler R, Hogan D, Jordan F. Physical injuries and fatalities resulting from the Oklahoma City bombing. JAMA. 1996;276(5):382-387.
20. Barillo DJ, Renz E, Broger K, Moak B, Wright G, Holcomb JB. An emergency medical bag set for long-range aeromedical transportation. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(2):79-86.
21. Seyedin SH, Aflatoonian MR, Ryan J. Adverse impact of international NGOs during and after the Bam earthquake: health system’s consumers’ points of view. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(3):173-179.
22. Merin O, Yitzhak A, Bader T. Medicine in a disaster area: lessons from the 2015 earthquake in Nepal. JAMA. 2015;175(9):1437-1438.
23. Ushizawa H, Foxwell AR, Bice S, et al. Needs for disaster medicine: lessons from the field of the great east Japan earthquake. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2013;4(1):51-55.
24. Campos-Outcalt D. Disaster medical response: maximizing your effectiveness. J Fam Pract. 2006;55(2):113-115.
25. Patton-Levine JK, Vest JR, Valadez AM. Caregivers and families in medical special needs shelters: an experience during Hurricane Rita. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(2):81-86.
26. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical theatre in rural Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):775-778.
27. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical training model for advanced emergency medics in Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):779-784.
28. Kirsch TD, Leidman E, Weiss W, Doocy S. The impact of the earthquake and humanitarian assistance on household economies and livelihoods of earthquake-affected populations in Haiti. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(2):85-94.
29. Noji EK. Public health in the aftermath of disasters. BMJ. 2005;330(7504):1379-1381.
30. Spiegel PB. Differences in world responses to natural disasters and complex emergencies. JAMA. 2005;293(15):1915-1918.
31. Watson JT, Gayer M, Connolly MA. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(1):1-5.
Environmental disasters can overpower local medical resources. Fortunately, such crises are rare in the U.S. This situation, however, has not always been the case. For example, in 1812, an earthquake along the New Madrid fault of the Mississippi Valley caused the Mississippi River to flow backward for 3 days.1 Today, in urbanized America, an earthquake of that magnitude would be devastating and severely overwhelm medical systems. All nations, including highly modernized nations, would need help in such disasters.2 A response system that is nimble, well-trained, scalable, and rapidly deployable can mitigate disaster sequelae. This article focuses on key aspects of effective rapid response, including speed, appropriate triage, quick-response strike teams, and disaster dynamics.
Why Speed Matters Most
Response time arguably is the most important factor in increasing survival in a disaster. In a 1996 study of earthquake disasters worldwide, Schultz and colleagues found a lower survival rate for victims who received medical care outside a 24-hour window.1 Studies of earthquakes in China have suggested that unless aid is rendered within 2 to 6 hours, fewer than half the victims will survive.3 Regarding a 1980 earthquake in Italy, de Bruycker and colleagues emphasized the importance of engaging in rescue activities within the first 48 hours.4 Safar reviewed mass disasters and reported that 25% to 50% of the injured and dead could have been saved if first aid had been provided immediately.5 In 1992 and 1994, Pretto and colleagues wrote that in earthquakes in Armenia and Costa Rica, many deaths could have been prevented had the victims received medical attention within the first 6 hours.6,7 The question is: How can responses to such crises be improved? Confederate Army Lt. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest’s dictum “[Get] there first with the most men” holds true in disaster medicine as well: get there fast with the right people, training, equipment, and supplies.8
Deaths in disasters can be described in a 3-phase distribution: immediate, early, and delayed. Stringent building codes and public warnings and evacuations reduce immediate deaths, but victims also die of catastrophic injury soon after an event. Early deaths are preventable with use of rapid interventions, such as tourniquets and airway adjuncts, but these must be administered within minutes or hours. Delayed deaths occur days or weeks after injury secondary to infection or organ system failure—which emphasizes the value of early wound care.
Emergency Supplies
What items are most needed? As each disaster is different, it would be presumptuous to provide a one-size-fits-all list, but some common supplies have been suggested. In 2010, Ginzberg and colleagues reported that during the first 24 hours of the Haiti earthquake of 1996, the overwhelming need was for IV hydration, narcotic analgesics, and casting supplies for the splinting of fractures.9 During the next 24 hours, IV stabilization was key, along with monitoring by Foley and suprapubic catheters. In the third 24-hour period, providers began to see sepsis-related deaths. In response to this challenge, teams began aggressive treatment with open surgical debridement of wounds, amputation of severely injured limbs, and administration of broad-spectrum IV antibiotics. Regional anesthesia with conscious sedation was mandatory because supplemental oxygen and ventilators were unavailable. By day 4, wound debridement, amputations, and fasciotomies were being provided by newly arrived anesthesiologists and orthopedic surgeons. Ginzberg and colleagues emphasized that rapid response was key in maximizing survival and by day 4, there was a greater need for surgical teams and broad-spectrum antibiotics (eg, piperacillin, tazobactam) to combat sepsis.
Pereira and colleagues reported that in a catastrophe caused by a tropical storm and landslides in Brazil, the most common injuries involved the extremities; the majority of wounds required only cleaning, debridement, and suture; and the most commonly performed operations were for orthopedic injuries.10 Incidentally, population baseline morbidity and mortality continue during disasters, and rescue personnel invariably sustain injuries, which contribute to the total medical burden. These additional injuries must be anticipated, and plans to manage them must be included in any disaster contingency planning.
Triage
Speed and correct triage are essential building blocks of disaster response. When resources are limited, triage is crucial in providing the right treatment to the right patient. There are numerous triage methods, some more rapid and straightforward; others more effective and cumbersome.11 In 2012, Sasser and colleagues wrote that the purpose of triage is to ensure injured patients are transported to a trauma center or the hospital best equipped to manage their specific injuries in an appropriate and timely manner.12 Their report focused on prehospital emergent care, not mass-casualty or disaster situations.
Triage is sometimes performed inconsistently. In a 2013 study, Kleber and colleagues found that 24% of providers overtriage and 16% undertriage.13 In the U.S., simple triage and rapid treatment (START) is commonly used to sort traumatized patients. All these methods take a “worst gets first treatment” approach. Depending on the magnitude of an event, however, providers may take a reverse-triage approach, in which they better use resources for the least injured patients and provide palliative care to the gravely ill.
During pandemic disasters, trauma triage protocols are ineffective. Instead, these events demand assessments that are sensitive to infectious diseases. Timely, didactic, hands-on training must be conducted before the fact so responders can adapt to react appropriately to a given disaster.14
Accurate, timely triage in mass-casualty incidents was conceptually demonstrated by Mekel and colleagues who reviewed the medical management of bombing victims in metropolitan Haifa, Israel during the period 2000 to 2006.15 Providers initiated a predetermined triage system in which patients are assigned to the appropriate echelon of care. Of 342 injured patients, 9.5% had severe injuries, 2.4% had moderate-severe injuries, and 88.9% had mild injuries. Correct and timely triage directed trauma victims to the appropriate medical care. Such action prevents the highest level facility from becoming overcrowded with less severely injured patients and ensures that the more critically injured receive a level of care comparable to that given under nondisaster circumstances.
The handheld ultrasound device, which can be used to correctly diagnose fractures, is an efficient triage resource for prehospital teams. In a 2008 study, McManus and colleagues suggested that ultrasound (vs traditional radiography) could be used to identify fractures in an emergency room.16 A handheld ultrasound device could be used outside the hospital, in the field, potentially reducing the number of referrals to overwhelmed orthopedic hospitals.
In 2007, Dean and colleagues reported on using ultrasound to rapidly triage disease during an earthquake in Guatemala.17 In that disaster, 23% of injuries presented within the first 24 hours, and a handheld ultrasound device was used to assess orthopedic injuries—ruling in 12% and ruling out 42%. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a tool that small medical teams can use to speed triage, enhance patient care, and relieve overcrowded medical centers of the unrelenting pressure.
On-Site vs Hospital
Complicating disaster response is self-triage. Victims with injuries of all severity levels go to the nearest hospital and overwhelm it. In 1991, Waeckerle reported that within the first 30 minutes of a disaster, a wave of victims arrives, usually with minor injuries, and impedes care for the more severely wounded.18 Correct triage instead would have directed these patients to a hospital other than the overwhelmed level I trauma center.15 This is not to say that patients with mild or moderate injuries are unimportant—just that their care may take scarce space and resources from the more severely injured.
Mallonee and colleagues reported that of the 759 people injured in the 1996 Oklahoma City bombing, 167 (22%) were fatalities, 83 (11%) were hospitalized, and 509 (67%) were treated on an outpatient basis.19 Most of the injuries could have been managed by quick-response medical teams operating in the affected area, outside the hospitals. This action would have reduced operational pressure on hospitals and improved severely injured patients’ access to care.
Specialized Teams
In 2008, Barillo and colleagues suggested that having standardized medic bags would allow a small detachment of medical professionals to provide care nimbly—and doing so would represent a leap forward in access to care.20
Because of their unique ability to understand the culture and coordinate military assets with local authorities, DoD international health specialists are crucial interfaces for any population, foreign or domestic. Seyedin and colleagues and Merin and colleagues suggested that in both the Bam earthquake in 2003 and the Nepal earthquake in 2015, understanding the culture played a vital role in health care delivery and in adhering to cultural norms in deciding when to perform surgery, making end-of-life decisions, communicating with family, establishing trust with local and regional leaders, and other matters.21,22
Strike teams are small groups of variably trained health care providers who are dispatched to underserved, outlying, or overwhelmed areas to deliver precached basic medical care and triage significant injuries to medical centers. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a strike team tool. During a local emergency, it is understood or assumed that response is inundated and that people are going untreated.
Crucially, strike teams must be trained, prepared, and readily dispatched ahead of larger response elements. Though quickly deployable, disaster medical assistance teams (DMATs) and National Guard Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and High-Yield Explosive Enhanced Response Force Package units, take time to mobilize. Therefore, strike teams should consist of community citizens or local National Guard assets, the latter being particularly suited to rapid response given their training, effective command and control, and intrinsic logistics.
The efficacy of strike teams was demonstrated during the 2011 earthquake in Japan.23 Disaster medical assistance teams were invaluable in triaging and treating patients during the first 3 days. A team left 34 minutes after the event to render aid to people caught in a roof collapse. During triage, 17% of the injuries were classified urgent, 22% intermediate, and 61% minor. On day 7, a DMAT was dispatched to assist with emergency medicine and primary care; 3% of the injuries were severe and required urgent care, 50% required intermediate care, and 47% required minor care.
The value of strike teams is 3-fold: It provides rapid, professional care at a crucial place and critical time; it correctly triages patients and thus allow hospitals to maintain resources for the more severely injured; and augments overwhelmed providers at crucial sites. The roles of strike teams were echoed in 2006 by Campos-Outcalt, who reported that DMATs deployed to austere locations had the flexibility to augment existing medical staff and to rapidly deploy, self-sustain, and treat patients until a situation was resolved.24 This nimble strike team mentality could become a rapid and flexible model to save more lives, relieve significant suffering, and offload pressure from local hospitals by treating the less critically injured.
After a disaster, space is at a premium, and nonmedical residents who make up 40% to 70% of the shelter population require resources as well.25 Family members and the lightly injured may be conscripted to augment the overwhelmed medical staff. In 1988, Halbert and colleagues described how Afghan volunteers with minimal medical experience were given training and supplies and served as advanced emergency medics, delivering medical care and performing well under austere conditions.26,27 Strike teams thus may provide on-scene training in addition to medical care.
In 2012, Kirsch and colleaguesfound that Haiti earthquake victims who received treatment and remained in camps showed no improvement in income, employment, or food access 1 year after the disaster compared with victims who remained outside the camps and in their own neighborhoods.28 This finding underscores the need for accurate and timely triage by strike teams outside hospitals and quick treatment and return of patients to their homes.
Conceptually, strike teams need not be confined to medical response. Team members also might be specialists in epidemiology, disease surveillance, public health, culinary water protection, municipal security, and civil engineering. Noji reported that malnutrition, diarrheal diseases, measles, acute respiratory infections, and malaria consistently accounted for 60% to 95% of reported deaths among refugees and displaced populations.29 In 2005, Spiegel found that the potential for epidemics of communicable diseases was increased by overcrowding and poor sanitation in both natural disasters and complex emergencies.30 In 2007, Watson and colleagues suggested that communicable diseases may account for two-thirds of the deaths in conflict areas, and malnutrition significantly increases the risk of these diseases.31 Effective disaster care may be better accomplished through decentralized strike team interventions, which avoid the pitfalls of displacement and overcrowding.
Conclusion
Crises of all magnitudes can be greatly eased by well-trained, quick-response, all-hazards medical detachments—small teams that can be rapidly mobilized and deployed to establish casualty collection points, provide accurate triage, and render emergency care. These highly mobile teams can bridge the gap between the occurrence of a disaster and the arrival of substantial assistance from state, federal, and nongovernmental organizations—a most vulnerable time. These competent, flexible teams then can be absorbed by the larger force when it arrives for sustained disaster operations. Predisaster planning must take into account the possibility of long-term care for casualties and the displaced. Careful attention should be given to the potential for epidemics—immunizations should be administered quickly to achieve herd immunity—and a program that will provide food, water, shelter, sanitation, and security should be established.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sarah M. Paulsen and members of the Utah Air National Guard and Morrocan military for their friendship and help in preparing the manuscript.
Environmental disasters can overpower local medical resources. Fortunately, such crises are rare in the U.S. This situation, however, has not always been the case. For example, in 1812, an earthquake along the New Madrid fault of the Mississippi Valley caused the Mississippi River to flow backward for 3 days.1 Today, in urbanized America, an earthquake of that magnitude would be devastating and severely overwhelm medical systems. All nations, including highly modernized nations, would need help in such disasters.2 A response system that is nimble, well-trained, scalable, and rapidly deployable can mitigate disaster sequelae. This article focuses on key aspects of effective rapid response, including speed, appropriate triage, quick-response strike teams, and disaster dynamics.
Why Speed Matters Most
Response time arguably is the most important factor in increasing survival in a disaster. In a 1996 study of earthquake disasters worldwide, Schultz and colleagues found a lower survival rate for victims who received medical care outside a 24-hour window.1 Studies of earthquakes in China have suggested that unless aid is rendered within 2 to 6 hours, fewer than half the victims will survive.3 Regarding a 1980 earthquake in Italy, de Bruycker and colleagues emphasized the importance of engaging in rescue activities within the first 48 hours.4 Safar reviewed mass disasters and reported that 25% to 50% of the injured and dead could have been saved if first aid had been provided immediately.5 In 1992 and 1994, Pretto and colleagues wrote that in earthquakes in Armenia and Costa Rica, many deaths could have been prevented had the victims received medical attention within the first 6 hours.6,7 The question is: How can responses to such crises be improved? Confederate Army Lt. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest’s dictum “[Get] there first with the most men” holds true in disaster medicine as well: get there fast with the right people, training, equipment, and supplies.8
Deaths in disasters can be described in a 3-phase distribution: immediate, early, and delayed. Stringent building codes and public warnings and evacuations reduce immediate deaths, but victims also die of catastrophic injury soon after an event. Early deaths are preventable with use of rapid interventions, such as tourniquets and airway adjuncts, but these must be administered within minutes or hours. Delayed deaths occur days or weeks after injury secondary to infection or organ system failure—which emphasizes the value of early wound care.
Emergency Supplies
What items are most needed? As each disaster is different, it would be presumptuous to provide a one-size-fits-all list, but some common supplies have been suggested. In 2010, Ginzberg and colleagues reported that during the first 24 hours of the Haiti earthquake of 1996, the overwhelming need was for IV hydration, narcotic analgesics, and casting supplies for the splinting of fractures.9 During the next 24 hours, IV stabilization was key, along with monitoring by Foley and suprapubic catheters. In the third 24-hour period, providers began to see sepsis-related deaths. In response to this challenge, teams began aggressive treatment with open surgical debridement of wounds, amputation of severely injured limbs, and administration of broad-spectrum IV antibiotics. Regional anesthesia with conscious sedation was mandatory because supplemental oxygen and ventilators were unavailable. By day 4, wound debridement, amputations, and fasciotomies were being provided by newly arrived anesthesiologists and orthopedic surgeons. Ginzberg and colleagues emphasized that rapid response was key in maximizing survival and by day 4, there was a greater need for surgical teams and broad-spectrum antibiotics (eg, piperacillin, tazobactam) to combat sepsis.
Pereira and colleagues reported that in a catastrophe caused by a tropical storm and landslides in Brazil, the most common injuries involved the extremities; the majority of wounds required only cleaning, debridement, and suture; and the most commonly performed operations were for orthopedic injuries.10 Incidentally, population baseline morbidity and mortality continue during disasters, and rescue personnel invariably sustain injuries, which contribute to the total medical burden. These additional injuries must be anticipated, and plans to manage them must be included in any disaster contingency planning.
Triage
Speed and correct triage are essential building blocks of disaster response. When resources are limited, triage is crucial in providing the right treatment to the right patient. There are numerous triage methods, some more rapid and straightforward; others more effective and cumbersome.11 In 2012, Sasser and colleagues wrote that the purpose of triage is to ensure injured patients are transported to a trauma center or the hospital best equipped to manage their specific injuries in an appropriate and timely manner.12 Their report focused on prehospital emergent care, not mass-casualty or disaster situations.
Triage is sometimes performed inconsistently. In a 2013 study, Kleber and colleagues found that 24% of providers overtriage and 16% undertriage.13 In the U.S., simple triage and rapid treatment (START) is commonly used to sort traumatized patients. All these methods take a “worst gets first treatment” approach. Depending on the magnitude of an event, however, providers may take a reverse-triage approach, in which they better use resources for the least injured patients and provide palliative care to the gravely ill.
During pandemic disasters, trauma triage protocols are ineffective. Instead, these events demand assessments that are sensitive to infectious diseases. Timely, didactic, hands-on training must be conducted before the fact so responders can adapt to react appropriately to a given disaster.14
Accurate, timely triage in mass-casualty incidents was conceptually demonstrated by Mekel and colleagues who reviewed the medical management of bombing victims in metropolitan Haifa, Israel during the period 2000 to 2006.15 Providers initiated a predetermined triage system in which patients are assigned to the appropriate echelon of care. Of 342 injured patients, 9.5% had severe injuries, 2.4% had moderate-severe injuries, and 88.9% had mild injuries. Correct and timely triage directed trauma victims to the appropriate medical care. Such action prevents the highest level facility from becoming overcrowded with less severely injured patients and ensures that the more critically injured receive a level of care comparable to that given under nondisaster circumstances.
The handheld ultrasound device, which can be used to correctly diagnose fractures, is an efficient triage resource for prehospital teams. In a 2008 study, McManus and colleagues suggested that ultrasound (vs traditional radiography) could be used to identify fractures in an emergency room.16 A handheld ultrasound device could be used outside the hospital, in the field, potentially reducing the number of referrals to overwhelmed orthopedic hospitals.
In 2007, Dean and colleagues reported on using ultrasound to rapidly triage disease during an earthquake in Guatemala.17 In that disaster, 23% of injuries presented within the first 24 hours, and a handheld ultrasound device was used to assess orthopedic injuries—ruling in 12% and ruling out 42%. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a tool that small medical teams can use to speed triage, enhance patient care, and relieve overcrowded medical centers of the unrelenting pressure.
On-Site vs Hospital
Complicating disaster response is self-triage. Victims with injuries of all severity levels go to the nearest hospital and overwhelm it. In 1991, Waeckerle reported that within the first 30 minutes of a disaster, a wave of victims arrives, usually with minor injuries, and impedes care for the more severely wounded.18 Correct triage instead would have directed these patients to a hospital other than the overwhelmed level I trauma center.15 This is not to say that patients with mild or moderate injuries are unimportant—just that their care may take scarce space and resources from the more severely injured.
Mallonee and colleagues reported that of the 759 people injured in the 1996 Oklahoma City bombing, 167 (22%) were fatalities, 83 (11%) were hospitalized, and 509 (67%) were treated on an outpatient basis.19 Most of the injuries could have been managed by quick-response medical teams operating in the affected area, outside the hospitals. This action would have reduced operational pressure on hospitals and improved severely injured patients’ access to care.
Specialized Teams
In 2008, Barillo and colleagues suggested that having standardized medic bags would allow a small detachment of medical professionals to provide care nimbly—and doing so would represent a leap forward in access to care.20
Because of their unique ability to understand the culture and coordinate military assets with local authorities, DoD international health specialists are crucial interfaces for any population, foreign or domestic. Seyedin and colleagues and Merin and colleagues suggested that in both the Bam earthquake in 2003 and the Nepal earthquake in 2015, understanding the culture played a vital role in health care delivery and in adhering to cultural norms in deciding when to perform surgery, making end-of-life decisions, communicating with family, establishing trust with local and regional leaders, and other matters.21,22
Strike teams are small groups of variably trained health care providers who are dispatched to underserved, outlying, or overwhelmed areas to deliver precached basic medical care and triage significant injuries to medical centers. The handheld ultrasound device is an example of a strike team tool. During a local emergency, it is understood or assumed that response is inundated and that people are going untreated.
Crucially, strike teams must be trained, prepared, and readily dispatched ahead of larger response elements. Though quickly deployable, disaster medical assistance teams (DMATs) and National Guard Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and High-Yield Explosive Enhanced Response Force Package units, take time to mobilize. Therefore, strike teams should consist of community citizens or local National Guard assets, the latter being particularly suited to rapid response given their training, effective command and control, and intrinsic logistics.
The efficacy of strike teams was demonstrated during the 2011 earthquake in Japan.23 Disaster medical assistance teams were invaluable in triaging and treating patients during the first 3 days. A team left 34 minutes after the event to render aid to people caught in a roof collapse. During triage, 17% of the injuries were classified urgent, 22% intermediate, and 61% minor. On day 7, a DMAT was dispatched to assist with emergency medicine and primary care; 3% of the injuries were severe and required urgent care, 50% required intermediate care, and 47% required minor care.
The value of strike teams is 3-fold: It provides rapid, professional care at a crucial place and critical time; it correctly triages patients and thus allow hospitals to maintain resources for the more severely injured; and augments overwhelmed providers at crucial sites. The roles of strike teams were echoed in 2006 by Campos-Outcalt, who reported that DMATs deployed to austere locations had the flexibility to augment existing medical staff and to rapidly deploy, self-sustain, and treat patients until a situation was resolved.24 This nimble strike team mentality could become a rapid and flexible model to save more lives, relieve significant suffering, and offload pressure from local hospitals by treating the less critically injured.
After a disaster, space is at a premium, and nonmedical residents who make up 40% to 70% of the shelter population require resources as well.25 Family members and the lightly injured may be conscripted to augment the overwhelmed medical staff. In 1988, Halbert and colleagues described how Afghan volunteers with minimal medical experience were given training and supplies and served as advanced emergency medics, delivering medical care and performing well under austere conditions.26,27 Strike teams thus may provide on-scene training in addition to medical care.
In 2012, Kirsch and colleaguesfound that Haiti earthquake victims who received treatment and remained in camps showed no improvement in income, employment, or food access 1 year after the disaster compared with victims who remained outside the camps and in their own neighborhoods.28 This finding underscores the need for accurate and timely triage by strike teams outside hospitals and quick treatment and return of patients to their homes.
Conceptually, strike teams need not be confined to medical response. Team members also might be specialists in epidemiology, disease surveillance, public health, culinary water protection, municipal security, and civil engineering. Noji reported that malnutrition, diarrheal diseases, measles, acute respiratory infections, and malaria consistently accounted for 60% to 95% of reported deaths among refugees and displaced populations.29 In 2005, Spiegel found that the potential for epidemics of communicable diseases was increased by overcrowding and poor sanitation in both natural disasters and complex emergencies.30 In 2007, Watson and colleagues suggested that communicable diseases may account for two-thirds of the deaths in conflict areas, and malnutrition significantly increases the risk of these diseases.31 Effective disaster care may be better accomplished through decentralized strike team interventions, which avoid the pitfalls of displacement and overcrowding.
Conclusion
Crises of all magnitudes can be greatly eased by well-trained, quick-response, all-hazards medical detachments—small teams that can be rapidly mobilized and deployed to establish casualty collection points, provide accurate triage, and render emergency care. These highly mobile teams can bridge the gap between the occurrence of a disaster and the arrival of substantial assistance from state, federal, and nongovernmental organizations—a most vulnerable time. These competent, flexible teams then can be absorbed by the larger force when it arrives for sustained disaster operations. Predisaster planning must take into account the possibility of long-term care for casualties and the displaced. Careful attention should be given to the potential for epidemics—immunizations should be administered quickly to achieve herd immunity—and a program that will provide food, water, shelter, sanitation, and security should be established.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sarah M. Paulsen and members of the Utah Air National Guard and Morrocan military for their friendship and help in preparing the manuscript.
1. Schultz CH, Koenig KL, Noji EK. A medical disaster response to reduce immediate mortality after an earthquake. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(7):438-444.
2. Merin O, Blumberg N, Raveh D, Bar A, Nishizawa M, Cohen-Marom O. Global responsibility in mass casualty events: the Israeli experience in Japan. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(1):61-64.
3. Sheng ZY. Medical support in the Tangshan earthquake: a review of the management of mass casualties and certain major injuries. J Trauma. 1987;27(10):1130-1135.
4. de Bruycker M, Greco D, Annino I, et al. The 1980 earthquake in southern Italy: rescue of trapped victims and mortality. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(6):1021-1025.
5. Safar P. Resuscitation potentials in mass disasters. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1986;2:34-47.
6. Pretto EA, Ricci E, Klain M, et al. Disaster reanimatology potentials: a structured interview study in Armenia III. Results, conclusions and recommendations. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1992;7:327-338.
7. Pretto EA, Angus DC, Abrams JI, et al. An analysis of prehospital mortality in an earthquake. Disaster Reanimatology Study Group. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1994;9(2):107-124.
8. Keyes R. The Quote Verifier: Who Said What, Where, and When. New York, NY: St. Martin’s Griffin; 2006.
9. Ginzberg E, O’Neill WW, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, de Marchena E, Pust D, Green BA. Rapid medical relief—Project Medishare and the Haitian earthquake. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(10):e31.
10. Pereira BM, Morales W, Cardoso RG, Fiorelli R, Fraga GP, Briggs SM. Lessons learned from a landslide catastrophe in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(4):253-258.
11. Cross KP, Cicero MX. Head-to-head comparison of disaster triage methods in pediatric, adult, and geriatric patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;61(6):668-676.e7.
12. Sasser SM, Hunt RC, Faul M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Guidelines for field triage of injured patients: recommendations of the National Expert Panel on Field Triage, 2011. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2012;61(RR-1):1-20.
13. Kleber C, Cwojdzinski D, Strehl M, Poloczek S, Haas NP. Results of in-hospital triage in 17 mass casualty trainings: underestimation of life-threatening injuries and need for re-triage. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(1):5-11.
14. Talmor D, Jones AE, Rubinson L, Howell MD, Shapiro NI. Simple triage scoring system predicting death and the need for critical care resources for use during epidemics. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5):1251-1256.
15. Mekel M, Bumenfeld A, Feigenberg Z, et al. Terrorist suicide bombings: lessons learned in metropolitan Haifa from September 2000 to January 2006. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(4):233-248.
16. McManus JG, Morton MJ, Crystal CS, et al. Use of ultrasound to assess acute fracture reduction in emergency care settings. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(4):241-247.
17. Dean AJ, Ku BS, Zeserson EM. The utility of handheld ultrasound in an austere medical setting in Guatemala after a natural disaster. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(5):249-256.
18. Waeckerle JF. Disaster planning and response. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(12):815-821.
19. Mallonee S, Shariat S, Stennies G, Waxweiler R, Hogan D, Jordan F. Physical injuries and fatalities resulting from the Oklahoma City bombing. JAMA. 1996;276(5):382-387.
20. Barillo DJ, Renz E, Broger K, Moak B, Wright G, Holcomb JB. An emergency medical bag set for long-range aeromedical transportation. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(2):79-86.
21. Seyedin SH, Aflatoonian MR, Ryan J. Adverse impact of international NGOs during and after the Bam earthquake: health system’s consumers’ points of view. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(3):173-179.
22. Merin O, Yitzhak A, Bader T. Medicine in a disaster area: lessons from the 2015 earthquake in Nepal. JAMA. 2015;175(9):1437-1438.
23. Ushizawa H, Foxwell AR, Bice S, et al. Needs for disaster medicine: lessons from the field of the great east Japan earthquake. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2013;4(1):51-55.
24. Campos-Outcalt D. Disaster medical response: maximizing your effectiveness. J Fam Pract. 2006;55(2):113-115.
25. Patton-Levine JK, Vest JR, Valadez AM. Caregivers and families in medical special needs shelters: an experience during Hurricane Rita. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(2):81-86.
26. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical theatre in rural Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):775-778.
27. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical training model for advanced emergency medics in Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):779-784.
28. Kirsch TD, Leidman E, Weiss W, Doocy S. The impact of the earthquake and humanitarian assistance on household economies and livelihoods of earthquake-affected populations in Haiti. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(2):85-94.
29. Noji EK. Public health in the aftermath of disasters. BMJ. 2005;330(7504):1379-1381.
30. Spiegel PB. Differences in world responses to natural disasters and complex emergencies. JAMA. 2005;293(15):1915-1918.
31. Watson JT, Gayer M, Connolly MA. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(1):1-5.
1. Schultz CH, Koenig KL, Noji EK. A medical disaster response to reduce immediate mortality after an earthquake. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(7):438-444.
2. Merin O, Blumberg N, Raveh D, Bar A, Nishizawa M, Cohen-Marom O. Global responsibility in mass casualty events: the Israeli experience in Japan. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(1):61-64.
3. Sheng ZY. Medical support in the Tangshan earthquake: a review of the management of mass casualties and certain major injuries. J Trauma. 1987;27(10):1130-1135.
4. de Bruycker M, Greco D, Annino I, et al. The 1980 earthquake in southern Italy: rescue of trapped victims and mortality. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(6):1021-1025.
5. Safar P. Resuscitation potentials in mass disasters. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1986;2:34-47.
6. Pretto EA, Ricci E, Klain M, et al. Disaster reanimatology potentials: a structured interview study in Armenia III. Results, conclusions and recommendations. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1992;7:327-338.
7. Pretto EA, Angus DC, Abrams JI, et al. An analysis of prehospital mortality in an earthquake. Disaster Reanimatology Study Group. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1994;9(2):107-124.
8. Keyes R. The Quote Verifier: Who Said What, Where, and When. New York, NY: St. Martin’s Griffin; 2006.
9. Ginzberg E, O’Neill WW, Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ, de Marchena E, Pust D, Green BA. Rapid medical relief—Project Medishare and the Haitian earthquake. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(10):e31.
10. Pereira BM, Morales W, Cardoso RG, Fiorelli R, Fraga GP, Briggs SM. Lessons learned from a landslide catastrophe in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(4):253-258.
11. Cross KP, Cicero MX. Head-to-head comparison of disaster triage methods in pediatric, adult, and geriatric patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;61(6):668-676.e7.
12. Sasser SM, Hunt RC, Faul M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Guidelines for field triage of injured patients: recommendations of the National Expert Panel on Field Triage, 2011. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2012;61(RR-1):1-20.
13. Kleber C, Cwojdzinski D, Strehl M, Poloczek S, Haas NP. Results of in-hospital triage in 17 mass casualty trainings: underestimation of life-threatening injuries and need for re-triage. Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(1):5-11.
14. Talmor D, Jones AE, Rubinson L, Howell MD, Shapiro NI. Simple triage scoring system predicting death and the need for critical care resources for use during epidemics. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(5):1251-1256.
15. Mekel M, Bumenfeld A, Feigenberg Z, et al. Terrorist suicide bombings: lessons learned in metropolitan Haifa from September 2000 to January 2006. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(4):233-248.
16. McManus JG, Morton MJ, Crystal CS, et al. Use of ultrasound to assess acute fracture reduction in emergency care settings. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(4):241-247.
17. Dean AJ, Ku BS, Zeserson EM. The utility of handheld ultrasound in an austere medical setting in Guatemala after a natural disaster. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(5):249-256.
18. Waeckerle JF. Disaster planning and response. N Engl J Med. 1991;324(12):815-821.
19. Mallonee S, Shariat S, Stennies G, Waxweiler R, Hogan D, Jordan F. Physical injuries and fatalities resulting from the Oklahoma City bombing. JAMA. 1996;276(5):382-387.
20. Barillo DJ, Renz E, Broger K, Moak B, Wright G, Holcomb JB. An emergency medical bag set for long-range aeromedical transportation. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(2):79-86.
21. Seyedin SH, Aflatoonian MR, Ryan J. Adverse impact of international NGOs during and after the Bam earthquake: health system’s consumers’ points of view. Am J Disaster Med. 2009;4(3):173-179.
22. Merin O, Yitzhak A, Bader T. Medicine in a disaster area: lessons from the 2015 earthquake in Nepal. JAMA. 2015;175(9):1437-1438.
23. Ushizawa H, Foxwell AR, Bice S, et al. Needs for disaster medicine: lessons from the field of the great east Japan earthquake. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2013;4(1):51-55.
24. Campos-Outcalt D. Disaster medical response: maximizing your effectiveness. J Fam Pract. 2006;55(2):113-115.
25. Patton-Levine JK, Vest JR, Valadez AM. Caregivers and families in medical special needs shelters: an experience during Hurricane Rita. Am J Disaster Med. 2007;2(2):81-86.
26. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical theatre in rural Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):775-778.
27. Halbert RJ, Simon RR, Nasraty Q. Surgical training model for advanced emergency medics in Afghanistan. Ann Emerg Med. 1988;17(8):779-784.
28. Kirsch TD, Leidman E, Weiss W, Doocy S. The impact of the earthquake and humanitarian assistance on household economies and livelihoods of earthquake-affected populations in Haiti. Am J Disaster Med. 2012;7(2):85-94.
29. Noji EK. Public health in the aftermath of disasters. BMJ. 2005;330(7504):1379-1381.
30. Spiegel PB. Differences in world responses to natural disasters and complex emergencies. JAMA. 2005;293(15):1915-1918.
31. Watson JT, Gayer M, Connolly MA. Epidemics after natural disasters. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13(1):1-5.
Cancer survivors report pros and cons of telehealth

Photo by Daniel Sone
Cancer survivors report a range of benefits and detriments related to telehealth, according to research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
Telehealth is the use of technology to provide remote, personalized healthcare to patients.
Telehealth services allow patients to have meetings and follow-up consultations with healthcare professionals either on the phone or through online services at a time that suits the patients.
Anna Cox, PhD, of the University of Surrey in the UK, and her colleagues examined 22 studies, published between 2006 and 2016, that reported cancer patients’ direct views on their experience of telehealth.
Some of the cancer survivors studied reported their appreciation of the flexibility and convenience of telehealth, which enabled them to engage with healthcare providers with minimum disruption to their lives and in a comfortable, familiar environment.
“Our research found that cancer survivors wanted to get back to their daily lives as quickly as possible,” Dr Cox said. “Telehealth helped facilitate this, as it removed the often burdensome visits to hospital and enabled the integration of care into daily routines.”
However, not all subjects viewed telehealth as a convenience. Of the Internet-based interventions studied, 2 were perceived as an extra burden, and 1 was considered too time-consuming.
In addition, some study participants viewed telehealth as an impersonal service that did not allow them to meet their healthcare team in person.
On the other hand, the invisibility and perceived anonymity that telehealth provided sometimes reduced cancer survivors’ sense of vulnerability and enabled them to raise concerns remotely that they would not have wanted to discuss face-to-face.
And, in 8 different studies, subjects said telehealth had educated them about ways they could improve or manage their symptoms, or it had raised their awareness of potential issues they might experience.
Unfortunately, some of the cancer survivors studied said they were unable to use telehealth due to personal circumstances, such as hearing issues and lack of computer literacy skills.
“For many cancer survivors, telehealth supported their independence and offered them reassurance,” Dr Cox noted. “However, it is all down to personal preference, as some cancer survivors still preferred traditional methods of care.” ![]()

Photo by Daniel Sone
Cancer survivors report a range of benefits and detriments related to telehealth, according to research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
Telehealth is the use of technology to provide remote, personalized healthcare to patients.
Telehealth services allow patients to have meetings and follow-up consultations with healthcare professionals either on the phone or through online services at a time that suits the patients.
Anna Cox, PhD, of the University of Surrey in the UK, and her colleagues examined 22 studies, published between 2006 and 2016, that reported cancer patients’ direct views on their experience of telehealth.
Some of the cancer survivors studied reported their appreciation of the flexibility and convenience of telehealth, which enabled them to engage with healthcare providers with minimum disruption to their lives and in a comfortable, familiar environment.
“Our research found that cancer survivors wanted to get back to their daily lives as quickly as possible,” Dr Cox said. “Telehealth helped facilitate this, as it removed the often burdensome visits to hospital and enabled the integration of care into daily routines.”
However, not all subjects viewed telehealth as a convenience. Of the Internet-based interventions studied, 2 were perceived as an extra burden, and 1 was considered too time-consuming.
In addition, some study participants viewed telehealth as an impersonal service that did not allow them to meet their healthcare team in person.
On the other hand, the invisibility and perceived anonymity that telehealth provided sometimes reduced cancer survivors’ sense of vulnerability and enabled them to raise concerns remotely that they would not have wanted to discuss face-to-face.
And, in 8 different studies, subjects said telehealth had educated them about ways they could improve or manage their symptoms, or it had raised their awareness of potential issues they might experience.
Unfortunately, some of the cancer survivors studied said they were unable to use telehealth due to personal circumstances, such as hearing issues and lack of computer literacy skills.
“For many cancer survivors, telehealth supported their independence and offered them reassurance,” Dr Cox noted. “However, it is all down to personal preference, as some cancer survivors still preferred traditional methods of care.” ![]()

Photo by Daniel Sone
Cancer survivors report a range of benefits and detriments related to telehealth, according to research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
Telehealth is the use of technology to provide remote, personalized healthcare to patients.
Telehealth services allow patients to have meetings and follow-up consultations with healthcare professionals either on the phone or through online services at a time that suits the patients.
Anna Cox, PhD, of the University of Surrey in the UK, and her colleagues examined 22 studies, published between 2006 and 2016, that reported cancer patients’ direct views on their experience of telehealth.
Some of the cancer survivors studied reported their appreciation of the flexibility and convenience of telehealth, which enabled them to engage with healthcare providers with minimum disruption to their lives and in a comfortable, familiar environment.
“Our research found that cancer survivors wanted to get back to their daily lives as quickly as possible,” Dr Cox said. “Telehealth helped facilitate this, as it removed the often burdensome visits to hospital and enabled the integration of care into daily routines.”
However, not all subjects viewed telehealth as a convenience. Of the Internet-based interventions studied, 2 were perceived as an extra burden, and 1 was considered too time-consuming.
In addition, some study participants viewed telehealth as an impersonal service that did not allow them to meet their healthcare team in person.
On the other hand, the invisibility and perceived anonymity that telehealth provided sometimes reduced cancer survivors’ sense of vulnerability and enabled them to raise concerns remotely that they would not have wanted to discuss face-to-face.
And, in 8 different studies, subjects said telehealth had educated them about ways they could improve or manage their symptoms, or it had raised their awareness of potential issues they might experience.
Unfortunately, some of the cancer survivors studied said they were unable to use telehealth due to personal circumstances, such as hearing issues and lack of computer literacy skills.
“For many cancer survivors, telehealth supported their independence and offered them reassurance,” Dr Cox noted. “However, it is all down to personal preference, as some cancer survivors still preferred traditional methods of care.” ![]()
B-cell energy levels linked to leukemic transformation

Photo from Business Wire
A pair of transcription factors protect B cells from malignant transformation by keeping the cells’ glucose and energy levels low, according to research published in Nature.
“While transformation to cancer and childhood leukemia takes large amounts of energy, we discovered that low energy levels in B cells protects from malignant transformation toward leukemia and cancer,” said study author Markus Müschen, MD, PhD, of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
“The low energy levels in normal B cells are simply too low to allow transformation to leukemia.”
Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that PAX5 and IKZF1, transcription factors that are critical for early B-cell development, “enforce a state of chronic energy deprivation” that results in constitutive activation of the energy-stress sensor AMPK.
However, dominant-negative mutants of PAX5 and IKZF1 reverse this effect.
Past research has suggested that mutations and deletions in the PAX5 and IKZF1 genes occur in more than 80% of cases of pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
In the current study, Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that heterozygous deletion of Pax5 in a mouse model of pre-B ALL greatly increased glucose uptake and ATP levels.
Similarly, when they reconstituted PAX5 and IKZF1 in samples from patients with pre-B ALL, the investigators observed “an energy crisis” that prompted leukemic cell death.
Dr Müschen and his colleagues also performed a CRISPR/Cas9-based screen of PAX5 and IKZF1 transcriptional targets. They said this revealed that NR3C1, TXNIP, and CNR2 are central effectors of B-lymphoid restriction of glucose and energy.
To build upon this finding, the investigators tested TXNIP and CNR2 agonists as well as a small-molecule AMPK inhibitor. They found these compounds synergized with glucocorticoids in patient-derived pre-B ALL cells.
The team therefore concluded that TXNIP, CNR2, and AMPK are potential therapeutic targets for pre-B ALL.
The investigators also said the results of this study support a previous finding that obese children with high blood sugar levels are much more likely to develop drug-resistant leukemia than children who are not overweight. So dieting could be an important consideration for children who have survived leukemia.
“Avoiding obesity and excessive energy supply may help to decrease the risk of leukemia relapse,” said study author Lai Chan, PhD, also of City of Hope.
To test that theory, Drs Chan and Müschen and their colleagues plan to perform experiments in animal models to evaluate the efficacy of dietary restriction on patient-derived childhood leukemia cells, and to assess the activity of drugs that reduce leukemia cells’ glucose and energy supply.
“Based on the outcome of these studies, we plan to introduce dietary restriction and/or glucose-restricting drugs into a clinical trial for children who are at risk to develop leukemia relapse,” Dr Müschen said. ![]()

Photo from Business Wire
A pair of transcription factors protect B cells from malignant transformation by keeping the cells’ glucose and energy levels low, according to research published in Nature.
“While transformation to cancer and childhood leukemia takes large amounts of energy, we discovered that low energy levels in B cells protects from malignant transformation toward leukemia and cancer,” said study author Markus Müschen, MD, PhD, of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
“The low energy levels in normal B cells are simply too low to allow transformation to leukemia.”
Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that PAX5 and IKZF1, transcription factors that are critical for early B-cell development, “enforce a state of chronic energy deprivation” that results in constitutive activation of the energy-stress sensor AMPK.
However, dominant-negative mutants of PAX5 and IKZF1 reverse this effect.
Past research has suggested that mutations and deletions in the PAX5 and IKZF1 genes occur in more than 80% of cases of pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
In the current study, Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that heterozygous deletion of Pax5 in a mouse model of pre-B ALL greatly increased glucose uptake and ATP levels.
Similarly, when they reconstituted PAX5 and IKZF1 in samples from patients with pre-B ALL, the investigators observed “an energy crisis” that prompted leukemic cell death.
Dr Müschen and his colleagues also performed a CRISPR/Cas9-based screen of PAX5 and IKZF1 transcriptional targets. They said this revealed that NR3C1, TXNIP, and CNR2 are central effectors of B-lymphoid restriction of glucose and energy.
To build upon this finding, the investigators tested TXNIP and CNR2 agonists as well as a small-molecule AMPK inhibitor. They found these compounds synergized with glucocorticoids in patient-derived pre-B ALL cells.
The team therefore concluded that TXNIP, CNR2, and AMPK are potential therapeutic targets for pre-B ALL.
The investigators also said the results of this study support a previous finding that obese children with high blood sugar levels are much more likely to develop drug-resistant leukemia than children who are not overweight. So dieting could be an important consideration for children who have survived leukemia.
“Avoiding obesity and excessive energy supply may help to decrease the risk of leukemia relapse,” said study author Lai Chan, PhD, also of City of Hope.
To test that theory, Drs Chan and Müschen and their colleagues plan to perform experiments in animal models to evaluate the efficacy of dietary restriction on patient-derived childhood leukemia cells, and to assess the activity of drugs that reduce leukemia cells’ glucose and energy supply.
“Based on the outcome of these studies, we plan to introduce dietary restriction and/or glucose-restricting drugs into a clinical trial for children who are at risk to develop leukemia relapse,” Dr Müschen said. ![]()

Photo from Business Wire
A pair of transcription factors protect B cells from malignant transformation by keeping the cells’ glucose and energy levels low, according to research published in Nature.
“While transformation to cancer and childhood leukemia takes large amounts of energy, we discovered that low energy levels in B cells protects from malignant transformation toward leukemia and cancer,” said study author Markus Müschen, MD, PhD, of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
“The low energy levels in normal B cells are simply too low to allow transformation to leukemia.”
Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that PAX5 and IKZF1, transcription factors that are critical for early B-cell development, “enforce a state of chronic energy deprivation” that results in constitutive activation of the energy-stress sensor AMPK.
However, dominant-negative mutants of PAX5 and IKZF1 reverse this effect.
Past research has suggested that mutations and deletions in the PAX5 and IKZF1 genes occur in more than 80% of cases of pre-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
In the current study, Dr Müschen and his colleagues found that heterozygous deletion of Pax5 in a mouse model of pre-B ALL greatly increased glucose uptake and ATP levels.
Similarly, when they reconstituted PAX5 and IKZF1 in samples from patients with pre-B ALL, the investigators observed “an energy crisis” that prompted leukemic cell death.
Dr Müschen and his colleagues also performed a CRISPR/Cas9-based screen of PAX5 and IKZF1 transcriptional targets. They said this revealed that NR3C1, TXNIP, and CNR2 are central effectors of B-lymphoid restriction of glucose and energy.
To build upon this finding, the investigators tested TXNIP and CNR2 agonists as well as a small-molecule AMPK inhibitor. They found these compounds synergized with glucocorticoids in patient-derived pre-B ALL cells.
The team therefore concluded that TXNIP, CNR2, and AMPK are potential therapeutic targets for pre-B ALL.
The investigators also said the results of this study support a previous finding that obese children with high blood sugar levels are much more likely to develop drug-resistant leukemia than children who are not overweight. So dieting could be an important consideration for children who have survived leukemia.
“Avoiding obesity and excessive energy supply may help to decrease the risk of leukemia relapse,” said study author Lai Chan, PhD, also of City of Hope.
To test that theory, Drs Chan and Müschen and their colleagues plan to perform experiments in animal models to evaluate the efficacy of dietary restriction on patient-derived childhood leukemia cells, and to assess the activity of drugs that reduce leukemia cells’ glucose and energy supply.
“Based on the outcome of these studies, we plan to introduce dietary restriction and/or glucose-restricting drugs into a clinical trial for children who are at risk to develop leukemia relapse,” Dr Müschen said. ![]()
Predicting the efficacy of malaria vaccines
Photo by Caitlin Kleiboer
Researchers say they have identified molecular signatures that could potentially be used to predict whether the malaria vaccine RTS,S will be effective.
The group says the research, published in PNAS, could inform decisions on how RTS,S or other malaria vaccines are deployed or modified.
RTS,S (also known as RTS,S/AS01 or Mosquirix) has been shown to provide partial protection against malaria in phase 2 and phase 3 trials.
The vaccine is scheduled for roll-out through pilot projects in 3 African countries next year, according to the World Health Organization.
With the current study, researchers used a systems biology approach to identify molecular signatures induced after subjects were vaccinated with RTS,S.
The team looked at 2 groups of subjects:
- Individuals vaccinated with the standard RTS,S vaccination regimen, which consists of 3 RTS,S immunizations (RRR)
- Individuals vaccinated first with recombinant adenovirus 35 (Ad35) expressing the circumsporozoite malaria antigen, followed by 2 immunizations with RTS,S (ARR).
Vaccinated subjects were exposed to mosquitoes infected with Plasmodium falciparum 3 weeks after their final immunization.
Both vaccination regimens resulted in about 50% protection from malaria infection. And the researchers identified markers in each group that were associated with protection.
In the RRR group, circumsporozoite protein-specific antibody titers, prior to the challenge with infected mosquitoes, were associated with protection from malaria infection.
In addition, molecular signatures of B and plasma cells detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were associated with pre-challenge antibody titers and protection from malaria infection in the RRR group.
In the ARR group, protection from infection was associated with polyfunctional CD4+ T-cell responses 2 weeks after priming with Ad35, early signatures of innate immunity, and dendritic cell activation.
In both groups, natural killer (NK) cell signatures were negatively correlated with protection.
“Many of the genes contained in the predictive signatures are known to be expressed in natural killer cells, which mediate critical immune functions against viruses,” said study author Bali Pulendran, PhD, of Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
“It was a surprise to see such a robust ‘NK cell signature’ in predicting success of vaccination against the malaria parasite and raises the hypothesis that such cells may be playing a vital role in orchestrating immunity against malaria.”
Dr Pulendran and his colleagues said the results of this research suggest protective immunity against P falciparum can be achieved via multiple mechanisms.
“The extent to which these candidate signatures of protection can successfully predict vaccine efficacy in other field trials remain to be determined,” Dr Pulendran noted. ![]()

Photo by Caitlin Kleiboer
Researchers say they have identified molecular signatures that could potentially be used to predict whether the malaria vaccine RTS,S will be effective.
The group says the research, published in PNAS, could inform decisions on how RTS,S or other malaria vaccines are deployed or modified.
RTS,S (also known as RTS,S/AS01 or Mosquirix) has been shown to provide partial protection against malaria in phase 2 and phase 3 trials.
The vaccine is scheduled for roll-out through pilot projects in 3 African countries next year, according to the World Health Organization.
With the current study, researchers used a systems biology approach to identify molecular signatures induced after subjects were vaccinated with RTS,S.
The team looked at 2 groups of subjects:
- Individuals vaccinated with the standard RTS,S vaccination regimen, which consists of 3 RTS,S immunizations (RRR)
- Individuals vaccinated first with recombinant adenovirus 35 (Ad35) expressing the circumsporozoite malaria antigen, followed by 2 immunizations with RTS,S (ARR).
Vaccinated subjects were exposed to mosquitoes infected with Plasmodium falciparum 3 weeks after their final immunization.
Both vaccination regimens resulted in about 50% protection from malaria infection. And the researchers identified markers in each group that were associated with protection.
In the RRR group, circumsporozoite protein-specific antibody titers, prior to the challenge with infected mosquitoes, were associated with protection from malaria infection.
In addition, molecular signatures of B and plasma cells detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were associated with pre-challenge antibody titers and protection from malaria infection in the RRR group.
In the ARR group, protection from infection was associated with polyfunctional CD4+ T-cell responses 2 weeks after priming with Ad35, early signatures of innate immunity, and dendritic cell activation.
In both groups, natural killer (NK) cell signatures were negatively correlated with protection.
“Many of the genes contained in the predictive signatures are known to be expressed in natural killer cells, which mediate critical immune functions against viruses,” said study author Bali Pulendran, PhD, of Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
“It was a surprise to see such a robust ‘NK cell signature’ in predicting success of vaccination against the malaria parasite and raises the hypothesis that such cells may be playing a vital role in orchestrating immunity against malaria.”
Dr Pulendran and his colleagues said the results of this research suggest protective immunity against P falciparum can be achieved via multiple mechanisms.
“The extent to which these candidate signatures of protection can successfully predict vaccine efficacy in other field trials remain to be determined,” Dr Pulendran noted. ![]()

Photo by Caitlin Kleiboer
Researchers say they have identified molecular signatures that could potentially be used to predict whether the malaria vaccine RTS,S will be effective.
The group says the research, published in PNAS, could inform decisions on how RTS,S or other malaria vaccines are deployed or modified.
RTS,S (also known as RTS,S/AS01 or Mosquirix) has been shown to provide partial protection against malaria in phase 2 and phase 3 trials.
The vaccine is scheduled for roll-out through pilot projects in 3 African countries next year, according to the World Health Organization.
With the current study, researchers used a systems biology approach to identify molecular signatures induced after subjects were vaccinated with RTS,S.
The team looked at 2 groups of subjects:
- Individuals vaccinated with the standard RTS,S vaccination regimen, which consists of 3 RTS,S immunizations (RRR)
- Individuals vaccinated first with recombinant adenovirus 35 (Ad35) expressing the circumsporozoite malaria antigen, followed by 2 immunizations with RTS,S (ARR).
Vaccinated subjects were exposed to mosquitoes infected with Plasmodium falciparum 3 weeks after their final immunization.
Both vaccination regimens resulted in about 50% protection from malaria infection. And the researchers identified markers in each group that were associated with protection.
In the RRR group, circumsporozoite protein-specific antibody titers, prior to the challenge with infected mosquitoes, were associated with protection from malaria infection.
In addition, molecular signatures of B and plasma cells detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were associated with pre-challenge antibody titers and protection from malaria infection in the RRR group.
In the ARR group, protection from infection was associated with polyfunctional CD4+ T-cell responses 2 weeks after priming with Ad35, early signatures of innate immunity, and dendritic cell activation.
In both groups, natural killer (NK) cell signatures were negatively correlated with protection.
“Many of the genes contained in the predictive signatures are known to be expressed in natural killer cells, which mediate critical immune functions against viruses,” said study author Bali Pulendran, PhD, of Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
“It was a surprise to see such a robust ‘NK cell signature’ in predicting success of vaccination against the malaria parasite and raises the hypothesis that such cells may be playing a vital role in orchestrating immunity against malaria.”
Dr Pulendran and his colleagues said the results of this research suggest protective immunity against P falciparum can be achieved via multiple mechanisms.
“The extent to which these candidate signatures of protection can successfully predict vaccine efficacy in other field trials remain to be determined,” Dr Pulendran noted. ![]()
Study reveals patterns of ED use in SCD patients

Photo courtesy of St. Jude
Children’s Research Hospital
Population-based surveillance data has revealed patterns of emergency department (ED) visits among Californians with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Previous research suggested that between one-half and two-thirds of SCD patients’ ED visits end in a discharge from the ED, called a treat-and-release visit.
The remainder result in admission to a hospital or other treatment facility.
The purpose of the current study was to use data from the Sickle Cell Data Collection program to describe patterns of ED use for treat-and-release visits by California’s SCD population and compare these new findings with results of previous studies.
The current study was published in Pediatric Blood and Cancer.
Researchers looked at ED and hospital discharge data in California from 2005 to 2014. This included 4636 patients with SCD.
The data showed that 88% of patients had 1 or more treat-and-release ED visits during the 10-year study period.
This group of 4100 patients had 90,904 treat-and-release ED visits. The average number of visits each year was 2.1 (rage, 0-185).
In a single year (2005):
- 53% of patients had no treat-and-release ED visits (no ED use)
- 35% had between 1 and 3 visits (low ED use)
- 9% had between 4 and 10 visits (medium ED use)
- 3% had 11 or more visits (high ED use).
The youngest patients (age 0 to 9.9) and the oldest patients (80 and older) were the least likely to have at least 1 treat-and-release ED visit.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 ED visit over the study period was:
- 68% among patients age 0 to 9.9 at the close of the study
- 80% among patients age 10 to 19.9
- 92% among patients age 20 to 29.9
- 94% among patients age 30 to 39.9
- 93% among patients age 40 to 49.9
- 92% among patients age 50 to 59.9
- 92% among patients age 60 to 69.9
- 85% among patients age 70 to 79.9
- 73% among patients age 80 and older.
The researchers said this study highlights the utility of a multisource, longitudinal data collection effort for SCD. And further study of patients with the highest ED utilization may highlight areas where changes could improve and extend the lives of patients with SCD. ![]()

Photo courtesy of St. Jude
Children’s Research Hospital
Population-based surveillance data has revealed patterns of emergency department (ED) visits among Californians with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Previous research suggested that between one-half and two-thirds of SCD patients’ ED visits end in a discharge from the ED, called a treat-and-release visit.
The remainder result in admission to a hospital or other treatment facility.
The purpose of the current study was to use data from the Sickle Cell Data Collection program to describe patterns of ED use for treat-and-release visits by California’s SCD population and compare these new findings with results of previous studies.
The current study was published in Pediatric Blood and Cancer.
Researchers looked at ED and hospital discharge data in California from 2005 to 2014. This included 4636 patients with SCD.
The data showed that 88% of patients had 1 or more treat-and-release ED visits during the 10-year study period.
This group of 4100 patients had 90,904 treat-and-release ED visits. The average number of visits each year was 2.1 (rage, 0-185).
In a single year (2005):
- 53% of patients had no treat-and-release ED visits (no ED use)
- 35% had between 1 and 3 visits (low ED use)
- 9% had between 4 and 10 visits (medium ED use)
- 3% had 11 or more visits (high ED use).
The youngest patients (age 0 to 9.9) and the oldest patients (80 and older) were the least likely to have at least 1 treat-and-release ED visit.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 ED visit over the study period was:
- 68% among patients age 0 to 9.9 at the close of the study
- 80% among patients age 10 to 19.9
- 92% among patients age 20 to 29.9
- 94% among patients age 30 to 39.9
- 93% among patients age 40 to 49.9
- 92% among patients age 50 to 59.9
- 92% among patients age 60 to 69.9
- 85% among patients age 70 to 79.9
- 73% among patients age 80 and older.
The researchers said this study highlights the utility of a multisource, longitudinal data collection effort for SCD. And further study of patients with the highest ED utilization may highlight areas where changes could improve and extend the lives of patients with SCD. ![]()

Photo courtesy of St. Jude
Children’s Research Hospital
Population-based surveillance data has revealed patterns of emergency department (ED) visits among Californians with sickle cell disease (SCD).
Previous research suggested that between one-half and two-thirds of SCD patients’ ED visits end in a discharge from the ED, called a treat-and-release visit.
The remainder result in admission to a hospital or other treatment facility.
The purpose of the current study was to use data from the Sickle Cell Data Collection program to describe patterns of ED use for treat-and-release visits by California’s SCD population and compare these new findings with results of previous studies.
The current study was published in Pediatric Blood and Cancer.
Researchers looked at ED and hospital discharge data in California from 2005 to 2014. This included 4636 patients with SCD.
The data showed that 88% of patients had 1 or more treat-and-release ED visits during the 10-year study period.
This group of 4100 patients had 90,904 treat-and-release ED visits. The average number of visits each year was 2.1 (rage, 0-185).
In a single year (2005):
- 53% of patients had no treat-and-release ED visits (no ED use)
- 35% had between 1 and 3 visits (low ED use)
- 9% had between 4 and 10 visits (medium ED use)
- 3% had 11 or more visits (high ED use).
The youngest patients (age 0 to 9.9) and the oldest patients (80 and older) were the least likely to have at least 1 treat-and-release ED visit.
The proportion of patients with at least 1 ED visit over the study period was:
- 68% among patients age 0 to 9.9 at the close of the study
- 80% among patients age 10 to 19.9
- 92% among patients age 20 to 29.9
- 94% among patients age 30 to 39.9
- 93% among patients age 40 to 49.9
- 92% among patients age 50 to 59.9
- 92% among patients age 60 to 69.9
- 85% among patients age 70 to 79.9
- 73% among patients age 80 and older.
The researchers said this study highlights the utility of a multisource, longitudinal data collection effort for SCD. And further study of patients with the highest ED utilization may highlight areas where changes could improve and extend the lives of patients with SCD. ![]()






