User login
Leveraging consumer technology in gastroenterology practice
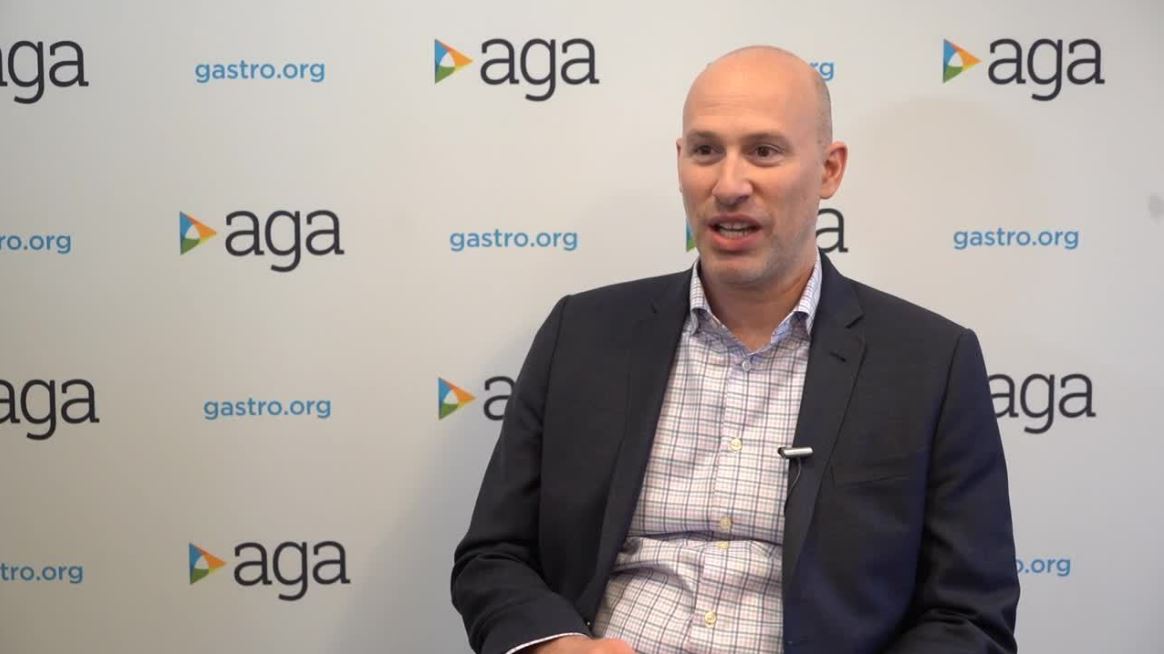
SAN FRANCISCO – Dr. Michael Docktor, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Boston Hospital, described myriad digital tools that physicians – especially gastroenterologists – as well as patients are now using. Some tools may be implemented to track stool output or diet for diseases like irritable bowel syndrome or Crohn’s disease, he said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
There are patient-facing applications that provide data that can be used by both patients and their physicians to better understand the disease. These data can help in diagnosis and management and give the GI doctor a “window into the 99% of the time that they aren’t with the patient.” Other apps can build a timeline of the disease that can help the patient get a better understanding of their disease and learn to distinguish a flare from a bad day with poor food choices. Dr. Docktor described the AGA Tech Summit as a place to try out new ideas and work with like-minded doctors.
SAN FRANCISCO – Dr. Michael Docktor, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Boston Hospital, described myriad digital tools that physicians – especially gastroenterologists – as well as patients are now using. Some tools may be implemented to track stool output or diet for diseases like irritable bowel syndrome or Crohn’s disease, he said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
There are patient-facing applications that provide data that can be used by both patients and their physicians to better understand the disease. These data can help in diagnosis and management and give the GI doctor a “window into the 99% of the time that they aren’t with the patient.” Other apps can build a timeline of the disease that can help the patient get a better understanding of their disease and learn to distinguish a flare from a bad day with poor food choices. Dr. Docktor described the AGA Tech Summit as a place to try out new ideas and work with like-minded doctors.
SAN FRANCISCO – Dr. Michael Docktor, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Boston Hospital, described myriad digital tools that physicians – especially gastroenterologists – as well as patients are now using. Some tools may be implemented to track stool output or diet for diseases like irritable bowel syndrome or Crohn’s disease, he said in an interview at the AGA Tech Summit, sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
There are patient-facing applications that provide data that can be used by both patients and their physicians to better understand the disease. These data can help in diagnosis and management and give the GI doctor a “window into the 99% of the time that they aren’t with the patient.” Other apps can build a timeline of the disease that can help the patient get a better understanding of their disease and learn to distinguish a flare from a bad day with poor food choices. Dr. Docktor described the AGA Tech Summit as a place to try out new ideas and work with like-minded doctors.
REPORTING FROM 2019 AGA TECH SUMMIT
Obeticholic acid reversed NASH liver fibrosis in phase 3 trial
VIENNA – making obeticholic acid the first agent proven to improve the course of this disease.
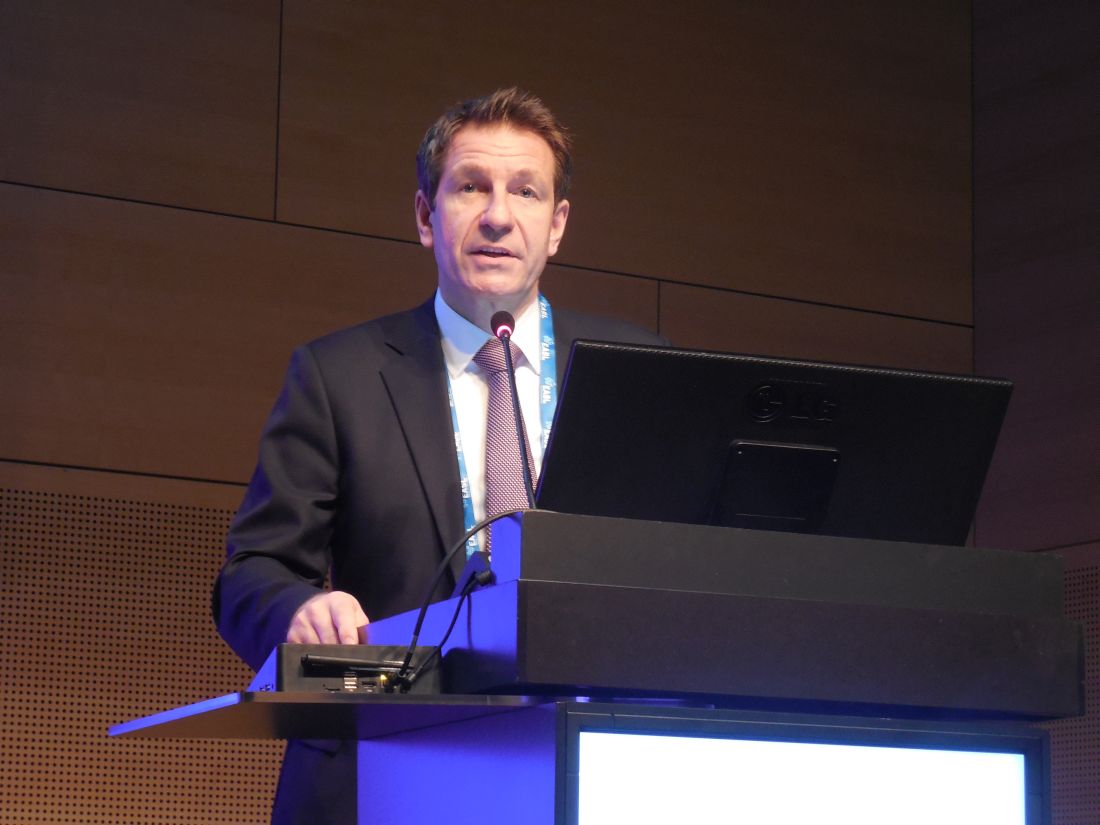
“There is no doubt that with these data we have changed the treatment” of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), Zobair M. Younossi, MD, of Inova Fairfax Medical Campus in Falls Church, Va., said at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. “We are at a watershed moment” in NASH treatment, Dr. Younossi added in a video interview.
Until now “we have had no effective treatments for NASH. This is the first success in a phase 3 trial; obeticholic acid looks very promising,” commented Philip N. Newsome, PhD, professor of experimental hepatology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Obeticholic acid (OCA), an agonist of the farnesoid X receptor, already has Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the indication of primary biliary cholangitis, a much rarer disease than NASH.
The REGENERATE (Randomized Global Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Impact on NASH With Fibrosis of Obeticholic Acid Treatment) trial has so far enrolled 931 patients at about 350 sites in 20 countries, including the United States, and followed them during 18 months of treatment, the prespecified time for an interim analysis. The study enrolled adults with biopsy-proven NASH and generally focused on patients with either stage 2 or 3 liver fibrosis and a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score of at least 4. Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, slightly more than half the enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes, and more than half had stage 3 fibrosis.
The study design included two coprimary endpoints, and specified that a statistically significant finding for either outcome meant a positive trial result, but the design also prespecified that the benefit would need to meet a stringent definition of statistical significance, compared with placebo patients, with a P value of no more than .01. REGENERATE tested two different OCA dosages, 10 mg or 25 mg, once daily. The results showed a trend for benefit from the smaller dosage, but these effects did not achieve statistical significance.
For the primary endpoint of regression of liver fibrosis by at least one stage with no worsening of NASH the intention-to-treat analysis showed after 18 months a 13% rate with placebo, a 21% rate with the 10-mg dosage, and a 23% rate with the 25-mg dosage, a statistically significant improvement over placebo for the higher dosage.
The second primary endpoint was resolution of NASH without worsening liver fibrosis, which occurred in 8% of placebo patients, 11% of patients on 10 mg OCA/day and 12% of those on 25 mg/day. The differences between each of the active groups and the controls were not statistically significant for this endpoint.
Among the 931 enrolled patients 668 (72%) actually received treatment fully consistent with the study protocol, and among these per-protocol patients the benefit from 25 mg/day OCA was even more striking: a 28% rate of fibrosis regression, compared with 13% in the control patients. Regression by at least two fibrotic stages occurred in 5% of placebo patients and 13% of those on 25 mg/day OCA. Many treated patients also showed normalizations of liver enzyme levels.
Adverse events on OCA were mostly mild or moderate, with similar rates of serious adverse events in the OCA groups and in control patients. The most common adverse effect on OCA treatment was pruritus, a previously described effect, reported by 51% of patients on the 25 mg/day dosage and by 19% of control patients.
REGENERATE will continue until a goal level of endpoint events occur, and may eventually enroll as many as 2,400 patients and extend for a few more years. By then, Dr. Younossi said, he hopes that an analysis will be possible of “harder” endpoints than fibrosis, such as development of cirrhosis. He noted, however, that the FDA has designated fibrosis regression as a valid surrogate endpoint for assessing treatment efficacy for NASH.
Already on the U.S. market, a single 10-mg OCA pill currently retails for almost $230; a 25-mg formulation is not currently marketed. Dr. Younossi said that subsequent studies will assess the cost-effectiveness of OCA treatment for NASH. He also hopes that further study of patient characteristics will identify which NASH patients are most likely to respond to OCA. Eventually, OCA may be part of a multidrug strategy for treating this disease, Dr. Younossi said.
REGENERATE was sponsored by Intercept, the company that markets obeticholic acid (Ocaliva). Dr. Younossi is a consultant to and has received research funding from Intercept. He has also been a consultant to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Quest, Siemens, Terns Pharmaceutical, and Viking Therapeutics. Dr. Newsome has been a consultant or speaker for Intercept as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Dignity Sciences, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, and Shire, and he has received research funding from Pharmaxis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
VIENNA – making obeticholic acid the first agent proven to improve the course of this disease.
“There is no doubt that with these data we have changed the treatment” of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), Zobair M. Younossi, MD, of Inova Fairfax Medical Campus in Falls Church, Va., said at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. “We are at a watershed moment” in NASH treatment, Dr. Younossi added in a video interview.
Until now “we have had no effective treatments for NASH. This is the first success in a phase 3 trial; obeticholic acid looks very promising,” commented Philip N. Newsome, PhD, professor of experimental hepatology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Obeticholic acid (OCA), an agonist of the farnesoid X receptor, already has Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the indication of primary biliary cholangitis, a much rarer disease than NASH.
The REGENERATE (Randomized Global Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Impact on NASH With Fibrosis of Obeticholic Acid Treatment) trial has so far enrolled 931 patients at about 350 sites in 20 countries, including the United States, and followed them during 18 months of treatment, the prespecified time for an interim analysis. The study enrolled adults with biopsy-proven NASH and generally focused on patients with either stage 2 or 3 liver fibrosis and a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score of at least 4. Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, slightly more than half the enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes, and more than half had stage 3 fibrosis.
The study design included two coprimary endpoints, and specified that a statistically significant finding for either outcome meant a positive trial result, but the design also prespecified that the benefit would need to meet a stringent definition of statistical significance, compared with placebo patients, with a P value of no more than .01. REGENERATE tested two different OCA dosages, 10 mg or 25 mg, once daily. The results showed a trend for benefit from the smaller dosage, but these effects did not achieve statistical significance.
For the primary endpoint of regression of liver fibrosis by at least one stage with no worsening of NASH the intention-to-treat analysis showed after 18 months a 13% rate with placebo, a 21% rate with the 10-mg dosage, and a 23% rate with the 25-mg dosage, a statistically significant improvement over placebo for the higher dosage.
The second primary endpoint was resolution of NASH without worsening liver fibrosis, which occurred in 8% of placebo patients, 11% of patients on 10 mg OCA/day and 12% of those on 25 mg/day. The differences between each of the active groups and the controls were not statistically significant for this endpoint.
Among the 931 enrolled patients 668 (72%) actually received treatment fully consistent with the study protocol, and among these per-protocol patients the benefit from 25 mg/day OCA was even more striking: a 28% rate of fibrosis regression, compared with 13% in the control patients. Regression by at least two fibrotic stages occurred in 5% of placebo patients and 13% of those on 25 mg/day OCA. Many treated patients also showed normalizations of liver enzyme levels.
Adverse events on OCA were mostly mild or moderate, with similar rates of serious adverse events in the OCA groups and in control patients. The most common adverse effect on OCA treatment was pruritus, a previously described effect, reported by 51% of patients on the 25 mg/day dosage and by 19% of control patients.
REGENERATE will continue until a goal level of endpoint events occur, and may eventually enroll as many as 2,400 patients and extend for a few more years. By then, Dr. Younossi said, he hopes that an analysis will be possible of “harder” endpoints than fibrosis, such as development of cirrhosis. He noted, however, that the FDA has designated fibrosis regression as a valid surrogate endpoint for assessing treatment efficacy for NASH.
Already on the U.S. market, a single 10-mg OCA pill currently retails for almost $230; a 25-mg formulation is not currently marketed. Dr. Younossi said that subsequent studies will assess the cost-effectiveness of OCA treatment for NASH. He also hopes that further study of patient characteristics will identify which NASH patients are most likely to respond to OCA. Eventually, OCA may be part of a multidrug strategy for treating this disease, Dr. Younossi said.
REGENERATE was sponsored by Intercept, the company that markets obeticholic acid (Ocaliva). Dr. Younossi is a consultant to and has received research funding from Intercept. He has also been a consultant to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Quest, Siemens, Terns Pharmaceutical, and Viking Therapeutics. Dr. Newsome has been a consultant or speaker for Intercept as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Dignity Sciences, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, and Shire, and he has received research funding from Pharmaxis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
VIENNA – making obeticholic acid the first agent proven to improve the course of this disease.
“There is no doubt that with these data we have changed the treatment” of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), Zobair M. Younossi, MD, of Inova Fairfax Medical Campus in Falls Church, Va., said at the meeting sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver. “We are at a watershed moment” in NASH treatment, Dr. Younossi added in a video interview.
Until now “we have had no effective treatments for NASH. This is the first success in a phase 3 trial; obeticholic acid looks very promising,” commented Philip N. Newsome, PhD, professor of experimental hepatology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Obeticholic acid (OCA), an agonist of the farnesoid X receptor, already has Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the indication of primary biliary cholangitis, a much rarer disease than NASH.
The REGENERATE (Randomized Global Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Impact on NASH With Fibrosis of Obeticholic Acid Treatment) trial has so far enrolled 931 patients at about 350 sites in 20 countries, including the United States, and followed them during 18 months of treatment, the prespecified time for an interim analysis. The study enrolled adults with biopsy-proven NASH and generally focused on patients with either stage 2 or 3 liver fibrosis and a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score of at least 4. Enrolled patients averaged about 55 years old, slightly more than half the enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes, and more than half had stage 3 fibrosis.
The study design included two coprimary endpoints, and specified that a statistically significant finding for either outcome meant a positive trial result, but the design also prespecified that the benefit would need to meet a stringent definition of statistical significance, compared with placebo patients, with a P value of no more than .01. REGENERATE tested two different OCA dosages, 10 mg or 25 mg, once daily. The results showed a trend for benefit from the smaller dosage, but these effects did not achieve statistical significance.
For the primary endpoint of regression of liver fibrosis by at least one stage with no worsening of NASH the intention-to-treat analysis showed after 18 months a 13% rate with placebo, a 21% rate with the 10-mg dosage, and a 23% rate with the 25-mg dosage, a statistically significant improvement over placebo for the higher dosage.
The second primary endpoint was resolution of NASH without worsening liver fibrosis, which occurred in 8% of placebo patients, 11% of patients on 10 mg OCA/day and 12% of those on 25 mg/day. The differences between each of the active groups and the controls were not statistically significant for this endpoint.
Among the 931 enrolled patients 668 (72%) actually received treatment fully consistent with the study protocol, and among these per-protocol patients the benefit from 25 mg/day OCA was even more striking: a 28% rate of fibrosis regression, compared with 13% in the control patients. Regression by at least two fibrotic stages occurred in 5% of placebo patients and 13% of those on 25 mg/day OCA. Many treated patients also showed normalizations of liver enzyme levels.
Adverse events on OCA were mostly mild or moderate, with similar rates of serious adverse events in the OCA groups and in control patients. The most common adverse effect on OCA treatment was pruritus, a previously described effect, reported by 51% of patients on the 25 mg/day dosage and by 19% of control patients.
REGENERATE will continue until a goal level of endpoint events occur, and may eventually enroll as many as 2,400 patients and extend for a few more years. By then, Dr. Younossi said, he hopes that an analysis will be possible of “harder” endpoints than fibrosis, such as development of cirrhosis. He noted, however, that the FDA has designated fibrosis regression as a valid surrogate endpoint for assessing treatment efficacy for NASH.
Already on the U.S. market, a single 10-mg OCA pill currently retails for almost $230; a 25-mg formulation is not currently marketed. Dr. Younossi said that subsequent studies will assess the cost-effectiveness of OCA treatment for NASH. He also hopes that further study of patient characteristics will identify which NASH patients are most likely to respond to OCA. Eventually, OCA may be part of a multidrug strategy for treating this disease, Dr. Younossi said.
REGENERATE was sponsored by Intercept, the company that markets obeticholic acid (Ocaliva). Dr. Younossi is a consultant to and has received research funding from Intercept. He has also been a consultant to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Quest, Siemens, Terns Pharmaceutical, and Viking Therapeutics. Dr. Newsome has been a consultant or speaker for Intercept as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Dignity Sciences, Johnson & Johnson, Novo Nordisk, and Shire, and he has received research funding from Pharmaxis and Boehringer Ingelheim.
REPORTING FROM ILC 2019
Nontraditional specialty physicians supplement hospitalist staffing
More HMGs cover inpatient and ED settings
Our profession continues to experience steady growth, and demand for hospitalist physicians exceeds supply. In a recent article in The Hospitalist, Andrew White, MD, SFHM, highlighted the fact that most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) are constantly recruiting and open positions are not uncommon.
When we think about recruitment and staffing, I bet many of us think principally of physicians trained in the general medicine specialties of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatrics. Yet, to help meet demand for hospital-based clinicians, HMGs sometimes turn to physicians certified in emergency medicine, critical care, geriatric medicine, palliative care, and other fields.
To gain a better understanding of the diversity within our profession, the Society of Hospital Medicine’s State of Hospital Medicine survey asked HMGs whether they employ at least one physician in these various specialties. Results published in the recently released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report show significant differences among groups, affected by location, group size, and type of employer.
At the core of our profession are physicians trained in internal medicine, present in 99.2% of adult medicine HMGs throughout the United States. No surprise given that our field was founded by internists and remains a popular career choice for IM residency graduates. Family physicians follow, with the highest percentage of groups employing at least one FP located in the southern United States at 70.3% and lowest in the west at 54.7%. Small-sized groups – fewer than 10 full-time equivalents (FTEs) – were also more likely to employ FPs.
This speaks to the challenge – often faced by smaller hospitals – of covering both adult and pediatric patient populations and limited workforce availability. Pediatrics- and internal medicine/pediatrics–trained physicians help meet this need and were prevalent within small-sized groups. Another distinction found in the report is that, while 92.1% of multistate hospitalist management companies employed family physicians, only 28.8% of academic university settings did so. Partly because of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements for IM-certified teaching attending for internal medicine residents, FP and other specialties are filling some non–teaching hospitalist positions within our academic programs.
What may be surprising is that emergency medicine and critical care had the largest increase in representation in hospital medicine. The two specialties showed similar growth trends, with a larger presence in the South and Midwest states and 56% of multistate hospitalist management companies employing them. Small- to medium-sized groups of up to 20 FTEs were also more likely to have physicians from these fields, with up to 44% of groups doing so. This is a significant change from 2016, when less than 3.4% of all HMGs overall had a physician certified in emergency or critical care medicine.
This finding seems to coincide with the growth in hospital medicine groups who are covering both ED and inpatient services. For small and rural hospitals, it has become necessary and beneficial to have physicians capable of covering both clinical settings.
Contrast this with geriatric medicine and palliative care. Here, we saw these two specialties to be present in our academic institutions at 26.8% and 22.5%, respectively. Large-sized HMGs were more likely to employ them, whereas their presence in multistate management groups or private multispecialty/primary care groups was quite low. Compared with our last survey in 2016, their overall prevalence in HMGs hasn’t changed significantly. Whether this will be different in the future with our aging population will be interesting to follow.
Published biannually, the SoHM report provides insight into these and other market-based dynamics that shape hospital medicine. The demand for hospital-based clinicians and the demands of acute inpatient care are leading to the broad and inclusive nature of hospital medicine. Our staffing will continue to be met not only by internal medicine and family medicine physicians but also through these other specialties joining our ranks and adding diversity to our profession.
Dr. Sites is the executive medical director of acute medicine at Providence St. Joseph Health, Oregon, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee. She leads the hospital medicine programs and is involved in strategy development and alignment of acute inpatient medicine services at eight member hospitals. She has been a practicing hospitalist for 20 years and volunteers on medical mission trips to Guatemala annually.
More HMGs cover inpatient and ED settings
More HMGs cover inpatient and ED settings
Our profession continues to experience steady growth, and demand for hospitalist physicians exceeds supply. In a recent article in The Hospitalist, Andrew White, MD, SFHM, highlighted the fact that most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) are constantly recruiting and open positions are not uncommon.
When we think about recruitment and staffing, I bet many of us think principally of physicians trained in the general medicine specialties of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatrics. Yet, to help meet demand for hospital-based clinicians, HMGs sometimes turn to physicians certified in emergency medicine, critical care, geriatric medicine, palliative care, and other fields.
To gain a better understanding of the diversity within our profession, the Society of Hospital Medicine’s State of Hospital Medicine survey asked HMGs whether they employ at least one physician in these various specialties. Results published in the recently released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report show significant differences among groups, affected by location, group size, and type of employer.
At the core of our profession are physicians trained in internal medicine, present in 99.2% of adult medicine HMGs throughout the United States. No surprise given that our field was founded by internists and remains a popular career choice for IM residency graduates. Family physicians follow, with the highest percentage of groups employing at least one FP located in the southern United States at 70.3% and lowest in the west at 54.7%. Small-sized groups – fewer than 10 full-time equivalents (FTEs) – were also more likely to employ FPs.
This speaks to the challenge – often faced by smaller hospitals – of covering both adult and pediatric patient populations and limited workforce availability. Pediatrics- and internal medicine/pediatrics–trained physicians help meet this need and were prevalent within small-sized groups. Another distinction found in the report is that, while 92.1% of multistate hospitalist management companies employed family physicians, only 28.8% of academic university settings did so. Partly because of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements for IM-certified teaching attending for internal medicine residents, FP and other specialties are filling some non–teaching hospitalist positions within our academic programs.
What may be surprising is that emergency medicine and critical care had the largest increase in representation in hospital medicine. The two specialties showed similar growth trends, with a larger presence in the South and Midwest states and 56% of multistate hospitalist management companies employing them. Small- to medium-sized groups of up to 20 FTEs were also more likely to have physicians from these fields, with up to 44% of groups doing so. This is a significant change from 2016, when less than 3.4% of all HMGs overall had a physician certified in emergency or critical care medicine.
This finding seems to coincide with the growth in hospital medicine groups who are covering both ED and inpatient services. For small and rural hospitals, it has become necessary and beneficial to have physicians capable of covering both clinical settings.
Contrast this with geriatric medicine and palliative care. Here, we saw these two specialties to be present in our academic institutions at 26.8% and 22.5%, respectively. Large-sized HMGs were more likely to employ them, whereas their presence in multistate management groups or private multispecialty/primary care groups was quite low. Compared with our last survey in 2016, their overall prevalence in HMGs hasn’t changed significantly. Whether this will be different in the future with our aging population will be interesting to follow.
Published biannually, the SoHM report provides insight into these and other market-based dynamics that shape hospital medicine. The demand for hospital-based clinicians and the demands of acute inpatient care are leading to the broad and inclusive nature of hospital medicine. Our staffing will continue to be met not only by internal medicine and family medicine physicians but also through these other specialties joining our ranks and adding diversity to our profession.
Dr. Sites is the executive medical director of acute medicine at Providence St. Joseph Health, Oregon, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee. She leads the hospital medicine programs and is involved in strategy development and alignment of acute inpatient medicine services at eight member hospitals. She has been a practicing hospitalist for 20 years and volunteers on medical mission trips to Guatemala annually.
Our profession continues to experience steady growth, and demand for hospitalist physicians exceeds supply. In a recent article in The Hospitalist, Andrew White, MD, SFHM, highlighted the fact that most hospital medicine groups (HMGs) are constantly recruiting and open positions are not uncommon.
When we think about recruitment and staffing, I bet many of us think principally of physicians trained in the general medicine specialties of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatrics. Yet, to help meet demand for hospital-based clinicians, HMGs sometimes turn to physicians certified in emergency medicine, critical care, geriatric medicine, palliative care, and other fields.
To gain a better understanding of the diversity within our profession, the Society of Hospital Medicine’s State of Hospital Medicine survey asked HMGs whether they employ at least one physician in these various specialties. Results published in the recently released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report show significant differences among groups, affected by location, group size, and type of employer.
At the core of our profession are physicians trained in internal medicine, present in 99.2% of adult medicine HMGs throughout the United States. No surprise given that our field was founded by internists and remains a popular career choice for IM residency graduates. Family physicians follow, with the highest percentage of groups employing at least one FP located in the southern United States at 70.3% and lowest in the west at 54.7%. Small-sized groups – fewer than 10 full-time equivalents (FTEs) – were also more likely to employ FPs.
This speaks to the challenge – often faced by smaller hospitals – of covering both adult and pediatric patient populations and limited workforce availability. Pediatrics- and internal medicine/pediatrics–trained physicians help meet this need and were prevalent within small-sized groups. Another distinction found in the report is that, while 92.1% of multistate hospitalist management companies employed family physicians, only 28.8% of academic university settings did so. Partly because of Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements for IM-certified teaching attending for internal medicine residents, FP and other specialties are filling some non–teaching hospitalist positions within our academic programs.
What may be surprising is that emergency medicine and critical care had the largest increase in representation in hospital medicine. The two specialties showed similar growth trends, with a larger presence in the South and Midwest states and 56% of multistate hospitalist management companies employing them. Small- to medium-sized groups of up to 20 FTEs were also more likely to have physicians from these fields, with up to 44% of groups doing so. This is a significant change from 2016, when less than 3.4% of all HMGs overall had a physician certified in emergency or critical care medicine.
This finding seems to coincide with the growth in hospital medicine groups who are covering both ED and inpatient services. For small and rural hospitals, it has become necessary and beneficial to have physicians capable of covering both clinical settings.
Contrast this with geriatric medicine and palliative care. Here, we saw these two specialties to be present in our academic institutions at 26.8% and 22.5%, respectively. Large-sized HMGs were more likely to employ them, whereas their presence in multistate management groups or private multispecialty/primary care groups was quite low. Compared with our last survey in 2016, their overall prevalence in HMGs hasn’t changed significantly. Whether this will be different in the future with our aging population will be interesting to follow.
Published biannually, the SoHM report provides insight into these and other market-based dynamics that shape hospital medicine. The demand for hospital-based clinicians and the demands of acute inpatient care are leading to the broad and inclusive nature of hospital medicine. Our staffing will continue to be met not only by internal medicine and family medicine physicians but also through these other specialties joining our ranks and adding diversity to our profession.
Dr. Sites is the executive medical director of acute medicine at Providence St. Joseph Health, Oregon, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee. She leads the hospital medicine programs and is involved in strategy development and alignment of acute inpatient medicine services at eight member hospitals. She has been a practicing hospitalist for 20 years and volunteers on medical mission trips to Guatemala annually.
FDA approves pembrolizumab for first-line stage III NSCLC
The who are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation, and for stage IV NSCLC.
Patients’ tumors must express programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) as determined by an FDA-approved test (tumor proportion score ≥1%) and have no epidermal growth factor receptor or anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutations.
The checkpoint inhibitor was previously approved as a single agent for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic disease with PD-L1 expression at a higher level (TPS ≥50%), the FDA said in a press statement.
Approval was based on statistically significant overall survival improvement with pembrolizumab, compared with investigator’s choice of a carboplatin-containing regimen with either pemetrexed or paclitaxel in KEYNOTE‑042. The trial enrolled 1,274 patients with stage III or IV NSCLC who had not received prior systemic treatment for metastatic NSCLC and whose tumors expressed PD-L1 (TPS ≥1%).
Overall survival was improved in all three subgroups for pembrolizumab, compared with chemotherapy: in the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the TPS ≥20% subgroup, and the overall population (TPS ≥1%). The median overall survival in the TPS ≥1% population was 16.7 for pembrolizumab and 12.1 months for the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio, 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.93; P = .0036). For the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the estimated median overall survival was 20 months for pembrolizumab and 12.2 months for the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.56-0.85; P = .0006).
The most common adverse reactions reported for patients who received pembrolizumab included fatigue, decreased appetite, dyspnea, cough, rash, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, hypothyroidism, pneumonia, pyrexia, and weight loss, the FDA said.
The recommended dose for NSCLC is 200 mg as an IV infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks.
The who are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation, and for stage IV NSCLC.
Patients’ tumors must express programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) as determined by an FDA-approved test (tumor proportion score ≥1%) and have no epidermal growth factor receptor or anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutations.
The checkpoint inhibitor was previously approved as a single agent for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic disease with PD-L1 expression at a higher level (TPS ≥50%), the FDA said in a press statement.
Approval was based on statistically significant overall survival improvement with pembrolizumab, compared with investigator’s choice of a carboplatin-containing regimen with either pemetrexed or paclitaxel in KEYNOTE‑042. The trial enrolled 1,274 patients with stage III or IV NSCLC who had not received prior systemic treatment for metastatic NSCLC and whose tumors expressed PD-L1 (TPS ≥1%).
Overall survival was improved in all three subgroups for pembrolizumab, compared with chemotherapy: in the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the TPS ≥20% subgroup, and the overall population (TPS ≥1%). The median overall survival in the TPS ≥1% population was 16.7 for pembrolizumab and 12.1 months for the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio, 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.93; P = .0036). For the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the estimated median overall survival was 20 months for pembrolizumab and 12.2 months for the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.56-0.85; P = .0006).
The most common adverse reactions reported for patients who received pembrolizumab included fatigue, decreased appetite, dyspnea, cough, rash, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, hypothyroidism, pneumonia, pyrexia, and weight loss, the FDA said.
The recommended dose for NSCLC is 200 mg as an IV infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks.
The who are not candidates for surgical resection or definitive chemoradiation, and for stage IV NSCLC.
Patients’ tumors must express programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) as determined by an FDA-approved test (tumor proportion score ≥1%) and have no epidermal growth factor receptor or anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutations.
The checkpoint inhibitor was previously approved as a single agent for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic disease with PD-L1 expression at a higher level (TPS ≥50%), the FDA said in a press statement.
Approval was based on statistically significant overall survival improvement with pembrolizumab, compared with investigator’s choice of a carboplatin-containing regimen with either pemetrexed or paclitaxel in KEYNOTE‑042. The trial enrolled 1,274 patients with stage III or IV NSCLC who had not received prior systemic treatment for metastatic NSCLC and whose tumors expressed PD-L1 (TPS ≥1%).
Overall survival was improved in all three subgroups for pembrolizumab, compared with chemotherapy: in the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the TPS ≥20% subgroup, and the overall population (TPS ≥1%). The median overall survival in the TPS ≥1% population was 16.7 for pembrolizumab and 12.1 months for the chemotherapy arms (hazard ratio, 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.93; P = .0036). For the TPS ≥50% subgroup, the estimated median overall survival was 20 months for pembrolizumab and 12.2 months for the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.69; 95% CI, 0.56-0.85; P = .0006).
The most common adverse reactions reported for patients who received pembrolizumab included fatigue, decreased appetite, dyspnea, cough, rash, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, hypothyroidism, pneumonia, pyrexia, and weight loss, the FDA said.
The recommended dose for NSCLC is 200 mg as an IV infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks.
Low LDL cholesterol may increase women’s risk of hemorrhagic stroke
, according to research published in Neurology.
“Women with very low LDL cholesterol or low triglycerides should be monitored by their doctors for other stroke risk factors that can be modified, like high blood pressure and smoking, in order to reduce their risk of hemorrhagic stroke,” said Pamela M. Rist, ScD, instructor in epidemiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Additional research is needed to determine how to lower the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in women with very low LDL and low triglycerides.”
Several meta-analyses have indicated that LDL cholesterol levels are inversely associated with the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Because lipid-lowering treatments are used to prevent cardiovascular disease, this potential association has implications for clinical practice. Most of the studies included in these meta-analyses had low numbers of events among women, which prevented researchers from stratifying their results by sex. Because women are at greater risk of stroke than men, Dr. Rist and her colleagues sought to evaluate the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
An analysis of the Women’s Health Study
The investigators examined data from the Women’s Health Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of low-dose aspirin and vitamin E for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer among female American health professionals aged 45 years or older. The study ended in March 2004, but follow-up is ongoing. At regular intervals, the women complete a questionnaire about disease outcomes, including stroke. Some participants agreed to provide a fasting venous blood sample before randomization. With the subjects’ permission, a committee of physicians examined medical records for women who reported a stroke on a follow-up questionnaire.
Dr. Rist and her colleagues analyzed 27,937 samples for levels of LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. They assigned each sample to one of five cholesterol level categories that were based on Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Cox proportional hazards models enabled the researchers to calculate the hazard ratio of incident hemorrhagic stroke events. They adjusted their results for covariates such as age, smoking status, menopausal status, body mass index, and alcohol consumption.
A U-shaped association
Women in the lowest category of LDL cholesterol level (less than 70 mg/dL) were younger, less likely to have a history of hypertension, and less likely to use cholesterol-lowering drugs than women in the reference group (100.0-129.9 mg/dL). Women with the lowest LDL cholesterol level were more likely to consume alcohol, have a normal weight, engage in physical activity, and be premenopausal than women in the reference group. The investigators confirmed 137 incident hemorrhagic stroke events during a mean 19.3 years of follow-up.
After data adjustment, the researchers found that women with the lowest level of LDL cholesterol had 2.17 times the risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with participants in the reference group. They found a trend toward increased risk among women with an LDL cholesterol level of 160 mg/dL or higher, but the result was not statistically significant. The highest risk for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) was among women with an LDL cholesterol level of less than 70 mg/dL (relative risk, 2.32), followed by women with a level of 160 mg/dL or higher (RR, 1.71).
In addition, after multivariable adjustment, women in the lowest quartile of triglycerides (less than or equal to 74 mg/dL for fasting and less than or equal to 85 mg/dL for nonfasting) had a significantly increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with women in the highest quartile (RR, 2.00). Low triglyceride levels were associated with an increased risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage, but not with an increased risk of ICH. Neither HDL cholesterol nor total cholesterol was associated with risk of hemorrhagic stroke, the researchers wrote.
Mechanism of increased risk unclear
The researchers do not yet know how low triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. One hypothesis is that low cholesterol promotes necrosis of the arterial medial layer’s smooth muscle cells. This impaired endothelium might be more susceptible to microaneurysms, which are common in patients with ICH, said the researchers.
The prospective design and the large sample size were two of the study’s strengths, but the study had important weaknesses as well, the researchers wrote. For example, few women were premenopausal at baseline, so the investigators could not evaluate whether menopausal status modifies the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke. In addition, lipid levels were measured only at baseline, which prevented an analysis of whether change in lipid levels over time modifies the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Dr. Rist reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Rist PM et al. Neurology. 2019 April 10. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007454.
, according to research published in Neurology.
“Women with very low LDL cholesterol or low triglycerides should be monitored by their doctors for other stroke risk factors that can be modified, like high blood pressure and smoking, in order to reduce their risk of hemorrhagic stroke,” said Pamela M. Rist, ScD, instructor in epidemiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Additional research is needed to determine how to lower the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in women with very low LDL and low triglycerides.”
Several meta-analyses have indicated that LDL cholesterol levels are inversely associated with the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Because lipid-lowering treatments are used to prevent cardiovascular disease, this potential association has implications for clinical practice. Most of the studies included in these meta-analyses had low numbers of events among women, which prevented researchers from stratifying their results by sex. Because women are at greater risk of stroke than men, Dr. Rist and her colleagues sought to evaluate the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
An analysis of the Women’s Health Study
The investigators examined data from the Women’s Health Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of low-dose aspirin and vitamin E for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer among female American health professionals aged 45 years or older. The study ended in March 2004, but follow-up is ongoing. At regular intervals, the women complete a questionnaire about disease outcomes, including stroke. Some participants agreed to provide a fasting venous blood sample before randomization. With the subjects’ permission, a committee of physicians examined medical records for women who reported a stroke on a follow-up questionnaire.
Dr. Rist and her colleagues analyzed 27,937 samples for levels of LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. They assigned each sample to one of five cholesterol level categories that were based on Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Cox proportional hazards models enabled the researchers to calculate the hazard ratio of incident hemorrhagic stroke events. They adjusted their results for covariates such as age, smoking status, menopausal status, body mass index, and alcohol consumption.
A U-shaped association
Women in the lowest category of LDL cholesterol level (less than 70 mg/dL) were younger, less likely to have a history of hypertension, and less likely to use cholesterol-lowering drugs than women in the reference group (100.0-129.9 mg/dL). Women with the lowest LDL cholesterol level were more likely to consume alcohol, have a normal weight, engage in physical activity, and be premenopausal than women in the reference group. The investigators confirmed 137 incident hemorrhagic stroke events during a mean 19.3 years of follow-up.
After data adjustment, the researchers found that women with the lowest level of LDL cholesterol had 2.17 times the risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with participants in the reference group. They found a trend toward increased risk among women with an LDL cholesterol level of 160 mg/dL or higher, but the result was not statistically significant. The highest risk for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) was among women with an LDL cholesterol level of less than 70 mg/dL (relative risk, 2.32), followed by women with a level of 160 mg/dL or higher (RR, 1.71).
In addition, after multivariable adjustment, women in the lowest quartile of triglycerides (less than or equal to 74 mg/dL for fasting and less than or equal to 85 mg/dL for nonfasting) had a significantly increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with women in the highest quartile (RR, 2.00). Low triglyceride levels were associated with an increased risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage, but not with an increased risk of ICH. Neither HDL cholesterol nor total cholesterol was associated with risk of hemorrhagic stroke, the researchers wrote.
Mechanism of increased risk unclear
The researchers do not yet know how low triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. One hypothesis is that low cholesterol promotes necrosis of the arterial medial layer’s smooth muscle cells. This impaired endothelium might be more susceptible to microaneurysms, which are common in patients with ICH, said the researchers.
The prospective design and the large sample size were two of the study’s strengths, but the study had important weaknesses as well, the researchers wrote. For example, few women were premenopausal at baseline, so the investigators could not evaluate whether menopausal status modifies the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke. In addition, lipid levels were measured only at baseline, which prevented an analysis of whether change in lipid levels over time modifies the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Dr. Rist reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Rist PM et al. Neurology. 2019 April 10. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007454.
, according to research published in Neurology.
“Women with very low LDL cholesterol or low triglycerides should be monitored by their doctors for other stroke risk factors that can be modified, like high blood pressure and smoking, in order to reduce their risk of hemorrhagic stroke,” said Pamela M. Rist, ScD, instructor in epidemiology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “Additional research is needed to determine how to lower the risk of hemorrhagic stroke in women with very low LDL and low triglycerides.”
Several meta-analyses have indicated that LDL cholesterol levels are inversely associated with the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Because lipid-lowering treatments are used to prevent cardiovascular disease, this potential association has implications for clinical practice. Most of the studies included in these meta-analyses had low numbers of events among women, which prevented researchers from stratifying their results by sex. Because women are at greater risk of stroke than men, Dr. Rist and her colleagues sought to evaluate the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
An analysis of the Women’s Health Study
The investigators examined data from the Women’s Health Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of low-dose aspirin and vitamin E for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer among female American health professionals aged 45 years or older. The study ended in March 2004, but follow-up is ongoing. At regular intervals, the women complete a questionnaire about disease outcomes, including stroke. Some participants agreed to provide a fasting venous blood sample before randomization. With the subjects’ permission, a committee of physicians examined medical records for women who reported a stroke on a follow-up questionnaire.
Dr. Rist and her colleagues analyzed 27,937 samples for levels of LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. They assigned each sample to one of five cholesterol level categories that were based on Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Cox proportional hazards models enabled the researchers to calculate the hazard ratio of incident hemorrhagic stroke events. They adjusted their results for covariates such as age, smoking status, menopausal status, body mass index, and alcohol consumption.
A U-shaped association
Women in the lowest category of LDL cholesterol level (less than 70 mg/dL) were younger, less likely to have a history of hypertension, and less likely to use cholesterol-lowering drugs than women in the reference group (100.0-129.9 mg/dL). Women with the lowest LDL cholesterol level were more likely to consume alcohol, have a normal weight, engage in physical activity, and be premenopausal than women in the reference group. The investigators confirmed 137 incident hemorrhagic stroke events during a mean 19.3 years of follow-up.
After data adjustment, the researchers found that women with the lowest level of LDL cholesterol had 2.17 times the risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with participants in the reference group. They found a trend toward increased risk among women with an LDL cholesterol level of 160 mg/dL or higher, but the result was not statistically significant. The highest risk for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) was among women with an LDL cholesterol level of less than 70 mg/dL (relative risk, 2.32), followed by women with a level of 160 mg/dL or higher (RR, 1.71).
In addition, after multivariable adjustment, women in the lowest quartile of triglycerides (less than or equal to 74 mg/dL for fasting and less than or equal to 85 mg/dL for nonfasting) had a significantly increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke, compared with women in the highest quartile (RR, 2.00). Low triglyceride levels were associated with an increased risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage, but not with an increased risk of ICH. Neither HDL cholesterol nor total cholesterol was associated with risk of hemorrhagic stroke, the researchers wrote.
Mechanism of increased risk unclear
The researchers do not yet know how low triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. One hypothesis is that low cholesterol promotes necrosis of the arterial medial layer’s smooth muscle cells. This impaired endothelium might be more susceptible to microaneurysms, which are common in patients with ICH, said the researchers.
The prospective design and the large sample size were two of the study’s strengths, but the study had important weaknesses as well, the researchers wrote. For example, few women were premenopausal at baseline, so the investigators could not evaluate whether menopausal status modifies the association between lipid levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke. In addition, lipid levels were measured only at baseline, which prevented an analysis of whether change in lipid levels over time modifies the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
Dr. Rist reported receiving a grant from the National Institutes of Health.
SOURCE: Rist PM et al. Neurology. 2019 April 10. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007454.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Proportion of women speaking at medical conferences rises over decade
The proportion of women speaking at medical conferences in the United States and Canada increased significantly between 2007 and 2017, while the proportion at surgical specialty conferences lagged noticeably behind, according to new research.
“Although female representation at academic meetings has been identified as an important gender equity issue, the proportion of conference speakers who are women has not yet been systematically measured across different medical subspecialties,” wrote Shannon M. Ruzycki, MD, and her colleagues from the University of Calgary (Alta.). The report is in JAMA Network Open.
Using the Web of Science Conference database, the investigators identified 181 conferences and 701 unique meetings (40 in 2007, 104 in 2013, 115 in 2014, 124 in 2015, 137 in 2016, and 181 in 2017). The list of names from each meeting program was analyzed by the Gender Balance Assessment Tool to identify the likely proportion of female speakers by assigning a probability of each name belonging to a gender, based on social media data.
In 2007, the proportion of female speakers was 24.6% , which increased to 34.1% by 2017, an average increase of 0.97% per year. The range of female speakers at each meeting ranged from 0% to 82.6%, with 82 (12%) of the 701 meetings having more than 50% female speakers. The proportion of female speakers was slightly less than the proportion of female doctors in the United States and Canada in 2007 (26.1%), but was slightly greater than the proportion of female doctors in 2015 (32.4%).
During the study period, the proportion of female speakers at surgical specialty conferences was significantly lower than that for medical specialty conferences (20.1% in 2007 and 28.4% in 2017 vs. 29.9% in 2007 and 38.8% in 2017). While the number of speakers at medical meetings in 2015 matched the proportion of doctors in the United States and Canada in that year, the proportion of speakers at surgical meetings was noticeably higher than the number of female surgeons.
“We hypothesize that the low proportion of female speakers at medical conferences reflects broader gender inequity within the medical profession, particularly in subspecialties where the majority of physicians are men. It has been shown that the presence of female role models in male-dominated career streams can increase engagement of young women,” the investigators wrote. “Exposure to female speakers at medical conferences may be a means of encouraging female medical students and residents to choose specialties that have historically been male dominated. Strategies to promote inclusivity of female speakers at academic conferences may therefore represent an important opportunity to influence gender equity within medicine,” they concluded.
The University of Calgary funded the study. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ruzycki SM et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 12. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2103.
The proportion of women speaking at medical conferences in the United States and Canada increased significantly between 2007 and 2017, while the proportion at surgical specialty conferences lagged noticeably behind, according to new research.
“Although female representation at academic meetings has been identified as an important gender equity issue, the proportion of conference speakers who are women has not yet been systematically measured across different medical subspecialties,” wrote Shannon M. Ruzycki, MD, and her colleagues from the University of Calgary (Alta.). The report is in JAMA Network Open.
Using the Web of Science Conference database, the investigators identified 181 conferences and 701 unique meetings (40 in 2007, 104 in 2013, 115 in 2014, 124 in 2015, 137 in 2016, and 181 in 2017). The list of names from each meeting program was analyzed by the Gender Balance Assessment Tool to identify the likely proportion of female speakers by assigning a probability of each name belonging to a gender, based on social media data.
In 2007, the proportion of female speakers was 24.6% , which increased to 34.1% by 2017, an average increase of 0.97% per year. The range of female speakers at each meeting ranged from 0% to 82.6%, with 82 (12%) of the 701 meetings having more than 50% female speakers. The proportion of female speakers was slightly less than the proportion of female doctors in the United States and Canada in 2007 (26.1%), but was slightly greater than the proportion of female doctors in 2015 (32.4%).
During the study period, the proportion of female speakers at surgical specialty conferences was significantly lower than that for medical specialty conferences (20.1% in 2007 and 28.4% in 2017 vs. 29.9% in 2007 and 38.8% in 2017). While the number of speakers at medical meetings in 2015 matched the proportion of doctors in the United States and Canada in that year, the proportion of speakers at surgical meetings was noticeably higher than the number of female surgeons.
“We hypothesize that the low proportion of female speakers at medical conferences reflects broader gender inequity within the medical profession, particularly in subspecialties where the majority of physicians are men. It has been shown that the presence of female role models in male-dominated career streams can increase engagement of young women,” the investigators wrote. “Exposure to female speakers at medical conferences may be a means of encouraging female medical students and residents to choose specialties that have historically been male dominated. Strategies to promote inclusivity of female speakers at academic conferences may therefore represent an important opportunity to influence gender equity within medicine,” they concluded.
The University of Calgary funded the study. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ruzycki SM et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 12. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2103.
The proportion of women speaking at medical conferences in the United States and Canada increased significantly between 2007 and 2017, while the proportion at surgical specialty conferences lagged noticeably behind, according to new research.
“Although female representation at academic meetings has been identified as an important gender equity issue, the proportion of conference speakers who are women has not yet been systematically measured across different medical subspecialties,” wrote Shannon M. Ruzycki, MD, and her colleagues from the University of Calgary (Alta.). The report is in JAMA Network Open.
Using the Web of Science Conference database, the investigators identified 181 conferences and 701 unique meetings (40 in 2007, 104 in 2013, 115 in 2014, 124 in 2015, 137 in 2016, and 181 in 2017). The list of names from each meeting program was analyzed by the Gender Balance Assessment Tool to identify the likely proportion of female speakers by assigning a probability of each name belonging to a gender, based on social media data.
In 2007, the proportion of female speakers was 24.6% , which increased to 34.1% by 2017, an average increase of 0.97% per year. The range of female speakers at each meeting ranged from 0% to 82.6%, with 82 (12%) of the 701 meetings having more than 50% female speakers. The proportion of female speakers was slightly less than the proportion of female doctors in the United States and Canada in 2007 (26.1%), but was slightly greater than the proportion of female doctors in 2015 (32.4%).
During the study period, the proportion of female speakers at surgical specialty conferences was significantly lower than that for medical specialty conferences (20.1% in 2007 and 28.4% in 2017 vs. 29.9% in 2007 and 38.8% in 2017). While the number of speakers at medical meetings in 2015 matched the proportion of doctors in the United States and Canada in that year, the proportion of speakers at surgical meetings was noticeably higher than the number of female surgeons.
“We hypothesize that the low proportion of female speakers at medical conferences reflects broader gender inequity within the medical profession, particularly in subspecialties where the majority of physicians are men. It has been shown that the presence of female role models in male-dominated career streams can increase engagement of young women,” the investigators wrote. “Exposure to female speakers at medical conferences may be a means of encouraging female medical students and residents to choose specialties that have historically been male dominated. Strategies to promote inclusivity of female speakers at academic conferences may therefore represent an important opportunity to influence gender equity within medicine,” they concluded.
The University of Calgary funded the study. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ruzycki SM et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 12. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2103.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Key clinical point: By 2015, the proportion of women presenting at medical conferences matched the proportion of women practicing medicine in the United States and Canada.
Major finding: Between 2007 and 2017, the proportion of women presenting at medical conferences rose from 24.60% to 34.10%, an average increase of 0.97% per year.
Study details: A review of presenters from 181 conferences and 701 unique meetings.
Disclosures: The University of Calgary funded the study. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Source: Ruzycki SM et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 12. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2103.
Negotiating an employment contract? Lawyer up
advised in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
In a presentation that outlined the essentials of reviewing an employment contract, Dr. Sinha of Harvard Medical School, Boston, advised hiring a lawyer with expertise in health care law and health care employment contracts once the letter of intent has been received. Understanding the contract process is helpful, “but ultimately the lawyer is going to be the one helping you with regional expertise. Perhaps they have already interacted with this employer and have a long-standing relationship. They are going to know state laws that are relevant to you. They are going to have a lot of insights that you are just not going to be able to bring to the table very easily.”
A lawyer also will have expertise in negotiation. “If you can form an alliance and negotiate as a team, you are much more likely to get the things you want out of a negotiation,” he said.
Dr. Sinha advised going into a contract knowing exactly what you want. He recommended coming up with six or seven things that matter to you, such as base pay and bonus structure, fringe benefits, relocation expenses, work hours and locations, terms, employee versus independent contractor, and no compete clauses. Even if you have only three key things you’re looking for out of the negotiations, still try to come up with six or seven items.
To get the best results, you need to do your homework. Find out starting salaries and use salary scales when available. Get a sense of who the prospective employer is, what their needs are, and who is competing with you for that contract. Talk to the staff to get a sense of what the work environment is like.
“And then, really speak to people in the community. ... I think this [factor] gets overlooked,” he said. “You can get a lot of valuable information, get a sense of public perception about a physician group, a hospital, a medical school. Those are important considerations as well.”
He also stressed understanding the economic viability of the organization and the growth opportunities for the organization, and recommended reading the contract multiple times. “Understanding the contract is the key to being able to negotiate the provisions.”
Finally, he emphasized that there is no need to accept the first offer made.
“There is always room for negotiating and the bottom line is both sides have to be happy with the contract they negotiated,” he said.
advised in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
In a presentation that outlined the essentials of reviewing an employment contract, Dr. Sinha of Harvard Medical School, Boston, advised hiring a lawyer with expertise in health care law and health care employment contracts once the letter of intent has been received. Understanding the contract process is helpful, “but ultimately the lawyer is going to be the one helping you with regional expertise. Perhaps they have already interacted with this employer and have a long-standing relationship. They are going to know state laws that are relevant to you. They are going to have a lot of insights that you are just not going to be able to bring to the table very easily.”
A lawyer also will have expertise in negotiation. “If you can form an alliance and negotiate as a team, you are much more likely to get the things you want out of a negotiation,” he said.
Dr. Sinha advised going into a contract knowing exactly what you want. He recommended coming up with six or seven things that matter to you, such as base pay and bonus structure, fringe benefits, relocation expenses, work hours and locations, terms, employee versus independent contractor, and no compete clauses. Even if you have only three key things you’re looking for out of the negotiations, still try to come up with six or seven items.
To get the best results, you need to do your homework. Find out starting salaries and use salary scales when available. Get a sense of who the prospective employer is, what their needs are, and who is competing with you for that contract. Talk to the staff to get a sense of what the work environment is like.
“And then, really speak to people in the community. ... I think this [factor] gets overlooked,” he said. “You can get a lot of valuable information, get a sense of public perception about a physician group, a hospital, a medical school. Those are important considerations as well.”
He also stressed understanding the economic viability of the organization and the growth opportunities for the organization, and recommended reading the contract multiple times. “Understanding the contract is the key to being able to negotiate the provisions.”
Finally, he emphasized that there is no need to accept the first offer made.
“There is always room for negotiating and the bottom line is both sides have to be happy with the contract they negotiated,” he said.
advised in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
In a presentation that outlined the essentials of reviewing an employment contract, Dr. Sinha of Harvard Medical School, Boston, advised hiring a lawyer with expertise in health care law and health care employment contracts once the letter of intent has been received. Understanding the contract process is helpful, “but ultimately the lawyer is going to be the one helping you with regional expertise. Perhaps they have already interacted with this employer and have a long-standing relationship. They are going to know state laws that are relevant to you. They are going to have a lot of insights that you are just not going to be able to bring to the table very easily.”
A lawyer also will have expertise in negotiation. “If you can form an alliance and negotiate as a team, you are much more likely to get the things you want out of a negotiation,” he said.
Dr. Sinha advised going into a contract knowing exactly what you want. He recommended coming up with six or seven things that matter to you, such as base pay and bonus structure, fringe benefits, relocation expenses, work hours and locations, terms, employee versus independent contractor, and no compete clauses. Even if you have only three key things you’re looking for out of the negotiations, still try to come up with six or seven items.
To get the best results, you need to do your homework. Find out starting salaries and use salary scales when available. Get a sense of who the prospective employer is, what their needs are, and who is competing with you for that contract. Talk to the staff to get a sense of what the work environment is like.
“And then, really speak to people in the community. ... I think this [factor] gets overlooked,” he said. “You can get a lot of valuable information, get a sense of public perception about a physician group, a hospital, a medical school. Those are important considerations as well.”
He also stressed understanding the economic viability of the organization and the growth opportunities for the organization, and recommended reading the contract multiple times. “Understanding the contract is the key to being able to negotiate the provisions.”
Finally, he emphasized that there is no need to accept the first offer made.
“There is always room for negotiating and the bottom line is both sides have to be happy with the contract they negotiated,” he said.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019
Updates in MS: Highlights From the ECTRIMS and ACTRIMS Annual Meetings
This supplement to Neurology Reviews compiles news briefs from the 2018 ECTRIMS annual meeting in Berlin and the 2019 annual ACTRIMS meeting in Dallas.
This supplement to Neurology Reviews compiles news briefs from the 2018 ECTRIMS annual meeting in Berlin and the 2019 annual ACTRIMS meeting in Dallas.
This supplement to Neurology Reviews compiles news briefs from the 2018 ECTRIMS annual meeting in Berlin and the 2019 annual ACTRIMS meeting in Dallas.
A chance to unite
Is America coming apart at the seams? According to the press, there are more things that divide us than bind us together. It’s red state versus blue state, it’s the privileged versus the disadvantaged, people of color versus the white majority. Could the great melting pot have cooled and its contents settled out into a dozen stratified layers?
Despite the image of a divided America that we see portrayed in the newspapers and on television, I continue to believe that there is more that we share in common than separate us, but it’s a struggle. The media operate on the assumption that conflict draws more readers than good news about cooperation and compromise. The situation is compounded by the apparent absence of a leader from either party who wants to unite us.
However, when one scratches the surface, there is surprising amount of agreement among Americans. For example, according to John Gramlich (“7 facts about guns in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Dec. 27, 2018), 89% of both Republicans and Democrats feel that people with mental illness should not be allowed to purchase a gun. And 79% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats favor background checks at gun shows and for private sales for purchase of a gun. As of 2018, 58% of Americans feel that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, and only 37% feel it should be illegal in all or most cases. (“Public Opinion on Abortion,” Pew Research Center, Oct. 15, 2018).
At the core of many of our struggles to unite is a question that has bedeviled democracies for millennia: How does one balance a citizen’s freedom of choice with the health and safety of the society in which that person lives? While resolutions on gun control and abortion seem unlikely in the foreseeable future, the current outbreaks of measles offer America a rare opportunity to unite on an issue that pits personal freedom against societal safety.
According to Virginia Villa (“5 facts about vaccines in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Mar. 19, 2019), 82% of adults in the United States believe that the MMR vaccine should be required for public school attendance, while only 17% believe that parents should be allowed to leave their child unvaccinated even if their decision creates a health risk for other children and adults.
Why should we expect the government to respond to protect the population from the risk posed by the unvaccinated minority when it has done very little to further gun control? Obviously a key difference is that the antivaccination minority lacks the financial resources and political muscle of a large organization such as the National Rifle Association. While we must never underestimate the power of social media, the publicity surfacing from the mainstream media as the measles outbreaks in the United States have continued has prompted several states to rethink their policies regarding vaccination requirements and school attendance. Here in Maine, there has been strong support among the legislature for eliminating exemptions for philosophic or religious exemptions.
It is probably unrealistic to expect the federal government to act on the health threat caused by the antivaccine movement. However, it is encouraging that, at least at the local level, there is hope for closing one of the wounds that divide us. As providers who care for children, we should seize this opportunity created by the measles outbreaks to promote legislation and policies that strike a sensible balance between the right of the individual and the safety of the society at large.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Is America coming apart at the seams? According to the press, there are more things that divide us than bind us together. It’s red state versus blue state, it’s the privileged versus the disadvantaged, people of color versus the white majority. Could the great melting pot have cooled and its contents settled out into a dozen stratified layers?
Despite the image of a divided America that we see portrayed in the newspapers and on television, I continue to believe that there is more that we share in common than separate us, but it’s a struggle. The media operate on the assumption that conflict draws more readers than good news about cooperation and compromise. The situation is compounded by the apparent absence of a leader from either party who wants to unite us.
However, when one scratches the surface, there is surprising amount of agreement among Americans. For example, according to John Gramlich (“7 facts about guns in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Dec. 27, 2018), 89% of both Republicans and Democrats feel that people with mental illness should not be allowed to purchase a gun. And 79% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats favor background checks at gun shows and for private sales for purchase of a gun. As of 2018, 58% of Americans feel that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, and only 37% feel it should be illegal in all or most cases. (“Public Opinion on Abortion,” Pew Research Center, Oct. 15, 2018).
At the core of many of our struggles to unite is a question that has bedeviled democracies for millennia: How does one balance a citizen’s freedom of choice with the health and safety of the society in which that person lives? While resolutions on gun control and abortion seem unlikely in the foreseeable future, the current outbreaks of measles offer America a rare opportunity to unite on an issue that pits personal freedom against societal safety.
According to Virginia Villa (“5 facts about vaccines in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Mar. 19, 2019), 82% of adults in the United States believe that the MMR vaccine should be required for public school attendance, while only 17% believe that parents should be allowed to leave their child unvaccinated even if their decision creates a health risk for other children and adults.
Why should we expect the government to respond to protect the population from the risk posed by the unvaccinated minority when it has done very little to further gun control? Obviously a key difference is that the antivaccination minority lacks the financial resources and political muscle of a large organization such as the National Rifle Association. While we must never underestimate the power of social media, the publicity surfacing from the mainstream media as the measles outbreaks in the United States have continued has prompted several states to rethink their policies regarding vaccination requirements and school attendance. Here in Maine, there has been strong support among the legislature for eliminating exemptions for philosophic or religious exemptions.
It is probably unrealistic to expect the federal government to act on the health threat caused by the antivaccine movement. However, it is encouraging that, at least at the local level, there is hope for closing one of the wounds that divide us. As providers who care for children, we should seize this opportunity created by the measles outbreaks to promote legislation and policies that strike a sensible balance between the right of the individual and the safety of the society at large.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Is America coming apart at the seams? According to the press, there are more things that divide us than bind us together. It’s red state versus blue state, it’s the privileged versus the disadvantaged, people of color versus the white majority. Could the great melting pot have cooled and its contents settled out into a dozen stratified layers?
Despite the image of a divided America that we see portrayed in the newspapers and on television, I continue to believe that there is more that we share in common than separate us, but it’s a struggle. The media operate on the assumption that conflict draws more readers than good news about cooperation and compromise. The situation is compounded by the apparent absence of a leader from either party who wants to unite us.
However, when one scratches the surface, there is surprising amount of agreement among Americans. For example, according to John Gramlich (“7 facts about guns in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Dec. 27, 2018), 89% of both Republicans and Democrats feel that people with mental illness should not be allowed to purchase a gun. And 79% of Republicans and 91% of Democrats favor background checks at gun shows and for private sales for purchase of a gun. As of 2018, 58% of Americans feel that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, and only 37% feel it should be illegal in all or most cases. (“Public Opinion on Abortion,” Pew Research Center, Oct. 15, 2018).
At the core of many of our struggles to unite is a question that has bedeviled democracies for millennia: How does one balance a citizen’s freedom of choice with the health and safety of the society in which that person lives? While resolutions on gun control and abortion seem unlikely in the foreseeable future, the current outbreaks of measles offer America a rare opportunity to unite on an issue that pits personal freedom against societal safety.
According to Virginia Villa (“5 facts about vaccines in the U.S.,” Pew Research Center, Mar. 19, 2019), 82% of adults in the United States believe that the MMR vaccine should be required for public school attendance, while only 17% believe that parents should be allowed to leave their child unvaccinated even if their decision creates a health risk for other children and adults.
Why should we expect the government to respond to protect the population from the risk posed by the unvaccinated minority when it has done very little to further gun control? Obviously a key difference is that the antivaccination minority lacks the financial resources and political muscle of a large organization such as the National Rifle Association. While we must never underestimate the power of social media, the publicity surfacing from the mainstream media as the measles outbreaks in the United States have continued has prompted several states to rethink their policies regarding vaccination requirements and school attendance. Here in Maine, there has been strong support among the legislature for eliminating exemptions for philosophic or religious exemptions.
It is probably unrealistic to expect the federal government to act on the health threat caused by the antivaccine movement. However, it is encouraging that, at least at the local level, there is hope for closing one of the wounds that divide us. As providers who care for children, we should seize this opportunity created by the measles outbreaks to promote legislation and policies that strike a sensible balance between the right of the individual and the safety of the society at large.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
ACP launches program to better implement QI projects
PHILADELPHIA – .

The program includes 12 months of virtual coaching for a cost, and free online module training, according to Daisy Smith, MD, FACP, who spoke at a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Smith, the ACP’s vice president of clinical programs, discussed additional aspects of ACP Advance with Selam Wubu, director of the ACP’s Center for Quality, in a video interview.
“We launched ACP Advance to engage physicians and their teams [and] empower them to engage and implement quality improvement that results in meaningful improvement for them and their patients,” Ms. Wubu said.
Dr. Smith and Ms. Wubu have no relevant disclosures.
PHILADELPHIA – .

The program includes 12 months of virtual coaching for a cost, and free online module training, according to Daisy Smith, MD, FACP, who spoke at a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Smith, the ACP’s vice president of clinical programs, discussed additional aspects of ACP Advance with Selam Wubu, director of the ACP’s Center for Quality, in a video interview.
“We launched ACP Advance to engage physicians and their teams [and] empower them to engage and implement quality improvement that results in meaningful improvement for them and their patients,” Ms. Wubu said.
Dr. Smith and Ms. Wubu have no relevant disclosures.
PHILADELPHIA – .

The program includes 12 months of virtual coaching for a cost, and free online module training, according to Daisy Smith, MD, FACP, who spoke at a press conference at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dr. Smith, the ACP’s vice president of clinical programs, discussed additional aspects of ACP Advance with Selam Wubu, director of the ACP’s Center for Quality, in a video interview.
“We launched ACP Advance to engage physicians and their teams [and] empower them to engage and implement quality improvement that results in meaningful improvement for them and their patients,” Ms. Wubu said.
Dr. Smith and Ms. Wubu have no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM INTERNAL MEDICINE 2019