User login
Parents’ smartphone addiction linked to children’s overuse of the devices
BALTIMORE – according to a new study. The findings suggest that excessive smartphone use also is associated with the stress of parenting.
“We really need to start raising awareness among parents that their behaviors possibly have an association with their children’s [behaviors] as well,” lead author Korena S. Klimczak of Old Dominion University, Norfolk, Va., said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies.
“I think a lot of parents are not really considering how their smartphone use might be possibly influencing their children,” Ms. Klimczak said. “I think that’s an area pediatricians can start to target as they see parents using the smartphone in the room or passing the phone off to their child in the room.”
Previous research already has linked excessive smartphone use with problematic parenting. Parents distracted by their phones tend to communicate less with their children in the moment, and parents with smartphone addiction symptoms are “less likely to actively mediate their child’s smartphone use,” Ms. Klimczak and her associates noted.
For this study, the researchers recruited 355 parents of children aged 6 months to 5 years from an urban Southeastern academic pediatric hospital clinic. Most of the participating parents were black (72%) and most were mothers (79%).
During a well-child visit, the parents filled out the Smartphone Addiction Scale (SAS), the Parental Stress Scale (PSS) and a 16-item survey on their demographics and their children’s smartphone use. The SAS provided a binary variable (yes/no) on whether parents were addicted to their phones.
Starting when the children were between 12 and 17 months old, parents reported their children’s increasing ability to open or turn on a smartphone. Forty percent of parents reported that their children could turn on phones at this age, and the proportion steadily rose to 79% for children aged 4-5 years (P less than .001).
About one-third of children could start applications on their parents’ phones at age 12-17 months, but more than half were watching videos on their parents’ phones at that age. By the time children were aged 18-24 months, 73% of parents reported that the toddlers could open applications on the phones.
Among parents with a smartphone addiction as defined by the SAS, 59% reported finding it difficult to take their phones away from their children, compared with about half as many parents (26%) without a smartphone addiction (P = .001).
That finding appeared to carry over into their children spending more time on their smartphones as well. Among parents with a smartphone addiction, 22% reported that their children spent more than 2 hours a day on their smartphones, compared with 4% of parents without a smartphone addiction (P = .012). Past research suggests that spending that much time on mobile phones can be an obstacle to emotional and cognitive development, Ms. Klimczak said.
The proportion of children who spent time on their parents’ phones for 5-30 minutes, 30-60 minutes, or 1-2 hours was otherwise relatively similar between parents with and without smartphone addiction.
“There were some possible behavioral issues involved with smartphone addiction in parents as well,” she said, given how much more difficulty these parents had with taking phones away from their children. These parents “were more likely to use corporal punishment as well,” she added.
When faced with a hypothetical situation in which the child broke the parent’s phone, parents with high levels of parental stress were “significantly more likely to discipline their child through either spanking or yelling” the researchers reported, and a positive correlation between parental stress and smartphone addiction existed as well (r = .352, P less than .001).
Ms. Klimczak acknowledged that pediatricians already have a lot of ground to cover in each well-child visit, and monitoring parents’ cell phone use does not necessarily need to be a formal screening measure.
“I think as you see the behavior, you can point it out and maybe gently bring it up,” she said. Pediatricians who notice parents focused on their phones or passing their phones to their children can ask parents at that moment: “I see you using your phone ...” or “I see you’re letting your child use the phone. How often do you let them use the phone [each] day?” Ms. Klimczak said. Gently asking those questions may at least get the parents to think about the issues.
She also recommended incorporating awareness of smartphone addiction and child use of phones into parent education programs in addition to information about safe sleep, breastfeeding, and similar topics. “With how prevalent smartphone use is today, I think it’s at least something to bring up and make them conscious of.”
Ms. Klimczak had no financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – according to a new study. The findings suggest that excessive smartphone use also is associated with the stress of parenting.
“We really need to start raising awareness among parents that their behaviors possibly have an association with their children’s [behaviors] as well,” lead author Korena S. Klimczak of Old Dominion University, Norfolk, Va., said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies.
“I think a lot of parents are not really considering how their smartphone use might be possibly influencing their children,” Ms. Klimczak said. “I think that’s an area pediatricians can start to target as they see parents using the smartphone in the room or passing the phone off to their child in the room.”
Previous research already has linked excessive smartphone use with problematic parenting. Parents distracted by their phones tend to communicate less with their children in the moment, and parents with smartphone addiction symptoms are “less likely to actively mediate their child’s smartphone use,” Ms. Klimczak and her associates noted.
For this study, the researchers recruited 355 parents of children aged 6 months to 5 years from an urban Southeastern academic pediatric hospital clinic. Most of the participating parents were black (72%) and most were mothers (79%).
During a well-child visit, the parents filled out the Smartphone Addiction Scale (SAS), the Parental Stress Scale (PSS) and a 16-item survey on their demographics and their children’s smartphone use. The SAS provided a binary variable (yes/no) on whether parents were addicted to their phones.
Starting when the children were between 12 and 17 months old, parents reported their children’s increasing ability to open or turn on a smartphone. Forty percent of parents reported that their children could turn on phones at this age, and the proportion steadily rose to 79% for children aged 4-5 years (P less than .001).
About one-third of children could start applications on their parents’ phones at age 12-17 months, but more than half were watching videos on their parents’ phones at that age. By the time children were aged 18-24 months, 73% of parents reported that the toddlers could open applications on the phones.
Among parents with a smartphone addiction as defined by the SAS, 59% reported finding it difficult to take their phones away from their children, compared with about half as many parents (26%) without a smartphone addiction (P = .001).
That finding appeared to carry over into their children spending more time on their smartphones as well. Among parents with a smartphone addiction, 22% reported that their children spent more than 2 hours a day on their smartphones, compared with 4% of parents without a smartphone addiction (P = .012). Past research suggests that spending that much time on mobile phones can be an obstacle to emotional and cognitive development, Ms. Klimczak said.
The proportion of children who spent time on their parents’ phones for 5-30 minutes, 30-60 minutes, or 1-2 hours was otherwise relatively similar between parents with and without smartphone addiction.
“There were some possible behavioral issues involved with smartphone addiction in parents as well,” she said, given how much more difficulty these parents had with taking phones away from their children. These parents “were more likely to use corporal punishment as well,” she added.
When faced with a hypothetical situation in which the child broke the parent’s phone, parents with high levels of parental stress were “significantly more likely to discipline their child through either spanking or yelling” the researchers reported, and a positive correlation between parental stress and smartphone addiction existed as well (r = .352, P less than .001).
Ms. Klimczak acknowledged that pediatricians already have a lot of ground to cover in each well-child visit, and monitoring parents’ cell phone use does not necessarily need to be a formal screening measure.
“I think as you see the behavior, you can point it out and maybe gently bring it up,” she said. Pediatricians who notice parents focused on their phones or passing their phones to their children can ask parents at that moment: “I see you using your phone ...” or “I see you’re letting your child use the phone. How often do you let them use the phone [each] day?” Ms. Klimczak said. Gently asking those questions may at least get the parents to think about the issues.
She also recommended incorporating awareness of smartphone addiction and child use of phones into parent education programs in addition to information about safe sleep, breastfeeding, and similar topics. “With how prevalent smartphone use is today, I think it’s at least something to bring up and make them conscious of.”
Ms. Klimczak had no financial disclosures.
BALTIMORE – according to a new study. The findings suggest that excessive smartphone use also is associated with the stress of parenting.
“We really need to start raising awareness among parents that their behaviors possibly have an association with their children’s [behaviors] as well,” lead author Korena S. Klimczak of Old Dominion University, Norfolk, Va., said in an interview at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies.
“I think a lot of parents are not really considering how their smartphone use might be possibly influencing their children,” Ms. Klimczak said. “I think that’s an area pediatricians can start to target as they see parents using the smartphone in the room or passing the phone off to their child in the room.”
Previous research already has linked excessive smartphone use with problematic parenting. Parents distracted by their phones tend to communicate less with their children in the moment, and parents with smartphone addiction symptoms are “less likely to actively mediate their child’s smartphone use,” Ms. Klimczak and her associates noted.
For this study, the researchers recruited 355 parents of children aged 6 months to 5 years from an urban Southeastern academic pediatric hospital clinic. Most of the participating parents were black (72%) and most were mothers (79%).
During a well-child visit, the parents filled out the Smartphone Addiction Scale (SAS), the Parental Stress Scale (PSS) and a 16-item survey on their demographics and their children’s smartphone use. The SAS provided a binary variable (yes/no) on whether parents were addicted to their phones.
Starting when the children were between 12 and 17 months old, parents reported their children’s increasing ability to open or turn on a smartphone. Forty percent of parents reported that their children could turn on phones at this age, and the proportion steadily rose to 79% for children aged 4-5 years (P less than .001).
About one-third of children could start applications on their parents’ phones at age 12-17 months, but more than half were watching videos on their parents’ phones at that age. By the time children were aged 18-24 months, 73% of parents reported that the toddlers could open applications on the phones.
Among parents with a smartphone addiction as defined by the SAS, 59% reported finding it difficult to take their phones away from their children, compared with about half as many parents (26%) without a smartphone addiction (P = .001).
That finding appeared to carry over into their children spending more time on their smartphones as well. Among parents with a smartphone addiction, 22% reported that their children spent more than 2 hours a day on their smartphones, compared with 4% of parents without a smartphone addiction (P = .012). Past research suggests that spending that much time on mobile phones can be an obstacle to emotional and cognitive development, Ms. Klimczak said.
The proportion of children who spent time on their parents’ phones for 5-30 minutes, 30-60 minutes, or 1-2 hours was otherwise relatively similar between parents with and without smartphone addiction.
“There were some possible behavioral issues involved with smartphone addiction in parents as well,” she said, given how much more difficulty these parents had with taking phones away from their children. These parents “were more likely to use corporal punishment as well,” she added.
When faced with a hypothetical situation in which the child broke the parent’s phone, parents with high levels of parental stress were “significantly more likely to discipline their child through either spanking or yelling” the researchers reported, and a positive correlation between parental stress and smartphone addiction existed as well (r = .352, P less than .001).
Ms. Klimczak acknowledged that pediatricians already have a lot of ground to cover in each well-child visit, and monitoring parents’ cell phone use does not necessarily need to be a formal screening measure.
“I think as you see the behavior, you can point it out and maybe gently bring it up,” she said. Pediatricians who notice parents focused on their phones or passing their phones to their children can ask parents at that moment: “I see you using your phone ...” or “I see you’re letting your child use the phone. How often do you let them use the phone [each] day?” Ms. Klimczak said. Gently asking those questions may at least get the parents to think about the issues.
She also recommended incorporating awareness of smartphone addiction and child use of phones into parent education programs in addition to information about safe sleep, breastfeeding, and similar topics. “With how prevalent smartphone use is today, I think it’s at least something to bring up and make them conscious of.”
Ms. Klimczak had no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM PAS 2019
Knowledge gaps about long-term osteoporosis drug therapy benefits, risks remain large
Long-term use of alendronate and zoledronic acid for more than 3 years reduces the rate of vertebral fracture in treatment-naive postmenopausal women with notable, yet rare, adverse events, but too little evidence exists to make determinations on the long-term benefit/risk profile of other bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis drugs besides raloxifene and oral hormone therapy, according to a report coming out of a recent National Institutes of Health workshop.
This situation leaves a large research gap that authors of an accompanying position paper hope to bridge with recommendations for studying therapy discontinuation and drug holidays during long-term osteoporosis drug treatment.
The NIH’s Pathways to Prevention (P2P) Workshop: Appropriate Use of Drug Therapies for Osteoporotic Fracture Prevention outlined the findings of the systematic review of long-term osteoporosis drug treatment (ODT), which was commissioned by the NIH Office of Disease Prevention. The systematic review and a position paper summarizing the workshop were published April 23 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Clinicians and patients need increased information on benefits and risks to inform shared decision making about the use of these treatments, taking into account patients’ values and preferences,” Albert Siu, MD, of the Brookdale Department of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and his colleagues wrote in the position paper (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961). “The research ... is urgently needed to advance prevention of osteoporosis-related mortality and morbidity.”
In the systematic review, by a group of researchers separate from the workshop, 48 studies were identified (35 trials, 13 observational studies) that compared men and postmenopausal women 50 years or older who used treatments such as alendronate, raloxifene, zoledronic acid, and hormone therapy. The researchers found that use of alendronate for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical fractures (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.82) and radiographic vertebral fractures (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.31-0.82) in women with osteoporosis. Raloxifene use for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical vertebral fractures (relative risk, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.43-0.79) and radiographic vertebral fractures (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.53-0.76) but not nonvertebral fractures. Zoledronic acid use for 6 years was associated with a lower rate of nonvertebral fractures (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.51-0.85) and clinical vertebral fractures (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.22-0.75) in women with both osteoporosis and osteopenia. Estrogen-progestin use for 5.6 years and unopposed estrogen for 7 years was associated with clinical fracture reduction in women with unspecified osteoporosis and osteopenia when compared with placebo (Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0533).
Controlled observational studies collectively show that long-term use of alendronate and of bisphosphonates as a class increased risk for radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture but by a small absolute amount, with less evidence for risks of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures without radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture features and osteonecrosis of the jaw. However, there were no eligible observational studies with long-term use of zoledronic acid that evaluated risk for these adverse events.
Long-term raloxifene therapy was associated with a threefold increased risk for deep venous thrombosis and a three- to fourfold increased risk for pulmonary embolism, although not all results were statistically significant, the researchers said. In two long-term trials, both estrogen and estrogen-progestin compared with placebo increased risk for cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment. Estrogen-progestin also increased risk for invasive breast cancer.
The researchers also studied abaloparatide, denosumab, ibandronate, risedronate, and teriparatide, but noted there were insufficient data to show the long-term effects of their use on fractures and other harms.
Dr. Siu and coauthors on the position paper made the following recommendations with regard to future research on long-term ODT:
• Using “innovative designs and approaches” for new research such as modeling studies, clinical trials, and observational studies of existing and potential treatments.
• Evaluating new agents or multicomponent interventions, such as fracture liaison services and oral care, that do not carry the downsides of antiresorptive therapies.
• Researching and preventing atypical femoral fracture and osteonecrosis of the jaw, particularly when associated with long-term denosumab or bisphosphonate use.
• Determining which patients are indicated for drug holidays, sequential therapies, and strategies for avoiding serious adverse events.
• Studying barriers to ODT.
“When we have information on these outcomes, such as how medication use after a fragility fracture is linked to future fractures or survival rates, we need to understand how to convey that information to patients so they can make more informed decisions about their care,” noted Dr. Siu and colleagues.
In an editorial related to both the position paper and the systematic review, Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, agreed that clinical trial data do not answer questions about shared decision making for women with multiple comorbid conditions, the long-term effects of ODT with regard to rare fracture risk, and which patients are well-suited for drug holidays.
“The National Institutes of Health should support research to answer these high-impact clinical questions, in addition to encouraging approaches for clinicians to determine which individual patients are at greater risk for harms related to long-term bisphosphonate use,” she said. “The need to rigorously study patient preferences in the context of ODT is pressing because of the complex dosing instructions of oral bisphosphonates and the dramatic underutilization of ODT among persons who have already had a vertebral or hip fracture.”
The systematic review was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors of the position paper and Dr. Crandall reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Siu A et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961.
Long-term use of alendronate and zoledronic acid for more than 3 years reduces the rate of vertebral fracture in treatment-naive postmenopausal women with notable, yet rare, adverse events, but too little evidence exists to make determinations on the long-term benefit/risk profile of other bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis drugs besides raloxifene and oral hormone therapy, according to a report coming out of a recent National Institutes of Health workshop.
This situation leaves a large research gap that authors of an accompanying position paper hope to bridge with recommendations for studying therapy discontinuation and drug holidays during long-term osteoporosis drug treatment.
The NIH’s Pathways to Prevention (P2P) Workshop: Appropriate Use of Drug Therapies for Osteoporotic Fracture Prevention outlined the findings of the systematic review of long-term osteoporosis drug treatment (ODT), which was commissioned by the NIH Office of Disease Prevention. The systematic review and a position paper summarizing the workshop were published April 23 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Clinicians and patients need increased information on benefits and risks to inform shared decision making about the use of these treatments, taking into account patients’ values and preferences,” Albert Siu, MD, of the Brookdale Department of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and his colleagues wrote in the position paper (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961). “The research ... is urgently needed to advance prevention of osteoporosis-related mortality and morbidity.”
In the systematic review, by a group of researchers separate from the workshop, 48 studies were identified (35 trials, 13 observational studies) that compared men and postmenopausal women 50 years or older who used treatments such as alendronate, raloxifene, zoledronic acid, and hormone therapy. The researchers found that use of alendronate for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical fractures (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.82) and radiographic vertebral fractures (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.31-0.82) in women with osteoporosis. Raloxifene use for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical vertebral fractures (relative risk, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.43-0.79) and radiographic vertebral fractures (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.53-0.76) but not nonvertebral fractures. Zoledronic acid use for 6 years was associated with a lower rate of nonvertebral fractures (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.51-0.85) and clinical vertebral fractures (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.22-0.75) in women with both osteoporosis and osteopenia. Estrogen-progestin use for 5.6 years and unopposed estrogen for 7 years was associated with clinical fracture reduction in women with unspecified osteoporosis and osteopenia when compared with placebo (Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0533).
Controlled observational studies collectively show that long-term use of alendronate and of bisphosphonates as a class increased risk for radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture but by a small absolute amount, with less evidence for risks of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures without radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture features and osteonecrosis of the jaw. However, there were no eligible observational studies with long-term use of zoledronic acid that evaluated risk for these adverse events.
Long-term raloxifene therapy was associated with a threefold increased risk for deep venous thrombosis and a three- to fourfold increased risk for pulmonary embolism, although not all results were statistically significant, the researchers said. In two long-term trials, both estrogen and estrogen-progestin compared with placebo increased risk for cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment. Estrogen-progestin also increased risk for invasive breast cancer.
The researchers also studied abaloparatide, denosumab, ibandronate, risedronate, and teriparatide, but noted there were insufficient data to show the long-term effects of their use on fractures and other harms.
Dr. Siu and coauthors on the position paper made the following recommendations with regard to future research on long-term ODT:
• Using “innovative designs and approaches” for new research such as modeling studies, clinical trials, and observational studies of existing and potential treatments.
• Evaluating new agents or multicomponent interventions, such as fracture liaison services and oral care, that do not carry the downsides of antiresorptive therapies.
• Researching and preventing atypical femoral fracture and osteonecrosis of the jaw, particularly when associated with long-term denosumab or bisphosphonate use.
• Determining which patients are indicated for drug holidays, sequential therapies, and strategies for avoiding serious adverse events.
• Studying barriers to ODT.
“When we have information on these outcomes, such as how medication use after a fragility fracture is linked to future fractures or survival rates, we need to understand how to convey that information to patients so they can make more informed decisions about their care,” noted Dr. Siu and colleagues.
In an editorial related to both the position paper and the systematic review, Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, agreed that clinical trial data do not answer questions about shared decision making for women with multiple comorbid conditions, the long-term effects of ODT with regard to rare fracture risk, and which patients are well-suited for drug holidays.
“The National Institutes of Health should support research to answer these high-impact clinical questions, in addition to encouraging approaches for clinicians to determine which individual patients are at greater risk for harms related to long-term bisphosphonate use,” she said. “The need to rigorously study patient preferences in the context of ODT is pressing because of the complex dosing instructions of oral bisphosphonates and the dramatic underutilization of ODT among persons who have already had a vertebral or hip fracture.”
The systematic review was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors of the position paper and Dr. Crandall reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Siu A et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961.
Long-term use of alendronate and zoledronic acid for more than 3 years reduces the rate of vertebral fracture in treatment-naive postmenopausal women with notable, yet rare, adverse events, but too little evidence exists to make determinations on the long-term benefit/risk profile of other bisphosphonates or other osteoporosis drugs besides raloxifene and oral hormone therapy, according to a report coming out of a recent National Institutes of Health workshop.
This situation leaves a large research gap that authors of an accompanying position paper hope to bridge with recommendations for studying therapy discontinuation and drug holidays during long-term osteoporosis drug treatment.
The NIH’s Pathways to Prevention (P2P) Workshop: Appropriate Use of Drug Therapies for Osteoporotic Fracture Prevention outlined the findings of the systematic review of long-term osteoporosis drug treatment (ODT), which was commissioned by the NIH Office of Disease Prevention. The systematic review and a position paper summarizing the workshop were published April 23 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Clinicians and patients need increased information on benefits and risks to inform shared decision making about the use of these treatments, taking into account patients’ values and preferences,” Albert Siu, MD, of the Brookdale Department of Geriatrics and Palliative Medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and his colleagues wrote in the position paper (Ann Intern Med. 2019 Apr 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961). “The research ... is urgently needed to advance prevention of osteoporosis-related mortality and morbidity.”
In the systematic review, by a group of researchers separate from the workshop, 48 studies were identified (35 trials, 13 observational studies) that compared men and postmenopausal women 50 years or older who used treatments such as alendronate, raloxifene, zoledronic acid, and hormone therapy. The researchers found that use of alendronate for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical fractures (hazard ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.50-0.82) and radiographic vertebral fractures (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.31-0.82) in women with osteoporosis. Raloxifene use for 4 years reduced the rate of clinical vertebral fractures (relative risk, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.43-0.79) and radiographic vertebral fractures (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.53-0.76) but not nonvertebral fractures. Zoledronic acid use for 6 years was associated with a lower rate of nonvertebral fractures (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.51-0.85) and clinical vertebral fractures (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.22-0.75) in women with both osteoporosis and osteopenia. Estrogen-progestin use for 5.6 years and unopposed estrogen for 7 years was associated with clinical fracture reduction in women with unspecified osteoporosis and osteopenia when compared with placebo (Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0533).
Controlled observational studies collectively show that long-term use of alendronate and of bisphosphonates as a class increased risk for radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture but by a small absolute amount, with less evidence for risks of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures without radiologically confirmed atypical femoral fracture features and osteonecrosis of the jaw. However, there were no eligible observational studies with long-term use of zoledronic acid that evaluated risk for these adverse events.
Long-term raloxifene therapy was associated with a threefold increased risk for deep venous thrombosis and a three- to fourfold increased risk for pulmonary embolism, although not all results were statistically significant, the researchers said. In two long-term trials, both estrogen and estrogen-progestin compared with placebo increased risk for cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment. Estrogen-progestin also increased risk for invasive breast cancer.
The researchers also studied abaloparatide, denosumab, ibandronate, risedronate, and teriparatide, but noted there were insufficient data to show the long-term effects of their use on fractures and other harms.
Dr. Siu and coauthors on the position paper made the following recommendations with regard to future research on long-term ODT:
• Using “innovative designs and approaches” for new research such as modeling studies, clinical trials, and observational studies of existing and potential treatments.
• Evaluating new agents or multicomponent interventions, such as fracture liaison services and oral care, that do not carry the downsides of antiresorptive therapies.
• Researching and preventing atypical femoral fracture and osteonecrosis of the jaw, particularly when associated with long-term denosumab or bisphosphonate use.
• Determining which patients are indicated for drug holidays, sequential therapies, and strategies for avoiding serious adverse events.
• Studying barriers to ODT.
“When we have information on these outcomes, such as how medication use after a fragility fracture is linked to future fractures or survival rates, we need to understand how to convey that information to patients so they can make more informed decisions about their care,” noted Dr. Siu and colleagues.
In an editorial related to both the position paper and the systematic review, Carolyn J. Crandall, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, agreed that clinical trial data do not answer questions about shared decision making for women with multiple comorbid conditions, the long-term effects of ODT with regard to rare fracture risk, and which patients are well-suited for drug holidays.
“The National Institutes of Health should support research to answer these high-impact clinical questions, in addition to encouraging approaches for clinicians to determine which individual patients are at greater risk for harms related to long-term bisphosphonate use,” she said. “The need to rigorously study patient preferences in the context of ODT is pressing because of the complex dosing instructions of oral bisphosphonates and the dramatic underutilization of ODT among persons who have already had a vertebral or hip fracture.”
The systematic review was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The authors of the position paper and Dr. Crandall reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Siu A et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 April 23. doi: 10.7326/M19-0961.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Rat race
My son and I used to play a game called CASHFLOW. It was invented by Robert Kiyosaki, the real estate magnate who originated the “Rich Dad Poor Dad” book series to educate the masses on the basics of real estate investing.
The object of the game was to acquire enough passive income to become independent of active income like salary. The hope was that by playing the game, participants would recognize the advantages of passive income and become entrepreneurs in real estate or business. The winner was no longer an employee, but happily self-employed and out of the rat race.
Alas, the lesson was lost on me and my son. Both of us are still very much in the rat race and dependent on salary.
But a rat race can be more than just a competitive quest for financial gain. In politics, the quest is more for power. In sports, the quest includes championships. In academic medicine – and hematology is usually practiced in an academic setting – the quest is often for power and prestige. Training for our hematologic quest began in high school.
In high school, superior grades were a given, but we also worked to excel in sports, extracurricular activities, and standardized tests in order to get into the best universities. The cycle was then repeated to allow entry into the best medical schools. The old adage that students who finished last in their medical school class are still addressed as “Doctor” notwithstanding, most of us pushed ourselves beyond good grades to volunteer work, research activities, and prestigious clerkships to ensure that we matched at the best residency programs. There, those inclined to hematology cozied up to influential faculty by helping with their research in order to obtain the cherished letter of recommendation that promised admission to the best fellowship program, where the cycle was again repeated in the hope of landing a position in the best academic medical center.
Through these pursuits, young recruits to medical academia are primed and ready to enter a rat race of individual accomplishment. The academic rat race is a particularly pernicious result of our training to be the best, and the “best” hematologists are found at the podium, not in the exam room.
Not content to be recognized for clinical excellence by their patients, academic hematologists often aspire more to be recognized for content expertise by their peers. Through the noble pursuit of advancing science, peer recognition bestows prestige and power in the form of promotions, grants, advisory boards, consultancies, and speaking opportunities all over the globe. For some, the academic rat race validates a life dedicated to being the best.
However, the demands of patient care can interfere with academic pursuits and stand as impediments to the march of science, with its attendant rewards in power and prestige. The most common complaint I get from my team is the inability to fully participate in all that is required to succeed academically because of clinical responsibilities. The difficulty is worsened when financial realities require even more time spent in the clinic to generate income. This makes it hard enough to keep a healthy balance between research and patient care. When the pressures of clinical and academic hematology are combined with the responsibility of family, the rat race can begin to lead to burnout.
A rat race forces us to compare ourselves to others, and we often find ourselves wanting. There is always someone who seems wealthier and wiser than we are. Our training often compels us to compete with whoever it is we are comparing ourselves to. That competition simultaneously drives us toward a laudable goal and away from a balanced, happy life.
Theodore Roosevelt said “Comparison is the thief of joy,” and that certainly seems to be the case among medical professionals. As physicians, we do not lack for wealth, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We do not lack for wisdom, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We’d see that we really lack very little and occupy a privileged place in society if we only took the time to be grateful for having had the talent and support to do so.
I enjoyed playing CASHFLOW when I was younger and naively thought that either my son or I might materially benefit from its lessons. I realize now that the real enjoyment of playing was not to win or to get rich, but rather to spend time with my son. Likewise, our training got us where we are, and it will sustain a happy fulfilling career, but it will also consume us if we let go of why we started playing the game in the first place.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He chairs the department of hematology and medical oncology at Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
My son and I used to play a game called CASHFLOW. It was invented by Robert Kiyosaki, the real estate magnate who originated the “Rich Dad Poor Dad” book series to educate the masses on the basics of real estate investing.
The object of the game was to acquire enough passive income to become independent of active income like salary. The hope was that by playing the game, participants would recognize the advantages of passive income and become entrepreneurs in real estate or business. The winner was no longer an employee, but happily self-employed and out of the rat race.
Alas, the lesson was lost on me and my son. Both of us are still very much in the rat race and dependent on salary.
But a rat race can be more than just a competitive quest for financial gain. In politics, the quest is more for power. In sports, the quest includes championships. In academic medicine – and hematology is usually practiced in an academic setting – the quest is often for power and prestige. Training for our hematologic quest began in high school.
In high school, superior grades were a given, but we also worked to excel in sports, extracurricular activities, and standardized tests in order to get into the best universities. The cycle was then repeated to allow entry into the best medical schools. The old adage that students who finished last in their medical school class are still addressed as “Doctor” notwithstanding, most of us pushed ourselves beyond good grades to volunteer work, research activities, and prestigious clerkships to ensure that we matched at the best residency programs. There, those inclined to hematology cozied up to influential faculty by helping with their research in order to obtain the cherished letter of recommendation that promised admission to the best fellowship program, where the cycle was again repeated in the hope of landing a position in the best academic medical center.
Through these pursuits, young recruits to medical academia are primed and ready to enter a rat race of individual accomplishment. The academic rat race is a particularly pernicious result of our training to be the best, and the “best” hematologists are found at the podium, not in the exam room.
Not content to be recognized for clinical excellence by their patients, academic hematologists often aspire more to be recognized for content expertise by their peers. Through the noble pursuit of advancing science, peer recognition bestows prestige and power in the form of promotions, grants, advisory boards, consultancies, and speaking opportunities all over the globe. For some, the academic rat race validates a life dedicated to being the best.
However, the demands of patient care can interfere with academic pursuits and stand as impediments to the march of science, with its attendant rewards in power and prestige. The most common complaint I get from my team is the inability to fully participate in all that is required to succeed academically because of clinical responsibilities. The difficulty is worsened when financial realities require even more time spent in the clinic to generate income. This makes it hard enough to keep a healthy balance between research and patient care. When the pressures of clinical and academic hematology are combined with the responsibility of family, the rat race can begin to lead to burnout.
A rat race forces us to compare ourselves to others, and we often find ourselves wanting. There is always someone who seems wealthier and wiser than we are. Our training often compels us to compete with whoever it is we are comparing ourselves to. That competition simultaneously drives us toward a laudable goal and away from a balanced, happy life.
Theodore Roosevelt said “Comparison is the thief of joy,” and that certainly seems to be the case among medical professionals. As physicians, we do not lack for wealth, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We do not lack for wisdom, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We’d see that we really lack very little and occupy a privileged place in society if we only took the time to be grateful for having had the talent and support to do so.
I enjoyed playing CASHFLOW when I was younger and naively thought that either my son or I might materially benefit from its lessons. I realize now that the real enjoyment of playing was not to win or to get rich, but rather to spend time with my son. Likewise, our training got us where we are, and it will sustain a happy fulfilling career, but it will also consume us if we let go of why we started playing the game in the first place.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He chairs the department of hematology and medical oncology at Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
My son and I used to play a game called CASHFLOW. It was invented by Robert Kiyosaki, the real estate magnate who originated the “Rich Dad Poor Dad” book series to educate the masses on the basics of real estate investing.
The object of the game was to acquire enough passive income to become independent of active income like salary. The hope was that by playing the game, participants would recognize the advantages of passive income and become entrepreneurs in real estate or business. The winner was no longer an employee, but happily self-employed and out of the rat race.
Alas, the lesson was lost on me and my son. Both of us are still very much in the rat race and dependent on salary.
But a rat race can be more than just a competitive quest for financial gain. In politics, the quest is more for power. In sports, the quest includes championships. In academic medicine – and hematology is usually practiced in an academic setting – the quest is often for power and prestige. Training for our hematologic quest began in high school.
In high school, superior grades were a given, but we also worked to excel in sports, extracurricular activities, and standardized tests in order to get into the best universities. The cycle was then repeated to allow entry into the best medical schools. The old adage that students who finished last in their medical school class are still addressed as “Doctor” notwithstanding, most of us pushed ourselves beyond good grades to volunteer work, research activities, and prestigious clerkships to ensure that we matched at the best residency programs. There, those inclined to hematology cozied up to influential faculty by helping with their research in order to obtain the cherished letter of recommendation that promised admission to the best fellowship program, where the cycle was again repeated in the hope of landing a position in the best academic medical center.
Through these pursuits, young recruits to medical academia are primed and ready to enter a rat race of individual accomplishment. The academic rat race is a particularly pernicious result of our training to be the best, and the “best” hematologists are found at the podium, not in the exam room.
Not content to be recognized for clinical excellence by their patients, academic hematologists often aspire more to be recognized for content expertise by their peers. Through the noble pursuit of advancing science, peer recognition bestows prestige and power in the form of promotions, grants, advisory boards, consultancies, and speaking opportunities all over the globe. For some, the academic rat race validates a life dedicated to being the best.
However, the demands of patient care can interfere with academic pursuits and stand as impediments to the march of science, with its attendant rewards in power and prestige. The most common complaint I get from my team is the inability to fully participate in all that is required to succeed academically because of clinical responsibilities. The difficulty is worsened when financial realities require even more time spent in the clinic to generate income. This makes it hard enough to keep a healthy balance between research and patient care. When the pressures of clinical and academic hematology are combined with the responsibility of family, the rat race can begin to lead to burnout.
A rat race forces us to compare ourselves to others, and we often find ourselves wanting. There is always someone who seems wealthier and wiser than we are. Our training often compels us to compete with whoever it is we are comparing ourselves to. That competition simultaneously drives us toward a laudable goal and away from a balanced, happy life.
Theodore Roosevelt said “Comparison is the thief of joy,” and that certainly seems to be the case among medical professionals. As physicians, we do not lack for wealth, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We do not lack for wisdom, unless we compare ourselves to those who have more. We’d see that we really lack very little and occupy a privileged place in society if we only took the time to be grateful for having had the talent and support to do so.
I enjoyed playing CASHFLOW when I was younger and naively thought that either my son or I might materially benefit from its lessons. I realize now that the real enjoyment of playing was not to win or to get rich, but rather to spend time with my son. Likewise, our training got us where we are, and it will sustain a happy fulfilling career, but it will also consume us if we let go of why we started playing the game in the first place.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He chairs the department of hematology and medical oncology at Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
An obese 48-year-old man with progressive fatigue and decreased libido
A 48-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because of progressively decreasing energy and gradual decline in both libido and erectile function for the past 18 months. He has noticed decreased morning erections as well. He rates his libido at 3 to 4 on a scale of 10 for the past 6 months. He also reports poor motivation, depressed mood, impaired concentration, and sleep disturbances. He reports no hair loss, headache, or dizziness, and no decrease in shaving frequency. Review of his systems is otherwise unremarkable.
He has had dyslipidemia for 3 years and is not known to have hypertension or diabetes. His medications include atorvastatin, vitamin E, and multivitamins.
He is married with 3 children and does not wish to have more. He works as a software engineer and leads a sedentary lifestyle. He is a nonsmoker and occasionally drinks alcohol on the weekends.
On physical examination, he is alert and oriented and appears well. His height is 5 feet 10 inches (178 cm), weight 230 lb (104 kg), and body mass index (BMI) 32.8 kg/m2. His blood pressure is 115/83 mm Hg and pulse rate is 82 beats per minute and regular. Findings on cardiovascular and pulmonary examination are normal. He has large fatty breasts but without palpable glandular tissue.
Genitourinary examination reveals normal hair distribution, a normal-sized penis, and slightly soft testes with testicular volume of 18–20 mL bilaterally.
His primary care physician suspects that he has low testosterone and orders some basic laboratory tests; the results are normal except for a low total testosterone level (Table 1).
FURTHER TESTING
1. Which of the following tests should his physician order next?
- Repeat total testosterone measurement
- Free testosterone measurement by commercial assay
- Calculated free testosterone
- Bioavailable testosterone measurement
- Serum inhibin B measurement
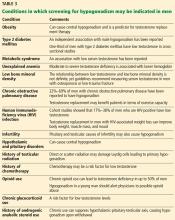
This patient presents with several nonspecific symptoms. But collectively they suggest testosterone deficiency (hypogonadism).
Together, erectile dysfunction, low libido, and decreased morning erections strongly suggest hypogonadism.2 Loss of body hair and decreased shaving frequency are specific symptoms of hypogonadism; however, they require years to develop.3 Gynecomastia can also occur due to loss of the inhibitory action of testosterone on breast growth and a relative increase in estradiol. This occurs more in primary hypogonadism, due to the increase in luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates the remaining Leydig cells to secrete estradiol rather than testosterone.4
To diagnose hypogonadism in men and to start treatment for it, current guidelines recommend that the patient should have clinical features as well as laboratory evidence of low testosterone.5,6
Measuring testosterone: Total, free, bound, and bioavailable
Testosterone, a steroid hormone, circulates in the serum either as free testosterone or bound to several plasma proteins, mainly sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin.
Total testosterone includes both the free and bound fractions, whereas bioavailable testosterone includes both free and the portion bound to albumin, which has low affinity and can dissociate and be used at the tissue level.11
Low levels of total testosterone do not necessarily reflect a hypogonadal state, as a man with altered SHBG levels or binding capabilities can have low total but normal free testosterone levels and no manifestations.12 Several conditions can alter the levels of SHBG, including obesity, diabetes, aging, thyroid dysfunction, and others.5,13
Because our patient is obese, his total testosterone level is not a reliable indicator of hypogonadism, and repeating its measurement will not add diagnostic value.
Therefore, an alternative measurement should be used to accurately reflect the testosterone levels. From a physiologic point of view, bioavailable testosterone is the active form of testosterone and is the most accurate to be measured in a patient with hypogonadism. Nevertheless, because of technical difficulties in its measurement and lack of evidence correlating bioavailable testosterone with the clinical picture of hypogonadism, it is recommended that the level of free testosterone be used.5
The gold standard for direct measurement of serum free testosterone is equilibrium dialysis, but this is expensive and time-consuming.14 Commercial assays for free testosterone exist but have been deemed unreliable.14,15 It is recommended that free testosterone be measured by equilibrium dialysis or calculated using equations based on total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin levels.5 These equations are reliable and give results very close to the values obtained by equilibrium dialysis.15 Therefore, in our patient, it would be suitable to calculate the free testosterone level next.
Serum levels of free testosterone vary according to several factors. Diurnal variation of testosterone has been established: levels are highest in the morning and decline throughout the day.16 Food decreases testosterone levels.17 In addition, there is considerable day-to-day variation.18 Therefore, at least 2 readings of fasting morning testosterone on 2 separate days are recommended for the diagnosis of hypogonadism.5
Inhibin B is a hormone produced by Sertoli cells in the testes in response to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulation. In turn, it acts as negative feedback, together with testosterone, to inhibit FSH release from the pituitary. Inhibin B has been shown to reflect spermatogenesis in the testes and therefore fertility.19 Inhibin B levels were found to be low in patients with central hypogonadism, due to less FSH release; however, they did not correlate with testosterone levels.20
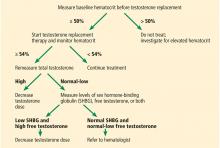
CASE RESUMED: CHARACTERIZING HIS HYPOGONADISM
The patient’s physician orders morning fasting total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin testing and calculates the free testosterone level, which yields a value of 3 ng/dL (reference range 4.5–17). This is confirmed by a repeat measurement, which yields a value of 2.9 ng/dL. Laboratory test results combined with his clinical presentation are consistent with hypogonadism.
2. What is the most appropriate next step?
- Measurement of serum LH and FSH
- Measurement of serum prolactin
- Scrotal ultrasonography
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test
- Semen analysis
After hypogonadism is diagnosed, it is important to distinguish if it is primary or central. This is achieved by measuring serum LH and FSH.5 All biotin supplements should be stopped at least 72 hours before measuring LH and FSH, as biotin can interfere with the assays, yielding false values.21
Secretion of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary is under the influence of pulsatile release of GnRH from the hypothalamus. LH acts on Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, whereas FSH acts on Sertoli cells, together with testosterone, to bring about spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules. Testosterone acts centrally as negative feedback to decrease the release of LH and FSH.
Primary hypogonadism occurs due to testicular failure, ie, the testes themselves fail to produce testosterone, leading to hypogonadism. The decrease in testosterone levels, together with inhibin B if Sertoli cells are damaged, lead to loss of negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary, and therefore increased levels of LH and FSH. This is termed hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Testicular failure may also result in impaired spermatogenesis and infertility due to destruction of testicular structures, in which case fertility cannot be restored.
Central hypogonadism occurs when the pituitary fails to produce LH and FSH (secondary hypogonadism) or when the hypothalamus fails to produce GnRH and subsequently the lack of secretion of LH and FSH from the pituitary (tertiary hypogonadism). The lack of LH will result in no stimulation of Leydig cells to produce testosterone, and therefore its deficiency. Serum hormone levels in central hypogonadism will reveal low testosterone, with either low or inappropriately normal gonadotropins (LH and FSH). This is termed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The lack of FSH, together with testosterone deficiency will also result in decreased spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. Testicular structures are preserved, however, and fertility can be restored with appropriate therapy, as discussed below.
Prolactin should be measured only if the patient has central hypogonadism. Its measurement is not warranted at this point in the patient’s workup. The implications of prolactin and its relationship to hypogonadism will be discussed later.
Although, this stepwise approach is not convenient for many patients, some physicians follow it because it is cost-effective, especially in those who are not insured. However, other physicians order FSH, LH, and sometimes prolactin with the confirmatory low testosterone measurement. Laboratories can also be instructed to wait to measure the pituitary hormones and to do so only if low testosterone is confirmed.
Varicocele, a possible cause of male infertility, can also impair Leydig cell function and cause low testosterone. In fact, surgical repair of varicocele has been demonstrated to increase serum testosterone.22 Scrotal ultrasonography is used to diagnose varicocele, but this also should be ordered at a later stage in the workup if primary hypogonadism is diagnosed.
The GnRH stimulation test is important for the diagnosis and evaluation of precocious or delayed puberty in children. In boys with delayed puberty, a poorer response to GnRH stimulation indicates central hypogonadism rather than constitutional delay.23 It has no role in the evaluation of postpubertal or adult-onset hypogonadism.
Semen analysis is important to evaluate fertility if the patient is interested in further procreation.5 Low testosterone levels may result in impaired spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. On the other hand, treatment with exogenous testosterone will also result in infertility, by feedback inhibition of LH and FSH and therefore inhibition of spermatogenesis. If the patient wishes to preserve fertility, treatment options other than testosterone should be considered; examples include clomiphene citrate, human menopausal gonadotropin, and human chorionic gonadotropin.23,24
Our patient has no desire to expand his family; therefore, a semen analysis and attempts to preserve spermatogenesis are not indicated.
CASE RESUMED: SEARCHING FOR CAUSES
His physician orders testing of serum LH and FSH, yielding the following values:
- LH 1.6 mIU/mL (reference range 1.8–12)
- FSH 1.9 mIU/mL (reference range 1.5–12.5).
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism is established.
3. Which investigation is the least appropriate in the further evaluation of this patient?
- Serum prolactin measurement
- Serum ferritin measurement
- Pituitary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Chromosomal karyotyping
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism warrants evaluation for possible causes. These are summarized in Table 4.
Serum free thyroxine and morning cortisol
Since this patient’s LH and FSH values are abnormal, it is important to evaluate the status of other anterior pituitary hormones. In patients with pituitary abnormalities, serum free T4 is a more reliable test for assessing thyroid function than thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), because of loss of the negative feedback of thyroid hormones on the diseased pituitary. In contrast, serum TSH is considered the best single thyroid test to assess primary thyroid dysfunction.
Other measurements include prolactin and morning cortisol (reflecting adrenocorticotropic hormone status).
Prolactin measurement
Prolactin measurement is important to evaluate for hyperprolactinemia, as this will lead to hypogonadism by inhibition of GnRH secretion.25 Different pathologic, pharmacologic, and physiologic conditions can result in hyperprolactinemia, including prolactinomas, other pituitary and hypothalamic lesions, primary hypothyroidism, and medications such as antipsychotics.25 Dopamine agonists are the mainstay treatment for hyperprolactinemia.
Ferritin measurement
Ferritin measurement is indicated to diagnose iron overload conditions such as hemochromatosis, which can result in primary hypogonadism via testicular damage or in secondary hypogonadism via pituitary damage.26
Pituitary MRI with contrast
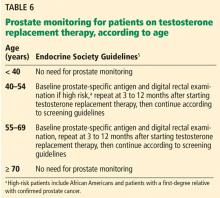
Pituitary MRI with contrast is used to diagnose structural lesions of the pituitary or hypothalamus. This diagnostic modality is indicated for patients with pituitary dysfunction, including central hypogonadism, manifestations of a mass effect (headache, visual field defects), persistent hyperprolactinemia, and panhypopituitarism, among others. To improve the diagnostic yield of pituitary MRI, the Endocrine Society guidelines recommend it for men with serum total testosterone levels below 150 ng/dL.5 However, some clinicians have a lower threshold for ordering pituitary MRI for patients with central hypogonadism. Physician judgment and expertise should be exercised and the decision made on an individual basis.
Chromosomal karyotyping
Chromosomal karyotyping is not indicated in our patient. It is reserved for those with primary hypogonadism to diagnose Klinefelter syndrome, which has a karyotype of 47,XXY.
CASE RESUMED: MOSH SYNDROME
Our patient’s prolactin, free T4, morning cortisol, and ferritin levels are measured, yielding normal values. No abnormalities are seen on pituitary MRI. A clinical reevaluation is conducted, revealing no history of head trauma or head and neck radiation. The lack of an obvious cause in our patient’s clinical presentation and workup, together with his obesity (BMI 32.8 kg/m2) supports the diagnosis of obesity as the cause of his hypogonadism.
Obesity can be a cause of secondary hypogonadism, which has led to the term “MOSH” (male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism) syndrome. In fact, a cross-sectional study has demonstrated that 40% of nondiabetic obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) men over age 45 have low serum free testosterone levels, compared with 26% for lean (BMI < 25 kg/m2) men.27 Moreover, obesity has been found to be a strong predictor of testosterone replacement therapy.28 Other studies have also found an inverse relationship between BMI and testosterone levels.29
Several mechanisms interact in the pathogenesis of MOSH syndrome. Adipose tissue possesses aromatase activity, which converts androgens into estrogens.30 Peripheral estrogen production can in turn exert feedback inhibition on pituitary gonadotropin secretion.31 In obese men, increased adipose tissue leads to increased aromatase activity and more estrogen, so more feedback inhibition on the pituitary and subsequently secondary hypogonadism.
Leptin, a hormone produced by adipocytes, is also increased in obesity, and was found to be inversely correlated with serum testosterone.32 Studies have demonstrated that leptin has an inhibitory effect on the enzymatic pathway that synthesizes testosterone in Leydig cells.33
Proinflammatory cytokines have also been implicated, as central obesity is associated with an increase in these cytokines, which in turn act negatively on the hypothalamus and impair GnRH release leading to lower testosterone.34,35
Treating obesity-related hypogonadism
In a pilot study,36 lifestyle attempts to reduce obesity were shown to improve hormonal levels. Bariatric surgery has also been demonstrated to be successful.37
Clomiphene citrate, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, increases endogenous testosterone secretion by inhibiting the negative feedback of estrogen on the hypothalamus and pituitary and thus increasing LH and FSH. It also preserves endogenous testosterone production, since it does not suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.38 This made clomiphene citrate a potential treatment for men with central hypogonadism including those with MOSH.39
Nevertheless, there are no randomized trials to prove its safety and efficacy in the management of central hypogonadism.5 Regarding its use in men wishing to preserve fertility, most studies did not show improvement. However, a meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant increased pregnancy rates in partners of men with idiopathic infertility if the men used 50 mg of clomiphene citrate daily.40
Testosterone deficiency can be a marker of metabolic syndrome, which needs to be managed more urgently than hypogonadism. A cross-sectional study found not only an association between metabolic syndrome and low serum testosterone, but also with each individual component of metabolic syndrome on its own, all of which need to be addressed.10
CASE CONTINUED: BEGINNING TREATMENT
The physician counsels the patient regarding the implications, potential adverse outcomes, and available treatments for his obesity, including lifestyle modification and bariatric surgery. The patient declines surgery and wishes to adopt a weight-reducing diet and exercise program, for which he is referred to a dietitian.
In addition, in view of the patient’s clinically and biochemically proven hypogonadism, his physician offers testosterone replacement therapy. He orders a serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, which is 1.3 ng/dL (reference range < 4 ng/dL). The patient is prescribed 5 g of 1% testosterone gel daily.
TESTOSTERONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY
4. Which is the most common adverse effect of testosterone replacement therapy?
- Cardiovascular events
- Erythrocytosis
- Prostate cancer
- Infertility
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Clinicians should be very cautious in initiating testosterone replacement therapy in any patient with an unstable medical condition.
There are several formulations of testosterone replacement therapy, including intramuscular injections, transdermal gels or patches, buccal tablets, an intranasal gel, and oral tablets. Of note, there are 2 different forms of oral testosterone preparations: testosterone undecanoate and 17-alpha alkylated testosterone. The former is unavailable in the United States and the latter is not recommended for use due to its proven hepatic toxicity.41
Testosterone and erythrocytosis
Meta-analyses have concluded that the most frequent adverse event of testosterone replacement therapy is a significant rise in hematocrit.42 This rise was found to be dose-dependent and was more marked in older men.43 Although all preparations can cause erythrocytosis, parenteral forms have been observed to raise it the most, particularly short-term injectables.44,45
The mechanism behind this increase is attributed to increased erythropoietin levels and improved usage of iron for red blood cell synthesis.46 In fact, testosterone replacement therapy has been shown to improve hemoglobin levels in patients with anemia.47 On the other hand, increasing hematocrit levels may lead to thrombotic and vasoocclusive events.44
Testosterone and prostate cancer
The relationship between testosterone treatment and prostate cancer has long been studied. Historically, testosterone replacement therapy was believed to increase the risk of prostate cancer; however, recent studies and meta-analyses have shown that this is not the case.42,48 Nevertheless, clinical guidelines still recommend prostate monitoring for men on testosterone replacement therapy.5,6
Testosterone and cardiovascular risk
The evidence regarding this issue has been contradictory and inconsistent. Meta-analyses have demonstrated that low testosterone is associated with higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.50 These studies argue for the use of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men to decrease the risk. However, other studies and meta-analyses have found that testosterone replacement therapy is associated with increased cardiovascular risk and have concluded that major adverse cardiac events are in fact a risk of testosterone replacement therapy.51
Current recommendations advocate against the use of testosterone replacement therapy in men with uncontrolled heart failure or with cardiovascular events in the past 3 to 6 months.5,6 Cardiovascular risk factors should be addressed and corrected, and patients should be educated on cardiovascular symptoms and the need to report them if they occur.
Testosterone and infertility
As described earlier, testosterone replacement therapy increases negative feedback on the pituitary and decreases LH and FSH production, leading to less spermatogenesis. Other treatment options should be sought for hypogonadal men wishing to preserve fertility.
Other adverse effects
Other adverse effects of testosterone replacement therapy include acne, oily skin, obstructive sleep apnea, gynecomastia, and balding.
Given all the adverse events that can be associated with testosterone replacement therapy, the risks and benefits of treating hypogonadism in each patient should be taken into consideration, and an individualized approach is required.
CASE RESUMED: FOLLOW-UP
The patient presents 3 months later for follow-up. He reports significant improvement in his presenting symptoms including energy, libido, and erectile function. He also reports some improvement in his mood and concentration. He has lost 12 lb (5.4 kg) and is still trying to improve his diet and exercise program. He is compliant with his testosterone gel therapy.
His serum calculated free testosterone level is 7.8 ng/dL (4.5–17), and his hematocrit is 46%. The patient is instructed to continue his treatment and to return after 9 months for further follow-up.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Men with hypogonadism usually present with nonspecific manifestations, so clinicians should keep a high index of suspicion.
- Both clinical and biochemical evidence of hypogonadism should be present to diagnose and start treatment for it.
- Low levels of serum total testosterone do not necessarily reflect hypogonadism.
- The hormonal profile of central hypogonadism reveals low serum testosterone with low or inappropriately normal serum LH and FSH levels.
Obesity can cause central hypogonadism and should be suspected after pituitary and other systemic causes are excluded.
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, et al. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(11):4241–4247. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1245
- Wu FCW, Tajar A, Beynon JM, et al; EMAS Group. Identification of late-onset hypogonadism in middle-aged and elderly men. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(2):123–135. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911101
- Arver S, Lehtihet M. Current guidelines for the diagnosis of testosterone deficiency. Front Horm Res 2009; 37:5–20. doi:10.1159/000175839
- Narula HS, Carlson HE. Gynaecomastia—pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2014; 10(11):684–698. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2014.139
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018; 103(5):1715–1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol 2018; 200(2):423–432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Balasubramanian V, Naing S. Hypogonadism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: incidence and effects. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2012; 18(2):112–117. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e32834feb37
- Atlantis E, Fahey P, Cochrane B, Wittert G, Smith S. Endogenous testosterone level and testosterone supplementation therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2013; 3(8)pii:e003127. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003127
- Bawor M, Bami H, Dennis BB, et al. Testosterone suppression in opioid users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend 2015; 149:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.01.038
- Tan WS, Ng CJ, Khoo EM, Low WY, Tan HM. The triad of erectile dysfunction, testosterone deficiency syndrome and metabolic syndrome: findings from a multi-ethnic Asian men study (The Subang Men's Health Study). Aging Male 2011; 14(4):231–236. doi:10.3109/13685538.2011.597463
- Goldman AL, Bhasin S, Wu FCW, Krishna M, Matsumoto AM, Jasuja R. A reappraisal of testosterone’s binding in circulation: physiological and clinical implications. Endocr Rev 2017; 38(4):302–324. doi:10.1210/er.2017-00025
- Antonio L, Wu FC, O’Neill TW, et al; European Male Ageing Study Study Group. Low free testosterone is associated with hypogonadal signs and symptoms in men with normal total testosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016; 101(7):2647–2657. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-4106
- Liu F, Shen X, Wang R, et al. Association of central obesity with sex hormone binding globulin: a cross-sectional study of 1166 Chinese men. Open Med (Wars) 2018; 13:196–202. doi:10.1515/med-2018-0030
- Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM. A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3666–3672. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6079
- Halmenschlager G, Rhoden EL, Riedner CE. Calculated free testosterone and radioimmunoassay free testosterone as a predictor of subnormal levels of total testosterone. Int Urol Nephrol 2012; 44(3):673–681. doi:10.1007/s11255-011-0066-z
- Brambilla DJ, Matsumoto AM, Araujo AB, McKinlay JB. The effect of diurnal variation on clinical measurement of serum testosterone and other sex hormone levels in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94(3):907–913. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1902
- Lehtihet M, Arver S, Bartuseviciene I, Pousette Å. S-testosterone decrease after a mixed meal in healthy men independent of SHBG and gonadotrophin levels. Andrologia 2012; 44(6):405–410. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.2012.01296.x
- Brambilla DJ, O’Donnell AB, Matsumoto AM, McKinlay JB. Intraindividual variation in levels of serum testosterone and other reproductive and adrenal hormones in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007; 67(6):853–862. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02976.x
- Manzoor SM, Sattar A, Hashim R, et al. Serum inhibin B as a diagnostic marker of male infertility. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2012; 24(3–4):113–116. pmid:24669628
- Kolb BA, Stanczyk FZ, Sokol RZ. Serum inhibin B levels in males with gonadal dysfunction. Fertil Steril 2000; 74(2):234–238. pmid:10927037
- Trambas CM, Sikaris KA, Lu ZX. More on biotin treatment mimicking Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med 2016; 375(17):1698. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1611875
- Li F, Yue H, Yamaguchi K, et al. Effect of surgical repair on testosterone production in infertile men with varicocele: a meta-analysis. Int J Urol 2012; 19(2):149–154. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2011.02890.x
- Crosnoe-Shipley LE, Elkelany OO, Rahnema CD, Kim ED. Treatment of hypogonadotropic male hypogonadism: case-based scenarios. World J Nephrol 2015; 4(2):245–253. doi:10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.245
- Majzoub A, Sabanegh E Jr. Testosterone replacement in the infertile man. Transl Androl Urol 2016; 5(6):859–865. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.08.03
- Majumdar A, Mangal NS. Hyperprolactinemia. J Hum Reprod Sci 2013; 6(3):168–175. doi:10.4103/0974-1208.121400
- El Osta R, Grandpre N, Monnin N, Hubert J, Koscinski I. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in men with hereditary hemochromatosis. Basic Clin Androl 2017; 27:13. doi:10.1186/s12610-017-0057-8
- Dhindsa S, Miller MG, McWhirter CL, et al. Testosterone concentrations in diabetic and nondiabetic obese men. Diabetes Care 2010; 33(6):1186–1192. doi:10.2337/dc09-1649
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med 2017; 32(3):304–311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Kaplan SA, Lee JY, O’Neill EA, Meehan AG, Kusek JW. Prevalence of low testosterone and its relationship to body mass index in older men with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Aging Male 2013; 16(4):169–172. doi:10.3109/13685538.2013.844786
- Lee HK, Lee JK, Cho B. The role of androgen in the adipose tissue of males. World J Mens Health 2013; 31(2):136–140. doi:10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.2.136
- Raven G, De Jong FH, Kaufman JM, De Ronde W. In men, peripheral estradiol levels directly reflect the action of estrogens at the hypothalamo-pituitary level to inhibit gonadotropin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91(9):3324–3328. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0462
- Hofny ER, Ali ME, Abdel-Hafez HZ, et al. Semen parameters and hormonal profile in obese fertile and infertile males. Fertil Steril 2010; 94(2):581–584. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.085
- Isidori AM, Caprio M, Strollo F, et al. Leptin and androgens in male obesity: evidence for leptin contribution to reduced androgen levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3673–3680. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6082
- El-Wakkad A, Hassan NM, Sibaii H, El-Zayat SR. Proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 2013; 61(2):682–687. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.11.010
- Maggio M, Basaria S, Ceda GP, et al. The relationship between testosterone and molecular markers of inflammation in older men. J Endocrinol Invest 2005; 28(suppl proceedings 11):116–119. pmid:16760639
- de Lorenzo A, Noce A, Moriconi E, et al. MOSH syndrome (male obesity secondary hypogonadism): clinical assessment and possible therapeutic approaches. Nutrients 2018; 10(4)pii:E474. doi:10.3390/nu10040474
- Escobar-Morreale HF, Santacruz E, Luque-Ramírez M, Botella Carretero JI. Prevalence of ‘obesity-associated gonadal dysfunction’ in severely obese men and women and its resolution after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 2017; 23(4):390–408. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmx012
- Lo EM, Rodriguez KM, Pastuszak AW, Khera M. Alternatives to testosterone therapy: a review. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):106–113. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.09.004
- Soares AH, Horie NC, Chiang LAP, et al. Effects of clomiphene citrate on male obesity-associated hypogonadism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2018; 42(5):953–963. doi:10.1038/s41366-018-0105-2
- Chua ME, Escusa KG, Luna S, Tapia LC, Dofitas B, Morales M. Revisiting oestrogen antagonists (clomiphene or tamoxifen) as medical empiric therapy for idiopathic male infertility: a meta-analysis. Andrology 2013; 1(5):749–757. doi:10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00107.x
- Westaby D, Ogle SJ, Paradinas FJ, Randell JB, Murray-Lyon IM. Liver damage from long-term methyltestosterone. Lancet 1977; 2(8032):262–263. pmid:69876
- Fernández-Balsells MM, Murad MH, Lane M, et al. Clinical review 1: Adverse effects of testosterone therapy in adult men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(6):2560–2575. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2575
- Coviello AD, Kaplan B, Lakshman KM, Chen T, Singh AB, Bhasin S. Effects of graded doses of testosterone on erythropoiesis in healthy young and older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93(3):914–919. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1692
- Ohlander SJ, Varghese B, Pastuszak AW. Erythrocytosis following testosterone therapy. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):77–85. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.04.001
- Jones SD Jr, Dukovac T, Sangkum P, Yafi FA, Hellstrom WJ. Erythrocytosis and polycythemia secondary to testosterone replacement therapy in the aging male. Sex Med Rev 2015; 3(2):101–112. doi:10.1002/smrj.43
- Bachman E, Travison TG, Basaria S, et al. Testosterone induces erythrocytosis via increased erythropoietin and suppressed hepcidin: evidence for a new erythropoietin/hemoglobin set point. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2014; 69(6):725–735. doi:10.1093/gerona/glt154
- Roy CN, Snyder PJ, Stephens-Shields AJ, et al. Association of testosterone levels with anemia in older men: a controlled clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2017; 177(4):480–490. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9540
- Klap J, Schmid M, Loughlin KR. The relationship between total testosterone levels and prostate cancer: a review of the continuing controversy. J Urol 2015; 193(2):403–413. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.07.123
- Gilbert SM, Cavallo CB, Kahane H, Lowe FC. Evidence suggesting PSA cutpoint of 2.5 ng/mL for prompting prostate biopsy: review of 36,316 biopsies. Urology 2005; 65(3):549–553. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2004.10.064
- Araujo AB, Dixon JM, Suarez EA, Murad MH, Guey LT, Wittert GA. Clinical review: Endogenous testosterone and mortality in men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96(10):3007–3019. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1137
- Xu L, Freeman G, Cowling BJ, Schooling CM. Testosterone therapy and cardiovascular events among men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. BMC Med 2013; 11:108. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-108
A 48-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because of progressively decreasing energy and gradual decline in both libido and erectile function for the past 18 months. He has noticed decreased morning erections as well. He rates his libido at 3 to 4 on a scale of 10 for the past 6 months. He also reports poor motivation, depressed mood, impaired concentration, and sleep disturbances. He reports no hair loss, headache, or dizziness, and no decrease in shaving frequency. Review of his systems is otherwise unremarkable.
He has had dyslipidemia for 3 years and is not known to have hypertension or diabetes. His medications include atorvastatin, vitamin E, and multivitamins.
He is married with 3 children and does not wish to have more. He works as a software engineer and leads a sedentary lifestyle. He is a nonsmoker and occasionally drinks alcohol on the weekends.
On physical examination, he is alert and oriented and appears well. His height is 5 feet 10 inches (178 cm), weight 230 lb (104 kg), and body mass index (BMI) 32.8 kg/m2. His blood pressure is 115/83 mm Hg and pulse rate is 82 beats per minute and regular. Findings on cardiovascular and pulmonary examination are normal. He has large fatty breasts but without palpable glandular tissue.
Genitourinary examination reveals normal hair distribution, a normal-sized penis, and slightly soft testes with testicular volume of 18–20 mL bilaterally.
His primary care physician suspects that he has low testosterone and orders some basic laboratory tests; the results are normal except for a low total testosterone level (Table 1).
FURTHER TESTING
1. Which of the following tests should his physician order next?
- Repeat total testosterone measurement
- Free testosterone measurement by commercial assay
- Calculated free testosterone
- Bioavailable testosterone measurement
- Serum inhibin B measurement
This patient presents with several nonspecific symptoms. But collectively they suggest testosterone deficiency (hypogonadism).
Together, erectile dysfunction, low libido, and decreased morning erections strongly suggest hypogonadism.2 Loss of body hair and decreased shaving frequency are specific symptoms of hypogonadism; however, they require years to develop.3 Gynecomastia can also occur due to loss of the inhibitory action of testosterone on breast growth and a relative increase in estradiol. This occurs more in primary hypogonadism, due to the increase in luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates the remaining Leydig cells to secrete estradiol rather than testosterone.4
To diagnose hypogonadism in men and to start treatment for it, current guidelines recommend that the patient should have clinical features as well as laboratory evidence of low testosterone.5,6
Measuring testosterone: Total, free, bound, and bioavailable
Testosterone, a steroid hormone, circulates in the serum either as free testosterone or bound to several plasma proteins, mainly sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin.
Total testosterone includes both the free and bound fractions, whereas bioavailable testosterone includes both free and the portion bound to albumin, which has low affinity and can dissociate and be used at the tissue level.11
Low levels of total testosterone do not necessarily reflect a hypogonadal state, as a man with altered SHBG levels or binding capabilities can have low total but normal free testosterone levels and no manifestations.12 Several conditions can alter the levels of SHBG, including obesity, diabetes, aging, thyroid dysfunction, and others.5,13
Because our patient is obese, his total testosterone level is not a reliable indicator of hypogonadism, and repeating its measurement will not add diagnostic value.
Therefore, an alternative measurement should be used to accurately reflect the testosterone levels. From a physiologic point of view, bioavailable testosterone is the active form of testosterone and is the most accurate to be measured in a patient with hypogonadism. Nevertheless, because of technical difficulties in its measurement and lack of evidence correlating bioavailable testosterone with the clinical picture of hypogonadism, it is recommended that the level of free testosterone be used.5
The gold standard for direct measurement of serum free testosterone is equilibrium dialysis, but this is expensive and time-consuming.14 Commercial assays for free testosterone exist but have been deemed unreliable.14,15 It is recommended that free testosterone be measured by equilibrium dialysis or calculated using equations based on total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin levels.5 These equations are reliable and give results very close to the values obtained by equilibrium dialysis.15 Therefore, in our patient, it would be suitable to calculate the free testosterone level next.
Serum levels of free testosterone vary according to several factors. Diurnal variation of testosterone has been established: levels are highest in the morning and decline throughout the day.16 Food decreases testosterone levels.17 In addition, there is considerable day-to-day variation.18 Therefore, at least 2 readings of fasting morning testosterone on 2 separate days are recommended for the diagnosis of hypogonadism.5
Inhibin B is a hormone produced by Sertoli cells in the testes in response to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulation. In turn, it acts as negative feedback, together with testosterone, to inhibit FSH release from the pituitary. Inhibin B has been shown to reflect spermatogenesis in the testes and therefore fertility.19 Inhibin B levels were found to be low in patients with central hypogonadism, due to less FSH release; however, they did not correlate with testosterone levels.20
CASE RESUMED: CHARACTERIZING HIS HYPOGONADISM
The patient’s physician orders morning fasting total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin testing and calculates the free testosterone level, which yields a value of 3 ng/dL (reference range 4.5–17). This is confirmed by a repeat measurement, which yields a value of 2.9 ng/dL. Laboratory test results combined with his clinical presentation are consistent with hypogonadism.
2. What is the most appropriate next step?
- Measurement of serum LH and FSH
- Measurement of serum prolactin
- Scrotal ultrasonography
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test
- Semen analysis
After hypogonadism is diagnosed, it is important to distinguish if it is primary or central. This is achieved by measuring serum LH and FSH.5 All biotin supplements should be stopped at least 72 hours before measuring LH and FSH, as biotin can interfere with the assays, yielding false values.21
Secretion of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary is under the influence of pulsatile release of GnRH from the hypothalamus. LH acts on Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, whereas FSH acts on Sertoli cells, together with testosterone, to bring about spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules. Testosterone acts centrally as negative feedback to decrease the release of LH and FSH.
Primary hypogonadism occurs due to testicular failure, ie, the testes themselves fail to produce testosterone, leading to hypogonadism. The decrease in testosterone levels, together with inhibin B if Sertoli cells are damaged, lead to loss of negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary, and therefore increased levels of LH and FSH. This is termed hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Testicular failure may also result in impaired spermatogenesis and infertility due to destruction of testicular structures, in which case fertility cannot be restored.
Central hypogonadism occurs when the pituitary fails to produce LH and FSH (secondary hypogonadism) or when the hypothalamus fails to produce GnRH and subsequently the lack of secretion of LH and FSH from the pituitary (tertiary hypogonadism). The lack of LH will result in no stimulation of Leydig cells to produce testosterone, and therefore its deficiency. Serum hormone levels in central hypogonadism will reveal low testosterone, with either low or inappropriately normal gonadotropins (LH and FSH). This is termed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The lack of FSH, together with testosterone deficiency will also result in decreased spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. Testicular structures are preserved, however, and fertility can be restored with appropriate therapy, as discussed below.
Prolactin should be measured only if the patient has central hypogonadism. Its measurement is not warranted at this point in the patient’s workup. The implications of prolactin and its relationship to hypogonadism will be discussed later.
Although, this stepwise approach is not convenient for many patients, some physicians follow it because it is cost-effective, especially in those who are not insured. However, other physicians order FSH, LH, and sometimes prolactin with the confirmatory low testosterone measurement. Laboratories can also be instructed to wait to measure the pituitary hormones and to do so only if low testosterone is confirmed.
Varicocele, a possible cause of male infertility, can also impair Leydig cell function and cause low testosterone. In fact, surgical repair of varicocele has been demonstrated to increase serum testosterone.22 Scrotal ultrasonography is used to diagnose varicocele, but this also should be ordered at a later stage in the workup if primary hypogonadism is diagnosed.
The GnRH stimulation test is important for the diagnosis and evaluation of precocious or delayed puberty in children. In boys with delayed puberty, a poorer response to GnRH stimulation indicates central hypogonadism rather than constitutional delay.23 It has no role in the evaluation of postpubertal or adult-onset hypogonadism.
Semen analysis is important to evaluate fertility if the patient is interested in further procreation.5 Low testosterone levels may result in impaired spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. On the other hand, treatment with exogenous testosterone will also result in infertility, by feedback inhibition of LH and FSH and therefore inhibition of spermatogenesis. If the patient wishes to preserve fertility, treatment options other than testosterone should be considered; examples include clomiphene citrate, human menopausal gonadotropin, and human chorionic gonadotropin.23,24
Our patient has no desire to expand his family; therefore, a semen analysis and attempts to preserve spermatogenesis are not indicated.
CASE RESUMED: SEARCHING FOR CAUSES
His physician orders testing of serum LH and FSH, yielding the following values:
- LH 1.6 mIU/mL (reference range 1.8–12)
- FSH 1.9 mIU/mL (reference range 1.5–12.5).
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism is established.
3. Which investigation is the least appropriate in the further evaluation of this patient?
- Serum prolactin measurement
- Serum ferritin measurement
- Pituitary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Chromosomal karyotyping
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism warrants evaluation for possible causes. These are summarized in Table 4.
Serum free thyroxine and morning cortisol
Since this patient’s LH and FSH values are abnormal, it is important to evaluate the status of other anterior pituitary hormones. In patients with pituitary abnormalities, serum free T4 is a more reliable test for assessing thyroid function than thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), because of loss of the negative feedback of thyroid hormones on the diseased pituitary. In contrast, serum TSH is considered the best single thyroid test to assess primary thyroid dysfunction.
Other measurements include prolactin and morning cortisol (reflecting adrenocorticotropic hormone status).
Prolactin measurement
Prolactin measurement is important to evaluate for hyperprolactinemia, as this will lead to hypogonadism by inhibition of GnRH secretion.25 Different pathologic, pharmacologic, and physiologic conditions can result in hyperprolactinemia, including prolactinomas, other pituitary and hypothalamic lesions, primary hypothyroidism, and medications such as antipsychotics.25 Dopamine agonists are the mainstay treatment for hyperprolactinemia.
Ferritin measurement
Ferritin measurement is indicated to diagnose iron overload conditions such as hemochromatosis, which can result in primary hypogonadism via testicular damage or in secondary hypogonadism via pituitary damage.26
Pituitary MRI with contrast
Pituitary MRI with contrast is used to diagnose structural lesions of the pituitary or hypothalamus. This diagnostic modality is indicated for patients with pituitary dysfunction, including central hypogonadism, manifestations of a mass effect (headache, visual field defects), persistent hyperprolactinemia, and panhypopituitarism, among others. To improve the diagnostic yield of pituitary MRI, the Endocrine Society guidelines recommend it for men with serum total testosterone levels below 150 ng/dL.5 However, some clinicians have a lower threshold for ordering pituitary MRI for patients with central hypogonadism. Physician judgment and expertise should be exercised and the decision made on an individual basis.
Chromosomal karyotyping
Chromosomal karyotyping is not indicated in our patient. It is reserved for those with primary hypogonadism to diagnose Klinefelter syndrome, which has a karyotype of 47,XXY.
CASE RESUMED: MOSH SYNDROME
Our patient’s prolactin, free T4, morning cortisol, and ferritin levels are measured, yielding normal values. No abnormalities are seen on pituitary MRI. A clinical reevaluation is conducted, revealing no history of head trauma or head and neck radiation. The lack of an obvious cause in our patient’s clinical presentation and workup, together with his obesity (BMI 32.8 kg/m2) supports the diagnosis of obesity as the cause of his hypogonadism.
Obesity can be a cause of secondary hypogonadism, which has led to the term “MOSH” (male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism) syndrome. In fact, a cross-sectional study has demonstrated that 40% of nondiabetic obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) men over age 45 have low serum free testosterone levels, compared with 26% for lean (BMI < 25 kg/m2) men.27 Moreover, obesity has been found to be a strong predictor of testosterone replacement therapy.28 Other studies have also found an inverse relationship between BMI and testosterone levels.29
Several mechanisms interact in the pathogenesis of MOSH syndrome. Adipose tissue possesses aromatase activity, which converts androgens into estrogens.30 Peripheral estrogen production can in turn exert feedback inhibition on pituitary gonadotropin secretion.31 In obese men, increased adipose tissue leads to increased aromatase activity and more estrogen, so more feedback inhibition on the pituitary and subsequently secondary hypogonadism.
Leptin, a hormone produced by adipocytes, is also increased in obesity, and was found to be inversely correlated with serum testosterone.32 Studies have demonstrated that leptin has an inhibitory effect on the enzymatic pathway that synthesizes testosterone in Leydig cells.33
Proinflammatory cytokines have also been implicated, as central obesity is associated with an increase in these cytokines, which in turn act negatively on the hypothalamus and impair GnRH release leading to lower testosterone.34,35
Treating obesity-related hypogonadism
In a pilot study,36 lifestyle attempts to reduce obesity were shown to improve hormonal levels. Bariatric surgery has also been demonstrated to be successful.37
Clomiphene citrate, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, increases endogenous testosterone secretion by inhibiting the negative feedback of estrogen on the hypothalamus and pituitary and thus increasing LH and FSH. It also preserves endogenous testosterone production, since it does not suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.38 This made clomiphene citrate a potential treatment for men with central hypogonadism including those with MOSH.39
Nevertheless, there are no randomized trials to prove its safety and efficacy in the management of central hypogonadism.5 Regarding its use in men wishing to preserve fertility, most studies did not show improvement. However, a meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant increased pregnancy rates in partners of men with idiopathic infertility if the men used 50 mg of clomiphene citrate daily.40
Testosterone deficiency can be a marker of metabolic syndrome, which needs to be managed more urgently than hypogonadism. A cross-sectional study found not only an association between metabolic syndrome and low serum testosterone, but also with each individual component of metabolic syndrome on its own, all of which need to be addressed.10
CASE CONTINUED: BEGINNING TREATMENT
The physician counsels the patient regarding the implications, potential adverse outcomes, and available treatments for his obesity, including lifestyle modification and bariatric surgery. The patient declines surgery and wishes to adopt a weight-reducing diet and exercise program, for which he is referred to a dietitian.
In addition, in view of the patient’s clinically and biochemically proven hypogonadism, his physician offers testosterone replacement therapy. He orders a serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, which is 1.3 ng/dL (reference range < 4 ng/dL). The patient is prescribed 5 g of 1% testosterone gel daily.
TESTOSTERONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY
4. Which is the most common adverse effect of testosterone replacement therapy?
- Cardiovascular events
- Erythrocytosis
- Prostate cancer
- Infertility
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Clinicians should be very cautious in initiating testosterone replacement therapy in any patient with an unstable medical condition.
There are several formulations of testosterone replacement therapy, including intramuscular injections, transdermal gels or patches, buccal tablets, an intranasal gel, and oral tablets. Of note, there are 2 different forms of oral testosterone preparations: testosterone undecanoate and 17-alpha alkylated testosterone. The former is unavailable in the United States and the latter is not recommended for use due to its proven hepatic toxicity.41
Testosterone and erythrocytosis
Meta-analyses have concluded that the most frequent adverse event of testosterone replacement therapy is a significant rise in hematocrit.42 This rise was found to be dose-dependent and was more marked in older men.43 Although all preparations can cause erythrocytosis, parenteral forms have been observed to raise it the most, particularly short-term injectables.44,45
The mechanism behind this increase is attributed to increased erythropoietin levels and improved usage of iron for red blood cell synthesis.46 In fact, testosterone replacement therapy has been shown to improve hemoglobin levels in patients with anemia.47 On the other hand, increasing hematocrit levels may lead to thrombotic and vasoocclusive events.44
Testosterone and prostate cancer
The relationship between testosterone treatment and prostate cancer has long been studied. Historically, testosterone replacement therapy was believed to increase the risk of prostate cancer; however, recent studies and meta-analyses have shown that this is not the case.42,48 Nevertheless, clinical guidelines still recommend prostate monitoring for men on testosterone replacement therapy.5,6
Testosterone and cardiovascular risk
The evidence regarding this issue has been contradictory and inconsistent. Meta-analyses have demonstrated that low testosterone is associated with higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.50 These studies argue for the use of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men to decrease the risk. However, other studies and meta-analyses have found that testosterone replacement therapy is associated with increased cardiovascular risk and have concluded that major adverse cardiac events are in fact a risk of testosterone replacement therapy.51
Current recommendations advocate against the use of testosterone replacement therapy in men with uncontrolled heart failure or with cardiovascular events in the past 3 to 6 months.5,6 Cardiovascular risk factors should be addressed and corrected, and patients should be educated on cardiovascular symptoms and the need to report them if they occur.
Testosterone and infertility
As described earlier, testosterone replacement therapy increases negative feedback on the pituitary and decreases LH and FSH production, leading to less spermatogenesis. Other treatment options should be sought for hypogonadal men wishing to preserve fertility.
Other adverse effects
Other adverse effects of testosterone replacement therapy include acne, oily skin, obstructive sleep apnea, gynecomastia, and balding.
Given all the adverse events that can be associated with testosterone replacement therapy, the risks and benefits of treating hypogonadism in each patient should be taken into consideration, and an individualized approach is required.
CASE RESUMED: FOLLOW-UP
The patient presents 3 months later for follow-up. He reports significant improvement in his presenting symptoms including energy, libido, and erectile function. He also reports some improvement in his mood and concentration. He has lost 12 lb (5.4 kg) and is still trying to improve his diet and exercise program. He is compliant with his testosterone gel therapy.
His serum calculated free testosterone level is 7.8 ng/dL (4.5–17), and his hematocrit is 46%. The patient is instructed to continue his treatment and to return after 9 months for further follow-up.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Men with hypogonadism usually present with nonspecific manifestations, so clinicians should keep a high index of suspicion.
- Both clinical and biochemical evidence of hypogonadism should be present to diagnose and start treatment for it.
- Low levels of serum total testosterone do not necessarily reflect hypogonadism.
- The hormonal profile of central hypogonadism reveals low serum testosterone with low or inappropriately normal serum LH and FSH levels.
Obesity can cause central hypogonadism and should be suspected after pituitary and other systemic causes are excluded.
A 48-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because of progressively decreasing energy and gradual decline in both libido and erectile function for the past 18 months. He has noticed decreased morning erections as well. He rates his libido at 3 to 4 on a scale of 10 for the past 6 months. He also reports poor motivation, depressed mood, impaired concentration, and sleep disturbances. He reports no hair loss, headache, or dizziness, and no decrease in shaving frequency. Review of his systems is otherwise unremarkable.
He has had dyslipidemia for 3 years and is not known to have hypertension or diabetes. His medications include atorvastatin, vitamin E, and multivitamins.
He is married with 3 children and does not wish to have more. He works as a software engineer and leads a sedentary lifestyle. He is a nonsmoker and occasionally drinks alcohol on the weekends.
On physical examination, he is alert and oriented and appears well. His height is 5 feet 10 inches (178 cm), weight 230 lb (104 kg), and body mass index (BMI) 32.8 kg/m2. His blood pressure is 115/83 mm Hg and pulse rate is 82 beats per minute and regular. Findings on cardiovascular and pulmonary examination are normal. He has large fatty breasts but without palpable glandular tissue.
Genitourinary examination reveals normal hair distribution, a normal-sized penis, and slightly soft testes with testicular volume of 18–20 mL bilaterally.
His primary care physician suspects that he has low testosterone and orders some basic laboratory tests; the results are normal except for a low total testosterone level (Table 1).
FURTHER TESTING
1. Which of the following tests should his physician order next?
- Repeat total testosterone measurement
- Free testosterone measurement by commercial assay
- Calculated free testosterone
- Bioavailable testosterone measurement
- Serum inhibin B measurement
This patient presents with several nonspecific symptoms. But collectively they suggest testosterone deficiency (hypogonadism).
Together, erectile dysfunction, low libido, and decreased morning erections strongly suggest hypogonadism.2 Loss of body hair and decreased shaving frequency are specific symptoms of hypogonadism; however, they require years to develop.3 Gynecomastia can also occur due to loss of the inhibitory action of testosterone on breast growth and a relative increase in estradiol. This occurs more in primary hypogonadism, due to the increase in luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates the remaining Leydig cells to secrete estradiol rather than testosterone.4
To diagnose hypogonadism in men and to start treatment for it, current guidelines recommend that the patient should have clinical features as well as laboratory evidence of low testosterone.5,6
Measuring testosterone: Total, free, bound, and bioavailable
Testosterone, a steroid hormone, circulates in the serum either as free testosterone or bound to several plasma proteins, mainly sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin.
Total testosterone includes both the free and bound fractions, whereas bioavailable testosterone includes both free and the portion bound to albumin, which has low affinity and can dissociate and be used at the tissue level.11
Low levels of total testosterone do not necessarily reflect a hypogonadal state, as a man with altered SHBG levels or binding capabilities can have low total but normal free testosterone levels and no manifestations.12 Several conditions can alter the levels of SHBG, including obesity, diabetes, aging, thyroid dysfunction, and others.5,13
Because our patient is obese, his total testosterone level is not a reliable indicator of hypogonadism, and repeating its measurement will not add diagnostic value.
Therefore, an alternative measurement should be used to accurately reflect the testosterone levels. From a physiologic point of view, bioavailable testosterone is the active form of testosterone and is the most accurate to be measured in a patient with hypogonadism. Nevertheless, because of technical difficulties in its measurement and lack of evidence correlating bioavailable testosterone with the clinical picture of hypogonadism, it is recommended that the level of free testosterone be used.5
The gold standard for direct measurement of serum free testosterone is equilibrium dialysis, but this is expensive and time-consuming.14 Commercial assays for free testosterone exist but have been deemed unreliable.14,15 It is recommended that free testosterone be measured by equilibrium dialysis or calculated using equations based on total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin levels.5 These equations are reliable and give results very close to the values obtained by equilibrium dialysis.15 Therefore, in our patient, it would be suitable to calculate the free testosterone level next.
Serum levels of free testosterone vary according to several factors. Diurnal variation of testosterone has been established: levels are highest in the morning and decline throughout the day.16 Food decreases testosterone levels.17 In addition, there is considerable day-to-day variation.18 Therefore, at least 2 readings of fasting morning testosterone on 2 separate days are recommended for the diagnosis of hypogonadism.5
Inhibin B is a hormone produced by Sertoli cells in the testes in response to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulation. In turn, it acts as negative feedback, together with testosterone, to inhibit FSH release from the pituitary. Inhibin B has been shown to reflect spermatogenesis in the testes and therefore fertility.19 Inhibin B levels were found to be low in patients with central hypogonadism, due to less FSH release; however, they did not correlate with testosterone levels.20
CASE RESUMED: CHARACTERIZING HIS HYPOGONADISM
The patient’s physician orders morning fasting total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin testing and calculates the free testosterone level, which yields a value of 3 ng/dL (reference range 4.5–17). This is confirmed by a repeat measurement, which yields a value of 2.9 ng/dL. Laboratory test results combined with his clinical presentation are consistent with hypogonadism.
2. What is the most appropriate next step?
- Measurement of serum LH and FSH
- Measurement of serum prolactin
- Scrotal ultrasonography
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test
- Semen analysis
After hypogonadism is diagnosed, it is important to distinguish if it is primary or central. This is achieved by measuring serum LH and FSH.5 All biotin supplements should be stopped at least 72 hours before measuring LH and FSH, as biotin can interfere with the assays, yielding false values.21
Secretion of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary is under the influence of pulsatile release of GnRH from the hypothalamus. LH acts on Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone, whereas FSH acts on Sertoli cells, together with testosterone, to bring about spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules. Testosterone acts centrally as negative feedback to decrease the release of LH and FSH.
Primary hypogonadism occurs due to testicular failure, ie, the testes themselves fail to produce testosterone, leading to hypogonadism. The decrease in testosterone levels, together with inhibin B if Sertoli cells are damaged, lead to loss of negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary, and therefore increased levels of LH and FSH. This is termed hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Testicular failure may also result in impaired spermatogenesis and infertility due to destruction of testicular structures, in which case fertility cannot be restored.
Central hypogonadism occurs when the pituitary fails to produce LH and FSH (secondary hypogonadism) or when the hypothalamus fails to produce GnRH and subsequently the lack of secretion of LH and FSH from the pituitary (tertiary hypogonadism). The lack of LH will result in no stimulation of Leydig cells to produce testosterone, and therefore its deficiency. Serum hormone levels in central hypogonadism will reveal low testosterone, with either low or inappropriately normal gonadotropins (LH and FSH). This is termed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The lack of FSH, together with testosterone deficiency will also result in decreased spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. Testicular structures are preserved, however, and fertility can be restored with appropriate therapy, as discussed below.
Prolactin should be measured only if the patient has central hypogonadism. Its measurement is not warranted at this point in the patient’s workup. The implications of prolactin and its relationship to hypogonadism will be discussed later.
Although, this stepwise approach is not convenient for many patients, some physicians follow it because it is cost-effective, especially in those who are not insured. However, other physicians order FSH, LH, and sometimes prolactin with the confirmatory low testosterone measurement. Laboratories can also be instructed to wait to measure the pituitary hormones and to do so only if low testosterone is confirmed.
Varicocele, a possible cause of male infertility, can also impair Leydig cell function and cause low testosterone. In fact, surgical repair of varicocele has been demonstrated to increase serum testosterone.22 Scrotal ultrasonography is used to diagnose varicocele, but this also should be ordered at a later stage in the workup if primary hypogonadism is diagnosed.
The GnRH stimulation test is important for the diagnosis and evaluation of precocious or delayed puberty in children. In boys with delayed puberty, a poorer response to GnRH stimulation indicates central hypogonadism rather than constitutional delay.23 It has no role in the evaluation of postpubertal or adult-onset hypogonadism.
Semen analysis is important to evaluate fertility if the patient is interested in further procreation.5 Low testosterone levels may result in impaired spermatogenesis and therefore infertility. On the other hand, treatment with exogenous testosterone will also result in infertility, by feedback inhibition of LH and FSH and therefore inhibition of spermatogenesis. If the patient wishes to preserve fertility, treatment options other than testosterone should be considered; examples include clomiphene citrate, human menopausal gonadotropin, and human chorionic gonadotropin.23,24
Our patient has no desire to expand his family; therefore, a semen analysis and attempts to preserve spermatogenesis are not indicated.
CASE RESUMED: SEARCHING FOR CAUSES
His physician orders testing of serum LH and FSH, yielding the following values:
- LH 1.6 mIU/mL (reference range 1.8–12)
- FSH 1.9 mIU/mL (reference range 1.5–12.5).
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism is established.
3. Which investigation is the least appropriate in the further evaluation of this patient?
- Serum prolactin measurement
- Serum ferritin measurement
- Pituitary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Chromosomal karyotyping
The diagnosis of central hypogonadism warrants evaluation for possible causes. These are summarized in Table 4.
Serum free thyroxine and morning cortisol
Since this patient’s LH and FSH values are abnormal, it is important to evaluate the status of other anterior pituitary hormones. In patients with pituitary abnormalities, serum free T4 is a more reliable test for assessing thyroid function than thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), because of loss of the negative feedback of thyroid hormones on the diseased pituitary. In contrast, serum TSH is considered the best single thyroid test to assess primary thyroid dysfunction.
Other measurements include prolactin and morning cortisol (reflecting adrenocorticotropic hormone status).
Prolactin measurement
Prolactin measurement is important to evaluate for hyperprolactinemia, as this will lead to hypogonadism by inhibition of GnRH secretion.25 Different pathologic, pharmacologic, and physiologic conditions can result in hyperprolactinemia, including prolactinomas, other pituitary and hypothalamic lesions, primary hypothyroidism, and medications such as antipsychotics.25 Dopamine agonists are the mainstay treatment for hyperprolactinemia.
Ferritin measurement
Ferritin measurement is indicated to diagnose iron overload conditions such as hemochromatosis, which can result in primary hypogonadism via testicular damage or in secondary hypogonadism via pituitary damage.26
Pituitary MRI with contrast
Pituitary MRI with contrast is used to diagnose structural lesions of the pituitary or hypothalamus. This diagnostic modality is indicated for patients with pituitary dysfunction, including central hypogonadism, manifestations of a mass effect (headache, visual field defects), persistent hyperprolactinemia, and panhypopituitarism, among others. To improve the diagnostic yield of pituitary MRI, the Endocrine Society guidelines recommend it for men with serum total testosterone levels below 150 ng/dL.5 However, some clinicians have a lower threshold for ordering pituitary MRI for patients with central hypogonadism. Physician judgment and expertise should be exercised and the decision made on an individual basis.
Chromosomal karyotyping
Chromosomal karyotyping is not indicated in our patient. It is reserved for those with primary hypogonadism to diagnose Klinefelter syndrome, which has a karyotype of 47,XXY.
CASE RESUMED: MOSH SYNDROME
Our patient’s prolactin, free T4, morning cortisol, and ferritin levels are measured, yielding normal values. No abnormalities are seen on pituitary MRI. A clinical reevaluation is conducted, revealing no history of head trauma or head and neck radiation. The lack of an obvious cause in our patient’s clinical presentation and workup, together with his obesity (BMI 32.8 kg/m2) supports the diagnosis of obesity as the cause of his hypogonadism.
Obesity can be a cause of secondary hypogonadism, which has led to the term “MOSH” (male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism) syndrome. In fact, a cross-sectional study has demonstrated that 40% of nondiabetic obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) men over age 45 have low serum free testosterone levels, compared with 26% for lean (BMI < 25 kg/m2) men.27 Moreover, obesity has been found to be a strong predictor of testosterone replacement therapy.28 Other studies have also found an inverse relationship between BMI and testosterone levels.29
Several mechanisms interact in the pathogenesis of MOSH syndrome. Adipose tissue possesses aromatase activity, which converts androgens into estrogens.30 Peripheral estrogen production can in turn exert feedback inhibition on pituitary gonadotropin secretion.31 In obese men, increased adipose tissue leads to increased aromatase activity and more estrogen, so more feedback inhibition on the pituitary and subsequently secondary hypogonadism.
Leptin, a hormone produced by adipocytes, is also increased in obesity, and was found to be inversely correlated with serum testosterone.32 Studies have demonstrated that leptin has an inhibitory effect on the enzymatic pathway that synthesizes testosterone in Leydig cells.33
Proinflammatory cytokines have also been implicated, as central obesity is associated with an increase in these cytokines, which in turn act negatively on the hypothalamus and impair GnRH release leading to lower testosterone.34,35
Treating obesity-related hypogonadism
In a pilot study,36 lifestyle attempts to reduce obesity were shown to improve hormonal levels. Bariatric surgery has also been demonstrated to be successful.37
Clomiphene citrate, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, increases endogenous testosterone secretion by inhibiting the negative feedback of estrogen on the hypothalamus and pituitary and thus increasing LH and FSH. It also preserves endogenous testosterone production, since it does not suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis.38 This made clomiphene citrate a potential treatment for men with central hypogonadism including those with MOSH.39
Nevertheless, there are no randomized trials to prove its safety and efficacy in the management of central hypogonadism.5 Regarding its use in men wishing to preserve fertility, most studies did not show improvement. However, a meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant increased pregnancy rates in partners of men with idiopathic infertility if the men used 50 mg of clomiphene citrate daily.40
Testosterone deficiency can be a marker of metabolic syndrome, which needs to be managed more urgently than hypogonadism. A cross-sectional study found not only an association between metabolic syndrome and low serum testosterone, but also with each individual component of metabolic syndrome on its own, all of which need to be addressed.10
CASE CONTINUED: BEGINNING TREATMENT
The physician counsels the patient regarding the implications, potential adverse outcomes, and available treatments for his obesity, including lifestyle modification and bariatric surgery. The patient declines surgery and wishes to adopt a weight-reducing diet and exercise program, for which he is referred to a dietitian.
In addition, in view of the patient’s clinically and biochemically proven hypogonadism, his physician offers testosterone replacement therapy. He orders a serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, which is 1.3 ng/dL (reference range < 4 ng/dL). The patient is prescribed 5 g of 1% testosterone gel daily.
TESTOSTERONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY
4. Which is the most common adverse effect of testosterone replacement therapy?
- Cardiovascular events
- Erythrocytosis
- Prostate cancer
- Infertility
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Clinicians should be very cautious in initiating testosterone replacement therapy in any patient with an unstable medical condition.
There are several formulations of testosterone replacement therapy, including intramuscular injections, transdermal gels or patches, buccal tablets, an intranasal gel, and oral tablets. Of note, there are 2 different forms of oral testosterone preparations: testosterone undecanoate and 17-alpha alkylated testosterone. The former is unavailable in the United States and the latter is not recommended for use due to its proven hepatic toxicity.41
Testosterone and erythrocytosis
Meta-analyses have concluded that the most frequent adverse event of testosterone replacement therapy is a significant rise in hematocrit.42 This rise was found to be dose-dependent and was more marked in older men.43 Although all preparations can cause erythrocytosis, parenteral forms have been observed to raise it the most, particularly short-term injectables.44,45
The mechanism behind this increase is attributed to increased erythropoietin levels and improved usage of iron for red blood cell synthesis.46 In fact, testosterone replacement therapy has been shown to improve hemoglobin levels in patients with anemia.47 On the other hand, increasing hematocrit levels may lead to thrombotic and vasoocclusive events.44
Testosterone and prostate cancer
The relationship between testosterone treatment and prostate cancer has long been studied. Historically, testosterone replacement therapy was believed to increase the risk of prostate cancer; however, recent studies and meta-analyses have shown that this is not the case.42,48 Nevertheless, clinical guidelines still recommend prostate monitoring for men on testosterone replacement therapy.5,6
Testosterone and cardiovascular risk
The evidence regarding this issue has been contradictory and inconsistent. Meta-analyses have demonstrated that low testosterone is associated with higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.50 These studies argue for the use of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men to decrease the risk. However, other studies and meta-analyses have found that testosterone replacement therapy is associated with increased cardiovascular risk and have concluded that major adverse cardiac events are in fact a risk of testosterone replacement therapy.51
Current recommendations advocate against the use of testosterone replacement therapy in men with uncontrolled heart failure or with cardiovascular events in the past 3 to 6 months.5,6 Cardiovascular risk factors should be addressed and corrected, and patients should be educated on cardiovascular symptoms and the need to report them if they occur.
Testosterone and infertility
As described earlier, testosterone replacement therapy increases negative feedback on the pituitary and decreases LH and FSH production, leading to less spermatogenesis. Other treatment options should be sought for hypogonadal men wishing to preserve fertility.
Other adverse effects
Other adverse effects of testosterone replacement therapy include acne, oily skin, obstructive sleep apnea, gynecomastia, and balding.
Given all the adverse events that can be associated with testosterone replacement therapy, the risks and benefits of treating hypogonadism in each patient should be taken into consideration, and an individualized approach is required.
CASE RESUMED: FOLLOW-UP
The patient presents 3 months later for follow-up. He reports significant improvement in his presenting symptoms including energy, libido, and erectile function. He also reports some improvement in his mood and concentration. He has lost 12 lb (5.4 kg) and is still trying to improve his diet and exercise program. He is compliant with his testosterone gel therapy.
His serum calculated free testosterone level is 7.8 ng/dL (4.5–17), and his hematocrit is 46%. The patient is instructed to continue his treatment and to return after 9 months for further follow-up.
TAKE-HOME POINTS
- Men with hypogonadism usually present with nonspecific manifestations, so clinicians should keep a high index of suspicion.
- Both clinical and biochemical evidence of hypogonadism should be present to diagnose and start treatment for it.
- Low levels of serum total testosterone do not necessarily reflect hypogonadism.
- The hormonal profile of central hypogonadism reveals low serum testosterone with low or inappropriately normal serum LH and FSH levels.
Obesity can cause central hypogonadism and should be suspected after pituitary and other systemic causes are excluded.
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, et al. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(11):4241–4247. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1245
- Wu FCW, Tajar A, Beynon JM, et al; EMAS Group. Identification of late-onset hypogonadism in middle-aged and elderly men. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(2):123–135. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911101
- Arver S, Lehtihet M. Current guidelines for the diagnosis of testosterone deficiency. Front Horm Res 2009; 37:5–20. doi:10.1159/000175839
- Narula HS, Carlson HE. Gynaecomastia—pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2014; 10(11):684–698. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2014.139
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018; 103(5):1715–1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol 2018; 200(2):423–432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Balasubramanian V, Naing S. Hypogonadism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: incidence and effects. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2012; 18(2):112–117. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e32834feb37
- Atlantis E, Fahey P, Cochrane B, Wittert G, Smith S. Endogenous testosterone level and testosterone supplementation therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2013; 3(8)pii:e003127. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003127
- Bawor M, Bami H, Dennis BB, et al. Testosterone suppression in opioid users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend 2015; 149:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.01.038
- Tan WS, Ng CJ, Khoo EM, Low WY, Tan HM. The triad of erectile dysfunction, testosterone deficiency syndrome and metabolic syndrome: findings from a multi-ethnic Asian men study (The Subang Men's Health Study). Aging Male 2011; 14(4):231–236. doi:10.3109/13685538.2011.597463
- Goldman AL, Bhasin S, Wu FCW, Krishna M, Matsumoto AM, Jasuja R. A reappraisal of testosterone’s binding in circulation: physiological and clinical implications. Endocr Rev 2017; 38(4):302–324. doi:10.1210/er.2017-00025
- Antonio L, Wu FC, O’Neill TW, et al; European Male Ageing Study Study Group. Low free testosterone is associated with hypogonadal signs and symptoms in men with normal total testosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016; 101(7):2647–2657. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-4106
- Liu F, Shen X, Wang R, et al. Association of central obesity with sex hormone binding globulin: a cross-sectional study of 1166 Chinese men. Open Med (Wars) 2018; 13:196–202. doi:10.1515/med-2018-0030
- Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM. A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3666–3672. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6079
- Halmenschlager G, Rhoden EL, Riedner CE. Calculated free testosterone and radioimmunoassay free testosterone as a predictor of subnormal levels of total testosterone. Int Urol Nephrol 2012; 44(3):673–681. doi:10.1007/s11255-011-0066-z
- Brambilla DJ, Matsumoto AM, Araujo AB, McKinlay JB. The effect of diurnal variation on clinical measurement of serum testosterone and other sex hormone levels in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94(3):907–913. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1902
- Lehtihet M, Arver S, Bartuseviciene I, Pousette Å. S-testosterone decrease after a mixed meal in healthy men independent of SHBG and gonadotrophin levels. Andrologia 2012; 44(6):405–410. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.2012.01296.x
- Brambilla DJ, O’Donnell AB, Matsumoto AM, McKinlay JB. Intraindividual variation in levels of serum testosterone and other reproductive and adrenal hormones in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007; 67(6):853–862. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02976.x
- Manzoor SM, Sattar A, Hashim R, et al. Serum inhibin B as a diagnostic marker of male infertility. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2012; 24(3–4):113–116. pmid:24669628
- Kolb BA, Stanczyk FZ, Sokol RZ. Serum inhibin B levels in males with gonadal dysfunction. Fertil Steril 2000; 74(2):234–238. pmid:10927037
- Trambas CM, Sikaris KA, Lu ZX. More on biotin treatment mimicking Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med 2016; 375(17):1698. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1611875
- Li F, Yue H, Yamaguchi K, et al. Effect of surgical repair on testosterone production in infertile men with varicocele: a meta-analysis. Int J Urol 2012; 19(2):149–154. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2011.02890.x
- Crosnoe-Shipley LE, Elkelany OO, Rahnema CD, Kim ED. Treatment of hypogonadotropic male hypogonadism: case-based scenarios. World J Nephrol 2015; 4(2):245–253. doi:10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.245
- Majzoub A, Sabanegh E Jr. Testosterone replacement in the infertile man. Transl Androl Urol 2016; 5(6):859–865. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.08.03
- Majumdar A, Mangal NS. Hyperprolactinemia. J Hum Reprod Sci 2013; 6(3):168–175. doi:10.4103/0974-1208.121400
- El Osta R, Grandpre N, Monnin N, Hubert J, Koscinski I. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in men with hereditary hemochromatosis. Basic Clin Androl 2017; 27:13. doi:10.1186/s12610-017-0057-8
- Dhindsa S, Miller MG, McWhirter CL, et al. Testosterone concentrations in diabetic and nondiabetic obese men. Diabetes Care 2010; 33(6):1186–1192. doi:10.2337/dc09-1649
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med 2017; 32(3):304–311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Kaplan SA, Lee JY, O’Neill EA, Meehan AG, Kusek JW. Prevalence of low testosterone and its relationship to body mass index in older men with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Aging Male 2013; 16(4):169–172. doi:10.3109/13685538.2013.844786
- Lee HK, Lee JK, Cho B. The role of androgen in the adipose tissue of males. World J Mens Health 2013; 31(2):136–140. doi:10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.2.136
- Raven G, De Jong FH, Kaufman JM, De Ronde W. In men, peripheral estradiol levels directly reflect the action of estrogens at the hypothalamo-pituitary level to inhibit gonadotropin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91(9):3324–3328. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0462
- Hofny ER, Ali ME, Abdel-Hafez HZ, et al. Semen parameters and hormonal profile in obese fertile and infertile males. Fertil Steril 2010; 94(2):581–584. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.085
- Isidori AM, Caprio M, Strollo F, et al. Leptin and androgens in male obesity: evidence for leptin contribution to reduced androgen levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3673–3680. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6082
- El-Wakkad A, Hassan NM, Sibaii H, El-Zayat SR. Proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 2013; 61(2):682–687. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.11.010
- Maggio M, Basaria S, Ceda GP, et al. The relationship between testosterone and molecular markers of inflammation in older men. J Endocrinol Invest 2005; 28(suppl proceedings 11):116–119. pmid:16760639
- de Lorenzo A, Noce A, Moriconi E, et al. MOSH syndrome (male obesity secondary hypogonadism): clinical assessment and possible therapeutic approaches. Nutrients 2018; 10(4)pii:E474. doi:10.3390/nu10040474
- Escobar-Morreale HF, Santacruz E, Luque-Ramírez M, Botella Carretero JI. Prevalence of ‘obesity-associated gonadal dysfunction’ in severely obese men and women and its resolution after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 2017; 23(4):390–408. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmx012
- Lo EM, Rodriguez KM, Pastuszak AW, Khera M. Alternatives to testosterone therapy: a review. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):106–113. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.09.004
- Soares AH, Horie NC, Chiang LAP, et al. Effects of clomiphene citrate on male obesity-associated hypogonadism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2018; 42(5):953–963. doi:10.1038/s41366-018-0105-2
- Chua ME, Escusa KG, Luna S, Tapia LC, Dofitas B, Morales M. Revisiting oestrogen antagonists (clomiphene or tamoxifen) as medical empiric therapy for idiopathic male infertility: a meta-analysis. Andrology 2013; 1(5):749–757. doi:10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00107.x
- Westaby D, Ogle SJ, Paradinas FJ, Randell JB, Murray-Lyon IM. Liver damage from long-term methyltestosterone. Lancet 1977; 2(8032):262–263. pmid:69876
- Fernández-Balsells MM, Murad MH, Lane M, et al. Clinical review 1: Adverse effects of testosterone therapy in adult men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(6):2560–2575. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2575
- Coviello AD, Kaplan B, Lakshman KM, Chen T, Singh AB, Bhasin S. Effects of graded doses of testosterone on erythropoiesis in healthy young and older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93(3):914–919. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1692
- Ohlander SJ, Varghese B, Pastuszak AW. Erythrocytosis following testosterone therapy. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):77–85. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.04.001
- Jones SD Jr, Dukovac T, Sangkum P, Yafi FA, Hellstrom WJ. Erythrocytosis and polycythemia secondary to testosterone replacement therapy in the aging male. Sex Med Rev 2015; 3(2):101–112. doi:10.1002/smrj.43
- Bachman E, Travison TG, Basaria S, et al. Testosterone induces erythrocytosis via increased erythropoietin and suppressed hepcidin: evidence for a new erythropoietin/hemoglobin set point. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2014; 69(6):725–735. doi:10.1093/gerona/glt154
- Roy CN, Snyder PJ, Stephens-Shields AJ, et al. Association of testosterone levels with anemia in older men: a controlled clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2017; 177(4):480–490. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9540
- Klap J, Schmid M, Loughlin KR. The relationship between total testosterone levels and prostate cancer: a review of the continuing controversy. J Urol 2015; 193(2):403–413. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.07.123
- Gilbert SM, Cavallo CB, Kahane H, Lowe FC. Evidence suggesting PSA cutpoint of 2.5 ng/mL for prompting prostate biopsy: review of 36,316 biopsies. Urology 2005; 65(3):549–553. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2004.10.064
- Araujo AB, Dixon JM, Suarez EA, Murad MH, Guey LT, Wittert GA. Clinical review: Endogenous testosterone and mortality in men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96(10):3007–3019. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1137
- Xu L, Freeman G, Cowling BJ, Schooling CM. Testosterone therapy and cardiovascular events among men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. BMC Med 2013; 11:108. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-108
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Kupelian V, et al. Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(11):4241–4247. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1245
- Wu FCW, Tajar A, Beynon JM, et al; EMAS Group. Identification of late-onset hypogonadism in middle-aged and elderly men. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(2):123–135. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0911101
- Arver S, Lehtihet M. Current guidelines for the diagnosis of testosterone deficiency. Front Horm Res 2009; 37:5–20. doi:10.1159/000175839
- Narula HS, Carlson HE. Gynaecomastia—pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2014; 10(11):684–698. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2014.139
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018; 103(5):1715–1744. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00229
- Mulhall JP, Trost LW, Brannigan RE, et al. Evaluation and management of testosterone deficiency: AUA guideline. J Urol 2018; 200(2):423–432. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.115
- Balasubramanian V, Naing S. Hypogonadism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: incidence and effects. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2012; 18(2):112–117. doi:10.1097/MCP.0b013e32834feb37
- Atlantis E, Fahey P, Cochrane B, Wittert G, Smith S. Endogenous testosterone level and testosterone supplementation therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2013; 3(8)pii:e003127. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003127
- Bawor M, Bami H, Dennis BB, et al. Testosterone suppression in opioid users: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend 2015; 149:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.01.038
- Tan WS, Ng CJ, Khoo EM, Low WY, Tan HM. The triad of erectile dysfunction, testosterone deficiency syndrome and metabolic syndrome: findings from a multi-ethnic Asian men study (The Subang Men's Health Study). Aging Male 2011; 14(4):231–236. doi:10.3109/13685538.2011.597463
- Goldman AL, Bhasin S, Wu FCW, Krishna M, Matsumoto AM, Jasuja R. A reappraisal of testosterone’s binding in circulation: physiological and clinical implications. Endocr Rev 2017; 38(4):302–324. doi:10.1210/er.2017-00025
- Antonio L, Wu FC, O’Neill TW, et al; European Male Ageing Study Study Group. Low free testosterone is associated with hypogonadal signs and symptoms in men with normal total testosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016; 101(7):2647–2657. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-4106
- Liu F, Shen X, Wang R, et al. Association of central obesity with sex hormone binding globulin: a cross-sectional study of 1166 Chinese men. Open Med (Wars) 2018; 13:196–202. doi:10.1515/med-2018-0030
- Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM. A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3666–3672. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6079
- Halmenschlager G, Rhoden EL, Riedner CE. Calculated free testosterone and radioimmunoassay free testosterone as a predictor of subnormal levels of total testosterone. Int Urol Nephrol 2012; 44(3):673–681. doi:10.1007/s11255-011-0066-z
- Brambilla DJ, Matsumoto AM, Araujo AB, McKinlay JB. The effect of diurnal variation on clinical measurement of serum testosterone and other sex hormone levels in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94(3):907–913. doi:10.1210/jc.2008-1902
- Lehtihet M, Arver S, Bartuseviciene I, Pousette Å. S-testosterone decrease after a mixed meal in healthy men independent of SHBG and gonadotrophin levels. Andrologia 2012; 44(6):405–410. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0272.2012.01296.x
- Brambilla DJ, O’Donnell AB, Matsumoto AM, McKinlay JB. Intraindividual variation in levels of serum testosterone and other reproductive and adrenal hormones in men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007; 67(6):853–862. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02976.x
- Manzoor SM, Sattar A, Hashim R, et al. Serum inhibin B as a diagnostic marker of male infertility. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2012; 24(3–4):113–116. pmid:24669628
- Kolb BA, Stanczyk FZ, Sokol RZ. Serum inhibin B levels in males with gonadal dysfunction. Fertil Steril 2000; 74(2):234–238. pmid:10927037
- Trambas CM, Sikaris KA, Lu ZX. More on biotin treatment mimicking Graves’ disease. N Engl J Med 2016; 375(17):1698. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1611875
- Li F, Yue H, Yamaguchi K, et al. Effect of surgical repair on testosterone production in infertile men with varicocele: a meta-analysis. Int J Urol 2012; 19(2):149–154. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2011.02890.x
- Crosnoe-Shipley LE, Elkelany OO, Rahnema CD, Kim ED. Treatment of hypogonadotropic male hypogonadism: case-based scenarios. World J Nephrol 2015; 4(2):245–253. doi:10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.245
- Majzoub A, Sabanegh E Jr. Testosterone replacement in the infertile man. Transl Androl Urol 2016; 5(6):859–865. doi:10.21037/tau.2016.08.03
- Majumdar A, Mangal NS. Hyperprolactinemia. J Hum Reprod Sci 2013; 6(3):168–175. doi:10.4103/0974-1208.121400
- El Osta R, Grandpre N, Monnin N, Hubert J, Koscinski I. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in men with hereditary hemochromatosis. Basic Clin Androl 2017; 27:13. doi:10.1186/s12610-017-0057-8
- Dhindsa S, Miller MG, McWhirter CL, et al. Testosterone concentrations in diabetic and nondiabetic obese men. Diabetes Care 2010; 33(6):1186–1192. doi:10.2337/dc09-1649
- Jasuja GK, Bhasin S, Reisman JI, et al. Who gets testosterone? Patient characteristics associated with testosterone prescribing in the Veteran Affairs system: a cross-sectional study. J Gen Intern Med 2017; 32(3):304–311. doi:10.1007/s11606-016-3940-7
- Kaplan SA, Lee JY, O’Neill EA, Meehan AG, Kusek JW. Prevalence of low testosterone and its relationship to body mass index in older men with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Aging Male 2013; 16(4):169–172. doi:10.3109/13685538.2013.844786
- Lee HK, Lee JK, Cho B. The role of androgen in the adipose tissue of males. World J Mens Health 2013; 31(2):136–140. doi:10.5534/wjmh.2013.31.2.136
- Raven G, De Jong FH, Kaufman JM, De Ronde W. In men, peripheral estradiol levels directly reflect the action of estrogens at the hypothalamo-pituitary level to inhibit gonadotropin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91(9):3324–3328. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0462
- Hofny ER, Ali ME, Abdel-Hafez HZ, et al. Semen parameters and hormonal profile in obese fertile and infertile males. Fertil Steril 2010; 94(2):581–584. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.03.085
- Isidori AM, Caprio M, Strollo F, et al. Leptin and androgens in male obesity: evidence for leptin contribution to reduced androgen levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(10):3673–3680. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.10.6082
- El-Wakkad A, Hassan NM, Sibaii H, El-Zayat SR. Proinflammatory, anti-inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 2013; 61(2):682–687. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.11.010
- Maggio M, Basaria S, Ceda GP, et al. The relationship between testosterone and molecular markers of inflammation in older men. J Endocrinol Invest 2005; 28(suppl proceedings 11):116–119. pmid:16760639
- de Lorenzo A, Noce A, Moriconi E, et al. MOSH syndrome (male obesity secondary hypogonadism): clinical assessment and possible therapeutic approaches. Nutrients 2018; 10(4)pii:E474. doi:10.3390/nu10040474
- Escobar-Morreale HF, Santacruz E, Luque-Ramírez M, Botella Carretero JI. Prevalence of ‘obesity-associated gonadal dysfunction’ in severely obese men and women and its resolution after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 2017; 23(4):390–408. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmx012
- Lo EM, Rodriguez KM, Pastuszak AW, Khera M. Alternatives to testosterone therapy: a review. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):106–113. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.09.004
- Soares AH, Horie NC, Chiang LAP, et al. Effects of clomiphene citrate on male obesity-associated hypogonadism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2018; 42(5):953–963. doi:10.1038/s41366-018-0105-2
- Chua ME, Escusa KG, Luna S, Tapia LC, Dofitas B, Morales M. Revisiting oestrogen antagonists (clomiphene or tamoxifen) as medical empiric therapy for idiopathic male infertility: a meta-analysis. Andrology 2013; 1(5):749–757. doi:10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00107.x
- Westaby D, Ogle SJ, Paradinas FJ, Randell JB, Murray-Lyon IM. Liver damage from long-term methyltestosterone. Lancet 1977; 2(8032):262–263. pmid:69876
- Fernández-Balsells MM, Murad MH, Lane M, et al. Clinical review 1: Adverse effects of testosterone therapy in adult men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(6):2560–2575. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2575
- Coviello AD, Kaplan B, Lakshman KM, Chen T, Singh AB, Bhasin S. Effects of graded doses of testosterone on erythropoiesis in healthy young and older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93(3):914–919. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-1692
- Ohlander SJ, Varghese B, Pastuszak AW. Erythrocytosis following testosterone therapy. Sex Med Rev 2018; 6(1):77–85. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.04.001
- Jones SD Jr, Dukovac T, Sangkum P, Yafi FA, Hellstrom WJ. Erythrocytosis and polycythemia secondary to testosterone replacement therapy in the aging male. Sex Med Rev 2015; 3(2):101–112. doi:10.1002/smrj.43
- Bachman E, Travison TG, Basaria S, et al. Testosterone induces erythrocytosis via increased erythropoietin and suppressed hepcidin: evidence for a new erythropoietin/hemoglobin set point. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2014; 69(6):725–735. doi:10.1093/gerona/glt154
- Roy CN, Snyder PJ, Stephens-Shields AJ, et al. Association of testosterone levels with anemia in older men: a controlled clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2017; 177(4):480–490. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9540
- Klap J, Schmid M, Loughlin KR. The relationship between total testosterone levels and prostate cancer: a review of the continuing controversy. J Urol 2015; 193(2):403–413. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.07.123
- Gilbert SM, Cavallo CB, Kahane H, Lowe FC. Evidence suggesting PSA cutpoint of 2.5 ng/mL for prompting prostate biopsy: review of 36,316 biopsies. Urology 2005; 65(3):549–553. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2004.10.064
- Araujo AB, Dixon JM, Suarez EA, Murad MH, Guey LT, Wittert GA. Clinical review: Endogenous testosterone and mortality in men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96(10):3007–3019. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1137
- Xu L, Freeman G, Cowling BJ, Schooling CM. Testosterone therapy and cardiovascular events among men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized trials. BMC Med 2013; 11:108. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-108
Evaluating and managing postural tachycardia syndrome
Some people, most of them relatively young women, experience lightheadedness, a racing heart, and other symptoms (but not hypotension) when they stand up, in a condition known as postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS).1 Although not known to shorten life,1 it can be physically and mentally debilitating.2,3 Therapy rarely cures it, but a multifaceted approach can substantially improve quality of life.
This review outlines the evaluation and diagnosis of POTS and provides guidance for a therapy regimen.
HOW IS POTS DEFINED?
POTS is a multifactorial syndrome rather than a specific disease. It is characterized by all of the following1,4–6:
- An increase in heart rate of ≥ 30 bpm, or ≥ 40 bpm for those under age 19, within 10 minutes of standing from a supine position
- Sustained tachycardia (> 30 seconds)
- Absence of orthostatic hypotension (a fall in blood pressure of ≥ 20/10 mm Hg)
- Frequent and chronic duration (≥ 6 months).
These features are critical to diagnosis. Hemodynamic criteria in isolation may describe postural tachycardia but are not sufficient to diagnose POTS.
The prevalence of POTS is estimated to be between 0.2% and 1.0%,7 affecting up to 3 million people in the United States. Most cases arise between ages 13 and 50, with a female-to-male ratio of 5:1.8
MANY NAMES, SAME CONDITION
In 1871, Da Costa9 described a condition he called “irritable heart syndrome” that had characteristics similar to those of POTS, including extreme fatigue and exercise intolerance. Decades later, Lewis10 and Wood11 provided more detailed descriptions of the disorder, renaming it “soldier’s heart” or “Da Costa syndrome.” As other cases were documented, more terms arose, including “effort syndrome” and “mitral valve prolapse syndrome.”
In 1982, Rosen and Cryer12 were the first to use the term “postural tachycardia syndrome” for patients with disabling tachycardia upon standing without orthostatic hypotension. In 1986, Fouad et al13 described patients with postural tachycardia, orthostatic intolerance, and a small degree of hypotension as having “idiopathic hypovolemia.”
In 1993, Schondorf and Low14 established the current definition of POTS, leading to increased awareness and research efforts to understand its pathophysiology.
MULTIFACTORIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
During the last 2 decades, several often-overlapping forms of POTS have been recognized, all of which share a final common pathway of sustained orthostatic tachycardia.15–19 In addition, a number of common comorbidities were identified through review of large clinic populations of POTS.20,21
Hypovolemic POTS
Up to 70% of patients with POTS have hypovolemia. The average plasma volume deficit is about 13%, which typically causes only insignificant changes in heart rate and norepinephrine levels while a patient is supine. However, blood pooling associated with upright posture further compromises cardiac output and consequently increases sympathetic nerve activity. Abnormalities in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone volume regulation system are also suspected to impair sodium retention, contributing to hypovolemia.1,22
Neuropathic POTS
About half of patients with POTS have partial sympathetic denervation (particularly in the lower limbs) and inadequate vasoconstriction upon standing, leading to reduced venous return and stroke volume.17,23 A compensatory increase in sympathetic tone results in tachycardia to maintain cardiac output and blood pressure.
Hyperadrenergic POTS
Up to 50% of patients with POTS have high norepinephrine levels (≥ 600 pg/mL) when upright. This subtype, hyperadrenergic POTS, is characterized by an increase in systolic blood pressure of at least 10 mm Hg within 10 minutes of standing, with concomitant tachycardia that can be similar to or greater than that seen in nonhyperadrenergic POTS. Patients with hyperadrenergic POTS tend to report more prominent symptoms of sympathetic activation, such as palpitations, anxiety, and tremulousness.24,25
Norepinephrine transporter deficiency
The norepinephrine transporter (NET) is on the presynaptic cleft of sympathetic neurons and serves to clear synaptic norepinephrine. NET deficiency leads to a hyperadrenergic state and elevated sympathetic nerve activation.18 NET deficiency may be induced by common antidepressants (eg, tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and attention-deficit disorder medications.4
Mast cell activation syndrome
The relationship between mast cell activation syndrome and POTS is poorly understood.4,26 Mast cell activation syndrome has been described in a subset of patients with POTS who have sinus tachycardia accompanied by severe episodic flushing. Patients with this subtype have a hyperadrenergic response to postural change and elevated urine methylhistamine during flushing episodes.
Patients with mast cell activation syndrome tend to have strong allergic symptoms and may also have severe gastrointestinal problems, food sensitivities, dermatographism, and neuropathy. Diagnosis can be difficult, as the condition is associated with numerous markers with varying sensitivity and specificity.
Autoimmune origin
A significant minority of patients report a viral-like illness before the onset of POTS symptoms, suggesting a possible autoimmune-mediated or inflammatory cause. Also, some autoimmune disorders (eg, Sjögren syndrome) can present with a POTS-like manifestation.
Research into the role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of POTS offers the potential to develop novel therapeutic targets. Autoantibodies that have been reported in POTS include those against M1 to M3 muscarinic receptors (present in over 87% of patients with POTS),27 cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins,28 adrenergic G-protein coupled receptors, alpha-1-adrenergic receptors, and beta-1- and beta-2-adrenergic receptors.29 Although commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays can assess for these antibody fragments, it is not known whether targeting the antibodies improves outcomes. At this time, antibody testing for POTS should be confined to the research setting.
LINKS TO OTHER SYNDROMES
POTS is often associated with other conditions whose symptoms cannot be explained by postural intolerance or tachycardia.
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes are a group of inherited heterogeneous disorders involving joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility.30 The hypermobile subtype is most commonly associated with POTS, with patients often having symptoms of autonomic dysregulation and autonomic test abnormalities.31–33 Patients with POTS may have a history of joint subluxations, joint pain, cervical instability, and spontaneous epidural leaks. The reason for the overlap between the two syndromes is not clear.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is characterized by persistent fatigue that does not resolve with rest and is not necessarily associated with orthostatic changes. More than 75% of patients with POTS report general fatigue as a major complaint, and up to 23% meet the full criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome.34
DIAGNOSTIC STRATEGY
A patient presenting with symptoms suggestive of POTS should first undergo a detailed history and physical examination. Other causes of sinus tachycardia should be considered.
Detailed history, symptom review
The history should focus on determining symptom burden, including tachycardia onset, frequency, severity, and triggers; the presence of syncope; and the impact of symptoms on daily function and quality of life.
Presyncope and its associated symptoms occur in less than one-third of patients with POTS, and syncope is not a principal feature.4 If syncope is the predominant complaint, alternative causes should be investigated. The usual cause of syncope in the general population is thought to be vasovagal.
In addition to orthostatic intolerance, gastrointestinal disturbances are common in POTS, presenting as abdominal pain, heartburn, irregular bowel movements, diarrhea, or constipation. Symptoms of gastroparesis are less common. Gastrointestinal symptoms tend to be prolonged, lasting hours and occurring multiple times a week. They tend not to improve in the supine position.35
POTS-associated symptoms may develop insidiously, but patients often report onset after an acute stressor such as pregnancy, major surgery, or a presumed viral illness.4 Whether these putative triggers are causative or coincidental is unknown. Symptoms of orthostatic intolerance tend to be exacerbated by dehydration, heat, alcohol, exercise, and menstruation.36,37
Consider the family history: 1 in 8 patients with POTS reports familial orthostatic intolerance,38 suggesting a genetic role in some patients. Inquire about symptoms or a previous diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and mast cell activation syndrome.
Consider other conditions
Pheochromocytoma causes hyperadrenergic symptoms (eg, palpitations, lightheadedness) like those in POTS, but patients with pheochromocytoma typically have these symptoms while supine. Pheochromocytoma is also characterized by plasma norepinephrine levels much higher than in POTS.4 Plasma metanephrine testing helps diagnose or rule out pheochromocytoma.5
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia, like pheochromocytoma, also has clinical features similar to those of POTS, as well as tachycardia present when supine. It involves higher sympathetic tone and lower parasympathetic tone compared with POTS; patients commonly have a daytime resting heart rate of at least 100 bpm or a 24-hour mean heart rate of at least 90 bpm.1,42 While the intrinsic heart rate is heightened in inappropriate sinus tachycardia, it is not different between POTS patients and healthy individuals.42,43 Distinguishing POTS from inappropriate sinus tachycardia is further complicated by the broad inclusion criteria of most studies of inappropriate sinus tachycardia, which failed to exclude patients with POTS.44 The Heart Rhythm Society recently adopted distinct definitions for the 2 conditions.1
Physical examination: Focus on vital signs
Dependent acrocyanosis—dark red-blue discoloration of the lower legs that is cold to the touch—occurs in about half of patients with POTS upon standing.4 Dependent acrocyanosis is associated with joint hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, so these conditions should also be considered if findings are positive.
Laboratory testing for other causes
Laboratory testing is used mainly to detect primary causes of sinus tachycardia. Tests should include:
- Complete blood cell count with hematocrit (for severe anemia)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level (for hyperthyroidism)
- Electrolyte panel (for significant electrolyte disturbances).
Evidence is insufficient to support routinely measuring the vitamin B12 level, iron indices, and serum markers for celiac disease, although these may be done if the history or physical examination suggests related problems.4 Sicca symptoms (severe dry eye or dry mouth) should trigger evaluation for Sjögren syndrome.
Electrocardiography needed
Electrocardiography should be performed to investigate for cardiac conduction abnormalities as well as for resting markers of a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. Extended ambulatory (Holter) monitoring may be useful to evaluate for a transient reentrant tachyarrhythmia4; however, it does not record body position, so it can be difficult to determine if detected episodes of tachycardia are related to posture.
Additional testing for select cases
Further investigation is usually not needed to diagnose POTS but should be considered in some cases. Advanced tests are typically performed at a tertiary care referral center and include:
- Quantitative sensory testing to evaluate for small-fiber neuropathy (ie, Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test, or QSART), which occurs in the neuropathic POTS subtype
- Formal autonomic function testing to characterize neurovascular responsiveness
- Supine and standing plasma norepinephrine levels (fractionated catecholamines) to characterize the net activation of the sympathetic nervous system
- Blood volume assessments to assess hypovolemia
- Formal exercise testing to objectively quantify exercise capacity.
GRADED MANAGEMENT
No single universal gold-standard therapy exists for POTS, and management should be individually determined with the primary goals of treating symptoms and restoring function. A graded approach should be used, starting with conservative nonpharmacologic therapies and adding medications as needed.
While the disease course varies substantially from patient to patient, proper management is strongly associated with eventual symptom improvement.1
NONPHARMACOLOGIC STEPS FIRST
Education
Patients should be informed of the nature of their condition and referred to appropriate healthcare personnel. POTS is a chronic illness requiring individualized coping strategies, intensive physician interaction, and support of a multidisciplinary team. Patients and family members can be reassured that most symptoms improve over time with appropriate diagnosis and treatment.1 Patients should be advised to avoid aggravating triggers and activities.
Exercise
Exercise programs are encouraged but should be introduced gradually, as physical activity can exacerbate symptoms, especially at the outset. Several studies have reported benefits from a short-term (3-month) program, in which the patient gradually progresses from non-upright exercise (eg, rowing machine, recumbent cycle, swimming) to upright endurance exercises. At the end of these programs, significant cardiac remodeling, improved quality of life, and reduced heart rate responses to standing have been reported, and benefits have been reported to persist in patients who continued exercising after the 3-month study period.46,47
Despite the benefits of exercise interventions, compliance is low.46,47 To prevent early discouragement, patients should be advised that it can take 4 to 6 weeks of continued exercise before benefits appear. Patients are encouraged to exercise every other day for 30 minutes or more. Regimens should primarily focus on aerobic conditioning, but resistance training, concentrating on thigh muscles, can also help. Exercise is a treatment and not a cure, and benefits can rapidly disappear if regular activity (at least 3 times per week) is stopped.48
Compression stockings
Compression stockings help reduce peripheral venous pooling and enhance venous return to the heart. Waist-high stockings with compression of at least 30 to 40 mm Hg offer the best results.
Diet
Increased fluid and salt intake is advisable for patients with suspected hypovolemia. At least 2 to 3 L of water accompanied by 10 to 12 g of daily sodium intake is recommended.1 This can usually be accomplished with diet and salt added to food, but salt tablets can be used if the patient prefers. The resultant plasma volume expansion may help reduce the reflex tachycardia upon standing.49
Check medications
Rescue therapy with saline infusion
Intravenous saline infusion can augment blood volume in patients who are clinically decompensated and present with severe symptoms.1 Intermittent infusion of 1 L of normal saline has been found to significantly reduce orthostatic tachycardia and related symptoms in patients with POTS, contributing to improved quality of life.51,52
Chronic saline infusions are not recommended for long-term care because of the risk of access complications and infection.1 Moak et al53 reported a high rate of bacteremia in a cohort of children with POTS with regular saline infusions, most of whom had a central line. On the other hand, Ruzieh et al54 reported significantly improved symptoms with regular saline infusions without a high rate of complications, but patients in this study received infusions for only a few months and through a peripheral intravenous catheter.
DRUG THERAPY
No medications are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or Health Canada specifically for treating POTS, making all pharmacologic recommendations off-label. Although the drugs discussed below have been evaluated for POTS in controlled laboratory settings, they have yet to be tested in robust clinical trials.
Blood volume expansion
Several drugs expand blood volume, which may reduce orthostatic tachycardia.
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic aldosterone analogue that enhances sodium and water retention. Although one observational study found that it normalizes hemodynamic changes in response to orthostatic stress, no high-level evidence exists for its effectiveness for POTS.55 It is generally well tolerated, although possible adverse effects include hyperkalemia, hypertension, fatigue, nausea, headache, and edema.5,56
Desmopressin is a synthetic version of a natural antidiuretic hormone that increases kidney-mediated free-water reabsorption without sodium retention. It significantly reduces upright heart rate in patients with POTS and improves symptom burden. Although potential adverse effects include edema and headache, hyponatremia is the primary concern with daily use, especially with the increased water intake advised for POTS.57 Patients should be advised to use desmopressin no more than once a week for the acute improvement of symptoms. Intermittent monitoring of serum sodium levels is recommended for safety.
Erythropoietin replacement has been suggested for treating POTS to address the significant deficit in red blood cell volume. Although erythropoietin therapy has a direct vasoconstrictive effect and largely improves red blood cell volume in patients with POTS, it does not expand plasma volume, so orthostatic tachycardia is not itself reduced.22 Nevertheless, it may significantly improve POTS symptoms refractory to more common methods of treatment, and it should be reserved for such cases. In addition to the lack of effect on orthostatic tachycardia, drawbacks to using erythropoietin include its high cost, the need for subcutaneous administration, and the risk of life-threatening complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke.58,59
Heart rate-lowering agents
Propranolol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist, can significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptoms at low dosages (10–20 mg). Higher dosages can further restrain orthostatic tachycardia but are not as well tolerated, mainly due to hypotension and worsening of existing symptoms such as fatigue.60 Regular-acting propranolol works for about 4 to 5 hours per dose, so full-day coverage often requires dosing 4 times per day.
Ivabradine is a selective blocker of the “funny” (If) channel that reduces the sinus node firing rate without affecting blood pressure, so it slows heart rate without causing supine hypertension or orthostatic hypotension.
A retrospective case series found that 60% of patients with POTS treated with ivabradine reported symptomatic improvement, and all patients experienced reduced tachycardia with continued use.61 Ivabradine has not been compared with placebo or propranolol in a randomized controlled trial, and it has not been well studied in pregnancy and so should be avoided because of potential teratogenic effects.
When prescribing ivabradine for women of childbearing age, a negative pregnancy test may be documented prior to initiation of therapy, and the use of highly effective methods of contraception is recommended. Ivabradine should be avoided in women contemplating pregnancy. Insurance coverage can limit access to ivabradine in the United States.
Central nervous system sympatholytics
Patients with prominent hyperadrenergic features may benefit from central sympatholytic agents. However, these drugs may not be well tolerated in patients with neuropathic POTS because of the effects of reduced systemic vascular resistance5 and the possible exacerbation of drowsiness, fatigue, and mental clouding.4 Patients can be extremely sensitive to these medications, so they should initially be prescribed at the lowest dose, then gradually increased as tolerated.
Clonidine, an alpha-2-adrenergic agonist, decreases central sympathetic tone. In hyperadrenergic patients, clonidine can stabilize heart rate and blood pressure, thereby reducing orthostatic symptoms.62
Methyldopa has effects similar to those of clonidine but is easier to titrate owing to its longer half-life.63 Methyldopa is typically started at 125 mg at bedtime and increased to 125 mg twice daily, if tolerated.
Other agents
Midodrine is a prodrug. The active form, an alpha-1-adrenergic agonist, constricts peripheral veins and arteries to increase vascular resistance and venous return, thereby reducing orthostatic tachycardia.52 It is most useful in patients with impaired peripheral vasoconstriction (eg, neuropathic POTS) and may be less effective in those with hyperadrenergic POTS.64 Major limitations of midodrine include worsening supine hypertension and possible urinary retention.39
Because of midodrine’s short half-life, frequent dosing is required during daytime hours (eg, 8 AM, noon, and 4 PM), but it should not be taken within 4 to 5 hours of sleep because of the risk of supine hypertension. Midodrine is typically started at 2.5 to 5 mg per dose and can be titrated up to 15 mg per dose.
Midodrine is an FDA pregnancy category C drug (adverse effects in pregnancy seen in animal models, but evidence lacking in humans). While ideally it should be avoided, we have used it safely in pregnant women with disabling POTS symptoms.
Pyridostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, increases cardiovagal tone and possibly sympathetic tone. It has been reported to significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptom burden in patients with POTS.65 However, pyridostigmine increases gastrointestinal mobility, leading to severe adverse effects in over 20% of patients, including abdominal cramps, nausea, and diarrhea.66
Droxidopa, a synthetic amino acid precursor of norepinephrine, improves dizziness and fatigue in POTS with minimal effects on blood pressure.67
Modafinil, a psychostimulant, may improve POTS-associated cognitive symptoms.4 It also raises upright blood pressure without significantly worsening standing heart rate or acute orthostatic symptoms.68
EFFECTS OF COMORBID DISORDERS ON MANAGEMENT
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Pharmacologic approaches to POTS should not be altered based on the presence of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, but because many of these patients are prone to joint dislocation, exercise prescriptions may need adjusting.
A medical genetics consult is recommended for patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Although the hypermobile type (the form most commonly associated with POTS) is not associated with aortopathy, it can be confused with classical and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, which require serial aortic screening.30
Mast cell activation syndrome
Consultation with an allergist or immunologist may help patients with severe symptoms.
Autoantibodies and autoimmunity
Treatment of the underlying disorder is recommended and can result in significantly improved POTS symptoms.
SPECIALTY CARE REFERRAL
POTS can be challenging to manage. Given the range of physiologic, emotional, and functional distress patients experience, it often requires significant physician time and multidisciplinary care. Patients with continued severe or debilitating symptoms may benefit from referral to a tertiary-care center with experience in autonomic nervous system disorders.
PROGNOSIS
Limited data are available on the long-term prognosis of POTS, and more studies are needed in pediatric and adult populations. No deaths have been reported in the handful of published cases of POTS in patients older than 50.1 Some pediatric studies suggest that some teenagers “outgrow” their POTS. However, these data are not robust, and an alternative explanation is that as they get older, they see adult physicians for their POTS symptoms and so are lost to study follow-up.6,44,69
We have not often seen POTS simply resolve without ongoing treatment. However, in our experience, most patients have improved symptoms and function with multimodal treatment (ie, exercise, salt, water, stockings, and some medications) and time.
- Sheldon RS, Grubb BP 2nd, Olshansky B, et al. 2015 Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and vasovagal syncope. Heart Rhythm 2015; 12(6):e41–e63. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.03.029
- Bagai K, Song Y, Ling JF, et al. Sleep disturbances and diminished quality of life in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med 2011; 7(2):204–210. pmid:21509337
- Benrud-Larson LM, Dewar MS, Sandroni P, Rummans TA, Haythornthwaite JA, Low PA. Quality of life in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 2002; 77(6):531–537. doi:10.4065/77.6.531
- Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). Circulation 2013; 127(23):2336–2342. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.144501
- Raj SR. The postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS): pathophysiology, diagnosis & management. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 2006; 6(2):84–99. pmid:16943900
- Singer W, Sletten DM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Brands CK, Fischer PR, Low PA. Postural tachycardia in children and adolescents: what is abnormal? J Pediatr 2012; 160(2):222–226. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.08.054
- Mar PL, Raj SR. Neuronal and hormonal perturbations in postural tachycardia syndrome. Front Physiol 2014; 5:220. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00220
- Garland EM, Raj SR, Black BK, Harris PA, Robertson D. The hemodynamic and neurohumoral phenotype of postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurology 2007; 69(8):790–798. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000267663.05398.40
- Da Costa JM. On irritable heart: a clinical study of a form of functional cardiac disorder and its consequences. Am J Med Sci 1871; 61(121):2–52.
- Lewis T. The tolerance of physical exertion, as shown by soldiers suffering from so-called “irritable heart.” Br Med J 1918; 1(2987):363–365. pmid:20768980
- Wood P. Da Costa’s syndrome (or effort syndrome): lecture I. Br Med J 1941; 1(4194):767–772. pmid:20783672
- Rosen SG, Cryer PE. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Reversal of sympathetic hyperresponsiveness and clinical improvement during sodium loading. Am J Med 1982; 72(5):847–850.
- Fouad FM, Tadena-Thome L, Bravo EL, Tarazi RC. Idiopathic hypovolemia. Ann Intern Med 1986; 104(3):298–303. pmid:3511818
- Schondorf R, Low PA. Idiopathic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: an attenuated form of acute pandysautonomia? Neurology 1993; 43(1):132–137. pmid:8423877
- Vernino S, Low PA, Fealey RD, Stewart JD, Farrugia G, Lennon VA. Autoantibodies to ganglionic acetylcholine receptors in autoimmune autonomic neuropathies. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(12):847–855. doi:10.1056/NEJM200009213431204
- Raj SR, Robertson D. Blood volume perturbations in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Am J Med Sci 2007; 334(1):57–60. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318063c6c0
- Jacob G, Costa F, Shannon JR, et al. The neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(14):1008–1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM200010053431404
- Shannon JR, Flattem NL, Jordan J, et al. Orthostatic intolerance and tachycardia associated with norepinephrine-transporter deficiency. N Engl J Med 2000; 342(8):541–549. doi:10.1056/NEJM200002243420803
- Jones PK, Shaw BH, Raj SR. Clinical challenges in the diagnosis and management of postural tachycardia syndrome. Pract Neurol 2016; 16(6):431–438. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2016-001405
- Gunning WT, Karabin BL, Blomquist TM, Grubb BP. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is associated with platelet storage pool deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(37):e4849. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004849
- Kanjwal K, Sheikh M, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Neurocardiogenic syncope coexisting with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in patients suffering from orthostatic intolerance: a combined form of autonomic dysfunction. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(5):549–554. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02994.x
- Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Yamhure PC, et al. Renin-aldosterone paradox and perturbed blood volume regulation underlying postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(13):1574–1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000160356.97313.5D
- Gibbons CH, Bonyhay I, Benson A, Wang N, Freeman R. Structural and functional small fiber abnormalities in the neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e84716. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084716
- Low PA, Sandroni P, Joyner M, Shen WK. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2009; 20(3):352–358. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2008.01407.x
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Clinical presentation and management of patients with hyperadrenergic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. A single center experience. Cardiol J 2011; 18(5):527–531. pmid:21947988
- Shibao C, Arzubiaga C, Roberts J, et al. Hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome in mast cell activation disorders. Hypertension 2005; 45(3):385–390. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000158259.68614.40
- Dubey D, Hopkins S, Vernino S. M1 and M2 muscarinic receptor antibodies among patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: potential disease biomarker [abstract]. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2016; 17(3):179S.
- Wang XL, Ling TY, Charlesworth MC, et al. Autoimmunoreactive IgGs against cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Transl Res 2013; 162(1):34–44. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.002
- Li H, Yu X, Liles C, et al. Autoimmune basis for postural tachycardia syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(1):e000755. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000755
- Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2017; 175(1):8–26. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31552
- Wallman D, Weinberg J, Hohler AD. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and postural tachycardia syndrome: a relationship study. J Neurol Sci 2014; 340(1-2):99–102. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2014.03.002
- De Wandele I, Calders P, Peersman W, et al. Autonomic symptom burden in the hypermobility type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a comparative study with two other EDS types, fibromyalgia, and healthy controls. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 44(3):353–361. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.05.013
- Gazit Y, Nahir AM, Grahame R, Jacob G. Dysautonomia in the joint hypermobility syndrome. Am J Med 2003; 115(1):33–40. pmid:12867232
- Okamoto LE, Raj SR, Peltier A, et al. Neurohumoral and haemodynamic profile in postural tachycardia and chronic fatigue syndromes. Clin Sci (Lond) 2012; 122(4):183–192. doi:10.1042/CS20110200
- Wang LB, Culbertson CJ, Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Huang H, Hohler AD. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Neurol Sci 2015; 359(1-2):193–196. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2015.10.052
- Raj S, Sheldon R. Management of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia and vasovagal syncope. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2016; 5(2):122–129. doi:10.15420/AER.2016.7.2
- Peggs KJ, Nguyen H, Enayat D, Keller NR, Al-Hendy A, Raj SR. Gynecologic disorders and menstrual cycle lightheadedness in postural tachycardia syndrome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012; 118(3):242–246. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.04.014
- Thieben MJ, Sandroni P, Sletten DM, et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo Clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc 2007; 82(3):308–313. doi:10.4065/82.3.308
- Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Culbertson CJ, Wang LB, Hohler AD. A survey-based analysis of symptoms in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 28(7):157–159. pmid:25829642
- Ertek S, Cicero AF. Hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular complications: a narrative review on the basis of pathophysiology. Arch Med Sci 2013; 9(5):944–952. doi:10.5114/aoms.2013.38685
- Rangno RE, Langlois S. Comparison of withdrawal phenomena after propranolol, metoprolol and pindolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1982; 13(suppl 2):345S–351S. pmid:6125187
- Nwazue VC, Paranjape SY, Black BK, et al. Postural tachycardia syndrome and inappropriate sinus tachycardia: role of autonomic modulation and sinus node automaticity. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(2):e000700. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000700
- Morillo CA, Klein GJ, Thakur RK, Li H, Zardini M, Yee R. Mechanism of “inappropriate” sinus tachycardia. Role of sympathovagal balance. Circulation 1994; 90(2):873–877. pmid:7913886
- Grubb BP. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2008; 117(21):2814–2817. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761643
- Bhatia R, Kizilbash SJ, Ahrens SP, et al. Outcomes of adolescent-onset postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Pediatr 2016; 173:149–153. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.035
- George SA, Bivens TB, Howden EJ, et al. The international POTS registry: evaluating the efficacy of an exercise training intervention in a community setting. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):943–950. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.012
- Fu Q, VanGundy TB, Galbreath MM, et al. Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55(25):2858–2868. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.043
- Raj SR. Row, row, row your way to treating postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):951–952. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.039
- Celedonio JE, Garland EM, Nwazue VC, et al. Effects of high sodium intake on blood volume and catecholamines in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome and healthy females [abstract]. Clin Auton Res 2014; 24:211.
- Garland EM, Celedonio JE, Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome: beyond orthostatic intolerance. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2015; 15(9):60. doi:10.1007/s11910-015-0583-8
- Gordon VM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Novak V, Low PA. Hemodynamic and symptomatic effects of acute interventions on tilt in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10:29–33. pmid:10750641
- Jacob G, Shannon JR, Black B, et al. Effects of volume loading and pressor agents in idiopathic orthostatic tachycardia. Circulation 1997; 96(2):575–580. pmid:9244228
- Moak JP, Leong D, Fabian R, et al. Intravenous hydration for management of medication-resistant orthostatic intolerance in the adolescent and young adult. Pediatr Cardiol 2016; 37(2):278–282. doi:10.1007/s00246-015-1274-6
- Ruzieh M, Baugh A, Dasa O, et al. Effects of intermittent intravenous saline infusions in patients with medication-refractory postural tachycardia syndrome. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2017; 48(3):255–260. doi:10.1007/s10840-017-0225-y
- Freitas J, Santos R, Azevedo E, Costa O, Carvalho M, de Freitas AF. Clinical improvement in patients with orthostatic intolerance after treatment with bisoprolol and fludrocortisone. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10(5):293–299. pmid:11198485
- Lee AK, Krahn AD. Evaluation of syncope: focus on diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2016; 14(6):725–736. doi:10.1586/14779072.2016.1164034
- Coffin ST, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Desmopressin acutely decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2012; 9(9):1484–1490. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.05.002
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Sheikh M, Grubb BP. Erythropoietin in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2012; 19(2):92–95. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ef621a
- Hoeldtke RD, Horvath GG, Bryner KD. Treatment of orthostatic tachycardia with erythropoietin. Am J Med 1995; 99(5):525–529. pmid:7485211
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Propranolol decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome: less is more. Circulation 2009; 120(9):725–734. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.846501
- McDonald C, Frith J, Newton JL. Single centre experience of ivabradine in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Europace 2011; 13(3):427–430. doi:10.1093/europace/euq390
- Gaffney FA, Lane LB, Pettinger W, Blomqvist G. Effects of long-term clonidine administration on the hemodynamic and neuroendocrine postural responses of patients with dysautonomia. Chest 1983; 83(suppl 2):436–438. pmid:6295714
- Jacob G, Biaggioni I. Idiopathic orthostatic intolerance and postural tachycardia syndromes. Am J Med Sci 1999; 317(2):88–101. pmid:10037112
- Ross AJ, Ocon AJ, Medow MS, Stewart JM. A double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study of the vascular effects of midodrine in neuropathic compared with hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014; 126(4):289–296. doi:10.1042/CS20130222
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, Harris PA, Robertson D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition improves tachycardia in postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(21):2734–2340. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.497594
- Kanjwal K, Karabin B, Sheikh M, et al. Pyridostigmine in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia: A single-center experience. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(6):750–755. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03047.x
- Ruzieh M, Dasa O, Pacenta A, Karabin B, Grubb B. Droxidopa in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2017; 24(2):e157–e161. doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000000468
- Kpaeyeh AG Jr, Mar PL, Raj V, et al. Hemodynamic profiles and tolerability of modafinil in the treatment of POTS: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2014; 34(6):738–741. doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000000221
- Lai CC, Fischer PR, Brands CK, et al. Outcomes in adolescents with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome treated with midodrine and beta-blockers. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2009; 32(2):234–238. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.02207.x
Some people, most of them relatively young women, experience lightheadedness, a racing heart, and other symptoms (but not hypotension) when they stand up, in a condition known as postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS).1 Although not known to shorten life,1 it can be physically and mentally debilitating.2,3 Therapy rarely cures it, but a multifaceted approach can substantially improve quality of life.
This review outlines the evaluation and diagnosis of POTS and provides guidance for a therapy regimen.
HOW IS POTS DEFINED?
POTS is a multifactorial syndrome rather than a specific disease. It is characterized by all of the following1,4–6:
- An increase in heart rate of ≥ 30 bpm, or ≥ 40 bpm for those under age 19, within 10 minutes of standing from a supine position
- Sustained tachycardia (> 30 seconds)
- Absence of orthostatic hypotension (a fall in blood pressure of ≥ 20/10 mm Hg)
- Frequent and chronic duration (≥ 6 months).
These features are critical to diagnosis. Hemodynamic criteria in isolation may describe postural tachycardia but are not sufficient to diagnose POTS.
The prevalence of POTS is estimated to be between 0.2% and 1.0%,7 affecting up to 3 million people in the United States. Most cases arise between ages 13 and 50, with a female-to-male ratio of 5:1.8
MANY NAMES, SAME CONDITION
In 1871, Da Costa9 described a condition he called “irritable heart syndrome” that had characteristics similar to those of POTS, including extreme fatigue and exercise intolerance. Decades later, Lewis10 and Wood11 provided more detailed descriptions of the disorder, renaming it “soldier’s heart” or “Da Costa syndrome.” As other cases were documented, more terms arose, including “effort syndrome” and “mitral valve prolapse syndrome.”
In 1982, Rosen and Cryer12 were the first to use the term “postural tachycardia syndrome” for patients with disabling tachycardia upon standing without orthostatic hypotension. In 1986, Fouad et al13 described patients with postural tachycardia, orthostatic intolerance, and a small degree of hypotension as having “idiopathic hypovolemia.”
In 1993, Schondorf and Low14 established the current definition of POTS, leading to increased awareness and research efforts to understand its pathophysiology.
MULTIFACTORIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
During the last 2 decades, several often-overlapping forms of POTS have been recognized, all of which share a final common pathway of sustained orthostatic tachycardia.15–19 In addition, a number of common comorbidities were identified through review of large clinic populations of POTS.20,21
Hypovolemic POTS
Up to 70% of patients with POTS have hypovolemia. The average plasma volume deficit is about 13%, which typically causes only insignificant changes in heart rate and norepinephrine levels while a patient is supine. However, blood pooling associated with upright posture further compromises cardiac output and consequently increases sympathetic nerve activity. Abnormalities in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone volume regulation system are also suspected to impair sodium retention, contributing to hypovolemia.1,22
Neuropathic POTS
About half of patients with POTS have partial sympathetic denervation (particularly in the lower limbs) and inadequate vasoconstriction upon standing, leading to reduced venous return and stroke volume.17,23 A compensatory increase in sympathetic tone results in tachycardia to maintain cardiac output and blood pressure.
Hyperadrenergic POTS
Up to 50% of patients with POTS have high norepinephrine levels (≥ 600 pg/mL) when upright. This subtype, hyperadrenergic POTS, is characterized by an increase in systolic blood pressure of at least 10 mm Hg within 10 minutes of standing, with concomitant tachycardia that can be similar to or greater than that seen in nonhyperadrenergic POTS. Patients with hyperadrenergic POTS tend to report more prominent symptoms of sympathetic activation, such as palpitations, anxiety, and tremulousness.24,25
Norepinephrine transporter deficiency
The norepinephrine transporter (NET) is on the presynaptic cleft of sympathetic neurons and serves to clear synaptic norepinephrine. NET deficiency leads to a hyperadrenergic state and elevated sympathetic nerve activation.18 NET deficiency may be induced by common antidepressants (eg, tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and attention-deficit disorder medications.4
Mast cell activation syndrome
The relationship between mast cell activation syndrome and POTS is poorly understood.4,26 Mast cell activation syndrome has been described in a subset of patients with POTS who have sinus tachycardia accompanied by severe episodic flushing. Patients with this subtype have a hyperadrenergic response to postural change and elevated urine methylhistamine during flushing episodes.
Patients with mast cell activation syndrome tend to have strong allergic symptoms and may also have severe gastrointestinal problems, food sensitivities, dermatographism, and neuropathy. Diagnosis can be difficult, as the condition is associated with numerous markers with varying sensitivity and specificity.
Autoimmune origin
A significant minority of patients report a viral-like illness before the onset of POTS symptoms, suggesting a possible autoimmune-mediated or inflammatory cause. Also, some autoimmune disorders (eg, Sjögren syndrome) can present with a POTS-like manifestation.
Research into the role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of POTS offers the potential to develop novel therapeutic targets. Autoantibodies that have been reported in POTS include those against M1 to M3 muscarinic receptors (present in over 87% of patients with POTS),27 cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins,28 adrenergic G-protein coupled receptors, alpha-1-adrenergic receptors, and beta-1- and beta-2-adrenergic receptors.29 Although commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays can assess for these antibody fragments, it is not known whether targeting the antibodies improves outcomes. At this time, antibody testing for POTS should be confined to the research setting.
LINKS TO OTHER SYNDROMES
POTS is often associated with other conditions whose symptoms cannot be explained by postural intolerance or tachycardia.
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes are a group of inherited heterogeneous disorders involving joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility.30 The hypermobile subtype is most commonly associated with POTS, with patients often having symptoms of autonomic dysregulation and autonomic test abnormalities.31–33 Patients with POTS may have a history of joint subluxations, joint pain, cervical instability, and spontaneous epidural leaks. The reason for the overlap between the two syndromes is not clear.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is characterized by persistent fatigue that does not resolve with rest and is not necessarily associated with orthostatic changes. More than 75% of patients with POTS report general fatigue as a major complaint, and up to 23% meet the full criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome.34
DIAGNOSTIC STRATEGY
A patient presenting with symptoms suggestive of POTS should first undergo a detailed history and physical examination. Other causes of sinus tachycardia should be considered.
Detailed history, symptom review
The history should focus on determining symptom burden, including tachycardia onset, frequency, severity, and triggers; the presence of syncope; and the impact of symptoms on daily function and quality of life.
Presyncope and its associated symptoms occur in less than one-third of patients with POTS, and syncope is not a principal feature.4 If syncope is the predominant complaint, alternative causes should be investigated. The usual cause of syncope in the general population is thought to be vasovagal.
In addition to orthostatic intolerance, gastrointestinal disturbances are common in POTS, presenting as abdominal pain, heartburn, irregular bowel movements, diarrhea, or constipation. Symptoms of gastroparesis are less common. Gastrointestinal symptoms tend to be prolonged, lasting hours and occurring multiple times a week. They tend not to improve in the supine position.35
POTS-associated symptoms may develop insidiously, but patients often report onset after an acute stressor such as pregnancy, major surgery, or a presumed viral illness.4 Whether these putative triggers are causative or coincidental is unknown. Symptoms of orthostatic intolerance tend to be exacerbated by dehydration, heat, alcohol, exercise, and menstruation.36,37
Consider the family history: 1 in 8 patients with POTS reports familial orthostatic intolerance,38 suggesting a genetic role in some patients. Inquire about symptoms or a previous diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and mast cell activation syndrome.
Consider other conditions
Pheochromocytoma causes hyperadrenergic symptoms (eg, palpitations, lightheadedness) like those in POTS, but patients with pheochromocytoma typically have these symptoms while supine. Pheochromocytoma is also characterized by plasma norepinephrine levels much higher than in POTS.4 Plasma metanephrine testing helps diagnose or rule out pheochromocytoma.5
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia, like pheochromocytoma, also has clinical features similar to those of POTS, as well as tachycardia present when supine. It involves higher sympathetic tone and lower parasympathetic tone compared with POTS; patients commonly have a daytime resting heart rate of at least 100 bpm or a 24-hour mean heart rate of at least 90 bpm.1,42 While the intrinsic heart rate is heightened in inappropriate sinus tachycardia, it is not different between POTS patients and healthy individuals.42,43 Distinguishing POTS from inappropriate sinus tachycardia is further complicated by the broad inclusion criteria of most studies of inappropriate sinus tachycardia, which failed to exclude patients with POTS.44 The Heart Rhythm Society recently adopted distinct definitions for the 2 conditions.1
Physical examination: Focus on vital signs
Dependent acrocyanosis—dark red-blue discoloration of the lower legs that is cold to the touch—occurs in about half of patients with POTS upon standing.4 Dependent acrocyanosis is associated with joint hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, so these conditions should also be considered if findings are positive.
Laboratory testing for other causes
Laboratory testing is used mainly to detect primary causes of sinus tachycardia. Tests should include:
- Complete blood cell count with hematocrit (for severe anemia)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level (for hyperthyroidism)
- Electrolyte panel (for significant electrolyte disturbances).
Evidence is insufficient to support routinely measuring the vitamin B12 level, iron indices, and serum markers for celiac disease, although these may be done if the history or physical examination suggests related problems.4 Sicca symptoms (severe dry eye or dry mouth) should trigger evaluation for Sjögren syndrome.
Electrocardiography needed
Electrocardiography should be performed to investigate for cardiac conduction abnormalities as well as for resting markers of a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. Extended ambulatory (Holter) monitoring may be useful to evaluate for a transient reentrant tachyarrhythmia4; however, it does not record body position, so it can be difficult to determine if detected episodes of tachycardia are related to posture.
Additional testing for select cases
Further investigation is usually not needed to diagnose POTS but should be considered in some cases. Advanced tests are typically performed at a tertiary care referral center and include:
- Quantitative sensory testing to evaluate for small-fiber neuropathy (ie, Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test, or QSART), which occurs in the neuropathic POTS subtype
- Formal autonomic function testing to characterize neurovascular responsiveness
- Supine and standing plasma norepinephrine levels (fractionated catecholamines) to characterize the net activation of the sympathetic nervous system
- Blood volume assessments to assess hypovolemia
- Formal exercise testing to objectively quantify exercise capacity.
GRADED MANAGEMENT
No single universal gold-standard therapy exists for POTS, and management should be individually determined with the primary goals of treating symptoms and restoring function. A graded approach should be used, starting with conservative nonpharmacologic therapies and adding medications as needed.
While the disease course varies substantially from patient to patient, proper management is strongly associated with eventual symptom improvement.1
NONPHARMACOLOGIC STEPS FIRST
Education
Patients should be informed of the nature of their condition and referred to appropriate healthcare personnel. POTS is a chronic illness requiring individualized coping strategies, intensive physician interaction, and support of a multidisciplinary team. Patients and family members can be reassured that most symptoms improve over time with appropriate diagnosis and treatment.1 Patients should be advised to avoid aggravating triggers and activities.
Exercise
Exercise programs are encouraged but should be introduced gradually, as physical activity can exacerbate symptoms, especially at the outset. Several studies have reported benefits from a short-term (3-month) program, in which the patient gradually progresses from non-upright exercise (eg, rowing machine, recumbent cycle, swimming) to upright endurance exercises. At the end of these programs, significant cardiac remodeling, improved quality of life, and reduced heart rate responses to standing have been reported, and benefits have been reported to persist in patients who continued exercising after the 3-month study period.46,47
Despite the benefits of exercise interventions, compliance is low.46,47 To prevent early discouragement, patients should be advised that it can take 4 to 6 weeks of continued exercise before benefits appear. Patients are encouraged to exercise every other day for 30 minutes or more. Regimens should primarily focus on aerobic conditioning, but resistance training, concentrating on thigh muscles, can also help. Exercise is a treatment and not a cure, and benefits can rapidly disappear if regular activity (at least 3 times per week) is stopped.48
Compression stockings
Compression stockings help reduce peripheral venous pooling and enhance venous return to the heart. Waist-high stockings with compression of at least 30 to 40 mm Hg offer the best results.
Diet
Increased fluid and salt intake is advisable for patients with suspected hypovolemia. At least 2 to 3 L of water accompanied by 10 to 12 g of daily sodium intake is recommended.1 This can usually be accomplished with diet and salt added to food, but salt tablets can be used if the patient prefers. The resultant plasma volume expansion may help reduce the reflex tachycardia upon standing.49
Check medications
Rescue therapy with saline infusion
Intravenous saline infusion can augment blood volume in patients who are clinically decompensated and present with severe symptoms.1 Intermittent infusion of 1 L of normal saline has been found to significantly reduce orthostatic tachycardia and related symptoms in patients with POTS, contributing to improved quality of life.51,52
Chronic saline infusions are not recommended for long-term care because of the risk of access complications and infection.1 Moak et al53 reported a high rate of bacteremia in a cohort of children with POTS with regular saline infusions, most of whom had a central line. On the other hand, Ruzieh et al54 reported significantly improved symptoms with regular saline infusions without a high rate of complications, but patients in this study received infusions for only a few months and through a peripheral intravenous catheter.
DRUG THERAPY
No medications are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or Health Canada specifically for treating POTS, making all pharmacologic recommendations off-label. Although the drugs discussed below have been evaluated for POTS in controlled laboratory settings, they have yet to be tested in robust clinical trials.
Blood volume expansion
Several drugs expand blood volume, which may reduce orthostatic tachycardia.
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic aldosterone analogue that enhances sodium and water retention. Although one observational study found that it normalizes hemodynamic changes in response to orthostatic stress, no high-level evidence exists for its effectiveness for POTS.55 It is generally well tolerated, although possible adverse effects include hyperkalemia, hypertension, fatigue, nausea, headache, and edema.5,56
Desmopressin is a synthetic version of a natural antidiuretic hormone that increases kidney-mediated free-water reabsorption without sodium retention. It significantly reduces upright heart rate in patients with POTS and improves symptom burden. Although potential adverse effects include edema and headache, hyponatremia is the primary concern with daily use, especially with the increased water intake advised for POTS.57 Patients should be advised to use desmopressin no more than once a week for the acute improvement of symptoms. Intermittent monitoring of serum sodium levels is recommended for safety.
Erythropoietin replacement has been suggested for treating POTS to address the significant deficit in red blood cell volume. Although erythropoietin therapy has a direct vasoconstrictive effect and largely improves red blood cell volume in patients with POTS, it does not expand plasma volume, so orthostatic tachycardia is not itself reduced.22 Nevertheless, it may significantly improve POTS symptoms refractory to more common methods of treatment, and it should be reserved for such cases. In addition to the lack of effect on orthostatic tachycardia, drawbacks to using erythropoietin include its high cost, the need for subcutaneous administration, and the risk of life-threatening complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke.58,59
Heart rate-lowering agents
Propranolol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist, can significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptoms at low dosages (10–20 mg). Higher dosages can further restrain orthostatic tachycardia but are not as well tolerated, mainly due to hypotension and worsening of existing symptoms such as fatigue.60 Regular-acting propranolol works for about 4 to 5 hours per dose, so full-day coverage often requires dosing 4 times per day.
Ivabradine is a selective blocker of the “funny” (If) channel that reduces the sinus node firing rate without affecting blood pressure, so it slows heart rate without causing supine hypertension or orthostatic hypotension.
A retrospective case series found that 60% of patients with POTS treated with ivabradine reported symptomatic improvement, and all patients experienced reduced tachycardia with continued use.61 Ivabradine has not been compared with placebo or propranolol in a randomized controlled trial, and it has not been well studied in pregnancy and so should be avoided because of potential teratogenic effects.
When prescribing ivabradine for women of childbearing age, a negative pregnancy test may be documented prior to initiation of therapy, and the use of highly effective methods of contraception is recommended. Ivabradine should be avoided in women contemplating pregnancy. Insurance coverage can limit access to ivabradine in the United States.
Central nervous system sympatholytics
Patients with prominent hyperadrenergic features may benefit from central sympatholytic agents. However, these drugs may not be well tolerated in patients with neuropathic POTS because of the effects of reduced systemic vascular resistance5 and the possible exacerbation of drowsiness, fatigue, and mental clouding.4 Patients can be extremely sensitive to these medications, so they should initially be prescribed at the lowest dose, then gradually increased as tolerated.
Clonidine, an alpha-2-adrenergic agonist, decreases central sympathetic tone. In hyperadrenergic patients, clonidine can stabilize heart rate and blood pressure, thereby reducing orthostatic symptoms.62
Methyldopa has effects similar to those of clonidine but is easier to titrate owing to its longer half-life.63 Methyldopa is typically started at 125 mg at bedtime and increased to 125 mg twice daily, if tolerated.
Other agents
Midodrine is a prodrug. The active form, an alpha-1-adrenergic agonist, constricts peripheral veins and arteries to increase vascular resistance and venous return, thereby reducing orthostatic tachycardia.52 It is most useful in patients with impaired peripheral vasoconstriction (eg, neuropathic POTS) and may be less effective in those with hyperadrenergic POTS.64 Major limitations of midodrine include worsening supine hypertension and possible urinary retention.39
Because of midodrine’s short half-life, frequent dosing is required during daytime hours (eg, 8 AM, noon, and 4 PM), but it should not be taken within 4 to 5 hours of sleep because of the risk of supine hypertension. Midodrine is typically started at 2.5 to 5 mg per dose and can be titrated up to 15 mg per dose.
Midodrine is an FDA pregnancy category C drug (adverse effects in pregnancy seen in animal models, but evidence lacking in humans). While ideally it should be avoided, we have used it safely in pregnant women with disabling POTS symptoms.
Pyridostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, increases cardiovagal tone and possibly sympathetic tone. It has been reported to significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptom burden in patients with POTS.65 However, pyridostigmine increases gastrointestinal mobility, leading to severe adverse effects in over 20% of patients, including abdominal cramps, nausea, and diarrhea.66
Droxidopa, a synthetic amino acid precursor of norepinephrine, improves dizziness and fatigue in POTS with minimal effects on blood pressure.67
Modafinil, a psychostimulant, may improve POTS-associated cognitive symptoms.4 It also raises upright blood pressure without significantly worsening standing heart rate or acute orthostatic symptoms.68
EFFECTS OF COMORBID DISORDERS ON MANAGEMENT
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Pharmacologic approaches to POTS should not be altered based on the presence of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, but because many of these patients are prone to joint dislocation, exercise prescriptions may need adjusting.
A medical genetics consult is recommended for patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Although the hypermobile type (the form most commonly associated with POTS) is not associated with aortopathy, it can be confused with classical and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, which require serial aortic screening.30
Mast cell activation syndrome
Consultation with an allergist or immunologist may help patients with severe symptoms.
Autoantibodies and autoimmunity
Treatment of the underlying disorder is recommended and can result in significantly improved POTS symptoms.
SPECIALTY CARE REFERRAL
POTS can be challenging to manage. Given the range of physiologic, emotional, and functional distress patients experience, it often requires significant physician time and multidisciplinary care. Patients with continued severe or debilitating symptoms may benefit from referral to a tertiary-care center with experience in autonomic nervous system disorders.
PROGNOSIS
Limited data are available on the long-term prognosis of POTS, and more studies are needed in pediatric and adult populations. No deaths have been reported in the handful of published cases of POTS in patients older than 50.1 Some pediatric studies suggest that some teenagers “outgrow” their POTS. However, these data are not robust, and an alternative explanation is that as they get older, they see adult physicians for their POTS symptoms and so are lost to study follow-up.6,44,69
We have not often seen POTS simply resolve without ongoing treatment. However, in our experience, most patients have improved symptoms and function with multimodal treatment (ie, exercise, salt, water, stockings, and some medications) and time.
Some people, most of them relatively young women, experience lightheadedness, a racing heart, and other symptoms (but not hypotension) when they stand up, in a condition known as postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS).1 Although not known to shorten life,1 it can be physically and mentally debilitating.2,3 Therapy rarely cures it, but a multifaceted approach can substantially improve quality of life.
This review outlines the evaluation and diagnosis of POTS and provides guidance for a therapy regimen.
HOW IS POTS DEFINED?
POTS is a multifactorial syndrome rather than a specific disease. It is characterized by all of the following1,4–6:
- An increase in heart rate of ≥ 30 bpm, or ≥ 40 bpm for those under age 19, within 10 minutes of standing from a supine position
- Sustained tachycardia (> 30 seconds)
- Absence of orthostatic hypotension (a fall in blood pressure of ≥ 20/10 mm Hg)
- Frequent and chronic duration (≥ 6 months).
These features are critical to diagnosis. Hemodynamic criteria in isolation may describe postural tachycardia but are not sufficient to diagnose POTS.
The prevalence of POTS is estimated to be between 0.2% and 1.0%,7 affecting up to 3 million people in the United States. Most cases arise between ages 13 and 50, with a female-to-male ratio of 5:1.8
MANY NAMES, SAME CONDITION
In 1871, Da Costa9 described a condition he called “irritable heart syndrome” that had characteristics similar to those of POTS, including extreme fatigue and exercise intolerance. Decades later, Lewis10 and Wood11 provided more detailed descriptions of the disorder, renaming it “soldier’s heart” or “Da Costa syndrome.” As other cases were documented, more terms arose, including “effort syndrome” and “mitral valve prolapse syndrome.”
In 1982, Rosen and Cryer12 were the first to use the term “postural tachycardia syndrome” for patients with disabling tachycardia upon standing without orthostatic hypotension. In 1986, Fouad et al13 described patients with postural tachycardia, orthostatic intolerance, and a small degree of hypotension as having “idiopathic hypovolemia.”
In 1993, Schondorf and Low14 established the current definition of POTS, leading to increased awareness and research efforts to understand its pathophysiology.
MULTIFACTORIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
During the last 2 decades, several often-overlapping forms of POTS have been recognized, all of which share a final common pathway of sustained orthostatic tachycardia.15–19 In addition, a number of common comorbidities were identified through review of large clinic populations of POTS.20,21
Hypovolemic POTS
Up to 70% of patients with POTS have hypovolemia. The average plasma volume deficit is about 13%, which typically causes only insignificant changes in heart rate and norepinephrine levels while a patient is supine. However, blood pooling associated with upright posture further compromises cardiac output and consequently increases sympathetic nerve activity. Abnormalities in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone volume regulation system are also suspected to impair sodium retention, contributing to hypovolemia.1,22
Neuropathic POTS
About half of patients with POTS have partial sympathetic denervation (particularly in the lower limbs) and inadequate vasoconstriction upon standing, leading to reduced venous return and stroke volume.17,23 A compensatory increase in sympathetic tone results in tachycardia to maintain cardiac output and blood pressure.
Hyperadrenergic POTS
Up to 50% of patients with POTS have high norepinephrine levels (≥ 600 pg/mL) when upright. This subtype, hyperadrenergic POTS, is characterized by an increase in systolic blood pressure of at least 10 mm Hg within 10 minutes of standing, with concomitant tachycardia that can be similar to or greater than that seen in nonhyperadrenergic POTS. Patients with hyperadrenergic POTS tend to report more prominent symptoms of sympathetic activation, such as palpitations, anxiety, and tremulousness.24,25
Norepinephrine transporter deficiency
The norepinephrine transporter (NET) is on the presynaptic cleft of sympathetic neurons and serves to clear synaptic norepinephrine. NET deficiency leads to a hyperadrenergic state and elevated sympathetic nerve activation.18 NET deficiency may be induced by common antidepressants (eg, tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and attention-deficit disorder medications.4
Mast cell activation syndrome
The relationship between mast cell activation syndrome and POTS is poorly understood.4,26 Mast cell activation syndrome has been described in a subset of patients with POTS who have sinus tachycardia accompanied by severe episodic flushing. Patients with this subtype have a hyperadrenergic response to postural change and elevated urine methylhistamine during flushing episodes.
Patients with mast cell activation syndrome tend to have strong allergic symptoms and may also have severe gastrointestinal problems, food sensitivities, dermatographism, and neuropathy. Diagnosis can be difficult, as the condition is associated with numerous markers with varying sensitivity and specificity.
Autoimmune origin
A significant minority of patients report a viral-like illness before the onset of POTS symptoms, suggesting a possible autoimmune-mediated or inflammatory cause. Also, some autoimmune disorders (eg, Sjögren syndrome) can present with a POTS-like manifestation.
Research into the role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of POTS offers the potential to develop novel therapeutic targets. Autoantibodies that have been reported in POTS include those against M1 to M3 muscarinic receptors (present in over 87% of patients with POTS),27 cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins,28 adrenergic G-protein coupled receptors, alpha-1-adrenergic receptors, and beta-1- and beta-2-adrenergic receptors.29 Although commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays can assess for these antibody fragments, it is not known whether targeting the antibodies improves outcomes. At this time, antibody testing for POTS should be confined to the research setting.
LINKS TO OTHER SYNDROMES
POTS is often associated with other conditions whose symptoms cannot be explained by postural intolerance or tachycardia.
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes are a group of inherited heterogeneous disorders involving joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility.30 The hypermobile subtype is most commonly associated with POTS, with patients often having symptoms of autonomic dysregulation and autonomic test abnormalities.31–33 Patients with POTS may have a history of joint subluxations, joint pain, cervical instability, and spontaneous epidural leaks. The reason for the overlap between the two syndromes is not clear.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is characterized by persistent fatigue that does not resolve with rest and is not necessarily associated with orthostatic changes. More than 75% of patients with POTS report general fatigue as a major complaint, and up to 23% meet the full criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome.34
DIAGNOSTIC STRATEGY
A patient presenting with symptoms suggestive of POTS should first undergo a detailed history and physical examination. Other causes of sinus tachycardia should be considered.
Detailed history, symptom review
The history should focus on determining symptom burden, including tachycardia onset, frequency, severity, and triggers; the presence of syncope; and the impact of symptoms on daily function and quality of life.
Presyncope and its associated symptoms occur in less than one-third of patients with POTS, and syncope is not a principal feature.4 If syncope is the predominant complaint, alternative causes should be investigated. The usual cause of syncope in the general population is thought to be vasovagal.
In addition to orthostatic intolerance, gastrointestinal disturbances are common in POTS, presenting as abdominal pain, heartburn, irregular bowel movements, diarrhea, or constipation. Symptoms of gastroparesis are less common. Gastrointestinal symptoms tend to be prolonged, lasting hours and occurring multiple times a week. They tend not to improve in the supine position.35
POTS-associated symptoms may develop insidiously, but patients often report onset after an acute stressor such as pregnancy, major surgery, or a presumed viral illness.4 Whether these putative triggers are causative or coincidental is unknown. Symptoms of orthostatic intolerance tend to be exacerbated by dehydration, heat, alcohol, exercise, and menstruation.36,37
Consider the family history: 1 in 8 patients with POTS reports familial orthostatic intolerance,38 suggesting a genetic role in some patients. Inquire about symptoms or a previous diagnosis of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and mast cell activation syndrome.
Consider other conditions
Pheochromocytoma causes hyperadrenergic symptoms (eg, palpitations, lightheadedness) like those in POTS, but patients with pheochromocytoma typically have these symptoms while supine. Pheochromocytoma is also characterized by plasma norepinephrine levels much higher than in POTS.4 Plasma metanephrine testing helps diagnose or rule out pheochromocytoma.5
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia, like pheochromocytoma, also has clinical features similar to those of POTS, as well as tachycardia present when supine. It involves higher sympathetic tone and lower parasympathetic tone compared with POTS; patients commonly have a daytime resting heart rate of at least 100 bpm or a 24-hour mean heart rate of at least 90 bpm.1,42 While the intrinsic heart rate is heightened in inappropriate sinus tachycardia, it is not different between POTS patients and healthy individuals.42,43 Distinguishing POTS from inappropriate sinus tachycardia is further complicated by the broad inclusion criteria of most studies of inappropriate sinus tachycardia, which failed to exclude patients with POTS.44 The Heart Rhythm Society recently adopted distinct definitions for the 2 conditions.1
Physical examination: Focus on vital signs
Dependent acrocyanosis—dark red-blue discoloration of the lower legs that is cold to the touch—occurs in about half of patients with POTS upon standing.4 Dependent acrocyanosis is associated with joint hypermobility and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, so these conditions should also be considered if findings are positive.
Laboratory testing for other causes
Laboratory testing is used mainly to detect primary causes of sinus tachycardia. Tests should include:
- Complete blood cell count with hematocrit (for severe anemia)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone level (for hyperthyroidism)
- Electrolyte panel (for significant electrolyte disturbances).
Evidence is insufficient to support routinely measuring the vitamin B12 level, iron indices, and serum markers for celiac disease, although these may be done if the history or physical examination suggests related problems.4 Sicca symptoms (severe dry eye or dry mouth) should trigger evaluation for Sjögren syndrome.
Electrocardiography needed
Electrocardiography should be performed to investigate for cardiac conduction abnormalities as well as for resting markers of a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. Extended ambulatory (Holter) monitoring may be useful to evaluate for a transient reentrant tachyarrhythmia4; however, it does not record body position, so it can be difficult to determine if detected episodes of tachycardia are related to posture.
Additional testing for select cases
Further investigation is usually not needed to diagnose POTS but should be considered in some cases. Advanced tests are typically performed at a tertiary care referral center and include:
- Quantitative sensory testing to evaluate for small-fiber neuropathy (ie, Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test, or QSART), which occurs in the neuropathic POTS subtype
- Formal autonomic function testing to characterize neurovascular responsiveness
- Supine and standing plasma norepinephrine levels (fractionated catecholamines) to characterize the net activation of the sympathetic nervous system
- Blood volume assessments to assess hypovolemia
- Formal exercise testing to objectively quantify exercise capacity.
GRADED MANAGEMENT
No single universal gold-standard therapy exists for POTS, and management should be individually determined with the primary goals of treating symptoms and restoring function. A graded approach should be used, starting with conservative nonpharmacologic therapies and adding medications as needed.
While the disease course varies substantially from patient to patient, proper management is strongly associated with eventual symptom improvement.1
NONPHARMACOLOGIC STEPS FIRST
Education
Patients should be informed of the nature of their condition and referred to appropriate healthcare personnel. POTS is a chronic illness requiring individualized coping strategies, intensive physician interaction, and support of a multidisciplinary team. Patients and family members can be reassured that most symptoms improve over time with appropriate diagnosis and treatment.1 Patients should be advised to avoid aggravating triggers and activities.
Exercise
Exercise programs are encouraged but should be introduced gradually, as physical activity can exacerbate symptoms, especially at the outset. Several studies have reported benefits from a short-term (3-month) program, in which the patient gradually progresses from non-upright exercise (eg, rowing machine, recumbent cycle, swimming) to upright endurance exercises. At the end of these programs, significant cardiac remodeling, improved quality of life, and reduced heart rate responses to standing have been reported, and benefits have been reported to persist in patients who continued exercising after the 3-month study period.46,47
Despite the benefits of exercise interventions, compliance is low.46,47 To prevent early discouragement, patients should be advised that it can take 4 to 6 weeks of continued exercise before benefits appear. Patients are encouraged to exercise every other day for 30 minutes or more. Regimens should primarily focus on aerobic conditioning, but resistance training, concentrating on thigh muscles, can also help. Exercise is a treatment and not a cure, and benefits can rapidly disappear if regular activity (at least 3 times per week) is stopped.48
Compression stockings
Compression stockings help reduce peripheral venous pooling and enhance venous return to the heart. Waist-high stockings with compression of at least 30 to 40 mm Hg offer the best results.
Diet
Increased fluid and salt intake is advisable for patients with suspected hypovolemia. At least 2 to 3 L of water accompanied by 10 to 12 g of daily sodium intake is recommended.1 This can usually be accomplished with diet and salt added to food, but salt tablets can be used if the patient prefers. The resultant plasma volume expansion may help reduce the reflex tachycardia upon standing.49
Check medications
Rescue therapy with saline infusion
Intravenous saline infusion can augment blood volume in patients who are clinically decompensated and present with severe symptoms.1 Intermittent infusion of 1 L of normal saline has been found to significantly reduce orthostatic tachycardia and related symptoms in patients with POTS, contributing to improved quality of life.51,52
Chronic saline infusions are not recommended for long-term care because of the risk of access complications and infection.1 Moak et al53 reported a high rate of bacteremia in a cohort of children with POTS with regular saline infusions, most of whom had a central line. On the other hand, Ruzieh et al54 reported significantly improved symptoms with regular saline infusions without a high rate of complications, but patients in this study received infusions for only a few months and through a peripheral intravenous catheter.
DRUG THERAPY
No medications are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or Health Canada specifically for treating POTS, making all pharmacologic recommendations off-label. Although the drugs discussed below have been evaluated for POTS in controlled laboratory settings, they have yet to be tested in robust clinical trials.
Blood volume expansion
Several drugs expand blood volume, which may reduce orthostatic tachycardia.
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic aldosterone analogue that enhances sodium and water retention. Although one observational study found that it normalizes hemodynamic changes in response to orthostatic stress, no high-level evidence exists for its effectiveness for POTS.55 It is generally well tolerated, although possible adverse effects include hyperkalemia, hypertension, fatigue, nausea, headache, and edema.5,56
Desmopressin is a synthetic version of a natural antidiuretic hormone that increases kidney-mediated free-water reabsorption without sodium retention. It significantly reduces upright heart rate in patients with POTS and improves symptom burden. Although potential adverse effects include edema and headache, hyponatremia is the primary concern with daily use, especially with the increased water intake advised for POTS.57 Patients should be advised to use desmopressin no more than once a week for the acute improvement of symptoms. Intermittent monitoring of serum sodium levels is recommended for safety.
Erythropoietin replacement has been suggested for treating POTS to address the significant deficit in red blood cell volume. Although erythropoietin therapy has a direct vasoconstrictive effect and largely improves red blood cell volume in patients with POTS, it does not expand plasma volume, so orthostatic tachycardia is not itself reduced.22 Nevertheless, it may significantly improve POTS symptoms refractory to more common methods of treatment, and it should be reserved for such cases. In addition to the lack of effect on orthostatic tachycardia, drawbacks to using erythropoietin include its high cost, the need for subcutaneous administration, and the risk of life-threatening complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke.58,59
Heart rate-lowering agents
Propranolol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist, can significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptoms at low dosages (10–20 mg). Higher dosages can further restrain orthostatic tachycardia but are not as well tolerated, mainly due to hypotension and worsening of existing symptoms such as fatigue.60 Regular-acting propranolol works for about 4 to 5 hours per dose, so full-day coverage often requires dosing 4 times per day.
Ivabradine is a selective blocker of the “funny” (If) channel that reduces the sinus node firing rate without affecting blood pressure, so it slows heart rate without causing supine hypertension or orthostatic hypotension.
A retrospective case series found that 60% of patients with POTS treated with ivabradine reported symptomatic improvement, and all patients experienced reduced tachycardia with continued use.61 Ivabradine has not been compared with placebo or propranolol in a randomized controlled trial, and it has not been well studied in pregnancy and so should be avoided because of potential teratogenic effects.
When prescribing ivabradine for women of childbearing age, a negative pregnancy test may be documented prior to initiation of therapy, and the use of highly effective methods of contraception is recommended. Ivabradine should be avoided in women contemplating pregnancy. Insurance coverage can limit access to ivabradine in the United States.
Central nervous system sympatholytics
Patients with prominent hyperadrenergic features may benefit from central sympatholytic agents. However, these drugs may not be well tolerated in patients with neuropathic POTS because of the effects of reduced systemic vascular resistance5 and the possible exacerbation of drowsiness, fatigue, and mental clouding.4 Patients can be extremely sensitive to these medications, so they should initially be prescribed at the lowest dose, then gradually increased as tolerated.
Clonidine, an alpha-2-adrenergic agonist, decreases central sympathetic tone. In hyperadrenergic patients, clonidine can stabilize heart rate and blood pressure, thereby reducing orthostatic symptoms.62
Methyldopa has effects similar to those of clonidine but is easier to titrate owing to its longer half-life.63 Methyldopa is typically started at 125 mg at bedtime and increased to 125 mg twice daily, if tolerated.
Other agents
Midodrine is a prodrug. The active form, an alpha-1-adrenergic agonist, constricts peripheral veins and arteries to increase vascular resistance and venous return, thereby reducing orthostatic tachycardia.52 It is most useful in patients with impaired peripheral vasoconstriction (eg, neuropathic POTS) and may be less effective in those with hyperadrenergic POTS.64 Major limitations of midodrine include worsening supine hypertension and possible urinary retention.39
Because of midodrine’s short half-life, frequent dosing is required during daytime hours (eg, 8 AM, noon, and 4 PM), but it should not be taken within 4 to 5 hours of sleep because of the risk of supine hypertension. Midodrine is typically started at 2.5 to 5 mg per dose and can be titrated up to 15 mg per dose.
Midodrine is an FDA pregnancy category C drug (adverse effects in pregnancy seen in animal models, but evidence lacking in humans). While ideally it should be avoided, we have used it safely in pregnant women with disabling POTS symptoms.
Pyridostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, increases cardiovagal tone and possibly sympathetic tone. It has been reported to significantly reduce standing heart rate and improve symptom burden in patients with POTS.65 However, pyridostigmine increases gastrointestinal mobility, leading to severe adverse effects in over 20% of patients, including abdominal cramps, nausea, and diarrhea.66
Droxidopa, a synthetic amino acid precursor of norepinephrine, improves dizziness and fatigue in POTS with minimal effects on blood pressure.67
Modafinil, a psychostimulant, may improve POTS-associated cognitive symptoms.4 It also raises upright blood pressure without significantly worsening standing heart rate or acute orthostatic symptoms.68
EFFECTS OF COMORBID DISORDERS ON MANAGEMENT
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Pharmacologic approaches to POTS should not be altered based on the presence of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, but because many of these patients are prone to joint dislocation, exercise prescriptions may need adjusting.
A medical genetics consult is recommended for patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Although the hypermobile type (the form most commonly associated with POTS) is not associated with aortopathy, it can be confused with classical and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndromes, which require serial aortic screening.30
Mast cell activation syndrome
Consultation with an allergist or immunologist may help patients with severe symptoms.
Autoantibodies and autoimmunity
Treatment of the underlying disorder is recommended and can result in significantly improved POTS symptoms.
SPECIALTY CARE REFERRAL
POTS can be challenging to manage. Given the range of physiologic, emotional, and functional distress patients experience, it often requires significant physician time and multidisciplinary care. Patients with continued severe or debilitating symptoms may benefit from referral to a tertiary-care center with experience in autonomic nervous system disorders.
PROGNOSIS
Limited data are available on the long-term prognosis of POTS, and more studies are needed in pediatric and adult populations. No deaths have been reported in the handful of published cases of POTS in patients older than 50.1 Some pediatric studies suggest that some teenagers “outgrow” their POTS. However, these data are not robust, and an alternative explanation is that as they get older, they see adult physicians for their POTS symptoms and so are lost to study follow-up.6,44,69
We have not often seen POTS simply resolve without ongoing treatment. However, in our experience, most patients have improved symptoms and function with multimodal treatment (ie, exercise, salt, water, stockings, and some medications) and time.
- Sheldon RS, Grubb BP 2nd, Olshansky B, et al. 2015 Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and vasovagal syncope. Heart Rhythm 2015; 12(6):e41–e63. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.03.029
- Bagai K, Song Y, Ling JF, et al. Sleep disturbances and diminished quality of life in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med 2011; 7(2):204–210. pmid:21509337
- Benrud-Larson LM, Dewar MS, Sandroni P, Rummans TA, Haythornthwaite JA, Low PA. Quality of life in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 2002; 77(6):531–537. doi:10.4065/77.6.531
- Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). Circulation 2013; 127(23):2336–2342. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.144501
- Raj SR. The postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS): pathophysiology, diagnosis & management. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 2006; 6(2):84–99. pmid:16943900
- Singer W, Sletten DM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Brands CK, Fischer PR, Low PA. Postural tachycardia in children and adolescents: what is abnormal? J Pediatr 2012; 160(2):222–226. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.08.054
- Mar PL, Raj SR. Neuronal and hormonal perturbations in postural tachycardia syndrome. Front Physiol 2014; 5:220. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00220
- Garland EM, Raj SR, Black BK, Harris PA, Robertson D. The hemodynamic and neurohumoral phenotype of postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurology 2007; 69(8):790–798. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000267663.05398.40
- Da Costa JM. On irritable heart: a clinical study of a form of functional cardiac disorder and its consequences. Am J Med Sci 1871; 61(121):2–52.
- Lewis T. The tolerance of physical exertion, as shown by soldiers suffering from so-called “irritable heart.” Br Med J 1918; 1(2987):363–365. pmid:20768980
- Wood P. Da Costa’s syndrome (or effort syndrome): lecture I. Br Med J 1941; 1(4194):767–772. pmid:20783672
- Rosen SG, Cryer PE. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Reversal of sympathetic hyperresponsiveness and clinical improvement during sodium loading. Am J Med 1982; 72(5):847–850.
- Fouad FM, Tadena-Thome L, Bravo EL, Tarazi RC. Idiopathic hypovolemia. Ann Intern Med 1986; 104(3):298–303. pmid:3511818
- Schondorf R, Low PA. Idiopathic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: an attenuated form of acute pandysautonomia? Neurology 1993; 43(1):132–137. pmid:8423877
- Vernino S, Low PA, Fealey RD, Stewart JD, Farrugia G, Lennon VA. Autoantibodies to ganglionic acetylcholine receptors in autoimmune autonomic neuropathies. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(12):847–855. doi:10.1056/NEJM200009213431204
- Raj SR, Robertson D. Blood volume perturbations in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Am J Med Sci 2007; 334(1):57–60. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318063c6c0
- Jacob G, Costa F, Shannon JR, et al. The neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(14):1008–1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM200010053431404
- Shannon JR, Flattem NL, Jordan J, et al. Orthostatic intolerance and tachycardia associated with norepinephrine-transporter deficiency. N Engl J Med 2000; 342(8):541–549. doi:10.1056/NEJM200002243420803
- Jones PK, Shaw BH, Raj SR. Clinical challenges in the diagnosis and management of postural tachycardia syndrome. Pract Neurol 2016; 16(6):431–438. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2016-001405
- Gunning WT, Karabin BL, Blomquist TM, Grubb BP. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is associated with platelet storage pool deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(37):e4849. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004849
- Kanjwal K, Sheikh M, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Neurocardiogenic syncope coexisting with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in patients suffering from orthostatic intolerance: a combined form of autonomic dysfunction. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(5):549–554. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02994.x
- Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Yamhure PC, et al. Renin-aldosterone paradox and perturbed blood volume regulation underlying postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(13):1574–1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000160356.97313.5D
- Gibbons CH, Bonyhay I, Benson A, Wang N, Freeman R. Structural and functional small fiber abnormalities in the neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e84716. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084716
- Low PA, Sandroni P, Joyner M, Shen WK. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2009; 20(3):352–358. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2008.01407.x
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Clinical presentation and management of patients with hyperadrenergic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. A single center experience. Cardiol J 2011; 18(5):527–531. pmid:21947988
- Shibao C, Arzubiaga C, Roberts J, et al. Hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome in mast cell activation disorders. Hypertension 2005; 45(3):385–390. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000158259.68614.40
- Dubey D, Hopkins S, Vernino S. M1 and M2 muscarinic receptor antibodies among patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: potential disease biomarker [abstract]. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2016; 17(3):179S.
- Wang XL, Ling TY, Charlesworth MC, et al. Autoimmunoreactive IgGs against cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Transl Res 2013; 162(1):34–44. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.002
- Li H, Yu X, Liles C, et al. Autoimmune basis for postural tachycardia syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(1):e000755. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000755
- Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2017; 175(1):8–26. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31552
- Wallman D, Weinberg J, Hohler AD. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and postural tachycardia syndrome: a relationship study. J Neurol Sci 2014; 340(1-2):99–102. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2014.03.002
- De Wandele I, Calders P, Peersman W, et al. Autonomic symptom burden in the hypermobility type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a comparative study with two other EDS types, fibromyalgia, and healthy controls. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 44(3):353–361. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.05.013
- Gazit Y, Nahir AM, Grahame R, Jacob G. Dysautonomia in the joint hypermobility syndrome. Am J Med 2003; 115(1):33–40. pmid:12867232
- Okamoto LE, Raj SR, Peltier A, et al. Neurohumoral and haemodynamic profile in postural tachycardia and chronic fatigue syndromes. Clin Sci (Lond) 2012; 122(4):183–192. doi:10.1042/CS20110200
- Wang LB, Culbertson CJ, Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Huang H, Hohler AD. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Neurol Sci 2015; 359(1-2):193–196. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2015.10.052
- Raj S, Sheldon R. Management of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia and vasovagal syncope. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2016; 5(2):122–129. doi:10.15420/AER.2016.7.2
- Peggs KJ, Nguyen H, Enayat D, Keller NR, Al-Hendy A, Raj SR. Gynecologic disorders and menstrual cycle lightheadedness in postural tachycardia syndrome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012; 118(3):242–246. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.04.014
- Thieben MJ, Sandroni P, Sletten DM, et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo Clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc 2007; 82(3):308–313. doi:10.4065/82.3.308
- Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Culbertson CJ, Wang LB, Hohler AD. A survey-based analysis of symptoms in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 28(7):157–159. pmid:25829642
- Ertek S, Cicero AF. Hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular complications: a narrative review on the basis of pathophysiology. Arch Med Sci 2013; 9(5):944–952. doi:10.5114/aoms.2013.38685
- Rangno RE, Langlois S. Comparison of withdrawal phenomena after propranolol, metoprolol and pindolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1982; 13(suppl 2):345S–351S. pmid:6125187
- Nwazue VC, Paranjape SY, Black BK, et al. Postural tachycardia syndrome and inappropriate sinus tachycardia: role of autonomic modulation and sinus node automaticity. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(2):e000700. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000700
- Morillo CA, Klein GJ, Thakur RK, Li H, Zardini M, Yee R. Mechanism of “inappropriate” sinus tachycardia. Role of sympathovagal balance. Circulation 1994; 90(2):873–877. pmid:7913886
- Grubb BP. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2008; 117(21):2814–2817. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761643
- Bhatia R, Kizilbash SJ, Ahrens SP, et al. Outcomes of adolescent-onset postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Pediatr 2016; 173:149–153. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.035
- George SA, Bivens TB, Howden EJ, et al. The international POTS registry: evaluating the efficacy of an exercise training intervention in a community setting. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):943–950. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.012
- Fu Q, VanGundy TB, Galbreath MM, et al. Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55(25):2858–2868. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.043
- Raj SR. Row, row, row your way to treating postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):951–952. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.039
- Celedonio JE, Garland EM, Nwazue VC, et al. Effects of high sodium intake on blood volume and catecholamines in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome and healthy females [abstract]. Clin Auton Res 2014; 24:211.
- Garland EM, Celedonio JE, Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome: beyond orthostatic intolerance. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2015; 15(9):60. doi:10.1007/s11910-015-0583-8
- Gordon VM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Novak V, Low PA. Hemodynamic and symptomatic effects of acute interventions on tilt in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10:29–33. pmid:10750641
- Jacob G, Shannon JR, Black B, et al. Effects of volume loading and pressor agents in idiopathic orthostatic tachycardia. Circulation 1997; 96(2):575–580. pmid:9244228
- Moak JP, Leong D, Fabian R, et al. Intravenous hydration for management of medication-resistant orthostatic intolerance in the adolescent and young adult. Pediatr Cardiol 2016; 37(2):278–282. doi:10.1007/s00246-015-1274-6
- Ruzieh M, Baugh A, Dasa O, et al. Effects of intermittent intravenous saline infusions in patients with medication-refractory postural tachycardia syndrome. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2017; 48(3):255–260. doi:10.1007/s10840-017-0225-y
- Freitas J, Santos R, Azevedo E, Costa O, Carvalho M, de Freitas AF. Clinical improvement in patients with orthostatic intolerance after treatment with bisoprolol and fludrocortisone. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10(5):293–299. pmid:11198485
- Lee AK, Krahn AD. Evaluation of syncope: focus on diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2016; 14(6):725–736. doi:10.1586/14779072.2016.1164034
- Coffin ST, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Desmopressin acutely decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2012; 9(9):1484–1490. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.05.002
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Sheikh M, Grubb BP. Erythropoietin in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2012; 19(2):92–95. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ef621a
- Hoeldtke RD, Horvath GG, Bryner KD. Treatment of orthostatic tachycardia with erythropoietin. Am J Med 1995; 99(5):525–529. pmid:7485211
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Propranolol decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome: less is more. Circulation 2009; 120(9):725–734. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.846501
- McDonald C, Frith J, Newton JL. Single centre experience of ivabradine in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Europace 2011; 13(3):427–430. doi:10.1093/europace/euq390
- Gaffney FA, Lane LB, Pettinger W, Blomqvist G. Effects of long-term clonidine administration on the hemodynamic and neuroendocrine postural responses of patients with dysautonomia. Chest 1983; 83(suppl 2):436–438. pmid:6295714
- Jacob G, Biaggioni I. Idiopathic orthostatic intolerance and postural tachycardia syndromes. Am J Med Sci 1999; 317(2):88–101. pmid:10037112
- Ross AJ, Ocon AJ, Medow MS, Stewart JM. A double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study of the vascular effects of midodrine in neuropathic compared with hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014; 126(4):289–296. doi:10.1042/CS20130222
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, Harris PA, Robertson D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition improves tachycardia in postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(21):2734–2340. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.497594
- Kanjwal K, Karabin B, Sheikh M, et al. Pyridostigmine in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia: A single-center experience. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(6):750–755. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03047.x
- Ruzieh M, Dasa O, Pacenta A, Karabin B, Grubb B. Droxidopa in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2017; 24(2):e157–e161. doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000000468
- Kpaeyeh AG Jr, Mar PL, Raj V, et al. Hemodynamic profiles and tolerability of modafinil in the treatment of POTS: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2014; 34(6):738–741. doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000000221
- Lai CC, Fischer PR, Brands CK, et al. Outcomes in adolescents with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome treated with midodrine and beta-blockers. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2009; 32(2):234–238. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.02207.x
- Sheldon RS, Grubb BP 2nd, Olshansky B, et al. 2015 Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and treatment of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and vasovagal syncope. Heart Rhythm 2015; 12(6):e41–e63. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.03.029
- Bagai K, Song Y, Ling JF, et al. Sleep disturbances and diminished quality of life in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med 2011; 7(2):204–210. pmid:21509337
- Benrud-Larson LM, Dewar MS, Sandroni P, Rummans TA, Haythornthwaite JA, Low PA. Quality of life in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 2002; 77(6):531–537. doi:10.4065/77.6.531
- Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). Circulation 2013; 127(23):2336–2342. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.144501
- Raj SR. The postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS): pathophysiology, diagnosis & management. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 2006; 6(2):84–99. pmid:16943900
- Singer W, Sletten DM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Brands CK, Fischer PR, Low PA. Postural tachycardia in children and adolescents: what is abnormal? J Pediatr 2012; 160(2):222–226. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.08.054
- Mar PL, Raj SR. Neuronal and hormonal perturbations in postural tachycardia syndrome. Front Physiol 2014; 5:220. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00220
- Garland EM, Raj SR, Black BK, Harris PA, Robertson D. The hemodynamic and neurohumoral phenotype of postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurology 2007; 69(8):790–798. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000267663.05398.40
- Da Costa JM. On irritable heart: a clinical study of a form of functional cardiac disorder and its consequences. Am J Med Sci 1871; 61(121):2–52.
- Lewis T. The tolerance of physical exertion, as shown by soldiers suffering from so-called “irritable heart.” Br Med J 1918; 1(2987):363–365. pmid:20768980
- Wood P. Da Costa’s syndrome (or effort syndrome): lecture I. Br Med J 1941; 1(4194):767–772. pmid:20783672
- Rosen SG, Cryer PE. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Reversal of sympathetic hyperresponsiveness and clinical improvement during sodium loading. Am J Med 1982; 72(5):847–850.
- Fouad FM, Tadena-Thome L, Bravo EL, Tarazi RC. Idiopathic hypovolemia. Ann Intern Med 1986; 104(3):298–303. pmid:3511818
- Schondorf R, Low PA. Idiopathic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: an attenuated form of acute pandysautonomia? Neurology 1993; 43(1):132–137. pmid:8423877
- Vernino S, Low PA, Fealey RD, Stewart JD, Farrugia G, Lennon VA. Autoantibodies to ganglionic acetylcholine receptors in autoimmune autonomic neuropathies. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(12):847–855. doi:10.1056/NEJM200009213431204
- Raj SR, Robertson D. Blood volume perturbations in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Am J Med Sci 2007; 334(1):57–60. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e318063c6c0
- Jacob G, Costa F, Shannon JR, et al. The neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000; 343(14):1008–1014. doi:10.1056/NEJM200010053431404
- Shannon JR, Flattem NL, Jordan J, et al. Orthostatic intolerance and tachycardia associated with norepinephrine-transporter deficiency. N Engl J Med 2000; 342(8):541–549. doi:10.1056/NEJM200002243420803
- Jones PK, Shaw BH, Raj SR. Clinical challenges in the diagnosis and management of postural tachycardia syndrome. Pract Neurol 2016; 16(6):431–438. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2016-001405
- Gunning WT, Karabin BL, Blomquist TM, Grubb BP. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is associated with platelet storage pool deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95(37):e4849. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000004849
- Kanjwal K, Sheikh M, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Neurocardiogenic syncope coexisting with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in patients suffering from orthostatic intolerance: a combined form of autonomic dysfunction. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(5):549–554. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2010.02994.x
- Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Yamhure PC, et al. Renin-aldosterone paradox and perturbed blood volume regulation underlying postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(13):1574–1582. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000160356.97313.5D
- Gibbons CH, Bonyhay I, Benson A, Wang N, Freeman R. Structural and functional small fiber abnormalities in the neuropathic postural tachycardia syndrome. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e84716. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084716
- Low PA, Sandroni P, Joyner M, Shen WK. Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2009; 20(3):352–358. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2008.01407.x
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Grubb BP. Clinical presentation and management of patients with hyperadrenergic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. A single center experience. Cardiol J 2011; 18(5):527–531. pmid:21947988
- Shibao C, Arzubiaga C, Roberts J, et al. Hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome in mast cell activation disorders. Hypertension 2005; 45(3):385–390. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000158259.68614.40
- Dubey D, Hopkins S, Vernino S. M1 and M2 muscarinic receptor antibodies among patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: potential disease biomarker [abstract]. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2016; 17(3):179S.
- Wang XL, Ling TY, Charlesworth MC, et al. Autoimmunoreactive IgGs against cardiac lipid raft-associated proteins in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Transl Res 2013; 162(1):34–44. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2013.03.002
- Li H, Yu X, Liles C, et al. Autoimmune basis for postural tachycardia syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(1):e000755. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000755
- Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2017; 175(1):8–26. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31552
- Wallman D, Weinberg J, Hohler AD. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and postural tachycardia syndrome: a relationship study. J Neurol Sci 2014; 340(1-2):99–102. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2014.03.002
- De Wandele I, Calders P, Peersman W, et al. Autonomic symptom burden in the hypermobility type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a comparative study with two other EDS types, fibromyalgia, and healthy controls. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2014; 44(3):353–361. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.05.013
- Gazit Y, Nahir AM, Grahame R, Jacob G. Dysautonomia in the joint hypermobility syndrome. Am J Med 2003; 115(1):33–40. pmid:12867232
- Okamoto LE, Raj SR, Peltier A, et al. Neurohumoral and haemodynamic profile in postural tachycardia and chronic fatigue syndromes. Clin Sci (Lond) 2012; 122(4):183–192. doi:10.1042/CS20110200
- Wang LB, Culbertson CJ, Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Huang H, Hohler AD. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in postural tachycardia syndrome. J Neurol Sci 2015; 359(1-2):193–196. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2015.10.052
- Raj S, Sheldon R. Management of postural tachycardia syndrome, inappropriate sinus tachycardia and vasovagal syncope. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2016; 5(2):122–129. doi:10.15420/AER.2016.7.2
- Peggs KJ, Nguyen H, Enayat D, Keller NR, Al-Hendy A, Raj SR. Gynecologic disorders and menstrual cycle lightheadedness in postural tachycardia syndrome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012; 118(3):242–246. doi:10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.04.014
- Thieben MJ, Sandroni P, Sletten DM, et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo Clinic experience. Mayo Clin Proc 2007; 82(3):308–313. doi:10.4065/82.3.308
- Deb A, Morgenshtern K, Culbertson CJ, Wang LB, Hohler AD. A survey-based analysis of symptoms in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 28(7):157–159. pmid:25829642
- Ertek S, Cicero AF. Hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular complications: a narrative review on the basis of pathophysiology. Arch Med Sci 2013; 9(5):944–952. doi:10.5114/aoms.2013.38685
- Rangno RE, Langlois S. Comparison of withdrawal phenomena after propranolol, metoprolol and pindolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1982; 13(suppl 2):345S–351S. pmid:6125187
- Nwazue VC, Paranjape SY, Black BK, et al. Postural tachycardia syndrome and inappropriate sinus tachycardia: role of autonomic modulation and sinus node automaticity. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3(2):e000700. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000700
- Morillo CA, Klein GJ, Thakur RK, Li H, Zardini M, Yee R. Mechanism of “inappropriate” sinus tachycardia. Role of sympathovagal balance. Circulation 1994; 90(2):873–877. pmid:7913886
- Grubb BP. Postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2008; 117(21):2814–2817. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761643
- Bhatia R, Kizilbash SJ, Ahrens SP, et al. Outcomes of adolescent-onset postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Pediatr 2016; 173:149–153. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.035
- George SA, Bivens TB, Howden EJ, et al. The international POTS registry: evaluating the efficacy of an exercise training intervention in a community setting. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):943–950. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.012
- Fu Q, VanGundy TB, Galbreath MM, et al. Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55(25):2858–2868. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.02.043
- Raj SR. Row, row, row your way to treating postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2016; 13(4):951–952. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.12.039
- Celedonio JE, Garland EM, Nwazue VC, et al. Effects of high sodium intake on blood volume and catecholamines in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome and healthy females [abstract]. Clin Auton Res 2014; 24:211.
- Garland EM, Celedonio JE, Raj SR. Postural tachycardia syndrome: beyond orthostatic intolerance. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2015; 15(9):60. doi:10.1007/s11910-015-0583-8
- Gordon VM, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Novak V, Low PA. Hemodynamic and symptomatic effects of acute interventions on tilt in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10:29–33. pmid:10750641
- Jacob G, Shannon JR, Black B, et al. Effects of volume loading and pressor agents in idiopathic orthostatic tachycardia. Circulation 1997; 96(2):575–580. pmid:9244228
- Moak JP, Leong D, Fabian R, et al. Intravenous hydration for management of medication-resistant orthostatic intolerance in the adolescent and young adult. Pediatr Cardiol 2016; 37(2):278–282. doi:10.1007/s00246-015-1274-6
- Ruzieh M, Baugh A, Dasa O, et al. Effects of intermittent intravenous saline infusions in patients with medication-refractory postural tachycardia syndrome. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 2017; 48(3):255–260. doi:10.1007/s10840-017-0225-y
- Freitas J, Santos R, Azevedo E, Costa O, Carvalho M, de Freitas AF. Clinical improvement in patients with orthostatic intolerance after treatment with bisoprolol and fludrocortisone. Clin Auton Res 2000; 10(5):293–299. pmid:11198485
- Lee AK, Krahn AD. Evaluation of syncope: focus on diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2016; 14(6):725–736. doi:10.1586/14779072.2016.1164034
- Coffin ST, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Desmopressin acutely decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2012; 9(9):1484–1490. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.05.002
- Kanjwal K, Saeed B, Karabin B, Kanjwal Y, Sheikh M, Grubb BP. Erythropoietin in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2012; 19(2):92–95. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ef621a
- Hoeldtke RD, Horvath GG, Bryner KD. Treatment of orthostatic tachycardia with erythropoietin. Am J Med 1995; 99(5):525–529. pmid:7485211
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, et al. Propranolol decreases tachycardia and improves symptoms in the postural tachycardia syndrome: less is more. Circulation 2009; 120(9):725–734. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.846501
- McDonald C, Frith J, Newton JL. Single centre experience of ivabradine in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Europace 2011; 13(3):427–430. doi:10.1093/europace/euq390
- Gaffney FA, Lane LB, Pettinger W, Blomqvist G. Effects of long-term clonidine administration on the hemodynamic and neuroendocrine postural responses of patients with dysautonomia. Chest 1983; 83(suppl 2):436–438. pmid:6295714
- Jacob G, Biaggioni I. Idiopathic orthostatic intolerance and postural tachycardia syndromes. Am J Med Sci 1999; 317(2):88–101. pmid:10037112
- Ross AJ, Ocon AJ, Medow MS, Stewart JM. A double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study of the vascular effects of midodrine in neuropathic compared with hyperadrenergic postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2014; 126(4):289–296. doi:10.1042/CS20130222
- Raj SR, Black BK, Biaggioni I, Harris PA, Robertson D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition improves tachycardia in postural tachycardia syndrome. Circulation 2005; 111(21):2734–2340. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.497594
- Kanjwal K, Karabin B, Sheikh M, et al. Pyridostigmine in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia: A single-center experience. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2011; 34(6):750–755. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2011.03047.x
- Ruzieh M, Dasa O, Pacenta A, Karabin B, Grubb B. Droxidopa in the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Am J Ther 2017; 24(2):e157–e161. doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000000468
- Kpaeyeh AG Jr, Mar PL, Raj V, et al. Hemodynamic profiles and tolerability of modafinil in the treatment of POTS: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2014; 34(6):738–741. doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000000221
- Lai CC, Fischer PR, Brands CK, et al. Outcomes in adolescents with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome treated with midodrine and beta-blockers. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2009; 32(2):234–238. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.02207.x
KEY POINTS
- Several POTS subtypes have been recognized, including hypovolemic, neuropathic, and hyperadrenergic forms, overlapping with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, mast cell activation, and autoimmune syndromes.
- Treatment should take a graded approach, beginning with increasing salt and water intake, exercise, and compression stockings.
- If needed, consider medications to expand blood volume, slow heart rate, or reduce central sympathetic tone.
- Certain medications, including venodilators, diuretics, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, can exacerbate symptoms and should be avoided.
Gastric outlet obstruction: A red flag, potentially manageable
A 72-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with progressive nausea and vomiting. One week earlier, she developed early satiety and nausea with vomiting after eating solid food. Three days later her symptoms progressed, and she became unable to take anything by mouth. The patient also experienced a 40-lb weight loss in the previous 3 months. She denies symptoms of abdominal pain, hematemesis, or melena. Her medical history includes cholecystectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus, diagnosed 1 year ago. She has no family history of gastrointestinal malignancy. She says she smoked 1 pack a day in her 20s. She does not consume alcohol.
On physical examination, she is normotensive with a heart rate of 105 beats per minute. The oral mucosa is dry, and the abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation in the epigastrium. Laboratory evaluation reveals hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
Computed tomography (CT) reveals a mass 3 cm by 4 cm in the pancreatic head. The mass has invaded the medial wall of the duodenum, with obstruction of the pancreatic and common bile ducts and extension into and occlusion of the superior mesenteric vein, with soft-tissue expansion around the superior mesenteric artery. CT also reveals retained stomach contents and an air-fluid level consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
INTRINSIC OR EXTRINSIC BLOCKAGE
Gastric outlet obstruction, also called pyloric obstruction, is caused by intrinsic or extrinsic mechanical blockage of gastric emptying, generally in the distal stomach, pyloric channel, or duodenum, with associated symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and early satiety. It is encountered in both the clinic and the hospital.
Here, we review the causes, diagnosis, and management of this disorder.
BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES
In a retrospective study of 76 patients hospitalized with gastric outlet obstruction between 2006 and 2015 at our institution,2 29 cases (38%) were due to malignancy and 47 (62%) were due to benign causes. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma accounted for 13 cases (17%), while gastric adenocarcinoma accounted for 5 cases (7%); less common malignant causes were cholangiocarcinoma, cancer of the ampulla of Vater, duodenal adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and metastatic disease. Of the benign causes, the most common were peptic ulcer disease (13 cases, 17%) and postoperative strictures or adhesions (11 cases, 14%).
These numbers reflect general trends around the world.
Less gastric cancer, more pancreatic cancer
The last several decades have seen a trend toward more cases due to cancer and fewer due to benign causes.3–14
In earlier studies in both developed and developing countries, gastric adenocarcinoma was the most common malignant cause of gastric outlet obstruction. Since then, it has become less common in Western countries, although it remains more common in Asia and Africa.7–14 This trend likely reflects environmental factors, including decreased prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection, a major risk factor for gastric cancer, in Western countries.15–17
At the same time, pancreatic cancer is on the rise,16 and up to 20% of patients with pancreatic cancer develop gastric outlet obstruction.18 In a prospective observational study of 108 patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction undergoing endoscopic stenting, pancreatic cancer was by far the most common malignancy, occurring in 54% of patients, followed by gastric cancer in 13%.19
Less peptic ulcer disease, but still common
Peptic ulcer disease used to account for up to 90% of cases of gastric outlet obstruction, and it is still the most common benign cause.
In 1990, gastric outlet obstruction was estimated to occur in 5% to 10% of all hospital admissions for ulcer-related complications, accounting for 2,000 operations annually.20,21 Gastric outlet obstruction now occurs in fewer than 5% of patients with duodenal ulcer disease and fewer than 2% of patients with gastric ulcer disease.22
Peptic ulcer disease remains an important cause of obstruction in countries with poor access to acid-suppressing drugs.23
Gastric outlet obstruction occurs in both acute and chronic peptic ulcer disease. In acute peptic ulcer disease, tissue inflammation and edema result in mechanical obstruction. Chronic peptic ulcer disease results in tissue scarring and fibrosis with strictures.20
Environmental factors, including improved diet, hygiene, physical activity, and the decreased prevalence of H pylori infection, also contribute to the decreased prevalence of peptic ulcer disease and its complications, including gastric outlet obstruction.3 The continued occurrence of peptic ulcer disease is associated with widespread use of low-dose aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the most common causes of peptic ulcer disease in Western countries.24,25
Other nonmalignant causes of gastric outlet obstruction are diverse and less common. They include caustic ingestion, postsurgical strictures, benign tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, Crohn disease, and pancreatic disorders including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudocyst, chronic pancreatitis, and annular pancreas. Intramural duodenal hematoma may cause obstruction after blunt abdominal trauma, endoscopic biopsy, or gastrostomy tube migration, especially in the setting of a bleeding disorder or anticoagulation.26
Tuberculosis should be suspected in countries in which it is common.7 In a prospective study of 64 patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction in India,27 16 (25%) had corrosive injury, 16 (25%) had tuberculosis, and 15 (23%) had peptic ulcer disease. Compared with patients with corrosive injury and peptic ulcer disease, patients with gastroduodenal tuberculosis had the best outcomes with appropriate treatment.
Other reported causes include Bouveret syndrome (an impacted gallstone in the proximal duodenum), phytobezoar, diaphragmatic hernia, gastric volvulus, and Ladd bands (peritoneal bands associated with intestinal malrotation).7,28,29
PRESENTING SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction include nausea, nonbilious vomiting, epigastric pain, early satiety, abdominal distention, and weight loss.
In our patients, the most common presenting symptoms were nausea and vomiting (80%), followed by abdominal pain (72%); weight loss (15%), abdominal distention (15%), and early satiety (9%) were less common.2
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to malignancy generally present with a shorter duration of symptoms than those with peptic ulcer disease and are more likely to be older.8,13 Other conditions with an acute onset of symptoms include gastric polyp prolapse, percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube migration, gastric volvulus, and gallstone impaction.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction associated with peptic ulcer disease generally have a long-standing history of symptoms, including dyspepsia and weight loss over several years.4
SIGNS ON EXAMINATION
On examination, look for signs of chronic gastric obstruction and its consequences, such as malnutrition, cachexia, volume depletion, and dental erosions.
A succussion splash may suggest gastric outlet obstruction. This is elicited by rocking the patient back and forth by the hips or abdomen while listening over the stomach for a splash, which may be heard without a stethoscope. The test is considered positive if present 3 or more hours after drinking fluids and suggests retention of gastric materials.30,31
In thin individuals, chronic gastric outlet obstruction makes the stomach dilate and hypertrophy, which may be evident by a palpably thickened stomach with visible gastric peristalsis.4
Other notable findings on physical examination may include a palpable abdominal mass, epigastric pain, or an abnormality suggestive of metastatic gastric cancer, such as an enlarged left supraclavicular lymph node (Virchow node) or periumbilical lymph node (Sister Mary Joseph nodule). The Virchow node is at the junction of the thoracic duct and the left subclavian vein where the lymphatic circulation from the body drains into the systemic circulation, and it may be the first sign of gastric cancer.32 Sister Mary Joseph nodule (named after a surgical assistant to Dr. William James Mayo) refers to a palpable mass at the umbilicus, generally resulting from metastasis of an abdominal malignancy.33
SIGNS ON FURTHER STUDIES
Laboratory evaluation may show signs of poor oral intake and electrolyte abnormalities secondary to chronic nausea, vomiting, and dehydration, including hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia.
The underlying cause of gastric outlet obstruction has major implications for treatment and prognosis and cannot be differentiated by clinical presentation alone.1,9 Diagnosis is based on clinical features and radiologic or endoscopic evaluation consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
Plain radiography may reveal an enlarged gastric bubble, and contrast studies may be useful to determine whether the obstruction is partial or complete, depending on whether the contrast passes into the small bowel.
Upper endoscopy is often needed to establish the diagnosis and cause. Emptying the stomach with a nasogastric tube is recommended before endoscopy to minimize the risk of aspiration during the procedure, and endotracheal intubation should be considered for airway protection.34 Findings of gastric outlet obstruction on upper endoscopy include retained food and liquid. Endoscopic biopsy is important to differentiate between benign and malignant causes. For patients with malignancy, endoscopic ultrasonography is useful for diagnosis via tissue sampling with fine-needle aspiration and locoregional staging.35
A strategy. Most patients whose clinical presentation suggests gastric outlet obstruction require cross-sectional radiologic imaging, upper endoscopy, or both.36 CT is the preferred imaging study to evaluate for intestinal obstruction.36,37 Patients with suspected complete obstruction or perforation should undergo CT before upper endoscopy. Oral contrast may interfere with endoscopy and should be avoided if endoscopy is planned. Additionally, giving oral contrast may worsen patient discomfort and increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, and aspiration.36,37
Following radiographic evaluation, upper endoscopy can be performed after gastric decompression to identify the location and extent of the obstruction and to potentially provide a definitive diagnosis with biopsy.36
DIFFERENTIATE FROM GASTROPARESIS
Gastroparesis is a chronic neuromuscular disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction.38 The most common causes are diabetes, surgery, and idiopathy. Other causes include viral infection, connective tissue diseases, ischemia, infiltrative disorders, radiation, neurologic disorders, and paraneoplastic syndromes.39,40
Gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis share clinical symptoms including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, early satiety, and weight loss and are important to differentiate.36,38 Although abdominal pain may be present in both gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis, in gastroparesis it tends not to be the dominant symptom.40
Gastric scintigraphy is most commonly used to objectively quantify delayed gastric emptying.39 Upper endoscopy is imperative to exclude mechanical obstruction.39
MANAGEMENT
Initially, patients with signs and symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction should be given:
- Nothing by mouth (NPO)
- Intravenous fluids to correct volume depletion and electrolyte abnormalities
- A nasogastric tube for gastric decompression and symptom relief if symptoms persist despite being NPO
- A parenteral proton pump inhibitor, regardless of the cause of obstruction, to decrease gastric secretions41
- Medications for pain and nausea, if needed.
Definitive treatment of gastric outlet obstruction depends on the underlying cause, whether benign or malignant.
Management of benign gastric outlet obstruction
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction resolve spontaneously in about half of cases caused by acute peptic ulcer disease, as acute inflammation resolves.9,22
Endoscopic dilation is an important option in patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction, including peptic ulcer disease. Peptic ulcer disease-induced gastric outlet obstruction can be safely treated with endoscopic balloon dilation. This treatment almost always relieves symptoms immediately; however, the long-term response has varied from 16% to 100%, and patients may require more than 1 dilation procedure.25,42,43 The need for 2 or more dilation procedures may predict need for surgery.44 Gastric outlet obstruction after caustic ingestion or endoscopic submucosal dissection may also respond to endoscopic balloon dilation.36
Eradication of H pylori may be effective and lead to complete resolution of symptoms in patients with gastric outlet obstruction due to this infection.45–47
NSAIDs should be discontinued in patients with peptic ulcer disease and gastric outlet obstruction. These drugs damage the gastrointestinal mucosa by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes and decreasing synthesis of prostaglandins, which are important for mucosal defense.48 Patients may be unaware of NSAIDs contained in over-the-counter medications and may have difficulty discontinuing NSAIDs taken for pain.49
These drugs are an important cause of refractory peptic ulcer disease and can be detected by platelet COX activity testing, although this test is not widely available. In a study of patients with peptic ulcer disease without definite NSAID use or H pylori infection, up to one-third had evidence of surreptitious NSAID use as detected by platelet COX activity testing.50 In another study,51 platelet COX activity testing discovered over 20% more aspirin users than clinical history alone.
Surgery for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction is used only when medical management and endoscopic dilation fail. Ideally, surgery should relieve the obstruction and target the underlying cause, such as peptic ulcer disease. Laparoscopic surgery is generally preferred to open surgery because patients can resume oral intake sooner, have a shorter hospital stay, and have less intraoperative blood loss.52 The simplest surgical procedure to relieve obstruction is laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction and peptic ulcer disease warrant laparoscopic vagotomy and antrectomy or distal gastrectomy. This removes the obstruction and the stimulus for gastric secretion.53 An alternative is vagotomy with a drainage procedure (pyloroplasty or gastrojejunostomy), which has a similar postoperative course and reduction in gastric acid secretion compared with antrectomy or distal gastrectomy.53,54
Daily proton pump inhibitors can be used for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction not associated with peptic ulcer disease or risk factors; for such cases, vagotomy is not required.
Management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction
Patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction may have intractable nausea and abdominal pain secondary to retention of gastric contents. The major goal of therapy is to improve symptoms and restore tolerance of an oral diet. The short-term prognosis of malignant gastric outlet obstruction is poor, with a median survival of 3 to 4 months, as these patients often have unresectable disease.55
Surgical bypass used to be the standard of care for palliation of malignant gastric obstruction, but that was before endoscopic stenting was developed.
Endoscopic stenting allows patients to resume oral intake and get out of the hospital sooner with fewer complications than with open surgical bypass. It may be a more appropriate option for palliation of symptoms in patients with malignant obstruction who have a poor prognosis and prefer a less invasive intervention.55,56
Endoscopic duodenal stenting of malignant gastric outlet obstruction has a success rate of greater than 90%, and most patients can tolerate a mechanical soft diet afterward.34 The procedure is usually performed with a 9-cm or 12-cm self-expanding duodenal stent, 22 mm in diameter, placed over a guide wire under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance (Figure 2). The stent is placed by removing the outer catheter, with distal-to-proximal stent deployment.
Patients who also have biliary obstruction may require biliary stent placement, which is generally performed before duodenal stenting. For patients with an endoscopic stent who develop biliary obstruction, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography can be attempted with placement of a biliary stent; however, these patients may require biliary drain placement by percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography or by endoscopic ultrasonographically guided transduodenal or transgastric biliary drainage.
From 20% to 30% of patients require repeated endoscopic stent placement, although most patients die within several months after stenting.34 Surgical options for patients who do not respond to endoscopic stenting include open or laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55
Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy may provide better long-term outcomes than duodenal stenting for patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction and a life expectancy longer than a few months.
A 2017 retrospective study of 155 patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to unresectable gastric cancer suggested that those who underwent laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy had better oral intake, better tolerance of chemotherapy, and longer overall survival than those who underwent duodenal stenting. Postsurgical complications were more common in the laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy group (16%) than in the duodenal stenting group (0%).57
In most of the studies comparing endoscopic stenting with surgery, the surgery was open gastrojejunostomy; there are limited data directly comparing stenting with laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55 Endoscopic stenting is estimated to be significantly less costly than surgery, with a median cost of $12,000 less than gastrojejunostomy.58 As an alternative to enteral stenting and surgical gastrojejunostomy, ultrasonography-guided endoscopic gastrojejunostomy or gastroenterostomy with placement of a lumen-apposing metal stent is emerging as a third treatment option and is under active investigation.59
Patients with malignancy that is potentially curable by resection should undergo surgical evaluation before consideration of endoscopic stenting. For patients who are not candidates for surgery or endoscopic stenting, a percutaneous gastrostomy tube can be considered for gastric decompression and symptom relief.
CASE CONCLUDED
The patient underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy with endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of her pancreatic mass. Before the procedure, she was intubated to minimize the risk of aspiration due to persistent nausea and retained gastric contents. A large submucosal mass was found in the duodenal bulb. Endoscopic ultrasonography showed a mass within the pancreatic head with pancreatic duct obstruction. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy was performed, and pathology study revealed pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The patient underwent stenting with a 22-mm by 12-cm WallFlex stent (Boston Scientific), which led to resolution of nausea and advancement to a mechanical soft diet on hospital discharge.
She was scheduled for follow-up in the outpatient clinic for treatment of pancreatic cancer.
- Johnson CD. Gastric outlet obstruction malignant until proved otherwise. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1740. pmid:7572886
- Koop AH, Palmer WC, Mareth K, Burton MC, Bowman A, Stancampiano F. Tu1335 - Pancreatic cancer most common cause of malignant gastric outlet obstruction at a tertiary referral center: a 10 year retrospective study [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2018; 154(6, suppl 1):S-1343.
- Hall R, Royston C, Bardhan KD. The scars of time: the disappearance of peptic ulcer-related pyloric stenosis through the 20th century. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2014; 44(3):201–208. doi:10.4997/JRCPE.2014.303
- Kreel L, Ellis H. Pyloric stenosis in adults: a clinical and radiological study of 100 consecutive patients. Gut 1965; 6(3):253–261. pmid:18668780
- Shone DN, Nikoomanesh P, Smith-Meek MM, Bender JS. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction in the era of H2 blockers. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1769–1770. pmid:7572891
- Ellis H. The diagnosis of benign and malignant pyloric obstruction. Clin Oncol 1976; 2(1):11–15. pmid:1277618
- Samad A, Khanzada TW, Shoukat I. Gastric outlet obstruction: change in etiology. Pak J Surg 2007; 23(1):29–32.
- Chowdhury A, Dhali GK, Banerjee PK. Etiology of gastric outlet obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(8):1679. pmid:8759707
- Johnson CD, Ellis H. Gastric outlet obstruction now predicts malignancy. Br J Surg 1990; 77(9):1023–1024. pmid:2207566
- Misra SP, Dwivedi M, Misra V. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction even in a developing country. Endoscopy 1998; 30(5):484–486. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1001313
- Essoun SD, Dakubo JCB. Update of aetiological patterns of adult gastric outlet obstruction in Accra, Ghana. Int J Clin Med 2014; 5(17):1059–1064. doi:10.4236/ijcm.2014.517136
- Jaka H, Mchembe MD, Rambau PF, Chalya PL. Gastric outlet obstruction at Bugando Medical Centre in Northwestern Tanzania: a prospective review of 184 cases. BMC Surg 2013; 13:41. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-13-41
- Sukumar V, Ravindran C, Prasad RV. Demographic and etiological patterns of gastric outlet obstruction in Kerala, South India. N Am J Med Sci 2015; 7(9):403–406. doi:10.4103/1947-2714.166220
- Yoursef M, Mirza MR, Khan S. Gastric outlet obstruction. Pak J Surg 2005; 10(4):48–50.
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015; 136(5):E359–E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
- Parkin DM, Stjernsward J, Muir CS. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of twelve major cancers. Bull World Health Organ 1984; 62(2):163–182. pmid:6610488
- Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2014; 23(5):700–713. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1057
- Jeurnink SM, Steyerberg EW, van Hooft JE, et al; Dutch SUSTENT Study Group. Surgical gastrojejunostomy or endoscopic stent placement for the palliation of malignant gastric outlet obstruction (SUSTENT) study): a multicenter randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 71(3):490–499. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2009.09.042
- Tringali A, Didden P, Repici A, et al. Endoscopic treatment of malignant gastric and duodenal strictures: a prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):66–75. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.06.032
- Malfertheiner P, Chan FK, McColl KE. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2009; 374(9699):1449–1461. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60938-7
- Gibson JB, Behrman SW, Fabian TC, Britt LG. Gastric outlet obstruction resulting from peptic ulcer disease requiring surgical intervention is infrequently associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Am Coll Surg 2000; 191(1):32–37. pmid:10898181
- Kochhar R, Kochhar S. Endoscopic balloon dilation for benign gastric outlet obstruction in adults. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(1):29–35. doi:10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.29
- Kotisso R. Gastric outlet obstruction in Northwestern Ethiopia. East Cent Afr J Surg 2000; 5(2):25-29.
- Hamzaoui L, Bouassida M, Ben Mansour I, et al. Balloon dilatation in patients with gastric outlet obstruction related to peptic ulcer disease. Arab J Gastroenterol 2015; 16(3–4):121–124. doi:10.1016/j.ajg.2015.07.004
- Najm WI. Peptic ulcer disease. Prim Care 2011; 38(3):383–394. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2011.05.001
- Veloso N, Amaro P, Ferreira M, Romaozinho JM, Sofia C. Acute pancreatitis associated with a nontraumatic, intramural duodenal hematoma. Endoscopy 2013; 45(suppl 2):E51–E52. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1325969
- Maharshi S, Puri AS, Sachdeva S, Kumar A, Dalal A, Gupta M. Aetiological spectrum of benign gastric outlet obstruction in India: new trends. Trop Doct 2016; 46(4):186–191. doi:10.1177/0049475515626032
- Sala MA, Ligabo AN, de Arruda MC, Indiani JM, Nacif MS. Intestinal malrotation associated with duodenal obstruction secondary to Ladd’s bands. Radiol Bras 2016; 49(4):271–272. doi:10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0106
- Alibegovic E, Kurtcehajic A, Hujdurovic A, Mujagic S, Alibegovic J, Kurtcehajic D. Bouveret syndrome or gallstone ileus. Am J Med 2018; 131(4):e175. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.10.044
- Lau JY, Chung SC, Sung JJ, et al. Through-the-scope balloon dilation for pyloric stenosis: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc 1996; 43(2 Pt 1):98–101. pmid:8635729
- Ray K, Snowden C, Khatri K, McFall M. Gastric outlet obstruction from a caecal volvulus, herniated through epiploic foramen: a case report. BMJ Case Rep 2009; pii:bcr05.2009.1880. doi:10.1136/bcr.05.2009.1880
- Baumgart DC, Fischer A. Virchow’s node. Lancet 2007; 370(9598):1568. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61661-4
- Dar IH, Kamili MA, Dar SH, Kuchaai FA. Sister Mary Joseph nodule—a case report with review of literature. J Res Med Sci 2009; 14(6):385–387. pmid:21772912
- Tang SJ. Endoscopic stent placement for gastric outlet obstruction. Video Journal and Encyclopedia of GI Endoscopy 2013; 1(1):133–136.
- Valero M, Robles-Medranda C. Endoscopic ultrasound in oncology: an update of clinical applications in the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(6):243–254.
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Fukami N, Anderson MA, Khan K, et al. The role of endoscopy in gastroduodenal obstruction and gastroparesis. Gastrointest Endosc 2011; 74(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.12.003
- Ros PR, Huprich JE. ACR appropriateness criteria on suspected small-bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Radiol 2006; 3(11):838–841. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2006.09.018
- Pasricha PJ, Parkman HP. Gastroparesis: definitions and diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2015; 44(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2014.11.001
- Stein B, Everhart KK, Lacy BE. Gastroparesis: a review of current diagnosis and treatment options. J Clin Gastroenterol 2015; 49(7):550–558. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000320
- Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L; American College of Gastroenterology. Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108(1):18–37.
- Gursoy O, Memis D, Sut N. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on gastric juice volume, gastric pH and gastric intramucosal pH in critically ill patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Drug Investig 2008; 28(12):777–782. doi:10.2165/0044011-200828120-00005
- Kuwada SK, Alexander GL. Long-term outcome of endoscopic dilation of nonmalignant pyloric stenosis. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 41(1):15–17. pmid:7698619
- Kochhar R, Sethy PK, Nagi B, Wig JD. Endoscopic balloon dilatation of benign gastric outlet obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 19(4):418–422. pmid:15012779
- Perng CL, Lin HJ, Lo WC, Lai CR, Guo WS, Lee SD. Characteristics of patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction requiring surgery after endoscopic balloon dilation. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(5):987–990. pmid:8633593
- Taskin V, Gurer I, Ozyilkan E, Sare M, Hilmioglu F. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on peptic ulcer disease complicated with outlet obstruction. Helicobacter 2000; 5(1):38–40. pmid:10672050
- de Boer WA, Driessen WM. Resolution of gastric outlet obstruction after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Gastroenterol 1995; 21(4):329–330. pmid:8583113
- Tursi A, Cammarota G, Papa A, Montalto M, Fedeli G, Gasbarrini G. Helicobacter pylori eradication helps resolve pyloric and duodenal stenosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1996; 23(2):157–158. pmid:8877648
- Schmassmann A. Mechanisms of ulcer healing and effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Med 1998; 104(3A):43S–51S; discussion 79S–80S. pmid:9572320
- Kim HU. Diagnostic and treatment approaches for refractory peptic ulcers. Clin Endosc 2015; 48(4):285–290. doi:10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.285
- Ong TZ, Hawkey CJ, Ho KY. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is a significant cause of peptic ulcer disease in a tertiary hospital in Singapore: a prospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2006; 40(9):795–800. doi:10.1097/01.mcg.0000225610.41105.7f
- Lanas A, Sekar MC, Hirschowitz BI. Objective evidence of aspirin use in both ulcer and nonulcer upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1992; 103(3):862–869. pmid:1499936
- Zhang LP, Tabrizian P, Nguyen S, Telem D, Divino C. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction. JSLS 2011; 15(2):169–173. doi:10.4293/108680811X13022985132074
- Lagoo J, Pappas TN, Perez A. A relic or still relevant: the narrowing role for vagotomy in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Am J Surg 2014; 207(1):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.02.012
- Csendes A, Maluenda F, Braghetto I, Schutte H, Burdiles P, Diaz JC. Prospective randomized study comparing three surgical techniques for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction secondary to duodenal ulcer. Am J Surg 1993; 166(1):45–49. pmid:8101050
- Ly J, O’Grady G, Mittal A, Plank L, Windsor JA. A systematic review of methods to palliate malignant gastric outlet obstruction. Surg Endosc 2010; 24(2):290–297. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0577-1
- Goldberg EM. Palliative treatment of gastric outlet obstruction in terminal patients: SEMS. Stent every malignant stricture! Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):76–78. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.056
- Min SH, Son SY, Jung DH, et al. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy versus duodenal stenting in unresectable gastric cancer with gastric outlet obstruction. Ann Surg Treat Res 2017; 93(3):130–136. doi:10.4174/astr.2017.93.3.130
- Roy A, Kim M, Christein J, Varadarajulu S. Stenting versus gastrojejunostomy for management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction: comparison of clinical outcomes and costs. Surg Endosc 2012; 26(11):3114–119. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2301-9
- Amin S, Sethi A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2017; 27(4):707–713. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2017.06.009
A 72-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with progressive nausea and vomiting. One week earlier, she developed early satiety and nausea with vomiting after eating solid food. Three days later her symptoms progressed, and she became unable to take anything by mouth. The patient also experienced a 40-lb weight loss in the previous 3 months. She denies symptoms of abdominal pain, hematemesis, or melena. Her medical history includes cholecystectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus, diagnosed 1 year ago. She has no family history of gastrointestinal malignancy. She says she smoked 1 pack a day in her 20s. She does not consume alcohol.
On physical examination, she is normotensive with a heart rate of 105 beats per minute. The oral mucosa is dry, and the abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation in the epigastrium. Laboratory evaluation reveals hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
Computed tomography (CT) reveals a mass 3 cm by 4 cm in the pancreatic head. The mass has invaded the medial wall of the duodenum, with obstruction of the pancreatic and common bile ducts and extension into and occlusion of the superior mesenteric vein, with soft-tissue expansion around the superior mesenteric artery. CT also reveals retained stomach contents and an air-fluid level consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
INTRINSIC OR EXTRINSIC BLOCKAGE
Gastric outlet obstruction, also called pyloric obstruction, is caused by intrinsic or extrinsic mechanical blockage of gastric emptying, generally in the distal stomach, pyloric channel, or duodenum, with associated symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and early satiety. It is encountered in both the clinic and the hospital.
Here, we review the causes, diagnosis, and management of this disorder.
BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES
In a retrospective study of 76 patients hospitalized with gastric outlet obstruction between 2006 and 2015 at our institution,2 29 cases (38%) were due to malignancy and 47 (62%) were due to benign causes. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma accounted for 13 cases (17%), while gastric adenocarcinoma accounted for 5 cases (7%); less common malignant causes were cholangiocarcinoma, cancer of the ampulla of Vater, duodenal adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and metastatic disease. Of the benign causes, the most common were peptic ulcer disease (13 cases, 17%) and postoperative strictures or adhesions (11 cases, 14%).
These numbers reflect general trends around the world.
Less gastric cancer, more pancreatic cancer
The last several decades have seen a trend toward more cases due to cancer and fewer due to benign causes.3–14
In earlier studies in both developed and developing countries, gastric adenocarcinoma was the most common malignant cause of gastric outlet obstruction. Since then, it has become less common in Western countries, although it remains more common in Asia and Africa.7–14 This trend likely reflects environmental factors, including decreased prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection, a major risk factor for gastric cancer, in Western countries.15–17
At the same time, pancreatic cancer is on the rise,16 and up to 20% of patients with pancreatic cancer develop gastric outlet obstruction.18 In a prospective observational study of 108 patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction undergoing endoscopic stenting, pancreatic cancer was by far the most common malignancy, occurring in 54% of patients, followed by gastric cancer in 13%.19
Less peptic ulcer disease, but still common
Peptic ulcer disease used to account for up to 90% of cases of gastric outlet obstruction, and it is still the most common benign cause.
In 1990, gastric outlet obstruction was estimated to occur in 5% to 10% of all hospital admissions for ulcer-related complications, accounting for 2,000 operations annually.20,21 Gastric outlet obstruction now occurs in fewer than 5% of patients with duodenal ulcer disease and fewer than 2% of patients with gastric ulcer disease.22
Peptic ulcer disease remains an important cause of obstruction in countries with poor access to acid-suppressing drugs.23
Gastric outlet obstruction occurs in both acute and chronic peptic ulcer disease. In acute peptic ulcer disease, tissue inflammation and edema result in mechanical obstruction. Chronic peptic ulcer disease results in tissue scarring and fibrosis with strictures.20
Environmental factors, including improved diet, hygiene, physical activity, and the decreased prevalence of H pylori infection, also contribute to the decreased prevalence of peptic ulcer disease and its complications, including gastric outlet obstruction.3 The continued occurrence of peptic ulcer disease is associated with widespread use of low-dose aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the most common causes of peptic ulcer disease in Western countries.24,25
Other nonmalignant causes of gastric outlet obstruction are diverse and less common. They include caustic ingestion, postsurgical strictures, benign tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, Crohn disease, and pancreatic disorders including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudocyst, chronic pancreatitis, and annular pancreas. Intramural duodenal hematoma may cause obstruction after blunt abdominal trauma, endoscopic biopsy, or gastrostomy tube migration, especially in the setting of a bleeding disorder or anticoagulation.26
Tuberculosis should be suspected in countries in which it is common.7 In a prospective study of 64 patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction in India,27 16 (25%) had corrosive injury, 16 (25%) had tuberculosis, and 15 (23%) had peptic ulcer disease. Compared with patients with corrosive injury and peptic ulcer disease, patients with gastroduodenal tuberculosis had the best outcomes with appropriate treatment.
Other reported causes include Bouveret syndrome (an impacted gallstone in the proximal duodenum), phytobezoar, diaphragmatic hernia, gastric volvulus, and Ladd bands (peritoneal bands associated with intestinal malrotation).7,28,29
PRESENTING SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction include nausea, nonbilious vomiting, epigastric pain, early satiety, abdominal distention, and weight loss.
In our patients, the most common presenting symptoms were nausea and vomiting (80%), followed by abdominal pain (72%); weight loss (15%), abdominal distention (15%), and early satiety (9%) were less common.2
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to malignancy generally present with a shorter duration of symptoms than those with peptic ulcer disease and are more likely to be older.8,13 Other conditions with an acute onset of symptoms include gastric polyp prolapse, percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube migration, gastric volvulus, and gallstone impaction.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction associated with peptic ulcer disease generally have a long-standing history of symptoms, including dyspepsia and weight loss over several years.4
SIGNS ON EXAMINATION
On examination, look for signs of chronic gastric obstruction and its consequences, such as malnutrition, cachexia, volume depletion, and dental erosions.
A succussion splash may suggest gastric outlet obstruction. This is elicited by rocking the patient back and forth by the hips or abdomen while listening over the stomach for a splash, which may be heard without a stethoscope. The test is considered positive if present 3 or more hours after drinking fluids and suggests retention of gastric materials.30,31
In thin individuals, chronic gastric outlet obstruction makes the stomach dilate and hypertrophy, which may be evident by a palpably thickened stomach with visible gastric peristalsis.4
Other notable findings on physical examination may include a palpable abdominal mass, epigastric pain, or an abnormality suggestive of metastatic gastric cancer, such as an enlarged left supraclavicular lymph node (Virchow node) or periumbilical lymph node (Sister Mary Joseph nodule). The Virchow node is at the junction of the thoracic duct and the left subclavian vein where the lymphatic circulation from the body drains into the systemic circulation, and it may be the first sign of gastric cancer.32 Sister Mary Joseph nodule (named after a surgical assistant to Dr. William James Mayo) refers to a palpable mass at the umbilicus, generally resulting from metastasis of an abdominal malignancy.33
SIGNS ON FURTHER STUDIES
Laboratory evaluation may show signs of poor oral intake and electrolyte abnormalities secondary to chronic nausea, vomiting, and dehydration, including hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia.
The underlying cause of gastric outlet obstruction has major implications for treatment and prognosis and cannot be differentiated by clinical presentation alone.1,9 Diagnosis is based on clinical features and radiologic or endoscopic evaluation consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
Plain radiography may reveal an enlarged gastric bubble, and contrast studies may be useful to determine whether the obstruction is partial or complete, depending on whether the contrast passes into the small bowel.
Upper endoscopy is often needed to establish the diagnosis and cause. Emptying the stomach with a nasogastric tube is recommended before endoscopy to minimize the risk of aspiration during the procedure, and endotracheal intubation should be considered for airway protection.34 Findings of gastric outlet obstruction on upper endoscopy include retained food and liquid. Endoscopic biopsy is important to differentiate between benign and malignant causes. For patients with malignancy, endoscopic ultrasonography is useful for diagnosis via tissue sampling with fine-needle aspiration and locoregional staging.35
A strategy. Most patients whose clinical presentation suggests gastric outlet obstruction require cross-sectional radiologic imaging, upper endoscopy, or both.36 CT is the preferred imaging study to evaluate for intestinal obstruction.36,37 Patients with suspected complete obstruction or perforation should undergo CT before upper endoscopy. Oral contrast may interfere with endoscopy and should be avoided if endoscopy is planned. Additionally, giving oral contrast may worsen patient discomfort and increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, and aspiration.36,37
Following radiographic evaluation, upper endoscopy can be performed after gastric decompression to identify the location and extent of the obstruction and to potentially provide a definitive diagnosis with biopsy.36
DIFFERENTIATE FROM GASTROPARESIS
Gastroparesis is a chronic neuromuscular disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction.38 The most common causes are diabetes, surgery, and idiopathy. Other causes include viral infection, connective tissue diseases, ischemia, infiltrative disorders, radiation, neurologic disorders, and paraneoplastic syndromes.39,40
Gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis share clinical symptoms including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, early satiety, and weight loss and are important to differentiate.36,38 Although abdominal pain may be present in both gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis, in gastroparesis it tends not to be the dominant symptom.40
Gastric scintigraphy is most commonly used to objectively quantify delayed gastric emptying.39 Upper endoscopy is imperative to exclude mechanical obstruction.39
MANAGEMENT
Initially, patients with signs and symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction should be given:
- Nothing by mouth (NPO)
- Intravenous fluids to correct volume depletion and electrolyte abnormalities
- A nasogastric tube for gastric decompression and symptom relief if symptoms persist despite being NPO
- A parenteral proton pump inhibitor, regardless of the cause of obstruction, to decrease gastric secretions41
- Medications for pain and nausea, if needed.
Definitive treatment of gastric outlet obstruction depends on the underlying cause, whether benign or malignant.
Management of benign gastric outlet obstruction
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction resolve spontaneously in about half of cases caused by acute peptic ulcer disease, as acute inflammation resolves.9,22
Endoscopic dilation is an important option in patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction, including peptic ulcer disease. Peptic ulcer disease-induced gastric outlet obstruction can be safely treated with endoscopic balloon dilation. This treatment almost always relieves symptoms immediately; however, the long-term response has varied from 16% to 100%, and patients may require more than 1 dilation procedure.25,42,43 The need for 2 or more dilation procedures may predict need for surgery.44 Gastric outlet obstruction after caustic ingestion or endoscopic submucosal dissection may also respond to endoscopic balloon dilation.36
Eradication of H pylori may be effective and lead to complete resolution of symptoms in patients with gastric outlet obstruction due to this infection.45–47
NSAIDs should be discontinued in patients with peptic ulcer disease and gastric outlet obstruction. These drugs damage the gastrointestinal mucosa by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes and decreasing synthesis of prostaglandins, which are important for mucosal defense.48 Patients may be unaware of NSAIDs contained in over-the-counter medications and may have difficulty discontinuing NSAIDs taken for pain.49
These drugs are an important cause of refractory peptic ulcer disease and can be detected by platelet COX activity testing, although this test is not widely available. In a study of patients with peptic ulcer disease without definite NSAID use or H pylori infection, up to one-third had evidence of surreptitious NSAID use as detected by platelet COX activity testing.50 In another study,51 platelet COX activity testing discovered over 20% more aspirin users than clinical history alone.
Surgery for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction is used only when medical management and endoscopic dilation fail. Ideally, surgery should relieve the obstruction and target the underlying cause, such as peptic ulcer disease. Laparoscopic surgery is generally preferred to open surgery because patients can resume oral intake sooner, have a shorter hospital stay, and have less intraoperative blood loss.52 The simplest surgical procedure to relieve obstruction is laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction and peptic ulcer disease warrant laparoscopic vagotomy and antrectomy or distal gastrectomy. This removes the obstruction and the stimulus for gastric secretion.53 An alternative is vagotomy with a drainage procedure (pyloroplasty or gastrojejunostomy), which has a similar postoperative course and reduction in gastric acid secretion compared with antrectomy or distal gastrectomy.53,54
Daily proton pump inhibitors can be used for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction not associated with peptic ulcer disease or risk factors; for such cases, vagotomy is not required.
Management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction
Patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction may have intractable nausea and abdominal pain secondary to retention of gastric contents. The major goal of therapy is to improve symptoms and restore tolerance of an oral diet. The short-term prognosis of malignant gastric outlet obstruction is poor, with a median survival of 3 to 4 months, as these patients often have unresectable disease.55
Surgical bypass used to be the standard of care for palliation of malignant gastric obstruction, but that was before endoscopic stenting was developed.
Endoscopic stenting allows patients to resume oral intake and get out of the hospital sooner with fewer complications than with open surgical bypass. It may be a more appropriate option for palliation of symptoms in patients with malignant obstruction who have a poor prognosis and prefer a less invasive intervention.55,56
Endoscopic duodenal stenting of malignant gastric outlet obstruction has a success rate of greater than 90%, and most patients can tolerate a mechanical soft diet afterward.34 The procedure is usually performed with a 9-cm or 12-cm self-expanding duodenal stent, 22 mm in diameter, placed over a guide wire under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance (Figure 2). The stent is placed by removing the outer catheter, with distal-to-proximal stent deployment.
Patients who also have biliary obstruction may require biliary stent placement, which is generally performed before duodenal stenting. For patients with an endoscopic stent who develop biliary obstruction, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography can be attempted with placement of a biliary stent; however, these patients may require biliary drain placement by percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography or by endoscopic ultrasonographically guided transduodenal or transgastric biliary drainage.
From 20% to 30% of patients require repeated endoscopic stent placement, although most patients die within several months after stenting.34 Surgical options for patients who do not respond to endoscopic stenting include open or laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55
Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy may provide better long-term outcomes than duodenal stenting for patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction and a life expectancy longer than a few months.
A 2017 retrospective study of 155 patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to unresectable gastric cancer suggested that those who underwent laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy had better oral intake, better tolerance of chemotherapy, and longer overall survival than those who underwent duodenal stenting. Postsurgical complications were more common in the laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy group (16%) than in the duodenal stenting group (0%).57
In most of the studies comparing endoscopic stenting with surgery, the surgery was open gastrojejunostomy; there are limited data directly comparing stenting with laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55 Endoscopic stenting is estimated to be significantly less costly than surgery, with a median cost of $12,000 less than gastrojejunostomy.58 As an alternative to enteral stenting and surgical gastrojejunostomy, ultrasonography-guided endoscopic gastrojejunostomy or gastroenterostomy with placement of a lumen-apposing metal stent is emerging as a third treatment option and is under active investigation.59
Patients with malignancy that is potentially curable by resection should undergo surgical evaluation before consideration of endoscopic stenting. For patients who are not candidates for surgery or endoscopic stenting, a percutaneous gastrostomy tube can be considered for gastric decompression and symptom relief.
CASE CONCLUDED
The patient underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy with endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of her pancreatic mass. Before the procedure, she was intubated to minimize the risk of aspiration due to persistent nausea and retained gastric contents. A large submucosal mass was found in the duodenal bulb. Endoscopic ultrasonography showed a mass within the pancreatic head with pancreatic duct obstruction. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy was performed, and pathology study revealed pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The patient underwent stenting with a 22-mm by 12-cm WallFlex stent (Boston Scientific), which led to resolution of nausea and advancement to a mechanical soft diet on hospital discharge.
She was scheduled for follow-up in the outpatient clinic for treatment of pancreatic cancer.
A 72-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with progressive nausea and vomiting. One week earlier, she developed early satiety and nausea with vomiting after eating solid food. Three days later her symptoms progressed, and she became unable to take anything by mouth. The patient also experienced a 40-lb weight loss in the previous 3 months. She denies symptoms of abdominal pain, hematemesis, or melena. Her medical history includes cholecystectomy and type 2 diabetes mellitus, diagnosed 1 year ago. She has no family history of gastrointestinal malignancy. She says she smoked 1 pack a day in her 20s. She does not consume alcohol.
On physical examination, she is normotensive with a heart rate of 105 beats per minute. The oral mucosa is dry, and the abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation in the epigastrium. Laboratory evaluation reveals hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
Computed tomography (CT) reveals a mass 3 cm by 4 cm in the pancreatic head. The mass has invaded the medial wall of the duodenum, with obstruction of the pancreatic and common bile ducts and extension into and occlusion of the superior mesenteric vein, with soft-tissue expansion around the superior mesenteric artery. CT also reveals retained stomach contents and an air-fluid level consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
INTRINSIC OR EXTRINSIC BLOCKAGE
Gastric outlet obstruction, also called pyloric obstruction, is caused by intrinsic or extrinsic mechanical blockage of gastric emptying, generally in the distal stomach, pyloric channel, or duodenum, with associated symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and early satiety. It is encountered in both the clinic and the hospital.
Here, we review the causes, diagnosis, and management of this disorder.
BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CAUSES
In a retrospective study of 76 patients hospitalized with gastric outlet obstruction between 2006 and 2015 at our institution,2 29 cases (38%) were due to malignancy and 47 (62%) were due to benign causes. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma accounted for 13 cases (17%), while gastric adenocarcinoma accounted for 5 cases (7%); less common malignant causes were cholangiocarcinoma, cancer of the ampulla of Vater, duodenal adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and metastatic disease. Of the benign causes, the most common were peptic ulcer disease (13 cases, 17%) and postoperative strictures or adhesions (11 cases, 14%).
These numbers reflect general trends around the world.
Less gastric cancer, more pancreatic cancer
The last several decades have seen a trend toward more cases due to cancer and fewer due to benign causes.3–14
In earlier studies in both developed and developing countries, gastric adenocarcinoma was the most common malignant cause of gastric outlet obstruction. Since then, it has become less common in Western countries, although it remains more common in Asia and Africa.7–14 This trend likely reflects environmental factors, including decreased prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection, a major risk factor for gastric cancer, in Western countries.15–17
At the same time, pancreatic cancer is on the rise,16 and up to 20% of patients with pancreatic cancer develop gastric outlet obstruction.18 In a prospective observational study of 108 patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction undergoing endoscopic stenting, pancreatic cancer was by far the most common malignancy, occurring in 54% of patients, followed by gastric cancer in 13%.19
Less peptic ulcer disease, but still common
Peptic ulcer disease used to account for up to 90% of cases of gastric outlet obstruction, and it is still the most common benign cause.
In 1990, gastric outlet obstruction was estimated to occur in 5% to 10% of all hospital admissions for ulcer-related complications, accounting for 2,000 operations annually.20,21 Gastric outlet obstruction now occurs in fewer than 5% of patients with duodenal ulcer disease and fewer than 2% of patients with gastric ulcer disease.22
Peptic ulcer disease remains an important cause of obstruction in countries with poor access to acid-suppressing drugs.23
Gastric outlet obstruction occurs in both acute and chronic peptic ulcer disease. In acute peptic ulcer disease, tissue inflammation and edema result in mechanical obstruction. Chronic peptic ulcer disease results in tissue scarring and fibrosis with strictures.20
Environmental factors, including improved diet, hygiene, physical activity, and the decreased prevalence of H pylori infection, also contribute to the decreased prevalence of peptic ulcer disease and its complications, including gastric outlet obstruction.3 The continued occurrence of peptic ulcer disease is associated with widespread use of low-dose aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the most common causes of peptic ulcer disease in Western countries.24,25
Other nonmalignant causes of gastric outlet obstruction are diverse and less common. They include caustic ingestion, postsurgical strictures, benign tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, Crohn disease, and pancreatic disorders including acute pancreatitis, pancreatic pseudocyst, chronic pancreatitis, and annular pancreas. Intramural duodenal hematoma may cause obstruction after blunt abdominal trauma, endoscopic biopsy, or gastrostomy tube migration, especially in the setting of a bleeding disorder or anticoagulation.26
Tuberculosis should be suspected in countries in which it is common.7 In a prospective study of 64 patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction in India,27 16 (25%) had corrosive injury, 16 (25%) had tuberculosis, and 15 (23%) had peptic ulcer disease. Compared with patients with corrosive injury and peptic ulcer disease, patients with gastroduodenal tuberculosis had the best outcomes with appropriate treatment.
Other reported causes include Bouveret syndrome (an impacted gallstone in the proximal duodenum), phytobezoar, diaphragmatic hernia, gastric volvulus, and Ladd bands (peritoneal bands associated with intestinal malrotation).7,28,29
PRESENTING SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction include nausea, nonbilious vomiting, epigastric pain, early satiety, abdominal distention, and weight loss.
In our patients, the most common presenting symptoms were nausea and vomiting (80%), followed by abdominal pain (72%); weight loss (15%), abdominal distention (15%), and early satiety (9%) were less common.2
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to malignancy generally present with a shorter duration of symptoms than those with peptic ulcer disease and are more likely to be older.8,13 Other conditions with an acute onset of symptoms include gastric polyp prolapse, percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube migration, gastric volvulus, and gallstone impaction.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction associated with peptic ulcer disease generally have a long-standing history of symptoms, including dyspepsia and weight loss over several years.4
SIGNS ON EXAMINATION
On examination, look for signs of chronic gastric obstruction and its consequences, such as malnutrition, cachexia, volume depletion, and dental erosions.
A succussion splash may suggest gastric outlet obstruction. This is elicited by rocking the patient back and forth by the hips or abdomen while listening over the stomach for a splash, which may be heard without a stethoscope. The test is considered positive if present 3 or more hours after drinking fluids and suggests retention of gastric materials.30,31
In thin individuals, chronic gastric outlet obstruction makes the stomach dilate and hypertrophy, which may be evident by a palpably thickened stomach with visible gastric peristalsis.4
Other notable findings on physical examination may include a palpable abdominal mass, epigastric pain, or an abnormality suggestive of metastatic gastric cancer, such as an enlarged left supraclavicular lymph node (Virchow node) or periumbilical lymph node (Sister Mary Joseph nodule). The Virchow node is at the junction of the thoracic duct and the left subclavian vein where the lymphatic circulation from the body drains into the systemic circulation, and it may be the first sign of gastric cancer.32 Sister Mary Joseph nodule (named after a surgical assistant to Dr. William James Mayo) refers to a palpable mass at the umbilicus, generally resulting from metastasis of an abdominal malignancy.33
SIGNS ON FURTHER STUDIES
Laboratory evaluation may show signs of poor oral intake and electrolyte abnormalities secondary to chronic nausea, vomiting, and dehydration, including hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia.
The underlying cause of gastric outlet obstruction has major implications for treatment and prognosis and cannot be differentiated by clinical presentation alone.1,9 Diagnosis is based on clinical features and radiologic or endoscopic evaluation consistent with gastric outlet obstruction.
Plain radiography may reveal an enlarged gastric bubble, and contrast studies may be useful to determine whether the obstruction is partial or complete, depending on whether the contrast passes into the small bowel.
Upper endoscopy is often needed to establish the diagnosis and cause. Emptying the stomach with a nasogastric tube is recommended before endoscopy to minimize the risk of aspiration during the procedure, and endotracheal intubation should be considered for airway protection.34 Findings of gastric outlet obstruction on upper endoscopy include retained food and liquid. Endoscopic biopsy is important to differentiate between benign and malignant causes. For patients with malignancy, endoscopic ultrasonography is useful for diagnosis via tissue sampling with fine-needle aspiration and locoregional staging.35
A strategy. Most patients whose clinical presentation suggests gastric outlet obstruction require cross-sectional radiologic imaging, upper endoscopy, or both.36 CT is the preferred imaging study to evaluate for intestinal obstruction.36,37 Patients with suspected complete obstruction or perforation should undergo CT before upper endoscopy. Oral contrast may interfere with endoscopy and should be avoided if endoscopy is planned. Additionally, giving oral contrast may worsen patient discomfort and increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, and aspiration.36,37
Following radiographic evaluation, upper endoscopy can be performed after gastric decompression to identify the location and extent of the obstruction and to potentially provide a definitive diagnosis with biopsy.36
DIFFERENTIATE FROM GASTROPARESIS
Gastroparesis is a chronic neuromuscular disorder characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction.38 The most common causes are diabetes, surgery, and idiopathy. Other causes include viral infection, connective tissue diseases, ischemia, infiltrative disorders, radiation, neurologic disorders, and paraneoplastic syndromes.39,40
Gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis share clinical symptoms including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, early satiety, and weight loss and are important to differentiate.36,38 Although abdominal pain may be present in both gastric outlet obstruction and gastroparesis, in gastroparesis it tends not to be the dominant symptom.40
Gastric scintigraphy is most commonly used to objectively quantify delayed gastric emptying.39 Upper endoscopy is imperative to exclude mechanical obstruction.39
MANAGEMENT
Initially, patients with signs and symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction should be given:
- Nothing by mouth (NPO)
- Intravenous fluids to correct volume depletion and electrolyte abnormalities
- A nasogastric tube for gastric decompression and symptom relief if symptoms persist despite being NPO
- A parenteral proton pump inhibitor, regardless of the cause of obstruction, to decrease gastric secretions41
- Medications for pain and nausea, if needed.
Definitive treatment of gastric outlet obstruction depends on the underlying cause, whether benign or malignant.
Management of benign gastric outlet obstruction
Symptoms of gastric outlet obstruction resolve spontaneously in about half of cases caused by acute peptic ulcer disease, as acute inflammation resolves.9,22
Endoscopic dilation is an important option in patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction, including peptic ulcer disease. Peptic ulcer disease-induced gastric outlet obstruction can be safely treated with endoscopic balloon dilation. This treatment almost always relieves symptoms immediately; however, the long-term response has varied from 16% to 100%, and patients may require more than 1 dilation procedure.25,42,43 The need for 2 or more dilation procedures may predict need for surgery.44 Gastric outlet obstruction after caustic ingestion or endoscopic submucosal dissection may also respond to endoscopic balloon dilation.36
Eradication of H pylori may be effective and lead to complete resolution of symptoms in patients with gastric outlet obstruction due to this infection.45–47
NSAIDs should be discontinued in patients with peptic ulcer disease and gastric outlet obstruction. These drugs damage the gastrointestinal mucosa by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes and decreasing synthesis of prostaglandins, which are important for mucosal defense.48 Patients may be unaware of NSAIDs contained in over-the-counter medications and may have difficulty discontinuing NSAIDs taken for pain.49
These drugs are an important cause of refractory peptic ulcer disease and can be detected by platelet COX activity testing, although this test is not widely available. In a study of patients with peptic ulcer disease without definite NSAID use or H pylori infection, up to one-third had evidence of surreptitious NSAID use as detected by platelet COX activity testing.50 In another study,51 platelet COX activity testing discovered over 20% more aspirin users than clinical history alone.
Surgery for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction is used only when medical management and endoscopic dilation fail. Ideally, surgery should relieve the obstruction and target the underlying cause, such as peptic ulcer disease. Laparoscopic surgery is generally preferred to open surgery because patients can resume oral intake sooner, have a shorter hospital stay, and have less intraoperative blood loss.52 The simplest surgical procedure to relieve obstruction is laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.
Patients with gastric outlet obstruction and peptic ulcer disease warrant laparoscopic vagotomy and antrectomy or distal gastrectomy. This removes the obstruction and the stimulus for gastric secretion.53 An alternative is vagotomy with a drainage procedure (pyloroplasty or gastrojejunostomy), which has a similar postoperative course and reduction in gastric acid secretion compared with antrectomy or distal gastrectomy.53,54
Daily proton pump inhibitors can be used for patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction not associated with peptic ulcer disease or risk factors; for such cases, vagotomy is not required.
Management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction
Patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction may have intractable nausea and abdominal pain secondary to retention of gastric contents. The major goal of therapy is to improve symptoms and restore tolerance of an oral diet. The short-term prognosis of malignant gastric outlet obstruction is poor, with a median survival of 3 to 4 months, as these patients often have unresectable disease.55
Surgical bypass used to be the standard of care for palliation of malignant gastric obstruction, but that was before endoscopic stenting was developed.
Endoscopic stenting allows patients to resume oral intake and get out of the hospital sooner with fewer complications than with open surgical bypass. It may be a more appropriate option for palliation of symptoms in patients with malignant obstruction who have a poor prognosis and prefer a less invasive intervention.55,56
Endoscopic duodenal stenting of malignant gastric outlet obstruction has a success rate of greater than 90%, and most patients can tolerate a mechanical soft diet afterward.34 The procedure is usually performed with a 9-cm or 12-cm self-expanding duodenal stent, 22 mm in diameter, placed over a guide wire under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance (Figure 2). The stent is placed by removing the outer catheter, with distal-to-proximal stent deployment.
Patients who also have biliary obstruction may require biliary stent placement, which is generally performed before duodenal stenting. For patients with an endoscopic stent who develop biliary obstruction, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography can be attempted with placement of a biliary stent; however, these patients may require biliary drain placement by percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography or by endoscopic ultrasonographically guided transduodenal or transgastric biliary drainage.
From 20% to 30% of patients require repeated endoscopic stent placement, although most patients die within several months after stenting.34 Surgical options for patients who do not respond to endoscopic stenting include open or laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55
Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy may provide better long-term outcomes than duodenal stenting for patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction and a life expectancy longer than a few months.
A 2017 retrospective study of 155 patients with gastric outlet obstruction secondary to unresectable gastric cancer suggested that those who underwent laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy had better oral intake, better tolerance of chemotherapy, and longer overall survival than those who underwent duodenal stenting. Postsurgical complications were more common in the laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy group (16%) than in the duodenal stenting group (0%).57
In most of the studies comparing endoscopic stenting with surgery, the surgery was open gastrojejunostomy; there are limited data directly comparing stenting with laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy.55 Endoscopic stenting is estimated to be significantly less costly than surgery, with a median cost of $12,000 less than gastrojejunostomy.58 As an alternative to enteral stenting and surgical gastrojejunostomy, ultrasonography-guided endoscopic gastrojejunostomy or gastroenterostomy with placement of a lumen-apposing metal stent is emerging as a third treatment option and is under active investigation.59
Patients with malignancy that is potentially curable by resection should undergo surgical evaluation before consideration of endoscopic stenting. For patients who are not candidates for surgery or endoscopic stenting, a percutaneous gastrostomy tube can be considered for gastric decompression and symptom relief.
CASE CONCLUDED
The patient underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy with endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of her pancreatic mass. Before the procedure, she was intubated to minimize the risk of aspiration due to persistent nausea and retained gastric contents. A large submucosal mass was found in the duodenal bulb. Endoscopic ultrasonography showed a mass within the pancreatic head with pancreatic duct obstruction. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy was performed, and pathology study revealed pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The patient underwent stenting with a 22-mm by 12-cm WallFlex stent (Boston Scientific), which led to resolution of nausea and advancement to a mechanical soft diet on hospital discharge.
She was scheduled for follow-up in the outpatient clinic for treatment of pancreatic cancer.
- Johnson CD. Gastric outlet obstruction malignant until proved otherwise. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1740. pmid:7572886
- Koop AH, Palmer WC, Mareth K, Burton MC, Bowman A, Stancampiano F. Tu1335 - Pancreatic cancer most common cause of malignant gastric outlet obstruction at a tertiary referral center: a 10 year retrospective study [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2018; 154(6, suppl 1):S-1343.
- Hall R, Royston C, Bardhan KD. The scars of time: the disappearance of peptic ulcer-related pyloric stenosis through the 20th century. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2014; 44(3):201–208. doi:10.4997/JRCPE.2014.303
- Kreel L, Ellis H. Pyloric stenosis in adults: a clinical and radiological study of 100 consecutive patients. Gut 1965; 6(3):253–261. pmid:18668780
- Shone DN, Nikoomanesh P, Smith-Meek MM, Bender JS. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction in the era of H2 blockers. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1769–1770. pmid:7572891
- Ellis H. The diagnosis of benign and malignant pyloric obstruction. Clin Oncol 1976; 2(1):11–15. pmid:1277618
- Samad A, Khanzada TW, Shoukat I. Gastric outlet obstruction: change in etiology. Pak J Surg 2007; 23(1):29–32.
- Chowdhury A, Dhali GK, Banerjee PK. Etiology of gastric outlet obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(8):1679. pmid:8759707
- Johnson CD, Ellis H. Gastric outlet obstruction now predicts malignancy. Br J Surg 1990; 77(9):1023–1024. pmid:2207566
- Misra SP, Dwivedi M, Misra V. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction even in a developing country. Endoscopy 1998; 30(5):484–486. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1001313
- Essoun SD, Dakubo JCB. Update of aetiological patterns of adult gastric outlet obstruction in Accra, Ghana. Int J Clin Med 2014; 5(17):1059–1064. doi:10.4236/ijcm.2014.517136
- Jaka H, Mchembe MD, Rambau PF, Chalya PL. Gastric outlet obstruction at Bugando Medical Centre in Northwestern Tanzania: a prospective review of 184 cases. BMC Surg 2013; 13:41. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-13-41
- Sukumar V, Ravindran C, Prasad RV. Demographic and etiological patterns of gastric outlet obstruction in Kerala, South India. N Am J Med Sci 2015; 7(9):403–406. doi:10.4103/1947-2714.166220
- Yoursef M, Mirza MR, Khan S. Gastric outlet obstruction. Pak J Surg 2005; 10(4):48–50.
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015; 136(5):E359–E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
- Parkin DM, Stjernsward J, Muir CS. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of twelve major cancers. Bull World Health Organ 1984; 62(2):163–182. pmid:6610488
- Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2014; 23(5):700–713. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1057
- Jeurnink SM, Steyerberg EW, van Hooft JE, et al; Dutch SUSTENT Study Group. Surgical gastrojejunostomy or endoscopic stent placement for the palliation of malignant gastric outlet obstruction (SUSTENT) study): a multicenter randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 71(3):490–499. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2009.09.042
- Tringali A, Didden P, Repici A, et al. Endoscopic treatment of malignant gastric and duodenal strictures: a prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):66–75. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.06.032
- Malfertheiner P, Chan FK, McColl KE. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2009; 374(9699):1449–1461. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60938-7
- Gibson JB, Behrman SW, Fabian TC, Britt LG. Gastric outlet obstruction resulting from peptic ulcer disease requiring surgical intervention is infrequently associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Am Coll Surg 2000; 191(1):32–37. pmid:10898181
- Kochhar R, Kochhar S. Endoscopic balloon dilation for benign gastric outlet obstruction in adults. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(1):29–35. doi:10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.29
- Kotisso R. Gastric outlet obstruction in Northwestern Ethiopia. East Cent Afr J Surg 2000; 5(2):25-29.
- Hamzaoui L, Bouassida M, Ben Mansour I, et al. Balloon dilatation in patients with gastric outlet obstruction related to peptic ulcer disease. Arab J Gastroenterol 2015; 16(3–4):121–124. doi:10.1016/j.ajg.2015.07.004
- Najm WI. Peptic ulcer disease. Prim Care 2011; 38(3):383–394. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2011.05.001
- Veloso N, Amaro P, Ferreira M, Romaozinho JM, Sofia C. Acute pancreatitis associated with a nontraumatic, intramural duodenal hematoma. Endoscopy 2013; 45(suppl 2):E51–E52. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1325969
- Maharshi S, Puri AS, Sachdeva S, Kumar A, Dalal A, Gupta M. Aetiological spectrum of benign gastric outlet obstruction in India: new trends. Trop Doct 2016; 46(4):186–191. doi:10.1177/0049475515626032
- Sala MA, Ligabo AN, de Arruda MC, Indiani JM, Nacif MS. Intestinal malrotation associated with duodenal obstruction secondary to Ladd’s bands. Radiol Bras 2016; 49(4):271–272. doi:10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0106
- Alibegovic E, Kurtcehajic A, Hujdurovic A, Mujagic S, Alibegovic J, Kurtcehajic D. Bouveret syndrome or gallstone ileus. Am J Med 2018; 131(4):e175. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.10.044
- Lau JY, Chung SC, Sung JJ, et al. Through-the-scope balloon dilation for pyloric stenosis: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc 1996; 43(2 Pt 1):98–101. pmid:8635729
- Ray K, Snowden C, Khatri K, McFall M. Gastric outlet obstruction from a caecal volvulus, herniated through epiploic foramen: a case report. BMJ Case Rep 2009; pii:bcr05.2009.1880. doi:10.1136/bcr.05.2009.1880
- Baumgart DC, Fischer A. Virchow’s node. Lancet 2007; 370(9598):1568. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61661-4
- Dar IH, Kamili MA, Dar SH, Kuchaai FA. Sister Mary Joseph nodule—a case report with review of literature. J Res Med Sci 2009; 14(6):385–387. pmid:21772912
- Tang SJ. Endoscopic stent placement for gastric outlet obstruction. Video Journal and Encyclopedia of GI Endoscopy 2013; 1(1):133–136.
- Valero M, Robles-Medranda C. Endoscopic ultrasound in oncology: an update of clinical applications in the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(6):243–254.
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Fukami N, Anderson MA, Khan K, et al. The role of endoscopy in gastroduodenal obstruction and gastroparesis. Gastrointest Endosc 2011; 74(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.12.003
- Ros PR, Huprich JE. ACR appropriateness criteria on suspected small-bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Radiol 2006; 3(11):838–841. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2006.09.018
- Pasricha PJ, Parkman HP. Gastroparesis: definitions and diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2015; 44(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2014.11.001
- Stein B, Everhart KK, Lacy BE. Gastroparesis: a review of current diagnosis and treatment options. J Clin Gastroenterol 2015; 49(7):550–558. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000320
- Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L; American College of Gastroenterology. Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108(1):18–37.
- Gursoy O, Memis D, Sut N. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on gastric juice volume, gastric pH and gastric intramucosal pH in critically ill patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Drug Investig 2008; 28(12):777–782. doi:10.2165/0044011-200828120-00005
- Kuwada SK, Alexander GL. Long-term outcome of endoscopic dilation of nonmalignant pyloric stenosis. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 41(1):15–17. pmid:7698619
- Kochhar R, Sethy PK, Nagi B, Wig JD. Endoscopic balloon dilatation of benign gastric outlet obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 19(4):418–422. pmid:15012779
- Perng CL, Lin HJ, Lo WC, Lai CR, Guo WS, Lee SD. Characteristics of patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction requiring surgery after endoscopic balloon dilation. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(5):987–990. pmid:8633593
- Taskin V, Gurer I, Ozyilkan E, Sare M, Hilmioglu F. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on peptic ulcer disease complicated with outlet obstruction. Helicobacter 2000; 5(1):38–40. pmid:10672050
- de Boer WA, Driessen WM. Resolution of gastric outlet obstruction after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Gastroenterol 1995; 21(4):329–330. pmid:8583113
- Tursi A, Cammarota G, Papa A, Montalto M, Fedeli G, Gasbarrini G. Helicobacter pylori eradication helps resolve pyloric and duodenal stenosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1996; 23(2):157–158. pmid:8877648
- Schmassmann A. Mechanisms of ulcer healing and effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Med 1998; 104(3A):43S–51S; discussion 79S–80S. pmid:9572320
- Kim HU. Diagnostic and treatment approaches for refractory peptic ulcers. Clin Endosc 2015; 48(4):285–290. doi:10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.285
- Ong TZ, Hawkey CJ, Ho KY. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is a significant cause of peptic ulcer disease in a tertiary hospital in Singapore: a prospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2006; 40(9):795–800. doi:10.1097/01.mcg.0000225610.41105.7f
- Lanas A, Sekar MC, Hirschowitz BI. Objective evidence of aspirin use in both ulcer and nonulcer upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1992; 103(3):862–869. pmid:1499936
- Zhang LP, Tabrizian P, Nguyen S, Telem D, Divino C. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction. JSLS 2011; 15(2):169–173. doi:10.4293/108680811X13022985132074
- Lagoo J, Pappas TN, Perez A. A relic or still relevant: the narrowing role for vagotomy in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Am J Surg 2014; 207(1):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.02.012
- Csendes A, Maluenda F, Braghetto I, Schutte H, Burdiles P, Diaz JC. Prospective randomized study comparing three surgical techniques for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction secondary to duodenal ulcer. Am J Surg 1993; 166(1):45–49. pmid:8101050
- Ly J, O’Grady G, Mittal A, Plank L, Windsor JA. A systematic review of methods to palliate malignant gastric outlet obstruction. Surg Endosc 2010; 24(2):290–297. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0577-1
- Goldberg EM. Palliative treatment of gastric outlet obstruction in terminal patients: SEMS. Stent every malignant stricture! Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):76–78. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.056
- Min SH, Son SY, Jung DH, et al. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy versus duodenal stenting in unresectable gastric cancer with gastric outlet obstruction. Ann Surg Treat Res 2017; 93(3):130–136. doi:10.4174/astr.2017.93.3.130
- Roy A, Kim M, Christein J, Varadarajulu S. Stenting versus gastrojejunostomy for management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction: comparison of clinical outcomes and costs. Surg Endosc 2012; 26(11):3114–119. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2301-9
- Amin S, Sethi A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2017; 27(4):707–713. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2017.06.009
- Johnson CD. Gastric outlet obstruction malignant until proved otherwise. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1740. pmid:7572886
- Koop AH, Palmer WC, Mareth K, Burton MC, Bowman A, Stancampiano F. Tu1335 - Pancreatic cancer most common cause of malignant gastric outlet obstruction at a tertiary referral center: a 10 year retrospective study [abstract]. Gastroenterology 2018; 154(6, suppl 1):S-1343.
- Hall R, Royston C, Bardhan KD. The scars of time: the disappearance of peptic ulcer-related pyloric stenosis through the 20th century. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 2014; 44(3):201–208. doi:10.4997/JRCPE.2014.303
- Kreel L, Ellis H. Pyloric stenosis in adults: a clinical and radiological study of 100 consecutive patients. Gut 1965; 6(3):253–261. pmid:18668780
- Shone DN, Nikoomanesh P, Smith-Meek MM, Bender JS. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction in the era of H2 blockers. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90(10):1769–1770. pmid:7572891
- Ellis H. The diagnosis of benign and malignant pyloric obstruction. Clin Oncol 1976; 2(1):11–15. pmid:1277618
- Samad A, Khanzada TW, Shoukat I. Gastric outlet obstruction: change in etiology. Pak J Surg 2007; 23(1):29–32.
- Chowdhury A, Dhali GK, Banerjee PK. Etiology of gastric outlet obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(8):1679. pmid:8759707
- Johnson CD, Ellis H. Gastric outlet obstruction now predicts malignancy. Br J Surg 1990; 77(9):1023–1024. pmid:2207566
- Misra SP, Dwivedi M, Misra V. Malignancy is the most common cause of gastric outlet obstruction even in a developing country. Endoscopy 1998; 30(5):484–486. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1001313
- Essoun SD, Dakubo JCB. Update of aetiological patterns of adult gastric outlet obstruction in Accra, Ghana. Int J Clin Med 2014; 5(17):1059–1064. doi:10.4236/ijcm.2014.517136
- Jaka H, Mchembe MD, Rambau PF, Chalya PL. Gastric outlet obstruction at Bugando Medical Centre in Northwestern Tanzania: a prospective review of 184 cases. BMC Surg 2013; 13:41. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-13-41
- Sukumar V, Ravindran C, Prasad RV. Demographic and etiological patterns of gastric outlet obstruction in Kerala, South India. N Am J Med Sci 2015; 7(9):403–406. doi:10.4103/1947-2714.166220
- Yoursef M, Mirza MR, Khan S. Gastric outlet obstruction. Pak J Surg 2005; 10(4):48–50.
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015; 136(5):E359–E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
- Parkin DM, Stjernsward J, Muir CS. Estimates of the worldwide frequency of twelve major cancers. Bull World Health Organ 1984; 62(2):163–182. pmid:6610488
- Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2014; 23(5):700–713. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-1057
- Jeurnink SM, Steyerberg EW, van Hooft JE, et al; Dutch SUSTENT Study Group. Surgical gastrojejunostomy or endoscopic stent placement for the palliation of malignant gastric outlet obstruction (SUSTENT) study): a multicenter randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 71(3):490–499. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2009.09.042
- Tringali A, Didden P, Repici A, et al. Endoscopic treatment of malignant gastric and duodenal strictures: a prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):66–75. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.06.032
- Malfertheiner P, Chan FK, McColl KE. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2009; 374(9699):1449–1461. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60938-7
- Gibson JB, Behrman SW, Fabian TC, Britt LG. Gastric outlet obstruction resulting from peptic ulcer disease requiring surgical intervention is infrequently associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Am Coll Surg 2000; 191(1):32–37. pmid:10898181
- Kochhar R, Kochhar S. Endoscopic balloon dilation for benign gastric outlet obstruction in adults. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2010; 2(1):29–35. doi:10.4253/wjge.v2.i1.29
- Kotisso R. Gastric outlet obstruction in Northwestern Ethiopia. East Cent Afr J Surg 2000; 5(2):25-29.
- Hamzaoui L, Bouassida M, Ben Mansour I, et al. Balloon dilatation in patients with gastric outlet obstruction related to peptic ulcer disease. Arab J Gastroenterol 2015; 16(3–4):121–124. doi:10.1016/j.ajg.2015.07.004
- Najm WI. Peptic ulcer disease. Prim Care 2011; 38(3):383–394. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2011.05.001
- Veloso N, Amaro P, Ferreira M, Romaozinho JM, Sofia C. Acute pancreatitis associated with a nontraumatic, intramural duodenal hematoma. Endoscopy 2013; 45(suppl 2):E51–E52. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1325969
- Maharshi S, Puri AS, Sachdeva S, Kumar A, Dalal A, Gupta M. Aetiological spectrum of benign gastric outlet obstruction in India: new trends. Trop Doct 2016; 46(4):186–191. doi:10.1177/0049475515626032
- Sala MA, Ligabo AN, de Arruda MC, Indiani JM, Nacif MS. Intestinal malrotation associated with duodenal obstruction secondary to Ladd’s bands. Radiol Bras 2016; 49(4):271–272. doi:10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0106
- Alibegovic E, Kurtcehajic A, Hujdurovic A, Mujagic S, Alibegovic J, Kurtcehajic D. Bouveret syndrome or gallstone ileus. Am J Med 2018; 131(4):e175. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.10.044
- Lau JY, Chung SC, Sung JJ, et al. Through-the-scope balloon dilation for pyloric stenosis: long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc 1996; 43(2 Pt 1):98–101. pmid:8635729
- Ray K, Snowden C, Khatri K, McFall M. Gastric outlet obstruction from a caecal volvulus, herniated through epiploic foramen: a case report. BMJ Case Rep 2009; pii:bcr05.2009.1880. doi:10.1136/bcr.05.2009.1880
- Baumgart DC, Fischer A. Virchow’s node. Lancet 2007; 370(9598):1568. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61661-4
- Dar IH, Kamili MA, Dar SH, Kuchaai FA. Sister Mary Joseph nodule—a case report with review of literature. J Res Med Sci 2009; 14(6):385–387. pmid:21772912
- Tang SJ. Endoscopic stent placement for gastric outlet obstruction. Video Journal and Encyclopedia of GI Endoscopy 2013; 1(1):133–136.
- Valero M, Robles-Medranda C. Endoscopic ultrasound in oncology: an update of clinical applications in the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2017; 9(6):243–254.
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Fukami N, Anderson MA, Khan K, et al. The role of endoscopy in gastroduodenal obstruction and gastroparesis. Gastrointest Endosc 2011; 74(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2010.12.003
- Ros PR, Huprich JE. ACR appropriateness criteria on suspected small-bowel obstruction. J Am Coll Radiol 2006; 3(11):838–841. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2006.09.018
- Pasricha PJ, Parkman HP. Gastroparesis: definitions and diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2015; 44(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.gtc.2014.11.001
- Stein B, Everhart KK, Lacy BE. Gastroparesis: a review of current diagnosis and treatment options. J Clin Gastroenterol 2015; 49(7):550–558. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000320
- Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L; American College of Gastroenterology. Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108(1):18–37.
- Gursoy O, Memis D, Sut N. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on gastric juice volume, gastric pH and gastric intramucosal pH in critically ill patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Drug Investig 2008; 28(12):777–782. doi:10.2165/0044011-200828120-00005
- Kuwada SK, Alexander GL. Long-term outcome of endoscopic dilation of nonmalignant pyloric stenosis. Gastrointest Endosc 1995; 41(1):15–17. pmid:7698619
- Kochhar R, Sethy PK, Nagi B, Wig JD. Endoscopic balloon dilatation of benign gastric outlet obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 19(4):418–422. pmid:15012779
- Perng CL, Lin HJ, Lo WC, Lai CR, Guo WS, Lee SD. Characteristics of patients with benign gastric outlet obstruction requiring surgery after endoscopic balloon dilation. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91(5):987–990. pmid:8633593
- Taskin V, Gurer I, Ozyilkan E, Sare M, Hilmioglu F. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on peptic ulcer disease complicated with outlet obstruction. Helicobacter 2000; 5(1):38–40. pmid:10672050
- de Boer WA, Driessen WM. Resolution of gastric outlet obstruction after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Gastroenterol 1995; 21(4):329–330. pmid:8583113
- Tursi A, Cammarota G, Papa A, Montalto M, Fedeli G, Gasbarrini G. Helicobacter pylori eradication helps resolve pyloric and duodenal stenosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1996; 23(2):157–158. pmid:8877648
- Schmassmann A. Mechanisms of ulcer healing and effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Med 1998; 104(3A):43S–51S; discussion 79S–80S. pmid:9572320
- Kim HU. Diagnostic and treatment approaches for refractory peptic ulcers. Clin Endosc 2015; 48(4):285–290. doi:10.5946/ce.2015.48.4.285
- Ong TZ, Hawkey CJ, Ho KY. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is a significant cause of peptic ulcer disease in a tertiary hospital in Singapore: a prospective study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2006; 40(9):795–800. doi:10.1097/01.mcg.0000225610.41105.7f
- Lanas A, Sekar MC, Hirschowitz BI. Objective evidence of aspirin use in both ulcer and nonulcer upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastroenterology 1992; 103(3):862–869. pmid:1499936
- Zhang LP, Tabrizian P, Nguyen S, Telem D, Divino C. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction. JSLS 2011; 15(2):169–173. doi:10.4293/108680811X13022985132074
- Lagoo J, Pappas TN, Perez A. A relic or still relevant: the narrowing role for vagotomy in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease. Am J Surg 2014; 207(1):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.02.012
- Csendes A, Maluenda F, Braghetto I, Schutte H, Burdiles P, Diaz JC. Prospective randomized study comparing three surgical techniques for the treatment of gastric outlet obstruction secondary to duodenal ulcer. Am J Surg 1993; 166(1):45–49. pmid:8101050
- Ly J, O’Grady G, Mittal A, Plank L, Windsor JA. A systematic review of methods to palliate malignant gastric outlet obstruction. Surg Endosc 2010; 24(2):290–297. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0577-1
- Goldberg EM. Palliative treatment of gastric outlet obstruction in terminal patients: SEMS. Stent every malignant stricture! Gastrointest Endosc 2014; 79(1):76–78. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.07.056
- Min SH, Son SY, Jung DH, et al. Laparoscopic gastrojejunostomy versus duodenal stenting in unresectable gastric cancer with gastric outlet obstruction. Ann Surg Treat Res 2017; 93(3):130–136. doi:10.4174/astr.2017.93.3.130
- Roy A, Kim M, Christein J, Varadarajulu S. Stenting versus gastrojejunostomy for management of malignant gastric outlet obstruction: comparison of clinical outcomes and costs. Surg Endosc 2012; 26(11):3114–119. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2301-9
- Amin S, Sethi A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastrojejunostomy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2017; 27(4):707–713. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2017.06.009
KEY POINTS
- Causes of gastric outlet obstruction fall into 2 categories: benign and malignant. The cause should be presumed to be malignant until proven otherwise.
- Peptic ulcer disease, a benign cause, used to account for most cases of gastric outlet obstruction. It is still common but has declined in frequency with the development of acid-suppressing drugs.
- Gastric cancer used to be the most common malignant cause but has declined in frequency in Western countries with treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. Now, pancreatic cancer predominates.
- Endoscopic stenting is an effective, minimally invasive treatment for patients with malignant gastric outlet obstruction and poor prognosis, allowing resumption of oral intake and improving quality of life.
Infection or not infection, that is the question—Is procalcitonin the answer?
Diagnostic algorithms have been proposed to help recognize infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rhinosinusitis syndrome, acute arthritis, pharyngitis, and possible sepsis. The algorithms have included laboratory tests and potential biomarkers, but all are imperfect despite achieving various degrees of acceptance in practice.
In this issue of the Journal, Dr. Fakheri updates us on using the data on serum procalcitonin levels to guide starting and stopping antibiotics in different clinical scenarios. As I read the paper, I wondered what was different about procalcitonin that might allow it to succeed where seemingly similar biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) have failed.
Procalcitonin is the approximately 15,000-kD product of the CALC1 gene and the precursor of calcitonin. Not surprisingly, then, it is increased in patients with thyroid medullary carcinoma, and it is also often elevated in nonthyroid neuroendocrine malignancies. Proteolytic cleavage of procalcitonin to active calcitonin takes place mainly or only in the thyroid, and under normal homeostatic conditions, procalcitonin is almost unmeasurable in the circulation. However, under major stress such as systemic inflammation, sepsis, or burns, the CALC1 gene is activated in parenchymal cells in many organs, and procalcitonin is synthesized and released. Notably, under these conditions, the procalcitonin does not seem to be of thyroid origin; hence, calcitonin levels do not rise markedly. The physiologic role of nonthyroidal procalcitonin is unknown.
Procalcitonin synthesis and secretion is turned on in nonthyroid tissue by multiple cytokines; the cytokines most likely relevant to its association with inflammation and infections are interleukin (IL) 1 beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, and IL-6. Since these same mediators drive the acute-phase response and elicit the increase in circulating CRP and fibrinogen (the major contributor to the ESR), the obvious question is why procalcitonin might be a more reliable biomarker to distinguish bacterial infection from inflammation or a viral infection than the CRP level or ESR. And although it does indeed seem to do so in several conditions, as Dr. Fakheri discusses, the explanation is not obvious. But it is intriguing to hypothesize.
Induction of procalcitonin by endotoxin-stimulated cytokines is rapid and seems to be slightly faster than that of CRP, although there may be issues of assay sensitivity. The half-life of procalcitonin is similar to that of CRP (about 24 hours). Its degradation does not seem to be altered in renal insufficiency, and its synthesis seems to rapidly shut off as the cytokine level drops. But interestingly, and perhaps relevant to its possible unique biomarker behavior, its synthesis seems to depend on factors other than the increase in inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. Under certain circumstances, in the same patient, there is a discrepancy between the levels of procalcitonin and CRP.
In a small study of patients with pulmonary embolism and fever, IL-6 levels increased in many with an expected accompanying increase in CRP and ESR, but procalcitonin did not markedly rise,1 although all 3 markers rose as expected in patients with bacterial pneumonia.
Even more provocative is another study in 69 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and bacterial infection (43 patients had sepsis, 11 of whom died). The CRP level rose dramatically in the infected patients, but procalcitonin did not.2
The intriguing aspect of this, assuming it holds true in other studies, is that interferon activity is high in lupus and many viral infections, and if interferon can suppress CALC1 gene activation3 but leave CRP activation unaffected, this may provide a clue as to why CRP but not procalcitonin is elevated in serious viral infections, thus allowing procalcitonin to more effectively distinguish bacterial from viral and other nonbacterial inflammatory responses.
The two studies I mention are small, some conflicting results have been published, and the results cannot yet be generalized. Plus, it has long been recognized there is sometimes discordance in a given patient between the elevation in ESR and CRP, not readily explained by the presence of a paraprotein, rheologic factors, or the different time course of decay in the ESR and CRP response. Whatever the explanation, procalcitonin’s biology is interesting, and clinical study results show promise. While tracking procalcitonin levels is not uniformly useful (eg, there is no convincing value in using procalcitonin in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections), there is accumulating evidence that it can guide us to using shorter but still effective courses of antibiotics in several clinical scenarios. Hopefully, more frequent use of the test will make a dent in our apparent excess use of antibiotics in patients with nonbacterial upper-respiratory infections.
- Köktürk N, Kanbay A, Bukan N, Ekim N. The value of serum procalcitonin in differential diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and community acquired pneumonia. Clin App Thromb Hemostasis 2011; 17(5):519–525. doi:10.1177/1076029610375425
- El-Serougy E, Zayed HS, Ibrahim NM, Maged LA. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: the controversy continues. Lupus 2018 Jan 1:961203318777101. doi:10.1177/0961203318777101 (e-pub ahead of print)
- Linscheid P, Seboek D, Nylen ES, et al. In vitro and in vivo calcitonin I gene expression in parenchymal cells: a novel product of human adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2003; 144(12): 5578–5584. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0854
Diagnostic algorithms have been proposed to help recognize infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rhinosinusitis syndrome, acute arthritis, pharyngitis, and possible sepsis. The algorithms have included laboratory tests and potential biomarkers, but all are imperfect despite achieving various degrees of acceptance in practice.
In this issue of the Journal, Dr. Fakheri updates us on using the data on serum procalcitonin levels to guide starting and stopping antibiotics in different clinical scenarios. As I read the paper, I wondered what was different about procalcitonin that might allow it to succeed where seemingly similar biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) have failed.
Procalcitonin is the approximately 15,000-kD product of the CALC1 gene and the precursor of calcitonin. Not surprisingly, then, it is increased in patients with thyroid medullary carcinoma, and it is also often elevated in nonthyroid neuroendocrine malignancies. Proteolytic cleavage of procalcitonin to active calcitonin takes place mainly or only in the thyroid, and under normal homeostatic conditions, procalcitonin is almost unmeasurable in the circulation. However, under major stress such as systemic inflammation, sepsis, or burns, the CALC1 gene is activated in parenchymal cells in many organs, and procalcitonin is synthesized and released. Notably, under these conditions, the procalcitonin does not seem to be of thyroid origin; hence, calcitonin levels do not rise markedly. The physiologic role of nonthyroidal procalcitonin is unknown.
Procalcitonin synthesis and secretion is turned on in nonthyroid tissue by multiple cytokines; the cytokines most likely relevant to its association with inflammation and infections are interleukin (IL) 1 beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, and IL-6. Since these same mediators drive the acute-phase response and elicit the increase in circulating CRP and fibrinogen (the major contributor to the ESR), the obvious question is why procalcitonin might be a more reliable biomarker to distinguish bacterial infection from inflammation or a viral infection than the CRP level or ESR. And although it does indeed seem to do so in several conditions, as Dr. Fakheri discusses, the explanation is not obvious. But it is intriguing to hypothesize.
Induction of procalcitonin by endotoxin-stimulated cytokines is rapid and seems to be slightly faster than that of CRP, although there may be issues of assay sensitivity. The half-life of procalcitonin is similar to that of CRP (about 24 hours). Its degradation does not seem to be altered in renal insufficiency, and its synthesis seems to rapidly shut off as the cytokine level drops. But interestingly, and perhaps relevant to its possible unique biomarker behavior, its synthesis seems to depend on factors other than the increase in inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. Under certain circumstances, in the same patient, there is a discrepancy between the levels of procalcitonin and CRP.
In a small study of patients with pulmonary embolism and fever, IL-6 levels increased in many with an expected accompanying increase in CRP and ESR, but procalcitonin did not markedly rise,1 although all 3 markers rose as expected in patients with bacterial pneumonia.
Even more provocative is another study in 69 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and bacterial infection (43 patients had sepsis, 11 of whom died). The CRP level rose dramatically in the infected patients, but procalcitonin did not.2
The intriguing aspect of this, assuming it holds true in other studies, is that interferon activity is high in lupus and many viral infections, and if interferon can suppress CALC1 gene activation3 but leave CRP activation unaffected, this may provide a clue as to why CRP but not procalcitonin is elevated in serious viral infections, thus allowing procalcitonin to more effectively distinguish bacterial from viral and other nonbacterial inflammatory responses.
The two studies I mention are small, some conflicting results have been published, and the results cannot yet be generalized. Plus, it has long been recognized there is sometimes discordance in a given patient between the elevation in ESR and CRP, not readily explained by the presence of a paraprotein, rheologic factors, or the different time course of decay in the ESR and CRP response. Whatever the explanation, procalcitonin’s biology is interesting, and clinical study results show promise. While tracking procalcitonin levels is not uniformly useful (eg, there is no convincing value in using procalcitonin in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections), there is accumulating evidence that it can guide us to using shorter but still effective courses of antibiotics in several clinical scenarios. Hopefully, more frequent use of the test will make a dent in our apparent excess use of antibiotics in patients with nonbacterial upper-respiratory infections.
Diagnostic algorithms have been proposed to help recognize infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rhinosinusitis syndrome, acute arthritis, pharyngitis, and possible sepsis. The algorithms have included laboratory tests and potential biomarkers, but all are imperfect despite achieving various degrees of acceptance in practice.
In this issue of the Journal, Dr. Fakheri updates us on using the data on serum procalcitonin levels to guide starting and stopping antibiotics in different clinical scenarios. As I read the paper, I wondered what was different about procalcitonin that might allow it to succeed where seemingly similar biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) have failed.
Procalcitonin is the approximately 15,000-kD product of the CALC1 gene and the precursor of calcitonin. Not surprisingly, then, it is increased in patients with thyroid medullary carcinoma, and it is also often elevated in nonthyroid neuroendocrine malignancies. Proteolytic cleavage of procalcitonin to active calcitonin takes place mainly or only in the thyroid, and under normal homeostatic conditions, procalcitonin is almost unmeasurable in the circulation. However, under major stress such as systemic inflammation, sepsis, or burns, the CALC1 gene is activated in parenchymal cells in many organs, and procalcitonin is synthesized and released. Notably, under these conditions, the procalcitonin does not seem to be of thyroid origin; hence, calcitonin levels do not rise markedly. The physiologic role of nonthyroidal procalcitonin is unknown.
Procalcitonin synthesis and secretion is turned on in nonthyroid tissue by multiple cytokines; the cytokines most likely relevant to its association with inflammation and infections are interleukin (IL) 1 beta, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, and IL-6. Since these same mediators drive the acute-phase response and elicit the increase in circulating CRP and fibrinogen (the major contributor to the ESR), the obvious question is why procalcitonin might be a more reliable biomarker to distinguish bacterial infection from inflammation or a viral infection than the CRP level or ESR. And although it does indeed seem to do so in several conditions, as Dr. Fakheri discusses, the explanation is not obvious. But it is intriguing to hypothesize.
Induction of procalcitonin by endotoxin-stimulated cytokines is rapid and seems to be slightly faster than that of CRP, although there may be issues of assay sensitivity. The half-life of procalcitonin is similar to that of CRP (about 24 hours). Its degradation does not seem to be altered in renal insufficiency, and its synthesis seems to rapidly shut off as the cytokine level drops. But interestingly, and perhaps relevant to its possible unique biomarker behavior, its synthesis seems to depend on factors other than the increase in inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. Under certain circumstances, in the same patient, there is a discrepancy between the levels of procalcitonin and CRP.
In a small study of patients with pulmonary embolism and fever, IL-6 levels increased in many with an expected accompanying increase in CRP and ESR, but procalcitonin did not markedly rise,1 although all 3 markers rose as expected in patients with bacterial pneumonia.
Even more provocative is another study in 69 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and bacterial infection (43 patients had sepsis, 11 of whom died). The CRP level rose dramatically in the infected patients, but procalcitonin did not.2
The intriguing aspect of this, assuming it holds true in other studies, is that interferon activity is high in lupus and many viral infections, and if interferon can suppress CALC1 gene activation3 but leave CRP activation unaffected, this may provide a clue as to why CRP but not procalcitonin is elevated in serious viral infections, thus allowing procalcitonin to more effectively distinguish bacterial from viral and other nonbacterial inflammatory responses.
The two studies I mention are small, some conflicting results have been published, and the results cannot yet be generalized. Plus, it has long been recognized there is sometimes discordance in a given patient between the elevation in ESR and CRP, not readily explained by the presence of a paraprotein, rheologic factors, or the different time course of decay in the ESR and CRP response. Whatever the explanation, procalcitonin’s biology is interesting, and clinical study results show promise. While tracking procalcitonin levels is not uniformly useful (eg, there is no convincing value in using procalcitonin in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections), there is accumulating evidence that it can guide us to using shorter but still effective courses of antibiotics in several clinical scenarios. Hopefully, more frequent use of the test will make a dent in our apparent excess use of antibiotics in patients with nonbacterial upper-respiratory infections.
- Köktürk N, Kanbay A, Bukan N, Ekim N. The value of serum procalcitonin in differential diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and community acquired pneumonia. Clin App Thromb Hemostasis 2011; 17(5):519–525. doi:10.1177/1076029610375425
- El-Serougy E, Zayed HS, Ibrahim NM, Maged LA. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: the controversy continues. Lupus 2018 Jan 1:961203318777101. doi:10.1177/0961203318777101 (e-pub ahead of print)
- Linscheid P, Seboek D, Nylen ES, et al. In vitro and in vivo calcitonin I gene expression in parenchymal cells: a novel product of human adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2003; 144(12): 5578–5584. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0854
- Köktürk N, Kanbay A, Bukan N, Ekim N. The value of serum procalcitonin in differential diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and community acquired pneumonia. Clin App Thromb Hemostasis 2011; 17(5):519–525. doi:10.1177/1076029610375425
- El-Serougy E, Zayed HS, Ibrahim NM, Maged LA. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus: the controversy continues. Lupus 2018 Jan 1:961203318777101. doi:10.1177/0961203318777101 (e-pub ahead of print)
- Linscheid P, Seboek D, Nylen ES, et al. In vitro and in vivo calcitonin I gene expression in parenchymal cells: a novel product of human adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2003; 144(12): 5578–5584. doi:10.1210/en.2003-0854
Dabigatran-induced esophagitis
A 74-year-old man presented to the gastroenterology clinic with a 2-day history of retrosternal discomfort. His vital signs were normal, and laboratory testing showed a normal leukocyte count.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed longitudinal sloughing mucosal casts in the middle and lower esophagus (Figure 1).
The patient had been taking dabigatran 110 mg twice daily for 2 years because of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. He was also taking amlodipine 2.5 mg/day for hypertension.
DABIGATRAN-INDUCED ESOPHAGITIS
Although no study has investigated the overall prevalence of dabigatran-induced esophagitis, a retrospective database review of 91 patients taking dabigatran and undergoing upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy reported that 19 (20.9%) had endoscopic signs of dabigatran-induced esophagitis.2
Typical symptoms are the acute onset of chest pain, epigastralgia, odynophagia, and dysphagia. But patients can also have no symptoms or only mild symptoms.2,3
Despite dabigatran’s anticoagulant activity, there have been few reports of bleeding, perhaps because the lesions tend to be superficial on the surface of the esophageal mucosa.
Symptoms usually resolve within 1 week after stopping dabigatran and starting a proton pump inhibitor. To prevent mucosal injury, patients should be instructed to take dabigatran with sufficient water and to remain in an upright position for at least 30 minutes afterward.4
- Baehr PH, McDonald GB. Esophageal infections: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology 1994; 106(2):509–532. pmid:7980741
- Toya Y, Nakamura S, Tomita K, et al. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis: the prevalence and endoscopic characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 31(3):610–614. doi:10.1111/jgh.13024
- Ueta E, Fujikawa T, Imagawa A. A case of a slightly symptomatic exfoliative oesophagitis. BMJ Case Rep 2015; pii:bcr2015211925. doi:10.1136/bcr-2015-211925
- Ootani A, Hayashi Y, Miyagi Y. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12(7):e55–e56. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.010
A 74-year-old man presented to the gastroenterology clinic with a 2-day history of retrosternal discomfort. His vital signs were normal, and laboratory testing showed a normal leukocyte count.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed longitudinal sloughing mucosal casts in the middle and lower esophagus (Figure 1).
The patient had been taking dabigatran 110 mg twice daily for 2 years because of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. He was also taking amlodipine 2.5 mg/day for hypertension.
DABIGATRAN-INDUCED ESOPHAGITIS
Although no study has investigated the overall prevalence of dabigatran-induced esophagitis, a retrospective database review of 91 patients taking dabigatran and undergoing upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy reported that 19 (20.9%) had endoscopic signs of dabigatran-induced esophagitis.2
Typical symptoms are the acute onset of chest pain, epigastralgia, odynophagia, and dysphagia. But patients can also have no symptoms or only mild symptoms.2,3
Despite dabigatran’s anticoagulant activity, there have been few reports of bleeding, perhaps because the lesions tend to be superficial on the surface of the esophageal mucosa.
Symptoms usually resolve within 1 week after stopping dabigatran and starting a proton pump inhibitor. To prevent mucosal injury, patients should be instructed to take dabigatran with sufficient water and to remain in an upright position for at least 30 minutes afterward.4
A 74-year-old man presented to the gastroenterology clinic with a 2-day history of retrosternal discomfort. His vital signs were normal, and laboratory testing showed a normal leukocyte count.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed longitudinal sloughing mucosal casts in the middle and lower esophagus (Figure 1).
The patient had been taking dabigatran 110 mg twice daily for 2 years because of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. He was also taking amlodipine 2.5 mg/day for hypertension.
DABIGATRAN-INDUCED ESOPHAGITIS
Although no study has investigated the overall prevalence of dabigatran-induced esophagitis, a retrospective database review of 91 patients taking dabigatran and undergoing upper-gastrointestinal endoscopy reported that 19 (20.9%) had endoscopic signs of dabigatran-induced esophagitis.2
Typical symptoms are the acute onset of chest pain, epigastralgia, odynophagia, and dysphagia. But patients can also have no symptoms or only mild symptoms.2,3
Despite dabigatran’s anticoagulant activity, there have been few reports of bleeding, perhaps because the lesions tend to be superficial on the surface of the esophageal mucosa.
Symptoms usually resolve within 1 week after stopping dabigatran and starting a proton pump inhibitor. To prevent mucosal injury, patients should be instructed to take dabigatran with sufficient water and to remain in an upright position for at least 30 minutes afterward.4
- Baehr PH, McDonald GB. Esophageal infections: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology 1994; 106(2):509–532. pmid:7980741
- Toya Y, Nakamura S, Tomita K, et al. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis: the prevalence and endoscopic characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 31(3):610–614. doi:10.1111/jgh.13024
- Ueta E, Fujikawa T, Imagawa A. A case of a slightly symptomatic exfoliative oesophagitis. BMJ Case Rep 2015; pii:bcr2015211925. doi:10.1136/bcr-2015-211925
- Ootani A, Hayashi Y, Miyagi Y. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12(7):e55–e56. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.010
- Baehr PH, McDonald GB. Esophageal infections: risk factors, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology 1994; 106(2):509–532. pmid:7980741
- Toya Y, Nakamura S, Tomita K, et al. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis: the prevalence and endoscopic characteristics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 31(3):610–614. doi:10.1111/jgh.13024
- Ueta E, Fujikawa T, Imagawa A. A case of a slightly symptomatic exfoliative oesophagitis. BMJ Case Rep 2015; pii:bcr2015211925. doi:10.1136/bcr-2015-211925
- Ootani A, Hayashi Y, Miyagi Y. Dabigatran-induced esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 12(7):e55–e56. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2013.09.010
Pyoderma gangrenosum mistaken for diabetic ulcer
A 55-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, anemia, and ulcerative colitis presented to the emergency department with an ulcer on his left leg (Figure 1). He said the lesion had started as a “large pimple” that ruptured one night while he was sleeping and then became drastically worse over the past week. He said the lesion was painful and was “oozing blood.”
On examination, the lesion was 7 cm by 6.5 cm, with fibrinous, necrotic tissue, purulence, and a violaceous tint at the borders. The patient’s body temperature was 100.5°F (38.1°C) and the white blood cell count was 8.1 x 109/L (reference range 4.0–11.0).
Based on the patient’s medical history, the lesion was initially diagnosed as an infected diabetic ulcer. He was admitted to the hospital and intravenous (IV) vancomycin and clindamycin were started. During this time, the lesion expanded in size, and a second lesion appeared on the right anterior thigh, in similar fashion to how the original lesion had started. The original lesion expanded to 8 cm by 8.5 cm by hospital day 2. The patient continued to have episodes of low-grade fever without leukocytosis.
Cultures of blood and tissue from the lesions were negative, ruling out bacterial infection. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left tibia was negative for osteomyelitis. Punch biopsy of the ulcer border was done on day 3 to evaluate for pyoderma gangrenosum.
On hospital day 5, the patient developed acute kidney injury, with a creatinine increase to 2.17 mg/dL over 24 hours from a baseline value of 0.82 mg/dL. The IV antibiotics were discontinued, and IV fluid hydration was started. At this time, diabetic ulcer secondary to infection and osteomyelitis were ruled out. The lesions were diagnosed as pyoderma gangrenosum.
The patient was started on prednisone 30 mg twice daily. After 2 days, the low-grade fevers resolved, both lesions began to heal, and his creatinine level returned to baseline (Figure 2). He was discharged on hospital day 10. The prednisone was tapered over 1 month, with wet-to-dry dressing changes for wound care.
After discharge, he remained adherent to his steroid regimen. At a follow-up visit to his dermatologist, the ulcers had fully closed, and the skin had begun to heal. Results of the punch biopsy study came back 2 days after the patient was discharged and further confirmed the diagnosis, with a mixed lymphocytic composition composed primarily of neutrophils.
APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
Pyoderma gangrenosum is rare, with an incidence of 3 to 10 cases per million people per year.1 It is a rapidly progressive ulcerative condition typically associated with inflammatory bowel disease.2 Despite its name, the condition involves neither gangrene nor infection. The ulcer typically appears on the legs and is rapidly growing, painful, and purulent, with tissue necrosis and a violaceous border.3
Pyoderma gangrenosum is often misdiagnosed as infective ulcer and inappropriately treated with antibiotics.2 It can also be mistreated with surgical debridement, which can result in severe complications such as pathergy.1
The differential diagnosis includes diabetic ulcer, peripheral vascular disease, vasculitis, bacterial infection, osteomyelitis, and malignancy. Because it presents as an open, necrotic ulcer, ruling out infection is a top priority.3 However, an initial workup to rule out infection or other conditions can delay diagnosis and treatment,1 and treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics poses the risk of nephrotoxicity and new complications during the hospital stay.
Diagnosis requires meeting 2 major criteria—ie, presence of the characteristic ulcerous lesion, and exclusion of other causes of skin ulceration—and at least 2 minor criteria including histologic confirmation of neutrophil infiltrate at the ulcer border, the presence of a systemic disease associated with pyoderma gangrenosum, and a rapid response to steroid treatment.4,5
Our patient was at high risk for an infected diabetic ulcer. After infection was ruled out, clinical suspicion for pyoderma gangrenosum was high, given the patient’s presentation and his history of ulcerative colitis.
TREATMENT
Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum begins with systemic corticosteroids, as was done in this patient. Additional measures depend on whether the disease is localized or extensive and can include wound care, topical treatments, immunosuppressants, and immunomodulators.1
- Bhat RM. Pyoderma gangrenosum: an update. Indian Dermatol Online J 2012; 3(1):7–13. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93482
- Marinopoulos S, Theofanakis C, Zacharouli T, Sotiropoulou M, Dimitrakakis C. Pyoderma gangrenosum of the breast: a case report study. Int J Surg Case Rep 2017; 31:203–205. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.01.036
- Gameiro A, Pereira N, Cardoso JC, Gonçalo M. Pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2015; 8:285–293. doi:10.2147/CCID.S61202
- Su WP, David MD, Weenig RH, Powell FC, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: clinicopathologic correlation and proposed diagnostic criteria. Int J Dermatol 2004; 43(11):790–800. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02128.x
- von den Driesch P. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a report of 44 cases with follow-up. Br J Dermatol 1997; 137(6):1000–1005. pmid:9470924
A 55-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, anemia, and ulcerative colitis presented to the emergency department with an ulcer on his left leg (Figure 1). He said the lesion had started as a “large pimple” that ruptured one night while he was sleeping and then became drastically worse over the past week. He said the lesion was painful and was “oozing blood.”
On examination, the lesion was 7 cm by 6.5 cm, with fibrinous, necrotic tissue, purulence, and a violaceous tint at the borders. The patient’s body temperature was 100.5°F (38.1°C) and the white blood cell count was 8.1 x 109/L (reference range 4.0–11.0).
Based on the patient’s medical history, the lesion was initially diagnosed as an infected diabetic ulcer. He was admitted to the hospital and intravenous (IV) vancomycin and clindamycin were started. During this time, the lesion expanded in size, and a second lesion appeared on the right anterior thigh, in similar fashion to how the original lesion had started. The original lesion expanded to 8 cm by 8.5 cm by hospital day 2. The patient continued to have episodes of low-grade fever without leukocytosis.
Cultures of blood and tissue from the lesions were negative, ruling out bacterial infection. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left tibia was negative for osteomyelitis. Punch biopsy of the ulcer border was done on day 3 to evaluate for pyoderma gangrenosum.
On hospital day 5, the patient developed acute kidney injury, with a creatinine increase to 2.17 mg/dL over 24 hours from a baseline value of 0.82 mg/dL. The IV antibiotics were discontinued, and IV fluid hydration was started. At this time, diabetic ulcer secondary to infection and osteomyelitis were ruled out. The lesions were diagnosed as pyoderma gangrenosum.
The patient was started on prednisone 30 mg twice daily. After 2 days, the low-grade fevers resolved, both lesions began to heal, and his creatinine level returned to baseline (Figure 2). He was discharged on hospital day 10. The prednisone was tapered over 1 month, with wet-to-dry dressing changes for wound care.
After discharge, he remained adherent to his steroid regimen. At a follow-up visit to his dermatologist, the ulcers had fully closed, and the skin had begun to heal. Results of the punch biopsy study came back 2 days after the patient was discharged and further confirmed the diagnosis, with a mixed lymphocytic composition composed primarily of neutrophils.
APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
Pyoderma gangrenosum is rare, with an incidence of 3 to 10 cases per million people per year.1 It is a rapidly progressive ulcerative condition typically associated with inflammatory bowel disease.2 Despite its name, the condition involves neither gangrene nor infection. The ulcer typically appears on the legs and is rapidly growing, painful, and purulent, with tissue necrosis and a violaceous border.3
Pyoderma gangrenosum is often misdiagnosed as infective ulcer and inappropriately treated with antibiotics.2 It can also be mistreated with surgical debridement, which can result in severe complications such as pathergy.1
The differential diagnosis includes diabetic ulcer, peripheral vascular disease, vasculitis, bacterial infection, osteomyelitis, and malignancy. Because it presents as an open, necrotic ulcer, ruling out infection is a top priority.3 However, an initial workup to rule out infection or other conditions can delay diagnosis and treatment,1 and treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics poses the risk of nephrotoxicity and new complications during the hospital stay.
Diagnosis requires meeting 2 major criteria—ie, presence of the characteristic ulcerous lesion, and exclusion of other causes of skin ulceration—and at least 2 minor criteria including histologic confirmation of neutrophil infiltrate at the ulcer border, the presence of a systemic disease associated with pyoderma gangrenosum, and a rapid response to steroid treatment.4,5
Our patient was at high risk for an infected diabetic ulcer. After infection was ruled out, clinical suspicion for pyoderma gangrenosum was high, given the patient’s presentation and his history of ulcerative colitis.
TREATMENT
Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum begins with systemic corticosteroids, as was done in this patient. Additional measures depend on whether the disease is localized or extensive and can include wound care, topical treatments, immunosuppressants, and immunomodulators.1
A 55-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, anemia, and ulcerative colitis presented to the emergency department with an ulcer on his left leg (Figure 1). He said the lesion had started as a “large pimple” that ruptured one night while he was sleeping and then became drastically worse over the past week. He said the lesion was painful and was “oozing blood.”
On examination, the lesion was 7 cm by 6.5 cm, with fibrinous, necrotic tissue, purulence, and a violaceous tint at the borders. The patient’s body temperature was 100.5°F (38.1°C) and the white blood cell count was 8.1 x 109/L (reference range 4.0–11.0).
Based on the patient’s medical history, the lesion was initially diagnosed as an infected diabetic ulcer. He was admitted to the hospital and intravenous (IV) vancomycin and clindamycin were started. During this time, the lesion expanded in size, and a second lesion appeared on the right anterior thigh, in similar fashion to how the original lesion had started. The original lesion expanded to 8 cm by 8.5 cm by hospital day 2. The patient continued to have episodes of low-grade fever without leukocytosis.
Cultures of blood and tissue from the lesions were negative, ruling out bacterial infection. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left tibia was negative for osteomyelitis. Punch biopsy of the ulcer border was done on day 3 to evaluate for pyoderma gangrenosum.
On hospital day 5, the patient developed acute kidney injury, with a creatinine increase to 2.17 mg/dL over 24 hours from a baseline value of 0.82 mg/dL. The IV antibiotics were discontinued, and IV fluid hydration was started. At this time, diabetic ulcer secondary to infection and osteomyelitis were ruled out. The lesions were diagnosed as pyoderma gangrenosum.
The patient was started on prednisone 30 mg twice daily. After 2 days, the low-grade fevers resolved, both lesions began to heal, and his creatinine level returned to baseline (Figure 2). He was discharged on hospital day 10. The prednisone was tapered over 1 month, with wet-to-dry dressing changes for wound care.
After discharge, he remained adherent to his steroid regimen. At a follow-up visit to his dermatologist, the ulcers had fully closed, and the skin had begun to heal. Results of the punch biopsy study came back 2 days after the patient was discharged and further confirmed the diagnosis, with a mixed lymphocytic composition composed primarily of neutrophils.
APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
Pyoderma gangrenosum is rare, with an incidence of 3 to 10 cases per million people per year.1 It is a rapidly progressive ulcerative condition typically associated with inflammatory bowel disease.2 Despite its name, the condition involves neither gangrene nor infection. The ulcer typically appears on the legs and is rapidly growing, painful, and purulent, with tissue necrosis and a violaceous border.3
Pyoderma gangrenosum is often misdiagnosed as infective ulcer and inappropriately treated with antibiotics.2 It can also be mistreated with surgical debridement, which can result in severe complications such as pathergy.1
The differential diagnosis includes diabetic ulcer, peripheral vascular disease, vasculitis, bacterial infection, osteomyelitis, and malignancy. Because it presents as an open, necrotic ulcer, ruling out infection is a top priority.3 However, an initial workup to rule out infection or other conditions can delay diagnosis and treatment,1 and treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics poses the risk of nephrotoxicity and new complications during the hospital stay.
Diagnosis requires meeting 2 major criteria—ie, presence of the characteristic ulcerous lesion, and exclusion of other causes of skin ulceration—and at least 2 minor criteria including histologic confirmation of neutrophil infiltrate at the ulcer border, the presence of a systemic disease associated with pyoderma gangrenosum, and a rapid response to steroid treatment.4,5
Our patient was at high risk for an infected diabetic ulcer. After infection was ruled out, clinical suspicion for pyoderma gangrenosum was high, given the patient’s presentation and his history of ulcerative colitis.
TREATMENT
Treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum begins with systemic corticosteroids, as was done in this patient. Additional measures depend on whether the disease is localized or extensive and can include wound care, topical treatments, immunosuppressants, and immunomodulators.1
- Bhat RM. Pyoderma gangrenosum: an update. Indian Dermatol Online J 2012; 3(1):7–13. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93482
- Marinopoulos S, Theofanakis C, Zacharouli T, Sotiropoulou M, Dimitrakakis C. Pyoderma gangrenosum of the breast: a case report study. Int J Surg Case Rep 2017; 31:203–205. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.01.036
- Gameiro A, Pereira N, Cardoso JC, Gonçalo M. Pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2015; 8:285–293. doi:10.2147/CCID.S61202
- Su WP, David MD, Weenig RH, Powell FC, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: clinicopathologic correlation and proposed diagnostic criteria. Int J Dermatol 2004; 43(11):790–800. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02128.x
- von den Driesch P. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a report of 44 cases with follow-up. Br J Dermatol 1997; 137(6):1000–1005. pmid:9470924
- Bhat RM. Pyoderma gangrenosum: an update. Indian Dermatol Online J 2012; 3(1):7–13. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.93482
- Marinopoulos S, Theofanakis C, Zacharouli T, Sotiropoulou M, Dimitrakakis C. Pyoderma gangrenosum of the breast: a case report study. Int J Surg Case Rep 2017; 31:203–205. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.01.036
- Gameiro A, Pereira N, Cardoso JC, Gonçalo M. Pyoderma gangrenosum: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2015; 8:285–293. doi:10.2147/CCID.S61202
- Su WP, David MD, Weenig RH, Powell FC, Perry HO. Pyoderma gangrenosum: clinicopathologic correlation and proposed diagnostic criteria. Int J Dermatol 2004; 43(11):790–800. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02128.x
- von den Driesch P. Pyoderma gangrenosum: a report of 44 cases with follow-up. Br J Dermatol 1997; 137(6):1000–1005. pmid:9470924
Can procalcitonin guide decisions about antibiotic management?
Yes, but with caution. Multiple randomized controlled trials showed that procalcitonin testing can help guide antibiotic management in a variety of clinical scenarios including sepsis, respiratory tract infection, and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and that procalcitonin guidance led to less antibiotic use with either unchanged or better outcomes. Moreover, observational studies have shown high negative predictive values for procalcitonin testing in other clinical situations such as bacteremia and bacterial meningitis, allowing clinicians to rule out these diagnoses if the clinical probability is low or moderate.
Nonetheless, clinical judgment must be exercised to consider the possibility of false- positive and false-negative results, especially if clinical suspicion for bacterial infection is high.
A RESPONSE TO BACTERIAL TOXIN
Procalcitonin is a peptide precursor of calcitonin that is produced by C cells of the thyroid and by neuroendocrine cells of the lung and intestine in response to bacterial toxin. In contrast, procalcitonin levels are down-regulated in viral infection.
Levels of procalcitonin increase 6 to 12 hours after stimulation, and the half-life is roughly 24 hours.1 This suggests levels should decrease by one-half daily if an infection is controlled and is responding to therapy (assuming normal clearance).
The test costs about $25, with a turnaround time of 20 to 60 minutes, or longer at institutions that send the test out or run the tests in batches.
Point-of-care procalcitonin testing is emerging but not yet commercially available in the United States. Despite extensive observational studies and randomized controlled trials over the past 20 years, procalcitonin’s physiologic role remains unclear. The large body of evidence of the clinical utility of procalcitonin measurement has been summarized in several meta-analyses in different diseases.
PROCALCITONIN TESTING IN SEPSIS
Trials of procalcitonin testing have had slightly different inclusion criteria that commonly overlap with similar diagnoses. Sepsis is the broadest cohort studied.
The Procalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Treatments in Acutely Ill Patients (PRORATA) trial2 randomized 621 patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with suspected bacterial infections to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin concentrations or to antibiotic therapy based on current guidelines. The source of infection varied, but 73% of patients had pulmonary infections.The procalcitonin algorithm was as follows:
- Starting antibiotics was discouraged if the procalcitonin concentration was less than 0.5 ng/mL, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.25 ng/mL
- Starting antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration was 0.5 ng/mL or higher, and strongly encouraged if 1 ng/mL or higher
- Stopping antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration dropped by at least 80% from the peak level or to a level greater than or equal to 0.25 ng/mL; stopping was strongly encouraged if the concentration fell below 0.25 ng/mL.
There was also guidance to change antibiotics if procalcitonin increased on therapy and was above 0.5 ng/mL.
Although the study physicians generally followed the algorithm, they were allowed to override it based on clinical judgment. The main results were that the number of days without antibiotics was higher in the procalcitonin group than in the controls (14.3 vs 11.6 days), with no other statistically significant difference between groups. These findings supported the idea that procalcitonin can guide clinicians to safely “deprescribe” antibiotics.
The Stop Antibiotics on Guidance of Procalcitonin Study (SAPS),3 published in 2016, was a larger trial with similar design, in 1,575 patients admitted to the ICU with suspected infection. Antibiotic use was less and the 28-day mortality rate was lower with procalcitonin guidance: 20% vs 25% in the intention-to-treat analysis.
ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION
The Procalcitonin Guided Antibiotic Therapy and Hospitalisation in Patients With Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (ProHOSP) trial4 randomized 1,381 patients to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin levels or standard guidelines. Most patients had community-acquired pneumonia, while the rest had exacerbations of COPD, acute bronchitis, or other lower respiratory tract infections.
In the study algorithm, starting or continuing antibiotics was discouraged if procalcitonin levels were 0.25 ng/mL or less, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.1 ng/mL. Starting or continuing antibiotics was encouraged if levels were greater than 0.25 ng/mL, and strongly encouraged if greater than 0.5 ng/mL.
The algorithm recommended stopping antibiotics if procalcitonin levels fell below 0.25 ng/mL or decreased by 80%, and strongly recommended stopping them if procalcitonin fell below 0.1 ng/mL or decreased by 90%.
The treating physician could override the algorithm if the patient was unstable, was in an ICU, or had Legionella infection.
Antibiotic use was less in the procalcitonin-guided arm (75.4% vs 87.7%; mean duration 5.7 days vs 8.7 days), as was the rate of adverse effects from antibiotics (19.8% vs 28.1%). Rates of recurrence or rehospitalization were also lower with procalcitonin guidance (3.7% vs 6.5%), presumably because of fewer antibiotic-related side effects or better diagnostic accuracy. Rates of death and ICU admission were similar in the 2 groups. These findings were similar to those of PRORATA and SAPS, demonstrating that guidance with procalcitonin levels decreased antibiotic utilization, with other outcomes either improved or unchanged.
Schuetz et al,5 in a 2018 meta-analysis, collected data on 6,708 patients from 26 trials in 12 countries and found that procalcitonin guidance decreased antibiotic exposure by 2.4 days and reduced the rate of antibiotic-related side effects (16% vs 22%). Although there was skepticism about the mortality benefit reported in the SAPS trial, a similar mortality benefit was found in this meta-analysis (30-day mortality rates were 9% vs 10%), suggesting that measuring procalcitonin not only reduces unnecessary antibiotic exposure, but also saves lives.
Although decreasing antibiotic exposure may not confer a survival benefit, procalcitonin guidance likely clarifies the diagnosis and thus expedites proper treatment in patients with sepsis-like syndromes that are actually due to a noninfectious pathology (eg, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, adrenal insufficiency).
Negative findings in ProACT
The Procalcitonin Antibiotic Consensus Trial (ProACT)6 subsequently reported findings discordant with those above but was flawed in that adherence to the procalcitonin guideline by physicians was only 62% in the subgroup of patients with low procalcitonin results, which accounted for almost 90% of patients. Overall adherence by physicians to the procalcitonin guideline was 65%, much lower than in other trials (ProHOSP had over 90% adherence).4 Further, ProACT was done in American centers unfamiliar with procalcitonin, and it seems they did not trust low procalcitonin values as a reason to stop or avoid antibiotics.
ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF COPD
Multiple small randomized controlled trials and subgroups of larger studies like ProHOSP have studied the use of procalcitonin in acute exacerbations of COPD. Most studies used a design similar to the algorithm in ProHOSP.
Mathioudakis et al,7 in a meta-analysis of 8 trials with a total of 1,062 patients with acute exacerbation of COPD, found that with procalcitonin guidance, prescription of antibiotics on admission decreased by almost one-half, and courses of antibiotics were approximately 4 days shorter without any statistically significant difference in rates of treatment failure, length of hospital stay, recurrence, rehospitalization, or overall mortality.
However, the quality of the studies included in the meta-analysis was deemed only low to moderate, and thus the authors concluded, “Procalcitonin-based protocols appear to be clinically effective; however, confirmatory trials with rigorous methodology are required.”7 Nonetheless, given the lack of data supporting current practices for patient selection for antibiotics in COPD exacerbations, a strategy involving procalcitonin seems to be reasonable.
BACTEREMIA
Observational studies from as far as back as 1999 have examined the association of procalcitonin levels with bacteremia. The study designs were generally similar, with procalcitonin levels checked at time of blood culture, mostly in emergency rooms, and the procalcitonin value correlated with blood culture results. The general conclusion has been that procalcitonin has diagnostic value in ruling out bacteremia but should be used in the context of pretest probability rather than in isolation.
Hattori et al8 performed one of the largest studies, in 1,331 patients, using a procalcitonin level cutoff of 0.9 ng/mL. The sensitivity was 72% and specificity was 69%, which are not impressive; however, the negative predictive value was 95%, and even higher at lower cutoff values. Further, procalcitonin was significantly better at predicting bacteremia than either the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level, with the latter two being hardly better than random chance.
Hoeboer et al9 performed a meta-analysis of various studies with a total of 16,514 patients. Using a cutoff of 0.5 ng/mL, they reported a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 69% with a negative predictive value of 97% in emergency rooms, 95% on regular wards, and 98% in ICUs. The high negative predictive value of procalcitonin can allow clinicians to stratify bacteremia risk to determine which patients need blood cultures, which in turn may help clinicians order blood cultures more appropriately and avoid unnecessary costs, delays, and harms associated with false-positive results, such as additional visits, additional testing, and unnecessary use of antibiotics.
MENINGITIS
As with bacteremia, observational studies have reported fairly high negative predictive values for procalcitonin in bacterial meningitis. The correlation is not surprising, given that most cases of bacterial meningitis occur due to hematogenous dissemination.
A 2015 meta-analysis of 9 studies and 725 patients reported a pooled sensitivity of 90%, specificity 90%, positive likelihood ratio 27.3, and negative likelihood ratio 0.13.10 Cutoffs for procalcitonin levels varied, but the most common value was 0.5 ng/mL. The authors also noted that the diagnostic utility of procalcitonin was far superior to C-reactive protein in this scenario, concluding that serum procalcitonin is a highly accurate test to distinguish between bacterial and viral causes in suspected meningitis.10
OTHER CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Postoperative infection
Small studies have assessed procalcitonin as a marker to rule out postoperative infections,11,12 but the heterogeneity of study designs and populations makes it difficult to combine the studies for meta-analysis. Nevertheless, the general trend is that there may be a role for procalcitonin, and that procalcitonin has better diagnostic yield than the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level. The optimal cutoff depends on the surgery, since a small elevation in procalcitonin can be expected with the stress of surgery; and since the degree of elevation varies with type of surgery, the result must be interpreted with caution.
Malignancy
In malignancy-associated conditions such as neutropenic fever and tumor fever, the clinical utility of procalcitonin is somewhat diminished, as malignancy can cause elevated procalcitonin levels (especially in metastatic disease), but a low concentration still has a fair negative predictive value (approximately 90%) for bloodstream infections.13
A retrospective study suggested that the ratio of procalcitonin to C-reactive protein could improve diagnostic accuracy in patients with malignancies, presumably because an elevation of procalcitonin out of proportion to elevation in C-reactive protein favored a bacterial infection rather than nonspecific inflammation related to malignancy.14
Cardiac syndromes
In cardiac syndromes, dyspnea and abnormal chest imaging may make it difficult to exclude respiratory infections. Schuetz et al15 reviewed the potential value of procalcitonin testing in a variety of cardiac disorders, especially in acute cardiovascular conditions whose presentation resembles that of sepsis or acute respiratory tract infection. They concluded it may have a role in diagnosis and prognosis in these settings, as well as guiding drug therapy.
Localized infections
Though localized infections such as cystitis, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis often do not affect procalcitonin levels, the test may help assess illness severity and rule out associated bacteremia.
One study found that a low procalcitonin level was insufficient to rule out urinary tract infection, but procalcitonin levels predicted bacteremia better than any other variable or combination of variables; moreover, procalcitonin had a negative predictive value as high as 97% for ruling out bacteremia associated with urinary tract infection.16
ROLE IN PROGNOSIS
In addition to being a useful marker for diagnosis of bacterial infections, the procalcitonin level has significant prognostic implications, as a high or persistently elevated level correlates with a higher rate of all-cause mortality.17 The prognostic capability may enhance triage decisions.
Because the procalcitonin level lacks specificity, clinicians need to be aware of noninfectious causes of elevations such as malignancy, surgery, impaired renal function,8 and myocardial infarction.18 In these scenarios, it is important to think critically about the procalcitonin result and consider an adjusted cutoff.
A study of procalcitonin to predict a positive blood culture in patients with renal disease suggested an optimal cutoff value of 1.06 ng/mL for patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m2, and a value of 2.50 ng/mL for a rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2.8
In a chronic process like malignancy, the procalcitonin level is usually not markedly elevated. But it can also remain persistently elevated, with no improvement associated with effective antibiotic treatment and no clinical deterioration associated with treatment failure.
Use of procalcitonin and troponin
For some patients, there may be diagnostic uncertainty about interpreting procalcitonin and troponin results, as both plaque-rupture myocardial infarction and demand ischemia from sepsis can cause elevation in both values. In a study of patients with acute myocardial infarction, the procalcitonin level peaked at 3.57 ng/mL and troponin peaked at 60 ng/mL at about 24 hours after admission.18 This suggests that a troponin-to-procalcitonin ratio may help distinguish acute myocardial infarction from demand ischemia, though the optimal cutoff is unknown.
Both troponin and procalcitonin levels can help rule out acute severe illness (eg, bloodstream infection, acute myocardial infarction). But both can be falsely negative in early presentation or in less severe disease (eg, localized infection, unstable angina), as well as in noninfectious inflammation and nonobstructive myocardial injury.
Both are important prognostic markers. Furthermore, both can be chronically elevated in patients with renal disease, but both still have a characteristic rise and fall in acute disease states. But neither should be used in isolation without information from electrocardiography, other tests, and the clinical context.
CAVEATS AND CHALLENGES
Based on clinical experience and reported studies, procalcitonin testing has proven valuable in the diagnosis, prognosis, and management of a range of diseases, particularly certain infections.
However, procalcitonin testing must be applied cautiously and judiciously. There is a potential for early false-negative results, and false-positive results can occur in conditions such as kidney disease, myocardial infarction, postoperative stress response, and malignancy, though there may be ways to factor these conditions into interpretation of procalcitonin results.
Widespread procalcitonin testing may lead to excessive costs, though the cost for each test is reasonable and probably offset by benefits of diagnostic clarification and decreased use of antibiotics, if appropriately applied.
The primary roles for procalcitonin testing are to rule out infection in patients with low probability of infection and to allow safe early cessation of antibiotic therapy in patients with presumed bacterial infection. Procalcitonin testing can enable providers to stop antibiotics safely, with the general trend showing decreased antibiotic utilization without patient harm. This can result in healthcare cost savings and improved patient outcomes such as decreased length of hospital stay, decreased readmission rates, fewer adverse effects from antibiotics, and possibly improved mortality rates.
Despite the potential benefits from procalcitonin testing, results must be interpreted within the clinical context because a host of factors can affect the values. Extreme values are more useful than intermediate values, which are difficult to interpret and have poor predictive value.
Although all current biomarkers for infection are imperfect, procalcitonin appears to have better diagnostic accuracy than other markers such as the white blood cell count and C-reactive protein in multiple clinical scenarios, and its appropriate use appears to improve important outcomes such as survival.
- Schuetz P, Albrich W, Mueller B. Procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection and guide to antibiotic decisions: past, present and future. BMC Med 2011; 9:107. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-107
- Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, et al; PRORATA trial group. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients' exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 375(9713):463–474. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61879-1
- de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2016; 16(7):819–827. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00053-0
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, et al; ProHOSP Study Group. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009; 302(10):1059–1066. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1297
- Schuetz P, Wirz Y, Sager R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic treatment on mortality in acute respiratory infections: a patient level meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(1):95–107. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30592-3
- Huang DT, Yealy DM, Filbin MR, et al; ProACT Investigators. Procalcitonin-guided use of antibiotics for lower respiratory tract infection. N Engl J Med 2018; 379(3):236–249. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1802670
- Mathioudakis AG, Chatzimavridou-Grigoriadou V, Corlateanu A, Vestbo J. Procalcitonin to guide antibiotic administration in COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev 2017; 26(143)pii:160073. doi:10.1183/16000617.0073-2016
- Hattori T, Nishiyama H, Kato H, et al. Clinical value of procalcitonin for patients with suspected bloodstream infection. Am J Clin Pathol 2014; 141(1):43–51. doi:10.1309/AJCP4GV7ZFDTANGC
- Hoeboer SH, van der Geest PJ, Nieboer D, Groeneveld AB. The diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin for bacteraemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015; 21(5):474–481. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2014.12.026
- Vikse J, Henry BM, Roy J, Ramakrishnan PK, Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA. The role of serum procalcitonin in the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2015; 38:68–76. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.07.011
- Aouifi A, Piriou V, Bastien O, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection in cardiac surgical patients. Crit Care Med 2000; 28(9):3171–3176. pmid:11008977
- Hunziker S, Hugle T, Schuchardt K, et al. The value of serum procalcitonin level for differentiation of infectious from noninfectious causes of fever after orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010; 92(1):138–148. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01600
- Shomali W, Hachem R, Chaftari AM, et al. Can procalcitonin distinguish infectious fever from tumor-related fever in non-neutropenic cancer patients? Cancer 2012; 118(23):5823–5829. doi:10.1002/cncr.27602
- Hangai S, Nannya Y, Kurokawa M. Role of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for discrimination between tumor fever and infection in patients with hematological diseases. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56(4):910–914. doi:10.3109/10428194.2014.938329
- Schuetz P, Daniels LB, Kulkarni P, Anker SD, Mueller B. Procalcitonin: a new biomarker for the cardiologist. Int J Cardiol 2016; 223:390–397. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.204
- van Nieuwkoop C, Bonten TN, van't Wout JW, et al. Procalcitonin reflects bacteremia and bacterial load in urosepsis syndrome: a prospective observational study. Crit Care 2010; 14(6):R206. doi:10.1186/cc9328
- Liu D, Su L, Han G, Yan P, Xie L. Prognostic value of procalcitonin in adult patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0129450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129450
- Kafkas N, Venetsanou K, Patsilinakos S, et al. Procalcitonin in acute myocardial infarction. Acute Card Care 2008; 10(1):30–36. doi:10.1080/17482940701534800
Yes, but with caution. Multiple randomized controlled trials showed that procalcitonin testing can help guide antibiotic management in a variety of clinical scenarios including sepsis, respiratory tract infection, and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and that procalcitonin guidance led to less antibiotic use with either unchanged or better outcomes. Moreover, observational studies have shown high negative predictive values for procalcitonin testing in other clinical situations such as bacteremia and bacterial meningitis, allowing clinicians to rule out these diagnoses if the clinical probability is low or moderate.
Nonetheless, clinical judgment must be exercised to consider the possibility of false- positive and false-negative results, especially if clinical suspicion for bacterial infection is high.
A RESPONSE TO BACTERIAL TOXIN
Procalcitonin is a peptide precursor of calcitonin that is produced by C cells of the thyroid and by neuroendocrine cells of the lung and intestine in response to bacterial toxin. In contrast, procalcitonin levels are down-regulated in viral infection.
Levels of procalcitonin increase 6 to 12 hours after stimulation, and the half-life is roughly 24 hours.1 This suggests levels should decrease by one-half daily if an infection is controlled and is responding to therapy (assuming normal clearance).
The test costs about $25, with a turnaround time of 20 to 60 minutes, or longer at institutions that send the test out or run the tests in batches.
Point-of-care procalcitonin testing is emerging but not yet commercially available in the United States. Despite extensive observational studies and randomized controlled trials over the past 20 years, procalcitonin’s physiologic role remains unclear. The large body of evidence of the clinical utility of procalcitonin measurement has been summarized in several meta-analyses in different diseases.
PROCALCITONIN TESTING IN SEPSIS
Trials of procalcitonin testing have had slightly different inclusion criteria that commonly overlap with similar diagnoses. Sepsis is the broadest cohort studied.
The Procalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Treatments in Acutely Ill Patients (PRORATA) trial2 randomized 621 patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with suspected bacterial infections to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin concentrations or to antibiotic therapy based on current guidelines. The source of infection varied, but 73% of patients had pulmonary infections.The procalcitonin algorithm was as follows:
- Starting antibiotics was discouraged if the procalcitonin concentration was less than 0.5 ng/mL, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.25 ng/mL
- Starting antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration was 0.5 ng/mL or higher, and strongly encouraged if 1 ng/mL or higher
- Stopping antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration dropped by at least 80% from the peak level or to a level greater than or equal to 0.25 ng/mL; stopping was strongly encouraged if the concentration fell below 0.25 ng/mL.
There was also guidance to change antibiotics if procalcitonin increased on therapy and was above 0.5 ng/mL.
Although the study physicians generally followed the algorithm, they were allowed to override it based on clinical judgment. The main results were that the number of days without antibiotics was higher in the procalcitonin group than in the controls (14.3 vs 11.6 days), with no other statistically significant difference between groups. These findings supported the idea that procalcitonin can guide clinicians to safely “deprescribe” antibiotics.
The Stop Antibiotics on Guidance of Procalcitonin Study (SAPS),3 published in 2016, was a larger trial with similar design, in 1,575 patients admitted to the ICU with suspected infection. Antibiotic use was less and the 28-day mortality rate was lower with procalcitonin guidance: 20% vs 25% in the intention-to-treat analysis.
ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION
The Procalcitonin Guided Antibiotic Therapy and Hospitalisation in Patients With Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (ProHOSP) trial4 randomized 1,381 patients to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin levels or standard guidelines. Most patients had community-acquired pneumonia, while the rest had exacerbations of COPD, acute bronchitis, or other lower respiratory tract infections.
In the study algorithm, starting or continuing antibiotics was discouraged if procalcitonin levels were 0.25 ng/mL or less, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.1 ng/mL. Starting or continuing antibiotics was encouraged if levels were greater than 0.25 ng/mL, and strongly encouraged if greater than 0.5 ng/mL.
The algorithm recommended stopping antibiotics if procalcitonin levels fell below 0.25 ng/mL or decreased by 80%, and strongly recommended stopping them if procalcitonin fell below 0.1 ng/mL or decreased by 90%.
The treating physician could override the algorithm if the patient was unstable, was in an ICU, or had Legionella infection.
Antibiotic use was less in the procalcitonin-guided arm (75.4% vs 87.7%; mean duration 5.7 days vs 8.7 days), as was the rate of adverse effects from antibiotics (19.8% vs 28.1%). Rates of recurrence or rehospitalization were also lower with procalcitonin guidance (3.7% vs 6.5%), presumably because of fewer antibiotic-related side effects or better diagnostic accuracy. Rates of death and ICU admission were similar in the 2 groups. These findings were similar to those of PRORATA and SAPS, demonstrating that guidance with procalcitonin levels decreased antibiotic utilization, with other outcomes either improved or unchanged.
Schuetz et al,5 in a 2018 meta-analysis, collected data on 6,708 patients from 26 trials in 12 countries and found that procalcitonin guidance decreased antibiotic exposure by 2.4 days and reduced the rate of antibiotic-related side effects (16% vs 22%). Although there was skepticism about the mortality benefit reported in the SAPS trial, a similar mortality benefit was found in this meta-analysis (30-day mortality rates were 9% vs 10%), suggesting that measuring procalcitonin not only reduces unnecessary antibiotic exposure, but also saves lives.
Although decreasing antibiotic exposure may not confer a survival benefit, procalcitonin guidance likely clarifies the diagnosis and thus expedites proper treatment in patients with sepsis-like syndromes that are actually due to a noninfectious pathology (eg, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, adrenal insufficiency).
Negative findings in ProACT
The Procalcitonin Antibiotic Consensus Trial (ProACT)6 subsequently reported findings discordant with those above but was flawed in that adherence to the procalcitonin guideline by physicians was only 62% in the subgroup of patients with low procalcitonin results, which accounted for almost 90% of patients. Overall adherence by physicians to the procalcitonin guideline was 65%, much lower than in other trials (ProHOSP had over 90% adherence).4 Further, ProACT was done in American centers unfamiliar with procalcitonin, and it seems they did not trust low procalcitonin values as a reason to stop or avoid antibiotics.
ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF COPD
Multiple small randomized controlled trials and subgroups of larger studies like ProHOSP have studied the use of procalcitonin in acute exacerbations of COPD. Most studies used a design similar to the algorithm in ProHOSP.
Mathioudakis et al,7 in a meta-analysis of 8 trials with a total of 1,062 patients with acute exacerbation of COPD, found that with procalcitonin guidance, prescription of antibiotics on admission decreased by almost one-half, and courses of antibiotics were approximately 4 days shorter without any statistically significant difference in rates of treatment failure, length of hospital stay, recurrence, rehospitalization, or overall mortality.
However, the quality of the studies included in the meta-analysis was deemed only low to moderate, and thus the authors concluded, “Procalcitonin-based protocols appear to be clinically effective; however, confirmatory trials with rigorous methodology are required.”7 Nonetheless, given the lack of data supporting current practices for patient selection for antibiotics in COPD exacerbations, a strategy involving procalcitonin seems to be reasonable.
BACTEREMIA
Observational studies from as far as back as 1999 have examined the association of procalcitonin levels with bacteremia. The study designs were generally similar, with procalcitonin levels checked at time of blood culture, mostly in emergency rooms, and the procalcitonin value correlated with blood culture results. The general conclusion has been that procalcitonin has diagnostic value in ruling out bacteremia but should be used in the context of pretest probability rather than in isolation.
Hattori et al8 performed one of the largest studies, in 1,331 patients, using a procalcitonin level cutoff of 0.9 ng/mL. The sensitivity was 72% and specificity was 69%, which are not impressive; however, the negative predictive value was 95%, and even higher at lower cutoff values. Further, procalcitonin was significantly better at predicting bacteremia than either the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level, with the latter two being hardly better than random chance.
Hoeboer et al9 performed a meta-analysis of various studies with a total of 16,514 patients. Using a cutoff of 0.5 ng/mL, they reported a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 69% with a negative predictive value of 97% in emergency rooms, 95% on regular wards, and 98% in ICUs. The high negative predictive value of procalcitonin can allow clinicians to stratify bacteremia risk to determine which patients need blood cultures, which in turn may help clinicians order blood cultures more appropriately and avoid unnecessary costs, delays, and harms associated with false-positive results, such as additional visits, additional testing, and unnecessary use of antibiotics.
MENINGITIS
As with bacteremia, observational studies have reported fairly high negative predictive values for procalcitonin in bacterial meningitis. The correlation is not surprising, given that most cases of bacterial meningitis occur due to hematogenous dissemination.
A 2015 meta-analysis of 9 studies and 725 patients reported a pooled sensitivity of 90%, specificity 90%, positive likelihood ratio 27.3, and negative likelihood ratio 0.13.10 Cutoffs for procalcitonin levels varied, but the most common value was 0.5 ng/mL. The authors also noted that the diagnostic utility of procalcitonin was far superior to C-reactive protein in this scenario, concluding that serum procalcitonin is a highly accurate test to distinguish between bacterial and viral causes in suspected meningitis.10
OTHER CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Postoperative infection
Small studies have assessed procalcitonin as a marker to rule out postoperative infections,11,12 but the heterogeneity of study designs and populations makes it difficult to combine the studies for meta-analysis. Nevertheless, the general trend is that there may be a role for procalcitonin, and that procalcitonin has better diagnostic yield than the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level. The optimal cutoff depends on the surgery, since a small elevation in procalcitonin can be expected with the stress of surgery; and since the degree of elevation varies with type of surgery, the result must be interpreted with caution.
Malignancy
In malignancy-associated conditions such as neutropenic fever and tumor fever, the clinical utility of procalcitonin is somewhat diminished, as malignancy can cause elevated procalcitonin levels (especially in metastatic disease), but a low concentration still has a fair negative predictive value (approximately 90%) for bloodstream infections.13
A retrospective study suggested that the ratio of procalcitonin to C-reactive protein could improve diagnostic accuracy in patients with malignancies, presumably because an elevation of procalcitonin out of proportion to elevation in C-reactive protein favored a bacterial infection rather than nonspecific inflammation related to malignancy.14
Cardiac syndromes
In cardiac syndromes, dyspnea and abnormal chest imaging may make it difficult to exclude respiratory infections. Schuetz et al15 reviewed the potential value of procalcitonin testing in a variety of cardiac disorders, especially in acute cardiovascular conditions whose presentation resembles that of sepsis or acute respiratory tract infection. They concluded it may have a role in diagnosis and prognosis in these settings, as well as guiding drug therapy.
Localized infections
Though localized infections such as cystitis, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis often do not affect procalcitonin levels, the test may help assess illness severity and rule out associated bacteremia.
One study found that a low procalcitonin level was insufficient to rule out urinary tract infection, but procalcitonin levels predicted bacteremia better than any other variable or combination of variables; moreover, procalcitonin had a negative predictive value as high as 97% for ruling out bacteremia associated with urinary tract infection.16
ROLE IN PROGNOSIS
In addition to being a useful marker for diagnosis of bacterial infections, the procalcitonin level has significant prognostic implications, as a high or persistently elevated level correlates with a higher rate of all-cause mortality.17 The prognostic capability may enhance triage decisions.
Because the procalcitonin level lacks specificity, clinicians need to be aware of noninfectious causes of elevations such as malignancy, surgery, impaired renal function,8 and myocardial infarction.18 In these scenarios, it is important to think critically about the procalcitonin result and consider an adjusted cutoff.
A study of procalcitonin to predict a positive blood culture in patients with renal disease suggested an optimal cutoff value of 1.06 ng/mL for patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m2, and a value of 2.50 ng/mL for a rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2.8
In a chronic process like malignancy, the procalcitonin level is usually not markedly elevated. But it can also remain persistently elevated, with no improvement associated with effective antibiotic treatment and no clinical deterioration associated with treatment failure.
Use of procalcitonin and troponin
For some patients, there may be diagnostic uncertainty about interpreting procalcitonin and troponin results, as both plaque-rupture myocardial infarction and demand ischemia from sepsis can cause elevation in both values. In a study of patients with acute myocardial infarction, the procalcitonin level peaked at 3.57 ng/mL and troponin peaked at 60 ng/mL at about 24 hours after admission.18 This suggests that a troponin-to-procalcitonin ratio may help distinguish acute myocardial infarction from demand ischemia, though the optimal cutoff is unknown.
Both troponin and procalcitonin levels can help rule out acute severe illness (eg, bloodstream infection, acute myocardial infarction). But both can be falsely negative in early presentation or in less severe disease (eg, localized infection, unstable angina), as well as in noninfectious inflammation and nonobstructive myocardial injury.
Both are important prognostic markers. Furthermore, both can be chronically elevated in patients with renal disease, but both still have a characteristic rise and fall in acute disease states. But neither should be used in isolation without information from electrocardiography, other tests, and the clinical context.
CAVEATS AND CHALLENGES
Based on clinical experience and reported studies, procalcitonin testing has proven valuable in the diagnosis, prognosis, and management of a range of diseases, particularly certain infections.
However, procalcitonin testing must be applied cautiously and judiciously. There is a potential for early false-negative results, and false-positive results can occur in conditions such as kidney disease, myocardial infarction, postoperative stress response, and malignancy, though there may be ways to factor these conditions into interpretation of procalcitonin results.
Widespread procalcitonin testing may lead to excessive costs, though the cost for each test is reasonable and probably offset by benefits of diagnostic clarification and decreased use of antibiotics, if appropriately applied.
The primary roles for procalcitonin testing are to rule out infection in patients with low probability of infection and to allow safe early cessation of antibiotic therapy in patients with presumed bacterial infection. Procalcitonin testing can enable providers to stop antibiotics safely, with the general trend showing decreased antibiotic utilization without patient harm. This can result in healthcare cost savings and improved patient outcomes such as decreased length of hospital stay, decreased readmission rates, fewer adverse effects from antibiotics, and possibly improved mortality rates.
Despite the potential benefits from procalcitonin testing, results must be interpreted within the clinical context because a host of factors can affect the values. Extreme values are more useful than intermediate values, which are difficult to interpret and have poor predictive value.
Although all current biomarkers for infection are imperfect, procalcitonin appears to have better diagnostic accuracy than other markers such as the white blood cell count and C-reactive protein in multiple clinical scenarios, and its appropriate use appears to improve important outcomes such as survival.
Yes, but with caution. Multiple randomized controlled trials showed that procalcitonin testing can help guide antibiotic management in a variety of clinical scenarios including sepsis, respiratory tract infection, and exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and that procalcitonin guidance led to less antibiotic use with either unchanged or better outcomes. Moreover, observational studies have shown high negative predictive values for procalcitonin testing in other clinical situations such as bacteremia and bacterial meningitis, allowing clinicians to rule out these diagnoses if the clinical probability is low or moderate.
Nonetheless, clinical judgment must be exercised to consider the possibility of false- positive and false-negative results, especially if clinical suspicion for bacterial infection is high.
A RESPONSE TO BACTERIAL TOXIN
Procalcitonin is a peptide precursor of calcitonin that is produced by C cells of the thyroid and by neuroendocrine cells of the lung and intestine in response to bacterial toxin. In contrast, procalcitonin levels are down-regulated in viral infection.
Levels of procalcitonin increase 6 to 12 hours after stimulation, and the half-life is roughly 24 hours.1 This suggests levels should decrease by one-half daily if an infection is controlled and is responding to therapy (assuming normal clearance).
The test costs about $25, with a turnaround time of 20 to 60 minutes, or longer at institutions that send the test out or run the tests in batches.
Point-of-care procalcitonin testing is emerging but not yet commercially available in the United States. Despite extensive observational studies and randomized controlled trials over the past 20 years, procalcitonin’s physiologic role remains unclear. The large body of evidence of the clinical utility of procalcitonin measurement has been summarized in several meta-analyses in different diseases.
PROCALCITONIN TESTING IN SEPSIS
Trials of procalcitonin testing have had slightly different inclusion criteria that commonly overlap with similar diagnoses. Sepsis is the broadest cohort studied.
The Procalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Treatments in Acutely Ill Patients (PRORATA) trial2 randomized 621 patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with suspected bacterial infections to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin concentrations or to antibiotic therapy based on current guidelines. The source of infection varied, but 73% of patients had pulmonary infections.The procalcitonin algorithm was as follows:
- Starting antibiotics was discouraged if the procalcitonin concentration was less than 0.5 ng/mL, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.25 ng/mL
- Starting antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration was 0.5 ng/mL or higher, and strongly encouraged if 1 ng/mL or higher
- Stopping antibiotics was encouraged if the concentration dropped by at least 80% from the peak level or to a level greater than or equal to 0.25 ng/mL; stopping was strongly encouraged if the concentration fell below 0.25 ng/mL.
There was also guidance to change antibiotics if procalcitonin increased on therapy and was above 0.5 ng/mL.
Although the study physicians generally followed the algorithm, they were allowed to override it based on clinical judgment. The main results were that the number of days without antibiotics was higher in the procalcitonin group than in the controls (14.3 vs 11.6 days), with no other statistically significant difference between groups. These findings supported the idea that procalcitonin can guide clinicians to safely “deprescribe” antibiotics.
The Stop Antibiotics on Guidance of Procalcitonin Study (SAPS),3 published in 2016, was a larger trial with similar design, in 1,575 patients admitted to the ICU with suspected infection. Antibiotic use was less and the 28-day mortality rate was lower with procalcitonin guidance: 20% vs 25% in the intention-to-treat analysis.
ACUTE RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTION
The Procalcitonin Guided Antibiotic Therapy and Hospitalisation in Patients With Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (ProHOSP) trial4 randomized 1,381 patients to antibiotic therapy guided by procalcitonin levels or standard guidelines. Most patients had community-acquired pneumonia, while the rest had exacerbations of COPD, acute bronchitis, or other lower respiratory tract infections.
In the study algorithm, starting or continuing antibiotics was discouraged if procalcitonin levels were 0.25 ng/mL or less, and strongly discouraged if less than 0.1 ng/mL. Starting or continuing antibiotics was encouraged if levels were greater than 0.25 ng/mL, and strongly encouraged if greater than 0.5 ng/mL.
The algorithm recommended stopping antibiotics if procalcitonin levels fell below 0.25 ng/mL or decreased by 80%, and strongly recommended stopping them if procalcitonin fell below 0.1 ng/mL or decreased by 90%.
The treating physician could override the algorithm if the patient was unstable, was in an ICU, or had Legionella infection.
Antibiotic use was less in the procalcitonin-guided arm (75.4% vs 87.7%; mean duration 5.7 days vs 8.7 days), as was the rate of adverse effects from antibiotics (19.8% vs 28.1%). Rates of recurrence or rehospitalization were also lower with procalcitonin guidance (3.7% vs 6.5%), presumably because of fewer antibiotic-related side effects or better diagnostic accuracy. Rates of death and ICU admission were similar in the 2 groups. These findings were similar to those of PRORATA and SAPS, demonstrating that guidance with procalcitonin levels decreased antibiotic utilization, with other outcomes either improved or unchanged.
Schuetz et al,5 in a 2018 meta-analysis, collected data on 6,708 patients from 26 trials in 12 countries and found that procalcitonin guidance decreased antibiotic exposure by 2.4 days and reduced the rate of antibiotic-related side effects (16% vs 22%). Although there was skepticism about the mortality benefit reported in the SAPS trial, a similar mortality benefit was found in this meta-analysis (30-day mortality rates were 9% vs 10%), suggesting that measuring procalcitonin not only reduces unnecessary antibiotic exposure, but also saves lives.
Although decreasing antibiotic exposure may not confer a survival benefit, procalcitonin guidance likely clarifies the diagnosis and thus expedites proper treatment in patients with sepsis-like syndromes that are actually due to a noninfectious pathology (eg, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, adrenal insufficiency).
Negative findings in ProACT
The Procalcitonin Antibiotic Consensus Trial (ProACT)6 subsequently reported findings discordant with those above but was flawed in that adherence to the procalcitonin guideline by physicians was only 62% in the subgroup of patients with low procalcitonin results, which accounted for almost 90% of patients. Overall adherence by physicians to the procalcitonin guideline was 65%, much lower than in other trials (ProHOSP had over 90% adherence).4 Further, ProACT was done in American centers unfamiliar with procalcitonin, and it seems they did not trust low procalcitonin values as a reason to stop or avoid antibiotics.
ACUTE EXACERBATIONS OF COPD
Multiple small randomized controlled trials and subgroups of larger studies like ProHOSP have studied the use of procalcitonin in acute exacerbations of COPD. Most studies used a design similar to the algorithm in ProHOSP.
Mathioudakis et al,7 in a meta-analysis of 8 trials with a total of 1,062 patients with acute exacerbation of COPD, found that with procalcitonin guidance, prescription of antibiotics on admission decreased by almost one-half, and courses of antibiotics were approximately 4 days shorter without any statistically significant difference in rates of treatment failure, length of hospital stay, recurrence, rehospitalization, or overall mortality.
However, the quality of the studies included in the meta-analysis was deemed only low to moderate, and thus the authors concluded, “Procalcitonin-based protocols appear to be clinically effective; however, confirmatory trials with rigorous methodology are required.”7 Nonetheless, given the lack of data supporting current practices for patient selection for antibiotics in COPD exacerbations, a strategy involving procalcitonin seems to be reasonable.
BACTEREMIA
Observational studies from as far as back as 1999 have examined the association of procalcitonin levels with bacteremia. The study designs were generally similar, with procalcitonin levels checked at time of blood culture, mostly in emergency rooms, and the procalcitonin value correlated with blood culture results. The general conclusion has been that procalcitonin has diagnostic value in ruling out bacteremia but should be used in the context of pretest probability rather than in isolation.
Hattori et al8 performed one of the largest studies, in 1,331 patients, using a procalcitonin level cutoff of 0.9 ng/mL. The sensitivity was 72% and specificity was 69%, which are not impressive; however, the negative predictive value was 95%, and even higher at lower cutoff values. Further, procalcitonin was significantly better at predicting bacteremia than either the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level, with the latter two being hardly better than random chance.
Hoeboer et al9 performed a meta-analysis of various studies with a total of 16,514 patients. Using a cutoff of 0.5 ng/mL, they reported a sensitivity of 76% and a specificity of 69% with a negative predictive value of 97% in emergency rooms, 95% on regular wards, and 98% in ICUs. The high negative predictive value of procalcitonin can allow clinicians to stratify bacteremia risk to determine which patients need blood cultures, which in turn may help clinicians order blood cultures more appropriately and avoid unnecessary costs, delays, and harms associated with false-positive results, such as additional visits, additional testing, and unnecessary use of antibiotics.
MENINGITIS
As with bacteremia, observational studies have reported fairly high negative predictive values for procalcitonin in bacterial meningitis. The correlation is not surprising, given that most cases of bacterial meningitis occur due to hematogenous dissemination.
A 2015 meta-analysis of 9 studies and 725 patients reported a pooled sensitivity of 90%, specificity 90%, positive likelihood ratio 27.3, and negative likelihood ratio 0.13.10 Cutoffs for procalcitonin levels varied, but the most common value was 0.5 ng/mL. The authors also noted that the diagnostic utility of procalcitonin was far superior to C-reactive protein in this scenario, concluding that serum procalcitonin is a highly accurate test to distinguish between bacterial and viral causes in suspected meningitis.10
OTHER CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Postoperative infection
Small studies have assessed procalcitonin as a marker to rule out postoperative infections,11,12 but the heterogeneity of study designs and populations makes it difficult to combine the studies for meta-analysis. Nevertheless, the general trend is that there may be a role for procalcitonin, and that procalcitonin has better diagnostic yield than the white blood cell count or C-reactive protein level. The optimal cutoff depends on the surgery, since a small elevation in procalcitonin can be expected with the stress of surgery; and since the degree of elevation varies with type of surgery, the result must be interpreted with caution.
Malignancy
In malignancy-associated conditions such as neutropenic fever and tumor fever, the clinical utility of procalcitonin is somewhat diminished, as malignancy can cause elevated procalcitonin levels (especially in metastatic disease), but a low concentration still has a fair negative predictive value (approximately 90%) for bloodstream infections.13
A retrospective study suggested that the ratio of procalcitonin to C-reactive protein could improve diagnostic accuracy in patients with malignancies, presumably because an elevation of procalcitonin out of proportion to elevation in C-reactive protein favored a bacterial infection rather than nonspecific inflammation related to malignancy.14
Cardiac syndromes
In cardiac syndromes, dyspnea and abnormal chest imaging may make it difficult to exclude respiratory infections. Schuetz et al15 reviewed the potential value of procalcitonin testing in a variety of cardiac disorders, especially in acute cardiovascular conditions whose presentation resembles that of sepsis or acute respiratory tract infection. They concluded it may have a role in diagnosis and prognosis in these settings, as well as guiding drug therapy.
Localized infections
Though localized infections such as cystitis, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis often do not affect procalcitonin levels, the test may help assess illness severity and rule out associated bacteremia.
One study found that a low procalcitonin level was insufficient to rule out urinary tract infection, but procalcitonin levels predicted bacteremia better than any other variable or combination of variables; moreover, procalcitonin had a negative predictive value as high as 97% for ruling out bacteremia associated with urinary tract infection.16
ROLE IN PROGNOSIS
In addition to being a useful marker for diagnosis of bacterial infections, the procalcitonin level has significant prognostic implications, as a high or persistently elevated level correlates with a higher rate of all-cause mortality.17 The prognostic capability may enhance triage decisions.
Because the procalcitonin level lacks specificity, clinicians need to be aware of noninfectious causes of elevations such as malignancy, surgery, impaired renal function,8 and myocardial infarction.18 In these scenarios, it is important to think critically about the procalcitonin result and consider an adjusted cutoff.
A study of procalcitonin to predict a positive blood culture in patients with renal disease suggested an optimal cutoff value of 1.06 ng/mL for patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m2, and a value of 2.50 ng/mL for a rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2.8
In a chronic process like malignancy, the procalcitonin level is usually not markedly elevated. But it can also remain persistently elevated, with no improvement associated with effective antibiotic treatment and no clinical deterioration associated with treatment failure.
Use of procalcitonin and troponin
For some patients, there may be diagnostic uncertainty about interpreting procalcitonin and troponin results, as both plaque-rupture myocardial infarction and demand ischemia from sepsis can cause elevation in both values. In a study of patients with acute myocardial infarction, the procalcitonin level peaked at 3.57 ng/mL and troponin peaked at 60 ng/mL at about 24 hours after admission.18 This suggests that a troponin-to-procalcitonin ratio may help distinguish acute myocardial infarction from demand ischemia, though the optimal cutoff is unknown.
Both troponin and procalcitonin levels can help rule out acute severe illness (eg, bloodstream infection, acute myocardial infarction). But both can be falsely negative in early presentation or in less severe disease (eg, localized infection, unstable angina), as well as in noninfectious inflammation and nonobstructive myocardial injury.
Both are important prognostic markers. Furthermore, both can be chronically elevated in patients with renal disease, but both still have a characteristic rise and fall in acute disease states. But neither should be used in isolation without information from electrocardiography, other tests, and the clinical context.
CAVEATS AND CHALLENGES
Based on clinical experience and reported studies, procalcitonin testing has proven valuable in the diagnosis, prognosis, and management of a range of diseases, particularly certain infections.
However, procalcitonin testing must be applied cautiously and judiciously. There is a potential for early false-negative results, and false-positive results can occur in conditions such as kidney disease, myocardial infarction, postoperative stress response, and malignancy, though there may be ways to factor these conditions into interpretation of procalcitonin results.
Widespread procalcitonin testing may lead to excessive costs, though the cost for each test is reasonable and probably offset by benefits of diagnostic clarification and decreased use of antibiotics, if appropriately applied.
The primary roles for procalcitonin testing are to rule out infection in patients with low probability of infection and to allow safe early cessation of antibiotic therapy in patients with presumed bacterial infection. Procalcitonin testing can enable providers to stop antibiotics safely, with the general trend showing decreased antibiotic utilization without patient harm. This can result in healthcare cost savings and improved patient outcomes such as decreased length of hospital stay, decreased readmission rates, fewer adverse effects from antibiotics, and possibly improved mortality rates.
Despite the potential benefits from procalcitonin testing, results must be interpreted within the clinical context because a host of factors can affect the values. Extreme values are more useful than intermediate values, which are difficult to interpret and have poor predictive value.
Although all current biomarkers for infection are imperfect, procalcitonin appears to have better diagnostic accuracy than other markers such as the white blood cell count and C-reactive protein in multiple clinical scenarios, and its appropriate use appears to improve important outcomes such as survival.
- Schuetz P, Albrich W, Mueller B. Procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection and guide to antibiotic decisions: past, present and future. BMC Med 2011; 9:107. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-107
- Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, et al; PRORATA trial group. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients' exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 375(9713):463–474. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61879-1
- de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2016; 16(7):819–827. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00053-0
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, et al; ProHOSP Study Group. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009; 302(10):1059–1066. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1297
- Schuetz P, Wirz Y, Sager R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic treatment on mortality in acute respiratory infections: a patient level meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(1):95–107. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30592-3
- Huang DT, Yealy DM, Filbin MR, et al; ProACT Investigators. Procalcitonin-guided use of antibiotics for lower respiratory tract infection. N Engl J Med 2018; 379(3):236–249. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1802670
- Mathioudakis AG, Chatzimavridou-Grigoriadou V, Corlateanu A, Vestbo J. Procalcitonin to guide antibiotic administration in COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev 2017; 26(143)pii:160073. doi:10.1183/16000617.0073-2016
- Hattori T, Nishiyama H, Kato H, et al. Clinical value of procalcitonin for patients with suspected bloodstream infection. Am J Clin Pathol 2014; 141(1):43–51. doi:10.1309/AJCP4GV7ZFDTANGC
- Hoeboer SH, van der Geest PJ, Nieboer D, Groeneveld AB. The diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin for bacteraemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015; 21(5):474–481. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2014.12.026
- Vikse J, Henry BM, Roy J, Ramakrishnan PK, Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA. The role of serum procalcitonin in the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2015; 38:68–76. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.07.011
- Aouifi A, Piriou V, Bastien O, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection in cardiac surgical patients. Crit Care Med 2000; 28(9):3171–3176. pmid:11008977
- Hunziker S, Hugle T, Schuchardt K, et al. The value of serum procalcitonin level for differentiation of infectious from noninfectious causes of fever after orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010; 92(1):138–148. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01600
- Shomali W, Hachem R, Chaftari AM, et al. Can procalcitonin distinguish infectious fever from tumor-related fever in non-neutropenic cancer patients? Cancer 2012; 118(23):5823–5829. doi:10.1002/cncr.27602
- Hangai S, Nannya Y, Kurokawa M. Role of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for discrimination between tumor fever and infection in patients with hematological diseases. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56(4):910–914. doi:10.3109/10428194.2014.938329
- Schuetz P, Daniels LB, Kulkarni P, Anker SD, Mueller B. Procalcitonin: a new biomarker for the cardiologist. Int J Cardiol 2016; 223:390–397. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.204
- van Nieuwkoop C, Bonten TN, van't Wout JW, et al. Procalcitonin reflects bacteremia and bacterial load in urosepsis syndrome: a prospective observational study. Crit Care 2010; 14(6):R206. doi:10.1186/cc9328
- Liu D, Su L, Han G, Yan P, Xie L. Prognostic value of procalcitonin in adult patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0129450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129450
- Kafkas N, Venetsanou K, Patsilinakos S, et al. Procalcitonin in acute myocardial infarction. Acute Card Care 2008; 10(1):30–36. doi:10.1080/17482940701534800
- Schuetz P, Albrich W, Mueller B. Procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection and guide to antibiotic decisions: past, present and future. BMC Med 2011; 9:107. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-107
- Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, et al; PRORATA trial group. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients' exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010; 375(9713):463–474. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61879-1
- de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2016; 16(7):819–827. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00053-0
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, et al; ProHOSP Study Group. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009; 302(10):1059–1066. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1297
- Schuetz P, Wirz Y, Sager R, et al. Effect of procalcitonin-guided antibiotic treatment on mortality in acute respiratory infections: a patient level meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(1):95–107. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30592-3
- Huang DT, Yealy DM, Filbin MR, et al; ProACT Investigators. Procalcitonin-guided use of antibiotics for lower respiratory tract infection. N Engl J Med 2018; 379(3):236–249. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1802670
- Mathioudakis AG, Chatzimavridou-Grigoriadou V, Corlateanu A, Vestbo J. Procalcitonin to guide antibiotic administration in COPD exacerbations: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir Rev 2017; 26(143)pii:160073. doi:10.1183/16000617.0073-2016
- Hattori T, Nishiyama H, Kato H, et al. Clinical value of procalcitonin for patients with suspected bloodstream infection. Am J Clin Pathol 2014; 141(1):43–51. doi:10.1309/AJCP4GV7ZFDTANGC
- Hoeboer SH, van der Geest PJ, Nieboer D, Groeneveld AB. The diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin for bacteraemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2015; 21(5):474–481. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2014.12.026
- Vikse J, Henry BM, Roy J, Ramakrishnan PK, Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA. The role of serum procalcitonin in the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis 2015; 38:68–76. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2015.07.011
- Aouifi A, Piriou V, Bastien O, et al. Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection in cardiac surgical patients. Crit Care Med 2000; 28(9):3171–3176. pmid:11008977
- Hunziker S, Hugle T, Schuchardt K, et al. The value of serum procalcitonin level for differentiation of infectious from noninfectious causes of fever after orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010; 92(1):138–148. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.01600
- Shomali W, Hachem R, Chaftari AM, et al. Can procalcitonin distinguish infectious fever from tumor-related fever in non-neutropenic cancer patients? Cancer 2012; 118(23):5823–5829. doi:10.1002/cncr.27602
- Hangai S, Nannya Y, Kurokawa M. Role of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for discrimination between tumor fever and infection in patients with hematological diseases. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 56(4):910–914. doi:10.3109/10428194.2014.938329
- Schuetz P, Daniels LB, Kulkarni P, Anker SD, Mueller B. Procalcitonin: a new biomarker for the cardiologist. Int J Cardiol 2016; 223:390–397. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.204
- van Nieuwkoop C, Bonten TN, van't Wout JW, et al. Procalcitonin reflects bacteremia and bacterial load in urosepsis syndrome: a prospective observational study. Crit Care 2010; 14(6):R206. doi:10.1186/cc9328
- Liu D, Su L, Han G, Yan P, Xie L. Prognostic value of procalcitonin in adult patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(6):e0129450. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129450
- Kafkas N, Venetsanou K, Patsilinakos S, et al. Procalcitonin in acute myocardial infarction. Acute Card Care 2008; 10(1):30–36. doi:10.1080/17482940701534800