User login
Ultrasound improves specificity of psoriatic arthritis referrals
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
The use of ultrasound in screening for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis could reduce the number of unnecessary referrals to rheumatologists, according to a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Up to one-third of patients with psoriasis have underlying psoriatic arthritis (PsA), but half of all patients with psoriasis experience nonspecific musculoskeletal complaints.
“Different screening tools have been developed for the dermatology practice to distinguish patients with a higher likelihood of having PsA; however, the low specificities of these tools limit their use in clinical practice,” wrote Dilek Solmaz, MD, and colleagues at the University of Ottawa.
In this prospective study, 51 patients with psoriasis were screened for referral to a rheumatologist using the Early Arthritis for Psoriatic Patients and Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool questionnaires. They also underwent a limited ultrasound scanning of wrists, hands, feet, and the most painful joint, which was reviewed by experienced rheumatologists.
A dermatologist was asked to make a decision on referral based on the questionnaire data alone, then invited to revisit that decision after viewing the ultrasound results. When basing their decision on the questionnaires only, the dermatologist decided to refer 92% of patients to a rheumatologist. Of these patients, 40% were subsequently diagnosed with PsA, which represented a sensitivity of 95% but specificity of just 9%.
After reviewing the ultrasound data, the dermatologist revised their recommendations and only referred 43% of patients. Of these, 68% were later diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis. Among the patients who were not referred after the ultrasound review, five were diagnosed with PsA, but two had isolated axial involvement with no peripheral joint disease. Excluding these two cases, the sensitivity decreased to 88% but specificity increased to 77%.
“Screening tools in psoriasis that have high sensitivities usually have low specificities, which means a higher number of patients to be referred to rheumatology than needed,” the authors wrote. “Our study demonstrated that a musculoskeletal [ultrasound] based on a predefined protocol improves the referrals made to rheumatology.”
The authors did note that the ultrasounds were reviewed by experienced rheumatologists, so the results might not be generalizable to less-experienced sonographers without experience in musculoskeletal disorders.
The study was funded by AbbVie. One author declared receiving funding for a fellowship from UCB. Two authors declared honoraria and advisory consultancies with the pharmaceutical sector, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Solmaz D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov 28. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18515.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
California researchers work to update EMS status epilepticus protocols
BALTIMORE – Investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, are working with medical directors across the state to update county emergency medical services protocols to ensure patients in status epilepticus get 10 mg IM midazolam in the field, per national treatment guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society.
The work comes in the wake of a recent research letter in JAMA where the UCSF team reported that, across 33 emergency medical services (EMS) in California, only 2 included 10 mg midazolam IM per the guidelines, advice based on randomized, controlled clinical trials that found it to be safe and effective for stopping prehospital seizures in adults.
“Making people aware of the problem [is having] an impact,” said investigator Elan Guterman, MD, a neurology hospitalist and assistant professor of neurology at the university.
In a follow-up review at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society, the team took a deep dive into the situation in Alameda County, just east of San Francisco and including the city of Oakland, as an indicator of what’s been going on across the state.
Patients had to have an EMS record of active seizures, meaning more than two within 5 minutes or a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes. Alameda ambulance crews, like most, carry intramuscular midazolam because it’s more shelf stable than the two other first-line options, lorazepam and diazepam, and doesn’t require an intravenous line.
Among the 2,494 adults treated for status epilepticus from 2013 to 2018, just 62% received intramuscular midazolam, and only 39% got a dose of 5 mg or more. Not a single patient received the recommended 10-mg IM injection.
In short, “at the time when it’s the most important to act quickly, patients were not receiving the care they needed,” and the problem isn’t likely limited to California, Dr. Guterman said.
When patients did get 5 mg or more, they were less likely to reseize and require additional doses (adjusted odds ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.4-0.86). Also – and counterintuitively given the concern about benzodiazepines and respiratory depression – the team found that higher initial doses of 5 mg or more were actually associated with a lower need for respiratory support, including intubation (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99).
It’s possible ambulance crews were erring on the side of caution. People who got midazolam were more likely to have an established diagnosis of epilepsy (68% vs. 62%; P less than .01) and less likely to have been abusing drugs or alcohol (12.5% vs. 16.3%; P less than .01).
But an abundance of caution doesn’t fully explain it; even among people known to have epilepsy, many weren’t treated with midazolam and none at the appropriate dose.
Dr. Guterman thinks the bigger issue is what was reported in the research letter: Local EMS protocols simply haven’t been updated to include current best practices. EMS services might not even be aware of them, which is why she and her colleagues have been meeting with county medical directors.
“The first step is making sure the EMS world is aware of this gap in care, and motivating them to address it,” she said.
Patients in the study were a mean of 53 years old, and just over half were men.
There was no industry funding for the study, and Dr. Guterman didn’t report any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Guterman E et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.394.
BALTIMORE – Investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, are working with medical directors across the state to update county emergency medical services protocols to ensure patients in status epilepticus get 10 mg IM midazolam in the field, per national treatment guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society.
The work comes in the wake of a recent research letter in JAMA where the UCSF team reported that, across 33 emergency medical services (EMS) in California, only 2 included 10 mg midazolam IM per the guidelines, advice based on randomized, controlled clinical trials that found it to be safe and effective for stopping prehospital seizures in adults.
“Making people aware of the problem [is having] an impact,” said investigator Elan Guterman, MD, a neurology hospitalist and assistant professor of neurology at the university.
In a follow-up review at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society, the team took a deep dive into the situation in Alameda County, just east of San Francisco and including the city of Oakland, as an indicator of what’s been going on across the state.
Patients had to have an EMS record of active seizures, meaning more than two within 5 minutes or a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes. Alameda ambulance crews, like most, carry intramuscular midazolam because it’s more shelf stable than the two other first-line options, lorazepam and diazepam, and doesn’t require an intravenous line.
Among the 2,494 adults treated for status epilepticus from 2013 to 2018, just 62% received intramuscular midazolam, and only 39% got a dose of 5 mg or more. Not a single patient received the recommended 10-mg IM injection.
In short, “at the time when it’s the most important to act quickly, patients were not receiving the care they needed,” and the problem isn’t likely limited to California, Dr. Guterman said.
When patients did get 5 mg or more, they were less likely to reseize and require additional doses (adjusted odds ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.4-0.86). Also – and counterintuitively given the concern about benzodiazepines and respiratory depression – the team found that higher initial doses of 5 mg or more were actually associated with a lower need for respiratory support, including intubation (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99).
It’s possible ambulance crews were erring on the side of caution. People who got midazolam were more likely to have an established diagnosis of epilepsy (68% vs. 62%; P less than .01) and less likely to have been abusing drugs or alcohol (12.5% vs. 16.3%; P less than .01).
But an abundance of caution doesn’t fully explain it; even among people known to have epilepsy, many weren’t treated with midazolam and none at the appropriate dose.
Dr. Guterman thinks the bigger issue is what was reported in the research letter: Local EMS protocols simply haven’t been updated to include current best practices. EMS services might not even be aware of them, which is why she and her colleagues have been meeting with county medical directors.
“The first step is making sure the EMS world is aware of this gap in care, and motivating them to address it,” she said.
Patients in the study were a mean of 53 years old, and just over half were men.
There was no industry funding for the study, and Dr. Guterman didn’t report any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Guterman E et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.394.
BALTIMORE – Investigators from the University of California, San Francisco, are working with medical directors across the state to update county emergency medical services protocols to ensure patients in status epilepticus get 10 mg IM midazolam in the field, per national treatment guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society.
The work comes in the wake of a recent research letter in JAMA where the UCSF team reported that, across 33 emergency medical services (EMS) in California, only 2 included 10 mg midazolam IM per the guidelines, advice based on randomized, controlled clinical trials that found it to be safe and effective for stopping prehospital seizures in adults.
“Making people aware of the problem [is having] an impact,” said investigator Elan Guterman, MD, a neurology hospitalist and assistant professor of neurology at the university.
In a follow-up review at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society, the team took a deep dive into the situation in Alameda County, just east of San Francisco and including the city of Oakland, as an indicator of what’s been going on across the state.
Patients had to have an EMS record of active seizures, meaning more than two within 5 minutes or a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes. Alameda ambulance crews, like most, carry intramuscular midazolam because it’s more shelf stable than the two other first-line options, lorazepam and diazepam, and doesn’t require an intravenous line.
Among the 2,494 adults treated for status epilepticus from 2013 to 2018, just 62% received intramuscular midazolam, and only 39% got a dose of 5 mg or more. Not a single patient received the recommended 10-mg IM injection.
In short, “at the time when it’s the most important to act quickly, patients were not receiving the care they needed,” and the problem isn’t likely limited to California, Dr. Guterman said.
When patients did get 5 mg or more, they were less likely to reseize and require additional doses (adjusted odds ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.4-0.86). Also – and counterintuitively given the concern about benzodiazepines and respiratory depression – the team found that higher initial doses of 5 mg or more were actually associated with a lower need for respiratory support, including intubation (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99).
It’s possible ambulance crews were erring on the side of caution. People who got midazolam were more likely to have an established diagnosis of epilepsy (68% vs. 62%; P less than .01) and less likely to have been abusing drugs or alcohol (12.5% vs. 16.3%; P less than .01).
But an abundance of caution doesn’t fully explain it; even among people known to have epilepsy, many weren’t treated with midazolam and none at the appropriate dose.
Dr. Guterman thinks the bigger issue is what was reported in the research letter: Local EMS protocols simply haven’t been updated to include current best practices. EMS services might not even be aware of them, which is why she and her colleagues have been meeting with county medical directors.
“The first step is making sure the EMS world is aware of this gap in care, and motivating them to address it,” she said.
Patients in the study were a mean of 53 years old, and just over half were men.
There was no industry funding for the study, and Dr. Guterman didn’t report any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Guterman E et al. AES 2019, Abstract 1.394.
REPORTING FROM AES 2019
My favorite natural treatments
I practice in Seattle, where many of my patients are interested in natural treatment options. I am always puzzled that so many people assume that natural treatment options would be safer than prescription medications. Tsunamis, wildfires, flooding, and earthquakes are all natural and are deadly. There are certainly many natural poisons. There are a number of natural treatments that are very helpful, and recommending them are an important part of my practice. I want to share a few with you.
A useful vein pursuit?
Case: A 60-year-old woman presents to clinic with increasing pain in her left leg. She had a deep vein thrombosis in her left leg 2 years ago, which involved a large portion of her superficial femoral vein. She has noticed edema over the past few weeks, and pain has been more severe over the past 3 months. On exam, varicosities on left lower extremity with grade 2+ edema. Duplex of the lower extremity does not show deep vein thrombosis, but does show a great deal of venous valvular incompetence. She has tried compression stockings for the past 2 weeks. What is the best treatment option?
A) Turmeric
B) Amitriptyline
C) Vitamin B12
D) Horse chestnut
The treatment option with positive data for this problem is horse chestnut. What is horse chestnut? Horse chestnut is a kind of tree, and the seed extract contains aescin which is believed to be the active ingredient. Diehm et al. studied horse chestnut seed extract (HCSE), compared with compression stockings and placebo for edema from chronic venous insufficiency in a study of 240 patients.1 Lower-leg volume decreased by 43 mL with HCSE, 46 mL with compression stockings, and increased by 9 mL with placebo (P less than .005 for HCSE and P less than .002 for compression). In a Cochrane review, HCSE was considered efficacious and safe for the short-term therapy for chronic venous insufficiency.2 Studies have shown both an improvement in pain as well as swelling in patients with chronic venous insufficiency.
The question of UTIs
Probably the most popular natural treatment for prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women is cranberry juice (or cranberry extract). Unfortunately, there is little evidence that this treatment is helpful. In a Cochrane analysis, the conclusion was, based on current evidence, cranberry juice cannot currently be recommended for the prevention of UTIs.3 A natural product that appears to be more promising is the sugar D-mannose. Kranjčec et al. studied 308 women with acute UTI who had a history of recurrent UTI.4 All the women were treated for their symptomatic infection with ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 1 week). The women were allocated equally to three groups for 6 months: D-mannose 2 g daily, nitrofurantoin 50 mg daily, or no prophylaxis. About 60% of the women who received no prophylaxis had a UTI during the study period, compared with 20% in the nitrofurantoin group and 15% in the D-mannose group. The relative risk for D-mannose, compared with no prophylaxis, was 0.24 and for nitrofurantoin was 0.34 (P less than .0001), compared with no prophylaxis.
Made for migraines?
Migraine prophylaxis is challenging because all medications that are commonly used have side effects that often limit patient adherence. Tricyclic antidepressants (dry mouth, dizziness and weight gain), beta-blockers (fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance), valproate (weight gain and fatigue), and topiramate (parasthesias and mental slowing) all have troubling side effects. Riboflavin is a vitamin with evidence of effectiveness for migraine prophylaxis. It is extremely well tolerated. In a recent study in children with migraines, Talebian et al. studied 90 children with migraines who were randomized to three groups (200 mg of riboflavin a day, 100 mg of riboflavin a day, or placebo) after observation during a 1-month baseline period.5 There was a significant reduction in migraine frequency and duration in patients receiving 200 mg of riboflavin daily, compared with placebo. Rahimdel et al. published an interesting study comparing high-dose riboflavin with valproate for migraine prophylaxis. A total of 90 patients were randomized to receive 400 mg of riboflavin or 500 mg of valproate over a 12-month study.6 Both treatments resulted in marked reduction in frequency, duration, and severity of migraines (not statistically significantly different from each other). The reduction in migraine frequency for the riboflavin group was from 9.2 headache days per month to 2.4. The American Academy of Neurology rates the level of evidence for riboflavin as B.
Pearl
References
1. Diehm C et al. Lancet. 1996;347(8997):292-4.
2. Pittler MH, Ernst E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD003230.
3. Jepson RG et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD001321.
4. Kranjčec B et al. World J Urol. 2014 Feb;32(1):79-84.
5. Talebian A et al. Electron Physician. Feb 25;10(2):6279-85.
6. Rahimdel A et al. Electron Physician. 2015 Oct 19;7(6):1344-8.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
I practice in Seattle, where many of my patients are interested in natural treatment options. I am always puzzled that so many people assume that natural treatment options would be safer than prescription medications. Tsunamis, wildfires, flooding, and earthquakes are all natural and are deadly. There are certainly many natural poisons. There are a number of natural treatments that are very helpful, and recommending them are an important part of my practice. I want to share a few with you.
A useful vein pursuit?
Case: A 60-year-old woman presents to clinic with increasing pain in her left leg. She had a deep vein thrombosis in her left leg 2 years ago, which involved a large portion of her superficial femoral vein. She has noticed edema over the past few weeks, and pain has been more severe over the past 3 months. On exam, varicosities on left lower extremity with grade 2+ edema. Duplex of the lower extremity does not show deep vein thrombosis, but does show a great deal of venous valvular incompetence. She has tried compression stockings for the past 2 weeks. What is the best treatment option?
A) Turmeric
B) Amitriptyline
C) Vitamin B12
D) Horse chestnut
The treatment option with positive data for this problem is horse chestnut. What is horse chestnut? Horse chestnut is a kind of tree, and the seed extract contains aescin which is believed to be the active ingredient. Diehm et al. studied horse chestnut seed extract (HCSE), compared with compression stockings and placebo for edema from chronic venous insufficiency in a study of 240 patients.1 Lower-leg volume decreased by 43 mL with HCSE, 46 mL with compression stockings, and increased by 9 mL with placebo (P less than .005 for HCSE and P less than .002 for compression). In a Cochrane review, HCSE was considered efficacious and safe for the short-term therapy for chronic venous insufficiency.2 Studies have shown both an improvement in pain as well as swelling in patients with chronic venous insufficiency.
The question of UTIs
Probably the most popular natural treatment for prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women is cranberry juice (or cranberry extract). Unfortunately, there is little evidence that this treatment is helpful. In a Cochrane analysis, the conclusion was, based on current evidence, cranberry juice cannot currently be recommended for the prevention of UTIs.3 A natural product that appears to be more promising is the sugar D-mannose. Kranjčec et al. studied 308 women with acute UTI who had a history of recurrent UTI.4 All the women were treated for their symptomatic infection with ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 1 week). The women were allocated equally to three groups for 6 months: D-mannose 2 g daily, nitrofurantoin 50 mg daily, or no prophylaxis. About 60% of the women who received no prophylaxis had a UTI during the study period, compared with 20% in the nitrofurantoin group and 15% in the D-mannose group. The relative risk for D-mannose, compared with no prophylaxis, was 0.24 and for nitrofurantoin was 0.34 (P less than .0001), compared with no prophylaxis.
Made for migraines?
Migraine prophylaxis is challenging because all medications that are commonly used have side effects that often limit patient adherence. Tricyclic antidepressants (dry mouth, dizziness and weight gain), beta-blockers (fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance), valproate (weight gain and fatigue), and topiramate (parasthesias and mental slowing) all have troubling side effects. Riboflavin is a vitamin with evidence of effectiveness for migraine prophylaxis. It is extremely well tolerated. In a recent study in children with migraines, Talebian et al. studied 90 children with migraines who were randomized to three groups (200 mg of riboflavin a day, 100 mg of riboflavin a day, or placebo) after observation during a 1-month baseline period.5 There was a significant reduction in migraine frequency and duration in patients receiving 200 mg of riboflavin daily, compared with placebo. Rahimdel et al. published an interesting study comparing high-dose riboflavin with valproate for migraine prophylaxis. A total of 90 patients were randomized to receive 400 mg of riboflavin or 500 mg of valproate over a 12-month study.6 Both treatments resulted in marked reduction in frequency, duration, and severity of migraines (not statistically significantly different from each other). The reduction in migraine frequency for the riboflavin group was from 9.2 headache days per month to 2.4. The American Academy of Neurology rates the level of evidence for riboflavin as B.
Pearl
References
1. Diehm C et al. Lancet. 1996;347(8997):292-4.
2. Pittler MH, Ernst E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD003230.
3. Jepson RG et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD001321.
4. Kranjčec B et al. World J Urol. 2014 Feb;32(1):79-84.
5. Talebian A et al. Electron Physician. Feb 25;10(2):6279-85.
6. Rahimdel A et al. Electron Physician. 2015 Oct 19;7(6):1344-8.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
I practice in Seattle, where many of my patients are interested in natural treatment options. I am always puzzled that so many people assume that natural treatment options would be safer than prescription medications. Tsunamis, wildfires, flooding, and earthquakes are all natural and are deadly. There are certainly many natural poisons. There are a number of natural treatments that are very helpful, and recommending them are an important part of my practice. I want to share a few with you.
A useful vein pursuit?
Case: A 60-year-old woman presents to clinic with increasing pain in her left leg. She had a deep vein thrombosis in her left leg 2 years ago, which involved a large portion of her superficial femoral vein. She has noticed edema over the past few weeks, and pain has been more severe over the past 3 months. On exam, varicosities on left lower extremity with grade 2+ edema. Duplex of the lower extremity does not show deep vein thrombosis, but does show a great deal of venous valvular incompetence. She has tried compression stockings for the past 2 weeks. What is the best treatment option?
A) Turmeric
B) Amitriptyline
C) Vitamin B12
D) Horse chestnut
The treatment option with positive data for this problem is horse chestnut. What is horse chestnut? Horse chestnut is a kind of tree, and the seed extract contains aescin which is believed to be the active ingredient. Diehm et al. studied horse chestnut seed extract (HCSE), compared with compression stockings and placebo for edema from chronic venous insufficiency in a study of 240 patients.1 Lower-leg volume decreased by 43 mL with HCSE, 46 mL with compression stockings, and increased by 9 mL with placebo (P less than .005 for HCSE and P less than .002 for compression). In a Cochrane review, HCSE was considered efficacious and safe for the short-term therapy for chronic venous insufficiency.2 Studies have shown both an improvement in pain as well as swelling in patients with chronic venous insufficiency.
The question of UTIs
Probably the most popular natural treatment for prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women is cranberry juice (or cranberry extract). Unfortunately, there is little evidence that this treatment is helpful. In a Cochrane analysis, the conclusion was, based on current evidence, cranberry juice cannot currently be recommended for the prevention of UTIs.3 A natural product that appears to be more promising is the sugar D-mannose. Kranjčec et al. studied 308 women with acute UTI who had a history of recurrent UTI.4 All the women were treated for their symptomatic infection with ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 1 week). The women were allocated equally to three groups for 6 months: D-mannose 2 g daily, nitrofurantoin 50 mg daily, or no prophylaxis. About 60% of the women who received no prophylaxis had a UTI during the study period, compared with 20% in the nitrofurantoin group and 15% in the D-mannose group. The relative risk for D-mannose, compared with no prophylaxis, was 0.24 and for nitrofurantoin was 0.34 (P less than .0001), compared with no prophylaxis.
Made for migraines?
Migraine prophylaxis is challenging because all medications that are commonly used have side effects that often limit patient adherence. Tricyclic antidepressants (dry mouth, dizziness and weight gain), beta-blockers (fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance), valproate (weight gain and fatigue), and topiramate (parasthesias and mental slowing) all have troubling side effects. Riboflavin is a vitamin with evidence of effectiveness for migraine prophylaxis. It is extremely well tolerated. In a recent study in children with migraines, Talebian et al. studied 90 children with migraines who were randomized to three groups (200 mg of riboflavin a day, 100 mg of riboflavin a day, or placebo) after observation during a 1-month baseline period.5 There was a significant reduction in migraine frequency and duration in patients receiving 200 mg of riboflavin daily, compared with placebo. Rahimdel et al. published an interesting study comparing high-dose riboflavin with valproate for migraine prophylaxis. A total of 90 patients were randomized to receive 400 mg of riboflavin or 500 mg of valproate over a 12-month study.6 Both treatments resulted in marked reduction in frequency, duration, and severity of migraines (not statistically significantly different from each other). The reduction in migraine frequency for the riboflavin group was from 9.2 headache days per month to 2.4. The American Academy of Neurology rates the level of evidence for riboflavin as B.
Pearl
References
1. Diehm C et al. Lancet. 1996;347(8997):292-4.
2. Pittler MH, Ernst E. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD003230.
3. Jepson RG et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;10:CD001321.
4. Kranjčec B et al. World J Urol. 2014 Feb;32(1):79-84.
5. Talebian A et al. Electron Physician. Feb 25;10(2):6279-85.
6. Rahimdel A et al. Electron Physician. 2015 Oct 19;7(6):1344-8.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
Verrucous Psoriasis Treated With Methotrexate and Acitretin Combination Therapy
To the Editor:
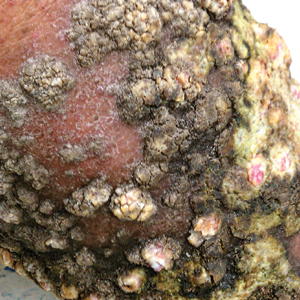
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.
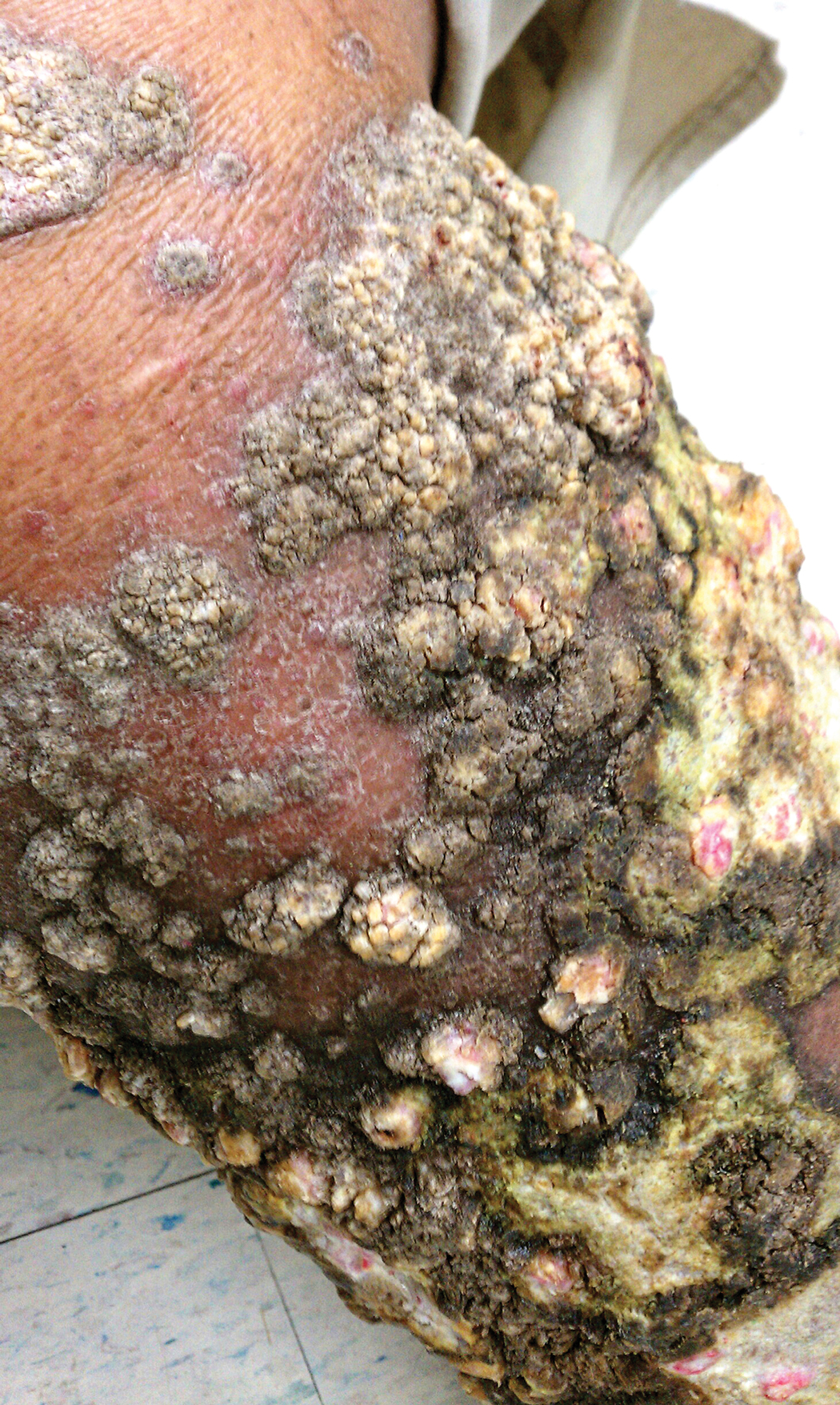
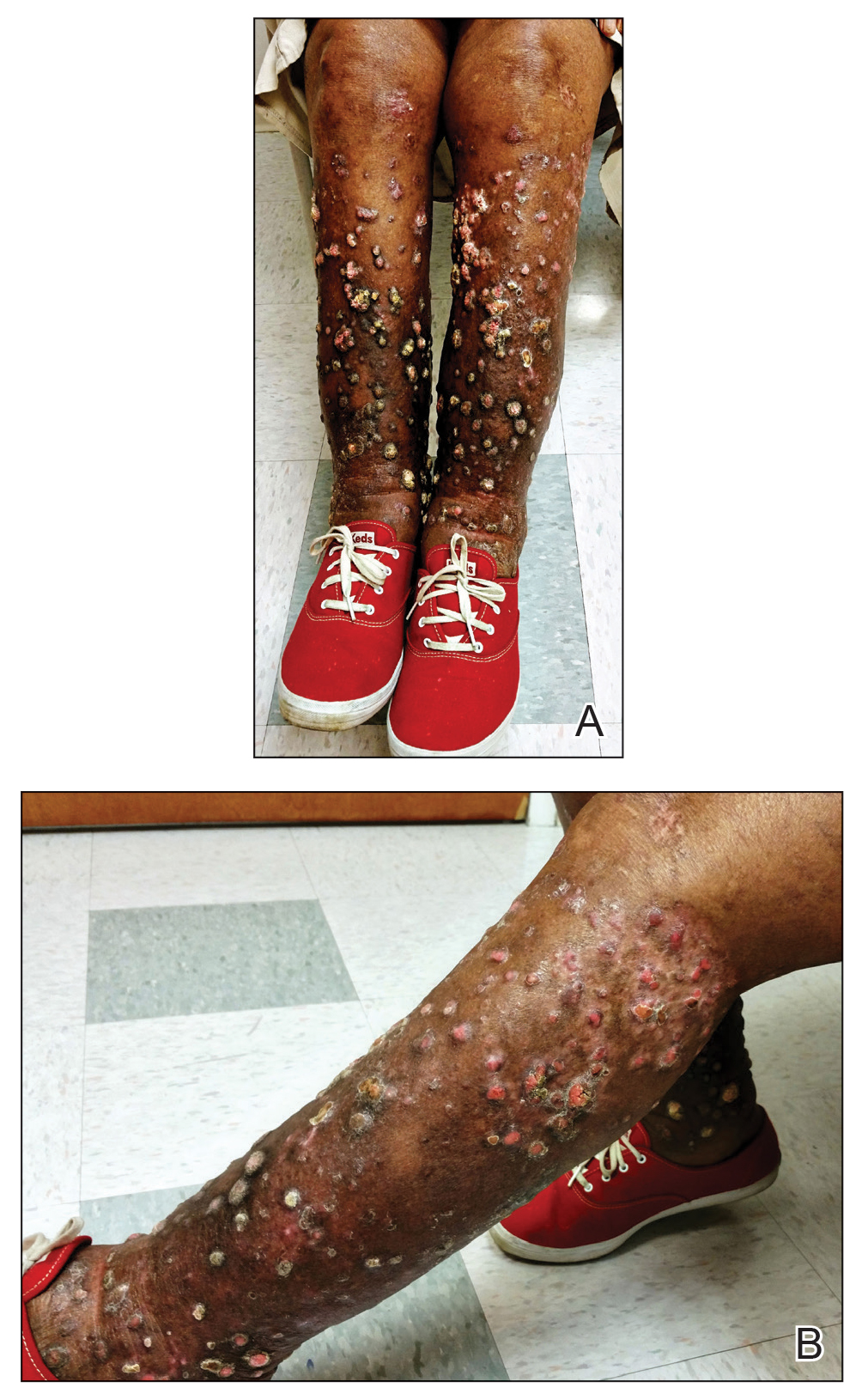
A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.
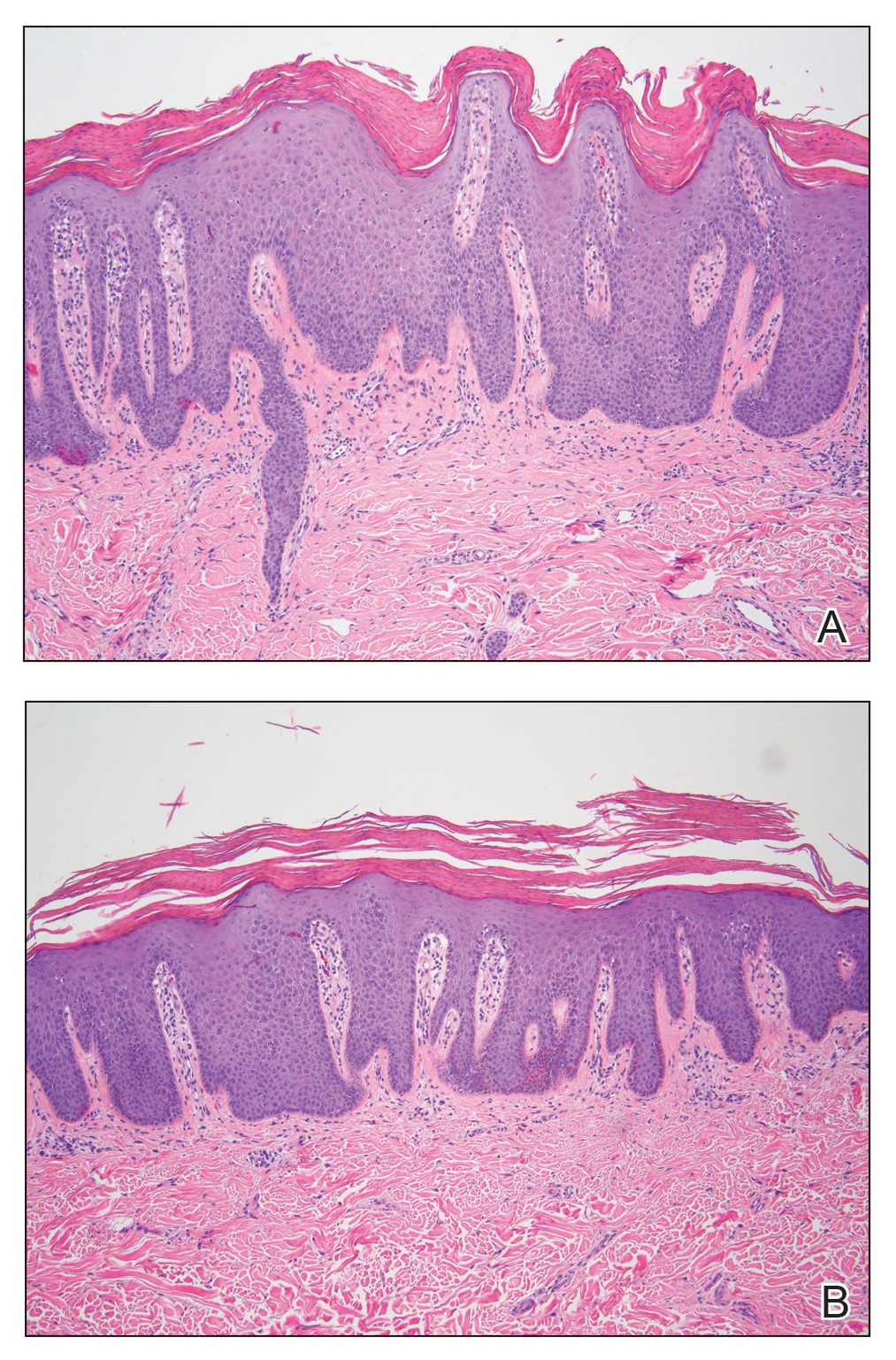
Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
To the Editor:
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.

A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.


Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
To the Editor:
A 76-year-old woman with venous insufficiency presented with numerous thick, hyperkeratotic, confluent papules and plaques involving both legs and thighs as well as the lower back. She initially developed lesions on the distal legs, which progressed to involve the thighs and lower back, slowly enlarging over 7 years (Figure 1). The eruption was associated with pruritus and was profoundly malodorous. The patient had been unsuccessfully treated with triamcinolone ointment, bleach baths, and several courses of oral antibiotics. Her history was remarkable for marked venous insufficiency and mild anemia, with a hemoglobin level of 11.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL). She had no other abnormalities on a comprehensive blood test, basic metabolic panel, or liver function test.

A punch biopsy specimen from the left lower back was obtained and demonstrated papillomatous psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with broad parakeratosis, few intracorneal neutrophils, hypogranulosis, and suprapapillary thinning (Figure 2). She was initially treated with oral methotrexate (20 mg weekly), resulting in partial improvement of plaques and complete resolution of pruritus and malodor. After 15 months of treatment with methotrexate, low-dose methotrexate (10 mg weekly) in combination with acitretin 25 mg daily was started, resulting in further improvement of hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). The patient also was given a compounded corticosteroid ointment containing liquor carbonis detergens, salicylic acid, and fluocinonide ointment, achieving minor additional benefit. Comprehensive metabolic panel, lipid panel, and liver function tests were obtained quarterly. Hemoglobin levels remained low, similar to baseline (11.3–12.5 g/dL), while all other values were within reference range. The patient tolerated treatment well, reporting mild dryness of lips on review of systems, which was attributed to acitretin and was treated with emollients.


Verrucous psoriasis is an uncommon variant of psoriasis that presents as localized annular, erythrodermic, or drug-induced disease, as reported in a patient with preexisting psoriasis after interferon treatment of hepatitis C.1,2 It is characterized by symmetric hypertrophic verrucous plaques that may have an erythematous base and involve the legs, arms, trunk, and dorsal aspect of the hands3; malodor is frequent.1 Histopathologically, overlapping features of verruca vulgaris and psoriasis have been described. Specifically, lesions display typical psoriasiform changes, including parakeratosis, epidermal acanthosis with elongation of rete ridges, suprapapillary thinning, epidermal hypogranulosis, dilated or tortuous capillaries, and neutrophil collections in the stratum corneum (Munro microabscesses) or stratum spinosum (spongiform pustules of Kogoj).3 Additional findings of papillomatosis and epithelial buttressing are highly suggestive of verrucous psoriasis,3 though epithelial buttressing is not universally present.4-6 Similarly, although eosinophils and plasma cells have been described in some patients with verrucous psoriasis, this finding has not been consistently reported.4-6 Our biopsy specimen (Figure 2) lacks the epithelial buttressing but does exhibit subtle papillomatous hyperplasia consistent with the diagnosis of psoriasis.
The etiology of this entity is unknown. An association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been proposed. Others have reported repeated trauma as contributing to the pathogenesis.1 For our patient, trauma secondary to scratching, long-standing venous insufficiency, and neglect likely contributed to the development of verrucous plaques.
The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis can be challenging because of its similarity to several other entities, including verruca vulgaris; epidermal nevus; and squamous cell carcinoma, particularly verrucous carcinoma.4,6,7 The diagnosis has been less challenging in areas where prior typical psoriatic lesions evolved into a verrucous morphology. Our patient presented a diagnostic challenge and draws attention to this unique variant of psoriasis that could easily be misdiagnosed and lead to inappropriate treatment.
Verrucous psoriasis can be recalcitrant to therapy. Although studies addressing treatment modalities are lacking, several recommendations can be derived from case reports and our patient. The use of topical therapies, including topical corticosteroids (eg, fluocinonide, clobetasol, halobetasol), keratolytic agents (eg, urea, salicylic acid), and calcipotriene, provide only minimal improvement when used as monotherapy.1 Better success has been reported with systemic therapies, mainly methotrexate and acitretin, with anecdotal reports favoring the use of oral retinoids.1,6 Conversely, biologic medications such as etanercept, ustekinumab, adalimumab, and infliximab have only provided a partial response.1 Combination therapies including intralesional triamcinolone plus methotrexate4 or methotrexate plus acitretin, as in our patient, seem to provide additional benefit. Methotrexate and acitretin combination therapy has traditionally been avoided because of the risk for hepatotoxicity. However, a case series has demonstrated a moderate safety profile with concurrent use of these drugs in treatment-resistant psoriasis.8 In our case, clinical response was most pronounced with combination therapy of methotrexate 10 mg weekly and acitretin 25 mg daily. Thus, strong consideration should be given for combination methotrexate-acitretin therapy in patients with recalcitrant verrucous psoriasis who lack comorbid conditions.
We present a case of verrucous psoriasis, a variant of psoriasis characterized by hypertrophic plaques. We propose that venous insufficiency and long-standing untreated disease was instrumental to the development of these lesions. Furthermore, retinoids, particularly in combination with methotrexate, provided the most benefit for our patient.
Acknowledgment
We thank Stephen Somach, MD (Cleveland, Ohio), for his help interpreting the microscopic findings in our biopsy specimen. He received no compensation.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
- Curtis AR, Yosipovitch G. Erythrodermic verrucous psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2012;23:215-218.
- Scavo S, Gurrera A, Mazzaglia C, et al. Verrucous psoriasis in a patient with chronic C hepatitis treated with interferon. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:427-429.
- Khalil FK, Keehn CA, Saeed S, et al. Verrucous psoriasis: a distinctive clinicopathologic variant of psoriasis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:204-207.
- Hall L, Marks V, Tyler W. Verrucous psoriasis: a clinical and histopathologic mimicker of verruca vulgaris [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68(suppl 1):AB218.
- Monroe HR, Hillman JD, Chiu MW. A case of verrucous psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:10.
- Larsen F, Susa JS, Cockerell CJ, et al. Case of multiple verrucous carcinomas responding to treatment with acetretin more likely to have been a case of verrucous psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:534-535.
- Kuan YZ, Hsu HC, Kuo TT, et al. Multiple verrucous carcinomas treated with acitretin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56(2 suppl):S29-S32.
- Lowenthal KE, Horn PJ, Kalb RE. Concurrent use of methotrexate and acitretin revisited. J Dermatolog Treat. 2008;19:22-26.
Practice Points
- Verrucous psoriasis in an uncommon but recalcitrant-to-treatment variant of psoriasis that is characterized by hypertrophic plaques.
- The diagnosis of verrucous psoriasis is challenging, as it can mimic other entities such as verruca vulgaris and squamous cell carcinoma.
- Although the etiology of this entity is unknown, an association with diabetes mellitus, pulmonary disease, lymphatic circulation disorders, and immunosuppression has been described.
- The combination of methotrexate and acitretin is a safe and effective option for these patients in the absence of comorbid conditions.
Oral paclitaxel bests IV version for tumor response, neuropathy incidence in mBC
SAN ANTONIO – An oral formulation of paclitaxel given with the P-glycoprotein pump inhibitor encequidar improved outcomes and reduced neuropathy risk, compared with intravenous paclitaxel, in women with metastatic breast cancer in a randomized, open-label, phase 3 study.
The primary study endpoint of radiologically confirmed tumor response rate was 35.8% among 265 patients randomized to receive oral paclitaxel plus encequidar, compared with 23.4% among 137 who received intravenous paclitaxel – a statistically significant 12.4% difference, Gerardo Umanzor, MD, reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In the prespecified modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population of patients who had evaluable scans at baseline and who received at least seven doses of oral therapy or one dose of intravenous therapy, the corresponding confirmed tumor response rates were 40.4% and 25.5% (absolute improvement, 14.8%), said Dr. Umanzor, a medical oncologist with Liga Contra el Cancer in San Pedro Sulas, Honduras.
Tumor responses in all clinically important subgroups were consistent with the overall confirmed response profiles, he said, noting that the responses were durable, with ongoing analyses showing median response durations of 39.0 weeks versus 30.1 weeks with oral versus intravenous therapy.
Further, a higher percentage of oral versus intravenous paclitaxel recipients were receiving ongoing treatment at the time of the study endpoint (19% vs. 13%, respectively), he said.
Progression-free survival also showed a trend toward improved outcome with oral therapy in ongoing analyses in the mITT population (9.3 vs. 8.3 months, respectively), and an early analysis of overall survival also showed significant improvement (27.9 vs. 16.9 months; P = .035), he said.
Oral paclitaxel also was associated with a lower incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy – a “highly debilitating side effect of IV paclitaxel,” he said, adding that “the difference between the arms is quite dramatic.”
The overall rates of neuropathy to week 23 were 17% versus 15% with oral versus intravenous therapy, and the rates of grade 3 neuropathy were 1% versus 8%, he said.
Alopecia incidence was reduced by about 50% with oral versus intravenous therapy, he added.
Toxicity was generally similar in the two groups, although the oral paclitaxel patients experienced higher rates of neutropenia and gastrointestinal effects. “These were low grade and manageable,” Dr. Umanzor said.
Study participants were patients with any type of metastatic breast cancer randomized 2:1 to receive a 15-mg tablet of encequidar followed by 205 mg/m2 of oral paclitaxel (about 11 capsules, each containing 30 mg of solubilized paclitaxel) for 3 consecutive days each week for 3 weeks or intravenous paclitaxel at the labeled dose of 175 mg/m2 over a 3-hour infusion every 3 weeks.
Confirmed tumor response rates were based on blinded assessment at two consecutive time points, 3-6 weeks apart, by study day 160.
The treatment groups were similar with respect to demographic characteristics and prior taxane therapy, he noted.
The findings have important implications, because while intravenous paclitaxel is an efficacious chemotherapeutic agent against metastatic breast cancer and multiple other cancers, it is associated in some patients with neuropathy.
“As an oncologist, it has been very frustrating to have an effective chemotherapy like paclitaxel, which a lot of patients cannot tolerate,” Dr. Umanzor said, noting that, in addition to eliminating the need for intravenous access and the risk of infusion hypersensitivity reactions, oral administration offers a number of potential benefits – particularly patient convenience.
Hypothesizing that the lower peak concentration of oral paclitaxel might result in lower systemic toxicity, Dr. Umanzor and colleagues developed the orally administered paclitaxel regimen used in this study to test that hypothesis. The paclitaxel was made bioavailable through combination with the encequidar, which promotes paclitaxel absorption into the blood stream, he explained, noting that the pharmacokinetic exposure matches that of intravenous paclitaxel when given at 80 mg/m2, but with peak concentrations that are approximately one-tenth of those seen with intravenous therapy.
In a phase 2 study of 26 patients with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer, the oral therapy was associated with an encouraging 42.3% partial response rate and a 46.2% stable disease rate, he said.
The oral paclitaxel plus encequidar combination used in this pivotal study is the first orally administered taxane to demonstrate improved and durable overall confirmed response rates with minimal clinically meaningful neuropathy, compared with intravenous paclitaxel given every 3 weeks, he said.
“Oral paclitaxel and encequidar provides an important oral therapeutic option for patients with metastatic breast cancer, representing a meaningful improvement in the clinical profile of paclitaxel,” he said.
He further noted in a press release that “[t]his oral form of paclitaxel provides a new therapeutic option for patients, in particular, for those who cannot easily travel. While blood counts still need to be monitored, oral administration allows patients to remain home during therapy, and avoid spending significant time in the chemotherapy unit.”
The next step will be testing the tolerability of oral paclitaxel in patients at high risk of developing peripheral neuropathy, he said, adding that the findings could also open the door for assessing this approach with other taxanes.
During a press briefing on the findings at the symposium, several attendees voiced concerns about patient compliance given the large number of capsules required for oral dosing, but Dr. Umanzor said “there were no complaints at all and no issues with adherence.”
“Patients were so excited that they were getting an oral treatment, and we had very good compliance,” he said.
The study was funded by Athenex, the maker of the oral form of paclitaxel. Dr. Umanzor reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Umanzor G et al. SABCS 2019, Abstract GS6-01.
SAN ANTONIO – An oral formulation of paclitaxel given with the P-glycoprotein pump inhibitor encequidar improved outcomes and reduced neuropathy risk, compared with intravenous paclitaxel, in women with metastatic breast cancer in a randomized, open-label, phase 3 study.
The primary study endpoint of radiologically confirmed tumor response rate was 35.8% among 265 patients randomized to receive oral paclitaxel plus encequidar, compared with 23.4% among 137 who received intravenous paclitaxel – a statistically significant 12.4% difference, Gerardo Umanzor, MD, reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In the prespecified modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population of patients who had evaluable scans at baseline and who received at least seven doses of oral therapy or one dose of intravenous therapy, the corresponding confirmed tumor response rates were 40.4% and 25.5% (absolute improvement, 14.8%), said Dr. Umanzor, a medical oncologist with Liga Contra el Cancer in San Pedro Sulas, Honduras.
Tumor responses in all clinically important subgroups were consistent with the overall confirmed response profiles, he said, noting that the responses were durable, with ongoing analyses showing median response durations of 39.0 weeks versus 30.1 weeks with oral versus intravenous therapy.
Further, a higher percentage of oral versus intravenous paclitaxel recipients were receiving ongoing treatment at the time of the study endpoint (19% vs. 13%, respectively), he said.
Progression-free survival also showed a trend toward improved outcome with oral therapy in ongoing analyses in the mITT population (9.3 vs. 8.3 months, respectively), and an early analysis of overall survival also showed significant improvement (27.9 vs. 16.9 months; P = .035), he said.
Oral paclitaxel also was associated with a lower incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy – a “highly debilitating side effect of IV paclitaxel,” he said, adding that “the difference between the arms is quite dramatic.”
The overall rates of neuropathy to week 23 were 17% versus 15% with oral versus intravenous therapy, and the rates of grade 3 neuropathy were 1% versus 8%, he said.
Alopecia incidence was reduced by about 50% with oral versus intravenous therapy, he added.
Toxicity was generally similar in the two groups, although the oral paclitaxel patients experienced higher rates of neutropenia and gastrointestinal effects. “These were low grade and manageable,” Dr. Umanzor said.
Study participants were patients with any type of metastatic breast cancer randomized 2:1 to receive a 15-mg tablet of encequidar followed by 205 mg/m2 of oral paclitaxel (about 11 capsules, each containing 30 mg of solubilized paclitaxel) for 3 consecutive days each week for 3 weeks or intravenous paclitaxel at the labeled dose of 175 mg/m2 over a 3-hour infusion every 3 weeks.
Confirmed tumor response rates were based on blinded assessment at two consecutive time points, 3-6 weeks apart, by study day 160.
The treatment groups were similar with respect to demographic characteristics and prior taxane therapy, he noted.
The findings have important implications, because while intravenous paclitaxel is an efficacious chemotherapeutic agent against metastatic breast cancer and multiple other cancers, it is associated in some patients with neuropathy.
“As an oncologist, it has been very frustrating to have an effective chemotherapy like paclitaxel, which a lot of patients cannot tolerate,” Dr. Umanzor said, noting that, in addition to eliminating the need for intravenous access and the risk of infusion hypersensitivity reactions, oral administration offers a number of potential benefits – particularly patient convenience.
Hypothesizing that the lower peak concentration of oral paclitaxel might result in lower systemic toxicity, Dr. Umanzor and colleagues developed the orally administered paclitaxel regimen used in this study to test that hypothesis. The paclitaxel was made bioavailable through combination with the encequidar, which promotes paclitaxel absorption into the blood stream, he explained, noting that the pharmacokinetic exposure matches that of intravenous paclitaxel when given at 80 mg/m2, but with peak concentrations that are approximately one-tenth of those seen with intravenous therapy.
In a phase 2 study of 26 patients with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer, the oral therapy was associated with an encouraging 42.3% partial response rate and a 46.2% stable disease rate, he said.
The oral paclitaxel plus encequidar combination used in this pivotal study is the first orally administered taxane to demonstrate improved and durable overall confirmed response rates with minimal clinically meaningful neuropathy, compared with intravenous paclitaxel given every 3 weeks, he said.
“Oral paclitaxel and encequidar provides an important oral therapeutic option for patients with metastatic breast cancer, representing a meaningful improvement in the clinical profile of paclitaxel,” he said.
He further noted in a press release that “[t]his oral form of paclitaxel provides a new therapeutic option for patients, in particular, for those who cannot easily travel. While blood counts still need to be monitored, oral administration allows patients to remain home during therapy, and avoid spending significant time in the chemotherapy unit.”
The next step will be testing the tolerability of oral paclitaxel in patients at high risk of developing peripheral neuropathy, he said, adding that the findings could also open the door for assessing this approach with other taxanes.
During a press briefing on the findings at the symposium, several attendees voiced concerns about patient compliance given the large number of capsules required for oral dosing, but Dr. Umanzor said “there were no complaints at all and no issues with adherence.”
“Patients were so excited that they were getting an oral treatment, and we had very good compliance,” he said.
The study was funded by Athenex, the maker of the oral form of paclitaxel. Dr. Umanzor reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Umanzor G et al. SABCS 2019, Abstract GS6-01.
SAN ANTONIO – An oral formulation of paclitaxel given with the P-glycoprotein pump inhibitor encequidar improved outcomes and reduced neuropathy risk, compared with intravenous paclitaxel, in women with metastatic breast cancer in a randomized, open-label, phase 3 study.
The primary study endpoint of radiologically confirmed tumor response rate was 35.8% among 265 patients randomized to receive oral paclitaxel plus encequidar, compared with 23.4% among 137 who received intravenous paclitaxel – a statistically significant 12.4% difference, Gerardo Umanzor, MD, reported at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
In the prespecified modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population of patients who had evaluable scans at baseline and who received at least seven doses of oral therapy or one dose of intravenous therapy, the corresponding confirmed tumor response rates were 40.4% and 25.5% (absolute improvement, 14.8%), said Dr. Umanzor, a medical oncologist with Liga Contra el Cancer in San Pedro Sulas, Honduras.
Tumor responses in all clinically important subgroups were consistent with the overall confirmed response profiles, he said, noting that the responses were durable, with ongoing analyses showing median response durations of 39.0 weeks versus 30.1 weeks with oral versus intravenous therapy.
Further, a higher percentage of oral versus intravenous paclitaxel recipients were receiving ongoing treatment at the time of the study endpoint (19% vs. 13%, respectively), he said.
Progression-free survival also showed a trend toward improved outcome with oral therapy in ongoing analyses in the mITT population (9.3 vs. 8.3 months, respectively), and an early analysis of overall survival also showed significant improvement (27.9 vs. 16.9 months; P = .035), he said.
Oral paclitaxel also was associated with a lower incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy – a “highly debilitating side effect of IV paclitaxel,” he said, adding that “the difference between the arms is quite dramatic.”
The overall rates of neuropathy to week 23 were 17% versus 15% with oral versus intravenous therapy, and the rates of grade 3 neuropathy were 1% versus 8%, he said.
Alopecia incidence was reduced by about 50% with oral versus intravenous therapy, he added.
Toxicity was generally similar in the two groups, although the oral paclitaxel patients experienced higher rates of neutropenia and gastrointestinal effects. “These were low grade and manageable,” Dr. Umanzor said.
Study participants were patients with any type of metastatic breast cancer randomized 2:1 to receive a 15-mg tablet of encequidar followed by 205 mg/m2 of oral paclitaxel (about 11 capsules, each containing 30 mg of solubilized paclitaxel) for 3 consecutive days each week for 3 weeks or intravenous paclitaxel at the labeled dose of 175 mg/m2 over a 3-hour infusion every 3 weeks.
Confirmed tumor response rates were based on blinded assessment at two consecutive time points, 3-6 weeks apart, by study day 160.
The treatment groups were similar with respect to demographic characteristics and prior taxane therapy, he noted.
The findings have important implications, because while intravenous paclitaxel is an efficacious chemotherapeutic agent against metastatic breast cancer and multiple other cancers, it is associated in some patients with neuropathy.
“As an oncologist, it has been very frustrating to have an effective chemotherapy like paclitaxel, which a lot of patients cannot tolerate,” Dr. Umanzor said, noting that, in addition to eliminating the need for intravenous access and the risk of infusion hypersensitivity reactions, oral administration offers a number of potential benefits – particularly patient convenience.
Hypothesizing that the lower peak concentration of oral paclitaxel might result in lower systemic toxicity, Dr. Umanzor and colleagues developed the orally administered paclitaxel regimen used in this study to test that hypothesis. The paclitaxel was made bioavailable through combination with the encequidar, which promotes paclitaxel absorption into the blood stream, he explained, noting that the pharmacokinetic exposure matches that of intravenous paclitaxel when given at 80 mg/m2, but with peak concentrations that are approximately one-tenth of those seen with intravenous therapy.
In a phase 2 study of 26 patients with heavily pretreated metastatic breast cancer, the oral therapy was associated with an encouraging 42.3% partial response rate and a 46.2% stable disease rate, he said.
The oral paclitaxel plus encequidar combination used in this pivotal study is the first orally administered taxane to demonstrate improved and durable overall confirmed response rates with minimal clinically meaningful neuropathy, compared with intravenous paclitaxel given every 3 weeks, he said.
“Oral paclitaxel and encequidar provides an important oral therapeutic option for patients with metastatic breast cancer, representing a meaningful improvement in the clinical profile of paclitaxel,” he said.
He further noted in a press release that “[t]his oral form of paclitaxel provides a new therapeutic option for patients, in particular, for those who cannot easily travel. While blood counts still need to be monitored, oral administration allows patients to remain home during therapy, and avoid spending significant time in the chemotherapy unit.”
The next step will be testing the tolerability of oral paclitaxel in patients at high risk of developing peripheral neuropathy, he said, adding that the findings could also open the door for assessing this approach with other taxanes.
During a press briefing on the findings at the symposium, several attendees voiced concerns about patient compliance given the large number of capsules required for oral dosing, but Dr. Umanzor said “there were no complaints at all and no issues with adherence.”
“Patients were so excited that they were getting an oral treatment, and we had very good compliance,” he said.
The study was funded by Athenex, the maker of the oral form of paclitaxel. Dr. Umanzor reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Umanzor G et al. SABCS 2019, Abstract GS6-01.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2019
High-dose progesterone to reverse mifepristone held still 'experimental'
A study of high-dose progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist to reverse medical abortion has been stopped early because of safety concerns, but the authors say mifepristone antagonization should not be considered impossible.
In Obstetrics & Gynecology, Mitchell D. Creinin, MD, of the University of California, Davis, and coauthors reported the outcomes of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating the efficacy and safety of high-dose oral progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist. The study intended to enroll more women at 44–63 days of gestation who were planning surgical abortion, but stopped enrolling after 12 patients because of hemorrhage concerns.
Women were given a 200-mg dose of oral mifepristone, then randomized to either 200 mg oral progesterone or placebo 24 hours later, taken twice daily for 3 days then once daily until their planned surgical abortion 14-16 days after enrollment.
The approved method of medical abortion in the United States involves a combination of mifepristone followed by the prostaglandin analogue misoprostol 24-48 hours later, a combination designed to improve efficacy of the treatment.
There have been reports of some patients changing their minds in between taking the mifepristone and the misoprostol. The fact that mifepristone binds strongly to the progesterone receptor has led to the idea that its action could be reversed with high-dose progesterone as an antagonist.
In this study, three women – two in the placebo group and one in the progesterone group – experienced severe bleeding requiring ambulance transport to the emergency department 2-3 days after taking the mifepristone.
The study found that four of the six patients in the progesterone group, and two of the six patients in the placebo group had continuing pregnancies at 2 weeks.
There were two patients – one in each group – who did not complete the study. One in the placebo group left after taking the mifepristone because of anxiety about bleeding, and had a suction aspiration. The second women completed two of the four doses of progesterone, then requested a suction aspiration.
Dr. Creinin and coauthors wrote that while the study ended early, they found that there were no significant differences in the side effects experienced by patients treated with progesterone, compared with those on placebo – apart from a worsening of some pregnancy symptoms such as vomiting and tiredness.
However, patients should be told of the risk of using mifepristone for medical abortion without using misoprostol, they said, as this was associated with severe hemorrhage even with progesterone treatment.
“Because of the potential dangers for patients who opt not to use misoprostol after mifepristone ingestion, any mifepristone antagonization treatment must be considered experimental,” Dr. Creinin and associates wrote.
The Society of Family Planning Research Fund supported the study. One author declared a consultancy with a laboratory providing medical consultation for clinicians regarding mifepristone, and a second author was an employee of Planned Parenthood. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Creinin M et al. Obstet Gynecol 2019 Dec 5. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003620.
I think that this study highlights the importance of scientific rigor approved by an institutional review board when we counsel and care for our patients. As ob.gyns., we have to remember the privilege that women entrust us with their health and well being. To a certain extent, we also care for their families within our scope of reproductive health. We practice based on the best evidence available and consider referral to another trusted provider when we feel that we cannot provide unbiased care. I also feel obligated to share my opinion that legislators should trust the scientific and clinical community to not only prioritize women and their health, but also avoid introducing legislation that infringes on medicine.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Creinin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is on the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
I think that this study highlights the importance of scientific rigor approved by an institutional review board when we counsel and care for our patients. As ob.gyns., we have to remember the privilege that women entrust us with their health and well being. To a certain extent, we also care for their families within our scope of reproductive health. We practice based on the best evidence available and consider referral to another trusted provider when we feel that we cannot provide unbiased care. I also feel obligated to share my opinion that legislators should trust the scientific and clinical community to not only prioritize women and their health, but also avoid introducing legislation that infringes on medicine.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Creinin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is on the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
I think that this study highlights the importance of scientific rigor approved by an institutional review board when we counsel and care for our patients. As ob.gyns., we have to remember the privilege that women entrust us with their health and well being. To a certain extent, we also care for their families within our scope of reproductive health. We practice based on the best evidence available and consider referral to another trusted provider when we feel that we cannot provide unbiased care. I also feel obligated to share my opinion that legislators should trust the scientific and clinical community to not only prioritize women and their health, but also avoid introducing legislation that infringes on medicine.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH, is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Creinin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is on the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
A study of high-dose progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist to reverse medical abortion has been stopped early because of safety concerns, but the authors say mifepristone antagonization should not be considered impossible.
In Obstetrics & Gynecology, Mitchell D. Creinin, MD, of the University of California, Davis, and coauthors reported the outcomes of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating the efficacy and safety of high-dose oral progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist. The study intended to enroll more women at 44–63 days of gestation who were planning surgical abortion, but stopped enrolling after 12 patients because of hemorrhage concerns.
Women were given a 200-mg dose of oral mifepristone, then randomized to either 200 mg oral progesterone or placebo 24 hours later, taken twice daily for 3 days then once daily until their planned surgical abortion 14-16 days after enrollment.
The approved method of medical abortion in the United States involves a combination of mifepristone followed by the prostaglandin analogue misoprostol 24-48 hours later, a combination designed to improve efficacy of the treatment.
There have been reports of some patients changing their minds in between taking the mifepristone and the misoprostol. The fact that mifepristone binds strongly to the progesterone receptor has led to the idea that its action could be reversed with high-dose progesterone as an antagonist.
In this study, three women – two in the placebo group and one in the progesterone group – experienced severe bleeding requiring ambulance transport to the emergency department 2-3 days after taking the mifepristone.
The study found that four of the six patients in the progesterone group, and two of the six patients in the placebo group had continuing pregnancies at 2 weeks.
There were two patients – one in each group – who did not complete the study. One in the placebo group left after taking the mifepristone because of anxiety about bleeding, and had a suction aspiration. The second women completed two of the four doses of progesterone, then requested a suction aspiration.
Dr. Creinin and coauthors wrote that while the study ended early, they found that there were no significant differences in the side effects experienced by patients treated with progesterone, compared with those on placebo – apart from a worsening of some pregnancy symptoms such as vomiting and tiredness.
However, patients should be told of the risk of using mifepristone for medical abortion without using misoprostol, they said, as this was associated with severe hemorrhage even with progesterone treatment.
“Because of the potential dangers for patients who opt not to use misoprostol after mifepristone ingestion, any mifepristone antagonization treatment must be considered experimental,” Dr. Creinin and associates wrote.
The Society of Family Planning Research Fund supported the study. One author declared a consultancy with a laboratory providing medical consultation for clinicians regarding mifepristone, and a second author was an employee of Planned Parenthood. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Creinin M et al. Obstet Gynecol 2019 Dec 5. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003620.
A study of high-dose progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist to reverse medical abortion has been stopped early because of safety concerns, but the authors say mifepristone antagonization should not be considered impossible.
In Obstetrics & Gynecology, Mitchell D. Creinin, MD, of the University of California, Davis, and coauthors reported the outcomes of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating the efficacy and safety of high-dose oral progesterone as a mifepristone antagonist. The study intended to enroll more women at 44–63 days of gestation who were planning surgical abortion, but stopped enrolling after 12 patients because of hemorrhage concerns.
Women were given a 200-mg dose of oral mifepristone, then randomized to either 200 mg oral progesterone or placebo 24 hours later, taken twice daily for 3 days then once daily until their planned surgical abortion 14-16 days after enrollment.
The approved method of medical abortion in the United States involves a combination of mifepristone followed by the prostaglandin analogue misoprostol 24-48 hours later, a combination designed to improve efficacy of the treatment.
There have been reports of some patients changing their minds in between taking the mifepristone and the misoprostol. The fact that mifepristone binds strongly to the progesterone receptor has led to the idea that its action could be reversed with high-dose progesterone as an antagonist.
In this study, three women – two in the placebo group and one in the progesterone group – experienced severe bleeding requiring ambulance transport to the emergency department 2-3 days after taking the mifepristone.
The study found that four of the six patients in the progesterone group, and two of the six patients in the placebo group had continuing pregnancies at 2 weeks.
There were two patients – one in each group – who did not complete the study. One in the placebo group left after taking the mifepristone because of anxiety about bleeding, and had a suction aspiration. The second women completed two of the four doses of progesterone, then requested a suction aspiration.
Dr. Creinin and coauthors wrote that while the study ended early, they found that there were no significant differences in the side effects experienced by patients treated with progesterone, compared with those on placebo – apart from a worsening of some pregnancy symptoms such as vomiting and tiredness.
However, patients should be told of the risk of using mifepristone for medical abortion without using misoprostol, they said, as this was associated with severe hemorrhage even with progesterone treatment.
“Because of the potential dangers for patients who opt not to use misoprostol after mifepristone ingestion, any mifepristone antagonization treatment must be considered experimental,” Dr. Creinin and associates wrote.
The Society of Family Planning Research Fund supported the study. One author declared a consultancy with a laboratory providing medical consultation for clinicians regarding mifepristone, and a second author was an employee of Planned Parenthood. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Creinin M et al. Obstet Gynecol 2019 Dec 5. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003620.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Appeals court rules ACA’s individual mandate is unconstitutional
A federal appeals court ruled Dec. 18 that the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is unconstitutional, but the panel sent the case back to a lower court to decide how much of the remainder of the law could topple along with it.
The three-judge panel of the New Orleans-based U.S. Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals said, “The individual mandate is unconstitutional because, under [a previous ruling, National Federation of Independent Business v Sebelius], it finds no constitutional footing in either the Interstate Commerce Clause or the Necessary and Proper Clause.”
The ruling upholds a December 2018 US District Court decision in which Judge Reed O’Connor found that the individual mandate that most Americans must have health insurance or pay a fine was unconstitutional and that without it the ACA itself was invalid.
In sending the case back to a Texas district court, however, the federal panel is asking for a central question to be resolved: Whether the individual mandate is “severable” from the rest of the law, while the rest of the law can be left intact.
If the district court eventually decides that the individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the ACA, the entire law will likely be ruled invalid, and some 24 million Americans could lose health coverage.
“Today’s ruling is the result of the Trump administration and congressional Republicans attempting to make dangerous health policy using the courts since they failed to succeed in Congress,” House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Richard E. Neal (D-Mass.) said in a statement. “This is a blow to our nation’s health care system and the millions of Americans who have gained coverage and protections under the Affordable Care Act. Democrats will continue to fight to protect Americans’ access to quality, affordable care.”
Some groups are applauding the decision, though. The Citizens’ Council for Health Freedom (CCHF), which filed an amicus brief with the Fifth Circuit arguing against the ACA, said it wants more.
“We are pleased with the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling, but it didn’t go far enough,” said Twila Brase, president and cofounder of CCHF, in a statement. “The individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the 2,700-page Affordable Care Act, thus the court should have ruled that the entire law is invalid, as the lower district court found.
“As the Court notes in the first paragraph of the ruling, we argued in our Amicus Brief, filed jointly with the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, that the Act ‘has deprived patients nationwide of a competitive market for affordable high-deductible health insurance,’ leaving ‘patients with no alternative to ... skyrocketing premiums,’ “ Ms. Brase added. “Sending it back to the lower court, which already ruled the right way, continues to deprive citizens and patients of the affordable coverage that freedom from Obamacare would bring.”
Future uncertain
The ruling in Texas v Azar is not a surprise because, during oral arguments in July, as reported by Medscape Medical News, at least two of the three judges – Jennifer Walker Elrod, appointed by President George W. Bush in 2007, and Kurt Engelhardt, appointed by President Donald J. Trump in 2018 – appeared to be more receptive to the arguments of a group of 18 Republican states and two individuals seeking to invalidate the ACA.
Judge Carolyn Dineen King, appointed by President Jimmy Carter in 1979, did not comment during the hearing.
The Trump administration chose not to defend the ACA, but it does not seem entirely prepared for what might happen if the law is overturned. In a briefing before the Fifth Circuit hearing, the administration argued that, if ultimately the law is ruled unconstitutional, it should be struck down only in the states seeking to overturn the law.
“A lot of this has to get sorted out – it’s complicated,” said August E. Flentje, a U.S. Department of Justice lawyer, at the oral arguments in July.
For now, though, the ACA remains.
“In 2012, the Supreme Court upheld Obamacare, despite serious constitutional issues with the federal government forcing Americans to purchase a product from a private company. Until an ultimate decision is made by the Supreme Court or Congress decides otherwise, the Affordable Care Act will remain the law of the land,” Senate Finance Committee Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), said in a statement.
And those who have led the court battle to keep the ACA intact plan to keep fighting. “For now, the President got the gift he wanted – uncertainty in the health care system and a pathway to repeal – so that the health care that seniors, workers, and families secured under the Affordable Care Act can be yanked from under them. This decision could take us to a dangerous and irresponsible place, not just for the 133 million Americans with pre-existing conditions, but for our seniors who use Medicare, our children under the age of 26, and the 20 million additional Americans covered directly through the ACA marketplace. California will move swiftly to challenge this decision because this could mean the difference between life and death for so many Americans and their families,” California Attorney General Xavier Becerra said in a statement.
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
A federal appeals court ruled Dec. 18 that the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is unconstitutional, but the panel sent the case back to a lower court to decide how much of the remainder of the law could topple along with it.
The three-judge panel of the New Orleans-based U.S. Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals said, “The individual mandate is unconstitutional because, under [a previous ruling, National Federation of Independent Business v Sebelius], it finds no constitutional footing in either the Interstate Commerce Clause or the Necessary and Proper Clause.”
The ruling upholds a December 2018 US District Court decision in which Judge Reed O’Connor found that the individual mandate that most Americans must have health insurance or pay a fine was unconstitutional and that without it the ACA itself was invalid.
In sending the case back to a Texas district court, however, the federal panel is asking for a central question to be resolved: Whether the individual mandate is “severable” from the rest of the law, while the rest of the law can be left intact.
If the district court eventually decides that the individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the ACA, the entire law will likely be ruled invalid, and some 24 million Americans could lose health coverage.
“Today’s ruling is the result of the Trump administration and congressional Republicans attempting to make dangerous health policy using the courts since they failed to succeed in Congress,” House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Richard E. Neal (D-Mass.) said in a statement. “This is a blow to our nation’s health care system and the millions of Americans who have gained coverage and protections under the Affordable Care Act. Democrats will continue to fight to protect Americans’ access to quality, affordable care.”
Some groups are applauding the decision, though. The Citizens’ Council for Health Freedom (CCHF), which filed an amicus brief with the Fifth Circuit arguing against the ACA, said it wants more.
“We are pleased with the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling, but it didn’t go far enough,” said Twila Brase, president and cofounder of CCHF, in a statement. “The individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the 2,700-page Affordable Care Act, thus the court should have ruled that the entire law is invalid, as the lower district court found.
“As the Court notes in the first paragraph of the ruling, we argued in our Amicus Brief, filed jointly with the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, that the Act ‘has deprived patients nationwide of a competitive market for affordable high-deductible health insurance,’ leaving ‘patients with no alternative to ... skyrocketing premiums,’ “ Ms. Brase added. “Sending it back to the lower court, which already ruled the right way, continues to deprive citizens and patients of the affordable coverage that freedom from Obamacare would bring.”
Future uncertain
The ruling in Texas v Azar is not a surprise because, during oral arguments in July, as reported by Medscape Medical News, at least two of the three judges – Jennifer Walker Elrod, appointed by President George W. Bush in 2007, and Kurt Engelhardt, appointed by President Donald J. Trump in 2018 – appeared to be more receptive to the arguments of a group of 18 Republican states and two individuals seeking to invalidate the ACA.
Judge Carolyn Dineen King, appointed by President Jimmy Carter in 1979, did not comment during the hearing.
The Trump administration chose not to defend the ACA, but it does not seem entirely prepared for what might happen if the law is overturned. In a briefing before the Fifth Circuit hearing, the administration argued that, if ultimately the law is ruled unconstitutional, it should be struck down only in the states seeking to overturn the law.
“A lot of this has to get sorted out – it’s complicated,” said August E. Flentje, a U.S. Department of Justice lawyer, at the oral arguments in July.
For now, though, the ACA remains.
“In 2012, the Supreme Court upheld Obamacare, despite serious constitutional issues with the federal government forcing Americans to purchase a product from a private company. Until an ultimate decision is made by the Supreme Court or Congress decides otherwise, the Affordable Care Act will remain the law of the land,” Senate Finance Committee Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), said in a statement.
And those who have led the court battle to keep the ACA intact plan to keep fighting. “For now, the President got the gift he wanted – uncertainty in the health care system and a pathway to repeal – so that the health care that seniors, workers, and families secured under the Affordable Care Act can be yanked from under them. This decision could take us to a dangerous and irresponsible place, not just for the 133 million Americans with pre-existing conditions, but for our seniors who use Medicare, our children under the age of 26, and the 20 million additional Americans covered directly through the ACA marketplace. California will move swiftly to challenge this decision because this could mean the difference between life and death for so many Americans and their families,” California Attorney General Xavier Becerra said in a statement.
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
A federal appeals court ruled Dec. 18 that the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) is unconstitutional, but the panel sent the case back to a lower court to decide how much of the remainder of the law could topple along with it.
The three-judge panel of the New Orleans-based U.S. Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals said, “The individual mandate is unconstitutional because, under [a previous ruling, National Federation of Independent Business v Sebelius], it finds no constitutional footing in either the Interstate Commerce Clause or the Necessary and Proper Clause.”
The ruling upholds a December 2018 US District Court decision in which Judge Reed O’Connor found that the individual mandate that most Americans must have health insurance or pay a fine was unconstitutional and that without it the ACA itself was invalid.
In sending the case back to a Texas district court, however, the federal panel is asking for a central question to be resolved: Whether the individual mandate is “severable” from the rest of the law, while the rest of the law can be left intact.
If the district court eventually decides that the individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the ACA, the entire law will likely be ruled invalid, and some 24 million Americans could lose health coverage.
“Today’s ruling is the result of the Trump administration and congressional Republicans attempting to make dangerous health policy using the courts since they failed to succeed in Congress,” House Ways and Means Committee Chairman Richard E. Neal (D-Mass.) said in a statement. “This is a blow to our nation’s health care system and the millions of Americans who have gained coverage and protections under the Affordable Care Act. Democrats will continue to fight to protect Americans’ access to quality, affordable care.”
Some groups are applauding the decision, though. The Citizens’ Council for Health Freedom (CCHF), which filed an amicus brief with the Fifth Circuit arguing against the ACA, said it wants more.
“We are pleased with the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling, but it didn’t go far enough,” said Twila Brase, president and cofounder of CCHF, in a statement. “The individual mandate cannot be severed from the rest of the 2,700-page Affordable Care Act, thus the court should have ruled that the entire law is invalid, as the lower district court found.
“As the Court notes in the first paragraph of the ruling, we argued in our Amicus Brief, filed jointly with the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, that the Act ‘has deprived patients nationwide of a competitive market for affordable high-deductible health insurance,’ leaving ‘patients with no alternative to ... skyrocketing premiums,’ “ Ms. Brase added. “Sending it back to the lower court, which already ruled the right way, continues to deprive citizens and patients of the affordable coverage that freedom from Obamacare would bring.”
Future uncertain
The ruling in Texas v Azar is not a surprise because, during oral arguments in July, as reported by Medscape Medical News, at least two of the three judges – Jennifer Walker Elrod, appointed by President George W. Bush in 2007, and Kurt Engelhardt, appointed by President Donald J. Trump in 2018 – appeared to be more receptive to the arguments of a group of 18 Republican states and two individuals seeking to invalidate the ACA.
Judge Carolyn Dineen King, appointed by President Jimmy Carter in 1979, did not comment during the hearing.
The Trump administration chose not to defend the ACA, but it does not seem entirely prepared for what might happen if the law is overturned. In a briefing before the Fifth Circuit hearing, the administration argued that, if ultimately the law is ruled unconstitutional, it should be struck down only in the states seeking to overturn the law.
“A lot of this has to get sorted out – it’s complicated,” said August E. Flentje, a U.S. Department of Justice lawyer, at the oral arguments in July.
For now, though, the ACA remains.
“In 2012, the Supreme Court upheld Obamacare, despite serious constitutional issues with the federal government forcing Americans to purchase a product from a private company. Until an ultimate decision is made by the Supreme Court or Congress decides otherwise, the Affordable Care Act will remain the law of the land,” Senate Finance Committee Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), said in a statement.
And those who have led the court battle to keep the ACA intact plan to keep fighting. “For now, the President got the gift he wanted – uncertainty in the health care system and a pathway to repeal – so that the health care that seniors, workers, and families secured under the Affordable Care Act can be yanked from under them. This decision could take us to a dangerous and irresponsible place, not just for the 133 million Americans with pre-existing conditions, but for our seniors who use Medicare, our children under the age of 26, and the 20 million additional Americans covered directly through the ACA marketplace. California will move swiftly to challenge this decision because this could mean the difference between life and death for so many Americans and their families,” California Attorney General Xavier Becerra said in a statement.
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Melanoma In Situ Within a Port-Wine Stain
To the Editor:
Port-wine stains (PWSs) are the most common type of vascular malformations. Patients rarely develop cancers in the overlying skin. However, we describe a case of melanoma in situ occurring within a long-standing facial PWS.
A 60-year-old white man with a history of a large unilateral facial PWS covering the right ear, lateral cheek, jaw, and neck presented to clinic with a new dark lesion on the right ear that had been growing for a few weeks or more. His PWS had been previously treated intermittently with a pulsed dye laser (PDL) for decades with variable improvement. He had not undergone any laser procedures in the last 8 months but wanted to restart treatment with the PDL. Upon further discussion, he reported a new darker area on the right earlobe that was growing. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer and was otherwise healthy. Physical examination revealed a large red vascular patch encompassing the ear, cheek, chin, and lateral neck. Within the PWS there was a black and dark brown patch with irregular borders on the right earlobe (Figure 1A). A shave biopsy was performed for histopathologic examination. The biopsy showed a confluent proliferation of atypical melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction extending down adnexal structures (Figure 2A) that stained positive for MART-1/Melan-A (Figure 2B). In the dermis, solar elastosis and prominent dilated and thin-walled vessels were present. These findings were consistent with a melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, overlying a capillary malformation.
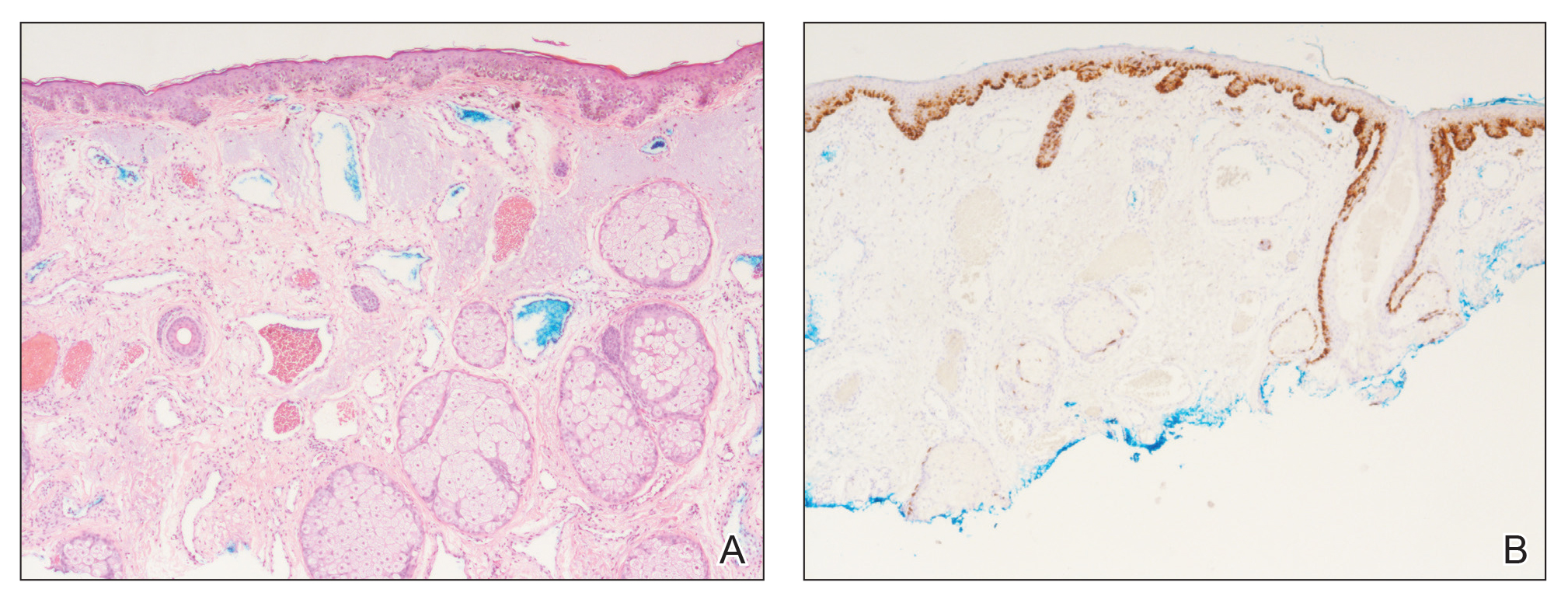
The patient underwent a wedge excision of the lesion with 5-mm margins, resulting in a final postoperative size of 2.5×3.5 cm. There was no excessive bleeding with surgery. A delayed repair was done after clear margins were confirmed by pathology (Figure 1B).
Port-wine stains are congenital vascular malformations that affect approximately 0.3% of individuals.1 Most are located on the head and neck along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. Cases are thought to occur sporadically, with recent evidence for somatic GNAQ mutations in both nonsyndromic cases and in Sturge-Weber syndrome.2 These lesions become progressively larger with time due to dilation of the capillary proliferation.3 Melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, usually affects white men in the sixth and seventh decades of life. It commonly arises on skin with chronic sun damage, particularly on the head and neck.4
Although uncommon, skin cancers have been known to arise in PWSs. Reports of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) and squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) have been published, but to date, there are no reports of melanoma or melanoma in situ arising in a PWS. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and port wine stain, squamous cell carcinoma and port wine stain, and basal cell carcinoma and port wine stain, fewer than 30 cases of BCCs in a PWS and only 4 cases of SCCs in a PWS have been documented, with 1 patient developing multiple BCCs and SCCs.1,5 Most BCCs (approximately 75%) and SCCs have been associated with historical treatments used to treat PWS before the development of laser therapy, such as grenz rays, topical thorium X, and other radiotherapy techniques.5,6 Interestingly, our patient’s PWS had only been treated with a PDL. Other risk factors for skin cancer in a PWS include sun exposure and smoking.5 There is no evidence that a PDL contributes to the development of skin cancer, but radiotherapy is a major factor.7
Treatment of these skin cancers is no different, with both Mohs micrographic surgery and standard excision used when appropriate. Despite the vascular nature of the lesion, there is only a minimal increase in bleeding risk.3 Most reports indicate no increase in perioperative bleeding.5,7 One case documented a hematoma developing postoperatively.6
This case of melanoma in situ arising in a PWS expands the range of skin cancer types known to arise in these malformations. Because of the potential for skin cancer to develop in a PWS, it is important to routinely examine these vascular proliferations.
- Hackett CB, Langtry JA. Basal cell carcinoma of the ala nasi arising in a port wine stain treated using Mohs micrographic surgery and local flap reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:590-592.
- Shirley MD, Tang H, Gallione CJ, et al. Sturge-Weber syndrome and port-wine stains caused by somatic mutation in GNAQ. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1971-1979.
- Cerrati EW, O TM, Binetter D, et al. Surgical treatment of head and neck port-wine stains by means of a staged zonal approach. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;134:1003-1012.
- Kallini JR, Jain SK, Khachemoune A. Lentigo maligna: review of salient characteristics and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:473-480.
- Rajan N, Ryan J, Langtry JA. Squamous cell carcinoma arising within a facial port-wine stain treated by Mohs micrographic surgical excision. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:864-866.
- Silapunt S, Goldberg LH, Thurber M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising in a port-wine stain. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1241-1245.
- Jasim ZF, Woo WK, Walsh MY, et al. Multifocal basal cell carcinoma developing in a facial port wine stain treated with argon and pulsed dye laser: a possible role for previous radiotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1155-1157.
To the Editor:
Port-wine stains (PWSs) are the most common type of vascular malformations. Patients rarely develop cancers in the overlying skin. However, we describe a case of melanoma in situ occurring within a long-standing facial PWS.
A 60-year-old white man with a history of a large unilateral facial PWS covering the right ear, lateral cheek, jaw, and neck presented to clinic with a new dark lesion on the right ear that had been growing for a few weeks or more. His PWS had been previously treated intermittently with a pulsed dye laser (PDL) for decades with variable improvement. He had not undergone any laser procedures in the last 8 months but wanted to restart treatment with the PDL. Upon further discussion, he reported a new darker area on the right earlobe that was growing. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer and was otherwise healthy. Physical examination revealed a large red vascular patch encompassing the ear, cheek, chin, and lateral neck. Within the PWS there was a black and dark brown patch with irregular borders on the right earlobe (Figure 1A). A shave biopsy was performed for histopathologic examination. The biopsy showed a confluent proliferation of atypical melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction extending down adnexal structures (Figure 2A) that stained positive for MART-1/Melan-A (Figure 2B). In the dermis, solar elastosis and prominent dilated and thin-walled vessels were present. These findings were consistent with a melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, overlying a capillary malformation.


The patient underwent a wedge excision of the lesion with 5-mm margins, resulting in a final postoperative size of 2.5×3.5 cm. There was no excessive bleeding with surgery. A delayed repair was done after clear margins were confirmed by pathology (Figure 1B).
Port-wine stains are congenital vascular malformations that affect approximately 0.3% of individuals.1 Most are located on the head and neck along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. Cases are thought to occur sporadically, with recent evidence for somatic GNAQ mutations in both nonsyndromic cases and in Sturge-Weber syndrome.2 These lesions become progressively larger with time due to dilation of the capillary proliferation.3 Melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, usually affects white men in the sixth and seventh decades of life. It commonly arises on skin with chronic sun damage, particularly on the head and neck.4
Although uncommon, skin cancers have been known to arise in PWSs. Reports of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) and squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) have been published, but to date, there are no reports of melanoma or melanoma in situ arising in a PWS. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and port wine stain, squamous cell carcinoma and port wine stain, and basal cell carcinoma and port wine stain, fewer than 30 cases of BCCs in a PWS and only 4 cases of SCCs in a PWS have been documented, with 1 patient developing multiple BCCs and SCCs.1,5 Most BCCs (approximately 75%) and SCCs have been associated with historical treatments used to treat PWS before the development of laser therapy, such as grenz rays, topical thorium X, and other radiotherapy techniques.5,6 Interestingly, our patient’s PWS had only been treated with a PDL. Other risk factors for skin cancer in a PWS include sun exposure and smoking.5 There is no evidence that a PDL contributes to the development of skin cancer, but radiotherapy is a major factor.7
Treatment of these skin cancers is no different, with both Mohs micrographic surgery and standard excision used when appropriate. Despite the vascular nature of the lesion, there is only a minimal increase in bleeding risk.3 Most reports indicate no increase in perioperative bleeding.5,7 One case documented a hematoma developing postoperatively.6
This case of melanoma in situ arising in a PWS expands the range of skin cancer types known to arise in these malformations. Because of the potential for skin cancer to develop in a PWS, it is important to routinely examine these vascular proliferations.
To the Editor:
Port-wine stains (PWSs) are the most common type of vascular malformations. Patients rarely develop cancers in the overlying skin. However, we describe a case of melanoma in situ occurring within a long-standing facial PWS.
A 60-year-old white man with a history of a large unilateral facial PWS covering the right ear, lateral cheek, jaw, and neck presented to clinic with a new dark lesion on the right ear that had been growing for a few weeks or more. His PWS had been previously treated intermittently with a pulsed dye laser (PDL) for decades with variable improvement. He had not undergone any laser procedures in the last 8 months but wanted to restart treatment with the PDL. Upon further discussion, he reported a new darker area on the right earlobe that was growing. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer and was otherwise healthy. Physical examination revealed a large red vascular patch encompassing the ear, cheek, chin, and lateral neck. Within the PWS there was a black and dark brown patch with irregular borders on the right earlobe (Figure 1A). A shave biopsy was performed for histopathologic examination. The biopsy showed a confluent proliferation of atypical melanocytes along the dermoepidermal junction extending down adnexal structures (Figure 2A) that stained positive for MART-1/Melan-A (Figure 2B). In the dermis, solar elastosis and prominent dilated and thin-walled vessels were present. These findings were consistent with a melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, overlying a capillary malformation.


The patient underwent a wedge excision of the lesion with 5-mm margins, resulting in a final postoperative size of 2.5×3.5 cm. There was no excessive bleeding with surgery. A delayed repair was done after clear margins were confirmed by pathology (Figure 1B).
Port-wine stains are congenital vascular malformations that affect approximately 0.3% of individuals.1 Most are located on the head and neck along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. Cases are thought to occur sporadically, with recent evidence for somatic GNAQ mutations in both nonsyndromic cases and in Sturge-Weber syndrome.2 These lesions become progressively larger with time due to dilation of the capillary proliferation.3 Melanoma in situ, lentigo maligna type, usually affects white men in the sixth and seventh decades of life. It commonly arises on skin with chronic sun damage, particularly on the head and neck.4
Although uncommon, skin cancers have been known to arise in PWSs. Reports of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) and squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) have been published, but to date, there are no reports of melanoma or melanoma in situ arising in a PWS. According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms melanoma and port wine stain, squamous cell carcinoma and port wine stain, and basal cell carcinoma and port wine stain, fewer than 30 cases of BCCs in a PWS and only 4 cases of SCCs in a PWS have been documented, with 1 patient developing multiple BCCs and SCCs.1,5 Most BCCs (approximately 75%) and SCCs have been associated with historical treatments used to treat PWS before the development of laser therapy, such as grenz rays, topical thorium X, and other radiotherapy techniques.5,6 Interestingly, our patient’s PWS had only been treated with a PDL. Other risk factors for skin cancer in a PWS include sun exposure and smoking.5 There is no evidence that a PDL contributes to the development of skin cancer, but radiotherapy is a major factor.7
Treatment of these skin cancers is no different, with both Mohs micrographic surgery and standard excision used when appropriate. Despite the vascular nature of the lesion, there is only a minimal increase in bleeding risk.3 Most reports indicate no increase in perioperative bleeding.5,7 One case documented a hematoma developing postoperatively.6
This case of melanoma in situ arising in a PWS expands the range of skin cancer types known to arise in these malformations. Because of the potential for skin cancer to develop in a PWS, it is important to routinely examine these vascular proliferations.
- Hackett CB, Langtry JA. Basal cell carcinoma of the ala nasi arising in a port wine stain treated using Mohs micrographic surgery and local flap reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:590-592.
- Shirley MD, Tang H, Gallione CJ, et al. Sturge-Weber syndrome and port-wine stains caused by somatic mutation in GNAQ. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1971-1979.
- Cerrati EW, O TM, Binetter D, et al. Surgical treatment of head and neck port-wine stains by means of a staged zonal approach. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;134:1003-1012.
- Kallini JR, Jain SK, Khachemoune A. Lentigo maligna: review of salient characteristics and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:473-480.
- Rajan N, Ryan J, Langtry JA. Squamous cell carcinoma arising within a facial port-wine stain treated by Mohs micrographic surgical excision. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:864-866.
- Silapunt S, Goldberg LH, Thurber M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising in a port-wine stain. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1241-1245.
- Jasim ZF, Woo WK, Walsh MY, et al. Multifocal basal cell carcinoma developing in a facial port wine stain treated with argon and pulsed dye laser: a possible role for previous radiotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1155-1157.
- Hackett CB, Langtry JA. Basal cell carcinoma of the ala nasi arising in a port wine stain treated using Mohs micrographic surgery and local flap reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:590-592.
- Shirley MD, Tang H, Gallione CJ, et al. Sturge-Weber syndrome and port-wine stains caused by somatic mutation in GNAQ. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1971-1979.
- Cerrati EW, O TM, Binetter D, et al. Surgical treatment of head and neck port-wine stains by means of a staged zonal approach. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;134:1003-1012.
- Kallini JR, Jain SK, Khachemoune A. Lentigo maligna: review of salient characteristics and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:473-480.
- Rajan N, Ryan J, Langtry JA. Squamous cell carcinoma arising within a facial port-wine stain treated by Mohs micrographic surgical excision. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:864-866.
- Silapunt S, Goldberg LH, Thurber M, et al. Basal cell carcinoma arising in a port-wine stain. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1241-1245.
- Jasim ZF, Woo WK, Walsh MY, et al. Multifocal basal cell carcinoma developing in a facial port wine stain treated with argon and pulsed dye laser: a possible role for previous radiotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:1155-1157.
Practice Points
- Nonmelanoma skin cancer is known to develop in port-wine stains, most commonly basal cell carcinoma.
- The range of skin cancer types known to arise in these malformations can be expanded to include melanoma in situ.
- It is important to routinely examine these vascular proliferations for new lesions.
Make the Diagnosis
A skin biopsy of one of the lesions showed granulomatous inflammation composed of lymphocytes, macrophages, and giant cells around hair follicles with negative mycobacterium stains and fungal stains, consistent with granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Tissue cultures from a skin biopsy for aerobic bacteria, mycobacteria, and fungus all were negative.
The patient initially was treated with erythromycin, but after 2 weeks, he reported abdominal pain and nausea and was unable to tolerate the medication. He was switched to clarithromycin, which he took for 6 weeks with clearance of the lesions.
A year later, some of the lesions recurred. He was treated again with clarithromycin and the lesions resolved.
Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (CGPD) is a benign skin eruption that occurs in prepubertal children. It also has been called facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption (FACE), and it tends to occur most commonly in children of darker skin types.1 but there are some cases reported of extra facial involvement.2 The lesions usually are not symptomatic, and they are more common in boys. The cause of this condition is not known, but possible triggers could include prior exposure to topical and systemic corticosteroids, as well as exposure to certain allergens such as formaldehyde.1
In histopathology, the lesions are characterized by granulomatous infiltrates around the hair follicles and the upper dermis. The granulomas are formed of macrophages, lymphocytes, and giant cell, as were seen in our patient.3
Several conditions can look very similar to CGPD; these include sarcoidosis, lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and granulomatous rosacea.
Sarcoidosis is a rare condition in children, and the lesions can be similar to the ones seen in our patient. Patients with sarcoidosis usually present with other systemic symptoms including fever, weight loss, respiratory symptoms, and fatigue; none of these were seen in our patient. Under the microscope, the lesions are characterized by “naked granulomas” instead of the inflammatory granulomas seen on our patient.
Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is a rare inflammatory skin condition commonly seen in young adults and is thought to be a variant of rosacea. It is characterized by skin-color to pink to yellow dome-shaped papules on the central face. Histologically, the lesions present as dermal epithelioid cell granulomas with central necrosis and surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells.4
Granulomatous rosacea and CGPD are considered two separate entities. Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a more chronic course, is not that common in children, and clinically presents with pustules, papules, and cysts around the eyes and cheeks.
Infectious processes like tuberculosis and fungal infections were ruled out in our patient with cultures and histopathology. Allergic contact dermatitis on the face can present with skin-color to pink papules, but they usually are very pruritic and improve with topical corticosteroids, while these medications can worsen CGPD.
CGPD can be a self-limiting condition. When mild, it can be treated with topical metronidazole, topical erythromycin, topical clindamycin solution, or pimecrolimus. Our patient failed treatment with pimecrolimus. For severe presentations, oral tetracyclines, erythromycin, and other macrolides, metronidazole, and oral isotretinoin can help clear the lesions.5
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Ann Dermatol. 2011 Aug;23(3):386-8.
2. Int J Dermatol. 2007 Feb;46(2):143-5.
3. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009 Feb 28;13(2):115-8.
4. An Bras Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;92(6):851-3.
5. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jan-Feb; 9(1):68-70.
A skin biopsy of one of the lesions showed granulomatous inflammation composed of lymphocytes, macrophages, and giant cells around hair follicles with negative mycobacterium stains and fungal stains, consistent with granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Tissue cultures from a skin biopsy for aerobic bacteria, mycobacteria, and fungus all were negative.
The patient initially was treated with erythromycin, but after 2 weeks, he reported abdominal pain and nausea and was unable to tolerate the medication. He was switched to clarithromycin, which he took for 6 weeks with clearance of the lesions.
A year later, some of the lesions recurred. He was treated again with clarithromycin and the lesions resolved.
Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (CGPD) is a benign skin eruption that occurs in prepubertal children. It also has been called facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption (FACE), and it tends to occur most commonly in children of darker skin types.1 but there are some cases reported of extra facial involvement.2 The lesions usually are not symptomatic, and they are more common in boys. The cause of this condition is not known, but possible triggers could include prior exposure to topical and systemic corticosteroids, as well as exposure to certain allergens such as formaldehyde.1
In histopathology, the lesions are characterized by granulomatous infiltrates around the hair follicles and the upper dermis. The granulomas are formed of macrophages, lymphocytes, and giant cell, as were seen in our patient.3
Several conditions can look very similar to CGPD; these include sarcoidosis, lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and granulomatous rosacea.
Sarcoidosis is a rare condition in children, and the lesions can be similar to the ones seen in our patient. Patients with sarcoidosis usually present with other systemic symptoms including fever, weight loss, respiratory symptoms, and fatigue; none of these were seen in our patient. Under the microscope, the lesions are characterized by “naked granulomas” instead of the inflammatory granulomas seen on our patient.
Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is a rare inflammatory skin condition commonly seen in young adults and is thought to be a variant of rosacea. It is characterized by skin-color to pink to yellow dome-shaped papules on the central face. Histologically, the lesions present as dermal epithelioid cell granulomas with central necrosis and surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells.4
Granulomatous rosacea and CGPD are considered two separate entities. Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a more chronic course, is not that common in children, and clinically presents with pustules, papules, and cysts around the eyes and cheeks.
Infectious processes like tuberculosis and fungal infections were ruled out in our patient with cultures and histopathology. Allergic contact dermatitis on the face can present with skin-color to pink papules, but they usually are very pruritic and improve with topical corticosteroids, while these medications can worsen CGPD.
CGPD can be a self-limiting condition. When mild, it can be treated with topical metronidazole, topical erythromycin, topical clindamycin solution, or pimecrolimus. Our patient failed treatment with pimecrolimus. For severe presentations, oral tetracyclines, erythromycin, and other macrolides, metronidazole, and oral isotretinoin can help clear the lesions.5
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Ann Dermatol. 2011 Aug;23(3):386-8.
2. Int J Dermatol. 2007 Feb;46(2):143-5.
3. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009 Feb 28;13(2):115-8.
4. An Bras Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;92(6):851-3.
5. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jan-Feb; 9(1):68-70.
A skin biopsy of one of the lesions showed granulomatous inflammation composed of lymphocytes, macrophages, and giant cells around hair follicles with negative mycobacterium stains and fungal stains, consistent with granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Tissue cultures from a skin biopsy for aerobic bacteria, mycobacteria, and fungus all were negative.
The patient initially was treated with erythromycin, but after 2 weeks, he reported abdominal pain and nausea and was unable to tolerate the medication. He was switched to clarithromycin, which he took for 6 weeks with clearance of the lesions.
A year later, some of the lesions recurred. He was treated again with clarithromycin and the lesions resolved.
Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (CGPD) is a benign skin eruption that occurs in prepubertal children. It also has been called facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption (FACE), and it tends to occur most commonly in children of darker skin types.1 but there are some cases reported of extra facial involvement.2 The lesions usually are not symptomatic, and they are more common in boys. The cause of this condition is not known, but possible triggers could include prior exposure to topical and systemic corticosteroids, as well as exposure to certain allergens such as formaldehyde.1
In histopathology, the lesions are characterized by granulomatous infiltrates around the hair follicles and the upper dermis. The granulomas are formed of macrophages, lymphocytes, and giant cell, as were seen in our patient.3
Several conditions can look very similar to CGPD; these include sarcoidosis, lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and granulomatous rosacea.
Sarcoidosis is a rare condition in children, and the lesions can be similar to the ones seen in our patient. Patients with sarcoidosis usually present with other systemic symptoms including fever, weight loss, respiratory symptoms, and fatigue; none of these were seen in our patient. Under the microscope, the lesions are characterized by “naked granulomas” instead of the inflammatory granulomas seen on our patient.
Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is a rare inflammatory skin condition commonly seen in young adults and is thought to be a variant of rosacea. It is characterized by skin-color to pink to yellow dome-shaped papules on the central face. Histologically, the lesions present as dermal epithelioid cell granulomas with central necrosis and surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells.4
Granulomatous rosacea and CGPD are considered two separate entities. Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a more chronic course, is not that common in children, and clinically presents with pustules, papules, and cysts around the eyes and cheeks.
Infectious processes like tuberculosis and fungal infections were ruled out in our patient with cultures and histopathology. Allergic contact dermatitis on the face can present with skin-color to pink papules, but they usually are very pruritic and improve with topical corticosteroids, while these medications can worsen CGPD.
CGPD can be a self-limiting condition. When mild, it can be treated with topical metronidazole, topical erythromycin, topical clindamycin solution, or pimecrolimus. Our patient failed treatment with pimecrolimus. For severe presentations, oral tetracyclines, erythromycin, and other macrolides, metronidazole, and oral isotretinoin can help clear the lesions.5
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Ann Dermatol. 2011 Aug;23(3):386-8.
2. Int J Dermatol. 2007 Feb;46(2):143-5.
3. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009 Feb 28;13(2):115-8.
4. An Bras Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;92(6):851-3.
5. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018 Jan-Feb; 9(1):68-70.
An 8-year-old African American male presented to our pediatric dermatology clinic for evaluation of a 3-month history of flesh-colored bumps on the face. According to the patient's mother, the lesions started with small pimple-like lesions around the nose and then spread to the whole face. Some lesions were crusty and somewhat itchy. He was treated with cephalexin and pimecrolimus with no improvement. The mother was very concerned because the lesions were close to the eyes and spreading.
He had no fevers, arthritis, or upper respiratory or gastrointestinal symptoms. He recently came back from a trip to Africa to visit his family. No other family members were affected. He used some new soaps, sunscreens, and moisturizers while he was in Africa.
On physical examination, the boy was in no acute distress. He had multiple flesh-colored papules on the face, especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth, where some lesions appeared crusted. There were no other skin lesions elsewhere on his body. There was no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly.
Red lesion on back
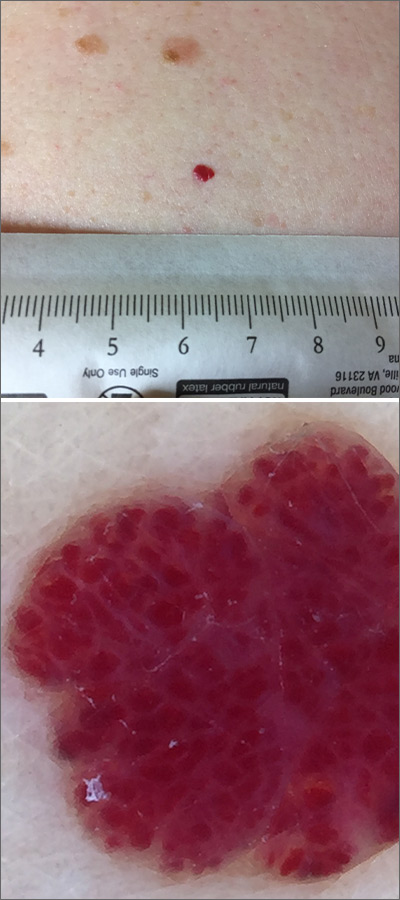
Dermoscopy was performed, which confirmed that this was a cherry angioma, also called a cherry hemangioma or Campbell de Morgan spot.
Cherry angiomas are benign proliferations that typically appear after age 30 as tiny bright erythematous macules that, over time, enlarge into papules. In their early, and smaller, stages they are typically maraschino cherry red, hence the name cherry angiomas. As they enlarge or become thrombosed, some lesions become darker red or even black in color. (The dermoscopy image shown here demonstrates the bright red globular red pattern that is classically seen with cherry angiomas.)
Cherry angiomas do not require treatment. If treatment is desired for cosmetic purposes, they can be treated with electrocautery, cryosurgery, or laser. The patient in this case was not worried about the appearance of the lesion and opted to leave it alone unless he developed symptoms.
Images and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

Dermoscopy was performed, which confirmed that this was a cherry angioma, also called a cherry hemangioma or Campbell de Morgan spot.
Cherry angiomas are benign proliferations that typically appear after age 30 as tiny bright erythematous macules that, over time, enlarge into papules. In their early, and smaller, stages they are typically maraschino cherry red, hence the name cherry angiomas. As they enlarge or become thrombosed, some lesions become darker red or even black in color. (The dermoscopy image shown here demonstrates the bright red globular red pattern that is classically seen with cherry angiomas.)
Cherry angiomas do not require treatment. If treatment is desired for cosmetic purposes, they can be treated with electrocautery, cryosurgery, or laser. The patient in this case was not worried about the appearance of the lesion and opted to leave it alone unless he developed symptoms.
Images and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

Dermoscopy was performed, which confirmed that this was a cherry angioma, also called a cherry hemangioma or Campbell de Morgan spot.
Cherry angiomas are benign proliferations that typically appear after age 30 as tiny bright erythematous macules that, over time, enlarge into papules. In their early, and smaller, stages they are typically maraschino cherry red, hence the name cherry angiomas. As they enlarge or become thrombosed, some lesions become darker red or even black in color. (The dermoscopy image shown here demonstrates the bright red globular red pattern that is classically seen with cherry angiomas.)
Cherry angiomas do not require treatment. If treatment is desired for cosmetic purposes, they can be treated with electrocautery, cryosurgery, or laser. The patient in this case was not worried about the appearance of the lesion and opted to leave it alone unless he developed symptoms.
Images and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.