User login
HIV shortens life expectancy 9 years, healthy life expectancy 16 years
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
Despite highly effective antiretroviral therapy, HIV still shortens life expectancy by 9 years and healthy life expectancy free of comorbidities 16 years, according to a review of HIV patients and matched controls at Kaiser Permanente facilities in California and the mid-Atlantic states during 2000-2016.
The good news is that starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) when CD4 counts are 500 cells/mm3 or higher closes the mortality gap. People who do so can expect to live into their mid-80s, the same as people without HIV, and the years they can expect to be free of diabetes and cancer is catching up to uninfected people, although the gap for other comorbidities hasn’t changed and the overall comorbidity gap remains 16 years, according to the report, which was presented at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections
“We were excited about finding no difference in lifespan for people starting ART with high CD4 counts, but we were surprised by how wide the gap was for the number of comorbidity free years. Greater attention to comorbidity prevention is needed,” said study lead Julia Marcus, PhD, an infectious disease epidemiologist and assistant professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The team estimated the average number of total and comorbidity-free years of life remaining at age 21 for 39,000 people with HIV who were matched 1:10 with 387,767 uninfected adults by sex, race/ethnicity, year, and medical center.
Overall, adults with HIV could expect to live until they were 77 years old, versus 86 years for people without HIV, during 2014-2016. It’s a large improvement over the 22 year gap during 2000-2003, when the numbers were 59 versus 81 years, respectively, Dr. Marcus reported at the virtual meeting, which was scheduled to be in Boston, but held online this year because of concerns about spreading the COVID-19 virus.
But the overall comorbidity gap didn’t budge during 2000-2016. People with HIV during 2014-2016 could expect to be comorbidity free until age 36 years, versus 52 years for the general population, the same 16-year difference during 2000-2003, when the numbers were age 32 versus age 48 years.
During 2014-2016, liver disease came 24 years sooner with HIV, and chronic kidney disease 17 years, chronic lung disease 16 years, cancer 9 years, and diabetes and cancer both 8 years sooner. Early ART didn’t narrow the gap for most comorbidities. Dr. Marcus didn’t address the reasons for the differences, except to note that “smoking rates were definitely higher among people with HIV.”
The results weren’t broken down by sex, but the majority of subjects, 88%, were men. The mean age was 41 years, and about half were white, with most of the rest either black or Hispanic. Transmission was among men who have sex with men in 70% of the cases, heterosexual sex in 20%, and IV drug accounted for the rest. Almost a third of the subjects started ART with CD4 counts at or above 500 cells/mm3.
Dr. Marcus said the results are likely generalizable to most insured people with HIV, but also that comorbidity screening might be higher in the HIV population, which could have affected the results.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Marcus is an adviser for Gilead.
SOURCE: Marcus JL et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 151.
FROM CROI 2020
Physicians pessimistic despite increased COVID-19 test kits
according to a survey.
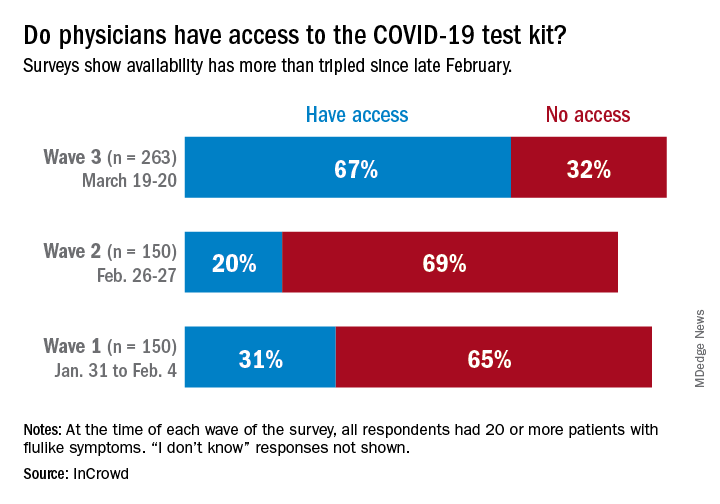
One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
according to a survey.

One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
according to a survey.

One positive finding from the physicians who participated in this survey March 19-20 was that the availability of COVID-19 test kits has more than doubled since late February.
Reported access to test kits went from 31% in the first wave of a series of surveys (Jan. 31–Feb. 4), down to 20% in the second (Feb. 26-27), and then jumped to 67% by the third wave (March 19-20), InCrowd reported March 26.
Views on several other COVID-related topics were negative among the majority of responding physicians – all of whom had or were currently treating 20 or more patients with flu-like symptoms at the time of the survey.
“Their frustrations and concerns about their ability to protect themselves while meeting upcoming patient care levels has increased significantly in the last 3 months,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, CEO and president of InCrowd, said in a written statement.
In the third wave, 78% of respondents were “concerned for the safety of loved ones due to my exposure as a physician to COVID-19” and only 16% believed that their facility was “staffed adequately to treat the influx of patients anticipated in the next 30 days,” InCrowd said.
One primary care physician from California elaborated on the issue of safety equipment: “First, [the CDC] said we need N95 masks and other masks would not protect us. As those are running out then they said just use regular surgical masks. Now they are saying use bandannas and scarves! It’s like they don’t care about the safety of the people who will be treating the ill! We don’t want to bring it home to our families!”
“Overall, morale appears low, with few optimistic about the efficacy of public-private collaboration (21%), their own safety given current PPE [personal protective equipment] supply (13%), and the U.S.’s ability to ‘flatten the curve’ (12%),” InCrowd noted in the report.
The first two waves each had 150 respondents, but the number increased to 263 for wave 3, with similar proportions – about 50% emergency medicine or critical care specialists, 25% pediatricians, and 25% primary care physicians – in all three.
Keep calm: Under 25s with diabetes aren't being hospitalized for COVID-19
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Reports from pediatric endocrinologists in COVID-19 hot spots globally indicate that children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes have so far not shown a different disease pattern with the virus compared to children and younger people who do not have diabetes.
Indeed, to date [as of March 24]” according to a new statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD), which currently has about 1,300 members around the globe and has instituted a discussion forum about the topic of treating children with both diabetes and COVID-19.
“We find these reports [from colleagues around the world], though anecdotal, to be reassuring,” it notes. However, there are real worries regarding other potentially dangerous effects. ISPAD has expressed concern, for example, that the COVID-19 pandemic will prevent youngsters with existing diabetes who are having diabetic emergencies from seeking hospital care.
Chinese physicians have reported to ISPAD a number of cases of delayed hospital admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children with known type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Andrea Scaramuzza, MD, a pediatric endocrinologist at Ospedale Maggiore di Cremona, Italy, has similarly reported multiple cases of patients presenting to emergency services there with severe DKA.
“These experiences reinforce the importance of continued attentiveness to standard diabetes care to avoid the need for hospitalization and emergency or urgent care visits,” says ISPAD, under the strapline: “Keep calm and mind your diabetes care.”
But it nevertheless stresses that these resources should be used “if needed.”
Worries that new-onset diabetes will be missed during COVID-19
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that there also are concerns regarding delays in diagnoses of new cases of type 1 diabetes “due to the fear families have to go to the emergency department because of COVID-19.”
Indeed, in Italy, a few patients have arrived with very serious DKA, he said. Dr. Scaramuzza noted a colleague from Naples, Dario Iafusco, MD, and colleagues have made a video to keep awareness high regarding new-onset diabetes.
“This coronavirus pandemic can be defeated if you stay at home, but if you know of a child who has excessive thirst, frequent urination, or who starts vomiting,” seek health care advice immediately. “This child could have [type 1] diabetes. Prevent severe DKA, or worse, death,” Dr. Iafusco of the Regional Centre of Paediatric Diabetology G.Stoppoloni Via S. Andrea delle Dame, Naples, said in the video.
Physicians from China have similar observations, reporting to ISPAD several cases of delayed admissions of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes because hospital services were closed for non–COVID-19 care.
Keep calm and mind your diabetes care; physicians use telemedicine
Meanwhile, last week ISPAD issued guidance for young people with diabetes and their carers about what to do if COVID-19 infection is suspected.
Most advice is the same as for the general public because reports of COVID-19 infection suggest it is much less severe in children and adolescents, and the summary currently serves “as reassurance that youth with diabetes are not more affected by COVID-19 than peers,” it adds.
“Our approach to treating a child with diabetes would be to follow the ISPAD sick-day guidelines, which provide generalized diabetes management in any flu-like illness. We wouldn’t do anything very different right now,” one of the authors, Jamie Wood, MD, associate professor of clinical pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“Any illness makes diabetes more difficult to manage and can increase the risk of DKA,” she emphasized.
“We would reinforce frequent monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels, to never stop insulin – in fact, when most people are ill, the body is stressed and requires more insulin – and to stay hydrated and treat the underlying symptoms.”
And make sure to “treat the fever,” she stressed. “When patients with type 1 diabetes get fever, they have a tendency to make more ketones, so we recommend aggressive control of fever.”
ISPAD recommends young people aim to keep blood glucose levels between 4 and 10 mmol/L (72-180 mg/dL) and blood ketones below 0.6 mmol/L (10.8 mg/dL) during illness and to never stop insulin.
Guidance is provided on when to seek urgent specialist advice with possible referral to emergency care, for example, in cases in which the patient has DKA symptoms, such as persistent and/or worsened fruity breath odor or vomiting.
Dr. Scaramuzza said in an interview that, in Italy, he and his colleagues have increased their use of telemedicine to keep monitoring their patients with diabetes even from a distance and that it was working very well.
“Technology – such as downloading [records from] insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and the possibility to use Skype or other platforms – really helps,” he noted.
“There has been a rapid increase in telehealth as a way to continue to care for youth with diabetes and decrease risk for infection,” said ISPAD.
“Communication between patients, families, and health care teams is vitally important. Methods to do so that avoid visits to clinics or hospitals can provide needed diabetes advice and reduce risk for COVID-19 transmission.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Less pain with a cancer drug to treat anal HPV, but it’s expensive
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
FROM CROI 2020
Visceral fat predicts NAFLD fibrosis, progression in HIV
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
Increased visceral fat predicts both the presence of hepatic fibrosis in HIV patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and also its progression, according to a report at the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections.
Among 58 people with NAFLD and well-controlled HIV, mostly men, a “striking 43% had evidence of fibrosis” on liver biopsy, a quarter with severe stage 3 fibrosis. Visceral fat content on MRI predicted fibrosis (284 cm2 among fibrotic patients vs. 212 cm2 among nonfibrotic patients, P = .005), but body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, subcutaneous fat, and hepatic fat content did not, said investigators led by Lindsay Fourman, MD, an attending physician at the Neuroendocrine & Pituitary Tumor Clinical Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Among 24 subjects with a second liver biopsy a year later, 38% had fibrosis progression, more than half from no fibrosis at baseline. Baseline visceral fat (306 cm2 among progressors versus 212 cm2, P = .04) again predicted progression, after adjustment for baseline BMI, hepatic fat content, and NAFLD activity score.
For every 25 cm2 rise in baseline visceral fat, the team found a 40% increased odds of fibrosis progression (P = .03). Body mass index was stable among subjects, so progression was not related to sudden weight gain. Dr. Fourman noted that people with HIV can have normal BMIs, but still significant accumulation of visceral fat.
The mean rate of progression was 0.2 stages per year. “To put this into perspective, the rate of fibrosis progression among NAFLD in the general population has been quoted to be about 0.03 stages per year.” Among HIV patients, it’s “more than sixfold higher,” she said in a video presentation of her research at the meeting, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting due to concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
Overall, visceral adiposity is “a novel clinical predictor of accelerated” progression in people with HIV. “Therapies to reduce visceral fat may be particularly effective in HIV-associated NAFLD,” she said.
The findings come from a trial of one such therapy, the growth hormone releasing hormone analogue tesamorelin (Egrifta). It’s approved for reduction of excess abdominal fat in HIV patients with lipodystrophy. Dr. Fourman and her colleagues recently reported a more than 30% reduction in liver fat, versus placebo, among HIV patients with NAFLD after a year of treatment, and a lower rate of fibrosis progression at 10.5% versus 37.5% (Lancet HIV. 2019 Dec;6[12]:e821-30).
In their follow-up study reported at the meeting, people with fibrosis at baseline also had higher NAFLD activity scores (3.6 points vs. 2.0 points; P < .0001), as well as higher ALT (41 U/L vs. 23 U/L, P = .002) and AST levels (44 U/L vs. 24 U/L; P = .0003).
Baseline BMI, liver fat content, NAFLD activity score, liver enzymes, waist circumference, CD4 count, and HIV duration, a median of 16 years in the study, did not predict progression, but activity scores, hemoglobin A1C, and C-reactive protein increased as fibrosis progressed.
“We really can’t speak from our own data” if HIV regimens might have had a role in progression. Sixty-two percent of the subjects were on integrase inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors are associated with weight gain, but their effect on visceral weight gain is unclear, plus BMIs were stable. Also, there was no difference in HIV regimens among the more than 100 people screened for the study between those with NAFDL and those without.
The subjects were 54 years old, on average. The average liver fat content at baseline was about 14%, and average baseline BMI just over 30 kg/m2. In addition to the 62% on integrase inhibitors, 40% were on nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and 24% were on protease inhibitors.
The work was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Fourman is a paid consultant to Theratechnologies, maker of tesamorelin.
SOURCE: Fourman LT et al. CROI 2020, Abstract 128
FROM CROI 2020
FMT appears safe and effective for IBD patients with recurrent C. difficile
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) appears safe and effective for treating recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to an ongoing prospective trial.
Most patients were cured of C. difficile after one fecal transplant, reported Jessica Allegretti, MD, associate director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“[For patients without IBD], fecal microbiota transplantation has been shown to be very effective for the treatment of recurrent C. diff,” Dr. Allegretti said at the annual Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit.
But similar data for patients with IBD are scarce, and this knowledge gap has high clinical relevance, Dr. Allegretti said. She noted that C. difficile infections are eight times more common among patients with IBD, and risk of recurrence is increased 4.5-fold.
According to Dr. Allegretti, three small clinical trials have tested FMT for treating recurrent C. difficile infections in patients with IBD.
“[These studies were] somewhat prospective, but [data] mainly retrospectively collected, as they relied heavily on chart review for the assessment of IBD disease activity,” she said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility..
Across the trials, C. difficile infection cure rates were comparable with non-IBD cohorts; but disease flare rates ranged from 17.9% to 54%, which raised concern that FMT may trigger inflammation.
To investigate further, Dr. Allegretti and her colleagues designed a prospective trial that is set to enroll 50 patients with IBD. Among 37 patients treated to date, a slight majority were women (56.8%), about one-third had Crohn’s disease (37.8%), and two-thirds had ulcerative colitis (62.2%). The average baseline calprotectin level, which measures inflammation in the intestines, was 1,804.8 microg/g of feces, which is far above the upper limit of 50 microg/g.
“This is a very inflamed patient population,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Out of these 37 patients, 34 (92%) were cured of C. difficile infection after only one fecal transplant, and the remaining three patients were cured after a second FMT.
“They all did very well,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Concerning IBD clinical scores, all patients with Crohn’s disease either had unchanged or improved disease. Among those with ulcerative colitis, almost all had unchanged or improved disease, except for one patient who had a de novo flare.
Early microbiome analyses showed patients had increased alpha diversity and richness after FMT that was sustained through week 12. Because only three patients had recurrence, numbers were too small to generate predictive data based on relative abundance.
Dr. Allegretti continued her presentation with a review of FMT for IBD in general.
“For Crohn’s disease, the role [of microbiome manipulation] seems a bit more clear,” Dr. Allegretti said, considering multiple effective treatments that alter gut flora, such as antibiotics.
In contrast, the role for microbiome manipulation in treating ulcerative colitis “has remained a bit unclear,” she said. Although some probiotics appear effective for treating mild disease, other microbiome-altering treatments, such as diversion of fecal stream, antibiotics, and bowel rest, have fallen short.
Still, pooled data from four randomized clinical trials showed that FMT led to remission in 28% of patients with ulcerative colitis, compared with 9% who receive placebo.
“You may be thinking that seems a bit underwhelming compared to the 90% or so cure rate we get for C. diff trials,” Dr. Allegretti said. “However, if you look at our other biologic trials in IBD, 28% puts FMT on par with our other IBD therapies.”
According to Dr. Allegretti, at least three stool-based, FMT-like therapeutics are poised to become commercially available in the next few years for the treatment of C. difficile infection, including broad- and narrow-spectrum enema bags and oral capsules.
“I certainly think we will start to see off-label usage in our IBD patients, and we will start to have an easier and more systemic way of utilizing these microbiome-based therapies,” Dr. Allegretti said. “They will be coming to market, and when they do, whether or not we are allowed to still do traditional FMT in its current form remains unseen. The FDA may not allow us to do that in the future when we have an FDA-approved product.”Dr. Allegretti disclosed relationships with Merck, Openbiome, Finch Therapeutics, and others.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) appears safe and effective for treating recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to an ongoing prospective trial.
Most patients were cured of C. difficile after one fecal transplant, reported Jessica Allegretti, MD, associate director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“[For patients without IBD], fecal microbiota transplantation has been shown to be very effective for the treatment of recurrent C. diff,” Dr. Allegretti said at the annual Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit.
But similar data for patients with IBD are scarce, and this knowledge gap has high clinical relevance, Dr. Allegretti said. She noted that C. difficile infections are eight times more common among patients with IBD, and risk of recurrence is increased 4.5-fold.
According to Dr. Allegretti, three small clinical trials have tested FMT for treating recurrent C. difficile infections in patients with IBD.
“[These studies were] somewhat prospective, but [data] mainly retrospectively collected, as they relied heavily on chart review for the assessment of IBD disease activity,” she said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility..
Across the trials, C. difficile infection cure rates were comparable with non-IBD cohorts; but disease flare rates ranged from 17.9% to 54%, which raised concern that FMT may trigger inflammation.
To investigate further, Dr. Allegretti and her colleagues designed a prospective trial that is set to enroll 50 patients with IBD. Among 37 patients treated to date, a slight majority were women (56.8%), about one-third had Crohn’s disease (37.8%), and two-thirds had ulcerative colitis (62.2%). The average baseline calprotectin level, which measures inflammation in the intestines, was 1,804.8 microg/g of feces, which is far above the upper limit of 50 microg/g.
“This is a very inflamed patient population,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Out of these 37 patients, 34 (92%) were cured of C. difficile infection after only one fecal transplant, and the remaining three patients were cured after a second FMT.
“They all did very well,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Concerning IBD clinical scores, all patients with Crohn’s disease either had unchanged or improved disease. Among those with ulcerative colitis, almost all had unchanged or improved disease, except for one patient who had a de novo flare.
Early microbiome analyses showed patients had increased alpha diversity and richness after FMT that was sustained through week 12. Because only three patients had recurrence, numbers were too small to generate predictive data based on relative abundance.
Dr. Allegretti continued her presentation with a review of FMT for IBD in general.
“For Crohn’s disease, the role [of microbiome manipulation] seems a bit more clear,” Dr. Allegretti said, considering multiple effective treatments that alter gut flora, such as antibiotics.
In contrast, the role for microbiome manipulation in treating ulcerative colitis “has remained a bit unclear,” she said. Although some probiotics appear effective for treating mild disease, other microbiome-altering treatments, such as diversion of fecal stream, antibiotics, and bowel rest, have fallen short.
Still, pooled data from four randomized clinical trials showed that FMT led to remission in 28% of patients with ulcerative colitis, compared with 9% who receive placebo.
“You may be thinking that seems a bit underwhelming compared to the 90% or so cure rate we get for C. diff trials,” Dr. Allegretti said. “However, if you look at our other biologic trials in IBD, 28% puts FMT on par with our other IBD therapies.”
According to Dr. Allegretti, at least three stool-based, FMT-like therapeutics are poised to become commercially available in the next few years for the treatment of C. difficile infection, including broad- and narrow-spectrum enema bags and oral capsules.
“I certainly think we will start to see off-label usage in our IBD patients, and we will start to have an easier and more systemic way of utilizing these microbiome-based therapies,” Dr. Allegretti said. “They will be coming to market, and when they do, whether or not we are allowed to still do traditional FMT in its current form remains unseen. The FDA may not allow us to do that in the future when we have an FDA-approved product.”Dr. Allegretti disclosed relationships with Merck, Openbiome, Finch Therapeutics, and others.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) appears safe and effective for treating recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to an ongoing prospective trial.
Most patients were cured of C. difficile after one fecal transplant, reported Jessica Allegretti, MD, associate director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“[For patients without IBD], fecal microbiota transplantation has been shown to be very effective for the treatment of recurrent C. diff,” Dr. Allegretti said at the annual Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit.
But similar data for patients with IBD are scarce, and this knowledge gap has high clinical relevance, Dr. Allegretti said. She noted that C. difficile infections are eight times more common among patients with IBD, and risk of recurrence is increased 4.5-fold.
According to Dr. Allegretti, three small clinical trials have tested FMT for treating recurrent C. difficile infections in patients with IBD.
“[These studies were] somewhat prospective, but [data] mainly retrospectively collected, as they relied heavily on chart review for the assessment of IBD disease activity,” she said at the meeting sponsored by the American Gastroenterological Association and the European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility..
Across the trials, C. difficile infection cure rates were comparable with non-IBD cohorts; but disease flare rates ranged from 17.9% to 54%, which raised concern that FMT may trigger inflammation.
To investigate further, Dr. Allegretti and her colleagues designed a prospective trial that is set to enroll 50 patients with IBD. Among 37 patients treated to date, a slight majority were women (56.8%), about one-third had Crohn’s disease (37.8%), and two-thirds had ulcerative colitis (62.2%). The average baseline calprotectin level, which measures inflammation in the intestines, was 1,804.8 microg/g of feces, which is far above the upper limit of 50 microg/g.
“This is a very inflamed patient population,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Out of these 37 patients, 34 (92%) were cured of C. difficile infection after only one fecal transplant, and the remaining three patients were cured after a second FMT.
“They all did very well,” Dr. Allegretti said.
Concerning IBD clinical scores, all patients with Crohn’s disease either had unchanged or improved disease. Among those with ulcerative colitis, almost all had unchanged or improved disease, except for one patient who had a de novo flare.
Early microbiome analyses showed patients had increased alpha diversity and richness after FMT that was sustained through week 12. Because only three patients had recurrence, numbers were too small to generate predictive data based on relative abundance.
Dr. Allegretti continued her presentation with a review of FMT for IBD in general.
“For Crohn’s disease, the role [of microbiome manipulation] seems a bit more clear,” Dr. Allegretti said, considering multiple effective treatments that alter gut flora, such as antibiotics.
In contrast, the role for microbiome manipulation in treating ulcerative colitis “has remained a bit unclear,” she said. Although some probiotics appear effective for treating mild disease, other microbiome-altering treatments, such as diversion of fecal stream, antibiotics, and bowel rest, have fallen short.
Still, pooled data from four randomized clinical trials showed that FMT led to remission in 28% of patients with ulcerative colitis, compared with 9% who receive placebo.
“You may be thinking that seems a bit underwhelming compared to the 90% or so cure rate we get for C. diff trials,” Dr. Allegretti said. “However, if you look at our other biologic trials in IBD, 28% puts FMT on par with our other IBD therapies.”
According to Dr. Allegretti, at least three stool-based, FMT-like therapeutics are poised to become commercially available in the next few years for the treatment of C. difficile infection, including broad- and narrow-spectrum enema bags and oral capsules.
“I certainly think we will start to see off-label usage in our IBD patients, and we will start to have an easier and more systemic way of utilizing these microbiome-based therapies,” Dr. Allegretti said. “They will be coming to market, and when they do, whether or not we are allowed to still do traditional FMT in its current form remains unseen. The FDA may not allow us to do that in the future when we have an FDA-approved product.”Dr. Allegretti disclosed relationships with Merck, Openbiome, Finch Therapeutics, and others.
FROM GMFH 2020
Elderly Americans carry heavier opioid burden
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.
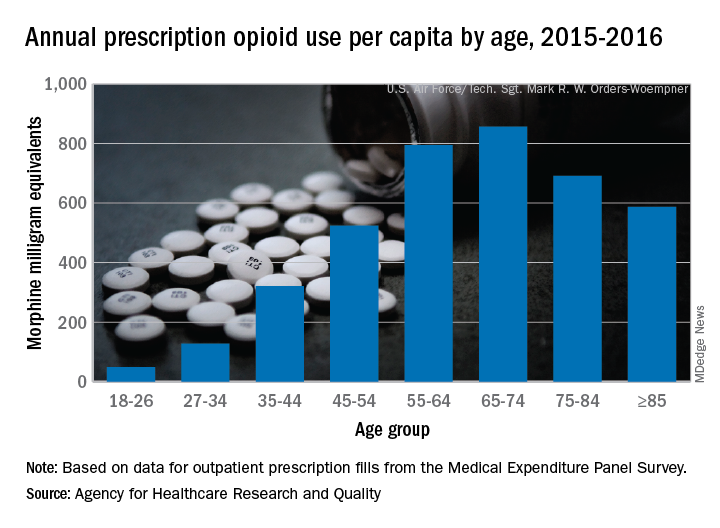
Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.

Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.

Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.
Focus groups seek transgender experience with HIV prevention
A pair of focus groups explored the experience of transgender patients with HIV prevention, finding many were discouraged by experiences of care that was not culturally competent and affirming.
The findings, including other important themes, were published in Pediatrics.
The pair of online asynchronous focus groups, conducted by Holly B. Fontenot, PhD, RN/NP, of the Fenway Institute in Boston, and colleagues, sought input from 30 transgender participants from across the United States. Eleven were aged 13-18 years, and 19 were aged 18-24 years, with an average age of 19. Most (70%) were white, and the remainder were African American (7%), Asian American (3%), multiracial (17%), and other (3%); 10% identified as Hispanic. Participants were given multiple options for reporting gender identity; 27% reported identifying as transgender males, 17% reported identifying as transgender females, and the rest identified with other terms, including 27% using one or more terms.
The quantitative analysis found four common themes, which the study explored in depth: “barriers to self-efficacy in sexual decision making; safety concerns, fear, and other challenges in forming romantic and/or sexual relationships; need for support and education; and desire for affirmative and culturally competent experiences and interactions.”
Based on their findings, the authors suggested ways of improving transgender youth experiences:
- Increasing provider knowledge and skills in providing affirming care through transgender health education programs.
- Addressing the barriers, such as stigma and lack of accessibility.
- Expanding sexual health education to be more inclusive regarding gender identities, sexual orientations, and definitions of sex.
Providers also need to include information on sexually transmitted infection and HIV prevention, including “discussion of safer sexual behaviors, negotiation and consent, sexual and physical assault, condoms, lubrication, STI and HIV testing, human papillomavirus vaccination, and PrEP [preexposure prophylaxis]” the authors emphasized.
Dr. Fontenot and associates determined that this study’s findings were consistent with what’s known about adult transgender patients, but this study provides more context regarding transgender youth experiences.
“It is important to elicit transgender youth experiences and perspectives related to HIV risk and preventive services,” they concluded. “This study provided a greater understanding of barriers to and facilitators of youth obtaining HIV preventive services and sexual health education.”
Limitations of the study included that non–English speaking participants were excluded, and that participants were predominantly white, non-Hispanic, and assigned female sex at birth.
This study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and NORC at The University of Chicago. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Fontenot HB et al., Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2204.
A pair of focus groups explored the experience of transgender patients with HIV prevention, finding many were discouraged by experiences of care that was not culturally competent and affirming.
The findings, including other important themes, were published in Pediatrics.
The pair of online asynchronous focus groups, conducted by Holly B. Fontenot, PhD, RN/NP, of the Fenway Institute in Boston, and colleagues, sought input from 30 transgender participants from across the United States. Eleven were aged 13-18 years, and 19 were aged 18-24 years, with an average age of 19. Most (70%) were white, and the remainder were African American (7%), Asian American (3%), multiracial (17%), and other (3%); 10% identified as Hispanic. Participants were given multiple options for reporting gender identity; 27% reported identifying as transgender males, 17% reported identifying as transgender females, and the rest identified with other terms, including 27% using one or more terms.
The quantitative analysis found four common themes, which the study explored in depth: “barriers to self-efficacy in sexual decision making; safety concerns, fear, and other challenges in forming romantic and/or sexual relationships; need for support and education; and desire for affirmative and culturally competent experiences and interactions.”
Based on their findings, the authors suggested ways of improving transgender youth experiences:
- Increasing provider knowledge and skills in providing affirming care through transgender health education programs.
- Addressing the barriers, such as stigma and lack of accessibility.
- Expanding sexual health education to be more inclusive regarding gender identities, sexual orientations, and definitions of sex.
Providers also need to include information on sexually transmitted infection and HIV prevention, including “discussion of safer sexual behaviors, negotiation and consent, sexual and physical assault, condoms, lubrication, STI and HIV testing, human papillomavirus vaccination, and PrEP [preexposure prophylaxis]” the authors emphasized.
Dr. Fontenot and associates determined that this study’s findings were consistent with what’s known about adult transgender patients, but this study provides more context regarding transgender youth experiences.
“It is important to elicit transgender youth experiences and perspectives related to HIV risk and preventive services,” they concluded. “This study provided a greater understanding of barriers to and facilitators of youth obtaining HIV preventive services and sexual health education.”
Limitations of the study included that non–English speaking participants were excluded, and that participants were predominantly white, non-Hispanic, and assigned female sex at birth.
This study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and NORC at The University of Chicago. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Fontenot HB et al., Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2204.
A pair of focus groups explored the experience of transgender patients with HIV prevention, finding many were discouraged by experiences of care that was not culturally competent and affirming.
The findings, including other important themes, were published in Pediatrics.
The pair of online asynchronous focus groups, conducted by Holly B. Fontenot, PhD, RN/NP, of the Fenway Institute in Boston, and colleagues, sought input from 30 transgender participants from across the United States. Eleven were aged 13-18 years, and 19 were aged 18-24 years, with an average age of 19. Most (70%) were white, and the remainder were African American (7%), Asian American (3%), multiracial (17%), and other (3%); 10% identified as Hispanic. Participants were given multiple options for reporting gender identity; 27% reported identifying as transgender males, 17% reported identifying as transgender females, and the rest identified with other terms, including 27% using one or more terms.
The quantitative analysis found four common themes, which the study explored in depth: “barriers to self-efficacy in sexual decision making; safety concerns, fear, and other challenges in forming romantic and/or sexual relationships; need for support and education; and desire for affirmative and culturally competent experiences and interactions.”
Based on their findings, the authors suggested ways of improving transgender youth experiences:
- Increasing provider knowledge and skills in providing affirming care through transgender health education programs.
- Addressing the barriers, such as stigma and lack of accessibility.
- Expanding sexual health education to be more inclusive regarding gender identities, sexual orientations, and definitions of sex.
Providers also need to include information on sexually transmitted infection and HIV prevention, including “discussion of safer sexual behaviors, negotiation and consent, sexual and physical assault, condoms, lubrication, STI and HIV testing, human papillomavirus vaccination, and PrEP [preexposure prophylaxis]” the authors emphasized.
Dr. Fontenot and associates determined that this study’s findings were consistent with what’s known about adult transgender patients, but this study provides more context regarding transgender youth experiences.
“It is important to elicit transgender youth experiences and perspectives related to HIV risk and preventive services,” they concluded. “This study provided a greater understanding of barriers to and facilitators of youth obtaining HIV preventive services and sexual health education.”
Limitations of the study included that non–English speaking participants were excluded, and that participants were predominantly white, non-Hispanic, and assigned female sex at birth.
This study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and NORC at The University of Chicago. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Fontenot HB et al., Pediatrics. 2020. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2204.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Guidelines on delaying cancer surgery during COVID-19
Cancer surgeries may need to be delayed as hospitals are forced to allocate resources to a surge of COVID-19 patients, says the American College of Surgeons, as it issues a new set of recommendations in reaction to the crisis.
Most surgeons have already curtailed or have ceased to perform elective operations, the ACS notes, and recommends that surgeons continue to do so in order to preserve the necessary resources for care of critically ill patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The new clinical guidance for elective surgical case triage during the pandemic includes recommendations for cancer surgery as well as for procedures that are specific to certain cancer types.
“These triage guidelines and joint recommendations are being issued as we appear to be entering a new phase of the COVID-19 pandemic with more hospitals facing a potential push beyond their resources to care for critically ill patients,” commented ACS Executive Director David B. Hoyt, MD, in a statement.
“ACS will continue to monitor the landscape for surgical care but we feel this guidance document provides a good foundation for surgeons to begin enacting these triage recommendations today to help them make the best decisions possible for their patients during COVID-19,” he said.
For cancer surgery, which is often not elective but essential to treatment, ACS has issued general guidance for triaging patients, taking into account the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation.
First, decisions about whether to proceed with elective surgeries must consider the available resources of local facilities. The parties responsible for preparing the facility to manage coronavirus patients should be sharing information at regular intervals about constraints on local resources, especially personal protective equipment (PPE), which is running low in many jurisdictions. For example, if an elective case has a high likelihood of needing postoperative ICU care, it is imperative to balance the risk of delay against the need of availability for patients with COVID-19.
Second, cancer care coordination should use virtual technologies as much as possible, and facilities with tumor boards may find it helpful to locate multidisciplinary experts by virtual means, to assist with decision making and establishing triage criteria.
Three Phases of Pandemic
The ACS has also organized decision making into three phases that reflect the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation:
- Phase I. Semi-Urgent Setting (Preparation Phase) – few COVID-19 patients, hospital resources not exhausted, institution still has ICU ventilator capacity and COVID-19 trajectory not in rapid escalation phase
- Phase II. Urgent Setting – many COVID-19 patients, ICU and ventilator capacity limited, operating room supplies limited
- Phase III. Hospital resources are all routed to COVID-19 patients, no ventilator or ICU capacity, operating room supplies exhausted; patients in whom death is likely within hours if surgery is deferred
Breast Cancer Surgery
The ACS also issued specific guidance for several tumor types, including guidance for breast cancer surgery.
For phase I, surgery should be restricted to patients who are likely to experience compromised survival if it is not performed within next 3 months. This includes patients completing neoadjuvant treatment, those with clinical stage T2 or N1 ERpos/PRpos/HER2-negative tumors, patients with triple negative or HER2-positive tumors, discordant biopsies that are likely to be malignant, and removal of a recurrent lesion.
Phase II would be restricted to patients whose survival is threatened if surgery is not performed within the next few days. These would include incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuating a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
In Phase III, surgical procedures would be restricted to patients who may not survive if surgery is not performed within a few hours. This includes incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuation of a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Guidance for colorectal cancer surgery is also split into the three phases of the pandemic.
Phase I would include cases needing surgical intervention as soon as feasible, while recognizing that the status of each hospital is likely to evolve over the next week or two. These patients would include those with nearly obstructing colon cancer or rectal cancer; cancers that require frequent transfusions; asymptomatic colon cancers; rectal cancers that do not respond to neoadjuvant chemoradiation; malignancies with a risk of local perforation and sepsis; and those with early stage rectal cancers that are not candidates for adjuvant therapy.
Phase II comprises patients needing surgery as soon as feasible, but recognizing that hospital status is likely to progress over the next few days. These cases include patients with a nearly obstructing colon cancer where stenting is not an option; those with nearly obstructing rectal cancer (should be diverted); cancers with high (inpatient) transfusion requirements; and cancers with pending evidence of local perforation and sepsis.
All colorectal procedures typically scheduled as routine should be delayed.
In Phase III, if the status of the facility is likely to progress within hours, the only surgery that should be performed would be for perforated, obstructed, or actively bleeding (inpatient transfusion dependent) cancers or those with sepsis. All other surgeries should be deferred.
Thoracic Cancer Surgery
Thoracic cancer surgery guidelines follow those for breast cancer. Phase I should be restricted to patients whose survival may be impacted if surgery is not performed within next 3 months. These include:
- Cases with solid or predominantly solid (>50%) lung cancer or presumed lung cancer (>2 cm), clinical node negative
- Node positive lung cancer
- Post-induction therapy cancer
- Esophageal cancer T1b or greater
- Chest wall tumors that are potentially aggressive and not manageable by alternative means
- Stenting for obstructing esophageal tumor
- Staging to start treatment (mediastinoscopy, diagnostic VATS for pleural dissemination)
- Symptomatic mediastinal tumors
- Patients who are enrolled in therapeutic clinical trials.
Phase II would permit surgery if survival will be impacted by a delay of a few days. These cases would include nonseptic perforated cancer of esophagus, a tumor-associated infection, and management of surgical complications in a hemodynamically stable patient.
All thoracic procedures considered to be routine/elective would be deferred.
Phase III restricts surgery to patients whose survival will be compromised if they do not undergo surgery within the next few hours. This group would include perforated cancer of esophagus in a septic patient, a patient with a threatened airway, sepsis associated with the cancer, and management of surgical complications in an unstable patient (active bleeding that requires surgery, dehiscence of airway, anastomotic leak with sepsis).
All other cases would be deferred.
Other Cancer Types
Although the ACS doesn’t have specific guidelines for all cancer types, a few are included in their general recommendations for the specialty.
For gynecologic surgeries, ACS lists cancer or suspected cancer as indications where significantly delayed surgery could cause “significant harm.”
Delays, in general, are not recommended for neurosurgery, which would include brain cancers. In pediatrics, most cancer surgery is considered “urgent,” where a delay of days to weeks could prove detrimental to the patient. This would comprise all solid tumors, including the initial biopsy and resection following neoadjuvant therapy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer surgeries may need to be delayed as hospitals are forced to allocate resources to a surge of COVID-19 patients, says the American College of Surgeons, as it issues a new set of recommendations in reaction to the crisis.
Most surgeons have already curtailed or have ceased to perform elective operations, the ACS notes, and recommends that surgeons continue to do so in order to preserve the necessary resources for care of critically ill patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The new clinical guidance for elective surgical case triage during the pandemic includes recommendations for cancer surgery as well as for procedures that are specific to certain cancer types.
“These triage guidelines and joint recommendations are being issued as we appear to be entering a new phase of the COVID-19 pandemic with more hospitals facing a potential push beyond their resources to care for critically ill patients,” commented ACS Executive Director David B. Hoyt, MD, in a statement.
“ACS will continue to monitor the landscape for surgical care but we feel this guidance document provides a good foundation for surgeons to begin enacting these triage recommendations today to help them make the best decisions possible for their patients during COVID-19,” he said.
For cancer surgery, which is often not elective but essential to treatment, ACS has issued general guidance for triaging patients, taking into account the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation.
First, decisions about whether to proceed with elective surgeries must consider the available resources of local facilities. The parties responsible for preparing the facility to manage coronavirus patients should be sharing information at regular intervals about constraints on local resources, especially personal protective equipment (PPE), which is running low in many jurisdictions. For example, if an elective case has a high likelihood of needing postoperative ICU care, it is imperative to balance the risk of delay against the need of availability for patients with COVID-19.
Second, cancer care coordination should use virtual technologies as much as possible, and facilities with tumor boards may find it helpful to locate multidisciplinary experts by virtual means, to assist with decision making and establishing triage criteria.
Three Phases of Pandemic
The ACS has also organized decision making into three phases that reflect the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation:
- Phase I. Semi-Urgent Setting (Preparation Phase) – few COVID-19 patients, hospital resources not exhausted, institution still has ICU ventilator capacity and COVID-19 trajectory not in rapid escalation phase
- Phase II. Urgent Setting – many COVID-19 patients, ICU and ventilator capacity limited, operating room supplies limited
- Phase III. Hospital resources are all routed to COVID-19 patients, no ventilator or ICU capacity, operating room supplies exhausted; patients in whom death is likely within hours if surgery is deferred
Breast Cancer Surgery
The ACS also issued specific guidance for several tumor types, including guidance for breast cancer surgery.
For phase I, surgery should be restricted to patients who are likely to experience compromised survival if it is not performed within next 3 months. This includes patients completing neoadjuvant treatment, those with clinical stage T2 or N1 ERpos/PRpos/HER2-negative tumors, patients with triple negative or HER2-positive tumors, discordant biopsies that are likely to be malignant, and removal of a recurrent lesion.
Phase II would be restricted to patients whose survival is threatened if surgery is not performed within the next few days. These would include incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuating a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
In Phase III, surgical procedures would be restricted to patients who may not survive if surgery is not performed within a few hours. This includes incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuation of a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Guidance for colorectal cancer surgery is also split into the three phases of the pandemic.
Phase I would include cases needing surgical intervention as soon as feasible, while recognizing that the status of each hospital is likely to evolve over the next week or two. These patients would include those with nearly obstructing colon cancer or rectal cancer; cancers that require frequent transfusions; asymptomatic colon cancers; rectal cancers that do not respond to neoadjuvant chemoradiation; malignancies with a risk of local perforation and sepsis; and those with early stage rectal cancers that are not candidates for adjuvant therapy.
Phase II comprises patients needing surgery as soon as feasible, but recognizing that hospital status is likely to progress over the next few days. These cases include patients with a nearly obstructing colon cancer where stenting is not an option; those with nearly obstructing rectal cancer (should be diverted); cancers with high (inpatient) transfusion requirements; and cancers with pending evidence of local perforation and sepsis.
All colorectal procedures typically scheduled as routine should be delayed.
In Phase III, if the status of the facility is likely to progress within hours, the only surgery that should be performed would be for perforated, obstructed, or actively bleeding (inpatient transfusion dependent) cancers or those with sepsis. All other surgeries should be deferred.
Thoracic Cancer Surgery
Thoracic cancer surgery guidelines follow those for breast cancer. Phase I should be restricted to patients whose survival may be impacted if surgery is not performed within next 3 months. These include:
- Cases with solid or predominantly solid (>50%) lung cancer or presumed lung cancer (>2 cm), clinical node negative
- Node positive lung cancer
- Post-induction therapy cancer
- Esophageal cancer T1b or greater
- Chest wall tumors that are potentially aggressive and not manageable by alternative means
- Stenting for obstructing esophageal tumor
- Staging to start treatment (mediastinoscopy, diagnostic VATS for pleural dissemination)
- Symptomatic mediastinal tumors
- Patients who are enrolled in therapeutic clinical trials.
Phase II would permit surgery if survival will be impacted by a delay of a few days. These cases would include nonseptic perforated cancer of esophagus, a tumor-associated infection, and management of surgical complications in a hemodynamically stable patient.
All thoracic procedures considered to be routine/elective would be deferred.
Phase III restricts surgery to patients whose survival will be compromised if they do not undergo surgery within the next few hours. This group would include perforated cancer of esophagus in a septic patient, a patient with a threatened airway, sepsis associated with the cancer, and management of surgical complications in an unstable patient (active bleeding that requires surgery, dehiscence of airway, anastomotic leak with sepsis).
All other cases would be deferred.
Other Cancer Types
Although the ACS doesn’t have specific guidelines for all cancer types, a few are included in their general recommendations for the specialty.
For gynecologic surgeries, ACS lists cancer or suspected cancer as indications where significantly delayed surgery could cause “significant harm.”
Delays, in general, are not recommended for neurosurgery, which would include brain cancers. In pediatrics, most cancer surgery is considered “urgent,” where a delay of days to weeks could prove detrimental to the patient. This would comprise all solid tumors, including the initial biopsy and resection following neoadjuvant therapy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer surgeries may need to be delayed as hospitals are forced to allocate resources to a surge of COVID-19 patients, says the American College of Surgeons, as it issues a new set of recommendations in reaction to the crisis.
Most surgeons have already curtailed or have ceased to perform elective operations, the ACS notes, and recommends that surgeons continue to do so in order to preserve the necessary resources for care of critically ill patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The new clinical guidance for elective surgical case triage during the pandemic includes recommendations for cancer surgery as well as for procedures that are specific to certain cancer types.
“These triage guidelines and joint recommendations are being issued as we appear to be entering a new phase of the COVID-19 pandemic with more hospitals facing a potential push beyond their resources to care for critically ill patients,” commented ACS Executive Director David B. Hoyt, MD, in a statement.
“ACS will continue to monitor the landscape for surgical care but we feel this guidance document provides a good foundation for surgeons to begin enacting these triage recommendations today to help them make the best decisions possible for their patients during COVID-19,” he said.
For cancer surgery, which is often not elective but essential to treatment, ACS has issued general guidance for triaging patients, taking into account the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation.
First, decisions about whether to proceed with elective surgeries must consider the available resources of local facilities. The parties responsible for preparing the facility to manage coronavirus patients should be sharing information at regular intervals about constraints on local resources, especially personal protective equipment (PPE), which is running low in many jurisdictions. For example, if an elective case has a high likelihood of needing postoperative ICU care, it is imperative to balance the risk of delay against the need of availability for patients with COVID-19.
Second, cancer care coordination should use virtual technologies as much as possible, and facilities with tumor boards may find it helpful to locate multidisciplinary experts by virtual means, to assist with decision making and establishing triage criteria.
Three Phases of Pandemic
The ACS has also organized decision making into three phases that reflect the acuity of the local COVID-19 situation:
- Phase I. Semi-Urgent Setting (Preparation Phase) – few COVID-19 patients, hospital resources not exhausted, institution still has ICU ventilator capacity and COVID-19 trajectory not in rapid escalation phase
- Phase II. Urgent Setting – many COVID-19 patients, ICU and ventilator capacity limited, operating room supplies limited
- Phase III. Hospital resources are all routed to COVID-19 patients, no ventilator or ICU capacity, operating room supplies exhausted; patients in whom death is likely within hours if surgery is deferred
Breast Cancer Surgery
The ACS also issued specific guidance for several tumor types, including guidance for breast cancer surgery.
For phase I, surgery should be restricted to patients who are likely to experience compromised survival if it is not performed within next 3 months. This includes patients completing neoadjuvant treatment, those with clinical stage T2 or N1 ERpos/PRpos/HER2-negative tumors, patients with triple negative or HER2-positive tumors, discordant biopsies that are likely to be malignant, and removal of a recurrent lesion.
Phase II would be restricted to patients whose survival is threatened if surgery is not performed within the next few days. These would include incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuating a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
In Phase III, surgical procedures would be restricted to patients who may not survive if surgery is not performed within a few hours. This includes incision and drainage of breast abscess, evacuation of a hematoma, revision of an ischemic mastectomy flap, and revascularization/revision of an autologous tissue flap (autologous reconstruction should be deferred).
Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Guidance for colorectal cancer surgery is also split into the three phases of the pandemic.
Phase I would include cases needing surgical intervention as soon as feasible, while recognizing that the status of each hospital is likely to evolve over the next week or two. These patients would include those with nearly obstructing colon cancer or rectal cancer; cancers that require frequent transfusions; asymptomatic colon cancers; rectal cancers that do not respond to neoadjuvant chemoradiation; malignancies with a risk of local perforation and sepsis; and those with early stage rectal cancers that are not candidates for adjuvant therapy.
Phase II comprises patients needing surgery as soon as feasible, but recognizing that hospital status is likely to progress over the next few days. These cases include patients with a nearly obstructing colon cancer where stenting is not an option; those with nearly obstructing rectal cancer (should be diverted); cancers with high (inpatient) transfusion requirements; and cancers with pending evidence of local perforation and sepsis.
All colorectal procedures typically scheduled as routine should be delayed.
In Phase III, if the status of the facility is likely to progress within hours, the only surgery that should be performed would be for perforated, obstructed, or actively bleeding (inpatient transfusion dependent) cancers or those with sepsis. All other surgeries should be deferred.
Thoracic Cancer Surgery
Thoracic cancer surgery guidelines follow those for breast cancer. Phase I should be restricted to patients whose survival may be impacted if surgery is not performed within next 3 months. These include:
- Cases with solid or predominantly solid (>50%) lung cancer or presumed lung cancer (>2 cm), clinical node negative
- Node positive lung cancer
- Post-induction therapy cancer
- Esophageal cancer T1b or greater
- Chest wall tumors that are potentially aggressive and not manageable by alternative means
- Stenting for obstructing esophageal tumor
- Staging to start treatment (mediastinoscopy, diagnostic VATS for pleural dissemination)
- Symptomatic mediastinal tumors
- Patients who are enrolled in therapeutic clinical trials.
Phase II would permit surgery if survival will be impacted by a delay of a few days. These cases would include nonseptic perforated cancer of esophagus, a tumor-associated infection, and management of surgical complications in a hemodynamically stable patient.
All thoracic procedures considered to be routine/elective would be deferred.
Phase III restricts surgery to patients whose survival will be compromised if they do not undergo surgery within the next few hours. This group would include perforated cancer of esophagus in a septic patient, a patient with a threatened airway, sepsis associated with the cancer, and management of surgical complications in an unstable patient (active bleeding that requires surgery, dehiscence of airway, anastomotic leak with sepsis).
All other cases would be deferred.
Other Cancer Types
Although the ACS doesn’t have specific guidelines for all cancer types, a few are included in their general recommendations for the specialty.
For gynecologic surgeries, ACS lists cancer or suspected cancer as indications where significantly delayed surgery could cause “significant harm.”
Delays, in general, are not recommended for neurosurgery, which would include brain cancers. In pediatrics, most cancer surgery is considered “urgent,” where a delay of days to weeks could prove detrimental to the patient. This would comprise all solid tumors, including the initial biopsy and resection following neoadjuvant therapy.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
White House expands seniors’ telehealth for COVID-19
“Medicare can pay for office, hospital, and other visits furnished via telehealth across the country and including in patients’ places of residence, starting March 6, 2020,” the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services said in a fact sheet issued March 17.
Some of the existing benefits were previously limited to rural communities.
“These services can also be provided in a variety of settings, including nursing homes, hospital outpatient departments, and more,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma during a March 17 White House press briefing on administration actions to contain the spread of COVID-19.
That means that seniors can continue to receive their routine care without having to leave the home and risk infection, or they can get medical guidance if they have mild symptoms, which would help mitigate the spread to others.
“This shift is very important for clinicians and providers who, over the coming weeks, will face considerable strain on their time and resources,” Dr. Verma said. “[It] allows the health care system to prioritize care for those who have more needs or who are in dire need, and it also preserves protective equipment.”
A range of providers will be able to deliver telehealth services, including doctors, nurse practitioners, clinical psychologists, and licensed clinical social workers. Visits using telehealth services will be considered the same as in-person visits and will be paid as if the patient were seen in the office.
This expansion of Medicare telehealth services will continue for the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency.
“In addition, the [Health & Human Services’] office of inspector general is providing flexibility for health care providers to reduce or waive cost-sharing for telehealth visits paid by federal health care programs,” the fact sheet states.Key to the expansion is that it will cover the entire United States and will not be limited to rural areas.
Dr. Verma also noted that the administration “will be temporarily suspending certain HIPAA requirements so that doctors can provide telehealth with their own phones.”
She added that state Medicaid agencies can expand their telehealth services without the approval of CMS during this emergency.
AGA has released a guide to commercial telehealth COVID-19 coding policies (http://ow.ly/8CIH30qsU0B) that supplements their guide to public payors.
“Medicare can pay for office, hospital, and other visits furnished via telehealth across the country and including in patients’ places of residence, starting March 6, 2020,” the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services said in a fact sheet issued March 17.
Some of the existing benefits were previously limited to rural communities.
“These services can also be provided in a variety of settings, including nursing homes, hospital outpatient departments, and more,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma during a March 17 White House press briefing on administration actions to contain the spread of COVID-19.
That means that seniors can continue to receive their routine care without having to leave the home and risk infection, or they can get medical guidance if they have mild symptoms, which would help mitigate the spread to others.
“This shift is very important for clinicians and providers who, over the coming weeks, will face considerable strain on their time and resources,” Dr. Verma said. “[It] allows the health care system to prioritize care for those who have more needs or who are in dire need, and it also preserves protective equipment.”
A range of providers will be able to deliver telehealth services, including doctors, nurse practitioners, clinical psychologists, and licensed clinical social workers. Visits using telehealth services will be considered the same as in-person visits and will be paid as if the patient were seen in the office.
This expansion of Medicare telehealth services will continue for the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency.
“In addition, the [Health & Human Services’] office of inspector general is providing flexibility for health care providers to reduce or waive cost-sharing for telehealth visits paid by federal health care programs,” the fact sheet states.Key to the expansion is that it will cover the entire United States and will not be limited to rural areas.
Dr. Verma also noted that the administration “will be temporarily suspending certain HIPAA requirements so that doctors can provide telehealth with their own phones.”
She added that state Medicaid agencies can expand their telehealth services without the approval of CMS during this emergency.
AGA has released a guide to commercial telehealth COVID-19 coding policies (http://ow.ly/8CIH30qsU0B) that supplements their guide to public payors.
“Medicare can pay for office, hospital, and other visits furnished via telehealth across the country and including in patients’ places of residence, starting March 6, 2020,” the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services said in a fact sheet issued March 17.
Some of the existing benefits were previously limited to rural communities.
“These services can also be provided in a variety of settings, including nursing homes, hospital outpatient departments, and more,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma during a March 17 White House press briefing on administration actions to contain the spread of COVID-19.
That means that seniors can continue to receive their routine care without having to leave the home and risk infection, or they can get medical guidance if they have mild symptoms, which would help mitigate the spread to others.
“This shift is very important for clinicians and providers who, over the coming weeks, will face considerable strain on their time and resources,” Dr. Verma said. “[It] allows the health care system to prioritize care for those who have more needs or who are in dire need, and it also preserves protective equipment.”
A range of providers will be able to deliver telehealth services, including doctors, nurse practitioners, clinical psychologists, and licensed clinical social workers. Visits using telehealth services will be considered the same as in-person visits and will be paid as if the patient were seen in the office.
This expansion of Medicare telehealth services will continue for the duration of the COVID-19 public health emergency.
“In addition, the [Health & Human Services’] office of inspector general is providing flexibility for health care providers to reduce or waive cost-sharing for telehealth visits paid by federal health care programs,” the fact sheet states.Key to the expansion is that it will cover the entire United States and will not be limited to rural areas.
Dr. Verma also noted that the administration “will be temporarily suspending certain HIPAA requirements so that doctors can provide telehealth with their own phones.”
She added that state Medicaid agencies can expand their telehealth services without the approval of CMS during this emergency.
AGA has released a guide to commercial telehealth COVID-19 coding policies (http://ow.ly/8CIH30qsU0B) that supplements their guide to public payors.





