User login
ADVANCES IN NEUROLOGY
New Supplement to Federal Practitioner: Advances in Neurology
Read more about:
- Lumbar Fusion With PEEK Rods Use for Patients With Degenerative Disease
- Systemic Literature Review of the Use of Virtual Reality for Rehabilitation in Parkinson Disease
- COVID-19 Vaccine in Veterans With Multiple Sclerosis: Protect the Vulnerable
Click here to read the supplement or click on the image
New Supplement to Federal Practitioner: Advances in Neurology
Read more about:
- Lumbar Fusion With PEEK Rods Use for Patients With Degenerative Disease
- Systemic Literature Review of the Use of Virtual Reality for Rehabilitation in Parkinson Disease
- COVID-19 Vaccine in Veterans With Multiple Sclerosis: Protect the Vulnerable
Click here to read the supplement or click on the image
New Supplement to Federal Practitioner: Advances in Neurology
Read more about:
- Lumbar Fusion With PEEK Rods Use for Patients With Degenerative Disease
- Systemic Literature Review of the Use of Virtual Reality for Rehabilitation in Parkinson Disease
- COVID-19 Vaccine in Veterans With Multiple Sclerosis: Protect the Vulnerable
Click here to read the supplement or click on the image
Feds let Illinois extend postpartum Medicaid coverage: HHS encourages other states to follow suit
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Highlights from ACTRIMS/ECTRIMS
Read the supplement here or by clicking on the image
Elevations in serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) are significantly linked to worse neurologic function, clinical disability, and lower brain volumes, according to new findings from a large, diverse population of patients with MS. “This is one of the largest studies to evaluate serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with MS,” said lead author Elias S. Sotirchos, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “An important strength of this cohort is that it is a realworld cohort of patients followed in U.S. and European MS centers,” he said. “The study captures the diversity of the MS population, including demographics, comorbidities, lifestyle factors, and clinical characteristics that may otherwise not be captured in a clinical trial population.” The research was presented at the 2021 ACTRIMS Forum.
Read the supplement here or by clicking on the image
Elevations in serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) are significantly linked to worse neurologic function, clinical disability, and lower brain volumes, according to new findings from a large, diverse population of patients with MS. “This is one of the largest studies to evaluate serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with MS,” said lead author Elias S. Sotirchos, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “An important strength of this cohort is that it is a realworld cohort of patients followed in U.S. and European MS centers,” he said. “The study captures the diversity of the MS population, including demographics, comorbidities, lifestyle factors, and clinical characteristics that may otherwise not be captured in a clinical trial population.” The research was presented at the 2021 ACTRIMS Forum.
Read the supplement here or by clicking on the image
Elevations in serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) are significantly linked to worse neurologic function, clinical disability, and lower brain volumes, according to new findings from a large, diverse population of patients with MS. “This is one of the largest studies to evaluate serum neurofilament light chain levels in people with MS,” said lead author Elias S. Sotirchos, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “An important strength of this cohort is that it is a realworld cohort of patients followed in U.S. and European MS centers,” he said. “The study captures the diversity of the MS population, including demographics, comorbidities, lifestyle factors, and clinical characteristics that may otherwise not be captured in a clinical trial population.” The research was presented at the 2021 ACTRIMS Forum.
Milk is overtaking nuts as top food allergy threat
When Lesley Solomon’s son was 10 years old, he was standing in an unlucky spot on the playground when a schoolmate kicked over a cup of hot chocolate, sending droplets flying into the air. For the young boy with a severe milk allergy, the hot liquid splattering was less of a hazard for him than the dairy stirred into the drink.
Ms. Solomon’s son quickly washed the fluids off his clothes and skin, took some Benadryl, and called his parents. But on the car ride home, his throat began to close and his pulse raced. It was one of about a dozen times he has needed an epinephrine injection, which increases blood flow, reduces swelling, and reverses anaphylaxis.
“Until you see a child going through that anaphylaxis and not being able to breathe, or throwing up so much that they can’t breathe, you don’t understand” how serious food allergies can be, said Ms. Solomon, who is senior vice president and chief innovation officer of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and cofounder of the Food Allergy Science Initiative, an independent nonprofit that funds food allergy research.
The rate of children hospitalized for food-induced anaphylaxis rose by 25% from 2006 to 2012 – from 1.2 to 1.5 per 100,000 – according to a 2019 analysis of data from pediatric hospitals in the United States. And severe symptoms were more often linked to milk than to peanuts or tree nuts, the study showed.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in children aged younger than 5 years, and accounts for about half of all food allergies in children younger than 1. Most children grow out of it, but when milk allergy persists into the teenage years and adulthood, it is more likely to cause severe reactions.
A dangerous allergy
“Cow’s milk allergy is the most distressing of the food allergies. Many people are unaware that it can cause anaphylaxis that is so severe,” said Carla Davis, MD, director of the food allergy program at the Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “People do not think about how much of this is in our food.”
And cow’s milk was shown to be the food allergy most likely to lead to death in school-aged children in the United Kingdom, according to an analysis of national data reported by this news organization.
Lack of awareness is what makes milk allergy so dangerous, said Paul Turner, BMBCh, PhD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist from Imperial College London, who was involved in the British analysis. “We need to get that information out to the public and businesses so they take the same level of care that they have with nuts, and when someone says they have milk allergy, they take it seriously.
In food allergy, the body treats certain proteins, such as the casein and whey in milk, as invaders, mounting an immune response. Antibodies known as IgE – which normally protect against bacteria, viruses, and parasites – trigger inflammation, the release of histamine, and can lead to symptoms, typically within minutes, ranging from rash and swelling to vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty breathing.
So, the very thing that makes milk a healthy choice for kids – its high protein content – can cause serious reactions in a small portion of children and adults. “You don’t need much milk to get a decent dose” of the allergen, Dr. Turner pointed out.
The mechanisms of milk allergy are complex, even compared with other food allergies. The IgE antibody can be detected with a skin-prick test or IgE blood test, but some people have positive results even though they are not allergic. To complicate things further, people can also have non–IgE-mediated milk allergy, which cannot be detected with testing and can lead to symptoms that emerge hours or even days after exposure.
More serious than lactose intolerance
Unfortunately, milk allergy is often confused with a milk-related digestive problem. Globally, about 70% of people lack the enzyme to break down the sugar in milk; the condition, known as lactose intolerance, can cause bloating, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea but is not life-threatening.
“Because lactose intolerance is so common, people don’t think of milk allergy as something that can be significant or severe,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Food Allergy and Asthma Research at the Northwestern University, Chicago.
In babies, colic, the regurgitation of milk-based formula, and rash are sometimes misinterpreted as a milk allergy, leading parents to buy expensive, specialized formula unnecessarily.
Frustrated by a lack of data about food allergies, Dr. Gupta and colleagues launched a nationally representative survey of 38,408 American parents in 2009, which was updated in 2015 and 2016.
On average, children with milk allergy had their first reaction before the age of 2, most commonly vomiting, diarrhea, hives, and eczema; this is a younger age of onset than for other food allergies. And children with milk allergy were twice as likely as children with other allergies to grow out of it.
Yet about one-third of milk-allergic children in the updated study were 11 years and older. And in a similar survey of adults who self-reported symptoms, milk allergy was as common as peanut allergy (1.9% vs 1.8%). “We don’t know why milk allergy is becoming more persistent,” Dr. Gupta said. And, she warned, only one in four children with a milk allergy had a current prescription for an epinephrine autoinjector, compared with about 70% of children with peanut allergy.
Food allergy can’t be caused by genetics alone, said Christine Olsen, MD, cofounder and CEO of the Food Allergy Science Initiative at the Broad Institute in Cambridge, Mass. “There may be a genetic predisposition, but there must be something environmental” that has influenced the development of food allergies.
One theory is that the body’s natural defense against noxious substances has been disrupted in the modern world by processed foods, chemical additives, and hygienic surroundings.
Dr. Olson’s own son vomited when he had his first small taste of hummus as a baby; he is severely allergic to sesame. The immediacy of his bodily reaction made Dr. Olsen think that the response involved neurons, not just a misguided immune system.
Researchers are currently looking for drug targets that could shut off the immune response as quickly as it starts. If you think of the fact that some kids outgrow their allergies and some adults get allergies, that suggests there’s some lever that you can turn on and off,” said Dr. Olsen, who is also a radiation oncologist.
Preventing allergy
The approach to food allergy prevention has already been transformed by the Learning Early About Peanut Allergy (LEAP) study conducted in the United Kingdom. LEAP investigators randomly assigned 640 infants to ingest regular amounts of peanut snacks or peanut butter or to avoid peanut products until they reached 5 years of age. The babies who had regular exposure to peanut from an early age were much less likely to develop a peanut allergy than those who avoided peanuts.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases revised its guidelines and now recommends that all babies be exposed to peanut-containing food at around 6 months of age; for high-risk babies, that can start as early as 4 months.
Allergy experts are planning to study that concept again with other foods, including cow’s milk. The 5-year iREACH study, launched by the Center for Food Allergy & Asthma Research at Northwestern and Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago, is currently enrolling 10,500 infants to test early exposure to peanuts, milk, egg, and cashew. A portion of the infants will have severe eczema, putting them at high risk for food allergies, and others will be low risk, said Dr. Gupta, who is the principal iREACH investigator.
“Hopefully in the next 5 years we will have data showing whether this prevention technique will work for other common food allergens, in addition to peanuts,” she said.
Introducing foods early “promotes tolerance rather than early sensitization,” explained Stephanie Leeds, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In the future, rather than just diagnosing and treating food allergies, allergists might work with pediatricians to help prevent them from ever happening.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Lesley Solomon’s son was 10 years old, he was standing in an unlucky spot on the playground when a schoolmate kicked over a cup of hot chocolate, sending droplets flying into the air. For the young boy with a severe milk allergy, the hot liquid splattering was less of a hazard for him than the dairy stirred into the drink.
Ms. Solomon’s son quickly washed the fluids off his clothes and skin, took some Benadryl, and called his parents. But on the car ride home, his throat began to close and his pulse raced. It was one of about a dozen times he has needed an epinephrine injection, which increases blood flow, reduces swelling, and reverses anaphylaxis.
“Until you see a child going through that anaphylaxis and not being able to breathe, or throwing up so much that they can’t breathe, you don’t understand” how serious food allergies can be, said Ms. Solomon, who is senior vice president and chief innovation officer of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and cofounder of the Food Allergy Science Initiative, an independent nonprofit that funds food allergy research.
The rate of children hospitalized for food-induced anaphylaxis rose by 25% from 2006 to 2012 – from 1.2 to 1.5 per 100,000 – according to a 2019 analysis of data from pediatric hospitals in the United States. And severe symptoms were more often linked to milk than to peanuts or tree nuts, the study showed.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in children aged younger than 5 years, and accounts for about half of all food allergies in children younger than 1. Most children grow out of it, but when milk allergy persists into the teenage years and adulthood, it is more likely to cause severe reactions.
A dangerous allergy
“Cow’s milk allergy is the most distressing of the food allergies. Many people are unaware that it can cause anaphylaxis that is so severe,” said Carla Davis, MD, director of the food allergy program at the Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “People do not think about how much of this is in our food.”
And cow’s milk was shown to be the food allergy most likely to lead to death in school-aged children in the United Kingdom, according to an analysis of national data reported by this news organization.
Lack of awareness is what makes milk allergy so dangerous, said Paul Turner, BMBCh, PhD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist from Imperial College London, who was involved in the British analysis. “We need to get that information out to the public and businesses so they take the same level of care that they have with nuts, and when someone says they have milk allergy, they take it seriously.
In food allergy, the body treats certain proteins, such as the casein and whey in milk, as invaders, mounting an immune response. Antibodies known as IgE – which normally protect against bacteria, viruses, and parasites – trigger inflammation, the release of histamine, and can lead to symptoms, typically within minutes, ranging from rash and swelling to vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty breathing.
So, the very thing that makes milk a healthy choice for kids – its high protein content – can cause serious reactions in a small portion of children and adults. “You don’t need much milk to get a decent dose” of the allergen, Dr. Turner pointed out.
The mechanisms of milk allergy are complex, even compared with other food allergies. The IgE antibody can be detected with a skin-prick test or IgE blood test, but some people have positive results even though they are not allergic. To complicate things further, people can also have non–IgE-mediated milk allergy, which cannot be detected with testing and can lead to symptoms that emerge hours or even days after exposure.
More serious than lactose intolerance
Unfortunately, milk allergy is often confused with a milk-related digestive problem. Globally, about 70% of people lack the enzyme to break down the sugar in milk; the condition, known as lactose intolerance, can cause bloating, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea but is not life-threatening.
“Because lactose intolerance is so common, people don’t think of milk allergy as something that can be significant or severe,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Food Allergy and Asthma Research at the Northwestern University, Chicago.
In babies, colic, the regurgitation of milk-based formula, and rash are sometimes misinterpreted as a milk allergy, leading parents to buy expensive, specialized formula unnecessarily.
Frustrated by a lack of data about food allergies, Dr. Gupta and colleagues launched a nationally representative survey of 38,408 American parents in 2009, which was updated in 2015 and 2016.
On average, children with milk allergy had their first reaction before the age of 2, most commonly vomiting, diarrhea, hives, and eczema; this is a younger age of onset than for other food allergies. And children with milk allergy were twice as likely as children with other allergies to grow out of it.
Yet about one-third of milk-allergic children in the updated study were 11 years and older. And in a similar survey of adults who self-reported symptoms, milk allergy was as common as peanut allergy (1.9% vs 1.8%). “We don’t know why milk allergy is becoming more persistent,” Dr. Gupta said. And, she warned, only one in four children with a milk allergy had a current prescription for an epinephrine autoinjector, compared with about 70% of children with peanut allergy.
Food allergy can’t be caused by genetics alone, said Christine Olsen, MD, cofounder and CEO of the Food Allergy Science Initiative at the Broad Institute in Cambridge, Mass. “There may be a genetic predisposition, but there must be something environmental” that has influenced the development of food allergies.
One theory is that the body’s natural defense against noxious substances has been disrupted in the modern world by processed foods, chemical additives, and hygienic surroundings.
Dr. Olson’s own son vomited when he had his first small taste of hummus as a baby; he is severely allergic to sesame. The immediacy of his bodily reaction made Dr. Olsen think that the response involved neurons, not just a misguided immune system.
Researchers are currently looking for drug targets that could shut off the immune response as quickly as it starts. If you think of the fact that some kids outgrow their allergies and some adults get allergies, that suggests there’s some lever that you can turn on and off,” said Dr. Olsen, who is also a radiation oncologist.
Preventing allergy
The approach to food allergy prevention has already been transformed by the Learning Early About Peanut Allergy (LEAP) study conducted in the United Kingdom. LEAP investigators randomly assigned 640 infants to ingest regular amounts of peanut snacks or peanut butter or to avoid peanut products until they reached 5 years of age. The babies who had regular exposure to peanut from an early age were much less likely to develop a peanut allergy than those who avoided peanuts.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases revised its guidelines and now recommends that all babies be exposed to peanut-containing food at around 6 months of age; for high-risk babies, that can start as early as 4 months.
Allergy experts are planning to study that concept again with other foods, including cow’s milk. The 5-year iREACH study, launched by the Center for Food Allergy & Asthma Research at Northwestern and Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago, is currently enrolling 10,500 infants to test early exposure to peanuts, milk, egg, and cashew. A portion of the infants will have severe eczema, putting them at high risk for food allergies, and others will be low risk, said Dr. Gupta, who is the principal iREACH investigator.
“Hopefully in the next 5 years we will have data showing whether this prevention technique will work for other common food allergens, in addition to peanuts,” she said.
Introducing foods early “promotes tolerance rather than early sensitization,” explained Stephanie Leeds, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In the future, rather than just diagnosing and treating food allergies, allergists might work with pediatricians to help prevent them from ever happening.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Lesley Solomon’s son was 10 years old, he was standing in an unlucky spot on the playground when a schoolmate kicked over a cup of hot chocolate, sending droplets flying into the air. For the young boy with a severe milk allergy, the hot liquid splattering was less of a hazard for him than the dairy stirred into the drink.
Ms. Solomon’s son quickly washed the fluids off his clothes and skin, took some Benadryl, and called his parents. But on the car ride home, his throat began to close and his pulse raced. It was one of about a dozen times he has needed an epinephrine injection, which increases blood flow, reduces swelling, and reverses anaphylaxis.
“Until you see a child going through that anaphylaxis and not being able to breathe, or throwing up so much that they can’t breathe, you don’t understand” how serious food allergies can be, said Ms. Solomon, who is senior vice president and chief innovation officer of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and cofounder of the Food Allergy Science Initiative, an independent nonprofit that funds food allergy research.
The rate of children hospitalized for food-induced anaphylaxis rose by 25% from 2006 to 2012 – from 1.2 to 1.5 per 100,000 – according to a 2019 analysis of data from pediatric hospitals in the United States. And severe symptoms were more often linked to milk than to peanuts or tree nuts, the study showed.
Cow’s milk is the most common food allergy in children aged younger than 5 years, and accounts for about half of all food allergies in children younger than 1. Most children grow out of it, but when milk allergy persists into the teenage years and adulthood, it is more likely to cause severe reactions.
A dangerous allergy
“Cow’s milk allergy is the most distressing of the food allergies. Many people are unaware that it can cause anaphylaxis that is so severe,” said Carla Davis, MD, director of the food allergy program at the Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “People do not think about how much of this is in our food.”
And cow’s milk was shown to be the food allergy most likely to lead to death in school-aged children in the United Kingdom, according to an analysis of national data reported by this news organization.
Lack of awareness is what makes milk allergy so dangerous, said Paul Turner, BMBCh, PhD, a pediatric allergist and immunologist from Imperial College London, who was involved in the British analysis. “We need to get that information out to the public and businesses so they take the same level of care that they have with nuts, and when someone says they have milk allergy, they take it seriously.
In food allergy, the body treats certain proteins, such as the casein and whey in milk, as invaders, mounting an immune response. Antibodies known as IgE – which normally protect against bacteria, viruses, and parasites – trigger inflammation, the release of histamine, and can lead to symptoms, typically within minutes, ranging from rash and swelling to vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and difficulty breathing.
So, the very thing that makes milk a healthy choice for kids – its high protein content – can cause serious reactions in a small portion of children and adults. “You don’t need much milk to get a decent dose” of the allergen, Dr. Turner pointed out.
The mechanisms of milk allergy are complex, even compared with other food allergies. The IgE antibody can be detected with a skin-prick test or IgE blood test, but some people have positive results even though they are not allergic. To complicate things further, people can also have non–IgE-mediated milk allergy, which cannot be detected with testing and can lead to symptoms that emerge hours or even days after exposure.
More serious than lactose intolerance
Unfortunately, milk allergy is often confused with a milk-related digestive problem. Globally, about 70% of people lack the enzyme to break down the sugar in milk; the condition, known as lactose intolerance, can cause bloating, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea but is not life-threatening.
“Because lactose intolerance is so common, people don’t think of milk allergy as something that can be significant or severe,” said Ruchi Gupta, MD, MPH, director of the Center for Food Allergy and Asthma Research at the Northwestern University, Chicago.
In babies, colic, the regurgitation of milk-based formula, and rash are sometimes misinterpreted as a milk allergy, leading parents to buy expensive, specialized formula unnecessarily.
Frustrated by a lack of data about food allergies, Dr. Gupta and colleagues launched a nationally representative survey of 38,408 American parents in 2009, which was updated in 2015 and 2016.
On average, children with milk allergy had their first reaction before the age of 2, most commonly vomiting, diarrhea, hives, and eczema; this is a younger age of onset than for other food allergies. And children with milk allergy were twice as likely as children with other allergies to grow out of it.
Yet about one-third of milk-allergic children in the updated study were 11 years and older. And in a similar survey of adults who self-reported symptoms, milk allergy was as common as peanut allergy (1.9% vs 1.8%). “We don’t know why milk allergy is becoming more persistent,” Dr. Gupta said. And, she warned, only one in four children with a milk allergy had a current prescription for an epinephrine autoinjector, compared with about 70% of children with peanut allergy.
Food allergy can’t be caused by genetics alone, said Christine Olsen, MD, cofounder and CEO of the Food Allergy Science Initiative at the Broad Institute in Cambridge, Mass. “There may be a genetic predisposition, but there must be something environmental” that has influenced the development of food allergies.
One theory is that the body’s natural defense against noxious substances has been disrupted in the modern world by processed foods, chemical additives, and hygienic surroundings.
Dr. Olson’s own son vomited when he had his first small taste of hummus as a baby; he is severely allergic to sesame. The immediacy of his bodily reaction made Dr. Olsen think that the response involved neurons, not just a misguided immune system.
Researchers are currently looking for drug targets that could shut off the immune response as quickly as it starts. If you think of the fact that some kids outgrow their allergies and some adults get allergies, that suggests there’s some lever that you can turn on and off,” said Dr. Olsen, who is also a radiation oncologist.
Preventing allergy
The approach to food allergy prevention has already been transformed by the Learning Early About Peanut Allergy (LEAP) study conducted in the United Kingdom. LEAP investigators randomly assigned 640 infants to ingest regular amounts of peanut snacks or peanut butter or to avoid peanut products until they reached 5 years of age. The babies who had regular exposure to peanut from an early age were much less likely to develop a peanut allergy than those who avoided peanuts.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases revised its guidelines and now recommends that all babies be exposed to peanut-containing food at around 6 months of age; for high-risk babies, that can start as early as 4 months.
Allergy experts are planning to study that concept again with other foods, including cow’s milk. The 5-year iREACH study, launched by the Center for Food Allergy & Asthma Research at Northwestern and Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago, is currently enrolling 10,500 infants to test early exposure to peanuts, milk, egg, and cashew. A portion of the infants will have severe eczema, putting them at high risk for food allergies, and others will be low risk, said Dr. Gupta, who is the principal iREACH investigator.
“Hopefully in the next 5 years we will have data showing whether this prevention technique will work for other common food allergens, in addition to peanuts,” she said.
Introducing foods early “promotes tolerance rather than early sensitization,” explained Stephanie Leeds, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. In the future, rather than just diagnosing and treating food allergies, allergists might work with pediatricians to help prevent them from ever happening.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
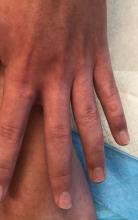
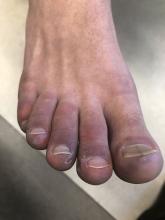
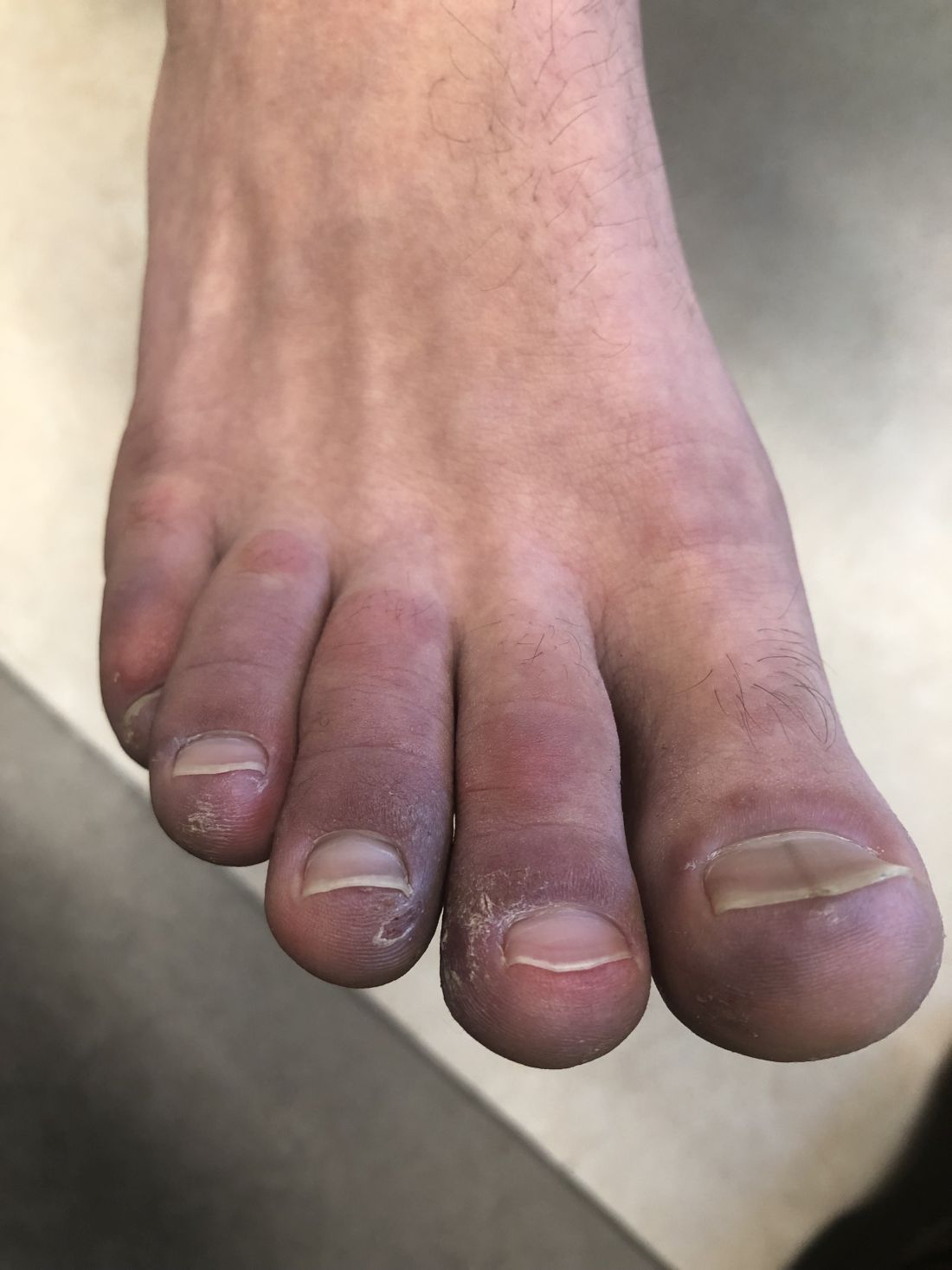
A 12-year-old male has persistent purple toes and new red lesions on his hands
A punch biopsy from one of the lesions on the feet showed subtle basal vacuolar interface inflammation on the epidermis and rare apoptotic keratinocytes. There was an underlying dermal lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate around the vascular plexus. Dermal mucin appeared slightly increased. The histologic findings are consistent with pernio. He had a negative direct immunofluorescence study.
Laboratory work-up showed an elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) of 1:620; positive anticardiolipin IgM was at 15.2. A complete blood count showed no anemia or lymphopenia, he had normal complement C3 and C4 levels, normal urinalysis, negative cryoglobulins and cold agglutinins, and a normal protein electrophoresis.
Given the chronicity of his lesions, the lack of improvement with weather changes, the histopathologic findings of a vacuolar interface dermatitis and the positive ANA titer he was diagnosed with chilblain lupus.
Chilblain lupus erythematosus (CLE) is an uncommon form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus that presents with tender pink to violaceous macules, papules, and/or nodules that sometimes can ulcerate and are present on the fingers, toes, and sometimes the nose and ears. The lesions are usually triggered by cold exposure.1 These patients also have clinical and laboratory findings consistent with lupus erythematosus.
Even though more studies are needed to clarify the clinical and histopathologic features of chilblain lupus, compared with idiopathic pernio, some authors suggest several characteristics: CLE lesions tend to persist in summer months, as occurred in our patient, and histopathologic evaluation usually shows vacuolar and interface inflammation on the basal cell layer and may also have a positive lupus band on direct immunofluorescence.2 About 20% of patient with CLE may later develop systemic lupus erythematosus.3
There is also a familial form of CLE which is usually inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. Mutations in TREX1, SAMHD1, and STING have been described in these patients.4 Affected children present with skin lesions at a young age and those with TREX1 mutations are at a higher risk to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.
The differential diagnosis of chilblain lupus includes idiopathic pernio or pernio secondary to other conditions. Other conditions that are thought to be associated with pernio, besides lupus erythematosus, include infectious causes (hepatitis B, COVID-19 infection),5 autoimmune conditions, malignancy and hematologic disorders (paraproteinemia).6 In histopathology, pernio lesions present with dermal edema and superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate.
The pathogenesis of pernio is not fully understood but is thought be related to vasospasm with secondary poor perfusion and ischemia and type I interferon (INF1) immune response. A recent review of the published studies trying to explain the causality between COVID 19 and pernio-like lesions, from January 2020 to December 2020, speculate several possible mechanisms: an increase in the vasoconstrictive, prothrombotic, and proinflammatory effects of the angiotensin II pathway through activation of the ACE2 by the virus; COVID-19 triggers a robust INF1 immune response in predisposed patients; pernio as a sign of mild disease, may be explained by genetic and hormonal differences in the patients affected.7
Another condition that can be confused with CLE is Raynaud phenomenon, were patients present with white to purple to red patches on the fingers and toes after exposure to cold, but in comparison with pernio, the lesions improve within minutes to hours after rewarming. Secondary Raynaud phenomenon can be seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in patients with other connective tissue disorders. The skin lesions in our patient were persistent and were not triggered by cold exposure, making Raynaud phenomenon less likely. Children with vasculitis can present with painful red, violaceous, or necrotic lesions on the extremities, which can mimic pernio. Vasculitis lesions tend to be more purpuric and angulated, compared with pernio lesions, though in severe cases of pernio with ulceration it may be difficult to distinguish between the two entities and a skin biopsy may be needed.
Sweet syndrome, also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a rare skin condition in which children present with edematous tender nodules on the hands and with less frequency in other parts of the body with associated fever, malaise, conjunctivitis, or joint pain and it is usually associated with infection or malignancy. Our patient denied any systemic symptoms and had no conjunctivitis nor arthritis.
Most patients with idiopathic pernio do not require a biopsy or further laboratory evaluation unless the lesions are atypical, chronic, or there is a suspected associated condition. The workup for patients with prolonged or atypical pernio-like lesions include a skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence, ANA, complete blood count, complement levels, antiphospholipid antibodies, cold agglutinins, and cryoglobulins.
Treatment of mild CLE is with moderate- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. In those patients not responding to topical measures and keeping the extremities warm, the use of hydroxychloroquine has been reported to be beneficial in some patients as well as the use of calcium-channel blockers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Su WP et al. Cutis. 1994 Dec;54(6):395-9.
2. Boada A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010 Feb;32(1):19-23.
3. Patel et al. SBMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013201165.
4. Genes Yi et al. BMC. 2020 Apr 15;18(1):32.
5. Battesti G et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(4):1219-22.
6. Cappel JA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Feb;89(2):207-15.
7. Cappel MA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(4):989-1005.
A punch biopsy from one of the lesions on the feet showed subtle basal vacuolar interface inflammation on the epidermis and rare apoptotic keratinocytes. There was an underlying dermal lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate around the vascular plexus. Dermal mucin appeared slightly increased. The histologic findings are consistent with pernio. He had a negative direct immunofluorescence study.
Laboratory work-up showed an elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) of 1:620; positive anticardiolipin IgM was at 15.2. A complete blood count showed no anemia or lymphopenia, he had normal complement C3 and C4 levels, normal urinalysis, negative cryoglobulins and cold agglutinins, and a normal protein electrophoresis.
Given the chronicity of his lesions, the lack of improvement with weather changes, the histopathologic findings of a vacuolar interface dermatitis and the positive ANA titer he was diagnosed with chilblain lupus.
Chilblain lupus erythematosus (CLE) is an uncommon form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus that presents with tender pink to violaceous macules, papules, and/or nodules that sometimes can ulcerate and are present on the fingers, toes, and sometimes the nose and ears. The lesions are usually triggered by cold exposure.1 These patients also have clinical and laboratory findings consistent with lupus erythematosus.
Even though more studies are needed to clarify the clinical and histopathologic features of chilblain lupus, compared with idiopathic pernio, some authors suggest several characteristics: CLE lesions tend to persist in summer months, as occurred in our patient, and histopathologic evaluation usually shows vacuolar and interface inflammation on the basal cell layer and may also have a positive lupus band on direct immunofluorescence.2 About 20% of patient with CLE may later develop systemic lupus erythematosus.3
There is also a familial form of CLE which is usually inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. Mutations in TREX1, SAMHD1, and STING have been described in these patients.4 Affected children present with skin lesions at a young age and those with TREX1 mutations are at a higher risk to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.
The differential diagnosis of chilblain lupus includes idiopathic pernio or pernio secondary to other conditions. Other conditions that are thought to be associated with pernio, besides lupus erythematosus, include infectious causes (hepatitis B, COVID-19 infection),5 autoimmune conditions, malignancy and hematologic disorders (paraproteinemia).6 In histopathology, pernio lesions present with dermal edema and superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate.
The pathogenesis of pernio is not fully understood but is thought be related to vasospasm with secondary poor perfusion and ischemia and type I interferon (INF1) immune response. A recent review of the published studies trying to explain the causality between COVID 19 and pernio-like lesions, from January 2020 to December 2020, speculate several possible mechanisms: an increase in the vasoconstrictive, prothrombotic, and proinflammatory effects of the angiotensin II pathway through activation of the ACE2 by the virus; COVID-19 triggers a robust INF1 immune response in predisposed patients; pernio as a sign of mild disease, may be explained by genetic and hormonal differences in the patients affected.7
Another condition that can be confused with CLE is Raynaud phenomenon, were patients present with white to purple to red patches on the fingers and toes after exposure to cold, but in comparison with pernio, the lesions improve within minutes to hours after rewarming. Secondary Raynaud phenomenon can be seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in patients with other connective tissue disorders. The skin lesions in our patient were persistent and were not triggered by cold exposure, making Raynaud phenomenon less likely. Children with vasculitis can present with painful red, violaceous, or necrotic lesions on the extremities, which can mimic pernio. Vasculitis lesions tend to be more purpuric and angulated, compared with pernio lesions, though in severe cases of pernio with ulceration it may be difficult to distinguish between the two entities and a skin biopsy may be needed.
Sweet syndrome, also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a rare skin condition in which children present with edematous tender nodules on the hands and with less frequency in other parts of the body with associated fever, malaise, conjunctivitis, or joint pain and it is usually associated with infection or malignancy. Our patient denied any systemic symptoms and had no conjunctivitis nor arthritis.
Most patients with idiopathic pernio do not require a biopsy or further laboratory evaluation unless the lesions are atypical, chronic, or there is a suspected associated condition. The workup for patients with prolonged or atypical pernio-like lesions include a skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence, ANA, complete blood count, complement levels, antiphospholipid antibodies, cold agglutinins, and cryoglobulins.
Treatment of mild CLE is with moderate- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. In those patients not responding to topical measures and keeping the extremities warm, the use of hydroxychloroquine has been reported to be beneficial in some patients as well as the use of calcium-channel blockers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Su WP et al. Cutis. 1994 Dec;54(6):395-9.
2. Boada A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010 Feb;32(1):19-23.
3. Patel et al. SBMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013201165.
4. Genes Yi et al. BMC. 2020 Apr 15;18(1):32.
5. Battesti G et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(4):1219-22.
6. Cappel JA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Feb;89(2):207-15.
7. Cappel MA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(4):989-1005.
A punch biopsy from one of the lesions on the feet showed subtle basal vacuolar interface inflammation on the epidermis and rare apoptotic keratinocytes. There was an underlying dermal lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate around the vascular plexus. Dermal mucin appeared slightly increased. The histologic findings are consistent with pernio. He had a negative direct immunofluorescence study.
Laboratory work-up showed an elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) of 1:620; positive anticardiolipin IgM was at 15.2. A complete blood count showed no anemia or lymphopenia, he had normal complement C3 and C4 levels, normal urinalysis, negative cryoglobulins and cold agglutinins, and a normal protein electrophoresis.
Given the chronicity of his lesions, the lack of improvement with weather changes, the histopathologic findings of a vacuolar interface dermatitis and the positive ANA titer he was diagnosed with chilblain lupus.
Chilblain lupus erythematosus (CLE) is an uncommon form of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus that presents with tender pink to violaceous macules, papules, and/or nodules that sometimes can ulcerate and are present on the fingers, toes, and sometimes the nose and ears. The lesions are usually triggered by cold exposure.1 These patients also have clinical and laboratory findings consistent with lupus erythematosus.
Even though more studies are needed to clarify the clinical and histopathologic features of chilblain lupus, compared with idiopathic pernio, some authors suggest several characteristics: CLE lesions tend to persist in summer months, as occurred in our patient, and histopathologic evaluation usually shows vacuolar and interface inflammation on the basal cell layer and may also have a positive lupus band on direct immunofluorescence.2 About 20% of patient with CLE may later develop systemic lupus erythematosus.3
There is also a familial form of CLE which is usually inherited as an autosomal-dominant trait. Mutations in TREX1, SAMHD1, and STING have been described in these patients.4 Affected children present with skin lesions at a young age and those with TREX1 mutations are at a higher risk to develop systemic lupus erythematosus.
The differential diagnosis of chilblain lupus includes idiopathic pernio or pernio secondary to other conditions. Other conditions that are thought to be associated with pernio, besides lupus erythematosus, include infectious causes (hepatitis B, COVID-19 infection),5 autoimmune conditions, malignancy and hematologic disorders (paraproteinemia).6 In histopathology, pernio lesions present with dermal edema and superficial and deep lymphocytic infiltrate.
The pathogenesis of pernio is not fully understood but is thought be related to vasospasm with secondary poor perfusion and ischemia and type I interferon (INF1) immune response. A recent review of the published studies trying to explain the causality between COVID 19 and pernio-like lesions, from January 2020 to December 2020, speculate several possible mechanisms: an increase in the vasoconstrictive, prothrombotic, and proinflammatory effects of the angiotensin II pathway through activation of the ACE2 by the virus; COVID-19 triggers a robust INF1 immune response in predisposed patients; pernio as a sign of mild disease, may be explained by genetic and hormonal differences in the patients affected.7
Another condition that can be confused with CLE is Raynaud phenomenon, were patients present with white to purple to red patches on the fingers and toes after exposure to cold, but in comparison with pernio, the lesions improve within minutes to hours after rewarming. Secondary Raynaud phenomenon can be seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and in patients with other connective tissue disorders. The skin lesions in our patient were persistent and were not triggered by cold exposure, making Raynaud phenomenon less likely. Children with vasculitis can present with painful red, violaceous, or necrotic lesions on the extremities, which can mimic pernio. Vasculitis lesions tend to be more purpuric and angulated, compared with pernio lesions, though in severe cases of pernio with ulceration it may be difficult to distinguish between the two entities and a skin biopsy may be needed.
Sweet syndrome, also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a rare skin condition in which children present with edematous tender nodules on the hands and with less frequency in other parts of the body with associated fever, malaise, conjunctivitis, or joint pain and it is usually associated with infection or malignancy. Our patient denied any systemic symptoms and had no conjunctivitis nor arthritis.
Most patients with idiopathic pernio do not require a biopsy or further laboratory evaluation unless the lesions are atypical, chronic, or there is a suspected associated condition. The workup for patients with prolonged or atypical pernio-like lesions include a skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence, ANA, complete blood count, complement levels, antiphospholipid antibodies, cold agglutinins, and cryoglobulins.
Treatment of mild CLE is with moderate- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. In those patients not responding to topical measures and keeping the extremities warm, the use of hydroxychloroquine has been reported to be beneficial in some patients as well as the use of calcium-channel blockers.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Su WP et al. Cutis. 1994 Dec;54(6):395-9.
2. Boada A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010 Feb;32(1):19-23.
3. Patel et al. SBMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013201165.
4. Genes Yi et al. BMC. 2020 Apr 15;18(1):32.
5. Battesti G et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(4):1219-22.
6. Cappel JA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Feb;89(2):207-15.
7. Cappel MA et al. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(4):989-1005.
He denied any hair loss, mouth sores, sun sensitivity, headaches, gastrointestinal complaints, joint pain, or muscle weakness.
He is not taking any medications.
He has been at home doing virtual school and has not traveled. He likes to play the piano. There is no family history of similar lesions, connective tissue disorder, or autoimmunity.
On physical exam he has purple discoloration on the toes with some violaceous and pink papules. On the fingers he has pink to violaceous papules and macules.
There is no joint edema or pain.
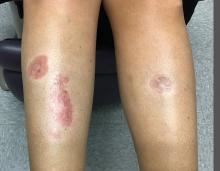
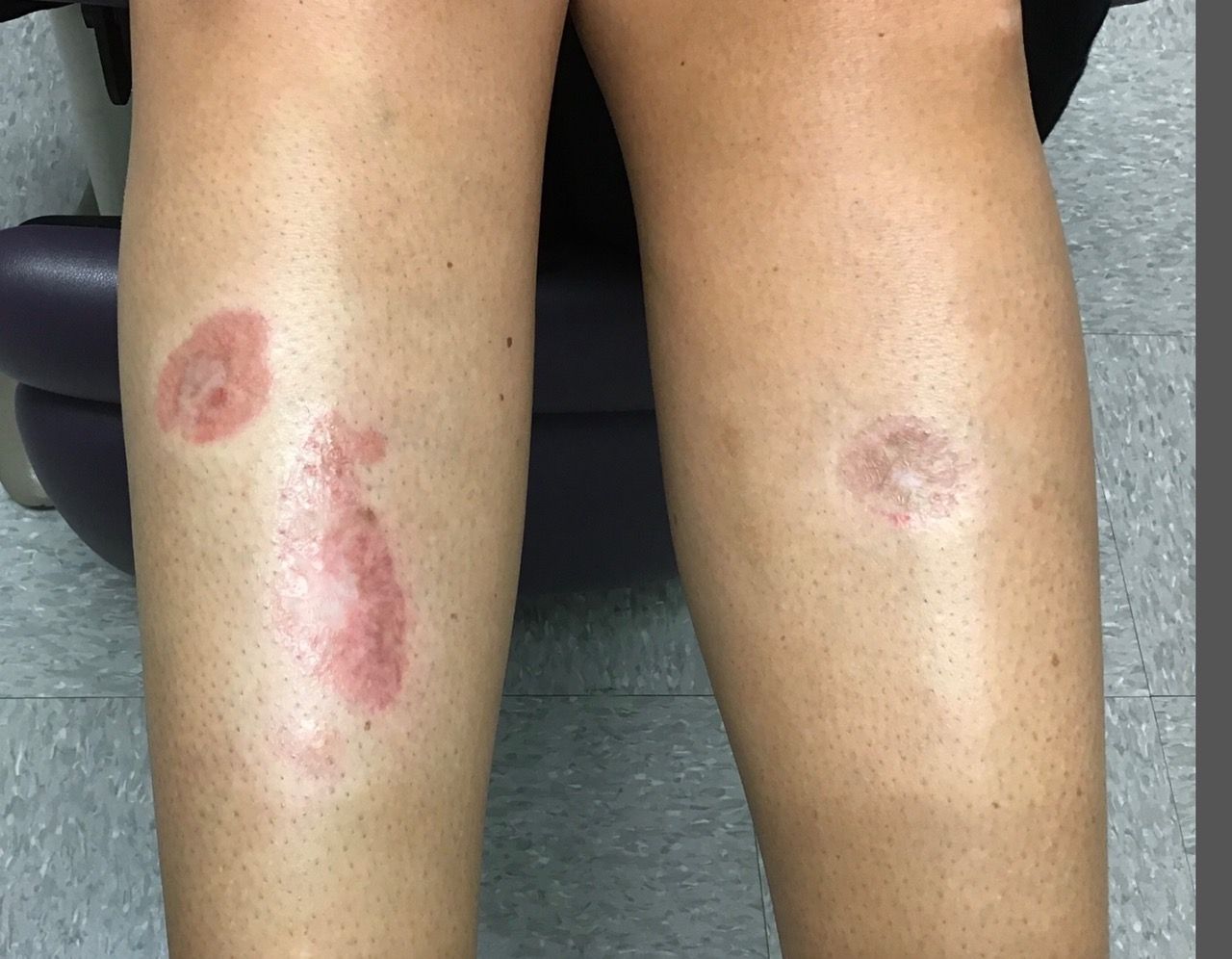
A woman with a history of diabetes, and plaques on both shins
. Women are often more affected than men. Patients often present in their 30s and 40s. The cause of NLD is unknown. Twenty percent of patients with NLD will have glucose intolerance or a family history of diabetes.1 The percentage of patients with NLD who have diabetes varies in reports from 11% to 65%.2 NLD may progress despite the diabetes treatment. Only 0.03% of patient with diabetes will have NLD.3
Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities, with shins being affected in most cases. They vary from asymptomatic to painful. Typically, lesions begin as small, firm erythematous papules that evolve into shiny, well-defined plaques. In older plaques, the center will often appear yellow, depressed, and atrophic, with telangiectasias. The periphery appears pink to violaceous to brown. Ulceration may be present, particularly after trauma, and there may be decreased sensation in the plaques. NLD is clinically distinct from diabetic dermopathy, which appear as brown macules, often in older patients with diabetes.
Ideally, biopsy should be taken at the edge of a lesion. Histologically, the epidermis appears normal or atrophic. A diffuse palisaded and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis consisting of histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, lymphocytes, and plasma cells is seen in the dermis. Granulomas are often oriented parallel to the epidermis. There is no mucin at the center of the granulomas (as seen in granuloma annulare). Inflammation may extend into the subcutaneous fat. Asteroid bodies (as seen in sarcoid) are absent.
Unfortunately, treatment of NLD is often unsuccessful. Treatment includes potent topical corticosteroids for early lesions and intralesional triamcinolone to the leading edge of lesions. Care should be taken to avoid injecting centrally where atrophy and ulceration may result. Systemic steroids may be helpful in some cases, but can elevate glucose levels. Other reported medical treatments include pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, and niacinamide. Some lesions may spontaneously resolve. Ulcerations may require surgical excision with grafting.
This case and photo are provided by Dr. Bilu Martin, who is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. James WD et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
2. Hashemi D et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Apr 1;155(4):455-9.
3. Bolognia JL et al. Dermatology. St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier, 2008.
. Women are often more affected than men. Patients often present in their 30s and 40s. The cause of NLD is unknown. Twenty percent of patients with NLD will have glucose intolerance or a family history of diabetes.1 The percentage of patients with NLD who have diabetes varies in reports from 11% to 65%.2 NLD may progress despite the diabetes treatment. Only 0.03% of patient with diabetes will have NLD.3
Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities, with shins being affected in most cases. They vary from asymptomatic to painful. Typically, lesions begin as small, firm erythematous papules that evolve into shiny, well-defined plaques. In older plaques, the center will often appear yellow, depressed, and atrophic, with telangiectasias. The periphery appears pink to violaceous to brown. Ulceration may be present, particularly after trauma, and there may be decreased sensation in the plaques. NLD is clinically distinct from diabetic dermopathy, which appear as brown macules, often in older patients with diabetes.
Ideally, biopsy should be taken at the edge of a lesion. Histologically, the epidermis appears normal or atrophic. A diffuse palisaded and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis consisting of histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, lymphocytes, and plasma cells is seen in the dermis. Granulomas are often oriented parallel to the epidermis. There is no mucin at the center of the granulomas (as seen in granuloma annulare). Inflammation may extend into the subcutaneous fat. Asteroid bodies (as seen in sarcoid) are absent.
Unfortunately, treatment of NLD is often unsuccessful. Treatment includes potent topical corticosteroids for early lesions and intralesional triamcinolone to the leading edge of lesions. Care should be taken to avoid injecting centrally where atrophy and ulceration may result. Systemic steroids may be helpful in some cases, but can elevate glucose levels. Other reported medical treatments include pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, and niacinamide. Some lesions may spontaneously resolve. Ulcerations may require surgical excision with grafting.
This case and photo are provided by Dr. Bilu Martin, who is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. James WD et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
2. Hashemi D et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Apr 1;155(4):455-9.
3. Bolognia JL et al. Dermatology. St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier, 2008.
. Women are often more affected than men. Patients often present in their 30s and 40s. The cause of NLD is unknown. Twenty percent of patients with NLD will have glucose intolerance or a family history of diabetes.1 The percentage of patients with NLD who have diabetes varies in reports from 11% to 65%.2 NLD may progress despite the diabetes treatment. Only 0.03% of patient with diabetes will have NLD.3
Lesions most commonly occur on the extremities, with shins being affected in most cases. They vary from asymptomatic to painful. Typically, lesions begin as small, firm erythematous papules that evolve into shiny, well-defined plaques. In older plaques, the center will often appear yellow, depressed, and atrophic, with telangiectasias. The periphery appears pink to violaceous to brown. Ulceration may be present, particularly after trauma, and there may be decreased sensation in the plaques. NLD is clinically distinct from diabetic dermopathy, which appear as brown macules, often in older patients with diabetes.
Ideally, biopsy should be taken at the edge of a lesion. Histologically, the epidermis appears normal or atrophic. A diffuse palisaded and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis consisting of histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells, lymphocytes, and plasma cells is seen in the dermis. Granulomas are often oriented parallel to the epidermis. There is no mucin at the center of the granulomas (as seen in granuloma annulare). Inflammation may extend into the subcutaneous fat. Asteroid bodies (as seen in sarcoid) are absent.
Unfortunately, treatment of NLD is often unsuccessful. Treatment includes potent topical corticosteroids for early lesions and intralesional triamcinolone to the leading edge of lesions. Care should be taken to avoid injecting centrally where atrophy and ulceration may result. Systemic steroids may be helpful in some cases, but can elevate glucose levels. Other reported medical treatments include pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, and niacinamide. Some lesions may spontaneously resolve. Ulcerations may require surgical excision with grafting.
This case and photo are provided by Dr. Bilu Martin, who is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. James WD et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
2. Hashemi D et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Apr 1;155(4):455-9.
3. Bolognia JL et al. Dermatology. St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier, 2008.
Tebentafusp improves OS: A first in metastatic uveal melanoma
Tebentafusp is the first investigational therapy in a phase 3 trial to improve OS in metastatic uveal melanoma, said Jessica Hassel, MD, of University Hospital Heidelberg in Germany, when presenting the results at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT002).
Dr. Hassel explained that tebentafusp is a bispecific fusion protein designed to target gp100 through a high affinity T-cell receptor binding domain and an anti-CD3 T-cell engaging domain, which redirects T cells to kill gp100-expressing tumor cells. Because the T-cell receptor binding domain only recognizes a specific gp100-derived peptide presented on HLA-A*02:01, tebentafusp can only be used to treat patients with this HLA type.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 378 treatment-naive HLA-A*02:01-positive patients with metastatic uveal melanoma. Their median age was 65 years, and 50% were men.
Patients were assigned 2:1 to receive tebentafusp (n = 252) or investigator’s choice of pembrolizumab (n = 103), ipilimumab (n = 16), or dacarbazine (n = 7).
Prolonged OS despite low response rate
At a median follow-up of 14.1 months, patients receiving tebentafusp had significantly longer OS than that of patients in the investigator’s choice arm – 21.7 months and 16.0 months, respectively. The estimated 1-year OS rate was 73.2% in the tebentafusp arm and 58.5% in the standard therapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.71; P < .0001). The OS benefit was consistent across subgroups, Dr. Hassel said.
At a median follow-up of 11.4 months, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 months in the tebentafusp arm and 2.9 months in the investigator’s choice arm (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.58-0.94; P = .0139).
The objective response rate was 9% in the tebentafusp arm and 5% in the investigator’s choice arm. There was only one complete response, and it was in the tebentafusp arm.
The disease control rate, defined as response or stable disease for 12 or more weeks, was 46% in the tebentafusp arm and 27% in the investigator’s choice arm. Rates of progressive disease were 52% and 62%, respectively.
Dr. Hassel pointed out that a landmark analysis of OS in patients with a best response of progressive disease, with patients continuing to receive treatment after progression, showed a hazard ratio of 0.4 (95% CI, 0.248-0.642) for those receiving tebentafusp vs. investigator’s choice. The OS benefit, despite low response rates, suggests that patients progress but are then stabilized with tebentafusp treatment.
“So this drug is slowing down developing disease,” she said.
‘Manageable’ adverse events
Target-mediated or cytokine-mediated adverse events were the most common side effects with tebentafusp. These included pyrexia (76%), pruritus (69%), and rash (83%), which decreased in frequency and severity after the first three to four doses.
While cytokine release syndrome was common (89%), the rate of grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome was very low (1%). Adverse events were generally manageable with standard interventions, Dr. Hassel said.
The discontinuation rate was lower in the tebentafusp arm than in the investigator’s choice arm – 2% and 4.5%, respectively. There were no tebentafusp-related deaths.
‘Practice-changing’ results
“This is the first randomized controlled trial to be positive for overall survival in uveal melanoma. These are seminal and practice-changing results,” said AACR discussant Caroline Robert, MD, PhD, of Gustave Roussy and Paris-Saclay University in France.
She observed that the biology of uveal melanoma is distinct from that of cutaneous melanoma, and future research will have to address why tebentafusp doesn’t work as well in cutaneous melanoma. Tebentafusp will be evaluated in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors as well, she added.
The major limitation of tebentafusp, Dr. Hassel observed, is that it can be used only in HLA-A*02:01-positive patients. “There still remains an unmet need for patients who do not have this particular surface protein,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Immunocore. Dr. Hassel disclosed relationships with Immunocore and other companies. Dr. Robert disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Novartis, and other companies.
Tebentafusp is the first investigational therapy in a phase 3 trial to improve OS in metastatic uveal melanoma, said Jessica Hassel, MD, of University Hospital Heidelberg in Germany, when presenting the results at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT002).
Dr. Hassel explained that tebentafusp is a bispecific fusion protein designed to target gp100 through a high affinity T-cell receptor binding domain and an anti-CD3 T-cell engaging domain, which redirects T cells to kill gp100-expressing tumor cells. Because the T-cell receptor binding domain only recognizes a specific gp100-derived peptide presented on HLA-A*02:01, tebentafusp can only be used to treat patients with this HLA type.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 378 treatment-naive HLA-A*02:01-positive patients with metastatic uveal melanoma. Their median age was 65 years, and 50% were men.
Patients were assigned 2:1 to receive tebentafusp (n = 252) or investigator’s choice of pembrolizumab (n = 103), ipilimumab (n = 16), or dacarbazine (n = 7).
Prolonged OS despite low response rate
At a median follow-up of 14.1 months, patients receiving tebentafusp had significantly longer OS than that of patients in the investigator’s choice arm – 21.7 months and 16.0 months, respectively. The estimated 1-year OS rate was 73.2% in the tebentafusp arm and 58.5% in the standard therapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.71; P < .0001). The OS benefit was consistent across subgroups, Dr. Hassel said.
At a median follow-up of 11.4 months, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 months in the tebentafusp arm and 2.9 months in the investigator’s choice arm (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.58-0.94; P = .0139).
The objective response rate was 9% in the tebentafusp arm and 5% in the investigator’s choice arm. There was only one complete response, and it was in the tebentafusp arm.
The disease control rate, defined as response or stable disease for 12 or more weeks, was 46% in the tebentafusp arm and 27% in the investigator’s choice arm. Rates of progressive disease were 52% and 62%, respectively.
Dr. Hassel pointed out that a landmark analysis of OS in patients with a best response of progressive disease, with patients continuing to receive treatment after progression, showed a hazard ratio of 0.4 (95% CI, 0.248-0.642) for those receiving tebentafusp vs. investigator’s choice. The OS benefit, despite low response rates, suggests that patients progress but are then stabilized with tebentafusp treatment.
“So this drug is slowing down developing disease,” she said.
‘Manageable’ adverse events
Target-mediated or cytokine-mediated adverse events were the most common side effects with tebentafusp. These included pyrexia (76%), pruritus (69%), and rash (83%), which decreased in frequency and severity after the first three to four doses.
While cytokine release syndrome was common (89%), the rate of grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome was very low (1%). Adverse events were generally manageable with standard interventions, Dr. Hassel said.
The discontinuation rate was lower in the tebentafusp arm than in the investigator’s choice arm – 2% and 4.5%, respectively. There were no tebentafusp-related deaths.
‘Practice-changing’ results
“This is the first randomized controlled trial to be positive for overall survival in uveal melanoma. These are seminal and practice-changing results,” said AACR discussant Caroline Robert, MD, PhD, of Gustave Roussy and Paris-Saclay University in France.
She observed that the biology of uveal melanoma is distinct from that of cutaneous melanoma, and future research will have to address why tebentafusp doesn’t work as well in cutaneous melanoma. Tebentafusp will be evaluated in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors as well, she added.
The major limitation of tebentafusp, Dr. Hassel observed, is that it can be used only in HLA-A*02:01-positive patients. “There still remains an unmet need for patients who do not have this particular surface protein,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Immunocore. Dr. Hassel disclosed relationships with Immunocore and other companies. Dr. Robert disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Novartis, and other companies.
Tebentafusp is the first investigational therapy in a phase 3 trial to improve OS in metastatic uveal melanoma, said Jessica Hassel, MD, of University Hospital Heidelberg in Germany, when presenting the results at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract CT002).
Dr. Hassel explained that tebentafusp is a bispecific fusion protein designed to target gp100 through a high affinity T-cell receptor binding domain and an anti-CD3 T-cell engaging domain, which redirects T cells to kill gp100-expressing tumor cells. Because the T-cell receptor binding domain only recognizes a specific gp100-derived peptide presented on HLA-A*02:01, tebentafusp can only be used to treat patients with this HLA type.
In the phase 3 trial, investigators enrolled 378 treatment-naive HLA-A*02:01-positive patients with metastatic uveal melanoma. Their median age was 65 years, and 50% were men.
Patients were assigned 2:1 to receive tebentafusp (n = 252) or investigator’s choice of pembrolizumab (n = 103), ipilimumab (n = 16), or dacarbazine (n = 7).
Prolonged OS despite low response rate
At a median follow-up of 14.1 months, patients receiving tebentafusp had significantly longer OS than that of patients in the investigator’s choice arm – 21.7 months and 16.0 months, respectively. The estimated 1-year OS rate was 73.2% in the tebentafusp arm and 58.5% in the standard therapy arm (hazard ratio, 0.51; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.71; P < .0001). The OS benefit was consistent across subgroups, Dr. Hassel said.
At a median follow-up of 11.4 months, the median progression-free survival was 3.3 months in the tebentafusp arm and 2.9 months in the investigator’s choice arm (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.58-0.94; P = .0139).
The objective response rate was 9% in the tebentafusp arm and 5% in the investigator’s choice arm. There was only one complete response, and it was in the tebentafusp arm.
The disease control rate, defined as response or stable disease for 12 or more weeks, was 46% in the tebentafusp arm and 27% in the investigator’s choice arm. Rates of progressive disease were 52% and 62%, respectively.
Dr. Hassel pointed out that a landmark analysis of OS in patients with a best response of progressive disease, with patients continuing to receive treatment after progression, showed a hazard ratio of 0.4 (95% CI, 0.248-0.642) for those receiving tebentafusp vs. investigator’s choice. The OS benefit, despite low response rates, suggests that patients progress but are then stabilized with tebentafusp treatment.
“So this drug is slowing down developing disease,” she said.
‘Manageable’ adverse events
Target-mediated or cytokine-mediated adverse events were the most common side effects with tebentafusp. These included pyrexia (76%), pruritus (69%), and rash (83%), which decreased in frequency and severity after the first three to four doses.
While cytokine release syndrome was common (89%), the rate of grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome was very low (1%). Adverse events were generally manageable with standard interventions, Dr. Hassel said.
The discontinuation rate was lower in the tebentafusp arm than in the investigator’s choice arm – 2% and 4.5%, respectively. There were no tebentafusp-related deaths.
‘Practice-changing’ results
“This is the first randomized controlled trial to be positive for overall survival in uveal melanoma. These are seminal and practice-changing results,” said AACR discussant Caroline Robert, MD, PhD, of Gustave Roussy and Paris-Saclay University in France.
She observed that the biology of uveal melanoma is distinct from that of cutaneous melanoma, and future research will have to address why tebentafusp doesn’t work as well in cutaneous melanoma. Tebentafusp will be evaluated in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors as well, she added.
The major limitation of tebentafusp, Dr. Hassel observed, is that it can be used only in HLA-A*02:01-positive patients. “There still remains an unmet need for patients who do not have this particular surface protein,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Immunocore. Dr. Hassel disclosed relationships with Immunocore and other companies. Dr. Robert disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Pierre Fabre, Novartis, and other companies.
FROM AACR 2021
Black patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis may have more systemic and CV disease
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
FROM SOC SOCIETY 2021
Clinical Edge Commentary: AML April 2021
In a study by Trembely et al. sponsored by Pfizer, an indirect comparison of both studies was performed using a simulated treatment comparison to account for differences in patient characteristics. As expected, the overall response rates were higher in the venetoclax study compared to the glasdegib study (48% vs. 24%), but overall survival was similar (hazard ratio 0.75 vs. HR 0.46). This study demonstrates again that CR/CRi cannot be used as a surrogate endpoint for survival in AML. In addition, with the negative study of V-LDAC vs. LDAC and the improved overall survival of the combination of azacytidine + venetoclax (Aza-ven) vs. azacitdine, the current standard of care of newly diagnosed patients with AML unbale to tolerate intensive chemotherapy is Aza-ven and V-LDAC is rarely used.
The success of Aza-ven is not without side effects. This was demonstrated recently in a retrospective study by Feld et al. In that study 72 patients with newly diagnosed AML (26), relapsed refractory AML (39) and MDS (7) received azacitdine + venetoclax. The main side effect was myelosuppression with only 15% of patients who were transfusion dependent become transfusion independent. In addition, 46% of patients had a neutropenic fever and 43.7% of patients requiring admission. Most patients (54.9%) required treatment interruption and 35.2% stopped venetoclax for toxicity.
This study highlighted that the optimal dose and frequency of venetoclax remains unclear. A shorted duration or lower dose of venetoclax maybe more ideal, however that may lead to less efficacy. In addition, bone marrow evaluation to assess for cellularity on D21 to D28 of the first cycle may help guide dose adjustments. Finally with the high CR/CRi rates in AML and short duration of response further studies are ongoing to further define molecular abnormalities that may refine prognosis or guide therapy. Two of those studies recently reported identified a prognostic and possible therapeutic role for both EZH2 and the PI3 kinase mTOR pathway.
In a study by Trembely et al. sponsored by Pfizer, an indirect comparison of both studies was performed using a simulated treatment comparison to account for differences in patient characteristics. As expected, the overall response rates were higher in the venetoclax study compared to the glasdegib study (48% vs. 24%), but overall survival was similar (hazard ratio 0.75 vs. HR 0.46). This study demonstrates again that CR/CRi cannot be used as a surrogate endpoint for survival in AML. In addition, with the negative study of V-LDAC vs. LDAC and the improved overall survival of the combination of azacytidine + venetoclax (Aza-ven) vs. azacitdine, the current standard of care of newly diagnosed patients with AML unbale to tolerate intensive chemotherapy is Aza-ven and V-LDAC is rarely used.
The success of Aza-ven is not without side effects. This was demonstrated recently in a retrospective study by Feld et al. In that study 72 patients with newly diagnosed AML (26), relapsed refractory AML (39) and MDS (7) received azacitdine + venetoclax. The main side effect was myelosuppression with only 15% of patients who were transfusion dependent become transfusion independent. In addition, 46% of patients had a neutropenic fever and 43.7% of patients requiring admission. Most patients (54.9%) required treatment interruption and 35.2% stopped venetoclax for toxicity.
This study highlighted that the optimal dose and frequency of venetoclax remains unclear. A shorted duration or lower dose of venetoclax maybe more ideal, however that may lead to less efficacy. In addition, bone marrow evaluation to assess for cellularity on D21 to D28 of the first cycle may help guide dose adjustments. Finally with the high CR/CRi rates in AML and short duration of response further studies are ongoing to further define molecular abnormalities that may refine prognosis or guide therapy. Two of those studies recently reported identified a prognostic and possible therapeutic role for both EZH2 and the PI3 kinase mTOR pathway.
In a study by Trembely et al. sponsored by Pfizer, an indirect comparison of both studies was performed using a simulated treatment comparison to account for differences in patient characteristics. As expected, the overall response rates were higher in the venetoclax study compared to the glasdegib study (48% vs. 24%), but overall survival was similar (hazard ratio 0.75 vs. HR 0.46). This study demonstrates again that CR/CRi cannot be used as a surrogate endpoint for survival in AML. In addition, with the negative study of V-LDAC vs. LDAC and the improved overall survival of the combination of azacytidine + venetoclax (Aza-ven) vs. azacitdine, the current standard of care of newly diagnosed patients with AML unbale to tolerate intensive chemotherapy is Aza-ven and V-LDAC is rarely used.
The success of Aza-ven is not without side effects. This was demonstrated recently in a retrospective study by Feld et al. In that study 72 patients with newly diagnosed AML (26), relapsed refractory AML (39) and MDS (7) received azacitdine + venetoclax. The main side effect was myelosuppression with only 15% of patients who were transfusion dependent become transfusion independent. In addition, 46% of patients had a neutropenic fever and 43.7% of patients requiring admission. Most patients (54.9%) required treatment interruption and 35.2% stopped venetoclax for toxicity.
This study highlighted that the optimal dose and frequency of venetoclax remains unclear. A shorted duration or lower dose of venetoclax maybe more ideal, however that may lead to less efficacy. In addition, bone marrow evaluation to assess for cellularity on D21 to D28 of the first cycle may help guide dose adjustments. Finally with the high CR/CRi rates in AML and short duration of response further studies are ongoing to further define molecular abnormalities that may refine prognosis or guide therapy. Two of those studies recently reported identified a prognostic and possible therapeutic role for both EZH2 and the PI3 kinase mTOR pathway.
Let me tell you about my vaccine
Welcome to our national obsession: Vaccines! You may have noticed – it’s all talk, all the time, with short breaks to discuss what we’re watching on Netflix.
For months, every session with almost every patient includes a commentary on someone they know who has gotten “the shot.” Before our state expanded eligibility to all adults, the discussion might include thoughts about who deserves to go first, who “cut the line,” how they did it, what vaccine is best, and worries about side effects.
And it’s not just my patients: With every friend, with every acquaintance, and even just walking by strangers who are conversing, the topic of discussion is vaccines. The narratives are similar; people want to talk about who has gotten vaccinated, why they qualified, where they went, which one they got, and what side effects they experienced. This is followed by a discussion about what they are now doing that they weren’t doing before being vaccinated, if anything. Some have returned to indoor restaurant dining, others only dine outdoors, still others continue to avoid public settings. There are the fully vaccinated, the partially vaccinated, and those scheduled for the first shot. In the unvaccinated/unregistered group there are the vaccine-hesitants and vaccine-refusers, with their concerns about everything from the safety of the agent to whether the government is using this as a way to insert tracker chips into all of us. There is enthusiasm, trepidation, anxiety, fear, excitement, relief, and absolute joy.
Recently I opened two emails from old friends I have not communicated with in a long time. Both emails began with, “I am fully vaccinated.” And yes, I heard the status of his wife and two children. In the course of one work day, I received distressed text messages from two patients about vaccines – one was anxious about having received the Janssen vaccine that was paused that morning, another was worried about getting a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine later in the week because he was having a symptom that could be indicative of COVID-19. I suggested that his primary care physician might be a better resource for this, but then added that he should probably get tested and delay having the second dose if positive. It seems I did have thoughts about a course of action after all.
Some psychiatrists have wondered how to handle patient questions about their own vaccination status. I have taken the stance that we are physicians, and that patients who may be seeing us – now or in the future – for in-person appointments are entitled to know if we pose a risk to their health, and so I have chosen to answer, without further exploration, when patients ask if I’ve received that coronavirus vaccine. Some psychiatrists feel it is our responsibility to share this information with our patients as a way of modeling safe behavior, and I have had one patient who said she would not be getting vaccinated until I told her that I thought she should.
“Did you get it?” she asked.
“I did,” I responded.
“Okay, if you got it, I will.” She soon discovered that vaccinations were hard to come by and that in her social group, being vaccinated was something of a status symbol. In addition to the worry about contracting a potentially fatal virus, her hesitancy yielded to “vaccine FOMO” or fear of missing out.
Some psychiatrists have felt uneasy with a question that pertains to their personal health, or have used the question as a springboard for exploration. Nicole Leistikow, MD (fully vaccinated, Moderna), is a psychiatrist in private practice in Baltimore. She notes, “Recently, I was discussing vaccination with a patient who wasn’t sure what information to believe or how much to trust the U.S. government. My careful exploration comparing different risks was not very helpful. I mentioned that I was vaccinated and that if he got vaccinated, he could come for a low-risk, in-person appointment after a year of telephone visits. This proved to be a winning argument and he called back later that day to say he had already had his first shot from leftover vaccine at his pharmacy.”
I grew up in a world that did not question vaccines. You got them and they were good things. No one asked which pharmaceutical company manufactured the vaccine. We trusted the system and our physicians. Schools asked for proof of vaccination, and it never occurred to me not to be vaccinated. Life has grown more complicated in the last 30 years, and the groups of people who are opposed to being vaccinated are more diverse. Those opposed to getting a COVID-19 vaccine are not necessarily the same as the broader group of anti-vaxxers that spawned from the fear that childhood vaccines cause autism. For some, it’s a personal issue related to their own health and risk perception, for others it’s a polarized political issue, and for another group there is the question of where their trust lies.
What lies ahead in our postvaccine world? This will be our next national conversation, and just as we negotiated our own levels of comfort with regard to working and socializing during the pandemic, I imagine the postvaccine world will have the same adjustment. There already are cases of COVID-19 in those who have been fully vaccinated, as well as the rare hospitalizations and deaths – we simply cannot expect a vaccine that did so well in controlled studies of tens of thousands of study subjects to do as well when given to tens of millions of uncontrolled citizens. One of the first deaths in a fully vaccinated person in late March was an older psychologist, and it remains unclear how effective the vaccine is for immunocompromised patients. Some people will play it very safe, eschewing all activities that entail risk, while others will choose to adhere to either their own intuition about what is safe, or to the recommendations of Anthony S. Fauci, MD, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
I’ll end with a final thought from the Twitter feed of Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the School of Public Health at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Jha tweeted, “Once you get fully vaccinated, it absolutely changes what you can do safely.” It seems our national conversation is not slated to change anytime soon.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
Welcome to our national obsession: Vaccines! You may have noticed – it’s all talk, all the time, with short breaks to discuss what we’re watching on Netflix.
For months, every session with almost every patient includes a commentary on someone they know who has gotten “the shot.” Before our state expanded eligibility to all adults, the discussion might include thoughts about who deserves to go first, who “cut the line,” how they did it, what vaccine is best, and worries about side effects.
And it’s not just my patients: With every friend, with every acquaintance, and even just walking by strangers who are conversing, the topic of discussion is vaccines. The narratives are similar; people want to talk about who has gotten vaccinated, why they qualified, where they went, which one they got, and what side effects they experienced. This is followed by a discussion about what they are now doing that they weren’t doing before being vaccinated, if anything. Some have returned to indoor restaurant dining, others only dine outdoors, still others continue to avoid public settings. There are the fully vaccinated, the partially vaccinated, and those scheduled for the first shot. In the unvaccinated/unregistered group there are the vaccine-hesitants and vaccine-refusers, with their concerns about everything from the safety of the agent to whether the government is using this as a way to insert tracker chips into all of us. There is enthusiasm, trepidation, anxiety, fear, excitement, relief, and absolute joy.
Recently I opened two emails from old friends I have not communicated with in a long time. Both emails began with, “I am fully vaccinated.” And yes, I heard the status of his wife and two children. In the course of one work day, I received distressed text messages from two patients about vaccines – one was anxious about having received the Janssen vaccine that was paused that morning, another was worried about getting a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine later in the week because he was having a symptom that could be indicative of COVID-19. I suggested that his primary care physician might be a better resource for this, but then added that he should probably get tested and delay having the second dose if positive. It seems I did have thoughts about a course of action after all.
Some psychiatrists have wondered how to handle patient questions about their own vaccination status. I have taken the stance that we are physicians, and that patients who may be seeing us – now or in the future – for in-person appointments are entitled to know if we pose a risk to their health, and so I have chosen to answer, without further exploration, when patients ask if I’ve received that coronavirus vaccine. Some psychiatrists feel it is our responsibility to share this information with our patients as a way of modeling safe behavior, and I have had one patient who said she would not be getting vaccinated until I told her that I thought she should.
“Did you get it?” she asked.
“I did,” I responded.
“Okay, if you got it, I will.” She soon discovered that vaccinations were hard to come by and that in her social group, being vaccinated was something of a status symbol. In addition to the worry about contracting a potentially fatal virus, her hesitancy yielded to “vaccine FOMO” or fear of missing out.
Some psychiatrists have felt uneasy with a question that pertains to their personal health, or have used the question as a springboard for exploration. Nicole Leistikow, MD (fully vaccinated, Moderna), is a psychiatrist in private practice in Baltimore. She notes, “Recently, I was discussing vaccination with a patient who wasn’t sure what information to believe or how much to trust the U.S. government. My careful exploration comparing different risks was not very helpful. I mentioned that I was vaccinated and that if he got vaccinated, he could come for a low-risk, in-person appointment after a year of telephone visits. This proved to be a winning argument and he called back later that day to say he had already had his first shot from leftover vaccine at his pharmacy.”
I grew up in a world that did not question vaccines. You got them and they were good things. No one asked which pharmaceutical company manufactured the vaccine. We trusted the system and our physicians. Schools asked for proof of vaccination, and it never occurred to me not to be vaccinated. Life has grown more complicated in the last 30 years, and the groups of people who are opposed to being vaccinated are more diverse. Those opposed to getting a COVID-19 vaccine are not necessarily the same as the broader group of anti-vaxxers that spawned from the fear that childhood vaccines cause autism. For some, it’s a personal issue related to their own health and risk perception, for others it’s a polarized political issue, and for another group there is the question of where their trust lies.
What lies ahead in our postvaccine world? This will be our next national conversation, and just as we negotiated our own levels of comfort with regard to working and socializing during the pandemic, I imagine the postvaccine world will have the same adjustment. There already are cases of COVID-19 in those who have been fully vaccinated, as well as the rare hospitalizations and deaths – we simply cannot expect a vaccine that did so well in controlled studies of tens of thousands of study subjects to do as well when given to tens of millions of uncontrolled citizens. One of the first deaths in a fully vaccinated person in late March was an older psychologist, and it remains unclear how effective the vaccine is for immunocompromised patients. Some people will play it very safe, eschewing all activities that entail risk, while others will choose to adhere to either their own intuition about what is safe, or to the recommendations of Anthony S. Fauci, MD, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
I’ll end with a final thought from the Twitter feed of Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the School of Public Health at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Jha tweeted, “Once you get fully vaccinated, it absolutely changes what you can do safely.” It seems our national conversation is not slated to change anytime soon.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
Welcome to our national obsession: Vaccines! You may have noticed – it’s all talk, all the time, with short breaks to discuss what we’re watching on Netflix.
For months, every session with almost every patient includes a commentary on someone they know who has gotten “the shot.” Before our state expanded eligibility to all adults, the discussion might include thoughts about who deserves to go first, who “cut the line,” how they did it, what vaccine is best, and worries about side effects.
And it’s not just my patients: With every friend, with every acquaintance, and even just walking by strangers who are conversing, the topic of discussion is vaccines. The narratives are similar; people want to talk about who has gotten vaccinated, why they qualified, where they went, which one they got, and what side effects they experienced. This is followed by a discussion about what they are now doing that they weren’t doing before being vaccinated, if anything. Some have returned to indoor restaurant dining, others only dine outdoors, still others continue to avoid public settings. There are the fully vaccinated, the partially vaccinated, and those scheduled for the first shot. In the unvaccinated/unregistered group there are the vaccine-hesitants and vaccine-refusers, with their concerns about everything from the safety of the agent to whether the government is using this as a way to insert tracker chips into all of us. There is enthusiasm, trepidation, anxiety, fear, excitement, relief, and absolute joy.
Recently I opened two emails from old friends I have not communicated with in a long time. Both emails began with, “I am fully vaccinated.” And yes, I heard the status of his wife and two children. In the course of one work day, I received distressed text messages from two patients about vaccines – one was anxious about having received the Janssen vaccine that was paused that morning, another was worried about getting a second dose of the Pfizer vaccine later in the week because he was having a symptom that could be indicative of COVID-19. I suggested that his primary care physician might be a better resource for this, but then added that he should probably get tested and delay having the second dose if positive. It seems I did have thoughts about a course of action after all.
Some psychiatrists have wondered how to handle patient questions about their own vaccination status. I have taken the stance that we are physicians, and that patients who may be seeing us – now or in the future – for in-person appointments are entitled to know if we pose a risk to their health, and so I have chosen to answer, without further exploration, when patients ask if I’ve received that coronavirus vaccine. Some psychiatrists feel it is our responsibility to share this information with our patients as a way of modeling safe behavior, and I have had one patient who said she would not be getting vaccinated until I told her that I thought she should.
“Did you get it?” she asked.
“I did,” I responded.
“Okay, if you got it, I will.” She soon discovered that vaccinations were hard to come by and that in her social group, being vaccinated was something of a status symbol. In addition to the worry about contracting a potentially fatal virus, her hesitancy yielded to “vaccine FOMO” or fear of missing out.
Some psychiatrists have felt uneasy with a question that pertains to their personal health, or have used the question as a springboard for exploration. Nicole Leistikow, MD (fully vaccinated, Moderna), is a psychiatrist in private practice in Baltimore. She notes, “Recently, I was discussing vaccination with a patient who wasn’t sure what information to believe or how much to trust the U.S. government. My careful exploration comparing different risks was not very helpful. I mentioned that I was vaccinated and that if he got vaccinated, he could come for a low-risk, in-person appointment after a year of telephone visits. This proved to be a winning argument and he called back later that day to say he had already had his first shot from leftover vaccine at his pharmacy.”
I grew up in a world that did not question vaccines. You got them and they were good things. No one asked which pharmaceutical company manufactured the vaccine. We trusted the system and our physicians. Schools asked for proof of vaccination, and it never occurred to me not to be vaccinated. Life has grown more complicated in the last 30 years, and the groups of people who are opposed to being vaccinated are more diverse. Those opposed to getting a COVID-19 vaccine are not necessarily the same as the broader group of anti-vaxxers that spawned from the fear that childhood vaccines cause autism. For some, it’s a personal issue related to their own health and risk perception, for others it’s a polarized political issue, and for another group there is the question of where their trust lies.
What lies ahead in our postvaccine world? This will be our next national conversation, and just as we negotiated our own levels of comfort with regard to working and socializing during the pandemic, I imagine the postvaccine world will have the same adjustment. There already are cases of COVID-19 in those who have been fully vaccinated, as well as the rare hospitalizations and deaths – we simply cannot expect a vaccine that did so well in controlled studies of tens of thousands of study subjects to do as well when given to tens of millions of uncontrolled citizens. One of the first deaths in a fully vaccinated person in late March was an older psychologist, and it remains unclear how effective the vaccine is for immunocompromised patients. Some people will play it very safe, eschewing all activities that entail risk, while others will choose to adhere to either their own intuition about what is safe, or to the recommendations of Anthony S. Fauci, MD, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
I’ll end with a final thought from the Twitter feed of Ashish K. Jha, MD, dean of the School of Public Health at Brown University, Providence, R.I. Dr. Jha tweeted, “Once you get fully vaccinated, it absolutely changes what you can do safely.” It seems our national conversation is not slated to change anytime soon.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.