User login
Things We Do for No Reason™: Calculating a “Corrected Calcium” Level
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A hospitalist admits a 75-year-old man for evaluation of acute pyelonephritis; the patient’s medical history is significant for chronic kidney disease and nephrotic syndrome. The patient endorses moderate flank pain upon palpation. Initial serum laboratory studies reveal an albumin level of 1.5 g/dL and a calcium level of 10.0 mg/dL. A repeat serum calcium assessment produces similar results. The hospitalist corrects calcium for albumin concentration by applying the most common formula (Payne’s formula), which results in a corrected calcium value of 12 mg/dL. The hospitalist then starts the patient on intravenous (IV) fluids to treat hypercalcemia and obtains serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels.
BACKGROUND
Our skeletons bind, with phosphate, nearly 99% of the body’s calcium, the most abundant mineral in our body. The remaining 1% of calcium (approximately 9-10.5 mg/dL) circulates in the blood. Approximately 40% of serum calcium is bound to albumin, with a smaller percentage bound to lactate and citrate. The remaining 4.5 to 5.5 mg/dL circulates unbound as free (ie, ionized) calcium (iCa).1 Calcium has many fundamental intra- and extracellular functions. Physiologic calcium homeostasis is maintained by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D.2 The amount of circulating iCa, rather than total plasma calcium, determines the many biologic effects of plasma calcium.
In the hospital setting, clinicians commonly encounter patients with derangements in calcium homeostasis.3 True hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia has significant clinical manifestations, including generalized fatigue, nephrolithiasis, cardiac arrhythmias, and, potentially, death. Thus, clinical practice requires correct and accurate assessment of serum calcium levels.1
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK CALCULATING A “CORRECTED CALCIUM” LEVEL IS HELPFUL
Although measuring biologically active calcium (ie, iCa) is the gold standard for assessing calcium levels, laboratories struggle to obtain a direct, accurate measurement of iCa due to the special handling and time constraints required to process samples.4 As a result, metabolic laboratory panels typically report the more easily measured total calcium, the sum of iCa and bound calcium.5 Changes in albumin levels, however, do not affect iCa levels. Since calcium has less available albumin for binding, hypoalbuminemia should theoretically decrease the amount of bound calcium and lead to a decreased reported total calcium. Therefore, a patient’s total calcium level may appear low even though their iCa is normal, which can lead to an incorrect diagnosis of hypocalcemia or overestimate of the extent of existing hypocalcemia. Moreover, these lower reported calcium levels can falsely report normocalcemia in patients with hypercalcemia or underestimate the extent of the patient’s hypercalcemia.
For years physicians have attempted to account for the underestimate in total calcium due to hypoalbuminemia by calculating a “corrected” calcium. The correction formulas use total calcium and serum albumin to estimate the expected iCa. Refinements to the original formula, developed by Payne et al in 1973, have resulted in the most commonly utilized formula today: corrected calcium = (0.8 x [normal albumin – patient’s albumin]) + serum calcium.6,7 Many commonly used clinical-decision resources recommend correcting serum calcium concentrations in patients with hypoalbuminemia.6
WHY CALCULATING A CORRECTED CALCIUM FOR ALBUMIN IS UNNECESSARY
While calculating corrected calcium should theoretically provide a more accurate estimate of physiologically active iCa in patients with hypoalbuminemia,4 the commonly used correction equations become less accurate as hypoalbuminemia worsens.8 Payne et al derived the original formula from 200 patients using a single laboratory; however, subsequent retrospective studies have not supported the use of albumin-corrected calcium calculations to estimate the iCa.4,9-11 For example, although Payne’s corrected calcium equations assume a constant relationship between albumin and calcium binding throughout all serum-albumin concentrations, studies have shown that as albumin falls, more calcium ions bind to each available gram of albumin. Payne’s assumption results in an overestimation of the total serum calcium after correction as compared to the iCa.8 In comparison, uncorrected total serum calcium assays more accurately reflect both the change in albumin binding that occurs with alterations in albumin concentration and the unchanged free calcium ions. Studies demonstrate superior correlation between iCa and uncorrected total calcium.4,9-11
Several large retrospective studies revealed the poor in vivo accuracy of equations used to correct calcium for albumin. In one study, Uppsala University Sweden researchers reviewed the laboratory records of more than 20,000 hospitalized patients from 2005 to 2013.9 This group compared seven corrected calcium formulas to direct measurements of iCa. All of the correction equations correlated poorly with iCa based on their intraclass correlation (ICC), a descriptive statistic for units that have been sorted into groups. (ICC describes how strongly the units in each group correlate or resemble each other—eg, the closer an ICC is to 1, the stronger the correlation is between each unit in the group.) ICC for the correcting equations ranged from 0.45-0.81. The formulas used to calculate corrected calcium levels performed especially poorly in patients with hypoalbuminemia. In this same patient population, the total serum calcium correlated well with directly assessed iCa, with an ICC of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.84-0.86). Moreover, the uncorrected total calcium classified the patient’s calcium level correctly in 82% of cases.
A second study of 5,500 patients in Australia comparing total and adjusted calcium with iCa similarly demonstrated that corrected calcium inaccurately predicts calcium status.10 Findings from this study showed that corrected calcium values correlated with iCa in only 55% to 65% of samples, but uncorrected total calcium correlated with iCa in 70% to 80% of samples. Notably, in patients with renal failure and/or serum albumin concentrations <3 g/dL, formulas used to correct calcium overestimated calcium levels when compared to directly assessed iCa. Correction formulas performed on serum albumin concentrations >3 g/dL correlated better with iCa (65%-77%), effectively negating the utility of the correction formulas.
Another large retrospective observational study from Norway reviewed laboratory data from more than 6,500 hospitalized and clinic patients.11 In this study, researchers calculated corrected calcium using several different albumin-adjusted formulas and compared results to laboratory-assessed iCa. As compared to corrected calcium, uncorrected total calcium more accurately determined clinically relevant free calcium.
Finally, a Canadian research group analyzed time-matched calcium, albumin, and iCa samples from 678 patients.4 They calculated each patient’s corrected calcium values using Payne’s formula. Results of this study showed that corrected calcium predicted iCa outcomes less reliably than uncorrected total calcium (ICC, 0.73 for corrected calcium vs 0.78 for uncorrected calcium).
Utilizing corrected calcium formulas in patients with hypoalbuminemia can overestimate serum calcium, resulting in false-positive findings and an incorrect diagnosis of hypercalcemia or normocalcemia.12 Incorrectly diagnosing hypercalcemia by using correction formulas prompts management that can lead to iatrogenic harm. Hypoalbuminemia is often associated with hepatic or renal disease. In this patient population, standard treatment of hypercalcemia with volume resuscitation (typically 2 to 4 L) and potentially IV loop diuretics will cause clinically significant volume overload and could worsen renal dysfunction.13 Notably, some of the correction formulas utilized in the studies discussed here performed well in hypercalcemic patients, particularly in those with preserved renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2).
Importantly, correction formulas can mask true hypocalcemia or the true severity of hypocalcemia. Applying correction formulas in patients with clinically significant hypocalcemia and hypoalbuminemia can make hospitalists believe that the calcium levels are normal or not as clinically significant as they first seemed. This can lead to the withholding of appropriate treatment.12
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
Based on the available literature, uncorrected total calcium values more accurately assess biologically active calcium. If a more certain calcium value will affect clinical outcomes, clinicians should obtain a direct measurement of iCa.4,9-11 Therefore, clinicians should assess iCa irrespective of the uncorrected serum calcium level in patients who are critically ill or who have known hypoparathyroidism or other derangements in iCa.14 Since iCa levels also fluctuate with pH, samples must be processed quickly and kept cool to slow blood cell metabolism, which alters pH levels.4 Using bedside point-of-care blood gas analyzers to obtain iCa removes a large logistical obstacle to obtaining an accurate iCa. Serum electrolyte interpretation with a properly calibrated point-of-care analyzer correlates well with a traditional laboratory analyzer.15
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Use serum calcium testing routinely to evaluate calcium homeostasis.
- Do not use corrected calcium equations to estimate total calcium.
- If a more accurate measurement of calcium will change medical management, obtain a direct iCa.
- Obtain a direct iCa measurement in critically ill patents and in patients with known hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, or other derangements in calcium homeostasis.
- Do not order a serum albumin test to assess calcium levels.
CONCLUSION
Returning to our clinical scenario, this patient did not have true hypercalcemia and experienced unnecessary evaluation and treatment. Multiple retrospective clinical trials do not support the practice of using corrected calcium equations to correct for serum albumin derangements.4,9-11 Hospitalists should therefore avoid the temptation to calculate a corrected calcium level in patients with hypoalbuminemia. For patients with clinically significant total serum hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, they should consider obtaining an iCa assay to better determine the true physiologic impact.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
1. Peacock M. Calcium metabolism in health and disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5 Suppl 1:S23-S30. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.05910809
2. Brown EM. Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid cell function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers. Physiol Rev. 1991;71(2):371-411. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.371
3. Aishah AB, Foo YN. A retrospective study of serum calcium levels in a hospital population in Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 1995;50(3):246-249.
4. Steen O, Clase C, Don-Wauchope A. Corrected calcium formula in routine clinical use does not accurately reflect ionized calcium in hospital patients. Can J Gen Int Med. 2016;11(3):14-21. https://doi.org/10.22374/cjgim.v11i3.150
5. Payne RB, Little AJ, Williams RB, Milner JR. Interpretation of serum calcium in patients with abnormal serum proteins. Br Med J. 1973;4(5893):643-646. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.4.5893.643
6. Shane E. Diagnostic approach to hypercalcemia. UpToDate website. Updated August 31, 2020. Accessed April 8, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnostic-approach-to-hypercalcemia
7. Ladenson JH, Lewis JW, Boyd JC. Failure of total calcium corrected for protein, albumin, and pH to correctly assess free calcium status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978;46(6):986-993. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-46-6-986
8. Besarab A, Caro JF. Increased absolute calcium binding to albumin in hypoalbuminaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1981;34(12):1368-1374. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.34.12.1368
9. Ridefelt P, Helmersson-Karlqvist J. Albumin adjustment of total calcium does not improve the estimation of calcium status. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2017;77(6):442-447. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2017.1336568
10. Smith JD, Wilson S, Schneider HG. Misclassification of calcium status based on albumin-adjusted calcium: studies in a tertiary hospital setting. Clin Chem. 2018;64(12):1713-1722. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2018.291377
11. Lian IA, Åsberg A. Should total calcium be adjusted for albumin? A retrospective observational study of laboratory data from central Norway. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e017703. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017703
12. Bowers GN Jr, Brassard C, Sena SF. Measurement of ionized calcium in serum with ion-selective electrodes: a mature technology that can meet the daily service needs. Clin Chem. 1986;32(8)1437-1447.
13. Myburgh JA. Fluid resuscitation in acute medicine: what is the current situation? J Intern Med. 2015;277(1):58-68. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12326
14. Aberegg SK. Ionized calcium in the ICU: should it be measured and corrected? Chest. 2016;149(3):846-855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2015.12.001
15. Mirzazadeh M, Morovat A, James T, Smith I, Kirby J, Shine B. Point-of-care testing of electrolytes and calcium using blood gas analysers: it is time we trusted the results. Emerg Med J. 2016;33(3):181-186. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2015-204669
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A hospitalist admits a 75-year-old man for evaluation of acute pyelonephritis; the patient’s medical history is significant for chronic kidney disease and nephrotic syndrome. The patient endorses moderate flank pain upon palpation. Initial serum laboratory studies reveal an albumin level of 1.5 g/dL and a calcium level of 10.0 mg/dL. A repeat serum calcium assessment produces similar results. The hospitalist corrects calcium for albumin concentration by applying the most common formula (Payne’s formula), which results in a corrected calcium value of 12 mg/dL. The hospitalist then starts the patient on intravenous (IV) fluids to treat hypercalcemia and obtains serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels.
BACKGROUND
Our skeletons bind, with phosphate, nearly 99% of the body’s calcium, the most abundant mineral in our body. The remaining 1% of calcium (approximately 9-10.5 mg/dL) circulates in the blood. Approximately 40% of serum calcium is bound to albumin, with a smaller percentage bound to lactate and citrate. The remaining 4.5 to 5.5 mg/dL circulates unbound as free (ie, ionized) calcium (iCa).1 Calcium has many fundamental intra- and extracellular functions. Physiologic calcium homeostasis is maintained by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D.2 The amount of circulating iCa, rather than total plasma calcium, determines the many biologic effects of plasma calcium.
In the hospital setting, clinicians commonly encounter patients with derangements in calcium homeostasis.3 True hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia has significant clinical manifestations, including generalized fatigue, nephrolithiasis, cardiac arrhythmias, and, potentially, death. Thus, clinical practice requires correct and accurate assessment of serum calcium levels.1
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK CALCULATING A “CORRECTED CALCIUM” LEVEL IS HELPFUL
Although measuring biologically active calcium (ie, iCa) is the gold standard for assessing calcium levels, laboratories struggle to obtain a direct, accurate measurement of iCa due to the special handling and time constraints required to process samples.4 As a result, metabolic laboratory panels typically report the more easily measured total calcium, the sum of iCa and bound calcium.5 Changes in albumin levels, however, do not affect iCa levels. Since calcium has less available albumin for binding, hypoalbuminemia should theoretically decrease the amount of bound calcium and lead to a decreased reported total calcium. Therefore, a patient’s total calcium level may appear low even though their iCa is normal, which can lead to an incorrect diagnosis of hypocalcemia or overestimate of the extent of existing hypocalcemia. Moreover, these lower reported calcium levels can falsely report normocalcemia in patients with hypercalcemia or underestimate the extent of the patient’s hypercalcemia.
For years physicians have attempted to account for the underestimate in total calcium due to hypoalbuminemia by calculating a “corrected” calcium. The correction formulas use total calcium and serum albumin to estimate the expected iCa. Refinements to the original formula, developed by Payne et al in 1973, have resulted in the most commonly utilized formula today: corrected calcium = (0.8 x [normal albumin – patient’s albumin]) + serum calcium.6,7 Many commonly used clinical-decision resources recommend correcting serum calcium concentrations in patients with hypoalbuminemia.6
WHY CALCULATING A CORRECTED CALCIUM FOR ALBUMIN IS UNNECESSARY
While calculating corrected calcium should theoretically provide a more accurate estimate of physiologically active iCa in patients with hypoalbuminemia,4 the commonly used correction equations become less accurate as hypoalbuminemia worsens.8 Payne et al derived the original formula from 200 patients using a single laboratory; however, subsequent retrospective studies have not supported the use of albumin-corrected calcium calculations to estimate the iCa.4,9-11 For example, although Payne’s corrected calcium equations assume a constant relationship between albumin and calcium binding throughout all serum-albumin concentrations, studies have shown that as albumin falls, more calcium ions bind to each available gram of albumin. Payne’s assumption results in an overestimation of the total serum calcium after correction as compared to the iCa.8 In comparison, uncorrected total serum calcium assays more accurately reflect both the change in albumin binding that occurs with alterations in albumin concentration and the unchanged free calcium ions. Studies demonstrate superior correlation between iCa and uncorrected total calcium.4,9-11
Several large retrospective studies revealed the poor in vivo accuracy of equations used to correct calcium for albumin. In one study, Uppsala University Sweden researchers reviewed the laboratory records of more than 20,000 hospitalized patients from 2005 to 2013.9 This group compared seven corrected calcium formulas to direct measurements of iCa. All of the correction equations correlated poorly with iCa based on their intraclass correlation (ICC), a descriptive statistic for units that have been sorted into groups. (ICC describes how strongly the units in each group correlate or resemble each other—eg, the closer an ICC is to 1, the stronger the correlation is between each unit in the group.) ICC for the correcting equations ranged from 0.45-0.81. The formulas used to calculate corrected calcium levels performed especially poorly in patients with hypoalbuminemia. In this same patient population, the total serum calcium correlated well with directly assessed iCa, with an ICC of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.84-0.86). Moreover, the uncorrected total calcium classified the patient’s calcium level correctly in 82% of cases.
A second study of 5,500 patients in Australia comparing total and adjusted calcium with iCa similarly demonstrated that corrected calcium inaccurately predicts calcium status.10 Findings from this study showed that corrected calcium values correlated with iCa in only 55% to 65% of samples, but uncorrected total calcium correlated with iCa in 70% to 80% of samples. Notably, in patients with renal failure and/or serum albumin concentrations <3 g/dL, formulas used to correct calcium overestimated calcium levels when compared to directly assessed iCa. Correction formulas performed on serum albumin concentrations >3 g/dL correlated better with iCa (65%-77%), effectively negating the utility of the correction formulas.
Another large retrospective observational study from Norway reviewed laboratory data from more than 6,500 hospitalized and clinic patients.11 In this study, researchers calculated corrected calcium using several different albumin-adjusted formulas and compared results to laboratory-assessed iCa. As compared to corrected calcium, uncorrected total calcium more accurately determined clinically relevant free calcium.
Finally, a Canadian research group analyzed time-matched calcium, albumin, and iCa samples from 678 patients.4 They calculated each patient’s corrected calcium values using Payne’s formula. Results of this study showed that corrected calcium predicted iCa outcomes less reliably than uncorrected total calcium (ICC, 0.73 for corrected calcium vs 0.78 for uncorrected calcium).
Utilizing corrected calcium formulas in patients with hypoalbuminemia can overestimate serum calcium, resulting in false-positive findings and an incorrect diagnosis of hypercalcemia or normocalcemia.12 Incorrectly diagnosing hypercalcemia by using correction formulas prompts management that can lead to iatrogenic harm. Hypoalbuminemia is often associated with hepatic or renal disease. In this patient population, standard treatment of hypercalcemia with volume resuscitation (typically 2 to 4 L) and potentially IV loop diuretics will cause clinically significant volume overload and could worsen renal dysfunction.13 Notably, some of the correction formulas utilized in the studies discussed here performed well in hypercalcemic patients, particularly in those with preserved renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2).
Importantly, correction formulas can mask true hypocalcemia or the true severity of hypocalcemia. Applying correction formulas in patients with clinically significant hypocalcemia and hypoalbuminemia can make hospitalists believe that the calcium levels are normal or not as clinically significant as they first seemed. This can lead to the withholding of appropriate treatment.12
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
Based on the available literature, uncorrected total calcium values more accurately assess biologically active calcium. If a more certain calcium value will affect clinical outcomes, clinicians should obtain a direct measurement of iCa.4,9-11 Therefore, clinicians should assess iCa irrespective of the uncorrected serum calcium level in patients who are critically ill or who have known hypoparathyroidism or other derangements in iCa.14 Since iCa levels also fluctuate with pH, samples must be processed quickly and kept cool to slow blood cell metabolism, which alters pH levels.4 Using bedside point-of-care blood gas analyzers to obtain iCa removes a large logistical obstacle to obtaining an accurate iCa. Serum electrolyte interpretation with a properly calibrated point-of-care analyzer correlates well with a traditional laboratory analyzer.15
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Use serum calcium testing routinely to evaluate calcium homeostasis.
- Do not use corrected calcium equations to estimate total calcium.
- If a more accurate measurement of calcium will change medical management, obtain a direct iCa.
- Obtain a direct iCa measurement in critically ill patents and in patients with known hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, or other derangements in calcium homeostasis.
- Do not order a serum albumin test to assess calcium levels.
CONCLUSION
Returning to our clinical scenario, this patient did not have true hypercalcemia and experienced unnecessary evaluation and treatment. Multiple retrospective clinical trials do not support the practice of using corrected calcium equations to correct for serum albumin derangements.4,9-11 Hospitalists should therefore avoid the temptation to calculate a corrected calcium level in patients with hypoalbuminemia. For patients with clinically significant total serum hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, they should consider obtaining an iCa assay to better determine the true physiologic impact.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
CLINICAL SCENARIO
A hospitalist admits a 75-year-old man for evaluation of acute pyelonephritis; the patient’s medical history is significant for chronic kidney disease and nephrotic syndrome. The patient endorses moderate flank pain upon palpation. Initial serum laboratory studies reveal an albumin level of 1.5 g/dL and a calcium level of 10.0 mg/dL. A repeat serum calcium assessment produces similar results. The hospitalist corrects calcium for albumin concentration by applying the most common formula (Payne’s formula), which results in a corrected calcium value of 12 mg/dL. The hospitalist then starts the patient on intravenous (IV) fluids to treat hypercalcemia and obtains serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone levels.
BACKGROUND
Our skeletons bind, with phosphate, nearly 99% of the body’s calcium, the most abundant mineral in our body. The remaining 1% of calcium (approximately 9-10.5 mg/dL) circulates in the blood. Approximately 40% of serum calcium is bound to albumin, with a smaller percentage bound to lactate and citrate. The remaining 4.5 to 5.5 mg/dL circulates unbound as free (ie, ionized) calcium (iCa).1 Calcium has many fundamental intra- and extracellular functions. Physiologic calcium homeostasis is maintained by parathyroid hormone and vitamin D.2 The amount of circulating iCa, rather than total plasma calcium, determines the many biologic effects of plasma calcium.
In the hospital setting, clinicians commonly encounter patients with derangements in calcium homeostasis.3 True hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia has significant clinical manifestations, including generalized fatigue, nephrolithiasis, cardiac arrhythmias, and, potentially, death. Thus, clinical practice requires correct and accurate assessment of serum calcium levels.1
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK CALCULATING A “CORRECTED CALCIUM” LEVEL IS HELPFUL
Although measuring biologically active calcium (ie, iCa) is the gold standard for assessing calcium levels, laboratories struggle to obtain a direct, accurate measurement of iCa due to the special handling and time constraints required to process samples.4 As a result, metabolic laboratory panels typically report the more easily measured total calcium, the sum of iCa and bound calcium.5 Changes in albumin levels, however, do not affect iCa levels. Since calcium has less available albumin for binding, hypoalbuminemia should theoretically decrease the amount of bound calcium and lead to a decreased reported total calcium. Therefore, a patient’s total calcium level may appear low even though their iCa is normal, which can lead to an incorrect diagnosis of hypocalcemia or overestimate of the extent of existing hypocalcemia. Moreover, these lower reported calcium levels can falsely report normocalcemia in patients with hypercalcemia or underestimate the extent of the patient’s hypercalcemia.
For years physicians have attempted to account for the underestimate in total calcium due to hypoalbuminemia by calculating a “corrected” calcium. The correction formulas use total calcium and serum albumin to estimate the expected iCa. Refinements to the original formula, developed by Payne et al in 1973, have resulted in the most commonly utilized formula today: corrected calcium = (0.8 x [normal albumin – patient’s albumin]) + serum calcium.6,7 Many commonly used clinical-decision resources recommend correcting serum calcium concentrations in patients with hypoalbuminemia.6
WHY CALCULATING A CORRECTED CALCIUM FOR ALBUMIN IS UNNECESSARY
While calculating corrected calcium should theoretically provide a more accurate estimate of physiologically active iCa in patients with hypoalbuminemia,4 the commonly used correction equations become less accurate as hypoalbuminemia worsens.8 Payne et al derived the original formula from 200 patients using a single laboratory; however, subsequent retrospective studies have not supported the use of albumin-corrected calcium calculations to estimate the iCa.4,9-11 For example, although Payne’s corrected calcium equations assume a constant relationship between albumin and calcium binding throughout all serum-albumin concentrations, studies have shown that as albumin falls, more calcium ions bind to each available gram of albumin. Payne’s assumption results in an overestimation of the total serum calcium after correction as compared to the iCa.8 In comparison, uncorrected total serum calcium assays more accurately reflect both the change in albumin binding that occurs with alterations in albumin concentration and the unchanged free calcium ions. Studies demonstrate superior correlation between iCa and uncorrected total calcium.4,9-11
Several large retrospective studies revealed the poor in vivo accuracy of equations used to correct calcium for albumin. In one study, Uppsala University Sweden researchers reviewed the laboratory records of more than 20,000 hospitalized patients from 2005 to 2013.9 This group compared seven corrected calcium formulas to direct measurements of iCa. All of the correction equations correlated poorly with iCa based on their intraclass correlation (ICC), a descriptive statistic for units that have been sorted into groups. (ICC describes how strongly the units in each group correlate or resemble each other—eg, the closer an ICC is to 1, the stronger the correlation is between each unit in the group.) ICC for the correcting equations ranged from 0.45-0.81. The formulas used to calculate corrected calcium levels performed especially poorly in patients with hypoalbuminemia. In this same patient population, the total serum calcium correlated well with directly assessed iCa, with an ICC of 0.85 (95% CI, 0.84-0.86). Moreover, the uncorrected total calcium classified the patient’s calcium level correctly in 82% of cases.
A second study of 5,500 patients in Australia comparing total and adjusted calcium with iCa similarly demonstrated that corrected calcium inaccurately predicts calcium status.10 Findings from this study showed that corrected calcium values correlated with iCa in only 55% to 65% of samples, but uncorrected total calcium correlated with iCa in 70% to 80% of samples. Notably, in patients with renal failure and/or serum albumin concentrations <3 g/dL, formulas used to correct calcium overestimated calcium levels when compared to directly assessed iCa. Correction formulas performed on serum albumin concentrations >3 g/dL correlated better with iCa (65%-77%), effectively negating the utility of the correction formulas.
Another large retrospective observational study from Norway reviewed laboratory data from more than 6,500 hospitalized and clinic patients.11 In this study, researchers calculated corrected calcium using several different albumin-adjusted formulas and compared results to laboratory-assessed iCa. As compared to corrected calcium, uncorrected total calcium more accurately determined clinically relevant free calcium.
Finally, a Canadian research group analyzed time-matched calcium, albumin, and iCa samples from 678 patients.4 They calculated each patient’s corrected calcium values using Payne’s formula. Results of this study showed that corrected calcium predicted iCa outcomes less reliably than uncorrected total calcium (ICC, 0.73 for corrected calcium vs 0.78 for uncorrected calcium).
Utilizing corrected calcium formulas in patients with hypoalbuminemia can overestimate serum calcium, resulting in false-positive findings and an incorrect diagnosis of hypercalcemia or normocalcemia.12 Incorrectly diagnosing hypercalcemia by using correction formulas prompts management that can lead to iatrogenic harm. Hypoalbuminemia is often associated with hepatic or renal disease. In this patient population, standard treatment of hypercalcemia with volume resuscitation (typically 2 to 4 L) and potentially IV loop diuretics will cause clinically significant volume overload and could worsen renal dysfunction.13 Notably, some of the correction formulas utilized in the studies discussed here performed well in hypercalcemic patients, particularly in those with preserved renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2).
Importantly, correction formulas can mask true hypocalcemia or the true severity of hypocalcemia. Applying correction formulas in patients with clinically significant hypocalcemia and hypoalbuminemia can make hospitalists believe that the calcium levels are normal or not as clinically significant as they first seemed. This can lead to the withholding of appropriate treatment.12
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
Based on the available literature, uncorrected total calcium values more accurately assess biologically active calcium. If a more certain calcium value will affect clinical outcomes, clinicians should obtain a direct measurement of iCa.4,9-11 Therefore, clinicians should assess iCa irrespective of the uncorrected serum calcium level in patients who are critically ill or who have known hypoparathyroidism or other derangements in iCa.14 Since iCa levels also fluctuate with pH, samples must be processed quickly and kept cool to slow blood cell metabolism, which alters pH levels.4 Using bedside point-of-care blood gas analyzers to obtain iCa removes a large logistical obstacle to obtaining an accurate iCa. Serum electrolyte interpretation with a properly calibrated point-of-care analyzer correlates well with a traditional laboratory analyzer.15
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Use serum calcium testing routinely to evaluate calcium homeostasis.
- Do not use corrected calcium equations to estimate total calcium.
- If a more accurate measurement of calcium will change medical management, obtain a direct iCa.
- Obtain a direct iCa measurement in critically ill patents and in patients with known hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, or other derangements in calcium homeostasis.
- Do not order a serum albumin test to assess calcium levels.
CONCLUSION
Returning to our clinical scenario, this patient did not have true hypercalcemia and experienced unnecessary evaluation and treatment. Multiple retrospective clinical trials do not support the practice of using corrected calcium equations to correct for serum albumin derangements.4,9-11 Hospitalists should therefore avoid the temptation to calculate a corrected calcium level in patients with hypoalbuminemia. For patients with clinically significant total serum hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, they should consider obtaining an iCa assay to better determine the true physiologic impact.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
1. Peacock M. Calcium metabolism in health and disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5 Suppl 1:S23-S30. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.05910809
2. Brown EM. Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid cell function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers. Physiol Rev. 1991;71(2):371-411. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.371
3. Aishah AB, Foo YN. A retrospective study of serum calcium levels in a hospital population in Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 1995;50(3):246-249.
4. Steen O, Clase C, Don-Wauchope A. Corrected calcium formula in routine clinical use does not accurately reflect ionized calcium in hospital patients. Can J Gen Int Med. 2016;11(3):14-21. https://doi.org/10.22374/cjgim.v11i3.150
5. Payne RB, Little AJ, Williams RB, Milner JR. Interpretation of serum calcium in patients with abnormal serum proteins. Br Med J. 1973;4(5893):643-646. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.4.5893.643
6. Shane E. Diagnostic approach to hypercalcemia. UpToDate website. Updated August 31, 2020. Accessed April 8, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnostic-approach-to-hypercalcemia
7. Ladenson JH, Lewis JW, Boyd JC. Failure of total calcium corrected for protein, albumin, and pH to correctly assess free calcium status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978;46(6):986-993. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-46-6-986
8. Besarab A, Caro JF. Increased absolute calcium binding to albumin in hypoalbuminaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1981;34(12):1368-1374. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.34.12.1368
9. Ridefelt P, Helmersson-Karlqvist J. Albumin adjustment of total calcium does not improve the estimation of calcium status. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2017;77(6):442-447. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2017.1336568
10. Smith JD, Wilson S, Schneider HG. Misclassification of calcium status based on albumin-adjusted calcium: studies in a tertiary hospital setting. Clin Chem. 2018;64(12):1713-1722. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2018.291377
11. Lian IA, Åsberg A. Should total calcium be adjusted for albumin? A retrospective observational study of laboratory data from central Norway. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e017703. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017703
12. Bowers GN Jr, Brassard C, Sena SF. Measurement of ionized calcium in serum with ion-selective electrodes: a mature technology that can meet the daily service needs. Clin Chem. 1986;32(8)1437-1447.
13. Myburgh JA. Fluid resuscitation in acute medicine: what is the current situation? J Intern Med. 2015;277(1):58-68. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12326
14. Aberegg SK. Ionized calcium in the ICU: should it be measured and corrected? Chest. 2016;149(3):846-855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2015.12.001
15. Mirzazadeh M, Morovat A, James T, Smith I, Kirby J, Shine B. Point-of-care testing of electrolytes and calcium using blood gas analysers: it is time we trusted the results. Emerg Med J. 2016;33(3):181-186. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2015-204669
1. Peacock M. Calcium metabolism in health and disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5 Suppl 1:S23-S30. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.05910809
2. Brown EM. Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid cell function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers. Physiol Rev. 1991;71(2):371-411. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.371
3. Aishah AB, Foo YN. A retrospective study of serum calcium levels in a hospital population in Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 1995;50(3):246-249.
4. Steen O, Clase C, Don-Wauchope A. Corrected calcium formula in routine clinical use does not accurately reflect ionized calcium in hospital patients. Can J Gen Int Med. 2016;11(3):14-21. https://doi.org/10.22374/cjgim.v11i3.150
5. Payne RB, Little AJ, Williams RB, Milner JR. Interpretation of serum calcium in patients with abnormal serum proteins. Br Med J. 1973;4(5893):643-646. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.4.5893.643
6. Shane E. Diagnostic approach to hypercalcemia. UpToDate website. Updated August 31, 2020. Accessed April 8, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnostic-approach-to-hypercalcemia
7. Ladenson JH, Lewis JW, Boyd JC. Failure of total calcium corrected for protein, albumin, and pH to correctly assess free calcium status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978;46(6):986-993. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-46-6-986
8. Besarab A, Caro JF. Increased absolute calcium binding to albumin in hypoalbuminaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1981;34(12):1368-1374. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.34.12.1368
9. Ridefelt P, Helmersson-Karlqvist J. Albumin adjustment of total calcium does not improve the estimation of calcium status. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2017;77(6):442-447. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2017.1336568
10. Smith JD, Wilson S, Schneider HG. Misclassification of calcium status based on albumin-adjusted calcium: studies in a tertiary hospital setting. Clin Chem. 2018;64(12):1713-1722. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2018.291377
11. Lian IA, Åsberg A. Should total calcium be adjusted for albumin? A retrospective observational study of laboratory data from central Norway. BMJ Open. 2018;8(4):e017703. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017703
12. Bowers GN Jr, Brassard C, Sena SF. Measurement of ionized calcium in serum with ion-selective electrodes: a mature technology that can meet the daily service needs. Clin Chem. 1986;32(8)1437-1447.
13. Myburgh JA. Fluid resuscitation in acute medicine: what is the current situation? J Intern Med. 2015;277(1):58-68. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12326
14. Aberegg SK. Ionized calcium in the ICU: should it be measured and corrected? Chest. 2016;149(3):846-855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2015.12.001
15. Mirzazadeh M, Morovat A, James T, Smith I, Kirby J, Shine B. Point-of-care testing of electrolytes and calcium using blood gas analysers: it is time we trusted the results. Emerg Med J. 2016;33(3):181-186. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2015-204669
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Pediatric Conditions Requiring Minimal Intervention or Observation After Interfacility Transfer
Regionalization of pediatric acute care is increasing across the United States, with rates of interfacility transfer for general medical conditions in children similar to those of high-risk conditions in adults.1 The inability for children to receive definitive care (ie, care provided to conclusively manage a patient’s condition without requiring an interfacility transfer) within their local community has implications on public health as well as family function and financial burden.1,2 Previous studies demonstrated that 30% to 80% of interfacility transfers are potentially unnecessary,3-6 as indicated by a high proportion of short lengths of stay after transfer.
To highlight conditions that referring hospitals may prioritize for pediatric capacity building, we aimed to identify the most common medical diagnoses among pediatric transfer patients that did not require advanced evaluation or intervention and that had high rates of discharge within 1 day of interfacility transfer.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional, descriptive study using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database, which contains administrative data from 48 geographically diverse US children’s hospitals.
We included children <18 years old who were transferred to a participating PHIS hospital in 2019, including emergency department (ED), observation, and inpatient encounters. We identified patients through the source-of-admission code labeled as “transfer.”
For each diagnosis, we determined the number of transfers and frequency of rapid discharge, defined as either discharge from the ED without admission or admission and discharge within 1 day from a general inpatient unit. As discharge times are not reliably available in PHIS, all patients discharged on the day of transfer or the following calendar day were identified as rapid discharge. Medical complexity was determined through applying the Pediatric Medical Complexity Algorithm (PMCA).8
For descriptive statistics, we calculated means for normally distributed variables, medians for continuous variables with nonnormal distributions, and percentages for binary variables. Comparisons were made using t-tests and chi-square tests.
This study was approved by the Seattle Children’s Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
We identified 286,905 transfers into participating PHIS hospitals in 2019. Of these, 89,519 (31.2%) were excluded (Appendix Table 2), leaving 197,386 (68.6%) transfers. Patients discharged within 1 day were more likely to have public or unknown insurance (65.1% vs 61.5%, P < 0.01), to have no co-occurring chronic conditions (60.2% vs 28.5%, P < 0.01), and to reside within the Northeast (35.0% vs 11.0%, P < 0.01) (Appendix Table 3).
The most common medical diagnoses among these transfers included acute bronchiolitis (4.3% of all interfacility transfers, n = 8,425), chemotherapy (4.0%, n = 7,819), and asthma (3.3%, n = 6,430) (Appendix Table 4); 45.9% of bronchiolitis, 15.0% of chemotherapy, and 67.4% of asthma transfers were rapidly discharged.
The Table shows the medical conditions among transfers that most frequently experienced rapid discharge (primary surgical diagnoses are presented in Appendix Table 5). 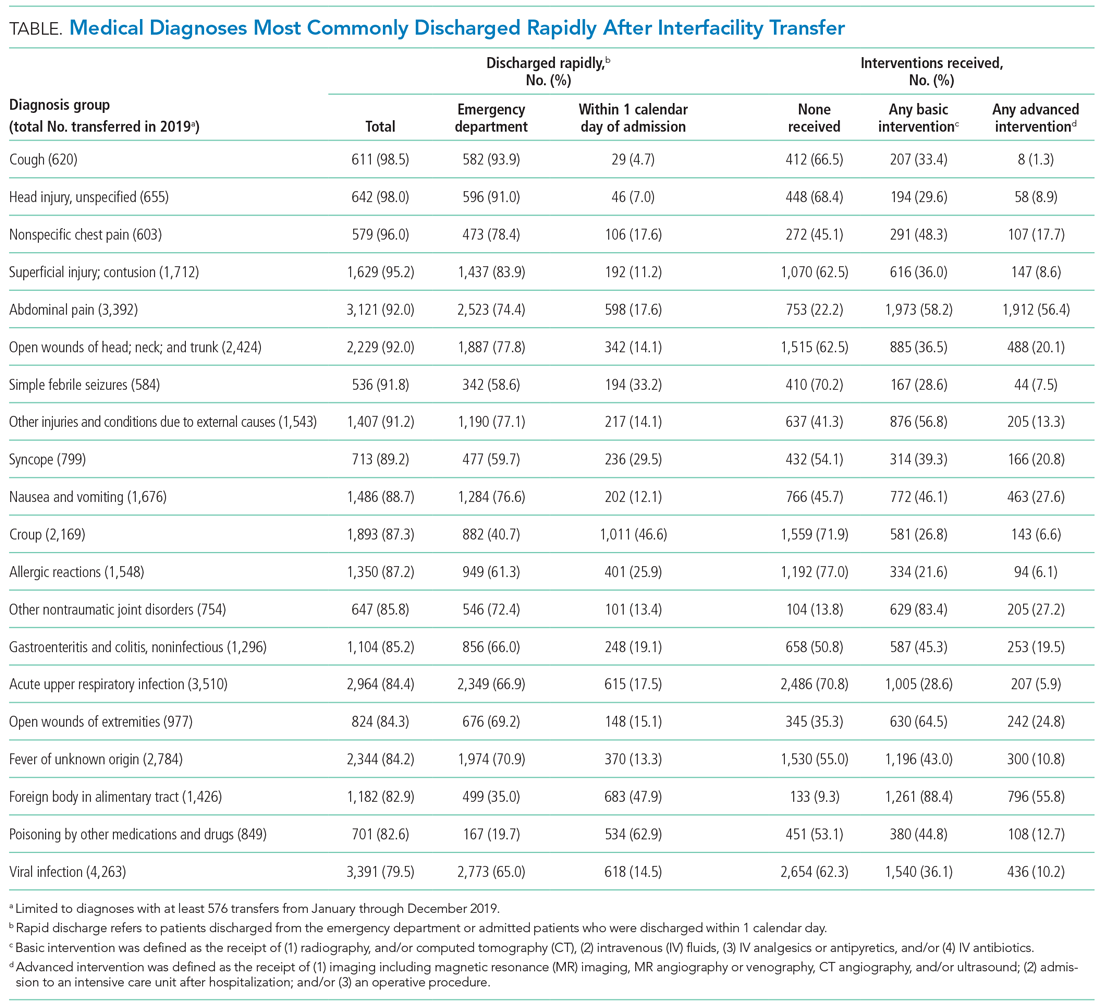
DISCUSSION
We have identified medical conditions that not only had high rates of rapid discharge after transfer, but also received minimal intervention from the accepting institution. Although bronchiolitis and chemotherapy were the most common conditions for which patients were transferred, the range of severity varied widely, with more than 50% of bronchiolitis and 85% of chemotherapy transfers requiring hospitalization for longer than 1 day
Identifying conditions as potential targets to reduce the number of interfacility transfers requires balancing a hospital’s capacity (or lack thereof) for pediatric admissions, perceived risk of decompensation, referring provider discomfort, and parental preference.9-11
The rapid upscale of telehealth may provide a unique opportunity to support the provision of pediatric care within local communities.12,13
Building infrastructure to prevent interfacility transfers may improve healthcare access for children in rural areas proportionately more than children in urban areas. Children in rural communities experience significantly higher rates of interfacility transfers than children in urban areas.14 This increases financial burden and causes additional distress and inconvenience for families.15 With constraints in staffing capacity, equipment, and finances, identifying a subset of medical conditions is a critical initial step to inform the design of targeted interventions to support pediatric healthcare delivery in local communities and avoid costly transfers, although it is not the wholesale solution. Additional utilization of tools such as informed shared decision-making resources and implementation of pediatric-specific protocols likely represent additional necessary steps.
Our study has several limitations. Because we used administrative data, there is a risk of misclassifying diagnoses. We attempted to mitigate this by using a standard ICD-10-based, pediatric-specific grouper.
CONCLUSION
Our exploration of pediatric interfacility transfers that experienced rapid discharge with minimal intervention provides a building block to support the provision of definitive pediatric care in non-pediatric hospitals and represents a step towards addressing limited access to care in general hospitals.
1. França UL, McManus ML. Availability of definitive hospital care for children. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(9):e171096. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1096
2. Mumford V, Baysari MT, Kalinin D, et al. Measuring the financial and productivity burden of paediatric hospitalisation on the wider family network. J Paediatr Child Health. 2018;54(9):987-996. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.13923
3. Richard KR, Glisson KL, Shah N, et al. Predictors of potentially unnecessary transfers to pediatric emergency departments. Hosp Pediatr. 2020;10(5):424-429. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2019-0307
4. Gattu RK, Teshome G, Cai L, Wright C, Lichenstein R. Interhospital pediatric patient transfers-factors influencing rapid disposition after transfer. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(1):26-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000000061
5. Li J, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG. Interfacility transfers of noncritically ill children to academic pediatric emergency departments. Pediatrics. 2012;130(1):83-92. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1819
6. Rosenthal JL, Lieng MK, Marcin JP, Romano PS. Profiling pediatric potentially avoidable transfers using procedure and diagnosis codes. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019 Mar 19;10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777
7. Pediatric clinical classification system (PECCS) codes. Children’s Hospital Association. December 11, 2020. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.childrenshospitals.org/Research-and-Data/Pediatric-Data-and-Trends/2020/Pediatric-Clinical-Classification-System-PECCS
8. Simon TD, Haaland W, Hawley K, Lambka K, Mangione-Smith R. Development and validation of the pediatric medical complexity algorithm (PMCA) version 3.0. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(5):577-580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2018.02.010
9. Rosenthal JL, Okumura MJ, Hernandez L, Li ST, Rehm RS. Interfacility transfers to general pediatric floors: a qualitative study exploring the role of communication. Acad Pediatr. 2016;16(7):692-699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2016.04.003
10. Rosenthal JL, Li ST, Hernandez L, Alvarez M, Rehm RS, Okumura MJ. Familial caregiver and physician perceptions of the family-physician interactions during interfacility transfers. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(6):344-351. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0017
11. Peebles ER, Miller MR, Lynch TP, Tijssen JA. Factors associated with discharge home after transfer to a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34(9):650-655. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001098
12. Labarbera JM, Ellenby MS, Bouressa P, Burrell J, Flori HR, Marcin JP. The impact of telemedicine intensivist support and a pediatric hospitalist program on a community hospital. Telemed J E Health. 2013;19(10):760-766. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2012.0303
13. Haynes SC, Dharmar M, Hill BC, et al. The impact of telemedicine on transfer rates of newborns at rural community hospitals. Acad Pediatr. 2020;20(5):636-641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2020.02.013
14. Michelson KA, Hudgins JD, Lyons TW, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG, Finkelstein JA. Trends in capability of hospitals to provide definitive acute care for children: 2008 to 2016. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-2203
15. Mohr NM, Harland KK, Shane DM, Miller SL, Torner JC. Potentially avoidable pediatric interfacility transfer is a costly burden for rural families: a cohort study. Acad Emerg Med. 2016;23(8):885-894. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.12972
Regionalization of pediatric acute care is increasing across the United States, with rates of interfacility transfer for general medical conditions in children similar to those of high-risk conditions in adults.1 The inability for children to receive definitive care (ie, care provided to conclusively manage a patient’s condition without requiring an interfacility transfer) within their local community has implications on public health as well as family function and financial burden.1,2 Previous studies demonstrated that 30% to 80% of interfacility transfers are potentially unnecessary,3-6 as indicated by a high proportion of short lengths of stay after transfer.
To highlight conditions that referring hospitals may prioritize for pediatric capacity building, we aimed to identify the most common medical diagnoses among pediatric transfer patients that did not require advanced evaluation or intervention and that had high rates of discharge within 1 day of interfacility transfer.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional, descriptive study using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database, which contains administrative data from 48 geographically diverse US children’s hospitals.
We included children <18 years old who were transferred to a participating PHIS hospital in 2019, including emergency department (ED), observation, and inpatient encounters. We identified patients through the source-of-admission code labeled as “transfer.”
For each diagnosis, we determined the number of transfers and frequency of rapid discharge, defined as either discharge from the ED without admission or admission and discharge within 1 day from a general inpatient unit. As discharge times are not reliably available in PHIS, all patients discharged on the day of transfer or the following calendar day were identified as rapid discharge. Medical complexity was determined through applying the Pediatric Medical Complexity Algorithm (PMCA).8
For descriptive statistics, we calculated means for normally distributed variables, medians for continuous variables with nonnormal distributions, and percentages for binary variables. Comparisons were made using t-tests and chi-square tests.
This study was approved by the Seattle Children’s Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
We identified 286,905 transfers into participating PHIS hospitals in 2019. Of these, 89,519 (31.2%) were excluded (Appendix Table 2), leaving 197,386 (68.6%) transfers. Patients discharged within 1 day were more likely to have public or unknown insurance (65.1% vs 61.5%, P < 0.01), to have no co-occurring chronic conditions (60.2% vs 28.5%, P < 0.01), and to reside within the Northeast (35.0% vs 11.0%, P < 0.01) (Appendix Table 3).
The most common medical diagnoses among these transfers included acute bronchiolitis (4.3% of all interfacility transfers, n = 8,425), chemotherapy (4.0%, n = 7,819), and asthma (3.3%, n = 6,430) (Appendix Table 4); 45.9% of bronchiolitis, 15.0% of chemotherapy, and 67.4% of asthma transfers were rapidly discharged.
The Table shows the medical conditions among transfers that most frequently experienced rapid discharge (primary surgical diagnoses are presented in Appendix Table 5). 
DISCUSSION
We have identified medical conditions that not only had high rates of rapid discharge after transfer, but also received minimal intervention from the accepting institution. Although bronchiolitis and chemotherapy were the most common conditions for which patients were transferred, the range of severity varied widely, with more than 50% of bronchiolitis and 85% of chemotherapy transfers requiring hospitalization for longer than 1 day
Identifying conditions as potential targets to reduce the number of interfacility transfers requires balancing a hospital’s capacity (or lack thereof) for pediatric admissions, perceived risk of decompensation, referring provider discomfort, and parental preference.9-11
The rapid upscale of telehealth may provide a unique opportunity to support the provision of pediatric care within local communities.12,13
Building infrastructure to prevent interfacility transfers may improve healthcare access for children in rural areas proportionately more than children in urban areas. Children in rural communities experience significantly higher rates of interfacility transfers than children in urban areas.14 This increases financial burden and causes additional distress and inconvenience for families.15 With constraints in staffing capacity, equipment, and finances, identifying a subset of medical conditions is a critical initial step to inform the design of targeted interventions to support pediatric healthcare delivery in local communities and avoid costly transfers, although it is not the wholesale solution. Additional utilization of tools such as informed shared decision-making resources and implementation of pediatric-specific protocols likely represent additional necessary steps.
Our study has several limitations. Because we used administrative data, there is a risk of misclassifying diagnoses. We attempted to mitigate this by using a standard ICD-10-based, pediatric-specific grouper.
CONCLUSION
Our exploration of pediatric interfacility transfers that experienced rapid discharge with minimal intervention provides a building block to support the provision of definitive pediatric care in non-pediatric hospitals and represents a step towards addressing limited access to care in general hospitals.
Regionalization of pediatric acute care is increasing across the United States, with rates of interfacility transfer for general medical conditions in children similar to those of high-risk conditions in adults.1 The inability for children to receive definitive care (ie, care provided to conclusively manage a patient’s condition without requiring an interfacility transfer) within their local community has implications on public health as well as family function and financial burden.1,2 Previous studies demonstrated that 30% to 80% of interfacility transfers are potentially unnecessary,3-6 as indicated by a high proportion of short lengths of stay after transfer.
To highlight conditions that referring hospitals may prioritize for pediatric capacity building, we aimed to identify the most common medical diagnoses among pediatric transfer patients that did not require advanced evaluation or intervention and that had high rates of discharge within 1 day of interfacility transfer.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective, cross-sectional, descriptive study using the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database, which contains administrative data from 48 geographically diverse US children’s hospitals.
We included children <18 years old who were transferred to a participating PHIS hospital in 2019, including emergency department (ED), observation, and inpatient encounters. We identified patients through the source-of-admission code labeled as “transfer.”
For each diagnosis, we determined the number of transfers and frequency of rapid discharge, defined as either discharge from the ED without admission or admission and discharge within 1 day from a general inpatient unit. As discharge times are not reliably available in PHIS, all patients discharged on the day of transfer or the following calendar day were identified as rapid discharge. Medical complexity was determined through applying the Pediatric Medical Complexity Algorithm (PMCA).8
For descriptive statistics, we calculated means for normally distributed variables, medians for continuous variables with nonnormal distributions, and percentages for binary variables. Comparisons were made using t-tests and chi-square tests.
This study was approved by the Seattle Children’s Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
We identified 286,905 transfers into participating PHIS hospitals in 2019. Of these, 89,519 (31.2%) were excluded (Appendix Table 2), leaving 197,386 (68.6%) transfers. Patients discharged within 1 day were more likely to have public or unknown insurance (65.1% vs 61.5%, P < 0.01), to have no co-occurring chronic conditions (60.2% vs 28.5%, P < 0.01), and to reside within the Northeast (35.0% vs 11.0%, P < 0.01) (Appendix Table 3).
The most common medical diagnoses among these transfers included acute bronchiolitis (4.3% of all interfacility transfers, n = 8,425), chemotherapy (4.0%, n = 7,819), and asthma (3.3%, n = 6,430) (Appendix Table 4); 45.9% of bronchiolitis, 15.0% of chemotherapy, and 67.4% of asthma transfers were rapidly discharged.
The Table shows the medical conditions among transfers that most frequently experienced rapid discharge (primary surgical diagnoses are presented in Appendix Table 5). 
DISCUSSION
We have identified medical conditions that not only had high rates of rapid discharge after transfer, but also received minimal intervention from the accepting institution. Although bronchiolitis and chemotherapy were the most common conditions for which patients were transferred, the range of severity varied widely, with more than 50% of bronchiolitis and 85% of chemotherapy transfers requiring hospitalization for longer than 1 day
Identifying conditions as potential targets to reduce the number of interfacility transfers requires balancing a hospital’s capacity (or lack thereof) for pediatric admissions, perceived risk of decompensation, referring provider discomfort, and parental preference.9-11
The rapid upscale of telehealth may provide a unique opportunity to support the provision of pediatric care within local communities.12,13
Building infrastructure to prevent interfacility transfers may improve healthcare access for children in rural areas proportionately more than children in urban areas. Children in rural communities experience significantly higher rates of interfacility transfers than children in urban areas.14 This increases financial burden and causes additional distress and inconvenience for families.15 With constraints in staffing capacity, equipment, and finances, identifying a subset of medical conditions is a critical initial step to inform the design of targeted interventions to support pediatric healthcare delivery in local communities and avoid costly transfers, although it is not the wholesale solution. Additional utilization of tools such as informed shared decision-making resources and implementation of pediatric-specific protocols likely represent additional necessary steps.
Our study has several limitations. Because we used administrative data, there is a risk of misclassifying diagnoses. We attempted to mitigate this by using a standard ICD-10-based, pediatric-specific grouper.
CONCLUSION
Our exploration of pediatric interfacility transfers that experienced rapid discharge with minimal intervention provides a building block to support the provision of definitive pediatric care in non-pediatric hospitals and represents a step towards addressing limited access to care in general hospitals.
1. França UL, McManus ML. Availability of definitive hospital care for children. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(9):e171096. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1096
2. Mumford V, Baysari MT, Kalinin D, et al. Measuring the financial and productivity burden of paediatric hospitalisation on the wider family network. J Paediatr Child Health. 2018;54(9):987-996. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.13923
3. Richard KR, Glisson KL, Shah N, et al. Predictors of potentially unnecessary transfers to pediatric emergency departments. Hosp Pediatr. 2020;10(5):424-429. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2019-0307
4. Gattu RK, Teshome G, Cai L, Wright C, Lichenstein R. Interhospital pediatric patient transfers-factors influencing rapid disposition after transfer. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(1):26-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000000061
5. Li J, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG. Interfacility transfers of noncritically ill children to academic pediatric emergency departments. Pediatrics. 2012;130(1):83-92. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1819
6. Rosenthal JL, Lieng MK, Marcin JP, Romano PS. Profiling pediatric potentially avoidable transfers using procedure and diagnosis codes. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019 Mar 19;10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777
7. Pediatric clinical classification system (PECCS) codes. Children’s Hospital Association. December 11, 2020. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.childrenshospitals.org/Research-and-Data/Pediatric-Data-and-Trends/2020/Pediatric-Clinical-Classification-System-PECCS
8. Simon TD, Haaland W, Hawley K, Lambka K, Mangione-Smith R. Development and validation of the pediatric medical complexity algorithm (PMCA) version 3.0. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(5):577-580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2018.02.010
9. Rosenthal JL, Okumura MJ, Hernandez L, Li ST, Rehm RS. Interfacility transfers to general pediatric floors: a qualitative study exploring the role of communication. Acad Pediatr. 2016;16(7):692-699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2016.04.003
10. Rosenthal JL, Li ST, Hernandez L, Alvarez M, Rehm RS, Okumura MJ. Familial caregiver and physician perceptions of the family-physician interactions during interfacility transfers. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(6):344-351. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0017
11. Peebles ER, Miller MR, Lynch TP, Tijssen JA. Factors associated with discharge home after transfer to a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34(9):650-655. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001098
12. Labarbera JM, Ellenby MS, Bouressa P, Burrell J, Flori HR, Marcin JP. The impact of telemedicine intensivist support and a pediatric hospitalist program on a community hospital. Telemed J E Health. 2013;19(10):760-766. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2012.0303
13. Haynes SC, Dharmar M, Hill BC, et al. The impact of telemedicine on transfer rates of newborns at rural community hospitals. Acad Pediatr. 2020;20(5):636-641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2020.02.013
14. Michelson KA, Hudgins JD, Lyons TW, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG, Finkelstein JA. Trends in capability of hospitals to provide definitive acute care for children: 2008 to 2016. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-2203
15. Mohr NM, Harland KK, Shane DM, Miller SL, Torner JC. Potentially avoidable pediatric interfacility transfer is a costly burden for rural families: a cohort study. Acad Emerg Med. 2016;23(8):885-894. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.12972
1. França UL, McManus ML. Availability of definitive hospital care for children. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(9):e171096. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1096
2. Mumford V, Baysari MT, Kalinin D, et al. Measuring the financial and productivity burden of paediatric hospitalisation on the wider family network. J Paediatr Child Health. 2018;54(9):987-996. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.13923
3. Richard KR, Glisson KL, Shah N, et al. Predictors of potentially unnecessary transfers to pediatric emergency departments. Hosp Pediatr. 2020;10(5):424-429. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2019-0307
4. Gattu RK, Teshome G, Cai L, Wright C, Lichenstein R. Interhospital pediatric patient transfers-factors influencing rapid disposition after transfer. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(1):26-30. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000000061
5. Li J, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG. Interfacility transfers of noncritically ill children to academic pediatric emergency departments. Pediatrics. 2012;130(1):83-92. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1819
6. Rosenthal JL, Lieng MK, Marcin JP, Romano PS. Profiling pediatric potentially avoidable transfers using procedure and diagnosis codes. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2019 Mar 19;10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001777
7. Pediatric clinical classification system (PECCS) codes. Children’s Hospital Association. December 11, 2020. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.childrenshospitals.org/Research-and-Data/Pediatric-Data-and-Trends/2020/Pediatric-Clinical-Classification-System-PECCS
8. Simon TD, Haaland W, Hawley K, Lambka K, Mangione-Smith R. Development and validation of the pediatric medical complexity algorithm (PMCA) version 3.0. Acad Pediatr. 2018;18(5):577-580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2018.02.010
9. Rosenthal JL, Okumura MJ, Hernandez L, Li ST, Rehm RS. Interfacility transfers to general pediatric floors: a qualitative study exploring the role of communication. Acad Pediatr. 2016;16(7):692-699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2016.04.003
10. Rosenthal JL, Li ST, Hernandez L, Alvarez M, Rehm RS, Okumura MJ. Familial caregiver and physician perceptions of the family-physician interactions during interfacility transfers. Hosp Pediatr. 2017;7(6):344-351. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2017-0017
11. Peebles ER, Miller MR, Lynch TP, Tijssen JA. Factors associated with discharge home after transfer to a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2018;34(9):650-655. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0000000000001098
12. Labarbera JM, Ellenby MS, Bouressa P, Burrell J, Flori HR, Marcin JP. The impact of telemedicine intensivist support and a pediatric hospitalist program on a community hospital. Telemed J E Health. 2013;19(10):760-766. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2012.0303
13. Haynes SC, Dharmar M, Hill BC, et al. The impact of telemedicine on transfer rates of newborns at rural community hospitals. Acad Pediatr. 2020;20(5):636-641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2020.02.013
14. Michelson KA, Hudgins JD, Lyons TW, Monuteaux MC, Bachur RG, Finkelstein JA. Trends in capability of hospitals to provide definitive acute care for children: 2008 to 2016. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-2203
15. Mohr NM, Harland KK, Shane DM, Miller SL, Torner JC. Potentially avoidable pediatric interfacility transfer is a costly burden for rural families: a cohort study. Acad Emerg Med. 2016;23(8):885-894. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.12972
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program and Observation Hospitalizations
The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) was designed to improve quality and safety for traditional Medicare beneficiaries.1 Since 2012, the program has reduced payments to institutions with excess inpatient rehospitalizations within 30 days of an index inpatient stay for targeted medical conditions. Observation hospitalizations, billed as outpatient and covered under Medicare Part B, are not counted as index or 30-day rehospitalizations under HRRP methods. Historically, observation occurred almost exclusively in observation units. Now, observation hospitalizations commonly occur on hospital wards, even in intensive care units, and are often clinically indistinguishable from inpatient hospitalizations billed under Medicare Part A.2 The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) state that beneficiaries expected to need 2 or more midnights of hospital care should generally be considered inpatients, yet observation hospitalizations commonly exceed 2 midnights.3,4
The increasing use of observation hospitalizations5,6 raises questions about its impact on HRRP measurements. While observation hospitalizations have been studied as part of 30-day follow-up (numerator) to index inpatient hospitalizations,5,6 little is known about how observation hospitalizations impact rates when they are factored in as both index stays (denominator) and in the 30-day rehospitalization rate (numerator).2,7 We analyzed the complete combinations of observation and inpatient hospitalizations, including observation as index hospitalization, rehospitalization, or both, to determine HRRP impact.
METHODS
Study Cohort
Medicare fee-for-service standard claim files for all beneficiaries (100% population file version) were used to examine qualifying index inpatient and observation hospitalizations between January 1, 2014, and November 30, 2014, as well as 30-day inpatient and observation rehospitalizations. We used CMS’s 30-day methodology, including previously described standard exclusions (Appendix Figure),8 except for the aforementioned inclusion of observation hospitalizations. Observation hospitalizations were identified using established methods,3,9,10 excluding those observation encounters coded with revenue center code 0761 only3,10 in order to be most conservative in identifying observation hospitalizations (Appendix Figure). These methods assign hospitalization type (observation or inpatient) based on the final (billed) status. The terms hospitalization and rehospitalization refer to both inpatient and observation encounters. The University of Wisconsin Health Sciences Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program
Index HRRP admissions for congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia were examined as a prespecified subgroup.1,11 Coronary artery bypass grafting, total hip replacement, and total knee replacement were excluded in this analysis, as no crosswalk exists between International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes and Current Procedural Terminology codes for these surgical conditions.11
Analysis
Analyses were conducted at the encounter level, consistent with CMS methods.8 Descriptive statistics were used to summarize index and 30-day outcomes.
RESULTS
Of 8,859,534 index hospitalizations for any reason or diagnosis, 1,597,837 (18%) were observation and 7,261,697 (82%) were inpatient. Including all hospitalizations, 23% (390,249/1,689,609) of rehospitalizations were excluded from readmission measurement by virtue of the index hospitalization and/or 30-day rehospitalization being observation (Table 1 and Table 2).
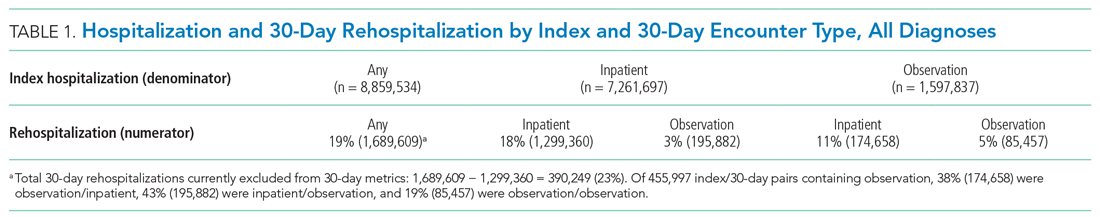
For the subgroup of HRRP conditions, 418,923 (11%) and 3,387,849 (89%) of 3,806,772 index hospitalizations were observation and inpatient, respectively. Including HRRP conditions only, 18% (155,553/876,033) of rehospitalizations were excluded from HRRP reporting owing to observation hospitalization as index, 30-day outcome, or both. Of 188,430 index/30-day pairs containing observation, 34% (63,740) were observation/inpatient, 53% (100,343) were inpatient/observation, and 13% (24,347) were observation/observation (Table 1 and Table 2).
DISCUSSION
By ignoring observation hospitalizations in 30-day HRRP quality metrics, nearly one of five potential rehospitalizations is missed. Observation hospitalizations commonly occur as either the index event or 30-day outcome, so accurately determining 30-day HRRP rates must include observation in both positions. Given hospital variability in observation use,3,7 these findings are critically important to accurately understand rehospitalization risk and indicate that HRRP may not be fulfilling its intended purpose.
Including all hospitalizations for any diagnosis, we found that observation and inpatient hospitalizations commonly occur within 30 days of each other. Nearly one in four hospitalization/rehospitalization pairs include observation as index, 30-day rehospitalization, or both. Although not directly related to HRRP metrics, these data demonstrate the growing importance and presence of outpatient (observation) hospitalizations in the Medicare program.
Our study adds to the evolving body of literature investigating quality measures under a two-tiered hospital system where inpatient hospitalizations are counted and observation hospitalizations are not. Figueroa and colleagues12 found that improvements in avoidable admission rates for patients with ambulatory care–sensitive conditions were largely attributable to a shift from counted inpatient to uncounted observation hospitalizations. In other words, hospitalizations were still occurring, but were not being tallied due to outpatient (observation) classification. Zuckerman et al5 and the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC)6 concluded that readmissions improvements recognized by the HRRP were not explained by a shift to more observation hospitalizations following an index inpatient hospitalization; however, both studies included observation hospitalizations as part of 30-day rehospitalization (numerator) only, not also as part of index hospitalizations (denominator). Our study confirms the importance of including observation hospitalizations in both the index (denominator) and 30-day (numerator) rehospitalization positions to determine the full impact of observation hospitalizations on Medicare’s HRRP metrics.
Our study has limitations. We focused on nonsurgical HRRP conditions, which may have impacted our findings. Additionally, some authors have suggested including emergency department (ED) visits in rehospitalization studies.7 Although ED visits occur at hospitals, they are not hospitalizations; we excluded them as a first step. Had we included ED visits, encounters excluded from HRRP measurements would have increased, suggesting that our findings, while sizeable, are likely conservative. Additionally, we could not determine the merits or medical necessity of hospitalizations (inpatient or outpatient observation), but this is an inherent limitation in a large claims dataset like this one. Finally, we only included a single year of data in this analysis, and it is possible that additional years of data would show different trends. However, we have no reason to believe the study year to be an aberrant year; if anything, observation rates have increased since 2014,6 again pointing out that while our findings are sizable, they are likely conservative. Future research could include additional years of data to confirm even greater proportions of rehospitalizations exempt from HRRP over time due to observation hospitalizations as index and/or 30-day events.
Outpatient observation hospitalizations can occur anywhere in the hospital and are often clinically similar to inpatient hospitalizations, yet observation hospitalizations are essentially invisible under inpatient quality metrics. Requiring the HRRP to include observation hospitalizations is the most obvious solution, but this could require major regulatory and legislative change11,13—change that would fix a metric but fail to address broad policy concerns inherent in the two-tiered observation and inpatient billing distinction. Instead, CMS and Congress might consider this an opportunity to address the oxymoron of “outpatient hospitalizations” by engaging in comprehensive observation reform.
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP). Accessed March 12, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/Readmissions-Reduction-Program
2. Sabbatini AK, Wright B. Excluding observation stays from readmission rates—what quality measures are missing. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2062-2065. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1800732
3. Sheehy AM, Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, et al. Thirty-day re-observation, chronic re-observation, and neighborhood disadvantage. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(12):2644-2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.059
4. US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Vulnerabilities remain under Medicare’s 2-midnight hospital policy. December 19, 2016. Accessed February 11, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-02-15-00020.asp
5. Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1543-1551. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa1513024
6. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Mandated report: the effects of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare and the Health Care Delivery System. 2018;3-31. Accessed March 17, 2021. Available at: http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/jun18_medpacreporttocongress_rev_nov2019_note_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
7. Wadhera RK, Yeh RW, Maddox KEJ. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program—time for a reboot. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2289-2291. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1901225
8. National Quality Forum. Measure #1789: Hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission measure. Accessed January 30, 2021. https://www.qualityforum.org/ProjectDescription.aspx?projectID=73619
9. Sheehy AM, Shi F, Kind AJH. Identifying observation stays in Medicare data: policy implications of a definition. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(2):96-100. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3038
10. Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, Kind AJH, Sheehy AM. What is an observation stay? Evaluating the use of hospital observation stays in Medicare. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(7):1568-1572. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.16441
11. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) Archives. Accessed February 10, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/HRRP-Archives
12. Figueroa JF, Burke LG, Zheng J, Orav EJ, Jha AK. Trends in hospitalization vs observation stay for ambulatory care-sensitive conditions. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12): 1714-1716. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.3177
13. Public Law 111-148, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, 111th Congress. March 23, 2010. Accessed March 12, 2021.https://www.congress.gov/111/plaws/publ148/PLAW-111publ148.pdf
The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) was designed to improve quality and safety for traditional Medicare beneficiaries.1 Since 2012, the program has reduced payments to institutions with excess inpatient rehospitalizations within 30 days of an index inpatient stay for targeted medical conditions. Observation hospitalizations, billed as outpatient and covered under Medicare Part B, are not counted as index or 30-day rehospitalizations under HRRP methods. Historically, observation occurred almost exclusively in observation units. Now, observation hospitalizations commonly occur on hospital wards, even in intensive care units, and are often clinically indistinguishable from inpatient hospitalizations billed under Medicare Part A.2 The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) state that beneficiaries expected to need 2 or more midnights of hospital care should generally be considered inpatients, yet observation hospitalizations commonly exceed 2 midnights.3,4
The increasing use of observation hospitalizations5,6 raises questions about its impact on HRRP measurements. While observation hospitalizations have been studied as part of 30-day follow-up (numerator) to index inpatient hospitalizations,5,6 little is known about how observation hospitalizations impact rates when they are factored in as both index stays (denominator) and in the 30-day rehospitalization rate (numerator).2,7 We analyzed the complete combinations of observation and inpatient hospitalizations, including observation as index hospitalization, rehospitalization, or both, to determine HRRP impact.
METHODS
Study Cohort
Medicare fee-for-service standard claim files for all beneficiaries (100% population file version) were used to examine qualifying index inpatient and observation hospitalizations between January 1, 2014, and November 30, 2014, as well as 30-day inpatient and observation rehospitalizations. We used CMS’s 30-day methodology, including previously described standard exclusions (Appendix Figure),8 except for the aforementioned inclusion of observation hospitalizations. Observation hospitalizations were identified using established methods,3,9,10 excluding those observation encounters coded with revenue center code 0761 only3,10 in order to be most conservative in identifying observation hospitalizations (Appendix Figure). These methods assign hospitalization type (observation or inpatient) based on the final (billed) status. The terms hospitalization and rehospitalization refer to both inpatient and observation encounters. The University of Wisconsin Health Sciences Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program
Index HRRP admissions for congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia were examined as a prespecified subgroup.1,11 Coronary artery bypass grafting, total hip replacement, and total knee replacement were excluded in this analysis, as no crosswalk exists between International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes and Current Procedural Terminology codes for these surgical conditions.11
Analysis
Analyses were conducted at the encounter level, consistent with CMS methods.8 Descriptive statistics were used to summarize index and 30-day outcomes.
RESULTS
Of 8,859,534 index hospitalizations for any reason or diagnosis, 1,597,837 (18%) were observation and 7,261,697 (82%) were inpatient. Including all hospitalizations, 23% (390,249/1,689,609) of rehospitalizations were excluded from readmission measurement by virtue of the index hospitalization and/or 30-day rehospitalization being observation (Table 1 and Table 2).

For the subgroup of HRRP conditions, 418,923 (11%) and 3,387,849 (89%) of 3,806,772 index hospitalizations were observation and inpatient, respectively. Including HRRP conditions only, 18% (155,553/876,033) of rehospitalizations were excluded from HRRP reporting owing to observation hospitalization as index, 30-day outcome, or both. Of 188,430 index/30-day pairs containing observation, 34% (63,740) were observation/inpatient, 53% (100,343) were inpatient/observation, and 13% (24,347) were observation/observation (Table 1 and Table 2).
DISCUSSION
By ignoring observation hospitalizations in 30-day HRRP quality metrics, nearly one of five potential rehospitalizations is missed. Observation hospitalizations commonly occur as either the index event or 30-day outcome, so accurately determining 30-day HRRP rates must include observation in both positions. Given hospital variability in observation use,3,7 these findings are critically important to accurately understand rehospitalization risk and indicate that HRRP may not be fulfilling its intended purpose.
Including all hospitalizations for any diagnosis, we found that observation and inpatient hospitalizations commonly occur within 30 days of each other. Nearly one in four hospitalization/rehospitalization pairs include observation as index, 30-day rehospitalization, or both. Although not directly related to HRRP metrics, these data demonstrate the growing importance and presence of outpatient (observation) hospitalizations in the Medicare program.
Our study adds to the evolving body of literature investigating quality measures under a two-tiered hospital system where inpatient hospitalizations are counted and observation hospitalizations are not. Figueroa and colleagues12 found that improvements in avoidable admission rates for patients with ambulatory care–sensitive conditions were largely attributable to a shift from counted inpatient to uncounted observation hospitalizations. In other words, hospitalizations were still occurring, but were not being tallied due to outpatient (observation) classification. Zuckerman et al5 and the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC)6 concluded that readmissions improvements recognized by the HRRP were not explained by a shift to more observation hospitalizations following an index inpatient hospitalization; however, both studies included observation hospitalizations as part of 30-day rehospitalization (numerator) only, not also as part of index hospitalizations (denominator). Our study confirms the importance of including observation hospitalizations in both the index (denominator) and 30-day (numerator) rehospitalization positions to determine the full impact of observation hospitalizations on Medicare’s HRRP metrics.
Our study has limitations. We focused on nonsurgical HRRP conditions, which may have impacted our findings. Additionally, some authors have suggested including emergency department (ED) visits in rehospitalization studies.7 Although ED visits occur at hospitals, they are not hospitalizations; we excluded them as a first step. Had we included ED visits, encounters excluded from HRRP measurements would have increased, suggesting that our findings, while sizeable, are likely conservative. Additionally, we could not determine the merits or medical necessity of hospitalizations (inpatient or outpatient observation), but this is an inherent limitation in a large claims dataset like this one. Finally, we only included a single year of data in this analysis, and it is possible that additional years of data would show different trends. However, we have no reason to believe the study year to be an aberrant year; if anything, observation rates have increased since 2014,6 again pointing out that while our findings are sizable, they are likely conservative. Future research could include additional years of data to confirm even greater proportions of rehospitalizations exempt from HRRP over time due to observation hospitalizations as index and/or 30-day events.
Outpatient observation hospitalizations can occur anywhere in the hospital and are often clinically similar to inpatient hospitalizations, yet observation hospitalizations are essentially invisible under inpatient quality metrics. Requiring the HRRP to include observation hospitalizations is the most obvious solution, but this could require major regulatory and legislative change11,13—change that would fix a metric but fail to address broad policy concerns inherent in the two-tiered observation and inpatient billing distinction. Instead, CMS and Congress might consider this an opportunity to address the oxymoron of “outpatient hospitalizations” by engaging in comprehensive observation reform.
The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) was designed to improve quality and safety for traditional Medicare beneficiaries.1 Since 2012, the program has reduced payments to institutions with excess inpatient rehospitalizations within 30 days of an index inpatient stay for targeted medical conditions. Observation hospitalizations, billed as outpatient and covered under Medicare Part B, are not counted as index or 30-day rehospitalizations under HRRP methods. Historically, observation occurred almost exclusively in observation units. Now, observation hospitalizations commonly occur on hospital wards, even in intensive care units, and are often clinically indistinguishable from inpatient hospitalizations billed under Medicare Part A.2 The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) state that beneficiaries expected to need 2 or more midnights of hospital care should generally be considered inpatients, yet observation hospitalizations commonly exceed 2 midnights.3,4
The increasing use of observation hospitalizations5,6 raises questions about its impact on HRRP measurements. While observation hospitalizations have been studied as part of 30-day follow-up (numerator) to index inpatient hospitalizations,5,6 little is known about how observation hospitalizations impact rates when they are factored in as both index stays (denominator) and in the 30-day rehospitalization rate (numerator).2,7 We analyzed the complete combinations of observation and inpatient hospitalizations, including observation as index hospitalization, rehospitalization, or both, to determine HRRP impact.
METHODS
Study Cohort
Medicare fee-for-service standard claim files for all beneficiaries (100% population file version) were used to examine qualifying index inpatient and observation hospitalizations between January 1, 2014, and November 30, 2014, as well as 30-day inpatient and observation rehospitalizations. We used CMS’s 30-day methodology, including previously described standard exclusions (Appendix Figure),8 except for the aforementioned inclusion of observation hospitalizations. Observation hospitalizations were identified using established methods,3,9,10 excluding those observation encounters coded with revenue center code 0761 only3,10 in order to be most conservative in identifying observation hospitalizations (Appendix Figure). These methods assign hospitalization type (observation or inpatient) based on the final (billed) status. The terms hospitalization and rehospitalization refer to both inpatient and observation encounters. The University of Wisconsin Health Sciences Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program
Index HRRP admissions for congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, myocardial infarction, and pneumonia were examined as a prespecified subgroup.1,11 Coronary artery bypass grafting, total hip replacement, and total knee replacement were excluded in this analysis, as no crosswalk exists between International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes and Current Procedural Terminology codes for these surgical conditions.11
Analysis
Analyses were conducted at the encounter level, consistent with CMS methods.8 Descriptive statistics were used to summarize index and 30-day outcomes.
RESULTS
Of 8,859,534 index hospitalizations for any reason or diagnosis, 1,597,837 (18%) were observation and 7,261,697 (82%) were inpatient. Including all hospitalizations, 23% (390,249/1,689,609) of rehospitalizations were excluded from readmission measurement by virtue of the index hospitalization and/or 30-day rehospitalization being observation (Table 1 and Table 2).

For the subgroup of HRRP conditions, 418,923 (11%) and 3,387,849 (89%) of 3,806,772 index hospitalizations were observation and inpatient, respectively. Including HRRP conditions only, 18% (155,553/876,033) of rehospitalizations were excluded from HRRP reporting owing to observation hospitalization as index, 30-day outcome, or both. Of 188,430 index/30-day pairs containing observation, 34% (63,740) were observation/inpatient, 53% (100,343) were inpatient/observation, and 13% (24,347) were observation/observation (Table 1 and Table 2).
DISCUSSION
By ignoring observation hospitalizations in 30-day HRRP quality metrics, nearly one of five potential rehospitalizations is missed. Observation hospitalizations commonly occur as either the index event or 30-day outcome, so accurately determining 30-day HRRP rates must include observation in both positions. Given hospital variability in observation use,3,7 these findings are critically important to accurately understand rehospitalization risk and indicate that HRRP may not be fulfilling its intended purpose.
Including all hospitalizations for any diagnosis, we found that observation and inpatient hospitalizations commonly occur within 30 days of each other. Nearly one in four hospitalization/rehospitalization pairs include observation as index, 30-day rehospitalization, or both. Although not directly related to HRRP metrics, these data demonstrate the growing importance and presence of outpatient (observation) hospitalizations in the Medicare program.
Our study adds to the evolving body of literature investigating quality measures under a two-tiered hospital system where inpatient hospitalizations are counted and observation hospitalizations are not. Figueroa and colleagues12 found that improvements in avoidable admission rates for patients with ambulatory care–sensitive conditions were largely attributable to a shift from counted inpatient to uncounted observation hospitalizations. In other words, hospitalizations were still occurring, but were not being tallied due to outpatient (observation) classification. Zuckerman et al5 and the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC)6 concluded that readmissions improvements recognized by the HRRP were not explained by a shift to more observation hospitalizations following an index inpatient hospitalization; however, both studies included observation hospitalizations as part of 30-day rehospitalization (numerator) only, not also as part of index hospitalizations (denominator). Our study confirms the importance of including observation hospitalizations in both the index (denominator) and 30-day (numerator) rehospitalization positions to determine the full impact of observation hospitalizations on Medicare’s HRRP metrics.
Our study has limitations. We focused on nonsurgical HRRP conditions, which may have impacted our findings. Additionally, some authors have suggested including emergency department (ED) visits in rehospitalization studies.7 Although ED visits occur at hospitals, they are not hospitalizations; we excluded them as a first step. Had we included ED visits, encounters excluded from HRRP measurements would have increased, suggesting that our findings, while sizeable, are likely conservative. Additionally, we could not determine the merits or medical necessity of hospitalizations (inpatient or outpatient observation), but this is an inherent limitation in a large claims dataset like this one. Finally, we only included a single year of data in this analysis, and it is possible that additional years of data would show different trends. However, we have no reason to believe the study year to be an aberrant year; if anything, observation rates have increased since 2014,6 again pointing out that while our findings are sizable, they are likely conservative. Future research could include additional years of data to confirm even greater proportions of rehospitalizations exempt from HRRP over time due to observation hospitalizations as index and/or 30-day events.
Outpatient observation hospitalizations can occur anywhere in the hospital and are often clinically similar to inpatient hospitalizations, yet observation hospitalizations are essentially invisible under inpatient quality metrics. Requiring the HRRP to include observation hospitalizations is the most obvious solution, but this could require major regulatory and legislative change11,13—change that would fix a metric but fail to address broad policy concerns inherent in the two-tiered observation and inpatient billing distinction. Instead, CMS and Congress might consider this an opportunity to address the oxymoron of “outpatient hospitalizations” by engaging in comprehensive observation reform.
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP). Accessed March 12, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/Readmissions-Reduction-Program
2. Sabbatini AK, Wright B. Excluding observation stays from readmission rates—what quality measures are missing. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2062-2065. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1800732
3. Sheehy AM, Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, et al. Thirty-day re-observation, chronic re-observation, and neighborhood disadvantage. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(12):2644-2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.059
4. US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Vulnerabilities remain under Medicare’s 2-midnight hospital policy. December 19, 2016. Accessed February 11, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-02-15-00020.asp
5. Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1543-1551. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa1513024
6. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Mandated report: the effects of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare and the Health Care Delivery System. 2018;3-31. Accessed March 17, 2021. Available at: http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/jun18_medpacreporttocongress_rev_nov2019_note_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
7. Wadhera RK, Yeh RW, Maddox KEJ. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program—time for a reboot. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2289-2291. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1901225
8. National Quality Forum. Measure #1789: Hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission measure. Accessed January 30, 2021. https://www.qualityforum.org/ProjectDescription.aspx?projectID=73619
9. Sheehy AM, Shi F, Kind AJH. Identifying observation stays in Medicare data: policy implications of a definition. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(2):96-100. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3038
10. Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, Kind AJH, Sheehy AM. What is an observation stay? Evaluating the use of hospital observation stays in Medicare. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(7):1568-1572. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.16441
11. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) Archives. Accessed February 10, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/HRRP-Archives
12. Figueroa JF, Burke LG, Zheng J, Orav EJ, Jha AK. Trends in hospitalization vs observation stay for ambulatory care-sensitive conditions. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12): 1714-1716. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.3177
13. Public Law 111-148, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, 111th Congress. March 23, 2010. Accessed March 12, 2021.https://www.congress.gov/111/plaws/publ148/PLAW-111publ148.pdf
1. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP). Accessed March 12, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/Readmissions-Reduction-Program
2. Sabbatini AK, Wright B. Excluding observation stays from readmission rates—what quality measures are missing. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2062-2065. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1800732
3. Sheehy AM, Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, et al. Thirty-day re-observation, chronic re-observation, and neighborhood disadvantage. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(12):2644-2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.059
4. US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Vulnerabilities remain under Medicare’s 2-midnight hospital policy. December 19, 2016. Accessed February 11, 2021. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-02-15-00020.asp
5. Zuckerman RB, Sheingold SH, Orav EJ, Ruhter J, Epstein AM. Readmissions, observation and the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(16):1543-1551. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa1513024
6. Medicare Payment Advisory Commission. Mandated report: the effects of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program. In: Report to the Congress: Medicare and the Health Care Delivery System. 2018;3-31. Accessed March 17, 2021. Available at: http://www.medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/jun18_medpacreporttocongress_rev_nov2019_note_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
7. Wadhera RK, Yeh RW, Maddox KEJ. The Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program—time for a reboot. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2289-2291. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1901225
8. National Quality Forum. Measure #1789: Hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission measure. Accessed January 30, 2021. https://www.qualityforum.org/ProjectDescription.aspx?projectID=73619
9. Sheehy AM, Shi F, Kind AJH. Identifying observation stays in Medicare data: policy implications of a definition. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(2):96-100. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3038
10. Powell WR, Kaiksow FA, Kind AJH, Sheehy AM. What is an observation stay? Evaluating the use of hospital observation stays in Medicare. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(7):1568-1572. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.16441
11. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP) Archives. Accessed February 10, 2021. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Payment/AcuteInpatientPPS/HRRP-Archives
12. Figueroa JF, Burke LG, Zheng J, Orav EJ, Jha AK. Trends in hospitalization vs observation stay for ambulatory care-sensitive conditions. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(12): 1714-1716. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.3177
13. Public Law 111-148, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, 111th Congress. March 23, 2010. Accessed March 12, 2021.https://www.congress.gov/111/plaws/publ148/PLAW-111publ148.pdf
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Scholarly Productivity and Rank in Academic Hospital Medicine
Hospital medicine has grown rapidly, with more than 50,000 hospitalists practicing nationally in 2016.1 Despite the remarkable increase in academic hospital medicine faculty (AHMF), scholarly productivity remains underdeveloped. Prior evidence suggests peer-reviewed publications remain an important aspect of promotion in academic hospital medicine.2 However, there are multiple barriers to robust scholarly productivity among AHMF, including inadequate mentorship,3 lack of protected scholarship time,4 and greater participation in nonclinical activities outside of peer-reviewed clinical research.5 Though research barriers have been described previously, the current state of scholarly productivity among AHMF has not been characterized. In this cross-sectional study, we describe the distribution of academic rank and scholarly output of a national sample of AHMF.
METHODS
Study Design and Data Source
We performed a cross-sectional study of AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residency programs as determined by Doximity.com as of February 1, 2020 (Appendix Table 1). Between March and August 2020, two authors (NS, MT) visited each residency program’s website, identified all faculty listed as members of the hospital medicine program, and extracted demographic data, including degrees, sex, residency, medical school, year of residency graduation, completion of chief residency, completion of fellowship, and rank. We categorized all academic titles into full professor, associate professor, assistant professor, and instructor/lecturer. Missing information was supplemented by searching state licensing websites and Doximity.com. Sex was validated using Genderize.io. We queried the Scopus database for each AHMF’s name and affiliated institution to extract publications, citations, and H-index (metric of productivity and impact, derived from the number of publications and their associated citations).6 We categorized medical schools by rank (top 25, top 50, or unranked), as defined by the 2020 US News Best Medical Schools, sorted by research7 and by location (United States, international Caribbean, and international non-Caribbean). We excluded programs without hospital medicine section/division webpages and AHMF with nonpromotion titles such as “adjunct professor” or “acting professor” or those with missing data that could not be identified using these methods.
Analysis
Summary statistics were generated using means with standard deviations and medians with interquartile ranges. We evaluated postresidency years 6 to 10 and 14 to 18 as conservative time frames for promotion to associate and full professor, respectively. These windows account for time spent for additional degrees, instructor years, and alternative career pathways. Demographic differences between academic ranks were determined using chi-square and Kruskal-Wallis analyses.
Because promotion occurs sequentially, a proportional odds logistic regression model was used to evaluate the association of academic rank and H-index, number of years post residency, completion of chief residency, graduation from a top 25 medical school, and sex. Since not all programs have the instructor/lecturer rank, only assistant, associate, and full professors were included in this model. Significance was assessed with the likelihood ratio test. The proportional odds assumption was assessed using the score test. All adjusted odds ratios and their associated 95% confidence intervals were recorded. A two-tailed P value < .05 was considered significant for this study, and SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used to conduct all analyses. This study was approved by the UT Southwestern Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
Cohort Demographics
Of the top 25 internal medicine programs, 3 were excluded because they did not have websites that listed AHMF. Of the remaining 22 programs, we identified 1,829 AHMF. We excluded 166 AHMF because we could not identify title or year of residency graduation and 109 for having nonpromotion titles, leaving 1,554 AHMF (Appendix Figure). The cohort characteristics are described in Table 1. 
Research Productivity
A total of 9,809 documents had been published by this cohort of academic hospitalists (Appendix Table 2). Overall mean (SD) and median (IQR) publications were 6.3 (24.3) and 0.0 (0.0-4.0), respectively. A total of 799 (51.4%) AHMF had no publications, 347 (22.3%) had one to three publications, 209 (13.4%) had 10 or more, and 39 (2.5%) had 50 or more. The median number of publications stratified by academic rank were 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-1.0) for instructors, 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-3.0) for assistant professors, 8.0 (IQR, 2.0-23.0) for associate professors, and 38.0 (IQR, 6.0-99.0) for full professors. Among men, 54.3% had published at least one manuscript, compared to 42.7% of women (P < .0001). The distribution of H-indices by years since residency graduation is shown in the Figure. The median number of documents published by faculty 6 to 10 years post residency was 1.0 (IQR, 0.0-4.0), with 46.8% of these faculty without a publication. For faculty 14 to 18 years post residency, the median number of documents was 3.0 (IQR, 0.0-11.0), with 30.1% of these faculty without a publication. Years post residency and academic rank were correlated with higher H-indices as well as more publications and citations (P < .0001).
Factors Associated With Academic Rank
Factors associated with rank are described in Appendix Table 3. In our multivariable ordinal regression model, H-index (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16 per single H-index point; 95% CI, 1.12-1.20), years post residency graduation (aOR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.11-1.17), completion of chief residency (aOR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.34-4.51), and graduation from a top 25 medical school (aOR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.44-3.06) were associated with promotion.
DISCUSSION
In this cross-sectional analysis of more than 1,500 AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residencies in the United States, 88.3% were instructors or assistant professors, while only 11.7% were associate or full professors. Furthermore, 51.4% were without a publication, and only 26.3% had published more than three manuscripts. Last, H-index, completion of a chief residency, years post residency, and graduation from a top 25 medical school were associated with higher academic rank.
Only 2.7% of the cohort were full professors, and 9.0% were associate professors. In comparison, academic cardiology faculty are 28.2% full professors and 22.9% associate professors.8 While the field of hospital medicine is relatively new, many faculty members had practiced for the expected duration of time for promotion consideration, with assistant professors or instructors constituting 89.9% of faculty at 6 to 10 years and 63.6% of faculty at 14 to 18 years post residency. We additionally observed a gender gap in publication history in hospital medicine, consistent with prior studies in hospital medicine that suggested gender disparities in scholarship.9,10 Increased focus will be needed in the future to ensure opportunities for scholarship are equitable for all faculty in hospital medicine.
Our findings suggest that scholarly productivity in academic hospital medicine remains a challenge. Prior studies have reported that less than half of academic hospitalists have ever published, and fewer than one in eight have received research funding.11,12 It is encouraging, however, that publications increase with time after residency. These data are consistent with the literature demonstrating a modest increase in hospitalists who had ever published, increasing from 43.0% in 2012 to 48.6% in 2020.12 Despite these trends, however, some early-career academic hospitalists report ambivalence toward academic productivity and promotion.13 Whether this ambivalence is the source of low scholarship output or the outcome of insufficient mentorship and limited research success is uncertain. But these factors, combined with the pressures of clinical productivity, the existing lack of mentorship, and inadequate protected research time represent barriers to successful scholarship in academic hospital medicine.3,14
Our study has several limitations. First, our inclusion criteria for the top 25 internal medicine residencies may have excluded hospital medicine divisions with substantial scholarly productivity. However, with 21 of the 25 programs listed on Doximity.com in the top 25 for internal medicine research funding, it is likely that our results overestimate scholarly productivity if compared to a complete, national cohort of AHMF.15 Second, our findings may not be generalizable to hospitalists who practice in nonacademic settings. Third, we were unable to account for differences in promotion criteria/tracks or scholarly output expectations between institutions. This limitation has been seen similarly in prior studies linking promotion and H-index.2 Furthermore, our study does not capture promotion via other pathways that may not depend on scholarly output, such as hospital leadership roles. Last, as data were abstracted from academic center websites, it is possible that not all information was accurate or updated. However, we randomly reevaluated 25% of hospital division webpages 6 months after our initial data collection and noted that all had been updated with new faculty and academic ranks, suggesting our data were accurate.
These data highlight that research productivity and academic promotion remain challenges in academic hospital medicine. Future studies may examine topics that include understanding pathways and milestones to promotion, reducing disparities in scholarship, and improving mentorship, protected time, and research funding in academic hospital medicine.
1. Wachter RM, Goldman L. Zero to 50,000—the 20th anniversary of the hospitalist. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(11):1009-1011. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1607958
2. Leykum LK, Parekh VI, Sharpe B, Boonyasai RT, Centor RM. Tried and true: a survey of successfully promoted academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(7):411-415. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.894
3. Harrison R, Hunter AJ, Sharpe B, Auerbach AD. Survey of US academic hospitalist leaders about mentorship and academic activities in hospitalist groups. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(1):5-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.836
4. Cumbler E, Rendón P, Yirdaw E, et al. Keys to career success: resources and barriers identified by early career academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33(5):588-589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-018-4336-7
5. Flanders SA, Centor B, Weber V, McGinn T, DeSalvo K, Auerbach A. Challenges and opportunities in academic hospital medicine: report from the Academic Hospital Medicine Summit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(4):240-246. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.497
6. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
7. 2021 Best Medical Schools: Research. U.S. News & World Report. Accessed April 23, 2021. https://www.usnews.com/best-graduate-schools/top-medical-schools/research-rankings
8. Blumenthal DM, Olenski AR, Yeh RW, et al. Sex differences in faculty rank among academic cardiologists in the United States. Circulation. 2017;135(6):506-517. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023520
9. Burden M, Frank MG, Keniston A, et al. Gender disparities in leadership and scholarly productivity of academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(8):481-485. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2340
10. Adler E, Hobbs A, Dhaliwal G, Babik JM. Gender differences in authorship of clinical problem-solving articles. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(8):475-478. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3465
11. Chopra V, Burden M, Jones CD, et al. State of research in adult hospital medicine: results of a national survey. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(4):207-211. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3136
12. Dang Do AN, Munchhof AM, Terry C, Emmett T, Kara A. Research and publication trends in hospital medicine. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):148-154. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2148
13. Cumbler E, Yirdaw E, Kneeland P, et al. What is career success for academic hospitalists? A qualitative analysis of early-career faculty perspectives. J Hosp Med. 2018;13(6):372-377. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2924
14. Reid MB, Misky GJ, Harrison RA, Sharpe B, Auerbach A, Glasheen JJ. Mentorship, productivity, and promotion among academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(1):23-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-011-1892-5
15. Roskoski R Jr, Parslow TG. Ranking tables of NIH funding to US medical schools in 2019. Accessed April 23, 2021. http://www.brimr.org/NIH_Awards/2019/NIH_Awards_2019.htm
Hospital medicine has grown rapidly, with more than 50,000 hospitalists practicing nationally in 2016.1 Despite the remarkable increase in academic hospital medicine faculty (AHMF), scholarly productivity remains underdeveloped. Prior evidence suggests peer-reviewed publications remain an important aspect of promotion in academic hospital medicine.2 However, there are multiple barriers to robust scholarly productivity among AHMF, including inadequate mentorship,3 lack of protected scholarship time,4 and greater participation in nonclinical activities outside of peer-reviewed clinical research.5 Though research barriers have been described previously, the current state of scholarly productivity among AHMF has not been characterized. In this cross-sectional study, we describe the distribution of academic rank and scholarly output of a national sample of AHMF.
METHODS
Study Design and Data Source
We performed a cross-sectional study of AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residency programs as determined by Doximity.com as of February 1, 2020 (Appendix Table 1). Between March and August 2020, two authors (NS, MT) visited each residency program’s website, identified all faculty listed as members of the hospital medicine program, and extracted demographic data, including degrees, sex, residency, medical school, year of residency graduation, completion of chief residency, completion of fellowship, and rank. We categorized all academic titles into full professor, associate professor, assistant professor, and instructor/lecturer. Missing information was supplemented by searching state licensing websites and Doximity.com. Sex was validated using Genderize.io. We queried the Scopus database for each AHMF’s name and affiliated institution to extract publications, citations, and H-index (metric of productivity and impact, derived from the number of publications and their associated citations).6 We categorized medical schools by rank (top 25, top 50, or unranked), as defined by the 2020 US News Best Medical Schools, sorted by research7 and by location (United States, international Caribbean, and international non-Caribbean). We excluded programs without hospital medicine section/division webpages and AHMF with nonpromotion titles such as “adjunct professor” or “acting professor” or those with missing data that could not be identified using these methods.
Analysis
Summary statistics were generated using means with standard deviations and medians with interquartile ranges. We evaluated postresidency years 6 to 10 and 14 to 18 as conservative time frames for promotion to associate and full professor, respectively. These windows account for time spent for additional degrees, instructor years, and alternative career pathways. Demographic differences between academic ranks were determined using chi-square and Kruskal-Wallis analyses.
Because promotion occurs sequentially, a proportional odds logistic regression model was used to evaluate the association of academic rank and H-index, number of years post residency, completion of chief residency, graduation from a top 25 medical school, and sex. Since not all programs have the instructor/lecturer rank, only assistant, associate, and full professors were included in this model. Significance was assessed with the likelihood ratio test. The proportional odds assumption was assessed using the score test. All adjusted odds ratios and their associated 95% confidence intervals were recorded. A two-tailed P value < .05 was considered significant for this study, and SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used to conduct all analyses. This study was approved by the UT Southwestern Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
Cohort Demographics
Of the top 25 internal medicine programs, 3 were excluded because they did not have websites that listed AHMF. Of the remaining 22 programs, we identified 1,829 AHMF. We excluded 166 AHMF because we could not identify title or year of residency graduation and 109 for having nonpromotion titles, leaving 1,554 AHMF (Appendix Figure). The cohort characteristics are described in Table 1. 

Research Productivity
A total of 9,809 documents had been published by this cohort of academic hospitalists (Appendix Table 2). Overall mean (SD) and median (IQR) publications were 6.3 (24.3) and 0.0 (0.0-4.0), respectively. A total of 799 (51.4%) AHMF had no publications, 347 (22.3%) had one to three publications, 209 (13.4%) had 10 or more, and 39 (2.5%) had 50 or more. The median number of publications stratified by academic rank were 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-1.0) for instructors, 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-3.0) for assistant professors, 8.0 (IQR, 2.0-23.0) for associate professors, and 38.0 (IQR, 6.0-99.0) for full professors. Among men, 54.3% had published at least one manuscript, compared to 42.7% of women (P < .0001). The distribution of H-indices by years since residency graduation is shown in the Figure. The median number of documents published by faculty 6 to 10 years post residency was 1.0 (IQR, 0.0-4.0), with 46.8% of these faculty without a publication. For faculty 14 to 18 years post residency, the median number of documents was 3.0 (IQR, 0.0-11.0), with 30.1% of these faculty without a publication. Years post residency and academic rank were correlated with higher H-indices as well as more publications and citations (P < .0001).
Factors Associated With Academic Rank
Factors associated with rank are described in Appendix Table 3. In our multivariable ordinal regression model, H-index (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16 per single H-index point; 95% CI, 1.12-1.20), years post residency graduation (aOR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.11-1.17), completion of chief residency (aOR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.34-4.51), and graduation from a top 25 medical school (aOR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.44-3.06) were associated with promotion.
DISCUSSION
In this cross-sectional analysis of more than 1,500 AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residencies in the United States, 88.3% were instructors or assistant professors, while only 11.7% were associate or full professors. Furthermore, 51.4% were without a publication, and only 26.3% had published more than three manuscripts. Last, H-index, completion of a chief residency, years post residency, and graduation from a top 25 medical school were associated with higher academic rank.
Only 2.7% of the cohort were full professors, and 9.0% were associate professors. In comparison, academic cardiology faculty are 28.2% full professors and 22.9% associate professors.8 While the field of hospital medicine is relatively new, many faculty members had practiced for the expected duration of time for promotion consideration, with assistant professors or instructors constituting 89.9% of faculty at 6 to 10 years and 63.6% of faculty at 14 to 18 years post residency. We additionally observed a gender gap in publication history in hospital medicine, consistent with prior studies in hospital medicine that suggested gender disparities in scholarship.9,10 Increased focus will be needed in the future to ensure opportunities for scholarship are equitable for all faculty in hospital medicine.
Our findings suggest that scholarly productivity in academic hospital medicine remains a challenge. Prior studies have reported that less than half of academic hospitalists have ever published, and fewer than one in eight have received research funding.11,12 It is encouraging, however, that publications increase with time after residency. These data are consistent with the literature demonstrating a modest increase in hospitalists who had ever published, increasing from 43.0% in 2012 to 48.6% in 2020.12 Despite these trends, however, some early-career academic hospitalists report ambivalence toward academic productivity and promotion.13 Whether this ambivalence is the source of low scholarship output or the outcome of insufficient mentorship and limited research success is uncertain. But these factors, combined with the pressures of clinical productivity, the existing lack of mentorship, and inadequate protected research time represent barriers to successful scholarship in academic hospital medicine.3,14
Our study has several limitations. First, our inclusion criteria for the top 25 internal medicine residencies may have excluded hospital medicine divisions with substantial scholarly productivity. However, with 21 of the 25 programs listed on Doximity.com in the top 25 for internal medicine research funding, it is likely that our results overestimate scholarly productivity if compared to a complete, national cohort of AHMF.15 Second, our findings may not be generalizable to hospitalists who practice in nonacademic settings. Third, we were unable to account for differences in promotion criteria/tracks or scholarly output expectations between institutions. This limitation has been seen similarly in prior studies linking promotion and H-index.2 Furthermore, our study does not capture promotion via other pathways that may not depend on scholarly output, such as hospital leadership roles. Last, as data were abstracted from academic center websites, it is possible that not all information was accurate or updated. However, we randomly reevaluated 25% of hospital division webpages 6 months after our initial data collection and noted that all had been updated with new faculty and academic ranks, suggesting our data were accurate.
These data highlight that research productivity and academic promotion remain challenges in academic hospital medicine. Future studies may examine topics that include understanding pathways and milestones to promotion, reducing disparities in scholarship, and improving mentorship, protected time, and research funding in academic hospital medicine.
Hospital medicine has grown rapidly, with more than 50,000 hospitalists practicing nationally in 2016.1 Despite the remarkable increase in academic hospital medicine faculty (AHMF), scholarly productivity remains underdeveloped. Prior evidence suggests peer-reviewed publications remain an important aspect of promotion in academic hospital medicine.2 However, there are multiple barriers to robust scholarly productivity among AHMF, including inadequate mentorship,3 lack of protected scholarship time,4 and greater participation in nonclinical activities outside of peer-reviewed clinical research.5 Though research barriers have been described previously, the current state of scholarly productivity among AHMF has not been characterized. In this cross-sectional study, we describe the distribution of academic rank and scholarly output of a national sample of AHMF.
METHODS
Study Design and Data Source
We performed a cross-sectional study of AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residency programs as determined by Doximity.com as of February 1, 2020 (Appendix Table 1). Between March and August 2020, two authors (NS, MT) visited each residency program’s website, identified all faculty listed as members of the hospital medicine program, and extracted demographic data, including degrees, sex, residency, medical school, year of residency graduation, completion of chief residency, completion of fellowship, and rank. We categorized all academic titles into full professor, associate professor, assistant professor, and instructor/lecturer. Missing information was supplemented by searching state licensing websites and Doximity.com. Sex was validated using Genderize.io. We queried the Scopus database for each AHMF’s name and affiliated institution to extract publications, citations, and H-index (metric of productivity and impact, derived from the number of publications and their associated citations).6 We categorized medical schools by rank (top 25, top 50, or unranked), as defined by the 2020 US News Best Medical Schools, sorted by research7 and by location (United States, international Caribbean, and international non-Caribbean). We excluded programs without hospital medicine section/division webpages and AHMF with nonpromotion titles such as “adjunct professor” or “acting professor” or those with missing data that could not be identified using these methods.
Analysis
Summary statistics were generated using means with standard deviations and medians with interquartile ranges. We evaluated postresidency years 6 to 10 and 14 to 18 as conservative time frames for promotion to associate and full professor, respectively. These windows account for time spent for additional degrees, instructor years, and alternative career pathways. Demographic differences between academic ranks were determined using chi-square and Kruskal-Wallis analyses.
Because promotion occurs sequentially, a proportional odds logistic regression model was used to evaluate the association of academic rank and H-index, number of years post residency, completion of chief residency, graduation from a top 25 medical school, and sex. Since not all programs have the instructor/lecturer rank, only assistant, associate, and full professors were included in this model. Significance was assessed with the likelihood ratio test. The proportional odds assumption was assessed using the score test. All adjusted odds ratios and their associated 95% confidence intervals were recorded. A two-tailed P value < .05 was considered significant for this study, and SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used to conduct all analyses. This study was approved by the UT Southwestern Institutional Review Board.
RESULTS
Cohort Demographics
Of the top 25 internal medicine programs, 3 were excluded because they did not have websites that listed AHMF. Of the remaining 22 programs, we identified 1,829 AHMF. We excluded 166 AHMF because we could not identify title or year of residency graduation and 109 for having nonpromotion titles, leaving 1,554 AHMF (Appendix Figure). The cohort characteristics are described in Table 1. 

Research Productivity
A total of 9,809 documents had been published by this cohort of academic hospitalists (Appendix Table 2). Overall mean (SD) and median (IQR) publications were 6.3 (24.3) and 0.0 (0.0-4.0), respectively. A total of 799 (51.4%) AHMF had no publications, 347 (22.3%) had one to three publications, 209 (13.4%) had 10 or more, and 39 (2.5%) had 50 or more. The median number of publications stratified by academic rank were 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-1.0) for instructors, 0.0 (IQR, 0.0-3.0) for assistant professors, 8.0 (IQR, 2.0-23.0) for associate professors, and 38.0 (IQR, 6.0-99.0) for full professors. Among men, 54.3% had published at least one manuscript, compared to 42.7% of women (P < .0001). The distribution of H-indices by years since residency graduation is shown in the Figure. The median number of documents published by faculty 6 to 10 years post residency was 1.0 (IQR, 0.0-4.0), with 46.8% of these faculty without a publication. For faculty 14 to 18 years post residency, the median number of documents was 3.0 (IQR, 0.0-11.0), with 30.1% of these faculty without a publication. Years post residency and academic rank were correlated with higher H-indices as well as more publications and citations (P < .0001).
Factors Associated With Academic Rank
Factors associated with rank are described in Appendix Table 3. In our multivariable ordinal regression model, H-index (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.16 per single H-index point; 95% CI, 1.12-1.20), years post residency graduation (aOR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.11-1.17), completion of chief residency (aOR, 2.46; 95% CI, 1.34-4.51), and graduation from a top 25 medical school (aOR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.44-3.06) were associated with promotion.
DISCUSSION
In this cross-sectional analysis of more than 1,500 AHMF at the top 25 internal medicine residencies in the United States, 88.3% were instructors or assistant professors, while only 11.7% were associate or full professors. Furthermore, 51.4% were without a publication, and only 26.3% had published more than three manuscripts. Last, H-index, completion of a chief residency, years post residency, and graduation from a top 25 medical school were associated with higher academic rank.
Only 2.7% of the cohort were full professors, and 9.0% were associate professors. In comparison, academic cardiology faculty are 28.2% full professors and 22.9% associate professors.8 While the field of hospital medicine is relatively new, many faculty members had practiced for the expected duration of time for promotion consideration, with assistant professors or instructors constituting 89.9% of faculty at 6 to 10 years and 63.6% of faculty at 14 to 18 years post residency. We additionally observed a gender gap in publication history in hospital medicine, consistent with prior studies in hospital medicine that suggested gender disparities in scholarship.9,10 Increased focus will be needed in the future to ensure opportunities for scholarship are equitable for all faculty in hospital medicine.
Our findings suggest that scholarly productivity in academic hospital medicine remains a challenge. Prior studies have reported that less than half of academic hospitalists have ever published, and fewer than one in eight have received research funding.11,12 It is encouraging, however, that publications increase with time after residency. These data are consistent with the literature demonstrating a modest increase in hospitalists who had ever published, increasing from 43.0% in 2012 to 48.6% in 2020.12 Despite these trends, however, some early-career academic hospitalists report ambivalence toward academic productivity and promotion.13 Whether this ambivalence is the source of low scholarship output or the outcome of insufficient mentorship and limited research success is uncertain. But these factors, combined with the pressures of clinical productivity, the existing lack of mentorship, and inadequate protected research time represent barriers to successful scholarship in academic hospital medicine.3,14
Our study has several limitations. First, our inclusion criteria for the top 25 internal medicine residencies may have excluded hospital medicine divisions with substantial scholarly productivity. However, with 21 of the 25 programs listed on Doximity.com in the top 25 for internal medicine research funding, it is likely that our results overestimate scholarly productivity if compared to a complete, national cohort of AHMF.15 Second, our findings may not be generalizable to hospitalists who practice in nonacademic settings. Third, we were unable to account for differences in promotion criteria/tracks or scholarly output expectations between institutions. This limitation has been seen similarly in prior studies linking promotion and H-index.2 Furthermore, our study does not capture promotion via other pathways that may not depend on scholarly output, such as hospital leadership roles. Last, as data were abstracted from academic center websites, it is possible that not all information was accurate or updated. However, we randomly reevaluated 25% of hospital division webpages 6 months after our initial data collection and noted that all had been updated with new faculty and academic ranks, suggesting our data were accurate.
These data highlight that research productivity and academic promotion remain challenges in academic hospital medicine. Future studies may examine topics that include understanding pathways and milestones to promotion, reducing disparities in scholarship, and improving mentorship, protected time, and research funding in academic hospital medicine.
1. Wachter RM, Goldman L. Zero to 50,000—the 20th anniversary of the hospitalist. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(11):1009-1011. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1607958
2. Leykum LK, Parekh VI, Sharpe B, Boonyasai RT, Centor RM. Tried and true: a survey of successfully promoted academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(7):411-415. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.894
3. Harrison R, Hunter AJ, Sharpe B, Auerbach AD. Survey of US academic hospitalist leaders about mentorship and academic activities in hospitalist groups. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(1):5-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.836
4. Cumbler E, Rendón P, Yirdaw E, et al. Keys to career success: resources and barriers identified by early career academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33(5):588-589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-018-4336-7
5. Flanders SA, Centor B, Weber V, McGinn T, DeSalvo K, Auerbach A. Challenges and opportunities in academic hospital medicine: report from the Academic Hospital Medicine Summit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(4):240-246. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.497
6. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
7. 2021 Best Medical Schools: Research. U.S. News & World Report. Accessed April 23, 2021. https://www.usnews.com/best-graduate-schools/top-medical-schools/research-rankings
8. Blumenthal DM, Olenski AR, Yeh RW, et al. Sex differences in faculty rank among academic cardiologists in the United States. Circulation. 2017;135(6):506-517. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023520
9. Burden M, Frank MG, Keniston A, et al. Gender disparities in leadership and scholarly productivity of academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(8):481-485. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2340
10. Adler E, Hobbs A, Dhaliwal G, Babik JM. Gender differences in authorship of clinical problem-solving articles. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(8):475-478. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3465
11. Chopra V, Burden M, Jones CD, et al. State of research in adult hospital medicine: results of a national survey. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(4):207-211. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3136
12. Dang Do AN, Munchhof AM, Terry C, Emmett T, Kara A. Research and publication trends in hospital medicine. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):148-154. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2148
13. Cumbler E, Yirdaw E, Kneeland P, et al. What is career success for academic hospitalists? A qualitative analysis of early-career faculty perspectives. J Hosp Med. 2018;13(6):372-377. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2924
14. Reid MB, Misky GJ, Harrison RA, Sharpe B, Auerbach A, Glasheen JJ. Mentorship, productivity, and promotion among academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(1):23-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-011-1892-5
15. Roskoski R Jr, Parslow TG. Ranking tables of NIH funding to US medical schools in 2019. Accessed April 23, 2021. http://www.brimr.org/NIH_Awards/2019/NIH_Awards_2019.htm
1. Wachter RM, Goldman L. Zero to 50,000—the 20th anniversary of the hospitalist. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(11):1009-1011. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp1607958
2. Leykum LK, Parekh VI, Sharpe B, Boonyasai RT, Centor RM. Tried and true: a survey of successfully promoted academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(7):411-415. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.894
3. Harrison R, Hunter AJ, Sharpe B, Auerbach AD. Survey of US academic hospitalist leaders about mentorship and academic activities in hospitalist groups. J Hosp Med. 2011;6(1):5-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.836
4. Cumbler E, Rendón P, Yirdaw E, et al. Keys to career success: resources and barriers identified by early career academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33(5):588-589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-018-4336-7
5. Flanders SA, Centor B, Weber V, McGinn T, DeSalvo K, Auerbach A. Challenges and opportunities in academic hospital medicine: report from the Academic Hospital Medicine Summit. J Hosp Med. 2009;4(4):240-246. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.497
6. Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102
7. 2021 Best Medical Schools: Research. U.S. News & World Report. Accessed April 23, 2021. https://www.usnews.com/best-graduate-schools/top-medical-schools/research-rankings
8. Blumenthal DM, Olenski AR, Yeh RW, et al. Sex differences in faculty rank among academic cardiologists in the United States. Circulation. 2017;135(6):506-517. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023520
9. Burden M, Frank MG, Keniston A, et al. Gender disparities in leadership and scholarly productivity of academic hospitalists. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(8):481-485. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2340
10. Adler E, Hobbs A, Dhaliwal G, Babik JM. Gender differences in authorship of clinical problem-solving articles. J Hosp Med. 2020;15(8):475-478. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3465
11. Chopra V, Burden M, Jones CD, et al. State of research in adult hospital medicine: results of a national survey. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(4):207-211. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3136
12. Dang Do AN, Munchhof AM, Terry C, Emmett T, Kara A. Research and publication trends in hospital medicine. J Hosp Med. 2014;9(3):148-154. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2148
13. Cumbler E, Yirdaw E, Kneeland P, et al. What is career success for academic hospitalists? A qualitative analysis of early-career faculty perspectives. J Hosp Med. 2018;13(6):372-377. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.2924
14. Reid MB, Misky GJ, Harrison RA, Sharpe B, Auerbach A, Glasheen JJ. Mentorship, productivity, and promotion among academic hospitalists. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(1):23-27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-011-1892-5
15. Roskoski R Jr, Parslow TG. Ranking tables of NIH funding to US medical schools in 2019. Accessed April 23, 2021. http://www.brimr.org/NIH_Awards/2019/NIH_Awards_2019.htm
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Coerced invasive procedures: Policy overriding indication in gastrostomy tube placement
Clinical scenario
An 83-year-old man is admitted with a hemiplegic cerebrovascular accident. He is found to have dysphagia, and a nasogastric feeding tube is placed. Over the next several days, his strength begins to recover, and he tolerates his tube feeding well. Discharge to a skilled nursing facility (SNF) for subacute rehabilitation is planned. His swallowing is showing signs of recovery; it has not recovered adequately but is expected to continue to improve such that he is predicted to be independent of tube feeding within 7-14 days. None of the facilities in the region are willing to admit a patient with a nasal feeding tube, despite the anticipated short duration. The patient is medically ready for discharge but is refusing the feeding gastrostomy. “Why would I want a hole in my stomach, if I’m only going to need it for 1-2 weeks and this tube in my nose is working fine and is comfortable?” he pleads with tears in his eyes.
Feeding dysphagic patients after stroke
Dysphagia, potentially leading to aspiration and/or pneumonia, is a common sequela of stroke – up to half of hospitalized patients are affected.1 When oral intake is contraindicated, patients are often fed by nasogastric tube (NGT) or by surgically or endoscopically placed gastrostomy tube (GT). Without good justification based on outcomes, NGTs are traditionally used when the need for feeding is thought to be short term (<4 weeks) and GTs are used for long term (>4 weeks). However, in 2005, a large multicenter randomized control trial found that the majority of stroke patients with dysphagia that would resolve had resolution within 2-3 weeks. Moreover, outcomes were equivalent or better for patients fed with an NGT versus GT.
The authors concluded by recommending feeding via NGT for 2-3 weeks, after which conversion to GT can be considered if dysphagia persists.1 Notably, the recommendation allows consideration, and no evidence-based guideline requires or recommends GT be placed based on duration of tube feed dependence. Currently, while nutrition and neurology authorities have adopted these recommendations,2,3 many authors have noted poor adherence to this guideline, and many find that the median period between stroke and GT placement is 7 days rather than the recommended minimum of 14.4,5,6 While ignorance can partially explain the lack of widespread compliance,6 the policies of posthospital facilities are another culprit. Increasingly, and for a variety of reasons unsupported by the literature, SNFs refuse NGT and require GT.4,7,8,9
Ethical considerations
The four principles of medical ethics – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice – can guide clinicians, patients, and family members in decision-making. In our case, by withholding needed and desired treatment (discharge to and treatment by a rehabilitation facility) the patient is being coerced to undergo a procedure he does not want, and clinicians participate in denying him autonomy. Further, given that the evidence, national guidelines, and in fact federal regulations indicate that his preferences are congruent with best practices, pressuring him to accept gastrostomy placement runs afoul of the principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence. Though the mechanism is unclear, early gastrostomy (<14-21 days) is associated with increased risk of death, worse functional outcomes, and a lower rate of return to oral feeding, as well as a significant procedure-specific complication rate.1,10 By insisting on gastrostomy, we neither act in this patient’s best interests nor “do no harm.”
However, the medical system is complex. The clinician at the bedside can evaluate this scenario, review the national guidelines, discuss the procedure and risks with the patient and family, and conclude that the patient should be discharged with a nasal feeding tube. Nevertheless, if no facility is willing to accept him without a gastrostomy, our decision-making model – previously limited to our patient’s best interests alone – is forced to change. Despite our misgivings, we often conclude that the harm done by an early gastrostomy is outweighed by the harm of remaining unnecessarily in the acute hospital setting. We further worry about other patients lingering in the emergency department for lack of an inpatient bed and the possible – though unknowable – harm done to them.
Looking forward
It is an unfortunate fact that medical decision-making must often include factors unrelated to the patient’s best interests, with financial considerations and structural barriers frequently driving deviation from ideal care. Providers and patients navigate these decisions to their best abilities, making compromises when forced. However, with education and professional activism, providers can advocate for the elimination of barriers to providing medically sound and ethically appropriate care. In our experience, delay of gastrostomy placement, until discharge is imminent and planning for postdischarge care is initiated, has resulted in a decrease by half the fraction of patients with tracheostomies who had gastrostomies placed prior to discharge.11 With aggressive outreach and education, we now have nursing homes willing to accept patients with NGTs.
Criteria for admission to discharge facilities can drive medical decision-making that is unethical and unsupported by evidence. Continued efforts to eliminate barriers to appropriate and ethical care have been successful and are encouraged.
Dr. Cowan is administrative chief resident in the department of surgery at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. Dr. Seres is professor of medicine in the Institute of Human Nutrition and associate clinical ethicist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Dennis MS et al. Lancet. 2005 Feb 26-Mar 4;365(9461):764-72.
2. Powers W. et al. Stroke. 2018 Mar;49(3):e46-e110.
3. Burgos R et al. Clin Nutr. 2018 Feb;37(1):354-96.
4. Wilmskoetter J et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016 Nov;25(11):2694-700.
5. George BP et al. Stroke. 2017 Feb;48(2):420-7.
6. Fessler TA. et al. Surg Endosc. 2019 Dec;33(12):4089-97.
7. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun;31(3):342-8.
8. Moran C and O’Mahoney S. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar;31(2):137-42.
9. Gomes CA et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD008096.
10. Joundi RA et al. Neurology. 2018 Feb 13;90(7):e544-52.
11. Bothra A et al. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018 Feb;42(2):491.
Clinical scenario
An 83-year-old man is admitted with a hemiplegic cerebrovascular accident. He is found to have dysphagia, and a nasogastric feeding tube is placed. Over the next several days, his strength begins to recover, and he tolerates his tube feeding well. Discharge to a skilled nursing facility (SNF) for subacute rehabilitation is planned. His swallowing is showing signs of recovery; it has not recovered adequately but is expected to continue to improve such that he is predicted to be independent of tube feeding within 7-14 days. None of the facilities in the region are willing to admit a patient with a nasal feeding tube, despite the anticipated short duration. The patient is medically ready for discharge but is refusing the feeding gastrostomy. “Why would I want a hole in my stomach, if I’m only going to need it for 1-2 weeks and this tube in my nose is working fine and is comfortable?” he pleads with tears in his eyes.
Feeding dysphagic patients after stroke
Dysphagia, potentially leading to aspiration and/or pneumonia, is a common sequela of stroke – up to half of hospitalized patients are affected.1 When oral intake is contraindicated, patients are often fed by nasogastric tube (NGT) or by surgically or endoscopically placed gastrostomy tube (GT). Without good justification based on outcomes, NGTs are traditionally used when the need for feeding is thought to be short term (<4 weeks) and GTs are used for long term (>4 weeks). However, in 2005, a large multicenter randomized control trial found that the majority of stroke patients with dysphagia that would resolve had resolution within 2-3 weeks. Moreover, outcomes were equivalent or better for patients fed with an NGT versus GT.
The authors concluded by recommending feeding via NGT for 2-3 weeks, after which conversion to GT can be considered if dysphagia persists.1 Notably, the recommendation allows consideration, and no evidence-based guideline requires or recommends GT be placed based on duration of tube feed dependence. Currently, while nutrition and neurology authorities have adopted these recommendations,2,3 many authors have noted poor adherence to this guideline, and many find that the median period between stroke and GT placement is 7 days rather than the recommended minimum of 14.4,5,6 While ignorance can partially explain the lack of widespread compliance,6 the policies of posthospital facilities are another culprit. Increasingly, and for a variety of reasons unsupported by the literature, SNFs refuse NGT and require GT.4,7,8,9
Ethical considerations
The four principles of medical ethics – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice – can guide clinicians, patients, and family members in decision-making. In our case, by withholding needed and desired treatment (discharge to and treatment by a rehabilitation facility) the patient is being coerced to undergo a procedure he does not want, and clinicians participate in denying him autonomy. Further, given that the evidence, national guidelines, and in fact federal regulations indicate that his preferences are congruent with best practices, pressuring him to accept gastrostomy placement runs afoul of the principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence. Though the mechanism is unclear, early gastrostomy (<14-21 days) is associated with increased risk of death, worse functional outcomes, and a lower rate of return to oral feeding, as well as a significant procedure-specific complication rate.1,10 By insisting on gastrostomy, we neither act in this patient’s best interests nor “do no harm.”
However, the medical system is complex. The clinician at the bedside can evaluate this scenario, review the national guidelines, discuss the procedure and risks with the patient and family, and conclude that the patient should be discharged with a nasal feeding tube. Nevertheless, if no facility is willing to accept him without a gastrostomy, our decision-making model – previously limited to our patient’s best interests alone – is forced to change. Despite our misgivings, we often conclude that the harm done by an early gastrostomy is outweighed by the harm of remaining unnecessarily in the acute hospital setting. We further worry about other patients lingering in the emergency department for lack of an inpatient bed and the possible – though unknowable – harm done to them.
Looking forward
It is an unfortunate fact that medical decision-making must often include factors unrelated to the patient’s best interests, with financial considerations and structural barriers frequently driving deviation from ideal care. Providers and patients navigate these decisions to their best abilities, making compromises when forced. However, with education and professional activism, providers can advocate for the elimination of barriers to providing medically sound and ethically appropriate care. In our experience, delay of gastrostomy placement, until discharge is imminent and planning for postdischarge care is initiated, has resulted in a decrease by half the fraction of patients with tracheostomies who had gastrostomies placed prior to discharge.11 With aggressive outreach and education, we now have nursing homes willing to accept patients with NGTs.
Criteria for admission to discharge facilities can drive medical decision-making that is unethical and unsupported by evidence. Continued efforts to eliminate barriers to appropriate and ethical care have been successful and are encouraged.
Dr. Cowan is administrative chief resident in the department of surgery at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. Dr. Seres is professor of medicine in the Institute of Human Nutrition and associate clinical ethicist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Dennis MS et al. Lancet. 2005 Feb 26-Mar 4;365(9461):764-72.
2. Powers W. et al. Stroke. 2018 Mar;49(3):e46-e110.
3. Burgos R et al. Clin Nutr. 2018 Feb;37(1):354-96.
4. Wilmskoetter J et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016 Nov;25(11):2694-700.
5. George BP et al. Stroke. 2017 Feb;48(2):420-7.
6. Fessler TA. et al. Surg Endosc. 2019 Dec;33(12):4089-97.
7. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun;31(3):342-8.
8. Moran C and O’Mahoney S. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar;31(2):137-42.
9. Gomes CA et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD008096.
10. Joundi RA et al. Neurology. 2018 Feb 13;90(7):e544-52.
11. Bothra A et al. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018 Feb;42(2):491.
Clinical scenario
An 83-year-old man is admitted with a hemiplegic cerebrovascular accident. He is found to have dysphagia, and a nasogastric feeding tube is placed. Over the next several days, his strength begins to recover, and he tolerates his tube feeding well. Discharge to a skilled nursing facility (SNF) for subacute rehabilitation is planned. His swallowing is showing signs of recovery; it has not recovered adequately but is expected to continue to improve such that he is predicted to be independent of tube feeding within 7-14 days. None of the facilities in the region are willing to admit a patient with a nasal feeding tube, despite the anticipated short duration. The patient is medically ready for discharge but is refusing the feeding gastrostomy. “Why would I want a hole in my stomach, if I’m only going to need it for 1-2 weeks and this tube in my nose is working fine and is comfortable?” he pleads with tears in his eyes.
Feeding dysphagic patients after stroke
Dysphagia, potentially leading to aspiration and/or pneumonia, is a common sequela of stroke – up to half of hospitalized patients are affected.1 When oral intake is contraindicated, patients are often fed by nasogastric tube (NGT) or by surgically or endoscopically placed gastrostomy tube (GT). Without good justification based on outcomes, NGTs are traditionally used when the need for feeding is thought to be short term (<4 weeks) and GTs are used for long term (>4 weeks). However, in 2005, a large multicenter randomized control trial found that the majority of stroke patients with dysphagia that would resolve had resolution within 2-3 weeks. Moreover, outcomes were equivalent or better for patients fed with an NGT versus GT.
The authors concluded by recommending feeding via NGT for 2-3 weeks, after which conversion to GT can be considered if dysphagia persists.1 Notably, the recommendation allows consideration, and no evidence-based guideline requires or recommends GT be placed based on duration of tube feed dependence. Currently, while nutrition and neurology authorities have adopted these recommendations,2,3 many authors have noted poor adherence to this guideline, and many find that the median period between stroke and GT placement is 7 days rather than the recommended minimum of 14.4,5,6 While ignorance can partially explain the lack of widespread compliance,6 the policies of posthospital facilities are another culprit. Increasingly, and for a variety of reasons unsupported by the literature, SNFs refuse NGT and require GT.4,7,8,9
Ethical considerations
The four principles of medical ethics – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice – can guide clinicians, patients, and family members in decision-making. In our case, by withholding needed and desired treatment (discharge to and treatment by a rehabilitation facility) the patient is being coerced to undergo a procedure he does not want, and clinicians participate in denying him autonomy. Further, given that the evidence, national guidelines, and in fact federal regulations indicate that his preferences are congruent with best practices, pressuring him to accept gastrostomy placement runs afoul of the principles of beneficence and nonmaleficence. Though the mechanism is unclear, early gastrostomy (<14-21 days) is associated with increased risk of death, worse functional outcomes, and a lower rate of return to oral feeding, as well as a significant procedure-specific complication rate.1,10 By insisting on gastrostomy, we neither act in this patient’s best interests nor “do no harm.”
However, the medical system is complex. The clinician at the bedside can evaluate this scenario, review the national guidelines, discuss the procedure and risks with the patient and family, and conclude that the patient should be discharged with a nasal feeding tube. Nevertheless, if no facility is willing to accept him without a gastrostomy, our decision-making model – previously limited to our patient’s best interests alone – is forced to change. Despite our misgivings, we often conclude that the harm done by an early gastrostomy is outweighed by the harm of remaining unnecessarily in the acute hospital setting. We further worry about other patients lingering in the emergency department for lack of an inpatient bed and the possible – though unknowable – harm done to them.
Looking forward
It is an unfortunate fact that medical decision-making must often include factors unrelated to the patient’s best interests, with financial considerations and structural barriers frequently driving deviation from ideal care. Providers and patients navigate these decisions to their best abilities, making compromises when forced. However, with education and professional activism, providers can advocate for the elimination of barriers to providing medically sound and ethically appropriate care. In our experience, delay of gastrostomy placement, until discharge is imminent and planning for postdischarge care is initiated, has resulted in a decrease by half the fraction of patients with tracheostomies who had gastrostomies placed prior to discharge.11 With aggressive outreach and education, we now have nursing homes willing to accept patients with NGTs.
Criteria for admission to discharge facilities can drive medical decision-making that is unethical and unsupported by evidence. Continued efforts to eliminate barriers to appropriate and ethical care have been successful and are encouraged.
Dr. Cowan is administrative chief resident in the department of surgery at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York. Dr. Seres is professor of medicine in the Institute of Human Nutrition and associate clinical ethicist at Columbia University Irving Medical Center. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Dennis MS et al. Lancet. 2005 Feb 26-Mar 4;365(9461):764-72.
2. Powers W. et al. Stroke. 2018 Mar;49(3):e46-e110.
3. Burgos R et al. Clin Nutr. 2018 Feb;37(1):354-96.
4. Wilmskoetter J et al. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016 Nov;25(11):2694-700.
5. George BP et al. Stroke. 2017 Feb;48(2):420-7.
6. Fessler TA. et al. Surg Endosc. 2019 Dec;33(12):4089-97.
7. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun;31(3):342-8.
8. Moran C and O’Mahoney S. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar;31(2):137-42.
9. Gomes CA et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD008096.
10. Joundi RA et al. Neurology. 2018 Feb 13;90(7):e544-52.
11. Bothra A et al. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2018 Feb;42(2):491.
Inpatient care for HS higher for Black and Hispanic patients
National Inpatient Sample.
The differences occurred despite Black and Hispanic patients being younger at the time of admission than White patients, and may reflect increased disease severity and management challenges in these patients with skin of color, Nishadh Sutaria, BS, a medical student at Tufts University, Boston, said at the annual Skin of Color Society symposium. “They may also reflect social inequities in access to dermatologists, with racial and ethnic minorities using inpatient services in lieu of outpatient care.”
Mr. Sutaria and coinvestigators, led by Shawn Kwatra, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, identified 8,040 HS admissions for White patients, 16,490 Black patients, and 2,405 for Hispanic patients during the 5-year period.
Black and Hispanic patients were significantly younger than White patients, with a mean age of 38.1 years and 35 years, respectively, compared with 42 years for White patients (P < .001 in each case). Compared with White patients, Black patients had more procedures (2.03 vs. 1.84, P = .006), a longer length of stay (5.82 days vs. 4.97 days, P = .001), and higher cost of care ($46,119 vs. $39,862, P = .010). Compared with White patients, Hispanic patients had higher cost of care ($52,334 vs. $39,862, P = .004).
“In these models, Black patients stayed almost a full day longer and accrued a charge of $8,000 more than White patients, and Hispanic patients stayed about a half-day longer and accrued a charge of almost $15,000 more than White patients,” Mr. Sutaria said.
In a multilinear regression analysis adjusting for age, sex, and insurance type, Black race correlated with more procedures, higher length of stay, and higher cost of care, and Hispanic ethnicity with more procedures and higher cost of care.
Prior research has shown that Black patients may be disproportionately affected by HS. A 2017 analysis of electronic health record data for tens of millions of patients nationally, for instance, showed an incidence of HS that was over 2.5 times greater in Blacks than Whites. And a recent analysis of electronic data in Wisconsin for patients with an HS diagnosis and 3 or more encounters for the disease showed that Blacks are more likely to have HS that is Hurley Stage 3, the most severe type.
Increased severity “has not been explicitly shown in Hispanic patients,” Dr. Kwatra said in an interview, “[but] there is a strong relationship between obesity/metabolic syndrome with HS. Because Hispanic patients have higher rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome, it’s [thought] that they may have more severe HS.”
HS patients with skin of color are underrepresented in clinical trials, he said. “Severe HS can be difficult to treat because there are few effective treatments,” he said, noting that adalimumab is the only Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy.
The National Inpatient Sample is a publicly available, all-payer inpatient care database developed for the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project.
Mr. Sutaria is a dermatology research fellow working under the guidance of Dr. Kwatra.
National Inpatient Sample.
The differences occurred despite Black and Hispanic patients being younger at the time of admission than White patients, and may reflect increased disease severity and management challenges in these patients with skin of color, Nishadh Sutaria, BS, a medical student at Tufts University, Boston, said at the annual Skin of Color Society symposium. “They may also reflect social inequities in access to dermatologists, with racial and ethnic minorities using inpatient services in lieu of outpatient care.”
Mr. Sutaria and coinvestigators, led by Shawn Kwatra, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, identified 8,040 HS admissions for White patients, 16,490 Black patients, and 2,405 for Hispanic patients during the 5-year period.
Black and Hispanic patients were significantly younger than White patients, with a mean age of 38.1 years and 35 years, respectively, compared with 42 years for White patients (P < .001 in each case). Compared with White patients, Black patients had more procedures (2.03 vs. 1.84, P = .006), a longer length of stay (5.82 days vs. 4.97 days, P = .001), and higher cost of care ($46,119 vs. $39,862, P = .010). Compared with White patients, Hispanic patients had higher cost of care ($52,334 vs. $39,862, P = .004).
“In these models, Black patients stayed almost a full day longer and accrued a charge of $8,000 more than White patients, and Hispanic patients stayed about a half-day longer and accrued a charge of almost $15,000 more than White patients,” Mr. Sutaria said.
In a multilinear regression analysis adjusting for age, sex, and insurance type, Black race correlated with more procedures, higher length of stay, and higher cost of care, and Hispanic ethnicity with more procedures and higher cost of care.
Prior research has shown that Black patients may be disproportionately affected by HS. A 2017 analysis of electronic health record data for tens of millions of patients nationally, for instance, showed an incidence of HS that was over 2.5 times greater in Blacks than Whites. And a recent analysis of electronic data in Wisconsin for patients with an HS diagnosis and 3 or more encounters for the disease showed that Blacks are more likely to have HS that is Hurley Stage 3, the most severe type.
Increased severity “has not been explicitly shown in Hispanic patients,” Dr. Kwatra said in an interview, “[but] there is a strong relationship between obesity/metabolic syndrome with HS. Because Hispanic patients have higher rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome, it’s [thought] that they may have more severe HS.”
HS patients with skin of color are underrepresented in clinical trials, he said. “Severe HS can be difficult to treat because there are few effective treatments,” he said, noting that adalimumab is the only Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy.
The National Inpatient Sample is a publicly available, all-payer inpatient care database developed for the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project.
Mr. Sutaria is a dermatology research fellow working under the guidance of Dr. Kwatra.
National Inpatient Sample.
The differences occurred despite Black and Hispanic patients being younger at the time of admission than White patients, and may reflect increased disease severity and management challenges in these patients with skin of color, Nishadh Sutaria, BS, a medical student at Tufts University, Boston, said at the annual Skin of Color Society symposium. “They may also reflect social inequities in access to dermatologists, with racial and ethnic minorities using inpatient services in lieu of outpatient care.”
Mr. Sutaria and coinvestigators, led by Shawn Kwatra, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, identified 8,040 HS admissions for White patients, 16,490 Black patients, and 2,405 for Hispanic patients during the 5-year period.
Black and Hispanic patients were significantly younger than White patients, with a mean age of 38.1 years and 35 years, respectively, compared with 42 years for White patients (P < .001 in each case). Compared with White patients, Black patients had more procedures (2.03 vs. 1.84, P = .006), a longer length of stay (5.82 days vs. 4.97 days, P = .001), and higher cost of care ($46,119 vs. $39,862, P = .010). Compared with White patients, Hispanic patients had higher cost of care ($52,334 vs. $39,862, P = .004).
“In these models, Black patients stayed almost a full day longer and accrued a charge of $8,000 more than White patients, and Hispanic patients stayed about a half-day longer and accrued a charge of almost $15,000 more than White patients,” Mr. Sutaria said.
In a multilinear regression analysis adjusting for age, sex, and insurance type, Black race correlated with more procedures, higher length of stay, and higher cost of care, and Hispanic ethnicity with more procedures and higher cost of care.
Prior research has shown that Black patients may be disproportionately affected by HS. A 2017 analysis of electronic health record data for tens of millions of patients nationally, for instance, showed an incidence of HS that was over 2.5 times greater in Blacks than Whites. And a recent analysis of electronic data in Wisconsin for patients with an HS diagnosis and 3 or more encounters for the disease showed that Blacks are more likely to have HS that is Hurley Stage 3, the most severe type.
Increased severity “has not been explicitly shown in Hispanic patients,” Dr. Kwatra said in an interview, “[but] there is a strong relationship between obesity/metabolic syndrome with HS. Because Hispanic patients have higher rates of obesity and metabolic syndrome, it’s [thought] that they may have more severe HS.”
HS patients with skin of color are underrepresented in clinical trials, he said. “Severe HS can be difficult to treat because there are few effective treatments,” he said, noting that adalimumab is the only Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy.
The National Inpatient Sample is a publicly available, all-payer inpatient care database developed for the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality’s Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project.
Mr. Sutaria is a dermatology research fellow working under the guidance of Dr. Kwatra.
FROM SOC SOCIETY 2021
‘Remarkable’ results for targeted therapy of rare CNS tumors
The results from three small studies of targeted therapy for rare brain tumors were “remarkable,” according to Jaishri Blakeley, MD, a neurology professor at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who discussed the studies after they were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting.
Although most patients don’t have targetable mutations, molecular testing “is well worth the effort,” for those that do. “I think it’s fair to say that precision medicine” – well established in other tumor types – “is finally here in full force for neuro-oncology,” Dr. Blakeley said.
A promising start
Fifteen of 16 patients (94%) in one study had newly diagnosed and untreated papillary craniopharyngiomas (PCPs) that harbored BRAF V600E mutations, a common finding in PCPs, which have no effective medical treatment.
Tumors shrunk 68%-99% in 14 patients (93%) after treatment with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib plus the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, which was included to stave off resistance to vemurafenib. The 24-month progression free survival was 93%.
The combination resulted in significant response in all patients who received at least one cycle of therapy, with a median 91% volume reduction. “Our study indicates that BRAF/MEK inhibitors could be a powerful tool in the treatment of previously untreated PCP, with the potential to avoid the morbidity associated with radiation and surgery,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Priscilla K. Brastianos, MD, associate professor of medicine at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston.
Thirty-three people in the second study had a mix of high and low grade gliomas or other CNS tumors positive for TRK gene fusions, a known oncogenic driver; the majority were children. They were treated with the TRK inhibitor larotrectinib after progressing on other systemic therapies.
The objective response rate was 30%, and the disease control rate was 73% at 24 weeks, with a median time to best response of 1.9 months. Tumors shrank in 82% of evaluable patients. Median progression-free survival was 18.3 months, and overall survival was not reached.
“These results support testing for TRK gene fusions for all patients with CNS tumors, especially if there is no known driver and especially in infants,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Sebastien Perreault, MD, a clinical assistant neurosciences professor at the University of Montreal.
The third study tested ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib in seven patients with adult-onset neuroblastoma, a rare and almost invariably fatal tumor known to be enriched for ALK mutations; the subjects were positive for them.
Their disease remained stable anywhere from 3.4 to 37.4 months. Median time to progression was 15.5 months, and median overall survival was 46.5 months.
ALK inhibitors “can be a well-tolerated options for treatment, improving time to progression. Development of resistance to one agent does not preclude use of other agents in the same drug class. ALK inhibitors should be considered when treating patients with this diagnosis,” said lead investigator and presenter Jessica Stiefel, MD, a pediatric hematology oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
A ‘strong’ recommendation
The data “are great news” across the board. Targeted therapy applied to the right CNS tumor can have “dramatic” benefit for tumor control, Dr. Blakeley said.
But organizing molecular testing is not straightforward and requires strategies to balance “the use of precious resources, such as time money, and tissue,” with the potential benefit. Interpretation of testing results isn’t straightforward either, and is best handled by a molecular tumor board. Clinical pharmacists are also key to accessing expensive medications off label for CNS tumors.
Adverse events are also a consideration. Most of the subjects in the PCP study had grade 3/4 toxicity. Three patients in the ALK inhibitor study had to stop because of adverse events. Almost 40% on larotrectinib had grade 3 or 4 toxicity; nobody came off treatment, but a third had to skip doses.
Once an actionable mutation is identified, Dr. Blakeley’s “strong recommendation” is to enroll patients in a clinical trial that targets it, to take advantage the structure already in place to secure treatment, managed patients, and assess outcomes.
The National Cancer Institute’s MATCH trial is one of several options.
The BRAF/MEK inhibitor study was funded by Genentech and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brastianos had ties to numerous companies, including Pfizer, Lilly, and Merck. The TRK inhibitor study was funded by Bayer/Lilly. Dr. Perreault is a speaker and researcher for the company and has other ties. Dr. Blakeley is an adviser and/or researcher for a number of companies, including AbbVie, Astellas, BMS, and Exelixis. Dr. Stiefel didn’t have any disclosures, and didn’t report outside funding.
The results from three small studies of targeted therapy for rare brain tumors were “remarkable,” according to Jaishri Blakeley, MD, a neurology professor at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who discussed the studies after they were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting.
Although most patients don’t have targetable mutations, molecular testing “is well worth the effort,” for those that do. “I think it’s fair to say that precision medicine” – well established in other tumor types – “is finally here in full force for neuro-oncology,” Dr. Blakeley said.
A promising start
Fifteen of 16 patients (94%) in one study had newly diagnosed and untreated papillary craniopharyngiomas (PCPs) that harbored BRAF V600E mutations, a common finding in PCPs, which have no effective medical treatment.
Tumors shrunk 68%-99% in 14 patients (93%) after treatment with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib plus the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, which was included to stave off resistance to vemurafenib. The 24-month progression free survival was 93%.
The combination resulted in significant response in all patients who received at least one cycle of therapy, with a median 91% volume reduction. “Our study indicates that BRAF/MEK inhibitors could be a powerful tool in the treatment of previously untreated PCP, with the potential to avoid the morbidity associated with radiation and surgery,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Priscilla K. Brastianos, MD, associate professor of medicine at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston.
Thirty-three people in the second study had a mix of high and low grade gliomas or other CNS tumors positive for TRK gene fusions, a known oncogenic driver; the majority were children. They were treated with the TRK inhibitor larotrectinib after progressing on other systemic therapies.
The objective response rate was 30%, and the disease control rate was 73% at 24 weeks, with a median time to best response of 1.9 months. Tumors shrank in 82% of evaluable patients. Median progression-free survival was 18.3 months, and overall survival was not reached.
“These results support testing for TRK gene fusions for all patients with CNS tumors, especially if there is no known driver and especially in infants,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Sebastien Perreault, MD, a clinical assistant neurosciences professor at the University of Montreal.
The third study tested ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib in seven patients with adult-onset neuroblastoma, a rare and almost invariably fatal tumor known to be enriched for ALK mutations; the subjects were positive for them.
Their disease remained stable anywhere from 3.4 to 37.4 months. Median time to progression was 15.5 months, and median overall survival was 46.5 months.
ALK inhibitors “can be a well-tolerated options for treatment, improving time to progression. Development of resistance to one agent does not preclude use of other agents in the same drug class. ALK inhibitors should be considered when treating patients with this diagnosis,” said lead investigator and presenter Jessica Stiefel, MD, a pediatric hematology oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
A ‘strong’ recommendation
The data “are great news” across the board. Targeted therapy applied to the right CNS tumor can have “dramatic” benefit for tumor control, Dr. Blakeley said.
But organizing molecular testing is not straightforward and requires strategies to balance “the use of precious resources, such as time money, and tissue,” with the potential benefit. Interpretation of testing results isn’t straightforward either, and is best handled by a molecular tumor board. Clinical pharmacists are also key to accessing expensive medications off label for CNS tumors.
Adverse events are also a consideration. Most of the subjects in the PCP study had grade 3/4 toxicity. Three patients in the ALK inhibitor study had to stop because of adverse events. Almost 40% on larotrectinib had grade 3 or 4 toxicity; nobody came off treatment, but a third had to skip doses.
Once an actionable mutation is identified, Dr. Blakeley’s “strong recommendation” is to enroll patients in a clinical trial that targets it, to take advantage the structure already in place to secure treatment, managed patients, and assess outcomes.
The National Cancer Institute’s MATCH trial is one of several options.
The BRAF/MEK inhibitor study was funded by Genentech and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brastianos had ties to numerous companies, including Pfizer, Lilly, and Merck. The TRK inhibitor study was funded by Bayer/Lilly. Dr. Perreault is a speaker and researcher for the company and has other ties. Dr. Blakeley is an adviser and/or researcher for a number of companies, including AbbVie, Astellas, BMS, and Exelixis. Dr. Stiefel didn’t have any disclosures, and didn’t report outside funding.
The results from three small studies of targeted therapy for rare brain tumors were “remarkable,” according to Jaishri Blakeley, MD, a neurology professor at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who discussed the studies after they were presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting.
Although most patients don’t have targetable mutations, molecular testing “is well worth the effort,” for those that do. “I think it’s fair to say that precision medicine” – well established in other tumor types – “is finally here in full force for neuro-oncology,” Dr. Blakeley said.
A promising start
Fifteen of 16 patients (94%) in one study had newly diagnosed and untreated papillary craniopharyngiomas (PCPs) that harbored BRAF V600E mutations, a common finding in PCPs, which have no effective medical treatment.
Tumors shrunk 68%-99% in 14 patients (93%) after treatment with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib plus the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, which was included to stave off resistance to vemurafenib. The 24-month progression free survival was 93%.
The combination resulted in significant response in all patients who received at least one cycle of therapy, with a median 91% volume reduction. “Our study indicates that BRAF/MEK inhibitors could be a powerful tool in the treatment of previously untreated PCP, with the potential to avoid the morbidity associated with radiation and surgery,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Priscilla K. Brastianos, MD, associate professor of medicine at Mass General Cancer Center, Boston.
Thirty-three people in the second study had a mix of high and low grade gliomas or other CNS tumors positive for TRK gene fusions, a known oncogenic driver; the majority were children. They were treated with the TRK inhibitor larotrectinib after progressing on other systemic therapies.
The objective response rate was 30%, and the disease control rate was 73% at 24 weeks, with a median time to best response of 1.9 months. Tumors shrank in 82% of evaluable patients. Median progression-free survival was 18.3 months, and overall survival was not reached.
“These results support testing for TRK gene fusions for all patients with CNS tumors, especially if there is no known driver and especially in infants,” concluded lead investigator and presenter Sebastien Perreault, MD, a clinical assistant neurosciences professor at the University of Montreal.
The third study tested ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib in seven patients with adult-onset neuroblastoma, a rare and almost invariably fatal tumor known to be enriched for ALK mutations; the subjects were positive for them.
Their disease remained stable anywhere from 3.4 to 37.4 months. Median time to progression was 15.5 months, and median overall survival was 46.5 months.
ALK inhibitors “can be a well-tolerated options for treatment, improving time to progression. Development of resistance to one agent does not preclude use of other agents in the same drug class. ALK inhibitors should be considered when treating patients with this diagnosis,” said lead investigator and presenter Jessica Stiefel, MD, a pediatric hematology oncology fellow at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
A ‘strong’ recommendation
The data “are great news” across the board. Targeted therapy applied to the right CNS tumor can have “dramatic” benefit for tumor control, Dr. Blakeley said.
But organizing molecular testing is not straightforward and requires strategies to balance “the use of precious resources, such as time money, and tissue,” with the potential benefit. Interpretation of testing results isn’t straightforward either, and is best handled by a molecular tumor board. Clinical pharmacists are also key to accessing expensive medications off label for CNS tumors.
Adverse events are also a consideration. Most of the subjects in the PCP study had grade 3/4 toxicity. Three patients in the ALK inhibitor study had to stop because of adverse events. Almost 40% on larotrectinib had grade 3 or 4 toxicity; nobody came off treatment, but a third had to skip doses.
Once an actionable mutation is identified, Dr. Blakeley’s “strong recommendation” is to enroll patients in a clinical trial that targets it, to take advantage the structure already in place to secure treatment, managed patients, and assess outcomes.
The National Cancer Institute’s MATCH trial is one of several options.
The BRAF/MEK inhibitor study was funded by Genentech and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brastianos had ties to numerous companies, including Pfizer, Lilly, and Merck. The TRK inhibitor study was funded by Bayer/Lilly. Dr. Perreault is a speaker and researcher for the company and has other ties. Dr. Blakeley is an adviser and/or researcher for a number of companies, including AbbVie, Astellas, BMS, and Exelixis. Dr. Stiefel didn’t have any disclosures, and didn’t report outside funding.
FROM ASCO 2021
Experimental antibody-drug conjugate shown active against r/r DLBCL
Patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas who are not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplant have a generally poor prognosis and few treatment options, but an experimental combination of the antibody-drug conjugate naratuximab with rituximab showed promising efficacy and acceptable safety in these patients in a phase 2 trial.
Among patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) the combination was associated with a 44.7% overall response rate, including 31.6% complete responses, and two-thirds of patients had responses lasting more than 12 months, reported Moshe Yair Levy, MD, from Texas Oncology–Baylor Charles A Sammons Cancer Center in Dallas.
“This is, in my viewpoint, very exciting therapy,” he said in a question-and-answer session following his presentation of the data in a late-breaking abstract session during the European Hematology Association annual congress. (Abstract LB1903).
Naratuximab emtansine is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) consisting of a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD37, a surface marker on B lymphocytes that is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), conjugated to a cytotoxic derivative of maitansine.
CD37 is also an internalizable cell-surface antigen, making it an attractive candidate for an ADC approach.
In a phase 1 trial, naratuximab monotherapy showed a good safety profile and a 22% overall response rate, Dr. Levy noted.
“What they found is that, if you coadminister this ADC with rituximab, you’re actually going to get more internalization of the CD37 monoclonal, therefore more payload delivered to your target cells,” he said.
He reported results of a multicenter, adaptive phase 2 study of the combination in patients with DLBCL and other relapsed/refractory NHL.
DLBCL and others
The trial was divided into two parts, with the first consisting of a safety run-in phase with expansion in patients with confirmed diagnoses of relapsed/refractory NHL, including DLBCL, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and marginal zone lymphoma.
Patients with double- or triple-hit disease (with translocations in MYC plus either BCL2 and/or BCL6), bulky disease, or transformed lymphoma were eligible.
The second part consisted of two cohorts of patients with DLBCL treated with naratuximab and rituximab either weekly or every 3 weeks.
All patients in the study had received one to six prior lines of therapy, and had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2. Patients with CNS lymphomas or prior anti-CD37 targeting therapy were excluded.
The safety population included 50 patients with DLBCL assigned to therapy every 3 weeks, 30 assigned to weekly therapy, and 20 patients with other NHL.
DLBCL efficacy
A total of 76 patients with DLBCL were evaluable for efficacy.
The ORR was 44% for patients in both the weekly and every 3 week cohorts, with 31.6% having complete responses.
Among 61 patients with nonbulky disease (longest diameter 7.5 cm or less), the ORR was 50.8%, and among 28 patients who had three or more prior lines of therapy the ORR was 46.4%, with 32.1% having a complete response.
Among responders followed for a median of 15 months, the median duration of response was not reached, and 66% had responses lasting beyond 12 months.
In the weekly dosing DLBCL cohort, 53.3% of patients discontinued treatment of both study drugs because of disease progression, as did 58% of those in the every 3 week cohort, and 30% of patients with other lymphomas. Only eight patients discontinued the combination because of treatment-emergent adverse events. Six patients had treatment-emergent adverse events leading to naratuximab dose reduction.
The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events were neutropenia, leukopenia, lymphopenia and thrombocytopenias. Dr. Levy commented that the use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which was not mandatory in the study, would likely have lowered the incidence of cytopenias.
There were 10 deaths during the study, 2 of which were considered to be treatment related, occurring in 1 patient each in the DLBCL dosing cohorts; 1 of the patients died from pneumonitis, and the other from left ventricular heart failure.
Other patients deaths were attributed to non–treatment-related cardiac arrest, acute renal failure, exacerbation of chronic heart failure, respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, lung infection, or colon adenocarcinoma.
Q 3 weeks suffices
In the question-and-answer session following the presentation, Kenny Lei, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong asked Dr. Levy what the half-life of naratuximab is, and what was the investigator’s rationale for testing a weekly dosing schedule.
“I think the reason they checked the two different regimens, the Q week and the Q 3-week group, is that they noted that [naratuximab] was cleared relatively quickly, and they wanted to see whether or not, by giving Q weekly, when you get a continuous CD37 site occupancy if they would have a better outcome. But as you saw, in the groups there was really no clinically relevant difference in outcome,” Dr. Levy said.
Andrew Davies, MD, PhD, from the University of Southampton (England), asked whether the neutropenia seen in the study was related to myeloid expression of the target of from the off-target deconjugated payload.
“I don’t know that I necessarily have the answer to that,” Dr. Levy replied. “Remember there is the CD20 monoclonal rituximab which we know can cause neutropenia, as well as the CD37 and the target payload. I don’t know if we have enough information to attribute it to one specific component of the therapy,” he said.
The study was funded by Debiopharm International. Dr. Levy disclosed speaker activities for multiple companies, not including Debiopharm. Dr. Lei and Dr. Davies had no disclosures relevant to the study.
Patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas who are not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplant have a generally poor prognosis and few treatment options, but an experimental combination of the antibody-drug conjugate naratuximab with rituximab showed promising efficacy and acceptable safety in these patients in a phase 2 trial.
Among patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) the combination was associated with a 44.7% overall response rate, including 31.6% complete responses, and two-thirds of patients had responses lasting more than 12 months, reported Moshe Yair Levy, MD, from Texas Oncology–Baylor Charles A Sammons Cancer Center in Dallas.
“This is, in my viewpoint, very exciting therapy,” he said in a question-and-answer session following his presentation of the data in a late-breaking abstract session during the European Hematology Association annual congress. (Abstract LB1903).
Naratuximab emtansine is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) consisting of a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD37, a surface marker on B lymphocytes that is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), conjugated to a cytotoxic derivative of maitansine.
CD37 is also an internalizable cell-surface antigen, making it an attractive candidate for an ADC approach.
In a phase 1 trial, naratuximab monotherapy showed a good safety profile and a 22% overall response rate, Dr. Levy noted.
“What they found is that, if you coadminister this ADC with rituximab, you’re actually going to get more internalization of the CD37 monoclonal, therefore more payload delivered to your target cells,” he said.
He reported results of a multicenter, adaptive phase 2 study of the combination in patients with DLBCL and other relapsed/refractory NHL.
DLBCL and others
The trial was divided into two parts, with the first consisting of a safety run-in phase with expansion in patients with confirmed diagnoses of relapsed/refractory NHL, including DLBCL, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and marginal zone lymphoma.
Patients with double- or triple-hit disease (with translocations in MYC plus either BCL2 and/or BCL6), bulky disease, or transformed lymphoma were eligible.
The second part consisted of two cohorts of patients with DLBCL treated with naratuximab and rituximab either weekly or every 3 weeks.
All patients in the study had received one to six prior lines of therapy, and had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2. Patients with CNS lymphomas or prior anti-CD37 targeting therapy were excluded.
The safety population included 50 patients with DLBCL assigned to therapy every 3 weeks, 30 assigned to weekly therapy, and 20 patients with other NHL.
DLBCL efficacy
A total of 76 patients with DLBCL were evaluable for efficacy.
The ORR was 44% for patients in both the weekly and every 3 week cohorts, with 31.6% having complete responses.
Among 61 patients with nonbulky disease (longest diameter 7.5 cm or less), the ORR was 50.8%, and among 28 patients who had three or more prior lines of therapy the ORR was 46.4%, with 32.1% having a complete response.
Among responders followed for a median of 15 months, the median duration of response was not reached, and 66% had responses lasting beyond 12 months.
In the weekly dosing DLBCL cohort, 53.3% of patients discontinued treatment of both study drugs because of disease progression, as did 58% of those in the every 3 week cohort, and 30% of patients with other lymphomas. Only eight patients discontinued the combination because of treatment-emergent adverse events. Six patients had treatment-emergent adverse events leading to naratuximab dose reduction.
The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events were neutropenia, leukopenia, lymphopenia and thrombocytopenias. Dr. Levy commented that the use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which was not mandatory in the study, would likely have lowered the incidence of cytopenias.
There were 10 deaths during the study, 2 of which were considered to be treatment related, occurring in 1 patient each in the DLBCL dosing cohorts; 1 of the patients died from pneumonitis, and the other from left ventricular heart failure.
Other patients deaths were attributed to non–treatment-related cardiac arrest, acute renal failure, exacerbation of chronic heart failure, respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, lung infection, or colon adenocarcinoma.
Q 3 weeks suffices
In the question-and-answer session following the presentation, Kenny Lei, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong asked Dr. Levy what the half-life of naratuximab is, and what was the investigator’s rationale for testing a weekly dosing schedule.
“I think the reason they checked the two different regimens, the Q week and the Q 3-week group, is that they noted that [naratuximab] was cleared relatively quickly, and they wanted to see whether or not, by giving Q weekly, when you get a continuous CD37 site occupancy if they would have a better outcome. But as you saw, in the groups there was really no clinically relevant difference in outcome,” Dr. Levy said.
Andrew Davies, MD, PhD, from the University of Southampton (England), asked whether the neutropenia seen in the study was related to myeloid expression of the target of from the off-target deconjugated payload.
“I don’t know that I necessarily have the answer to that,” Dr. Levy replied. “Remember there is the CD20 monoclonal rituximab which we know can cause neutropenia, as well as the CD37 and the target payload. I don’t know if we have enough information to attribute it to one specific component of the therapy,” he said.
The study was funded by Debiopharm International. Dr. Levy disclosed speaker activities for multiple companies, not including Debiopharm. Dr. Lei and Dr. Davies had no disclosures relevant to the study.
Patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas who are not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplant have a generally poor prognosis and few treatment options, but an experimental combination of the antibody-drug conjugate naratuximab with rituximab showed promising efficacy and acceptable safety in these patients in a phase 2 trial.
Among patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) the combination was associated with a 44.7% overall response rate, including 31.6% complete responses, and two-thirds of patients had responses lasting more than 12 months, reported Moshe Yair Levy, MD, from Texas Oncology–Baylor Charles A Sammons Cancer Center in Dallas.
“This is, in my viewpoint, very exciting therapy,” he said in a question-and-answer session following his presentation of the data in a late-breaking abstract session during the European Hematology Association annual congress. (Abstract LB1903).
Naratuximab emtansine is an investigational antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) consisting of a humanized monoclonal antibody against CD37, a surface marker on B lymphocytes that is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), conjugated to a cytotoxic derivative of maitansine.
CD37 is also an internalizable cell-surface antigen, making it an attractive candidate for an ADC approach.
In a phase 1 trial, naratuximab monotherapy showed a good safety profile and a 22% overall response rate, Dr. Levy noted.
“What they found is that, if you coadminister this ADC with rituximab, you’re actually going to get more internalization of the CD37 monoclonal, therefore more payload delivered to your target cells,” he said.
He reported results of a multicenter, adaptive phase 2 study of the combination in patients with DLBCL and other relapsed/refractory NHL.
DLBCL and others
The trial was divided into two parts, with the first consisting of a safety run-in phase with expansion in patients with confirmed diagnoses of relapsed/refractory NHL, including DLBCL, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and marginal zone lymphoma.
Patients with double- or triple-hit disease (with translocations in MYC plus either BCL2 and/or BCL6), bulky disease, or transformed lymphoma were eligible.
The second part consisted of two cohorts of patients with DLBCL treated with naratuximab and rituximab either weekly or every 3 weeks.
All patients in the study had received one to six prior lines of therapy, and had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-2. Patients with CNS lymphomas or prior anti-CD37 targeting therapy were excluded.
The safety population included 50 patients with DLBCL assigned to therapy every 3 weeks, 30 assigned to weekly therapy, and 20 patients with other NHL.
DLBCL efficacy
A total of 76 patients with DLBCL were evaluable for efficacy.
The ORR was 44% for patients in both the weekly and every 3 week cohorts, with 31.6% having complete responses.
Among 61 patients with nonbulky disease (longest diameter 7.5 cm or less), the ORR was 50.8%, and among 28 patients who had three or more prior lines of therapy the ORR was 46.4%, with 32.1% having a complete response.
Among responders followed for a median of 15 months, the median duration of response was not reached, and 66% had responses lasting beyond 12 months.
In the weekly dosing DLBCL cohort, 53.3% of patients discontinued treatment of both study drugs because of disease progression, as did 58% of those in the every 3 week cohort, and 30% of patients with other lymphomas. Only eight patients discontinued the combination because of treatment-emergent adverse events. Six patients had treatment-emergent adverse events leading to naratuximab dose reduction.
The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events were neutropenia, leukopenia, lymphopenia and thrombocytopenias. Dr. Levy commented that the use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which was not mandatory in the study, would likely have lowered the incidence of cytopenias.
There were 10 deaths during the study, 2 of which were considered to be treatment related, occurring in 1 patient each in the DLBCL dosing cohorts; 1 of the patients died from pneumonitis, and the other from left ventricular heart failure.
Other patients deaths were attributed to non–treatment-related cardiac arrest, acute renal failure, exacerbation of chronic heart failure, respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, lung infection, or colon adenocarcinoma.
Q 3 weeks suffices
In the question-and-answer session following the presentation, Kenny Lei, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong asked Dr. Levy what the half-life of naratuximab is, and what was the investigator’s rationale for testing a weekly dosing schedule.
“I think the reason they checked the two different regimens, the Q week and the Q 3-week group, is that they noted that [naratuximab] was cleared relatively quickly, and they wanted to see whether or not, by giving Q weekly, when you get a continuous CD37 site occupancy if they would have a better outcome. But as you saw, in the groups there was really no clinically relevant difference in outcome,” Dr. Levy said.
Andrew Davies, MD, PhD, from the University of Southampton (England), asked whether the neutropenia seen in the study was related to myeloid expression of the target of from the off-target deconjugated payload.
“I don’t know that I necessarily have the answer to that,” Dr. Levy replied. “Remember there is the CD20 monoclonal rituximab which we know can cause neutropenia, as well as the CD37 and the target payload. I don’t know if we have enough information to attribute it to one specific component of the therapy,” he said.
The study was funded by Debiopharm International. Dr. Levy disclosed speaker activities for multiple companies, not including Debiopharm. Dr. Lei and Dr. Davies had no disclosures relevant to the study.
FROM EHA 2021
Secukinumab provides clinical benefit in phase 3 juvenile arthritis trial
Favorable safety sustained at 104 weeks
Secukinumab (Cosentyx), an interleukin-17A inhibitor, is effective and reasonably well tolerated for treatment of enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) in children and adolescents, according to a phase 3 trial presented at a late breaking abstracts session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
On the primary outcome of time to flare, the curves for secukinumab and placebo separated almost immediately, with fewer than half the number of flares occurring in the experimental arm over the course of the study, according to Nicolino Ruperto, MD, senior research scientist at IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini in Genoa, Italy.
The trial, called JUNIPERA, was conducted over 2 years and included an open-label treatment period (TP1) and then a randomized, placebo-controlled comparison (TP2). In TP1, 86 children were initiated on open-label secukinumab administered subcutaneously on weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 12. The dose was 75 mg for children less than 50 kg and 150 kg for those heavier.
Average patient age was 13.1 years
Of these 86 children, 52 had ERA and 34 had JPsA. Disease duration of at least 6 months was required for entry. Patients up to the age of 18 years were permitted to enroll. The average age was 13.1 years. Most patients, two-thirds of whom were male, had received an immunomodulator prior to study entry.
At the end of TP1, 69.9% of patients had achieved 70% improvement in the Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis American College of Rheumatology joint score (JIA ACR70). The 90.4% of patients who achieved JIA ACR30 were invited to enroll in TP2. A total of 75 patients did so.
At the end of TP2, response rates strongly favored secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR30 (89.2% vs. 64.9%; P = .014) and JIA ACR70 (67.7% vs. 43.2%; P = .042). Higher but not statistically significant differences in response rates were seen for secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR50 (78.4% vs. 62.2%; P = .152), JIA ACR90 (51.4% vs. 40.5%; P = .431) and JIA ACR100 (43.2% vs. 37.8%; P = .755).
During TP2, there were 10 flares in the group randomized to secukinumab versus 21 flares in the placebo group, translating by hazard ratio (HR) into a 72% risk reduction (HR, 0.28; P < .001).
Side effects similar to those in adults
The types and rates of serious adverse events were similar to those reported previously in adult patients, according to Dr. Ruperto. Although the rate of serious adverse events (14.6% vs. 10.6%) was only moderately higher in the experimental arm, more patients randomized to secukinumab than placebo discontinued therapy (13.2% vs. 6.3%) before the end of follow-up.
The side effects that occurred more commonly on secukinumab included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea (22.9% vs. 15.8%). Other adverse events occurring in more than 10% of patients included headache and nasopharyngitis, but most side effects were mild and resolved.
Although the proportion of patients with flare increased over time in both groups, Dr. Ruperto reported that protection against flares and relative improvement in clinical markers of disease activity relative to placebo “were sustained out to 2 years of follow-up.”
The submission of these data to regulatory agencies is anticipated. If secukinumab is given an indication for these forms of arthritis, it will join an indication for plaque psoriasis in children that was granted just a few days before these data were presented. The psoriasis indication is the only current use approved for children in the United States.
More biologics needed for JPsA
Additional biologics will be helpful for children with arthritis who are poorly controlled on available treatments, according to Natasha M. Ruth, MD, director of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. Dr. Ruth was senior author of a case study published 2 years ago in which secukinumab was used to control psoriatic arthritis and nail manifestations of psoriasis.
“It was a girl who had already failed to improve adequately to TNF inhibitors,” reported Dr. Ruth, who had said the child and her parent were very concerned about the nail appearance.
“The nail involvement completely resolved, so it was a very good result in a difficult situation,” Dr. Ruth explained. She said that the decision to try secukinumab was made collaboratively in a clinic in which dermatologists and rheumatologists at her institution work together on difficult cases.
“There is a need for more biologics with different mechanisms of action,” Dr. Ruth said. Based on her experience, secukinumab could be an important addition to treatment options.
Dr. Ruperto reported having financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, which provided financial support for this trial. Many coauthors had financial relationships with multiple companies, including Novartis, and some were employees of the company. Dr. Ruth reported having no potential conflicts of interest.
Favorable safety sustained at 104 weeks
Favorable safety sustained at 104 weeks
Secukinumab (Cosentyx), an interleukin-17A inhibitor, is effective and reasonably well tolerated for treatment of enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) in children and adolescents, according to a phase 3 trial presented at a late breaking abstracts session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
On the primary outcome of time to flare, the curves for secukinumab and placebo separated almost immediately, with fewer than half the number of flares occurring in the experimental arm over the course of the study, according to Nicolino Ruperto, MD, senior research scientist at IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini in Genoa, Italy.
The trial, called JUNIPERA, was conducted over 2 years and included an open-label treatment period (TP1) and then a randomized, placebo-controlled comparison (TP2). In TP1, 86 children were initiated on open-label secukinumab administered subcutaneously on weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 12. The dose was 75 mg for children less than 50 kg and 150 kg for those heavier.
Average patient age was 13.1 years
Of these 86 children, 52 had ERA and 34 had JPsA. Disease duration of at least 6 months was required for entry. Patients up to the age of 18 years were permitted to enroll. The average age was 13.1 years. Most patients, two-thirds of whom were male, had received an immunomodulator prior to study entry.
At the end of TP1, 69.9% of patients had achieved 70% improvement in the Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis American College of Rheumatology joint score (JIA ACR70). The 90.4% of patients who achieved JIA ACR30 were invited to enroll in TP2. A total of 75 patients did so.
At the end of TP2, response rates strongly favored secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR30 (89.2% vs. 64.9%; P = .014) and JIA ACR70 (67.7% vs. 43.2%; P = .042). Higher but not statistically significant differences in response rates were seen for secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR50 (78.4% vs. 62.2%; P = .152), JIA ACR90 (51.4% vs. 40.5%; P = .431) and JIA ACR100 (43.2% vs. 37.8%; P = .755).
During TP2, there were 10 flares in the group randomized to secukinumab versus 21 flares in the placebo group, translating by hazard ratio (HR) into a 72% risk reduction (HR, 0.28; P < .001).
Side effects similar to those in adults
The types and rates of serious adverse events were similar to those reported previously in adult patients, according to Dr. Ruperto. Although the rate of serious adverse events (14.6% vs. 10.6%) was only moderately higher in the experimental arm, more patients randomized to secukinumab than placebo discontinued therapy (13.2% vs. 6.3%) before the end of follow-up.
The side effects that occurred more commonly on secukinumab included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea (22.9% vs. 15.8%). Other adverse events occurring in more than 10% of patients included headache and nasopharyngitis, but most side effects were mild and resolved.
Although the proportion of patients with flare increased over time in both groups, Dr. Ruperto reported that protection against flares and relative improvement in clinical markers of disease activity relative to placebo “were sustained out to 2 years of follow-up.”
The submission of these data to regulatory agencies is anticipated. If secukinumab is given an indication for these forms of arthritis, it will join an indication for plaque psoriasis in children that was granted just a few days before these data were presented. The psoriasis indication is the only current use approved for children in the United States.
More biologics needed for JPsA
Additional biologics will be helpful for children with arthritis who are poorly controlled on available treatments, according to Natasha M. Ruth, MD, director of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. Dr. Ruth was senior author of a case study published 2 years ago in which secukinumab was used to control psoriatic arthritis and nail manifestations of psoriasis.
“It was a girl who had already failed to improve adequately to TNF inhibitors,” reported Dr. Ruth, who had said the child and her parent were very concerned about the nail appearance.
“The nail involvement completely resolved, so it was a very good result in a difficult situation,” Dr. Ruth explained. She said that the decision to try secukinumab was made collaboratively in a clinic in which dermatologists and rheumatologists at her institution work together on difficult cases.
“There is a need for more biologics with different mechanisms of action,” Dr. Ruth said. Based on her experience, secukinumab could be an important addition to treatment options.
Dr. Ruperto reported having financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, which provided financial support for this trial. Many coauthors had financial relationships with multiple companies, including Novartis, and some were employees of the company. Dr. Ruth reported having no potential conflicts of interest.
Secukinumab (Cosentyx), an interleukin-17A inhibitor, is effective and reasonably well tolerated for treatment of enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) in children and adolescents, according to a phase 3 trial presented at a late breaking abstracts session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
On the primary outcome of time to flare, the curves for secukinumab and placebo separated almost immediately, with fewer than half the number of flares occurring in the experimental arm over the course of the study, according to Nicolino Ruperto, MD, senior research scientist at IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini in Genoa, Italy.
The trial, called JUNIPERA, was conducted over 2 years and included an open-label treatment period (TP1) and then a randomized, placebo-controlled comparison (TP2). In TP1, 86 children were initiated on open-label secukinumab administered subcutaneously on weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, and 12. The dose was 75 mg for children less than 50 kg and 150 kg for those heavier.
Average patient age was 13.1 years
Of these 86 children, 52 had ERA and 34 had JPsA. Disease duration of at least 6 months was required for entry. Patients up to the age of 18 years were permitted to enroll. The average age was 13.1 years. Most patients, two-thirds of whom were male, had received an immunomodulator prior to study entry.
At the end of TP1, 69.9% of patients had achieved 70% improvement in the Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis American College of Rheumatology joint score (JIA ACR70). The 90.4% of patients who achieved JIA ACR30 were invited to enroll in TP2. A total of 75 patients did so.
At the end of TP2, response rates strongly favored secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR30 (89.2% vs. 64.9%; P = .014) and JIA ACR70 (67.7% vs. 43.2%; P = .042). Higher but not statistically significant differences in response rates were seen for secukinumab over placebo for JIA ACR50 (78.4% vs. 62.2%; P = .152), JIA ACR90 (51.4% vs. 40.5%; P = .431) and JIA ACR100 (43.2% vs. 37.8%; P = .755).
During TP2, there were 10 flares in the group randomized to secukinumab versus 21 flares in the placebo group, translating by hazard ratio (HR) into a 72% risk reduction (HR, 0.28; P < .001).
Side effects similar to those in adults
The types and rates of serious adverse events were similar to those reported previously in adult patients, according to Dr. Ruperto. Although the rate of serious adverse events (14.6% vs. 10.6%) was only moderately higher in the experimental arm, more patients randomized to secukinumab than placebo discontinued therapy (13.2% vs. 6.3%) before the end of follow-up.
The side effects that occurred more commonly on secukinumab included gastrointestinal complaints, such as diarrhea (22.9% vs. 15.8%). Other adverse events occurring in more than 10% of patients included headache and nasopharyngitis, but most side effects were mild and resolved.
Although the proportion of patients with flare increased over time in both groups, Dr. Ruperto reported that protection against flares and relative improvement in clinical markers of disease activity relative to placebo “were sustained out to 2 years of follow-up.”
The submission of these data to regulatory agencies is anticipated. If secukinumab is given an indication for these forms of arthritis, it will join an indication for plaque psoriasis in children that was granted just a few days before these data were presented. The psoriasis indication is the only current use approved for children in the United States.
More biologics needed for JPsA
Additional biologics will be helpful for children with arthritis who are poorly controlled on available treatments, according to Natasha M. Ruth, MD, director of the division of pediatric rheumatology at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. Dr. Ruth was senior author of a case study published 2 years ago in which secukinumab was used to control psoriatic arthritis and nail manifestations of psoriasis.
“It was a girl who had already failed to improve adequately to TNF inhibitors,” reported Dr. Ruth, who had said the child and her parent were very concerned about the nail appearance.
“The nail involvement completely resolved, so it was a very good result in a difficult situation,” Dr. Ruth explained. She said that the decision to try secukinumab was made collaboratively in a clinic in which dermatologists and rheumatologists at her institution work together on difficult cases.
“There is a need for more biologics with different mechanisms of action,” Dr. Ruth said. Based on her experience, secukinumab could be an important addition to treatment options.
Dr. Ruperto reported having financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis, which provided financial support for this trial. Many coauthors had financial relationships with multiple companies, including Novartis, and some were employees of the company. Dr. Ruth reported having no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE EULAR 2021 CONGRESS
As new cases fall, U.S. passes 4 million children with COVID-19
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.


