User login
Western and proinflammatory diets are important drivers of gout risk
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE EULAR 2021 CONGRESS
The aducanumab revolution
The approval was hailed by advocacy groups and some practitioners as a victory for patients and families, as the drug – the first anti-Alzheimer’s agent to reach the market in 18 years – is a potentially disease-modifying therapy, which acts to clear amyloid plaques from the brain.
But several prominent Alzheimer’s researchers lambasted the agency’s decision, citing unclear evidence of benefit, trials that did not meet their primary endpoints, and reliance on a post hoc analysis of a high-dose subgroup of patients in a halted trial to argue that aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen, and Eisai), slowed cognitive and functional decline by 22% on one measure. In November 2020, 10 of 11 members of an independent FDA advisory committee voted against aducanumab’s approval, citing holes in the data and concerns about the quality of the evidence. After the agency went on to approve anyway, three members of that committee resigned in protest.
The FDA decision on aducanumab was made using the agency’s accelerated approval pathway, which allows for the use of a surrogate endpoint – in this case imaging that showed amyloid clearance from the brain – to predict clinical benefit. But amyloid clearance, which a number of experimental antiamyloid antibodies have been shown capable of, has not been definitively linked to clinical benefit. Aducanumab, which is delivered by monthly intravenous infusion, will be marketed pending results from a phase 4 clinical trial, which the manufacturer has nearly a decade to complete. The drug’s price was announced at $56,000 per year, underscoring concern over its modest-at-best benefits.
Clinicians prescribing aducanumab must obtain magnetic resonance imaging at baseline and repeatedly during the course of treatment to detect brain edema and microhemorrhages, which occurred in a third of high-dose patients in clinical trials. Beyond this, there are few restrictions. The FDA label allows for its use in any patient deemed to have Alzheimer’s disease, without stipulations as to disease stage or evidence of brain amyloid. Payers, of course, are likely to restrict use to certain patient groups, and to require evidence of amyloid positivity. The FDA offered no guidance on when treatment should be ceased, leaving payers to make that call as well. Whatever aducanumab’s value and role turns out to be, the first-in-class treatment for Alzheimer’s disease is likely to have a major impact on how patients are assessed and treated in the coming years, and embolden manufactures of similar agents to seek FDA approval.
This news organization reached out to researchers, advocates, and specialists in the community to learn how they see this change playing out.
Fielding broad interest
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Association, which was a strong proponent of aducanumab’s approval, acknowledged in an interview that the months to come are likely to be confusing for practitioners and families alike as the drug makes its way into community practices.
“We understand that off the bat millions of Americans will not have access to this tomorrow, but over time that will build. And the physician community, the specialists most likely to be prescribing this, over the next few years will even expand further,” Dr. Carrillo said.
For now, those specialists are mostly just struggling to respond responsibly to a deluge of inquiries from patients and their families.
“I’ve gotten like 20 calls in the just the past 2 days,” said neurologist Philip R. Delio, MD, who practices in Santa Barbara, Calif. “This is a longstanding issue that physicians have with patients’ access to information. Patients are getting information about a drug which isn’t available yet. They don’t know that it’s not ready to be sold. They don’t necessarily realize that a biopharma company won’t go into production until the FDA approves the drug.”
Many patients, Dr. Delio said, are aware of the controversy surrounding aducanumab and eager to hear their neurologist’s opinion. “I have tried to let them know that I want to see the trial data and to better understand the FDA’s rationale in approving it. I always caution patients that the devil will be in the details.”
While aducanumab’s label gives physicians remarkably wide latitude in whom to treat, clinicians say that until payers weigh in, the label is all but meaningless. Neurologist Douglas Scharre, MD, of the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, and a site investigator on a trial of aducanumab, said that he and his colleagues at the university’s memory center have tried to anticipate who might be deemed eligible by triaging calls.
Dr. Scharre and colleagues have been working under the assumption that payers will support aducanumab only for patients like those who seemed to benefit in the trials – people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or in the earliest stages of dementia with evidence of brain amyloid.
“I don’t want to fill up our new patient slots with people who are not even appropriate for this drug,” Dr. Scharre said. “We have a call center, and we have a few triage questions. After that a nurse practitioner collects some more data, and there’s a review process. Only then do we decide whether that person could be a candidate. If we deem that they are, we will want them in and to order an amyloid PET” – a type of brain scan that is seldom used outside research settings and not reimbursed by Medicare.
Dr. Scharre predicts that regardless of payer limitations, “there will be people hounding for the drug who are not appropriate for the drug. There will be very wealthy people who will want to pay for tests and get it no matter what.” Another concern, he said, was that having poorly selected patients on the drug could make definitive trial results even more elusive.
“The label the way it’s written is not going to help the drug in phase 4 trials,” he said. “It’s good to have real-world patient data, but if you have all these people in your cohort who are too early or too late, you won’t have good results.”
The challenge of delivery
Intravenous infusions are new to Alzheimer’s disease and pose all sorts of logistical hurdles. The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo described the situation as “manageable,” noting that infusions are standard of care for many diseases, and that neurologists now have more than 15 years’ experience with them for multiple sclerosis.
Still, most clinicians treating Alzheimer’s disease in the community – neurologists, geriatricians, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians – do not have infusion centers in their practices. Virtually none have experience with or access to PET-amyloid, or with screening for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-e) on MRI, as required by the FDA.
“I contacted the hospital infusion center we use and said I could end up sending five or six patients a week, can you handle this? They only have so many chairs,” Dr. Delio said. “I am one neurologist in a local community, and I might have 50 candidates for this drug. That’s a lot for them.” Patients with cognitive impairment are also difficult to infuse and may need to be treated at home, he noted.
“MRIs are easy enough to do,” Dr. Delio said. “But do we know what ARIA-e looks like on imaging? You’d have to talk to the radiologists – this is another element of uncertainty. Do we even know what we’re looking for with these scans? Will we recognize this?”
Neurologist Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, a vocal proponent of aducanumab and lead author of a May 2021 paper defending the evidence for it, acknowledged that the field was unprepared for a wide-scale adoption of infusions in dementia treatment, pointing to a Rand Corporation study from 2017 that warned that screening, diagnosis, and availability of infusion chairs would have to be drastically scaled up to meet demand.
“There are few clinicians who know how to identify MCI, too few imaging centers, too few radiologists who know how to identify ARIA-e on MRI, so all of these things will be required to be put into place. The label doesn’t specify any of this, but good clinical practice will require that, and getting this up and running will take 18 to 24 months,” Dr. Cummings said.
Neurologist David S. Knopman, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., a leading critic of the evidence for aducanumab who recently resigned his position on the independent committee that advises the FDA on neurology drugs, said that for large research institutions like his that have served as trial sites, the transition to offering PET-amyloid, MRI, and infusions in clinical practice will be easier.
“We have all this because this is what we do every day. And we have a very extensive understanding of MCI and mild dementia staging,” Dr. Knopman said. “But the amount of infrastructure that is implied by this, and all the extra steps it would take, would be a real challenge for people in general neurology practice.”
In addition to routine use of PET-amyloid and MRI screening for ARIA-e, Dr. Knopman said, clinicians will have to provide genetic screening and counseling before administering aducanumab, as clinical trials showed that treated patients have a higher risk of developing ARIA-e if they have APOE4, a risk variant for Alzheimer’s disease. “And that has real implications for the families and the children of patients,” he said.
Uncertainty over costs
Aducanumab’s true costs, to patients and to taxpayers, remain unknown. The $56,000 per year currently cited by its manufacturer “doesn’t count the PET scans and MRIs,” Dr. Knopman noted. “We’re probably pushing $100,00 a year for the first year of treatment.”
Most of that expense will likely be borne by Medicare, he said, and if not, “that will exacerbate existing health care disparities. People who can pay out of pocket are a pretty limited group.”
Dr. Scharre agreed that the costs of treatment were concerning, and that “at least you should be able to narrow it down and hopefully just use health care dollars for people who might stand to benefit,” he said – namely patients in an earlier stage of disease.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo declined to address the high price of aducanumab or its implications, saying only that the association is “very invested in all aspects of access including covering costs associated with the drug and the rest of treatment.”
Access also means “infrastructure, access to physicians to diagnose, access to diagnostics,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Dr. Cummings said aducanumab’s price would likely come down through negotiations with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, copayments, and bulk purchases.
The FDA has offered no guidance on how long treatment with aducanumab should last, or what should prompt withdrawal of treatment, meaning that patients could, in theory, stay on it to the end of their lives – raising costs further.
Critics have also noted that a built-in financial incentive under Medicare Part B, which covers infusion drugs, could result in overprescription of aducanumab. Under Medicare Part B, prescribing physicians are reimbursed 6% of a drug’s average sales price.
Geriatricians wary
On social media and in the lay press, geriatricians have been among the most outspoken opponents of the FDA decision and the Alzheimer’s Association’s advocacy of aducanumab.
Eric Widera, MD, a geriatrician at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the specialty might be less likely than others to embrace aducanumab. “I think part of the reasons geriatricians don’t make a lot of money is they have strong commitment to their values,” Dr. Widera said.
The American Geriatrics Society opposed the drug’s approval, citing concerns about evidence, side effects, and cost. “Additional considerations are the unintended consequences of overstressing Medicare’s limited financial reserves, and of challenging health care systems … to divert precious resources to an expensive treatment of uncertain value,” the society’s president, Peter Hollmann, MD, and chief executive officer, Nancy E. Lundebjerg, wrote in a June 2 letter to the FDA.
Dr. Widera said the approval was likely to undermine confidence in the FDA and in the Alzheimer’s Association, which receives significant funding from drug manufacturers, including Biogen and Eisai. “There’s a lot of reasons that the Geriatrics Society could have done what the Alzheimer’s Association did, and yet they came out against it, which I applaud.”
Dr. Widera pointed to a study showing that dementia patients were less likely to be on an antidementia drug if they were treated by a geriatrician, compared with a psychiatrist or a neurologist. But whether the specialty will prove as cautious with aducanumab remains to be seen. Some geriatricians will be tempted to open lucrative infusion centers, he predicted.
What is especially worrisome, Dr. Widera said, is that aducanumab’s label offers no guidance as to when to withdraw treatment. “We’ll probably see something similar to what happened with the cholinesterase inhibitors” – the class of marginally effective antidementia drugs that includes donepezil (Aricept, Pfizer) and rivastigmine (Exelon, Novartis). “No one thinks about deprescribing them. People are prescribed them even in their last months of life. There is no reason to think these infusions won’t be continued for a very long time, well beyond how long people were dosed in the trials.”
“Taking care of someone with dementia is hard enough,” Dr. Widera added. “We can’t even get normal support in the home for someone with dementia. But we are more than happy to throw money to Biogen for a drug they have not yet showed benefit for. Hopefully in 5 years we’ll have a drug that actually works,” Dr. Widera said. “After 5 years of giving this to people at $50,000 a year.”
A fractured research community
Ever since October 2019, when Biogen and Eisai announced that despite two trials halted for futility, they would go ahead and seek FDA approval for aducanumab, the Alzheimer’s research community has been bitterly divided over the drug and the FDA’s accelerated approval process.
Top researchers published critical editorials in journals, with some eventually taking their case to major newspapers as well. The Alzheimer’s Association’s position on the drug has clashed with that of many researchers whose work it supports.
“The Alzheimer’s community has been wonderfully collegial – we all have a common purpose,” Dr. Cummings said. “Now we have people taking extreme positions and I’m hoping this will not result in a permanent fracturing of the community.”
Chief among the critics’ concerns is that the FDA decision ratified the use of antiamyloid therapies based on biomarker evidence, opening the door for makers of similar drugs – those still under development or even those whose development has been halted – to seek approval on weak evidence of clinical benefit.
Whether the approval will chill research into drugs targeting pathways other than amyloid is uncertain.
Dr. Cummings said he felt that while the aducanumab decision would spur other manufacturers of antiamyloid drugs to seek accelerated approval, other classes of Alzheimer’s therapies in development also stand to get a boost. Many Alzheimer’s experts believe that a combination of drugs targeting different elements of the disease pathway – not just amyloid – will be needed in the long run.
Dr. Scharre said that the buzz over aducanumab’s approval will have at least one concrete benefit: people getting into doctors’ offices sooner.
“The people who come into our memory centers represent only a fraction of people walking around with MCI – there are people out there who may have heard that it’s normal aging; they have decreased insight; there’s denial, there’s embarrassment – there’s hundreds of reasons people avoid getting seen,” he said.
“Perhaps they come in and learn that they don’t have any degenerative process but their thyroid is out of whack, or there’s something else causing cognitive impairment. And if they do have a degenerative process, they’ll have time to start [aducanumab], and hopefully get to see a reduction in the decline.”
Dr. Knopman was a site investigator for the Biogen aducanumab trials and has consulted for Samus Therapeutics, Third Rock, Roche, and Alzeca Biosciences. A former member of the FDA’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee, he was recused from the Nov. 6, 2020, meeting that voted against aducanumab. Dr. Cummings has consulted for Biogen, Eisai, and other manufacturers. Dr. Scharre reports financial relationships with Biogen, Brain Test, Acadia, and Vascular Scientific. Dr. Widera has no disclosures. Dr. Delio is a speaker for Gore Medical, Allergan, and Biohaven Pharmaceuticals.
The approval was hailed by advocacy groups and some practitioners as a victory for patients and families, as the drug – the first anti-Alzheimer’s agent to reach the market in 18 years – is a potentially disease-modifying therapy, which acts to clear amyloid plaques from the brain.
But several prominent Alzheimer’s researchers lambasted the agency’s decision, citing unclear evidence of benefit, trials that did not meet their primary endpoints, and reliance on a post hoc analysis of a high-dose subgroup of patients in a halted trial to argue that aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen, and Eisai), slowed cognitive and functional decline by 22% on one measure. In November 2020, 10 of 11 members of an independent FDA advisory committee voted against aducanumab’s approval, citing holes in the data and concerns about the quality of the evidence. After the agency went on to approve anyway, three members of that committee resigned in protest.
The FDA decision on aducanumab was made using the agency’s accelerated approval pathway, which allows for the use of a surrogate endpoint – in this case imaging that showed amyloid clearance from the brain – to predict clinical benefit. But amyloid clearance, which a number of experimental antiamyloid antibodies have been shown capable of, has not been definitively linked to clinical benefit. Aducanumab, which is delivered by monthly intravenous infusion, will be marketed pending results from a phase 4 clinical trial, which the manufacturer has nearly a decade to complete. The drug’s price was announced at $56,000 per year, underscoring concern over its modest-at-best benefits.
Clinicians prescribing aducanumab must obtain magnetic resonance imaging at baseline and repeatedly during the course of treatment to detect brain edema and microhemorrhages, which occurred in a third of high-dose patients in clinical trials. Beyond this, there are few restrictions. The FDA label allows for its use in any patient deemed to have Alzheimer’s disease, without stipulations as to disease stage or evidence of brain amyloid. Payers, of course, are likely to restrict use to certain patient groups, and to require evidence of amyloid positivity. The FDA offered no guidance on when treatment should be ceased, leaving payers to make that call as well. Whatever aducanumab’s value and role turns out to be, the first-in-class treatment for Alzheimer’s disease is likely to have a major impact on how patients are assessed and treated in the coming years, and embolden manufactures of similar agents to seek FDA approval.
This news organization reached out to researchers, advocates, and specialists in the community to learn how they see this change playing out.
Fielding broad interest
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Association, which was a strong proponent of aducanumab’s approval, acknowledged in an interview that the months to come are likely to be confusing for practitioners and families alike as the drug makes its way into community practices.
“We understand that off the bat millions of Americans will not have access to this tomorrow, but over time that will build. And the physician community, the specialists most likely to be prescribing this, over the next few years will even expand further,” Dr. Carrillo said.
For now, those specialists are mostly just struggling to respond responsibly to a deluge of inquiries from patients and their families.
“I’ve gotten like 20 calls in the just the past 2 days,” said neurologist Philip R. Delio, MD, who practices in Santa Barbara, Calif. “This is a longstanding issue that physicians have with patients’ access to information. Patients are getting information about a drug which isn’t available yet. They don’t know that it’s not ready to be sold. They don’t necessarily realize that a biopharma company won’t go into production until the FDA approves the drug.”
Many patients, Dr. Delio said, are aware of the controversy surrounding aducanumab and eager to hear their neurologist’s opinion. “I have tried to let them know that I want to see the trial data and to better understand the FDA’s rationale in approving it. I always caution patients that the devil will be in the details.”
While aducanumab’s label gives physicians remarkably wide latitude in whom to treat, clinicians say that until payers weigh in, the label is all but meaningless. Neurologist Douglas Scharre, MD, of the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, and a site investigator on a trial of aducanumab, said that he and his colleagues at the university’s memory center have tried to anticipate who might be deemed eligible by triaging calls.
Dr. Scharre and colleagues have been working under the assumption that payers will support aducanumab only for patients like those who seemed to benefit in the trials – people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or in the earliest stages of dementia with evidence of brain amyloid.
“I don’t want to fill up our new patient slots with people who are not even appropriate for this drug,” Dr. Scharre said. “We have a call center, and we have a few triage questions. After that a nurse practitioner collects some more data, and there’s a review process. Only then do we decide whether that person could be a candidate. If we deem that they are, we will want them in and to order an amyloid PET” – a type of brain scan that is seldom used outside research settings and not reimbursed by Medicare.
Dr. Scharre predicts that regardless of payer limitations, “there will be people hounding for the drug who are not appropriate for the drug. There will be very wealthy people who will want to pay for tests and get it no matter what.” Another concern, he said, was that having poorly selected patients on the drug could make definitive trial results even more elusive.
“The label the way it’s written is not going to help the drug in phase 4 trials,” he said. “It’s good to have real-world patient data, but if you have all these people in your cohort who are too early or too late, you won’t have good results.”
The challenge of delivery
Intravenous infusions are new to Alzheimer’s disease and pose all sorts of logistical hurdles. The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo described the situation as “manageable,” noting that infusions are standard of care for many diseases, and that neurologists now have more than 15 years’ experience with them for multiple sclerosis.
Still, most clinicians treating Alzheimer’s disease in the community – neurologists, geriatricians, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians – do not have infusion centers in their practices. Virtually none have experience with or access to PET-amyloid, or with screening for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-e) on MRI, as required by the FDA.
“I contacted the hospital infusion center we use and said I could end up sending five or six patients a week, can you handle this? They only have so many chairs,” Dr. Delio said. “I am one neurologist in a local community, and I might have 50 candidates for this drug. That’s a lot for them.” Patients with cognitive impairment are also difficult to infuse and may need to be treated at home, he noted.
“MRIs are easy enough to do,” Dr. Delio said. “But do we know what ARIA-e looks like on imaging? You’d have to talk to the radiologists – this is another element of uncertainty. Do we even know what we’re looking for with these scans? Will we recognize this?”
Neurologist Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, a vocal proponent of aducanumab and lead author of a May 2021 paper defending the evidence for it, acknowledged that the field was unprepared for a wide-scale adoption of infusions in dementia treatment, pointing to a Rand Corporation study from 2017 that warned that screening, diagnosis, and availability of infusion chairs would have to be drastically scaled up to meet demand.
“There are few clinicians who know how to identify MCI, too few imaging centers, too few radiologists who know how to identify ARIA-e on MRI, so all of these things will be required to be put into place. The label doesn’t specify any of this, but good clinical practice will require that, and getting this up and running will take 18 to 24 months,” Dr. Cummings said.
Neurologist David S. Knopman, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., a leading critic of the evidence for aducanumab who recently resigned his position on the independent committee that advises the FDA on neurology drugs, said that for large research institutions like his that have served as trial sites, the transition to offering PET-amyloid, MRI, and infusions in clinical practice will be easier.
“We have all this because this is what we do every day. And we have a very extensive understanding of MCI and mild dementia staging,” Dr. Knopman said. “But the amount of infrastructure that is implied by this, and all the extra steps it would take, would be a real challenge for people in general neurology practice.”
In addition to routine use of PET-amyloid and MRI screening for ARIA-e, Dr. Knopman said, clinicians will have to provide genetic screening and counseling before administering aducanumab, as clinical trials showed that treated patients have a higher risk of developing ARIA-e if they have APOE4, a risk variant for Alzheimer’s disease. “And that has real implications for the families and the children of patients,” he said.
Uncertainty over costs
Aducanumab’s true costs, to patients and to taxpayers, remain unknown. The $56,000 per year currently cited by its manufacturer “doesn’t count the PET scans and MRIs,” Dr. Knopman noted. “We’re probably pushing $100,00 a year for the first year of treatment.”
Most of that expense will likely be borne by Medicare, he said, and if not, “that will exacerbate existing health care disparities. People who can pay out of pocket are a pretty limited group.”
Dr. Scharre agreed that the costs of treatment were concerning, and that “at least you should be able to narrow it down and hopefully just use health care dollars for people who might stand to benefit,” he said – namely patients in an earlier stage of disease.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo declined to address the high price of aducanumab or its implications, saying only that the association is “very invested in all aspects of access including covering costs associated with the drug and the rest of treatment.”
Access also means “infrastructure, access to physicians to diagnose, access to diagnostics,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Dr. Cummings said aducanumab’s price would likely come down through negotiations with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, copayments, and bulk purchases.
The FDA has offered no guidance on how long treatment with aducanumab should last, or what should prompt withdrawal of treatment, meaning that patients could, in theory, stay on it to the end of their lives – raising costs further.
Critics have also noted that a built-in financial incentive under Medicare Part B, which covers infusion drugs, could result in overprescription of aducanumab. Under Medicare Part B, prescribing physicians are reimbursed 6% of a drug’s average sales price.
Geriatricians wary
On social media and in the lay press, geriatricians have been among the most outspoken opponents of the FDA decision and the Alzheimer’s Association’s advocacy of aducanumab.
Eric Widera, MD, a geriatrician at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the specialty might be less likely than others to embrace aducanumab. “I think part of the reasons geriatricians don’t make a lot of money is they have strong commitment to their values,” Dr. Widera said.
The American Geriatrics Society opposed the drug’s approval, citing concerns about evidence, side effects, and cost. “Additional considerations are the unintended consequences of overstressing Medicare’s limited financial reserves, and of challenging health care systems … to divert precious resources to an expensive treatment of uncertain value,” the society’s president, Peter Hollmann, MD, and chief executive officer, Nancy E. Lundebjerg, wrote in a June 2 letter to the FDA.
Dr. Widera said the approval was likely to undermine confidence in the FDA and in the Alzheimer’s Association, which receives significant funding from drug manufacturers, including Biogen and Eisai. “There’s a lot of reasons that the Geriatrics Society could have done what the Alzheimer’s Association did, and yet they came out against it, which I applaud.”
Dr. Widera pointed to a study showing that dementia patients were less likely to be on an antidementia drug if they were treated by a geriatrician, compared with a psychiatrist or a neurologist. But whether the specialty will prove as cautious with aducanumab remains to be seen. Some geriatricians will be tempted to open lucrative infusion centers, he predicted.
What is especially worrisome, Dr. Widera said, is that aducanumab’s label offers no guidance as to when to withdraw treatment. “We’ll probably see something similar to what happened with the cholinesterase inhibitors” – the class of marginally effective antidementia drugs that includes donepezil (Aricept, Pfizer) and rivastigmine (Exelon, Novartis). “No one thinks about deprescribing them. People are prescribed them even in their last months of life. There is no reason to think these infusions won’t be continued for a very long time, well beyond how long people were dosed in the trials.”
“Taking care of someone with dementia is hard enough,” Dr. Widera added. “We can’t even get normal support in the home for someone with dementia. But we are more than happy to throw money to Biogen for a drug they have not yet showed benefit for. Hopefully in 5 years we’ll have a drug that actually works,” Dr. Widera said. “After 5 years of giving this to people at $50,000 a year.”
A fractured research community
Ever since October 2019, when Biogen and Eisai announced that despite two trials halted for futility, they would go ahead and seek FDA approval for aducanumab, the Alzheimer’s research community has been bitterly divided over the drug and the FDA’s accelerated approval process.
Top researchers published critical editorials in journals, with some eventually taking their case to major newspapers as well. The Alzheimer’s Association’s position on the drug has clashed with that of many researchers whose work it supports.
“The Alzheimer’s community has been wonderfully collegial – we all have a common purpose,” Dr. Cummings said. “Now we have people taking extreme positions and I’m hoping this will not result in a permanent fracturing of the community.”
Chief among the critics’ concerns is that the FDA decision ratified the use of antiamyloid therapies based on biomarker evidence, opening the door for makers of similar drugs – those still under development or even those whose development has been halted – to seek approval on weak evidence of clinical benefit.
Whether the approval will chill research into drugs targeting pathways other than amyloid is uncertain.
Dr. Cummings said he felt that while the aducanumab decision would spur other manufacturers of antiamyloid drugs to seek accelerated approval, other classes of Alzheimer’s therapies in development also stand to get a boost. Many Alzheimer’s experts believe that a combination of drugs targeting different elements of the disease pathway – not just amyloid – will be needed in the long run.
Dr. Scharre said that the buzz over aducanumab’s approval will have at least one concrete benefit: people getting into doctors’ offices sooner.
“The people who come into our memory centers represent only a fraction of people walking around with MCI – there are people out there who may have heard that it’s normal aging; they have decreased insight; there’s denial, there’s embarrassment – there’s hundreds of reasons people avoid getting seen,” he said.
“Perhaps they come in and learn that they don’t have any degenerative process but their thyroid is out of whack, or there’s something else causing cognitive impairment. And if they do have a degenerative process, they’ll have time to start [aducanumab], and hopefully get to see a reduction in the decline.”
Dr. Knopman was a site investigator for the Biogen aducanumab trials and has consulted for Samus Therapeutics, Third Rock, Roche, and Alzeca Biosciences. A former member of the FDA’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee, he was recused from the Nov. 6, 2020, meeting that voted against aducanumab. Dr. Cummings has consulted for Biogen, Eisai, and other manufacturers. Dr. Scharre reports financial relationships with Biogen, Brain Test, Acadia, and Vascular Scientific. Dr. Widera has no disclosures. Dr. Delio is a speaker for Gore Medical, Allergan, and Biohaven Pharmaceuticals.
The approval was hailed by advocacy groups and some practitioners as a victory for patients and families, as the drug – the first anti-Alzheimer’s agent to reach the market in 18 years – is a potentially disease-modifying therapy, which acts to clear amyloid plaques from the brain.
But several prominent Alzheimer’s researchers lambasted the agency’s decision, citing unclear evidence of benefit, trials that did not meet their primary endpoints, and reliance on a post hoc analysis of a high-dose subgroup of patients in a halted trial to argue that aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen, and Eisai), slowed cognitive and functional decline by 22% on one measure. In November 2020, 10 of 11 members of an independent FDA advisory committee voted against aducanumab’s approval, citing holes in the data and concerns about the quality of the evidence. After the agency went on to approve anyway, three members of that committee resigned in protest.
The FDA decision on aducanumab was made using the agency’s accelerated approval pathway, which allows for the use of a surrogate endpoint – in this case imaging that showed amyloid clearance from the brain – to predict clinical benefit. But amyloid clearance, which a number of experimental antiamyloid antibodies have been shown capable of, has not been definitively linked to clinical benefit. Aducanumab, which is delivered by monthly intravenous infusion, will be marketed pending results from a phase 4 clinical trial, which the manufacturer has nearly a decade to complete. The drug’s price was announced at $56,000 per year, underscoring concern over its modest-at-best benefits.
Clinicians prescribing aducanumab must obtain magnetic resonance imaging at baseline and repeatedly during the course of treatment to detect brain edema and microhemorrhages, which occurred in a third of high-dose patients in clinical trials. Beyond this, there are few restrictions. The FDA label allows for its use in any patient deemed to have Alzheimer’s disease, without stipulations as to disease stage or evidence of brain amyloid. Payers, of course, are likely to restrict use to certain patient groups, and to require evidence of amyloid positivity. The FDA offered no guidance on when treatment should be ceased, leaving payers to make that call as well. Whatever aducanumab’s value and role turns out to be, the first-in-class treatment for Alzheimer’s disease is likely to have a major impact on how patients are assessed and treated in the coming years, and embolden manufactures of similar agents to seek FDA approval.
This news organization reached out to researchers, advocates, and specialists in the community to learn how they see this change playing out.
Fielding broad interest
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Association, which was a strong proponent of aducanumab’s approval, acknowledged in an interview that the months to come are likely to be confusing for practitioners and families alike as the drug makes its way into community practices.
“We understand that off the bat millions of Americans will not have access to this tomorrow, but over time that will build. And the physician community, the specialists most likely to be prescribing this, over the next few years will even expand further,” Dr. Carrillo said.
For now, those specialists are mostly just struggling to respond responsibly to a deluge of inquiries from patients and their families.
“I’ve gotten like 20 calls in the just the past 2 days,” said neurologist Philip R. Delio, MD, who practices in Santa Barbara, Calif. “This is a longstanding issue that physicians have with patients’ access to information. Patients are getting information about a drug which isn’t available yet. They don’t know that it’s not ready to be sold. They don’t necessarily realize that a biopharma company won’t go into production until the FDA approves the drug.”
Many patients, Dr. Delio said, are aware of the controversy surrounding aducanumab and eager to hear their neurologist’s opinion. “I have tried to let them know that I want to see the trial data and to better understand the FDA’s rationale in approving it. I always caution patients that the devil will be in the details.”
While aducanumab’s label gives physicians remarkably wide latitude in whom to treat, clinicians say that until payers weigh in, the label is all but meaningless. Neurologist Douglas Scharre, MD, of the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, and a site investigator on a trial of aducanumab, said that he and his colleagues at the university’s memory center have tried to anticipate who might be deemed eligible by triaging calls.
Dr. Scharre and colleagues have been working under the assumption that payers will support aducanumab only for patients like those who seemed to benefit in the trials – people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or in the earliest stages of dementia with evidence of brain amyloid.
“I don’t want to fill up our new patient slots with people who are not even appropriate for this drug,” Dr. Scharre said. “We have a call center, and we have a few triage questions. After that a nurse practitioner collects some more data, and there’s a review process. Only then do we decide whether that person could be a candidate. If we deem that they are, we will want them in and to order an amyloid PET” – a type of brain scan that is seldom used outside research settings and not reimbursed by Medicare.
Dr. Scharre predicts that regardless of payer limitations, “there will be people hounding for the drug who are not appropriate for the drug. There will be very wealthy people who will want to pay for tests and get it no matter what.” Another concern, he said, was that having poorly selected patients on the drug could make definitive trial results even more elusive.
“The label the way it’s written is not going to help the drug in phase 4 trials,” he said. “It’s good to have real-world patient data, but if you have all these people in your cohort who are too early or too late, you won’t have good results.”
The challenge of delivery
Intravenous infusions are new to Alzheimer’s disease and pose all sorts of logistical hurdles. The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo described the situation as “manageable,” noting that infusions are standard of care for many diseases, and that neurologists now have more than 15 years’ experience with them for multiple sclerosis.
Still, most clinicians treating Alzheimer’s disease in the community – neurologists, geriatricians, psychiatrists, and primary care physicians – do not have infusion centers in their practices. Virtually none have experience with or access to PET-amyloid, or with screening for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-e) on MRI, as required by the FDA.
“I contacted the hospital infusion center we use and said I could end up sending five or six patients a week, can you handle this? They only have so many chairs,” Dr. Delio said. “I am one neurologist in a local community, and I might have 50 candidates for this drug. That’s a lot for them.” Patients with cognitive impairment are also difficult to infuse and may need to be treated at home, he noted.
“MRIs are easy enough to do,” Dr. Delio said. “But do we know what ARIA-e looks like on imaging? You’d have to talk to the radiologists – this is another element of uncertainty. Do we even know what we’re looking for with these scans? Will we recognize this?”
Neurologist Jeffrey L. Cummings, MD, ScD, of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, a vocal proponent of aducanumab and lead author of a May 2021 paper defending the evidence for it, acknowledged that the field was unprepared for a wide-scale adoption of infusions in dementia treatment, pointing to a Rand Corporation study from 2017 that warned that screening, diagnosis, and availability of infusion chairs would have to be drastically scaled up to meet demand.
“There are few clinicians who know how to identify MCI, too few imaging centers, too few radiologists who know how to identify ARIA-e on MRI, so all of these things will be required to be put into place. The label doesn’t specify any of this, but good clinical practice will require that, and getting this up and running will take 18 to 24 months,” Dr. Cummings said.
Neurologist David S. Knopman, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., a leading critic of the evidence for aducanumab who recently resigned his position on the independent committee that advises the FDA on neurology drugs, said that for large research institutions like his that have served as trial sites, the transition to offering PET-amyloid, MRI, and infusions in clinical practice will be easier.
“We have all this because this is what we do every day. And we have a very extensive understanding of MCI and mild dementia staging,” Dr. Knopman said. “But the amount of infrastructure that is implied by this, and all the extra steps it would take, would be a real challenge for people in general neurology practice.”
In addition to routine use of PET-amyloid and MRI screening for ARIA-e, Dr. Knopman said, clinicians will have to provide genetic screening and counseling before administering aducanumab, as clinical trials showed that treated patients have a higher risk of developing ARIA-e if they have APOE4, a risk variant for Alzheimer’s disease. “And that has real implications for the families and the children of patients,” he said.
Uncertainty over costs
Aducanumab’s true costs, to patients and to taxpayers, remain unknown. The $56,000 per year currently cited by its manufacturer “doesn’t count the PET scans and MRIs,” Dr. Knopman noted. “We’re probably pushing $100,00 a year for the first year of treatment.”
Most of that expense will likely be borne by Medicare, he said, and if not, “that will exacerbate existing health care disparities. People who can pay out of pocket are a pretty limited group.”
Dr. Scharre agreed that the costs of treatment were concerning, and that “at least you should be able to narrow it down and hopefully just use health care dollars for people who might stand to benefit,” he said – namely patients in an earlier stage of disease.
The Alzheimer’s Association’s Dr. Carrillo declined to address the high price of aducanumab or its implications, saying only that the association is “very invested in all aspects of access including covering costs associated with the drug and the rest of treatment.”
Access also means “infrastructure, access to physicians to diagnose, access to diagnostics,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Dr. Cummings said aducanumab’s price would likely come down through negotiations with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, copayments, and bulk purchases.
The FDA has offered no guidance on how long treatment with aducanumab should last, or what should prompt withdrawal of treatment, meaning that patients could, in theory, stay on it to the end of their lives – raising costs further.
Critics have also noted that a built-in financial incentive under Medicare Part B, which covers infusion drugs, could result in overprescription of aducanumab. Under Medicare Part B, prescribing physicians are reimbursed 6% of a drug’s average sales price.
Geriatricians wary
On social media and in the lay press, geriatricians have been among the most outspoken opponents of the FDA decision and the Alzheimer’s Association’s advocacy of aducanumab.
Eric Widera, MD, a geriatrician at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the specialty might be less likely than others to embrace aducanumab. “I think part of the reasons geriatricians don’t make a lot of money is they have strong commitment to their values,” Dr. Widera said.
The American Geriatrics Society opposed the drug’s approval, citing concerns about evidence, side effects, and cost. “Additional considerations are the unintended consequences of overstressing Medicare’s limited financial reserves, and of challenging health care systems … to divert precious resources to an expensive treatment of uncertain value,” the society’s president, Peter Hollmann, MD, and chief executive officer, Nancy E. Lundebjerg, wrote in a June 2 letter to the FDA.
Dr. Widera said the approval was likely to undermine confidence in the FDA and in the Alzheimer’s Association, which receives significant funding from drug manufacturers, including Biogen and Eisai. “There’s a lot of reasons that the Geriatrics Society could have done what the Alzheimer’s Association did, and yet they came out against it, which I applaud.”
Dr. Widera pointed to a study showing that dementia patients were less likely to be on an antidementia drug if they were treated by a geriatrician, compared with a psychiatrist or a neurologist. But whether the specialty will prove as cautious with aducanumab remains to be seen. Some geriatricians will be tempted to open lucrative infusion centers, he predicted.
What is especially worrisome, Dr. Widera said, is that aducanumab’s label offers no guidance as to when to withdraw treatment. “We’ll probably see something similar to what happened with the cholinesterase inhibitors” – the class of marginally effective antidementia drugs that includes donepezil (Aricept, Pfizer) and rivastigmine (Exelon, Novartis). “No one thinks about deprescribing them. People are prescribed them even in their last months of life. There is no reason to think these infusions won’t be continued for a very long time, well beyond how long people were dosed in the trials.”
“Taking care of someone with dementia is hard enough,” Dr. Widera added. “We can’t even get normal support in the home for someone with dementia. But we are more than happy to throw money to Biogen for a drug they have not yet showed benefit for. Hopefully in 5 years we’ll have a drug that actually works,” Dr. Widera said. “After 5 years of giving this to people at $50,000 a year.”
A fractured research community
Ever since October 2019, when Biogen and Eisai announced that despite two trials halted for futility, they would go ahead and seek FDA approval for aducanumab, the Alzheimer’s research community has been bitterly divided over the drug and the FDA’s accelerated approval process.
Top researchers published critical editorials in journals, with some eventually taking their case to major newspapers as well. The Alzheimer’s Association’s position on the drug has clashed with that of many researchers whose work it supports.
“The Alzheimer’s community has been wonderfully collegial – we all have a common purpose,” Dr. Cummings said. “Now we have people taking extreme positions and I’m hoping this will not result in a permanent fracturing of the community.”
Chief among the critics’ concerns is that the FDA decision ratified the use of antiamyloid therapies based on biomarker evidence, opening the door for makers of similar drugs – those still under development or even those whose development has been halted – to seek approval on weak evidence of clinical benefit.
Whether the approval will chill research into drugs targeting pathways other than amyloid is uncertain.
Dr. Cummings said he felt that while the aducanumab decision would spur other manufacturers of antiamyloid drugs to seek accelerated approval, other classes of Alzheimer’s therapies in development also stand to get a boost. Many Alzheimer’s experts believe that a combination of drugs targeting different elements of the disease pathway – not just amyloid – will be needed in the long run.
Dr. Scharre said that the buzz over aducanumab’s approval will have at least one concrete benefit: people getting into doctors’ offices sooner.
“The people who come into our memory centers represent only a fraction of people walking around with MCI – there are people out there who may have heard that it’s normal aging; they have decreased insight; there’s denial, there’s embarrassment – there’s hundreds of reasons people avoid getting seen,” he said.
“Perhaps they come in and learn that they don’t have any degenerative process but their thyroid is out of whack, or there’s something else causing cognitive impairment. And if they do have a degenerative process, they’ll have time to start [aducanumab], and hopefully get to see a reduction in the decline.”
Dr. Knopman was a site investigator for the Biogen aducanumab trials and has consulted for Samus Therapeutics, Third Rock, Roche, and Alzeca Biosciences. A former member of the FDA’s Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee, he was recused from the Nov. 6, 2020, meeting that voted against aducanumab. Dr. Cummings has consulted for Biogen, Eisai, and other manufacturers. Dr. Scharre reports financial relationships with Biogen, Brain Test, Acadia, and Vascular Scientific. Dr. Widera has no disclosures. Dr. Delio is a speaker for Gore Medical, Allergan, and Biohaven Pharmaceuticals.
CAR T cells rescue younger children with relapsed/refractory ALL
Even the youngest patients with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) may be able to benefit from chimeric antigen reception T-cell (CAR T) therapy, investigators in an international consortium say.
Among 30 children aged under 2 years at the time of (B-ALL diagnosis, manufacturing of the CAR T product tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) was feasible in 28 patients, and treatment resulted in high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, complete responses, event-free survival, and overall survival, reported Sara Ghorashian, MD from the University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, on behalf of the International BFM Resistant Disease Committee.
“The disease-related outcomes noted in this cohort of younger children predominantly with relapsed/refractory infant [mixed lineage leukemia]–rearranged ALL were at least as good as for the ELIANA study,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the European Hematology Association annual congress (Abstract S116).
The international, single-arm, open-label, ELIANA study was a phase 2 trial that included 97 patients aged 3-24 years with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL, most of whom had previously undergone a hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Of those patients, 79 patients went on to receive a single infusion of the CAR T therapy.
“It’s fantastic data,” said Kevin J. Curran, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist specializing in stem cell transplants and cellular therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“Pediatric leukemia, while it’s the most common malignancy that happens in children, when you get down to this really small group, this under 3-year-old group, it’s hard to get a cohort, and for them to put together 30 patients, and show these great results is groundbreaking,” he said in an interview.
“Most importantly, it gives hope to parents who have young children who have really difficult to treat leukemia,” he said.
Dr. Curran was not involved in the study.
Scarce data on ALL in infants
“Children under 3 years of age were excluded from the ELIANA study, yet in terms of having often highly aggressive disease, with traditionally poor outcomes with conventional therapy, the need for novel forms of therapy for children with relapsed infant ALL is important,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Because there is a paucity of data on outcomes in the youngest children, some health authorities will not support the use of tisagenlecleucel in this age group, and there are concerns about difficulties with performing leukapheresis in children weighing less than 10 kg, she noted.
To gain a better understanding of outcomes, members of the International BFM (Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster) Study Group conducted a retrospective analysis of data on all patients assessed for tisagenlecleucel for B-ALL who were aged under 3 years at screening at 1 of 15 centers in Europe and Israel.
A total of 30 patients were screened and had T cells harvested. Of this group, three patients did not receive CAR T infusions, two because of manufacturing failures, and one because of progressive disease.
Of the 27 patients who received CAR T infusions, 26 were evaluable for disease outcomes (1 had yet to reach the 30-day post infusion at the time of data cutoff).
The median age at diagnosis was 4.4 months, and the median age at infusion was 17.4 months; 19 of the 30 children in the entire cohort were boys. Mixed lineage leukemia rearrangements were found in 24 children, and 21 had undergone a stem cell transplant.
The children had a median of two prior lines of therapy, not including transplant. Seven of the children had received inotuzumab (Besponsa) and 11 had received blinotumumab (Blincyto).
High success rate
Of the 27 patients infused, 17 had sufficient cells harvested in a single day, and the remainder required 2-4 days. As noted, the CAR T product was successfully manufactured in 28 patients, with a median dose of 2.3 x 106/kg of patient weight.
The treatment failed for 2 of the 26 efficacy-evaluable patients, resulting in an MRD-negative rate of 92%.
Event-free survival at 6 months was 67%, similar to that in ELIANA (73%), and the 12-month event-free survival was 58%, which was superior to that in ELIANA (50%).
The 6-month and 12-month overall survival rates among the younger children were identical at 88%, compared with 90% and 76%, respectively, in ELIANA.
The 6- and 12-month probability of ongoing B-cell depletion, indicating CAR T persistence, were 77% and 68%, respectively. In ELIANA, the 6-month probability of B-cell depletion was 83%.
A total of 10 of the 27 patients received further therapy, including 3 who were given maintenance therapy for poor CAR T persistence, 2 who underwent chemotherapy for relapse, and 5 who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant.
Of six patients who experienced a relapse after having a complete response, two had CD19 relapse.
Low rate of serious CRS
At 30 days post infusion, grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome (CRS) had occurred in two patients, severe neurotoxicity occurred in one, and grade 3 or greater prolonged cytopenias occurred in eight patients.
The toxicity profile in this study was generally favorable in comparison with ELIANA, with shorter median duration of CRS, shorter median duration of CRS-related ICU stay, and a lower frequency of tocilizumab use. It should be noted, however, that the I-BFM investigators used American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy CRS consenus criteria, whereas the ELIANA investigators used University of Pennsylvania criteria.
“If the longer-term follow-up data are encouraging, it might suggest that the outcomes from tisagenlecleucel therapy are comparable to that of stem cell transplantation in high-risk relapsed infant ALL, without the associated late effects, and possibly supports CAR T-cell therapy eventually replace stem cell transplantation in this setting,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Dr. Curran, who leads the CAR T effort at MSK Kids, the children’s division of MSKCC, agreed that the goal is for CAR T to replace stem cell transplants.
“I hope I put my clinical practice out of business with my research practice,” he said, but added that “I think we need to do more research in figuring out how to best use CAR T cells, either earlier, or as some data suggest, by treating patients with lower disease burden we would get better durability.
“Because obviously in kids’ cancer one relapse is too much, and we want to be able to raise that bar and provide hope and a cure for all of our children,” he said.
The study was sponsored by the I-BFM Resistant Disease Committee and member institutions. Dr. Ghorashian disclosed advisory board activity for Novartis, maker of tisagenlecleucel, and patents and royalties from UCL Business. Dr. Curran research funding and consulting fees from Novartis.
Even the youngest patients with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) may be able to benefit from chimeric antigen reception T-cell (CAR T) therapy, investigators in an international consortium say.
Among 30 children aged under 2 years at the time of (B-ALL diagnosis, manufacturing of the CAR T product tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) was feasible in 28 patients, and treatment resulted in high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, complete responses, event-free survival, and overall survival, reported Sara Ghorashian, MD from the University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, on behalf of the International BFM Resistant Disease Committee.
“The disease-related outcomes noted in this cohort of younger children predominantly with relapsed/refractory infant [mixed lineage leukemia]–rearranged ALL were at least as good as for the ELIANA study,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the European Hematology Association annual congress (Abstract S116).
The international, single-arm, open-label, ELIANA study was a phase 2 trial that included 97 patients aged 3-24 years with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL, most of whom had previously undergone a hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Of those patients, 79 patients went on to receive a single infusion of the CAR T therapy.
“It’s fantastic data,” said Kevin J. Curran, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist specializing in stem cell transplants and cellular therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“Pediatric leukemia, while it’s the most common malignancy that happens in children, when you get down to this really small group, this under 3-year-old group, it’s hard to get a cohort, and for them to put together 30 patients, and show these great results is groundbreaking,” he said in an interview.
“Most importantly, it gives hope to parents who have young children who have really difficult to treat leukemia,” he said.
Dr. Curran was not involved in the study.
Scarce data on ALL in infants
“Children under 3 years of age were excluded from the ELIANA study, yet in terms of having often highly aggressive disease, with traditionally poor outcomes with conventional therapy, the need for novel forms of therapy for children with relapsed infant ALL is important,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Because there is a paucity of data on outcomes in the youngest children, some health authorities will not support the use of tisagenlecleucel in this age group, and there are concerns about difficulties with performing leukapheresis in children weighing less than 10 kg, she noted.
To gain a better understanding of outcomes, members of the International BFM (Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster) Study Group conducted a retrospective analysis of data on all patients assessed for tisagenlecleucel for B-ALL who were aged under 3 years at screening at 1 of 15 centers in Europe and Israel.
A total of 30 patients were screened and had T cells harvested. Of this group, three patients did not receive CAR T infusions, two because of manufacturing failures, and one because of progressive disease.
Of the 27 patients who received CAR T infusions, 26 were evaluable for disease outcomes (1 had yet to reach the 30-day post infusion at the time of data cutoff).
The median age at diagnosis was 4.4 months, and the median age at infusion was 17.4 months; 19 of the 30 children in the entire cohort were boys. Mixed lineage leukemia rearrangements were found in 24 children, and 21 had undergone a stem cell transplant.
The children had a median of two prior lines of therapy, not including transplant. Seven of the children had received inotuzumab (Besponsa) and 11 had received blinotumumab (Blincyto).
High success rate
Of the 27 patients infused, 17 had sufficient cells harvested in a single day, and the remainder required 2-4 days. As noted, the CAR T product was successfully manufactured in 28 patients, with a median dose of 2.3 x 106/kg of patient weight.
The treatment failed for 2 of the 26 efficacy-evaluable patients, resulting in an MRD-negative rate of 92%.
Event-free survival at 6 months was 67%, similar to that in ELIANA (73%), and the 12-month event-free survival was 58%, which was superior to that in ELIANA (50%).
The 6-month and 12-month overall survival rates among the younger children were identical at 88%, compared with 90% and 76%, respectively, in ELIANA.
The 6- and 12-month probability of ongoing B-cell depletion, indicating CAR T persistence, were 77% and 68%, respectively. In ELIANA, the 6-month probability of B-cell depletion was 83%.
A total of 10 of the 27 patients received further therapy, including 3 who were given maintenance therapy for poor CAR T persistence, 2 who underwent chemotherapy for relapse, and 5 who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant.
Of six patients who experienced a relapse after having a complete response, two had CD19 relapse.
Low rate of serious CRS
At 30 days post infusion, grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome (CRS) had occurred in two patients, severe neurotoxicity occurred in one, and grade 3 or greater prolonged cytopenias occurred in eight patients.
The toxicity profile in this study was generally favorable in comparison with ELIANA, with shorter median duration of CRS, shorter median duration of CRS-related ICU stay, and a lower frequency of tocilizumab use. It should be noted, however, that the I-BFM investigators used American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy CRS consenus criteria, whereas the ELIANA investigators used University of Pennsylvania criteria.
“If the longer-term follow-up data are encouraging, it might suggest that the outcomes from tisagenlecleucel therapy are comparable to that of stem cell transplantation in high-risk relapsed infant ALL, without the associated late effects, and possibly supports CAR T-cell therapy eventually replace stem cell transplantation in this setting,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Dr. Curran, who leads the CAR T effort at MSK Kids, the children’s division of MSKCC, agreed that the goal is for CAR T to replace stem cell transplants.
“I hope I put my clinical practice out of business with my research practice,” he said, but added that “I think we need to do more research in figuring out how to best use CAR T cells, either earlier, or as some data suggest, by treating patients with lower disease burden we would get better durability.
“Because obviously in kids’ cancer one relapse is too much, and we want to be able to raise that bar and provide hope and a cure for all of our children,” he said.
The study was sponsored by the I-BFM Resistant Disease Committee and member institutions. Dr. Ghorashian disclosed advisory board activity for Novartis, maker of tisagenlecleucel, and patents and royalties from UCL Business. Dr. Curran research funding and consulting fees from Novartis.
Even the youngest patients with relapsed or refractory B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) may be able to benefit from chimeric antigen reception T-cell (CAR T) therapy, investigators in an international consortium say.
Among 30 children aged under 2 years at the time of (B-ALL diagnosis, manufacturing of the CAR T product tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) was feasible in 28 patients, and treatment resulted in high rates of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, complete responses, event-free survival, and overall survival, reported Sara Ghorashian, MD from the University College London Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, on behalf of the International BFM Resistant Disease Committee.
“The disease-related outcomes noted in this cohort of younger children predominantly with relapsed/refractory infant [mixed lineage leukemia]–rearranged ALL were at least as good as for the ELIANA study,” she said in an oral abstract presented during the European Hematology Association annual congress (Abstract S116).
The international, single-arm, open-label, ELIANA study was a phase 2 trial that included 97 patients aged 3-24 years with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL, most of whom had previously undergone a hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Of those patients, 79 patients went on to receive a single infusion of the CAR T therapy.
“It’s fantastic data,” said Kevin J. Curran, MD, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist specializing in stem cell transplants and cellular therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York.
“Pediatric leukemia, while it’s the most common malignancy that happens in children, when you get down to this really small group, this under 3-year-old group, it’s hard to get a cohort, and for them to put together 30 patients, and show these great results is groundbreaking,” he said in an interview.
“Most importantly, it gives hope to parents who have young children who have really difficult to treat leukemia,” he said.
Dr. Curran was not involved in the study.
Scarce data on ALL in infants
“Children under 3 years of age were excluded from the ELIANA study, yet in terms of having often highly aggressive disease, with traditionally poor outcomes with conventional therapy, the need for novel forms of therapy for children with relapsed infant ALL is important,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Because there is a paucity of data on outcomes in the youngest children, some health authorities will not support the use of tisagenlecleucel in this age group, and there are concerns about difficulties with performing leukapheresis in children weighing less than 10 kg, she noted.
To gain a better understanding of outcomes, members of the International BFM (Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster) Study Group conducted a retrospective analysis of data on all patients assessed for tisagenlecleucel for B-ALL who were aged under 3 years at screening at 1 of 15 centers in Europe and Israel.
A total of 30 patients were screened and had T cells harvested. Of this group, three patients did not receive CAR T infusions, two because of manufacturing failures, and one because of progressive disease.
Of the 27 patients who received CAR T infusions, 26 were evaluable for disease outcomes (1 had yet to reach the 30-day post infusion at the time of data cutoff).
The median age at diagnosis was 4.4 months, and the median age at infusion was 17.4 months; 19 of the 30 children in the entire cohort were boys. Mixed lineage leukemia rearrangements were found in 24 children, and 21 had undergone a stem cell transplant.
The children had a median of two prior lines of therapy, not including transplant. Seven of the children had received inotuzumab (Besponsa) and 11 had received blinotumumab (Blincyto).
High success rate
Of the 27 patients infused, 17 had sufficient cells harvested in a single day, and the remainder required 2-4 days. As noted, the CAR T product was successfully manufactured in 28 patients, with a median dose of 2.3 x 106/kg of patient weight.
The treatment failed for 2 of the 26 efficacy-evaluable patients, resulting in an MRD-negative rate of 92%.
Event-free survival at 6 months was 67%, similar to that in ELIANA (73%), and the 12-month event-free survival was 58%, which was superior to that in ELIANA (50%).
The 6-month and 12-month overall survival rates among the younger children were identical at 88%, compared with 90% and 76%, respectively, in ELIANA.
The 6- and 12-month probability of ongoing B-cell depletion, indicating CAR T persistence, were 77% and 68%, respectively. In ELIANA, the 6-month probability of B-cell depletion was 83%.
A total of 10 of the 27 patients received further therapy, including 3 who were given maintenance therapy for poor CAR T persistence, 2 who underwent chemotherapy for relapse, and 5 who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplant.
Of six patients who experienced a relapse after having a complete response, two had CD19 relapse.
Low rate of serious CRS
At 30 days post infusion, grade 3 or greater cytokine release syndrome (CRS) had occurred in two patients, severe neurotoxicity occurred in one, and grade 3 or greater prolonged cytopenias occurred in eight patients.
The toxicity profile in this study was generally favorable in comparison with ELIANA, with shorter median duration of CRS, shorter median duration of CRS-related ICU stay, and a lower frequency of tocilizumab use. It should be noted, however, that the I-BFM investigators used American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy CRS consenus criteria, whereas the ELIANA investigators used University of Pennsylvania criteria.
“If the longer-term follow-up data are encouraging, it might suggest that the outcomes from tisagenlecleucel therapy are comparable to that of stem cell transplantation in high-risk relapsed infant ALL, without the associated late effects, and possibly supports CAR T-cell therapy eventually replace stem cell transplantation in this setting,” Dr. Ghorashian said.
Dr. Curran, who leads the CAR T effort at MSK Kids, the children’s division of MSKCC, agreed that the goal is for CAR T to replace stem cell transplants.
“I hope I put my clinical practice out of business with my research practice,” he said, but added that “I think we need to do more research in figuring out how to best use CAR T cells, either earlier, or as some data suggest, by treating patients with lower disease burden we would get better durability.
“Because obviously in kids’ cancer one relapse is too much, and we want to be able to raise that bar and provide hope and a cure for all of our children,” he said.
The study was sponsored by the I-BFM Resistant Disease Committee and member institutions. Dr. Ghorashian disclosed advisory board activity for Novartis, maker of tisagenlecleucel, and patents and royalties from UCL Business. Dr. Curran research funding and consulting fees from Novartis.
FROM EHA 2021
Bariatric surgery’s cardiovascular benefit extends to 7 years
Patients with obesity who had bariatric surgery had a lower risk of having a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) or dying from all causes during a median 7-year follow-up, compared with similar patients who did not undergo surgery.
These findings, from a province-wide retrospective cohort study from Quebec, follow two recent, slightly shorter similar trials.
Now we need a large randomized clinical trial (RCT), experts say, to definitively establish cardiovascular and mortality benefits in people with obesity who have metabolic/bariatric surgery. And such a trial is just beginning.
Philippe Bouchard, MD, a general surgery resident from McGill University in Montreal presented the Quebec study in a top papers session at the annual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery.
The findings showed that, among obese patients with metabolic syndrome, bariatric/metabolic surgery is associated with a sustained decrease in the incidence of MACE and all-cause mortality of at least 5 years, Dr. Bouchard said.
“The results of this population-based observational study should be validated in randomized controlled trials,” he concluded.
In the meantime, “we believe our study adds to the body of evidence in mainly two ways,” Dr. Bouchard told this news organization in an email.
It has a longer follow-up than recent observational studies, “a median of 7 years, compared to 3.9 years in a study from the Cleveland Clinic, and 4.6 years in one from Ontario, he said.
“This allows us to [estimate] an absolute risk reduction of MACE of 5.11% at 10 years,” he added. This is a smaller risk reduction than the roughly 40% risk reduction seen in the other two studies, possibly because of selection bias, Dr. Bouchard speculated.
“Second, most of the larger cohorts are heavily weighted on Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,” he continued. In contrast, their study included diverse procedures, including sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal switch, and adjustable gastric banding.
“Given the rise in popularity of a derivative of the duodenal switch – the single-anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADi-S) – we believe this information is timely and relevant to clinicians,” Dr. Bouchard said.
RCT on the subject is coming
“I totally agree that we need a large randomized controlled trial of bariatric surgery versus optimal medical therapy to conclusively establish” the impact of bariatric surgery on cardiovascular outcomes, said the assigned discussant, Mehran Anvari, MD. And their research group is just about to begin one.
In the absence of RCT data, clinicians “may currently not refer [eligible] patients for bariatric surgery because of the high risk they pose,” said Dr. Anvari, professor and director of the Centre for Minimal Access Surgery of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and senior author in the Ontario study.
Furthermore, an important point is that the current trial extended the follow-up to 7 years, he told this news organization in an email.
That study included patients with diabetes and hypertension, he added, whereas his group included patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and/or heart failure.
“We hope these studies encourage general practitioners and cardiologists to consider bariatric surgery as a viable treatment option to prevent and reduce the risk of MACE in the obese patients [body mass index >35 kg/m2] with significant cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“We have embarked on a pilot RCT among bariatric centers of excellence in Ontario,” Dr. Anvari added, which showed the feasibility and safety of such a study.
He estimates that the RCT will need to recruit 2,000 patients to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of bariatric surgery in reducing MACE and cardiac and all-cause mortality among patients with existing cardiovascular disease.
This “will require international collaboration,” he added, “and our group is currently establishing collaboration with sites in North America, Europe, and Australia to conduct such a study.”
Patients matched for age, sex, number of comorbidities
Quebec has a single public health care system that covers the cost of bariatric surgery for eligible patients; that is, those with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and comorbidities or a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2.
Using this provincial health care database, which covers over 97% of the population, the researchers identified 3,637 patients with diabetes and/or hypertension who had bariatric surgery during 2007-2012.
They matched the surgery patients with 5,420 control patients with obesity who lived in the same geographic region and had a similar age, sex, and number of Charlson Comorbidity Index comorbidities, but did not undergo bariatric surgery.
The patients had a mean age of 50 and 64% were women.
Half had zero to one comorbidities, a quarter had two comorbidities, and another quarter had at least three comorbidities.
Most patients in the surgery group had type 2 diabetes (70%) and 50% had hypertension, whereas in the control group, most patients had hypertension (82%) and 41% had diabetes.
The most common type of bariatric surgery was adjustable gastric banding (42% of patients), followed by duodenal switch (24%), sleeve gastrectomy (23%), and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (11%).
The primary outcome was the incidence of MACE, defined as coronary artery events (including myocardial infarction, percutaneous coronary intervention, and coronary artery bypass graft), stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality,
After a median follow-up of 7-11 years, fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had MACE (20% vs. 25%) or died from all causes (4.1% vs. 6.3%, both statistically significant at P < .01)
Similarly, significantly fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had a coronary artery event or heart failure (each P < .01).
However, there were no significant between-group difference in the rate of stroke, possibly because of the small number of strokes.
The risk of MACE was 17% lower in the group that had bariatric surgery than in the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.89), after adjusting for age, sex, and number of comorbidities.
In subgroup analysis, patients who had adjustable gastric banding, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, or duodenal switch had a significantly lower risk of MACE than control patients.
The risk of MACE was similar in patients who had sleeve gastrectomy and in control patients.
However, these subgroup results need to be interpreted with caution since the surgery and control patients in each surgery type subgroup were not matched for age, sex, and comorbidities, said Dr. Bouchard.
He acknowledged that study limitations include a lack of information about the patients’ BMI, weight, medications, and glycemic control (hemoglobin A1c).
Dr. Bouchard and Dr. Anvari have no relevant financial disclosures.
Patients with obesity who had bariatric surgery had a lower risk of having a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) or dying from all causes during a median 7-year follow-up, compared with similar patients who did not undergo surgery.
These findings, from a province-wide retrospective cohort study from Quebec, follow two recent, slightly shorter similar trials.
Now we need a large randomized clinical trial (RCT), experts say, to definitively establish cardiovascular and mortality benefits in people with obesity who have metabolic/bariatric surgery. And such a trial is just beginning.
Philippe Bouchard, MD, a general surgery resident from McGill University in Montreal presented the Quebec study in a top papers session at the annual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery.
The findings showed that, among obese patients with metabolic syndrome, bariatric/metabolic surgery is associated with a sustained decrease in the incidence of MACE and all-cause mortality of at least 5 years, Dr. Bouchard said.
“The results of this population-based observational study should be validated in randomized controlled trials,” he concluded.
In the meantime, “we believe our study adds to the body of evidence in mainly two ways,” Dr. Bouchard told this news organization in an email.
It has a longer follow-up than recent observational studies, “a median of 7 years, compared to 3.9 years in a study from the Cleveland Clinic, and 4.6 years in one from Ontario, he said.
“This allows us to [estimate] an absolute risk reduction of MACE of 5.11% at 10 years,” he added. This is a smaller risk reduction than the roughly 40% risk reduction seen in the other two studies, possibly because of selection bias, Dr. Bouchard speculated.
“Second, most of the larger cohorts are heavily weighted on Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,” he continued. In contrast, their study included diverse procedures, including sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal switch, and adjustable gastric banding.
“Given the rise in popularity of a derivative of the duodenal switch – the single-anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADi-S) – we believe this information is timely and relevant to clinicians,” Dr. Bouchard said.
RCT on the subject is coming
“I totally agree that we need a large randomized controlled trial of bariatric surgery versus optimal medical therapy to conclusively establish” the impact of bariatric surgery on cardiovascular outcomes, said the assigned discussant, Mehran Anvari, MD. And their research group is just about to begin one.
In the absence of RCT data, clinicians “may currently not refer [eligible] patients for bariatric surgery because of the high risk they pose,” said Dr. Anvari, professor and director of the Centre for Minimal Access Surgery of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and senior author in the Ontario study.
Furthermore, an important point is that the current trial extended the follow-up to 7 years, he told this news organization in an email.
That study included patients with diabetes and hypertension, he added, whereas his group included patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and/or heart failure.
“We hope these studies encourage general practitioners and cardiologists to consider bariatric surgery as a viable treatment option to prevent and reduce the risk of MACE in the obese patients [body mass index >35 kg/m2] with significant cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“We have embarked on a pilot RCT among bariatric centers of excellence in Ontario,” Dr. Anvari added, which showed the feasibility and safety of such a study.
He estimates that the RCT will need to recruit 2,000 patients to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of bariatric surgery in reducing MACE and cardiac and all-cause mortality among patients with existing cardiovascular disease.
This “will require international collaboration,” he added, “and our group is currently establishing collaboration with sites in North America, Europe, and Australia to conduct such a study.”
Patients matched for age, sex, number of comorbidities
Quebec has a single public health care system that covers the cost of bariatric surgery for eligible patients; that is, those with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and comorbidities or a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2.
Using this provincial health care database, which covers over 97% of the population, the researchers identified 3,637 patients with diabetes and/or hypertension who had bariatric surgery during 2007-2012.
They matched the surgery patients with 5,420 control patients with obesity who lived in the same geographic region and had a similar age, sex, and number of Charlson Comorbidity Index comorbidities, but did not undergo bariatric surgery.
The patients had a mean age of 50 and 64% were women.
Half had zero to one comorbidities, a quarter had two comorbidities, and another quarter had at least three comorbidities.
Most patients in the surgery group had type 2 diabetes (70%) and 50% had hypertension, whereas in the control group, most patients had hypertension (82%) and 41% had diabetes.
The most common type of bariatric surgery was adjustable gastric banding (42% of patients), followed by duodenal switch (24%), sleeve gastrectomy (23%), and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (11%).
The primary outcome was the incidence of MACE, defined as coronary artery events (including myocardial infarction, percutaneous coronary intervention, and coronary artery bypass graft), stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality,
After a median follow-up of 7-11 years, fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had MACE (20% vs. 25%) or died from all causes (4.1% vs. 6.3%, both statistically significant at P < .01)
Similarly, significantly fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had a coronary artery event or heart failure (each P < .01).
However, there were no significant between-group difference in the rate of stroke, possibly because of the small number of strokes.
The risk of MACE was 17% lower in the group that had bariatric surgery than in the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.89), after adjusting for age, sex, and number of comorbidities.
In subgroup analysis, patients who had adjustable gastric banding, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, or duodenal switch had a significantly lower risk of MACE than control patients.
The risk of MACE was similar in patients who had sleeve gastrectomy and in control patients.
However, these subgroup results need to be interpreted with caution since the surgery and control patients in each surgery type subgroup were not matched for age, sex, and comorbidities, said Dr. Bouchard.
He acknowledged that study limitations include a lack of information about the patients’ BMI, weight, medications, and glycemic control (hemoglobin A1c).
Dr. Bouchard and Dr. Anvari have no relevant financial disclosures.
Patients with obesity who had bariatric surgery had a lower risk of having a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) or dying from all causes during a median 7-year follow-up, compared with similar patients who did not undergo surgery.
These findings, from a province-wide retrospective cohort study from Quebec, follow two recent, slightly shorter similar trials.
Now we need a large randomized clinical trial (RCT), experts say, to definitively establish cardiovascular and mortality benefits in people with obesity who have metabolic/bariatric surgery. And such a trial is just beginning.
Philippe Bouchard, MD, a general surgery resident from McGill University in Montreal presented the Quebec study in a top papers session at the annual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery.
The findings showed that, among obese patients with metabolic syndrome, bariatric/metabolic surgery is associated with a sustained decrease in the incidence of MACE and all-cause mortality of at least 5 years, Dr. Bouchard said.
“The results of this population-based observational study should be validated in randomized controlled trials,” he concluded.
In the meantime, “we believe our study adds to the body of evidence in mainly two ways,” Dr. Bouchard told this news organization in an email.
It has a longer follow-up than recent observational studies, “a median of 7 years, compared to 3.9 years in a study from the Cleveland Clinic, and 4.6 years in one from Ontario, he said.
“This allows us to [estimate] an absolute risk reduction of MACE of 5.11% at 10 years,” he added. This is a smaller risk reduction than the roughly 40% risk reduction seen in the other two studies, possibly because of selection bias, Dr. Bouchard speculated.
“Second, most of the larger cohorts are heavily weighted on Roux-en-Y gastric bypass,” he continued. In contrast, their study included diverse procedures, including sleeve gastrectomy, duodenal switch, and adjustable gastric banding.
“Given the rise in popularity of a derivative of the duodenal switch – the single-anastomosis duodenal-ileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy (SADi-S) – we believe this information is timely and relevant to clinicians,” Dr. Bouchard said.
RCT on the subject is coming
“I totally agree that we need a large randomized controlled trial of bariatric surgery versus optimal medical therapy to conclusively establish” the impact of bariatric surgery on cardiovascular outcomes, said the assigned discussant, Mehran Anvari, MD. And their research group is just about to begin one.
In the absence of RCT data, clinicians “may currently not refer [eligible] patients for bariatric surgery because of the high risk they pose,” said Dr. Anvari, professor and director of the Centre for Minimal Access Surgery of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and senior author in the Ontario study.
Furthermore, an important point is that the current trial extended the follow-up to 7 years, he told this news organization in an email.
That study included patients with diabetes and hypertension, he added, whereas his group included patients with a history of cardiovascular disease and/or heart failure.
“We hope these studies encourage general practitioners and cardiologists to consider bariatric surgery as a viable treatment option to prevent and reduce the risk of MACE in the obese patients [body mass index >35 kg/m2] with significant cardiovascular disease,” he said.
“We have embarked on a pilot RCT among bariatric centers of excellence in Ontario,” Dr. Anvari added, which showed the feasibility and safety of such a study.
He estimates that the RCT will need to recruit 2,000 patients to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of bariatric surgery in reducing MACE and cardiac and all-cause mortality among patients with existing cardiovascular disease.
This “will require international collaboration,” he added, “and our group is currently establishing collaboration with sites in North America, Europe, and Australia to conduct such a study.”
Patients matched for age, sex, number of comorbidities
Quebec has a single public health care system that covers the cost of bariatric surgery for eligible patients; that is, those with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and comorbidities or a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2.
Using this provincial health care database, which covers over 97% of the population, the researchers identified 3,637 patients with diabetes and/or hypertension who had bariatric surgery during 2007-2012.
They matched the surgery patients with 5,420 control patients with obesity who lived in the same geographic region and had a similar age, sex, and number of Charlson Comorbidity Index comorbidities, but did not undergo bariatric surgery.
The patients had a mean age of 50 and 64% were women.
Half had zero to one comorbidities, a quarter had two comorbidities, and another quarter had at least three comorbidities.
Most patients in the surgery group had type 2 diabetes (70%) and 50% had hypertension, whereas in the control group, most patients had hypertension (82%) and 41% had diabetes.
The most common type of bariatric surgery was adjustable gastric banding (42% of patients), followed by duodenal switch (24%), sleeve gastrectomy (23%), and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (11%).
The primary outcome was the incidence of MACE, defined as coronary artery events (including myocardial infarction, percutaneous coronary intervention, and coronary artery bypass graft), stroke, heart failure, and all-cause mortality,
After a median follow-up of 7-11 years, fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had MACE (20% vs. 25%) or died from all causes (4.1% vs. 6.3%, both statistically significant at P < .01)
Similarly, significantly fewer patients in the surgical group than in the control group had a coronary artery event or heart failure (each P < .01).
However, there were no significant between-group difference in the rate of stroke, possibly because of the small number of strokes.
The risk of MACE was 17% lower in the group that had bariatric surgery than in the control group (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-0.89), after adjusting for age, sex, and number of comorbidities.
In subgroup analysis, patients who had adjustable gastric banding, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, or duodenal switch had a significantly lower risk of MACE than control patients.
The risk of MACE was similar in patients who had sleeve gastrectomy and in control patients.
However, these subgroup results need to be interpreted with caution since the surgery and control patients in each surgery type subgroup were not matched for age, sex, and comorbidities, said Dr. Bouchard.
He acknowledged that study limitations include a lack of information about the patients’ BMI, weight, medications, and glycemic control (hemoglobin A1c).
Dr. Bouchard and Dr. Anvari have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ASMBS 2021
Prediction rule identifies low infection risk in febrile infants
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PAS 2021
Healthy with obesity? The latest study casts doubt
compared with people without obesity and or adverse metabolic profiles, new research suggests.
The latest data on this controversial subject come from an analysis of nearly 400,000 people in the U.K. Biobank. Although the data also showed that metabolically healthy obesity poses less risk than “metabolically unhealthy” obesity, the risk of progression from healthy to unhealthy within 3-5 years was high.
“People with metabolically healthy obesity are not ‘healthy’ as they are at higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], heart failure, and respiratory diseases, compared with nonobese people with a normal metabolic profile. As such, weight management could be beneficial to all people with obesity irrespective of metabolic profile,” Ziyi Zhou and colleagues wrote in their report, published June 10, 2021, in Diabetologia.
Moreover, they advised avoiding the term metabolically healthy obesity entirely in clinical medicine “as it is misleading, and different strategies for risk stratification should be explored.”
In interviews, two experts provided somewhat different takes on the study and the overall subject.
‘Lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight’
Yoni Freedhoff, MD, medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, said “clinicians and patients need to be aware that obesity increases a person’s risk of various medical problems, and in turn this might lead to more frequent screening. This increased screening might be analogous to that of a person with a strong familial history of cancer who of course we would never describe as being ‘unhealthy’ as a consequence of their increased risk.”
In addition to screening, “lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight, and if a person’s weight is not affecting their health or their quality of life, a clinician need only let the patient know that, were they to want to discuss weight management options in the future, that they’d be there for them,” said Dr. Freedhoff.
‘Metabolically healthy obesity’ has had many definitions
Matthias Schulze, DrPH, head of the molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Potsdam, and professor at the University of Potsdam, pointed out that the way metabolically healthy obesity is defined and the outcomes assessed make a difference.
In the current study, the term is defined as having a body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2 and at least four of six metabolically healthy criteria: blood pressure, C-reactive protein, triacylglycerols, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and hemoglobin A1c.
In May 2021, Dr. Schulze and associates reported in JAMA Network Open on a different definition that they found to identify individuals who do not have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease death and total mortality. Interestingly, they also used the U.K. Biobank as their validation cohort.
“We derived a new definition of metabolic health ... that is different from those used in [the current] article. Importantly, we included a measure of body fat distribution, waist-to-hip ratio. On the other side, we investigated only mortality outcomes and we can therefore not exclude the possibility that other outcomes may still be related. [For example], a higher diabetes risk may still be present among those we have defined as having metabolically healthy obesity.”
Dr. Schulze also said that several previous studies and meta-analyses have suggested that “previous common definitions of metabolically healthy obesity do not identify a subgroup without risk, or being at risk comparable to normal-weight metabolically healthy. Thus, this study confirms this conclusion. [But] this doesn’t rule out that there are better ways of defining subgroups.”
Clinically, he said “given that we investigated only mortality, we cannot conclude that our ‘metabolically healthy obesity’ group doesn’t require intervention.”
Higher rates of diabetes, ASCVD, heart failure, death
The current population-based study included 381,363 U.K. Biobank participants who were followed up for a median 11.2 years. Overall, about 55% did not have obesity or metabolic abnormalities, 9% had metabolically healthy obesity, 20% were metabolically unhealthy but did not have obesity, and 16% had metabolically unhealthy obesity as defined by the investigators.
The investigators adjusted the data for several potential confounders, including age, sex, ethnicity, education, socioeconomic status, smoking status, physical activity, and dietary factors.
Compared with individuals without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher rates of incident diabetes (hazard ratio, 4.32), ASCVD (HR, 1.18), myocardial infarction (HR, 1.23), stroke (HR, 1.10), heart failure (HR, 1.76), respiratory diseases (HR, 1.28), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HR, 1.19).
In general, rates of cardiovascular and respiratory outcomes were highest in metabolically unhealthy obesity, followed by those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities and those with metabolically healthy obesity. However, for incident and fatal heart failure and incident respiratory diseases, those with metabolically healthy obesity had higher rates than did those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities.
Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher all-cause mortality rates (HR, 1.22). And, compared with those without obesity (regardless of metabolic status) at baseline, those with metabolically healthy obesity were significantly more likely to have diabetes (HR, 2.06), heart failure (HR, 1.6), and respiratory diseases (HR, 1.2), but not ASCVD. The association was also significant for all-cause and heart failure mortality (HR, 1.12 and 1.44, respectively), but not for other causes of death.
Progression from metabolically healthy to unhealthy is common
Among 8,512 participants for whom longitudinal data were available for a median of 4.4 years, half of those with metabolically healthy obesity remained in that category, 20% no longer had obesity, and more than a quarter transitioned to metabolically unhealthy obesity. Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities throughout, those who transitioned from metabolically healthy to metabolically unhealthy had significantly higher rates of incident ASCVD (HR, 2.46) and all-cause mortality (HR, 3.07).
But those who remained in the metabolically healthy obesity category throughout did not have significantly increased risks for the adverse outcomes measured.
Ms. Zhou and colleagues noted that the data demonstrate heterogeneity among people with obesity, which offers the potential to stratify risk based on prognosis. For example, “people with [metabolically unhealthy obesity] were at a higher risk of mortality and morbidity than everyone else, and thus they should be prioritized for intervention.”
However, they add, “Obesity is associated with a wide range of diseases, and using a single label or categorical risk algorithm is unlikely to be effective compared with prediction algorithms based on disease-specific and continuous risk markers.”
Ms. Zhou has no disclosures. One coauthor has relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies; the rest have none. Dr. Freedhoff has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for the Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health. He is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Obesity Canada and Novo Nordisk, received research grant from Novo Nordisk, and received income of at least $250 from WebMD, CTV, and Random House. Dr/ Schulze has received grants from German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
compared with people without obesity and or adverse metabolic profiles, new research suggests.
The latest data on this controversial subject come from an analysis of nearly 400,000 people in the U.K. Biobank. Although the data also showed that metabolically healthy obesity poses less risk than “metabolically unhealthy” obesity, the risk of progression from healthy to unhealthy within 3-5 years was high.
“People with metabolically healthy obesity are not ‘healthy’ as they are at higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], heart failure, and respiratory diseases, compared with nonobese people with a normal metabolic profile. As such, weight management could be beneficial to all people with obesity irrespective of metabolic profile,” Ziyi Zhou and colleagues wrote in their report, published June 10, 2021, in Diabetologia.
Moreover, they advised avoiding the term metabolically healthy obesity entirely in clinical medicine “as it is misleading, and different strategies for risk stratification should be explored.”
In interviews, two experts provided somewhat different takes on the study and the overall subject.
‘Lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight’
Yoni Freedhoff, MD, medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, said “clinicians and patients need to be aware that obesity increases a person’s risk of various medical problems, and in turn this might lead to more frequent screening. This increased screening might be analogous to that of a person with a strong familial history of cancer who of course we would never describe as being ‘unhealthy’ as a consequence of their increased risk.”
In addition to screening, “lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight, and if a person’s weight is not affecting their health or their quality of life, a clinician need only let the patient know that, were they to want to discuss weight management options in the future, that they’d be there for them,” said Dr. Freedhoff.
‘Metabolically healthy obesity’ has had many definitions
Matthias Schulze, DrPH, head of the molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Potsdam, and professor at the University of Potsdam, pointed out that the way metabolically healthy obesity is defined and the outcomes assessed make a difference.
In the current study, the term is defined as having a body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2 and at least four of six metabolically healthy criteria: blood pressure, C-reactive protein, triacylglycerols, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and hemoglobin A1c.
In May 2021, Dr. Schulze and associates reported in JAMA Network Open on a different definition that they found to identify individuals who do not have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease death and total mortality. Interestingly, they also used the U.K. Biobank as their validation cohort.
“We derived a new definition of metabolic health ... that is different from those used in [the current] article. Importantly, we included a measure of body fat distribution, waist-to-hip ratio. On the other side, we investigated only mortality outcomes and we can therefore not exclude the possibility that other outcomes may still be related. [For example], a higher diabetes risk may still be present among those we have defined as having metabolically healthy obesity.”
Dr. Schulze also said that several previous studies and meta-analyses have suggested that “previous common definitions of metabolically healthy obesity do not identify a subgroup without risk, or being at risk comparable to normal-weight metabolically healthy. Thus, this study confirms this conclusion. [But] this doesn’t rule out that there are better ways of defining subgroups.”
Clinically, he said “given that we investigated only mortality, we cannot conclude that our ‘metabolically healthy obesity’ group doesn’t require intervention.”
Higher rates of diabetes, ASCVD, heart failure, death
The current population-based study included 381,363 U.K. Biobank participants who were followed up for a median 11.2 years. Overall, about 55% did not have obesity or metabolic abnormalities, 9% had metabolically healthy obesity, 20% were metabolically unhealthy but did not have obesity, and 16% had metabolically unhealthy obesity as defined by the investigators.
The investigators adjusted the data for several potential confounders, including age, sex, ethnicity, education, socioeconomic status, smoking status, physical activity, and dietary factors.
Compared with individuals without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher rates of incident diabetes (hazard ratio, 4.32), ASCVD (HR, 1.18), myocardial infarction (HR, 1.23), stroke (HR, 1.10), heart failure (HR, 1.76), respiratory diseases (HR, 1.28), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HR, 1.19).
In general, rates of cardiovascular and respiratory outcomes were highest in metabolically unhealthy obesity, followed by those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities and those with metabolically healthy obesity. However, for incident and fatal heart failure and incident respiratory diseases, those with metabolically healthy obesity had higher rates than did those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities.
Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher all-cause mortality rates (HR, 1.22). And, compared with those without obesity (regardless of metabolic status) at baseline, those with metabolically healthy obesity were significantly more likely to have diabetes (HR, 2.06), heart failure (HR, 1.6), and respiratory diseases (HR, 1.2), but not ASCVD. The association was also significant for all-cause and heart failure mortality (HR, 1.12 and 1.44, respectively), but not for other causes of death.
Progression from metabolically healthy to unhealthy is common
Among 8,512 participants for whom longitudinal data were available for a median of 4.4 years, half of those with metabolically healthy obesity remained in that category, 20% no longer had obesity, and more than a quarter transitioned to metabolically unhealthy obesity. Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities throughout, those who transitioned from metabolically healthy to metabolically unhealthy had significantly higher rates of incident ASCVD (HR, 2.46) and all-cause mortality (HR, 3.07).
But those who remained in the metabolically healthy obesity category throughout did not have significantly increased risks for the adverse outcomes measured.
Ms. Zhou and colleagues noted that the data demonstrate heterogeneity among people with obesity, which offers the potential to stratify risk based on prognosis. For example, “people with [metabolically unhealthy obesity] were at a higher risk of mortality and morbidity than everyone else, and thus they should be prioritized for intervention.”
However, they add, “Obesity is associated with a wide range of diseases, and using a single label or categorical risk algorithm is unlikely to be effective compared with prediction algorithms based on disease-specific and continuous risk markers.”
Ms. Zhou has no disclosures. One coauthor has relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies; the rest have none. Dr. Freedhoff has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for the Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health. He is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Obesity Canada and Novo Nordisk, received research grant from Novo Nordisk, and received income of at least $250 from WebMD, CTV, and Random House. Dr/ Schulze has received grants from German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
compared with people without obesity and or adverse metabolic profiles, new research suggests.
The latest data on this controversial subject come from an analysis of nearly 400,000 people in the U.K. Biobank. Although the data also showed that metabolically healthy obesity poses less risk than “metabolically unhealthy” obesity, the risk of progression from healthy to unhealthy within 3-5 years was high.
“People with metabolically healthy obesity are not ‘healthy’ as they are at higher risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [ASCVD], heart failure, and respiratory diseases, compared with nonobese people with a normal metabolic profile. As such, weight management could be beneficial to all people with obesity irrespective of metabolic profile,” Ziyi Zhou and colleagues wrote in their report, published June 10, 2021, in Diabetologia.
Moreover, they advised avoiding the term metabolically healthy obesity entirely in clinical medicine “as it is misleading, and different strategies for risk stratification should be explored.”
In interviews, two experts provided somewhat different takes on the study and the overall subject.
‘Lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight’
Yoni Freedhoff, MD, medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, said “clinicians and patients need to be aware that obesity increases a person’s risk of various medical problems, and in turn this might lead to more frequent screening. This increased screening might be analogous to that of a person with a strong familial history of cancer who of course we would never describe as being ‘unhealthy’ as a consequence of their increased risk.”
In addition to screening, “lifestyle should be explored with every single patient regardless of their weight, and if a person’s weight is not affecting their health or their quality of life, a clinician need only let the patient know that, were they to want to discuss weight management options in the future, that they’d be there for them,” said Dr. Freedhoff.
‘Metabolically healthy obesity’ has had many definitions
Matthias Schulze, DrPH, head of the molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Potsdam, and professor at the University of Potsdam, pointed out that the way metabolically healthy obesity is defined and the outcomes assessed make a difference.
In the current study, the term is defined as having a body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2 and at least four of six metabolically healthy criteria: blood pressure, C-reactive protein, triacylglycerols, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and hemoglobin A1c.
In May 2021, Dr. Schulze and associates reported in JAMA Network Open on a different definition that they found to identify individuals who do not have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease death and total mortality. Interestingly, they also used the U.K. Biobank as their validation cohort.
“We derived a new definition of metabolic health ... that is different from those used in [the current] article. Importantly, we included a measure of body fat distribution, waist-to-hip ratio. On the other side, we investigated only mortality outcomes and we can therefore not exclude the possibility that other outcomes may still be related. [For example], a higher diabetes risk may still be present among those we have defined as having metabolically healthy obesity.”
Dr. Schulze also said that several previous studies and meta-analyses have suggested that “previous common definitions of metabolically healthy obesity do not identify a subgroup without risk, or being at risk comparable to normal-weight metabolically healthy. Thus, this study confirms this conclusion. [But] this doesn’t rule out that there are better ways of defining subgroups.”
Clinically, he said “given that we investigated only mortality, we cannot conclude that our ‘metabolically healthy obesity’ group doesn’t require intervention.”
Higher rates of diabetes, ASCVD, heart failure, death
The current population-based study included 381,363 U.K. Biobank participants who were followed up for a median 11.2 years. Overall, about 55% did not have obesity or metabolic abnormalities, 9% had metabolically healthy obesity, 20% were metabolically unhealthy but did not have obesity, and 16% had metabolically unhealthy obesity as defined by the investigators.
The investigators adjusted the data for several potential confounders, including age, sex, ethnicity, education, socioeconomic status, smoking status, physical activity, and dietary factors.
Compared with individuals without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher rates of incident diabetes (hazard ratio, 4.32), ASCVD (HR, 1.18), myocardial infarction (HR, 1.23), stroke (HR, 1.10), heart failure (HR, 1.76), respiratory diseases (HR, 1.28), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (HR, 1.19).
In general, rates of cardiovascular and respiratory outcomes were highest in metabolically unhealthy obesity, followed by those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities and those with metabolically healthy obesity. However, for incident and fatal heart failure and incident respiratory diseases, those with metabolically healthy obesity had higher rates than did those without obesity but with metabolic abnormalities.
Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities, those with metabolically healthy obesity had significantly higher all-cause mortality rates (HR, 1.22). And, compared with those without obesity (regardless of metabolic status) at baseline, those with metabolically healthy obesity were significantly more likely to have diabetes (HR, 2.06), heart failure (HR, 1.6), and respiratory diseases (HR, 1.2), but not ASCVD. The association was also significant for all-cause and heart failure mortality (HR, 1.12 and 1.44, respectively), but not for other causes of death.
Progression from metabolically healthy to unhealthy is common
Among 8,512 participants for whom longitudinal data were available for a median of 4.4 years, half of those with metabolically healthy obesity remained in that category, 20% no longer had obesity, and more than a quarter transitioned to metabolically unhealthy obesity. Compared with those without obesity or metabolic abnormalities throughout, those who transitioned from metabolically healthy to metabolically unhealthy had significantly higher rates of incident ASCVD (HR, 2.46) and all-cause mortality (HR, 3.07).
But those who remained in the metabolically healthy obesity category throughout did not have significantly increased risks for the adverse outcomes measured.
Ms. Zhou and colleagues noted that the data demonstrate heterogeneity among people with obesity, which offers the potential to stratify risk based on prognosis. For example, “people with [metabolically unhealthy obesity] were at a higher risk of mortality and morbidity than everyone else, and thus they should be prioritized for intervention.”
However, they add, “Obesity is associated with a wide range of diseases, and using a single label or categorical risk algorithm is unlikely to be effective compared with prediction algorithms based on disease-specific and continuous risk markers.”
Ms. Zhou has no disclosures. One coauthor has relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies; the rest have none. Dr. Freedhoff has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for the Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health. He is a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Obesity Canada and Novo Nordisk, received research grant from Novo Nordisk, and received income of at least $250 from WebMD, CTV, and Random House. Dr/ Schulze has received grants from German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
FROM DIABETOLOGIA
AMA: ‘Excited delirium’ not a legitimate medical diagnosis
Current evidence does not support use of “excited delirium” or “excited delirium syndrome” as a medical diagnosis, the American Medical Association said June 14, and the term should not be used unless clear diagnostic criteria are validated.
The term is disproportionately applied to people of color, “for whom inappropriate and excessive pharmacotherapy continues to be the norm instead of behavioral deescalation,” the report by the AMA’s Council on Science and Public Health stated, and is therefore indicative of systemic racism.
That conclusion was one of many included in CSAPH Report 2, which was adopted June 14 at the special meeting of the AMA House of Delegates.
The AMA also opposes “use of sedative/hypnotic and dissociative agents, including ketamine, as a pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting, when done solely for a law enforcement purpose.”
Medications typically used for restraint include dissociative ketamine, benzodiazepine sedatives such as midazolam, and antipsychotic medications including olanzapine or haloperidol, alone or in combination.
Kenneth Certa, MD, from the American Psychiatric Association, speaking on behalf of the section council on psychiatry, said in a reference committee hearing: “We have been very concerned over the years with the development of the inexact diagnosis of ‘agitated delirium’ or ‘excited delirium,’ especially after having had a number of individuals, more than what’s reported in the press, die by the use of ketamine in the field for this inexact diagnosis.”
Tamaan Osbourne-Roberts, MD, a delegate and CSAPH member, said the diagnosis lacks scientific evidence and is “disproportionately applied to otherwise healthy Black men in their mid-30s and these men are most likely to die from resulting first-responder actions.”
Dr. Osbourne-Roberts testified that deescalation training should be more widely used and that crisis intervention team models in which behavioral health specialists are first deployed to respond to behavioral health emergencies should be more prevalent.
Andrew Rudawsky, MD, an assistant medical director of two emergency departments and delegate from Ohio, speaking as an individual, testified: “I can tell you from first-hand experience that ‘excited delirium’ is very real. These acutely ill, unstable patients have an emergency medical condition best cared for by an emergency medicine physician.”
The report recognizes that drugs used outside a hospital setting by nonphysicians come with significant risks, particularly for those with underlying conditions and in terms of drug–drug interactions.
“I completely agree that medicine should not be practiced by law enforcement,” Dr. Rudawsky said. “I’m gravely concerned by the legal ramifications of stating that this condition doesn’t exist.”
He said he is optimistic that the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) will be updated to include “excited delirium.”
in medical and mental health emergencies in local communities.
Additionally, the report urges that “administration of any pharmacologic treatments in the out-of-hospital setting be done equitably, in an evidence-based, antiracist, and stigma-free way.”
The report calls on law enforcement and frontline emergency medical service personnel, who are a part of the “dual response” in emergency situations, to engage in training overseen by EMS medical directors. “The training should minimally include deescalation techniques and the appropriate use of pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting,” the report states.
Recommendation on oversight draws controversy
Several commenters were emergency physicians and medical directors who expressed concern that investigation of potential cases of inappropriate pharmacologic intervention would be overseen by nonphysicians.
The CSAPH authors write that independent investigators are appropriate, whereas those in emergency medicine say EMS medical directors should lead oversight.
Stephen Epstein, MD, chair of the section council on emergency medicine, speaking on behalf of the section council, had moved for referral of the portion of the report that deals with oversight of EMS.
“We’re concerned that recommendation 6, by calling for independent investigators, would put nonphysicians in the position of supervising the practice of medicine of a board-approved specialty. This would set an unfortunate precedent for our AMA,” he said.
Dr. Epstein also said the American College of Emergency Physicians will soon release a report on “excited delirium,” which will add key information for debating the issue.
He added that a new report on the safety of ketamine in out-of-hospital use was published just last week in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The authors reviewed more than 11,000 cases of the pharmacologic intervention over the past 2 years.
“We believe this information may add substantively to the recommendation in this report,” Dr. Epstein said.
Recommendation 6 was referred to the AMA Board for a decision, but the rest of the report was overwhelmingly adopted.
Dr. Certa, Dr. Osbourne-Roberts, Dr. Rudawsky, and Dr. Epstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Current evidence does not support use of “excited delirium” or “excited delirium syndrome” as a medical diagnosis, the American Medical Association said June 14, and the term should not be used unless clear diagnostic criteria are validated.
The term is disproportionately applied to people of color, “for whom inappropriate and excessive pharmacotherapy continues to be the norm instead of behavioral deescalation,” the report by the AMA’s Council on Science and Public Health stated, and is therefore indicative of systemic racism.
That conclusion was one of many included in CSAPH Report 2, which was adopted June 14 at the special meeting of the AMA House of Delegates.
The AMA also opposes “use of sedative/hypnotic and dissociative agents, including ketamine, as a pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting, when done solely for a law enforcement purpose.”
Medications typically used for restraint include dissociative ketamine, benzodiazepine sedatives such as midazolam, and antipsychotic medications including olanzapine or haloperidol, alone or in combination.
Kenneth Certa, MD, from the American Psychiatric Association, speaking on behalf of the section council on psychiatry, said in a reference committee hearing: “We have been very concerned over the years with the development of the inexact diagnosis of ‘agitated delirium’ or ‘excited delirium,’ especially after having had a number of individuals, more than what’s reported in the press, die by the use of ketamine in the field for this inexact diagnosis.”
Tamaan Osbourne-Roberts, MD, a delegate and CSAPH member, said the diagnosis lacks scientific evidence and is “disproportionately applied to otherwise healthy Black men in their mid-30s and these men are most likely to die from resulting first-responder actions.”
Dr. Osbourne-Roberts testified that deescalation training should be more widely used and that crisis intervention team models in which behavioral health specialists are first deployed to respond to behavioral health emergencies should be more prevalent.
Andrew Rudawsky, MD, an assistant medical director of two emergency departments and delegate from Ohio, speaking as an individual, testified: “I can tell you from first-hand experience that ‘excited delirium’ is very real. These acutely ill, unstable patients have an emergency medical condition best cared for by an emergency medicine physician.”
The report recognizes that drugs used outside a hospital setting by nonphysicians come with significant risks, particularly for those with underlying conditions and in terms of drug–drug interactions.
“I completely agree that medicine should not be practiced by law enforcement,” Dr. Rudawsky said. “I’m gravely concerned by the legal ramifications of stating that this condition doesn’t exist.”
He said he is optimistic that the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) will be updated to include “excited delirium.”
in medical and mental health emergencies in local communities.
Additionally, the report urges that “administration of any pharmacologic treatments in the out-of-hospital setting be done equitably, in an evidence-based, antiracist, and stigma-free way.”
The report calls on law enforcement and frontline emergency medical service personnel, who are a part of the “dual response” in emergency situations, to engage in training overseen by EMS medical directors. “The training should minimally include deescalation techniques and the appropriate use of pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting,” the report states.
Recommendation on oversight draws controversy
Several commenters were emergency physicians and medical directors who expressed concern that investigation of potential cases of inappropriate pharmacologic intervention would be overseen by nonphysicians.
The CSAPH authors write that independent investigators are appropriate, whereas those in emergency medicine say EMS medical directors should lead oversight.
Stephen Epstein, MD, chair of the section council on emergency medicine, speaking on behalf of the section council, had moved for referral of the portion of the report that deals with oversight of EMS.
“We’re concerned that recommendation 6, by calling for independent investigators, would put nonphysicians in the position of supervising the practice of medicine of a board-approved specialty. This would set an unfortunate precedent for our AMA,” he said.
Dr. Epstein also said the American College of Emergency Physicians will soon release a report on “excited delirium,” which will add key information for debating the issue.
He added that a new report on the safety of ketamine in out-of-hospital use was published just last week in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The authors reviewed more than 11,000 cases of the pharmacologic intervention over the past 2 years.
“We believe this information may add substantively to the recommendation in this report,” Dr. Epstein said.
Recommendation 6 was referred to the AMA Board for a decision, but the rest of the report was overwhelmingly adopted.
Dr. Certa, Dr. Osbourne-Roberts, Dr. Rudawsky, and Dr. Epstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Current evidence does not support use of “excited delirium” or “excited delirium syndrome” as a medical diagnosis, the American Medical Association said June 14, and the term should not be used unless clear diagnostic criteria are validated.
The term is disproportionately applied to people of color, “for whom inappropriate and excessive pharmacotherapy continues to be the norm instead of behavioral deescalation,” the report by the AMA’s Council on Science and Public Health stated, and is therefore indicative of systemic racism.
That conclusion was one of many included in CSAPH Report 2, which was adopted June 14 at the special meeting of the AMA House of Delegates.
The AMA also opposes “use of sedative/hypnotic and dissociative agents, including ketamine, as a pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting, when done solely for a law enforcement purpose.”
Medications typically used for restraint include dissociative ketamine, benzodiazepine sedatives such as midazolam, and antipsychotic medications including olanzapine or haloperidol, alone or in combination.
Kenneth Certa, MD, from the American Psychiatric Association, speaking on behalf of the section council on psychiatry, said in a reference committee hearing: “We have been very concerned over the years with the development of the inexact diagnosis of ‘agitated delirium’ or ‘excited delirium,’ especially after having had a number of individuals, more than what’s reported in the press, die by the use of ketamine in the field for this inexact diagnosis.”
Tamaan Osbourne-Roberts, MD, a delegate and CSAPH member, said the diagnosis lacks scientific evidence and is “disproportionately applied to otherwise healthy Black men in their mid-30s and these men are most likely to die from resulting first-responder actions.”
Dr. Osbourne-Roberts testified that deescalation training should be more widely used and that crisis intervention team models in which behavioral health specialists are first deployed to respond to behavioral health emergencies should be more prevalent.
Andrew Rudawsky, MD, an assistant medical director of two emergency departments and delegate from Ohio, speaking as an individual, testified: “I can tell you from first-hand experience that ‘excited delirium’ is very real. These acutely ill, unstable patients have an emergency medical condition best cared for by an emergency medicine physician.”
The report recognizes that drugs used outside a hospital setting by nonphysicians come with significant risks, particularly for those with underlying conditions and in terms of drug–drug interactions.
“I completely agree that medicine should not be practiced by law enforcement,” Dr. Rudawsky said. “I’m gravely concerned by the legal ramifications of stating that this condition doesn’t exist.”
He said he is optimistic that the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) will be updated to include “excited delirium.”
in medical and mental health emergencies in local communities.
Additionally, the report urges that “administration of any pharmacologic treatments in the out-of-hospital setting be done equitably, in an evidence-based, antiracist, and stigma-free way.”
The report calls on law enforcement and frontline emergency medical service personnel, who are a part of the “dual response” in emergency situations, to engage in training overseen by EMS medical directors. “The training should minimally include deescalation techniques and the appropriate use of pharmacologic intervention for agitated individuals in the out-of-hospital setting,” the report states.
Recommendation on oversight draws controversy
Several commenters were emergency physicians and medical directors who expressed concern that investigation of potential cases of inappropriate pharmacologic intervention would be overseen by nonphysicians.
The CSAPH authors write that independent investigators are appropriate, whereas those in emergency medicine say EMS medical directors should lead oversight.
Stephen Epstein, MD, chair of the section council on emergency medicine, speaking on behalf of the section council, had moved for referral of the portion of the report that deals with oversight of EMS.
“We’re concerned that recommendation 6, by calling for independent investigators, would put nonphysicians in the position of supervising the practice of medicine of a board-approved specialty. This would set an unfortunate precedent for our AMA,” he said.
Dr. Epstein also said the American College of Emergency Physicians will soon release a report on “excited delirium,” which will add key information for debating the issue.
He added that a new report on the safety of ketamine in out-of-hospital use was published just last week in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The authors reviewed more than 11,000 cases of the pharmacologic intervention over the past 2 years.
“We believe this information may add substantively to the recommendation in this report,” Dr. Epstein said.
Recommendation 6 was referred to the AMA Board for a decision, but the rest of the report was overwhelmingly adopted.
Dr. Certa, Dr. Osbourne-Roberts, Dr. Rudawsky, and Dr. Epstein have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reducing Overuse of Proton Pump Inhibitors for Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis and Nonvariceal Gastrointestinal Bleeding in the Hospital: A Narrative Review and Implementation Guide
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are among the most commonly used drugs worldwide to treat dyspepsia and prevent gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB).1 Between 40% and 70% of hospitalized patients receive acid-suppressive therapy (AST; defined as PPIs or histamine-receptor antagonists), and nearly half of these are initiated during the inpatient stay.2,3 While up to 50% of inpatients who received a new AST were discharged on these medications,2 there were no evidence-based indications for a majority of the prescriptions.2,3
Growing evidence shows that PPIs are overutilized and may be associated with wide-ranging adverse events, such as acute and chronic kidney disease,4Clostridium difficile infection,5 hypomagnesemia,6 and fractures.7 Because of the widespread overuse and the potential harm associated with PPIs, a concerted effort to promote their appropriate use in the inpatient setting is necessary. It is important to note that reducing the use of PPIs does not increase the risks of GIB or worsening dyspepsia. Rather, reducing overuse of PPIs lowers the risk of harm to patients. The efforts to reduce overuse, however, are complex and difficult.
This article summarizes evidence regarding interventions to reduce overuse and offers an implementation guide based on this evidence. This guide promotes value-based quality improvement and provides a blueprint for implementing an institution-wide program to reduce PPI overuse in the inpatient setting. We begin with a discussion about quality initiatives to reduce PPI overuse, followed by a review of the safety outcomes associated with reduced use of PPIs.
METHODS
A focused search of the US National Library of Medicine’s PubMed database was performed to identify English-language articles published between 2000 and 2018 that addressed strategies to reduce PPI overuse for stress ulcer prophylaxis (SUP) and nonvariceal GIB. The following search terms were used: PPI and inappropriate use; acid-suppressive therapy and inappropriate use; PPI and discontinuation; acid-suppressive (or suppressant) therapy and discontinuation; SUP and cost; and histamine receptor antagonist and PPI. Inpatient or outpatient studies of patients aged 18 years or older were considered for inclusion in this narrative review, and all study types were included. The primary exclusion criterion was patients aged younger than 18 years. A manual review of the full text of the retrieved articles was performed and references were reviewed for missed citations.
RESULTS
We identified a total of 1,497 unique citations through our initial search. After performing a manual review, we excluded 1,483 of the references and added an additional 2, resulting in 16 articles selected for inclusion. The selected articles addressed interventions falling into three main groupings: implementation of institutional guidelines with or without electronic health record (EHR)–based decision support, educational interventions alone, and multifaceted interventions. Each of these interventions is discussed in the sections that follow. Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 summarize the results of the studies included in our narrative review.
QUALITY INITIATIVES TO REDUCE PPI OVERUSE
Institutional Guidelines With or Without EHR-Based Decision Support
Table 1 summarizes institutional guidelines, with or without EHR-based decision support, to reduce inappropriate PPI use. The implementation of institutional guidelines for the appropriate reduction of PPI use has had some success. Coursol and Sanzari evaluated the impact of a treatment algorithm on the appropriateness of prescriptions for SUP in the intensive care unit (ICU).8 Risk factors of patients in this study included mechanical ventilation for 48 hours, coagulopathy for 24 hours, postoperative transplant, severe burns, active gastrointestinal (GI) disease, multiple trauma, multiple organ failure, and septicemia. The three treatment options chosen for the algorithm were intravenous (IV) famotidine (if the oral route was unavailable or impractical), omeprazole tablets (if oral access was available), and omeprazole suspension (in cases of dysphagia and presence of nasogastric or orogastric tube). After implementation of the treatment algorithm, the proportion of inappropriate prophylaxis decreased from 95.7% to 88.2% (P = .033), and the cost per patient decreased from $11.11 to $8.49 Canadian dollars (P = .003).
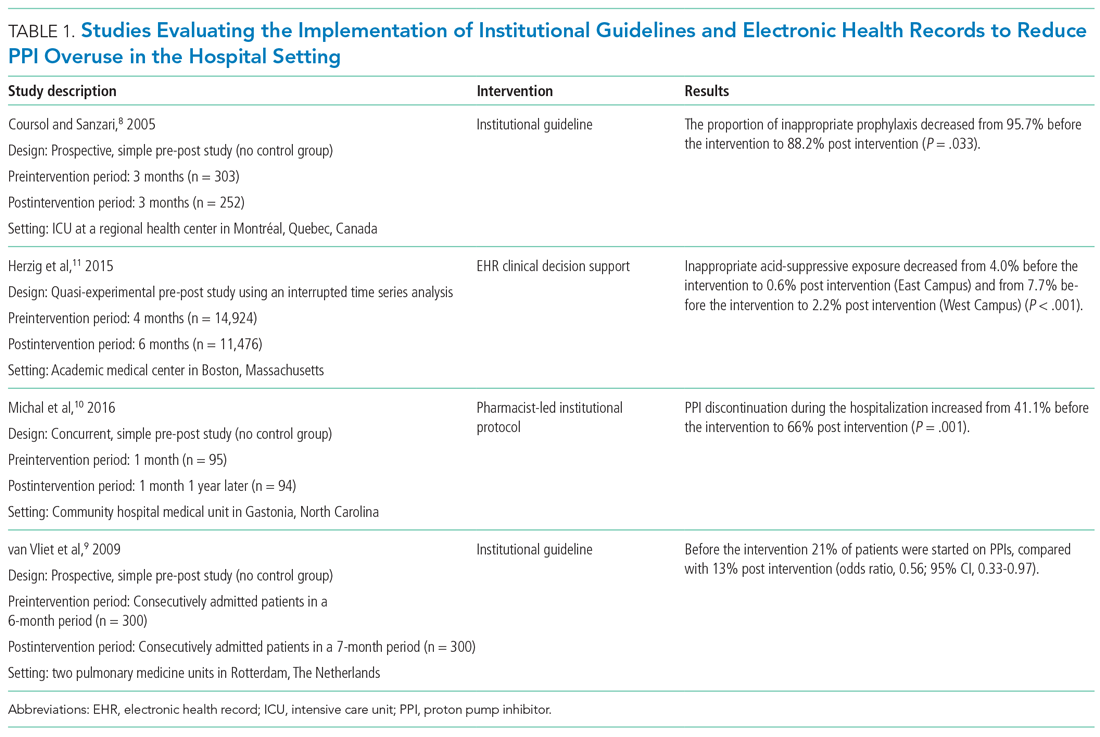
Van Vliet et al implemented a clinical practice guideline listing specific criteria for prescribing a PPI.9 Their criteria included the presence of gastric or duodenal ulcer and use of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or aspirin, plus at least one additional risk factor (eg, history of gastroduodenal hemorrhage or age >70 years). The proportion of patients started on PPIs during hospitalization decreased from 21% to 13% (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.33-0.97).
Michal et al utilized an institutional pharmacist-driven protocol that stipulated criteria for appropriate PPI use (eg, upper GIB, mechanical ventilation, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, coagulopathy).10 Pharmacists in the study evaluated patients for PPI appropriateness and recommended changes in medication or discontinuation of use. This institutional intervention decreased PPI use in non-ICU hospitalized adults. Discontinuation of PPIs increased from 41% of patients in the preintervention group to 66% of patients in the postintervention group (P = .001).
In addition to implementing guidelines and intervention strategies, institutions have also adopted changes to the EHR to reduce inappropriate PPI use. Herzig et al utilized a computerized clinical decision support intervention to decrease SUP in non-ICU hospitalized patients.11 Of the available response options for acid-suppressive medication, when SUP was chosen as the only indication for PPI use a prompt alerted the clinician that “[SUP] is not recommended for patients outside the [ICU]”; the alert resulted in a significant reduction in AST for the sole purpose of SUP. With this intervention, the percentage of patients who had any inappropriate acid-suppressive exposure decreased from 4.0% to 0.6% (P < .001).
EDUCATION
Table 2 summarizes educational interventions to reduce inappropriate PPI use.
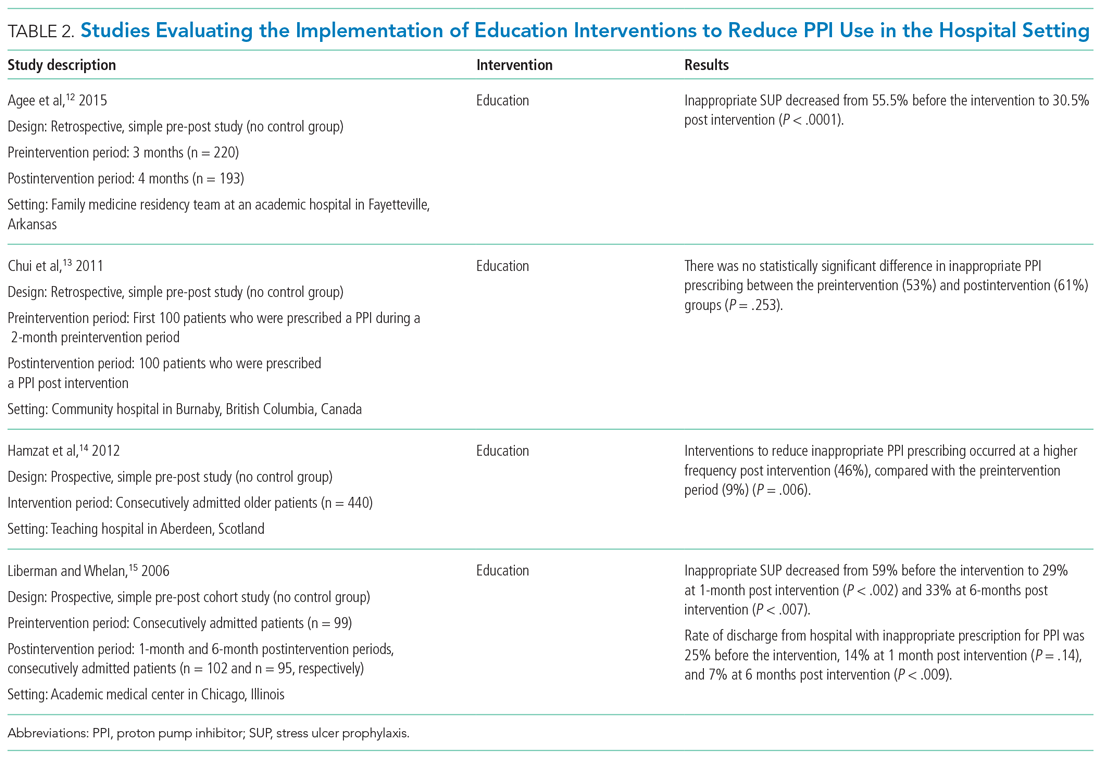
Agee et al employed a pharmacist-led educational seminar that described SUP indications, risks, and costs.12 Inappropriate SUP prescriptions decreased from 55.5% to 30.5% after the intervention (P < .0001). However, there was no reduction in the percentage of patients discharged on inappropriate AST.
Chui et al performed an intervention with academic detailing wherein a one-on-one visit with a physician took place, providing education to improve physician prescribing behavior.13 In this study, academic detailing focused on the most common instances for which PPIs were inappropriately utilized at that hospital (eg, surgical prophylaxis, anemia). Inappropriate use of double-dose PPIs was also targeted. Despite these efforts, no significant difference in inappropriate PPI prescribing was observed post intervention.
Hamzat et al implemented an educational strategy to reduce inappropriate PPI prescribing during hospital stays, which included dissemination of fliers, posters, emails, and presentations over a 4-week period.14 Educational efforts targeted clinical pharmacists, nurses, physicians, and patients. Appropriate indications for PPI use in this study included peptic ulcer disease (current or previous), H pylori infection, and treatment or prevention of an NSAID-induced ulcer. The primary outcome was a reduction in PPI dose or discontinuation of PPI during the hospital admission, which increased from 9% in the preintervention (pre-education) phase to 43% during the intervention (education) phase and to 46% in the postintervention (posteducation) phase (P = .006).
Liberman and Whelan also implemented an educational intervention among internal medicine residents to reduce inappropriate use of SUP; this intervention was based on practice-based learning and improvement methodology.15 They noted that the rate of inappropriate prophylaxis with AST decreased from 59% preintervention to 33% post intervention (P < .007).
MULTIFACETED APPROACHES
Table 3 summarizes several multifaceted approaches aimed at reducing inappropriate PPI use. Belfield et al utilized an intervention consisting of an institutional guideline review, education, and monitoring of AST by clinical pharmacists to reduce inappropriate use of PPI for SUP.16 With this intervention, the primary outcome of total inappropriate days of AST during hospitalization decreased from 279 to 116 (48% relative reduction in risk, P < .01, across 142 patients studied). Furthermore, inappropriate AST prescriptions at discharge decreased from 32% to 8% (P = .006). The one case of GIB noted in this study occurred in the control group.
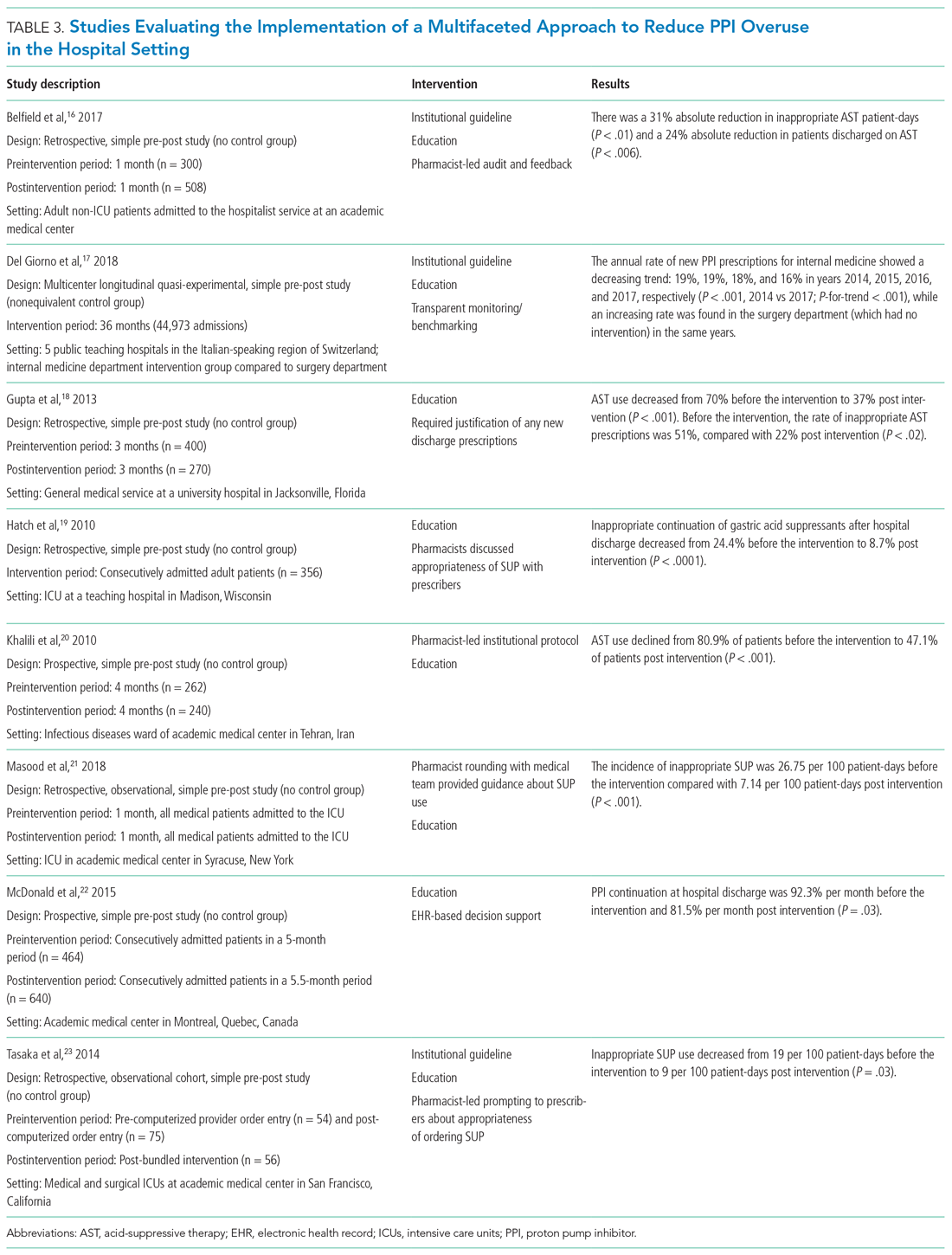
Del Giorno et al combined audit and feedback with education to reduce new PPI prescriptions at the time of discharge from the hospital.17 The educational component of this intervention included guidance regarding potentially inappropriate PPI use and associated side effects and targeted multiple departments in the hospital. This intervention led to a sustained reduction in new PPI prescriptions at discharge during the 3-year study period. The annual rate of new PPI prescriptions was 19%, 19%, 18%, and 16% in years 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, in the internal medicine department (postintervention group), compared with rates of 30%, 29%, 36%, 36% (P < .001) for the same years in the surgery department (control group).
Education and the use of medication reconciliation forms on admission and discharge were utilized by Gupta et al to reduce inappropriate AST in hospitalized patients from 51% prior to intervention to 22% post intervention (P < .001).18 Furthermore, the proportion of patients discharged on inappropriate AST decreased from 69% to 20% (P < .001).
Hatch et al also used educational resources and pharmacist-led medication reconciliation to reduce use of SUP.19 Before the intervention, 24.4% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge in the absence of a clear indication for use; post intervention, 11% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge (of these patients, 8.7% had no clear indication for use). This represented a 64.4% decrease in inappropriately prescribed SUP after discharge (P < .0001).
Khalili et al combined an educational intervention with an institutional guideline in an infectious disease ward to reduce inappropriate use of SUP.20 This intervention reduced the inappropriate use of AST from 80.9% before the intervention to 47.1% post intervention (P < .001).
Masood et al implemented two interventions wherein pharmacists reviewed SUP indications for each patient during daily team rounds, and ICU residents and fellows received education about indications for SUP and the implemented initiative on a bimonthly basis.21 Inappropriate AST decreased from 26.75 to 7.14 prescriptions per 100 patient-days of care (P < .001).
McDonald et al combined education with a web-based quality improvement tool to reduce inappropriate exit prescriptions for PPIs.22 The proportion of PPIs discontinued at hospital discharge increased from 7.7% per month to 18.5% per month (P = .03).
Finally, the initiative implemented by Tasaka et al to reduce overutilization of SUP included an institutional guideline, a pharmacist-led intervention, and an institutional education and awareness campaign.23 Their initiative led to a reduction in inappropriate SUP both at the time of transfer out of the ICU (8% before intervention, 4% post intervention, P = .54) and at the time of discharge from the hospital (7% before intervention, 0% post intervention, P = .22).
REDUCING PPI USE AND SAFETY OUTCOMES
Proton pump inhibitors are often initiated in the hospital setting, with up to half of these new prescriptions continued at discharge.2,24,25 Inappropriate prescriptions for PPIs expose patients to excess risk of long-term adverse events.26 De-escalating PPIs, however, raises concern among clinicians and patients for potential recurrence of dyspepsia and GIB. There is limited evidence regarding long-term safety outcomes (including GIB) following the discontinuation of PPIs deemed to have been inappropriately initiated in the hospital. In view of this, clinicians should educate and monitor individual patients for symptom relapse to ensure timely and appropriate resumption of AST.
LIMITATIONS
Our literature search for this narrative review and implementation guide has limitations. First, the time frame we included (2000-2018) may have excluded relevant articles published before our starting year. We did not include articles published before 2000 based on concerns these might contain outdated information. Also, there may have been incomplete retrieval of relevant studies/articles due to the labor-intensive nature involved in determining whether PPI prescriptions are appropriate or inappropriate.
We noted that interventional studies aimed at reducing overuse of PPIs were often limited by a low number of participants; these studies were also more likely to be single-center interventions, which limits generalizability. In addition, the studies often had low methodological rigor and lacked randomization or controls. Moreover, to fully evaluate the sustainability of interventions, some of the studies had a limited postimplementation period. For multifaceted interventions, the efficacy of individual components of the interventions was not clearly evaluated. Moreover, there was a high risk of bias in many of the included studies. Some of the larger studies used overall AST prescriptions as a surrogate for more appropriate use. It would be advantageous for a site to perform a pilot study that provides well-defined parameters for appropriate prescribing, and then correlate with the total number of prescriptions (automated and much easier) thereafter. Further, although the evidence regarding appropriate PPI use for SUP and GIB has shifted rapidly in recent years, society guidelines have not been updated to reflect this change. As such, quality improvement interventions have predominantly focused on reducing PPI use for the indications reflected by these guidelines.
IMPLEMENTATION BLUEPRINT
The following are our recommendations for successfully implementing an evidence-based, institution-wide initiative to promote the appropriate use of PPIs during hospitalization. These recommendations are informed by the evidence review and reflect the consensus of the combined committees coauthoring this review.
For an initiative to succeed, participation from multiple disciplines is necessary to formulate local guidelines and design and implement interventions. Such an interdisciplinary approach requires advocates to closely monitor and evaluate the program; sustainability will be greatly facilitated by the active engagement of key stakeholders, including the hospital’s executive administration, supply chain, pharmacists, and gastroenterologists. Lack of adequate buy-in on the part of key stakeholders is a barrier to the success of any intervention. Accordingly, before selecting a particular intervention, it is important to understand local factors driving the overuse of PPI.
1. Develop evidence-based institutional guidelines for both SUP and nonvariceal upper GIB through an interdisciplinary workgroup.
- Establish an interdisciplinary group including, but not limited to, pharmacists, hospitalists, gastroenterologists, and intensivists so that changes in practice will be widely adopted as institutional policy.
- Incorporate the best evidence and clearly convey appropriate and inappropriate uses.
2. Integrate changes to the EHR.
- If possible, the EHR should be leveraged to implement changes in PPI ordering practices.
- While integrating changes to the EHR, it is important to consider informatics and implementation science, since the utility of hard stops and best practice alerts has been questioned in the setting of operational inefficiencies and alert fatigue.
- Options for integrating changes to the EHR include the following:
- Create an ordering pathway that provides clinical decision support for PPI use.
- Incorporate a best practice alert in the EMR to notify clinicians of institutional guidelines when they initiate an order for PPI outside of the pathway.
- Consider restricting the authority to order IV PPIs by requiring a code or password or implement another means of using the EHR to limit the supply of PPI.
- Limit the duration of IV PPI by requiring daily renewal of IV PPI dosing or by altering the period of time that use of IV PPI is permitted (eg, 48 to 72 hours).
- PPIs should be removed from any current order sets that include medications for SUP.
3. Foster pharmacy-driven interventions.
- Consider requiring pharmacist approval for IV PPIs.
- Pharmacist-led review and feedback to clinicians for discontinuation of inappropriate PPIs can be effective in decreasing inappropriate utilization.
4. Provide education, audit data, and obtain feedback.
- Data auditing is needed to measure the efficacy of interventions. Outcome measures may include the number of non-ICU and ICU patients who are started on a PPI during an admission; the audit should be continued through discharge. A process measure may be the number of pharmacist calls for inappropriate PPIs. A balancing measure would be ulcer-specific upper GIB in patients who do not receive SUP during their admission. (Upper GIB from other etiologies, such as varices, portal hypertensive gastropathy, and Mallory-Weiss tear would not be affected by PPI SUP.)
- Run or control charts should be utilized, and data should be shared with project champions and ordering clinicians—in real time if possible.
- Project champions should provide feedback to colleagues; they should also work with hospital leadership to develop new strategies to improve adherence.
- Provide ongoing education about appropriate indications for PPIs and potential adverse effects associated with their use. Whenever possible, point-of-care or just-in-time teaching is the preferred format.
CONCLUSION
Excessive use of PPIs during hospitalization is prevalent; however, quality improvement interventions can be effective in achieving sustainable reductions in overuse. There is a need for the American College of Gastroenterology to revisit and update their guidelines for management of patients with ulcer bleeding to include stronger evidence-based recommendations on the proper use of PPIs.27 These updated guidelines could be used to update the implementation blueprint.
Quality improvement teams have an opportunity to use the principles of value-based healthcare to reduce inappropriate PPI use. By following the blueprint outlined in this article, institutions can safely and effectively tailor the use of PPIs to suitable patients in the appropriate settings. Reduction of PPI overuse can be employed as an institutional catalyst to promote implementation of further value-based measures to improve efficiency and quality of patient care.
1. Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, et al. Proton pump inhibitors: use and misuse in the clinical setting. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11(11):1123-1134. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2018.1531703
2. Nardino RJ, Vender RJ, Herbert PN. Overuse of acid-suppressive therapy in hospitalized patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(11):3118-3122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03259.x
3. Ahrens D, Behrens G, Himmel W, Kochen MM, Chenot JF. Appropriateness of proton pump inhibitor recommendations at hospital discharge and continuation in primary care. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(8):767-773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2012.02973.x
4. Moledina DG, Perazella MA. PPIs and kidney disease: from AIN to CKD. J Nephrol. 2016;29(5):611-616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0309-2
5. Kwok CS, Arthur AK, Anibueze CI, Singh S, Cavallazzi R, Loke YK. Risk of Clostridium difficile infection with acid suppressing drugs and antibiotics: meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(7):1011-1019. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.108
6. Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Kittanamongkolchai W, et al. Proton pump inhibitors linked to hypomagnesemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ren Fail. 2015;37(7):1237-1241. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022x.2015.1057800
7. Yang YX, Lewis JD, Epstein S, Metz DC. Long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy and risk of hip fracture. JAMA. 2006;296(24):2947-2953. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.296.24.2947
8. Coursol CJ, Sanzari SE. Impact of stress ulcer prophylaxis algorithm study. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(5):810-816. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1d129
9. van Vliet EPM, Steyerberg EW, Otten HJ, et al. The effects of guideline implementation for proton pump inhibitor prescription on two pulmonary medicine wards. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29(2):213-221. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03875.x
10. Michal J, Henry T, Street C. Impact of a pharmacist-driven protocol to decrease proton pump inhibitor use in non-intensive care hospitalized adults. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(17 Suppl 4):S126-S132. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp150519
11. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2260
12. Agee C, Coulter L, Hudson J. Effects of pharmacy resident led education on resident physician prescribing habits associated with stress ulcer prophylaxis in non-intensive care unit patients. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(11 Suppl 1):S48-S52. https://doi.org/10.2146/sp150013
13. Chui D, Young F, Tejani AM, Dillon EC. Impact of academic detailing on proton pump inhibitor prescribing behaviour in a community hospital. Can Pharm J (Ott). 2011;144(2):66-71. https://doi.org/10.3821/1913-701X-144.2.66
14. Hamzat H, Sun H, Ford JC, Macleod J, Soiza RL, Mangoni AA. Inappropriate prescribing of proton pump inhibitors in older patients: effects of an educational strategy. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(8):681-690. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03262283
15. Liberman JD, Whelan CT. Brief report: Reducing inappropriate usage of stress ulcer prophylaxis among internal medicine residents. A practice-based educational intervention. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):498-500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00435.x
16. Belfield KD, Kuyumjian AG, Teran R, Amadi M, Blatt M, Bicking K. Impact of a collaborative strategy to reduce the inappropriate use of acid suppressive therapy in non-intensive care unit patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2017;51(7):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028017698797
17. Del Giorno R, Ceschi A, Pironi M, Zasa A, Greco A, Gabutti L. Multifaceted intervention to curb in-hospital over-prescription of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal multicenter quasi-experimental before-and-after study. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;50:52-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2017.11.002
18. Gupta R, Marshall J, Munoz JC, Kottoor R, Jamal MM, Vega KJ. Decreased acid suppression therapy overuse after education and medication reconciliation. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(1):60-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12046
19. Hatch JB, Schulz L, Fish JT. Stress ulcer prophylaxis: reducing non-indicated prescribing after hospital discharge. Ann Pharmacother. 2010;44(10):1565-1571. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1p167
20. Khalili H, Dashti-Khavidaki S, Hossein Talasaz AH, Tabeefar H, Hendoiee N. Descriptive analysis of a clinical pharmacy intervention to improve the appropriate use of stress ulcer prophylaxis in a hospital infectious disease ward. J Manag Care Pharm. 2010;16(2):114-121. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2010.16.2.114
21. Masood U, Sharma A, Bhatti Z, et al. A successful pharmacist-based quality initiative to reduce inappropriate stress ulcer prophylaxis use in an academic medical intensive care unit. Inquiry. 2018;55:46958018759116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0046958018759116
22. McDonald EG, Jones J, Green L, Jayaraman D, Lee TC. Reduction of inappropriate exit prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors: a before-after study using education paired with a web-based quality-improvement tool. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(5):281-286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2330
23. Tasaka CL, Burg C, VanOsdol SJ, et al. An interprofessional approach to reducing the overutilization of stress ulcer prophylaxis in adult medical and surgical intensive care units. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(4):462-469. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028013517088
24. Zink DA, Pohlman M, Barnes M, Cannon ME. Long-term use of acid suppression started inappropriately during hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(10):1203-1209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02454.x
25. Pham CQ, Regal RE, Bostwick TR, Knauf KS. Acid suppressive therapy use on an inpatient internal medicine service. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40(7-8):1261-1266. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1g703
26. Schoenfeld AJ, Grady D. Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitors [editorial]. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(2):172-174. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7927
27. Laine L, Jensen DM. Management of patients with ulcer bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(3):345-360; quiz 361. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.480
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are among the most commonly used drugs worldwide to treat dyspepsia and prevent gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB).1 Between 40% and 70% of hospitalized patients receive acid-suppressive therapy (AST; defined as PPIs or histamine-receptor antagonists), and nearly half of these are initiated during the inpatient stay.2,3 While up to 50% of inpatients who received a new AST were discharged on these medications,2 there were no evidence-based indications for a majority of the prescriptions.2,3
Growing evidence shows that PPIs are overutilized and may be associated with wide-ranging adverse events, such as acute and chronic kidney disease,4Clostridium difficile infection,5 hypomagnesemia,6 and fractures.7 Because of the widespread overuse and the potential harm associated with PPIs, a concerted effort to promote their appropriate use in the inpatient setting is necessary. It is important to note that reducing the use of PPIs does not increase the risks of GIB or worsening dyspepsia. Rather, reducing overuse of PPIs lowers the risk of harm to patients. The efforts to reduce overuse, however, are complex and difficult.
This article summarizes evidence regarding interventions to reduce overuse and offers an implementation guide based on this evidence. This guide promotes value-based quality improvement and provides a blueprint for implementing an institution-wide program to reduce PPI overuse in the inpatient setting. We begin with a discussion about quality initiatives to reduce PPI overuse, followed by a review of the safety outcomes associated with reduced use of PPIs.
METHODS
A focused search of the US National Library of Medicine’s PubMed database was performed to identify English-language articles published between 2000 and 2018 that addressed strategies to reduce PPI overuse for stress ulcer prophylaxis (SUP) and nonvariceal GIB. The following search terms were used: PPI and inappropriate use; acid-suppressive therapy and inappropriate use; PPI and discontinuation; acid-suppressive (or suppressant) therapy and discontinuation; SUP and cost; and histamine receptor antagonist and PPI. Inpatient or outpatient studies of patients aged 18 years or older were considered for inclusion in this narrative review, and all study types were included. The primary exclusion criterion was patients aged younger than 18 years. A manual review of the full text of the retrieved articles was performed and references were reviewed for missed citations.
RESULTS
We identified a total of 1,497 unique citations through our initial search. After performing a manual review, we excluded 1,483 of the references and added an additional 2, resulting in 16 articles selected for inclusion. The selected articles addressed interventions falling into three main groupings: implementation of institutional guidelines with or without electronic health record (EHR)–based decision support, educational interventions alone, and multifaceted interventions. Each of these interventions is discussed in the sections that follow. Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 summarize the results of the studies included in our narrative review.
QUALITY INITIATIVES TO REDUCE PPI OVERUSE
Institutional Guidelines With or Without EHR-Based Decision Support
Table 1 summarizes institutional guidelines, with or without EHR-based decision support, to reduce inappropriate PPI use. The implementation of institutional guidelines for the appropriate reduction of PPI use has had some success. Coursol and Sanzari evaluated the impact of a treatment algorithm on the appropriateness of prescriptions for SUP in the intensive care unit (ICU).8 Risk factors of patients in this study included mechanical ventilation for 48 hours, coagulopathy for 24 hours, postoperative transplant, severe burns, active gastrointestinal (GI) disease, multiple trauma, multiple organ failure, and septicemia. The three treatment options chosen for the algorithm were intravenous (IV) famotidine (if the oral route was unavailable or impractical), omeprazole tablets (if oral access was available), and omeprazole suspension (in cases of dysphagia and presence of nasogastric or orogastric tube). After implementation of the treatment algorithm, the proportion of inappropriate prophylaxis decreased from 95.7% to 88.2% (P = .033), and the cost per patient decreased from $11.11 to $8.49 Canadian dollars (P = .003).

Van Vliet et al implemented a clinical practice guideline listing specific criteria for prescribing a PPI.9 Their criteria included the presence of gastric or duodenal ulcer and use of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or aspirin, plus at least one additional risk factor (eg, history of gastroduodenal hemorrhage or age >70 years). The proportion of patients started on PPIs during hospitalization decreased from 21% to 13% (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.33-0.97).
Michal et al utilized an institutional pharmacist-driven protocol that stipulated criteria for appropriate PPI use (eg, upper GIB, mechanical ventilation, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, coagulopathy).10 Pharmacists in the study evaluated patients for PPI appropriateness and recommended changes in medication or discontinuation of use. This institutional intervention decreased PPI use in non-ICU hospitalized adults. Discontinuation of PPIs increased from 41% of patients in the preintervention group to 66% of patients in the postintervention group (P = .001).
In addition to implementing guidelines and intervention strategies, institutions have also adopted changes to the EHR to reduce inappropriate PPI use. Herzig et al utilized a computerized clinical decision support intervention to decrease SUP in non-ICU hospitalized patients.11 Of the available response options for acid-suppressive medication, when SUP was chosen as the only indication for PPI use a prompt alerted the clinician that “[SUP] is not recommended for patients outside the [ICU]”; the alert resulted in a significant reduction in AST for the sole purpose of SUP. With this intervention, the percentage of patients who had any inappropriate acid-suppressive exposure decreased from 4.0% to 0.6% (P < .001).
EDUCATION
Table 2 summarizes educational interventions to reduce inappropriate PPI use.

Agee et al employed a pharmacist-led educational seminar that described SUP indications, risks, and costs.12 Inappropriate SUP prescriptions decreased from 55.5% to 30.5% after the intervention (P < .0001). However, there was no reduction in the percentage of patients discharged on inappropriate AST.
Chui et al performed an intervention with academic detailing wherein a one-on-one visit with a physician took place, providing education to improve physician prescribing behavior.13 In this study, academic detailing focused on the most common instances for which PPIs were inappropriately utilized at that hospital (eg, surgical prophylaxis, anemia). Inappropriate use of double-dose PPIs was also targeted. Despite these efforts, no significant difference in inappropriate PPI prescribing was observed post intervention.
Hamzat et al implemented an educational strategy to reduce inappropriate PPI prescribing during hospital stays, which included dissemination of fliers, posters, emails, and presentations over a 4-week period.14 Educational efforts targeted clinical pharmacists, nurses, physicians, and patients. Appropriate indications for PPI use in this study included peptic ulcer disease (current or previous), H pylori infection, and treatment or prevention of an NSAID-induced ulcer. The primary outcome was a reduction in PPI dose or discontinuation of PPI during the hospital admission, which increased from 9% in the preintervention (pre-education) phase to 43% during the intervention (education) phase and to 46% in the postintervention (posteducation) phase (P = .006).
Liberman and Whelan also implemented an educational intervention among internal medicine residents to reduce inappropriate use of SUP; this intervention was based on practice-based learning and improvement methodology.15 They noted that the rate of inappropriate prophylaxis with AST decreased from 59% preintervention to 33% post intervention (P < .007).
MULTIFACETED APPROACHES
Table 3 summarizes several multifaceted approaches aimed at reducing inappropriate PPI use. Belfield et al utilized an intervention consisting of an institutional guideline review, education, and monitoring of AST by clinical pharmacists to reduce inappropriate use of PPI for SUP.16 With this intervention, the primary outcome of total inappropriate days of AST during hospitalization decreased from 279 to 116 (48% relative reduction in risk, P < .01, across 142 patients studied). Furthermore, inappropriate AST prescriptions at discharge decreased from 32% to 8% (P = .006). The one case of GIB noted in this study occurred in the control group.

Del Giorno et al combined audit and feedback with education to reduce new PPI prescriptions at the time of discharge from the hospital.17 The educational component of this intervention included guidance regarding potentially inappropriate PPI use and associated side effects and targeted multiple departments in the hospital. This intervention led to a sustained reduction in new PPI prescriptions at discharge during the 3-year study period. The annual rate of new PPI prescriptions was 19%, 19%, 18%, and 16% in years 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, in the internal medicine department (postintervention group), compared with rates of 30%, 29%, 36%, 36% (P < .001) for the same years in the surgery department (control group).
Education and the use of medication reconciliation forms on admission and discharge were utilized by Gupta et al to reduce inappropriate AST in hospitalized patients from 51% prior to intervention to 22% post intervention (P < .001).18 Furthermore, the proportion of patients discharged on inappropriate AST decreased from 69% to 20% (P < .001).
Hatch et al also used educational resources and pharmacist-led medication reconciliation to reduce use of SUP.19 Before the intervention, 24.4% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge in the absence of a clear indication for use; post intervention, 11% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge (of these patients, 8.7% had no clear indication for use). This represented a 64.4% decrease in inappropriately prescribed SUP after discharge (P < .0001).
Khalili et al combined an educational intervention with an institutional guideline in an infectious disease ward to reduce inappropriate use of SUP.20 This intervention reduced the inappropriate use of AST from 80.9% before the intervention to 47.1% post intervention (P < .001).
Masood et al implemented two interventions wherein pharmacists reviewed SUP indications for each patient during daily team rounds, and ICU residents and fellows received education about indications for SUP and the implemented initiative on a bimonthly basis.21 Inappropriate AST decreased from 26.75 to 7.14 prescriptions per 100 patient-days of care (P < .001).
McDonald et al combined education with a web-based quality improvement tool to reduce inappropriate exit prescriptions for PPIs.22 The proportion of PPIs discontinued at hospital discharge increased from 7.7% per month to 18.5% per month (P = .03).
Finally, the initiative implemented by Tasaka et al to reduce overutilization of SUP included an institutional guideline, a pharmacist-led intervention, and an institutional education and awareness campaign.23 Their initiative led to a reduction in inappropriate SUP both at the time of transfer out of the ICU (8% before intervention, 4% post intervention, P = .54) and at the time of discharge from the hospital (7% before intervention, 0% post intervention, P = .22).
REDUCING PPI USE AND SAFETY OUTCOMES
Proton pump inhibitors are often initiated in the hospital setting, with up to half of these new prescriptions continued at discharge.2,24,25 Inappropriate prescriptions for PPIs expose patients to excess risk of long-term adverse events.26 De-escalating PPIs, however, raises concern among clinicians and patients for potential recurrence of dyspepsia and GIB. There is limited evidence regarding long-term safety outcomes (including GIB) following the discontinuation of PPIs deemed to have been inappropriately initiated in the hospital. In view of this, clinicians should educate and monitor individual patients for symptom relapse to ensure timely and appropriate resumption of AST.
LIMITATIONS
Our literature search for this narrative review and implementation guide has limitations. First, the time frame we included (2000-2018) may have excluded relevant articles published before our starting year. We did not include articles published before 2000 based on concerns these might contain outdated information. Also, there may have been incomplete retrieval of relevant studies/articles due to the labor-intensive nature involved in determining whether PPI prescriptions are appropriate or inappropriate.
We noted that interventional studies aimed at reducing overuse of PPIs were often limited by a low number of participants; these studies were also more likely to be single-center interventions, which limits generalizability. In addition, the studies often had low methodological rigor and lacked randomization or controls. Moreover, to fully evaluate the sustainability of interventions, some of the studies had a limited postimplementation period. For multifaceted interventions, the efficacy of individual components of the interventions was not clearly evaluated. Moreover, there was a high risk of bias in many of the included studies. Some of the larger studies used overall AST prescriptions as a surrogate for more appropriate use. It would be advantageous for a site to perform a pilot study that provides well-defined parameters for appropriate prescribing, and then correlate with the total number of prescriptions (automated and much easier) thereafter. Further, although the evidence regarding appropriate PPI use for SUP and GIB has shifted rapidly in recent years, society guidelines have not been updated to reflect this change. As such, quality improvement interventions have predominantly focused on reducing PPI use for the indications reflected by these guidelines.
IMPLEMENTATION BLUEPRINT
The following are our recommendations for successfully implementing an evidence-based, institution-wide initiative to promote the appropriate use of PPIs during hospitalization. These recommendations are informed by the evidence review and reflect the consensus of the combined committees coauthoring this review.
For an initiative to succeed, participation from multiple disciplines is necessary to formulate local guidelines and design and implement interventions. Such an interdisciplinary approach requires advocates to closely monitor and evaluate the program; sustainability will be greatly facilitated by the active engagement of key stakeholders, including the hospital’s executive administration, supply chain, pharmacists, and gastroenterologists. Lack of adequate buy-in on the part of key stakeholders is a barrier to the success of any intervention. Accordingly, before selecting a particular intervention, it is important to understand local factors driving the overuse of PPI.
1. Develop evidence-based institutional guidelines for both SUP and nonvariceal upper GIB through an interdisciplinary workgroup.
- Establish an interdisciplinary group including, but not limited to, pharmacists, hospitalists, gastroenterologists, and intensivists so that changes in practice will be widely adopted as institutional policy.
- Incorporate the best evidence and clearly convey appropriate and inappropriate uses.
2. Integrate changes to the EHR.
- If possible, the EHR should be leveraged to implement changes in PPI ordering practices.
- While integrating changes to the EHR, it is important to consider informatics and implementation science, since the utility of hard stops and best practice alerts has been questioned in the setting of operational inefficiencies and alert fatigue.
- Options for integrating changes to the EHR include the following:
- Create an ordering pathway that provides clinical decision support for PPI use.
- Incorporate a best practice alert in the EMR to notify clinicians of institutional guidelines when they initiate an order for PPI outside of the pathway.
- Consider restricting the authority to order IV PPIs by requiring a code or password or implement another means of using the EHR to limit the supply of PPI.
- Limit the duration of IV PPI by requiring daily renewal of IV PPI dosing or by altering the period of time that use of IV PPI is permitted (eg, 48 to 72 hours).
- PPIs should be removed from any current order sets that include medications for SUP.
3. Foster pharmacy-driven interventions.
- Consider requiring pharmacist approval for IV PPIs.
- Pharmacist-led review and feedback to clinicians for discontinuation of inappropriate PPIs can be effective in decreasing inappropriate utilization.
4. Provide education, audit data, and obtain feedback.
- Data auditing is needed to measure the efficacy of interventions. Outcome measures may include the number of non-ICU and ICU patients who are started on a PPI during an admission; the audit should be continued through discharge. A process measure may be the number of pharmacist calls for inappropriate PPIs. A balancing measure would be ulcer-specific upper GIB in patients who do not receive SUP during their admission. (Upper GIB from other etiologies, such as varices, portal hypertensive gastropathy, and Mallory-Weiss tear would not be affected by PPI SUP.)
- Run or control charts should be utilized, and data should be shared with project champions and ordering clinicians—in real time if possible.
- Project champions should provide feedback to colleagues; they should also work with hospital leadership to develop new strategies to improve adherence.
- Provide ongoing education about appropriate indications for PPIs and potential adverse effects associated with their use. Whenever possible, point-of-care or just-in-time teaching is the preferred format.
CONCLUSION
Excessive use of PPIs during hospitalization is prevalent; however, quality improvement interventions can be effective in achieving sustainable reductions in overuse. There is a need for the American College of Gastroenterology to revisit and update their guidelines for management of patients with ulcer bleeding to include stronger evidence-based recommendations on the proper use of PPIs.27 These updated guidelines could be used to update the implementation blueprint.
Quality improvement teams have an opportunity to use the principles of value-based healthcare to reduce inappropriate PPI use. By following the blueprint outlined in this article, institutions can safely and effectively tailor the use of PPIs to suitable patients in the appropriate settings. Reduction of PPI overuse can be employed as an institutional catalyst to promote implementation of further value-based measures to improve efficiency and quality of patient care.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are among the most commonly used drugs worldwide to treat dyspepsia and prevent gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB).1 Between 40% and 70% of hospitalized patients receive acid-suppressive therapy (AST; defined as PPIs or histamine-receptor antagonists), and nearly half of these are initiated during the inpatient stay.2,3 While up to 50% of inpatients who received a new AST were discharged on these medications,2 there were no evidence-based indications for a majority of the prescriptions.2,3
Growing evidence shows that PPIs are overutilized and may be associated with wide-ranging adverse events, such as acute and chronic kidney disease,4Clostridium difficile infection,5 hypomagnesemia,6 and fractures.7 Because of the widespread overuse and the potential harm associated with PPIs, a concerted effort to promote their appropriate use in the inpatient setting is necessary. It is important to note that reducing the use of PPIs does not increase the risks of GIB or worsening dyspepsia. Rather, reducing overuse of PPIs lowers the risk of harm to patients. The efforts to reduce overuse, however, are complex and difficult.
This article summarizes evidence regarding interventions to reduce overuse and offers an implementation guide based on this evidence. This guide promotes value-based quality improvement and provides a blueprint for implementing an institution-wide program to reduce PPI overuse in the inpatient setting. We begin with a discussion about quality initiatives to reduce PPI overuse, followed by a review of the safety outcomes associated with reduced use of PPIs.
METHODS
A focused search of the US National Library of Medicine’s PubMed database was performed to identify English-language articles published between 2000 and 2018 that addressed strategies to reduce PPI overuse for stress ulcer prophylaxis (SUP) and nonvariceal GIB. The following search terms were used: PPI and inappropriate use; acid-suppressive therapy and inappropriate use; PPI and discontinuation; acid-suppressive (or suppressant) therapy and discontinuation; SUP and cost; and histamine receptor antagonist and PPI. Inpatient or outpatient studies of patients aged 18 years or older were considered for inclusion in this narrative review, and all study types were included. The primary exclusion criterion was patients aged younger than 18 years. A manual review of the full text of the retrieved articles was performed and references were reviewed for missed citations.
RESULTS
We identified a total of 1,497 unique citations through our initial search. After performing a manual review, we excluded 1,483 of the references and added an additional 2, resulting in 16 articles selected for inclusion. The selected articles addressed interventions falling into three main groupings: implementation of institutional guidelines with or without electronic health record (EHR)–based decision support, educational interventions alone, and multifaceted interventions. Each of these interventions is discussed in the sections that follow. Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 summarize the results of the studies included in our narrative review.
QUALITY INITIATIVES TO REDUCE PPI OVERUSE
Institutional Guidelines With or Without EHR-Based Decision Support
Table 1 summarizes institutional guidelines, with or without EHR-based decision support, to reduce inappropriate PPI use. The implementation of institutional guidelines for the appropriate reduction of PPI use has had some success. Coursol and Sanzari evaluated the impact of a treatment algorithm on the appropriateness of prescriptions for SUP in the intensive care unit (ICU).8 Risk factors of patients in this study included mechanical ventilation for 48 hours, coagulopathy for 24 hours, postoperative transplant, severe burns, active gastrointestinal (GI) disease, multiple trauma, multiple organ failure, and septicemia. The three treatment options chosen for the algorithm were intravenous (IV) famotidine (if the oral route was unavailable or impractical), omeprazole tablets (if oral access was available), and omeprazole suspension (in cases of dysphagia and presence of nasogastric or orogastric tube). After implementation of the treatment algorithm, the proportion of inappropriate prophylaxis decreased from 95.7% to 88.2% (P = .033), and the cost per patient decreased from $11.11 to $8.49 Canadian dollars (P = .003).

Van Vliet et al implemented a clinical practice guideline listing specific criteria for prescribing a PPI.9 Their criteria included the presence of gastric or duodenal ulcer and use of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or aspirin, plus at least one additional risk factor (eg, history of gastroduodenal hemorrhage or age >70 years). The proportion of patients started on PPIs during hospitalization decreased from 21% to 13% (odds ratio, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.33-0.97).
Michal et al utilized an institutional pharmacist-driven protocol that stipulated criteria for appropriate PPI use (eg, upper GIB, mechanical ventilation, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, coagulopathy).10 Pharmacists in the study evaluated patients for PPI appropriateness and recommended changes in medication or discontinuation of use. This institutional intervention decreased PPI use in non-ICU hospitalized adults. Discontinuation of PPIs increased from 41% of patients in the preintervention group to 66% of patients in the postintervention group (P = .001).
In addition to implementing guidelines and intervention strategies, institutions have also adopted changes to the EHR to reduce inappropriate PPI use. Herzig et al utilized a computerized clinical decision support intervention to decrease SUP in non-ICU hospitalized patients.11 Of the available response options for acid-suppressive medication, when SUP was chosen as the only indication for PPI use a prompt alerted the clinician that “[SUP] is not recommended for patients outside the [ICU]”; the alert resulted in a significant reduction in AST for the sole purpose of SUP. With this intervention, the percentage of patients who had any inappropriate acid-suppressive exposure decreased from 4.0% to 0.6% (P < .001).
EDUCATION
Table 2 summarizes educational interventions to reduce inappropriate PPI use.

Agee et al employed a pharmacist-led educational seminar that described SUP indications, risks, and costs.12 Inappropriate SUP prescriptions decreased from 55.5% to 30.5% after the intervention (P < .0001). However, there was no reduction in the percentage of patients discharged on inappropriate AST.
Chui et al performed an intervention with academic detailing wherein a one-on-one visit with a physician took place, providing education to improve physician prescribing behavior.13 In this study, academic detailing focused on the most common instances for which PPIs were inappropriately utilized at that hospital (eg, surgical prophylaxis, anemia). Inappropriate use of double-dose PPIs was also targeted. Despite these efforts, no significant difference in inappropriate PPI prescribing was observed post intervention.
Hamzat et al implemented an educational strategy to reduce inappropriate PPI prescribing during hospital stays, which included dissemination of fliers, posters, emails, and presentations over a 4-week period.14 Educational efforts targeted clinical pharmacists, nurses, physicians, and patients. Appropriate indications for PPI use in this study included peptic ulcer disease (current or previous), H pylori infection, and treatment or prevention of an NSAID-induced ulcer. The primary outcome was a reduction in PPI dose or discontinuation of PPI during the hospital admission, which increased from 9% in the preintervention (pre-education) phase to 43% during the intervention (education) phase and to 46% in the postintervention (posteducation) phase (P = .006).
Liberman and Whelan also implemented an educational intervention among internal medicine residents to reduce inappropriate use of SUP; this intervention was based on practice-based learning and improvement methodology.15 They noted that the rate of inappropriate prophylaxis with AST decreased from 59% preintervention to 33% post intervention (P < .007).
MULTIFACETED APPROACHES
Table 3 summarizes several multifaceted approaches aimed at reducing inappropriate PPI use. Belfield et al utilized an intervention consisting of an institutional guideline review, education, and monitoring of AST by clinical pharmacists to reduce inappropriate use of PPI for SUP.16 With this intervention, the primary outcome of total inappropriate days of AST during hospitalization decreased from 279 to 116 (48% relative reduction in risk, P < .01, across 142 patients studied). Furthermore, inappropriate AST prescriptions at discharge decreased from 32% to 8% (P = .006). The one case of GIB noted in this study occurred in the control group.

Del Giorno et al combined audit and feedback with education to reduce new PPI prescriptions at the time of discharge from the hospital.17 The educational component of this intervention included guidance regarding potentially inappropriate PPI use and associated side effects and targeted multiple departments in the hospital. This intervention led to a sustained reduction in new PPI prescriptions at discharge during the 3-year study period. The annual rate of new PPI prescriptions was 19%, 19%, 18%, and 16% in years 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, in the internal medicine department (postintervention group), compared with rates of 30%, 29%, 36%, 36% (P < .001) for the same years in the surgery department (control group).
Education and the use of medication reconciliation forms on admission and discharge were utilized by Gupta et al to reduce inappropriate AST in hospitalized patients from 51% prior to intervention to 22% post intervention (P < .001).18 Furthermore, the proportion of patients discharged on inappropriate AST decreased from 69% to 20% (P < .001).
Hatch et al also used educational resources and pharmacist-led medication reconciliation to reduce use of SUP.19 Before the intervention, 24.4% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge in the absence of a clear indication for use; post intervention, 11% of patients were continued on SUP after hospital discharge (of these patients, 8.7% had no clear indication for use). This represented a 64.4% decrease in inappropriately prescribed SUP after discharge (P < .0001).
Khalili et al combined an educational intervention with an institutional guideline in an infectious disease ward to reduce inappropriate use of SUP.20 This intervention reduced the inappropriate use of AST from 80.9% before the intervention to 47.1% post intervention (P < .001).
Masood et al implemented two interventions wherein pharmacists reviewed SUP indications for each patient during daily team rounds, and ICU residents and fellows received education about indications for SUP and the implemented initiative on a bimonthly basis.21 Inappropriate AST decreased from 26.75 to 7.14 prescriptions per 100 patient-days of care (P < .001).
McDonald et al combined education with a web-based quality improvement tool to reduce inappropriate exit prescriptions for PPIs.22 The proportion of PPIs discontinued at hospital discharge increased from 7.7% per month to 18.5% per month (P = .03).
Finally, the initiative implemented by Tasaka et al to reduce overutilization of SUP included an institutional guideline, a pharmacist-led intervention, and an institutional education and awareness campaign.23 Their initiative led to a reduction in inappropriate SUP both at the time of transfer out of the ICU (8% before intervention, 4% post intervention, P = .54) and at the time of discharge from the hospital (7% before intervention, 0% post intervention, P = .22).
REDUCING PPI USE AND SAFETY OUTCOMES
Proton pump inhibitors are often initiated in the hospital setting, with up to half of these new prescriptions continued at discharge.2,24,25 Inappropriate prescriptions for PPIs expose patients to excess risk of long-term adverse events.26 De-escalating PPIs, however, raises concern among clinicians and patients for potential recurrence of dyspepsia and GIB. There is limited evidence regarding long-term safety outcomes (including GIB) following the discontinuation of PPIs deemed to have been inappropriately initiated in the hospital. In view of this, clinicians should educate and monitor individual patients for symptom relapse to ensure timely and appropriate resumption of AST.
LIMITATIONS
Our literature search for this narrative review and implementation guide has limitations. First, the time frame we included (2000-2018) may have excluded relevant articles published before our starting year. We did not include articles published before 2000 based on concerns these might contain outdated information. Also, there may have been incomplete retrieval of relevant studies/articles due to the labor-intensive nature involved in determining whether PPI prescriptions are appropriate or inappropriate.
We noted that interventional studies aimed at reducing overuse of PPIs were often limited by a low number of participants; these studies were also more likely to be single-center interventions, which limits generalizability. In addition, the studies often had low methodological rigor and lacked randomization or controls. Moreover, to fully evaluate the sustainability of interventions, some of the studies had a limited postimplementation period. For multifaceted interventions, the efficacy of individual components of the interventions was not clearly evaluated. Moreover, there was a high risk of bias in many of the included studies. Some of the larger studies used overall AST prescriptions as a surrogate for more appropriate use. It would be advantageous for a site to perform a pilot study that provides well-defined parameters for appropriate prescribing, and then correlate with the total number of prescriptions (automated and much easier) thereafter. Further, although the evidence regarding appropriate PPI use for SUP and GIB has shifted rapidly in recent years, society guidelines have not been updated to reflect this change. As such, quality improvement interventions have predominantly focused on reducing PPI use for the indications reflected by these guidelines.
IMPLEMENTATION BLUEPRINT
The following are our recommendations for successfully implementing an evidence-based, institution-wide initiative to promote the appropriate use of PPIs during hospitalization. These recommendations are informed by the evidence review and reflect the consensus of the combined committees coauthoring this review.
For an initiative to succeed, participation from multiple disciplines is necessary to formulate local guidelines and design and implement interventions. Such an interdisciplinary approach requires advocates to closely monitor and evaluate the program; sustainability will be greatly facilitated by the active engagement of key stakeholders, including the hospital’s executive administration, supply chain, pharmacists, and gastroenterologists. Lack of adequate buy-in on the part of key stakeholders is a barrier to the success of any intervention. Accordingly, before selecting a particular intervention, it is important to understand local factors driving the overuse of PPI.
1. Develop evidence-based institutional guidelines for both SUP and nonvariceal upper GIB through an interdisciplinary workgroup.
- Establish an interdisciplinary group including, but not limited to, pharmacists, hospitalists, gastroenterologists, and intensivists so that changes in practice will be widely adopted as institutional policy.
- Incorporate the best evidence and clearly convey appropriate and inappropriate uses.
2. Integrate changes to the EHR.
- If possible, the EHR should be leveraged to implement changes in PPI ordering practices.
- While integrating changes to the EHR, it is important to consider informatics and implementation science, since the utility of hard stops and best practice alerts has been questioned in the setting of operational inefficiencies and alert fatigue.
- Options for integrating changes to the EHR include the following:
- Create an ordering pathway that provides clinical decision support for PPI use.
- Incorporate a best practice alert in the EMR to notify clinicians of institutional guidelines when they initiate an order for PPI outside of the pathway.
- Consider restricting the authority to order IV PPIs by requiring a code or password or implement another means of using the EHR to limit the supply of PPI.
- Limit the duration of IV PPI by requiring daily renewal of IV PPI dosing or by altering the period of time that use of IV PPI is permitted (eg, 48 to 72 hours).
- PPIs should be removed from any current order sets that include medications for SUP.
3. Foster pharmacy-driven interventions.
- Consider requiring pharmacist approval for IV PPIs.
- Pharmacist-led review and feedback to clinicians for discontinuation of inappropriate PPIs can be effective in decreasing inappropriate utilization.
4. Provide education, audit data, and obtain feedback.
- Data auditing is needed to measure the efficacy of interventions. Outcome measures may include the number of non-ICU and ICU patients who are started on a PPI during an admission; the audit should be continued through discharge. A process measure may be the number of pharmacist calls for inappropriate PPIs. A balancing measure would be ulcer-specific upper GIB in patients who do not receive SUP during their admission. (Upper GIB from other etiologies, such as varices, portal hypertensive gastropathy, and Mallory-Weiss tear would not be affected by PPI SUP.)
- Run or control charts should be utilized, and data should be shared with project champions and ordering clinicians—in real time if possible.
- Project champions should provide feedback to colleagues; they should also work with hospital leadership to develop new strategies to improve adherence.
- Provide ongoing education about appropriate indications for PPIs and potential adverse effects associated with their use. Whenever possible, point-of-care or just-in-time teaching is the preferred format.
CONCLUSION
Excessive use of PPIs during hospitalization is prevalent; however, quality improvement interventions can be effective in achieving sustainable reductions in overuse. There is a need for the American College of Gastroenterology to revisit and update their guidelines for management of patients with ulcer bleeding to include stronger evidence-based recommendations on the proper use of PPIs.27 These updated guidelines could be used to update the implementation blueprint.
Quality improvement teams have an opportunity to use the principles of value-based healthcare to reduce inappropriate PPI use. By following the blueprint outlined in this article, institutions can safely and effectively tailor the use of PPIs to suitable patients in the appropriate settings. Reduction of PPI overuse can be employed as an institutional catalyst to promote implementation of further value-based measures to improve efficiency and quality of patient care.
1. Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, et al. Proton pump inhibitors: use and misuse in the clinical setting. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11(11):1123-1134. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2018.1531703
2. Nardino RJ, Vender RJ, Herbert PN. Overuse of acid-suppressive therapy in hospitalized patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(11):3118-3122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03259.x
3. Ahrens D, Behrens G, Himmel W, Kochen MM, Chenot JF. Appropriateness of proton pump inhibitor recommendations at hospital discharge and continuation in primary care. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(8):767-773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2012.02973.x
4. Moledina DG, Perazella MA. PPIs and kidney disease: from AIN to CKD. J Nephrol. 2016;29(5):611-616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0309-2
5. Kwok CS, Arthur AK, Anibueze CI, Singh S, Cavallazzi R, Loke YK. Risk of Clostridium difficile infection with acid suppressing drugs and antibiotics: meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(7):1011-1019. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.108
6. Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Kittanamongkolchai W, et al. Proton pump inhibitors linked to hypomagnesemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ren Fail. 2015;37(7):1237-1241. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022x.2015.1057800
7. Yang YX, Lewis JD, Epstein S, Metz DC. Long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy and risk of hip fracture. JAMA. 2006;296(24):2947-2953. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.296.24.2947
8. Coursol CJ, Sanzari SE. Impact of stress ulcer prophylaxis algorithm study. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(5):810-816. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1d129
9. van Vliet EPM, Steyerberg EW, Otten HJ, et al. The effects of guideline implementation for proton pump inhibitor prescription on two pulmonary medicine wards. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29(2):213-221. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03875.x
10. Michal J, Henry T, Street C. Impact of a pharmacist-driven protocol to decrease proton pump inhibitor use in non-intensive care hospitalized adults. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(17 Suppl 4):S126-S132. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp150519
11. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2260
12. Agee C, Coulter L, Hudson J. Effects of pharmacy resident led education on resident physician prescribing habits associated with stress ulcer prophylaxis in non-intensive care unit patients. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(11 Suppl 1):S48-S52. https://doi.org/10.2146/sp150013
13. Chui D, Young F, Tejani AM, Dillon EC. Impact of academic detailing on proton pump inhibitor prescribing behaviour in a community hospital. Can Pharm J (Ott). 2011;144(2):66-71. https://doi.org/10.3821/1913-701X-144.2.66
14. Hamzat H, Sun H, Ford JC, Macleod J, Soiza RL, Mangoni AA. Inappropriate prescribing of proton pump inhibitors in older patients: effects of an educational strategy. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(8):681-690. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03262283
15. Liberman JD, Whelan CT. Brief report: Reducing inappropriate usage of stress ulcer prophylaxis among internal medicine residents. A practice-based educational intervention. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):498-500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00435.x
16. Belfield KD, Kuyumjian AG, Teran R, Amadi M, Blatt M, Bicking K. Impact of a collaborative strategy to reduce the inappropriate use of acid suppressive therapy in non-intensive care unit patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2017;51(7):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028017698797
17. Del Giorno R, Ceschi A, Pironi M, Zasa A, Greco A, Gabutti L. Multifaceted intervention to curb in-hospital over-prescription of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal multicenter quasi-experimental before-and-after study. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;50:52-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2017.11.002
18. Gupta R, Marshall J, Munoz JC, Kottoor R, Jamal MM, Vega KJ. Decreased acid suppression therapy overuse after education and medication reconciliation. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(1):60-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12046
19. Hatch JB, Schulz L, Fish JT. Stress ulcer prophylaxis: reducing non-indicated prescribing after hospital discharge. Ann Pharmacother. 2010;44(10):1565-1571. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1p167
20. Khalili H, Dashti-Khavidaki S, Hossein Talasaz AH, Tabeefar H, Hendoiee N. Descriptive analysis of a clinical pharmacy intervention to improve the appropriate use of stress ulcer prophylaxis in a hospital infectious disease ward. J Manag Care Pharm. 2010;16(2):114-121. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2010.16.2.114
21. Masood U, Sharma A, Bhatti Z, et al. A successful pharmacist-based quality initiative to reduce inappropriate stress ulcer prophylaxis use in an academic medical intensive care unit. Inquiry. 2018;55:46958018759116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0046958018759116
22. McDonald EG, Jones J, Green L, Jayaraman D, Lee TC. Reduction of inappropriate exit prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors: a before-after study using education paired with a web-based quality-improvement tool. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(5):281-286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2330
23. Tasaka CL, Burg C, VanOsdol SJ, et al. An interprofessional approach to reducing the overutilization of stress ulcer prophylaxis in adult medical and surgical intensive care units. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(4):462-469. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028013517088
24. Zink DA, Pohlman M, Barnes M, Cannon ME. Long-term use of acid suppression started inappropriately during hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(10):1203-1209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02454.x
25. Pham CQ, Regal RE, Bostwick TR, Knauf KS. Acid suppressive therapy use on an inpatient internal medicine service. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40(7-8):1261-1266. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1g703
26. Schoenfeld AJ, Grady D. Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitors [editorial]. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(2):172-174. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7927
27. Laine L, Jensen DM. Management of patients with ulcer bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(3):345-360; quiz 361. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.480
1. Savarino V, Marabotto E, Zentilin P, et al. Proton pump inhibitors: use and misuse in the clinical setting. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11(11):1123-1134. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2018.1531703
2. Nardino RJ, Vender RJ, Herbert PN. Overuse of acid-suppressive therapy in hospitalized patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(11):3118-3122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03259.x
3. Ahrens D, Behrens G, Himmel W, Kochen MM, Chenot JF. Appropriateness of proton pump inhibitor recommendations at hospital discharge and continuation in primary care. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(8):767-773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2012.02973.x
4. Moledina DG, Perazella MA. PPIs and kidney disease: from AIN to CKD. J Nephrol. 2016;29(5):611-616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0309-2
5. Kwok CS, Arthur AK, Anibueze CI, Singh S, Cavallazzi R, Loke YK. Risk of Clostridium difficile infection with acid suppressing drugs and antibiotics: meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(7):1011-1019. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.108
6. Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Kittanamongkolchai W, et al. Proton pump inhibitors linked to hypomagnesemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ren Fail. 2015;37(7):1237-1241. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022x.2015.1057800
7. Yang YX, Lewis JD, Epstein S, Metz DC. Long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy and risk of hip fracture. JAMA. 2006;296(24):2947-2953. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.296.24.2947
8. Coursol CJ, Sanzari SE. Impact of stress ulcer prophylaxis algorithm study. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(5):810-816. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1d129
9. van Vliet EPM, Steyerberg EW, Otten HJ, et al. The effects of guideline implementation for proton pump inhibitor prescription on two pulmonary medicine wards. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29(2):213-221. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2008.03875.x
10. Michal J, Henry T, Street C. Impact of a pharmacist-driven protocol to decrease proton pump inhibitor use in non-intensive care hospitalized adults. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(17 Suppl 4):S126-S132. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp150519
11. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2260
12. Agee C, Coulter L, Hudson J. Effects of pharmacy resident led education on resident physician prescribing habits associated with stress ulcer prophylaxis in non-intensive care unit patients. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72(11 Suppl 1):S48-S52. https://doi.org/10.2146/sp150013
13. Chui D, Young F, Tejani AM, Dillon EC. Impact of academic detailing on proton pump inhibitor prescribing behaviour in a community hospital. Can Pharm J (Ott). 2011;144(2):66-71. https://doi.org/10.3821/1913-701X-144.2.66
14. Hamzat H, Sun H, Ford JC, Macleod J, Soiza RL, Mangoni AA. Inappropriate prescribing of proton pump inhibitors in older patients: effects of an educational strategy. Drugs Aging. 2012;29(8):681-690. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03262283
15. Liberman JD, Whelan CT. Brief report: Reducing inappropriate usage of stress ulcer prophylaxis among internal medicine residents. A practice-based educational intervention. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(5):498-500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00435.x
16. Belfield KD, Kuyumjian AG, Teran R, Amadi M, Blatt M, Bicking K. Impact of a collaborative strategy to reduce the inappropriate use of acid suppressive therapy in non-intensive care unit patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2017;51(7):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028017698797
17. Del Giorno R, Ceschi A, Pironi M, Zasa A, Greco A, Gabutti L. Multifaceted intervention to curb in-hospital over-prescription of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal multicenter quasi-experimental before-and-after study. Eur J Intern Med. 2018;50:52-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2017.11.002
18. Gupta R, Marshall J, Munoz JC, Kottoor R, Jamal MM, Vega KJ. Decreased acid suppression therapy overuse after education and medication reconciliation. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(1):60-65. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12046
19. Hatch JB, Schulz L, Fish JT. Stress ulcer prophylaxis: reducing non-indicated prescribing after hospital discharge. Ann Pharmacother. 2010;44(10):1565-1571. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1p167
20. Khalili H, Dashti-Khavidaki S, Hossein Talasaz AH, Tabeefar H, Hendoiee N. Descriptive analysis of a clinical pharmacy intervention to improve the appropriate use of stress ulcer prophylaxis in a hospital infectious disease ward. J Manag Care Pharm. 2010;16(2):114-121. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2010.16.2.114
21. Masood U, Sharma A, Bhatti Z, et al. A successful pharmacist-based quality initiative to reduce inappropriate stress ulcer prophylaxis use in an academic medical intensive care unit. Inquiry. 2018;55:46958018759116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0046958018759116
22. McDonald EG, Jones J, Green L, Jayaraman D, Lee TC. Reduction of inappropriate exit prescriptions for proton pump inhibitors: a before-after study using education paired with a web-based quality-improvement tool. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(5):281-286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.2330
23. Tasaka CL, Burg C, VanOsdol SJ, et al. An interprofessional approach to reducing the overutilization of stress ulcer prophylaxis in adult medical and surgical intensive care units. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(4):462-469. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028013517088
24. Zink DA, Pohlman M, Barnes M, Cannon ME. Long-term use of acid suppression started inappropriately during hospitalization. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;21(10):1203-1209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02454.x
25. Pham CQ, Regal RE, Bostwick TR, Knauf KS. Acid suppressive therapy use on an inpatient internal medicine service. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40(7-8):1261-1266. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1g703
26. Schoenfeld AJ, Grady D. Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitors [editorial]. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176(2):172-174. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7927
27. Laine L, Jensen DM. Management of patients with ulcer bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(3):345-360; quiz 361. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.480
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Things We Do For No Reason™: Rasburicase for Adult Patients With Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely ® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
A 35-year-old man with a history of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), who most recently received treatment 12 months earlier, presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and constipation. A computed tomography scan of the abdomen reveals retroperitoneal and mesenteric lymphadenopathy causing small bowel obstruction. The basic metabolic panel reveals a creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL, calcium of 8.5 mg/dL, phosphorus of 4 mg/dL, potassium of 4.5 mEq/L, and uric acid of 7.3 mg/dL. The admitting team contemplates using allopurinol or rasburicase for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) prevention in the setting of recurrent DLBCL.
BACKGROUND
Tumor lysis syndrome is characterized by metabolic derangement and end-organ damage in the setting of cytotoxic chemotherapy, chemosensitive malignancy, and/or increased tumor burden.1 Risk stratification for TLS takes into account patient and disease characteristics (Table 1). Other risk factors include tumor bulk, elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase, and certain types of chemotherapy (eg, cisplatin, cytarabine, etoposide, paclitaxel, cytotoxic therapies), immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.2 Elevated serum levels of uric acid, potassium, and phosphorus, as well as preexisting renal dysfunction, predispose patients to clinical TLS.3
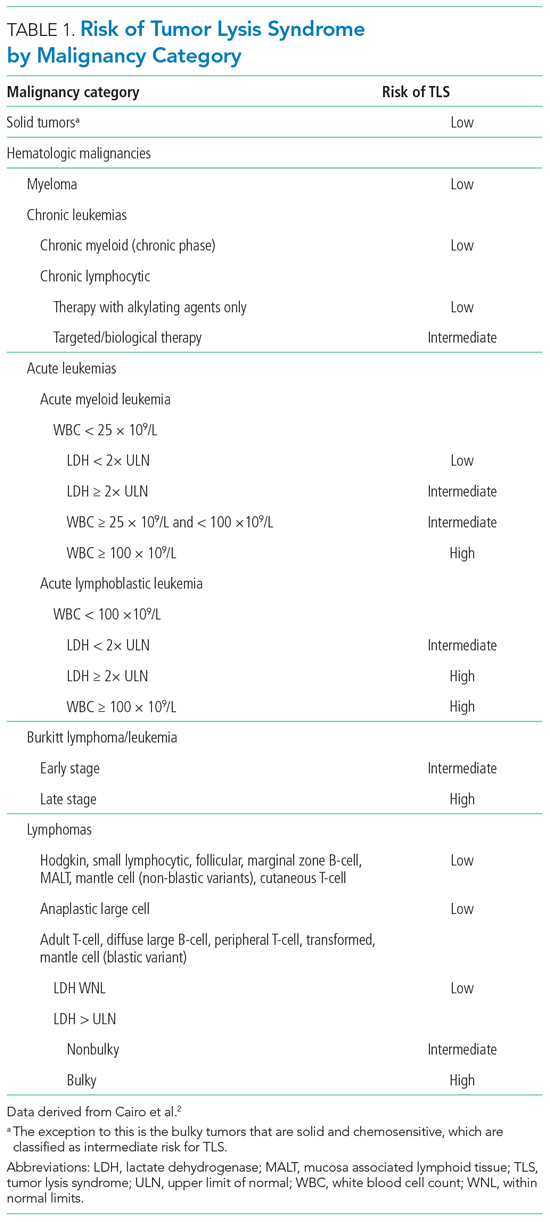
The Cairo-Bishop classification system is most frequently used to diagnose TLS (Table 2).3 Laboratory features include hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and hypocalcemia secondary to lysis of proliferating tumor cells and their nuclei. Clinical features include arrhythmias, seizures, and acute kidney injury (AKI).1 Acute kidney injury, the most common clinical complication of TLS, results from crystallization of markedly elevated plasma uric acid, leading to tubular obstruction.1,4 The development of AKI can predict morbidity (namely, the need for renal replacement therapy [RRT]) and mortality in this patient population.1
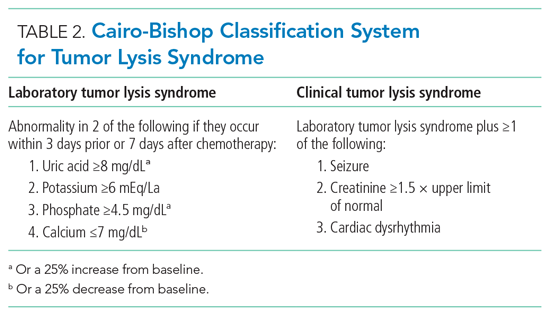
Stratifying a patient’s baseline risk of developing TLS often dictates the prevention and management plan. Therapeutic prophylaxis and management strategies for TLS include aggressive fluid resuscitation, diuresis, plasma uric acid (PUA) levels, monitoring electrolyte levels, and, in certain life-threatening situations, dialysis. Oncologists presume reducing uric acid levels prevents and treats TLS.
Current methods to reduce PUA as a means of preventing or treating TLS include xanthine oxidase inhibitors (eg, allopurinol) or urate oxidase (eg, rasburicase). Before the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval of rasburicase to manage TLS, providers combined allopurinol (a purine analog that inhibits the enzyme xanthine oxidase, decreasing uric acid level) with aggressive fluid resuscitation. Approved by the FDA in 2002, rasburicase offers an alternative treatment for hyperuricemia by directly decreasing levels of uric acid instead of merely preventing the increased formation of uric acid. As a urate oxidase, rasburicase converts uric acid to the non-nephrotoxic, water-soluble, and freely excreted allantoin.
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK YOU SHOULD USE URATE OXIDASE IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME FOR THE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Rasburicase is often considered the standard-of-care treatment for hyperuricemia due to its ability to reduce circulating uric acid levels rapidly. The primary goal of uric acid reduction is to prevent the occurrence of AKI.
Based upon bioplausible relevance to clinically meaningful endpoints, researchers selected PUA reduction as the primary outcome in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies to justify treatment with rasburicase. In RCTs, compassionate trials, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses, rasburicase demonstrated a more rapid reduction in uric acid levels compared to allopurinol.5 Specifically, in one study by Goldman et al,6 rasburicase decreased baseline uric acid levels in pediatric oncology patients by 86% (statistically significant) 4 hours after administration, compared to allopurinol, which only reduced baseline uric acid by 12%. According to a study by Cairo et al, allopurinol may take up to 1 day to reduce PUA.3
WHY URATE OXIDASE MAY NOT IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS AT RISK FOR OR WITH TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
Randomized controlled trials examining the safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in adult patients remain sparse. Both RCTs and systematic reviews and meta-analyses rely on PUA levels as a surrogate endpoint and fail to include clinically meaningful primary endpoints (eg, change in baseline creatinine or need for RRT), raising the question as to whether rasburicase improves patient-centered outcomes.5 Since previous studies in the oncology literature show low or modest correlations between PUA reduction and patient-oriented outcomes, we must question whether PUA reduction serves as a meaningful surrogate endpoint.
Treatment of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Two meta-analyses focusing on the treatment of TLS by Dinnel et al5 and Lopez-Olivo et al8 each included only three unique RCTs (two of the three RCTs were referenced in both meta-analyses). Moreover, both studies included only one RCT comparing rasburicase directly to allopurinol (a 2010 RCT by Cortes et al9) while the other RCTs compared the impact of different rasburicase dosing regimens. Researchers powered the head-to-head RCT by Cortes et al9 to detect a difference in PUA levels across three different arms: rasburicase, rasburicase plus allopurinol, or allopurinol alone. All three treatment arms resulted in a statistically significant reduction in serum PUA levels (87%, 78%, 66%, respectively; P = .001) without a change in the secondary, underpowered clinical outcomes such as clinical TLS or reduced renal function (defined in this study as increased creatinine, renal failure/impairment, or acute renal failure).
More recently, retrospective analyses of patients with AKI secondary to TLS found no difference in creatinine improvement, renal recovery, or prevention of RRT based on whether the patients received either rasburicase or allopurinol.10,11 While rasburicase is associated with greater PUA reduction compared to allopurinol, according to meaningful RCT and observational data as discussed previously and described further in the following section, this does not translate to clinically important risk reduction.
Prevention of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Furthermore, there exists little compelling evidence to support the use of rasburicase for preventing AKI secondary to TLS. Even among patients at high-risk for TLS (the only group for whom rasburicase is currently recommended),5 rasburicase does not definitively prevent AKI. Data suggest that despite lowering uric acid levels, rasburicase does not consistently prevent renal injury11 or decrease the total number of subsequent inpatient days.12 The only phase 3 trial that compared the efficacy of rasburicase to allopurinol for the prevention of TLS and included clinically meaningful endpoints (eg, renal failure) found that, while rasburicase reduced uric acid levels faster than allopurinol, it did not decrease rates of clinical TLS.9
The published literature offers limited efficacy data of rasburicase in preventing TLS in low-risk patients; however, the absence of benefit of rasburicase in preventing renal failure in high-risk patients warrants skepticism as to its potential efficacy in low-risk patients.8,10
Costs-Effectiveness and Other Ethical Considerations
Rasburicase is an expensive treatment. The estimated cost of the FDA-recommended dosing is around $37,500.13 Moreover, studies comparing the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase to allopurinol focus primarily on patients at high-risk for TLS, which overestimates the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in patients at low-to-intermediate risk for TLS.14,15 Unfortunately, some providers inappropriately prescribe rasburicase regularly to patients at low or intermediate risk for TLS. Based on observational studies of rasburicase in various clinical scenarios, including inpatient and emergency department settings, inappropriate use of rasburicase (eg, in the setting of hyperuricemia without evidence of a high-risk TLS tumor, no prior trial of allopurinol, preserved renal function, no laboratory evaluation) ranges from 32% to 70%.14,15
Finally, while <1% of patients experience rasburicase-induced anaphylaxis, 20% to 50% of patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms and viral-syndrome-like symptoms.16 Meanwhile, major side effects from allopurinol that occur with 1% to 10% frequency include maculopapular rash, pruritis, gout, nausea, vomiting, and renal failure syndrome.17 Even if the cost for rasburicase and allopurinol were similar, the lack of improved efficacy and the side-effect profiles of the two medications should make us question whether to prescribe rasburicase preferentially over allopurinol.
WHEN MIGHT URATE OXIDASE BE HELPFUL IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
While some experts recommend rasburicase prophylaxis in patients at high risk for developing TLS, such recommendations rely on low-quality evidence.2 When prescribing rasburicase, the hospitalist must ensure correct dosing. The FDA approved rasburicase for weight-based dosing at 0.2 mg/kg, though current evidence favors a single, fixed dose of 3 mg.16,17 Compared to weight-based dosing, which has an estimated cost-effectiveness ratio ranging from $27,982.77 to $119,643.59 per quality-adjusted life-year, single dosing has equivalent efficacy at approximately 50% lower cost per dose.11,17,18
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
As a preventive treatment for TLS, clinicians should only consider prescribing rasburicase as a single fixed dose of 3 mg to high-risk patients.17 In the event of AKI secondary to TLS, clinicians should proceed with the mainstay treatment of resuscitation with aggressive fluid resuscitation, with a goal urine output of at least 2 mL/kg/h.1 Fluid resuscitation should be used cautiously in patients with oliguric or anuric AKI, pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure, and hemodynamically significant valvular disease. Clinicians should provide continuous cardiac monitoring during the initial presentation to monitor for electrocardiographic changes in the setting of hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, and they should consult nephrology, oncology, and critical care services early in the disease course to maximize coordination of care.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Prevention
- Identify patients at high-risk of TLS (Table 1) and consider a single 3-mg dose of rasburicase.
- Manage low- and intermediate-risk patients with allopurinol and hydration.
Treatment
- Identify patients with TLS using the clinical and laboratory findings outlined in the Cairo-Bishop classification system (Table 2).
- Initiate aggressive fluid resuscitation and manage electrolyte abnormalities.
- If urate-lowering therapy is part of local hospital guidelines for TLS management, consider a single dose regimen of rasburicase utilizing shared decision-making.
CONCLUSION
Tumor lysis syndrome remains a metabolic emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and management to prevent morbidity and mortality. Current data show rasburicase rapidly decreases PUA compared to allopurinol. However, the current literature does not provide compelling evidence that rapidly lowering uric acid with rasburicase to prevent TLS or to treat AKI secondary to TLS improves patient-oriented outcomes.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
1. Howard SC, Jones DP, Pui CH. The tumor lysis syndrome. N Engl J Med.2011;364(19):1844-1854. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra0904569
2. Cairo MS, Coiffier B, Reiter A, Younes A; TLS Expert Panel. Recommendations for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149(4):578-586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08143.x
3. Cairo MS, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol.. 2004;127(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05094.x
4. Durani U, Shah ND, Go RS. In-hospital outcomes of tumor lysis syndrome: a population-based study using the National Inpatient Sample. Oncologist. 2017;22(12):1506-1509. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0147
5. Dinnel J, Moore BL, Skiver BM, Bose P. Rasburicase in the management of tumor lysis: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid.. 2015;10:23-38. https://doi.org/10.2147/ce.s54995
6. Goldman SC, Holcenberg JS, Finklestein JZ, et al. A randomized comparison between rasburicase and allopurinol in children with lymphoma or leukemia at high risk for tumor lysis. Blood. 2001;97(10):2998-3003. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v97.10.2998
7. Haslam A, Hey SP, Gill J, Prasad V. A systematic review of trial-level meta-analyses measuring the strength of association between surrogate end-points and overall survival in oncology. Eur J Cancer. 1990. 2019;106:196-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.11.012
8. Lopez-Olivo MA, Pratt G, Palla SL, Salahudeen A. Rasburicase in tumor lysis syndrome of the adult: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(3):481-492. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.378
9. Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, et al. Control of plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor lysis syndrome: efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone—results of a multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4207-4213. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.8896
10. Martens KL, Khalighi PR, Li S, et al. Comparative effectiveness of rasburicase versus allopurinol for cancer patients with renal dysfunction and hyperuricemia. Leuk Res. 2020;89:106298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106298
11. Personett HA, Barreto EF, McCullough K, Dierkhising R, Leung N, Habermann TM. Impact of early rasburicase on incidence and outcomes of clinical tumor lysis syndrome in lymphoma. Blood. 2019;60(9)2271-2277. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2019.1574000
12. Howard SC, Cockerham AR, Yvonne Barnes DN, Ryan M, Irish W, Gordan L. Real-world analysis of outpatient rasburicase to prevent and manage tumor lysis syndrome in newly diagnosed adults with leukemia or lymphoma. J Clin Pathways. 2020;6(2):46-51.
13. Abu-Hashyeh AM, Shenouda M, Al-Sharedi M. The efficacy of cost-effective fixed dose of rasburicase compared to weight-based dose in treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3.5):QIM20-119. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.7516
14. Patel KK, Brown TJ, Gupta A, et al. Decreasing inappropriate use of rasburicase to promote cost-effective care. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15(2):e178-e186. https://doi.org/10.1200/jop.18.00528
15. Khalighi PR, Martens KL, White AA, et al. Utilization patterns and clinical outcomes of rasburicase administration according to tumor risk stratification. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020;26(3):529-535. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155219851543
16. Elitek. Prescribing information. Sanofi-Aventis U.S., LLC; 2019. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://products.sanofi.us/elitek/Elitek.html
17. Allopurinol. Drugs & Diseases. Medscape. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://reference.medscape.com/drug/zyloprim-aloprim-allopurinol-342811
18. Jones GL, Will A, Jackson GH, Webb NJA, Rule S; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169(5):661‐671. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13403
19. Boutin A, Blackman A, O’Sullivan DM, Forcello N. The value of fixed rasburicase dosing versus weight-based dosing in the treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019;25(3):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155217752075
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely ® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
A 35-year-old man with a history of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), who most recently received treatment 12 months earlier, presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and constipation. A computed tomography scan of the abdomen reveals retroperitoneal and mesenteric lymphadenopathy causing small bowel obstruction. The basic metabolic panel reveals a creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL, calcium of 8.5 mg/dL, phosphorus of 4 mg/dL, potassium of 4.5 mEq/L, and uric acid of 7.3 mg/dL. The admitting team contemplates using allopurinol or rasburicase for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) prevention in the setting of recurrent DLBCL.
BACKGROUND
Tumor lysis syndrome is characterized by metabolic derangement and end-organ damage in the setting of cytotoxic chemotherapy, chemosensitive malignancy, and/or increased tumor burden.1 Risk stratification for TLS takes into account patient and disease characteristics (Table 1). Other risk factors include tumor bulk, elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase, and certain types of chemotherapy (eg, cisplatin, cytarabine, etoposide, paclitaxel, cytotoxic therapies), immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.2 Elevated serum levels of uric acid, potassium, and phosphorus, as well as preexisting renal dysfunction, predispose patients to clinical TLS.3

The Cairo-Bishop classification system is most frequently used to diagnose TLS (Table 2).3 Laboratory features include hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and hypocalcemia secondary to lysis of proliferating tumor cells and their nuclei. Clinical features include arrhythmias, seizures, and acute kidney injury (AKI).1 Acute kidney injury, the most common clinical complication of TLS, results from crystallization of markedly elevated plasma uric acid, leading to tubular obstruction.1,4 The development of AKI can predict morbidity (namely, the need for renal replacement therapy [RRT]) and mortality in this patient population.1

Stratifying a patient’s baseline risk of developing TLS often dictates the prevention and management plan. Therapeutic prophylaxis and management strategies for TLS include aggressive fluid resuscitation, diuresis, plasma uric acid (PUA) levels, monitoring electrolyte levels, and, in certain life-threatening situations, dialysis. Oncologists presume reducing uric acid levels prevents and treats TLS.
Current methods to reduce PUA as a means of preventing or treating TLS include xanthine oxidase inhibitors (eg, allopurinol) or urate oxidase (eg, rasburicase). Before the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval of rasburicase to manage TLS, providers combined allopurinol (a purine analog that inhibits the enzyme xanthine oxidase, decreasing uric acid level) with aggressive fluid resuscitation. Approved by the FDA in 2002, rasburicase offers an alternative treatment for hyperuricemia by directly decreasing levels of uric acid instead of merely preventing the increased formation of uric acid. As a urate oxidase, rasburicase converts uric acid to the non-nephrotoxic, water-soluble, and freely excreted allantoin.
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK YOU SHOULD USE URATE OXIDASE IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME FOR THE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Rasburicase is often considered the standard-of-care treatment for hyperuricemia due to its ability to reduce circulating uric acid levels rapidly. The primary goal of uric acid reduction is to prevent the occurrence of AKI.
Based upon bioplausible relevance to clinically meaningful endpoints, researchers selected PUA reduction as the primary outcome in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies to justify treatment with rasburicase. In RCTs, compassionate trials, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses, rasburicase demonstrated a more rapid reduction in uric acid levels compared to allopurinol.5 Specifically, in one study by Goldman et al,6 rasburicase decreased baseline uric acid levels in pediatric oncology patients by 86% (statistically significant) 4 hours after administration, compared to allopurinol, which only reduced baseline uric acid by 12%. According to a study by Cairo et al, allopurinol may take up to 1 day to reduce PUA.3
WHY URATE OXIDASE MAY NOT IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS AT RISK FOR OR WITH TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
Randomized controlled trials examining the safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in adult patients remain sparse. Both RCTs and systematic reviews and meta-analyses rely on PUA levels as a surrogate endpoint and fail to include clinically meaningful primary endpoints (eg, change in baseline creatinine or need for RRT), raising the question as to whether rasburicase improves patient-centered outcomes.5 Since previous studies in the oncology literature show low or modest correlations between PUA reduction and patient-oriented outcomes, we must question whether PUA reduction serves as a meaningful surrogate endpoint.
Treatment of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Two meta-analyses focusing on the treatment of TLS by Dinnel et al5 and Lopez-Olivo et al8 each included only three unique RCTs (two of the three RCTs were referenced in both meta-analyses). Moreover, both studies included only one RCT comparing rasburicase directly to allopurinol (a 2010 RCT by Cortes et al9) while the other RCTs compared the impact of different rasburicase dosing regimens. Researchers powered the head-to-head RCT by Cortes et al9 to detect a difference in PUA levels across three different arms: rasburicase, rasburicase plus allopurinol, or allopurinol alone. All three treatment arms resulted in a statistically significant reduction in serum PUA levels (87%, 78%, 66%, respectively; P = .001) without a change in the secondary, underpowered clinical outcomes such as clinical TLS or reduced renal function (defined in this study as increased creatinine, renal failure/impairment, or acute renal failure).
More recently, retrospective analyses of patients with AKI secondary to TLS found no difference in creatinine improvement, renal recovery, or prevention of RRT based on whether the patients received either rasburicase or allopurinol.10,11 While rasburicase is associated with greater PUA reduction compared to allopurinol, according to meaningful RCT and observational data as discussed previously and described further in the following section, this does not translate to clinically important risk reduction.
Prevention of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Furthermore, there exists little compelling evidence to support the use of rasburicase for preventing AKI secondary to TLS. Even among patients at high-risk for TLS (the only group for whom rasburicase is currently recommended),5 rasburicase does not definitively prevent AKI. Data suggest that despite lowering uric acid levels, rasburicase does not consistently prevent renal injury11 or decrease the total number of subsequent inpatient days.12 The only phase 3 trial that compared the efficacy of rasburicase to allopurinol for the prevention of TLS and included clinically meaningful endpoints (eg, renal failure) found that, while rasburicase reduced uric acid levels faster than allopurinol, it did not decrease rates of clinical TLS.9
The published literature offers limited efficacy data of rasburicase in preventing TLS in low-risk patients; however, the absence of benefit of rasburicase in preventing renal failure in high-risk patients warrants skepticism as to its potential efficacy in low-risk patients.8,10
Costs-Effectiveness and Other Ethical Considerations
Rasburicase is an expensive treatment. The estimated cost of the FDA-recommended dosing is around $37,500.13 Moreover, studies comparing the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase to allopurinol focus primarily on patients at high-risk for TLS, which overestimates the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in patients at low-to-intermediate risk for TLS.14,15 Unfortunately, some providers inappropriately prescribe rasburicase regularly to patients at low or intermediate risk for TLS. Based on observational studies of rasburicase in various clinical scenarios, including inpatient and emergency department settings, inappropriate use of rasburicase (eg, in the setting of hyperuricemia without evidence of a high-risk TLS tumor, no prior trial of allopurinol, preserved renal function, no laboratory evaluation) ranges from 32% to 70%.14,15
Finally, while <1% of patients experience rasburicase-induced anaphylaxis, 20% to 50% of patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms and viral-syndrome-like symptoms.16 Meanwhile, major side effects from allopurinol that occur with 1% to 10% frequency include maculopapular rash, pruritis, gout, nausea, vomiting, and renal failure syndrome.17 Even if the cost for rasburicase and allopurinol were similar, the lack of improved efficacy and the side-effect profiles of the two medications should make us question whether to prescribe rasburicase preferentially over allopurinol.
WHEN MIGHT URATE OXIDASE BE HELPFUL IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
While some experts recommend rasburicase prophylaxis in patients at high risk for developing TLS, such recommendations rely on low-quality evidence.2 When prescribing rasburicase, the hospitalist must ensure correct dosing. The FDA approved rasburicase for weight-based dosing at 0.2 mg/kg, though current evidence favors a single, fixed dose of 3 mg.16,17 Compared to weight-based dosing, which has an estimated cost-effectiveness ratio ranging from $27,982.77 to $119,643.59 per quality-adjusted life-year, single dosing has equivalent efficacy at approximately 50% lower cost per dose.11,17,18
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
As a preventive treatment for TLS, clinicians should only consider prescribing rasburicase as a single fixed dose of 3 mg to high-risk patients.17 In the event of AKI secondary to TLS, clinicians should proceed with the mainstay treatment of resuscitation with aggressive fluid resuscitation, with a goal urine output of at least 2 mL/kg/h.1 Fluid resuscitation should be used cautiously in patients with oliguric or anuric AKI, pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure, and hemodynamically significant valvular disease. Clinicians should provide continuous cardiac monitoring during the initial presentation to monitor for electrocardiographic changes in the setting of hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, and they should consult nephrology, oncology, and critical care services early in the disease course to maximize coordination of care.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Prevention
- Identify patients at high-risk of TLS (Table 1) and consider a single 3-mg dose of rasburicase.
- Manage low- and intermediate-risk patients with allopurinol and hydration.
Treatment
- Identify patients with TLS using the clinical and laboratory findings outlined in the Cairo-Bishop classification system (Table 2).
- Initiate aggressive fluid resuscitation and manage electrolyte abnormalities.
- If urate-lowering therapy is part of local hospital guidelines for TLS management, consider a single dose regimen of rasburicase utilizing shared decision-making.
CONCLUSION
Tumor lysis syndrome remains a metabolic emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and management to prevent morbidity and mortality. Current data show rasburicase rapidly decreases PUA compared to allopurinol. However, the current literature does not provide compelling evidence that rapidly lowering uric acid with rasburicase to prevent TLS or to treat AKI secondary to TLS improves patient-oriented outcomes.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
Inspired by the ABIM Foundation’s Choosing Wisely ® campaign, the “Things We Do for No Reason™” (TWDFNR) series reviews practices that have become common parts of hospital care but may provide little value to our patients. Practices reviewed in the TWDFNR series do not represent clear-cut conclusions or clinical practice standards but are meant as a starting place for research and active discussions among hospitalists and patients. We invite you to be part of that discussion.
A 35-year-old man with a history of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), who most recently received treatment 12 months earlier, presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and constipation. A computed tomography scan of the abdomen reveals retroperitoneal and mesenteric lymphadenopathy causing small bowel obstruction. The basic metabolic panel reveals a creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL, calcium of 8.5 mg/dL, phosphorus of 4 mg/dL, potassium of 4.5 mEq/L, and uric acid of 7.3 mg/dL. The admitting team contemplates using allopurinol or rasburicase for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) prevention in the setting of recurrent DLBCL.
BACKGROUND
Tumor lysis syndrome is characterized by metabolic derangement and end-organ damage in the setting of cytotoxic chemotherapy, chemosensitive malignancy, and/or increased tumor burden.1 Risk stratification for TLS takes into account patient and disease characteristics (Table 1). Other risk factors include tumor bulk, elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase, and certain types of chemotherapy (eg, cisplatin, cytarabine, etoposide, paclitaxel, cytotoxic therapies), immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.2 Elevated serum levels of uric acid, potassium, and phosphorus, as well as preexisting renal dysfunction, predispose patients to clinical TLS.3

The Cairo-Bishop classification system is most frequently used to diagnose TLS (Table 2).3 Laboratory features include hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and hypocalcemia secondary to lysis of proliferating tumor cells and their nuclei. Clinical features include arrhythmias, seizures, and acute kidney injury (AKI).1 Acute kidney injury, the most common clinical complication of TLS, results from crystallization of markedly elevated plasma uric acid, leading to tubular obstruction.1,4 The development of AKI can predict morbidity (namely, the need for renal replacement therapy [RRT]) and mortality in this patient population.1

Stratifying a patient’s baseline risk of developing TLS often dictates the prevention and management plan. Therapeutic prophylaxis and management strategies for TLS include aggressive fluid resuscitation, diuresis, plasma uric acid (PUA) levels, monitoring electrolyte levels, and, in certain life-threatening situations, dialysis. Oncologists presume reducing uric acid levels prevents and treats TLS.
Current methods to reduce PUA as a means of preventing or treating TLS include xanthine oxidase inhibitors (eg, allopurinol) or urate oxidase (eg, rasburicase). Before the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) approval of rasburicase to manage TLS, providers combined allopurinol (a purine analog that inhibits the enzyme xanthine oxidase, decreasing uric acid level) with aggressive fluid resuscitation. Approved by the FDA in 2002, rasburicase offers an alternative treatment for hyperuricemia by directly decreasing levels of uric acid instead of merely preventing the increased formation of uric acid. As a urate oxidase, rasburicase converts uric acid to the non-nephrotoxic, water-soluble, and freely excreted allantoin.
WHY YOU MIGHT THINK YOU SHOULD USE URATE OXIDASE IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME FOR THE PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
Rasburicase is often considered the standard-of-care treatment for hyperuricemia due to its ability to reduce circulating uric acid levels rapidly. The primary goal of uric acid reduction is to prevent the occurrence of AKI.
Based upon bioplausible relevance to clinically meaningful endpoints, researchers selected PUA reduction as the primary outcome in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies to justify treatment with rasburicase. In RCTs, compassionate trials, and systematic reviews and meta-analyses, rasburicase demonstrated a more rapid reduction in uric acid levels compared to allopurinol.5 Specifically, in one study by Goldman et al,6 rasburicase decreased baseline uric acid levels in pediatric oncology patients by 86% (statistically significant) 4 hours after administration, compared to allopurinol, which only reduced baseline uric acid by 12%. According to a study by Cairo et al, allopurinol may take up to 1 day to reduce PUA.3
WHY URATE OXIDASE MAY NOT IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS AT RISK FOR OR WITH TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
Randomized controlled trials examining the safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in adult patients remain sparse. Both RCTs and systematic reviews and meta-analyses rely on PUA levels as a surrogate endpoint and fail to include clinically meaningful primary endpoints (eg, change in baseline creatinine or need for RRT), raising the question as to whether rasburicase improves patient-centered outcomes.5 Since previous studies in the oncology literature show low or modest correlations between PUA reduction and patient-oriented outcomes, we must question whether PUA reduction serves as a meaningful surrogate endpoint.
Treatment of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Two meta-analyses focusing on the treatment of TLS by Dinnel et al5 and Lopez-Olivo et al8 each included only three unique RCTs (two of the three RCTs were referenced in both meta-analyses). Moreover, both studies included only one RCT comparing rasburicase directly to allopurinol (a 2010 RCT by Cortes et al9) while the other RCTs compared the impact of different rasburicase dosing regimens. Researchers powered the head-to-head RCT by Cortes et al9 to detect a difference in PUA levels across three different arms: rasburicase, rasburicase plus allopurinol, or allopurinol alone. All three treatment arms resulted in a statistically significant reduction in serum PUA levels (87%, 78%, 66%, respectively; P = .001) without a change in the secondary, underpowered clinical outcomes such as clinical TLS or reduced renal function (defined in this study as increased creatinine, renal failure/impairment, or acute renal failure).
More recently, retrospective analyses of patients with AKI secondary to TLS found no difference in creatinine improvement, renal recovery, or prevention of RRT based on whether the patients received either rasburicase or allopurinol.10,11 While rasburicase is associated with greater PUA reduction compared to allopurinol, according to meaningful RCT and observational data as discussed previously and described further in the following section, this does not translate to clinically important risk reduction.
Prevention of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Furthermore, there exists little compelling evidence to support the use of rasburicase for preventing AKI secondary to TLS. Even among patients at high-risk for TLS (the only group for whom rasburicase is currently recommended),5 rasburicase does not definitively prevent AKI. Data suggest that despite lowering uric acid levels, rasburicase does not consistently prevent renal injury11 or decrease the total number of subsequent inpatient days.12 The only phase 3 trial that compared the efficacy of rasburicase to allopurinol for the prevention of TLS and included clinically meaningful endpoints (eg, renal failure) found that, while rasburicase reduced uric acid levels faster than allopurinol, it did not decrease rates of clinical TLS.9
The published literature offers limited efficacy data of rasburicase in preventing TLS in low-risk patients; however, the absence of benefit of rasburicase in preventing renal failure in high-risk patients warrants skepticism as to its potential efficacy in low-risk patients.8,10
Costs-Effectiveness and Other Ethical Considerations
Rasburicase is an expensive treatment. The estimated cost of the FDA-recommended dosing is around $37,500.13 Moreover, studies comparing the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase to allopurinol focus primarily on patients at high-risk for TLS, which overestimates the cost-effectiveness of rasburicase in patients at low-to-intermediate risk for TLS.14,15 Unfortunately, some providers inappropriately prescribe rasburicase regularly to patients at low or intermediate risk for TLS. Based on observational studies of rasburicase in various clinical scenarios, including inpatient and emergency department settings, inappropriate use of rasburicase (eg, in the setting of hyperuricemia without evidence of a high-risk TLS tumor, no prior trial of allopurinol, preserved renal function, no laboratory evaluation) ranges from 32% to 70%.14,15
Finally, while <1% of patients experience rasburicase-induced anaphylaxis, 20% to 50% of patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms and viral-syndrome-like symptoms.16 Meanwhile, major side effects from allopurinol that occur with 1% to 10% frequency include maculopapular rash, pruritis, gout, nausea, vomiting, and renal failure syndrome.17 Even if the cost for rasburicase and allopurinol were similar, the lack of improved efficacy and the side-effect profiles of the two medications should make us question whether to prescribe rasburicase preferentially over allopurinol.
WHEN MIGHT URATE OXIDASE BE HELPFUL IN TUMOR LYSIS SYNDROME
While some experts recommend rasburicase prophylaxis in patients at high risk for developing TLS, such recommendations rely on low-quality evidence.2 When prescribing rasburicase, the hospitalist must ensure correct dosing. The FDA approved rasburicase for weight-based dosing at 0.2 mg/kg, though current evidence favors a single, fixed dose of 3 mg.16,17 Compared to weight-based dosing, which has an estimated cost-effectiveness ratio ranging from $27,982.77 to $119,643.59 per quality-adjusted life-year, single dosing has equivalent efficacy at approximately 50% lower cost per dose.11,17,18
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO INSTEAD
As a preventive treatment for TLS, clinicians should only consider prescribing rasburicase as a single fixed dose of 3 mg to high-risk patients.17 In the event of AKI secondary to TLS, clinicians should proceed with the mainstay treatment of resuscitation with aggressive fluid resuscitation, with a goal urine output of at least 2 mL/kg/h.1 Fluid resuscitation should be used cautiously in patients with oliguric or anuric AKI, pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure, and hemodynamically significant valvular disease. Clinicians should provide continuous cardiac monitoring during the initial presentation to monitor for electrocardiographic changes in the setting of hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia, and they should consult nephrology, oncology, and critical care services early in the disease course to maximize coordination of care.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Prevention
- Identify patients at high-risk of TLS (Table 1) and consider a single 3-mg dose of rasburicase.
- Manage low- and intermediate-risk patients with allopurinol and hydration.
Treatment
- Identify patients with TLS using the clinical and laboratory findings outlined in the Cairo-Bishop classification system (Table 2).
- Initiate aggressive fluid resuscitation and manage electrolyte abnormalities.
- If urate-lowering therapy is part of local hospital guidelines for TLS management, consider a single dose regimen of rasburicase utilizing shared decision-making.
CONCLUSION
Tumor lysis syndrome remains a metabolic emergency that requires rapid diagnosis and management to prevent morbidity and mortality. Current data show rasburicase rapidly decreases PUA compared to allopurinol. However, the current literature does not provide compelling evidence that rapidly lowering uric acid with rasburicase to prevent TLS or to treat AKI secondary to TLS improves patient-oriented outcomes.
Do you think this is a low-value practice? Is this truly a “Thing We Do for No Reason™”? Share what you do in your practice and join in the conversation online by retweeting it on Twitter (#TWDFNR) and liking it on Facebook. We invite you to propose ideas for other “Things We Do for No Reason™” topics by emailing [email protected]
1. Howard SC, Jones DP, Pui CH. The tumor lysis syndrome. N Engl J Med.2011;364(19):1844-1854. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra0904569
2. Cairo MS, Coiffier B, Reiter A, Younes A; TLS Expert Panel. Recommendations for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149(4):578-586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08143.x
3. Cairo MS, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol.. 2004;127(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05094.x
4. Durani U, Shah ND, Go RS. In-hospital outcomes of tumor lysis syndrome: a population-based study using the National Inpatient Sample. Oncologist. 2017;22(12):1506-1509. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0147
5. Dinnel J, Moore BL, Skiver BM, Bose P. Rasburicase in the management of tumor lysis: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid.. 2015;10:23-38. https://doi.org/10.2147/ce.s54995
6. Goldman SC, Holcenberg JS, Finklestein JZ, et al. A randomized comparison between rasburicase and allopurinol in children with lymphoma or leukemia at high risk for tumor lysis. Blood. 2001;97(10):2998-3003. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v97.10.2998
7. Haslam A, Hey SP, Gill J, Prasad V. A systematic review of trial-level meta-analyses measuring the strength of association between surrogate end-points and overall survival in oncology. Eur J Cancer. 1990. 2019;106:196-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.11.012
8. Lopez-Olivo MA, Pratt G, Palla SL, Salahudeen A. Rasburicase in tumor lysis syndrome of the adult: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(3):481-492. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.378
9. Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, et al. Control of plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor lysis syndrome: efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone—results of a multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4207-4213. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.8896
10. Martens KL, Khalighi PR, Li S, et al. Comparative effectiveness of rasburicase versus allopurinol for cancer patients with renal dysfunction and hyperuricemia. Leuk Res. 2020;89:106298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106298
11. Personett HA, Barreto EF, McCullough K, Dierkhising R, Leung N, Habermann TM. Impact of early rasburicase on incidence and outcomes of clinical tumor lysis syndrome in lymphoma. Blood. 2019;60(9)2271-2277. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2019.1574000
12. Howard SC, Cockerham AR, Yvonne Barnes DN, Ryan M, Irish W, Gordan L. Real-world analysis of outpatient rasburicase to prevent and manage tumor lysis syndrome in newly diagnosed adults with leukemia or lymphoma. J Clin Pathways. 2020;6(2):46-51.
13. Abu-Hashyeh AM, Shenouda M, Al-Sharedi M. The efficacy of cost-effective fixed dose of rasburicase compared to weight-based dose in treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3.5):QIM20-119. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.7516
14. Patel KK, Brown TJ, Gupta A, et al. Decreasing inappropriate use of rasburicase to promote cost-effective care. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15(2):e178-e186. https://doi.org/10.1200/jop.18.00528
15. Khalighi PR, Martens KL, White AA, et al. Utilization patterns and clinical outcomes of rasburicase administration according to tumor risk stratification. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020;26(3):529-535. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155219851543
16. Elitek. Prescribing information. Sanofi-Aventis U.S., LLC; 2019. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://products.sanofi.us/elitek/Elitek.html
17. Allopurinol. Drugs & Diseases. Medscape. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://reference.medscape.com/drug/zyloprim-aloprim-allopurinol-342811
18. Jones GL, Will A, Jackson GH, Webb NJA, Rule S; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169(5):661‐671. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13403
19. Boutin A, Blackman A, O’Sullivan DM, Forcello N. The value of fixed rasburicase dosing versus weight-based dosing in the treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019;25(3):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155217752075
1. Howard SC, Jones DP, Pui CH. The tumor lysis syndrome. N Engl J Med.2011;364(19):1844-1854. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra0904569
2. Cairo MS, Coiffier B, Reiter A, Younes A; TLS Expert Panel. Recommendations for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149(4):578-586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08143.x
3. Cairo MS, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol.. 2004;127(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05094.x
4. Durani U, Shah ND, Go RS. In-hospital outcomes of tumor lysis syndrome: a population-based study using the National Inpatient Sample. Oncologist. 2017;22(12):1506-1509. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0147
5. Dinnel J, Moore BL, Skiver BM, Bose P. Rasburicase in the management of tumor lysis: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid.. 2015;10:23-38. https://doi.org/10.2147/ce.s54995
6. Goldman SC, Holcenberg JS, Finklestein JZ, et al. A randomized comparison between rasburicase and allopurinol in children with lymphoma or leukemia at high risk for tumor lysis. Blood. 2001;97(10):2998-3003. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v97.10.2998
7. Haslam A, Hey SP, Gill J, Prasad V. A systematic review of trial-level meta-analyses measuring the strength of association between surrogate end-points and overall survival in oncology. Eur J Cancer. 1990. 2019;106:196-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.11.012
8. Lopez-Olivo MA, Pratt G, Palla SL, Salahudeen A. Rasburicase in tumor lysis syndrome of the adult: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(3):481-492. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.378
9. Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, et al. Control of plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor lysis syndrome: efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone—results of a multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4207-4213. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.8896
10. Martens KL, Khalighi PR, Li S, et al. Comparative effectiveness of rasburicase versus allopurinol for cancer patients with renal dysfunction and hyperuricemia. Leuk Res. 2020;89:106298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106298
11. Personett HA, Barreto EF, McCullough K, Dierkhising R, Leung N, Habermann TM. Impact of early rasburicase on incidence and outcomes of clinical tumor lysis syndrome in lymphoma. Blood. 2019;60(9)2271-2277. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2019.1574000
12. Howard SC, Cockerham AR, Yvonne Barnes DN, Ryan M, Irish W, Gordan L. Real-world analysis of outpatient rasburicase to prevent and manage tumor lysis syndrome in newly diagnosed adults with leukemia or lymphoma. J Clin Pathways. 2020;6(2):46-51.
13. Abu-Hashyeh AM, Shenouda M, Al-Sharedi M. The efficacy of cost-effective fixed dose of rasburicase compared to weight-based dose in treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(3.5):QIM20-119. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.7516
14. Patel KK, Brown TJ, Gupta A, et al. Decreasing inappropriate use of rasburicase to promote cost-effective care. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15(2):e178-e186. https://doi.org/10.1200/jop.18.00528
15. Khalighi PR, Martens KL, White AA, et al. Utilization patterns and clinical outcomes of rasburicase administration according to tumor risk stratification. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020;26(3):529-535. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155219851543
16. Elitek. Prescribing information. Sanofi-Aventis U.S., LLC; 2019. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://products.sanofi.us/elitek/Elitek.html
17. Allopurinol. Drugs & Diseases. Medscape. Accessed June 1, 2021. https://reference.medscape.com/drug/zyloprim-aloprim-allopurinol-342811
18. Jones GL, Will A, Jackson GH, Webb NJA, Rule S; British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169(5):661‐671. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13403
19. Boutin A, Blackman A, O’Sullivan DM, Forcello N. The value of fixed rasburicase dosing versus weight-based dosing in the treatment and prevention of tumor lysis syndrome. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019;25(3):577-583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155217752075
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine
Debriefing During a Mental Health Crisis
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals across the country face a crisis in identifying resources for the surging needs of patients with mental health conditions. Compared with 2019, survey and utilization data from 2020 suggest an increase in suicidal ideation and other symptoms among adults,1 and an escalation in mental health-related visits to pediatric emergency departments, respectively.2 Unfortunately, mental health resources have dwindled during this period. Available inpatient psychiatric beds and 24-hour residential treatment beds—already on the decline over the past 5 years—have been massively affected by the pandemic due to capacity constraints and facility closures.3
These factors have placed general medical hospitals (hospitals) at the front lines of a mental health crisis4 for which most are ill prepared. Indeed, once a patient with acute mental health needs is “medically cleared,” they must wait for an available bed at a psychiatric or residential treatment facility.3 This waiting period often delays necessary patient care, as most consultation-liaison psychiatry models are not designed to provide intensive services.5
This waiting period can also place hospital staff in unfamiliar and potentially unsafe scenarios related to physical and psychological stressors. Staff may encounter patient behaviors that risk harm to patients and staff (ie, behavioral crisis events), which may require seclusion (ie, confinement to a locked room) or restraints (chemical, physical, and mechanical). Even in inpatient psychiatric units, an estimated 70% of nurses have been assaulted at least once during their career.6 Such violent behaviors and the interventions required to subdue them can be traumatizing for both patients and staff.7 In fact, the “cost of caring” may be higher for mental health nurses, who often suffer from secondary posttraumatic stress.8 Staff lacking mental health training may encounter additional stressors from feeling powerless to help their patients.
Facing this crisis, hospitals must develop a strategic response that encompasses the needs of both patients and staff. Beyond intensive interventions (eg, additional staffing resources), this response should include lower-effort interventions. In this perspective, we review two debriefing practices—clinical event debriefing and psychological debriefing—that hospitals can feasibly implement during this crisis. These respective practices can ensure safe and effective care of patients by reducing use of restraints and seclusion while also providing crucial support for staff.
CLINICAL EVENT DEBRIEFING
Broadly defined as a facilitated discussion of significant clinical events, clinical event debriefing (CED) can improve both individual and team performance in resuscitation events and patient outcomes.9-11 While CED is often utilized for clinical deterioration events, it can also apply to behavioral crises in a diversity of settings.6
In recent decades, researchers have developed several frameworks for reducing seclusion and restraint practices in psychiatric care settings.6 A common framework is Huckshorn’s Six Core Strategies,6,12,13 which can reduce seclusion and restraint use14 and is feasible to implement.15 This framework advocates for an immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. A unit supervisor or senior staff member not involved in the event should lead the CED, which has several goals. The first priorities, however, are ensuring the physical safety of all staff and returning the unit to normal operations. More broadly, the CED group should review event documentation and interview staff who were present at the time of the event. These processes can help identify antecedents as well as short- and long-term practices, systems, and environmental modifications to prevent reoccurence.12 However, little is known about this practice outside of inpatient psychiatric units.
Our pediatric hospital implemented a CED process in our medical behavioral unit (MBU), a 10-bed unit designed for patients with comorbid mental health needs requiring a higher level of psychosocial resources. The MBU is not an inpatient psychiatric unit, yet more than 50% of patients admitted to the MBU at any given time are hospitalized with a primary psychiatric diagnosis requiring intensive services due to a lack of resources in the community.
Preventing use of restraints is an institutional priority for all areas of our hospital. To reduce restraint use in the MBU, staff are asked to perform immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. This process involves both clinical (eg, nurses, physicians, psychiatric technicians) and nonclinical staff (eg, unit clerks, security officers). All staff involved in the event are invited to attend. A senior staff member not involved in the event typically organizes and leads the CED. The group uses a facilitative guide to (1) review the patient’s history; (2) identify potential triggers for the event; (3) reflect on areas of strength and weakness in unit response; (4) identify systems issues impacting the patient or the unit response; and (5) generate a strategy to prevent reoccurrence. The process is designed to take 5 to 10 minutes. The guide also serves as a data collection tool that unit leaders use to screen for generalizable learnings and improvement ideas (Appendix). For example, if a behavioral trigger is identified for a patient, unit leaders disseminate this information to create situational awareness and to ensure care plans are updated.
PSYCHOLOGICAL DEBRIEFING
Psychological debriefing is an application of Critical Incident Stress Management, a comprehensive approach that was developed in the 1970s to help emergency service workers process the thoughts and emotions arising from their exposure to trauma in their work.8,16 More recently, it has become a standard practice in many settings, including healthcare. Notably, psychological debriefing and event debriefing are often conflated. While not mutually exclusive, psychological debriefing has the unique aim of providing support to groups who work together in stressful situations.
Strategies for psychological debriefing are less well described in healthcare. However, our hospital has found it to be a useful tool for MBU staff. Operationally, this process takes the form of a weekly multidisciplinary team meeting with unit clinical staff. Typically, a psychologist or social worker initiates this meeting, which is held at a dedicated time and in a protected space. Discussion centers on patients who have been admitted to the unit for more than 30 days. A goal of the meeting is to review and update patient care plans, but there is also an important goal of emotional processing (Appendix).
In this meeting, staff reflect collectively on the unique stressors they encounter in their work, and they generate situational awareness and potential interventions for these stressors. The psychosocial providers often share recommendations, such as strategies to promote effective communication with patients and families. Peer support is a major component of this meeting and is often utilized to navigate stressful situations, such as disagreements with families regarding behavioral management. Staff also review and reinforce the Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports framework—a preventive framework that can reduce seclusion and restraint use in pediatric psychiatric units, among other positive outcomes.17 This framework includes setting expectations for patients and families regarding behaviors on the unit. In reviewing these guidelines, staff are encouraged to recognize and report inappropriate behaviors (from patients or families) that can be traumatizing, especially over prolonged hospitalizations. This framework also provides a common language for staff to express behavioral expectations in a positive manner (eg, “Let’s use our walking feet” rather than “No running”). Overall, staff view this meeting as a resilience-building activity that empowers them in their routine work.
IMPLEMENTATION CONSIDERATIONS
While the MBU is a specialized unit with dedicated psychosocial resources, the debriefing practices we describe can be translated to multiple care settings. However, successful implementation relies on intentional process design. First, debriefing indications must be made clear to staff (eg, events of restraint). There should be a role or group accountable for organizing and leading debriefings, which should be held at a time that promotes participation from frontline staff,particularly for CED. Debriefings—especially psychological debriefings—should be held in a protected space. They should have a clear organization, such as use of a survey-based debriefing guide that allows for data collection. Importantly, there should be a unit or hospital leader accountable for disseminating learnings and improvement ideas to relevant staff and ensuring action items are completed. Finally, accountable leaders should evaluate the process’ feasibility, efficacy, and sustainability to inform implementation.
Hospitals must also consider how to train debriefing leaders to facilitate difficult conversations. Some hospitals may have formal communication training programs, but it may also be helpful to leverage the skills of social workers and psychosocial staff.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Debriefing relies on a climate in which staff of diverse backgrounds and professional status feel comfortable speaking up. Psychological safety is critical in any crisis, and hospital leaders should consider how to make staff feel comfortable during this mental health crisis.18 Leaders must also be prepared to support staff beyond debriefing if resources are required for secondary posttraumatic stress, burnout, or compassion fatigue.8,19,20 Employee assistance programs may be a useful resource.
CONCLUSION
Debriefing practices can help hospitals contend with the unique challenges facing patients and staff in a mental health crisis. While debriefing may vary based on need and setting, hospitals should consider CED as a strategy for reducing seclusion and restraint use, which adversely impact patients and staff. Psychological debriefing can also help staff mitigate the psychosocial stressors of their work.
1. Czeisler MÉ, Lane RI, Petrosky E, et al. Mental health, substance use, and suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, June 24–30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1049-1057. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6932a1
2. Leeb RT, Bitsko RH, Radhakrishnan L, et al. Mental health–related emergency department visits among children aged <18 years during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, January 1–October 17, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1675-1680. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6945a3
3. Rapoport R. ‘Every day is an emergency’: The pandemic is worsening psychiatric bed shortages nationwide. Stat News. December 23, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2021. https://www.statnews.com/2020/12/23/mental-health-covid19-psychiatric-beds/
4. A step to ease the pandemic mental health crisis. Scientific American. February 1, 2021. Accessed April 14, 2021. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/a-step-to-ease-the-pandemic-mental-health-crisis/
5. Sharpe M, Toynbee M, Walker J. Proactive Integrated Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry: A new service model for the psychiatric care of general hospital inpatients. Gen Hosp Psych. 2020;66:9-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.005
6. Mangaoil RA, Cleverley K, Peter E. Immediate staff debriefing following seclusions or restraint use in inpatient mental health settings: a scoping review. Clin Nurs Res. 2020;29(7):479-495. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773818791085
7. Needham I, Abderhalden C, Zeller A, et al. The effect of a training course on nursing students’ attitudes toward, perceptions of, and confidence in managing patient aggression. J Nurs Educ. 2005;44:415-420.
8. Missouridou E. Secondary posttraumatic stress and nurses’ emotional responses to patient’s trauma. J Trauma Nurs. 2017;24(2):110-115. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTN.0000000000000274
9. Blankenship BAC, Fernandez RP, Joy BF, et al. Multidisciplinary review of code events in a heart center. Am J Crit Care. 2016;25(4):90-98. https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2016302
10. Wolfe H, Zebuhr C, Topjian AA, et al. Interdisciplinary ICU cardiac arrest debriefing improves survival outcomes. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(7):1688-1695. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000327
11. Tannenbaum SI, Cerasoli CP. Do team and individual debriefs enhance performance? A meta-analysis. Hum Factors. 2013;55(1):231-245. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720812448394
12. Huckshorn KA. Reducing seclusion restraint in mental health use settings: core strategies for prevention. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 2004;42:22-33.
13. Goulet MH, Larue C, Dumais A. Evaluation of seclusion and restraint reduction programs in mental health: a systematic review. Agress Violent Behav. 2017;34:139-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2017.01.019
14. Azeem MW, Aujila A, Rammerth M, et al, Effectiveness of six core strategies based on trauma informed care in reducing seclusions and restraints at a child and adolescent psychiatric hospital. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs. 2011;24:11-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcap.12190
15. Wieman DA, Camacho-Gonsalves T, Huckshorn KA, et al. Multisite study of an evidence-based practice to reduce seclusion and restraint in psychiatric inpatient facilities. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(3):345-351. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300210
16. Everly GS. A primer on critical incident stress management: what’s really in a name? Int J Emerg Ment Health. 1999;1(2):77-79.
17. Reynolds EK, Grados MA, Praglowski N, et al. Use of modified positive behavioral interventions and supports in a psychiatric inpatient unit for high-risk youths. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):570-573. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201500039
18. Devaraj LR, Cooper C, Begin AS. Creating psychological safety on medical teams in times of crisis. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(1):47-49. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3541
19. Bride BE, Radey M, Figley CR. Measuring compassion fatigue. Clin Soc Work J. 2007;35:155-163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-007-0091-7
20. Figley CR. Compassion fatigue: psychotherapists’ lack of self care. J Clin Psychol. 2002;58(11):1433-1441. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.10090
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals across the country face a crisis in identifying resources for the surging needs of patients with mental health conditions. Compared with 2019, survey and utilization data from 2020 suggest an increase in suicidal ideation and other symptoms among adults,1 and an escalation in mental health-related visits to pediatric emergency departments, respectively.2 Unfortunately, mental health resources have dwindled during this period. Available inpatient psychiatric beds and 24-hour residential treatment beds—already on the decline over the past 5 years—have been massively affected by the pandemic due to capacity constraints and facility closures.3
These factors have placed general medical hospitals (hospitals) at the front lines of a mental health crisis4 for which most are ill prepared. Indeed, once a patient with acute mental health needs is “medically cleared,” they must wait for an available bed at a psychiatric or residential treatment facility.3 This waiting period often delays necessary patient care, as most consultation-liaison psychiatry models are not designed to provide intensive services.5
This waiting period can also place hospital staff in unfamiliar and potentially unsafe scenarios related to physical and psychological stressors. Staff may encounter patient behaviors that risk harm to patients and staff (ie, behavioral crisis events), which may require seclusion (ie, confinement to a locked room) or restraints (chemical, physical, and mechanical). Even in inpatient psychiatric units, an estimated 70% of nurses have been assaulted at least once during their career.6 Such violent behaviors and the interventions required to subdue them can be traumatizing for both patients and staff.7 In fact, the “cost of caring” may be higher for mental health nurses, who often suffer from secondary posttraumatic stress.8 Staff lacking mental health training may encounter additional stressors from feeling powerless to help their patients.
Facing this crisis, hospitals must develop a strategic response that encompasses the needs of both patients and staff. Beyond intensive interventions (eg, additional staffing resources), this response should include lower-effort interventions. In this perspective, we review two debriefing practices—clinical event debriefing and psychological debriefing—that hospitals can feasibly implement during this crisis. These respective practices can ensure safe and effective care of patients by reducing use of restraints and seclusion while also providing crucial support for staff.
CLINICAL EVENT DEBRIEFING
Broadly defined as a facilitated discussion of significant clinical events, clinical event debriefing (CED) can improve both individual and team performance in resuscitation events and patient outcomes.9-11 While CED is often utilized for clinical deterioration events, it can also apply to behavioral crises in a diversity of settings.6
In recent decades, researchers have developed several frameworks for reducing seclusion and restraint practices in psychiatric care settings.6 A common framework is Huckshorn’s Six Core Strategies,6,12,13 which can reduce seclusion and restraint use14 and is feasible to implement.15 This framework advocates for an immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. A unit supervisor or senior staff member not involved in the event should lead the CED, which has several goals. The first priorities, however, are ensuring the physical safety of all staff and returning the unit to normal operations. More broadly, the CED group should review event documentation and interview staff who were present at the time of the event. These processes can help identify antecedents as well as short- and long-term practices, systems, and environmental modifications to prevent reoccurence.12 However, little is known about this practice outside of inpatient psychiatric units.
Our pediatric hospital implemented a CED process in our medical behavioral unit (MBU), a 10-bed unit designed for patients with comorbid mental health needs requiring a higher level of psychosocial resources. The MBU is not an inpatient psychiatric unit, yet more than 50% of patients admitted to the MBU at any given time are hospitalized with a primary psychiatric diagnosis requiring intensive services due to a lack of resources in the community.
Preventing use of restraints is an institutional priority for all areas of our hospital. To reduce restraint use in the MBU, staff are asked to perform immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. This process involves both clinical (eg, nurses, physicians, psychiatric technicians) and nonclinical staff (eg, unit clerks, security officers). All staff involved in the event are invited to attend. A senior staff member not involved in the event typically organizes and leads the CED. The group uses a facilitative guide to (1) review the patient’s history; (2) identify potential triggers for the event; (3) reflect on areas of strength and weakness in unit response; (4) identify systems issues impacting the patient or the unit response; and (5) generate a strategy to prevent reoccurrence. The process is designed to take 5 to 10 minutes. The guide also serves as a data collection tool that unit leaders use to screen for generalizable learnings and improvement ideas (Appendix). For example, if a behavioral trigger is identified for a patient, unit leaders disseminate this information to create situational awareness and to ensure care plans are updated.
PSYCHOLOGICAL DEBRIEFING
Psychological debriefing is an application of Critical Incident Stress Management, a comprehensive approach that was developed in the 1970s to help emergency service workers process the thoughts and emotions arising from their exposure to trauma in their work.8,16 More recently, it has become a standard practice in many settings, including healthcare. Notably, psychological debriefing and event debriefing are often conflated. While not mutually exclusive, psychological debriefing has the unique aim of providing support to groups who work together in stressful situations.
Strategies for psychological debriefing are less well described in healthcare. However, our hospital has found it to be a useful tool for MBU staff. Operationally, this process takes the form of a weekly multidisciplinary team meeting with unit clinical staff. Typically, a psychologist or social worker initiates this meeting, which is held at a dedicated time and in a protected space. Discussion centers on patients who have been admitted to the unit for more than 30 days. A goal of the meeting is to review and update patient care plans, but there is also an important goal of emotional processing (Appendix).
In this meeting, staff reflect collectively on the unique stressors they encounter in their work, and they generate situational awareness and potential interventions for these stressors. The psychosocial providers often share recommendations, such as strategies to promote effective communication with patients and families. Peer support is a major component of this meeting and is often utilized to navigate stressful situations, such as disagreements with families regarding behavioral management. Staff also review and reinforce the Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports framework—a preventive framework that can reduce seclusion and restraint use in pediatric psychiatric units, among other positive outcomes.17 This framework includes setting expectations for patients and families regarding behaviors on the unit. In reviewing these guidelines, staff are encouraged to recognize and report inappropriate behaviors (from patients or families) that can be traumatizing, especially over prolonged hospitalizations. This framework also provides a common language for staff to express behavioral expectations in a positive manner (eg, “Let’s use our walking feet” rather than “No running”). Overall, staff view this meeting as a resilience-building activity that empowers them in their routine work.
IMPLEMENTATION CONSIDERATIONS
While the MBU is a specialized unit with dedicated psychosocial resources, the debriefing practices we describe can be translated to multiple care settings. However, successful implementation relies on intentional process design. First, debriefing indications must be made clear to staff (eg, events of restraint). There should be a role or group accountable for organizing and leading debriefings, which should be held at a time that promotes participation from frontline staff,particularly for CED. Debriefings—especially psychological debriefings—should be held in a protected space. They should have a clear organization, such as use of a survey-based debriefing guide that allows for data collection. Importantly, there should be a unit or hospital leader accountable for disseminating learnings and improvement ideas to relevant staff and ensuring action items are completed. Finally, accountable leaders should evaluate the process’ feasibility, efficacy, and sustainability to inform implementation.
Hospitals must also consider how to train debriefing leaders to facilitate difficult conversations. Some hospitals may have formal communication training programs, but it may also be helpful to leverage the skills of social workers and psychosocial staff.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Debriefing relies on a climate in which staff of diverse backgrounds and professional status feel comfortable speaking up. Psychological safety is critical in any crisis, and hospital leaders should consider how to make staff feel comfortable during this mental health crisis.18 Leaders must also be prepared to support staff beyond debriefing if resources are required for secondary posttraumatic stress, burnout, or compassion fatigue.8,19,20 Employee assistance programs may be a useful resource.
CONCLUSION
Debriefing practices can help hospitals contend with the unique challenges facing patients and staff in a mental health crisis. While debriefing may vary based on need and setting, hospitals should consider CED as a strategy for reducing seclusion and restraint use, which adversely impact patients and staff. Psychological debriefing can also help staff mitigate the psychosocial stressors of their work.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals across the country face a crisis in identifying resources for the surging needs of patients with mental health conditions. Compared with 2019, survey and utilization data from 2020 suggest an increase in suicidal ideation and other symptoms among adults,1 and an escalation in mental health-related visits to pediatric emergency departments, respectively.2 Unfortunately, mental health resources have dwindled during this period. Available inpatient psychiatric beds and 24-hour residential treatment beds—already on the decline over the past 5 years—have been massively affected by the pandemic due to capacity constraints and facility closures.3
These factors have placed general medical hospitals (hospitals) at the front lines of a mental health crisis4 for which most are ill prepared. Indeed, once a patient with acute mental health needs is “medically cleared,” they must wait for an available bed at a psychiatric or residential treatment facility.3 This waiting period often delays necessary patient care, as most consultation-liaison psychiatry models are not designed to provide intensive services.5
This waiting period can also place hospital staff in unfamiliar and potentially unsafe scenarios related to physical and psychological stressors. Staff may encounter patient behaviors that risk harm to patients and staff (ie, behavioral crisis events), which may require seclusion (ie, confinement to a locked room) or restraints (chemical, physical, and mechanical). Even in inpatient psychiatric units, an estimated 70% of nurses have been assaulted at least once during their career.6 Such violent behaviors and the interventions required to subdue them can be traumatizing for both patients and staff.7 In fact, the “cost of caring” may be higher for mental health nurses, who often suffer from secondary posttraumatic stress.8 Staff lacking mental health training may encounter additional stressors from feeling powerless to help their patients.
Facing this crisis, hospitals must develop a strategic response that encompasses the needs of both patients and staff. Beyond intensive interventions (eg, additional staffing resources), this response should include lower-effort interventions. In this perspective, we review two debriefing practices—clinical event debriefing and psychological debriefing—that hospitals can feasibly implement during this crisis. These respective practices can ensure safe and effective care of patients by reducing use of restraints and seclusion while also providing crucial support for staff.
CLINICAL EVENT DEBRIEFING
Broadly defined as a facilitated discussion of significant clinical events, clinical event debriefing (CED) can improve both individual and team performance in resuscitation events and patient outcomes.9-11 While CED is often utilized for clinical deterioration events, it can also apply to behavioral crises in a diversity of settings.6
In recent decades, researchers have developed several frameworks for reducing seclusion and restraint practices in psychiatric care settings.6 A common framework is Huckshorn’s Six Core Strategies,6,12,13 which can reduce seclusion and restraint use14 and is feasible to implement.15 This framework advocates for an immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. A unit supervisor or senior staff member not involved in the event should lead the CED, which has several goals. The first priorities, however, are ensuring the physical safety of all staff and returning the unit to normal operations. More broadly, the CED group should review event documentation and interview staff who were present at the time of the event. These processes can help identify antecedents as well as short- and long-term practices, systems, and environmental modifications to prevent reoccurence.12 However, little is known about this practice outside of inpatient psychiatric units.
Our pediatric hospital implemented a CED process in our medical behavioral unit (MBU), a 10-bed unit designed for patients with comorbid mental health needs requiring a higher level of psychosocial resources. The MBU is not an inpatient psychiatric unit, yet more than 50% of patients admitted to the MBU at any given time are hospitalized with a primary psychiatric diagnosis requiring intensive services due to a lack of resources in the community.
Preventing use of restraints is an institutional priority for all areas of our hospital. To reduce restraint use in the MBU, staff are asked to perform immediate CED following behavioral crisis events. This process involves both clinical (eg, nurses, physicians, psychiatric technicians) and nonclinical staff (eg, unit clerks, security officers). All staff involved in the event are invited to attend. A senior staff member not involved in the event typically organizes and leads the CED. The group uses a facilitative guide to (1) review the patient’s history; (2) identify potential triggers for the event; (3) reflect on areas of strength and weakness in unit response; (4) identify systems issues impacting the patient or the unit response; and (5) generate a strategy to prevent reoccurrence. The process is designed to take 5 to 10 minutes. The guide also serves as a data collection tool that unit leaders use to screen for generalizable learnings and improvement ideas (Appendix). For example, if a behavioral trigger is identified for a patient, unit leaders disseminate this information to create situational awareness and to ensure care plans are updated.
PSYCHOLOGICAL DEBRIEFING
Psychological debriefing is an application of Critical Incident Stress Management, a comprehensive approach that was developed in the 1970s to help emergency service workers process the thoughts and emotions arising from their exposure to trauma in their work.8,16 More recently, it has become a standard practice in many settings, including healthcare. Notably, psychological debriefing and event debriefing are often conflated. While not mutually exclusive, psychological debriefing has the unique aim of providing support to groups who work together in stressful situations.
Strategies for psychological debriefing are less well described in healthcare. However, our hospital has found it to be a useful tool for MBU staff. Operationally, this process takes the form of a weekly multidisciplinary team meeting with unit clinical staff. Typically, a psychologist or social worker initiates this meeting, which is held at a dedicated time and in a protected space. Discussion centers on patients who have been admitted to the unit for more than 30 days. A goal of the meeting is to review and update patient care plans, but there is also an important goal of emotional processing (Appendix).
In this meeting, staff reflect collectively on the unique stressors they encounter in their work, and they generate situational awareness and potential interventions for these stressors. The psychosocial providers often share recommendations, such as strategies to promote effective communication with patients and families. Peer support is a major component of this meeting and is often utilized to navigate stressful situations, such as disagreements with families regarding behavioral management. Staff also review and reinforce the Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports framework—a preventive framework that can reduce seclusion and restraint use in pediatric psychiatric units, among other positive outcomes.17 This framework includes setting expectations for patients and families regarding behaviors on the unit. In reviewing these guidelines, staff are encouraged to recognize and report inappropriate behaviors (from patients or families) that can be traumatizing, especially over prolonged hospitalizations. This framework also provides a common language for staff to express behavioral expectations in a positive manner (eg, “Let’s use our walking feet” rather than “No running”). Overall, staff view this meeting as a resilience-building activity that empowers them in their routine work.
IMPLEMENTATION CONSIDERATIONS
While the MBU is a specialized unit with dedicated psychosocial resources, the debriefing practices we describe can be translated to multiple care settings. However, successful implementation relies on intentional process design. First, debriefing indications must be made clear to staff (eg, events of restraint). There should be a role or group accountable for organizing and leading debriefings, which should be held at a time that promotes participation from frontline staff,particularly for CED. Debriefings—especially psychological debriefings—should be held in a protected space. They should have a clear organization, such as use of a survey-based debriefing guide that allows for data collection. Importantly, there should be a unit or hospital leader accountable for disseminating learnings and improvement ideas to relevant staff and ensuring action items are completed. Finally, accountable leaders should evaluate the process’ feasibility, efficacy, and sustainability to inform implementation.
Hospitals must also consider how to train debriefing leaders to facilitate difficult conversations. Some hospitals may have formal communication training programs, but it may also be helpful to leverage the skills of social workers and psychosocial staff.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Debriefing relies on a climate in which staff of diverse backgrounds and professional status feel comfortable speaking up. Psychological safety is critical in any crisis, and hospital leaders should consider how to make staff feel comfortable during this mental health crisis.18 Leaders must also be prepared to support staff beyond debriefing if resources are required for secondary posttraumatic stress, burnout, or compassion fatigue.8,19,20 Employee assistance programs may be a useful resource.
CONCLUSION
Debriefing practices can help hospitals contend with the unique challenges facing patients and staff in a mental health crisis. While debriefing may vary based on need and setting, hospitals should consider CED as a strategy for reducing seclusion and restraint use, which adversely impact patients and staff. Psychological debriefing can also help staff mitigate the psychosocial stressors of their work.
1. Czeisler MÉ, Lane RI, Petrosky E, et al. Mental health, substance use, and suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, June 24–30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1049-1057. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6932a1
2. Leeb RT, Bitsko RH, Radhakrishnan L, et al. Mental health–related emergency department visits among children aged <18 years during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, January 1–October 17, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1675-1680. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6945a3
3. Rapoport R. ‘Every day is an emergency’: The pandemic is worsening psychiatric bed shortages nationwide. Stat News. December 23, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2021. https://www.statnews.com/2020/12/23/mental-health-covid19-psychiatric-beds/
4. A step to ease the pandemic mental health crisis. Scientific American. February 1, 2021. Accessed April 14, 2021. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/a-step-to-ease-the-pandemic-mental-health-crisis/
5. Sharpe M, Toynbee M, Walker J. Proactive Integrated Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry: A new service model for the psychiatric care of general hospital inpatients. Gen Hosp Psych. 2020;66:9-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.005
6. Mangaoil RA, Cleverley K, Peter E. Immediate staff debriefing following seclusions or restraint use in inpatient mental health settings: a scoping review. Clin Nurs Res. 2020;29(7):479-495. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773818791085
7. Needham I, Abderhalden C, Zeller A, et al. The effect of a training course on nursing students’ attitudes toward, perceptions of, and confidence in managing patient aggression. J Nurs Educ. 2005;44:415-420.
8. Missouridou E. Secondary posttraumatic stress and nurses’ emotional responses to patient’s trauma. J Trauma Nurs. 2017;24(2):110-115. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTN.0000000000000274
9. Blankenship BAC, Fernandez RP, Joy BF, et al. Multidisciplinary review of code events in a heart center. Am J Crit Care. 2016;25(4):90-98. https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2016302
10. Wolfe H, Zebuhr C, Topjian AA, et al. Interdisciplinary ICU cardiac arrest debriefing improves survival outcomes. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(7):1688-1695. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000327
11. Tannenbaum SI, Cerasoli CP. Do team and individual debriefs enhance performance? A meta-analysis. Hum Factors. 2013;55(1):231-245. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720812448394
12. Huckshorn KA. Reducing seclusion restraint in mental health use settings: core strategies for prevention. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 2004;42:22-33.
13. Goulet MH, Larue C, Dumais A. Evaluation of seclusion and restraint reduction programs in mental health: a systematic review. Agress Violent Behav. 2017;34:139-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2017.01.019
14. Azeem MW, Aujila A, Rammerth M, et al, Effectiveness of six core strategies based on trauma informed care in reducing seclusions and restraints at a child and adolescent psychiatric hospital. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs. 2011;24:11-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcap.12190
15. Wieman DA, Camacho-Gonsalves T, Huckshorn KA, et al. Multisite study of an evidence-based practice to reduce seclusion and restraint in psychiatric inpatient facilities. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(3):345-351. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300210
16. Everly GS. A primer on critical incident stress management: what’s really in a name? Int J Emerg Ment Health. 1999;1(2):77-79.
17. Reynolds EK, Grados MA, Praglowski N, et al. Use of modified positive behavioral interventions and supports in a psychiatric inpatient unit for high-risk youths. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):570-573. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201500039
18. Devaraj LR, Cooper C, Begin AS. Creating psychological safety on medical teams in times of crisis. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(1):47-49. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3541
19. Bride BE, Radey M, Figley CR. Measuring compassion fatigue. Clin Soc Work J. 2007;35:155-163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-007-0091-7
20. Figley CR. Compassion fatigue: psychotherapists’ lack of self care. J Clin Psychol. 2002;58(11):1433-1441. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.10090
1. Czeisler MÉ, Lane RI, Petrosky E, et al. Mental health, substance use, and suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, June 24–30, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1049-1057. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6932a1
2. Leeb RT, Bitsko RH, Radhakrishnan L, et al. Mental health–related emergency department visits among children aged <18 years during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, January 1–October 17, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1675-1680. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6945a3
3. Rapoport R. ‘Every day is an emergency’: The pandemic is worsening psychiatric bed shortages nationwide. Stat News. December 23, 2020. Accessed January 22, 2021. https://www.statnews.com/2020/12/23/mental-health-covid19-psychiatric-beds/
4. A step to ease the pandemic mental health crisis. Scientific American. February 1, 2021. Accessed April 14, 2021. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/a-step-to-ease-the-pandemic-mental-health-crisis/
5. Sharpe M, Toynbee M, Walker J. Proactive Integrated Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry: A new service model for the psychiatric care of general hospital inpatients. Gen Hosp Psych. 2020;66:9-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.005
6. Mangaoil RA, Cleverley K, Peter E. Immediate staff debriefing following seclusions or restraint use in inpatient mental health settings: a scoping review. Clin Nurs Res. 2020;29(7):479-495. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773818791085
7. Needham I, Abderhalden C, Zeller A, et al. The effect of a training course on nursing students’ attitudes toward, perceptions of, and confidence in managing patient aggression. J Nurs Educ. 2005;44:415-420.
8. Missouridou E. Secondary posttraumatic stress and nurses’ emotional responses to patient’s trauma. J Trauma Nurs. 2017;24(2):110-115. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTN.0000000000000274
9. Blankenship BAC, Fernandez RP, Joy BF, et al. Multidisciplinary review of code events in a heart center. Am J Crit Care. 2016;25(4):90-98. https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2016302
10. Wolfe H, Zebuhr C, Topjian AA, et al. Interdisciplinary ICU cardiac arrest debriefing improves survival outcomes. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(7):1688-1695. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000327
11. Tannenbaum SI, Cerasoli CP. Do team and individual debriefs enhance performance? A meta-analysis. Hum Factors. 2013;55(1):231-245. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720812448394
12. Huckshorn KA. Reducing seclusion restraint in mental health use settings: core strategies for prevention. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 2004;42:22-33.
13. Goulet MH, Larue C, Dumais A. Evaluation of seclusion and restraint reduction programs in mental health: a systematic review. Agress Violent Behav. 2017;34:139-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2017.01.019
14. Azeem MW, Aujila A, Rammerth M, et al, Effectiveness of six core strategies based on trauma informed care in reducing seclusions and restraints at a child and adolescent psychiatric hospital. J Child Adolesc Psychiatr Nurs. 2011;24:11-15. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcap.12190
15. Wieman DA, Camacho-Gonsalves T, Huckshorn KA, et al. Multisite study of an evidence-based practice to reduce seclusion and restraint in psychiatric inpatient facilities. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(3):345-351. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300210
16. Everly GS. A primer on critical incident stress management: what’s really in a name? Int J Emerg Ment Health. 1999;1(2):77-79.
17. Reynolds EK, Grados MA, Praglowski N, et al. Use of modified positive behavioral interventions and supports in a psychiatric inpatient unit for high-risk youths. Psychiatr Serv. 2016;67(5):570-573. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201500039
18. Devaraj LR, Cooper C, Begin AS. Creating psychological safety on medical teams in times of crisis. J Hosp Med. 2021;16(1):47-49. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3541
19. Bride BE, Radey M, Figley CR. Measuring compassion fatigue. Clin Soc Work J. 2007;35:155-163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-007-0091-7
20. Figley CR. Compassion fatigue: psychotherapists’ lack of self care. J Clin Psychol. 2002;58(11):1433-1441. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.10090
© 2021 Society of Hospital Medicine