User login
Pembro provides DFS benefit in early NSCLC
Adjuvant pembrolizumab significantly improves disease-free survival (DFS) compared to placebo in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have undergone complete resection, according to findings from the phase 3 PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 (PEARLS) study.
Patients in the pembrolizumab arm demonstrated median DFS nearly 12 months longer than those in the placebo arm (53.6 vs. 42.0 months). Investigators observed a DFS benefit for patients with any programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression.
“We believe that pembrolizumab has the potential to become a new adjuvant treatment option for patient with [stage IB to IIIA] non–small cell lung cancer following complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy when recommended,” concluded first author Luis Paz-Ares, MD, chair of the clinical research unit at Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, CNIO & Universidad Complutense, Madrid. “Pembrolizumab provided a benefit regardless of pathological stage and PD-L1 progression subgroup.”
The findings were presented by Dr. Paz-Ares at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) March virtual plenary session and published March 17 in Annals of Oncology.
Pembrolizumab is the standard treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC, but its efficacy in early-stage disease remains unclear. To determine whether patients with early-stage disease benefit from pembrolizumab, Dr. Paz-Ares and colleagues randomized 1,177 adults with stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC to 200 mg of pembrolizumab (n = 590) or placebo (n = 587) every 3 weeks.
All patients had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1, and any level of PD-L1 expression. Of the study participants, 168 in the pembrolizumab arm and 165 in the placebo arm had PD-L1 expression and a tumor proportion score (TPS) of at least 50%.
Overall, patients receiving pembrolizumab had a DFS of 53.6 months compared to 42.0 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P = .0014). The DFS benefit was generally consistent across patients with PD-L1 TPS <1%, 1%-49%, and ≥50%. In the subset of patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥50%, a slightly higher percentage of patients in the pembrolizumab group demonstrated DFS at 18 months (71.7% vs. 70.2%), but the difference did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.82; P = .14).
Overall survival (OS) at 18 months was 91.7% in the treatment arm and 91.3% in the placebo arm (HR, 0.87; P = .17), but the data were immature.
“The disease-free survival benefit was observed across most prespecified subgroups,” Dr. Paz-Ares said.
No new safety concerns were raised. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 34.1% of patients in the treatment arm and 25.8% in the placebo arm. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 19.8% of patients receiving pembrolizumab and 5.9% of patients in the placebo group.
Invited discussant Martin Reck, MD, said these findings represent forward progress. “We do see many patients with distant relapse, which indicates that we have to improve our control of the systemic relapse,” said Dr. Reck, head of the department of thoracic oncology and the clinical trial department at the Lungen Clinic Grosshansdorf, Germany.
Prior data provide a rationale for using immune checkpoint inhibition in early-stage NSCLC, and both the PEARLS study and the IMpower010 trial evaluating atezolizumab in a similar setting have demonstrated relevant improvements in DFS.
“I think we are entering the times of perioperative immunotherapies. We are seeing the first signals of efficacy for adjuvant immunotherapy in two large, randomized trials,” Dr. Reck said.
Based on the PEARLS trial results, Dr. Reck said that PD-L1 appears to have predictive and prognostic value but noted that “several other clinical trials say PD-L1 expression is a poor prognostic marker” for sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitor. Given this potential inconsistency, Dr. Reck called for further follow-up in this patient population and for studies in larger groups of patients to further delineate the role of PD-L1 as well as EGFR mutations and adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early NSCLC.
The PEARLS study was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. Dr. Paz-Ares and Dr. Reck disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
Adjuvant pembrolizumab significantly improves disease-free survival (DFS) compared to placebo in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have undergone complete resection, according to findings from the phase 3 PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 (PEARLS) study.
Patients in the pembrolizumab arm demonstrated median DFS nearly 12 months longer than those in the placebo arm (53.6 vs. 42.0 months). Investigators observed a DFS benefit for patients with any programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression.
“We believe that pembrolizumab has the potential to become a new adjuvant treatment option for patient with [stage IB to IIIA] non–small cell lung cancer following complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy when recommended,” concluded first author Luis Paz-Ares, MD, chair of the clinical research unit at Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, CNIO & Universidad Complutense, Madrid. “Pembrolizumab provided a benefit regardless of pathological stage and PD-L1 progression subgroup.”
The findings were presented by Dr. Paz-Ares at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) March virtual plenary session and published March 17 in Annals of Oncology.
Pembrolizumab is the standard treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC, but its efficacy in early-stage disease remains unclear. To determine whether patients with early-stage disease benefit from pembrolizumab, Dr. Paz-Ares and colleagues randomized 1,177 adults with stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC to 200 mg of pembrolizumab (n = 590) or placebo (n = 587) every 3 weeks.
All patients had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1, and any level of PD-L1 expression. Of the study participants, 168 in the pembrolizumab arm and 165 in the placebo arm had PD-L1 expression and a tumor proportion score (TPS) of at least 50%.
Overall, patients receiving pembrolizumab had a DFS of 53.6 months compared to 42.0 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P = .0014). The DFS benefit was generally consistent across patients with PD-L1 TPS <1%, 1%-49%, and ≥50%. In the subset of patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥50%, a slightly higher percentage of patients in the pembrolizumab group demonstrated DFS at 18 months (71.7% vs. 70.2%), but the difference did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.82; P = .14).
Overall survival (OS) at 18 months was 91.7% in the treatment arm and 91.3% in the placebo arm (HR, 0.87; P = .17), but the data were immature.
“The disease-free survival benefit was observed across most prespecified subgroups,” Dr. Paz-Ares said.
No new safety concerns were raised. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 34.1% of patients in the treatment arm and 25.8% in the placebo arm. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 19.8% of patients receiving pembrolizumab and 5.9% of patients in the placebo group.
Invited discussant Martin Reck, MD, said these findings represent forward progress. “We do see many patients with distant relapse, which indicates that we have to improve our control of the systemic relapse,” said Dr. Reck, head of the department of thoracic oncology and the clinical trial department at the Lungen Clinic Grosshansdorf, Germany.
Prior data provide a rationale for using immune checkpoint inhibition in early-stage NSCLC, and both the PEARLS study and the IMpower010 trial evaluating atezolizumab in a similar setting have demonstrated relevant improvements in DFS.
“I think we are entering the times of perioperative immunotherapies. We are seeing the first signals of efficacy for adjuvant immunotherapy in two large, randomized trials,” Dr. Reck said.
Based on the PEARLS trial results, Dr. Reck said that PD-L1 appears to have predictive and prognostic value but noted that “several other clinical trials say PD-L1 expression is a poor prognostic marker” for sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitor. Given this potential inconsistency, Dr. Reck called for further follow-up in this patient population and for studies in larger groups of patients to further delineate the role of PD-L1 as well as EGFR mutations and adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early NSCLC.
The PEARLS study was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. Dr. Paz-Ares and Dr. Reck disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
Adjuvant pembrolizumab significantly improves disease-free survival (DFS) compared to placebo in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have undergone complete resection, according to findings from the phase 3 PEARLS/KEYNOTE-091 (PEARLS) study.
Patients in the pembrolizumab arm demonstrated median DFS nearly 12 months longer than those in the placebo arm (53.6 vs. 42.0 months). Investigators observed a DFS benefit for patients with any programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression.
“We believe that pembrolizumab has the potential to become a new adjuvant treatment option for patient with [stage IB to IIIA] non–small cell lung cancer following complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy when recommended,” concluded first author Luis Paz-Ares, MD, chair of the clinical research unit at Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, CNIO & Universidad Complutense, Madrid. “Pembrolizumab provided a benefit regardless of pathological stage and PD-L1 progression subgroup.”
The findings were presented by Dr. Paz-Ares at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) March virtual plenary session and published March 17 in Annals of Oncology.
Pembrolizumab is the standard treatment for patients with advanced NSCLC, but its efficacy in early-stage disease remains unclear. To determine whether patients with early-stage disease benefit from pembrolizumab, Dr. Paz-Ares and colleagues randomized 1,177 adults with stage IB, II, or IIIA NSCLC to 200 mg of pembrolizumab (n = 590) or placebo (n = 587) every 3 weeks.
All patients had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1, and any level of PD-L1 expression. Of the study participants, 168 in the pembrolizumab arm and 165 in the placebo arm had PD-L1 expression and a tumor proportion score (TPS) of at least 50%.
Overall, patients receiving pembrolizumab had a DFS of 53.6 months compared to 42.0 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; P = .0014). The DFS benefit was generally consistent across patients with PD-L1 TPS <1%, 1%-49%, and ≥50%. In the subset of patients with PD-L1 TPS ≥50%, a slightly higher percentage of patients in the pembrolizumab group demonstrated DFS at 18 months (71.7% vs. 70.2%), but the difference did not reach statistical significance (HR, 0.82; P = .14).
Overall survival (OS) at 18 months was 91.7% in the treatment arm and 91.3% in the placebo arm (HR, 0.87; P = .17), but the data were immature.
“The disease-free survival benefit was observed across most prespecified subgroups,” Dr. Paz-Ares said.
No new safety concerns were raised. Grade 3 or greater adverse events occurred in 34.1% of patients in the treatment arm and 25.8% in the placebo arm. Adverse events led to discontinuation in 19.8% of patients receiving pembrolizumab and 5.9% of patients in the placebo group.
Invited discussant Martin Reck, MD, said these findings represent forward progress. “We do see many patients with distant relapse, which indicates that we have to improve our control of the systemic relapse,” said Dr. Reck, head of the department of thoracic oncology and the clinical trial department at the Lungen Clinic Grosshansdorf, Germany.
Prior data provide a rationale for using immune checkpoint inhibition in early-stage NSCLC, and both the PEARLS study and the IMpower010 trial evaluating atezolizumab in a similar setting have demonstrated relevant improvements in DFS.
“I think we are entering the times of perioperative immunotherapies. We are seeing the first signals of efficacy for adjuvant immunotherapy in two large, randomized trials,” Dr. Reck said.
Based on the PEARLS trial results, Dr. Reck said that PD-L1 appears to have predictive and prognostic value but noted that “several other clinical trials say PD-L1 expression is a poor prognostic marker” for sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitor. Given this potential inconsistency, Dr. Reck called for further follow-up in this patient population and for studies in larger groups of patients to further delineate the role of PD-L1 as well as EGFR mutations and adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early NSCLC.
The PEARLS study was funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. Dr. Paz-Ares and Dr. Reck disclosed numerous relationships with pharmaceutical companies.
FROM THE ESMO MARCH PLENARY
New COVID combo-variant XE found in U.K.
As of last week, the U.K. Health Security Agency had found 637 cases of the variant, known as XE. The earliest case was found Jan. 19.
The new strain is known as a recombinant, which means it is a combination of two variants or viruses.
XE makes up less than 1% of sequenced cases in the United Kingdom so far, and there is no evidence yet that the strain leads to more severe disease or less vaccine protection.
“Right now, there’s really no public health concern,” John Brownstein, PhD, an epidemiologist and chief innovation officer at Boston Children’s Hospital, told ABC. “Recombinant variants happen over and over. In fact, the reason that this is the XE variant recombinant is that we’ve had XA, XB, XC, XD already, and none of those have turned out to be any real concern.”
A World Health Organization update published March 29 notes XE’s high transmissibility and says it may have a growth advantage of 10% over the BA.2 subvariant that now makes up more than 70% of cases in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As of last week, the U.K. Health Security Agency had found 637 cases of the variant, known as XE. The earliest case was found Jan. 19.
The new strain is known as a recombinant, which means it is a combination of two variants or viruses.
XE makes up less than 1% of sequenced cases in the United Kingdom so far, and there is no evidence yet that the strain leads to more severe disease or less vaccine protection.
“Right now, there’s really no public health concern,” John Brownstein, PhD, an epidemiologist and chief innovation officer at Boston Children’s Hospital, told ABC. “Recombinant variants happen over and over. In fact, the reason that this is the XE variant recombinant is that we’ve had XA, XB, XC, XD already, and none of those have turned out to be any real concern.”
A World Health Organization update published March 29 notes XE’s high transmissibility and says it may have a growth advantage of 10% over the BA.2 subvariant that now makes up more than 70% of cases in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As of last week, the U.K. Health Security Agency had found 637 cases of the variant, known as XE. The earliest case was found Jan. 19.
The new strain is known as a recombinant, which means it is a combination of two variants or viruses.
XE makes up less than 1% of sequenced cases in the United Kingdom so far, and there is no evidence yet that the strain leads to more severe disease or less vaccine protection.
“Right now, there’s really no public health concern,” John Brownstein, PhD, an epidemiologist and chief innovation officer at Boston Children’s Hospital, told ABC. “Recombinant variants happen over and over. In fact, the reason that this is the XE variant recombinant is that we’ve had XA, XB, XC, XD already, and none of those have turned out to be any real concern.”
A World Health Organization update published March 29 notes XE’s high transmissibility and says it may have a growth advantage of 10% over the BA.2 subvariant that now makes up more than 70% of cases in the United States.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID-19: Decline in new cases may be leveling off
Even as a number of states see increases in new COVID-19 cases among all ages, the trend remains downward for children, albeit at a slower pace than in recent weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New pediatric cases in the United States totaled 27,521 for the most recent week, March 25-31, down by 5.2% from the previous week. Earlier weekly declines, going backward through March and into late February, were 9.3%, 23%, 39.5%, and 46%, according to data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health agencies. The lowest weekly total recorded since the initial wave in 2020 was just under 8,500 during the week of June 18-24, 2021.
Reported COVID-19 cases in children now total over 12.8 million since the beginning of the pandemic in March 2020, and those infections represent 19.0% of all cases. That share of new cases has not increased in the last 7 weeks, the AAP and CHA noted in their weekly COVID report, suggesting that children have not been bearing a disproportionate share of the declining Omicron burden.
As for Omicron, the BA.2 subvariant now makes up about 55% of COVID-19 infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review, and New York, Massachusetts, and New Jersey are among the states reporting BA.2-driven increases in new cases of as much as 30%, the New York Times said.
Rates of new cases for the latest week available (March 27 to April 2) and at their Omicron peaks in January were 11.3 per 100,000 and 1,011 per 100,000 (ages 0-4 years), 12.5 and 1,505 per 100,000 (5-11 years), 12.7 and 1,779 per 100,000 (12-15 years), and 13.1 and 1,982 per 100,000 (16-17 years), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalization rates, however, were a bit of a mixed bag. The last 2 weeks (March 13-19 and March 20-26) of data available from the CDC’s COVID-NET show that hospitalizations were up slightly in children aged 0-4 years (1.3 per 100,000 to 1.4 per 100,000), down for 5- to 11-year-olds (0.6 to 0.2), and steady for those aged 12-17 (0.4 to 0.4). COVID-NET collects data from nearly 100 counties in 10 states and from a separate four-state network.
Vaccinations got a small boost in the last week, the first one since early February. Initial doses and completions climbed slightly in the 12- to 17-year-olds, while just first doses were up a bit among the 5- to 11-year-olds during the week of March 24-30, compared with the previous week, although both groups are still well below the highest counts recorded so far in 2022, which are, in turn, far short of 2021’s peaks, according to CDC data analyzed by the AAP.
Even as a number of states see increases in new COVID-19 cases among all ages, the trend remains downward for children, albeit at a slower pace than in recent weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New pediatric cases in the United States totaled 27,521 for the most recent week, March 25-31, down by 5.2% from the previous week. Earlier weekly declines, going backward through March and into late February, were 9.3%, 23%, 39.5%, and 46%, according to data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health agencies. The lowest weekly total recorded since the initial wave in 2020 was just under 8,500 during the week of June 18-24, 2021.
Reported COVID-19 cases in children now total over 12.8 million since the beginning of the pandemic in March 2020, and those infections represent 19.0% of all cases. That share of new cases has not increased in the last 7 weeks, the AAP and CHA noted in their weekly COVID report, suggesting that children have not been bearing a disproportionate share of the declining Omicron burden.
As for Omicron, the BA.2 subvariant now makes up about 55% of COVID-19 infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review, and New York, Massachusetts, and New Jersey are among the states reporting BA.2-driven increases in new cases of as much as 30%, the New York Times said.
Rates of new cases for the latest week available (March 27 to April 2) and at their Omicron peaks in January were 11.3 per 100,000 and 1,011 per 100,000 (ages 0-4 years), 12.5 and 1,505 per 100,000 (5-11 years), 12.7 and 1,779 per 100,000 (12-15 years), and 13.1 and 1,982 per 100,000 (16-17 years), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalization rates, however, were a bit of a mixed bag. The last 2 weeks (March 13-19 and March 20-26) of data available from the CDC’s COVID-NET show that hospitalizations were up slightly in children aged 0-4 years (1.3 per 100,000 to 1.4 per 100,000), down for 5- to 11-year-olds (0.6 to 0.2), and steady for those aged 12-17 (0.4 to 0.4). COVID-NET collects data from nearly 100 counties in 10 states and from a separate four-state network.
Vaccinations got a small boost in the last week, the first one since early February. Initial doses and completions climbed slightly in the 12- to 17-year-olds, while just first doses were up a bit among the 5- to 11-year-olds during the week of March 24-30, compared with the previous week, although both groups are still well below the highest counts recorded so far in 2022, which are, in turn, far short of 2021’s peaks, according to CDC data analyzed by the AAP.
Even as a number of states see increases in new COVID-19 cases among all ages, the trend remains downward for children, albeit at a slower pace than in recent weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
New pediatric cases in the United States totaled 27,521 for the most recent week, March 25-31, down by 5.2% from the previous week. Earlier weekly declines, going backward through March and into late February, were 9.3%, 23%, 39.5%, and 46%, according to data collected by the AAP and CHA from state and territorial health agencies. The lowest weekly total recorded since the initial wave in 2020 was just under 8,500 during the week of June 18-24, 2021.
Reported COVID-19 cases in children now total over 12.8 million since the beginning of the pandemic in March 2020, and those infections represent 19.0% of all cases. That share of new cases has not increased in the last 7 weeks, the AAP and CHA noted in their weekly COVID report, suggesting that children have not been bearing a disproportionate share of the declining Omicron burden.
As for Omicron, the BA.2 subvariant now makes up about 55% of COVID-19 infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said in its COVID Data Tracker Weekly Review, and New York, Massachusetts, and New Jersey are among the states reporting BA.2-driven increases in new cases of as much as 30%, the New York Times said.
Rates of new cases for the latest week available (March 27 to April 2) and at their Omicron peaks in January were 11.3 per 100,000 and 1,011 per 100,000 (ages 0-4 years), 12.5 and 1,505 per 100,000 (5-11 years), 12.7 and 1,779 per 100,000 (12-15 years), and 13.1 and 1,982 per 100,000 (16-17 years), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Hospitalization rates, however, were a bit of a mixed bag. The last 2 weeks (March 13-19 and March 20-26) of data available from the CDC’s COVID-NET show that hospitalizations were up slightly in children aged 0-4 years (1.3 per 100,000 to 1.4 per 100,000), down for 5- to 11-year-olds (0.6 to 0.2), and steady for those aged 12-17 (0.4 to 0.4). COVID-NET collects data from nearly 100 counties in 10 states and from a separate four-state network.
Vaccinations got a small boost in the last week, the first one since early February. Initial doses and completions climbed slightly in the 12- to 17-year-olds, while just first doses were up a bit among the 5- to 11-year-olds during the week of March 24-30, compared with the previous week, although both groups are still well below the highest counts recorded so far in 2022, which are, in turn, far short of 2021’s peaks, according to CDC data analyzed by the AAP.
Photoprotection strategies for melasma are increasing
BOSTON – Untinted chemical sunscreens on the market are not sufficient to protect the skin from the effects of visible light, complicating sun protection efforts for patients with melasma and other conditions aggravated by sun exposure, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
A , Dr. Lim, former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health, Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Tinted sunscreens contain iron oxides; some also contain pigmentary titanium dioxide.
“Black, red, and yellow iron oxide all reflect visible light,” he added, noting that currently, there are no regulations as to how tinted sunscreens are marketed, making it difficult for practicing clinicians to advise patients about what products to choose. However, he said, “unlike ‘SPF’ and ‘broad spectrum’ labeling, there is no specific guidance on tinted sunscreens. “ ‘Universal’ shade is a good start but might not be ideal for users with very fair or deep skin tones,” he noted.
In December 2021, a guide to tinted sunscreens, written by Dr. Lim and colleagues, was published, recommending that consumers choose a product that contains iron oxides, is labeled as broad spectrum, and has an SPF of at least 30.
A comprehensive list of 54 tinted sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or greater that contain iron oxide is also available . The authors of the guide contributed to this resource, which lists sunscreens by average price per ounce.
At the meeting, Dr. Lim highlighted tinted sunscreens that cost about $20 or less per ounce. They include Supergoop 100% Mineral CC Cream (SPF 50); Bare Republic Mineral Tinted Face Sunscreen Lotion (SPF 30); CeraVe Hydrating Sunscreen with Sheer Tint (SPF 30); Tizo Ultra Zinc Body & Face Sunscreen (SPF 40); Vichy Capital Soleil Tinted Face Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 60); EltaMD UV Elements Tinted (SPF 44); La Roche-Posay Anthelios Ultra-Light Tinted Mineral (SPF 50), SkinMedica Essential Defense Mineral Shield (SPF 32), ISDIN Eryfotona Ageless Ultralight Tinted Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 50), and SkinCeuticals Physical Fusion UV Defense (SPF 50).
Sunscreens with antioxidants
Sunscreens with biologically active antioxidants may be another option for patients with melasma. A proof-of-concept study that Dr. Lim and colleagues conducted in 20 patients found that application of a blend of topical antioxidants (2%) was associated with less erythema at the application sites among those with skin phototypes I-III and less pigmentation at the application sites among those with skin phototypes IV-VI after exposure to visible light and UVA-1, compared with controls.
Certain antioxidants have been added to sunscreens currently on the market, including niacinamide (vitamin B3), licochalcone A, carotenoids (beta-carotene), vitamin E, vitamin C, glycyrrhetinic acid, and diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate.
A recently published paper on the role of antioxidants and free radical quenchers in protecting skin from visible light referred to unpublished data from Dr. Lim (the first author) and colleagues, which demonstrated a significant reduction in visual light–induced hyperpigmentation on skin with sunscreen that contained the antioxidants vitamin E, vitamin C, diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate, licochalcone A, and a glycyrrhetinic acid, compared with sunscreen that had no antioxidants.
Novel filters
Another emerging option is sunscreen with new filters that cover UVA-1 and visible light. In a randomized, controlled trial of 19 patients, researchers evaluated the addition of methoxypropylamino cyclohexenylidene ethoxyethylcyanoacetate (MCE) absorber, a new UVA-1 filter known as Mexoryl 400, which has a peak absorption of 385 nm, to a sunscreen formulation.
“Currently, peak absorption in the U.S. is with avobenzone, which peaks at about 357 nm,” but MCE “covers a longer spectrum of UVA-1,” Dr. Lim said. The researchers found that the addition of MCE reduced UVA-1-induced dermal and epidermal alterations at cellular, biochemical, and molecular levels; and decreased UVA-1-induced pigmentation.
Another relatively new filter, phenylene bis-diphenyltriazine (also known as TriAsorB) not only protects against UVA but it extends into the blue light portion of visible light, according to a recently published paper. According to a press release from Pierre Fabre, which has developed the filter, studies have shown that TriAsorB is not toxic for three key species of marine biodiversity: a coral species, a phytoplankton species, and a zooplankton.
This filter and MCE are available in Europe but not in the United States.
Dr. Lim reported that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oréal, Pfizer, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
BOSTON – Untinted chemical sunscreens on the market are not sufficient to protect the skin from the effects of visible light, complicating sun protection efforts for patients with melasma and other conditions aggravated by sun exposure, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
A , Dr. Lim, former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health, Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Tinted sunscreens contain iron oxides; some also contain pigmentary titanium dioxide.
“Black, red, and yellow iron oxide all reflect visible light,” he added, noting that currently, there are no regulations as to how tinted sunscreens are marketed, making it difficult for practicing clinicians to advise patients about what products to choose. However, he said, “unlike ‘SPF’ and ‘broad spectrum’ labeling, there is no specific guidance on tinted sunscreens. “ ‘Universal’ shade is a good start but might not be ideal for users with very fair or deep skin tones,” he noted.
In December 2021, a guide to tinted sunscreens, written by Dr. Lim and colleagues, was published, recommending that consumers choose a product that contains iron oxides, is labeled as broad spectrum, and has an SPF of at least 30.
A comprehensive list of 54 tinted sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or greater that contain iron oxide is also available . The authors of the guide contributed to this resource, which lists sunscreens by average price per ounce.
At the meeting, Dr. Lim highlighted tinted sunscreens that cost about $20 or less per ounce. They include Supergoop 100% Mineral CC Cream (SPF 50); Bare Republic Mineral Tinted Face Sunscreen Lotion (SPF 30); CeraVe Hydrating Sunscreen with Sheer Tint (SPF 30); Tizo Ultra Zinc Body & Face Sunscreen (SPF 40); Vichy Capital Soleil Tinted Face Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 60); EltaMD UV Elements Tinted (SPF 44); La Roche-Posay Anthelios Ultra-Light Tinted Mineral (SPF 50), SkinMedica Essential Defense Mineral Shield (SPF 32), ISDIN Eryfotona Ageless Ultralight Tinted Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 50), and SkinCeuticals Physical Fusion UV Defense (SPF 50).
Sunscreens with antioxidants
Sunscreens with biologically active antioxidants may be another option for patients with melasma. A proof-of-concept study that Dr. Lim and colleagues conducted in 20 patients found that application of a blend of topical antioxidants (2%) was associated with less erythema at the application sites among those with skin phototypes I-III and less pigmentation at the application sites among those with skin phototypes IV-VI after exposure to visible light and UVA-1, compared with controls.
Certain antioxidants have been added to sunscreens currently on the market, including niacinamide (vitamin B3), licochalcone A, carotenoids (beta-carotene), vitamin E, vitamin C, glycyrrhetinic acid, and diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate.
A recently published paper on the role of antioxidants and free radical quenchers in protecting skin from visible light referred to unpublished data from Dr. Lim (the first author) and colleagues, which demonstrated a significant reduction in visual light–induced hyperpigmentation on skin with sunscreen that contained the antioxidants vitamin E, vitamin C, diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate, licochalcone A, and a glycyrrhetinic acid, compared with sunscreen that had no antioxidants.
Novel filters
Another emerging option is sunscreen with new filters that cover UVA-1 and visible light. In a randomized, controlled trial of 19 patients, researchers evaluated the addition of methoxypropylamino cyclohexenylidene ethoxyethylcyanoacetate (MCE) absorber, a new UVA-1 filter known as Mexoryl 400, which has a peak absorption of 385 nm, to a sunscreen formulation.
“Currently, peak absorption in the U.S. is with avobenzone, which peaks at about 357 nm,” but MCE “covers a longer spectrum of UVA-1,” Dr. Lim said. The researchers found that the addition of MCE reduced UVA-1-induced dermal and epidermal alterations at cellular, biochemical, and molecular levels; and decreased UVA-1-induced pigmentation.
Another relatively new filter, phenylene bis-diphenyltriazine (also known as TriAsorB) not only protects against UVA but it extends into the blue light portion of visible light, according to a recently published paper. According to a press release from Pierre Fabre, which has developed the filter, studies have shown that TriAsorB is not toxic for three key species of marine biodiversity: a coral species, a phytoplankton species, and a zooplankton.
This filter and MCE are available in Europe but not in the United States.
Dr. Lim reported that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oréal, Pfizer, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
BOSTON – Untinted chemical sunscreens on the market are not sufficient to protect the skin from the effects of visible light, complicating sun protection efforts for patients with melasma and other conditions aggravated by sun exposure, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
A , Dr. Lim, former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health, Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Tinted sunscreens contain iron oxides; some also contain pigmentary titanium dioxide.
“Black, red, and yellow iron oxide all reflect visible light,” he added, noting that currently, there are no regulations as to how tinted sunscreens are marketed, making it difficult for practicing clinicians to advise patients about what products to choose. However, he said, “unlike ‘SPF’ and ‘broad spectrum’ labeling, there is no specific guidance on tinted sunscreens. “ ‘Universal’ shade is a good start but might not be ideal for users with very fair or deep skin tones,” he noted.
In December 2021, a guide to tinted sunscreens, written by Dr. Lim and colleagues, was published, recommending that consumers choose a product that contains iron oxides, is labeled as broad spectrum, and has an SPF of at least 30.
A comprehensive list of 54 tinted sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or greater that contain iron oxide is also available . The authors of the guide contributed to this resource, which lists sunscreens by average price per ounce.
At the meeting, Dr. Lim highlighted tinted sunscreens that cost about $20 or less per ounce. They include Supergoop 100% Mineral CC Cream (SPF 50); Bare Republic Mineral Tinted Face Sunscreen Lotion (SPF 30); CeraVe Hydrating Sunscreen with Sheer Tint (SPF 30); Tizo Ultra Zinc Body & Face Sunscreen (SPF 40); Vichy Capital Soleil Tinted Face Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 60); EltaMD UV Elements Tinted (SPF 44); La Roche-Posay Anthelios Ultra-Light Tinted Mineral (SPF 50), SkinMedica Essential Defense Mineral Shield (SPF 32), ISDIN Eryfotona Ageless Ultralight Tinted Mineral Sunscreen (SPF 50), and SkinCeuticals Physical Fusion UV Defense (SPF 50).
Sunscreens with antioxidants
Sunscreens with biologically active antioxidants may be another option for patients with melasma. A proof-of-concept study that Dr. Lim and colleagues conducted in 20 patients found that application of a blend of topical antioxidants (2%) was associated with less erythema at the application sites among those with skin phototypes I-III and less pigmentation at the application sites among those with skin phototypes IV-VI after exposure to visible light and UVA-1, compared with controls.
Certain antioxidants have been added to sunscreens currently on the market, including niacinamide (vitamin B3), licochalcone A, carotenoids (beta-carotene), vitamin E, vitamin C, glycyrrhetinic acid, and diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate.
A recently published paper on the role of antioxidants and free radical quenchers in protecting skin from visible light referred to unpublished data from Dr. Lim (the first author) and colleagues, which demonstrated a significant reduction in visual light–induced hyperpigmentation on skin with sunscreen that contained the antioxidants vitamin E, vitamin C, diethylhexyl syringylidenemalonate, licochalcone A, and a glycyrrhetinic acid, compared with sunscreen that had no antioxidants.
Novel filters
Another emerging option is sunscreen with new filters that cover UVA-1 and visible light. In a randomized, controlled trial of 19 patients, researchers evaluated the addition of methoxypropylamino cyclohexenylidene ethoxyethylcyanoacetate (MCE) absorber, a new UVA-1 filter known as Mexoryl 400, which has a peak absorption of 385 nm, to a sunscreen formulation.
“Currently, peak absorption in the U.S. is with avobenzone, which peaks at about 357 nm,” but MCE “covers a longer spectrum of UVA-1,” Dr. Lim said. The researchers found that the addition of MCE reduced UVA-1-induced dermal and epidermal alterations at cellular, biochemical, and molecular levels; and decreased UVA-1-induced pigmentation.
Another relatively new filter, phenylene bis-diphenyltriazine (also known as TriAsorB) not only protects against UVA but it extends into the blue light portion of visible light, according to a recently published paper. According to a press release from Pierre Fabre, which has developed the filter, studies have shown that TriAsorB is not toxic for three key species of marine biodiversity: a coral species, a phytoplankton species, and a zooplankton.
This filter and MCE are available in Europe but not in the United States.
Dr. Lim reported that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oréal, Pfizer, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
AT AAD 22
On the receiving end of care
It’s tough being on the receiving end of care. I’ve tried to avoid it as much as possible, being ever mindful of the law from Samuel Shem’s The House of God: “They can always hurt you more.”
Fortunately, each procedure went more smoothly than the prior one.
The first was not so elective. I had some uncomfortable symptoms while exercising and, not wanting to totally be in denial, contacted my doctor to ensure that it was not cardiac in origin since symptoms are often atypical in women.
My physician promptly saw me, then scheduled a nuclear stress test. There was a series of needless glitches. Registration at the diagnostic center had me on their schedule but did not have an order. They would have canceled the procedure had I not been able to get hold of the doctor’s office. Why isn’t an order automatically entered when the physician schedules the test?
While I was given the euphemistic “Patient Rights” brochure, asking to have reports sent to a physician outside of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center empire is apparently not included.
The staff canceled the stress test because I was not fasting. I had received no instructions from diagnostic cardiology. They suggested it was my internist’s responsibility.
I deliberately ate (2 hours earlier) because my trainer always wants me to eat a light meal so I don’t get hypoglycemic during our workouts, and an exercise stress test, is, of course, a workout. The nurse practitioner said that they were concerned I would vomit. I offered to sign a waiver. She parried, saying they would not be able to get adequate images, so I was out of luck.
When I expressed concern about getting hypoglycemic and having difficulty with the test if fasting, the tech said I should bring a soda and snack. Who tells a “borderline” diabetic to bring a soda?
The tech also said she had called our home to give instructions but encountered a busy signal and had not had time to call back. I had not left the house during the prior week (or most of the past 2 years), so this was a pretty lame excuse.
I suggested to the administration that the hospital offer to email the patient instructions well ahead of time (and perhaps ask for confirmation of receipt). If calling, they should try more than once. They should also have patient instruction sheets at the physician’s office and perhaps have them on their website.
It turns out that the hospital mailed me instructions, not on the date it was ordered, but with the postmark being the day of the procedure itself. With Trump donor Louis DeJoy in charge of the U.S. Postal Service, mail across town now has to travel to Baltimore, 3 hours away, be sorted, and returned.
I did finally have the stress test, which was reassuringly normal. I was not surprised, given that the fury I felt on the first attempt had not precipitated symptoms. The hospital sent a patient ombudsman to meet me there to discuss my previous complaints. I have no idea if they implemented any of the changes I had suggested. In 2021, when I urgently had to take my husband to the ED, I couldn’t see the sign pointing toward the ED and had to ask for directions at the main entrance. They said they would fix that promptly but still have not improved the signage. How I miss the friendly community hospital we had before!
Next was trigger-finger surgery. I had developed that in 1978 from using crutches after a fall. I figured that the relative lull in COVID and my activities made it as good a time as any to finally have it fixed. The surgicenter was great; the surgeon was someone I had worked with and respected for decades. The only glitch was not really knowing how long I was going to be out of commission.
The third encounter (at yet another institution) went really well, despite some early administrative glitches. My major complaint was with the lack of communication between preoperative anesthesia and the operating room and the lack of personalization of preoperative instructions. Despite EPIC, medicines were not correctly reconciled between the different encounters, even on the same day!
After about 15 years of diplopia, which has been gradually worsening, my eye doc had suggested that I consider strabismus surgery as a sort of last-ditch effort to improve my quality of life.
Anesthesiology has stock instructions, which they made no effort to individualize. For example, there is no reason to stop NSAIDs a week before such minor surgery. That’s a problem if you depend on NSAIDs for pain control. Similarly, nothing by mouth after midnight is passé and could be tailored for the patient. I felt particularly inconvenienced that I had to go out of town for the preoperative visit and then have a redundant preoperative clearance by my physician.
The nurses in the preoperative area made me feel quite comfortable and as relaxed as I could be under the circumstances. They had a good sense of humor, which helped too. And from the time I met him a few weeks earlier, I instantly liked my surgeon and felt very comfortable with him and had complete trust.
I was pleased that the chief anesthesiologist responded promptly and undefensively to my letter expressing concerns. I do believe that he will try to improve the systemic problems.
The best part: The surgery appears to have been successful and I should have a significantly improved quality of life.
Hospitals could do so much better by improving communications with patients and by viewing them as customers whose loyalty they must earn and will value. With monopolies growing, memories of such care are quickly fading, soon to be as extinct as the family doc who made house calls.
Dr. Stone is an infectious disease specialist and author of Resilience: One Family’s Story of Hope and Triumph over Evil and Conducting Clinical Research: A Practical Guide. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s tough being on the receiving end of care. I’ve tried to avoid it as much as possible, being ever mindful of the law from Samuel Shem’s The House of God: “They can always hurt you more.”
Fortunately, each procedure went more smoothly than the prior one.
The first was not so elective. I had some uncomfortable symptoms while exercising and, not wanting to totally be in denial, contacted my doctor to ensure that it was not cardiac in origin since symptoms are often atypical in women.
My physician promptly saw me, then scheduled a nuclear stress test. There was a series of needless glitches. Registration at the diagnostic center had me on their schedule but did not have an order. They would have canceled the procedure had I not been able to get hold of the doctor’s office. Why isn’t an order automatically entered when the physician schedules the test?
While I was given the euphemistic “Patient Rights” brochure, asking to have reports sent to a physician outside of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center empire is apparently not included.
The staff canceled the stress test because I was not fasting. I had received no instructions from diagnostic cardiology. They suggested it was my internist’s responsibility.
I deliberately ate (2 hours earlier) because my trainer always wants me to eat a light meal so I don’t get hypoglycemic during our workouts, and an exercise stress test, is, of course, a workout. The nurse practitioner said that they were concerned I would vomit. I offered to sign a waiver. She parried, saying they would not be able to get adequate images, so I was out of luck.
When I expressed concern about getting hypoglycemic and having difficulty with the test if fasting, the tech said I should bring a soda and snack. Who tells a “borderline” diabetic to bring a soda?
The tech also said she had called our home to give instructions but encountered a busy signal and had not had time to call back. I had not left the house during the prior week (or most of the past 2 years), so this was a pretty lame excuse.
I suggested to the administration that the hospital offer to email the patient instructions well ahead of time (and perhaps ask for confirmation of receipt). If calling, they should try more than once. They should also have patient instruction sheets at the physician’s office and perhaps have them on their website.
It turns out that the hospital mailed me instructions, not on the date it was ordered, but with the postmark being the day of the procedure itself. With Trump donor Louis DeJoy in charge of the U.S. Postal Service, mail across town now has to travel to Baltimore, 3 hours away, be sorted, and returned.
I did finally have the stress test, which was reassuringly normal. I was not surprised, given that the fury I felt on the first attempt had not precipitated symptoms. The hospital sent a patient ombudsman to meet me there to discuss my previous complaints. I have no idea if they implemented any of the changes I had suggested. In 2021, when I urgently had to take my husband to the ED, I couldn’t see the sign pointing toward the ED and had to ask for directions at the main entrance. They said they would fix that promptly but still have not improved the signage. How I miss the friendly community hospital we had before!
Next was trigger-finger surgery. I had developed that in 1978 from using crutches after a fall. I figured that the relative lull in COVID and my activities made it as good a time as any to finally have it fixed. The surgicenter was great; the surgeon was someone I had worked with and respected for decades. The only glitch was not really knowing how long I was going to be out of commission.
The third encounter (at yet another institution) went really well, despite some early administrative glitches. My major complaint was with the lack of communication between preoperative anesthesia and the operating room and the lack of personalization of preoperative instructions. Despite EPIC, medicines were not correctly reconciled between the different encounters, even on the same day!
After about 15 years of diplopia, which has been gradually worsening, my eye doc had suggested that I consider strabismus surgery as a sort of last-ditch effort to improve my quality of life.
Anesthesiology has stock instructions, which they made no effort to individualize. For example, there is no reason to stop NSAIDs a week before such minor surgery. That’s a problem if you depend on NSAIDs for pain control. Similarly, nothing by mouth after midnight is passé and could be tailored for the patient. I felt particularly inconvenienced that I had to go out of town for the preoperative visit and then have a redundant preoperative clearance by my physician.
The nurses in the preoperative area made me feel quite comfortable and as relaxed as I could be under the circumstances. They had a good sense of humor, which helped too. And from the time I met him a few weeks earlier, I instantly liked my surgeon and felt very comfortable with him and had complete trust.
I was pleased that the chief anesthesiologist responded promptly and undefensively to my letter expressing concerns. I do believe that he will try to improve the systemic problems.
The best part: The surgery appears to have been successful and I should have a significantly improved quality of life.
Hospitals could do so much better by improving communications with patients and by viewing them as customers whose loyalty they must earn and will value. With monopolies growing, memories of such care are quickly fading, soon to be as extinct as the family doc who made house calls.
Dr. Stone is an infectious disease specialist and author of Resilience: One Family’s Story of Hope and Triumph over Evil and Conducting Clinical Research: A Practical Guide. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s tough being on the receiving end of care. I’ve tried to avoid it as much as possible, being ever mindful of the law from Samuel Shem’s The House of God: “They can always hurt you more.”
Fortunately, each procedure went more smoothly than the prior one.
The first was not so elective. I had some uncomfortable symptoms while exercising and, not wanting to totally be in denial, contacted my doctor to ensure that it was not cardiac in origin since symptoms are often atypical in women.
My physician promptly saw me, then scheduled a nuclear stress test. There was a series of needless glitches. Registration at the diagnostic center had me on their schedule but did not have an order. They would have canceled the procedure had I not been able to get hold of the doctor’s office. Why isn’t an order automatically entered when the physician schedules the test?
While I was given the euphemistic “Patient Rights” brochure, asking to have reports sent to a physician outside of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center empire is apparently not included.
The staff canceled the stress test because I was not fasting. I had received no instructions from diagnostic cardiology. They suggested it was my internist’s responsibility.
I deliberately ate (2 hours earlier) because my trainer always wants me to eat a light meal so I don’t get hypoglycemic during our workouts, and an exercise stress test, is, of course, a workout. The nurse practitioner said that they were concerned I would vomit. I offered to sign a waiver. She parried, saying they would not be able to get adequate images, so I was out of luck.
When I expressed concern about getting hypoglycemic and having difficulty with the test if fasting, the tech said I should bring a soda and snack. Who tells a “borderline” diabetic to bring a soda?
The tech also said she had called our home to give instructions but encountered a busy signal and had not had time to call back. I had not left the house during the prior week (or most of the past 2 years), so this was a pretty lame excuse.
I suggested to the administration that the hospital offer to email the patient instructions well ahead of time (and perhaps ask for confirmation of receipt). If calling, they should try more than once. They should also have patient instruction sheets at the physician’s office and perhaps have them on their website.
It turns out that the hospital mailed me instructions, not on the date it was ordered, but with the postmark being the day of the procedure itself. With Trump donor Louis DeJoy in charge of the U.S. Postal Service, mail across town now has to travel to Baltimore, 3 hours away, be sorted, and returned.
I did finally have the stress test, which was reassuringly normal. I was not surprised, given that the fury I felt on the first attempt had not precipitated symptoms. The hospital sent a patient ombudsman to meet me there to discuss my previous complaints. I have no idea if they implemented any of the changes I had suggested. In 2021, when I urgently had to take my husband to the ED, I couldn’t see the sign pointing toward the ED and had to ask for directions at the main entrance. They said they would fix that promptly but still have not improved the signage. How I miss the friendly community hospital we had before!
Next was trigger-finger surgery. I had developed that in 1978 from using crutches after a fall. I figured that the relative lull in COVID and my activities made it as good a time as any to finally have it fixed. The surgicenter was great; the surgeon was someone I had worked with and respected for decades. The only glitch was not really knowing how long I was going to be out of commission.
The third encounter (at yet another institution) went really well, despite some early administrative glitches. My major complaint was with the lack of communication between preoperative anesthesia and the operating room and the lack of personalization of preoperative instructions. Despite EPIC, medicines were not correctly reconciled between the different encounters, even on the same day!
After about 15 years of diplopia, which has been gradually worsening, my eye doc had suggested that I consider strabismus surgery as a sort of last-ditch effort to improve my quality of life.
Anesthesiology has stock instructions, which they made no effort to individualize. For example, there is no reason to stop NSAIDs a week before such minor surgery. That’s a problem if you depend on NSAIDs for pain control. Similarly, nothing by mouth after midnight is passé and could be tailored for the patient. I felt particularly inconvenienced that I had to go out of town for the preoperative visit and then have a redundant preoperative clearance by my physician.
The nurses in the preoperative area made me feel quite comfortable and as relaxed as I could be under the circumstances. They had a good sense of humor, which helped too. And from the time I met him a few weeks earlier, I instantly liked my surgeon and felt very comfortable with him and had complete trust.
I was pleased that the chief anesthesiologist responded promptly and undefensively to my letter expressing concerns. I do believe that he will try to improve the systemic problems.
The best part: The surgery appears to have been successful and I should have a significantly improved quality of life.
Hospitals could do so much better by improving communications with patients and by viewing them as customers whose loyalty they must earn and will value. With monopolies growing, memories of such care are quickly fading, soon to be as extinct as the family doc who made house calls.
Dr. Stone is an infectious disease specialist and author of Resilience: One Family’s Story of Hope and Triumph over Evil and Conducting Clinical Research: A Practical Guide. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Global melanoma incidence high and on the rise
Even by cautious calculations,
An estimated 325,000 people worldwide received a new diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in 2020, and if present trends continue, the incidence of new cases is predicted to increase by about 50% in 2040, with melanoma deaths expected to rise by almost 70%, Melina Arnold, PhD, from the Cancer Surveillance Branch of the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon, France, and colleagues reported.
“Melanoma is the most lethal form of skin cancer; this epidemiological assessment found a heavy public health and economic burden, and our projections suggest that it will remain so in the coming decades,” they wrote in a study published online in JAMA Dermatology.
In an accompanying editorial, Mavis Obeng-Kusi, MPharm and Ivo Abraham, PhD from the Center for Health Outcomes and PharmacoEconomic Research at the University of Arizona, Tucson, commented that the findings are “sobering,” but may substantially underestimate the gravity of the problem in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).
“The study by Arnold et al. brings to the fore a public health concern that requires global attention and initiates conversations particularly related to LMIC settings, where the incidence and mortality of melanoma is thought to be minimal and for which preventive measures may be insufficient,” they wrote.
Down Under nations lead
Dr. Arnold and colleagues looked at data on age-standardized melanoma incidence and mortality rates per 100,000 person-years (PY) by country, each of 20 world regions as defined by the United Nations, and according to the UN’s four-tier Human Development Index, which stratifies countries into low-, medium-, high-, and very high–income categories.
As noted previously, the researchers estimated that there were 325,000 new melanoma cases worldwide in 2020 (174,000 cases in males and 151,000 in females). There were 57,000 estimated melanoma deaths the same year (32,000 in males and 25,000 in females.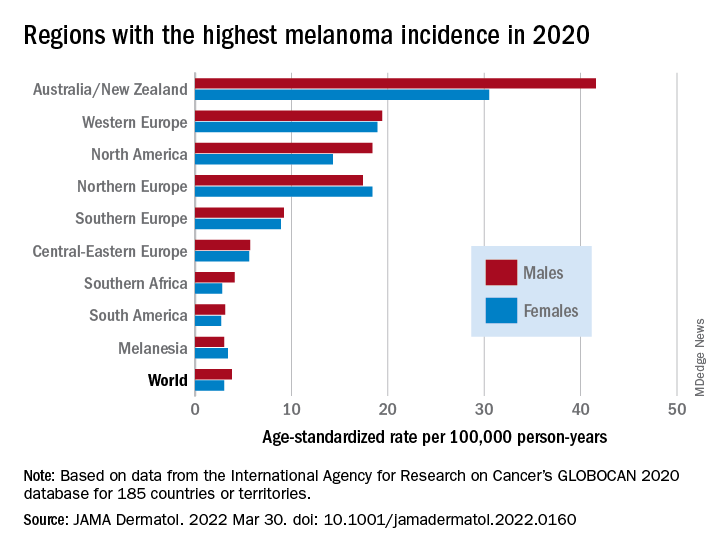
The highest incidence rates were seen in Australia and New Zealand, at 42 per 100,000 PY among males and 31 per 100,000 PY in females, followed by Western Europe with 19 per 100,000 PY in both males and females, North America with 18 and 14 cases per 100,000 PY in males and females respectively, and Northern Europe, with 17 per 100,000 PY in males, and 18 per 100,000 PY in females.
In contrast, in most African and Asian countries melanoma was rare, with rates commonly less than 1 per 100,000 PY, the investigators noted.
The melanoma mortality rate was highest in New Zealand, at 5 per 100,000 PY. Mortality rates worldwide varied less widely than incidence rates. In most other regions of the world, mortality rates were “much lower,” ranging between 0.2-1.0 per 100,000 PY, they wrote.
The authors estimated that, if 2020 rates remain stable, the global burden from melanoma in 2040 will increase to approximately 510,000 new cases and 96,000 deaths.
Public health efforts needed
In their editorial, Ms. Obeng-Kusi and Dr. Abraham pointed out that the study was hampered by the limited availability of cancer data from LMICs, leading the authors to estimate incidence and mortality rates based on proxy data, such as statistical modeling or averaged rates from neighboring countries.
They emphasized the need for going beyond the statistics: “Specific to cutaneous melanoma data, what is most important globally, knowing the exact numbers of cases and deaths or understanding the order of magnitude of the present and future epidemiology? No doubt the latter. Melanoma can be treated more easily if caught at earlier stages.”
Projections such as those provided by Dr. Arnold and colleagues could help to raise awareness of the importance of decreasing exposure to UV radiation, which accounts for three-fourths of all incident melanomas, the editorialists said.
The study was funded in part by a grant to coauthor Anna E. Cust, PhD, MPH. Dr. Cust reported receiving a fellowship from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council outside the submitted work. Dr. Arnold had no conflicts of interested to disclose. Dr. Abraham reported financial relationships with various entities. Ms. Obeng-Kusi had no disclosures.
Even by cautious calculations,
An estimated 325,000 people worldwide received a new diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in 2020, and if present trends continue, the incidence of new cases is predicted to increase by about 50% in 2040, with melanoma deaths expected to rise by almost 70%, Melina Arnold, PhD, from the Cancer Surveillance Branch of the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon, France, and colleagues reported.
“Melanoma is the most lethal form of skin cancer; this epidemiological assessment found a heavy public health and economic burden, and our projections suggest that it will remain so in the coming decades,” they wrote in a study published online in JAMA Dermatology.
In an accompanying editorial, Mavis Obeng-Kusi, MPharm and Ivo Abraham, PhD from the Center for Health Outcomes and PharmacoEconomic Research at the University of Arizona, Tucson, commented that the findings are “sobering,” but may substantially underestimate the gravity of the problem in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).
“The study by Arnold et al. brings to the fore a public health concern that requires global attention and initiates conversations particularly related to LMIC settings, where the incidence and mortality of melanoma is thought to be minimal and for which preventive measures may be insufficient,” they wrote.
Down Under nations lead
Dr. Arnold and colleagues looked at data on age-standardized melanoma incidence and mortality rates per 100,000 person-years (PY) by country, each of 20 world regions as defined by the United Nations, and according to the UN’s four-tier Human Development Index, which stratifies countries into low-, medium-, high-, and very high–income categories.
As noted previously, the researchers estimated that there were 325,000 new melanoma cases worldwide in 2020 (174,000 cases in males and 151,000 in females). There were 57,000 estimated melanoma deaths the same year (32,000 in males and 25,000 in females.
The highest incidence rates were seen in Australia and New Zealand, at 42 per 100,000 PY among males and 31 per 100,000 PY in females, followed by Western Europe with 19 per 100,000 PY in both males and females, North America with 18 and 14 cases per 100,000 PY in males and females respectively, and Northern Europe, with 17 per 100,000 PY in males, and 18 per 100,000 PY in females.
In contrast, in most African and Asian countries melanoma was rare, with rates commonly less than 1 per 100,000 PY, the investigators noted.
The melanoma mortality rate was highest in New Zealand, at 5 per 100,000 PY. Mortality rates worldwide varied less widely than incidence rates. In most other regions of the world, mortality rates were “much lower,” ranging between 0.2-1.0 per 100,000 PY, they wrote.
The authors estimated that, if 2020 rates remain stable, the global burden from melanoma in 2040 will increase to approximately 510,000 new cases and 96,000 deaths.
Public health efforts needed
In their editorial, Ms. Obeng-Kusi and Dr. Abraham pointed out that the study was hampered by the limited availability of cancer data from LMICs, leading the authors to estimate incidence and mortality rates based on proxy data, such as statistical modeling or averaged rates from neighboring countries.
They emphasized the need for going beyond the statistics: “Specific to cutaneous melanoma data, what is most important globally, knowing the exact numbers of cases and deaths or understanding the order of magnitude of the present and future epidemiology? No doubt the latter. Melanoma can be treated more easily if caught at earlier stages.”
Projections such as those provided by Dr. Arnold and colleagues could help to raise awareness of the importance of decreasing exposure to UV radiation, which accounts for three-fourths of all incident melanomas, the editorialists said.
The study was funded in part by a grant to coauthor Anna E. Cust, PhD, MPH. Dr. Cust reported receiving a fellowship from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council outside the submitted work. Dr. Arnold had no conflicts of interested to disclose. Dr. Abraham reported financial relationships with various entities. Ms. Obeng-Kusi had no disclosures.
Even by cautious calculations,
An estimated 325,000 people worldwide received a new diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma in 2020, and if present trends continue, the incidence of new cases is predicted to increase by about 50% in 2040, with melanoma deaths expected to rise by almost 70%, Melina Arnold, PhD, from the Cancer Surveillance Branch of the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon, France, and colleagues reported.
“Melanoma is the most lethal form of skin cancer; this epidemiological assessment found a heavy public health and economic burden, and our projections suggest that it will remain so in the coming decades,” they wrote in a study published online in JAMA Dermatology.
In an accompanying editorial, Mavis Obeng-Kusi, MPharm and Ivo Abraham, PhD from the Center for Health Outcomes and PharmacoEconomic Research at the University of Arizona, Tucson, commented that the findings are “sobering,” but may substantially underestimate the gravity of the problem in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).
“The study by Arnold et al. brings to the fore a public health concern that requires global attention and initiates conversations particularly related to LMIC settings, where the incidence and mortality of melanoma is thought to be minimal and for which preventive measures may be insufficient,” they wrote.
Down Under nations lead
Dr. Arnold and colleagues looked at data on age-standardized melanoma incidence and mortality rates per 100,000 person-years (PY) by country, each of 20 world regions as defined by the United Nations, and according to the UN’s four-tier Human Development Index, which stratifies countries into low-, medium-, high-, and very high–income categories.
As noted previously, the researchers estimated that there were 325,000 new melanoma cases worldwide in 2020 (174,000 cases in males and 151,000 in females). There were 57,000 estimated melanoma deaths the same year (32,000 in males and 25,000 in females.
The highest incidence rates were seen in Australia and New Zealand, at 42 per 100,000 PY among males and 31 per 100,000 PY in females, followed by Western Europe with 19 per 100,000 PY in both males and females, North America with 18 and 14 cases per 100,000 PY in males and females respectively, and Northern Europe, with 17 per 100,000 PY in males, and 18 per 100,000 PY in females.
In contrast, in most African and Asian countries melanoma was rare, with rates commonly less than 1 per 100,000 PY, the investigators noted.
The melanoma mortality rate was highest in New Zealand, at 5 per 100,000 PY. Mortality rates worldwide varied less widely than incidence rates. In most other regions of the world, mortality rates were “much lower,” ranging between 0.2-1.0 per 100,000 PY, they wrote.
The authors estimated that, if 2020 rates remain stable, the global burden from melanoma in 2040 will increase to approximately 510,000 new cases and 96,000 deaths.
Public health efforts needed
In their editorial, Ms. Obeng-Kusi and Dr. Abraham pointed out that the study was hampered by the limited availability of cancer data from LMICs, leading the authors to estimate incidence and mortality rates based on proxy data, such as statistical modeling or averaged rates from neighboring countries.
They emphasized the need for going beyond the statistics: “Specific to cutaneous melanoma data, what is most important globally, knowing the exact numbers of cases and deaths or understanding the order of magnitude of the present and future epidemiology? No doubt the latter. Melanoma can be treated more easily if caught at earlier stages.”
Projections such as those provided by Dr. Arnold and colleagues could help to raise awareness of the importance of decreasing exposure to UV radiation, which accounts for three-fourths of all incident melanomas, the editorialists said.
The study was funded in part by a grant to coauthor Anna E. Cust, PhD, MPH. Dr. Cust reported receiving a fellowship from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council outside the submitted work. Dr. Arnold had no conflicts of interested to disclose. Dr. Abraham reported financial relationships with various entities. Ms. Obeng-Kusi had no disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Some reproductive factors linked with risk of dementia
Certain reproductive factors are associated with greater or lower risk of dementia, according to researchers who conducted a large population-based study with UK Biobank data.
Jessica Gong, a PhD candidate at the George Institute for Global Health at University of New South Wales in Australia, and coauthors found a greater dementia risk in women with early and late menarche, women who were younger when they first gave birth, and those who had had a hysterectomy, especially those who had a hysterectomy without concomitant oophorectomy or with a previous oophorectomy.
After controlling for key confounders, the researchers found lower risk of all-cause dementia if women had ever been pregnant, ever had an abortion, had a longer reproductive span, or had later menopause.
Use of oral contraceptive pills was associated with a lower dementia risk, they found.
In this study, there was no evidence that hormone therapy (HT) was associated with dementia risk (hazard ratio, 0.99, 95% confidence interval [0.90-1.09], P =.0828).
The analysis, published online April 5 in PLOS Medicine, comprised 273,240 women and 228,957 men without prevalent dementia.
The authors noted that dementia rates are increasing. Globally, 50 million people live with dementia, and the number is expected to triple by 2050, according to Alzheimer’s Disease International.
“Our study identified certain reproductive factors related to shorter exposure to endogenous estrogen were associated with increased risk of dementia, highlighting the susceptibility in dementia risk pertaining to women,” Ms. Gong told this publication.
Risk comparison of men and women
Men were included in this study to compare the association between number of children fathered and the risk of all-cause dementia, with the association in their female counterparts.
The U-shaped associations between the number of children and dementia risk were similar for both sexes, suggesting that the risk difference in women may not be associated with factors associated with childbearing
“It may be more related to social and behavioral factors in parenthood, rather than biological factors involved in childbearing,” Ms. Gong said.
Compared with those with two children, for those without children, the multiple adjusted HR (95% CI) was 1.18 (1.04, 1.33) (P = .027) for women and 1.10 (0.98-1.23) P = .164) for men.
For those with four or more children, the HR was 1.14 (0.98, 1.33) (P = .132) for women and 1.26 (1.10-1.45) (P = .003) for men.
Rachel Buckley, PhD, assistant professor of neurology with a dual appointment at Brigham and Women’s and Massachusetts General hospitals in Boston, told this publication she found the comparison of dementia risk with number of children in men and women “fascinating.”
She said the argument usually is that if women have had more births, then they have had more estrogen through their body because women get a huge injection of hormones in pregnancy.
“The idea is that the more pregnancies you have the more protected you are. But this study put that on its head, because if men and women are showing increased [dementia] risk in the number of children they have, it suggests there must be something about having the children – not necessarily the circulating hormones – that might be having an impact,” Dr. Buckley said.
“I had never thought to compare the number of children in men. I do find that very interesting,” she said.
As for the lack of a link between HT and dementia risk, in this study she said, she wouldn’t shut the door on that discussion just yet.
She noted the long history of controversy in the field about whether there is a protective factor against dementia for estrogen or whether exposure to estrogen leads to increased risk.
Before the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study in the 1990s, she pointed out, there was evidence in many observational studies that women who had longer exposure to estrogen – whether that was earlier age at first period and later age at menopause combined or women had taken hormone therapy at some point, had less risk for dementia.
Dr. Buckley said that in a secondary outcome of WHI, however, “there was increased risk for progression to dementia in women who were taking hormone therapy which essentially flipped the field on its ahead because until that point everybody thought that estrogen was a protective factor.”
She said although this study found no association with dementia, she still thinks HT has a role to play and that it may just need to be better tailored to individuals.
“If you think about it, we have our tailored cocktail of hormones in our body and who’s to say that my hormones are going to be the same as yours? Why should you and I be put on the same hormone therapy and assume that will give us the same outcome? I think we could do a lot better with customization and calibration of hormones to aid in women’s health.”
Lifetime approach to dementia
Ms. Gong says future dementia risk-reduction strategies should consider sex-specific risk, and consider the reproductive events that took place in women’s lifespans as well as their entire hormone history when assessing dementia risk, to ensure that the strategies are sex sensitive.
Dr. Buckley agrees: “I don’t think we should ever think about dementia in terms of 65 onwards. We know this disease is insidious and it starts very, very early.”
Regarding limitations, the authors noted that it was a retrospective study that included self-reported measures of reproductive factors, which may be inherently subject to recall bias.
A coauthor does consultant work for Amgen, Freeline, and Kirin outside the submitted work. There were no other relevant financial disclosures.
Certain reproductive factors are associated with greater or lower risk of dementia, according to researchers who conducted a large population-based study with UK Biobank data.
Jessica Gong, a PhD candidate at the George Institute for Global Health at University of New South Wales in Australia, and coauthors found a greater dementia risk in women with early and late menarche, women who were younger when they first gave birth, and those who had had a hysterectomy, especially those who had a hysterectomy without concomitant oophorectomy or with a previous oophorectomy.
After controlling for key confounders, the researchers found lower risk of all-cause dementia if women had ever been pregnant, ever had an abortion, had a longer reproductive span, or had later menopause.
Use of oral contraceptive pills was associated with a lower dementia risk, they found.
In this study, there was no evidence that hormone therapy (HT) was associated with dementia risk (hazard ratio, 0.99, 95% confidence interval [0.90-1.09], P =.0828).
The analysis, published online April 5 in PLOS Medicine, comprised 273,240 women and 228,957 men without prevalent dementia.
The authors noted that dementia rates are increasing. Globally, 50 million people live with dementia, and the number is expected to triple by 2050, according to Alzheimer’s Disease International.
“Our study identified certain reproductive factors related to shorter exposure to endogenous estrogen were associated with increased risk of dementia, highlighting the susceptibility in dementia risk pertaining to women,” Ms. Gong told this publication.
Risk comparison of men and women
Men were included in this study to compare the association between number of children fathered and the risk of all-cause dementia, with the association in their female counterparts.
The U-shaped associations between the number of children and dementia risk were similar for both sexes, suggesting that the risk difference in women may not be associated with factors associated with childbearing
“It may be more related to social and behavioral factors in parenthood, rather than biological factors involved in childbearing,” Ms. Gong said.
Compared with those with two children, for those without children, the multiple adjusted HR (95% CI) was 1.18 (1.04, 1.33) (P = .027) for women and 1.10 (0.98-1.23) P = .164) for men.
For those with four or more children, the HR was 1.14 (0.98, 1.33) (P = .132) for women and 1.26 (1.10-1.45) (P = .003) for men.
Rachel Buckley, PhD, assistant professor of neurology with a dual appointment at Brigham and Women’s and Massachusetts General hospitals in Boston, told this publication she found the comparison of dementia risk with number of children in men and women “fascinating.”
She said the argument usually is that if women have had more births, then they have had more estrogen through their body because women get a huge injection of hormones in pregnancy.
“The idea is that the more pregnancies you have the more protected you are. But this study put that on its head, because if men and women are showing increased [dementia] risk in the number of children they have, it suggests there must be something about having the children – not necessarily the circulating hormones – that might be having an impact,” Dr. Buckley said.
“I had never thought to compare the number of children in men. I do find that very interesting,” she said.
As for the lack of a link between HT and dementia risk, in this study she said, she wouldn’t shut the door on that discussion just yet.
She noted the long history of controversy in the field about whether there is a protective factor against dementia for estrogen or whether exposure to estrogen leads to increased risk.
Before the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study in the 1990s, she pointed out, there was evidence in many observational studies that women who had longer exposure to estrogen – whether that was earlier age at first period and later age at menopause combined or women had taken hormone therapy at some point, had less risk for dementia.
Dr. Buckley said that in a secondary outcome of WHI, however, “there was increased risk for progression to dementia in women who were taking hormone therapy which essentially flipped the field on its ahead because until that point everybody thought that estrogen was a protective factor.”
She said although this study found no association with dementia, she still thinks HT has a role to play and that it may just need to be better tailored to individuals.
“If you think about it, we have our tailored cocktail of hormones in our body and who’s to say that my hormones are going to be the same as yours? Why should you and I be put on the same hormone therapy and assume that will give us the same outcome? I think we could do a lot better with customization and calibration of hormones to aid in women’s health.”
Lifetime approach to dementia
Ms. Gong says future dementia risk-reduction strategies should consider sex-specific risk, and consider the reproductive events that took place in women’s lifespans as well as their entire hormone history when assessing dementia risk, to ensure that the strategies are sex sensitive.
Dr. Buckley agrees: “I don’t think we should ever think about dementia in terms of 65 onwards. We know this disease is insidious and it starts very, very early.”
Regarding limitations, the authors noted that it was a retrospective study that included self-reported measures of reproductive factors, which may be inherently subject to recall bias.
A coauthor does consultant work for Amgen, Freeline, and Kirin outside the submitted work. There were no other relevant financial disclosures.
Certain reproductive factors are associated with greater or lower risk of dementia, according to researchers who conducted a large population-based study with UK Biobank data.
Jessica Gong, a PhD candidate at the George Institute for Global Health at University of New South Wales in Australia, and coauthors found a greater dementia risk in women with early and late menarche, women who were younger when they first gave birth, and those who had had a hysterectomy, especially those who had a hysterectomy without concomitant oophorectomy or with a previous oophorectomy.
After controlling for key confounders, the researchers found lower risk of all-cause dementia if women had ever been pregnant, ever had an abortion, had a longer reproductive span, or had later menopause.
Use of oral contraceptive pills was associated with a lower dementia risk, they found.
In this study, there was no evidence that hormone therapy (HT) was associated with dementia risk (hazard ratio, 0.99, 95% confidence interval [0.90-1.09], P =.0828).
The analysis, published online April 5 in PLOS Medicine, comprised 273,240 women and 228,957 men without prevalent dementia.
The authors noted that dementia rates are increasing. Globally, 50 million people live with dementia, and the number is expected to triple by 2050, according to Alzheimer’s Disease International.
“Our study identified certain reproductive factors related to shorter exposure to endogenous estrogen were associated with increased risk of dementia, highlighting the susceptibility in dementia risk pertaining to women,” Ms. Gong told this publication.
Risk comparison of men and women
Men were included in this study to compare the association between number of children fathered and the risk of all-cause dementia, with the association in their female counterparts.
The U-shaped associations between the number of children and dementia risk were similar for both sexes, suggesting that the risk difference in women may not be associated with factors associated with childbearing
“It may be more related to social and behavioral factors in parenthood, rather than biological factors involved in childbearing,” Ms. Gong said.
Compared with those with two children, for those without children, the multiple adjusted HR (95% CI) was 1.18 (1.04, 1.33) (P = .027) for women and 1.10 (0.98-1.23) P = .164) for men.
For those with four or more children, the HR was 1.14 (0.98, 1.33) (P = .132) for women and 1.26 (1.10-1.45) (P = .003) for men.
Rachel Buckley, PhD, assistant professor of neurology with a dual appointment at Brigham and Women’s and Massachusetts General hospitals in Boston, told this publication she found the comparison of dementia risk with number of children in men and women “fascinating.”
She said the argument usually is that if women have had more births, then they have had more estrogen through their body because women get a huge injection of hormones in pregnancy.
“The idea is that the more pregnancies you have the more protected you are. But this study put that on its head, because if men and women are showing increased [dementia] risk in the number of children they have, it suggests there must be something about having the children – not necessarily the circulating hormones – that might be having an impact,” Dr. Buckley said.
“I had never thought to compare the number of children in men. I do find that very interesting,” she said.
As for the lack of a link between HT and dementia risk, in this study she said, she wouldn’t shut the door on that discussion just yet.
She noted the long history of controversy in the field about whether there is a protective factor against dementia for estrogen or whether exposure to estrogen leads to increased risk.
Before the landmark Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study in the 1990s, she pointed out, there was evidence in many observational studies that women who had longer exposure to estrogen – whether that was earlier age at first period and later age at menopause combined or women had taken hormone therapy at some point, had less risk for dementia.
Dr. Buckley said that in a secondary outcome of WHI, however, “there was increased risk for progression to dementia in women who were taking hormone therapy which essentially flipped the field on its ahead because until that point everybody thought that estrogen was a protective factor.”
She said although this study found no association with dementia, she still thinks HT has a role to play and that it may just need to be better tailored to individuals.
“If you think about it, we have our tailored cocktail of hormones in our body and who’s to say that my hormones are going to be the same as yours? Why should you and I be put on the same hormone therapy and assume that will give us the same outcome? I think we could do a lot better with customization and calibration of hormones to aid in women’s health.”
Lifetime approach to dementia
Ms. Gong says future dementia risk-reduction strategies should consider sex-specific risk, and consider the reproductive events that took place in women’s lifespans as well as their entire hormone history when assessing dementia risk, to ensure that the strategies are sex sensitive.
Dr. Buckley agrees: “I don’t think we should ever think about dementia in terms of 65 onwards. We know this disease is insidious and it starts very, very early.”
Regarding limitations, the authors noted that it was a retrospective study that included self-reported measures of reproductive factors, which may be inherently subject to recall bias.
A coauthor does consultant work for Amgen, Freeline, and Kirin outside the submitted work. There were no other relevant financial disclosures.
FROM PLOS MEDICINE
‘Eye-opening’ experience on the other side of the hospital bed
The 5 days that she spent at her mother’s bedside were eye-opening for an oncologist used to being on the other side of the clinician–patient relationship.
“As a physician, I thought I had a unique perspective of things that were done well – and things that were not,” commented Pamela Kunz, MD.
Dr. Kunz, who was named the 2021 Woman Oncologist of the Year, is director of the Center for Gastrointestinal Cancers at Smilow Cancer Hospital and of the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.
But she was propelled into quite a different role when her mother was admitted to the hospital.
Her mom, who has trouble hearing, was easily confused by jargon and by “all of the people coming in and out with no introductions,” she explained.
“She needed someone to translate what was going on because she didn’t feel well,” she added.
Seeing inpatient care through her mother’s eyes was enlightening, and at times it was “shocking to be on the other side.”
Physicians get used to “checking boxes, getting through the day,” she said. “It’s easy to forget the human side.”
“Seeing a loved one sick, [struggling] through this – I just wished I had seen things done differently,” added Dr. Kunz.
Her thread has since garnered thousands of “likes” and scores of comments and retweets.
She began the Twitter thread explaining what prompted her comments:
“I spent many hours last week observing the practice of medicine while sitting at my mom’s hospital bedside and was reminded of some important communication pearls. Some musings ...”
“1. Introduce yourself by full name, role, and team and have ID badges visible. It can get very confusing for [patients] and family members with the number of people in and out of rooms. E.g. ‘My name is Dr. X. I’m the intern on the primary internal medicine team.’
2. End your patient visit with a summary of the plan for the day.
3. Avoid medical jargon & speak slowly, clearly, and logically. Remember you are a teacher for your [patients] and their family.
4. Masks make it harder to hear, especially for [patients] with hearing loss (and they no longer have the aid of lip reading).
5. Many older [patients] get confused in the hospital. Repetition is a good thing.
6. Speak to a family member at least once per day to relay the plan.
7. Try to avoid last minute or surprise discharges – they make [patients] and family members anxious. Talk about discharge planning from day 1 and what milestones must occur prior to a safe discharge. ‘In order for you to leave the hospital, X, Y, X must happen.’
8. Talk with your [patients] about something other than what brought them to the hospital (a tip I once learned from a wise mentor).
9. When possible, sit at eye level with your patient (I love these stools from @YNHH).
10. Take time to listen.”
Dr. Kunz closed with her golden rule: “Lastly, treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.”
Twitter user @BrunaPellini replied: “I love this, especially ‘Treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.’ My mom and grandma always said that to me since I was a med student, and this is definitely one of my core values.”
Other clinicians shared similar experiences, and some added to Dr. Kunz’s list.
“Agree entirely, love the list – and while none of us can always practice perfectly, my experiences with my own mother’s illness taught me an enormous amount about communication,” @hoperugo responded.
Twitter user @mariejacork added: “Everyone in health care please read ... if you are lucky enough to not have had a loved one unwell in hospital, these may get forgotten. Having sat with my dad for a few days before he died a few years ago, I felt a lot of these, and it changed my practice forever.”
@bjcohenmd provided additional advice: “And use the dry erase board that should be in every room. Never start a medication without explaining it. Many docs will see the patient and then go to the computer, decide to order a med, but never go back to explain it.”
Patients also shared experiences and offered suggestions.
“As a chronic pain patient I’d add – we know it’s frustrating you can’t cure us but PLEASE do not SIGH if we say something didn’t work or [tell] us to be more positive. Just say ‘I know this is very hard, I’m here to listen.’ We don’t expect a cure, we do expect to be believed,” said @ppenguinsmt. “It makes me feel like I’m causing distress to you if I say the pain has been unrelenting. I leave feeling worse. ...You may have heard 10 [people] in pain before me but this is MY only [appointment].”
Twitter user @KatieCahoots added: “These are perfect. I wish doctors would do this not only in the hospital but in the doctor’s office, as well. I would add one caveat: When you try not to use medical jargon, don’t dumb it down as though I don’t know anything about science or haven’t done any of my own research.”
Dr. Kunz said she was taken aback but pleased by the response to her Tweet.
“It’s an example of the human side of medicine, so it resonates with physicians and with patients,” she commented. Seeing through her mom’s eyes how care was provided made her realize that medical training should include more emphasis on communication, including “real-time feedback to interns, residents, fellows, and students.”
Yes, it takes time, and “we don’t all have a lot of extra time,” she acknowledged.
“But some of these elements don’t take that much more time to do. They can help build trust and can, in the long run, actually save time if patients understand and family members feel engaged and like they are participants,” she said. “I think a little time investment will go a long way.”
In her case, she very much appreciated the one trainee who tried to call her and update her about her mother’s care each afternoon. “I really valued that,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 5 days that she spent at her mother’s bedside were eye-opening for an oncologist used to being on the other side of the clinician–patient relationship.
“As a physician, I thought I had a unique perspective of things that were done well – and things that were not,” commented Pamela Kunz, MD.
Dr. Kunz, who was named the 2021 Woman Oncologist of the Year, is director of the Center for Gastrointestinal Cancers at Smilow Cancer Hospital and of the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.
But she was propelled into quite a different role when her mother was admitted to the hospital.
Her mom, who has trouble hearing, was easily confused by jargon and by “all of the people coming in and out with no introductions,” she explained.
“She needed someone to translate what was going on because she didn’t feel well,” she added.
Seeing inpatient care through her mother’s eyes was enlightening, and at times it was “shocking to be on the other side.”
Physicians get used to “checking boxes, getting through the day,” she said. “It’s easy to forget the human side.”
“Seeing a loved one sick, [struggling] through this – I just wished I had seen things done differently,” added Dr. Kunz.
Her thread has since garnered thousands of “likes” and scores of comments and retweets.
She began the Twitter thread explaining what prompted her comments:
“I spent many hours last week observing the practice of medicine while sitting at my mom’s hospital bedside and was reminded of some important communication pearls. Some musings ...”
“1. Introduce yourself by full name, role, and team and have ID badges visible. It can get very confusing for [patients] and family members with the number of people in and out of rooms. E.g. ‘My name is Dr. X. I’m the intern on the primary internal medicine team.’
2. End your patient visit with a summary of the plan for the day.
3. Avoid medical jargon & speak slowly, clearly, and logically. Remember you are a teacher for your [patients] and their family.
4. Masks make it harder to hear, especially for [patients] with hearing loss (and they no longer have the aid of lip reading).
5. Many older [patients] get confused in the hospital. Repetition is a good thing.
6. Speak to a family member at least once per day to relay the plan.
7. Try to avoid last minute or surprise discharges – they make [patients] and family members anxious. Talk about discharge planning from day 1 and what milestones must occur prior to a safe discharge. ‘In order for you to leave the hospital, X, Y, X must happen.’
8. Talk with your [patients] about something other than what brought them to the hospital (a tip I once learned from a wise mentor).
9. When possible, sit at eye level with your patient (I love these stools from @YNHH).
10. Take time to listen.”
Dr. Kunz closed with her golden rule: “Lastly, treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.”
Twitter user @BrunaPellini replied: “I love this, especially ‘Treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.’ My mom and grandma always said that to me since I was a med student, and this is definitely one of my core values.”
Other clinicians shared similar experiences, and some added to Dr. Kunz’s list.
“Agree entirely, love the list – and while none of us can always practice perfectly, my experiences with my own mother’s illness taught me an enormous amount about communication,” @hoperugo responded.
Twitter user @mariejacork added: “Everyone in health care please read ... if you are lucky enough to not have had a loved one unwell in hospital, these may get forgotten. Having sat with my dad for a few days before he died a few years ago, I felt a lot of these, and it changed my practice forever.”
@bjcohenmd provided additional advice: “And use the dry erase board that should be in every room. Never start a medication without explaining it. Many docs will see the patient and then go to the computer, decide to order a med, but never go back to explain it.”
Patients also shared experiences and offered suggestions.
“As a chronic pain patient I’d add – we know it’s frustrating you can’t cure us but PLEASE do not SIGH if we say something didn’t work or [tell] us to be more positive. Just say ‘I know this is very hard, I’m here to listen.’ We don’t expect a cure, we do expect to be believed,” said @ppenguinsmt. “It makes me feel like I’m causing distress to you if I say the pain has been unrelenting. I leave feeling worse. ...You may have heard 10 [people] in pain before me but this is MY only [appointment].”
Twitter user @KatieCahoots added: “These are perfect. I wish doctors would do this not only in the hospital but in the doctor’s office, as well. I would add one caveat: When you try not to use medical jargon, don’t dumb it down as though I don’t know anything about science or haven’t done any of my own research.”
Dr. Kunz said she was taken aback but pleased by the response to her Tweet.
“It’s an example of the human side of medicine, so it resonates with physicians and with patients,” she commented. Seeing through her mom’s eyes how care was provided made her realize that medical training should include more emphasis on communication, including “real-time feedback to interns, residents, fellows, and students.”
Yes, it takes time, and “we don’t all have a lot of extra time,” she acknowledged.
“But some of these elements don’t take that much more time to do. They can help build trust and can, in the long run, actually save time if patients understand and family members feel engaged and like they are participants,” she said. “I think a little time investment will go a long way.”
In her case, she very much appreciated the one trainee who tried to call her and update her about her mother’s care each afternoon. “I really valued that,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 5 days that she spent at her mother’s bedside were eye-opening for an oncologist used to being on the other side of the clinician–patient relationship.
“As a physician, I thought I had a unique perspective of things that were done well – and things that were not,” commented Pamela Kunz, MD.
Dr. Kunz, who was named the 2021 Woman Oncologist of the Year, is director of the Center for Gastrointestinal Cancers at Smilow Cancer Hospital and of the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.
But she was propelled into quite a different role when her mother was admitted to the hospital.
Her mom, who has trouble hearing, was easily confused by jargon and by “all of the people coming in and out with no introductions,” she explained.
“She needed someone to translate what was going on because she didn’t feel well,” she added.
Seeing inpatient care through her mother’s eyes was enlightening, and at times it was “shocking to be on the other side.”
Physicians get used to “checking boxes, getting through the day,” she said. “It’s easy to forget the human side.”
“Seeing a loved one sick, [struggling] through this – I just wished I had seen things done differently,” added Dr. Kunz.
Her thread has since garnered thousands of “likes” and scores of comments and retweets.
She began the Twitter thread explaining what prompted her comments:
“I spent many hours last week observing the practice of medicine while sitting at my mom’s hospital bedside and was reminded of some important communication pearls. Some musings ...”
“1. Introduce yourself by full name, role, and team and have ID badges visible. It can get very confusing for [patients] and family members with the number of people in and out of rooms. E.g. ‘My name is Dr. X. I’m the intern on the primary internal medicine team.’
2. End your patient visit with a summary of the plan for the day.
3. Avoid medical jargon & speak slowly, clearly, and logically. Remember you are a teacher for your [patients] and their family.
4. Masks make it harder to hear, especially for [patients] with hearing loss (and they no longer have the aid of lip reading).
5. Many older [patients] get confused in the hospital. Repetition is a good thing.
6. Speak to a family member at least once per day to relay the plan.
7. Try to avoid last minute or surprise discharges – they make [patients] and family members anxious. Talk about discharge planning from day 1 and what milestones must occur prior to a safe discharge. ‘In order for you to leave the hospital, X, Y, X must happen.’
8. Talk with your [patients] about something other than what brought them to the hospital (a tip I once learned from a wise mentor).
9. When possible, sit at eye level with your patient (I love these stools from @YNHH).
10. Take time to listen.”
Dr. Kunz closed with her golden rule: “Lastly, treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.”
Twitter user @BrunaPellini replied: “I love this, especially ‘Treat your patients how you would want your own family member treated.’ My mom and grandma always said that to me since I was a med student, and this is definitely one of my core values.”
Other clinicians shared similar experiences, and some added to Dr. Kunz’s list.
“Agree entirely, love the list – and while none of us can always practice perfectly, my experiences with my own mother’s illness taught me an enormous amount about communication,” @hoperugo responded.
Twitter user @mariejacork added: “Everyone in health care please read ... if you are lucky enough to not have had a loved one unwell in hospital, these may get forgotten. Having sat with my dad for a few days before he died a few years ago, I felt a lot of these, and it changed my practice forever.”
@bjcohenmd provided additional advice: “And use the dry erase board that should be in every room. Never start a medication without explaining it. Many docs will see the patient and then go to the computer, decide to order a med, but never go back to explain it.”
Patients also shared experiences and offered suggestions.
“As a chronic pain patient I’d add – we know it’s frustrating you can’t cure us but PLEASE do not SIGH if we say something didn’t work or [tell] us to be more positive. Just say ‘I know this is very hard, I’m here to listen.’ We don’t expect a cure, we do expect to be believed,” said @ppenguinsmt. “It makes me feel like I’m causing distress to you if I say the pain has been unrelenting. I leave feeling worse. ...You may have heard 10 [people] in pain before me but this is MY only [appointment].”
Twitter user @KatieCahoots added: “These are perfect. I wish doctors would do this not only in the hospital but in the doctor’s office, as well. I would add one caveat: When you try not to use medical jargon, don’t dumb it down as though I don’t know anything about science or haven’t done any of my own research.”
Dr. Kunz said she was taken aback but pleased by the response to her Tweet.
“It’s an example of the human side of medicine, so it resonates with physicians and with patients,” she commented. Seeing through her mom’s eyes how care was provided made her realize that medical training should include more emphasis on communication, including “real-time feedback to interns, residents, fellows, and students.”
Yes, it takes time, and “we don’t all have a lot of extra time,” she acknowledged.
“But some of these elements don’t take that much more time to do. They can help build trust and can, in the long run, actually save time if patients understand and family members feel engaged and like they are participants,” she said. “I think a little time investment will go a long way.”
In her case, she very much appreciated the one trainee who tried to call her and update her about her mother’s care each afternoon. “I really valued that,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We all struggle with the unwritten rules of medical culture
There is a two-lane bridge in my town. It is quaint and picturesque, and when we first moved here, I would gaze out at the water as I drove, letting my mind wander along with the seagulls drifting alongside the car. Until one day, crossing back over, I passed a school bus stopped in the other lane, and instead of waving back, the driver gave me such a fierce look of disapproval I felt like I’d been to the principal’s office. What had I done?
I started paying more attention to the pattern of the other cars on the bridge. Although it appeared to be a standard two-lane width, the lanes weren’t quite wide enough if a school bus or large truck needed to cross at the same time as a car coming from the opposite direction. They had to wait until the other lane was clear. It was an unwritten rule of the town that if you saw a school bus on the other side, you stopped your car and yielded the bridge to the bus. It took me weeks to figure this out. When I did, I felt like I finally belonged in the community. Before, I’d been an outsider.
This got me thinking about culture. Every place has its unwritten rules, whether a community or a workplace. But how do we know the culture of a place? It’s pretty much impossible until we experience it for ourselves.
When I did figure out the bridge, I had a little bit of anger, to be honest. How was I supposed to know about the lanes? There weren’t any signs. Geez.
Now, when I approach the bridge, I don’t even think about it. I know what to do if I see a bus coming.
But sometimes I remember that time of confusion before I deciphered the unwritten rule. I still have a twinge of guilt for having done something wrong, even though it hadn’t been my fault.
It reminded me of a memory from medical training. I was an MS4, and my ER rotation was in a busy county hospital with a level I trauma center. To say that the place was chaotic would be an understatement.
On the first morning, I was shown the chart rack (yes, this was back in the day of paper charts). Charts were placed in the order that patients arrived. Med students and residents were to take a chart in chronological order, go triage and assess the patient, and then find an attending. Once finished, you put the chart back on the rack and picked up the next one. This was the extent of my orientation to the ER.
The days and weeks of the rotation flew by. It was a busy and exciting time. By the end of the month, I’d come to feel a part of the team.
Until one day, after finishing discharging a patient, an attending asked me, “Where’s the billing sheet?”
I had no idea what she was talking about. No one had ever shown me a billing sheet. But by this point, as an MS4, I knew well that if an attending asked you something you didn’t know the answer to, you shouldn’t just say that you didn’t know. You should try to figure out if you could at least approximate an answer first.
As I scrambled in my mind to figure out what she was asking me, she took one look at the apprehension in my eyes and asked again, raising her voice, “You haven’t been doing the billing sheets?”
I thought back to the first day of the rotation. The cursory 30-second orientation. Chart rack. Take one. See the patient. Put it back. See the next patient. Nothing about billing sheets.
“No,” I said. “No one ever told me about – ”
But the attending didn’t care that I hadn’t been instructed on the billing sheets. She ripped into me, yelling about how she couldn’t believe I’d been working there the entire month and was not doing the billing sheets. She showed me what they were and where they were supposed to be going and, in front of the whole staff, treated me like not only the biggest idiot she’d ever worked with but that the hospital had ever seen.
As she berated me, I thought about all the patients I’d seen that month. All the billing sheets I hadn’t placed in the pile. All the attendings who hadn’t gotten credit for the patients they’d staffed with me.
But how could I have known? I wanted to ask. How could I have known if nobody showed me or told me?
It was like the bridge. I was in a new environment and somehow expected to know the rules without anyone telling me; and when I didn’t know, people treated me like I’d done it the wrong way on purpose.
I didn’t end up saying anything more to that attending. What could I have said? She had already unleashed a mountain of her pent-up anger at me.
What I did decide in that moment was that I would never be an attending like that.
Like the bridge, this memory years later can still make me feel guilt and shame for doing something wrong. Even though it wasn’t my fault.
I was thinking about this recently with the Match. Thousands of freshly graduated medical students embarking on their new positions as interns in teaching hospitals across the country.
If someone treats you poorly for not knowing something, you are not an idiot. You’ve worked incredibly hard to get where you are, and you deserve to be there.
For attendings and more senior trainees, remember what it was like to be starting in a new place. We all make mistakes, and often it’s simply because of a lack of information.
Trainees shouldn’t have to suffer and be made to feel like outsiders until they figure out the unwritten rules of the place. They belong.
Dr. Lycette is medical director of Providence Oncology and Hematology Care Clinic, Seaside, Ore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is a two-lane bridge in my town. It is quaint and picturesque, and when we first moved here, I would gaze out at the water as I drove, letting my mind wander along with the seagulls drifting alongside the car. Until one day, crossing back over, I passed a school bus stopped in the other lane, and instead of waving back, the driver gave me such a fierce look of disapproval I felt like I’d been to the principal’s office. What had I done?
I started paying more attention to the pattern of the other cars on the bridge. Although it appeared to be a standard two-lane width, the lanes weren’t quite wide enough if a school bus or large truck needed to cross at the same time as a car coming from the opposite direction. They had to wait until the other lane was clear. It was an unwritten rule of the town that if you saw a school bus on the other side, you stopped your car and yielded the bridge to the bus. It took me weeks to figure this out. When I did, I felt like I finally belonged in the community. Before, I’d been an outsider.
This got me thinking about culture. Every place has its unwritten rules, whether a community or a workplace. But how do we know the culture of a place? It’s pretty much impossible until we experience it for ourselves.
When I did figure out the bridge, I had a little bit of anger, to be honest. How was I supposed to know about the lanes? There weren’t any signs. Geez.
Now, when I approach the bridge, I don’t even think about it. I know what to do if I see a bus coming.
But sometimes I remember that time of confusion before I deciphered the unwritten rule. I still have a twinge of guilt for having done something wrong, even though it hadn’t been my fault.
It reminded me of a memory from medical training. I was an MS4, and my ER rotation was in a busy county hospital with a level I trauma center. To say that the place was chaotic would be an understatement.
On the first morning, I was shown the chart rack (yes, this was back in the day of paper charts). Charts were placed in the order that patients arrived. Med students and residents were to take a chart in chronological order, go triage and assess the patient, and then find an attending. Once finished, you put the chart back on the rack and picked up the next one. This was the extent of my orientation to the ER.
The days and weeks of the rotation flew by. It was a busy and exciting time. By the end of the month, I’d come to feel a part of the team.
Until one day, after finishing discharging a patient, an attending asked me, “Where’s the billing sheet?”
I had no idea what she was talking about. No one had ever shown me a billing sheet. But by this point, as an MS4, I knew well that if an attending asked you something you didn’t know the answer to, you shouldn’t just say that you didn’t know. You should try to figure out if you could at least approximate an answer first.
As I scrambled in my mind to figure out what she was asking me, she took one look at the apprehension in my eyes and asked again, raising her voice, “You haven’t been doing the billing sheets?”
I thought back to the first day of the rotation. The cursory 30-second orientation. Chart rack. Take one. See the patient. Put it back. See the next patient. Nothing about billing sheets.
“No,” I said. “No one ever told me about – ”
But the attending didn’t care that I hadn’t been instructed on the billing sheets. She ripped into me, yelling about how she couldn’t believe I’d been working there the entire month and was not doing the billing sheets. She showed me what they were and where they were supposed to be going and, in front of the whole staff, treated me like not only the biggest idiot she’d ever worked with but that the hospital had ever seen.
As she berated me, I thought about all the patients I’d seen that month. All the billing sheets I hadn’t placed in the pile. All the attendings who hadn’t gotten credit for the patients they’d staffed with me.
But how could I have known? I wanted to ask. How could I have known if nobody showed me or told me?
It was like the bridge. I was in a new environment and somehow expected to know the rules without anyone telling me; and when I didn’t know, people treated me like I’d done it the wrong way on purpose.
I didn’t end up saying anything more to that attending. What could I have said? She had already unleashed a mountain of her pent-up anger at me.
What I did decide in that moment was that I would never be an attending like that.
Like the bridge, this memory years later can still make me feel guilt and shame for doing something wrong. Even though it wasn’t my fault.
I was thinking about this recently with the Match. Thousands of freshly graduated medical students embarking on their new positions as interns in teaching hospitals across the country.
If someone treats you poorly for not knowing something, you are not an idiot. You’ve worked incredibly hard to get where you are, and you deserve to be there.
For attendings and more senior trainees, remember what it was like to be starting in a new place. We all make mistakes, and often it’s simply because of a lack of information.
Trainees shouldn’t have to suffer and be made to feel like outsiders until they figure out the unwritten rules of the place. They belong.
Dr. Lycette is medical director of Providence Oncology and Hematology Care Clinic, Seaside, Ore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There is a two-lane bridge in my town. It is quaint and picturesque, and when we first moved here, I would gaze out at the water as I drove, letting my mind wander along with the seagulls drifting alongside the car. Until one day, crossing back over, I passed a school bus stopped in the other lane, and instead of waving back, the driver gave me such a fierce look of disapproval I felt like I’d been to the principal’s office. What had I done?
I started paying more attention to the pattern of the other cars on the bridge. Although it appeared to be a standard two-lane width, the lanes weren’t quite wide enough if a school bus or large truck needed to cross at the same time as a car coming from the opposite direction. They had to wait until the other lane was clear. It was an unwritten rule of the town that if you saw a school bus on the other side, you stopped your car and yielded the bridge to the bus. It took me weeks to figure this out. When I did, I felt like I finally belonged in the community. Before, I’d been an outsider.
This got me thinking about culture. Every place has its unwritten rules, whether a community or a workplace. But how do we know the culture of a place? It’s pretty much impossible until we experience it for ourselves.
When I did figure out the bridge, I had a little bit of anger, to be honest. How was I supposed to know about the lanes? There weren’t any signs. Geez.
Now, when I approach the bridge, I don’t even think about it. I know what to do if I see a bus coming.
But sometimes I remember that time of confusion before I deciphered the unwritten rule. I still have a twinge of guilt for having done something wrong, even though it hadn’t been my fault.
It reminded me of a memory from medical training. I was an MS4, and my ER rotation was in a busy county hospital with a level I trauma center. To say that the place was chaotic would be an understatement.
On the first morning, I was shown the chart rack (yes, this was back in the day of paper charts). Charts were placed in the order that patients arrived. Med students and residents were to take a chart in chronological order, go triage and assess the patient, and then find an attending. Once finished, you put the chart back on the rack and picked up the next one. This was the extent of my orientation to the ER.
The days and weeks of the rotation flew by. It was a busy and exciting time. By the end of the month, I’d come to feel a part of the team.
Until one day, after finishing discharging a patient, an attending asked me, “Where’s the billing sheet?”
I had no idea what she was talking about. No one had ever shown me a billing sheet. But by this point, as an MS4, I knew well that if an attending asked you something you didn’t know the answer to, you shouldn’t just say that you didn’t know. You should try to figure out if you could at least approximate an answer first.
As I scrambled in my mind to figure out what she was asking me, she took one look at the apprehension in my eyes and asked again, raising her voice, “You haven’t been doing the billing sheets?”
I thought back to the first day of the rotation. The cursory 30-second orientation. Chart rack. Take one. See the patient. Put it back. See the next patient. Nothing about billing sheets.
“No,” I said. “No one ever told me about – ”
But the attending didn’t care that I hadn’t been instructed on the billing sheets. She ripped into me, yelling about how she couldn’t believe I’d been working there the entire month and was not doing the billing sheets. She showed me what they were and where they were supposed to be going and, in front of the whole staff, treated me like not only the biggest idiot she’d ever worked with but that the hospital had ever seen.
As she berated me, I thought about all the patients I’d seen that month. All the billing sheets I hadn’t placed in the pile. All the attendings who hadn’t gotten credit for the patients they’d staffed with me.
But how could I have known? I wanted to ask. How could I have known if nobody showed me or told me?
It was like the bridge. I was in a new environment and somehow expected to know the rules without anyone telling me; and when I didn’t know, people treated me like I’d done it the wrong way on purpose.
I didn’t end up saying anything more to that attending. What could I have said? She had already unleashed a mountain of her pent-up anger at me.
What I did decide in that moment was that I would never be an attending like that.
Like the bridge, this memory years later can still make me feel guilt and shame for doing something wrong. Even though it wasn’t my fault.
I was thinking about this recently with the Match. Thousands of freshly graduated medical students embarking on their new positions as interns in teaching hospitals across the country.
If someone treats you poorly for not knowing something, you are not an idiot. You’ve worked incredibly hard to get where you are, and you deserve to be there.
For attendings and more senior trainees, remember what it was like to be starting in a new place. We all make mistakes, and often it’s simply because of a lack of information.
Trainees shouldn’t have to suffer and be made to feel like outsiders until they figure out the unwritten rules of the place. They belong.
Dr. Lycette is medical director of Providence Oncology and Hematology Care Clinic, Seaside, Ore. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flu vaccines cut seasonal death in heart failure patients
WASHINGTON – Patients with heart failure who received an annual influenza vaccine for 3 years running had significantly fewer all-cause hospitalizations and significantly fewer cases of pneumonia during that time, compared with placebo-treated patients with heart failure, in a prospective, randomized, global trial with 5,129 participants.
Although the results failed to show a significant reduction in all-cause deaths linked to influenza vaccination, compared with controls during the entire 3 years of the study, the results did show a significant 21% relative mortality-risk reduction by vaccination during periods of peak influenza circulation, and a significant 23% reduction in cardiovascular deaths, compared with controls during peak seasons.
“This is the first randomized, controlled trial of influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure, and we showed that vaccination reduces deaths” during peak influenza seasons, Mark Loeb, MD, said during a press briefing at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The results send “an important global message that patients with heart failure should receive the influenza vaccine,” said Dr. Loeb, a professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who specializes in clinical epidemiology and infectious diseases.
Dr. Loeb admitted that he and his associates erred when they picked the time window to assess the two primary endpoints for the trial: the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke, and this combined endpoint plus hospitalizations for heart failure.
The time window they selected was the entirety of all 3 years following three annual immunizations. That was a mistake.
No flu vaccine benefit outside flu season
“We know that the influenza vaccine will not have any effect outside of when influenza is circulating. In retrospect, we should have done that,” Dr. Loeb bemoaned during his talk. He chalked up the bad choice to concern over collecting enough endpoints to see a significant between-group difference when the researchers designed the study.
For the entire 3 years of follow-up, influenza vaccination was tied to a nonsignificant 7% relative risk reduction for the first primary endpoint, and a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction for the second primary endpoint, he reported.
But Dr. Loeb lobbied for the relevance of several significant secondary endpoints that collectively showed a compelling pattern of benefit during his talk. These included, for the full 3-years of follow-up, important, significant reductions relative to placebo of 16% for first all-cause hospitalizations (P = .01), and a 42% relative risk reduction in first cases of pneumonia (P = .0006).
Then there were the benefits that appeared during influenza season. In that analysis, first events for the first primary endpoint fell after vaccination by a significant 18% relative to placebo. The in-season analysis also showed the significant cuts in both all-cause and cardiovascular deaths.
Despite the neutral primary endpoints, “if you look at these data as a whole I think they speak to the importance of vaccinating patients with heart failure against influenza,” Dr. Loeb maintained.
‘Totality of evidence supports vaccination’
“I agree that the totality of evidence supports influenza vaccination,” commented Mark H. Drazner, MD, professor and clinical chief of cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, who was designated discussant for the report.
“The message should be to offer influenza vaccine to patients with heart failure,” Dr. Drazner said in an interview. “Previous data on influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure were largely observational. This was a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial. That’s a step forward. Proving efficacy in a randomized trial is important.”
Dr Drazner added that his institution already promotes a “strong mandate” to vaccinate patients with heart failure against influenza.
“The influenza vaccine is a very effective and cost-efficient public health measure. Preventing hospitalizations of patients with heart failure has so many benefits,” commented Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of professional services at Baptist Health in Paducah, Ky., and a discussant during the press briefing.
The Influenza Vaccine To Prevent Adverse Vascular Events (IVVE) trial enrolled people with heart failure in New York Heart Association functional class II, III, or IV from any of 10 low- and middle-income countries including China, India, the Philippines, and multiple countries from Africa and the Middle East. They averaged 57 years of age, and slightly more than half were women.
IVVE was sponsored by McMaster University; the only commercial support that IVVE received was a free supply of influenza vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Loeb, Dr. Drazner, and Dr. Beavers had no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Patients with heart failure who received an annual influenza vaccine for 3 years running had significantly fewer all-cause hospitalizations and significantly fewer cases of pneumonia during that time, compared with placebo-treated patients with heart failure, in a prospective, randomized, global trial with 5,129 participants.
Although the results failed to show a significant reduction in all-cause deaths linked to influenza vaccination, compared with controls during the entire 3 years of the study, the results did show a significant 21% relative mortality-risk reduction by vaccination during periods of peak influenza circulation, and a significant 23% reduction in cardiovascular deaths, compared with controls during peak seasons.
“This is the first randomized, controlled trial of influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure, and we showed that vaccination reduces deaths” during peak influenza seasons, Mark Loeb, MD, said during a press briefing at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The results send “an important global message that patients with heart failure should receive the influenza vaccine,” said Dr. Loeb, a professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who specializes in clinical epidemiology and infectious diseases.
Dr. Loeb admitted that he and his associates erred when they picked the time window to assess the two primary endpoints for the trial: the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke, and this combined endpoint plus hospitalizations for heart failure.
The time window they selected was the entirety of all 3 years following three annual immunizations. That was a mistake.
No flu vaccine benefit outside flu season
“We know that the influenza vaccine will not have any effect outside of when influenza is circulating. In retrospect, we should have done that,” Dr. Loeb bemoaned during his talk. He chalked up the bad choice to concern over collecting enough endpoints to see a significant between-group difference when the researchers designed the study.
For the entire 3 years of follow-up, influenza vaccination was tied to a nonsignificant 7% relative risk reduction for the first primary endpoint, and a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction for the second primary endpoint, he reported.
But Dr. Loeb lobbied for the relevance of several significant secondary endpoints that collectively showed a compelling pattern of benefit during his talk. These included, for the full 3-years of follow-up, important, significant reductions relative to placebo of 16% for first all-cause hospitalizations (P = .01), and a 42% relative risk reduction in first cases of pneumonia (P = .0006).
Then there were the benefits that appeared during influenza season. In that analysis, first events for the first primary endpoint fell after vaccination by a significant 18% relative to placebo. The in-season analysis also showed the significant cuts in both all-cause and cardiovascular deaths.
Despite the neutral primary endpoints, “if you look at these data as a whole I think they speak to the importance of vaccinating patients with heart failure against influenza,” Dr. Loeb maintained.
‘Totality of evidence supports vaccination’
“I agree that the totality of evidence supports influenza vaccination,” commented Mark H. Drazner, MD, professor and clinical chief of cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, who was designated discussant for the report.
“The message should be to offer influenza vaccine to patients with heart failure,” Dr. Drazner said in an interview. “Previous data on influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure were largely observational. This was a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial. That’s a step forward. Proving efficacy in a randomized trial is important.”
Dr Drazner added that his institution already promotes a “strong mandate” to vaccinate patients with heart failure against influenza.
“The influenza vaccine is a very effective and cost-efficient public health measure. Preventing hospitalizations of patients with heart failure has so many benefits,” commented Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of professional services at Baptist Health in Paducah, Ky., and a discussant during the press briefing.
The Influenza Vaccine To Prevent Adverse Vascular Events (IVVE) trial enrolled people with heart failure in New York Heart Association functional class II, III, or IV from any of 10 low- and middle-income countries including China, India, the Philippines, and multiple countries from Africa and the Middle East. They averaged 57 years of age, and slightly more than half were women.
IVVE was sponsored by McMaster University; the only commercial support that IVVE received was a free supply of influenza vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Loeb, Dr. Drazner, and Dr. Beavers had no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Patients with heart failure who received an annual influenza vaccine for 3 years running had significantly fewer all-cause hospitalizations and significantly fewer cases of pneumonia during that time, compared with placebo-treated patients with heart failure, in a prospective, randomized, global trial with 5,129 participants.
Although the results failed to show a significant reduction in all-cause deaths linked to influenza vaccination, compared with controls during the entire 3 years of the study, the results did show a significant 21% relative mortality-risk reduction by vaccination during periods of peak influenza circulation, and a significant 23% reduction in cardiovascular deaths, compared with controls during peak seasons.
“This is the first randomized, controlled trial of influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure, and we showed that vaccination reduces deaths” during peak influenza seasons, Mark Loeb, MD, said during a press briefing at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology. The results send “an important global message that patients with heart failure should receive the influenza vaccine,” said Dr. Loeb, a professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who specializes in clinical epidemiology and infectious diseases.
Dr. Loeb admitted that he and his associates erred when they picked the time window to assess the two primary endpoints for the trial: the combined rate of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke, and this combined endpoint plus hospitalizations for heart failure.
The time window they selected was the entirety of all 3 years following three annual immunizations. That was a mistake.
No flu vaccine benefit outside flu season
“We know that the influenza vaccine will not have any effect outside of when influenza is circulating. In retrospect, we should have done that,” Dr. Loeb bemoaned during his talk. He chalked up the bad choice to concern over collecting enough endpoints to see a significant between-group difference when the researchers designed the study.
For the entire 3 years of follow-up, influenza vaccination was tied to a nonsignificant 7% relative risk reduction for the first primary endpoint, and a nonsignificant 9% relative risk reduction for the second primary endpoint, he reported.
But Dr. Loeb lobbied for the relevance of several significant secondary endpoints that collectively showed a compelling pattern of benefit during his talk. These included, for the full 3-years of follow-up, important, significant reductions relative to placebo of 16% for first all-cause hospitalizations (P = .01), and a 42% relative risk reduction in first cases of pneumonia (P = .0006).
Then there were the benefits that appeared during influenza season. In that analysis, first events for the first primary endpoint fell after vaccination by a significant 18% relative to placebo. The in-season analysis also showed the significant cuts in both all-cause and cardiovascular deaths.
Despite the neutral primary endpoints, “if you look at these data as a whole I think they speak to the importance of vaccinating patients with heart failure against influenza,” Dr. Loeb maintained.
‘Totality of evidence supports vaccination’
“I agree that the totality of evidence supports influenza vaccination,” commented Mark H. Drazner, MD, professor and clinical chief of cardiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, who was designated discussant for the report.
“The message should be to offer influenza vaccine to patients with heart failure,” Dr. Drazner said in an interview. “Previous data on influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure were largely observational. This was a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled trial. That’s a step forward. Proving efficacy in a randomized trial is important.”
Dr Drazner added that his institution already promotes a “strong mandate” to vaccinate patients with heart failure against influenza.
“The influenza vaccine is a very effective and cost-efficient public health measure. Preventing hospitalizations of patients with heart failure has so many benefits,” commented Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of professional services at Baptist Health in Paducah, Ky., and a discussant during the press briefing.
The Influenza Vaccine To Prevent Adverse Vascular Events (IVVE) trial enrolled people with heart failure in New York Heart Association functional class II, III, or IV from any of 10 low- and middle-income countries including China, India, the Philippines, and multiple countries from Africa and the Middle East. They averaged 57 years of age, and slightly more than half were women.
IVVE was sponsored by McMaster University; the only commercial support that IVVE received was a free supply of influenza vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Loeb, Dr. Drazner, and Dr. Beavers had no disclosures.
AT ACC 2022







