User login
The Mysterious Latch
While there may be some lactation consultants who disagree, in my experience counseling women attempting to breastfeed is more art than science. Well before the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) began to offer mini courses on breastfeeding for practitioners I was left to help new mothers based on watching my wife nurse our three children and what scraps of common sense I could sweep up off the floor.
Using my own benchmarks of success I would say I did a decent job with dyads who sought my help. I began by accepting that even under optimal conditions, not every woman and/or child can successfully breastfeed. None of the infants died or was hospitalized with dehydration. A few may have required some additional phototherapy, but they all completed infancy in good shape. On the maternal side I am sure there were a few mothers who had lingering feelings of inadequacy because they had “failed” at breastfeeding. But, for the most part, I think I succeeded in helping new mothers remain as mentally healthy as they could be given the rigors of motherhood. At least I gave it my best shot.
If I had a strategy, it was a focus on maintaining a routine (schedule can have an ugly aura about it) that allowed mothers to achieve spells of restorative rest. Helping mothers with the difficult task of deciding whether their infant was hungry, or tired, or uncomfortable was always a struggle, but well worth the effort when we succeeded. Finally, I tried to help mothers step back off the ledge and look at the bigger picture — breastfeeding was not the only way to feed their baby while we were working to overcome the bumps in the road.
Where I failed was in my inability to effectively counsel when it came to the mysteries of the latch. In large part it was because I was a man and helping the dyad succeed at latching on to the breast can require a hands-on approach with which I felt a bit uncomfortable. I could certainly test a baby’s suck and oral architecture with my pinky but otherwise I had to rely on women to help if latching was a problem. I think even trained lactation consultants have difficulty with this mysterious process, which is completely hidden from view inside the baby’s mouth.
Fortunately for me and the dyads I was working with, we rarely considered ankyloglossia as a problem. My training had been that tongue-tie seldom, if ever, contributed to speech problems and even less commonly hindered latch. I think I recall snipping a couple of lingual frenulums early in my career in a bloodless and seemingly painless procedure. But, for the life of me I can’t recall the motivation. It may have been that the ankyloglossia was so obvious that I couldn’t convince the parents it would resolve or it was at the request of a lactation consultant.
But, obviously after I stopped seeing newborns a decade and a half ago the lingual frenulum became a target of surgical assault with, at times, unfortunate results that made breastfeeding painful and more difficult. It’s hard for me to imagine why anyone would consider using a laser for such a simple procedure. But, then I haven’t invested in a laser that allowed me to charge $800 for the procedure. I doubt I even charged for it. It wouldn’t have been worth the time and effort to look up the code. But, then, technology and money can be powerful motivators.
The good news is the AAP has been watching and recently issued a clinical report in which they state what many of us have known from personal observation — They further note that “the symptoms of ankyloglossia overlap those of other breastfeeding difficulties.”
So there you have it. Another fad has been squashed and we’ve come full circle. The latch still remains mystery hidden from view. I think we have to suspect that there exists a small number of dyads in which tongue-tie creates a problem with nursing. And, there may be some safe imaging technique coming along that gives us a glimpse of what happens in the dark recesses of a nursing baby’s mouth. Until then we must rely on masters of the art of lactation consulting, the “Latch Whisperers.”
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
While there may be some lactation consultants who disagree, in my experience counseling women attempting to breastfeed is more art than science. Well before the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) began to offer mini courses on breastfeeding for practitioners I was left to help new mothers based on watching my wife nurse our three children and what scraps of common sense I could sweep up off the floor.
Using my own benchmarks of success I would say I did a decent job with dyads who sought my help. I began by accepting that even under optimal conditions, not every woman and/or child can successfully breastfeed. None of the infants died or was hospitalized with dehydration. A few may have required some additional phototherapy, but they all completed infancy in good shape. On the maternal side I am sure there were a few mothers who had lingering feelings of inadequacy because they had “failed” at breastfeeding. But, for the most part, I think I succeeded in helping new mothers remain as mentally healthy as they could be given the rigors of motherhood. At least I gave it my best shot.
If I had a strategy, it was a focus on maintaining a routine (schedule can have an ugly aura about it) that allowed mothers to achieve spells of restorative rest. Helping mothers with the difficult task of deciding whether their infant was hungry, or tired, or uncomfortable was always a struggle, but well worth the effort when we succeeded. Finally, I tried to help mothers step back off the ledge and look at the bigger picture — breastfeeding was not the only way to feed their baby while we were working to overcome the bumps in the road.
Where I failed was in my inability to effectively counsel when it came to the mysteries of the latch. In large part it was because I was a man and helping the dyad succeed at latching on to the breast can require a hands-on approach with which I felt a bit uncomfortable. I could certainly test a baby’s suck and oral architecture with my pinky but otherwise I had to rely on women to help if latching was a problem. I think even trained lactation consultants have difficulty with this mysterious process, which is completely hidden from view inside the baby’s mouth.
Fortunately for me and the dyads I was working with, we rarely considered ankyloglossia as a problem. My training had been that tongue-tie seldom, if ever, contributed to speech problems and even less commonly hindered latch. I think I recall snipping a couple of lingual frenulums early in my career in a bloodless and seemingly painless procedure. But, for the life of me I can’t recall the motivation. It may have been that the ankyloglossia was so obvious that I couldn’t convince the parents it would resolve or it was at the request of a lactation consultant.
But, obviously after I stopped seeing newborns a decade and a half ago the lingual frenulum became a target of surgical assault with, at times, unfortunate results that made breastfeeding painful and more difficult. It’s hard for me to imagine why anyone would consider using a laser for such a simple procedure. But, then I haven’t invested in a laser that allowed me to charge $800 for the procedure. I doubt I even charged for it. It wouldn’t have been worth the time and effort to look up the code. But, then, technology and money can be powerful motivators.
The good news is the AAP has been watching and recently issued a clinical report in which they state what many of us have known from personal observation — They further note that “the symptoms of ankyloglossia overlap those of other breastfeeding difficulties.”
So there you have it. Another fad has been squashed and we’ve come full circle. The latch still remains mystery hidden from view. I think we have to suspect that there exists a small number of dyads in which tongue-tie creates a problem with nursing. And, there may be some safe imaging technique coming along that gives us a glimpse of what happens in the dark recesses of a nursing baby’s mouth. Until then we must rely on masters of the art of lactation consulting, the “Latch Whisperers.”
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
While there may be some lactation consultants who disagree, in my experience counseling women attempting to breastfeed is more art than science. Well before the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) began to offer mini courses on breastfeeding for practitioners I was left to help new mothers based on watching my wife nurse our three children and what scraps of common sense I could sweep up off the floor.
Using my own benchmarks of success I would say I did a decent job with dyads who sought my help. I began by accepting that even under optimal conditions, not every woman and/or child can successfully breastfeed. None of the infants died or was hospitalized with dehydration. A few may have required some additional phototherapy, but they all completed infancy in good shape. On the maternal side I am sure there were a few mothers who had lingering feelings of inadequacy because they had “failed” at breastfeeding. But, for the most part, I think I succeeded in helping new mothers remain as mentally healthy as they could be given the rigors of motherhood. At least I gave it my best shot.
If I had a strategy, it was a focus on maintaining a routine (schedule can have an ugly aura about it) that allowed mothers to achieve spells of restorative rest. Helping mothers with the difficult task of deciding whether their infant was hungry, or tired, or uncomfortable was always a struggle, but well worth the effort when we succeeded. Finally, I tried to help mothers step back off the ledge and look at the bigger picture — breastfeeding was not the only way to feed their baby while we were working to overcome the bumps in the road.
Where I failed was in my inability to effectively counsel when it came to the mysteries of the latch. In large part it was because I was a man and helping the dyad succeed at latching on to the breast can require a hands-on approach with which I felt a bit uncomfortable. I could certainly test a baby’s suck and oral architecture with my pinky but otherwise I had to rely on women to help if latching was a problem. I think even trained lactation consultants have difficulty with this mysterious process, which is completely hidden from view inside the baby’s mouth.
Fortunately for me and the dyads I was working with, we rarely considered ankyloglossia as a problem. My training had been that tongue-tie seldom, if ever, contributed to speech problems and even less commonly hindered latch. I think I recall snipping a couple of lingual frenulums early in my career in a bloodless and seemingly painless procedure. But, for the life of me I can’t recall the motivation. It may have been that the ankyloglossia was so obvious that I couldn’t convince the parents it would resolve or it was at the request of a lactation consultant.
But, obviously after I stopped seeing newborns a decade and a half ago the lingual frenulum became a target of surgical assault with, at times, unfortunate results that made breastfeeding painful and more difficult. It’s hard for me to imagine why anyone would consider using a laser for such a simple procedure. But, then I haven’t invested in a laser that allowed me to charge $800 for the procedure. I doubt I even charged for it. It wouldn’t have been worth the time and effort to look up the code. But, then, technology and money can be powerful motivators.
The good news is the AAP has been watching and recently issued a clinical report in which they state what many of us have known from personal observation — They further note that “the symptoms of ankyloglossia overlap those of other breastfeeding difficulties.”
So there you have it. Another fad has been squashed and we’ve come full circle. The latch still remains mystery hidden from view. I think we have to suspect that there exists a small number of dyads in which tongue-tie creates a problem with nursing. And, there may be some safe imaging technique coming along that gives us a glimpse of what happens in the dark recesses of a nursing baby’s mouth. Until then we must rely on masters of the art of lactation consulting, the “Latch Whisperers.”
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
NODDI and DTI in Remote Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
, according to authors of a recent study. In particular, they said, using neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) to monitor long-term mTBI impact on brain regions related to cognitive and emotional processing can help clinicians assess recovery, predict progression, and optimize treatment.
“Currently,” said co-senior study author Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD, “there is a lack of minimally invasive, quantitative diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring progression or recovery after mild TBI. However, mild TBI can be quite disabling, with many patients reporting symptoms months or even years after injury. This is the most difficult part to diagnose.” Dr. Yeh is a researcher at the National Intrepid Center of Excellence (NICoE) at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Maryland.
The NICoE, a Department of Defense organization and the senior member of Defense Intrepid Network for Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Health, is among several centers charged with improving support for injured service members’ recovery, rehabilitation, and reintegration into their communities. The overarching goal, said Dr. Yeh, is to enable community neurologists to refer service members and veterans to these centers for treatment and advanced imaging when needed.
Invisible Wounds
Limitations of conventional MRI and CT make it tough to discern which patients with mTBI will return to baseline functioning, and which will develop long-term complications. Addressing the silent or invisible wounds of mTBI will require improved diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools, he said.
For their study, published in JAMA Network Open, Dr. Yeh and colleagues compared diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and NODDI data from 65 male service members with remote (more than 2 years old) mTBI against scans of 33 noninjured controls matched for age, sex, and active-duty status.
“Although DTI is very sensitive in detecting microstructural changes in mild TBI,” he said, “it is not specific to the underlying pathophysiological changes.”
Conversely, NODDI uses biophysical modeling of intracellular diffusion, extracellular diffusion, and free water to help physicians to understand subtle pathophysiological changes with greater sensitivity and specificity than does DTI. “This will allow us to correlate symptoms with brain structural changes, making the invisible wound visible.”
In the study, the greatest differences between injured and control patients appeared in the following NODDI metrics (P <.001 in all analyses):
- Intracellular volume fraction (ICVF) of the right corticospinal tract (CST)
- Orientation dispersion index (ODI) of the left posterior thalamic radiation (PTR)
- ODI of the left uncinate fasciculus (UNC)
Regarding patient-reported neurobehavioral symptoms, Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory cognitive subscores were associated with fractional anisotropy of the left UNC. In addition, PTSD Checklist–Civilian version total scores and avoidance subscores corresponded, respectively, with isotropic volume fraction (ISOVF) of the genu of corpus callosum and with ODI of the left fornix and stria terminalis.
Next Steps
Presently, Dr. Yeh said, conventional MRI and CT usually cannot differentiate between axonal injury, axonal inflammation (which develops during the chronic phase of mTBI), and demyelination. “But newer biophysical modeling, such as NODDI, will allow us to tell the difference.” Along with providing prognostic information, he said, such technology can guide appropriate treatment, such as anti-inflammatory agents for chronic inflammation.
Most community neurologists refer patients with persistent mTBI symptoms in the absence of red flags using CT and conventional MRI for advanced neuroimaging, said Dr. Yeh. But because few community neurologists are familiar with NODDI, he said, broadening its reach will require educating these providers. Additional steps that Dr. Yeh said could occur over the next decade or more include boosting advanced dMRI sensitivity levels through improved hardware, software, and diagnostic tools.
“We need to make these techniques clinically feasible,” he added. Currently, protocols that allow advanced dMRI scans in about 10 minutes can be achievable.
The investments required to implement advanced dMRI techniques will be substantial. A state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner that can support NODDI and DTI can easily cost $1 million, said Dr. Yeh. Factor in additional equipment options and construction costs, he added, and the total price tag can easily exceed $2 million. But rather than replacing all existing MRI systems, said Dr. Yeh, AI one day may help translate high-gradient capability even to widely used lower-field MRI scanners operating at 0.5T.
Streamlining systems that incorporate disparate scanners with different acquisition parameters will require standardized data acquisition and sharing parameters. Along with helping to evaluate new techniques as they become available, data harmonization and sharing can facilitate a shift from research comparisons between large groups to comparing a single patient against many others — a move that Dr. Yeh said must occur for advanced dMRI techniques to achieve clinical relevance.
In addition, experts will need to revise clinical guidelines for use of new technologies as their availability grows. “Improper use of these techniques will not only increase health costs, but also probably result in adverse health results.” Such guidelines could be very useful in evaluating the suitability and quality of referrals for diagnostic images, Dr. Yeh said.
Dr. Yeh reports no relevant financial interests. The project was partially funded by the US Army Medical Research and Materiel Command.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Case Series: Upadacitinib Effective for Granulomatous Cheilitis
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
in a small retrospective case series.
METHODOLOGY:
- Granulomatous cheilitis is a rare, nonnecrotizing granulomatous inflammatory disorder characterized by intermittent or persistent swelling of the lips.
- In a retrospective case series of five patients (median age, 30 years; four women) with granulomatous cheilitis resistant to systemic treatments at a Belgian hospital between June 2023 and March 2024, all five were treated with a high dose of upadacitinib (30 mg daily).
- The primary endpoint was objective clinical improvement in lip swelling and infiltration over a median follow-up of 7.2 months.
- Three patients had concomitant dormant Crohn’s disease (CD); a secondary outcome was disease activity in these patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Upadacitinib treatment resulted in a complete response in four patients (80%) within a median of 3.8 months and a partial response in one patient.
- CD remained dormant in the three patients with CD.
- The safety profile of upadacitinib was favorable, and no serious adverse events were reported. Two patients experienced headaches, acne, mild changes in lipids, and/or transaminitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Upadacitinib was effective in treating patients with recalcitrant and long-lasting granulomatous cheilitis, even in cases of concomitant CD, which could substantially improve the quality of life of affected patients,” the authors wrote. More studies are needed to confirm these results in larger groups of patients over longer periods of time, “and with other JAK inhibitors.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Axel De Greef, MD, Department of Dermatology, Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain), Brussels, Belgium. It was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and short follow-up may limit the generalizability of the findings to a larger population of patients with granulomatous cheilitis.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not report any funding sources. Some authors reported receiving nonfinancial support and personal fees from various pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychiatric, Autoimmune Comorbidities Increased in Patients with Alopecia Areata
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and were at greater risk of developing those comorbidities after diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated 63,384 patients with AA and 3,309,107 individuals without AA (aged 12-64 years) from the Merative MarketScan Research Databases.
- The matched cohorts included 16,512 patients with AA and 66,048 control individuals.
- Outcomes were the prevalence of psychiatric and autoimmune diseases at baseline and the incidence of new-onset psychiatric and autoimmune diseases during the year after diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, patients with AA showed a greater prevalence of any psychiatric disease (30.9% vs 26.8%; P < .001) and any immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (16.1% vs 8.9%; P < .0001) than those with controls.
- In matched cohorts, patients with AA also showed a higher incidence of any new-onset psychiatric diseases (10.2% vs 6.8%; P < .001) or immune-mediated or autoimmune disease (6.2% vs 1.5%; P <.001) within the first 12 months of AA diagnosis than those with controls.
- Among patients with AA, the risk of developing a psychiatric comorbidity was higher (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.3; 95% CI, 1.3-1.4). The highest risks were seen for adjustment disorder (aHR, 1.5), panic disorder (aHR, 1.4), and sexual dysfunction (aHR, 1.4).
- Compared with controls, patients with AA were also at an increased risk of developing immune-mediated or autoimmune comorbidities (aHR, 2.7; 95% CI, 2.5-2.8), with the highest for systemic lupus (aHR, 5.7), atopic dermatitis (aHR, 4.3), and vitiligo (aHR, 3.8).
IN PRACTICE:
“Routine monitoring of patients with AA, especially those at risk of developing comorbidities, may permit earlier and more effective intervention,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPA, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard University, Boston. It was published online on July 31, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Causality could not be inferred because of the retrospective nature of the study. Comorbidities were solely diagnosed on the basis of diagnostic codes, and researchers did not have access to characteristics such as lab values that could have indicated any underlying comorbidity before the AA diagnosis. This study also did not account for the varying levels of severity of the disease, which may have led to an underestimation of disease burden and the risk for comorbidities.
DISCLOSURES:
AbbVie provided funding for this study. Mostaghimi disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbvie and several other companies outside of this work. The other four authors were current or former employees of Abbvie and have or may have stock and/or stock options in AbbVie.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Expanded Surface Area Safe, Well-Tolerated for AK treatment
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 multicenter, single-arm trial evaluated the safety and tolerability of tirbanibulin ointment 1% in 105 adults with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AKs on the face or balding scalp from June to December 2022 in the United States. (In June 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved a supplemental new drug application for tirbanibulin 1%, a microtubule inhibitor, allowing the expansion of the surface area treated for AKs of the face or scalp from 25 cm2 to 100 cm2.)
- Participants applied tirbanibulin ointment 1% once daily for 5 days over a treatment field of about 100 cm2 on the face or balding scalp. A total of 102 patients completed the study.
- Safety and tolerability were evaluated with reports of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and a composite score of six local tolerability signs on days 5, 8, 15, and 29, and on completion of the evaluation period on day 57.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common local effects of treatment were erythema (96.1% of patients) and flaking or scaling (84.4%), with severe cases reported in 5.8% and 8.7% of the patients, respectively.
- The mean maximum local tolerability composite score was 4.1 out of 18, which peaked around day 8 and returned to baseline by day 29.
- TEAEs considered related to the treatment were reported in 18.1% of patients; the most frequent were application site pruritus (10.5%) and application site pain (8.6%). No adverse events led to the discontinuation of treatment.
- The mean percent reduction in the lesion count from baseline was 77.8% at day 57, with a mean lesion count of 1.8 at the end of the study.
IN PRACTICE:
In this study, “local tolerability and safety profiles were well characterized in patients with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AK lesions in a field of 100 cm2 and were consistent with those previously reported in patients with AK treated in pivotal trials with tirbanibulin over a smaller field (25 cm2),” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Neal Bhatia, MD, of Therapeutics Clinical Research, San Diego, was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of a placebo group and the absence of long-term follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Almirall. Five authors reported being employees of Almirall. Other authors declared having ties with various other sources, including Almirall.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 multicenter, single-arm trial evaluated the safety and tolerability of tirbanibulin ointment 1% in 105 adults with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AKs on the face or balding scalp from June to December 2022 in the United States. (In June 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved a supplemental new drug application for tirbanibulin 1%, a microtubule inhibitor, allowing the expansion of the surface area treated for AKs of the face or scalp from 25 cm2 to 100 cm2.)
- Participants applied tirbanibulin ointment 1% once daily for 5 days over a treatment field of about 100 cm2 on the face or balding scalp. A total of 102 patients completed the study.
- Safety and tolerability were evaluated with reports of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and a composite score of six local tolerability signs on days 5, 8, 15, and 29, and on completion of the evaluation period on day 57.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common local effects of treatment were erythema (96.1% of patients) and flaking or scaling (84.4%), with severe cases reported in 5.8% and 8.7% of the patients, respectively.
- The mean maximum local tolerability composite score was 4.1 out of 18, which peaked around day 8 and returned to baseline by day 29.
- TEAEs considered related to the treatment were reported in 18.1% of patients; the most frequent were application site pruritus (10.5%) and application site pain (8.6%). No adverse events led to the discontinuation of treatment.
- The mean percent reduction in the lesion count from baseline was 77.8% at day 57, with a mean lesion count of 1.8 at the end of the study.
IN PRACTICE:
In this study, “local tolerability and safety profiles were well characterized in patients with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AK lesions in a field of 100 cm2 and were consistent with those previously reported in patients with AK treated in pivotal trials with tirbanibulin over a smaller field (25 cm2),” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Neal Bhatia, MD, of Therapeutics Clinical Research, San Diego, was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of a placebo group and the absence of long-term follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Almirall. Five authors reported being employees of Almirall. Other authors declared having ties with various other sources, including Almirall.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 multicenter, single-arm trial evaluated the safety and tolerability of tirbanibulin ointment 1% in 105 adults with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AKs on the face or balding scalp from June to December 2022 in the United States. (In June 2024, the Food and Drug Administration approved a supplemental new drug application for tirbanibulin 1%, a microtubule inhibitor, allowing the expansion of the surface area treated for AKs of the face or scalp from 25 cm2 to 100 cm2.)
- Participants applied tirbanibulin ointment 1% once daily for 5 days over a treatment field of about 100 cm2 on the face or balding scalp. A total of 102 patients completed the study.
- Safety and tolerability were evaluated with reports of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and a composite score of six local tolerability signs on days 5, 8, 15, and 29, and on completion of the evaluation period on day 57.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common local effects of treatment were erythema (96.1% of patients) and flaking or scaling (84.4%), with severe cases reported in 5.8% and 8.7% of the patients, respectively.
- The mean maximum local tolerability composite score was 4.1 out of 18, which peaked around day 8 and returned to baseline by day 29.
- TEAEs considered related to the treatment were reported in 18.1% of patients; the most frequent were application site pruritus (10.5%) and application site pain (8.6%). No adverse events led to the discontinuation of treatment.
- The mean percent reduction in the lesion count from baseline was 77.8% at day 57, with a mean lesion count of 1.8 at the end of the study.
IN PRACTICE:
In this study, “local tolerability and safety profiles were well characterized in patients with 4-12 clinically typical, visible, and discrete AK lesions in a field of 100 cm2 and were consistent with those previously reported in patients with AK treated in pivotal trials with tirbanibulin over a smaller field (25 cm2),” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Neal Bhatia, MD, of Therapeutics Clinical Research, San Diego, was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the lack of a placebo group and the absence of long-term follow-up.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Almirall. Five authors reported being employees of Almirall. Other authors declared having ties with various other sources, including Almirall.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Skin Dxs in Children in Refugee Camps Include Fungal Infections, Leishmaniasis
on the topic, a literature review showed. However, likely culprits include infectious diseases with cutaneous manifestations, such as pediculosis, tinea capitis, and scabies.
“Current data indicates that one in two refugees are children,” one of the study investigators, Mehar Maju, MPH, a fourth-year student at of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in an interview following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the results were presented during a poster session.
“The number of refugees continues to rise to unprecedented levels every year,” and climate change continues to drive increases in migration, “impacting those residing in camps,” she said. “As we continue to think about what this means for best supporting those residing in camps, I think it’s also important to consider how to best support refugees, specifically children, when they arrive in the United States. Part of this is to know what conditions are most prevalent and what type of social support this vulnerable population needs.”
To identify the common dermatologic conditions among children living in refugee camps, Ms. Maju and fellow fourth-year University of Washington medical student Nadia Siddiqui searched PubMed and Google Scholar for studies that were published in English and reported on the skin disease prevalence and management for refugees who are children. Key search terms used included “refugees,” “children,” “dermatology,” and “skin disease.” Of approximately 105 potential studies identified, 19 underwent analysis. Of these, only five were included in the final review.
One of the five studies was conducted in rural Nyala, Sudan. The study found that 88.8% of those living in orphanages and refugee camps were reported to have a skin disorder, commonly fungal or bacterial infections and dermatitis. In a separate case series, researchers found that cutaneous leishmaniasis was rising among Syrian refugee children.
A study that looked at morbidity and disease burden in mainland Greece refugee camps found that the skin was the second-most common site of communicable diseases among children, behind those of the respiratory tract. In another study that investigated the health of children in Australian immigration detention centers, complaints related to skin conditions were significantly elevated among children who were detained offshore, compared with those who were detained onshore.
Finally, in a study of 125 children between the ages of 1 and 15 years at a Sierra Leone–based displacement camp, the prevalence of scabies was 77% among those aged < 5 years and peaked to 86% among those aged 5-9 years.
“It was surprising to see the limited information about dermatologic diseases impacting children in refugee camps,” Ms. Maju said. “I expected that there would be more information on the specific proportion of diseases beyond those of infectious etiology. For example, I had believed that we would have more information on the prevalence of atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, and other more chronic skin diseases.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, mainly the lack of published information on the skin health of pediatric refugees. “A study that evaluates the health status and dermatologic prevalence of disease among children residing in camps and those newly arrived in the United States from camps would provide unprecedented insight into this topic,” Ms. Maju said. “The results could guide public health efforts in improving care delivery and preparedness in camps and clinicians serving this particular population when they arrive in the United States.”
She and Ms. Siddiqui reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on the topic, a literature review showed. However, likely culprits include infectious diseases with cutaneous manifestations, such as pediculosis, tinea capitis, and scabies.
“Current data indicates that one in two refugees are children,” one of the study investigators, Mehar Maju, MPH, a fourth-year student at of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in an interview following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the results were presented during a poster session.
“The number of refugees continues to rise to unprecedented levels every year,” and climate change continues to drive increases in migration, “impacting those residing in camps,” she said. “As we continue to think about what this means for best supporting those residing in camps, I think it’s also important to consider how to best support refugees, specifically children, when they arrive in the United States. Part of this is to know what conditions are most prevalent and what type of social support this vulnerable population needs.”
To identify the common dermatologic conditions among children living in refugee camps, Ms. Maju and fellow fourth-year University of Washington medical student Nadia Siddiqui searched PubMed and Google Scholar for studies that were published in English and reported on the skin disease prevalence and management for refugees who are children. Key search terms used included “refugees,” “children,” “dermatology,” and “skin disease.” Of approximately 105 potential studies identified, 19 underwent analysis. Of these, only five were included in the final review.
One of the five studies was conducted in rural Nyala, Sudan. The study found that 88.8% of those living in orphanages and refugee camps were reported to have a skin disorder, commonly fungal or bacterial infections and dermatitis. In a separate case series, researchers found that cutaneous leishmaniasis was rising among Syrian refugee children.
A study that looked at morbidity and disease burden in mainland Greece refugee camps found that the skin was the second-most common site of communicable diseases among children, behind those of the respiratory tract. In another study that investigated the health of children in Australian immigration detention centers, complaints related to skin conditions were significantly elevated among children who were detained offshore, compared with those who were detained onshore.
Finally, in a study of 125 children between the ages of 1 and 15 years at a Sierra Leone–based displacement camp, the prevalence of scabies was 77% among those aged < 5 years and peaked to 86% among those aged 5-9 years.
“It was surprising to see the limited information about dermatologic diseases impacting children in refugee camps,” Ms. Maju said. “I expected that there would be more information on the specific proportion of diseases beyond those of infectious etiology. For example, I had believed that we would have more information on the prevalence of atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, and other more chronic skin diseases.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, mainly the lack of published information on the skin health of pediatric refugees. “A study that evaluates the health status and dermatologic prevalence of disease among children residing in camps and those newly arrived in the United States from camps would provide unprecedented insight into this topic,” Ms. Maju said. “The results could guide public health efforts in improving care delivery and preparedness in camps and clinicians serving this particular population when they arrive in the United States.”
She and Ms. Siddiqui reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
on the topic, a literature review showed. However, likely culprits include infectious diseases with cutaneous manifestations, such as pediculosis, tinea capitis, and scabies.
“Current data indicates that one in two refugees are children,” one of the study investigators, Mehar Maju, MPH, a fourth-year student at of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said in an interview following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the results were presented during a poster session.
“The number of refugees continues to rise to unprecedented levels every year,” and climate change continues to drive increases in migration, “impacting those residing in camps,” she said. “As we continue to think about what this means for best supporting those residing in camps, I think it’s also important to consider how to best support refugees, specifically children, when they arrive in the United States. Part of this is to know what conditions are most prevalent and what type of social support this vulnerable population needs.”
To identify the common dermatologic conditions among children living in refugee camps, Ms. Maju and fellow fourth-year University of Washington medical student Nadia Siddiqui searched PubMed and Google Scholar for studies that were published in English and reported on the skin disease prevalence and management for refugees who are children. Key search terms used included “refugees,” “children,” “dermatology,” and “skin disease.” Of approximately 105 potential studies identified, 19 underwent analysis. Of these, only five were included in the final review.
One of the five studies was conducted in rural Nyala, Sudan. The study found that 88.8% of those living in orphanages and refugee camps were reported to have a skin disorder, commonly fungal or bacterial infections and dermatitis. In a separate case series, researchers found that cutaneous leishmaniasis was rising among Syrian refugee children.
A study that looked at morbidity and disease burden in mainland Greece refugee camps found that the skin was the second-most common site of communicable diseases among children, behind those of the respiratory tract. In another study that investigated the health of children in Australian immigration detention centers, complaints related to skin conditions were significantly elevated among children who were detained offshore, compared with those who were detained onshore.
Finally, in a study of 125 children between the ages of 1 and 15 years at a Sierra Leone–based displacement camp, the prevalence of scabies was 77% among those aged < 5 years and peaked to 86% among those aged 5-9 years.
“It was surprising to see the limited information about dermatologic diseases impacting children in refugee camps,” Ms. Maju said. “I expected that there would be more information on the specific proportion of diseases beyond those of infectious etiology. For example, I had believed that we would have more information on the prevalence of atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, and other more chronic skin diseases.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, mainly the lack of published information on the skin health of pediatric refugees. “A study that evaluates the health status and dermatologic prevalence of disease among children residing in camps and those newly arrived in the United States from camps would provide unprecedented insight into this topic,” Ms. Maju said. “The results could guide public health efforts in improving care delivery and preparedness in camps and clinicians serving this particular population when they arrive in the United States.”
She and Ms. Siddiqui reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Eruptive Syringoma Manifesting as a Widespread Rash in 3 Patients
To the Editor:
Syringoma is a relatively common benign adnexal neoplasm originating in the ducts of eccrine sweat glands. It can be
A 28-year-old man presented with multiple asymptomatic papules on the trunk and upper arms of 20 years’ duration (patient 1). He had been diagnosed with Darier disease 3 years prior to the current presentation and was treated with oral and topical retinoic acid without a response. After 3 months of oral treatment, the retinoic acid was stopped due to elevated liver enzymes. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed multiple smooth, firm, nonfused, 1- to 4-mm
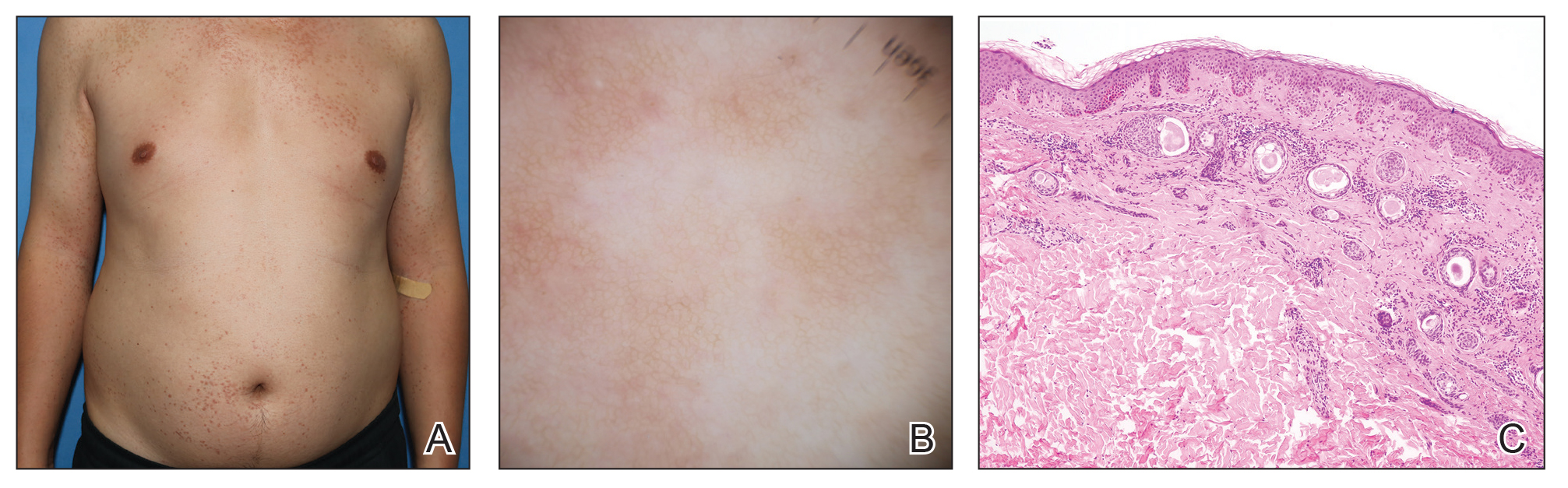
A 27-year-old woman presented with widespread asymptomatic papules

A 43-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with brownish flat-topped papules on the chest and abdomen of 19 years’ duration (Figure 3A)(patient 3). The lesions had remained stable and did not progress. He denied any treatment.
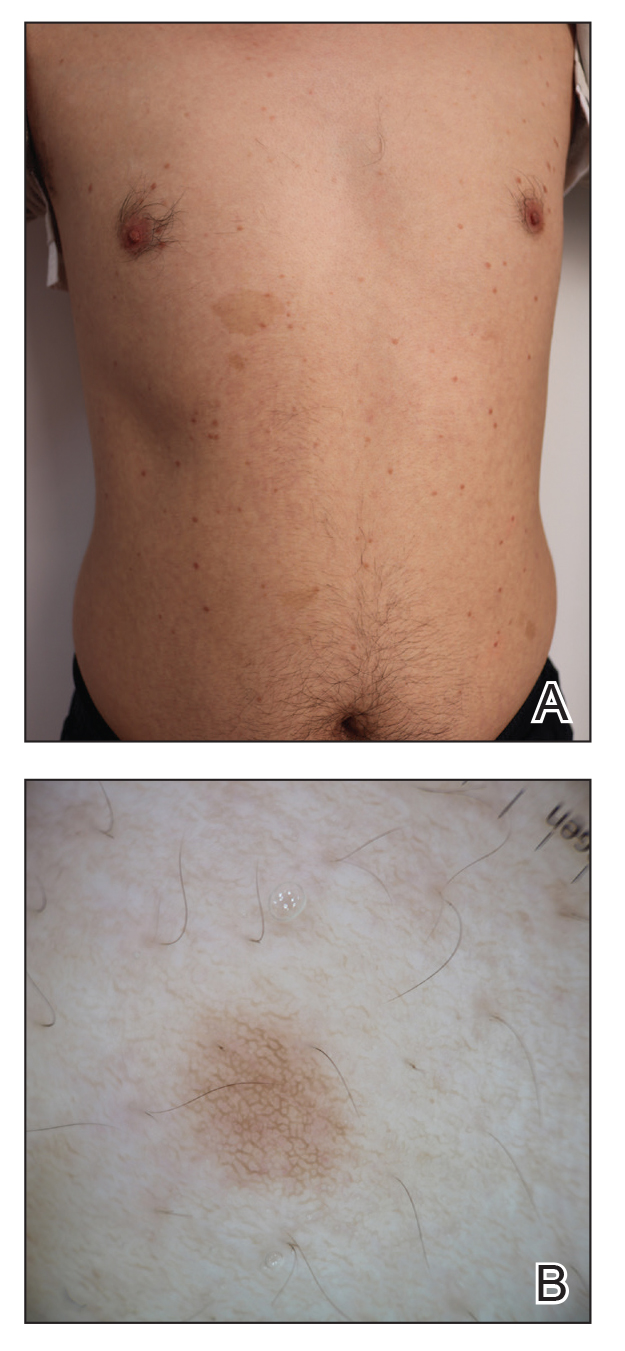
All 3 patients demonstrated classic histopathologic features of syringoma, and none had a family history of similar skin lesions. The clinical and dermoscopic findings along with the histopathology in all 3 patients were consistent with ES.
The pathogenesis of ES is
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.e1239. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Jacquet L, Darier J.
Hidradénomes éruptifs, I.épithéliomes adenoids des glandes sudoripares ou adénomes sudoripares. Ann Dermatol Venerol. 1887;8:317-323. - Huang A, Taylor G, Liebman TN. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt0hb8q22g..
- Maeda T, Natsuga K, Nishie W, et al. Extensive eruptive syringoma after liver transplantation. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:119-120. doi:10.2340/00015555-2814
- Lerner TH, Barr RJ, Dolezal JF, et al. Syringomatous hyperplasia and eccrine squamous syringometaplasia associated with benoxaprofen therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1202-1204. doi:10.1001/archderm.1987.01660330113022
- Ozturk F, Ermertcan AT, Bilac C, et al.
A case report of postpubertal eruptive syringoma triggered with antiepileptic drugs. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:707-710. - Guitart J, Rosenbaum MM, Requena L. ‘Eruptive syringoma’: a misnomer for a reactive eccrine gland ductal proliferation? J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:202-205. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00023.x
- Dupre A, Carrere S, Bonafe JL, et al. Eruptive generalized syringomas, milium and atrophoderma vermiculata. Nicolau and Balus’ syndrome (author’s transl). Dermatologica. 1981;162:281-286.
- Schepis C, Torre V, Siragusa M, et al. Eruptive syringomas with calcium deposits in a young woman with Down’s syndrome. Dermatology. 2001;203:345-347. doi:10.1159/000051788
- Samia AM, Donthi D, Nenow J, et al. A case study and review of literature of eruptive syringoma in a six-year-old. Cureus. 2021;13:E14634. doi:10.7759/cureus.14634
- Soler-Carrillo J, Estrach T, Mascaró JM. Eruptive syringoma: 27 new cases and review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:242-246. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2001.00235.x
- Aleissa M, Aljarbou O, AlJasser MI. Dermoscopy of eruptive syringoma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2021;7:401-403. doi:10.1159/000515443
- Botsali A, Caliskan E, Coskun A, et al. Eruptive syringoma: two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1159/000508656
- Dutra Rezende H, Madia ACT, Elias BM, et al. Comment on: eruptive syringoma—two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2022;8:81-82. doi:10.1159/000518158
- Silva-Hirschberg C, Cabrera R, Rollán MP, et al. Darier disease: the use of dermoscopy in monitoring acitretin treatment. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:644-647. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.05.021
- Singal A, Kaur I, Jakhar D. Fox-Fordyce disease: dermoscopic perspective. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:247-249. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Brau Javier CN, Morales A, Sanchez JL. Histopathology attributes of Fox-Fordyce disease. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1313-1318. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Horie K, Shinkuma S, Fujita Y, et al. Efficacy of N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)-anthranilic acid (tranilast) against eruptive syringoma: report of two cases and review of published work. J Dermatol. 2012;39:1044-1046. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01612.x
- Sanchez TS, Dauden E, Casas AP, et al. Eruptive pruritic syringomas: treatment with topical atropine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:148-149. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.109854
To the Editor:
Syringoma is a relatively common benign adnexal neoplasm originating in the ducts of eccrine sweat glands. It can be
A 28-year-old man presented with multiple asymptomatic papules on the trunk and upper arms of 20 years’ duration (patient 1). He had been diagnosed with Darier disease 3 years prior to the current presentation and was treated with oral and topical retinoic acid without a response. After 3 months of oral treatment, the retinoic acid was stopped due to elevated liver enzymes. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed multiple smooth, firm, nonfused, 1- to 4-mm

A 27-year-old woman presented with widespread asymptomatic papules

A 43-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with brownish flat-topped papules on the chest and abdomen of 19 years’ duration (Figure 3A)(patient 3). The lesions had remained stable and did not progress. He denied any treatment.

All 3 patients demonstrated classic histopathologic features of syringoma, and none had a family history of similar skin lesions. The clinical and dermoscopic findings along with the histopathology in all 3 patients were consistent with ES.
The pathogenesis of ES is
To the Editor:
Syringoma is a relatively common benign adnexal neoplasm originating in the ducts of eccrine sweat glands. It can be
A 28-year-old man presented with multiple asymptomatic papules on the trunk and upper arms of 20 years’ duration (patient 1). He had been diagnosed with Darier disease 3 years prior to the current presentation and was treated with oral and topical retinoic acid without a response. After 3 months of oral treatment, the retinoic acid was stopped due to elevated liver enzymes. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed multiple smooth, firm, nonfused, 1- to 4-mm

A 27-year-old woman presented with widespread asymptomatic papules

A 43-year-old man who was otherwise healthy presented with brownish flat-topped papules on the chest and abdomen of 19 years’ duration (Figure 3A)(patient 3). The lesions had remained stable and did not progress. He denied any treatment.

All 3 patients demonstrated classic histopathologic features of syringoma, and none had a family history of similar skin lesions. The clinical and dermoscopic findings along with the histopathology in all 3 patients were consistent with ES.
The pathogenesis of ES is
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.e1239. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Jacquet L, Darier J.
Hidradénomes éruptifs, I.épithéliomes adenoids des glandes sudoripares ou adénomes sudoripares. Ann Dermatol Venerol. 1887;8:317-323. - Huang A, Taylor G, Liebman TN. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt0hb8q22g..
- Maeda T, Natsuga K, Nishie W, et al. Extensive eruptive syringoma after liver transplantation. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:119-120. doi:10.2340/00015555-2814
- Lerner TH, Barr RJ, Dolezal JF, et al. Syringomatous hyperplasia and eccrine squamous syringometaplasia associated with benoxaprofen therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1202-1204. doi:10.1001/archderm.1987.01660330113022
- Ozturk F, Ermertcan AT, Bilac C, et al.
A case report of postpubertal eruptive syringoma triggered with antiepileptic drugs. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:707-710. - Guitart J, Rosenbaum MM, Requena L. ‘Eruptive syringoma’: a misnomer for a reactive eccrine gland ductal proliferation? J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:202-205. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00023.x
- Dupre A, Carrere S, Bonafe JL, et al. Eruptive generalized syringomas, milium and atrophoderma vermiculata. Nicolau and Balus’ syndrome (author’s transl). Dermatologica. 1981;162:281-286.
- Schepis C, Torre V, Siragusa M, et al. Eruptive syringomas with calcium deposits in a young woman with Down’s syndrome. Dermatology. 2001;203:345-347. doi:10.1159/000051788
- Samia AM, Donthi D, Nenow J, et al. A case study and review of literature of eruptive syringoma in a six-year-old. Cureus. 2021;13:E14634. doi:10.7759/cureus.14634
- Soler-Carrillo J, Estrach T, Mascaró JM. Eruptive syringoma: 27 new cases and review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:242-246. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2001.00235.x
- Aleissa M, Aljarbou O, AlJasser MI. Dermoscopy of eruptive syringoma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2021;7:401-403. doi:10.1159/000515443
- Botsali A, Caliskan E, Coskun A, et al. Eruptive syringoma: two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1159/000508656
- Dutra Rezende H, Madia ACT, Elias BM, et al. Comment on: eruptive syringoma—two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2022;8:81-82. doi:10.1159/000518158
- Silva-Hirschberg C, Cabrera R, Rollán MP, et al. Darier disease: the use of dermoscopy in monitoring acitretin treatment. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:644-647. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.05.021
- Singal A, Kaur I, Jakhar D. Fox-Fordyce disease: dermoscopic perspective. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:247-249. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Brau Javier CN, Morales A, Sanchez JL. Histopathology attributes of Fox-Fordyce disease. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1313-1318. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Horie K, Shinkuma S, Fujita Y, et al. Efficacy of N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)-anthranilic acid (tranilast) against eruptive syringoma: report of two cases and review of published work. J Dermatol. 2012;39:1044-1046. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01612.x
- Sanchez TS, Dauden E, Casas AP, et al. Eruptive pruritic syringomas: treatment with topical atropine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:148-149. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.109854
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.e1239. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Jacquet L, Darier J.
Hidradénomes éruptifs, I.épithéliomes adenoids des glandes sudoripares ou adénomes sudoripares. Ann Dermatol Venerol. 1887;8:317-323. - Huang A, Taylor G, Liebman TN. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt0hb8q22g..
- Maeda T, Natsuga K, Nishie W, et al. Extensive eruptive syringoma after liver transplantation. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:119-120. doi:10.2340/00015555-2814
- Lerner TH, Barr RJ, Dolezal JF, et al. Syringomatous hyperplasia and eccrine squamous syringometaplasia associated with benoxaprofen therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1202-1204. doi:10.1001/archderm.1987.01660330113022
- Ozturk F, Ermertcan AT, Bilac C, et al.
A case report of postpubertal eruptive syringoma triggered with antiepileptic drugs. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:707-710. - Guitart J, Rosenbaum MM, Requena L. ‘Eruptive syringoma’: a misnomer for a reactive eccrine gland ductal proliferation? J Cutan Pathol. 2003;30:202-205. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0560.2003.00023.x
- Dupre A, Carrere S, Bonafe JL, et al. Eruptive generalized syringomas, milium and atrophoderma vermiculata. Nicolau and Balus’ syndrome (author’s transl). Dermatologica. 1981;162:281-286.
- Schepis C, Torre V, Siragusa M, et al. Eruptive syringomas with calcium deposits in a young woman with Down’s syndrome. Dermatology. 2001;203:345-347. doi:10.1159/000051788
- Samia AM, Donthi D, Nenow J, et al. A case study and review of literature of eruptive syringoma in a six-year-old. Cureus. 2021;13:E14634. doi:10.7759/cureus.14634
- Soler-Carrillo J, Estrach T, Mascaró JM. Eruptive syringoma: 27 new cases and review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2001;15:242-246. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2001.00235.x
- Aleissa M, Aljarbou O, AlJasser MI. Dermoscopy of eruptive syringoma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2021;7:401-403. doi:10.1159/000515443
- Botsali A, Caliskan E, Coskun A, et al. Eruptive syringoma: two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:319-322. doi:10.1159/000508656
- Dutra Rezende H, Madia ACT, Elias BM, et al. Comment on: eruptive syringoma—two cases with dermoscopic features. Skin Appendage Disord. 2022;8:81-82. doi:10.1159/000518158
- Silva-Hirschberg C, Cabrera R, Rollán MP, et al. Darier disease: the use of dermoscopy in monitoring acitretin treatment. An Bras Dermatol. 2022;97:644-647. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.05.021
- Singal A, Kaur I, Jakhar D. Fox-Fordyce disease: dermoscopic perspective. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:247-249. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Brau Javier CN, Morales A, Sanchez JL. Histopathology attributes of Fox-Fordyce disease. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1313-1318. doi:10.1159/000508201
- Horie K, Shinkuma S, Fujita Y, et al. Efficacy of N-(3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl)-anthranilic acid (tranilast) against eruptive syringoma: report of two cases and review of published work. J Dermatol. 2012;39:1044-1046. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01612.x
- Sanchez TS, Dauden E, Casas AP, et al. Eruptive pruritic syringomas: treatment with topical atropine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:148-149. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.109854
Practice Points
- Eruptive syringoma (ES) is a benign cutaneous adnexal neoplasm that typically does not require treatment.
- Dermoscopy and biopsy are helpful for the diagnosis of ES, which often is missed or misdiagnosed clinically.
Sjögren Disease Treatments in Early Trials Have Mostly Positive Results
VIENNA — Nipocalimab, iscalimab, and tibulizumab, but not lusvertikimab, appear to be promising new agents for Sjögren disease that warrant further investigation, suggest the results of four separate early clinical trials reported at the recent annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR).
This is potentially good news for patients, as discovering new treatments that work for managing the various symptoms of Sjögren disease is a high priority, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg, MD, PhD, said when he presented the results of the phase 2 DAHLIAS study of nipocalimab during a late-breaking abstract session.
“All patients suffer from high burden of symptoms — pain, fatigue, and dryness; nearly 50% of patients have systemic complications; mortality is increased, so there is a high unmet need since no specific drug has been accepted so far,” said Dr. Gottenberg, who works at Strasbourg University Hospital in Strasbourg, France.
“The pathogenesis of the disease involves high B-cell activation, resulting in high IgG levels, and secretion of autoantibodies,” such as anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type A (anti-SSA), and anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type B antibodies, Dr. Gottenberg said.
Thus, one approach to reducing the disease burden is to try to lower circulating immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels and IgG-associated autoantibodies, which is how the monoclonal antibody nipocalimab works. Nipocalimab essentially blocks the interaction of IgG with the neonatal fragment crystallizable receptor and has already been shown to have efficacy in other autoimmune conditions such as myasthenia gravis and fetal and neonatal hemolytic disease, although not as hoped in rheumatoid arthritis.
The DAHLIAS Phase 2 Study
Now, results from the DAHLIAS study show that nipocalimab may also work in Sjögren disease, with significant improvement vs placebo seen in the primary endpoint of the total EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index (clinESSDAI) at 24 weeks for one of the two doses of the drug that were tested.
The multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was conducted in 163 patients with moderate to severely active primary Sjögren disease. The latter was determined by having a clinESSDAI of 6 or higher and seropositivity for anti-Ro60, anti-Ro52, or both autoantibodies.
Dr. Gottenberg reported that the mean age of patients was 48 years; the majority (92.6%) were women and of White ethnicity (90.8%). The baseline clinESSDAI was a mean of 9.9; 98.1% had anti-Ro60, 80.6% had anti-Ro52, and 71.9% had anti-La antibodies.
In addition to standard of care, patients were randomly allocated to receive intravenous treatment every 2 weeks with nipocalimab 5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg, or placebo.
At 24 weeks, the least squares mean (LSM) change in clinESSDAI from baseline was −3.74 for placebo, −4.08 for nipocalimab 5 mg/kg (P = not significant vs placebo), and −6.40 for nipocalimab 15 mg/kg (P = .02 vs placebo).
Nipocalimab 15 mg/kg also “demonstrated similar and consistent trends in other key efficacy endpoints,” Dr. Gottenberg said. This included improvements in the ESSDAI and EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) and composite measures such as the Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR), Composite of Relevant Endpoints for Sjögren’s Syndrome (CRESS), and the Disease Activity Level. There were also improvements in the unstimulated salivary flow rate.
Safety findings showed no new concerns, with adverse events reported in 62.5% of placebo-treated patients and by 79.2% and 79.6% of patients receiving nipocalimab 5 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg, respectively. Serious adverse events were reported in a respective 5.4%, 7.5%, and 7.4%, including severe infections or infections requiring intravenous anti-infectives in 1.8%, 3.8%, and 1.9% of participants, although none was thought to be related to the study treatment. No opportunistic infections or any deaths were reported.
Thomas Schindler, PhD, senior clinical scientist at F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., in Basel, Switzerland, commented from the audience: “This was a very impressive set of results, and I’m very surprised that its safety profile is so benign.”
Dr. Schindler wanted to know if there were any changes in the serum albumin level and if this manifested as any laboratory abnormalities, but there were no reported cases of severe hypoalbuminemia in the study.
The TWINSS Phase 2 Study
Similarly hopeful results were reported for iscalimab, a fully human IgG1 anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody that is given by subcutaneous injection, during a clinical abstracts session. Xavier Mariette, MD, PhD, head of the Rheumatology Department at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University in Paris, France, reported updated results of the phase 2b dose-ranging TWINSS study, showing sustained benefits at 48 weeks. The primary endpoint results at 24 weeks were recently published in The Lancet.
TWINSS was set up to assess the safety and efficacy of iscalimab given every 2 weeks vs placebo in two distinct cohorts of patients with Sjögren disease — one with moderate to severe disease with both systemic and symptomatic involvement and the other with low systemic involvement but high symptom burden.
Whereas patients in the first cohort who had moderate to severe disease (n = 173) were randomly allocated to one of three doses (150, 300, and 600 mg) of iscalimab or placebo for the initial 24 weeks, those in the second cohort (n = 100) were randomly allocated to a 600-mg dose or placebo. After the double-blind period ended, patients taking iscalimab continued on the dose they were taking for another 24 weeks, with those in the placebo arms switching to the 600-mg dose in cohort 1 and the 300-mg dose in cohort 2.
Topline results for those in cohort 1 with moderate to severe Sjögren disease were that the significant improvements in ESSDAI that had been seen at week 24 were maintained in those who continued iscalimab and improved in those who had switched from placebo.
LSM change from baseline in ESSDAI vs placebo at week 24 had been −3.0, −1.4, and −2.9 for the 150-, 300-, and 600-mg doses of iscalimab, respectively. Results at week 48 were a respective −7.6, −5.7, and −7.9. The LSM change for the placebo-treated patients who had switched to the 600-mg dose was −6.7.
Dr. Mariette reported “consistent improvement” in patient-reported outcomes, including ESSPRI, the Sjögren’s Syndrome Symptom Diary, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue measure, and the Impact of Dry Eye on Everyday Life instrument. There was also a significant improvement in stimulated salivary flow rates.
Similar benefits were seen in the second cohort of patients who did not have systemic involvement but had a high burden of symptoms, with improved ESSPRI scores of a LSM change from baseline vs placebo of −2.29 for patients continuing iscalimab 600 mg treatment and −1.14 for those taking the 300-mg dose after being treated with placebo. Improvements were also seen in the other patient-reported outcomes used.
Regarding safety, Dr. Mariette reported that there were “no specific issues” seen in the patients who switched from placebo to iscalimab, either at the 300-mg or 600-mg dose. Any adverse event occurred in around 80% of placebo-treated patients and roughly 90% of those given iscalimab, and serious adverse events occurred in 11.4%, 14.3%, and 11.4% pf patients treated with iscalimab 150, 300, and 600 mg, and 4.9% of those given placebo and then 600 mg iscalimab.
“The safety seems equivalent to patients having received iscalimab from the beginning of the trial,” Dr. Mariette said, adding “the risk-benefit [analysis] seems positive in patients up to week 48.”
Phase 1 Trial of Tibulizumab
Further positive early trial results were reported by Michael Howell, PhD, chief scientific officer for Zura Bio, a biotech company based in Henderson, Nevada. During a poster tour at EULAR 2024, Dr. Howell presented some preliminary findings from a phase 1 trial of tibulizumab, a dual antagonist of interleukin (IL)-17A and the B-cell–activating factor (BAFF) engineered by fusing elements of ixekizumab (Taltz) and tabalumab together.
“The headline result for me is that the molecule does what it’s supposed to,” Dr. Howell told this news organization. “We have potent engagement of the IL-17 and BAFF pathways, and this sets the tone for additional exploration in rheumatologic diseases where there’s known activation of those two pathways,” he said.
Dr. Howell reported that total B-cell counts and lower levels of type 1 T helper cells were seen during the trial.
Over the years, Dr. Howell, an immunologist, has been involved in the development of many therapeutics, such as risankizumab (Skyrizi) and spesolimab (Spevigo).
“When I look at the molecules and the opportunity we have to do broader antagonism of pathways in a safe aspect, this is probably one of the most exciting,” he said.
The trial he presented included 25 people with a confirmed diagnosis of Sjögren disease and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies. Patients received tibulizumab or a placebo for a total of 12 weeks via a subcutaneous injection. Various doses were tested: 30 mg, 100 mg, or 300 mg every 4 weeks, or 300 mg every 2 weeks.
Serum levels of both BAFF and IL-17A increased as expected in the tibulizumab-treated patients, and Dr. Howell reported that “it’s well tolerated. There’s no adverse event profile that caused any concern.”
As a phase 1 study, it was not powered to look at efficacy, but there were positive signals, Dr. Howell said, meaning that the drug is likely to be tested further in a phase 2 trial.
Lusvertikimab Phase 2 Trial
During the same poster tour, the null findings of a phase 2 trial of the anti-IL-7 monoclonal antibody lusvertikimab were presented by Benjamin Fisher, MD, professor of rheumatology at Birmingham University in Birmingham, England.
Dr. Fisher told this news organization: “It’s a negative study, at least over the 3-month period that we’ve studied it.” Whether longer durations of treatment may be needed is a question that currently cannot be answered, he added.
A total of 48 patients with Sjögren disease had been included in the trial from 19 different centers in Europe, the United States, and Australia. The mean age of the participants was 53.7 years, 87% were women, and the mean duration of disease was 5.0 years. Baseline ESSDAI and ESSPRI were 12.1 and 7.0, respectively. Half were receiving other background treatment, and 72.9% were anti-Ro or anti-SSA positive.
Lusvertikimab 750 mg or a matching placebo was given via intravenous infusion at weeks 0, 2, 4, 7, and 10.
The primary endpoint was the mean change in ESSDAI from baseline to week 13, which was the same, at −3.9, in both groups. There was also no significant difference between the groups in any of the other secondary endpoints that were used, including ESSPRI, Schirmer’s test, the ocular staining score, salivary flow rate, physician and patient global assessment, assessment of fatigue, quality of life, or the composite measures STAR and CRESS.
“This isn’t going anywhere,” said Dr. Fisher, asking what was going to happen next and if this meant the end of IL-7-focused therapy.
“For years, there’s been quite a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Fisher said. Sjögren disease is characterized by a sort of focal inflammation of the saliva glands, which is composed of both T and B cells in the early stages, probably a T-cell component and a B-cell component, he explained.
“IL-7 is thought to be an important cytokine for homeostasis of the T-cell compartment, so for maintenance of T central memory and effector memory cells,” he said. “So, the idea is that, if you block IL-7, you switch off T cells, and you may rebalance the immune system towards a more regulatory phenotype. Just that it didn’t work,” Dr. Fisher said.
“There’s large unmet need,” he said. “Sjögren’s is associated with poor health-related quality of life, [and] a large part that is symptom-driven — dryness and fatigue — which we have no real interventions yet for patients; there’s no licensed therapeutics for it.”
Dr. Fisher cited ianalumab as one of the front-runners for becoming the first licensed treatment for Sjögren disease. The novel BAFF-targeting antibody is already in phase 3 trials and is also showing promise for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
“Then there are CD40-targeting drugs; the ones most advanced are dazodalibep and iscalimab.” Commenting on the potential of iscalimab, Dr. Fisher said that it “seems to work — it improves systemic disease activity; it also leads to some symptomatic improvement, which has been difficult to demonstrate in Sjögren’s.”
Dr. Fisher added that “the nipocalimab data looks interesting, as do data on TYK2 inhibition.”
The DAHLIAS study was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Gottenberg has consulted for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. The TWINSS study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Mariette has consulted for BMS, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Servier. The tibulizumab phase 1 study was funded by Eli Lilly & Company. Dr. Howell is an employee of the developer, Zura Bio. The Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier sponsored the lusvertikimab trial. Dr. Fisher has consulted for Novartis, Roche, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Servier, UCB, and Sanofi and received funding to his institution for collaborative research from Janssen, Celgene, Galapagos, and Servier.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Nipocalimab, iscalimab, and tibulizumab, but not lusvertikimab, appear to be promising new agents for Sjögren disease that warrant further investigation, suggest the results of four separate early clinical trials reported at the recent annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR).
This is potentially good news for patients, as discovering new treatments that work for managing the various symptoms of Sjögren disease is a high priority, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg, MD, PhD, said when he presented the results of the phase 2 DAHLIAS study of nipocalimab during a late-breaking abstract session.
“All patients suffer from high burden of symptoms — pain, fatigue, and dryness; nearly 50% of patients have systemic complications; mortality is increased, so there is a high unmet need since no specific drug has been accepted so far,” said Dr. Gottenberg, who works at Strasbourg University Hospital in Strasbourg, France.
“The pathogenesis of the disease involves high B-cell activation, resulting in high IgG levels, and secretion of autoantibodies,” such as anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type A (anti-SSA), and anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type B antibodies, Dr. Gottenberg said.
Thus, one approach to reducing the disease burden is to try to lower circulating immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels and IgG-associated autoantibodies, which is how the monoclonal antibody nipocalimab works. Nipocalimab essentially blocks the interaction of IgG with the neonatal fragment crystallizable receptor and has already been shown to have efficacy in other autoimmune conditions such as myasthenia gravis and fetal and neonatal hemolytic disease, although not as hoped in rheumatoid arthritis.
The DAHLIAS Phase 2 Study
Now, results from the DAHLIAS study show that nipocalimab may also work in Sjögren disease, with significant improvement vs placebo seen in the primary endpoint of the total EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index (clinESSDAI) at 24 weeks for one of the two doses of the drug that were tested.
The multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was conducted in 163 patients with moderate to severely active primary Sjögren disease. The latter was determined by having a clinESSDAI of 6 or higher and seropositivity for anti-Ro60, anti-Ro52, or both autoantibodies.
Dr. Gottenberg reported that the mean age of patients was 48 years; the majority (92.6%) were women and of White ethnicity (90.8%). The baseline clinESSDAI was a mean of 9.9; 98.1% had anti-Ro60, 80.6% had anti-Ro52, and 71.9% had anti-La antibodies.
In addition to standard of care, patients were randomly allocated to receive intravenous treatment every 2 weeks with nipocalimab 5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg, or placebo.
At 24 weeks, the least squares mean (LSM) change in clinESSDAI from baseline was −3.74 for placebo, −4.08 for nipocalimab 5 mg/kg (P = not significant vs placebo), and −6.40 for nipocalimab 15 mg/kg (P = .02 vs placebo).
Nipocalimab 15 mg/kg also “demonstrated similar and consistent trends in other key efficacy endpoints,” Dr. Gottenberg said. This included improvements in the ESSDAI and EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) and composite measures such as the Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR), Composite of Relevant Endpoints for Sjögren’s Syndrome (CRESS), and the Disease Activity Level. There were also improvements in the unstimulated salivary flow rate.
Safety findings showed no new concerns, with adverse events reported in 62.5% of placebo-treated patients and by 79.2% and 79.6% of patients receiving nipocalimab 5 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg, respectively. Serious adverse events were reported in a respective 5.4%, 7.5%, and 7.4%, including severe infections or infections requiring intravenous anti-infectives in 1.8%, 3.8%, and 1.9% of participants, although none was thought to be related to the study treatment. No opportunistic infections or any deaths were reported.
Thomas Schindler, PhD, senior clinical scientist at F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., in Basel, Switzerland, commented from the audience: “This was a very impressive set of results, and I’m very surprised that its safety profile is so benign.”
Dr. Schindler wanted to know if there were any changes in the serum albumin level and if this manifested as any laboratory abnormalities, but there were no reported cases of severe hypoalbuminemia in the study.
The TWINSS Phase 2 Study
Similarly hopeful results were reported for iscalimab, a fully human IgG1 anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody that is given by subcutaneous injection, during a clinical abstracts session. Xavier Mariette, MD, PhD, head of the Rheumatology Department at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University in Paris, France, reported updated results of the phase 2b dose-ranging TWINSS study, showing sustained benefits at 48 weeks. The primary endpoint results at 24 weeks were recently published in The Lancet.
TWINSS was set up to assess the safety and efficacy of iscalimab given every 2 weeks vs placebo in two distinct cohorts of patients with Sjögren disease — one with moderate to severe disease with both systemic and symptomatic involvement and the other with low systemic involvement but high symptom burden.
Whereas patients in the first cohort who had moderate to severe disease (n = 173) were randomly allocated to one of three doses (150, 300, and 600 mg) of iscalimab or placebo for the initial 24 weeks, those in the second cohort (n = 100) were randomly allocated to a 600-mg dose or placebo. After the double-blind period ended, patients taking iscalimab continued on the dose they were taking for another 24 weeks, with those in the placebo arms switching to the 600-mg dose in cohort 1 and the 300-mg dose in cohort 2.
Topline results for those in cohort 1 with moderate to severe Sjögren disease were that the significant improvements in ESSDAI that had been seen at week 24 were maintained in those who continued iscalimab and improved in those who had switched from placebo.
LSM change from baseline in ESSDAI vs placebo at week 24 had been −3.0, −1.4, and −2.9 for the 150-, 300-, and 600-mg doses of iscalimab, respectively. Results at week 48 were a respective −7.6, −5.7, and −7.9. The LSM change for the placebo-treated patients who had switched to the 600-mg dose was −6.7.
Dr. Mariette reported “consistent improvement” in patient-reported outcomes, including ESSPRI, the Sjögren’s Syndrome Symptom Diary, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue measure, and the Impact of Dry Eye on Everyday Life instrument. There was also a significant improvement in stimulated salivary flow rates.
Similar benefits were seen in the second cohort of patients who did not have systemic involvement but had a high burden of symptoms, with improved ESSPRI scores of a LSM change from baseline vs placebo of −2.29 for patients continuing iscalimab 600 mg treatment and −1.14 for those taking the 300-mg dose after being treated with placebo. Improvements were also seen in the other patient-reported outcomes used.
Regarding safety, Dr. Mariette reported that there were “no specific issues” seen in the patients who switched from placebo to iscalimab, either at the 300-mg or 600-mg dose. Any adverse event occurred in around 80% of placebo-treated patients and roughly 90% of those given iscalimab, and serious adverse events occurred in 11.4%, 14.3%, and 11.4% pf patients treated with iscalimab 150, 300, and 600 mg, and 4.9% of those given placebo and then 600 mg iscalimab.
“The safety seems equivalent to patients having received iscalimab from the beginning of the trial,” Dr. Mariette said, adding “the risk-benefit [analysis] seems positive in patients up to week 48.”
Phase 1 Trial of Tibulizumab
Further positive early trial results were reported by Michael Howell, PhD, chief scientific officer for Zura Bio, a biotech company based in Henderson, Nevada. During a poster tour at EULAR 2024, Dr. Howell presented some preliminary findings from a phase 1 trial of tibulizumab, a dual antagonist of interleukin (IL)-17A and the B-cell–activating factor (BAFF) engineered by fusing elements of ixekizumab (Taltz) and tabalumab together.
“The headline result for me is that the molecule does what it’s supposed to,” Dr. Howell told this news organization. “We have potent engagement of the IL-17 and BAFF pathways, and this sets the tone for additional exploration in rheumatologic diseases where there’s known activation of those two pathways,” he said.
Dr. Howell reported that total B-cell counts and lower levels of type 1 T helper cells were seen during the trial.
Over the years, Dr. Howell, an immunologist, has been involved in the development of many therapeutics, such as risankizumab (Skyrizi) and spesolimab (Spevigo).
“When I look at the molecules and the opportunity we have to do broader antagonism of pathways in a safe aspect, this is probably one of the most exciting,” he said.
The trial he presented included 25 people with a confirmed diagnosis of Sjögren disease and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies. Patients received tibulizumab or a placebo for a total of 12 weeks via a subcutaneous injection. Various doses were tested: 30 mg, 100 mg, or 300 mg every 4 weeks, or 300 mg every 2 weeks.
Serum levels of both BAFF and IL-17A increased as expected in the tibulizumab-treated patients, and Dr. Howell reported that “it’s well tolerated. There’s no adverse event profile that caused any concern.”
As a phase 1 study, it was not powered to look at efficacy, but there were positive signals, Dr. Howell said, meaning that the drug is likely to be tested further in a phase 2 trial.
Lusvertikimab Phase 2 Trial
During the same poster tour, the null findings of a phase 2 trial of the anti-IL-7 monoclonal antibody lusvertikimab were presented by Benjamin Fisher, MD, professor of rheumatology at Birmingham University in Birmingham, England.
Dr. Fisher told this news organization: “It’s a negative study, at least over the 3-month period that we’ve studied it.” Whether longer durations of treatment may be needed is a question that currently cannot be answered, he added.
A total of 48 patients with Sjögren disease had been included in the trial from 19 different centers in Europe, the United States, and Australia. The mean age of the participants was 53.7 years, 87% were women, and the mean duration of disease was 5.0 years. Baseline ESSDAI and ESSPRI were 12.1 and 7.0, respectively. Half were receiving other background treatment, and 72.9% were anti-Ro or anti-SSA positive.
Lusvertikimab 750 mg or a matching placebo was given via intravenous infusion at weeks 0, 2, 4, 7, and 10.
The primary endpoint was the mean change in ESSDAI from baseline to week 13, which was the same, at −3.9, in both groups. There was also no significant difference between the groups in any of the other secondary endpoints that were used, including ESSPRI, Schirmer’s test, the ocular staining score, salivary flow rate, physician and patient global assessment, assessment of fatigue, quality of life, or the composite measures STAR and CRESS.
“This isn’t going anywhere,” said Dr. Fisher, asking what was going to happen next and if this meant the end of IL-7-focused therapy.
“For years, there’s been quite a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Fisher said. Sjögren disease is characterized by a sort of focal inflammation of the saliva glands, which is composed of both T and B cells in the early stages, probably a T-cell component and a B-cell component, he explained.
“IL-7 is thought to be an important cytokine for homeostasis of the T-cell compartment, so for maintenance of T central memory and effector memory cells,” he said. “So, the idea is that, if you block IL-7, you switch off T cells, and you may rebalance the immune system towards a more regulatory phenotype. Just that it didn’t work,” Dr. Fisher said.
“There’s large unmet need,” he said. “Sjögren’s is associated with poor health-related quality of life, [and] a large part that is symptom-driven — dryness and fatigue — which we have no real interventions yet for patients; there’s no licensed therapeutics for it.”
Dr. Fisher cited ianalumab as one of the front-runners for becoming the first licensed treatment for Sjögren disease. The novel BAFF-targeting antibody is already in phase 3 trials and is also showing promise for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
“Then there are CD40-targeting drugs; the ones most advanced are dazodalibep and iscalimab.” Commenting on the potential of iscalimab, Dr. Fisher said that it “seems to work — it improves systemic disease activity; it also leads to some symptomatic improvement, which has been difficult to demonstrate in Sjögren’s.”
Dr. Fisher added that “the nipocalimab data looks interesting, as do data on TYK2 inhibition.”
The DAHLIAS study was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Gottenberg has consulted for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. The TWINSS study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Mariette has consulted for BMS, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Servier. The tibulizumab phase 1 study was funded by Eli Lilly & Company. Dr. Howell is an employee of the developer, Zura Bio. The Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier sponsored the lusvertikimab trial. Dr. Fisher has consulted for Novartis, Roche, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Servier, UCB, and Sanofi and received funding to his institution for collaborative research from Janssen, Celgene, Galapagos, and Servier.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Nipocalimab, iscalimab, and tibulizumab, but not lusvertikimab, appear to be promising new agents for Sjögren disease that warrant further investigation, suggest the results of four separate early clinical trials reported at the recent annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR).
This is potentially good news for patients, as discovering new treatments that work for managing the various symptoms of Sjögren disease is a high priority, Jacques-Eric Gottenberg, MD, PhD, said when he presented the results of the phase 2 DAHLIAS study of nipocalimab during a late-breaking abstract session.
“All patients suffer from high burden of symptoms — pain, fatigue, and dryness; nearly 50% of patients have systemic complications; mortality is increased, so there is a high unmet need since no specific drug has been accepted so far,” said Dr. Gottenberg, who works at Strasbourg University Hospital in Strasbourg, France.
“The pathogenesis of the disease involves high B-cell activation, resulting in high IgG levels, and secretion of autoantibodies,” such as anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type A (anti-SSA), and anti-Sjögren’s syndrome type B antibodies, Dr. Gottenberg said.
Thus, one approach to reducing the disease burden is to try to lower circulating immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels and IgG-associated autoantibodies, which is how the monoclonal antibody nipocalimab works. Nipocalimab essentially blocks the interaction of IgG with the neonatal fragment crystallizable receptor and has already been shown to have efficacy in other autoimmune conditions such as myasthenia gravis and fetal and neonatal hemolytic disease, although not as hoped in rheumatoid arthritis.
The DAHLIAS Phase 2 Study
Now, results from the DAHLIAS study show that nipocalimab may also work in Sjögren disease, with significant improvement vs placebo seen in the primary endpoint of the total EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Disease Activity Index (clinESSDAI) at 24 weeks for one of the two doses of the drug that were tested.
The multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was conducted in 163 patients with moderate to severely active primary Sjögren disease. The latter was determined by having a clinESSDAI of 6 or higher and seropositivity for anti-Ro60, anti-Ro52, or both autoantibodies.
Dr. Gottenberg reported that the mean age of patients was 48 years; the majority (92.6%) were women and of White ethnicity (90.8%). The baseline clinESSDAI was a mean of 9.9; 98.1% had anti-Ro60, 80.6% had anti-Ro52, and 71.9% had anti-La antibodies.
In addition to standard of care, patients were randomly allocated to receive intravenous treatment every 2 weeks with nipocalimab 5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg, or placebo.
At 24 weeks, the least squares mean (LSM) change in clinESSDAI from baseline was −3.74 for placebo, −4.08 for nipocalimab 5 mg/kg (P = not significant vs placebo), and −6.40 for nipocalimab 15 mg/kg (P = .02 vs placebo).
Nipocalimab 15 mg/kg also “demonstrated similar and consistent trends in other key efficacy endpoints,” Dr. Gottenberg said. This included improvements in the ESSDAI and EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) and composite measures such as the Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR), Composite of Relevant Endpoints for Sjögren’s Syndrome (CRESS), and the Disease Activity Level. There were also improvements in the unstimulated salivary flow rate.
Safety findings showed no new concerns, with adverse events reported in 62.5% of placebo-treated patients and by 79.2% and 79.6% of patients receiving nipocalimab 5 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg, respectively. Serious adverse events were reported in a respective 5.4%, 7.5%, and 7.4%, including severe infections or infections requiring intravenous anti-infectives in 1.8%, 3.8%, and 1.9% of participants, although none was thought to be related to the study treatment. No opportunistic infections or any deaths were reported.
Thomas Schindler, PhD, senior clinical scientist at F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., in Basel, Switzerland, commented from the audience: “This was a very impressive set of results, and I’m very surprised that its safety profile is so benign.”
Dr. Schindler wanted to know if there were any changes in the serum albumin level and if this manifested as any laboratory abnormalities, but there were no reported cases of severe hypoalbuminemia in the study.
The TWINSS Phase 2 Study
Similarly hopeful results were reported for iscalimab, a fully human IgG1 anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody that is given by subcutaneous injection, during a clinical abstracts session. Xavier Mariette, MD, PhD, head of the Rheumatology Department at Bicêtre Hospital, Paris-Saclay University in Paris, France, reported updated results of the phase 2b dose-ranging TWINSS study, showing sustained benefits at 48 weeks. The primary endpoint results at 24 weeks were recently published in The Lancet.
TWINSS was set up to assess the safety and efficacy of iscalimab given every 2 weeks vs placebo in two distinct cohorts of patients with Sjögren disease — one with moderate to severe disease with both systemic and symptomatic involvement and the other with low systemic involvement but high symptom burden.
Whereas patients in the first cohort who had moderate to severe disease (n = 173) were randomly allocated to one of three doses (150, 300, and 600 mg) of iscalimab or placebo for the initial 24 weeks, those in the second cohort (n = 100) were randomly allocated to a 600-mg dose or placebo. After the double-blind period ended, patients taking iscalimab continued on the dose they were taking for another 24 weeks, with those in the placebo arms switching to the 600-mg dose in cohort 1 and the 300-mg dose in cohort 2.
Topline results for those in cohort 1 with moderate to severe Sjögren disease were that the significant improvements in ESSDAI that had been seen at week 24 were maintained in those who continued iscalimab and improved in those who had switched from placebo.
LSM change from baseline in ESSDAI vs placebo at week 24 had been −3.0, −1.4, and −2.9 for the 150-, 300-, and 600-mg doses of iscalimab, respectively. Results at week 48 were a respective −7.6, −5.7, and −7.9. The LSM change for the placebo-treated patients who had switched to the 600-mg dose was −6.7.
Dr. Mariette reported “consistent improvement” in patient-reported outcomes, including ESSPRI, the Sjögren’s Syndrome Symptom Diary, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue measure, and the Impact of Dry Eye on Everyday Life instrument. There was also a significant improvement in stimulated salivary flow rates.
Similar benefits were seen in the second cohort of patients who did not have systemic involvement but had a high burden of symptoms, with improved ESSPRI scores of a LSM change from baseline vs placebo of −2.29 for patients continuing iscalimab 600 mg treatment and −1.14 for those taking the 300-mg dose after being treated with placebo. Improvements were also seen in the other patient-reported outcomes used.
Regarding safety, Dr. Mariette reported that there were “no specific issues” seen in the patients who switched from placebo to iscalimab, either at the 300-mg or 600-mg dose. Any adverse event occurred in around 80% of placebo-treated patients and roughly 90% of those given iscalimab, and serious adverse events occurred in 11.4%, 14.3%, and 11.4% pf patients treated with iscalimab 150, 300, and 600 mg, and 4.9% of those given placebo and then 600 mg iscalimab.
“The safety seems equivalent to patients having received iscalimab from the beginning of the trial,” Dr. Mariette said, adding “the risk-benefit [analysis] seems positive in patients up to week 48.”
Phase 1 Trial of Tibulizumab
Further positive early trial results were reported by Michael Howell, PhD, chief scientific officer for Zura Bio, a biotech company based in Henderson, Nevada. During a poster tour at EULAR 2024, Dr. Howell presented some preliminary findings from a phase 1 trial of tibulizumab, a dual antagonist of interleukin (IL)-17A and the B-cell–activating factor (BAFF) engineered by fusing elements of ixekizumab (Taltz) and tabalumab together.
“The headline result for me is that the molecule does what it’s supposed to,” Dr. Howell told this news organization. “We have potent engagement of the IL-17 and BAFF pathways, and this sets the tone for additional exploration in rheumatologic diseases where there’s known activation of those two pathways,” he said.
Dr. Howell reported that total B-cell counts and lower levels of type 1 T helper cells were seen during the trial.
Over the years, Dr. Howell, an immunologist, has been involved in the development of many therapeutics, such as risankizumab (Skyrizi) and spesolimab (Spevigo).
“When I look at the molecules and the opportunity we have to do broader antagonism of pathways in a safe aspect, this is probably one of the most exciting,” he said.
The trial he presented included 25 people with a confirmed diagnosis of Sjögren disease and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies. Patients received tibulizumab or a placebo for a total of 12 weeks via a subcutaneous injection. Various doses were tested: 30 mg, 100 mg, or 300 mg every 4 weeks, or 300 mg every 2 weeks.
Serum levels of both BAFF and IL-17A increased as expected in the tibulizumab-treated patients, and Dr. Howell reported that “it’s well tolerated. There’s no adverse event profile that caused any concern.”
As a phase 1 study, it was not powered to look at efficacy, but there were positive signals, Dr. Howell said, meaning that the drug is likely to be tested further in a phase 2 trial.
Lusvertikimab Phase 2 Trial
During the same poster tour, the null findings of a phase 2 trial of the anti-IL-7 monoclonal antibody lusvertikimab were presented by Benjamin Fisher, MD, professor of rheumatology at Birmingham University in Birmingham, England.
Dr. Fisher told this news organization: “It’s a negative study, at least over the 3-month period that we’ve studied it.” Whether longer durations of treatment may be needed is a question that currently cannot be answered, he added.
A total of 48 patients with Sjögren disease had been included in the trial from 19 different centers in Europe, the United States, and Australia. The mean age of the participants was 53.7 years, 87% were women, and the mean duration of disease was 5.0 years. Baseline ESSDAI and ESSPRI were 12.1 and 7.0, respectively. Half were receiving other background treatment, and 72.9% were anti-Ro or anti-SSA positive.
Lusvertikimab 750 mg or a matching placebo was given via intravenous infusion at weeks 0, 2, 4, 7, and 10.
The primary endpoint was the mean change in ESSDAI from baseline to week 13, which was the same, at −3.9, in both groups. There was also no significant difference between the groups in any of the other secondary endpoints that were used, including ESSPRI, Schirmer’s test, the ocular staining score, salivary flow rate, physician and patient global assessment, assessment of fatigue, quality of life, or the composite measures STAR and CRESS.
“This isn’t going anywhere,” said Dr. Fisher, asking what was going to happen next and if this meant the end of IL-7-focused therapy.
“For years, there’s been quite a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Fisher said. Sjögren disease is characterized by a sort of focal inflammation of the saliva glands, which is composed of both T and B cells in the early stages, probably a T-cell component and a B-cell component, he explained.
“IL-7 is thought to be an important cytokine for homeostasis of the T-cell compartment, so for maintenance of T central memory and effector memory cells,” he said. “So, the idea is that, if you block IL-7, you switch off T cells, and you may rebalance the immune system towards a more regulatory phenotype. Just that it didn’t work,” Dr. Fisher said.
“There’s large unmet need,” he said. “Sjögren’s is associated with poor health-related quality of life, [and] a large part that is symptom-driven — dryness and fatigue — which we have no real interventions yet for patients; there’s no licensed therapeutics for it.”
Dr. Fisher cited ianalumab as one of the front-runners for becoming the first licensed treatment for Sjögren disease. The novel BAFF-targeting antibody is already in phase 3 trials and is also showing promise for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
“Then there are CD40-targeting drugs; the ones most advanced are dazodalibep and iscalimab.” Commenting on the potential of iscalimab, Dr. Fisher said that it “seems to work — it improves systemic disease activity; it also leads to some symptomatic improvement, which has been difficult to demonstrate in Sjögren’s.”
Dr. Fisher added that “the nipocalimab data looks interesting, as do data on TYK2 inhibition.”
The DAHLIAS study was funded by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Gottenberg has consulted for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. The TWINSS study was funded by Novartis. Dr. Mariette has consulted for BMS, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Servier. The tibulizumab phase 1 study was funded by Eli Lilly & Company. Dr. Howell is an employee of the developer, Zura Bio. The Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier sponsored the lusvertikimab trial. Dr. Fisher has consulted for Novartis, Roche, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Servier, UCB, and Sanofi and received funding to his institution for collaborative research from Janssen, Celgene, Galapagos, and Servier.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EULAR 2024
Saxophone Penis: A Forgotten Manifestation of Hidradenitis Suppurativa
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting 1% to 4% of Europeans. It is characterized by recurrent inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts in intertriginous regions.1 The genital area is affected in 11% of cases2 and usually is connected to severe forms of HS in both men and women.3 The prevalence of HS-associated genital lymphedema remains unknown.
Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation of the major penile lymphatic vessels that cause fibrosis of the surrounding connective tissue. Poor blood flow further causes contracture and distortion of the penile axis.4 Saxophone penis also has been associated with primary lymphedema, lymphogranuloma venereum, filariasis,5 and administration of paraffin injections.6 We describe 3 men with HS who presented with saxophone penis.
A 33-year-old man with Hurley stage III HS presented with a medical history of groin lesions and progressive penoscrotal edema of 13 years’ duration. He had a body mass index (BMI) of 37, no family history of HS or comorbidities, and a 15-year history of smoking 20 cigarettes per day. After repeated surgical drainage of the HS lesions as well as antibiotic treatment with clindamycin 600 mg/d and rifampicin 600 mg/d, the patient was kept on a maintenance therapy with adalimumab 40 mg/wk. Due to lack of response, treatment was discontinued at week 16. Clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg were immediately reintroduced with no benefit on the genital lesions. The patient underwent genital reconstruction, including penile degloving, scrotoplasty, infrapubic fat pad removal, and perineoplasty (Figure 1). The patient currently is not undergoing any therapies.
A 55-year-old man presented with Hurley stage II HS of 33 years’ duration. He had a BMI of 52; a history of hypertension, hyperuricemia, severe hip and knee osteoarthritis, and orchiopexy in childhood; a smoking history of 40 cigarettes per day; and an alcohol consumption history of 200 mL per day since 18 years of age. He had radical excision of axillary lesions 8 years prior. One year later, he was treated with concomitant clindamycin and rifampicin 300 mg twice daily for 3 months with no desirable effects. Adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. After 12 weeks of treatment, he experienced 80% improvement in all areas except the genital region. He continued adalimumab for 3 years with good clinical response in all HS-affected sites except the genital region.
A 66-year-old man presented with Hurley stage III HS of 37 years’ duration. He had a smoking history of 10 cigarettes per day for 30 years, a BMI of 24.6, and a medical history of long-standing hypertension and hypothyroidism. A 3-month course of clindamycin and rifampicin 600 mg/d was ineffective; adalimumab 40 mg/wk was initiated. All affected areas improved, except for the saxophone penis. He continues his fifth year of therapy with adalimumab (Figure 2).

Hidradenitis suppurativa is associated with chronic pain, purulent malodor, and scarring with structural deformity. Repetitive inflammation causes fibrosis, scar formation, and soft-tissue destruction of lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema; primary lymphedema of the genitals in men has been reported to result in a saxophone penis.4
The only approved biologic treatments for moderate to severe HS are the tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab and anti-IL-17 secukinumab.1 All 3 of our patients with HS were treated with adalimumab with reasonable success; however, the penile condition remained refractory, which we speculate may be due to adalimumab’s ability to control only active inflammatory lesions but not scars or fibrotic tissue.7 Higher adalimumab dosages were unlikely to be beneficial for their penile condition; some improvements have been reported following fluoroquinolone therapy. To our knowledge, there is no effective medical treatment for saxophone penis. However, surgery showed good results in one of our patients. Among our 3 adalimumab-treated patients, only 1 patient had corrective surgery that resulted in improvement in the penile deformity, further confirming adalimumab’s limited role in genital lymphedema.7 Extensive resection of the lymphedematous tissue, scrotoplasty, and Charles procedure are treatment options.8
Genital lymphedema has been associated with lymphangiectasia, lymphangioma circumscriptum, infections, and neoplasms such as lymphangiosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma.9 Our patients reported discomfort, hygiene issues, and swelling. One patient reported micturition, and 2 patients reported sexual dysfunction.
Saxophone penis remains a disabling sequela of HS. Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Fertitta L, Hotz C, Wolkenstein P, et al. Efficacy and satisfaction of surgical treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:839-845.
- Micieli R, Alavi A. Lymphedema in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review of published literature. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:1471-1480.
- Maatouk I, Moutran R. Saxophone penis. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:802.
- Koley S, Mandal RK. Saxophone penis after unilateral inguinal bubo of lymphogranuloma venereum. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2013;34:149-151.
- D’Antuono A, Lambertini M, Gaspari V, et al. Visual dermatology: self-induced chronic saxophone penis due to paraffin injections. J Cutan Med Surg. 2019;23:330.
- Musumeci ML, Scilletta A, Sorci F, et al. Genital lymphedema associated with hidradenitis suppurativa unresponsive to adalimumab treatment. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:326-328.
- Jain V, Singh S, Garge S, et al. Saxophone penis due to primary lymphoedema. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009;14:230-231.
- Moosbrugger EA, Mutasim DF. Hidradenitis suppurativa complicated by severe lymphedema and lymphangiectasias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:1223-1224.
Practice Points
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial chronic inflammatory skin disease.
- Saxophone penis is a specific penile malformation characterized by a saxophone shape due to inflammation.
- Repetitive inflammation within the context of HS may cause structural deformity of the penis, resulting in a saxophone penis.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of HS may help prevent development of this condition.
Government Accuses Health System of Paying Docs Outrageous Salaries for Patient Referrals
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Strapped for cash and searching for new profits, Tennessee-based Erlanger Health System illegally paid excessive salaries to physicians in exchange for patient referrals, the US government alleged in a federal lawsuit.
Erlanger changed its compensation model to entice revenue-generating doctors, paying some two to three times the median salary for their specialty, according to the complaint.
The physicians in turn referred numerous patients to Erlanger, and the health system submitted claims to Medicare for the referred services in violation of the Stark Law, according to the suit, filed in US District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.
The government’s complaint “serves as a warning” to healthcare providers who try to boost profits through improper financial arrangements with referring physicians, said Tamala E. Miles, Special Agent in Charge for the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG).
In a statement provided to this news organization, Erlanger denied the allegations and said it would “vigorously” defend the lawsuit.
“Erlanger paid physicians based on amounts that outside experts advised was fair market value,” Erlanger officials said in the statement. “Erlanger did not pay for referrals. A complete picture of the facts will demonstrate that the allegations lack merit and tell a very different story than what the government now claims.”
The Erlanger case is a reminder to physicians to consult their own knowledgeable advisors when considering financial arrangements with hospitals, said William Sarraille, JD, adjunct professor for the University of Maryland Francis King Carey School of Law in Baltimore and a regulatory consultant.
“There is a tendency by physicians when contracting ... to rely on [hospitals’] perceived compliance and legal expertise,” Mr. Sarraille told this news organization. “This case illustrates the risks in doing so. Sometimes bigger doesn’t translate into more sophisticated or more effective from a compliance perspective.”
Stark Law Prohibits Kickbacks
The Stark Law prohibits hospitals from billing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for services referred by a physician with whom the hospital has an improper financial relationship.
CMS paid Erlanger about $27.8 million for claims stemming from the improper financial arrangements, the government contends.
“HHS-OIG will continue to investigate such deals to prevent financial arrangements that could compromise impartial medical judgment, increase healthcare costs, and erode public trust in the healthcare system,” Ms. Miles said in a statement.
Suit: Health System’s Money Woes Led to Illegal Arrangements
Erlanger’s financial troubles allegedly started after a previous run-in with the US government over false claims.
In 2005, Erlanger Health System agreed to pay the government $40 million to resolve allegations that it knowingly submitted false claims to Medicare, according to the government’s complaint. At the time, Erlanger entered into a Corporate Integrity Agreement (CIA) with the OIG that required Erlanger to put controls in place to ensure its financial relationships did not violate the Stark Law.
Erlanger’s agreement with OIG ended in 2010. Over the next 3 years, the health system lost nearly $32 million and in fiscal year 2013, had only 65 days of cash on hand, according to the government’s lawsuit.
Beginning in 2013, Erlanger allegedly implemented a strategy to increase profits by employing more physicians, particularly specialists from competing hospitals whose patients would need costly hospital stays, according to the complaint.
Once hired, Erlanger’s physicians were expected to treat patients at Erlanger’s hospitals and refer them to other providers within the health system, the suit claims. Erlanger also relaxed or eliminated the oversight and controls on physician compensation put in place under the CIA. For example, Erlanger’s CEO signed some compensation contracts before its chief compliance officer could review them and no longer allowed the compliance officer to vote on whether to approve compensation arrangements, according to the complaint.
Erlanger also changed its compensation model to include large salaries for medical director and academic positions and allegedly paid such salaries to physicians without ensuring the required work was performed. As a result, Erlanger physicians with profitable referrals were among the highest paid in the nation for their specialties, the government claims. For example, according to the complaint:
- Erlanger paid an electrophysiologist an annual clinical salary of $816,701, a medical director salary of $101,080, an academic salary of $59,322, and a productivity incentive based on work relative value units (wRVUs). The medical director and academic salaries paid were near the 90th percentile of comparable salaries in the specialty.
- The health system paid a neurosurgeon a base salary of $654,735, a productivity incentive based on wRVUs, and payments for excess call coverage ranging from $400 to $1000 per 24-hour shift. In 2016, the neurosurgeon made $500,000 in excess call payments.
- Erlanger paid a cardiothoracic surgeon a base clinical salary of $1,070,000, a sign-on bonus of $150,000, a retention bonus of $100,000 (payable in the 4th year of the contract), and a program incentive of up to $150,000 per year.
In addition, Erlanger ignored patient safety concerns about some of its high revenue-generating physicians, the government claims.
For instance, Erlanger received multiple complaints that a cardiothoracic surgeon was misusing an expensive form of life support in which pumps and oxygenators take over heart and lung function. Overuse of the equipment prolonged patients’ hospital stays and increased the hospital fees generated by the surgeon, according to the complaint. Staff also raised concerns about the cardiothoracic surgeon’s patient outcomes.
But Erlanger disregarded the concerns and in 2018, increased the cardiothoracic surgeon’s retention bonus from $100,000 to $250,000, the suit alleges. A year later, the health system increased his base salary from $1,070,000 to $1,195,000.
Health care compensation and billing consultants alerted Erlanger that it was overpaying salaries and handing out bonuses based on measures that overstated the work physicians were performing, but Erlanger ignored the warnings, according to the complaint.
Administrators allegedly resisted efforts by the chief compliance officer to hire an outside consultant to review its compensation models. Erlanger fired the compliance officer in 2019.
The former chief compliance officer and another administrator filed a whistleblower lawsuit against Erlanger in 2021. The two administrators are relators in the government’s July 2024 lawsuit.
How to Protect Yourself From Illegal Hospital Deals
The Erlanger case is the latest in a series of recent complaints by the federal government involving financial arrangements between hospitals and physicians.
In December 2023, Indianapolis-based Community Health Network Inc. agreed to pay the government $345 million to resolve claims that it paid physicians above fair market value and awarded bonuses tied to referrals in violation of the Stark Law.
Also in 2023, Saginaw, Michigan–based Covenant HealthCare and two physicians paid the government $69 million to settle allegations that administrators engaged in improper financial arrangements with referring physicians and a physician-owned investment group. In another 2023 case, Massachusetts Eye and Ear in Boston agreed to pay $5.7 million to resolve claims that some of its physician compensation plans violated the Stark Law.
Before you enter into a financial arrangement with a hospital, it’s also important to examine what percentile the aggregate compensation would reflect, law professor Mr. Sarraille said. The Erlanger case highlights federal officials’ suspicion of compensation, in aggregate, that exceeds the 90th percentile and increased attention to compensation that exceeds the 75th percentile, he said.
To research compensation levels, doctors can review the Medical Group Management Association’s annual compensation report or search its compensation data.
Before signing any contracts, Mr. Sarraille suggests, physicians should also consider whether the hospital shares the same values. Ask physicians at the hospital what they have to say about the hospital’s culture, vision, and values. Have physicians left the hospital after their practices were acquired? Consider speaking with them to learn why.
Keep in mind that a doctor’s reputation could be impacted by a compliance complaint, regardless of whether it’s directed at the hospital and not the employed physician, Mr. Sarraille said.
“The [Erlanger] complaint focuses on the compensation of specific, named physicians saying they were wildly overcompensated,” he said. “The implication is that they sold their referral power in exchange for a pay day. It’s a bad look, no matter how the case evolves from here.”
Physicians could also face their own liability risk under the Stark Law and False Claims Act, depending on the circumstances. In the event of related quality-of-care issues, medical liability could come into play, Mr. Sarraille noted. In such cases, plaintiffs’ attorneys may see an opportunity to boost their claims with allegations that the patient harm was a function of “chasing compensation dollars,” Mr. Sarraille said.
“Where that happens, plaintiff lawyers see the potential for crippling punitive damages, which might not be covered by an insurer,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.