User login
Does Headache Surgery Really Work? Neurologists Remain Unconvinced
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey E. Janis, MD, is on a mission. The professor of plastic surgery, surgery, neurosurgery, and neurology at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, wants to convince neurologists of the safety and efficacy of nerve decompression surgery for treatment-resistant headache. However, many neurologists remain unconvinced.
There’s 24 years of evidence behind this surgical technique across hundreds of different studies with different study designs,” Dr. Janis said.
Yet this treatment approach — surgery on peripheral nerves rather than the brain or spinal cord — hasn’t garnered much support from neurologists. A scan of the agenda of topics at the recently held 2024 annual meeting of the American Headache Society showed few if any studies or presentations on this topic. And neurologists this news organization spoke to said they believe the surgery is experimental and unproven.
Experts do agree drugs don’t work for all patients with migraines. Up to 30% of patients don’t respond to the “laundry list of medications” available to treat the condition, said Dr. Janis.
Many patients have also tried, and failed, alternative treatment approaches such as massage, acupuncture, craniosacral therapy, transdermal patches, electrical stimulation, cryoablation, neurostimulation, and radiofrequency ablation.
If nothing else works, is surgery for headaches the answer?
Long-Held Theory
The idea that pinched, irritated, or compressed peripheral nerves can trigger migraine attacks has been around for nearly 25 years. Studies suggest that in addition to migraine, nerve compression can lead to other headache conditions, including occipital neuralgia, supraorbital neuralgia , and post-traumatic headaches.
This has led to the development of surgical techniques to deactivate various compression trigger sites — what Dr. Janis calls “pinch points” — which could involve muscles, bone, fascia, blood vessels, or scar tissue from prior trauma or surgery.
The procedure is predominantly performed by plastic surgeons, but to a lesser degree by neurosurgeons and ear, nose, and throat specialists.
Target nerves in surgical interventions include those in the frontal region of the head above the eye, temporal region, neck region, and nasal region. Affected areas are usually identified either through patient self-reports or by using a nerve block agent such as lidocaine or Botox at specific points, Dr. Janis noted. If pain subsides after an injection, that location is marked as a target.
One of the barriers to referring complicated patients for surgery is that neurologists evaluating migraine treatments “speak a different language” than surgeons performing the procedure, said Dr. Janis.
Neurologists tend to focus on reduction in monthly migraine days (MMD), while surgeons typically use the Migraine Headache Index that incorporates the frequency, intensity, and duration of migraine attacks.
“Rather than try to convince somebody to speak a different language, we thought, why don’t we just learn their language so we can build bridges and take down barriers,” said Dr. Janis, coauthor of a systematic review and meta-analysis published online recently in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.
Investigators examined 19 studies in the review, including five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), published from January 2020 to September 2023, with a total of 1603 participants who were mostly female and ranged in age from 9 to 72 years. Study follow-ups extended from 6 to 38 months. All but three studies were carried out in the United States, and six different compression sites were addressed during surgery.
Investigators found that across studies and by a number of measures, migraine frequency and severity improved after surgery.
Monthly migraine days decreased by 36%-92% and the number of overall migraine attacks per month dropped 25%-87.5%. Patients also reported decreases in attack duration of 41%-75% and intensity of 28%-82% across studies.
“Even using the neurologist-standard language of monthly migraine days, this surgery works,” said Dr. Janis. “Now this is documented both in the surgical literature and the nonsurgical literature.”
The most common complications were ecchymosis, hair loss or thinning, itching, dryness, and rhinorrhea, all of which Dr. Janis described as “fairly minor.” Major complications such as intraoperative bleeding and wound dehiscence were rare, occurring in 1% or less of participants.
‘One And Done?’
These surgeries are usually done on an outpatient basis and generally offer long-term results, Dr. Janis said.
“The idea is one and done,” he said. “The literature around this type of surgery says that whatever type of effect you get at 1 year is likely to be permanent.”
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons agrees. A 2018 position paper developed by experts and commissioned by the society reports that the intervention is safe and effective for appropriate patients, based on a comprehensive literature search and review of a large body of peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
“There is substantial, extensively replicated clinical data that demonstrates a significant reduction in [migraine headache] symptoms and frequency (even complete elimination of headache pain) following trigger site surgery,” the authors noted.
Pamela Blake, MD, a neurologist, board-certified headache specialist, and medical director at the Headache Center of River Oaks, Houston, is a proponent of what she said can be “lifesaving” headache surgery.
“If a doctor told you that you can either treat this problem with medications that you’ll need to take for the rest of your life or you can have a surgical procedure as an outpatient that has extremely low risk and has, in my experience, a 75% chance of reducing or eliminating your pain, you probably would be interested in surgery,” she said.
Continued Skepticism
However, other neurologists and clinicians appear doubtful about this intervention, including Hans-Christoph Diener, MD, PhD, professor of neurology and director, Essen Headache Centre, University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany.
During a debate on the topic a decade ago at the International Headache Congress, Dr. Diener argued that, as migraine is a complex multigene-related disorder of the brain, it doesn’t make sense that surgery would affect the epigenetics of 22 different genes.
Recently, he said that his views have not changed.
The topic remains controversial, and some neurologists are uncomfortable even openly discussing the procedure. Two clinicians who previously commented on this article later asked not to be included.
One neurologist, who asked to remain anonymous, said that Dr. Janis’s review article is “merely a review collecting 19 studies over the previous 10-plus years.”
Other limitations cited by this neurologist are the lack of consistency in procedures among the various studies and the inclusion of only four RCTs, the most recent of which was published 8 years ago, suggesting “the study was probably done closer to 9 or 10 years ago,” the neurologist said.
Dr. Blake suggested some neurologists’ reluctance could be due to limited background on the procedure, which she said isn’t widely discussed at headache meetings and is covered mostly in plastic surgery journals, not neurology literature. Access to surgery is further limited by a lack of specialists who perform the procedure and inconsistent insurance coverage.
A closer collaboration between neurologists and surgeons who perform the procedure could benefit patients, Dr. Blake noted.
“The headache doctor’s role is to identify who’s a candidate for surgery, who meets the criteria for nerve compression, and then follow that patient postoperatively, managing their medications, although usually we get them off their medications,” she added.
From Dr. Janis’s perspective, things are starting to change.
“I’m definitely seeing a greater comfort level among neurologists who are understanding where this sits in the algorithm for treatment, especially for complicated patients,” he said.
Dr. Janis receives royalties from Thieme and Springer Publishing. Dr. Blake reported no relevant conflicts. Dr. Diener received research support from the German Research Council; serves on the editorial boards of Cephalalgia, Lancet Neurology, and Drugs; and has received honoraria for participation in clinical trials, contribution to advisory boards, or oral presentations from AbbVie, Lilly, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Teva, Weber & Weber, and WebMD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Epidermal Tumors Arising on Donor Sites From Autologous Skin Grafts: A Systematic Review
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.
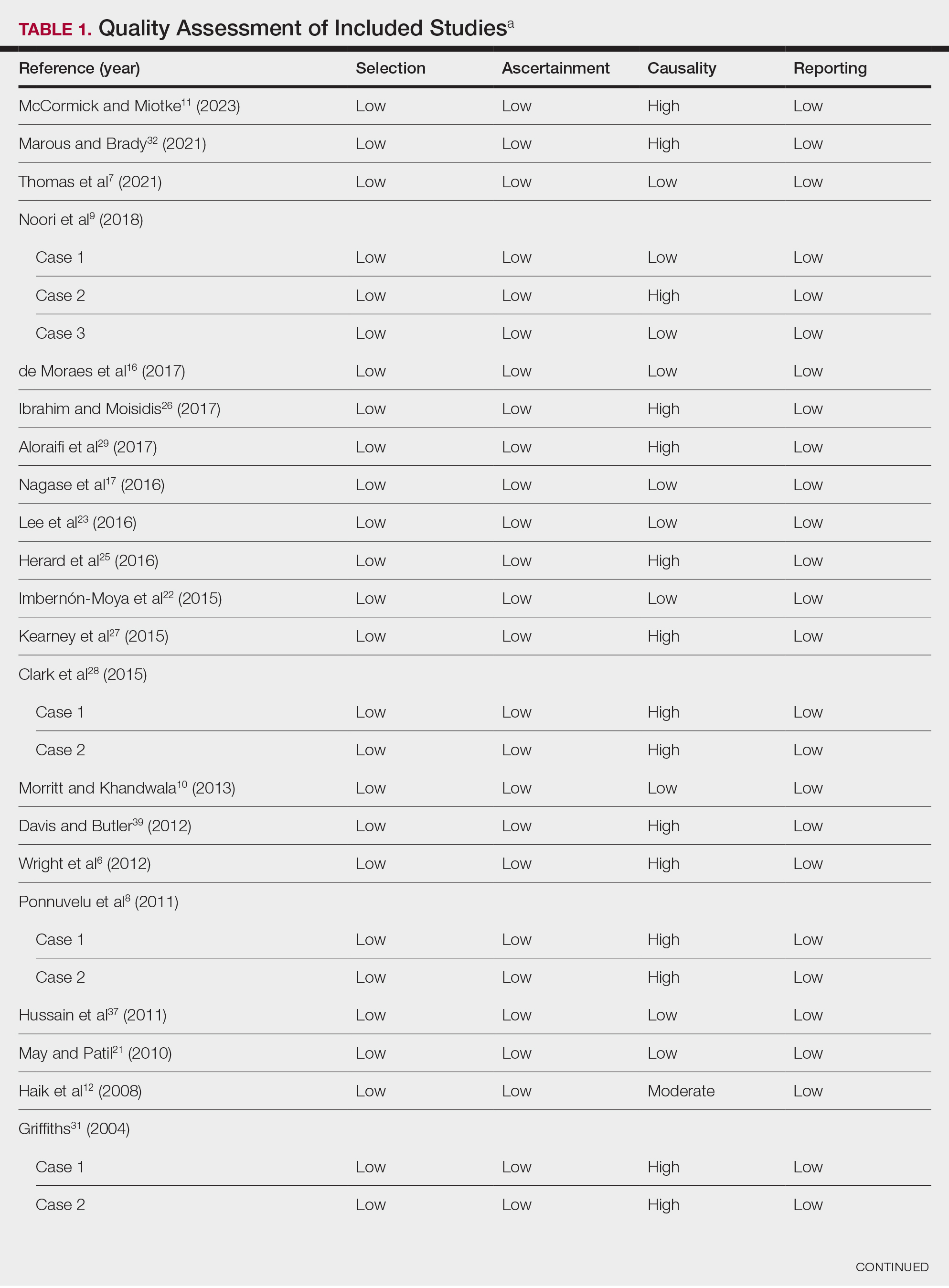
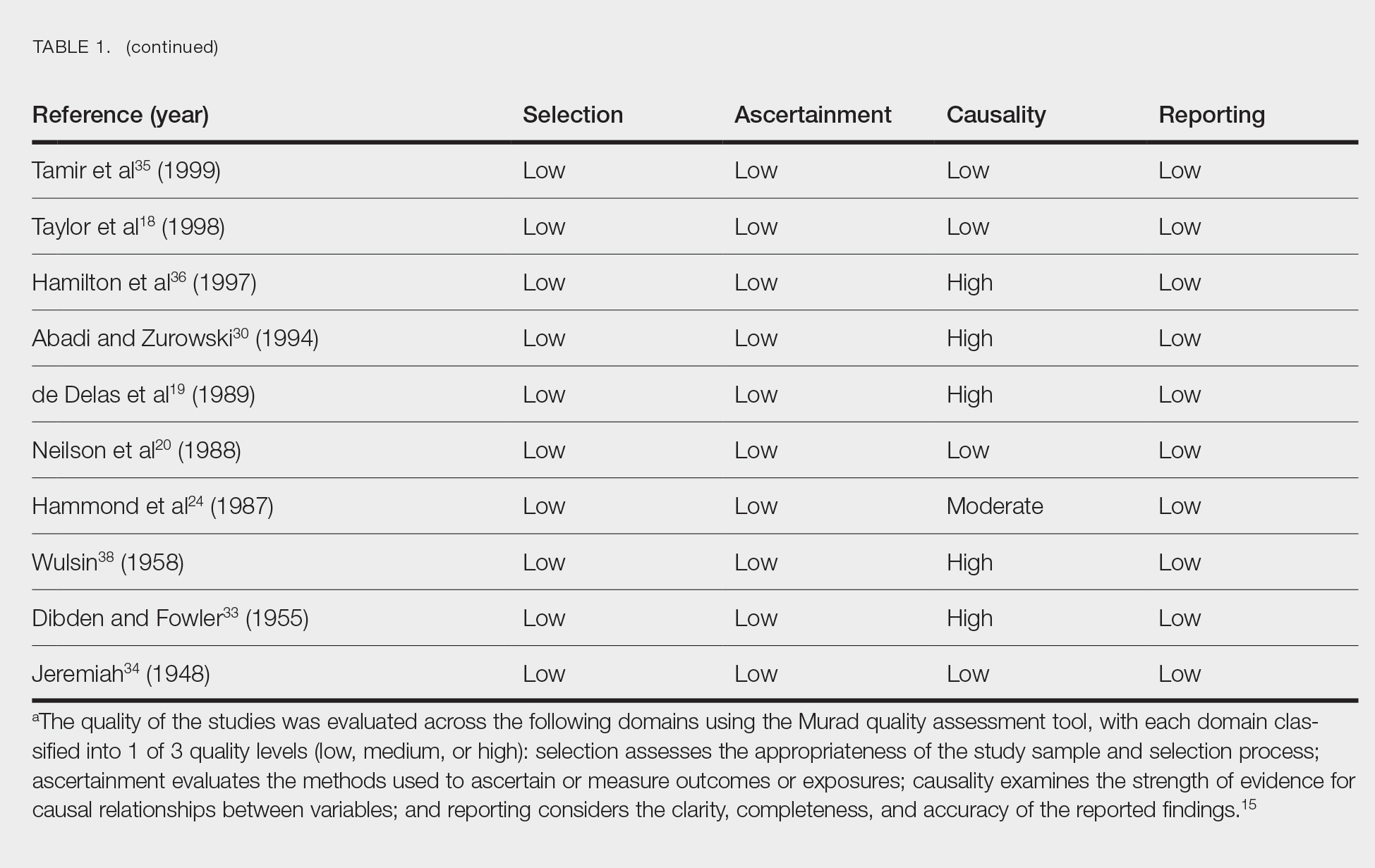
Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
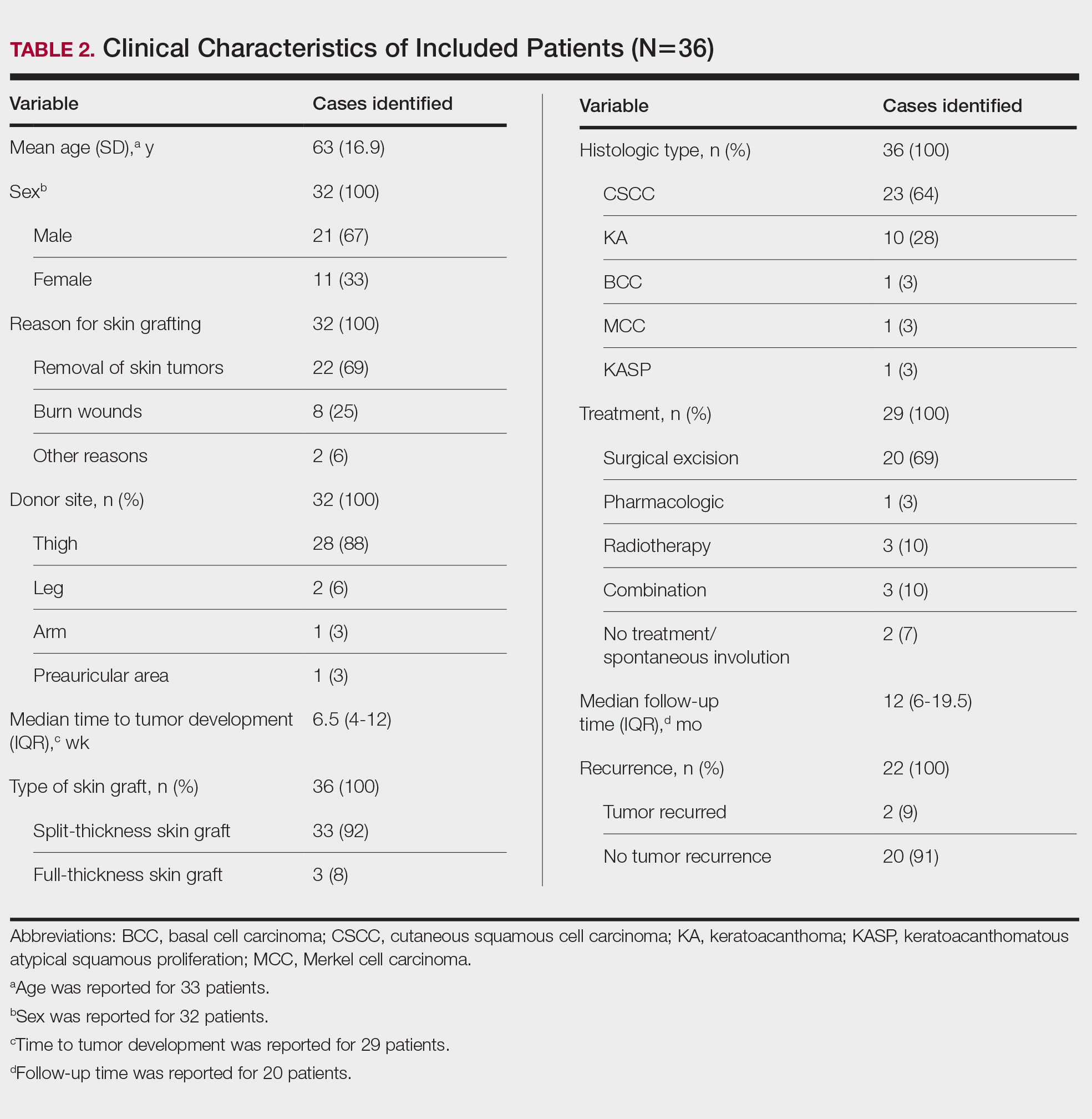
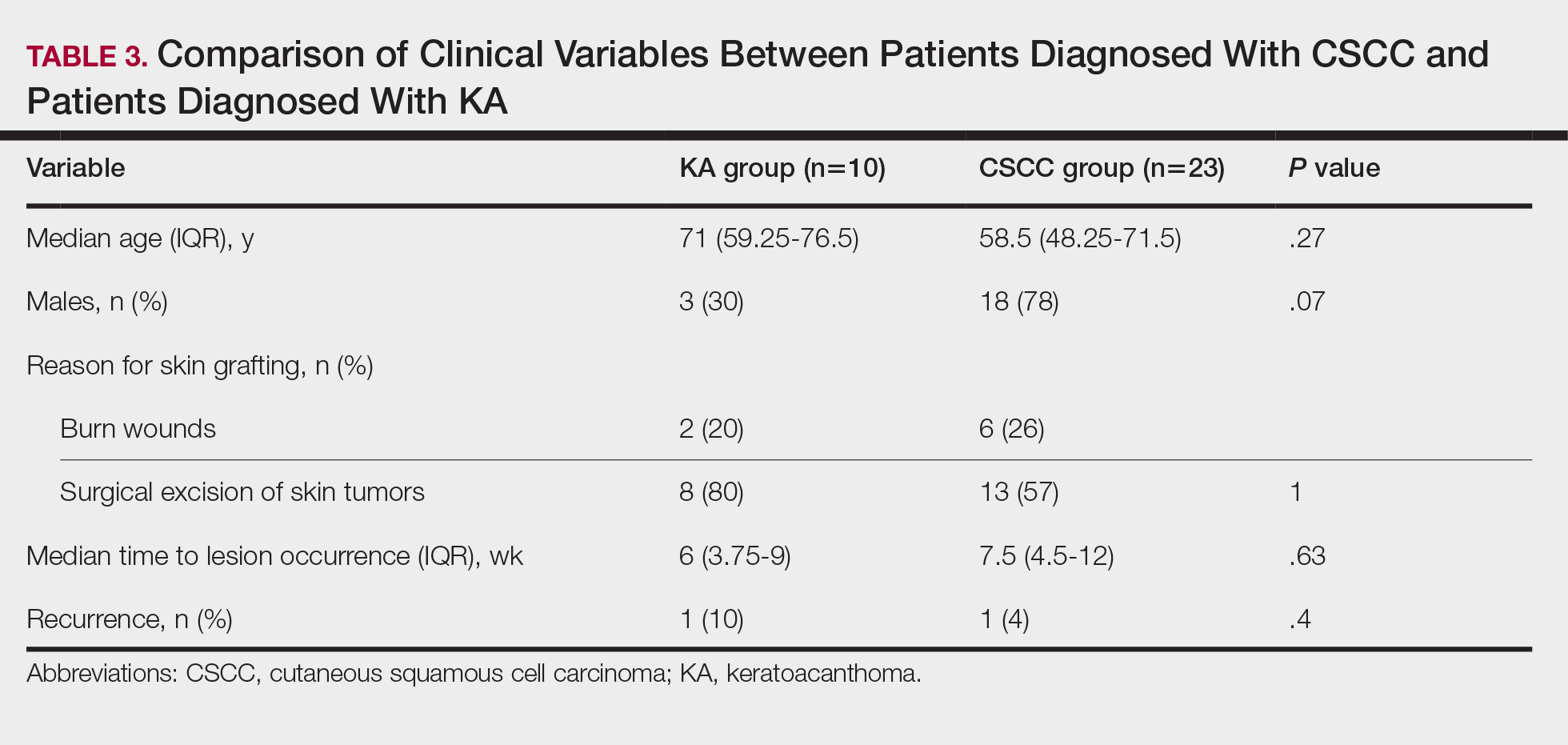
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.
Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.


Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.


Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
Skin grafting is a surgical technique used to cover skin defects resulting from the removal of skin tumors, ulcers, or burn injuries.1-3 Complications can occur at both donor and recipient sites and may include bleeding, hematoma/seroma formation, postoperative pain, infection, scarring, paresthesia, skin pigmentation, graft contracture, and graft failure.1,2,4,5 The development of epidermal tumors is not commonly reported among the complications of skin grafting; however, cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites during the postoperative period have been reported.6-12
We performed a systematic review of the literature for cases of epidermal tumor development on skin graft donor sites in patients undergoing autologous skin graft surgery. We present the clinical characteristics of these cases and discuss the nature of these tumors.
Methods
Search Strategy and Study Selection—A literature search was conducted by 2 independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) for articles published before December 2022 in the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library, OpenGrey, Google Scholar, and WorldCat. Search terms included all possible combinations of the following: keratoacanthoma, molluscum sebaceum, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, acanthoma, wart, Merkel cell carcinoma, verruca, Bowen disease, keratosis, skin cancer, cutaneous cancer, skin neoplasia, cutaneous neoplasia, and skin tumor. The literature search terms were selected based on the World Health Organization classification of skin tumors.13 Manual bibliography checks were performed on all eligible search results for possible relevant studies. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and, if needed, mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). To be included, a study had to report a case(s) of epidermal tumor(s) that was confirmed by histopathology and arose on a graft donor site in a patient receiving autologous skin grafts for any reason. No language, geographic, or report date restrictions were set.
Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis—We adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.14 Two independent researchers (Z.P. and V.P.) retrieved the data from the included studies. We have used the terms case and patient interchangeably, and 1 month was measured as 4 weeks for simplicity. Disagreements were resolved by discussion and mediation by a third researcher (N.C.). The quality of the included studies was assessed by 2 researchers (M.P. and V.P.) using the tool proposed by Murad et al.15
We used descriptive statistical analysis to analyze clinical characteristics of the included cases. We performed separate descriptive analyses based on the most frequently reported types of epidermal tumors and compared the differences between different groups using the Mann-Whitney U test, χ2 test, and Fisher exact test. The level of significance was set at P<.05. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS (version 29).
Results
Literature Search and Characteristics of Included Studies—The initial literature search identified 1378 studies, which were screened based on title and abstract. After removing duplicate and irrelevant studies and evaluating the full text of eligible studies, 31 studies (4 case series and 27 case reports) were included in the systematic review (Figure).6-12,16-39 Quality assessment of the included studies is presented in Table 1.


Clinical Characteristics of Included Patients—Our systematic review included 36 patients with a mean age of 63 years and a male to female ratio of 2:1. The 2 most common causes for skin grafting were burn wounds and surgical excision of skin tumors. Most grafts were harvested from the thighs. The development of a solitary lesion on the donor area was reported in two-thirds of the patients, while more than 1 lesion developed in the remaining one-third of patients. The median time to tumor development was 6.5 weeks. In most cases, a split-thickness skin graft was used.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (CSCCs) were found in 23 patients, with well-differentiated CSCCs in 19 of these cases. Additionally, keratoacanthomas (KAs) were found in 10 patients. The majority of patients underwent surgical excision of the tumor. The median follow-up time was 12 months, during which recurrences were noted in a small percentage of cases. Clinical characteristics of included patients are presented in Table 2.


Comment
Reasons for Tumor Development on Skin Graft Donor Sites—The etiology behind epidermal tumor development on graft donor sites is unclear. According to one theory, iatrogenic contamination of the donor site during the removal of a primary epidermal tumor could be responsible. However, contemporary surgical procedures dictate the use of different sets of instruments for separate surgical sites. Moreover, this theory cannot explain the occurrence of epidermal tumors on donor sites in patients who have undergone skin grafting for the repair of burn wounds.37
Another theory suggests that hematogenous and/or lymphatic spread can occur from the site of the primary epidermal tumor to the donor site, which has increased vascularization.16,37 However, this theory also fails to provide an explanation for the development of epidermal tumors in patients who receive skin grafts for burn wounds.
A third theory states that the microenvironment of the donor site is key to tumor development. The donor site undergoes acute inflammation due to the trauma from harvesting the skin graft. According to this theory, acute inflammation could promote neoplastic growth and thus explain the development of epidermal tumors on the donor site.8,26 However, the relationship between acute inflammation and carcinogenesis remains unclear. What is known to date is that the development of CSCC has been documented primarily in chronically inflamed tissues, whereas the development of KA—a variant of CSCC with distinctive and more benign clinical characteristics—can be expected in the setting of acute trauma-related inflammation.13,40,41
Based on our systematic review, we propose that well-differentiated CSCC on graft donor sites might actually be misdiagnosed KA, given that the histopathologic differential diagnosis between CSCC and KA is extremely challenging.42 This hypothesis could explain the development of well-differentiated CSCC and KA on graft donor sites.
Conclusion
Development of CSCC and KA on graft donor sites can be listed among the postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting. Patients and physicians should be aware of this potential complication, and donor sites should be monitored for the occurrence of epidermal tumors.
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
- Adams DC, Ramsey ML. Grafts in dermatologic surgery: review and update on full- and split-thickness skin grafts, free cartilage grafts, and composite grafts. Dermatologic Surg. 2005;31(8, pt 2):1055-1067. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31831
- Shimizu R, Kishi K. Skin graft. Plast Surg Int. 2012;2012:563493. doi:10.1155/2012/563493
- Reddy S, El-Haddawi F, Fancourt M, et al. The incidence and risk factors for lower limb skin graft failure. Dermatol Res Pract. 2014;2014:582080. doi:10.1155/2014/582080
- Coughlin MJ, Dockery GD, Crawford ME, et al. Lower Extremity Soft Tissue & Cutaneous Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed. Saunders Ltd; 2012.
- Herskovitz I, Hughes OB, Macquhae F, et al. Epidermal skin grafting. Int Wound J. 2016;13(suppl 3):52-56. doi:10.1111/iwj.12631
- Wright H, McKinnell TH, Dunkin C. Recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at remote limb donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:1265-1266. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2012.01.022
- Thomas W, Rezzadeh K, Rossi K, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising at a skin graft donor site: case report and review of the literature. Plast Surg Case Stud. 2021;7:2513826X211008425. doi:10.1177/2513826X211008425
- Ponnuvelu G, Ng MFY, Connolly CM, et al. Inflammation to skin malignancy, time to rethink the link: SCC in skin graft donor sites. Surgeon. 2011;9:168-169. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2010.08.006
- Noori VJ, Trehan K, Savetamal A, et al. New onset squamous cell carcinoma in previous split-thickness skin graft donor site. Int J Surg. 2018;52:16-19. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.047
- Morritt DG, Khandwala AR. The development of squamous cell carcinomas in split-thickness skin graft donor sites. Eur J Plast Surg. 2013;36:377-380.
- McCormick M, Miotke S. Squamous cell carcinoma at split thickness skin graft donor site: a case report and review of the literature. J Burn Care Res. 2023;44:210-213. doi:10.1093/jbcr/irac137
- Haik J, Georgiou I, Farber N, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. Burns. 2008;34:891-893. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2007.06.006
- Elder DE, Massi D, Scolyer RA WR. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. 4th ed. IARC Press; 2018.
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:264-269, W64. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
- Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, et al. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ. 2018;23:60-63. doi:10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
- de Moraes LPB, Burchett I, Nicholls S, et al. Large solitary distant metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to skin graft site with complete response following definitive radiotherapy. Int J Bioautomation. 2017;21:103-108.
- Nagase K, Suzuki Y, Misago N, et al. Acute development of keratoacanthoma at a full-thickness skin graft donor site shortly after surgery. J Dermatol. 2016;43:1232-1233. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13368
- Taylor CD, Snelling CF, Nickerson D, et al. Acute development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1998;19:382-385. doi:10.1097/00004630-199809000-00004
- de Delas J, Leache A, Vazquez Doval J, et al. Keratoacanthoma over the donor site of a laminar skin graft. Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1989;17:225-228.
- Neilson D, Emerson DJ, Dunn L. Squamous cell carcinoma of skin developing in a skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1988;41:417-419. doi:10.1016/0007-1226(88)90086-0
- May JT, Patil YJ. Keratoacanthoma-type squamous cell carcinoma developing in a skin graft donor site after tumor extirpation at a distant site. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010;89:E11-E13.
- Imbernón-Moya A, Vargas-Laguna E, Lobato-Berezo A, et al. Simultaneous onset of basal cell carcinoma over skin graft and donor site. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:244-246. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.05.004
- Lee S, Coutts I, Ryan A, et al. Keratoacanthoma formation after skin grafting: a brief report and pathophysiological hypothesis. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:e117-e119. doi:10.1111/ajd.12501
- Hammond JS, Thomsen S, Ward CG. Scar carcinoma arising acutelyin a skin graft donor site. J Trauma. 1987;27:681-683. doi:10.1097/00005373-198706000-00017
- Herard C, Arnaud D, Goga D, et al. Rapid onset of squamous cell carcinoma in a thin skin graft donor site. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2016;143:457-461. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2015.03.027
- Ibrahim A, Moisidis E. Case series: rapidly growing squamous cell carcinoma after cutaneous surgical intervention. JPRAS Open. 2017;14:27-32. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2017.08.004
- Kearney L, Dolan RT, Parfrey NA, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in a skin graft donor site following melanoma extirpation at a distant site: a case report and review of the literature. JPRAS Open. 2015;3:35-38. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2015.02.002
- Clark MA, Guitart J, Gerami P, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomatous atypical squamous proliferations (KASPs) arising in skin graft sites. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1:274-276. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.06.009
- Aloraifi F, Mulgrew S, James NK. Secondary Merkel cell carcinoma arising from a graft donor site. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:167-169. doi:10.1177/1203475416676805
- Abadir R, Zurowski S. Case report: squamous cell carcinoma of the skin in both palms, axillary node, donor skin graft site and both soles—associated hyperkeratosis and porokeratosis. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:507-510. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-797-507
- Griffiths RW. Keratoacanthoma observed. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:485-501. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2004.05.007
- Marous M, Brady K. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in a split thickness skin graft donor site in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatologic Surg. 2021;47:1106-1107. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002955
- Dibden FA, Fowler M. The multiple growth of molluscum sebaceum in donor and recipient sites of skin graft. Aust N Z J Surg. 1955;25:157-159. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1955.tb05122.x
- Jeremiah BS. Squamous cell carcinoma development on donor area following removal of a split thickness skin graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1948;3:718-721.
- Tamir G, Morgenstern S, Ben-Amitay D, et al. Synchronous appearance of keratoacanthomas in burn scar and skin graft donor site shortly after injury. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(5, pt 2):870-871. doi:10.1053/jd.1999.v40.a94419
- Hamilton SA, Dickson WA, O’Brien CJ. Keratoacanthoma developing in a split skin graft donor site. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:560-561. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91308-4
- Hussain A, Ekwobi C, Watson S. Metastatic implantation squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:690-692. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.06.004
- Wulsin JH. Keratoacanthoma: a benign cutaneous tumors arising in a skin graft donor site. Am Surg. 1958;24:689-692.
- Davis L, Butler D. Acute development of squamous cell carcinoma in a split-thickness skin graft donor site [abstract]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB208. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.11.874
- Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002;16:217-226, 229; discussion 230-232.
- Piotrowski I, Kulcenty K, Suchorska W. Interplay between inflammation and cancer. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020;25:422-427. doi:10.1016/j.rpor.2020.04.004
- Carr RA, Houghton JP. Histopathologists’ approach to keratoacanthoma: a multisite survey of regional variation in Great Britain and Ireland. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:637-638. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202255
Practice Points
- Donor site cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) and keratoacanthoma (KA) can be postoperative complications of autologous skin grafting.
- Surgical excision of donor site CSCC and KA typically is curative.
Management, Evaluation of Chronic Itch in Older Adults
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — , Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the ElderDerm conference on dermatology in older patients hosted by the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences.
“We found a few years ago that eosinophils seem to differentiate this group, and now we’re finding that IgE and CBC [complete blood count] differential can help you get a little better sense of who has an immune-driven itch vs something more neuropathic,” said Dr. Kwatra, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, who founded and directed the Johns Hopkins Itch Center before coming to the University of Maryland in 2023. Not all patients with immune-driven itch will have these biomarkers, “but it’s a helpful tool,” he said.
CPUO is the term that is increasingly being used, he said, to describe intense, chronic pruritus without primary skin lesions or rashes and without any known systemic cause. It becomes more common as people get older and is sometimes debilitating. The initial evaluation should be kept “simple and straightforward,” he advised, with heightened concern for underlying malignancy in those who present with an itch of less than 12 months’ duration.
Biologics, JAK Inhibitors: Case Reports, Ongoing Research
Research conducted by Dr. Kwatra and Jaya Manjunath, a fourth-year medical student at The George Washington University, Washington, documented higher levels of Th2-associated cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with CPUO who had elevated IgE or eosinophil levels, or both than in patients with itch who had low IgE and eosinophil levels. The patients with higher levels also had a greater response to off-label treatment with immunomodulatory therapy.
“Multiple Th2-related inflammatory markers, like IL [interleukin]-5 and eotaxin-3, were reduced after dupilumab” in patients who responded to the therapy, said Ms. Manjunath, who co-presented the meeting session on chronic itch with Dr. Kwatra. Other changes in the plasma cytokine profile included a reduction in the serum level of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, which is a biomarker for atopic dermatitis. The research is under review for publication.
Meanwhile, a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CPUO-CHIC) of dupilumab for CPUO is currently underway, Dr. Kwatra noted. Investigators are randomizing patients with severe pruritus (Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale [WI-NRS] ≥ 7) to dupilumab or placebo for 12 or 24 weeks.
In one of several cases shared by Dr. Kwatra and Ms. Manjunath, a 71-year-old Black woman with a 6-month history of generalized itch (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease was found to have elevated eosinophil levels and a negative malignancy workup. Previous therapies included antihistamines and topical steroids. She was started on a 600-mg loading dose of subcutaneous dupilumab followed by 300 mg every 14 days. At the 2-month follow-up, her WI-NRS score was 0.
Because “dupilumab is off label right now for this form of itch, oftentimes our first line is methotrexate,” Dr. Kwatra said. Patients “can have a good response with this therapeutic.”
He also described the case of a 72-year-old Black woman with total body itch for 2 years (WI-NRS = 10) and a history of seasonal allergies, thyroid disease, and hypertension. Previous therapies included prednisone, antihistamines, topical steroids, and gabapentin. The patient was found to have high IgE (447 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.9%), was started on methotrexate, and had an itch score of 0 at the 8-month follow-up.
JAK inhibitors may also have a role in the management of CPUO. A phase 2 nonrandomized controlled trial of abrocitinib for adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) or CPUO, recently published in JAMA Dermatology, showed itch scores decreased by 53.7% in the CPUO group (and 78.3% in the PN group) after 12 weeks of treatment with oral abrocitinib 200 mg daily. Patients had significant improvements in quality of life and no serious adverse events, said Dr. Kwatra, the lead author of the paper.
One of these patients was a 73-year-old White man who had experienced total body itch for 1.5 years (predominantly affecting his upper extremities; WI-NRS = 10) and a history of ascending aortic aneurysm, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Previous failed therapies included dupilumab (> 6 months), topical steroids, tacrolimus, and antihistamines. Labs showed elevated IgE (456 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (11.7%). After 12 weeks of treatment with abrocitinib, the WI-NRS decreased to 2.
PD-1 Inhibitors As a Trigger
Chronic pruritus caused by the anticancer PD-1 inhibitors is becoming more common as the utilization of these immune checkpoint inhibitors increases, Dr. Kwatra noted. “You don’t see much in the skin, but [these patients have] very high IgE and eosinophils,” he said. “We’ve been seeing more reports recently of utilizing agents that target type 2 inflammation off label for PD-1 inhibitor–related skin manifestations.”
One such patient with PD-1 inhibitor–induced pruritus was a 65-year-old White man with metastatic melanoma who reported a 6-month history of itching that began 3 weeks after the start of treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembrolizumab. His WI-NRS score was 10 despite treatment with topical steroids and antihistamines. He had a history of psoriasis. Labs showed elevated IgE (1350 kU/L) and eosinophil levels (4.5%). At a 4-month follow-up after treatment with off-label dupilumab (a 600-mg subcutaneous loading dose followed by 300 mg every 14 days), his WI-NRS score was 0.
In a paper recently published in JAAD International, Dr. Kwatra, Ms. Manjunath, and coinvestigators reported on a series of 15 patients who developed chronic pruritus following an immune stimulus exposure, including immunotherapy and vaccination (2024 Apr 7:16:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2024.03.022). Most immunotherapy-treated patients experienced pruritus during treatment or after 21-60 days of receiving treatment, and the patients with vaccine-stimulated pruritus (after Tdap and messenger RNA COVID-19 vaccination) developed pruritus within a week of vaccination.
In addition to the elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils, plasma cytokine analysis showed elevated levels of IL-5, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and other Th2-related cytokines and inflammatory markers in patients with immune-stimulated pruritus compared with healthy controls, Ms. Manjunath said at the meeting.
When a Malignancy Workup Becomes Important
The initial part of any diagnostic workup for CPUO should include CBC with differential, liver function tests, renal function tests, and thyroid function testing, said Kwatra, referring to a diagnostic algorithm he developed, which was published as part of a CME review in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022.
Then, as indicated by risk factors in the history and physical, one could order other tests such as HIV serology, hepatitis B/C serologies, bullous pemphigoid testing, chest x-rays, evaluation for gammopathies, stool examination for ova and parasites, or heavy metal testing. “Do you do everything at once? We like to keep it straightforward,” Dr. Kwatra said. “Depending on the patient’s risk factors, you could order more or less.”
A malignancy workup should be strongly considered in patients whose itch duration is less than 12 months — and especially if the duration is less than 3 months — with an emphasis on cancers more frequently associated with itch: Hematologic and hepatobiliary cancers. This is “when concern should be heightened ... when there should be a lower threshold for workup,” he said.
The 12-month recommendation stems from a Danish cohort study published in 2014 that demonstrated a twofold increased incidence of cancer among patients with pruritus in the first 3 months after the diagnosis of pruritus. The 1-year absolute cancer risk was 1.63%.
Other risk factors for underlying malignancy or malignancy development in patients with CPUO include age older than 60 years, male sex, liver disease, and current or prior smoking, according to another study, noted Dr. Kwatra.
Dr. Kwatra disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and other companies and an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Manjunath served as the codirector of the ElderDerm conference.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ELDERDERM 2024
Cognitive Breakdown: The New Memory Condition Primary Care Needs to Know
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients experiencing memory problems often come to neurologist David Jones, MD, for second opinions. They repeat questions and sometimes misplace items. Their primary care clinician has suggested they may have Alzheimer’s disease or something else.
In many cases, Dr. Jones, a neurologist with Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, performs a series of investigations and finds the patient instead has a different type of neurodegenerative syndrome, one that progresses slowly, seems limited chiefly to loss of memory, and which tests show affects only the limbic system.
The news of diagnosis can be reassuring to patients.
“Memory problems are not always Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Jones said. “It’s important to broaden the differential diagnosis and seek diagnostic clarity and precision for patients who experience problems with brain functioning later in life.”
Dr. Jones and colleagues recently published clinical criteria for what they call limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome (LANS).
Various underlying etiologies are known to cause degeneration of the limbic system, the most frequent being a buildup of deposits of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) protein referred to as limbic-predominant, age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathological change (LATE-NC). LATE-NC first involves the amygdala, followed by the hippocampus, and then the middle frontal gyrus, and is found in about 40% of autopsied brains in people over age of 85 years.
By contrast, amnestic syndromes originating from neocortical degeneration are largely caused by neuropathological changes from Alzheimer’s disease and often present with non-memory features.
Criteria for LANS
Broken down into core, standard, and advanced features
Core clinical features:
The patient must present with a slow, amnestic, predominant neurodegenerative syndrome — an insidious onset with gradual progression over 2 or more years — without another condition that better accounts for the clinical deficits.
Standard supportive features:
1. Older age at evaluation.
- Most patients are at least the age of 75 years. Older age increases the likelihood that the amnestic syndrome is caused by degeneration of the limbic system.
2. Mild clinical syndrome.
- A diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment or mild amnestic dementia (ie, a score of ≤ 4 on the Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes [CDR-SB]) at the first visit.
3. Hippocampal atrophy out of proportion to syndrome severity.
- Hippocampal volume was smaller than expected on MRI, compared with the CDR-SB score.
4. Mildly impaired semantic memory.
Advanced supportive features:
1.Limbic hypometabolism and absence of neocortical degenerative pattern on fludeoxyglucose-18-PET imaging.
2. Low likelihood of significant neocortical tau pathology.
Dr. Jones and colleagues also classified a degree of certainty for LANS to use when making a diagnosis. Those with the highest likelihood meet all core, standard, and advanced features.
Patients with a high likelihood of having LANS meet core features, at least three standard features and one advanced feature; or meet core features, at least two standard features as well as two advanced features. Those with a moderate likelihood meet core features and at least three standard features or meet core features and at least two standard features and one advanced feature. Those with a low likelihood of LANS meet core features and two or fewer standard features.
To develop these criteria, the group screened 218 autopsied patients participating in databases for the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging and the multicenter Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. They conducted neuropathological assessments, reviewed MRI and PET scans of the brains, and studied fluid biomarkers from samples of cerebrospinal fluid.
In LANS, the neocortex exhibits normal function, Dr. Jones said. High-level language functions, visual spatial functions, and executive function are preserved, and the disease stays mild for many years. LANS is highly associated with LATE, for which no biomarkers are yet available.
The National Institute on Aging in May 2023 held a workshop on LATE, and a consensus group was formed to publish criteria to help with the diagnosis. Many LANS criteria likely will be in that publication as well, Dr. Jones said.
Several steps lay ahead to improve the definition of LANS, the authors wrote, including conducting prospective studies and developing clinical tools that are sensitive and specific to its cognitive features. The development of in vivo diagnostic markers of TDP-43 pathology is needed to embed LANS into a disease state driven by LATE-NC, according to Dr. Jones’ group. Because LANS is newly defined, clinical trials are needed to determine the best treatments.
Heterogeneous Dementia
“We are increasingly recognizing that the syndrome of dementia in older adults is heterogeneous,” said Sudha Seshadri, MD, DM, a behavioral neurologist and founding director of the Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
LANS “is something that needs to be diagnosed early but also needs to be worked up in a nuanced manner, with assessment of the pattern of cognitive deficits, the pattern of brain shrinkage on MRI, and also how the disease progresses over, say, a year,” said Dr. Seshadri. “We need to have both some primary care physicians and geriatricians who are comfortable doing this kind of nuanced advising and others who may refer patients to behavioral neurologists, geriatricians, or psychiatrists who have that kind of expertise.”
About 10% of people presenting to dementia clinics potentially could fit the LANS definition, Dr. Seshadri said. Dr. Seshadri was not a coauthor of the classification article but sees patients in the clinic who fit this description.
“It may be that as we start more freely giving the diagnosis of a possible LANS, the proportion of people will go up,” Dr. Seshadri said.
Primary care physicians can use a variety of assessments to help diagnose dementias, she said. These include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which takes about 10 minutes to administer, or an MRI to determine the level of hippocampal atrophy. Blood tests for p-tau 217 and other plasma tests can stratify risk and guide referrals to a neurologist. Clinicians also should look for reversible causes of memory complaints, such as deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or the thyroid hormone.
“There aren’t enough behavioral neurologists around to work up every single person who has memory problems,” Dr. Seshadri said. “We really need to partner on educating and learning from our primary care partners as to what challenges they face, advocating for them to be able to address that, and then sharing what we know, because what we know is an evolving thing.”
Other tools primary care clinicians can use in the initial evaluation of dementia include the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition and the Mini-Cog, as part of annual Medicare wellness visits or in response to patient or caregiver concerns about memory, said Allison Kaplan, MD, a family physician at Desert Grove Family Medical in Gilbert, Arizona, who coauthored a point-of-care guide for the American Academy of Family Physicians. Each of these tests takes just 3-4 minutes to administer.
If a patient has a positive result on the Mini-Cog or similar test, they should return for further dementia evaluation using the MoCA, Mini-Mental State Examination, or Saint Louis University Mental Status examination, she said. Physicians also can order brain imaging and lab work, as Dr. Seshadri noted. Dementias often accompany some type of cardiovascular disease, which should be managed.
Even if a patient or family member doesn’t express concern about memory, physicians can look for certain signs during medical visits.
“Patients will keep asking the same question, or you notice they’re having difficulty taking care of themselves, especially independent activities of daily living, which could clue you in to a dementia diagnosis,” she said.
Dr. Jones ,Dr. Seshadri, and Dr. Kaplan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BRAIN COMMUNICATION
Weight Loss in Obesity May Create ‘Positive’ Hormone Changes
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In middle-aged patients with severe obesity, changes in endogenous sex hormones may be proportional to the amount of weight loss after bariatric surgery and dietary intervention, leading to an improved hormonal balance, with more pronounced androgen changes in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Obesity-related hormonal imbalances are common among those seeking weight loss treatment.
- This prospective observational study evaluated the incremental effect of weight loss by three bariatric procedures and a dietary intervention on endogenous sex hormones in men and women over 3 years.
- The study included 61 adults (median age, 50.9 years; baseline mean body mass index, 40.2; 72% women) from obesity clinics and private bariatric services in Sydney, Australia, between 2009 and 2012, who underwent bariatric surgery or received dietary interventions based on their probability of diabetes remission.
- The researchers evaluated weight loss and hormone levels at baseline and at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months.
- Changes in hormones were also compared among patients who received dietary intervention and those who underwent bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and laparoscopic gastric banding.
TAKEAWAY:
- In women, testosterone levels decreased and sex hormone–binding globulin (SHBG) levels increased at 6 months; these changes were maintained at 24 and 36 months and remained statistically significant when controlled for age and menopausal status.
- In men, testosterone levels were significantly higher at 12, 24, and 36 months, and SHBG levels increased at 12 and 24 months. There were no differences in the estradiol levels among men and women.
- Women who underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery experienced the greatest weight loss and the largest reduction (54%) in testosterone levels (P = .004), and sleeve gastrectomy led to an increase of 51% in SHBG levels (P = .0001), all compared with dietary interventions. In men, there were no differences in testosterone and SHBG levels between the diet and surgical groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ongoing monitoring of hormone levels and metabolic parameters is crucial for patients undergoing bariatric procedures to ensure long-term optimal health outcomes,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Malgorzata M. Brzozowska, MD, PhD, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, Australia, and was published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The main limitations were a small sample size, lack of randomization, and absence of data on clinical outcomes related to hormone changes. Additionally, the researchers did not evaluate women for polycystic ovary syndrome or menstrual irregularities, and the clinical significance of testosterone reductions within the normal range remains unknown.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council. Some authors have received honoraria and consulting and research support from various pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves First Targeted Therapy for Gliomas With IDH Mutations
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specifically, the oral targeted inhibitor of IDH1 and IDH2 was approved for use after surgery in adults and children aged 12 years or older who have grade 2 astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation. According to the FDA, surgery includes biopsy, subtotal resection, or gross total resection.
Mutations in IDH1 are present in around 80% of grade 2 gliomas, whereas IDH2 mutations are more infrequent, occurring in about 4%.
Prior to the approval, which was based on progression-free survival (PFS) and safety findings from the pivotal phase 3 INDIGO trial, patients with this type of glioma had limited treatment options, said a Servier spokesperson.
The approval of vorasidenib marks “one of the biggest advances in low-grade glioma in more than two decades” and “will empower patients to take active control of their disease with a once-daily pill,” according to the spokesperson.
In the INDIGO trial, 331 patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of vorasidenib once daily (n = 168) or placebo (n = 163). At a median follow-up of 14.2 months, the median PFS was more than twice as long among those who received vorasidenib vs placebo: 27.7 months vs 11.1 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR] for disease progression or death, 0.39). The time to next intervention was also significantly longer with vorasidenib vs placebo (median not reached vs 17.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.26).
The 61% reduction in the risk for tumor progression or death observed in the trial represents “a significant sign of efficacy that has the potential to change the landscape in this disease,” first author Ingo K. Mellinghoff, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, told this news organization in 2023, when presenting the findings at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology conference. These findings were simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Glenn Lesser, MD, a discussant at the 2023 meeting, commented on the “striking” findings. The results are “statistically highly significant, and more importantly, they’re clinically very, very significant,” said Dr. Lesser, from Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Vorasidenib can also potentially delay the use of toxic chemotherapies and radiation for many years in patients with these tumors, Dr. Lesser added.
Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 22.8% of those who received vorasidenib and in 13.5% of those in the placebo group. Increased alanine aminotransferase levels of grade 3 or higher occurred in 9.6 vs 0% of patients in the groups, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions with vorasidenib, affecting at least 15% of treated patients, include fatigue, headache, COVID-19, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and seizure. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were increased alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as well as decreased neutrophils.
The recommended dose of vorasidenib for adults is 40 mg given orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In children aged 12 or older, the recommended dose is 40 mg given orally once daily for those weighing ≥ 40 kg, and 20 mg given orally once daily for those weighing < 40 kg.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tool Can Help Predict Futile Surgery in Pancreatic Cancer
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Immediate resection is associated with a high incidence of postoperative complications and disease recurrence within a year of surgery in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Predicting which patients likely won’t benefit from upfront pancreatectomy is important.
- To identify preoperative risk factors for futile pancreatectomy, researchers evaluated 1426 patients (median age, 69 years; 53.2% men) with anatomically resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent pancreatic resection between January 2010 and December 2021.
- The patients were divided into derivation (n = 885) and validation (n = 541) cohorts.
- The primary outcome was the rate of futile upfront pancreatectomy, defined as death or disease recurrence within 6 months of surgery. Patients were divided into three risk categories — low, intermediate, and high risk — each with escalating likelihoods of futile resection, worse pathological features, and worse outcomes.
- The secondary endpoint was to develop criteria for surgical candidacy, setting a futility likelihood threshold of < 20%. This threshold corresponds to the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (CI) for postneoadjuvant resection rates (resection rate, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.80-1.01) from recent meta-analyses.
TAKEAWAY:
- The futility rate for pancreatectomy was 18.9% — 19.2% in the development cohort and 18.6% in the validation cohort. Three independent risk factors for futile resection included American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class (95% CI for coefficients, 0.68-0.87), preoperative cancer antigen 19.9 serum levels (95% CI for coefficients, 0.05-0.75), and radiologic tumor size (95% CI for coefficients, 0.28-0.46).
- Using these independent risk factors, the predictive model demonstrated adequate calibration and discrimination in both the derivation and validation cohorts.
- The researchers then identified three risk groups. In the derivation cohort, the rate of futile pancreatectomy was 9.2% in the low-risk group, 18.0% in the intermediate-risk group, and 28.7% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend). In the validation cohort, the futility rate was 10.9% in the low-risk group, 20.2% in the intermediate-risk group, and 29.2% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend).
- Researchers identified four conditions associated with a futility likelihood below 20%, where larger tumor size is paired with lower cancer antigen 19.9 levels (defined as cancer antigen 19.9–adjusted-to-size). Patients who met these criteria experienced significantly longer disease-free survival (median 18.4 months vs 11.2 months) and overall survival (38.5 months vs 22.1 months).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the study provides an easy-to-use calculator for clinical decision-making, there are some methodological limitations,” according to the authors of accompanying commentary. These limitations include failing to accurately describe how ASA class, cancer antigen 19.9 level, and tumor size were chosen for the model. “While we do not think the model is yet ready for standard clinical use, it may prove to be a viable tool if tested in future randomized trials comparing the neoadjuvant approach to upfront surgery in resectable pancreatic cancer,” the editorialists added.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, Division of Pancreatic Surgery, Pancreas Translational and Clinical Research Center, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy, and the accompanying commentary were published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
In addition to the limitations noted by the editorialists, others include the study’s retrospective design, which could introduce bias. Because preoperative imaging was not revised, the assigned resectability classes could show variability. Institutional differences existed in the selection process for upfront pancreatectomy. The model cannot be applied to cancer antigen 19.9 nonsecretors and was not externally validated.
DISCLOSURES:
The Italian Association for Cancer Research Special Program in Metastatic Disease and Italian Ministry of Health/Italian Foundation for the Research of Pancreatic Diseases supported the study in the form of a grant. Two authors reported receiving personal fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Immediate resection is associated with a high incidence of postoperative complications and disease recurrence within a year of surgery in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Predicting which patients likely won’t benefit from upfront pancreatectomy is important.
- To identify preoperative risk factors for futile pancreatectomy, researchers evaluated 1426 patients (median age, 69 years; 53.2% men) with anatomically resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent pancreatic resection between January 2010 and December 2021.
- The patients were divided into derivation (n = 885) and validation (n = 541) cohorts.
- The primary outcome was the rate of futile upfront pancreatectomy, defined as death or disease recurrence within 6 months of surgery. Patients were divided into three risk categories — low, intermediate, and high risk — each with escalating likelihoods of futile resection, worse pathological features, and worse outcomes.
- The secondary endpoint was to develop criteria for surgical candidacy, setting a futility likelihood threshold of < 20%. This threshold corresponds to the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (CI) for postneoadjuvant resection rates (resection rate, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.80-1.01) from recent meta-analyses.
TAKEAWAY:
- The futility rate for pancreatectomy was 18.9% — 19.2% in the development cohort and 18.6% in the validation cohort. Three independent risk factors for futile resection included American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class (95% CI for coefficients, 0.68-0.87), preoperative cancer antigen 19.9 serum levels (95% CI for coefficients, 0.05-0.75), and radiologic tumor size (95% CI for coefficients, 0.28-0.46).
- Using these independent risk factors, the predictive model demonstrated adequate calibration and discrimination in both the derivation and validation cohorts.
- The researchers then identified three risk groups. In the derivation cohort, the rate of futile pancreatectomy was 9.2% in the low-risk group, 18.0% in the intermediate-risk group, and 28.7% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend). In the validation cohort, the futility rate was 10.9% in the low-risk group, 20.2% in the intermediate-risk group, and 29.2% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend).
- Researchers identified four conditions associated with a futility likelihood below 20%, where larger tumor size is paired with lower cancer antigen 19.9 levels (defined as cancer antigen 19.9–adjusted-to-size). Patients who met these criteria experienced significantly longer disease-free survival (median 18.4 months vs 11.2 months) and overall survival (38.5 months vs 22.1 months).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the study provides an easy-to-use calculator for clinical decision-making, there are some methodological limitations,” according to the authors of accompanying commentary. These limitations include failing to accurately describe how ASA class, cancer antigen 19.9 level, and tumor size were chosen for the model. “While we do not think the model is yet ready for standard clinical use, it may prove to be a viable tool if tested in future randomized trials comparing the neoadjuvant approach to upfront surgery in resectable pancreatic cancer,” the editorialists added.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, Division of Pancreatic Surgery, Pancreas Translational and Clinical Research Center, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy, and the accompanying commentary were published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
In addition to the limitations noted by the editorialists, others include the study’s retrospective design, which could introduce bias. Because preoperative imaging was not revised, the assigned resectability classes could show variability. Institutional differences existed in the selection process for upfront pancreatectomy. The model cannot be applied to cancer antigen 19.9 nonsecretors and was not externally validated.
DISCLOSURES:
The Italian Association for Cancer Research Special Program in Metastatic Disease and Italian Ministry of Health/Italian Foundation for the Research of Pancreatic Diseases supported the study in the form of a grant. Two authors reported receiving personal fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Immediate resection is associated with a high incidence of postoperative complications and disease recurrence within a year of surgery in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Predicting which patients likely won’t benefit from upfront pancreatectomy is important.
- To identify preoperative risk factors for futile pancreatectomy, researchers evaluated 1426 patients (median age, 69 years; 53.2% men) with anatomically resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma who underwent pancreatic resection between January 2010 and December 2021.
- The patients were divided into derivation (n = 885) and validation (n = 541) cohorts.
- The primary outcome was the rate of futile upfront pancreatectomy, defined as death or disease recurrence within 6 months of surgery. Patients were divided into three risk categories — low, intermediate, and high risk — each with escalating likelihoods of futile resection, worse pathological features, and worse outcomes.
- The secondary endpoint was to develop criteria for surgical candidacy, setting a futility likelihood threshold of < 20%. This threshold corresponds to the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (CI) for postneoadjuvant resection rates (resection rate, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.80-1.01) from recent meta-analyses.
TAKEAWAY:
- The futility rate for pancreatectomy was 18.9% — 19.2% in the development cohort and 18.6% in the validation cohort. Three independent risk factors for futile resection included American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class (95% CI for coefficients, 0.68-0.87), preoperative cancer antigen 19.9 serum levels (95% CI for coefficients, 0.05-0.75), and radiologic tumor size (95% CI for coefficients, 0.28-0.46).
- Using these independent risk factors, the predictive model demonstrated adequate calibration and discrimination in both the derivation and validation cohorts.
- The researchers then identified three risk groups. In the derivation cohort, the rate of futile pancreatectomy was 9.2% in the low-risk group, 18.0% in the intermediate-risk group, and 28.7% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend). In the validation cohort, the futility rate was 10.9% in the low-risk group, 20.2% in the intermediate-risk group, and 29.2% in the high-risk group (P < .001 for trend).
- Researchers identified four conditions associated with a futility likelihood below 20%, where larger tumor size is paired with lower cancer antigen 19.9 levels (defined as cancer antigen 19.9–adjusted-to-size). Patients who met these criteria experienced significantly longer disease-free survival (median 18.4 months vs 11.2 months) and overall survival (38.5 months vs 22.1 months).
IN PRACTICE:
“Although the study provides an easy-to-use calculator for clinical decision-making, there are some methodological limitations,” according to the authors of accompanying commentary. These limitations include failing to accurately describe how ASA class, cancer antigen 19.9 level, and tumor size were chosen for the model. “While we do not think the model is yet ready for standard clinical use, it may prove to be a viable tool if tested in future randomized trials comparing the neoadjuvant approach to upfront surgery in resectable pancreatic cancer,” the editorialists added.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Stefano Crippa, MD, PhD, Division of Pancreatic Surgery, Pancreas Translational and Clinical Research Center, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Milan, Italy, and the accompanying commentary were published online in JAMA Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
In addition to the limitations noted by the editorialists, others include the study’s retrospective design, which could introduce bias. Because preoperative imaging was not revised, the assigned resectability classes could show variability. Institutional differences existed in the selection process for upfront pancreatectomy. The model cannot be applied to cancer antigen 19.9 nonsecretors and was not externally validated.
DISCLOSURES:
The Italian Association for Cancer Research Special Program in Metastatic Disease and Italian Ministry of Health/Italian Foundation for the Research of Pancreatic Diseases supported the study in the form of a grant. Two authors reported receiving personal fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metastasis-Directed Therapy Ups PFS in Pancreatic Cancer
TOPLINE:
Adding metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) to systemic therapy improves progression-free survival (PFS) to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone in patients with oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 2 multicenter, randomized basket trial involving 41 patients with oligometastatic PDAC in the EXTEND trial.
- Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive MDT plus systemic therapy or systemic therapy alone.
- MDT included definitive local therapy, with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy recommended when feasible. Members of the control group were allowed to receive MDT if their disease progressed.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, measured from random assignment to radiologic progression, clinical progression, or death.
- “Secondary endpoints included overall survival, time to next-line systemic therapy, time to local failure, time to new lesion formation, toxicity, and quality of life,” the authors said.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, adding MDT to systemic therapy significantly improved PFS to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone (P = .030).
- The hazard ratio for PFS was 0.43 (95% CI, 0.20-0.94), indicating a substantial reduction in the risk for disease progression or death with MDT.
- No grade 4 or 5 treatment-emergent adverse events were observed, suggesting that MDT is a safe addition to systemic therapy.
- Longer PFS and overall survival were associated with activated systemic immunity after MDT, suggesting that “an activated systemic immune profile, supported by a diverse T-cell receptor repertoire, might promote immunosurveillance of distant microscopic disease.”
IN PRACTICE:
“No other PDAC-specific trials have been reported, and tumor-agnostic studies, such as SABR-COMET or the National Health Service single-arm registry study, have not published PDAC-specific outcomes. Thus, the EXTEND trial provides the strongest evidence to date in favor of the existence of an oligometastatic state in PDAC.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ethan B. Ludmir, MD, and Alexander D. Sherry, MD, both of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. It was published online on August 5 in The Journal of Clinical Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s broad enrollment criteria may have introduced heterogeneity in the patient population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings. The study was not powered to evaluate overall survival, and the small sample size may have limited the robustness of the results. Crossover and non–cancer-related deaths could have influenced the comparisons, and quality-of-life data were limited because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The definition of oligometastasis used in the trial may have oversimplified the complex spectrum of the disease.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Ludmir disclosed employment with Alaunos Therapeutics and consulting for Xerient. Dr. Sherry reported employment with MD Anderson Cancer Center and honoraria from Sermo. One coauthor has an uncompensated relationship with Polaris Consulting. Another coauthor has stock ownership in BriaCell and a consulting or an advisory role with Regeneron. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) to systemic therapy improves progression-free survival (PFS) to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone in patients with oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 2 multicenter, randomized basket trial involving 41 patients with oligometastatic PDAC in the EXTEND trial.
- Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive MDT plus systemic therapy or systemic therapy alone.
- MDT included definitive local therapy, with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy recommended when feasible. Members of the control group were allowed to receive MDT if their disease progressed.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, measured from random assignment to radiologic progression, clinical progression, or death.
- “Secondary endpoints included overall survival, time to next-line systemic therapy, time to local failure, time to new lesion formation, toxicity, and quality of life,” the authors said.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, adding MDT to systemic therapy significantly improved PFS to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone (P = .030).
- The hazard ratio for PFS was 0.43 (95% CI, 0.20-0.94), indicating a substantial reduction in the risk for disease progression or death with MDT.
- No grade 4 or 5 treatment-emergent adverse events were observed, suggesting that MDT is a safe addition to systemic therapy.
- Longer PFS and overall survival were associated with activated systemic immunity after MDT, suggesting that “an activated systemic immune profile, supported by a diverse T-cell receptor repertoire, might promote immunosurveillance of distant microscopic disease.”
IN PRACTICE:
“No other PDAC-specific trials have been reported, and tumor-agnostic studies, such as SABR-COMET or the National Health Service single-arm registry study, have not published PDAC-specific outcomes. Thus, the EXTEND trial provides the strongest evidence to date in favor of the existence of an oligometastatic state in PDAC.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ethan B. Ludmir, MD, and Alexander D. Sherry, MD, both of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. It was published online on August 5 in The Journal of Clinical Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s broad enrollment criteria may have introduced heterogeneity in the patient population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings. The study was not powered to evaluate overall survival, and the small sample size may have limited the robustness of the results. Crossover and non–cancer-related deaths could have influenced the comparisons, and quality-of-life data were limited because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The definition of oligometastasis used in the trial may have oversimplified the complex spectrum of the disease.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Ludmir disclosed employment with Alaunos Therapeutics and consulting for Xerient. Dr. Sherry reported employment with MD Anderson Cancer Center and honoraria from Sermo. One coauthor has an uncompensated relationship with Polaris Consulting. Another coauthor has stock ownership in BriaCell and a consulting or an advisory role with Regeneron. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) to systemic therapy improves progression-free survival (PFS) to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone in patients with oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 2 multicenter, randomized basket trial involving 41 patients with oligometastatic PDAC in the EXTEND trial.
- Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive MDT plus systemic therapy or systemic therapy alone.
- MDT included definitive local therapy, with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy recommended when feasible. Members of the control group were allowed to receive MDT if their disease progressed.
- The primary endpoint was PFS, measured from random assignment to radiologic progression, clinical progression, or death.
- “Secondary endpoints included overall survival, time to next-line systemic therapy, time to local failure, time to new lesion formation, toxicity, and quality of life,” the authors said.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, adding MDT to systemic therapy significantly improved PFS to 10.3 months vs 2.5 months with systemic therapy alone (P = .030).
- The hazard ratio for PFS was 0.43 (95% CI, 0.20-0.94), indicating a substantial reduction in the risk for disease progression or death with MDT.
- No grade 4 or 5 treatment-emergent adverse events were observed, suggesting that MDT is a safe addition to systemic therapy.
- Longer PFS and overall survival were associated with activated systemic immunity after MDT, suggesting that “an activated systemic immune profile, supported by a diverse T-cell receptor repertoire, might promote immunosurveillance of distant microscopic disease.”
IN PRACTICE:
“No other PDAC-specific trials have been reported, and tumor-agnostic studies, such as SABR-COMET or the National Health Service single-arm registry study, have not published PDAC-specific outcomes. Thus, the EXTEND trial provides the strongest evidence to date in favor of the existence of an oligometastatic state in PDAC.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ethan B. Ludmir, MD, and Alexander D. Sherry, MD, both of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. It was published online on August 5 in The Journal of Clinical Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s broad enrollment criteria may have introduced heterogeneity in the patient population, potentially affecting the generalizability of the findings. The study was not powered to evaluate overall survival, and the small sample size may have limited the robustness of the results. Crossover and non–cancer-related deaths could have influenced the comparisons, and quality-of-life data were limited because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The definition of oligometastasis used in the trial may have oversimplified the complex spectrum of the disease.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Ludmir disclosed employment with Alaunos Therapeutics and consulting for Xerient. Dr. Sherry reported employment with MD Anderson Cancer Center and honoraria from Sermo. One coauthor has an uncompensated relationship with Polaris Consulting. Another coauthor has stock ownership in BriaCell and a consulting or an advisory role with Regeneron. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gut Microbiota Tied to Food Addiction Vulnerability
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Food addiction, characterized by a loss of control over food intake, may promote obesity and alter gut microbiota composition.
- Researchers used the Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 criteria to classify extreme food addiction and nonaddiction in mouse models and humans.
- The gut microbiota between addicted and nonaddicted mice were compared to identify factors related to food addiction in the murine model. Researchers subsequently gave mice drinking water with the prebiotics lactulose or rhamnose and the bacterium Blautia wexlerae, which has been associated with a reduced risk for obesity and diabetes.
- Gut microbiota signatures were also analyzed in 15 individuals with food addiction and 13 matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- In both humans and mice, gut microbiome signatures suggested possible nonbeneficial effects of bacteria in the Proteobacteria phylum and potential protective effects of Actinobacteria against the development of food addiction.
- In correlational analyses, decreased relative abundance of the species B wexlerae was observed in addicted humans and of the Blautia genus in addicted mice.
- Administration of the nondigestible carbohydrates lactulose and rhamnose, known to favor Blautia growth, led to increased relative abundance of Blautia in mouse feces, as well as “dramatic improvements” in food addiction.
- In functional validation experiments, oral administration of B wexlerae in mice led to similar improvement.
IN PRACTICE:
“This novel understanding of the role of gut microbiota in the development of food addiction may open new approaches for developing biomarkers and innovative therapies for food addiction and related eating disorders,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Solveiga Samulėnaitė, a doctoral student at Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania, was published online in Gut.
LIMITATIONS:
Further research is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms underlying the potential use of gut microbiota for treating food addiction and to test the safety and efficacy in humans.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by La Caixa Health and numerous grants from Spanish ministries and institutions and the European Union. No competing interests were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Food addiction, characterized by a loss of control over food intake, may promote obesity and alter gut microbiota composition.
- Researchers used the Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 criteria to classify extreme food addiction and nonaddiction in mouse models and humans.
- The gut microbiota between addicted and nonaddicted mice were compared to identify factors related to food addiction in the murine model. Researchers subsequently gave mice drinking water with the prebiotics lactulose or rhamnose and the bacterium Blautia wexlerae, which has been associated with a reduced risk for obesity and diabetes.
- Gut microbiota signatures were also analyzed in 15 individuals with food addiction and 13 matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- In both humans and mice, gut microbiome signatures suggested possible nonbeneficial effects of bacteria in the Proteobacteria phylum and potential protective effects of Actinobacteria against the development of food addiction.
- In correlational analyses, decreased relative abundance of the species B wexlerae was observed in addicted humans and of the Blautia genus in addicted mice.
- Administration of the nondigestible carbohydrates lactulose and rhamnose, known to favor Blautia growth, led to increased relative abundance of Blautia in mouse feces, as well as “dramatic improvements” in food addiction.
- In functional validation experiments, oral administration of B wexlerae in mice led to similar improvement.
IN PRACTICE:
“This novel understanding of the role of gut microbiota in the development of food addiction may open new approaches for developing biomarkers and innovative therapies for food addiction and related eating disorders,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Solveiga Samulėnaitė, a doctoral student at Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania, was published online in Gut.
LIMITATIONS:
Further research is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms underlying the potential use of gut microbiota for treating food addiction and to test the safety and efficacy in humans.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by La Caixa Health and numerous grants from Spanish ministries and institutions and the European Union. No competing interests were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Food addiction, characterized by a loss of control over food intake, may promote obesity and alter gut microbiota composition.
- Researchers used the Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 criteria to classify extreme food addiction and nonaddiction in mouse models and humans.
- The gut microbiota between addicted and nonaddicted mice were compared to identify factors related to food addiction in the murine model. Researchers subsequently gave mice drinking water with the prebiotics lactulose or rhamnose and the bacterium Blautia wexlerae, which has been associated with a reduced risk for obesity and diabetes.
- Gut microbiota signatures were also analyzed in 15 individuals with food addiction and 13 matched controls.
TAKEAWAY:
- In both humans and mice, gut microbiome signatures suggested possible nonbeneficial effects of bacteria in the Proteobacteria phylum and potential protective effects of Actinobacteria against the development of food addiction.
- In correlational analyses, decreased relative abundance of the species B wexlerae was observed in addicted humans and of the Blautia genus in addicted mice.
- Administration of the nondigestible carbohydrates lactulose and rhamnose, known to favor Blautia growth, led to increased relative abundance of Blautia in mouse feces, as well as “dramatic improvements” in food addiction.
- In functional validation experiments, oral administration of B wexlerae in mice led to similar improvement.
IN PRACTICE:
“This novel understanding of the role of gut microbiota in the development of food addiction may open new approaches for developing biomarkers and innovative therapies for food addiction and related eating disorders,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Solveiga Samulėnaitė, a doctoral student at Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania, was published online in Gut.
LIMITATIONS:
Further research is needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms underlying the potential use of gut microbiota for treating food addiction and to test the safety and efficacy in humans.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by La Caixa Health and numerous grants from Spanish ministries and institutions and the European Union. No competing interests were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last Call for Alcohol? Probably Not
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
For most of my formative years in medicine it was taken as gospel that 1-2 drinks/day, particularly red wine, was good for you.
Today though, the pendulum has swung the other way (granted, that could change in a year).
Recent re-analysis of the data now suggests there’s no benefit to any amount of alcohol. Zero. Zip. Nada.
This certainly isn’t the first time in medicine this has happened. It’s amazing how many studies end up getting re-analyzed, and re-re-analyzed, years later, with different conclusions reached.
It makes you wonder how these things happen. Possible explanations include flawed methodologies that either weren’t recognized at the time, confirmation bias, a rush to publish, and, rarely, outright fraud.
All of them, except for the last, are understandable. We all make mistakes. We’re all susceptible to the same statistical and psychological biases. Isn’t that part of the reason we do the peer-review process, so more than one pair of eyes can look for errors?
So, basically, no amount of alcohol is good for you.
Do I really think this is going to change anything? Hell no.
A huge amount of our culture revolves around alcohol. I’m not much of a drinker, but have no desire to give up my 2-3 beers per month, either. Just shopping in the store you see T-shirts, kitchen towels, gift bags, etc., that say things like “wine is just fruit salad” or “1 tequila, 2, tequila, 3 tequila, floor.”
The archaeological record suggests we began making alcoholic beverages 13,000 years ago. That’s a long time, and a pretty hard cultural habit to break. For comparison, tobacco has only been used for 3000 years.
In one of our strangest moments, America launched a 13-year experiment in prohibition, which failed miserably. Think about that. One hundred years ago, in 1924, you couldn’t legally buy alcohol anywhere in the United States. You had to break the law to get a drink, which most people did. Even then it was dangerous —in order to keep industrial ethanol from being sold to the public it was denatured with various toxins. As a result several thousand Americans died from their routine nightcap — with the government’s blessing.
Basically, alcohol isn’t going away. Not now, probably not ever.
There may be some out there who will alter their drinking habits based on the study, but I doubt it. I just don’t see too many people having a glass solely for the same reason they might take Lipitor or a multivitamin.
But I have no issue with correcting the original data. In medicine, and life in general, finding out what works is just as important as learning what doesn’t.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.



