User login
Childhood type 1 diabetes tests suggested at ages 2 and 6
, new data suggest.
Both genetic screening and islet-cell autoantibody screening for type 1 diabetes risk have become less expensive in recent years. Nonetheless, as of now, most children who receive such screening do so through programs that screen relatives of people who already have the condition, such as the global TrialNet program.
Some in the type 1 diabetes field have urged wider screening, with the rationale that knowledge of increased risk can prepare families to recognize the early signs of hyperglycemia and seek medical help to prevent the onset of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Moreover, potential therapies to prevent or delay type 1 diabetes are currently in development, including the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio).
However, given that the incidence of type 1 diabetes is about 1 in 300 children, any population-wide screening program would need to be implemented in the most efficient and cost-effective way possible with limited numbers of tests, say Mohamed Ghalwash, PhD, of the Center for Computational Health, IBM Research, Yorktown Heights, N.Y., and colleagues.
Results from their analysis of nearly 25,000 children from five prospective cohorts in Europe and the United States were published online in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Screening in kids feasible, but may need geographic tweaking
“Our results show that initial screening for islet autoantibodies at two ages (2 years and 6 years) is sensitive and efficient for public health translation but might require adjustment by country on the basis of population-specific disease characteristics,” Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues write.
In an accompanying editorial, pediatric endocrinologist Maria J. Redondo, MD, PhD, writes: “This study is timely because recent successes in preventing type 1 diabetes highlight the need to identify the best candidates for intervention ... This paper constitutes an important contribution to the literature.”
However, Dr. Redondo, of Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, also cautioned: “It remains to be seen whether Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues’ strategy could work in the general population, because all the participants in the combined dataset had genetic risk factors for the disease or a relative with type 1 diabetes, in whom performance is expected to be higher.”
She also noted that most participants were of northern European ancestry and that it is unknown whether the same or a similar screening strategy could be applied to individuals older than 15 years, in whom preclinical type 1 diabetes progresses more slowly.
Two-time childhood screening yielded high sensitivity, specificity
The data from a total of 24,662 participants were pooled from five prospective cohorts from Finland (DIPP), Germany (BABYDIAB), Sweden (DiPiS), and the United States (DAISY and DEW-IT).
All were at elevated risk for type 1 diabetes based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotyping, and some had first-degree relatives with the condition. Participants were screened annually for three type 1 diabetes–associated autoantibodies up to age 15 years or the onset of type 1 diabetes.
During follow-up, 672 children developed type 1 diabetes by age 15 years and 6,050 did not. (The rest hadn’t yet reached age 15 years or type 1 diabetes onset.) The median age at first appearance of islet autoantibodies was 4.5 years.
A two-age screening strategy at 2 years and 6 years was more sensitive than screening at just one age, with a sensitivity of 82% and a positive predictive value of 79% for the development of type 1 diabetes by age 15 years.
The predictive value increased with the number of autoantibodies tested. For example, a single islet autoantibody at age 2 years indicated a 4-year risk of developing type 1 diabetes by age 5.99 years of 31%, while multiple antibody positivity at age 2 years carried a 4-year risk of 55%.
By age 6 years, the risk over the next 9 years was 39% if the test had been negative at age 2 years and 70% if the test had been positive at 2 years. But overall, a 6-year-old with multiple autoantibodies had an overall 83% risk of type 1 diabetes regardless of the test result at 2 years.
The predictive performance of sensitivity by age differed by country, suggesting that the optimal ages for autoantibody testing might differ by geographic region, Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues say.
Dr. Redondo commented, “The model might require adaptation to local factors that affect the progression and prevalence of type 1 diabetes.” And, she added, “important aspects, such as screening cost, global access, acceptability, and follow-up support will need to be addressed for this strategy to be a viable public health option.”
The study was funded by JDRF. Dr. Ghalwash and another author are employees of IBM. A third author was a JDRF employee when the research was done and is now an employee of Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Redondo has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
Both genetic screening and islet-cell autoantibody screening for type 1 diabetes risk have become less expensive in recent years. Nonetheless, as of now, most children who receive such screening do so through programs that screen relatives of people who already have the condition, such as the global TrialNet program.
Some in the type 1 diabetes field have urged wider screening, with the rationale that knowledge of increased risk can prepare families to recognize the early signs of hyperglycemia and seek medical help to prevent the onset of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Moreover, potential therapies to prevent or delay type 1 diabetes are currently in development, including the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio).
However, given that the incidence of type 1 diabetes is about 1 in 300 children, any population-wide screening program would need to be implemented in the most efficient and cost-effective way possible with limited numbers of tests, say Mohamed Ghalwash, PhD, of the Center for Computational Health, IBM Research, Yorktown Heights, N.Y., and colleagues.
Results from their analysis of nearly 25,000 children from five prospective cohorts in Europe and the United States were published online in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Screening in kids feasible, but may need geographic tweaking
“Our results show that initial screening for islet autoantibodies at two ages (2 years and 6 years) is sensitive and efficient for public health translation but might require adjustment by country on the basis of population-specific disease characteristics,” Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues write.
In an accompanying editorial, pediatric endocrinologist Maria J. Redondo, MD, PhD, writes: “This study is timely because recent successes in preventing type 1 diabetes highlight the need to identify the best candidates for intervention ... This paper constitutes an important contribution to the literature.”
However, Dr. Redondo, of Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, also cautioned: “It remains to be seen whether Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues’ strategy could work in the general population, because all the participants in the combined dataset had genetic risk factors for the disease or a relative with type 1 diabetes, in whom performance is expected to be higher.”
She also noted that most participants were of northern European ancestry and that it is unknown whether the same or a similar screening strategy could be applied to individuals older than 15 years, in whom preclinical type 1 diabetes progresses more slowly.
Two-time childhood screening yielded high sensitivity, specificity
The data from a total of 24,662 participants were pooled from five prospective cohorts from Finland (DIPP), Germany (BABYDIAB), Sweden (DiPiS), and the United States (DAISY and DEW-IT).
All were at elevated risk for type 1 diabetes based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotyping, and some had first-degree relatives with the condition. Participants were screened annually for three type 1 diabetes–associated autoantibodies up to age 15 years or the onset of type 1 diabetes.
During follow-up, 672 children developed type 1 diabetes by age 15 years and 6,050 did not. (The rest hadn’t yet reached age 15 years or type 1 diabetes onset.) The median age at first appearance of islet autoantibodies was 4.5 years.
A two-age screening strategy at 2 years and 6 years was more sensitive than screening at just one age, with a sensitivity of 82% and a positive predictive value of 79% for the development of type 1 diabetes by age 15 years.
The predictive value increased with the number of autoantibodies tested. For example, a single islet autoantibody at age 2 years indicated a 4-year risk of developing type 1 diabetes by age 5.99 years of 31%, while multiple antibody positivity at age 2 years carried a 4-year risk of 55%.
By age 6 years, the risk over the next 9 years was 39% if the test had been negative at age 2 years and 70% if the test had been positive at 2 years. But overall, a 6-year-old with multiple autoantibodies had an overall 83% risk of type 1 diabetes regardless of the test result at 2 years.
The predictive performance of sensitivity by age differed by country, suggesting that the optimal ages for autoantibody testing might differ by geographic region, Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues say.
Dr. Redondo commented, “The model might require adaptation to local factors that affect the progression and prevalence of type 1 diabetes.” And, she added, “important aspects, such as screening cost, global access, acceptability, and follow-up support will need to be addressed for this strategy to be a viable public health option.”
The study was funded by JDRF. Dr. Ghalwash and another author are employees of IBM. A third author was a JDRF employee when the research was done and is now an employee of Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Redondo has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
Both genetic screening and islet-cell autoantibody screening for type 1 diabetes risk have become less expensive in recent years. Nonetheless, as of now, most children who receive such screening do so through programs that screen relatives of people who already have the condition, such as the global TrialNet program.
Some in the type 1 diabetes field have urged wider screening, with the rationale that knowledge of increased risk can prepare families to recognize the early signs of hyperglycemia and seek medical help to prevent the onset of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Moreover, potential therapies to prevent or delay type 1 diabetes are currently in development, including the anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody teplizumab (Tzield, Provention Bio).
However, given that the incidence of type 1 diabetes is about 1 in 300 children, any population-wide screening program would need to be implemented in the most efficient and cost-effective way possible with limited numbers of tests, say Mohamed Ghalwash, PhD, of the Center for Computational Health, IBM Research, Yorktown Heights, N.Y., and colleagues.
Results from their analysis of nearly 25,000 children from five prospective cohorts in Europe and the United States were published online in Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Screening in kids feasible, but may need geographic tweaking
“Our results show that initial screening for islet autoantibodies at two ages (2 years and 6 years) is sensitive and efficient for public health translation but might require adjustment by country on the basis of population-specific disease characteristics,” Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues write.
In an accompanying editorial, pediatric endocrinologist Maria J. Redondo, MD, PhD, writes: “This study is timely because recent successes in preventing type 1 diabetes highlight the need to identify the best candidates for intervention ... This paper constitutes an important contribution to the literature.”
However, Dr. Redondo, of Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, also cautioned: “It remains to be seen whether Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues’ strategy could work in the general population, because all the participants in the combined dataset had genetic risk factors for the disease or a relative with type 1 diabetes, in whom performance is expected to be higher.”
She also noted that most participants were of northern European ancestry and that it is unknown whether the same or a similar screening strategy could be applied to individuals older than 15 years, in whom preclinical type 1 diabetes progresses more slowly.
Two-time childhood screening yielded high sensitivity, specificity
The data from a total of 24,662 participants were pooled from five prospective cohorts from Finland (DIPP), Germany (BABYDIAB), Sweden (DiPiS), and the United States (DAISY and DEW-IT).
All were at elevated risk for type 1 diabetes based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotyping, and some had first-degree relatives with the condition. Participants were screened annually for three type 1 diabetes–associated autoantibodies up to age 15 years or the onset of type 1 diabetes.
During follow-up, 672 children developed type 1 diabetes by age 15 years and 6,050 did not. (The rest hadn’t yet reached age 15 years or type 1 diabetes onset.) The median age at first appearance of islet autoantibodies was 4.5 years.
A two-age screening strategy at 2 years and 6 years was more sensitive than screening at just one age, with a sensitivity of 82% and a positive predictive value of 79% for the development of type 1 diabetes by age 15 years.
The predictive value increased with the number of autoantibodies tested. For example, a single islet autoantibody at age 2 years indicated a 4-year risk of developing type 1 diabetes by age 5.99 years of 31%, while multiple antibody positivity at age 2 years carried a 4-year risk of 55%.
By age 6 years, the risk over the next 9 years was 39% if the test had been negative at age 2 years and 70% if the test had been positive at 2 years. But overall, a 6-year-old with multiple autoantibodies had an overall 83% risk of type 1 diabetes regardless of the test result at 2 years.
The predictive performance of sensitivity by age differed by country, suggesting that the optimal ages for autoantibody testing might differ by geographic region, Dr. Ghalwash and colleagues say.
Dr. Redondo commented, “The model might require adaptation to local factors that affect the progression and prevalence of type 1 diabetes.” And, she added, “important aspects, such as screening cost, global access, acceptability, and follow-up support will need to be addressed for this strategy to be a viable public health option.”
The study was funded by JDRF. Dr. Ghalwash and another author are employees of IBM. A third author was a JDRF employee when the research was done and is now an employee of Janssen Research and Development. Dr. Redondo has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
Social media in the lives of adolescents
Adolescence is a time of growing autonomy fueled by puberty, intellectual development, and identity formation. Social media engages adolescents by giving them easy access to (semi) private communication with peers, the ability to safely explore their sexuality, and easily investigate issues of intellectual curiosity, as they move from childhood to older adolescence. Social media facilitates the creation of a teenager’s own world, separate and distinct from adult concern or scrutiny. It is clearly compelling for adolescents, but we are in the early days of understanding the effect of various types of digital activities on the health and well-being of youth. There is evidence that for some, the addictive potential of these applications is potent, exacerbating or triggering mood, anxiety, and eating disorder symptoms. Their drive to explore their identity and relationships and their immature capacity to regulate emotions and behaviors make the risks of overuse substantial. But it would be impossible (and probably socially very costly) to simply avoid social media. So how to discuss its healthy use with your patients and their parents?
The data
Social media are digital communication platforms that allow users to build a public profile and then accumulate a network of followers, and follow other users, based on shared interests. They include FaceBook, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube, and Twitter. Surveys demonstrated that 90% of U.S. adolescents use social media, with 75% having at least one social media profile and over half visiting social media sites at least once daily. Adolescents spend over 7 hours daily on their phones, not including time devoted to online schoolwork, and 8- to 12-year-olds are not far behind at almost 5 hours of daily phone use. On average, 39% of adolescent screen time is spent on passive consumption, 26% on social media, 25% on interactive activities (browsing the web, interactive video gaming) and 3% on content creation (coding, etc). There was considerable variability in survey results, and differences between genders, with boys engaged in video games almost eight times as often as girls, and girls in social media nearly twice as often as boys.1
The research
There is a growing body of research devoted to understanding the effects of all of this digital activity on youth health and well-being.
A large, longitudinal study of Canadian 13- to 17-year-olds found that time spent on social media or watching television was strongly associated with depressive and anxiety symptoms, with a robust dose-response relationship.2 However, causality is not clear, as anxious, shy, and depressed adolescents may use more social media as a consequence of their mood. Interestingly, there was no such relationship with mood and anxiety symptoms and time spent on video games.3 For youth with depression and anxiety, time spent on social media has been strongly associated with increased levels of self-reported distress, self-injury and suicidality, but again, causality is hard to prove.
One very large study from the United Kingdom (including more than 10,000 participants), demonstrated a strong relationship between time spent on social media and severity of depressive symptoms, with a more pronounced effect in girls than in boys.4 Many more nuanced studies have demonstrated that excessive time spent on social media, the presence of an addictive pattern of use, and the degree to which an adolescent’s sense of well-being is connected to social media are the variables that strongly predict an association with worsening depressive or anxiety symptoms.5
Several studies have demonstrated that low to moderate use of social media, and use to gather information and make plans were associated with better scores of emotional self-regulation and lower rates of depressive symptoms in teens.6 It seems safe to say that social media can be useful and fun, but that too much can be bad for you. So help your adolescent patients to expand their perspective on its use by discussing it with them.
Make them curious about quantity
Most teens feel they do not have enough time for all of the things they need to do, so invite them to play detective by using their phone’s applications that can track their time spent online and in different apps.
Remind them that these apps were designed to be so engaging that for some addiction is a real problem. As with tobacco, addiction is the business model by which these companies earn advertising dollars. Indeed, adolescents are the target demographic, as they are most sensitive to social rewards and are the most valuable audience for advertisers. Engage their natural suspicion of authority by pointing out that with every hour on Insta, someone else is making a lot of money. They get to choose how they want to relax, connect with friends, and explore the world, so help them to be aware of how these apps are designed to keep them from choosing.
Raise awareness of vulnerability
Adolescents who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder already have difficulty with impulse control and with shifting their attention to less engaging activities. Adolescents with anxiety are prone to avoid stressful situations, but still hunger for knowledge and connections. Adolescents with depression are managing low motivation and self-esteem, and the rewards of social media may keep them from exercise and actual social engagement that are critical to their treatment. Youth with eating disorders are especially prone to critical comparison of themselves to others, feeding their distorted body images. Help your patients with these common illnesses to be aware of how social media may make their treatment harder, rather than being the source of relief it may feel like.
Protect their health
For all young people, too much time spent in virtual activities and passive media consumption may not leave enough time to explore potential interests, talents, or relationships. These are important activities throughout life, but they are the central developmental tasks of adolescence. They also need 8-10 hours of sleep nightly and regular exercise. And of course, they have homework! Help them to think about how to use their time wisely to support satisfying relationships and activities, with time for relaxation and good health.
Keep parents in the room for these discussions
State that most of us have difficulty putting down our phones. Children and teens need adults who model striving for balance in all areas of choice. Just as we try to teach them to make good choices about food, getting excellent nutrition while still valuing taste and pleasure, we can talk about how to balance virtual activities with actual activities, work with play, and effort with relaxation. You can help expand your young patients’ self-awareness, acknowledge the fun and utility of their digital time, and enhance their sense of how we must all learn how to put screens down sometimes. In so doing, you can help families to ensure that they are engaging with the digital tools and toys available to all of us in ways that can support their health and well-being.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Geena Davis Institute on Gender and Media. The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Teens and Tweens, 2015.
2. Abi-Jaoude E et al. CMAJ 2020;192(6):E136-41.
3. Boers E et al. Can J Psychiatry. 2020 Mar;65(3):206-8.
4. Kelly Y et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2019 Jan 4;6:59-68.
5. Vidal C et al. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2020 May;32(3):235-53.
6. Coyne SM et al. J Res Adolescence. 2019;29(4):897-907.
Adolescence is a time of growing autonomy fueled by puberty, intellectual development, and identity formation. Social media engages adolescents by giving them easy access to (semi) private communication with peers, the ability to safely explore their sexuality, and easily investigate issues of intellectual curiosity, as they move from childhood to older adolescence. Social media facilitates the creation of a teenager’s own world, separate and distinct from adult concern or scrutiny. It is clearly compelling for adolescents, but we are in the early days of understanding the effect of various types of digital activities on the health and well-being of youth. There is evidence that for some, the addictive potential of these applications is potent, exacerbating or triggering mood, anxiety, and eating disorder symptoms. Their drive to explore their identity and relationships and their immature capacity to regulate emotions and behaviors make the risks of overuse substantial. But it would be impossible (and probably socially very costly) to simply avoid social media. So how to discuss its healthy use with your patients and their parents?
The data
Social media are digital communication platforms that allow users to build a public profile and then accumulate a network of followers, and follow other users, based on shared interests. They include FaceBook, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube, and Twitter. Surveys demonstrated that 90% of U.S. adolescents use social media, with 75% having at least one social media profile and over half visiting social media sites at least once daily. Adolescents spend over 7 hours daily on their phones, not including time devoted to online schoolwork, and 8- to 12-year-olds are not far behind at almost 5 hours of daily phone use. On average, 39% of adolescent screen time is spent on passive consumption, 26% on social media, 25% on interactive activities (browsing the web, interactive video gaming) and 3% on content creation (coding, etc). There was considerable variability in survey results, and differences between genders, with boys engaged in video games almost eight times as often as girls, and girls in social media nearly twice as often as boys.1
The research
There is a growing body of research devoted to understanding the effects of all of this digital activity on youth health and well-being.
A large, longitudinal study of Canadian 13- to 17-year-olds found that time spent on social media or watching television was strongly associated with depressive and anxiety symptoms, with a robust dose-response relationship.2 However, causality is not clear, as anxious, shy, and depressed adolescents may use more social media as a consequence of their mood. Interestingly, there was no such relationship with mood and anxiety symptoms and time spent on video games.3 For youth with depression and anxiety, time spent on social media has been strongly associated with increased levels of self-reported distress, self-injury and suicidality, but again, causality is hard to prove.
One very large study from the United Kingdom (including more than 10,000 participants), demonstrated a strong relationship between time spent on social media and severity of depressive symptoms, with a more pronounced effect in girls than in boys.4 Many more nuanced studies have demonstrated that excessive time spent on social media, the presence of an addictive pattern of use, and the degree to which an adolescent’s sense of well-being is connected to social media are the variables that strongly predict an association with worsening depressive or anxiety symptoms.5
Several studies have demonstrated that low to moderate use of social media, and use to gather information and make plans were associated with better scores of emotional self-regulation and lower rates of depressive symptoms in teens.6 It seems safe to say that social media can be useful and fun, but that too much can be bad for you. So help your adolescent patients to expand their perspective on its use by discussing it with them.
Make them curious about quantity
Most teens feel they do not have enough time for all of the things they need to do, so invite them to play detective by using their phone’s applications that can track their time spent online and in different apps.
Remind them that these apps were designed to be so engaging that for some addiction is a real problem. As with tobacco, addiction is the business model by which these companies earn advertising dollars. Indeed, adolescents are the target demographic, as they are most sensitive to social rewards and are the most valuable audience for advertisers. Engage their natural suspicion of authority by pointing out that with every hour on Insta, someone else is making a lot of money. They get to choose how they want to relax, connect with friends, and explore the world, so help them to be aware of how these apps are designed to keep them from choosing.
Raise awareness of vulnerability
Adolescents who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder already have difficulty with impulse control and with shifting their attention to less engaging activities. Adolescents with anxiety are prone to avoid stressful situations, but still hunger for knowledge and connections. Adolescents with depression are managing low motivation and self-esteem, and the rewards of social media may keep them from exercise and actual social engagement that are critical to their treatment. Youth with eating disorders are especially prone to critical comparison of themselves to others, feeding their distorted body images. Help your patients with these common illnesses to be aware of how social media may make their treatment harder, rather than being the source of relief it may feel like.
Protect their health
For all young people, too much time spent in virtual activities and passive media consumption may not leave enough time to explore potential interests, talents, or relationships. These are important activities throughout life, but they are the central developmental tasks of adolescence. They also need 8-10 hours of sleep nightly and regular exercise. And of course, they have homework! Help them to think about how to use their time wisely to support satisfying relationships and activities, with time for relaxation and good health.
Keep parents in the room for these discussions
State that most of us have difficulty putting down our phones. Children and teens need adults who model striving for balance in all areas of choice. Just as we try to teach them to make good choices about food, getting excellent nutrition while still valuing taste and pleasure, we can talk about how to balance virtual activities with actual activities, work with play, and effort with relaxation. You can help expand your young patients’ self-awareness, acknowledge the fun and utility of their digital time, and enhance their sense of how we must all learn how to put screens down sometimes. In so doing, you can help families to ensure that they are engaging with the digital tools and toys available to all of us in ways that can support their health and well-being.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Geena Davis Institute on Gender and Media. The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Teens and Tweens, 2015.
2. Abi-Jaoude E et al. CMAJ 2020;192(6):E136-41.
3. Boers E et al. Can J Psychiatry. 2020 Mar;65(3):206-8.
4. Kelly Y et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2019 Jan 4;6:59-68.
5. Vidal C et al. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2020 May;32(3):235-53.
6. Coyne SM et al. J Res Adolescence. 2019;29(4):897-907.
Adolescence is a time of growing autonomy fueled by puberty, intellectual development, and identity formation. Social media engages adolescents by giving them easy access to (semi) private communication with peers, the ability to safely explore their sexuality, and easily investigate issues of intellectual curiosity, as they move from childhood to older adolescence. Social media facilitates the creation of a teenager’s own world, separate and distinct from adult concern or scrutiny. It is clearly compelling for adolescents, but we are in the early days of understanding the effect of various types of digital activities on the health and well-being of youth. There is evidence that for some, the addictive potential of these applications is potent, exacerbating or triggering mood, anxiety, and eating disorder symptoms. Their drive to explore their identity and relationships and their immature capacity to regulate emotions and behaviors make the risks of overuse substantial. But it would be impossible (and probably socially very costly) to simply avoid social media. So how to discuss its healthy use with your patients and their parents?
The data
Social media are digital communication platforms that allow users to build a public profile and then accumulate a network of followers, and follow other users, based on shared interests. They include FaceBook, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube, and Twitter. Surveys demonstrated that 90% of U.S. adolescents use social media, with 75% having at least one social media profile and over half visiting social media sites at least once daily. Adolescents spend over 7 hours daily on their phones, not including time devoted to online schoolwork, and 8- to 12-year-olds are not far behind at almost 5 hours of daily phone use. On average, 39% of adolescent screen time is spent on passive consumption, 26% on social media, 25% on interactive activities (browsing the web, interactive video gaming) and 3% on content creation (coding, etc). There was considerable variability in survey results, and differences between genders, with boys engaged in video games almost eight times as often as girls, and girls in social media nearly twice as often as boys.1
The research
There is a growing body of research devoted to understanding the effects of all of this digital activity on youth health and well-being.
A large, longitudinal study of Canadian 13- to 17-year-olds found that time spent on social media or watching television was strongly associated with depressive and anxiety symptoms, with a robust dose-response relationship.2 However, causality is not clear, as anxious, shy, and depressed adolescents may use more social media as a consequence of their mood. Interestingly, there was no such relationship with mood and anxiety symptoms and time spent on video games.3 For youth with depression and anxiety, time spent on social media has been strongly associated with increased levels of self-reported distress, self-injury and suicidality, but again, causality is hard to prove.
One very large study from the United Kingdom (including more than 10,000 participants), demonstrated a strong relationship between time spent on social media and severity of depressive symptoms, with a more pronounced effect in girls than in boys.4 Many more nuanced studies have demonstrated that excessive time spent on social media, the presence of an addictive pattern of use, and the degree to which an adolescent’s sense of well-being is connected to social media are the variables that strongly predict an association with worsening depressive or anxiety symptoms.5
Several studies have demonstrated that low to moderate use of social media, and use to gather information and make plans were associated with better scores of emotional self-regulation and lower rates of depressive symptoms in teens.6 It seems safe to say that social media can be useful and fun, but that too much can be bad for you. So help your adolescent patients to expand their perspective on its use by discussing it with them.
Make them curious about quantity
Most teens feel they do not have enough time for all of the things they need to do, so invite them to play detective by using their phone’s applications that can track their time spent online and in different apps.
Remind them that these apps were designed to be so engaging that for some addiction is a real problem. As with tobacco, addiction is the business model by which these companies earn advertising dollars. Indeed, adolescents are the target demographic, as they are most sensitive to social rewards and are the most valuable audience for advertisers. Engage their natural suspicion of authority by pointing out that with every hour on Insta, someone else is making a lot of money. They get to choose how they want to relax, connect with friends, and explore the world, so help them to be aware of how these apps are designed to keep them from choosing.
Raise awareness of vulnerability
Adolescents who have attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder already have difficulty with impulse control and with shifting their attention to less engaging activities. Adolescents with anxiety are prone to avoid stressful situations, but still hunger for knowledge and connections. Adolescents with depression are managing low motivation and self-esteem, and the rewards of social media may keep them from exercise and actual social engagement that are critical to their treatment. Youth with eating disorders are especially prone to critical comparison of themselves to others, feeding their distorted body images. Help your patients with these common illnesses to be aware of how social media may make their treatment harder, rather than being the source of relief it may feel like.
Protect their health
For all young people, too much time spent in virtual activities and passive media consumption may not leave enough time to explore potential interests, talents, or relationships. These are important activities throughout life, but they are the central developmental tasks of adolescence. They also need 8-10 hours of sleep nightly and regular exercise. And of course, they have homework! Help them to think about how to use their time wisely to support satisfying relationships and activities, with time for relaxation and good health.
Keep parents in the room for these discussions
State that most of us have difficulty putting down our phones. Children and teens need adults who model striving for balance in all areas of choice. Just as we try to teach them to make good choices about food, getting excellent nutrition while still valuing taste and pleasure, we can talk about how to balance virtual activities with actual activities, work with play, and effort with relaxation. You can help expand your young patients’ self-awareness, acknowledge the fun and utility of their digital time, and enhance their sense of how we must all learn how to put screens down sometimes. In so doing, you can help families to ensure that they are engaging with the digital tools and toys available to all of us in ways that can support their health and well-being.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Geena Davis Institute on Gender and Media. The Common Sense Census: Media Use by Teens and Tweens, 2015.
2. Abi-Jaoude E et al. CMAJ 2020;192(6):E136-41.
3. Boers E et al. Can J Psychiatry. 2020 Mar;65(3):206-8.
4. Kelly Y et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2019 Jan 4;6:59-68.
5. Vidal C et al. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2020 May;32(3):235-53.
6. Coyne SM et al. J Res Adolescence. 2019;29(4):897-907.
Transplanted pig hearts functioned normally in deceased persons on ventilator support
A team of surgeons successfully transplanted genetically engineered pig hearts into two recently deceased people whose bodies were being maintained on ventilatory support – not in the hope of restoring life, but as a proof-of-concept experiment in xenotransplantation that could eventually help to ease the critical shortage of donor organs.
The surgeries were performed on June 16 and July 6, 2022, using porcine hearts from animals genetically engineered to prevent organ rejection and promote adaptive immunity by human recipients
without utilizing unapproved devices or techniques or medications,” said Nader Moazami, MD, surgical director of heart transplantation and chief of the division of heart and lung transplantation and mechanical circulatory support at NYU Langone Health, New York.
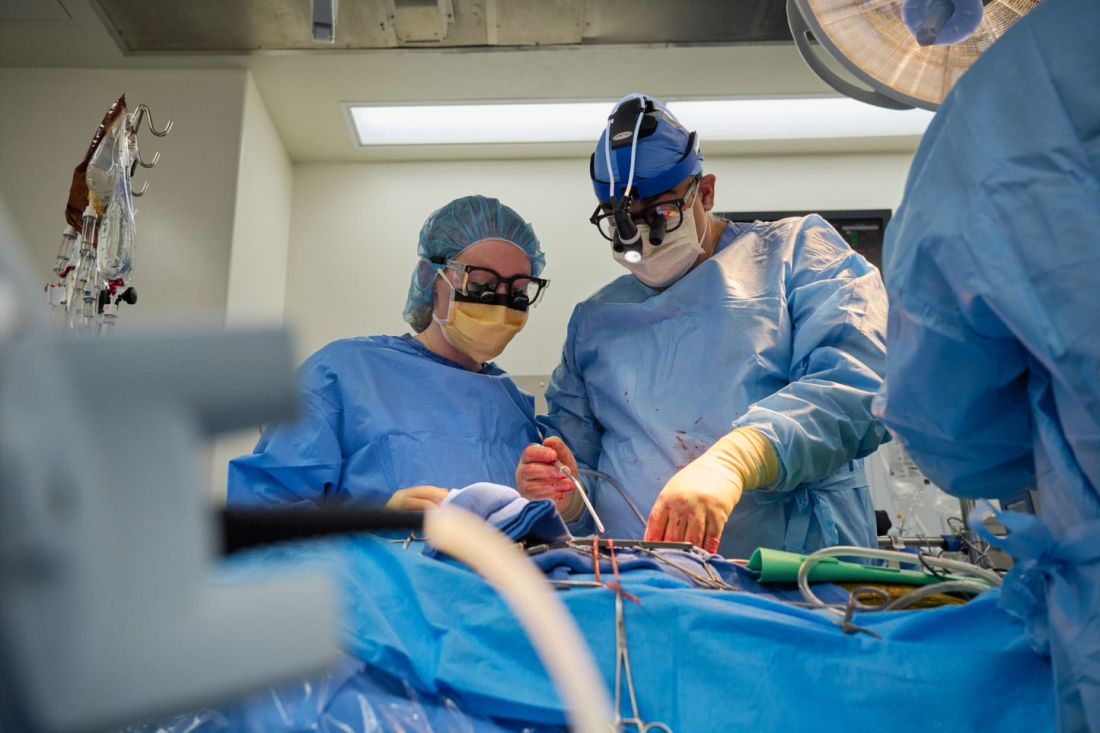
Through 72 hours of postoperative monitoring “we evaluated the heart for functionality and the heart function was completely normal with excellent contractility,” he said at a press briefing announcing early results of the experimental program.
He acknowledged that for the first of the two procedures some surgical modification of the pig heart was required, primarily because of size differences between the donor and recipient.
“Nevertheless, we learned a tremendous amount from the first operation, and when that experience was translated into the second operation it even performed better,” he said.
Alex Reyentovich, MD, medical director of heart transplantation and director of the NYU Langone advanced heart failure program noted that “there are 6 million individuals with heart failure in the United States. About 100,000 of those individuals have end-stage heart failure, and we only do about 3,500 heart transplants a year in the United States, so we have a tremendous deficiency in organs, and there are many people dying waiting for a heart.”
Infection protocols
To date there has been only one xenotransplant of a genetically modified pig heart into a living human recipient, David Bennett Sr., age 57. The surgery, performed at the University of Maryland in January 2022, was initially successful, with the patient able to sit up in bed a few days after the procedure, and the heart performing like a “rock star” according to transplant surgeon Bartley Griffith, MD.
However, Mr. Bennett died 2 months after the procedure from compromise of the organ by an as yet undetermined cause, of which one may have been the heart's infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (CMV).
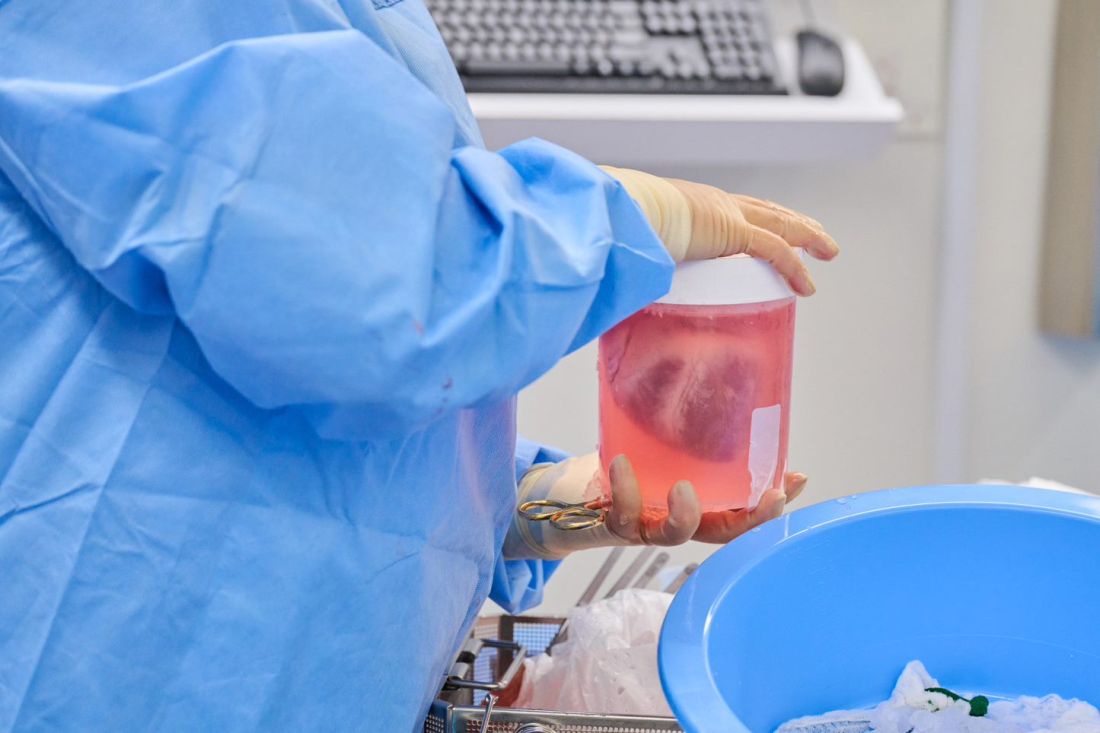
The NYU team, mindful of this potential setback, used more sensitive assays to screen the donor organs for porcine CMV, and implemented protocols to prevent and to monitor for potential zoonotic transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus.
The procedure used a dedicated operating room and equipment that will not be used for clinical procedures, the team emphasized.
An organ transplant specialist who was not involved in the study commented that there can be unwelcome surprises even with the most rigorous infection prophylaxis protocols.
“I think these are important steps, but they don’t resolve the question of infectious risk. Sometimes viruses or latent infections are only manifested later,” said Jay A. Fishman, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Transplant Center and director of the transplant infectious diseases and compromised host program at the hospital, which is in Boston.
“I think these are important steps, but as you may recall from the Maryland heart transplant experience, when porcine cytomegalovirus was activated, it was a long way into that patient’s course, and so we just don’t know whether something would have been reactivated later,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Fishman noted that experience with xenotransplantation at the University of Maryland and other centers has suggested that immunosuppressive regimens used for human-to-human transplants may not be suited for animal-to-human grafts.
The hearts were taken from pigs genetically modified with knockouts of four porcine genes to prevent rejection – including a gene for a growth hormone that would otherwise cause the heart to continue to expand in the recipient’s chest – and with the addition of six human transgenes encoding for expression of proteins regulating biologic pathways that might be disrupted by incompatibilities across species.
Vietnam veteran
The organ recipients were recently deceased patients who had expressed the clear wish to be organ donors but whose organs were for clinical reasons unsuitable for transplant.
The first recipient was Lawrence Kelly, a Vietnam War veteran and welder who died from heart failure at the age of 72.
“He was an organ donor, and would be so happy to know how much his contribution to this research will help people like him with this heart disease. He was a hero his whole life, and he went out a hero,” said Alice Michael, Mr. Kelly’s partner of 33 years, who also spoke at the briefing.
“It was, I think, one of the most incredible things to see a pig heart pounding away and beating inside the chest of a human being,” said Robert A. Montgomery, MD, DPhil, director of the NYU Transplant Institute, and himself a heart transplant recipient.
Dr. Fishman said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated on 7/12/22 and 7/14/22.
A team of surgeons successfully transplanted genetically engineered pig hearts into two recently deceased people whose bodies were being maintained on ventilatory support – not in the hope of restoring life, but as a proof-of-concept experiment in xenotransplantation that could eventually help to ease the critical shortage of donor organs.
The surgeries were performed on June 16 and July 6, 2022, using porcine hearts from animals genetically engineered to prevent organ rejection and promote adaptive immunity by human recipients
without utilizing unapproved devices or techniques or medications,” said Nader Moazami, MD, surgical director of heart transplantation and chief of the division of heart and lung transplantation and mechanical circulatory support at NYU Langone Health, New York.

Through 72 hours of postoperative monitoring “we evaluated the heart for functionality and the heart function was completely normal with excellent contractility,” he said at a press briefing announcing early results of the experimental program.
He acknowledged that for the first of the two procedures some surgical modification of the pig heart was required, primarily because of size differences between the donor and recipient.
“Nevertheless, we learned a tremendous amount from the first operation, and when that experience was translated into the second operation it even performed better,” he said.
Alex Reyentovich, MD, medical director of heart transplantation and director of the NYU Langone advanced heart failure program noted that “there are 6 million individuals with heart failure in the United States. About 100,000 of those individuals have end-stage heart failure, and we only do about 3,500 heart transplants a year in the United States, so we have a tremendous deficiency in organs, and there are many people dying waiting for a heart.”
Infection protocols
To date there has been only one xenotransplant of a genetically modified pig heart into a living human recipient, David Bennett Sr., age 57. The surgery, performed at the University of Maryland in January 2022, was initially successful, with the patient able to sit up in bed a few days after the procedure, and the heart performing like a “rock star” according to transplant surgeon Bartley Griffith, MD.
However, Mr. Bennett died 2 months after the procedure from compromise of the organ by an as yet undetermined cause, of which one may have been the heart's infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (CMV).

The NYU team, mindful of this potential setback, used more sensitive assays to screen the donor organs for porcine CMV, and implemented protocols to prevent and to monitor for potential zoonotic transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus.
The procedure used a dedicated operating room and equipment that will not be used for clinical procedures, the team emphasized.
An organ transplant specialist who was not involved in the study commented that there can be unwelcome surprises even with the most rigorous infection prophylaxis protocols.
“I think these are important steps, but they don’t resolve the question of infectious risk. Sometimes viruses or latent infections are only manifested later,” said Jay A. Fishman, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Transplant Center and director of the transplant infectious diseases and compromised host program at the hospital, which is in Boston.
“I think these are important steps, but as you may recall from the Maryland heart transplant experience, when porcine cytomegalovirus was activated, it was a long way into that patient’s course, and so we just don’t know whether something would have been reactivated later,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Fishman noted that experience with xenotransplantation at the University of Maryland and other centers has suggested that immunosuppressive regimens used for human-to-human transplants may not be suited for animal-to-human grafts.
The hearts were taken from pigs genetically modified with knockouts of four porcine genes to prevent rejection – including a gene for a growth hormone that would otherwise cause the heart to continue to expand in the recipient’s chest – and with the addition of six human transgenes encoding for expression of proteins regulating biologic pathways that might be disrupted by incompatibilities across species.
Vietnam veteran
The organ recipients were recently deceased patients who had expressed the clear wish to be organ donors but whose organs were for clinical reasons unsuitable for transplant.
The first recipient was Lawrence Kelly, a Vietnam War veteran and welder who died from heart failure at the age of 72.
“He was an organ donor, and would be so happy to know how much his contribution to this research will help people like him with this heart disease. He was a hero his whole life, and he went out a hero,” said Alice Michael, Mr. Kelly’s partner of 33 years, who also spoke at the briefing.
“It was, I think, one of the most incredible things to see a pig heart pounding away and beating inside the chest of a human being,” said Robert A. Montgomery, MD, DPhil, director of the NYU Transplant Institute, and himself a heart transplant recipient.
Dr. Fishman said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated on 7/12/22 and 7/14/22.
A team of surgeons successfully transplanted genetically engineered pig hearts into two recently deceased people whose bodies were being maintained on ventilatory support – not in the hope of restoring life, but as a proof-of-concept experiment in xenotransplantation that could eventually help to ease the critical shortage of donor organs.
The surgeries were performed on June 16 and July 6, 2022, using porcine hearts from animals genetically engineered to prevent organ rejection and promote adaptive immunity by human recipients
without utilizing unapproved devices or techniques or medications,” said Nader Moazami, MD, surgical director of heart transplantation and chief of the division of heart and lung transplantation and mechanical circulatory support at NYU Langone Health, New York.

Through 72 hours of postoperative monitoring “we evaluated the heart for functionality and the heart function was completely normal with excellent contractility,” he said at a press briefing announcing early results of the experimental program.
He acknowledged that for the first of the two procedures some surgical modification of the pig heart was required, primarily because of size differences between the donor and recipient.
“Nevertheless, we learned a tremendous amount from the first operation, and when that experience was translated into the second operation it even performed better,” he said.
Alex Reyentovich, MD, medical director of heart transplantation and director of the NYU Langone advanced heart failure program noted that “there are 6 million individuals with heart failure in the United States. About 100,000 of those individuals have end-stage heart failure, and we only do about 3,500 heart transplants a year in the United States, so we have a tremendous deficiency in organs, and there are many people dying waiting for a heart.”
Infection protocols
To date there has been only one xenotransplant of a genetically modified pig heart into a living human recipient, David Bennett Sr., age 57. The surgery, performed at the University of Maryland in January 2022, was initially successful, with the patient able to sit up in bed a few days after the procedure, and the heart performing like a “rock star” according to transplant surgeon Bartley Griffith, MD.
However, Mr. Bennett died 2 months after the procedure from compromise of the organ by an as yet undetermined cause, of which one may have been the heart's infection by porcine cytomegalovirus (CMV).

The NYU team, mindful of this potential setback, used more sensitive assays to screen the donor organs for porcine CMV, and implemented protocols to prevent and to monitor for potential zoonotic transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus.
The procedure used a dedicated operating room and equipment that will not be used for clinical procedures, the team emphasized.
An organ transplant specialist who was not involved in the study commented that there can be unwelcome surprises even with the most rigorous infection prophylaxis protocols.
“I think these are important steps, but they don’t resolve the question of infectious risk. Sometimes viruses or latent infections are only manifested later,” said Jay A. Fishman, MD, associate director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Transplant Center and director of the transplant infectious diseases and compromised host program at the hospital, which is in Boston.
“I think these are important steps, but as you may recall from the Maryland heart transplant experience, when porcine cytomegalovirus was activated, it was a long way into that patient’s course, and so we just don’t know whether something would have been reactivated later,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Fishman noted that experience with xenotransplantation at the University of Maryland and other centers has suggested that immunosuppressive regimens used for human-to-human transplants may not be suited for animal-to-human grafts.
The hearts were taken from pigs genetically modified with knockouts of four porcine genes to prevent rejection – including a gene for a growth hormone that would otherwise cause the heart to continue to expand in the recipient’s chest – and with the addition of six human transgenes encoding for expression of proteins regulating biologic pathways that might be disrupted by incompatibilities across species.
Vietnam veteran
The organ recipients were recently deceased patients who had expressed the clear wish to be organ donors but whose organs were for clinical reasons unsuitable for transplant.
The first recipient was Lawrence Kelly, a Vietnam War veteran and welder who died from heart failure at the age of 72.
“He was an organ donor, and would be so happy to know how much his contribution to this research will help people like him with this heart disease. He was a hero his whole life, and he went out a hero,” said Alice Michael, Mr. Kelly’s partner of 33 years, who also spoke at the briefing.
“It was, I think, one of the most incredible things to see a pig heart pounding away and beating inside the chest of a human being,” said Robert A. Montgomery, MD, DPhil, director of the NYU Transplant Institute, and himself a heart transplant recipient.
Dr. Fishman said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated on 7/12/22 and 7/14/22.
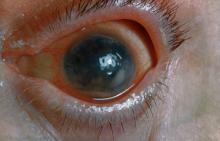
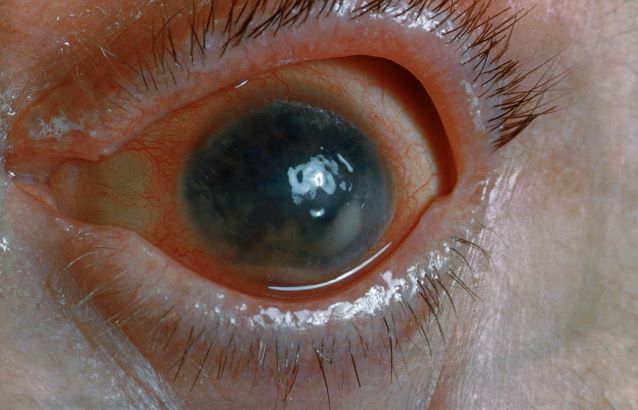
Pain and photophobia
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
On the basis of the patient's medical history and presentation, this is probably a case of uveitis, a common extra-articular manifestation of psoriatic disease. In fact, the presence of uveitis can help distinguish PsA from osteoarthritis. Uveitis is characterized by inflammation of the uvea tract, with the retina, optic nerve, vitreous body, and sclera potentially becoming inflamed as well. Among patients with PsA, the prevalence of uveitis rises with ongoing disease duration, though the condition may also precede the development of PsA in patients with psoriasis, and is common among patients with severe psoriatic disease in Western and Asian populations. Overall, the prevalence of uveitis has been estimated to be 6%-9%. HLA-B27 genotype is strongly associated with uveitis in patients with concomitant PsA.
Symptoms of uveitis, as seen in the present case, include blurred vision, photophobia, pain, and ciliary flush. The condition is classified as anterior, intermediate, posterior, or panuveitis, with the majority of cases diagnosed as anterior. In anterior uveitis, the inflamed pupil may become constricted or take on an irregular shape caused by iris adhesions to the anterior lens capsule. Uveitis in PsA is bilateral and has a chronic relapsing course. Onset is typically insidious.
Workup for uveitis should comprise visual acuity testing, slit lamp biomicroscopy, measurement of intraocular pressures, and a dilated eye exam. Conditions in the differential which threaten a patient's sight include retinal vasculitis, vitritis, cystoid macular edema, Behçet disease, and tubulo-interstitial nephritis. Other autoimmune diseases which can cause uveitis with systemic manifestations (multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, lupus) should be investigated. Infectious causes must also be eliminated. However, considering this patient's history of psoriatic disease, uveitis should be highly suspected.
Uveitis demands urgent treatment to control ocular inflammation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors are the recommended first-line and second-line treatment for PsA, including in patients with complications such as uveitis. However, etanercept should not be used as it is less effective than adalimumab or other TNF inhibitors for uveitis. Because uveitis may sometimes respond to MTX therapy, patients with severe PsA may use a biologic agent in combination with MTX if they have had a partial response to current MTX therapy, as recommended by the American College of Rheumatology.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, Professor of Medicine (retired), Temple University School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh; Chairman, Department of Medicine Emeritus, Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA.
Herbert S. Diamond, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 48-year-old male patient presents with blurred vision, pain, and photophobia. He recently had a routine visit with an ophthalmologist, which was normal. The affected pupil appears irregular in shape. The anterior chamber appears foggy. Local ciliary flush is observed on slit lamp exam. The physical examination is also notable for axial arthropathy. The patient has an 11-year history of moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis (PsA) which he typically manages with methotrexate (MTX) therapy, to which he has had a partial response. He was initially diagnosed when he presented with worsening psoriasis and enthesitis on the insertion sites of the plantar fascia, as well as dactylitis.
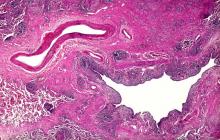
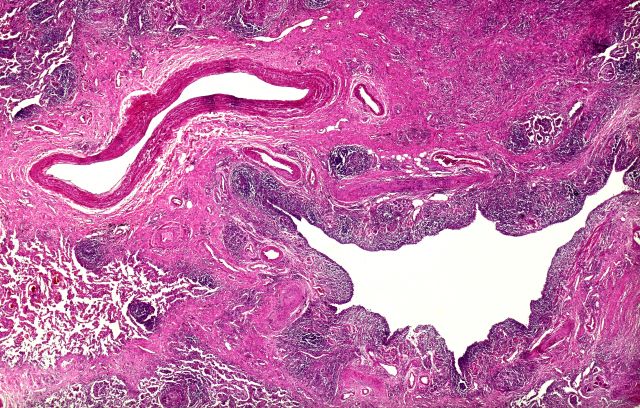
Dry cough and dyspnea
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Based on the patient's presentation and workup, the likely diagnosis is adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a relatively rare subtype of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adenosquamous carcinoma displays qualities of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma; for definitive diagnosis, the cancer must contain 10% of each of these major NSCLC subtypes. Maeda and colleagues concluded that adenosquamous carcinoma occurs more frequently among men and that the age at the time of diagnosis is higher among such cancers compared with adenocarcinoma. Several studies have confirmed that adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is also more prevalent among smokers.
Though a diagnosis of adenosquamous carcinoma may be suspected after small biopsies, cytology, or excisional biopsies, definitive diagnosis necessitates a resection specimen. If any adenocarcinoma component is observed in a biopsy specimen that is otherwise squamous, as in the present case, this finding is an indication for molecular testing. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations may be present in adenosquamous carcinoma cancers, despite a majority of cancers with EGFR mutations being among nonsmokers or former light smokers with adenocarcinoma histology. In addition, even for patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma should be considered if genetic testing suggests EGFR mutations.
Relative to adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma has higher grade malignancy, more advanced postoperative stage, and stronger lymph nodal invasiveness. In terms of treatment, surgical resection is the curative option for adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, with lobectomy with lymphadenectomy considered for first-line treatment. Though the most beneficial chemotherapy regimen for patients with adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung remains the subject of investigation, platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the current standard treatment option. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors may be an effective option for EGFR-positive patients.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 58-year-old man with a 20-year–pack history of smoking initially presented with a persistent dry cough and dyspnea. Clubbing was noted on physical examination and breath sounds in the right upper lung were weak. Other than hypertension, which the patient manages with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, medical history is unremarkable. The patient notes that this medication has always made him cough, but dyspnea has only developed over the past 6 weeks. Respiratory symptoms prompted a chest radiograph which revealed a mass in the upper lobe of the right lung. Transbronchial lung biopsy of the right lung reveals components of adenocarcinoma; the specimen is otherwise squamous.
Drugging the undruggable
including 68% of pancreatic tumors and 20% of all non–small cell lung cancers (NSCLC).
We now have a treatment – sotorasib – for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC that is driven by a KRAS mutation (G12C). And, now, there is a second treatment – adagrasib – under study, which, according to a presentation recently made at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, looks promising.
Ras is a membrane-bound regulatory protein (G protein) belonging to the family of guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Ras functions as a guanosine diphosphate/triphosphate binary switch by cycling between the active GTP-bound and the inactive GDP-bound states in response to extracellular stimuli. The KRAS (G12C) mutation affects the active form of KRAS and results in abnormally high concentrations of GTP-bound KRAS leading to hyperactivation of downstream oncogenic pathways and uncontrolled cell growth, specifically of ERK and MEK signaling pathways.
At the ASCO annual meeting in June, Spira and colleagues reported the results of cohort A of the KRYSTAL-1 study evaluating adagrasib as second-line therapy patients with advanced solid tumors harboring a KRAS (G12C) mutation. Like sotorasib, adagrasib is a KRAS (G12C) inhibitor that irreversibly and selectively binds KRAS (G12C), locking it in its inactive state. In this study, patients had to have failed first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy with 43% of lung cancer patients responding. The 12-month overall survival (OS) was 51%, median overall survival was 12.6 and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.5 months. Twenty-five patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC and active, untreated central nervous system metastases received adagrasib in a phase 1b cohort. The intracranial overall response rate was 31.6% and median intracranial PFS was 4.2 months. Systemic ORR was 35.0% (7/20), the disease control rate was 80.0% (16/20) and median duration of response was 9.6 months. Based on these data, a phase 3 trial evaluating adagrasib monotherapy versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with KRAS (G12C) mutant NSCLC is ongoing.
The Food and Drug Administration approval of sotorasib in 2021 was, in part, based on the results of a single-arm, phase 2, second-line study of patients who had previously received platinum-based chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy. An ORR rate of 37.1% was reported with a median PFS of 6.8 months and median OS of 12.5 months leading to the FDA approval. Responses were observed across the range of baseline PD-L1 expression levels: 48% of PD-L1 negative, 39% with PD-L1 between 1%-49%, and 22% of patients with a PD-L1 of greater than 50% having a response.
The major toxicities observed in these studies were gastrointestinal (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) and hepatic (elevated liver enzymes). About 97% of patients on adagrasib experienced any treatment-related adverse events, and 43% experienced a grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event leading to dose reduction in 52% of patients, a dose interruption in 61% of patients, and a 7% discontinuation rate. About 70% of patients treated with sotorasib had a treatment-related adverse event of any grade, and 21% reported grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events.
A subgroup in the KRYSTAL-1 trial reported an intracranial ORR of 32% in patients with active, untreated CNS metastases. Median overall survival has not yet reached concordance between systemic and intracranial disease control was 88%. In addition, preliminary data from two patients with untreated CNS metastases from a phase 1b cohort found cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of adagrasib with a mean ratio of unbound brain-to-plasma concentration of 0.47, which is comparable or exceeds values for known CNS-penetrant tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Unfortunately, KRAS (G12C) is not the only KRAS mutation out there. There are a myriad of others, such as G12V and G12D. Hopefully, we will be seeing more drugs aimed at this set of important mutations. Another question, of course, is when and if these drugs will move to the first-line setting.
Dr. Schiller is a medical oncologist and founding member of Oncologists United for Climate and Health. She is a former board member of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer and a current board member of the Lung Cancer Research Foundation.
including 68% of pancreatic tumors and 20% of all non–small cell lung cancers (NSCLC).
We now have a treatment – sotorasib – for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC that is driven by a KRAS mutation (G12C). And, now, there is a second treatment – adagrasib – under study, which, according to a presentation recently made at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, looks promising.
Ras is a membrane-bound regulatory protein (G protein) belonging to the family of guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Ras functions as a guanosine diphosphate/triphosphate binary switch by cycling between the active GTP-bound and the inactive GDP-bound states in response to extracellular stimuli. The KRAS (G12C) mutation affects the active form of KRAS and results in abnormally high concentrations of GTP-bound KRAS leading to hyperactivation of downstream oncogenic pathways and uncontrolled cell growth, specifically of ERK and MEK signaling pathways.
At the ASCO annual meeting in June, Spira and colleagues reported the results of cohort A of the KRYSTAL-1 study evaluating adagrasib as second-line therapy patients with advanced solid tumors harboring a KRAS (G12C) mutation. Like sotorasib, adagrasib is a KRAS (G12C) inhibitor that irreversibly and selectively binds KRAS (G12C), locking it in its inactive state. In this study, patients had to have failed first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy with 43% of lung cancer patients responding. The 12-month overall survival (OS) was 51%, median overall survival was 12.6 and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.5 months. Twenty-five patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC and active, untreated central nervous system metastases received adagrasib in a phase 1b cohort. The intracranial overall response rate was 31.6% and median intracranial PFS was 4.2 months. Systemic ORR was 35.0% (7/20), the disease control rate was 80.0% (16/20) and median duration of response was 9.6 months. Based on these data, a phase 3 trial evaluating adagrasib monotherapy versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with KRAS (G12C) mutant NSCLC is ongoing.
The Food and Drug Administration approval of sotorasib in 2021 was, in part, based on the results of a single-arm, phase 2, second-line study of patients who had previously received platinum-based chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy. An ORR rate of 37.1% was reported with a median PFS of 6.8 months and median OS of 12.5 months leading to the FDA approval. Responses were observed across the range of baseline PD-L1 expression levels: 48% of PD-L1 negative, 39% with PD-L1 between 1%-49%, and 22% of patients with a PD-L1 of greater than 50% having a response.
The major toxicities observed in these studies were gastrointestinal (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) and hepatic (elevated liver enzymes). About 97% of patients on adagrasib experienced any treatment-related adverse events, and 43% experienced a grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event leading to dose reduction in 52% of patients, a dose interruption in 61% of patients, and a 7% discontinuation rate. About 70% of patients treated with sotorasib had a treatment-related adverse event of any grade, and 21% reported grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events.
A subgroup in the KRYSTAL-1 trial reported an intracranial ORR of 32% in patients with active, untreated CNS metastases. Median overall survival has not yet reached concordance between systemic and intracranial disease control was 88%. In addition, preliminary data from two patients with untreated CNS metastases from a phase 1b cohort found cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of adagrasib with a mean ratio of unbound brain-to-plasma concentration of 0.47, which is comparable or exceeds values for known CNS-penetrant tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Unfortunately, KRAS (G12C) is not the only KRAS mutation out there. There are a myriad of others, such as G12V and G12D. Hopefully, we will be seeing more drugs aimed at this set of important mutations. Another question, of course, is when and if these drugs will move to the first-line setting.
Dr. Schiller is a medical oncologist and founding member of Oncologists United for Climate and Health. She is a former board member of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer and a current board member of the Lung Cancer Research Foundation.
including 68% of pancreatic tumors and 20% of all non–small cell lung cancers (NSCLC).
We now have a treatment – sotorasib – for patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC that is driven by a KRAS mutation (G12C). And, now, there is a second treatment – adagrasib – under study, which, according to a presentation recently made at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, looks promising.
Ras is a membrane-bound regulatory protein (G protein) belonging to the family of guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Ras functions as a guanosine diphosphate/triphosphate binary switch by cycling between the active GTP-bound and the inactive GDP-bound states in response to extracellular stimuli. The KRAS (G12C) mutation affects the active form of KRAS and results in abnormally high concentrations of GTP-bound KRAS leading to hyperactivation of downstream oncogenic pathways and uncontrolled cell growth, specifically of ERK and MEK signaling pathways.
At the ASCO annual meeting in June, Spira and colleagues reported the results of cohort A of the KRYSTAL-1 study evaluating adagrasib as second-line therapy patients with advanced solid tumors harboring a KRAS (G12C) mutation. Like sotorasib, adagrasib is a KRAS (G12C) inhibitor that irreversibly and selectively binds KRAS (G12C), locking it in its inactive state. In this study, patients had to have failed first-line chemotherapy and immunotherapy with 43% of lung cancer patients responding. The 12-month overall survival (OS) was 51%, median overall survival was 12.6 and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.5 months. Twenty-five patients with KRAS (G12C)–mutant NSCLC and active, untreated central nervous system metastases received adagrasib in a phase 1b cohort. The intracranial overall response rate was 31.6% and median intracranial PFS was 4.2 months. Systemic ORR was 35.0% (7/20), the disease control rate was 80.0% (16/20) and median duration of response was 9.6 months. Based on these data, a phase 3 trial evaluating adagrasib monotherapy versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with KRAS (G12C) mutant NSCLC is ongoing.
The Food and Drug Administration approval of sotorasib in 2021 was, in part, based on the results of a single-arm, phase 2, second-line study of patients who had previously received platinum-based chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy. An ORR rate of 37.1% was reported with a median PFS of 6.8 months and median OS of 12.5 months leading to the FDA approval. Responses were observed across the range of baseline PD-L1 expression levels: 48% of PD-L1 negative, 39% with PD-L1 between 1%-49%, and 22% of patients with a PD-L1 of greater than 50% having a response.
The major toxicities observed in these studies were gastrointestinal (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) and hepatic (elevated liver enzymes). About 97% of patients on adagrasib experienced any treatment-related adverse events, and 43% experienced a grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse event leading to dose reduction in 52% of patients, a dose interruption in 61% of patients, and a 7% discontinuation rate. About 70% of patients treated with sotorasib had a treatment-related adverse event of any grade, and 21% reported grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events.
A subgroup in the KRYSTAL-1 trial reported an intracranial ORR of 32% in patients with active, untreated CNS metastases. Median overall survival has not yet reached concordance between systemic and intracranial disease control was 88%. In addition, preliminary data from two patients with untreated CNS metastases from a phase 1b cohort found cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of adagrasib with a mean ratio of unbound brain-to-plasma concentration of 0.47, which is comparable or exceeds values for known CNS-penetrant tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Unfortunately, KRAS (G12C) is not the only KRAS mutation out there. There are a myriad of others, such as G12V and G12D. Hopefully, we will be seeing more drugs aimed at this set of important mutations. Another question, of course, is when and if these drugs will move to the first-line setting.
Dr. Schiller is a medical oncologist and founding member of Oncologists United for Climate and Health. She is a former board member of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer and a current board member of the Lung Cancer Research Foundation.
Aggression toward health care providers common during pandemic
After an aggressive event or abuse occurred, 56% of providers considered changing their care tasks, and more than a third considered quitting their profession.
“Aggression of any sort against health care providers is not a new social phenomenon, and it has existed as far as medicine and health care is reported in literature. However, the phenomenon of aggression against health care providers during the pandemic grew worse,” senior study author Adrian Baranchuk, MD, a professor of medicine at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., told this news organization.
The study was published online in Current Problems in Cardiology
Survey snapshot
Dr. Baranchuk and colleagues, with the support of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology, developed a survey to characterize the frequency and types of abuse that frontline health professionals faced. They invited health care professionals from Latin America who had provided care since March 2020 to participate.
Between January and February 2022, 3,544 participants from 19 countries took the survey. Among them, 70.8% were physicians, 16% were nurses, and 13.2% were other health team members, such as administrative staff and technicians. About 58.5% were women, and 74.7% provided direct care to patients with COVID-19.
Overall, 54.8% of respondents reported acts of aggression. Of this group, 95.6% reported verbal abuse, 11.1% reported physical abuse, and 19.9% reported other types of abuse, including microaggressions.
About 13% of respondents reported experiencing some form of aggression daily, 26.4% experienced abuse weekly, and 38.8% reported violence a few times per month. Typically, the incidents involved patients’ relatives or both the patients and their relatives.
Nearly half of those who reported abuse experienced psychosomatic symptoms after the event, and 12% sought psychological care.
Administrative staff were 3.5 times more likely to experience abuse than other health care workers. Doctors and nurses were about twice as likely to experience abuse.
In addition, women, younger staff, and those who worked directly with COVID-19 patients were more likely to report abuse.
‘Shocking results’
Dr. Baranchuk, a native of Argentina, said people initially celebrated doctors and nurses for keeping communities safe. In several countries across Latin America, for instance, people lit candles, applauded at certain hours, and posted support on social media. As pandemic-related policies changed, however, health care providers faced unrest as people grew tired of wearing masks, maintaining social distance, and obeying restrictions at public spaces such as clubs and restaurants.
“This fatigue toward the social changes grew, but people didn’t have a specific target, and slowly and gradually, health care providers became the target of frustration and hate,” said Dr. Baranchuk. “In areas of the world where legislation is more flexible and less strict in charging individuals with poor or unacceptable behavior toward members of the health care team, aggression and microaggression became more frequent.”
“The results we obtained were more shocking than we expected,” Sebastián García-Zamora, MD, the lead study author and head of the coronary care unit at the Delta Clinic, Buenos Aires, said in an interview.
Dr. García-Zamora, also the coordinator of the International Society of Electrocardiology Young Community, noted the particularly high numbers of reports among young health care workers and women.
“Unfortunately, young women seem to be the most vulnerable staff to suffering violence, regardless of the work they perform in the health system,” he said. “Notably, less than one in four health team members that suffered workplace violence pursued legal action based on the events.”
The research team is now conducting additional analyses on the different types of aggression based on gender, region, and task performed by the health care team. They’re trying to understand who is most vulnerable to physical attacks, as well as the consequences.
“The most important thing to highlight is that this problem exists, it is more frequent than we think, and we can only solve it if we all get involved in it,” Dr. García-Zamora said.
‘Complete systematic failure’
Health care workers in certain communities faced more aggression as well. In a CMAJ Open study published in November 2021, Asian Canadian and Asian American health care workers experienced discrimination, racial microaggressions, threats of violence, and violent acts during the pandemic. Women and frontline workers with direct patient contact were more likely to face verbal and physical abuse.
“This highlights that we need to continue the fight against misogyny, racism, and health care worker discrimination,” lead study author Zhida Shang, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, told this news organization.
“As we are managing to live with the COVID-19 pandemic, it is important to study our successes and shortcomings. I sincerely believe that during the pandemic, the treatment of various racialized communities, including Asian Americans and Asian Canadians, was a complete systematic failure,” he said. “It is crucial to continue to examine, reflect, and learn from these lessons so that there will be equitable outcomes during the next public health emergency.”
The study was conducted without funding support. Dr. Baranchuk, Dr. García-Zamora, and Ms. Shang report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After an aggressive event or abuse occurred, 56% of providers considered changing their care tasks, and more than a third considered quitting their profession.
“Aggression of any sort against health care providers is not a new social phenomenon, and it has existed as far as medicine and health care is reported in literature. However, the phenomenon of aggression against health care providers during the pandemic grew worse,” senior study author Adrian Baranchuk, MD, a professor of medicine at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., told this news organization.
The study was published online in Current Problems in Cardiology
Survey snapshot
Dr. Baranchuk and colleagues, with the support of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology, developed a survey to characterize the frequency and types of abuse that frontline health professionals faced. They invited health care professionals from Latin America who had provided care since March 2020 to participate.
Between January and February 2022, 3,544 participants from 19 countries took the survey. Among them, 70.8% were physicians, 16% were nurses, and 13.2% were other health team members, such as administrative staff and technicians. About 58.5% were women, and 74.7% provided direct care to patients with COVID-19.
Overall, 54.8% of respondents reported acts of aggression. Of this group, 95.6% reported verbal abuse, 11.1% reported physical abuse, and 19.9% reported other types of abuse, including microaggressions.
About 13% of respondents reported experiencing some form of aggression daily, 26.4% experienced abuse weekly, and 38.8% reported violence a few times per month. Typically, the incidents involved patients’ relatives or both the patients and their relatives.
Nearly half of those who reported abuse experienced psychosomatic symptoms after the event, and 12% sought psychological care.
Administrative staff were 3.5 times more likely to experience abuse than other health care workers. Doctors and nurses were about twice as likely to experience abuse.
In addition, women, younger staff, and those who worked directly with COVID-19 patients were more likely to report abuse.
‘Shocking results’
Dr. Baranchuk, a native of Argentina, said people initially celebrated doctors and nurses for keeping communities safe. In several countries across Latin America, for instance, people lit candles, applauded at certain hours, and posted support on social media. As pandemic-related policies changed, however, health care providers faced unrest as people grew tired of wearing masks, maintaining social distance, and obeying restrictions at public spaces such as clubs and restaurants.
“This fatigue toward the social changes grew, but people didn’t have a specific target, and slowly and gradually, health care providers became the target of frustration and hate,” said Dr. Baranchuk. “In areas of the world where legislation is more flexible and less strict in charging individuals with poor or unacceptable behavior toward members of the health care team, aggression and microaggression became more frequent.”
“The results we obtained were more shocking than we expected,” Sebastián García-Zamora, MD, the lead study author and head of the coronary care unit at the Delta Clinic, Buenos Aires, said in an interview.
Dr. García-Zamora, also the coordinator of the International Society of Electrocardiology Young Community, noted the particularly high numbers of reports among young health care workers and women.
“Unfortunately, young women seem to be the most vulnerable staff to suffering violence, regardless of the work they perform in the health system,” he said. “Notably, less than one in four health team members that suffered workplace violence pursued legal action based on the events.”
The research team is now conducting additional analyses on the different types of aggression based on gender, region, and task performed by the health care team. They’re trying to understand who is most vulnerable to physical attacks, as well as the consequences.
“The most important thing to highlight is that this problem exists, it is more frequent than we think, and we can only solve it if we all get involved in it,” Dr. García-Zamora said.
‘Complete systematic failure’
Health care workers in certain communities faced more aggression as well. In a CMAJ Open study published in November 2021, Asian Canadian and Asian American health care workers experienced discrimination, racial microaggressions, threats of violence, and violent acts during the pandemic. Women and frontline workers with direct patient contact were more likely to face verbal and physical abuse.
“This highlights that we need to continue the fight against misogyny, racism, and health care worker discrimination,” lead study author Zhida Shang, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, told this news organization.
“As we are managing to live with the COVID-19 pandemic, it is important to study our successes and shortcomings. I sincerely believe that during the pandemic, the treatment of various racialized communities, including Asian Americans and Asian Canadians, was a complete systematic failure,” he said. “It is crucial to continue to examine, reflect, and learn from these lessons so that there will be equitable outcomes during the next public health emergency.”
The study was conducted without funding support. Dr. Baranchuk, Dr. García-Zamora, and Ms. Shang report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After an aggressive event or abuse occurred, 56% of providers considered changing their care tasks, and more than a third considered quitting their profession.
“Aggression of any sort against health care providers is not a new social phenomenon, and it has existed as far as medicine and health care is reported in literature. However, the phenomenon of aggression against health care providers during the pandemic grew worse,” senior study author Adrian Baranchuk, MD, a professor of medicine at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., told this news organization.
The study was published online in Current Problems in Cardiology
Survey snapshot
Dr. Baranchuk and colleagues, with the support of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology, developed a survey to characterize the frequency and types of abuse that frontline health professionals faced. They invited health care professionals from Latin America who had provided care since March 2020 to participate.
Between January and February 2022, 3,544 participants from 19 countries took the survey. Among them, 70.8% were physicians, 16% were nurses, and 13.2% were other health team members, such as administrative staff and technicians. About 58.5% were women, and 74.7% provided direct care to patients with COVID-19.
Overall, 54.8% of respondents reported acts of aggression. Of this group, 95.6% reported verbal abuse, 11.1% reported physical abuse, and 19.9% reported other types of abuse, including microaggressions.
About 13% of respondents reported experiencing some form of aggression daily, 26.4% experienced abuse weekly, and 38.8% reported violence a few times per month. Typically, the incidents involved patients’ relatives or both the patients and their relatives.
Nearly half of those who reported abuse experienced psychosomatic symptoms after the event, and 12% sought psychological care.
Administrative staff were 3.5 times more likely to experience abuse than other health care workers. Doctors and nurses were about twice as likely to experience abuse.
In addition, women, younger staff, and those who worked directly with COVID-19 patients were more likely to report abuse.
‘Shocking results’
Dr. Baranchuk, a native of Argentina, said people initially celebrated doctors and nurses for keeping communities safe. In several countries across Latin America, for instance, people lit candles, applauded at certain hours, and posted support on social media. As pandemic-related policies changed, however, health care providers faced unrest as people grew tired of wearing masks, maintaining social distance, and obeying restrictions at public spaces such as clubs and restaurants.
“This fatigue toward the social changes grew, but people didn’t have a specific target, and slowly and gradually, health care providers became the target of frustration and hate,” said Dr. Baranchuk. “In areas of the world where legislation is more flexible and less strict in charging individuals with poor or unacceptable behavior toward members of the health care team, aggression and microaggression became more frequent.”
“The results we obtained were more shocking than we expected,” Sebastián García-Zamora, MD, the lead study author and head of the coronary care unit at the Delta Clinic, Buenos Aires, said in an interview.
Dr. García-Zamora, also the coordinator of the International Society of Electrocardiology Young Community, noted the particularly high numbers of reports among young health care workers and women.
“Unfortunately, young women seem to be the most vulnerable staff to suffering violence, regardless of the work they perform in the health system,” he said. “Notably, less than one in four health team members that suffered workplace violence pursued legal action based on the events.”
The research team is now conducting additional analyses on the different types of aggression based on gender, region, and task performed by the health care team. They’re trying to understand who is most vulnerable to physical attacks, as well as the consequences.
“The most important thing to highlight is that this problem exists, it is more frequent than we think, and we can only solve it if we all get involved in it,” Dr. García-Zamora said.
‘Complete systematic failure’
Health care workers in certain communities faced more aggression as well. In a CMAJ Open study published in November 2021, Asian Canadian and Asian American health care workers experienced discrimination, racial microaggressions, threats of violence, and violent acts during the pandemic. Women and frontline workers with direct patient contact were more likely to face verbal and physical abuse.
“This highlights that we need to continue the fight against misogyny, racism, and health care worker discrimination,” lead study author Zhida Shang, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, told this news organization.
“As we are managing to live with the COVID-19 pandemic, it is important to study our successes and shortcomings. I sincerely believe that during the pandemic, the treatment of various racialized communities, including Asian Americans and Asian Canadians, was a complete systematic failure,” he said. “It is crucial to continue to examine, reflect, and learn from these lessons so that there will be equitable outcomes during the next public health emergency.”
The study was conducted without funding support. Dr. Baranchuk, Dr. García-Zamora, and Ms. Shang report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inflation and health care: The prognosis for doctors
Rampant inflation doesn’t just mean a spike in everyday expenses like gas and groceries. It’s also bound to have a significant impact on the cost of health care – and on your practice. A recent report from McKinsey & Company predicts that the current inflationary spiral will force health care providers to charge higher reimbursement rates, and those costs inevitably will be passed along to both employers and consumers. Bottom line: Your patients will likely have to pay more out of pocket.
How, precisely, will inflation affect your practice, and what’s the best way to minimize the damage?
Step 1: Maintain operational standards
“Based on the conversations we’ve had with our physician clients that own practices, we see the potential for cost inflation to outrun revenue inflation over the next year,” said Michael Ashley Schulman, CFA, partner and chief investment officer at Running Point Capital, El Segundo, Calif. “Staff wages, as well as office equipment and medical supply costs, are increasing faster than insurance and Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement amounts.” Even so, topflight employees are essential to keep your practice running smoothly. Prioritize excellent nursing. Instead of adding a new hire, compensate your best nurse as well as possible. The same goes for an efficient office manager: On that front, too, you should go the extra mile, even if it means trimming expenses elsewhere.
Step 2: Plan ahead for insurance challenges
Many insurers, including Medicare, set health care costs a year in advance, based on projected growth. This means insurance payouts will stay largely the same for the time being. “Almost all physicians employed by large groups won’t see costs due to inflation rise until next year,” said Mark V. Pauly, PhD, Bendheim Professor in the department of health care management at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “For self-employed physicians, there will also be a cushion.”
“The big issue with inflation is that more patients will likely be underinsured,” said Tiffany Johnson, MBA, CFP, co-CEO and financial advisor at Piece of Wealth Planning in Atlanta. “With more out-of-pocket costs ... these patients may not seek out medical treatment or go to see a specialist if they do not believe it is necessary.” A new study from Johns Hopkins found that patients under financial pressure often delay or forgo medical treatment because of food insecurity. Compassionate care is the solution: Direct these patients to financial aid and other resources they may qualify for. That way, they can continue to receive the care they need from you, and your need to pass on costs may be lower.
Step 3: Rely on your affiliated health care organization
These are tough times when it comes to expansion. “Since we are in an environment where inflation and interest rates are both high, it will be much harder for physicians to have the capital to invest in new technology to grow or advance their practice,” Ms. Johnson said. With that in mind, keep the lines of communication between you and your affiliated hospital/health care organization more open than ever. Combining practices with another doctor is one way to increase revenue; you might ask if any affiliated doctors are seeking to team up. It’s also vital to attend meetings and pay close attention to budget cuts your organization may be making. And don’t be shy about asking your administrator for profit-boosting recommendations.
Step 4: Revisit vendor relationships
Find out if your vendors will continue to supply you with the goods you need at reasonable rates, and switch now if they won’t. Be proactive. “Test new medical suppliers,” Mr. Schulman advised. “Reread equipment leasing contracts to check if the interest rates have increased. See if buyout, prepay, or refinancing options are more economical. Also, investigate [bringing down] your rental expense by reducing square footage or moving to a lower-cost location.” In light of ongoing supply chain issues, it’s wise to consider alternative products. But stay focused on quality – you don’t want to be stuck with cheap, possibly defective equipment. Spend where it’s essential and cut the fat somewhere else.
Step 5: Don’t waste your assets
Analyze your budget in minute detail. “Now is the time to review your current inventory and overhead costs,” Ms. Johnson said. “Many physicians let their office staff handle the restocking of inventory and office supplies. While this can be efficient for their practice, it also leaves room for unnecessary business expenses.” Take a cold, hard look at your supply closet – what’s in there that you can live without? Don’t reorder it. Then seek out any revenue stream you may be overlooking. “It’s important to review billing to make sure all the services are reimbursable,” Ms. Johnson added. Small mistakes can yield dividends if you find them.
Step 6: Be poised to pivot
Get creative. “To minimize a profit decline, use video consulting – it’s more efficient and less equipment intensive,” Mr. Schulman said. “Look at how remote work and flexible hours can maximize the work your practice accomplishes while cutting office costs.”
Ms. Johnson suggests adding concierge services, noting that “concierge doctors offer personalized care and direct access for an up-front fee.” With this approach, you may see fewer patients, but your payout paperwork will decrease, and that up-front fee can be profitable. Another outside-the-box idea: Start making house calls. A Scripps study found that home health visits requested via app can result in patient care delivered by a doctor and medical assistant in less than 2 hours. House calls can be an effective and profitable solution when it comes to providing nonemergency care and preventive treatment to patients who aren’t mobile, not to mention patients who just appreciate the convenience.
Step 7: Maintain transparency
Any economic changes your practice will implement must be communicated to your staff and patients clearly and directly. Keep everyone in the loop and be ready to answer questions immediately. Show those you work with and care for that, regardless of the economy, it’s they who matter to you most. That simple reassurance will prove invaluable.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rampant inflation doesn’t just mean a spike in everyday expenses like gas and groceries. It’s also bound to have a significant impact on the cost of health care – and on your practice. A recent report from McKinsey & Company predicts that the current inflationary spiral will force health care providers to charge higher reimbursement rates, and those costs inevitably will be passed along to both employers and consumers. Bottom line: Your patients will likely have to pay more out of pocket.
How, precisely, will inflation affect your practice, and what’s the best way to minimize the damage?
Step 1: Maintain operational standards
“Based on the conversations we’ve had with our physician clients that own practices, we see the potential for cost inflation to outrun revenue inflation over the next year,” said Michael Ashley Schulman, CFA, partner and chief investment officer at Running Point Capital, El Segundo, Calif. “Staff wages, as well as office equipment and medical supply costs, are increasing faster than insurance and Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement amounts.” Even so, topflight employees are essential to keep your practice running smoothly. Prioritize excellent nursing. Instead of adding a new hire, compensate your best nurse as well as possible. The same goes for an efficient office manager: On that front, too, you should go the extra mile, even if it means trimming expenses elsewhere.
Step 2: Plan ahead for insurance challenges
Many insurers, including Medicare, set health care costs a year in advance, based on projected growth. This means insurance payouts will stay largely the same for the time being. “Almost all physicians employed by large groups won’t see costs due to inflation rise until next year,” said Mark V. Pauly, PhD, Bendheim Professor in the department of health care management at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “For self-employed physicians, there will also be a cushion.”
“The big issue with inflation is that more patients will likely be underinsured,” said Tiffany Johnson, MBA, CFP, co-CEO and financial advisor at Piece of Wealth Planning in Atlanta. “With more out-of-pocket costs ... these patients may not seek out medical treatment or go to see a specialist if they do not believe it is necessary.” A new study from Johns Hopkins found that patients under financial pressure often delay or forgo medical treatment because of food insecurity. Compassionate care is the solution: Direct these patients to financial aid and other resources they may qualify for. That way, they can continue to receive the care they need from you, and your need to pass on costs may be lower.
Step 3: Rely on your affiliated health care organization
These are tough times when it comes to expansion. “Since we are in an environment where inflation and interest rates are both high, it will be much harder for physicians to have the capital to invest in new technology to grow or advance their practice,” Ms. Johnson said. With that in mind, keep the lines of communication between you and your affiliated hospital/health care organization more open than ever. Combining practices with another doctor is one way to increase revenue; you might ask if any affiliated doctors are seeking to team up. It’s also vital to attend meetings and pay close attention to budget cuts your organization may be making. And don’t be shy about asking your administrator for profit-boosting recommendations.
Step 4: Revisit vendor relationships
Find out if your vendors will continue to supply you with the goods you need at reasonable rates, and switch now if they won’t. Be proactive. “Test new medical suppliers,” Mr. Schulman advised. “Reread equipment leasing contracts to check if the interest rates have increased. See if buyout, prepay, or refinancing options are more economical. Also, investigate [bringing down] your rental expense by reducing square footage or moving to a lower-cost location.” In light of ongoing supply chain issues, it’s wise to consider alternative products. But stay focused on quality – you don’t want to be stuck with cheap, possibly defective equipment. Spend where it’s essential and cut the fat somewhere else.
Step 5: Don’t waste your assets
Analyze your budget in minute detail. “Now is the time to review your current inventory and overhead costs,” Ms. Johnson said. “Many physicians let their office staff handle the restocking of inventory and office supplies. While this can be efficient for their practice, it also leaves room for unnecessary business expenses.” Take a cold, hard look at your supply closet – what’s in there that you can live without? Don’t reorder it. Then seek out any revenue stream you may be overlooking. “It’s important to review billing to make sure all the services are reimbursable,” Ms. Johnson added. Small mistakes can yield dividends if you find them.
Step 6: Be poised to pivot
Get creative. “To minimize a profit decline, use video consulting – it’s more efficient and less equipment intensive,” Mr. Schulman said. “Look at how remote work and flexible hours can maximize the work your practice accomplishes while cutting office costs.”
Ms. Johnson suggests adding concierge services, noting that “concierge doctors offer personalized care and direct access for an up-front fee.” With this approach, you may see fewer patients, but your payout paperwork will decrease, and that up-front fee can be profitable. Another outside-the-box idea: Start making house calls. A Scripps study found that home health visits requested via app can result in patient care delivered by a doctor and medical assistant in less than 2 hours. House calls can be an effective and profitable solution when it comes to providing nonemergency care and preventive treatment to patients who aren’t mobile, not to mention patients who just appreciate the convenience.
Step 7: Maintain transparency
Any economic changes your practice will implement must be communicated to your staff and patients clearly and directly. Keep everyone in the loop and be ready to answer questions immediately. Show those you work with and care for that, regardless of the economy, it’s they who matter to you most. That simple reassurance will prove invaluable.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rampant inflation doesn’t just mean a spike in everyday expenses like gas and groceries. It’s also bound to have a significant impact on the cost of health care – and on your practice. A recent report from McKinsey & Company predicts that the current inflationary spiral will force health care providers to charge higher reimbursement rates, and those costs inevitably will be passed along to both employers and consumers. Bottom line: Your patients will likely have to pay more out of pocket.
How, precisely, will inflation affect your practice, and what’s the best way to minimize the damage?
Step 1: Maintain operational standards
“Based on the conversations we’ve had with our physician clients that own practices, we see the potential for cost inflation to outrun revenue inflation over the next year,” said Michael Ashley Schulman, CFA, partner and chief investment officer at Running Point Capital, El Segundo, Calif. “Staff wages, as well as office equipment and medical supply costs, are increasing faster than insurance and Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement amounts.” Even so, topflight employees are essential to keep your practice running smoothly. Prioritize excellent nursing. Instead of adding a new hire, compensate your best nurse as well as possible. The same goes for an efficient office manager: On that front, too, you should go the extra mile, even if it means trimming expenses elsewhere.
Step 2: Plan ahead for insurance challenges
Many insurers, including Medicare, set health care costs a year in advance, based on projected growth. This means insurance payouts will stay largely the same for the time being. “Almost all physicians employed by large groups won’t see costs due to inflation rise until next year,” said Mark V. Pauly, PhD, Bendheim Professor in the department of health care management at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “For self-employed physicians, there will also be a cushion.”
“The big issue with inflation is that more patients will likely be underinsured,” said Tiffany Johnson, MBA, CFP, co-CEO and financial advisor at Piece of Wealth Planning in Atlanta. “With more out-of-pocket costs ... these patients may not seek out medical treatment or go to see a specialist if they do not believe it is necessary.” A new study from Johns Hopkins found that patients under financial pressure often delay or forgo medical treatment because of food insecurity. Compassionate care is the solution: Direct these patients to financial aid and other resources they may qualify for. That way, they can continue to receive the care they need from you, and your need to pass on costs may be lower.
Step 3: Rely on your affiliated health care organization
These are tough times when it comes to expansion. “Since we are in an environment where inflation and interest rates are both high, it will be much harder for physicians to have the capital to invest in new technology to grow or advance their practice,” Ms. Johnson said. With that in mind, keep the lines of communication between you and your affiliated hospital/health care organization more open than ever. Combining practices with another doctor is one way to increase revenue; you might ask if any affiliated doctors are seeking to team up. It’s also vital to attend meetings and pay close attention to budget cuts your organization may be making. And don’t be shy about asking your administrator for profit-boosting recommendations.
Step 4: Revisit vendor relationships
Find out if your vendors will continue to supply you with the goods you need at reasonable rates, and switch now if they won’t. Be proactive. “Test new medical suppliers,” Mr. Schulman advised. “Reread equipment leasing contracts to check if the interest rates have increased. See if buyout, prepay, or refinancing options are more economical. Also, investigate [bringing down] your rental expense by reducing square footage or moving to a lower-cost location.” In light of ongoing supply chain issues, it’s wise to consider alternative products. But stay focused on quality – you don’t want to be stuck with cheap, possibly defective equipment. Spend where it’s essential and cut the fat somewhere else.
Step 5: Don’t waste your assets
Analyze your budget in minute detail. “Now is the time to review your current inventory and overhead costs,” Ms. Johnson said. “Many physicians let their office staff handle the restocking of inventory and office supplies. While this can be efficient for their practice, it also leaves room for unnecessary business expenses.” Take a cold, hard look at your supply closet – what’s in there that you can live without? Don’t reorder it. Then seek out any revenue stream you may be overlooking. “It’s important to review billing to make sure all the services are reimbursable,” Ms. Johnson added. Small mistakes can yield dividends if you find them.
Step 6: Be poised to pivot
Get creative. “To minimize a profit decline, use video consulting – it’s more efficient and less equipment intensive,” Mr. Schulman said. “Look at how remote work and flexible hours can maximize the work your practice accomplishes while cutting office costs.”
Ms. Johnson suggests adding concierge services, noting that “concierge doctors offer personalized care and direct access for an up-front fee.” With this approach, you may see fewer patients, but your payout paperwork will decrease, and that up-front fee can be profitable. Another outside-the-box idea: Start making house calls. A Scripps study found that home health visits requested via app can result in patient care delivered by a doctor and medical assistant in less than 2 hours. House calls can be an effective and profitable solution when it comes to providing nonemergency care and preventive treatment to patients who aren’t mobile, not to mention patients who just appreciate the convenience.
Step 7: Maintain transparency
Any economic changes your practice will implement must be communicated to your staff and patients clearly and directly. Keep everyone in the loop and be ready to answer questions immediately. Show those you work with and care for that, regardless of the economy, it’s they who matter to you most. That simple reassurance will prove invaluable.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do behavioral interventions improve nighttime sleep in children < 1 year old?
Most interventions resulted in at least modest improvements in sleep
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 279 newborn infants and their mothers evaluated developmentally appropriate sleep interventions.1 Mothers were given guidance on bedtime sleep routines, including starting the routine 30 to 45 minutes before bedtime, choosing age-appropriate calming bedtime activities, not using feeding as the last step before bedtime, and offering the child choices with their routine. Mothers were also given guidance on sleep location and behaviors, including recommendations on the best bedtime (between 7 and 8
These interventions were compared to a control group that received instructions on crib safety, sudden infant death syndrome prevention, and other sleep safety recommendations. Infant nocturnal sleep duration was determined by maternal report using the Brief Infant Sleep Questionnaire (BISQ). After 40 weeks, infants in the intervention group demonstrated longer sleep duration than did those in the control group (624.6 ± 67.6 minutes vs 602.9 ± 76.1 minutes; P = .01).1
An RCT of 82 infants (ages 2-4 months) and their mothers evaluated the effect of behavioral sleep interventions on maternal and infant sleep.2 Parents were offered either a 90-minute class and take-home booklet about behavioral sleep interventions or a 30-minute training on general infant safety with an accompanying pamphlet.
The behavioral interventions booklet included instructions on differentiating day and night routines for baby, avoiding digital devices and television in the evenings, playing more active games in the morning, dimming lights and reducing house noises in the afternoon, and having a consistent nighttime routine with consistent bedtime and sleep space. Participants completed an infant sleep diary prior to the intervention and repeated the sleep diary 8 weeks after the intervention. The infants whose mothers received the education on behavioral sleep interventions demonstrated an increase in nighttime sleep duration when compared to the control group (7.4 to 8.8 hours vs 7.3 to 7.5 hours; ANCOVA P < .001).
An RCT of 235 families with infants ages 6 to 8 months evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education regarding normal infant sleep, effects of inadequate sleep, setting limits around infant sleep, importance of daytime routines, and negative sleep associations combined with a booklet and weekly phone follow-ups.3 This intervention was compared to routine infant education. At age 6 weeks, infants were monitored for 48 hours with actigraphy and the mothers completed a sleep diary to correlate activities. There was no difference in average nightly waking (2 nightly wakes; risk difference = –0.2%; 95% CI, –1.32 to 0.91).
An RCT of 268 families with infants (ages 2-3 weeks) evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education on behavioral sleep interventions including the cyclical nature of infant sleep, environmental factors that influence sleep, and parent-independent sleep cues (eg, leaving a settling infant alone for 5 minutes before responding) combined with written information.4 This was compared to infants receiving standard care without parental sleep intervention education. Participants recorded sleep diaries for 7 days when their infant reached age 6 weeks and again at age 12 weeks. At both 6 weeks and 12 weeks, there was a significant increase in infant nocturnal sleep time in the intervention group vs the control group (mean difference [MD] at 6 weeks = 0.5 hours; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.69 vs MD at 12 weeks = 0.64 hours; 95% CI, 0.19 to 0.89).
A nonrandomized controlled trial with 84 mothers and infants (ages 0-6 months) evaluated the effectiveness of a multifaceted intervention involving brief focused negotiation by pediatricians, motivational counseling by a health educator, and group parenting workshops, compared to mother–infant pairs receiving standard care.5 Parents completed the BISQ at 0 and 6 months to assess nocturnal sleep duration. At 6 months, the intervention group had a significantly higher increase in infant nocturnal sleep duration compared to the control group (mean increase = 1.9 vs 1.3 hours; P = .05).
In a prospective cohort study involving 79 infants (ages 3-24 months) with parent- or pediatrician-reported day and night sleep problems, parents were given education on the promotion of nighttime sleep by gradually reducing contact with the infant over several nights and only leaving the room after the infant fell asleep or allowing the child to self-soothe for 1-3 minutes.6 The intervention was performed over 3 weeks, with in-person follow-up performed on Day 15 and phone follow-up on Days 8 and 21. Infants in this study demonstrated an increase in the average hours of total night sleep from 10.2 to 10.5 hours (P < .001).
Editor’s takeaway
Providing behavioral recommendations to parents about infant sleep routines improves sleep duration. This increased sleep duration, and the supporting evidence, is modest, but the low cost and risk of these interventions make them worthwhile.
1. Paul IM, Savage JS, Anzman-Frasca S, et al. INSIGHT responsive parenting intervention and infant sleep. Pediatrics. 2016;138:e20160762. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-0762
2. Rouzafzoon M, Farnam F, Khakbazan Z. The effects of infant behavioural sleep interventions on maternal sleep and mood, and infant sleep: a randomised controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2021;30:e13344. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13344
3. Hall WA, Hutton E, Brant RF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of an intervention for infants’ behavioral sleep problems. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15:181. doi:10.1186/s12887-015-0492-7
4. Symon BG, Marley JE, Martin AJ, et al. Effect of a consultation teaching behaviour modification on sleep performance in infants: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Aust. 2005;182:215-218. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2005.tb06669.x
5. Taveras EM, Blackburn K, Gillman MW, et al. First steps for mommy and me: a pilot intervention to improve nutrition and physical activity behaviors of postpartum mothers and their infants. Matern Child Health J. 2011;15:1217-1227. doi: 10.1007/s10995-010-0696-2
6. Skuladottir A, Thome M, Ramel A. Improving day and night sleep problems in infants by changing day time sleep rhythm: a single group before and after study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2005;42:843-850. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.12.004
Most interventions resulted in at least modest improvements in sleep
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 279 newborn infants and their mothers evaluated developmentally appropriate sleep interventions.1 Mothers were given guidance on bedtime sleep routines, including starting the routine 30 to 45 minutes before bedtime, choosing age-appropriate calming bedtime activities, not using feeding as the last step before bedtime, and offering the child choices with their routine. Mothers were also given guidance on sleep location and behaviors, including recommendations on the best bedtime (between 7 and 8
These interventions were compared to a control group that received instructions on crib safety, sudden infant death syndrome prevention, and other sleep safety recommendations. Infant nocturnal sleep duration was determined by maternal report using the Brief Infant Sleep Questionnaire (BISQ). After 40 weeks, infants in the intervention group demonstrated longer sleep duration than did those in the control group (624.6 ± 67.6 minutes vs 602.9 ± 76.1 minutes; P = .01).1
An RCT of 82 infants (ages 2-4 months) and their mothers evaluated the effect of behavioral sleep interventions on maternal and infant sleep.2 Parents were offered either a 90-minute class and take-home booklet about behavioral sleep interventions or a 30-minute training on general infant safety with an accompanying pamphlet.
The behavioral interventions booklet included instructions on differentiating day and night routines for baby, avoiding digital devices and television in the evenings, playing more active games in the morning, dimming lights and reducing house noises in the afternoon, and having a consistent nighttime routine with consistent bedtime and sleep space. Participants completed an infant sleep diary prior to the intervention and repeated the sleep diary 8 weeks after the intervention. The infants whose mothers received the education on behavioral sleep interventions demonstrated an increase in nighttime sleep duration when compared to the control group (7.4 to 8.8 hours vs 7.3 to 7.5 hours; ANCOVA P < .001).
An RCT of 235 families with infants ages 6 to 8 months evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education regarding normal infant sleep, effects of inadequate sleep, setting limits around infant sleep, importance of daytime routines, and negative sleep associations combined with a booklet and weekly phone follow-ups.3 This intervention was compared to routine infant education. At age 6 weeks, infants were monitored for 48 hours with actigraphy and the mothers completed a sleep diary to correlate activities. There was no difference in average nightly waking (2 nightly wakes; risk difference = –0.2%; 95% CI, –1.32 to 0.91).
An RCT of 268 families with infants (ages 2-3 weeks) evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education on behavioral sleep interventions including the cyclical nature of infant sleep, environmental factors that influence sleep, and parent-independent sleep cues (eg, leaving a settling infant alone for 5 minutes before responding) combined with written information.4 This was compared to infants receiving standard care without parental sleep intervention education. Participants recorded sleep diaries for 7 days when their infant reached age 6 weeks and again at age 12 weeks. At both 6 weeks and 12 weeks, there was a significant increase in infant nocturnal sleep time in the intervention group vs the control group (mean difference [MD] at 6 weeks = 0.5 hours; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.69 vs MD at 12 weeks = 0.64 hours; 95% CI, 0.19 to 0.89).
A nonrandomized controlled trial with 84 mothers and infants (ages 0-6 months) evaluated the effectiveness of a multifaceted intervention involving brief focused negotiation by pediatricians, motivational counseling by a health educator, and group parenting workshops, compared to mother–infant pairs receiving standard care.5 Parents completed the BISQ at 0 and 6 months to assess nocturnal sleep duration. At 6 months, the intervention group had a significantly higher increase in infant nocturnal sleep duration compared to the control group (mean increase = 1.9 vs 1.3 hours; P = .05).
In a prospective cohort study involving 79 infants (ages 3-24 months) with parent- or pediatrician-reported day and night sleep problems, parents were given education on the promotion of nighttime sleep by gradually reducing contact with the infant over several nights and only leaving the room after the infant fell asleep or allowing the child to self-soothe for 1-3 minutes.6 The intervention was performed over 3 weeks, with in-person follow-up performed on Day 15 and phone follow-up on Days 8 and 21. Infants in this study demonstrated an increase in the average hours of total night sleep from 10.2 to 10.5 hours (P < .001).
Editor’s takeaway
Providing behavioral recommendations to parents about infant sleep routines improves sleep duration. This increased sleep duration, and the supporting evidence, is modest, but the low cost and risk of these interventions make them worthwhile.
Most interventions resulted in at least modest improvements in sleep
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 279 newborn infants and their mothers evaluated developmentally appropriate sleep interventions.1 Mothers were given guidance on bedtime sleep routines, including starting the routine 30 to 45 minutes before bedtime, choosing age-appropriate calming bedtime activities, not using feeding as the last step before bedtime, and offering the child choices with their routine. Mothers were also given guidance on sleep location and behaviors, including recommendations on the best bedtime (between 7 and 8
These interventions were compared to a control group that received instructions on crib safety, sudden infant death syndrome prevention, and other sleep safety recommendations. Infant nocturnal sleep duration was determined by maternal report using the Brief Infant Sleep Questionnaire (BISQ). After 40 weeks, infants in the intervention group demonstrated longer sleep duration than did those in the control group (624.6 ± 67.6 minutes vs 602.9 ± 76.1 minutes; P = .01).1
An RCT of 82 infants (ages 2-4 months) and their mothers evaluated the effect of behavioral sleep interventions on maternal and infant sleep.2 Parents were offered either a 90-minute class and take-home booklet about behavioral sleep interventions or a 30-minute training on general infant safety with an accompanying pamphlet.
The behavioral interventions booklet included instructions on differentiating day and night routines for baby, avoiding digital devices and television in the evenings, playing more active games in the morning, dimming lights and reducing house noises in the afternoon, and having a consistent nighttime routine with consistent bedtime and sleep space. Participants completed an infant sleep diary prior to the intervention and repeated the sleep diary 8 weeks after the intervention. The infants whose mothers received the education on behavioral sleep interventions demonstrated an increase in nighttime sleep duration when compared to the control group (7.4 to 8.8 hours vs 7.3 to 7.5 hours; ANCOVA P < .001).
An RCT of 235 families with infants ages 6 to 8 months evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education regarding normal infant sleep, effects of inadequate sleep, setting limits around infant sleep, importance of daytime routines, and negative sleep associations combined with a booklet and weekly phone follow-ups.3 This intervention was compared to routine infant education. At age 6 weeks, infants were monitored for 48 hours with actigraphy and the mothers completed a sleep diary to correlate activities. There was no difference in average nightly waking (2 nightly wakes; risk difference = –0.2%; 95% CI, –1.32 to 0.91).
An RCT of 268 families with infants (ages 2-3 weeks) evaluated the effect of 45 minutes of nurse-provided education on behavioral sleep interventions including the cyclical nature of infant sleep, environmental factors that influence sleep, and parent-independent sleep cues (eg, leaving a settling infant alone for 5 minutes before responding) combined with written information.4 This was compared to infants receiving standard care without parental sleep intervention education. Participants recorded sleep diaries for 7 days when their infant reached age 6 weeks and again at age 12 weeks. At both 6 weeks and 12 weeks, there was a significant increase in infant nocturnal sleep time in the intervention group vs the control group (mean difference [MD] at 6 weeks = 0.5 hours; 95% CI, 0.32 to 0.69 vs MD at 12 weeks = 0.64 hours; 95% CI, 0.19 to 0.89).
A nonrandomized controlled trial with 84 mothers and infants (ages 0-6 months) evaluated the effectiveness of a multifaceted intervention involving brief focused negotiation by pediatricians, motivational counseling by a health educator, and group parenting workshops, compared to mother–infant pairs receiving standard care.5 Parents completed the BISQ at 0 and 6 months to assess nocturnal sleep duration. At 6 months, the intervention group had a significantly higher increase in infant nocturnal sleep duration compared to the control group (mean increase = 1.9 vs 1.3 hours; P = .05).
In a prospective cohort study involving 79 infants (ages 3-24 months) with parent- or pediatrician-reported day and night sleep problems, parents were given education on the promotion of nighttime sleep by gradually reducing contact with the infant over several nights and only leaving the room after the infant fell asleep or allowing the child to self-soothe for 1-3 minutes.6 The intervention was performed over 3 weeks, with in-person follow-up performed on Day 15 and phone follow-up on Days 8 and 21. Infants in this study demonstrated an increase in the average hours of total night sleep from 10.2 to 10.5 hours (P < .001).
Editor’s takeaway
Providing behavioral recommendations to parents about infant sleep routines improves sleep duration. This increased sleep duration, and the supporting evidence, is modest, but the low cost and risk of these interventions make them worthwhile.
1. Paul IM, Savage JS, Anzman-Frasca S, et al. INSIGHT responsive parenting intervention and infant sleep. Pediatrics. 2016;138:e20160762. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-0762
2. Rouzafzoon M, Farnam F, Khakbazan Z. The effects of infant behavioural sleep interventions on maternal sleep and mood, and infant sleep: a randomised controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2021;30:e13344. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13344
3. Hall WA, Hutton E, Brant RF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of an intervention for infants’ behavioral sleep problems. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15:181. doi:10.1186/s12887-015-0492-7
4. Symon BG, Marley JE, Martin AJ, et al. Effect of a consultation teaching behaviour modification on sleep performance in infants: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Aust. 2005;182:215-218. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2005.tb06669.x
5. Taveras EM, Blackburn K, Gillman MW, et al. First steps for mommy and me: a pilot intervention to improve nutrition and physical activity behaviors of postpartum mothers and their infants. Matern Child Health J. 2011;15:1217-1227. doi: 10.1007/s10995-010-0696-2
6. Skuladottir A, Thome M, Ramel A. Improving day and night sleep problems in infants by changing day time sleep rhythm: a single group before and after study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2005;42:843-850. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.12.004
1. Paul IM, Savage JS, Anzman-Frasca S, et al. INSIGHT responsive parenting intervention and infant sleep. Pediatrics. 2016;138:e20160762. doi:10.1542/peds.2016-0762
2. Rouzafzoon M, Farnam F, Khakbazan Z. The effects of infant behavioural sleep interventions on maternal sleep and mood, and infant sleep: a randomised controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2021;30:e13344. doi: 10.1111/jsr.13344
3. Hall WA, Hutton E, Brant RF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of an intervention for infants’ behavioral sleep problems. BMC Pediatr. 2015;15:181. doi:10.1186/s12887-015-0492-7
4. Symon BG, Marley JE, Martin AJ, et al. Effect of a consultation teaching behaviour modification on sleep performance in infants: a randomised controlled trial. Med J Aust. 2005;182:215-218. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2005.tb06669.x
5. Taveras EM, Blackburn K, Gillman MW, et al. First steps for mommy and me: a pilot intervention to improve nutrition and physical activity behaviors of postpartum mothers and their infants. Matern Child Health J. 2011;15:1217-1227. doi: 10.1007/s10995-010-0696-2
6. Skuladottir A, Thome M, Ramel A. Improving day and night sleep problems in infants by changing day time sleep rhythm: a single group before and after study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2005;42:843-850. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.12.004
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
YES. Infants respond to behavioral interventions, although objective data are limited. Behavioral interventions include establishing regular daytime and sleep routines for the infant, reducing environmental noises or distractions, and allowing for self-soothing at bedtime (strength of recommendation: B, based on multiple randomized and nonrandomized studies).
Are antipsychotics effective adjunctive Tx for patients with moderate-to-severe depression?
Evidence summary
Depression symptoms improved with any of 4 antipsychotics
A 2021 systematic review of 16 RCTs (N = 3649) assessed data from trials that used an atypical antipsychotic—either aripiprazole, quetiapine, olanzapine, or risperidone—as augmentation therapy to an antidepressant vs placebo.1 Study participants included adults ages 18 to 65 who experienced an episode of depression and did not respond adequately to at least 1 optimally dosed antidepressant. In most studies, treatment-resistant depression (TRD) was defined as the failure of at least 1 major class of antidepressants. Trial lengths ranged from 4 to 12 weeks.
Six RCTs evaluated the effectiveness of augmentation with aripiprazole (2-20 mg/d) in patients with unipolar depression, with 5 trials demonstrating greater improvement in clinical symptoms with aripiprazole compared to placebo. Augmentation with quetiapine (150-300 mg/d) was evaluated in 5 trials, with all trials showing improvement in depression symptoms; however, in 1 trial the difference in remission rates was not significant, and in another trial significant improvement was seen only at a quetia-pine dose of 300 mg/d. Two trials examining olanzapine found that patients receiving fluoxetine plus olanzapine augmentation demonstrated greater improvement in depression symptoms than did those receiving either agent alone. Three trials examined augmentation with risperidone (0.5-3 mg/d); in all 3, risperidone demonstrated significant improvement in depression symptoms and remission rates compared to placebo.1
This systematic review was limited by small sample size and heterogeneity of antipsychotic dosages in the RCTs included, as well as the lack of a standardized and globally accepted definition of TRD.
Augmentation reduced symptom severity, but dropout rates were high
A 2019 Cochrane review of 10 RCTs (N = 2731) compared 5 strategies, including augmenting treatment with an antipsychotic vs continuing antidepressant monotherapy.2 Participants were adults ages 18 to 74 with unipolar depression who had not responded to a minimum of 4 weeks of antidepressant treatment at a recommended dose. The primary outcome was depressive symptom severity, as measured by the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS; range of 0-60) or the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D; range, 0-52).
Compared with continued antidepressant monotherapy, symptom severity was reduced when current treatment was augmented with cariprazine 1-4.5 mg/d (1 trial; N = 808; mean difference [MD] on MADRS = –1.5; 95% CI, –2.7 to –0.25; high-quality evidence); quetiapine 150-300 mg/d (3 trials; N = 977; standardized MD = –0.32; 95% CI, –0.46 to –0.18; high-quality evidence); ziprasidone 40-160 mg/d (2 trials; N = 199; MD on HAM-D = –2.7; 95% CI, –4.5 to –0.93; moderate-quality evidence); or olanzapine 5-20 mg/d (1 trial; N = 20; MD on MADRS = –12; 95% CI, –22 to –2.4; low-quality evidence). One trial did not show a significant difference on the HAM-D for olanzapine (1 trial; N = 20; MD = –7.9; 95% CI, –17 to 0.96; low-quality evidence).2
Dropout rates, which were most commonly secondary to adverse effects, ranged from 10% to 39% in the groups augmented with an antipsychotic and from 12% to 23% in the comparison groups.2 This systematic review was limited by the small number of studies included in the various comparisons.
Antipsychotic augmentation was effective but came with adverse effects
A 2017 RCT (N = 1522) examined the effectiveness of augmenting an antidepressant with aripiprazole in patients with TRD.3 Participants were adults (mean age, 54.4 years; 85% men) at 35 US Veterans Health Administration (VA) medical centers who had a diagnosis of nonpsychotic major depressive disorder that was unresponsive to at least 1 antidepressant course meeting minimal standards for treatment dose and duration.
Continue to: Patients were randomly...
Patients were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 different treatment groups, which included switching to a different antidepressant (bupropion sustained release 150-500 mg/d); augmenting current treatment with bupropion; or augmenting with an atypical antipsychotic (aripiprazole 2-15 mg/d) for 12 to 36 weeks. The primary outcome was remission rate at 12 weeks, which was defined as a score ≤ 5 on the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Clinician Rated (QIDS-C; range, 0-27) at 2 consecutive visits. The secondary outcome, symptom response to treatment, was defined as ≥ 50% reduction on QIDS-C score.
The augment-aripiprazole group (N = 146) exceeded the switch group (N = 114) in remission rate (absolute remission rates = 28.9% vs 22.3%; relative risk [RR] = 1.3; 95% CI, 1.1-1.6; number needed to treat [NNT] = 15), but had similar remission rates to the augment-bupropion group (N = 136; absolute remission rate = 26.9%; RR = 1.1; 95% CI, 0.88-1.3). Symptom response in the augment-aripiprazole group (74.3%) was higher than in either the switch group (62.4%; RR = 1.19; 95% CI, 1.09-1.29; NNT = 8) or the augment-bupropion group (65.6%; RR = 1.13; 95% CI, 1.0-1.2; NNT = 11). There was no difference noted in response rate between the switch group and the augment-bupropion group (RR = 1.05; 95% CI, 0.96-1.15).3
The adverse events that occurred more often in the augment-aripiprazole group than in the other groups included weight gain ≥ 7% (25% at 36 weeks) and extrapyramidal symptoms (19%).3 Limitations of the study included the evaluation of only 1 antipsychotic and 1 antidepressant, the dropout rate (only 75% of patients completed the 12-week follow-up), and the homogeneity of the patient population (older, male, veterans), all of which may limit the effect size.
Editor’s takeaway
Multiple trials show that adjunctive antipsychotic medications such as aripiprazole and quetiapine more effectively treat resistant depression than adding a placebo, increasing antidepressant dosage, switching to a different antidepressant, or adding another antidepressant. However, while primary care physicians should be comfortable with this option, the magnitude of difference between these options was modest, and adverse effects were common. All options can still be reasonably considered.
1. Cantù F, Ciappolino V, Enrico P, et al. Augmentation with atypical antipsychotics for treatment-resistant depression. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(pt A):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.11.006
2. Davies P, Ijaz S, Williams CJ, et al. Pharmacological interventions for treatment-resistant depression in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;12:CD010557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010557.pub2
3. Mohamed S, Johnson GR, Chen P, et al. Effect of antidepressant switching vs augmentation on remission among patients with major depressive disorder unresponsive to antidepressant treatment: the VAST-D randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:132-145. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.8036
Evidence summary
Depression symptoms improved with any of 4 antipsychotics
A 2021 systematic review of 16 RCTs (N = 3649) assessed data from trials that used an atypical antipsychotic—either aripiprazole, quetiapine, olanzapine, or risperidone—as augmentation therapy to an antidepressant vs placebo.1 Study participants included adults ages 18 to 65 who experienced an episode of depression and did not respond adequately to at least 1 optimally dosed antidepressant. In most studies, treatment-resistant depression (TRD) was defined as the failure of at least 1 major class of antidepressants. Trial lengths ranged from 4 to 12 weeks.
Six RCTs evaluated the effectiveness of augmentation with aripiprazole (2-20 mg/d) in patients with unipolar depression, with 5 trials demonstrating greater improvement in clinical symptoms with aripiprazole compared to placebo. Augmentation with quetiapine (150-300 mg/d) was evaluated in 5 trials, with all trials showing improvement in depression symptoms; however, in 1 trial the difference in remission rates was not significant, and in another trial significant improvement was seen only at a quetia-pine dose of 300 mg/d. Two trials examining olanzapine found that patients receiving fluoxetine plus olanzapine augmentation demonstrated greater improvement in depression symptoms than did those receiving either agent alone. Three trials examined augmentation with risperidone (0.5-3 mg/d); in all 3, risperidone demonstrated significant improvement in depression symptoms and remission rates compared to placebo.1
This systematic review was limited by small sample size and heterogeneity of antipsychotic dosages in the RCTs included, as well as the lack of a standardized and globally accepted definition of TRD.
Augmentation reduced symptom severity, but dropout rates were high
A 2019 Cochrane review of 10 RCTs (N = 2731) compared 5 strategies, including augmenting treatment with an antipsychotic vs continuing antidepressant monotherapy.2 Participants were adults ages 18 to 74 with unipolar depression who had not responded to a minimum of 4 weeks of antidepressant treatment at a recommended dose. The primary outcome was depressive symptom severity, as measured by the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS; range of 0-60) or the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D; range, 0-52).
Compared with continued antidepressant monotherapy, symptom severity was reduced when current treatment was augmented with cariprazine 1-4.5 mg/d (1 trial; N = 808; mean difference [MD] on MADRS = –1.5; 95% CI, –2.7 to –0.25; high-quality evidence); quetiapine 150-300 mg/d (3 trials; N = 977; standardized MD = –0.32; 95% CI, –0.46 to –0.18; high-quality evidence); ziprasidone 40-160 mg/d (2 trials; N = 199; MD on HAM-D = –2.7; 95% CI, –4.5 to –0.93; moderate-quality evidence); or olanzapine 5-20 mg/d (1 trial; N = 20; MD on MADRS = –12; 95% CI, –22 to –2.4; low-quality evidence). One trial did not show a significant difference on the HAM-D for olanzapine (1 trial; N = 20; MD = –7.9; 95% CI, –17 to 0.96; low-quality evidence).2
Dropout rates, which were most commonly secondary to adverse effects, ranged from 10% to 39% in the groups augmented with an antipsychotic and from 12% to 23% in the comparison groups.2 This systematic review was limited by the small number of studies included in the various comparisons.
Antipsychotic augmentation was effective but came with adverse effects
A 2017 RCT (N = 1522) examined the effectiveness of augmenting an antidepressant with aripiprazole in patients with TRD.3 Participants were adults (mean age, 54.4 years; 85% men) at 35 US Veterans Health Administration (VA) medical centers who had a diagnosis of nonpsychotic major depressive disorder that was unresponsive to at least 1 antidepressant course meeting minimal standards for treatment dose and duration.
Continue to: Patients were randomly...
Patients were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 different treatment groups, which included switching to a different antidepressant (bupropion sustained release 150-500 mg/d); augmenting current treatment with bupropion; or augmenting with an atypical antipsychotic (aripiprazole 2-15 mg/d) for 12 to 36 weeks. The primary outcome was remission rate at 12 weeks, which was defined as a score ≤ 5 on the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Clinician Rated (QIDS-C; range, 0-27) at 2 consecutive visits. The secondary outcome, symptom response to treatment, was defined as ≥ 50% reduction on QIDS-C score.
The augment-aripiprazole group (N = 146) exceeded the switch group (N = 114) in remission rate (absolute remission rates = 28.9% vs 22.3%; relative risk [RR] = 1.3; 95% CI, 1.1-1.6; number needed to treat [NNT] = 15), but had similar remission rates to the augment-bupropion group (N = 136; absolute remission rate = 26.9%; RR = 1.1; 95% CI, 0.88-1.3). Symptom response in the augment-aripiprazole group (74.3%) was higher than in either the switch group (62.4%; RR = 1.19; 95% CI, 1.09-1.29; NNT = 8) or the augment-bupropion group (65.6%; RR = 1.13; 95% CI, 1.0-1.2; NNT = 11). There was no difference noted in response rate between the switch group and the augment-bupropion group (RR = 1.05; 95% CI, 0.96-1.15).3
The adverse events that occurred more often in the augment-aripiprazole group than in the other groups included weight gain ≥ 7% (25% at 36 weeks) and extrapyramidal symptoms (19%).3 Limitations of the study included the evaluation of only 1 antipsychotic and 1 antidepressant, the dropout rate (only 75% of patients completed the 12-week follow-up), and the homogeneity of the patient population (older, male, veterans), all of which may limit the effect size.
Editor’s takeaway
Multiple trials show that adjunctive antipsychotic medications such as aripiprazole and quetiapine more effectively treat resistant depression than adding a placebo, increasing antidepressant dosage, switching to a different antidepressant, or adding another antidepressant. However, while primary care physicians should be comfortable with this option, the magnitude of difference between these options was modest, and adverse effects were common. All options can still be reasonably considered.
Evidence summary
Depression symptoms improved with any of 4 antipsychotics
A 2021 systematic review of 16 RCTs (N = 3649) assessed data from trials that used an atypical antipsychotic—either aripiprazole, quetiapine, olanzapine, or risperidone—as augmentation therapy to an antidepressant vs placebo.1 Study participants included adults ages 18 to 65 who experienced an episode of depression and did not respond adequately to at least 1 optimally dosed antidepressant. In most studies, treatment-resistant depression (TRD) was defined as the failure of at least 1 major class of antidepressants. Trial lengths ranged from 4 to 12 weeks.
Six RCTs evaluated the effectiveness of augmentation with aripiprazole (2-20 mg/d) in patients with unipolar depression, with 5 trials demonstrating greater improvement in clinical symptoms with aripiprazole compared to placebo. Augmentation with quetiapine (150-300 mg/d) was evaluated in 5 trials, with all trials showing improvement in depression symptoms; however, in 1 trial the difference in remission rates was not significant, and in another trial significant improvement was seen only at a quetia-pine dose of 300 mg/d. Two trials examining olanzapine found that patients receiving fluoxetine plus olanzapine augmentation demonstrated greater improvement in depression symptoms than did those receiving either agent alone. Three trials examined augmentation with risperidone (0.5-3 mg/d); in all 3, risperidone demonstrated significant improvement in depression symptoms and remission rates compared to placebo.1
This systematic review was limited by small sample size and heterogeneity of antipsychotic dosages in the RCTs included, as well as the lack of a standardized and globally accepted definition of TRD.
Augmentation reduced symptom severity, but dropout rates were high
A 2019 Cochrane review of 10 RCTs (N = 2731) compared 5 strategies, including augmenting treatment with an antipsychotic vs continuing antidepressant monotherapy.2 Participants were adults ages 18 to 74 with unipolar depression who had not responded to a minimum of 4 weeks of antidepressant treatment at a recommended dose. The primary outcome was depressive symptom severity, as measured by the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS; range of 0-60) or the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D; range, 0-52).
Compared with continued antidepressant monotherapy, symptom severity was reduced when current treatment was augmented with cariprazine 1-4.5 mg/d (1 trial; N = 808; mean difference [MD] on MADRS = –1.5; 95% CI, –2.7 to –0.25; high-quality evidence); quetiapine 150-300 mg/d (3 trials; N = 977; standardized MD = –0.32; 95% CI, –0.46 to –0.18; high-quality evidence); ziprasidone 40-160 mg/d (2 trials; N = 199; MD on HAM-D = –2.7; 95% CI, –4.5 to –0.93; moderate-quality evidence); or olanzapine 5-20 mg/d (1 trial; N = 20; MD on MADRS = –12; 95% CI, –22 to –2.4; low-quality evidence). One trial did not show a significant difference on the HAM-D for olanzapine (1 trial; N = 20; MD = –7.9; 95% CI, –17 to 0.96; low-quality evidence).2
Dropout rates, which were most commonly secondary to adverse effects, ranged from 10% to 39% in the groups augmented with an antipsychotic and from 12% to 23% in the comparison groups.2 This systematic review was limited by the small number of studies included in the various comparisons.
Antipsychotic augmentation was effective but came with adverse effects
A 2017 RCT (N = 1522) examined the effectiveness of augmenting an antidepressant with aripiprazole in patients with TRD.3 Participants were adults (mean age, 54.4 years; 85% men) at 35 US Veterans Health Administration (VA) medical centers who had a diagnosis of nonpsychotic major depressive disorder that was unresponsive to at least 1 antidepressant course meeting minimal standards for treatment dose and duration.
Continue to: Patients were randomly...
Patients were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 different treatment groups, which included switching to a different antidepressant (bupropion sustained release 150-500 mg/d); augmenting current treatment with bupropion; or augmenting with an atypical antipsychotic (aripiprazole 2-15 mg/d) for 12 to 36 weeks. The primary outcome was remission rate at 12 weeks, which was defined as a score ≤ 5 on the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Clinician Rated (QIDS-C; range, 0-27) at 2 consecutive visits. The secondary outcome, symptom response to treatment, was defined as ≥ 50% reduction on QIDS-C score.
The augment-aripiprazole group (N = 146) exceeded the switch group (N = 114) in remission rate (absolute remission rates = 28.9% vs 22.3%; relative risk [RR] = 1.3; 95% CI, 1.1-1.6; number needed to treat [NNT] = 15), but had similar remission rates to the augment-bupropion group (N = 136; absolute remission rate = 26.9%; RR = 1.1; 95% CI, 0.88-1.3). Symptom response in the augment-aripiprazole group (74.3%) was higher than in either the switch group (62.4%; RR = 1.19; 95% CI, 1.09-1.29; NNT = 8) or the augment-bupropion group (65.6%; RR = 1.13; 95% CI, 1.0-1.2; NNT = 11). There was no difference noted in response rate between the switch group and the augment-bupropion group (RR = 1.05; 95% CI, 0.96-1.15).3
The adverse events that occurred more often in the augment-aripiprazole group than in the other groups included weight gain ≥ 7% (25% at 36 weeks) and extrapyramidal symptoms (19%).3 Limitations of the study included the evaluation of only 1 antipsychotic and 1 antidepressant, the dropout rate (only 75% of patients completed the 12-week follow-up), and the homogeneity of the patient population (older, male, veterans), all of which may limit the effect size.
Editor’s takeaway
Multiple trials show that adjunctive antipsychotic medications such as aripiprazole and quetiapine more effectively treat resistant depression than adding a placebo, increasing antidepressant dosage, switching to a different antidepressant, or adding another antidepressant. However, while primary care physicians should be comfortable with this option, the magnitude of difference between these options was modest, and adverse effects were common. All options can still be reasonably considered.
1. Cantù F, Ciappolino V, Enrico P, et al. Augmentation with atypical antipsychotics for treatment-resistant depression. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(pt A):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.11.006
2. Davies P, Ijaz S, Williams CJ, et al. Pharmacological interventions for treatment-resistant depression in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;12:CD010557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010557.pub2
3. Mohamed S, Johnson GR, Chen P, et al. Effect of antidepressant switching vs augmentation on remission among patients with major depressive disorder unresponsive to antidepressant treatment: the VAST-D randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:132-145. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.8036
1. Cantù F, Ciappolino V, Enrico P, et al. Augmentation with atypical antipsychotics for treatment-resistant depression. J Affect Disord. 2021;280(pt A):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.11.006
2. Davies P, Ijaz S, Williams CJ, et al. Pharmacological interventions for treatment-resistant depression in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;12:CD010557. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010557.pub2
3. Mohamed S, Johnson GR, Chen P, et al. Effect of antidepressant switching vs augmentation on remission among patients with major depressive disorder unresponsive to antidepressant treatment: the VAST-D randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318:132-145. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.8036
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
YES. Augmentation with second- generation antipsychotics, especially aripiprazole and quetiapine, appears to be effective in patients with moderate-to-severe depression who have had a suboptimal response to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor or a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, based on a systematic review of randomized controlled trials [RCTs] and an individual RCT). Augmenting antidepressant therapy with cariprazine, ziprasidone, or olanzapine also appears to improve depressive symptoms over the short term. All antipsychotics studied carried an increased likelihood of adverse effects that could lead to discontinuation (SOR: A, based on a systematic review of RCTs).