User login
Long COVID case study: persistent hormone deficiencies
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A case study of a 65-year-old man in Japan with long COVID describes how he recovered from certain impaired hormone deficiencies that persisted for more than a year.
Days after the patient recovered from respiratory failure and came off a ventilator, he had a sudden drop in blood pressure, which responded to hydrocortisone.
The patient was found to have low levels of growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), hypopituitarism, that persisted for more than a year. He also had low levels of testosterone that remained low at 15 months (the study end).
“An important finding in the present case is the eventual recovery from hypopituitarism over time but not from hypogonadism,” the researchers write in their study published in Endocrine Journal.
, which was confirmed using an insulin tolerance test, Kai Yoshimura, Kakogawa Medical Center, Japan, and colleagues report.
The findings show that “pituitary insufficiency should be considered in patients with prolonged symptoms of COVID-19,” they report, since it can be treated with hormone supplements that markedly improve symptoms and quality of life.
“It might be worthwhile to screen for endocrine dysfunction in patients with such persistent symptoms after their recovery from the acute disease,” the researchers conclude.
Case study timeline
The patient in this study was healthy without obesity, previous endocrine disease, or steroid use. He was admitted to hospital because he had dyspnea and fever for 8 days and a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test that was positive for COVID-19.
He received ciclesonide 200 mcg/day for 2 days. Then he was put on a ventilator and the drug was discontinued and “favipiravir, ritonavir, and lopinavir, a standard regimen during the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, were initiated;” the researchers explain.
On day 25 of his hospital stay the patient had recovered from respiratory failure and was extubated.
On day 31, he had a negative PCR test for COVID-19.
On day 36, the patient’s blood pressure suddenly dropped from 120/80 mmHg to 80/50 mmHg. His plasma ACTH and serum cortisol levels were low, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency. The low blood pressure responded to hydrocortisone 100 mg, which was gradually tapered.
At day 96, the patient was discharged from hospital with a dose of 15 mg/day hydrocortisone.
At 3 months after discharge, an insulin tolerance test revealed that the patient’s ACTH and cortisol responses were blunted, suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The patient also had moderate growth hormone deficiency and symptoms of hypogonadism.
At 6 months after discharge, the patient started testosterone therapy because his dysspermatism had worsened.
At 12 months after discharge, a repeat insulin tolerance test showed that both ACTH and cortisol responses were low but improved. The patient was no longer deficient in growth hormone.
At 15 months after discharge, early morning levels of ACTH and cortisol were now in the normal range. The patient discontinued testosterone treatment, but the symptoms returned, so he resumed it.
Long COVID symptoms, possible biological mechanism
The present case shows how certain COVID-19–associated conditions develop after the onset of, or the recovery from, respiratory disorders, the authors note.
Symptoms of long COVID-19 include fatigue, weakness, hair loss, diarrhea, arthralgia, and depression, and these symptoms are associated with pituitary insufficiency, especially secondary adrenocortical insufficiency.
In addition, an estimated 25% of sexually active men who recover from COVID have semen disorders such as azoospermia and oligospermia.
The underlying mechanism by which COVID-19 might trigger pituitary insufficiency is unknown, but other viral infections such as influenza-A and herpes simplex are also associated with transient hypopituitarism. An exaggerated immune response triggered by SARS-CoV-2 may explain the dysfunction of multiple endocrine organs, the researchers write.
The researchers have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low urate limits for gout questioned in study
Lower limits on serum urate levels applied in gout management may be based on a misreading of data on mortality risks, researchers say.
Low urate levels may not in themselves pose a risk of death but may be a sign of some other illness, said Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“It points us towards being more reassured that we can be aggressive in treating gout without a concern about long-term effects for our patients,” he said in an interview. He and colleagues published their findings online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Previous research has linked high levels of urate with excessive fat and low levels of urate with loss of skeletal muscle mass. And epidemiologic studies have shown a U-shaped relationship between urate levels and mortality, suggesting that very high and very low levels of urate could be harmful.
Based on this correlation, and the theory that urate could have antioxidant benefits, some professional societies have recommended not lowering urate levels below a defined threshold when treating gout. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology has recommended a lower limit of 3 mg/dL.
But the evidence doesn’t entirely support this caution. For example, in a clinical trial of pegloticase (Krystexxa) in patients with refractory gout, patients whose mean serum urate dropped below 2 mg/dL did not die in higher proportions than patients with higher urate levels.
To better understand the risk of low urate, Dr. Baker and colleagues analyzed data on 13,979 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 1999-2006. The dataset included whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measures as well as urate levels.
The researchers argue this measurement reveals more about a person’s overall health than body mass index (BMI), which doesn’t distinguish between mass from fat and mass from muscle.
They defined low lean body mass, or sarcopenia, as an appendicular lean mass index relative to fat mass index z score of –1. And they defined low urate as less than 2.5 mg/dL in women and less than 3.5 mg/dL in men.
They found that 29% of people with low urate had low lean body mass, compared with 16% of people with normal urate levels. The difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
They found an association between low urate and increased mortality (hazard ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-2.28; P = .008). But that association lost its statistical significance when the researchers adjusted for body composition and weight loss (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 0.92-1.85; P = .13).
Dr. Baker thinks the association between elevated mortality and low urate can be explained by conditions such as cancer or lung inflammation that might on one hand increase the risk of death and on the other hand lower urate levels by lowering muscle mass. “Low uric acid levels are observed in people who have lost weight for unhealthy reasons, and that can explain relationships with long-term outcomes,” he said.
Proportions of muscle and fat could not account for the risk of mortality associated with high levels of urate, the researchers found. Those participants with urate levels above 5.7 mg/dL had a higher risk of death with higher levels of urate, and this persisted even after statistical adjustment for body composition.
The study sheds light on an important area of controversy, said Mehdi Fini, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who was not involved in the research.
But body composition does not entirely explain the relationship between urate and mortality, he told this news organization. Medications used to lower urate can cause side effects that might increase mortality, he said.
Also, he said, it’s important to understand the role of comorbidities. He cited evidence that low urate is associated with renal, cardiovascular, and pulmonary conditions. Safe levels of urate might differ depending on these factors. So rather than applying the same target serum level to all patients, perhaps researchers should investigate whether lowering urate by a percentage of the patient’s current level is safer and more effective, he suggested.
He agreed with an editorial that also appeared in Arthritis & Rheumatology saying that there is no evidence for a benefit in lowering urate much below 5 mg/dL. “No matter what, I think we should just be careful,” Dr. Fini said.
Dr. Fini and Dr. Baker report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baker acknowledged support from a VA Clinical Science Research & Development Merit Award and a Rehabilitation R&D Merit Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lower limits on serum urate levels applied in gout management may be based on a misreading of data on mortality risks, researchers say.
Low urate levels may not in themselves pose a risk of death but may be a sign of some other illness, said Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“It points us towards being more reassured that we can be aggressive in treating gout without a concern about long-term effects for our patients,” he said in an interview. He and colleagues published their findings online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Previous research has linked high levels of urate with excessive fat and low levels of urate with loss of skeletal muscle mass. And epidemiologic studies have shown a U-shaped relationship between urate levels and mortality, suggesting that very high and very low levels of urate could be harmful.
Based on this correlation, and the theory that urate could have antioxidant benefits, some professional societies have recommended not lowering urate levels below a defined threshold when treating gout. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology has recommended a lower limit of 3 mg/dL.
But the evidence doesn’t entirely support this caution. For example, in a clinical trial of pegloticase (Krystexxa) in patients with refractory gout, patients whose mean serum urate dropped below 2 mg/dL did not die in higher proportions than patients with higher urate levels.
To better understand the risk of low urate, Dr. Baker and colleagues analyzed data on 13,979 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 1999-2006. The dataset included whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measures as well as urate levels.
The researchers argue this measurement reveals more about a person’s overall health than body mass index (BMI), which doesn’t distinguish between mass from fat and mass from muscle.
They defined low lean body mass, or sarcopenia, as an appendicular lean mass index relative to fat mass index z score of –1. And they defined low urate as less than 2.5 mg/dL in women and less than 3.5 mg/dL in men.
They found that 29% of people with low urate had low lean body mass, compared with 16% of people with normal urate levels. The difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
They found an association between low urate and increased mortality (hazard ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-2.28; P = .008). But that association lost its statistical significance when the researchers adjusted for body composition and weight loss (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 0.92-1.85; P = .13).
Dr. Baker thinks the association between elevated mortality and low urate can be explained by conditions such as cancer or lung inflammation that might on one hand increase the risk of death and on the other hand lower urate levels by lowering muscle mass. “Low uric acid levels are observed in people who have lost weight for unhealthy reasons, and that can explain relationships with long-term outcomes,” he said.
Proportions of muscle and fat could not account for the risk of mortality associated with high levels of urate, the researchers found. Those participants with urate levels above 5.7 mg/dL had a higher risk of death with higher levels of urate, and this persisted even after statistical adjustment for body composition.
The study sheds light on an important area of controversy, said Mehdi Fini, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who was not involved in the research.
But body composition does not entirely explain the relationship between urate and mortality, he told this news organization. Medications used to lower urate can cause side effects that might increase mortality, he said.
Also, he said, it’s important to understand the role of comorbidities. He cited evidence that low urate is associated with renal, cardiovascular, and pulmonary conditions. Safe levels of urate might differ depending on these factors. So rather than applying the same target serum level to all patients, perhaps researchers should investigate whether lowering urate by a percentage of the patient’s current level is safer and more effective, he suggested.
He agreed with an editorial that also appeared in Arthritis & Rheumatology saying that there is no evidence for a benefit in lowering urate much below 5 mg/dL. “No matter what, I think we should just be careful,” Dr. Fini said.
Dr. Fini and Dr. Baker report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baker acknowledged support from a VA Clinical Science Research & Development Merit Award and a Rehabilitation R&D Merit Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lower limits on serum urate levels applied in gout management may be based on a misreading of data on mortality risks, researchers say.
Low urate levels may not in themselves pose a risk of death but may be a sign of some other illness, said Joshua F. Baker, MD, MSCE, associate professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“It points us towards being more reassured that we can be aggressive in treating gout without a concern about long-term effects for our patients,” he said in an interview. He and colleagues published their findings online in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
Previous research has linked high levels of urate with excessive fat and low levels of urate with loss of skeletal muscle mass. And epidemiologic studies have shown a U-shaped relationship between urate levels and mortality, suggesting that very high and very low levels of urate could be harmful.
Based on this correlation, and the theory that urate could have antioxidant benefits, some professional societies have recommended not lowering urate levels below a defined threshold when treating gout. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology has recommended a lower limit of 3 mg/dL.
But the evidence doesn’t entirely support this caution. For example, in a clinical trial of pegloticase (Krystexxa) in patients with refractory gout, patients whose mean serum urate dropped below 2 mg/dL did not die in higher proportions than patients with higher urate levels.
To better understand the risk of low urate, Dr. Baker and colleagues analyzed data on 13,979 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) during 1999-2006. The dataset included whole-body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measures as well as urate levels.
The researchers argue this measurement reveals more about a person’s overall health than body mass index (BMI), which doesn’t distinguish between mass from fat and mass from muscle.
They defined low lean body mass, or sarcopenia, as an appendicular lean mass index relative to fat mass index z score of –1. And they defined low urate as less than 2.5 mg/dL in women and less than 3.5 mg/dL in men.
They found that 29% of people with low urate had low lean body mass, compared with 16% of people with normal urate levels. The difference was statistically significant (P = .001).
They found an association between low urate and increased mortality (hazard ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.14-2.28; P = .008). But that association lost its statistical significance when the researchers adjusted for body composition and weight loss (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 0.92-1.85; P = .13).
Dr. Baker thinks the association between elevated mortality and low urate can be explained by conditions such as cancer or lung inflammation that might on one hand increase the risk of death and on the other hand lower urate levels by lowering muscle mass. “Low uric acid levels are observed in people who have lost weight for unhealthy reasons, and that can explain relationships with long-term outcomes,” he said.
Proportions of muscle and fat could not account for the risk of mortality associated with high levels of urate, the researchers found. Those participants with urate levels above 5.7 mg/dL had a higher risk of death with higher levels of urate, and this persisted even after statistical adjustment for body composition.
The study sheds light on an important area of controversy, said Mehdi Fini, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who was not involved in the research.
But body composition does not entirely explain the relationship between urate and mortality, he told this news organization. Medications used to lower urate can cause side effects that might increase mortality, he said.
Also, he said, it’s important to understand the role of comorbidities. He cited evidence that low urate is associated with renal, cardiovascular, and pulmonary conditions. Safe levels of urate might differ depending on these factors. So rather than applying the same target serum level to all patients, perhaps researchers should investigate whether lowering urate by a percentage of the patient’s current level is safer and more effective, he suggested.
He agreed with an editorial that also appeared in Arthritis & Rheumatology saying that there is no evidence for a benefit in lowering urate much below 5 mg/dL. “No matter what, I think we should just be careful,” Dr. Fini said.
Dr. Fini and Dr. Baker report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baker acknowledged support from a VA Clinical Science Research & Development Merit Award and a Rehabilitation R&D Merit Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Large study amplifies evidence of COVID vaccine safety in pregnancy
The research team wrote in the BMJ that their reassuring findings – drawn from a registry of all births in Ontario over an 8-month period – “can inform evidence-based decision-making” about COVID vaccination during pregnancy.
Previous research has found that pregnant patients are at higher risk of severe complications and death if they become infected with COVID and that vaccination before or during pregnancy prevents such outcomes and reduces the risk of newborn infection, noted Jeffrey Ecker, chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
This new study “adds to a growing body of information arguing clearly and reassuringly that vaccination during pregnancy is not associated with complications during pregnancy,” said Dr. Ecker, who was not involved in the new study.
He added that it “should help obstetric providers further reassure those who are hesitant that vaccination is safe and best both for the pregnant patient and their pregnancy.”
Methods and results
For the new study, researchers tapped a provincial registry of all live and stillborn infants with a gestational age of at least 20 weeks or birth weight of at least 500 g. Unique health card numbers were used to link birth records to a database of COVID vaccinations.
Of 85,162 infants born from May through December of 2021, 43,099 (50.6%) were born to individuals who received at least one vaccine dose during pregnancy. Among those, 99.7% received an mRNA vaccine such as Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna.
Vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with greater risk of overall preterm birth (6.5% among vaccinated individuals versus 6.9% among unvaccinated; hazard ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.96-1.08), spontaneous preterm birth (3.7% versus 4.4%; hazard ratio, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.90-1.03) or very preterm birth (0.59% versus 0.89%; hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95).
Likewise, no increase was observed in the risk of an infant being small for gestational age at birth (9.1% versus 9.2%; hazard ratio, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.93-1.03).
The researchers observed a reduction in the risk of stillbirth, even after adjusting for potential confounders. Stillbirths occurred in 0.25% of vaccinated individuals, compared with 0.44% of unvaccinated individuals (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.51-0.84).
A reduced risk of stillbirth – albeit to a smaller degree – was also found in a Scandinavian registry study that included 28,506 babies born to individuals who were vaccinated during pregnancy.
“Collectively, the findings from these two studies are reassuring and are consistent with no increased risk of stillbirth after COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy. In contrast, COVID-19 disease during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth,” the researchers wrote.
Findings did not vary by which mRNA vaccine a mother received, the number of doses she received, or the trimester in which a vaccine was given, the researchers reported.
Stillbirth findings will be ‘very reassuring’ for patients
The lead investigator, Deshayne Fell, PhD, said in an interview, the fact that the study comprised the entire population of pregnant people in Ontario during the study period “increases our confidence” about the validity and relevance of the findings for other geographic settings.
Dr. Fell, an associate professor in epidemiology and public health at the University of Ottawa and a scientist at the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, Ottawa, said the evaluation of stillbirth in particular, “a rare but devastating outcome,” will be “very reassuring and useful for clinical counseling.”
A limitation cited by the research team included a lack of data on vaccination prior to pregnancy.
In the new study, Dr, Ecker said, “Though the investigators were able to adjust for many variables they cannot be certain that some unmeasured variable that, accordingly, was not adjusted for does not hide a small risk. This seems very unlikely, however.”
The Canadian research team said similar studies of non-mRNA COVID vaccines “should be a research priority.” However, such studies are not underway in Canada, where only mRNA vaccines are used in pregnancy, Dr. Fell said.
This study was supported by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Dr. Fell and Dr. Ecker reported no competing financial interests.
The research team wrote in the BMJ that their reassuring findings – drawn from a registry of all births in Ontario over an 8-month period – “can inform evidence-based decision-making” about COVID vaccination during pregnancy.
Previous research has found that pregnant patients are at higher risk of severe complications and death if they become infected with COVID and that vaccination before or during pregnancy prevents such outcomes and reduces the risk of newborn infection, noted Jeffrey Ecker, chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
This new study “adds to a growing body of information arguing clearly and reassuringly that vaccination during pregnancy is not associated with complications during pregnancy,” said Dr. Ecker, who was not involved in the new study.
He added that it “should help obstetric providers further reassure those who are hesitant that vaccination is safe and best both for the pregnant patient and their pregnancy.”
Methods and results
For the new study, researchers tapped a provincial registry of all live and stillborn infants with a gestational age of at least 20 weeks or birth weight of at least 500 g. Unique health card numbers were used to link birth records to a database of COVID vaccinations.
Of 85,162 infants born from May through December of 2021, 43,099 (50.6%) were born to individuals who received at least one vaccine dose during pregnancy. Among those, 99.7% received an mRNA vaccine such as Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna.
Vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with greater risk of overall preterm birth (6.5% among vaccinated individuals versus 6.9% among unvaccinated; hazard ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.96-1.08), spontaneous preterm birth (3.7% versus 4.4%; hazard ratio, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.90-1.03) or very preterm birth (0.59% versus 0.89%; hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95).
Likewise, no increase was observed in the risk of an infant being small for gestational age at birth (9.1% versus 9.2%; hazard ratio, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.93-1.03).
The researchers observed a reduction in the risk of stillbirth, even after adjusting for potential confounders. Stillbirths occurred in 0.25% of vaccinated individuals, compared with 0.44% of unvaccinated individuals (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.51-0.84).
A reduced risk of stillbirth – albeit to a smaller degree – was also found in a Scandinavian registry study that included 28,506 babies born to individuals who were vaccinated during pregnancy.
“Collectively, the findings from these two studies are reassuring and are consistent with no increased risk of stillbirth after COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy. In contrast, COVID-19 disease during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth,” the researchers wrote.
Findings did not vary by which mRNA vaccine a mother received, the number of doses she received, or the trimester in which a vaccine was given, the researchers reported.
Stillbirth findings will be ‘very reassuring’ for patients
The lead investigator, Deshayne Fell, PhD, said in an interview, the fact that the study comprised the entire population of pregnant people in Ontario during the study period “increases our confidence” about the validity and relevance of the findings for other geographic settings.
Dr. Fell, an associate professor in epidemiology and public health at the University of Ottawa and a scientist at the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, Ottawa, said the evaluation of stillbirth in particular, “a rare but devastating outcome,” will be “very reassuring and useful for clinical counseling.”
A limitation cited by the research team included a lack of data on vaccination prior to pregnancy.
In the new study, Dr, Ecker said, “Though the investigators were able to adjust for many variables they cannot be certain that some unmeasured variable that, accordingly, was not adjusted for does not hide a small risk. This seems very unlikely, however.”
The Canadian research team said similar studies of non-mRNA COVID vaccines “should be a research priority.” However, such studies are not underway in Canada, where only mRNA vaccines are used in pregnancy, Dr. Fell said.
This study was supported by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Dr. Fell and Dr. Ecker reported no competing financial interests.
The research team wrote in the BMJ that their reassuring findings – drawn from a registry of all births in Ontario over an 8-month period – “can inform evidence-based decision-making” about COVID vaccination during pregnancy.
Previous research has found that pregnant patients are at higher risk of severe complications and death if they become infected with COVID and that vaccination before or during pregnancy prevents such outcomes and reduces the risk of newborn infection, noted Jeffrey Ecker, chief of obstetrics and gynecology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
This new study “adds to a growing body of information arguing clearly and reassuringly that vaccination during pregnancy is not associated with complications during pregnancy,” said Dr. Ecker, who was not involved in the new study.
He added that it “should help obstetric providers further reassure those who are hesitant that vaccination is safe and best both for the pregnant patient and their pregnancy.”
Methods and results
For the new study, researchers tapped a provincial registry of all live and stillborn infants with a gestational age of at least 20 weeks or birth weight of at least 500 g. Unique health card numbers were used to link birth records to a database of COVID vaccinations.
Of 85,162 infants born from May through December of 2021, 43,099 (50.6%) were born to individuals who received at least one vaccine dose during pregnancy. Among those, 99.7% received an mRNA vaccine such as Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna.
Vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with greater risk of overall preterm birth (6.5% among vaccinated individuals versus 6.9% among unvaccinated; hazard ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.96-1.08), spontaneous preterm birth (3.7% versus 4.4%; hazard ratio, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.90-1.03) or very preterm birth (0.59% versus 0.89%; hazard ratio, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.67-0.95).
Likewise, no increase was observed in the risk of an infant being small for gestational age at birth (9.1% versus 9.2%; hazard ratio, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.93-1.03).
The researchers observed a reduction in the risk of stillbirth, even after adjusting for potential confounders. Stillbirths occurred in 0.25% of vaccinated individuals, compared with 0.44% of unvaccinated individuals (hazard ratio, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.51-0.84).
A reduced risk of stillbirth – albeit to a smaller degree – was also found in a Scandinavian registry study that included 28,506 babies born to individuals who were vaccinated during pregnancy.
“Collectively, the findings from these two studies are reassuring and are consistent with no increased risk of stillbirth after COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy. In contrast, COVID-19 disease during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of stillbirth,” the researchers wrote.
Findings did not vary by which mRNA vaccine a mother received, the number of doses she received, or the trimester in which a vaccine was given, the researchers reported.
Stillbirth findings will be ‘very reassuring’ for patients
The lead investigator, Deshayne Fell, PhD, said in an interview, the fact that the study comprised the entire population of pregnant people in Ontario during the study period “increases our confidence” about the validity and relevance of the findings for other geographic settings.
Dr. Fell, an associate professor in epidemiology and public health at the University of Ottawa and a scientist at the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, Ottawa, said the evaluation of stillbirth in particular, “a rare but devastating outcome,” will be “very reassuring and useful for clinical counseling.”
A limitation cited by the research team included a lack of data on vaccination prior to pregnancy.
In the new study, Dr, Ecker said, “Though the investigators were able to adjust for many variables they cannot be certain that some unmeasured variable that, accordingly, was not adjusted for does not hide a small risk. This seems very unlikely, however.”
The Canadian research team said similar studies of non-mRNA COVID vaccines “should be a research priority.” However, such studies are not underway in Canada, where only mRNA vaccines are used in pregnancy, Dr. Fell said.
This study was supported by the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Dr. Fell and Dr. Ecker reported no competing financial interests.
FROM BMJ
Exercise limitations in COPD – not everyone needs more inhalers
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is defined by airway obstruction and alveolar damage caused by exposure to noxious air particles. The physiologic results include varying degrees of gas-exchange abnormality and mechanical respiratory limitation, often in the form of dynamic hyperinflation. There’s a third major contributor, though – skeletal muscle deconditioning. Only one of these abnormalities responds to inhalers.
When your patients with COPD report dyspnea or exercise intolerance, what do you do? Do you attempt to determine its character to pinpoint its origin? Do you quiz them about their baseline activity levels to quantify their conditioning? I bet you get right to the point and order a cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET). That way you’ll be able to tease out all the contributors. Nah. Most likely you add an inhaler before continuing to rush through your COPD quality metrics: Vaccines? Check. Lung cancer screening? Check. Smoking cessation? Check.
The physiology of dyspnea and exercise limitation in COPD has been extensively studied. Work-of-breathing, dynamic hyperinflation, and gas-exchange inefficiencies interact with each other in complex ways to produce symptoms. The presence of deconditioning simply magnifies the existing abnormalities within the respiratory system by creating more strain at lower work rates. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) and oral corticosteroids further aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction.
The Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) Report directs clinicians to use inhalers to manage dyspnea. If they’re already on one inhaler, they get another. This continues until they’re stabilized on a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS). The GOLD report also advises pulmonary rehabilitation for any patient with grade B through D disease. Unfortunately, the pulmonary rehabilitation recommendation is buried in the text and doesn’t appear within the popularized pharmacologic algorithms in the report’s figures.
The data for adding inhalers on top of each other to reduce AECOPD and improve overall quality of life (QOL) are good. However, although GOLD tells us to keep adding inhalers for the dyspneic patient with COPD, the authors acknowledge that this hasn’t been systematically tested. The difference? A statement doesn’t require the same formal, rigorous scientific analysis known as the GRADE approach. Using this kind of analysis, a recent clinical practice guideline by the American Thoracic Society found no benefit in dyspnea or respiratory QOL with step-up from inhaler monotherapy.
Inhalers won’t do anything for gas-exchange inefficiencies and deconditioning, at least not directly. A recent CPET study from the CanCOLD network found ventilatory inefficiency in 23% of GOLD 1 and 26% of GOLD 2-4 COPD patients. The numbers were higher for those who reported dyspnea. Skeletal muscle dysfunction rates are equally high.
Thus, dyspnea and exercise intolerance are major determinants of QOL in COPD, but inhalers will only get you so far. At a minimum, make sure you get an activity/exercise history from your patients with COPD. For those who are sedentary, provide an exercise prescription (really, it’s not that hard to do). If dyspnea persists despite LABA or LAMA monotherapy, clarify the complaint before doubling down. Finally, try to get the patient into a good pulmonary rehabilitation program. They’ll thank you afterwards.
Dr. Holley is Associate Professor, department of medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and Program Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Fellowship, department of medicine, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, both in Bethesda, Md. He reported receiving research grants from Fisher-Paykel and receiving income from the American College of Chest Physicians.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
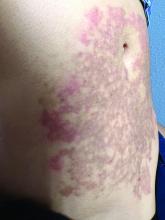
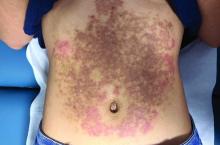
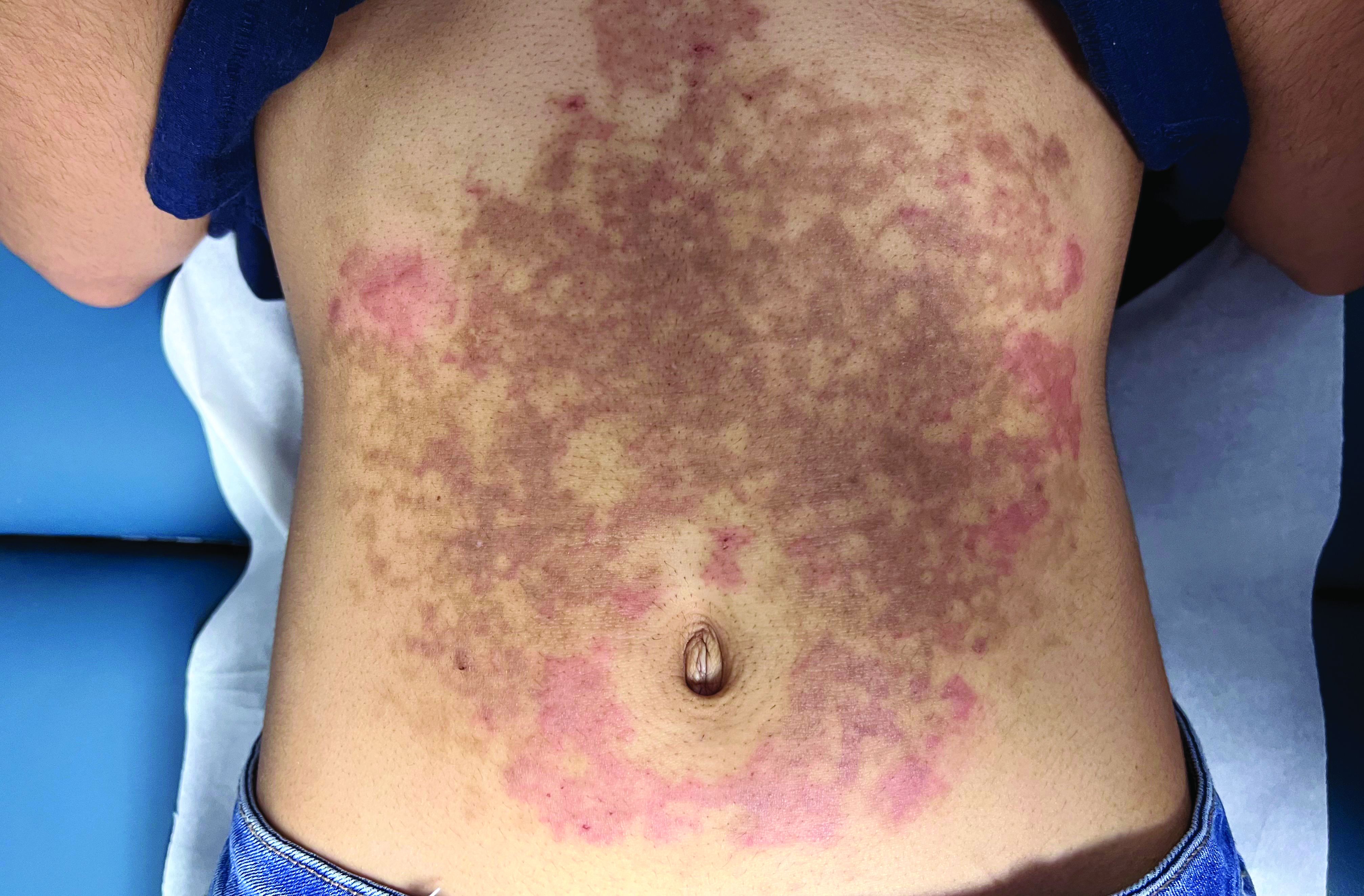
A White female presented with pruritic, reticulated, erythematous plaques on the abdomen
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
Real-world study shows subcutaneous vedolizumab effective for maintenance in IBD
Switching from intravenous to subcutaneous vedolizumab for maintenance treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases appears to be effective, according to a study providing real-world data.
Subcutaneous treatment could reduce direct health care costs because no infusion equipment is necessary, as well as societal costs because patients don’t need to take time off work or travel to infusion locations, wrote the researchers, led by Adriaan Volkers, MD, a doctoral candidate in gastroenterology and hepatology at the Amsterdam Gastroenterology Endocrinology Metabolism Research Institute at the University of Amsterdam in The Netherlands.
“The option of a SC formulation of VDZ [vedolizumab] offers patients a choice regarding the route of administration,” they wrote. The study was published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Dr. Volkers and colleagues assessed the effectiveness, safety, drug discontinuation, and pharmacokinetics of a switch from intravenous to subcutaneous maintenance vedolizumab in a prospective real-world cohort of patients from two separate studies in The Netherlands between July 2020 and November 2021.
The cohort comprised 135 adults who had greater than 4 months of IV vedolizumab: 82 patients with Crohn’s disease and 53 with ulcerative colitis. Prospective follow-up took place during scheduled outpatient clinic visits at weeks 12 and 24 after switching administration. Patients received 108 mg of subcutaneous vedolizumab once every 2 weeks.
Overall, 16 patients (11.9%) discontinued subcutaneous administration, including 11 patients (13.4%) with Crohn’s disease who stopped after a median of 18 weeks, as well as 5 patients (9.4%) with ulcerative colitis who stopped after a median of 6 weeks. Four patients, who all had Crohn’s disease, discontinued vedolizumab and switched to a different treatment because of loss of response. Nine patients switched back to IV administration because of adverse events, and three switched back because of fear of needles.
In total, there were 59 adverse events and 13 infections that were possibly or probably related to subcutaneous injection among 42 patients. The most common adverse events that were probably related were injection site reactions such as pain or swelling, reported among 15 patients, and headaches, reported among 6 patients.
At the initiation of therapy, 57 of 81 Crohn’s disease patients (70.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 53 of 80 (66.3%) were in biochemical remission, which was defined as C-reactive protein levels of 5 mg/L or less and fecal calprotectin levels of 250 mcg/g or less. For ulcerative colitis patients, 35 of 49 (71.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 41 of 51 (80.4%) were in biochemical remission. Median clinical and biochemical disease levels remained stable after the switch to subcutaneous treatment and weren’t significantly different, compared with baseline measurements.
Median vedolizumab serum concentrations increased from 19 mcg/mL at the time of the switch to 31 mcg/mL at 12 weeks after the switch and 37 mcg/mL at 24 weeks. Serum concentrations of less than 25 mcg/mL were associated with lower rates of corticosteroid-free clinical remission, and serum concentrations of greater than 40 mcg/mL were associated with higher biochemical remission rates.
Importantly, there was no association between vedolizumab serum concentrations and the risk of adverse events that were deemed probably related to subcutaneous injection or infections.
“The most important point to understand here is that SC VDZ can be used to maintain clinical remission after IV VDZ induction in a real-world setting,” said Brian DeBosch, MD, PhD, associate professor of cell biology and physiology at Washington University, St. Louis.
Dr. DeBosch, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that previous data have indicated that switching from intravenous to subcutaneous treatment after a 6-week induction is superior to placebo in maintaining clinical and biochemical remission. However, studies haven’t quantified the optimal timing and therapeutic efficacy of switching.
“This is critical to quantify because SC VDZ has slower and lower peak bioavailability when compared with IV administration,” he said. “These data indicate that IV induction overcomes the known pharmacokinetic limitations of SC VDZ during the induction phase.”
However, there are still some limitations and areas for future research around switching administration, Dr. DeBosch noted.
“A key comparison lacking in the study is the mean and trough serum VDZ, and proportion of patients with relapsing disease in patients on continued IV VDZ,” he said. “Yet, these data nevertheless indicate that tandem IV-SC drug administration can maximize the induction and maintenance of remission in IBD, while also mitigating some of the barriers associated with long-term, continued IV VDZ administration.”
The study authors reported advisory fees and speaker fees from several pharmaceutical companies, and some authors have received funding or served on advisory boards for Takeda Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures vedolizumab. Dr. DeBosch reported no relevant disclosures.
Switching from intravenous to subcutaneous vedolizumab for maintenance treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases appears to be effective, according to a study providing real-world data.
Subcutaneous treatment could reduce direct health care costs because no infusion equipment is necessary, as well as societal costs because patients don’t need to take time off work or travel to infusion locations, wrote the researchers, led by Adriaan Volkers, MD, a doctoral candidate in gastroenterology and hepatology at the Amsterdam Gastroenterology Endocrinology Metabolism Research Institute at the University of Amsterdam in The Netherlands.
“The option of a SC formulation of VDZ [vedolizumab] offers patients a choice regarding the route of administration,” they wrote. The study was published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Dr. Volkers and colleagues assessed the effectiveness, safety, drug discontinuation, and pharmacokinetics of a switch from intravenous to subcutaneous maintenance vedolizumab in a prospective real-world cohort of patients from two separate studies in The Netherlands between July 2020 and November 2021.
The cohort comprised 135 adults who had greater than 4 months of IV vedolizumab: 82 patients with Crohn’s disease and 53 with ulcerative colitis. Prospective follow-up took place during scheduled outpatient clinic visits at weeks 12 and 24 after switching administration. Patients received 108 mg of subcutaneous vedolizumab once every 2 weeks.
Overall, 16 patients (11.9%) discontinued subcutaneous administration, including 11 patients (13.4%) with Crohn’s disease who stopped after a median of 18 weeks, as well as 5 patients (9.4%) with ulcerative colitis who stopped after a median of 6 weeks. Four patients, who all had Crohn’s disease, discontinued vedolizumab and switched to a different treatment because of loss of response. Nine patients switched back to IV administration because of adverse events, and three switched back because of fear of needles.
In total, there were 59 adverse events and 13 infections that were possibly or probably related to subcutaneous injection among 42 patients. The most common adverse events that were probably related were injection site reactions such as pain or swelling, reported among 15 patients, and headaches, reported among 6 patients.
At the initiation of therapy, 57 of 81 Crohn’s disease patients (70.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 53 of 80 (66.3%) were in biochemical remission, which was defined as C-reactive protein levels of 5 mg/L or less and fecal calprotectin levels of 250 mcg/g or less. For ulcerative colitis patients, 35 of 49 (71.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 41 of 51 (80.4%) were in biochemical remission. Median clinical and biochemical disease levels remained stable after the switch to subcutaneous treatment and weren’t significantly different, compared with baseline measurements.
Median vedolizumab serum concentrations increased from 19 mcg/mL at the time of the switch to 31 mcg/mL at 12 weeks after the switch and 37 mcg/mL at 24 weeks. Serum concentrations of less than 25 mcg/mL were associated with lower rates of corticosteroid-free clinical remission, and serum concentrations of greater than 40 mcg/mL were associated with higher biochemical remission rates.
Importantly, there was no association between vedolizumab serum concentrations and the risk of adverse events that were deemed probably related to subcutaneous injection or infections.
“The most important point to understand here is that SC VDZ can be used to maintain clinical remission after IV VDZ induction in a real-world setting,” said Brian DeBosch, MD, PhD, associate professor of cell biology and physiology at Washington University, St. Louis.
Dr. DeBosch, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that previous data have indicated that switching from intravenous to subcutaneous treatment after a 6-week induction is superior to placebo in maintaining clinical and biochemical remission. However, studies haven’t quantified the optimal timing and therapeutic efficacy of switching.
“This is critical to quantify because SC VDZ has slower and lower peak bioavailability when compared with IV administration,” he said. “These data indicate that IV induction overcomes the known pharmacokinetic limitations of SC VDZ during the induction phase.”
However, there are still some limitations and areas for future research around switching administration, Dr. DeBosch noted.
“A key comparison lacking in the study is the mean and trough serum VDZ, and proportion of patients with relapsing disease in patients on continued IV VDZ,” he said. “Yet, these data nevertheless indicate that tandem IV-SC drug administration can maximize the induction and maintenance of remission in IBD, while also mitigating some of the barriers associated with long-term, continued IV VDZ administration.”
The study authors reported advisory fees and speaker fees from several pharmaceutical companies, and some authors have received funding or served on advisory boards for Takeda Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures vedolizumab. Dr. DeBosch reported no relevant disclosures.
Switching from intravenous to subcutaneous vedolizumab for maintenance treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases appears to be effective, according to a study providing real-world data.
Subcutaneous treatment could reduce direct health care costs because no infusion equipment is necessary, as well as societal costs because patients don’t need to take time off work or travel to infusion locations, wrote the researchers, led by Adriaan Volkers, MD, a doctoral candidate in gastroenterology and hepatology at the Amsterdam Gastroenterology Endocrinology Metabolism Research Institute at the University of Amsterdam in The Netherlands.
“The option of a SC formulation of VDZ [vedolizumab] offers patients a choice regarding the route of administration,” they wrote. The study was published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Dr. Volkers and colleagues assessed the effectiveness, safety, drug discontinuation, and pharmacokinetics of a switch from intravenous to subcutaneous maintenance vedolizumab in a prospective real-world cohort of patients from two separate studies in The Netherlands between July 2020 and November 2021.
The cohort comprised 135 adults who had greater than 4 months of IV vedolizumab: 82 patients with Crohn’s disease and 53 with ulcerative colitis. Prospective follow-up took place during scheduled outpatient clinic visits at weeks 12 and 24 after switching administration. Patients received 108 mg of subcutaneous vedolizumab once every 2 weeks.
Overall, 16 patients (11.9%) discontinued subcutaneous administration, including 11 patients (13.4%) with Crohn’s disease who stopped after a median of 18 weeks, as well as 5 patients (9.4%) with ulcerative colitis who stopped after a median of 6 weeks. Four patients, who all had Crohn’s disease, discontinued vedolizumab and switched to a different treatment because of loss of response. Nine patients switched back to IV administration because of adverse events, and three switched back because of fear of needles.
In total, there were 59 adverse events and 13 infections that were possibly or probably related to subcutaneous injection among 42 patients. The most common adverse events that were probably related were injection site reactions such as pain or swelling, reported among 15 patients, and headaches, reported among 6 patients.
At the initiation of therapy, 57 of 81 Crohn’s disease patients (70.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 53 of 80 (66.3%) were in biochemical remission, which was defined as C-reactive protein levels of 5 mg/L or less and fecal calprotectin levels of 250 mcg/g or less. For ulcerative colitis patients, 35 of 49 (71.4%) were in corticosteroid-free clinical remission and 41 of 51 (80.4%) were in biochemical remission. Median clinical and biochemical disease levels remained stable after the switch to subcutaneous treatment and weren’t significantly different, compared with baseline measurements.
Median vedolizumab serum concentrations increased from 19 mcg/mL at the time of the switch to 31 mcg/mL at 12 weeks after the switch and 37 mcg/mL at 24 weeks. Serum concentrations of less than 25 mcg/mL were associated with lower rates of corticosteroid-free clinical remission, and serum concentrations of greater than 40 mcg/mL were associated with higher biochemical remission rates.
Importantly, there was no association between vedolizumab serum concentrations and the risk of adverse events that were deemed probably related to subcutaneous injection or infections.
“The most important point to understand here is that SC VDZ can be used to maintain clinical remission after IV VDZ induction in a real-world setting,” said Brian DeBosch, MD, PhD, associate professor of cell biology and physiology at Washington University, St. Louis.
Dr. DeBosch, who wasn’t involved with this study, noted that previous data have indicated that switching from intravenous to subcutaneous treatment after a 6-week induction is superior to placebo in maintaining clinical and biochemical remission. However, studies haven’t quantified the optimal timing and therapeutic efficacy of switching.
“This is critical to quantify because SC VDZ has slower and lower peak bioavailability when compared with IV administration,” he said. “These data indicate that IV induction overcomes the known pharmacokinetic limitations of SC VDZ during the induction phase.”
However, there are still some limitations and areas for future research around switching administration, Dr. DeBosch noted.
“A key comparison lacking in the study is the mean and trough serum VDZ, and proportion of patients with relapsing disease in patients on continued IV VDZ,” he said. “Yet, these data nevertheless indicate that tandem IV-SC drug administration can maximize the induction and maintenance of remission in IBD, while also mitigating some of the barriers associated with long-term, continued IV VDZ administration.”
The study authors reported advisory fees and speaker fees from several pharmaceutical companies, and some authors have received funding or served on advisory boards for Takeda Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures vedolizumab. Dr. DeBosch reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM ALIMENTARY PHARMACOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS
‘Stop pretending’ there’s a magic formula to weight loss
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a diet or weight-loss program out there that doesn’t work for those who stick with it during its first 12 weeks?
Truly, the world’s most backwards, upside-down, anti-science, nonsensical diets work over the short haul, fueled by the fact that short-term suffering for weight loss is a skill set that humanity has assiduously cultivated for at least the past 100 years. We’re really good at it!
It’s the keeping the weight off, though, that’s the hitch. Which leads me to the question, why are medical journals, even preeminent nonpredatory ones, publishing 12-week weight-loss program studies as if they have value? And does anyone truly imagine that after over 100 years of trying, there’ll be a short-term diet or program that’ll have the durable, reproducible results that no other short-term diet or program ever has?
Take this study published by Obesity: “Pragmatic implementation of a fully automated online obesity treatment in primary care.” It details a 12-week online, automated, weight-loss program that led completers to lose the roughly 5% of weight that many diets and programs see lost over their first 12 weeks. By its description, aside from its automated provision, the program sounds like pretty much the same boilerplate weight management advice and recommendations that haven’t been shown to lead large numbers of people to sustain long-term weight loss.
Participants were provided with weekly lessons which no doubt in some manner told them that high-calorie foods had high numbers of calories and should be minimized, along with other weight-loss secrets. Users were to upload weekly self-monitored weight, energy intake, and exercise minutes and were told to use a food diary. Their goal was losing 10% of their body weight by consuming 1,200-1,500 calories per day if they weighed less than 250 pounds (113 kg) and 1,500-1,800 calories if they weighed more than 250 pounds, while also telling them to aim for 200 minutes per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity.
What was found was wholly unsurprising. Perhaps speaking to the tremendous and wide-ranging degrees of privilege that are required to prioritize intentional behavior change in the name of health, 79% of those who were given a prescription for the program either didn’t start it or stopped it before the end of the first week.
Of those who actually started the program and completed more than 1 week, despite having been selected as appropriate and interested participants by their physicians, only 20% watched all of the automated programs’ video lessons while only 32% actually bothered to submit all 12 weeks of weight data. Of course, the authors found that those who watched the greatest number of videos and submitted the most self-reported weights lost more weight and ascribed that loss to the program. What the authors did not entertain was the possibility that those who weren’t losing weight, or who were gaining, might simply be less inclined to continue with a program that wasn’t leading them to their desired outcomes or to want to submit their lack of loss or gains.
Short-term weight-loss studies help no one and when, as in this case, the outcomes aren’t even mediocre, and the completion and engagement rates are terrible, the study is still presented as significant and important. This bolsters the harmful stereotype that weight management is achievable by way of simple messages and generic goals. It suggests that it’s individuals who fail programs by not trying hard enough and that those who do, or who want it the most, will succeed. It may also lead patients and clinicians to second-guess the use of antiobesity medications, the current generation of which lead to far greater weight loss and reproducibility than any behavioral program or diet ever has.
The good news here at least is that the small percentage of participants who made it through this program’s 12 weeks are being randomly assigned to differing 9-month maintenance programs which at least will then lead to a 1-year analysis on the completers.
Why this study was published now, rather than pushed until the 1-year data were available, speaks to the pervasiveness of the toxic weight-biased notion that simple education will overcome the physiology forged over millions of years of extreme dietary insecurity.
Our food environment is a veritable floodplain of hyperpalatable foods, and social determinants of health make intentional behavior change in the name of health an unattainable luxury for a huge swath of the population.
Dr. Freedhoff is an associate professor of family medicine at the University of Ottawa and medical director of the Bariatric Medical Institute. He reported serving as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Bariatric Medical Institute and Constant Health and receiving research grants from Novo Nordisk. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lung adverse effects in patients taking trastuzumab deruxtecan
although the benefit-to-risk relationship with use of the drug is still positive, say researchers who report a review of early clinical trials with the drug.
T-DXd is a monoclonal antibody that targets HER2. It is approved for use in HER2-positive breast, gastric, and lung cancers.
In the new study, investigators analyzed data from early clinical trials that involved patients with advanced cancers who had been heavily pretreated. They found an incidence of just over 15% for interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis associated with the drug. Most patients (77.4%) had grade 1 or 2 ILD, but 2.2% of patients had grade 5 ILD.
“Interstitial lung disease is a known risk factor in patients treated with antibody conjugates for cancer,” commented lead author Charles Powell, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This adverse effect can lead to lung fibrosis and can become severe, life threatening, and even fatal, the authors warned.
The authors also discussed management of the event, which involves corticosteroids, and recommended that any patient who develops ILD of grade 3 or higher be hospitalized.
Close monitoring and proactive management may reduce the risk of ILD, they suggested.
Indeed, the incidence of this adverse effect was lower in a later phase 3 trial of the drug (10.5% in the DESTINY-Breast03 trial) and that the adverse events were less severe in this patient population (none of these events were of grade 4 or 5).
“Increased knowledge ... and implementation of ILD/pneumonitis monitoring, diagnosis, and management guidelines” may have resulted in this adverse effect being identified early and treated before it progressed, they commented.
ILD is highlighted in a boxed warning on the product label.
The study was published online in ESMO Open.
In their review, the investigators evaluated nine early-stage monotherapy clinical trials (phases 1 and 2) involving a total of 1,150 patients (breast cancer, 44.3%; gastric cancer, 25.6%; lung cancer, 17.7%; colorectal cancer, 9.3%, other cancers, 3.0%).
These patients had advanced cancer and had been heavily pretreated with a median of four prior lines of therapy. They received one or more doses of at least 5.4 mg/kg of T-DXd.
Nearly half of the cohort were treated for more than 6 months. A total of 276 potential ILD/pneumonitis events were sent for adjudication; of those, 85% were adjudicated as ILD/pneumonitis.
The overall incidence of adjudicated ILD/pneumonitis events was 15.4%; most were low-grade events. Some 87% of patients experienced their first ILD event within 12 months of treatment. The median time to experiencing an ILD/pneumonitis event was 5.4 months.
Some of the patients who developed grade 1 ILD/pneumonitis were treated and the adverse event resolved. These patients were then rechallenged with the drug. Only 3 of the 47 rechallenged patients experienced recurrence of ILD/pneumonitis, the authors noted.
“Rechallenge with T-DXd after complete resolution of grade 1 events is possible and warrants further investigation,” they commented. They cautioned, however, that rechallenge is not recommended for all patients, at least not for those with grade 2 or higher ILD/pneumonitis.
Overall, the authors concluded that the “benefit-risk of T-DXd treatment is positive,” but they warned that some patients may be at increased risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis
Baseline factors that increase the risk of developing an ILD/pneumonitis event include the following: being younger than 65 years, receiving a T-DXd dose of more than6.4 mg/kg, having a baseline oxygen saturation level of less than 95%, having moderate to severe renal impairment, and having lung comorbidities. In addition, patients who had initially been diagnosed with cancer more than 4 years before receiving the drug were at higher risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis.
“Using learnings from the early clinical trials experience, physician education and patient management protocols were revised and disseminated by the study sponsors [and] more recent trial data in earlier lines of therapy has demonstrated lower rates of ILD events, suggesting close monitoring and proactive management of ILD/pneumonitis is warranted for all patients,” Dr. Powell said in a statement.
The T-DXd clinical trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Powell has received fees from Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and Voluntis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
although the benefit-to-risk relationship with use of the drug is still positive, say researchers who report a review of early clinical trials with the drug.
T-DXd is a monoclonal antibody that targets HER2. It is approved for use in HER2-positive breast, gastric, and lung cancers.
In the new study, investigators analyzed data from early clinical trials that involved patients with advanced cancers who had been heavily pretreated. They found an incidence of just over 15% for interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis associated with the drug. Most patients (77.4%) had grade 1 or 2 ILD, but 2.2% of patients had grade 5 ILD.
“Interstitial lung disease is a known risk factor in patients treated with antibody conjugates for cancer,” commented lead author Charles Powell, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This adverse effect can lead to lung fibrosis and can become severe, life threatening, and even fatal, the authors warned.
The authors also discussed management of the event, which involves corticosteroids, and recommended that any patient who develops ILD of grade 3 or higher be hospitalized.
Close monitoring and proactive management may reduce the risk of ILD, they suggested.
Indeed, the incidence of this adverse effect was lower in a later phase 3 trial of the drug (10.5% in the DESTINY-Breast03 trial) and that the adverse events were less severe in this patient population (none of these events were of grade 4 or 5).
“Increased knowledge ... and implementation of ILD/pneumonitis monitoring, diagnosis, and management guidelines” may have resulted in this adverse effect being identified early and treated before it progressed, they commented.
ILD is highlighted in a boxed warning on the product label.
The study was published online in ESMO Open.
In their review, the investigators evaluated nine early-stage monotherapy clinical trials (phases 1 and 2) involving a total of 1,150 patients (breast cancer, 44.3%; gastric cancer, 25.6%; lung cancer, 17.7%; colorectal cancer, 9.3%, other cancers, 3.0%).
These patients had advanced cancer and had been heavily pretreated with a median of four prior lines of therapy. They received one or more doses of at least 5.4 mg/kg of T-DXd.
Nearly half of the cohort were treated for more than 6 months. A total of 276 potential ILD/pneumonitis events were sent for adjudication; of those, 85% were adjudicated as ILD/pneumonitis.
The overall incidence of adjudicated ILD/pneumonitis events was 15.4%; most were low-grade events. Some 87% of patients experienced their first ILD event within 12 months of treatment. The median time to experiencing an ILD/pneumonitis event was 5.4 months.
Some of the patients who developed grade 1 ILD/pneumonitis were treated and the adverse event resolved. These patients were then rechallenged with the drug. Only 3 of the 47 rechallenged patients experienced recurrence of ILD/pneumonitis, the authors noted.
“Rechallenge with T-DXd after complete resolution of grade 1 events is possible and warrants further investigation,” they commented. They cautioned, however, that rechallenge is not recommended for all patients, at least not for those with grade 2 or higher ILD/pneumonitis.
Overall, the authors concluded that the “benefit-risk of T-DXd treatment is positive,” but they warned that some patients may be at increased risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis
Baseline factors that increase the risk of developing an ILD/pneumonitis event include the following: being younger than 65 years, receiving a T-DXd dose of more than6.4 mg/kg, having a baseline oxygen saturation level of less than 95%, having moderate to severe renal impairment, and having lung comorbidities. In addition, patients who had initially been diagnosed with cancer more than 4 years before receiving the drug were at higher risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis.
“Using learnings from the early clinical trials experience, physician education and patient management protocols were revised and disseminated by the study sponsors [and] more recent trial data in earlier lines of therapy has demonstrated lower rates of ILD events, suggesting close monitoring and proactive management of ILD/pneumonitis is warranted for all patients,” Dr. Powell said in a statement.
The T-DXd clinical trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Powell has received fees from Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and Voluntis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
although the benefit-to-risk relationship with use of the drug is still positive, say researchers who report a review of early clinical trials with the drug.
T-DXd is a monoclonal antibody that targets HER2. It is approved for use in HER2-positive breast, gastric, and lung cancers.
In the new study, investigators analyzed data from early clinical trials that involved patients with advanced cancers who had been heavily pretreated. They found an incidence of just over 15% for interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis associated with the drug. Most patients (77.4%) had grade 1 or 2 ILD, but 2.2% of patients had grade 5 ILD.
“Interstitial lung disease is a known risk factor in patients treated with antibody conjugates for cancer,” commented lead author Charles Powell, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. This adverse effect can lead to lung fibrosis and can become severe, life threatening, and even fatal, the authors warned.
The authors also discussed management of the event, which involves corticosteroids, and recommended that any patient who develops ILD of grade 3 or higher be hospitalized.
Close monitoring and proactive management may reduce the risk of ILD, they suggested.
Indeed, the incidence of this adverse effect was lower in a later phase 3 trial of the drug (10.5% in the DESTINY-Breast03 trial) and that the adverse events were less severe in this patient population (none of these events were of grade 4 or 5).
“Increased knowledge ... and implementation of ILD/pneumonitis monitoring, diagnosis, and management guidelines” may have resulted in this adverse effect being identified early and treated before it progressed, they commented.
ILD is highlighted in a boxed warning on the product label.
The study was published online in ESMO Open.
In their review, the investigators evaluated nine early-stage monotherapy clinical trials (phases 1 and 2) involving a total of 1,150 patients (breast cancer, 44.3%; gastric cancer, 25.6%; lung cancer, 17.7%; colorectal cancer, 9.3%, other cancers, 3.0%).
These patients had advanced cancer and had been heavily pretreated with a median of four prior lines of therapy. They received one or more doses of at least 5.4 mg/kg of T-DXd.
Nearly half of the cohort were treated for more than 6 months. A total of 276 potential ILD/pneumonitis events were sent for adjudication; of those, 85% were adjudicated as ILD/pneumonitis.
The overall incidence of adjudicated ILD/pneumonitis events was 15.4%; most were low-grade events. Some 87% of patients experienced their first ILD event within 12 months of treatment. The median time to experiencing an ILD/pneumonitis event was 5.4 months.
Some of the patients who developed grade 1 ILD/pneumonitis were treated and the adverse event resolved. These patients were then rechallenged with the drug. Only 3 of the 47 rechallenged patients experienced recurrence of ILD/pneumonitis, the authors noted.
“Rechallenge with T-DXd after complete resolution of grade 1 events is possible and warrants further investigation,” they commented. They cautioned, however, that rechallenge is not recommended for all patients, at least not for those with grade 2 or higher ILD/pneumonitis.
Overall, the authors concluded that the “benefit-risk of T-DXd treatment is positive,” but they warned that some patients may be at increased risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis
Baseline factors that increase the risk of developing an ILD/pneumonitis event include the following: being younger than 65 years, receiving a T-DXd dose of more than6.4 mg/kg, having a baseline oxygen saturation level of less than 95%, having moderate to severe renal impairment, and having lung comorbidities. In addition, patients who had initially been diagnosed with cancer more than 4 years before receiving the drug were at higher risk of developing ILD/pneumonitis.
“Using learnings from the early clinical trials experience, physician education and patient management protocols were revised and disseminated by the study sponsors [and] more recent trial data in earlier lines of therapy has demonstrated lower rates of ILD events, suggesting close monitoring and proactive management of ILD/pneumonitis is warranted for all patients,” Dr. Powell said in a statement.
The T-DXd clinical trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Powell has received fees from Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and Voluntis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO OPEN
The ‘great dynamism’ of radiation oncology
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF CANCER
At 100, Guinness’s oldest practicing doctor shows no signs of slowing down
In the same year that Howard Tucker, MD, began practicing neurology, the average loaf of bread cost 13 cents, the microwave oven became commercially available, and Jackie Robinson took the field for the Brooklyn Dodgers as the first Black person to play Major League Baseball.
Since 1947, Dr. Tucker has witnessed major changes in health care, from President Harry S. Truman proposing a national health care plan to Congress to the current day, when patients carry their digital records around with them.
Dr. Tucker has been a resident of Cleveland Heights, Ohio, since 1922, the year he was born.
After graduating high school in 1940, Dr. Tucker attended Ohio State University, Columbus, where he received his undergraduate and medical degrees. During the Korean War, he served as chief neurologist for the Atlantic fleet at a U.S. Naval Hospital in Philadelphia. Following the war, he completed his residency at the Cleveland Clinic and trained at the Neurological Institute of New York.
Dr. Tucker chose to return to Cleveland, where he practiced at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Hillcrest Hospital for several decades.
Not content with just a medical degree, at the age of 67, Dr. Tucker attended Cleveland State University Cleveland Marshall College of Law. In 1989, he received his Juris Doctor degree and passed the Ohio bar examination.
And as if that weren’t enough career accomplishments, Guinness World Records dubbed him the world’s oldest practicing doctor at 98 years and 231 days. Dr. Tucker continues to practice into his 100th year. He celebrated his birthday in July.
Owing to the compelling and inspiring nature of his upbringing, Dr. Tucker has become the subject of a feature documentary film entitled “What’s Next?” The film is currently in production. It is being produced by his grandson, Austin Tucker, and is directed by Taylor Taglianetti.
This news organization recently spoke with Dr. Tucker about his life’s work in medicine.
Question: Why did you choose neurology?
Dr. Tucker: Well, I think I was just fascinated with medicine from about the seventh or eighth grade. I chose my specialty because it was a very cerebral one in those days. It was an intellectual pursuit. It was before the CAT scan, and you had to work hard to make a diagnosis. You even had to look at the spinal fluid. You had to look at EEGs, and it was a very detailed history taking.
Question: How has neurology changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: The MRI came in, so we don’t have to use spinal taps anymore. Lumbar puncture fluid and EEG aren’t needed as often either. Now we use EEG for convulsive disorders, but rarely when we suspect tumors like we used to. Also, when I was in med school, they said to use Dilaudid; don’t use morphine. And now, you can’t even find Dilaudin in emergency rooms anymore.
Question: How has medicine overall changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: Computers have made everything a different specialty.
In the old days, we would see a patient, call the referring doctor, and discuss [the case] with them in a very pleasant way. Now, when you call a doctor, he’ll say to you, “Let me read your note,” and that’s the end of it. He doesn’t want to talk to you. Medicine has changed dramatically.
It used to be a very warm relationship between you and your patients. You looked at your patient, you studied their expressions, and now you look at the screen and very rarely look at the patient.
Question: Why do you still enjoy practicing medicine?
Dr. Tucker: The challenge, the excitement of patients, and now I’m doing a lot of teaching, and I do love that part, too.
I teach neurology to residents and medical students that rotate through. When I retired from the Cleveland Clinic, 2 months of retirement was too much for me, so I went back to St. Vincent. It’s a smaller hospital but still has good residents and good teaching.
Question: What lessons do you teach to your residents?
Dr. Tucker: I ask my residents and physicians to think through a problem before they look at the CAT scan and imaging studies. Think through it, then you’ll know what questions you want to ask specifically before you even examine the patient, know exactly what you are going to find.
The complete neurological examination, aside from taking the history and checking mental status, is 5 minutes. You have them walk, check for excessive finger tapping, have them touch their nose, check their reflexes, check their strength – it’s over. That doesn’t take much time if you know what you’re looking for.
Residents say to me all the time, “55-year-old man, CAT scan shows ...” I have to say to them: “Slow down. Let’s talk about this first.”
Question: What advice do you have for physicians and medical students?
Dr. Tucker: Take a very careful history. Know the course of the illness. Make sure you have a diagnosis in your head and, specifically for medical residents, ask questions. You have to be smarter than the patients are, you have to know what to ask.
If someone hits their head on their steering wheel, they don’t know that they’ve lost their sense of smell. You have to ask that specifically, hence, why you have to be smarter than they are. Take a careful history before you do imaging studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the same year that Howard Tucker, MD, began practicing neurology, the average loaf of bread cost 13 cents, the microwave oven became commercially available, and Jackie Robinson took the field for the Brooklyn Dodgers as the first Black person to play Major League Baseball.
Since 1947, Dr. Tucker has witnessed major changes in health care, from President Harry S. Truman proposing a national health care plan to Congress to the current day, when patients carry their digital records around with them.
Dr. Tucker has been a resident of Cleveland Heights, Ohio, since 1922, the year he was born.
After graduating high school in 1940, Dr. Tucker attended Ohio State University, Columbus, where he received his undergraduate and medical degrees. During the Korean War, he served as chief neurologist for the Atlantic fleet at a U.S. Naval Hospital in Philadelphia. Following the war, he completed his residency at the Cleveland Clinic and trained at the Neurological Institute of New York.
Dr. Tucker chose to return to Cleveland, where he practiced at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Hillcrest Hospital for several decades.
Not content with just a medical degree, at the age of 67, Dr. Tucker attended Cleveland State University Cleveland Marshall College of Law. In 1989, he received his Juris Doctor degree and passed the Ohio bar examination.
And as if that weren’t enough career accomplishments, Guinness World Records dubbed him the world’s oldest practicing doctor at 98 years and 231 days. Dr. Tucker continues to practice into his 100th year. He celebrated his birthday in July.
Owing to the compelling and inspiring nature of his upbringing, Dr. Tucker has become the subject of a feature documentary film entitled “What’s Next?” The film is currently in production. It is being produced by his grandson, Austin Tucker, and is directed by Taylor Taglianetti.
This news organization recently spoke with Dr. Tucker about his life’s work in medicine.
Question: Why did you choose neurology?
Dr. Tucker: Well, I think I was just fascinated with medicine from about the seventh or eighth grade. I chose my specialty because it was a very cerebral one in those days. It was an intellectual pursuit. It was before the CAT scan, and you had to work hard to make a diagnosis. You even had to look at the spinal fluid. You had to look at EEGs, and it was a very detailed history taking.
Question: How has neurology changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: The MRI came in, so we don’t have to use spinal taps anymore. Lumbar puncture fluid and EEG aren’t needed as often either. Now we use EEG for convulsive disorders, but rarely when we suspect tumors like we used to. Also, when I was in med school, they said to use Dilaudid; don’t use morphine. And now, you can’t even find Dilaudin in emergency rooms anymore.
Question: How has medicine overall changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: Computers have made everything a different specialty.
In the old days, we would see a patient, call the referring doctor, and discuss [the case] with them in a very pleasant way. Now, when you call a doctor, he’ll say to you, “Let me read your note,” and that’s the end of it. He doesn’t want to talk to you. Medicine has changed dramatically.
It used to be a very warm relationship between you and your patients. You looked at your patient, you studied their expressions, and now you look at the screen and very rarely look at the patient.
Question: Why do you still enjoy practicing medicine?
Dr. Tucker: The challenge, the excitement of patients, and now I’m doing a lot of teaching, and I do love that part, too.
I teach neurology to residents and medical students that rotate through. When I retired from the Cleveland Clinic, 2 months of retirement was too much for me, so I went back to St. Vincent. It’s a smaller hospital but still has good residents and good teaching.
Question: What lessons do you teach to your residents?
Dr. Tucker: I ask my residents and physicians to think through a problem before they look at the CAT scan and imaging studies. Think through it, then you’ll know what questions you want to ask specifically before you even examine the patient, know exactly what you are going to find.
The complete neurological examination, aside from taking the history and checking mental status, is 5 minutes. You have them walk, check for excessive finger tapping, have them touch their nose, check their reflexes, check their strength – it’s over. That doesn’t take much time if you know what you’re looking for.
Residents say to me all the time, “55-year-old man, CAT scan shows ...” I have to say to them: “Slow down. Let’s talk about this first.”
Question: What advice do you have for physicians and medical students?
Dr. Tucker: Take a very careful history. Know the course of the illness. Make sure you have a diagnosis in your head and, specifically for medical residents, ask questions. You have to be smarter than the patients are, you have to know what to ask.
If someone hits their head on their steering wheel, they don’t know that they’ve lost their sense of smell. You have to ask that specifically, hence, why you have to be smarter than they are. Take a careful history before you do imaging studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the same year that Howard Tucker, MD, began practicing neurology, the average loaf of bread cost 13 cents, the microwave oven became commercially available, and Jackie Robinson took the field for the Brooklyn Dodgers as the first Black person to play Major League Baseball.
Since 1947, Dr. Tucker has witnessed major changes in health care, from President Harry S. Truman proposing a national health care plan to Congress to the current day, when patients carry their digital records around with them.
Dr. Tucker has been a resident of Cleveland Heights, Ohio, since 1922, the year he was born.
After graduating high school in 1940, Dr. Tucker attended Ohio State University, Columbus, where he received his undergraduate and medical degrees. During the Korean War, he served as chief neurologist for the Atlantic fleet at a U.S. Naval Hospital in Philadelphia. Following the war, he completed his residency at the Cleveland Clinic and trained at the Neurological Institute of New York.
Dr. Tucker chose to return to Cleveland, where he practiced at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and Hillcrest Hospital for several decades.
Not content with just a medical degree, at the age of 67, Dr. Tucker attended Cleveland State University Cleveland Marshall College of Law. In 1989, he received his Juris Doctor degree and passed the Ohio bar examination.
And as if that weren’t enough career accomplishments, Guinness World Records dubbed him the world’s oldest practicing doctor at 98 years and 231 days. Dr. Tucker continues to practice into his 100th year. He celebrated his birthday in July.
Owing to the compelling and inspiring nature of his upbringing, Dr. Tucker has become the subject of a feature documentary film entitled “What’s Next?” The film is currently in production. It is being produced by his grandson, Austin Tucker, and is directed by Taylor Taglianetti.
This news organization recently spoke with Dr. Tucker about his life’s work in medicine.
Question: Why did you choose neurology?
Dr. Tucker: Well, I think I was just fascinated with medicine from about the seventh or eighth grade. I chose my specialty because it was a very cerebral one in those days. It was an intellectual pursuit. It was before the CAT scan, and you had to work hard to make a diagnosis. You even had to look at the spinal fluid. You had to look at EEGs, and it was a very detailed history taking.
Question: How has neurology changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: The MRI came in, so we don’t have to use spinal taps anymore. Lumbar puncture fluid and EEG aren’t needed as often either. Now we use EEG for convulsive disorders, but rarely when we suspect tumors like we used to. Also, when I was in med school, they said to use Dilaudid; don’t use morphine. And now, you can’t even find Dilaudin in emergency rooms anymore.
Question: How has medicine overall changed since you started practicing?
Dr. Tucker: Computers have made everything a different specialty.
In the old days, we would see a patient, call the referring doctor, and discuss [the case] with them in a very pleasant way. Now, when you call a doctor, he’ll say to you, “Let me read your note,” and that’s the end of it. He doesn’t want to talk to you. Medicine has changed dramatically.
It used to be a very warm relationship between you and your patients. You looked at your patient, you studied their expressions, and now you look at the screen and very rarely look at the patient.
Question: Why do you still enjoy practicing medicine?
Dr. Tucker: The challenge, the excitement of patients, and now I’m doing a lot of teaching, and I do love that part, too.
I teach neurology to residents and medical students that rotate through. When I retired from the Cleveland Clinic, 2 months of retirement was too much for me, so I went back to St. Vincent. It’s a smaller hospital but still has good residents and good teaching.
Question: What lessons do you teach to your residents?
Dr. Tucker: I ask my residents and physicians to think through a problem before they look at the CAT scan and imaging studies. Think through it, then you’ll know what questions you want to ask specifically before you even examine the patient, know exactly what you are going to find.
The complete neurological examination, aside from taking the history and checking mental status, is 5 minutes. You have them walk, check for excessive finger tapping, have them touch their nose, check their reflexes, check their strength – it’s over. That doesn’t take much time if you know what you’re looking for.
Residents say to me all the time, “55-year-old man, CAT scan shows ...” I have to say to them: “Slow down. Let’s talk about this first.”
Question: What advice do you have for physicians and medical students?
Dr. Tucker: Take a very careful history. Know the course of the illness. Make sure you have a diagnosis in your head and, specifically for medical residents, ask questions. You have to be smarter than the patients are, you have to know what to ask.
If someone hits their head on their steering wheel, they don’t know that they’ve lost their sense of smell. You have to ask that specifically, hence, why you have to be smarter than they are. Take a careful history before you do imaging studies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.