User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
High-Potency Cannabis Tied to Impaired Brain Development, Psychosis, Cannabis-Use Disorder
It’s becoming clear that (CUD).
That was the message delivered by Yasmin Hurd, PhD, director of the Addiction Institute at Mount Sinai in New York, during a press briefing at the American Psychiatric Association (APA) 2024 annual meeting.
“We’re actually in historic times in that we now have highly concentrated, highly potent cannabis products that are administered in various routes,” Dr. Hurd told reporters.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations in cannabis products have increased over the years, from around 2%-4% to 15%-24% now, Dr. Hurd noted.
Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote in a commentary on the developmental trajectory of CUD published simultaneously in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Dramatic Increase in Teen Cannabis Use
A recent study from Oregon Health & Science University showed that adolescent cannabis abuse in the United States has increased dramatically, by about 245%, since 2000.
“Drug abuse is often driven by what is in front of you,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, noted in an interview.
“Right now, cannabis is widely available. So, guess what? Cannabis becomes the drug that people take. Nicotine is much harder to get. It is regulated to a much greater extent than cannabis, so fewer teenagers are consuming nicotine than are consuming cannabis,” Dr. Volkow said.
Cannabis exposure during neurodevelopment has the potential to alter the endocannabinoid system, which in turn, can affect the development of neural pathways that mediate reward; emotional regulation; and multiple cognitive domains including executive functioning and decision-making, learning, abstraction, and attention — all processes central to substance use disorder and other psychiatric disorders, Dr. Hurd said at the briefing.
Dr. Volkow said that cannabis use in adolescence and young adulthood is “very concerning because that’s also the age of risk for psychosis, particularly schizophrenia, with one study showing that use of cannabis in high doses can trigger psychotic episodes, particularly among young males.”
Dr. Hurd noted that not all young people who use cannabis develop CUD, “but a significant number do,” and large-scale studies have consistently reported two main factors associated with CUD risk.
The first is age, both for the onset and frequency of use at younger age. Those who start using cannabis before age 16 years are at the highest risk for CUD. The risk for CUD also increases significantly among youth who use cannabis at least weekly, with the highest prevalence among youth who use cannabis daily. One large study linked increased frequency of use with up to a 17-fold increased risk for CUD.
The second factor consistently associated with the risk for CUD is biologic sex, with CUD rates typically higher in male individuals.
Treatment Challenges
For young people who develop CUD, access to and uptake of treatment can be challenging.
“Given that the increased potency of cannabis and cannabinoid products is expected to increase CUD risk, it is disturbing that less than 10% of youth who meet the criteria for a substance use disorder, including CUD, receive treatment,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues point out in their commentary.
Another challenge is that treatment strategies for CUD are currently limited and consist mainly of motivational enhancement and cognitive-behavioral therapies.
“Clearly new treatment strategies are needed to address the mounting challenge of CUD risk in teens and young adults,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
Summing up, Dr. Hurd told reporters, “We now know that most psychiatric disorders have a developmental origin, and the adolescent time period is a critical window for cannabis use disorder risk.”
Yet, on a positive note, the “plasticity of the developing brain that makes it vulnerable to cannabis use disorder and psychiatric comorbidities also provides an opportunity for prevention and early intervention to change that trajectory,” Dr. Hurd said.
The changing legal landscape of cannabis — the US Drug Enforcement Agency is moving forward with plans to move marijuana from a Schedule I to a Schedule III controlled substance under the Controlled Substance Act — makes addressing these risks all the timelier.
“As states vie to leverage tax dollars from the growing cannabis industry, a significant portion of such funds must be used for early intervention/prevention strategies to reduce the impact of cannabis on the developing brain,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
This research was supported in part by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hurd and Dr. Volkow have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that (CUD).
That was the message delivered by Yasmin Hurd, PhD, director of the Addiction Institute at Mount Sinai in New York, during a press briefing at the American Psychiatric Association (APA) 2024 annual meeting.
“We’re actually in historic times in that we now have highly concentrated, highly potent cannabis products that are administered in various routes,” Dr. Hurd told reporters.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations in cannabis products have increased over the years, from around 2%-4% to 15%-24% now, Dr. Hurd noted.
Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote in a commentary on the developmental trajectory of CUD published simultaneously in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Dramatic Increase in Teen Cannabis Use
A recent study from Oregon Health & Science University showed that adolescent cannabis abuse in the United States has increased dramatically, by about 245%, since 2000.
“Drug abuse is often driven by what is in front of you,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, noted in an interview.
“Right now, cannabis is widely available. So, guess what? Cannabis becomes the drug that people take. Nicotine is much harder to get. It is regulated to a much greater extent than cannabis, so fewer teenagers are consuming nicotine than are consuming cannabis,” Dr. Volkow said.
Cannabis exposure during neurodevelopment has the potential to alter the endocannabinoid system, which in turn, can affect the development of neural pathways that mediate reward; emotional regulation; and multiple cognitive domains including executive functioning and decision-making, learning, abstraction, and attention — all processes central to substance use disorder and other psychiatric disorders, Dr. Hurd said at the briefing.
Dr. Volkow said that cannabis use in adolescence and young adulthood is “very concerning because that’s also the age of risk for psychosis, particularly schizophrenia, with one study showing that use of cannabis in high doses can trigger psychotic episodes, particularly among young males.”
Dr. Hurd noted that not all young people who use cannabis develop CUD, “but a significant number do,” and large-scale studies have consistently reported two main factors associated with CUD risk.
The first is age, both for the onset and frequency of use at younger age. Those who start using cannabis before age 16 years are at the highest risk for CUD. The risk for CUD also increases significantly among youth who use cannabis at least weekly, with the highest prevalence among youth who use cannabis daily. One large study linked increased frequency of use with up to a 17-fold increased risk for CUD.
The second factor consistently associated with the risk for CUD is biologic sex, with CUD rates typically higher in male individuals.
Treatment Challenges
For young people who develop CUD, access to and uptake of treatment can be challenging.
“Given that the increased potency of cannabis and cannabinoid products is expected to increase CUD risk, it is disturbing that less than 10% of youth who meet the criteria for a substance use disorder, including CUD, receive treatment,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues point out in their commentary.
Another challenge is that treatment strategies for CUD are currently limited and consist mainly of motivational enhancement and cognitive-behavioral therapies.
“Clearly new treatment strategies are needed to address the mounting challenge of CUD risk in teens and young adults,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
Summing up, Dr. Hurd told reporters, “We now know that most psychiatric disorders have a developmental origin, and the adolescent time period is a critical window for cannabis use disorder risk.”
Yet, on a positive note, the “plasticity of the developing brain that makes it vulnerable to cannabis use disorder and psychiatric comorbidities also provides an opportunity for prevention and early intervention to change that trajectory,” Dr. Hurd said.
The changing legal landscape of cannabis — the US Drug Enforcement Agency is moving forward with plans to move marijuana from a Schedule I to a Schedule III controlled substance under the Controlled Substance Act — makes addressing these risks all the timelier.
“As states vie to leverage tax dollars from the growing cannabis industry, a significant portion of such funds must be used for early intervention/prevention strategies to reduce the impact of cannabis on the developing brain,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
This research was supported in part by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hurd and Dr. Volkow have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that (CUD).
That was the message delivered by Yasmin Hurd, PhD, director of the Addiction Institute at Mount Sinai in New York, during a press briefing at the American Psychiatric Association (APA) 2024 annual meeting.
“We’re actually in historic times in that we now have highly concentrated, highly potent cannabis products that are administered in various routes,” Dr. Hurd told reporters.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations in cannabis products have increased over the years, from around 2%-4% to 15%-24% now, Dr. Hurd noted.
Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote in a commentary on the developmental trajectory of CUD published simultaneously in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Dramatic Increase in Teen Cannabis Use
A recent study from Oregon Health & Science University showed that adolescent cannabis abuse in the United States has increased dramatically, by about 245%, since 2000.
“Drug abuse is often driven by what is in front of you,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, noted in an interview.
“Right now, cannabis is widely available. So, guess what? Cannabis becomes the drug that people take. Nicotine is much harder to get. It is regulated to a much greater extent than cannabis, so fewer teenagers are consuming nicotine than are consuming cannabis,” Dr. Volkow said.
Cannabis exposure during neurodevelopment has the potential to alter the endocannabinoid system, which in turn, can affect the development of neural pathways that mediate reward; emotional regulation; and multiple cognitive domains including executive functioning and decision-making, learning, abstraction, and attention — all processes central to substance use disorder and other psychiatric disorders, Dr. Hurd said at the briefing.
Dr. Volkow said that cannabis use in adolescence and young adulthood is “very concerning because that’s also the age of risk for psychosis, particularly schizophrenia, with one study showing that use of cannabis in high doses can trigger psychotic episodes, particularly among young males.”
Dr. Hurd noted that not all young people who use cannabis develop CUD, “but a significant number do,” and large-scale studies have consistently reported two main factors associated with CUD risk.
The first is age, both for the onset and frequency of use at younger age. Those who start using cannabis before age 16 years are at the highest risk for CUD. The risk for CUD also increases significantly among youth who use cannabis at least weekly, with the highest prevalence among youth who use cannabis daily. One large study linked increased frequency of use with up to a 17-fold increased risk for CUD.
The second factor consistently associated with the risk for CUD is biologic sex, with CUD rates typically higher in male individuals.
Treatment Challenges
For young people who develop CUD, access to and uptake of treatment can be challenging.
“Given that the increased potency of cannabis and cannabinoid products is expected to increase CUD risk, it is disturbing that less than 10% of youth who meet the criteria for a substance use disorder, including CUD, receive treatment,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues point out in their commentary.
Another challenge is that treatment strategies for CUD are currently limited and consist mainly of motivational enhancement and cognitive-behavioral therapies.
“Clearly new treatment strategies are needed to address the mounting challenge of CUD risk in teens and young adults,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
Summing up, Dr. Hurd told reporters, “We now know that most psychiatric disorders have a developmental origin, and the adolescent time period is a critical window for cannabis use disorder risk.”
Yet, on a positive note, the “plasticity of the developing brain that makes it vulnerable to cannabis use disorder and psychiatric comorbidities also provides an opportunity for prevention and early intervention to change that trajectory,” Dr. Hurd said.
The changing legal landscape of cannabis — the US Drug Enforcement Agency is moving forward with plans to move marijuana from a Schedule I to a Schedule III controlled substance under the Controlled Substance Act — makes addressing these risks all the timelier.
“As states vie to leverage tax dollars from the growing cannabis industry, a significant portion of such funds must be used for early intervention/prevention strategies to reduce the impact of cannabis on the developing brain,” Dr. Hurd and colleagues wrote.
This research was supported in part by the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Hurd and Dr. Volkow have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM APA 2024
Widespread, Long-Held Practice in Dementia Called Into Question
Hospitalized patients with dementia and dysphagia are often prescribed a “dysphagia diet,” made up of texture-modified foods and thickened liquids in an effort to reduce the risk for aspiration or other problems. However, a new study calls this widespread and long-held practice into question.
Investigators found no evidence that the use of thickened liquids reduced mortality or respiratory complications, such as pneumonia, aspiration, or choking, compared with thin-liquid diets in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) and dysphagia. Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to be intubated, but they were actually more likely to have respiratory complications.
“When hospitalized patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias are found to have dysphagia, our go-to solution is to use a thick liquid diet,” senior author Liron Sinvani, MD, with the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, New York, said in a news release.
“However, there is no concrete evidence that thick liquids improve health outcomes, and we also know that thick liquids can lead to decreased palatability, poor oral intake, dehydration, malnutrition, and worse quality of life,” added Dr. Sinvani, director of the geriatric hospitalist service at Northwell Health in New York.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Challenging a Go-To Solution
The researchers compared outcomes in a propensity score-matched cohort of patients with ADRD and dysphagia (mean age, 86 years; 54% women) receiving mostly thick liquids versus thin liquids during their hospitalization. There were 4458 patients in each group.
They found no significant difference in hospital mortality between the thick liquids and thin liquids groups (hazard ratio [HR], 0.92; P = .46).
Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to require intubation (odds ratio [OR], 0.66; 95% CI, 0.54-0.80) but were more likely to develop respiratory complications (OR, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.56-1.91).
The two groups did not differ significantly in terms of risk for dehydration, hospital length of stay, or rate of 30-day readmission.
“This cohort study emphasizes the need for prospective studies that evaluate whether thick liquids are associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with ADRD and dysphagia,” the authors wrote.
Because few patients received a Modified Barium Swallow Study at baseline, researchers were unable to confirm the presence of dysphagia or account for dysphagia severity and impairment. It’s possible that patients in the thick liquid group had more severe dysphagia than those in the thin liquid group.
Another limitation is that the type of dementia and severity were not characterized. Also, the study could not account for factors like oral hygiene, immune status, and diet adherence that could impact risks like aspiration pneumonia.
Theoretical Benefit, No Evidence
In an invited commentary on the study, Eric Widera, MD, with University of California San Francisco, noted that medicine is “littered with interventions that have become the standard of practice based on theoretical benefits without clinical evidence”.
One example is percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes for individuals with dysphagia and dementia.
“For decades, these tubes were regularly used in individuals with dementia on the assumption that bypassing the oropharyngeal route would decrease rates of aspiration and, therefore, decrease adverse outcomes like pressure ulcers, malnutrition, pneumonia, and death. However, similar to what we see with thickened liquids, evidence slowly built that this standard of practice was not evidence-based practice,” Dr. Widera wrote.
When thinking about thick liquid diets, Dr. Widera encouraged clinicians to “acknowledge the limitations of the evidence both for and against thickened-liquid diets.”
He also encouraged clinicians to “put yourself in the shoes of the patients who will be asked to adhere to this modified diet. For 12 hours, drink your tea, coffee, wine, and water as thickened liquids,” Dr. Widera suggested. “The goal is not to convince yourself never to prescribe thickened liquids, but rather to be mindful of how a thickened liquid diet affects patients’ liquid and food intake, how it changes the mouthfeel and taste of different drinks, and how it affects patients’ quality of life.”
Clinicians also should “proactively engage speech-language pathologists, but do not ask them if it is safe for a patient with dementia to eat or drink normally. Instead, ask what we can do to meet the patient’s goals and maintain quality of life given the current evidence base,” Dr. Widera wrote.
“For some, when the patient’s goals are focused on comfort, this may lead to a recommendation for thickened liquids if their use may resolve significant coughing distress after drinking thin liquids. Alternatively, even when the patient’s goals are focused on prolonging life, the risks of thickened liquids, including dehydration and decreased food and fluid intake, as well as the thin evidence for mortality improvement, will argue against their use,” Dr. Widera added.
Funding for the study was provided by grants from the National Institute on Aging and by the William S. Middleton Veteran Affairs Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin. Dr. Sinvani and Dr. Widera declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Hospitalized patients with dementia and dysphagia are often prescribed a “dysphagia diet,” made up of texture-modified foods and thickened liquids in an effort to reduce the risk for aspiration or other problems. However, a new study calls this widespread and long-held practice into question.
Investigators found no evidence that the use of thickened liquids reduced mortality or respiratory complications, such as pneumonia, aspiration, or choking, compared with thin-liquid diets in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) and dysphagia. Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to be intubated, but they were actually more likely to have respiratory complications.
“When hospitalized patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias are found to have dysphagia, our go-to solution is to use a thick liquid diet,” senior author Liron Sinvani, MD, with the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, New York, said in a news release.
“However, there is no concrete evidence that thick liquids improve health outcomes, and we also know that thick liquids can lead to decreased palatability, poor oral intake, dehydration, malnutrition, and worse quality of life,” added Dr. Sinvani, director of the geriatric hospitalist service at Northwell Health in New York.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Challenging a Go-To Solution
The researchers compared outcomes in a propensity score-matched cohort of patients with ADRD and dysphagia (mean age, 86 years; 54% women) receiving mostly thick liquids versus thin liquids during their hospitalization. There were 4458 patients in each group.
They found no significant difference in hospital mortality between the thick liquids and thin liquids groups (hazard ratio [HR], 0.92; P = .46).
Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to require intubation (odds ratio [OR], 0.66; 95% CI, 0.54-0.80) but were more likely to develop respiratory complications (OR, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.56-1.91).
The two groups did not differ significantly in terms of risk for dehydration, hospital length of stay, or rate of 30-day readmission.
“This cohort study emphasizes the need for prospective studies that evaluate whether thick liquids are associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with ADRD and dysphagia,” the authors wrote.
Because few patients received a Modified Barium Swallow Study at baseline, researchers were unable to confirm the presence of dysphagia or account for dysphagia severity and impairment. It’s possible that patients in the thick liquid group had more severe dysphagia than those in the thin liquid group.
Another limitation is that the type of dementia and severity were not characterized. Also, the study could not account for factors like oral hygiene, immune status, and diet adherence that could impact risks like aspiration pneumonia.
Theoretical Benefit, No Evidence
In an invited commentary on the study, Eric Widera, MD, with University of California San Francisco, noted that medicine is “littered with interventions that have become the standard of practice based on theoretical benefits without clinical evidence”.
One example is percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes for individuals with dysphagia and dementia.
“For decades, these tubes were regularly used in individuals with dementia on the assumption that bypassing the oropharyngeal route would decrease rates of aspiration and, therefore, decrease adverse outcomes like pressure ulcers, malnutrition, pneumonia, and death. However, similar to what we see with thickened liquids, evidence slowly built that this standard of practice was not evidence-based practice,” Dr. Widera wrote.
When thinking about thick liquid diets, Dr. Widera encouraged clinicians to “acknowledge the limitations of the evidence both for and against thickened-liquid diets.”
He also encouraged clinicians to “put yourself in the shoes of the patients who will be asked to adhere to this modified diet. For 12 hours, drink your tea, coffee, wine, and water as thickened liquids,” Dr. Widera suggested. “The goal is not to convince yourself never to prescribe thickened liquids, but rather to be mindful of how a thickened liquid diet affects patients’ liquid and food intake, how it changes the mouthfeel and taste of different drinks, and how it affects patients’ quality of life.”
Clinicians also should “proactively engage speech-language pathologists, but do not ask them if it is safe for a patient with dementia to eat or drink normally. Instead, ask what we can do to meet the patient’s goals and maintain quality of life given the current evidence base,” Dr. Widera wrote.
“For some, when the patient’s goals are focused on comfort, this may lead to a recommendation for thickened liquids if their use may resolve significant coughing distress after drinking thin liquids. Alternatively, even when the patient’s goals are focused on prolonging life, the risks of thickened liquids, including dehydration and decreased food and fluid intake, as well as the thin evidence for mortality improvement, will argue against their use,” Dr. Widera added.
Funding for the study was provided by grants from the National Institute on Aging and by the William S. Middleton Veteran Affairs Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin. Dr. Sinvani and Dr. Widera declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Hospitalized patients with dementia and dysphagia are often prescribed a “dysphagia diet,” made up of texture-modified foods and thickened liquids in an effort to reduce the risk for aspiration or other problems. However, a new study calls this widespread and long-held practice into question.
Investigators found no evidence that the use of thickened liquids reduced mortality or respiratory complications, such as pneumonia, aspiration, or choking, compared with thin-liquid diets in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) and dysphagia. Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to be intubated, but they were actually more likely to have respiratory complications.
“When hospitalized patients with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias are found to have dysphagia, our go-to solution is to use a thick liquid diet,” senior author Liron Sinvani, MD, with the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, New York, said in a news release.
“However, there is no concrete evidence that thick liquids improve health outcomes, and we also know that thick liquids can lead to decreased palatability, poor oral intake, dehydration, malnutrition, and worse quality of life,” added Dr. Sinvani, director of the geriatric hospitalist service at Northwell Health in New York.
The study was published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Challenging a Go-To Solution
The researchers compared outcomes in a propensity score-matched cohort of patients with ADRD and dysphagia (mean age, 86 years; 54% women) receiving mostly thick liquids versus thin liquids during their hospitalization. There were 4458 patients in each group.
They found no significant difference in hospital mortality between the thick liquids and thin liquids groups (hazard ratio [HR], 0.92; P = .46).
Patients receiving thick liquids were less likely to require intubation (odds ratio [OR], 0.66; 95% CI, 0.54-0.80) but were more likely to develop respiratory complications (OR, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.56-1.91).
The two groups did not differ significantly in terms of risk for dehydration, hospital length of stay, or rate of 30-day readmission.
“This cohort study emphasizes the need for prospective studies that evaluate whether thick liquids are associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with ADRD and dysphagia,” the authors wrote.
Because few patients received a Modified Barium Swallow Study at baseline, researchers were unable to confirm the presence of dysphagia or account for dysphagia severity and impairment. It’s possible that patients in the thick liquid group had more severe dysphagia than those in the thin liquid group.
Another limitation is that the type of dementia and severity were not characterized. Also, the study could not account for factors like oral hygiene, immune status, and diet adherence that could impact risks like aspiration pneumonia.
Theoretical Benefit, No Evidence
In an invited commentary on the study, Eric Widera, MD, with University of California San Francisco, noted that medicine is “littered with interventions that have become the standard of practice based on theoretical benefits without clinical evidence”.
One example is percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes for individuals with dysphagia and dementia.
“For decades, these tubes were regularly used in individuals with dementia on the assumption that bypassing the oropharyngeal route would decrease rates of aspiration and, therefore, decrease adverse outcomes like pressure ulcers, malnutrition, pneumonia, and death. However, similar to what we see with thickened liquids, evidence slowly built that this standard of practice was not evidence-based practice,” Dr. Widera wrote.
When thinking about thick liquid diets, Dr. Widera encouraged clinicians to “acknowledge the limitations of the evidence both for and against thickened-liquid diets.”
He also encouraged clinicians to “put yourself in the shoes of the patients who will be asked to adhere to this modified diet. For 12 hours, drink your tea, coffee, wine, and water as thickened liquids,” Dr. Widera suggested. “The goal is not to convince yourself never to prescribe thickened liquids, but rather to be mindful of how a thickened liquid diet affects patients’ liquid and food intake, how it changes the mouthfeel and taste of different drinks, and how it affects patients’ quality of life.”
Clinicians also should “proactively engage speech-language pathologists, but do not ask them if it is safe for a patient with dementia to eat or drink normally. Instead, ask what we can do to meet the patient’s goals and maintain quality of life given the current evidence base,” Dr. Widera wrote.
“For some, when the patient’s goals are focused on comfort, this may lead to a recommendation for thickened liquids if their use may resolve significant coughing distress after drinking thin liquids. Alternatively, even when the patient’s goals are focused on prolonging life, the risks of thickened liquids, including dehydration and decreased food and fluid intake, as well as the thin evidence for mortality improvement, will argue against their use,” Dr. Widera added.
Funding for the study was provided by grants from the National Institute on Aging and by the William S. Middleton Veteran Affairs Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin. Dr. Sinvani and Dr. Widera declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
It Would Be Nice if Olive Oil Really Did Prevent Dementia
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As you all know by now, I’m always looking out for lifestyle changes that are both pleasurable and healthy. They are hard to find, especially when it comes to diet. My kids complain about this all the time: “When you say ‘healthy food,’ you just mean yucky food.” And yes, French fries are amazing, and no, we can’t have them three times a day.
So, when I saw an article claiming that olive oil reduces the risk for dementia, I was interested. I love olive oil; I cook with it all the time. But as is always the case in the world of nutritional epidemiology, we need to be careful. There are a lot of reasons to doubt the results of this study — and one reason to believe it’s true.
The study I’m talking about is “Consumption of Olive Oil and Diet Quality and Risk of Dementia-Related Death,” appearing in JAMA Network Open and following a well-trod formula in the nutritional epidemiology space.
Nearly 100,000 participants, all healthcare workers, filled out a food frequency questionnaire every 4 years with 130 questions touching on all aspects of diet: How often do you eat bananas, bacon, olive oil? Participants were followed for more than 20 years, and if they died, the cause of death was flagged as being dementia-related or not. Over that time frame there were around 38,000 deaths, of which 4751 were due to dementia.
The rest is just statistics. The authors show that those who reported consuming more olive oil were less likely to die from dementia — about 50% less likely, if you compare those who reported eating more than 7 grams of olive oil a day with those who reported eating none.
Is It What You Eat, or What You Don’t Eat?
And we could stop there if we wanted to; I’m sure big olive oil would be happy with that. Is there such a thing as “big olive oil”? But no, we need to dig deeper here because this study has the same problems as all nutritional epidemiology studies. Number one, no one is sitting around drinking small cups of olive oil. They consume it with other foods. And it was clear from the food frequency questionnaire that people who consumed more olive oil also consumed less red meat, more fruits and vegetables, more whole grains, more butter, and less margarine. And those are just the findings reported in the paper. I suspect that people who eat more olive oil also eat more tomatoes, for example, though data this granular aren’t shown. So, it can be really hard, in studies like this, to know for sure that it’s actually the olive oil that is helpful rather than some other constituent in the diet.
The flip side of that coin presents another issue. The food you eat is also a marker of the food you don’t eat. People who ate olive oil consumed less margarine, for example. At the time of this study, margarine was still adulterated with trans-fats, which a pretty solid evidence base suggests are really bad for your vascular system. So perhaps it’s not that olive oil is particularly good for you but that something else is bad for you. In other words, simply adding olive oil to your diet without changing anything else may not do anything.
The other major problem with studies of this sort is that people don’t consume food at random. The type of person who eats a lot of olive oil is simply different from the type of person who doesn›t. For one thing, olive oil is expensive. A 25-ounce bottle of olive oil is on sale at my local supermarket right now for $11.00. A similar-sized bottle of vegetable oil goes for $4.00.
Isn’t it interesting that food that costs more money tends to be associated with better health outcomes? (I’m looking at you, red wine.) Perhaps it’s not the food; perhaps it’s the money. We aren’t provided data on household income in this study, but we can see that the heavy olive oil users were less likely to be current smokers and they got more physical activity.
Now, the authors are aware of these limitations and do their best to account for them. In multivariable models, they adjust for other stuff in the diet, and even for income (sort of; they use census tract as a proxy for income, which is really a broad brush), and still find a significant though weakened association showing a protective effect of olive oil on dementia-related death. But still — adjustment is never perfect, and the small effect size here could definitely be due to residual confounding.
Evidence More Convincing
Now, I did tell you that there is one reason to believe that this study is true, but it’s not really from this study.
It’s from the PREDIMED randomized trial.
This is nutritional epidemiology I can get behind. Published in 2018, investigators in Spain randomized around 7500 participants to receive a liter of olive oil once a week vs mixed nuts, vs small nonfood gifts, the idea here being that if you have olive oil around, you’ll use it more. And people who were randomly assigned to get the olive oil had a 30% lower rate of cardiovascular events. A secondary analysis of that study found that the rate of development of mild cognitive impairment was 65% lower in those who were randomly assigned to olive oil. That’s an impressive result.
So, there might be something to this olive oil thing, but I’m not quite ready to add it to my “pleasurable things that are still good for you” list just yet. Though it does make me wonder: Can we make French fries in the stuff?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As you all know by now, I’m always looking out for lifestyle changes that are both pleasurable and healthy. They are hard to find, especially when it comes to diet. My kids complain about this all the time: “When you say ‘healthy food,’ you just mean yucky food.” And yes, French fries are amazing, and no, we can’t have them three times a day.
So, when I saw an article claiming that olive oil reduces the risk for dementia, I was interested. I love olive oil; I cook with it all the time. But as is always the case in the world of nutritional epidemiology, we need to be careful. There are a lot of reasons to doubt the results of this study — and one reason to believe it’s true.
The study I’m talking about is “Consumption of Olive Oil and Diet Quality and Risk of Dementia-Related Death,” appearing in JAMA Network Open and following a well-trod formula in the nutritional epidemiology space.
Nearly 100,000 participants, all healthcare workers, filled out a food frequency questionnaire every 4 years with 130 questions touching on all aspects of diet: How often do you eat bananas, bacon, olive oil? Participants were followed for more than 20 years, and if they died, the cause of death was flagged as being dementia-related or not. Over that time frame there were around 38,000 deaths, of which 4751 were due to dementia.
The rest is just statistics. The authors show that those who reported consuming more olive oil were less likely to die from dementia — about 50% less likely, if you compare those who reported eating more than 7 grams of olive oil a day with those who reported eating none.
Is It What You Eat, or What You Don’t Eat?
And we could stop there if we wanted to; I’m sure big olive oil would be happy with that. Is there such a thing as “big olive oil”? But no, we need to dig deeper here because this study has the same problems as all nutritional epidemiology studies. Number one, no one is sitting around drinking small cups of olive oil. They consume it with other foods. And it was clear from the food frequency questionnaire that people who consumed more olive oil also consumed less red meat, more fruits and vegetables, more whole grains, more butter, and less margarine. And those are just the findings reported in the paper. I suspect that people who eat more olive oil also eat more tomatoes, for example, though data this granular aren’t shown. So, it can be really hard, in studies like this, to know for sure that it’s actually the olive oil that is helpful rather than some other constituent in the diet.
The flip side of that coin presents another issue. The food you eat is also a marker of the food you don’t eat. People who ate olive oil consumed less margarine, for example. At the time of this study, margarine was still adulterated with trans-fats, which a pretty solid evidence base suggests are really bad for your vascular system. So perhaps it’s not that olive oil is particularly good for you but that something else is bad for you. In other words, simply adding olive oil to your diet without changing anything else may not do anything.
The other major problem with studies of this sort is that people don’t consume food at random. The type of person who eats a lot of olive oil is simply different from the type of person who doesn›t. For one thing, olive oil is expensive. A 25-ounce bottle of olive oil is on sale at my local supermarket right now for $11.00. A similar-sized bottle of vegetable oil goes for $4.00.
Isn’t it interesting that food that costs more money tends to be associated with better health outcomes? (I’m looking at you, red wine.) Perhaps it’s not the food; perhaps it’s the money. We aren’t provided data on household income in this study, but we can see that the heavy olive oil users were less likely to be current smokers and they got more physical activity.
Now, the authors are aware of these limitations and do their best to account for them. In multivariable models, they adjust for other stuff in the diet, and even for income (sort of; they use census tract as a proxy for income, which is really a broad brush), and still find a significant though weakened association showing a protective effect of olive oil on dementia-related death. But still — adjustment is never perfect, and the small effect size here could definitely be due to residual confounding.
Evidence More Convincing
Now, I did tell you that there is one reason to believe that this study is true, but it’s not really from this study.
It’s from the PREDIMED randomized trial.
This is nutritional epidemiology I can get behind. Published in 2018, investigators in Spain randomized around 7500 participants to receive a liter of olive oil once a week vs mixed nuts, vs small nonfood gifts, the idea here being that if you have olive oil around, you’ll use it more. And people who were randomly assigned to get the olive oil had a 30% lower rate of cardiovascular events. A secondary analysis of that study found that the rate of development of mild cognitive impairment was 65% lower in those who were randomly assigned to olive oil. That’s an impressive result.
So, there might be something to this olive oil thing, but I’m not quite ready to add it to my “pleasurable things that are still good for you” list just yet. Though it does make me wonder: Can we make French fries in the stuff?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
As you all know by now, I’m always looking out for lifestyle changes that are both pleasurable and healthy. They are hard to find, especially when it comes to diet. My kids complain about this all the time: “When you say ‘healthy food,’ you just mean yucky food.” And yes, French fries are amazing, and no, we can’t have them three times a day.
So, when I saw an article claiming that olive oil reduces the risk for dementia, I was interested. I love olive oil; I cook with it all the time. But as is always the case in the world of nutritional epidemiology, we need to be careful. There are a lot of reasons to doubt the results of this study — and one reason to believe it’s true.
The study I’m talking about is “Consumption of Olive Oil and Diet Quality and Risk of Dementia-Related Death,” appearing in JAMA Network Open and following a well-trod formula in the nutritional epidemiology space.
Nearly 100,000 participants, all healthcare workers, filled out a food frequency questionnaire every 4 years with 130 questions touching on all aspects of diet: How often do you eat bananas, bacon, olive oil? Participants were followed for more than 20 years, and if they died, the cause of death was flagged as being dementia-related or not. Over that time frame there were around 38,000 deaths, of which 4751 were due to dementia.
The rest is just statistics. The authors show that those who reported consuming more olive oil were less likely to die from dementia — about 50% less likely, if you compare those who reported eating more than 7 grams of olive oil a day with those who reported eating none.
Is It What You Eat, or What You Don’t Eat?
And we could stop there if we wanted to; I’m sure big olive oil would be happy with that. Is there such a thing as “big olive oil”? But no, we need to dig deeper here because this study has the same problems as all nutritional epidemiology studies. Number one, no one is sitting around drinking small cups of olive oil. They consume it with other foods. And it was clear from the food frequency questionnaire that people who consumed more olive oil also consumed less red meat, more fruits and vegetables, more whole grains, more butter, and less margarine. And those are just the findings reported in the paper. I suspect that people who eat more olive oil also eat more tomatoes, for example, though data this granular aren’t shown. So, it can be really hard, in studies like this, to know for sure that it’s actually the olive oil that is helpful rather than some other constituent in the diet.
The flip side of that coin presents another issue. The food you eat is also a marker of the food you don’t eat. People who ate olive oil consumed less margarine, for example. At the time of this study, margarine was still adulterated with trans-fats, which a pretty solid evidence base suggests are really bad for your vascular system. So perhaps it’s not that olive oil is particularly good for you but that something else is bad for you. In other words, simply adding olive oil to your diet without changing anything else may not do anything.
The other major problem with studies of this sort is that people don’t consume food at random. The type of person who eats a lot of olive oil is simply different from the type of person who doesn›t. For one thing, olive oil is expensive. A 25-ounce bottle of olive oil is on sale at my local supermarket right now for $11.00. A similar-sized bottle of vegetable oil goes for $4.00.
Isn’t it interesting that food that costs more money tends to be associated with better health outcomes? (I’m looking at you, red wine.) Perhaps it’s not the food; perhaps it’s the money. We aren’t provided data on household income in this study, but we can see that the heavy olive oil users were less likely to be current smokers and they got more physical activity.
Now, the authors are aware of these limitations and do their best to account for them. In multivariable models, they adjust for other stuff in the diet, and even for income (sort of; they use census tract as a proxy for income, which is really a broad brush), and still find a significant though weakened association showing a protective effect of olive oil on dementia-related death. But still — adjustment is never perfect, and the small effect size here could definitely be due to residual confounding.
Evidence More Convincing
Now, I did tell you that there is one reason to believe that this study is true, but it’s not really from this study.
It’s from the PREDIMED randomized trial.
This is nutritional epidemiology I can get behind. Published in 2018, investigators in Spain randomized around 7500 participants to receive a liter of olive oil once a week vs mixed nuts, vs small nonfood gifts, the idea here being that if you have olive oil around, you’ll use it more. And people who were randomly assigned to get the olive oil had a 30% lower rate of cardiovascular events. A secondary analysis of that study found that the rate of development of mild cognitive impairment was 65% lower in those who were randomly assigned to olive oil. That’s an impressive result.
So, there might be something to this olive oil thing, but I’m not quite ready to add it to my “pleasurable things that are still good for you” list just yet. Though it does make me wonder: Can we make French fries in the stuff?
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Inappropriate Medication Use Persists in Older Adults With Dementia
Medications that could have a negative effect on cognition are often used by older adults with dementia, according to data from approximately 13 million individuals presented at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
Classes of medications including anticholinergics, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, and non-benzodiazepine sedatives (Z drugs) have been identified as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) in patients with dementia, according to The American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults.
The medications that could worsen dementia or cognition are known as CogPIMs, said presenting author Caroline M. Mak, a doctor of pharmacy candidate at the University at Buffalo School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, New York.
Previous research has characterized the prevalence of use of CogPIMs, but data connecting use of CogPIMs and healthcare use are lacking, Ms. Mak said.
Ms. Mak and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from 2011 to 2015 from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), a national survey with data on medication and healthcare use. The researchers included approximately 13 million survey respondents older than 65 years with dementia.
Exposure to CogPIMs was defined as filling a prescription for one or more of the CogPIMs during the study period. Population estimates of the prevalence of use of the CogPIMs were created using survey-weighted procedures, and prevalence trends were assessed using the Cochran-Armitage test.
Overall, the prevalence was 15.9%, 11.5%, 7.5%, and 3.8% for use of benzodiazepines, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and Z drugs, respectively, during the study period.
Of these, benzodiazepines showed a significant trend with an increase in prevalence from 8.9% in 2011 to 16.4% in 2015 (P = .02).
The odds of hospitalization were more than twice as likely in individuals who reported using Z drugs (odds ratio, 2.57; P = .02) based on logistic regression. In addition, exposure to antipsychotics was significantly associated with an increased rate of hospitalization based on a binomial model for incidence rate ratio (IRR, 1.51; P = .02).
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and the lack of more recent data.
However, the results show that CogPIMs are often used by older adults with dementia, and antipsychotics and Z drugs could be targets for interventions to prevent harm from medication interactions and side effects, the researchers concluded.
Findings Highlight Need for Drug Awareness
The current study is important because of the expansion in the aging population and an increase in the number of patients with dementia, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “In both our older population and dementia patients, there are certain medication considerations that we need to take into account, and certain drugs that should be avoided if possible,” she said. Clinicians have been trying to use the Beers criteria to reduce potential medication harm, she noted. “One group of investigators (Hilmer et al.), has proposed a narrower focus on anticholinergic and sedative/hypnotic medication in the Drug Burden Index (DBI); the CogPIMs are a subset of both approaches (Beers and DBI) and represent a collection of medications that pose potential risks to our patients,” said Ms. Mak.
Continued reassessment is needed on appropriateness of anticholinergics, Z drugs, benzodiazepines, and antipsychotics in older patients with dementia, she added.
“Even though the only group to have a significant increase in prevalence [of use] was the benzodiazepine group, we didn’t see a decrease in any of the other groups,” said Ms. Mak. The current research provides a benchmark for CogPIMs use that can be monitored in the future for increases or, ideally, decreases, she said.
Part of a Bigger Picture
The current study is part of the work of Team Alice, a national deprescribing group affiliated with the University at Buffalo that was inspired by the tragic death of Alice Brennan, triggered by preventable medication harm, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “Team Alice consists of an array of academic, primary care, health plan, and regional health information partners that have designed patient-driven interventions to reduce medication harm, especially within primary care settings,” she said. “Their mission is to save people like Alice by pursuing multiple strategies to deprescribe unsafe medication, reduce harm, and foster successful aging. By characterizing the use of CogPIMs, we can design better intervention strategies,” she said.
Although Ms. Mak was not surprised by the emergence of benzodiazepines as the most commonly used drug groups, she was surprised by the increase during the study period.
“Unfortunately, our dataset was not rich enough to include reasons for this increase,” she said. In practice, “I have seen patients getting short-term, as needed, prescriptions for a benzodiazepine to address the anxiety and/or insomnia after the loss of a loved one; this may account for a small proportion of benzodiazepine use that appears to be inappropriate because of a lack of associated appropriate diagnosis,” she noted.
Also, the findings of increased hospitalization associated with Z drugs raises concerns, Ms. Mak said. Although the findings are consistent with other research, they illustrate the need for further investigation to identify strategies to prevent this harm, she said. “Not finding associations with hospitalization related to benzodiazepine or anticholinergics was a mild surprise,” Ms. Mak said in an interview. “However, while we know that these drugs can have a negative effect on older people, the effects may not have been severe enough to result in hospitalizations,” she said.
Looking ahead, Ms. Mak said she would like to see the study rerun with a more current data set, especially with regard to benzodiazepines and antipsychotics.
Seek Strategies to Reduce Medication Use
The current study was notable for its community-based population and attention to hospitalizations, Shelly Gray, PharmD, a professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
“Most studies examining potentially inappropriate medications that may impair cognition have been conducted in nursing homes, while this study focuses on community dwelling older adults where most people with dementia live,” said Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented.
In addition, “A unique aspect of this study was to examine how these medications are related to hospitalizations,” she said.
Given recent efforts to reduce use of potentially inappropriate medications in people with dementia, the increase in prevalence of use over the study period was surprising, especially for benzodiazepines, said Dr. Gray.
In clinical practice, “health care providers should continue to look for opportunities to deprescribe medications that may worsen cognition in people with dementia,” she said. However, more research is needed to examine trends in the years beyond 2015 for a more contemporary picture of medication use in this population, she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Medications that could have a negative effect on cognition are often used by older adults with dementia, according to data from approximately 13 million individuals presented at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
Classes of medications including anticholinergics, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, and non-benzodiazepine sedatives (Z drugs) have been identified as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) in patients with dementia, according to The American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults.
The medications that could worsen dementia or cognition are known as CogPIMs, said presenting author Caroline M. Mak, a doctor of pharmacy candidate at the University at Buffalo School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, New York.
Previous research has characterized the prevalence of use of CogPIMs, but data connecting use of CogPIMs and healthcare use are lacking, Ms. Mak said.
Ms. Mak and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from 2011 to 2015 from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), a national survey with data on medication and healthcare use. The researchers included approximately 13 million survey respondents older than 65 years with dementia.
Exposure to CogPIMs was defined as filling a prescription for one or more of the CogPIMs during the study period. Population estimates of the prevalence of use of the CogPIMs were created using survey-weighted procedures, and prevalence trends were assessed using the Cochran-Armitage test.
Overall, the prevalence was 15.9%, 11.5%, 7.5%, and 3.8% for use of benzodiazepines, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and Z drugs, respectively, during the study period.
Of these, benzodiazepines showed a significant trend with an increase in prevalence from 8.9% in 2011 to 16.4% in 2015 (P = .02).
The odds of hospitalization were more than twice as likely in individuals who reported using Z drugs (odds ratio, 2.57; P = .02) based on logistic regression. In addition, exposure to antipsychotics was significantly associated with an increased rate of hospitalization based on a binomial model for incidence rate ratio (IRR, 1.51; P = .02).
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and the lack of more recent data.
However, the results show that CogPIMs are often used by older adults with dementia, and antipsychotics and Z drugs could be targets for interventions to prevent harm from medication interactions and side effects, the researchers concluded.
Findings Highlight Need for Drug Awareness
The current study is important because of the expansion in the aging population and an increase in the number of patients with dementia, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “In both our older population and dementia patients, there are certain medication considerations that we need to take into account, and certain drugs that should be avoided if possible,” she said. Clinicians have been trying to use the Beers criteria to reduce potential medication harm, she noted. “One group of investigators (Hilmer et al.), has proposed a narrower focus on anticholinergic and sedative/hypnotic medication in the Drug Burden Index (DBI); the CogPIMs are a subset of both approaches (Beers and DBI) and represent a collection of medications that pose potential risks to our patients,” said Ms. Mak.
Continued reassessment is needed on appropriateness of anticholinergics, Z drugs, benzodiazepines, and antipsychotics in older patients with dementia, she added.
“Even though the only group to have a significant increase in prevalence [of use] was the benzodiazepine group, we didn’t see a decrease in any of the other groups,” said Ms. Mak. The current research provides a benchmark for CogPIMs use that can be monitored in the future for increases or, ideally, decreases, she said.
Part of a Bigger Picture
The current study is part of the work of Team Alice, a national deprescribing group affiliated with the University at Buffalo that was inspired by the tragic death of Alice Brennan, triggered by preventable medication harm, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “Team Alice consists of an array of academic, primary care, health plan, and regional health information partners that have designed patient-driven interventions to reduce medication harm, especially within primary care settings,” she said. “Their mission is to save people like Alice by pursuing multiple strategies to deprescribe unsafe medication, reduce harm, and foster successful aging. By characterizing the use of CogPIMs, we can design better intervention strategies,” she said.
Although Ms. Mak was not surprised by the emergence of benzodiazepines as the most commonly used drug groups, she was surprised by the increase during the study period.
“Unfortunately, our dataset was not rich enough to include reasons for this increase,” she said. In practice, “I have seen patients getting short-term, as needed, prescriptions for a benzodiazepine to address the anxiety and/or insomnia after the loss of a loved one; this may account for a small proportion of benzodiazepine use that appears to be inappropriate because of a lack of associated appropriate diagnosis,” she noted.
Also, the findings of increased hospitalization associated with Z drugs raises concerns, Ms. Mak said. Although the findings are consistent with other research, they illustrate the need for further investigation to identify strategies to prevent this harm, she said. “Not finding associations with hospitalization related to benzodiazepine or anticholinergics was a mild surprise,” Ms. Mak said in an interview. “However, while we know that these drugs can have a negative effect on older people, the effects may not have been severe enough to result in hospitalizations,” she said.
Looking ahead, Ms. Mak said she would like to see the study rerun with a more current data set, especially with regard to benzodiazepines and antipsychotics.
Seek Strategies to Reduce Medication Use
The current study was notable for its community-based population and attention to hospitalizations, Shelly Gray, PharmD, a professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
“Most studies examining potentially inappropriate medications that may impair cognition have been conducted in nursing homes, while this study focuses on community dwelling older adults where most people with dementia live,” said Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented.
In addition, “A unique aspect of this study was to examine how these medications are related to hospitalizations,” she said.
Given recent efforts to reduce use of potentially inappropriate medications in people with dementia, the increase in prevalence of use over the study period was surprising, especially for benzodiazepines, said Dr. Gray.
In clinical practice, “health care providers should continue to look for opportunities to deprescribe medications that may worsen cognition in people with dementia,” she said. However, more research is needed to examine trends in the years beyond 2015 for a more contemporary picture of medication use in this population, she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Medications that could have a negative effect on cognition are often used by older adults with dementia, according to data from approximately 13 million individuals presented at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
Classes of medications including anticholinergics, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, and non-benzodiazepine sedatives (Z drugs) have been identified as potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) in patients with dementia, according to The American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults.
The medications that could worsen dementia or cognition are known as CogPIMs, said presenting author Caroline M. Mak, a doctor of pharmacy candidate at the University at Buffalo School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, New York.
Previous research has characterized the prevalence of use of CogPIMs, but data connecting use of CogPIMs and healthcare use are lacking, Ms. Mak said.
Ms. Mak and colleagues conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from 2011 to 2015 from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), a national survey with data on medication and healthcare use. The researchers included approximately 13 million survey respondents older than 65 years with dementia.
Exposure to CogPIMs was defined as filling a prescription for one or more of the CogPIMs during the study period. Population estimates of the prevalence of use of the CogPIMs were created using survey-weighted procedures, and prevalence trends were assessed using the Cochran-Armitage test.
Overall, the prevalence was 15.9%, 11.5%, 7.5%, and 3.8% for use of benzodiazepines, anticholinergics, antipsychotics, and Z drugs, respectively, during the study period.
Of these, benzodiazepines showed a significant trend with an increase in prevalence from 8.9% in 2011 to 16.4% in 2015 (P = .02).
The odds of hospitalization were more than twice as likely in individuals who reported using Z drugs (odds ratio, 2.57; P = .02) based on logistic regression. In addition, exposure to antipsychotics was significantly associated with an increased rate of hospitalization based on a binomial model for incidence rate ratio (IRR, 1.51; P = .02).
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, reliance on self-reports, and the lack of more recent data.
However, the results show that CogPIMs are often used by older adults with dementia, and antipsychotics and Z drugs could be targets for interventions to prevent harm from medication interactions and side effects, the researchers concluded.
Findings Highlight Need for Drug Awareness
The current study is important because of the expansion in the aging population and an increase in the number of patients with dementia, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “In both our older population and dementia patients, there are certain medication considerations that we need to take into account, and certain drugs that should be avoided if possible,” she said. Clinicians have been trying to use the Beers criteria to reduce potential medication harm, she noted. “One group of investigators (Hilmer et al.), has proposed a narrower focus on anticholinergic and sedative/hypnotic medication in the Drug Burden Index (DBI); the CogPIMs are a subset of both approaches (Beers and DBI) and represent a collection of medications that pose potential risks to our patients,” said Ms. Mak.
Continued reassessment is needed on appropriateness of anticholinergics, Z drugs, benzodiazepines, and antipsychotics in older patients with dementia, she added.
“Even though the only group to have a significant increase in prevalence [of use] was the benzodiazepine group, we didn’t see a decrease in any of the other groups,” said Ms. Mak. The current research provides a benchmark for CogPIMs use that can be monitored in the future for increases or, ideally, decreases, she said.
Part of a Bigger Picture
The current study is part of the work of Team Alice, a national deprescribing group affiliated with the University at Buffalo that was inspired by the tragic death of Alice Brennan, triggered by preventable medication harm, Ms. Mak said in an interview. “Team Alice consists of an array of academic, primary care, health plan, and regional health information partners that have designed patient-driven interventions to reduce medication harm, especially within primary care settings,” she said. “Their mission is to save people like Alice by pursuing multiple strategies to deprescribe unsafe medication, reduce harm, and foster successful aging. By characterizing the use of CogPIMs, we can design better intervention strategies,” she said.
Although Ms. Mak was not surprised by the emergence of benzodiazepines as the most commonly used drug groups, she was surprised by the increase during the study period.
“Unfortunately, our dataset was not rich enough to include reasons for this increase,” she said. In practice, “I have seen patients getting short-term, as needed, prescriptions for a benzodiazepine to address the anxiety and/or insomnia after the loss of a loved one; this may account for a small proportion of benzodiazepine use that appears to be inappropriate because of a lack of associated appropriate diagnosis,” she noted.
Also, the findings of increased hospitalization associated with Z drugs raises concerns, Ms. Mak said. Although the findings are consistent with other research, they illustrate the need for further investigation to identify strategies to prevent this harm, she said. “Not finding associations with hospitalization related to benzodiazepine or anticholinergics was a mild surprise,” Ms. Mak said in an interview. “However, while we know that these drugs can have a negative effect on older people, the effects may not have been severe enough to result in hospitalizations,” she said.
Looking ahead, Ms. Mak said she would like to see the study rerun with a more current data set, especially with regard to benzodiazepines and antipsychotics.
Seek Strategies to Reduce Medication Use
The current study was notable for its community-based population and attention to hospitalizations, Shelly Gray, PharmD, a professor of pharmacy at the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, said in an interview.
“Most studies examining potentially inappropriate medications that may impair cognition have been conducted in nursing homes, while this study focuses on community dwelling older adults where most people with dementia live,” said Dr. Gray, who served as a moderator for the session in which the study was presented.
In addition, “A unique aspect of this study was to examine how these medications are related to hospitalizations,” she said.
Given recent efforts to reduce use of potentially inappropriate medications in people with dementia, the increase in prevalence of use over the study period was surprising, especially for benzodiazepines, said Dr. Gray.
In clinical practice, “health care providers should continue to look for opportunities to deprescribe medications that may worsen cognition in people with dementia,” she said. However, more research is needed to examine trends in the years beyond 2015 for a more contemporary picture of medication use in this population, she noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Gray had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AGS 2024
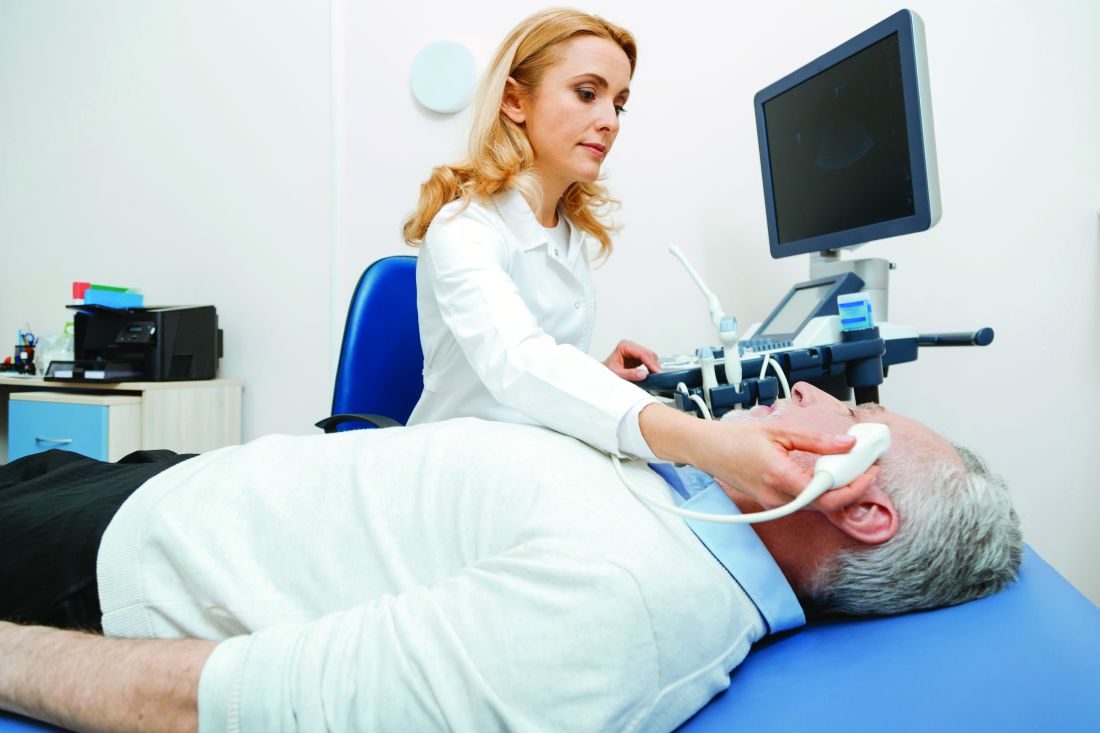
Diagnosing Giant Cell Arteritis Using Ultrasound First Proves Accurate, Avoids Biopsy in Many Cases
Temporal artery ultrasound alone was sufficient to accurately diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA) in over half of patients in a new prospective study.
The findings provide further evidence that “[ultrasound] of temporal arteries could really take the place of traditional temporal artery biopsy (TAB)” in patients with high clinical suspicion of GCA, lead author Guillaume Denis, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier de Rochefort in Rochefort, France, told this news organization.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) already recommends ultrasound as a first-line diagnostic tool for patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis, and the 2022 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/EULAR classification criteria for GCA weighs positive TAB or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound equally.
Guidelines from the ACR and the Vasculitis Foundation still recommend TAB over ultrasound.
“In general, rheumatologists and radiologists in the US are less experienced in using ultrasound to diagnose temporal artery involvement in GCA compared to their counterparts in Europe,” the 2021 guidelines stated. “In centers with appropriate training and expertise in using temporal artery ultrasound, ultrasound may be a useful and complementary tool for diagnosing GCA.”
Methodology
In the study, researchers recruited 165 individuals with high clinical suspicion of GCA from August 2016 through February 2020 at six French hospitals. Only patients older than 50 years of age and with biologic inflammatory syndrome with C-reactive protein elevation (≥ 6 mg/L) qualified for the study. Patients also needed to have at least one of these factors:
- Clinical signs of GCA (abnormal temporal arteries, scalp hyperesthesia, jaw claudication, or vision loss)
- General signs of GCA (headache, fever, or impaired general condition)
- Large-vessel vasculitis visible on imaging (CT angiography [CTA], MR angiography [MRA], and/or PET/CT)
All participants underwent a color Doppler ultrasound of the temporal artery, performed less than 1 week after the initiation of corticosteroid therapy. (Previous research demonstrated that corticosteroids can change the hallmark halo sign of vasculitis detectable via ultrasound as early as 1 week after initiation of therapy, the authors noted.) In this study, the time between consultation with a specialist and ultrasound was less than 1 day.
“Patients with halo signs detected around the lumen of both temporal arteries (that is, bilateral temporal halo sign) were considered as ultrasound-positive,” Guillaume Denis, MD, and colleagues explained. “Patients with no halo sign, or bilateral halo signs in the axillary arteries, or a unilateral halo sign in the temporal artery were considered as ultrasound-negative.”
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine on May 7.
Results
In total, 73 participants (44%) had positive ultrasounds and were diagnosed with GCA. These patients also underwent a second ultrasound a month later to document if the halo sign remained unchanged, reduced, or disappeared.
The remaining 92 patients with negative ultrasound results underwent TAB, which was conducted on average 4.5 days after the ultrasound. A total of 28 patients (30%) had a positive TAB result. Physicians diagnosed 35 TAB-negative patients with GCA using clinical, imaging, and biologic data, and 29 patients received alternative diagnoses. These other diagnoses included polymyalgia rheumatica, infectious diseases, cancer, and other systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
All patients diagnosed with GCA via ultrasound had their diagnoses reconfirmed at 1 month and for up to 2 years of follow-up.
“In summary, our study showed that the use of temporal artery ultrasound may be an efficient way to make the diagnosis of GCA in patients with high clinical suspicion and to reduce imaging costs and the need for biopsy, thereby limiting complications and the need for a surgeon,” the authors concluded.
Qualifications and Limitations
While over half of patients ultimately diagnosed with GCA were diagnosed using ultrasound, that percentage was “a bit lower than expected,” said Mark Matza, MD, MBA, the co-clinical director of rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. By comparison, one systematic review calculated ultrasound’s pooled sensitivity at 88% and pooled specificity at 96% for the diagnosis of GCA.
“In this [current] study, 30% of patients who had negative ultrasound were then found to have positive biopsy, indicating that ultrasound missed a substantial portion of patients who were ultimately diagnosed with GCA,” he continued.
Ultrasound is “very operator dependent,” he added, and there has been “variability in test performance of ultrasound.”
The authors acknowledged that techniques for ultrasound of the temporal arteries have also evolved over the study period, and thus, findings may not have been consistent.
However, about one in four patients with GCA were diagnosed after having both negative ultrasound and TAB results.
“One of the things that this paper shows is that even the gold standard of temporal artery biopsy isn’t 100% either,” noted Minna Kohler, MD, who directs the rheumatology musculoskeletal ultrasound program at Massachusetts General Hospital. “That’s why clinically, there is an increasing emphasis on using multimodality imaging to assist in the diagnosis of GCA along with a physician’s clinical intuition,” she said.
While ultrasound can visualize axillary, subclavian, and carotid arteries, other imaging modalities such as CTA, MRA, and PET/CT are better to fully assess supra-aortic and aortic vessels, she continued. However, “this imaging is more expensive and takes more time to coordinate, schedule, whereas ultrasound of temporal and axillary arteries can easily be done within the clinic with an immediate answer.”
This study was supported by a grant from “Recherche CH-CHU Poitou-Charentes 2014.” Dr. Denis disclosed relationships with Leo Pharma, Janssen, Novartis, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Matza reported honoraria from the Ultrasound School of North American Rheumatologists. Kohler had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Temporal artery ultrasound alone was sufficient to accurately diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA) in over half of patients in a new prospective study.
The findings provide further evidence that “[ultrasound] of temporal arteries could really take the place of traditional temporal artery biopsy (TAB)” in patients with high clinical suspicion of GCA, lead author Guillaume Denis, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier de Rochefort in Rochefort, France, told this news organization.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) already recommends ultrasound as a first-line diagnostic tool for patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis, and the 2022 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/EULAR classification criteria for GCA weighs positive TAB or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound equally.
Guidelines from the ACR and the Vasculitis Foundation still recommend TAB over ultrasound.
“In general, rheumatologists and radiologists in the US are less experienced in using ultrasound to diagnose temporal artery involvement in GCA compared to their counterparts in Europe,” the 2021 guidelines stated. “In centers with appropriate training and expertise in using temporal artery ultrasound, ultrasound may be a useful and complementary tool for diagnosing GCA.”
Methodology
In the study, researchers recruited 165 individuals with high clinical suspicion of GCA from August 2016 through February 2020 at six French hospitals. Only patients older than 50 years of age and with biologic inflammatory syndrome with C-reactive protein elevation (≥ 6 mg/L) qualified for the study. Patients also needed to have at least one of these factors:
- Clinical signs of GCA (abnormal temporal arteries, scalp hyperesthesia, jaw claudication, or vision loss)
- General signs of GCA (headache, fever, or impaired general condition)
- Large-vessel vasculitis visible on imaging (CT angiography [CTA], MR angiography [MRA], and/or PET/CT)
All participants underwent a color Doppler ultrasound of the temporal artery, performed less than 1 week after the initiation of corticosteroid therapy. (Previous research demonstrated that corticosteroids can change the hallmark halo sign of vasculitis detectable via ultrasound as early as 1 week after initiation of therapy, the authors noted.) In this study, the time between consultation with a specialist and ultrasound was less than 1 day.
“Patients with halo signs detected around the lumen of both temporal arteries (that is, bilateral temporal halo sign) were considered as ultrasound-positive,” Guillaume Denis, MD, and colleagues explained. “Patients with no halo sign, or bilateral halo signs in the axillary arteries, or a unilateral halo sign in the temporal artery were considered as ultrasound-negative.”
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine on May 7.
Results
In total, 73 participants (44%) had positive ultrasounds and were diagnosed with GCA. These patients also underwent a second ultrasound a month later to document if the halo sign remained unchanged, reduced, or disappeared.
The remaining 92 patients with negative ultrasound results underwent TAB, which was conducted on average 4.5 days after the ultrasound. A total of 28 patients (30%) had a positive TAB result. Physicians diagnosed 35 TAB-negative patients with GCA using clinical, imaging, and biologic data, and 29 patients received alternative diagnoses. These other diagnoses included polymyalgia rheumatica, infectious diseases, cancer, and other systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
All patients diagnosed with GCA via ultrasound had their diagnoses reconfirmed at 1 month and for up to 2 years of follow-up.
“In summary, our study showed that the use of temporal artery ultrasound may be an efficient way to make the diagnosis of GCA in patients with high clinical suspicion and to reduce imaging costs and the need for biopsy, thereby limiting complications and the need for a surgeon,” the authors concluded.
Qualifications and Limitations
While over half of patients ultimately diagnosed with GCA were diagnosed using ultrasound, that percentage was “a bit lower than expected,” said Mark Matza, MD, MBA, the co-clinical director of rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. By comparison, one systematic review calculated ultrasound’s pooled sensitivity at 88% and pooled specificity at 96% for the diagnosis of GCA.
“In this [current] study, 30% of patients who had negative ultrasound were then found to have positive biopsy, indicating that ultrasound missed a substantial portion of patients who were ultimately diagnosed with GCA,” he continued.
Ultrasound is “very operator dependent,” he added, and there has been “variability in test performance of ultrasound.”
The authors acknowledged that techniques for ultrasound of the temporal arteries have also evolved over the study period, and thus, findings may not have been consistent.
However, about one in four patients with GCA were diagnosed after having both negative ultrasound and TAB results.
“One of the things that this paper shows is that even the gold standard of temporal artery biopsy isn’t 100% either,” noted Minna Kohler, MD, who directs the rheumatology musculoskeletal ultrasound program at Massachusetts General Hospital. “That’s why clinically, there is an increasing emphasis on using multimodality imaging to assist in the diagnosis of GCA along with a physician’s clinical intuition,” she said.
While ultrasound can visualize axillary, subclavian, and carotid arteries, other imaging modalities such as CTA, MRA, and PET/CT are better to fully assess supra-aortic and aortic vessels, she continued. However, “this imaging is more expensive and takes more time to coordinate, schedule, whereas ultrasound of temporal and axillary arteries can easily be done within the clinic with an immediate answer.”
This study was supported by a grant from “Recherche CH-CHU Poitou-Charentes 2014.” Dr. Denis disclosed relationships with Leo Pharma, Janssen, Novartis, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Matza reported honoraria from the Ultrasound School of North American Rheumatologists. Kohler had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Temporal artery ultrasound alone was sufficient to accurately diagnose giant cell arteritis (GCA) in over half of patients in a new prospective study.
The findings provide further evidence that “[ultrasound] of temporal arteries could really take the place of traditional temporal artery biopsy (TAB)” in patients with high clinical suspicion of GCA, lead author Guillaume Denis, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier de Rochefort in Rochefort, France, told this news organization.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) already recommends ultrasound as a first-line diagnostic tool for patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis, and the 2022 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/EULAR classification criteria for GCA weighs positive TAB or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound equally.
Guidelines from the ACR and the Vasculitis Foundation still recommend TAB over ultrasound.
“In general, rheumatologists and radiologists in the US are less experienced in using ultrasound to diagnose temporal artery involvement in GCA compared to their counterparts in Europe,” the 2021 guidelines stated. “In centers with appropriate training and expertise in using temporal artery ultrasound, ultrasound may be a useful and complementary tool for diagnosing GCA.”
Methodology
In the study, researchers recruited 165 individuals with high clinical suspicion of GCA from August 2016 through February 2020 at six French hospitals. Only patients older than 50 years of age and with biologic inflammatory syndrome with C-reactive protein elevation (≥ 6 mg/L) qualified for the study. Patients also needed to have at least one of these factors:
- Clinical signs of GCA (abnormal temporal arteries, scalp hyperesthesia, jaw claudication, or vision loss)
- General signs of GCA (headache, fever, or impaired general condition)
- Large-vessel vasculitis visible on imaging (CT angiography [CTA], MR angiography [MRA], and/or PET/CT)
All participants underwent a color Doppler ultrasound of the temporal artery, performed less than 1 week after the initiation of corticosteroid therapy. (Previous research demonstrated that corticosteroids can change the hallmark halo sign of vasculitis detectable via ultrasound as early as 1 week after initiation of therapy, the authors noted.) In this study, the time between consultation with a specialist and ultrasound was less than 1 day.
“Patients with halo signs detected around the lumen of both temporal arteries (that is, bilateral temporal halo sign) were considered as ultrasound-positive,” Guillaume Denis, MD, and colleagues explained. “Patients with no halo sign, or bilateral halo signs in the axillary arteries, or a unilateral halo sign in the temporal artery were considered as ultrasound-negative.”
The findings were published in Annals of Internal Medicine on May 7.
Results
In total, 73 participants (44%) had positive ultrasounds and were diagnosed with GCA. These patients also underwent a second ultrasound a month later to document if the halo sign remained unchanged, reduced, or disappeared.
The remaining 92 patients with negative ultrasound results underwent TAB, which was conducted on average 4.5 days after the ultrasound. A total of 28 patients (30%) had a positive TAB result. Physicians diagnosed 35 TAB-negative patients with GCA using clinical, imaging, and biologic data, and 29 patients received alternative diagnoses. These other diagnoses included polymyalgia rheumatica, infectious diseases, cancer, and other systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
All patients diagnosed with GCA via ultrasound had their diagnoses reconfirmed at 1 month and for up to 2 years of follow-up.
“In summary, our study showed that the use of temporal artery ultrasound may be an efficient way to make the diagnosis of GCA in patients with high clinical suspicion and to reduce imaging costs and the need for biopsy, thereby limiting complications and the need for a surgeon,” the authors concluded.
Qualifications and Limitations
While over half of patients ultimately diagnosed with GCA were diagnosed using ultrasound, that percentage was “a bit lower than expected,” said Mark Matza, MD, MBA, the co-clinical director of rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. By comparison, one systematic review calculated ultrasound’s pooled sensitivity at 88% and pooled specificity at 96% for the diagnosis of GCA.
“In this [current] study, 30% of patients who had negative ultrasound were then found to have positive biopsy, indicating that ultrasound missed a substantial portion of patients who were ultimately diagnosed with GCA,” he continued.
Ultrasound is “very operator dependent,” he added, and there has been “variability in test performance of ultrasound.”
The authors acknowledged that techniques for ultrasound of the temporal arteries have also evolved over the study period, and thus, findings may not have been consistent.
However, about one in four patients with GCA were diagnosed after having both negative ultrasound and TAB results.
“One of the things that this paper shows is that even the gold standard of temporal artery biopsy isn’t 100% either,” noted Minna Kohler, MD, who directs the rheumatology musculoskeletal ultrasound program at Massachusetts General Hospital. “That’s why clinically, there is an increasing emphasis on using multimodality imaging to assist in the diagnosis of GCA along with a physician’s clinical intuition,” she said.
While ultrasound can visualize axillary, subclavian, and carotid arteries, other imaging modalities such as CTA, MRA, and PET/CT are better to fully assess supra-aortic and aortic vessels, she continued. However, “this imaging is more expensive and takes more time to coordinate, schedule, whereas ultrasound of temporal and axillary arteries can easily be done within the clinic with an immediate answer.”
This study was supported by a grant from “Recherche CH-CHU Poitou-Charentes 2014.” Dr. Denis disclosed relationships with Leo Pharma, Janssen, Novartis, Takeda, and Sanofi. Dr. Matza reported honoraria from the Ultrasound School of North American Rheumatologists. Kohler had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Traffic Noise Negatively Impacts Health
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research by Thomas Münzel, MD, senior professor of cardiology at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz in Mainz, Germany, and colleagues again emphasized the harmful effects of noise on the heart and blood vessels. An analysis of current epidemiologic data provided strong indications that transportation noise is closely related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, according to a statement on the data analysis. The results were published in Circulation Research.
Morbidity and Mortality
Epidemiologic studies have shown that road, rail, or air traffic noise increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, with strong evidence for ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, according to the scientists. These factors could favor vascular (endothelial) dysfunction, inflammation, and hypertension, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.
Consequences and Pathomechanisms
In the current publication, the authors provided an overview of epidemiologic research on the effects of transportation noise on cardiovascular risk factors and diseases, discussed mechanistic insights from the latest clinical and experimental studies, and proposed new risk markers to address noise-induced cardiovascular effects in the general population. An integrated analysis in the article demonstrated that for every 10 dB(A) increase, the risk for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure significantly increases by 3.2%.
The authors also explained the possible effects of noise on changes in gene networks, epigenetic pathways, circadian rhythms, signal transmission along the neuronal-cardiovascular axis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolism. Finally, current and future noise protection strategies are described, and the existing evidence on noise as a cardiovascular risk factor is discussed.
Confirmed Cardiovascular Risk Factor
“As an increasing proportion of the population is exposed to harmful traffic noise, efforts to reduce noise and laws for noise reduction are of great importance for future public health,” said Dr. Münzel. “It is also important for us that due to the strong evidence, traffic noise is finally recognized as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.”
Heart Attack Outcomes
Dr. Münzel and other researchers from Mainz have been studying the cardiovascular consequences of air pollution and traffic noise for several years. For example, they found that heart attacks in people and animals exposed to high noise levels earlier in life healed poorly. These results were published last year in Cardiovascular Research. According to the authors, the findings suggest that traffic noise may play a significant role in the development and course of coronary heart disease, such as after a heart attack.
The scientists initially found in animal experiments that exposure to aircraft noise for 4 days led to increased inflammation in the vessels. Compared with mice not exposed to aircraft noise, the noise-exposed animals showed an increase in free radicals; these animals exhibited a significant inflammatory response and had impaired vessel function.
The researchers explained that the experimental data showed aircraft noise alone triggers a proinflammatory transcription program that promotes the infiltration of immune cells into cardiovascular tissue in animals with acute myocardial infarction. They noted an increased infiltration of CD45+ cells into the vessels and heart, dominated by neutrophils in vessel tissue and Ly6Chigh monocytes in heart tissue. This infiltration creates a proinflammatory milieu that adversely affects the outcome after myocardial infarction by predisposing the heart tissue to greater ischemic damage and functional impairment. Exposure of animals to aircraft noise before induction of myocardial infarction by left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation impaired left ventricular function and increased infarct size after cardiac ischemia. In addition, noise exposure exacerbated infarct-induced endothelial dysfunction of peripheral vessels as early as 24 hours after LAD ligation.
Clinical Confirmation
These experimental results were confirmed by observations in the population-based Gutenberg Health Study. The researchers analyzed data from 100 patients with heart attack. The lead and senior authors of the study Michael Molitor, MD, and Philip Wenzel, MD, of the University of Mainz, explained, “From our studies, we have learned that exposure to aircraft noise before a heart attack significantly amplifies subsequent cardiovascular inflammation and exacerbates ischemic heart failure, which is favored by inflammation-promoting vascular conditioning. Our translational results show that people who have been exposed to noise in the past have a worse course if they experience a heart attack later in life.”
Study participants who had experienced a heart attack in their medical history had elevated levels of C-reactive protein if they had been exposed to aircraft noise in the past and subsequently developed noise annoyance reactions (0.305 vs 1.5; P = .0094). In addition, left ventricular ejection fraction in these patients after a heart attack was worse than that in patients with infarction without noise exposure in their medical history (62.5 vs 65.6; P = .0053).
The results suggest that measures to reduce environmental noise could help improve the clinical outcomes of heart attack patients, according to the authors.
Mental Health Effects
Traffic noise also may be associated with an increased risk for depression and anxiety disorders, as reported 2 years ago by the German Society for Psychosomatic Medicine and Medical Psychotherapy. Evolution has programmed the human organism to perceive noises as indicators of potential sources of danger — even during sleep. “Noise puts the body on alert,” explained Manfred E. Beutel, MD, director of the Clinic for Psychosomatic Medicine and Psychotherapy at the University of Mainz. As a result, the autonomic nervous system activates stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. If noise becomes chronic, chronic diseases can develop. “Indeed, observational and experimental studies have shown that persistent noise annoyance promotes incident hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Beutel.
Depression Risk Doubled
Among the negative effects of noise annoyance are also mental illnesses, as has become increasingly clear. “Noise annoyance disrupts daily activities and interferes with feelings and thoughts, sleep, and recovery,” said Dr. Beutel. The interruptions trigger negative emotional reactions such as anger, distress, exhaustion, flight impulses, and stress symptoms. “Such conditions promote the development of depression over time,” said Dr. Beutel. This observation was confirmed by the large-scale Gutenberg Health Study using the example of the Mainz population, which suffers to a large extent from noise annoyance because of the nearby Frankfurt Airport. “With increasing noise annoyance, the rates of depression and anxiety disorders steadily increased, until the risks eventually doubled with extreme annoyance,” said Dr. Beutel. Other studies point in the same direction. For example, a meta-analysis found a 12% increase in the risk for depression per 10-dB increase in noise. Another study found an association between nocturnal noise annoyance and the use of antidepressants.
Fine Particulate Matter
According to an evaluation of the Gutenberg Study, people perceive noise annoyance from aircraft noise as the most pronounced, followed by road, neighborhood, industrial, and railway noise. Noise occurs most frequently in urban areas that also produce air pollution such as fine particulate matter. “Fine particulate matter is also suspected of promoting anxiety and depression,” said Dr. Beutel, “because the small particles of fine particulate matter can enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammatory processes there, which in turn are closely related to depression.”
This story was translated from Univadis Germany, which is part of the Medscape professional network, using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New mRNA Vaccines in Development for Cancer and Infections
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Martina Prelog, MD, a pediatric and adolescent medicine specialist at the University Hospital of Würzburg in Germany, reported on the principles, research status, and perspectives for these vaccines at the 25th Travel and Health Forum of the Center for Travel Medicine in Berlin.
To understand the future, the immunologist first examined the past. “The induction of cellular and humoral immune responses by externally injected mRNA was discovered in the 1990s,” she said.
Instability Challenge
Significant hurdles in mRNA vaccinations included the instability of mRNA and the immune system’s ability to identify foreign mRNA as a threat and destroy mRNA fragments. “The breakthrough toward vaccination came through Dr. Katalin Karikó, who, along with Dr. Drew Weissman, both of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, discovered in 2005 that modifications of mRNA (replacing the nucleoside uridine with pseudouridine) enable better stability of mRNA, reduced immunogenicity, and higher translational capacity at the ribosomes,” said Dr. Prelog.
With this discovery, the two researchers paved the way for the development of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases. They were awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for their discovery last year.
Improved Scalability
“Since 2009, mRNA vaccines have been studied as a treatment option for cancer,” said Dr. Prelog. “Since 2012, they have been studied for the influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus [RSV].” Consequently, several mRNA vaccines are currently in development or in approval studies. “The mRNA technology offers the advantage of quickly and flexibly responding to new variants of pathogens and the ability to scale up production when there is high demand for a particular vaccine.”
Different forms and designations of mRNA vaccines are used, depending on the application and desired effect, said Dr. Prelog.
In nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines, modifications in the mRNA sequence enable the mRNA to remain in the body longer and to induce protein synthesis more effectively.
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–encapsulated mRNA vaccines protect the coding mRNA sequences against degradation by the body’s enzymes and facilitate the uptake of mRNA into cells, where it then triggers the production of the desired protein. In addition, LNPs are involved in cell stimulation and support the self-adjuvant effect of mRNA vaccines, thus eliminating the need for adjuvants.
Self-amplifying mRNA vaccines include a special mRNA that replicates itself in the cell and contains a sequence for RNA replicase, in addition to the coding sequence for the protein. This composition enables increased production of the target protein without the need for a high amount of external mRNA administration. Such vaccines could trigger a longer and stronger immune response because the immune system has more time to interact with the protein.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Dr. Prelog also discussed personalized vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Personalized mRNA vaccines are tailored to the patient’s genetic characteristics and antigens. They could be used in cancer immunotherapy to activate the immune system selectively against tumor cells.
Multivalent mRNA vaccines contain mRNA that codes for multiple antigens rather than just one protein to generate an immune response. These vaccines could be particularly useful in fighting pathogens with variable or changing surface structures or in eliciting protection against multiple pathogens simultaneously.
The technology of mRNA-encoded antibodies involves introducing mRNA into the cell, which creates light and heavy chains of antibodies. This step leads to the formation of antibodies targeted against toxins (eg, diphtheria and tetanus), animal venoms, infectious agents, or tumor cells.
Genetic Engineering
Dr. Prelog also reviewed genetic engineering techniques. In regenerative therapy or protein replacement therapy, skin fibroblasts or other cells are transfected with mRNA to enable conversion into induced pluripotent stem cells. This approach avoids the risk for DNA integration into the genome and associated mutation risks.
Another approach is making post-transcriptional modifications through RNA interference. For example, RNA structures can be used to inhibit the translation of disease-causing proteins. This technique is currently being tested against HIV and tumors such as melanoma.
In addition, mRNA technologies can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 technology (“gene scissors”) to influence the creation of gene products even more precisely. The advantage of this technique is that mRNA is only transiently expressed, thus preventing unwanted side effects. Furthermore, mRNA is translated directly in the cytoplasm, leading to a faster initiation of gene editing.
Of the numerous ongoing clinical mRNA vaccine studies, around 70% focus on infections, about 12% on cancer, and the rest on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders, said Dr. Prelog.
Research in Infections
Research in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology is the most advanced: mRNA vaccines against influenza and RSV are already in advanced clinical trials, Dr. Prelog told this news organization.
“Conventional influenza vaccines contain immunogenic surface molecules against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in various combinations of influenza strains A and B and are produced in egg or cell cultures,” she said. “This is a time-consuming manufacturing process that takes months and, particularly with the egg-based process, bears the risk of changing the vaccine strain.”
“Additionally, influenza viruses undergo antigenic shift and drift through recombination, thus requiring annual adjustments to the vaccines. Thus, these influenza vaccines often lose accuracy in targeting circulating seasonal influenza strains.”
Several mRNA vaccines being tested contain not only coding sequences against hemagglutinin and neuraminidase but also for structural proteins of influenza viruses. “These are more conserved and mutate less easily, meaning they could serve as the basis for universal pandemic influenza vaccines,” said Dr. Prelog.
An advantage of mRNA vaccines, she added, is the strong cellular immune response that they elicit. This response is intended to provide additional protection alongside specific antibodies. An mRNA vaccine with coding sequences for the pre-fusion protein of RSV is in phase 3 trials for approval for vaccination in patients aged 60 years and older. It shows high effectiveness even in older patients and those with comorbidities.
Elaborate Purification Process
Bacterial origin plasmid DNA is used to produce mRNA vaccines. The mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 raised concerns that production-related DNA residues could pose a safety risk and cause autoimmune diseases.
These vaccines “typically undergo a very elaborate purification process,” said Dr. Prelog. “This involves enzymatic digestion with DNase to fragment and deplete plasmid DNA, followed by purification using chromatography columns, so that no safety-relevant DNA fragments should remain afterward.”
Thus, the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut also pointed out the very small, fragmented plasmid DNA residues of bacterial origin in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines pose no risk, unlike residual DNA from animal cell culture might pose in other vaccines.
Prevention and Therapy
In addition to the numerous advantages of mRNA vaccines (such as rapid adaptability to new or mutated pathogens, scalability, rapid production capability, self-adjuvant effect, strong induction of cellular immune responses, and safety), there are also challenges in RNA technology as a preventive and therapeutic measure, according to Dr. Prelog.
“Stability and storability, as well as the costs of new vaccine developments, play a role, as do the long-term effects regarding the persistence of antibody and cellular responses,” she said. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, for example, showed a well-maintained cellular immune response despite a tendency toward a rapid decline in humoral immune response.
“The experience with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the new vaccine developments based on mRNA technology give hope for an efficient and safe preventive and therapeutic use, particularly in the fields of infectious diseases and oncology,” Dr. Prelog concluded.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Jumpstart Your AI Learning: The Very Best Resources for Doctors
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Like it or not, artificial intelligence (AI) is coming to medicine. For many physicians — maybe you — it’s already here.
More than a third of physicians use AI in their practice. And the vast majority of healthcare companies — 94%, according to Morgan Stanley — use some kind of AI machine learning.
“It’s incumbent on physicians, as well as physicians in training, to become familiar with at least the basics [of AI],” said internist Matthew DeCamp, MD, PhD, an associate professor in the Center for Bioethics and Humanities at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Frankly, the people who are deciding whether to implement algorithms in our day-to-day lives are oftentimes not physicians,” noted Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania and director of augmented and artificial intelligence at the Penn Center for Cancer Care Innovation, Philadelphia. Yet, physicians are most qualified to assess an AI tool’s usefulness in clinical practice.
That brings us to the best starting place for your AI education: Your own institution. Find out what AI tools your organization is implementing — and how you can influence them.
“Getting involved with our hospital data governance is the best way not only to learn practically what these AI tools do but also to influence the development process in positive ways,” Dr. Parikh said.
From there, consider the following resources to enhance your AI knowledge.
Get a Lay of the Land: Free Primers
Many clinical societies and interest groups have put out AI primers, an easy way to get a broad overview of the technology. The following were recommended or developed by the experts we spoke to, and all are free:
- The American Medical Association’s (AMA’s) framework for advancing healthcare AI lays out actionable guidance. Ask three key questions, the AMA recommends: Does it work? Does it work for my patients? Does it improve health outcomes?
- The Coalition for Health AI’s Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare provides a high-level summary of how to evaluate AI in healthcare, plus steps for implementing it. AI systems should be useful, safe, accountable, explainable, fair, and secure, the report asserted.
- The National Academy of Medicine’s draft code of conduct for AI in healthcare proposes core principles and commitments. These “reflect simple guideposts to guide and gauge behavior in a complex system and provide a starting point for real-time decision-making,” the report said.
- Health AI Partnership — a collaboration of Duke Health and Microsoft — outlines eight key decision points to consider at any stage of AI implementation, whether you’re still planning how to use it or you’ve started but want to improve it. The site also provides a breakdown of standards by regulatory agencies, organizations, and oversight bodies — so you can make sure your practices align with their guidance.
Make the Most of Conferences
Next time you’re at a conference, check the agenda for sessions on AI. “For someone who’s interested in this, I would be looking for content in my next national meeting because, undoubtedly, it’s going to be there,” said Dr. DeCamp. In a fast-moving field like AI, it’s a great way to get fresh, up-to-the-moment insights.
Listen to This Podcast
The New England Journal of Medicine’s free monthly podcast AI Grand Rounds is made for researchers and clinicians. Available on Apple, Spotify, and YouTube, the pod is good for “someone who’s looking to see both where the field is going [and to hear] a retrospective on big-name papers,” said Dr. Parikh . Episodes run for about an hour.
To learn about the challenges of applying AI to biology: Listen to Daphne Koller, PhD, founder of AI-driven drug discovery and development company insitro. For insights on the potential of AI in medicine, tune into the one with Eric Horvitz, MD, PhD, Microsoft’s chief scientific officer.
Consider a Class
Look for courses that focus on AI applications in clinical practice rather than a deep dive into theory. (You need to understand how these tools will influence your work, not the intricacies of large language model development.) Be wary of corporate-funded training that centers on one product , which could present conflicts of interest, said Dr. DeCamp. See the chart for courses that meet these criteria.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Big Pharma, Small Payments
A recent review of the Open Payments database found that, over the last 10 years, the evil forces of Big Pharma have paid doctors $12.1 billion dollars.
That’s a lot.
Of course, there are also quite a few doctors out there, and the word “paid” is kind of a misnomer. Yes, some people did get paid directly — cash for research, speaking engagements, teaching other docs — but a lot of the money was really spent on marketing. It may show that Dr. Jones was “paid” $200 one day, when in reality that was the cost of providing lunch to her, her five-person office staff, and the medical student following her around that afternoon.
In the last 10 years, I’ve accepted “payments” of one pizza and three iced coffees, so I guess I’m on there, too.
When you actually break it down, this comes out to a national average of (drum roll) $48 per doctor over 10 years.
Let’s face it, if your prescribing habits can be bought for $4.80 a year ... that’s pretty sad. They say everyone has their price, but hopefully it’s not that of a Happy Meal.
I understand the reasons for tracking this sort of thing. The system certainly can be — and has been — gamed for abuse. If one doctor is getting a ridiculous amount of money for doing nothing but writing scripts for Walletgouge-XR, that certainly needs to be known. Something is rotten in the state of Denmark (or wherever).
But the headline, especially when used in the lay media, makes it sound like all docs are on payola, and further erodes trust in the medical field. The fact that it works out to $4.80 per doctor each year is going to buried deeper in the article, by which time most readers will have moved on to see what Taylor Swift is up to.
Perhaps I’ve taken it to an extreme, but since the pizza (2014) I haven’t done lunch at my office. I still meet with reps, but they’re told now that I don’t do lunch, or bagels, or even iced coffee anymore. Tell me what I need to know about the new drug, but at this point in my career I’d rather have time. By not meeting a rep over lunch, or coffee, it adds 30-60 minutes to my day to use for reviewing tests, returning calls, and typing up notes. Those are things I’m going to have to do at some point, so I’d rather do them at my office and have the extra time at home, even if it’s just to do a jigsaw puzzle with my daughter.
That’s worth more than $4.80 per year.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
A recent review of the Open Payments database found that, over the last 10 years, the evil forces of Big Pharma have paid doctors $12.1 billion dollars.
That’s a lot.
Of course, there are also quite a few doctors out there, and the word “paid” is kind of a misnomer. Yes, some people did get paid directly — cash for research, speaking engagements, teaching other docs — but a lot of the money was really spent on marketing. It may show that Dr. Jones was “paid” $200 one day, when in reality that was the cost of providing lunch to her, her five-person office staff, and the medical student following her around that afternoon.
In the last 10 years, I’ve accepted “payments” of one pizza and three iced coffees, so I guess I’m on there, too.
When you actually break it down, this comes out to a national average of (drum roll) $48 per doctor over 10 years.
Let’s face it, if your prescribing habits can be bought for $4.80 a year ... that’s pretty sad. They say everyone has their price, but hopefully it’s not that of a Happy Meal.
I understand the reasons for tracking this sort of thing. The system certainly can be — and has been — gamed for abuse. If one doctor is getting a ridiculous amount of money for doing nothing but writing scripts for Walletgouge-XR, that certainly needs to be known. Something is rotten in the state of Denmark (or wherever).
But the headline, especially when used in the lay media, makes it sound like all docs are on payola, and further erodes trust in the medical field. The fact that it works out to $4.80 per doctor each year is going to buried deeper in the article, by which time most readers will have moved on to see what Taylor Swift is up to.
Perhaps I’ve taken it to an extreme, but since the pizza (2014) I haven’t done lunch at my office. I still meet with reps, but they’re told now that I don’t do lunch, or bagels, or even iced coffee anymore. Tell me what I need to know about the new drug, but at this point in my career I’d rather have time. By not meeting a rep over lunch, or coffee, it adds 30-60 minutes to my day to use for reviewing tests, returning calls, and typing up notes. Those are things I’m going to have to do at some point, so I’d rather do them at my office and have the extra time at home, even if it’s just to do a jigsaw puzzle with my daughter.
That’s worth more than $4.80 per year.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
A recent review of the Open Payments database found that, over the last 10 years, the evil forces of Big Pharma have paid doctors $12.1 billion dollars.
That’s a lot.
Of course, there are also quite a few doctors out there, and the word “paid” is kind of a misnomer. Yes, some people did get paid directly — cash for research, speaking engagements, teaching other docs — but a lot of the money was really spent on marketing. It may show that Dr. Jones was “paid” $200 one day, when in reality that was the cost of providing lunch to her, her five-person office staff, and the medical student following her around that afternoon.
In the last 10 years, I’ve accepted “payments” of one pizza and three iced coffees, so I guess I’m on there, too.
When you actually break it down, this comes out to a national average of (drum roll) $48 per doctor over 10 years.
Let’s face it, if your prescribing habits can be bought for $4.80 a year ... that’s pretty sad. They say everyone has their price, but hopefully it’s not that of a Happy Meal.
I understand the reasons for tracking this sort of thing. The system certainly can be — and has been — gamed for abuse. If one doctor is getting a ridiculous amount of money for doing nothing but writing scripts for Walletgouge-XR, that certainly needs to be known. Something is rotten in the state of Denmark (or wherever).
But the headline, especially when used in the lay media, makes it sound like all docs are on payola, and further erodes trust in the medical field. The fact that it works out to $4.80 per doctor each year is going to buried deeper in the article, by which time most readers will have moved on to see what Taylor Swift is up to.
Perhaps I’ve taken it to an extreme, but since the pizza (2014) I haven’t done lunch at my office. I still meet with reps, but they’re told now that I don’t do lunch, or bagels, or even iced coffee anymore. Tell me what I need to know about the new drug, but at this point in my career I’d rather have time. By not meeting a rep over lunch, or coffee, it adds 30-60 minutes to my day to use for reviewing tests, returning calls, and typing up notes. Those are things I’m going to have to do at some point, so I’d rather do them at my office and have the extra time at home, even if it’s just to do a jigsaw puzzle with my daughter.
That’s worth more than $4.80 per year.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
COVID Vaccines and New-Onset Seizures: New Data
There is no association between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and the risk for new-onset seizure, data from a new meta-analysis of six randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials (RCTs) showed.
Results of the pooled analysis that included 63,500 individuals vaccinated with SARS-CoV-2 and 55,000 who received a placebo vaccine showed there was no significant difference between the two groups with respect to new-onset seizures at 28- or 43-day follow-up.
Regarding new-onset seizures in the general population, there was no statistically significant difference in risk for seizure incidence among vaccinated individuals vs placebo recipients, according to our meta-analysis, wrote the investigators, led by Ali Rafati, MD, MPH, Iran University of Medical Sciences in Tehran.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Mixed Results
Results from previous research have been mixed regarding the link between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and new-onset seizures, with some showing an association.
To learn more about the possible association between the vaccines and new-onset seizures, the researchers conducted a literature review and identified six RCTs that measured adverse events following SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations (including messenger RNA, viral vector, and inactivated virus) vs placebo or other vaccines.
While five of the studies defined new-onset seizures according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities, trial investigators in the sixth RCT assessed and determined new-onset seizures in participants.
Participants received two vaccinations 28 days apart in five RCTs and only one vaccine in the sixth trial.
The research team searched the data for new-onset seizure in the 28 days following one or both COVID vaccinations.
No Link Found
After comparing the incidence of new-onset seizure between the 63,500 vaccine (nine new-onset seizures, 0.014%) and 55,000 placebo recipients (one new-onset seizure, 0.002%), investigators found no significant difference between the two groups (odds ratio [OR], 2.70; 95% CI, 0.76-9.57; P = .12)
Investigators also sliced the data several ways to see if it would yield different results. When they analyzed data by vaccine platform (viral vector) and age group (children), they didn’t observe significant differences in new-onset data.
The researchers also searched for data beyond the month following the injection to encompass the entire blinded phase, so they analyzed the results of three RCTs that reported adverse events up to 162 days after the vaccine.
After pooling the results from the three studies, investigators found no statistical difference between the vaccine and placebo groups in terms of the new-onset seizure (OR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86%-3.23; P > .99)
Study limitations included the missing information on vaccine doses or risk factors for the development of seizures. Also, the RCTs included in the meta-analysis were conducted at different times, so the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines may have differed in their composition and efficacy.
“The global vaccination drive against SARS-CoV-2 has been a monumental effort in combating the pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations that are now available appear safe and appropriate,” the authors wrote.
There were no study funding sources or disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
There is no association between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and the risk for new-onset seizure, data from a new meta-analysis of six randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials (RCTs) showed.
Results of the pooled analysis that included 63,500 individuals vaccinated with SARS-CoV-2 and 55,000 who received a placebo vaccine showed there was no significant difference between the two groups with respect to new-onset seizures at 28- or 43-day follow-up.
Regarding new-onset seizures in the general population, there was no statistically significant difference in risk for seizure incidence among vaccinated individuals vs placebo recipients, according to our meta-analysis, wrote the investigators, led by Ali Rafati, MD, MPH, Iran University of Medical Sciences in Tehran.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Mixed Results
Results from previous research have been mixed regarding the link between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and new-onset seizures, with some showing an association.
To learn more about the possible association between the vaccines and new-onset seizures, the researchers conducted a literature review and identified six RCTs that measured adverse events following SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations (including messenger RNA, viral vector, and inactivated virus) vs placebo or other vaccines.
While five of the studies defined new-onset seizures according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities, trial investigators in the sixth RCT assessed and determined new-onset seizures in participants.
Participants received two vaccinations 28 days apart in five RCTs and only one vaccine in the sixth trial.
The research team searched the data for new-onset seizure in the 28 days following one or both COVID vaccinations.
No Link Found
After comparing the incidence of new-onset seizure between the 63,500 vaccine (nine new-onset seizures, 0.014%) and 55,000 placebo recipients (one new-onset seizure, 0.002%), investigators found no significant difference between the two groups (odds ratio [OR], 2.70; 95% CI, 0.76-9.57; P = .12)
Investigators also sliced the data several ways to see if it would yield different results. When they analyzed data by vaccine platform (viral vector) and age group (children), they didn’t observe significant differences in new-onset data.
The researchers also searched for data beyond the month following the injection to encompass the entire blinded phase, so they analyzed the results of three RCTs that reported adverse events up to 162 days after the vaccine.
After pooling the results from the three studies, investigators found no statistical difference between the vaccine and placebo groups in terms of the new-onset seizure (OR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86%-3.23; P > .99)
Study limitations included the missing information on vaccine doses or risk factors for the development of seizures. Also, the RCTs included in the meta-analysis were conducted at different times, so the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines may have differed in their composition and efficacy.
“The global vaccination drive against SARS-CoV-2 has been a monumental effort in combating the pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations that are now available appear safe and appropriate,” the authors wrote.
There were no study funding sources or disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
There is no association between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and the risk for new-onset seizure, data from a new meta-analysis of six randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials (RCTs) showed.
Results of the pooled analysis that included 63,500 individuals vaccinated with SARS-CoV-2 and 55,000 who received a placebo vaccine showed there was no significant difference between the two groups with respect to new-onset seizures at 28- or 43-day follow-up.
Regarding new-onset seizures in the general population, there was no statistically significant difference in risk for seizure incidence among vaccinated individuals vs placebo recipients, according to our meta-analysis, wrote the investigators, led by Ali Rafati, MD, MPH, Iran University of Medical Sciences in Tehran.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Mixed Results
Results from previous research have been mixed regarding the link between the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and new-onset seizures, with some showing an association.
To learn more about the possible association between the vaccines and new-onset seizures, the researchers conducted a literature review and identified six RCTs that measured adverse events following SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations (including messenger RNA, viral vector, and inactivated virus) vs placebo or other vaccines.
While five of the studies defined new-onset seizures according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities, trial investigators in the sixth RCT assessed and determined new-onset seizures in participants.
Participants received two vaccinations 28 days apart in five RCTs and only one vaccine in the sixth trial.
The research team searched the data for new-onset seizure in the 28 days following one or both COVID vaccinations.
No Link Found
After comparing the incidence of new-onset seizure between the 63,500 vaccine (nine new-onset seizures, 0.014%) and 55,000 placebo recipients (one new-onset seizure, 0.002%), investigators found no significant difference between the two groups (odds ratio [OR], 2.70; 95% CI, 0.76-9.57; P = .12)
Investigators also sliced the data several ways to see if it would yield different results. When they analyzed data by vaccine platform (viral vector) and age group (children), they didn’t observe significant differences in new-onset data.
The researchers also searched for data beyond the month following the injection to encompass the entire blinded phase, so they analyzed the results of three RCTs that reported adverse events up to 162 days after the vaccine.
After pooling the results from the three studies, investigators found no statistical difference between the vaccine and placebo groups in terms of the new-onset seizure (OR, 2.31; 95% CI, 0.86%-3.23; P > .99)
Study limitations included the missing information on vaccine doses or risk factors for the development of seizures. Also, the RCTs included in the meta-analysis were conducted at different times, so the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines may have differed in their composition and efficacy.
“The global vaccination drive against SARS-CoV-2 has been a monumental effort in combating the pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations that are now available appear safe and appropriate,” the authors wrote.
There were no study funding sources or disclosures reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.