User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Record number of U.S. drug overdoses in 2020
More Americans died from drug overdoses in 2020 than in any other year, the CDC said July 14.
, according to the provisional data the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
The spikes are largely attributed to the rise in use of fentanyl and other synthetic opioids.
The Washington Post reported that more than 69,000 overdose deaths involved opioids, up from 50,963 in 2019.
Amid the crush of overdoses, the White House announced that President Joe Biden has nominated Rahul Gupta, MD, to lead the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy.
Dr. Gupta is a former health commissioner of West Virginia, and is chief medical and health officer for the March of Dimes.
“Dr. Gupta led efforts in West Virginia to address the opioid crisis, gaining national prominence as a leader in tackling this issue,” March of Dimes President and CEO Stacey Stewart said in a statement. “At March of Dimes, he has advocated for policies and programs to prevent and treat substance use, with a focus on the safety and care of pregnant women and infants.”
Healthday contributed to this report. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More Americans died from drug overdoses in 2020 than in any other year, the CDC said July 14.
, according to the provisional data the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
The spikes are largely attributed to the rise in use of fentanyl and other synthetic opioids.
The Washington Post reported that more than 69,000 overdose deaths involved opioids, up from 50,963 in 2019.
Amid the crush of overdoses, the White House announced that President Joe Biden has nominated Rahul Gupta, MD, to lead the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy.
Dr. Gupta is a former health commissioner of West Virginia, and is chief medical and health officer for the March of Dimes.
“Dr. Gupta led efforts in West Virginia to address the opioid crisis, gaining national prominence as a leader in tackling this issue,” March of Dimes President and CEO Stacey Stewart said in a statement. “At March of Dimes, he has advocated for policies and programs to prevent and treat substance use, with a focus on the safety and care of pregnant women and infants.”
Healthday contributed to this report. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More Americans died from drug overdoses in 2020 than in any other year, the CDC said July 14.
, according to the provisional data the National Center for Health Statistics reported.
The spikes are largely attributed to the rise in use of fentanyl and other synthetic opioids.
The Washington Post reported that more than 69,000 overdose deaths involved opioids, up from 50,963 in 2019.
Amid the crush of overdoses, the White House announced that President Joe Biden has nominated Rahul Gupta, MD, to lead the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy.
Dr. Gupta is a former health commissioner of West Virginia, and is chief medical and health officer for the March of Dimes.
“Dr. Gupta led efforts in West Virginia to address the opioid crisis, gaining national prominence as a leader in tackling this issue,” March of Dimes President and CEO Stacey Stewart said in a statement. “At March of Dimes, he has advocated for policies and programs to prevent and treat substance use, with a focus on the safety and care of pregnant women and infants.”
Healthday contributed to this report. A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
State-of-the-art psych unit designed with recovery in mind
Calming wall colors, nature-themed murals, and soft nighttime lighting are all part of a unique new state-of-the-art inpatient psychiatric unit that focuses especially on children and adolescents who have experienced significant trauma.
The 16-bed unit, which has been in the works for 3½ years and opened June 30 at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), in Baltimore, Maryland, treats youth aged 5 to 17 years. It has separate wings for younger children and for adolescents.
“We offer a really warm and welcoming environment that we think is going to promote health and healing,” the unit’s head, Sarah Edwards, DO, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at UMMC and assistant professor of psychiatry, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), Baltimore, said in an interview.
Previous research shows that 1 in 4 children experience some kind of maltreatment, whether physical, sexual, or emotional, and that 1 in 5 develop a diagnosable mental health disorder.
, Dr. Edwards noted. Recent data show that the rate of suicidal ideation among youth has increased significantly during the COVID-19 crisis.
“Urban children have unfortunately suffered a lot of what we call traumatic stress, so they might be victims of physical or sexual abuse but also face layers of stressful situations – for example, living in unsafe neighborhoods and attending schools that might not be so welcoming and safe,” said Dr. Edwards.
Safety first
Typical conditions treated at the new unit will include depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, psychotic spectrum, as well as trauma disorders.
Some of these young patients have been through the foster care system and show signs of trauma and poor attachment, Dr. Edwards noted. As a result, they may have difficulty regulating their thoughts and emotions and at times exhibit dangerous behavior.
The new unit is designed both architecturally and clinically to deliver “trauma-informed” care. This type of approach “recognizes the pervasive nature of trauma” and promotes settings that facilitate recovery, Dr. Edwards added.
The idea is to treat individuals “in a way that doesn’t re-traumatize them or make their condition worse,” she added.
Safety is of the utmost importance in the unit, Jill RachBeisel, MD, chief of psychiatry at UMMC and professor and chair in the department of psychiatry at UMSOM, said in an interview.
“Health care workers must recognize and respond to the effects of trauma – and one very important way is to provide care in settings that emphasize physical and emotional safety, which helps instill a sense of control and empowerment,” Dr. RachBeisel said.
Providing youth with options is an important way to provide that sense of control, Dr. Edwards added. For example, residents can choose their own music in their bedroom, such as sounds of nature, running water, or birds chirping. They can also draw or write personal notes on a large whiteboard in their unit.
Circadian-rhythm lighting
Other unique elements of the new unit include walls painted soothing shades and murals of natural scenery, created by a local artist.
These murals perfectly capture “the kind of overall spirit of what we were trying to induce,” said Dr. Edwards.
A part of the unit dubbed the “front porch” has a large mural depicting “a landscape of beautiful trees and water and animals,” she noted. Kids can gather here to relax or just hang out.
The lighting at the unit mirrors circadian rhythms. It’s brighter during the day to promote wakefulness and participation in activities and gradually dims toward the evening hours to help induce restful nighttime sleep.
Safe and empowering and adopt productive behaviors and coping skills, Dr. Edwards noted.
The staff for the interprofessional unit includes psychiatrists, psychologists, psychiatric nurses, occupational therapists, and others trained in pediatric care.
Advice for other centers
“Our new unit is designed to provide the highest standard in mental health care and incorporates a high-tech approach to create a calming, soothing, and engaging setting,” said Dr. RachBeisel.
School-transition specialists help connect discharged patients and their families to vital services and peer support. These services represent “an essential component of the continuum of care” for youth experiencing mental distress, she added.
Other organizations considering establishing a similar type of psychiatric unit should consult all stakeholders.
“We had staff, no matter what their role, be part of every step of this process, including helping with the design, picking out furniture they thought would make the most sense, and helping choose the artwork,” she said.
It is also important to incorporate feedback from youth themselves, Dr. Edwards added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Calming wall colors, nature-themed murals, and soft nighttime lighting are all part of a unique new state-of-the-art inpatient psychiatric unit that focuses especially on children and adolescents who have experienced significant trauma.
The 16-bed unit, which has been in the works for 3½ years and opened June 30 at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), in Baltimore, Maryland, treats youth aged 5 to 17 years. It has separate wings for younger children and for adolescents.
“We offer a really warm and welcoming environment that we think is going to promote health and healing,” the unit’s head, Sarah Edwards, DO, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at UMMC and assistant professor of psychiatry, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), Baltimore, said in an interview.
Previous research shows that 1 in 4 children experience some kind of maltreatment, whether physical, sexual, or emotional, and that 1 in 5 develop a diagnosable mental health disorder.
, Dr. Edwards noted. Recent data show that the rate of suicidal ideation among youth has increased significantly during the COVID-19 crisis.
“Urban children have unfortunately suffered a lot of what we call traumatic stress, so they might be victims of physical or sexual abuse but also face layers of stressful situations – for example, living in unsafe neighborhoods and attending schools that might not be so welcoming and safe,” said Dr. Edwards.
Safety first
Typical conditions treated at the new unit will include depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, psychotic spectrum, as well as trauma disorders.
Some of these young patients have been through the foster care system and show signs of trauma and poor attachment, Dr. Edwards noted. As a result, they may have difficulty regulating their thoughts and emotions and at times exhibit dangerous behavior.
The new unit is designed both architecturally and clinically to deliver “trauma-informed” care. This type of approach “recognizes the pervasive nature of trauma” and promotes settings that facilitate recovery, Dr. Edwards added.
The idea is to treat individuals “in a way that doesn’t re-traumatize them or make their condition worse,” she added.
Safety is of the utmost importance in the unit, Jill RachBeisel, MD, chief of psychiatry at UMMC and professor and chair in the department of psychiatry at UMSOM, said in an interview.
“Health care workers must recognize and respond to the effects of trauma – and one very important way is to provide care in settings that emphasize physical and emotional safety, which helps instill a sense of control and empowerment,” Dr. RachBeisel said.
Providing youth with options is an important way to provide that sense of control, Dr. Edwards added. For example, residents can choose their own music in their bedroom, such as sounds of nature, running water, or birds chirping. They can also draw or write personal notes on a large whiteboard in their unit.
Circadian-rhythm lighting
Other unique elements of the new unit include walls painted soothing shades and murals of natural scenery, created by a local artist.
These murals perfectly capture “the kind of overall spirit of what we were trying to induce,” said Dr. Edwards.
A part of the unit dubbed the “front porch” has a large mural depicting “a landscape of beautiful trees and water and animals,” she noted. Kids can gather here to relax or just hang out.
The lighting at the unit mirrors circadian rhythms. It’s brighter during the day to promote wakefulness and participation in activities and gradually dims toward the evening hours to help induce restful nighttime sleep.
Safe and empowering and adopt productive behaviors and coping skills, Dr. Edwards noted.
The staff for the interprofessional unit includes psychiatrists, psychologists, psychiatric nurses, occupational therapists, and others trained in pediatric care.
Advice for other centers
“Our new unit is designed to provide the highest standard in mental health care and incorporates a high-tech approach to create a calming, soothing, and engaging setting,” said Dr. RachBeisel.
School-transition specialists help connect discharged patients and their families to vital services and peer support. These services represent “an essential component of the continuum of care” for youth experiencing mental distress, she added.
Other organizations considering establishing a similar type of psychiatric unit should consult all stakeholders.
“We had staff, no matter what their role, be part of every step of this process, including helping with the design, picking out furniture they thought would make the most sense, and helping choose the artwork,” she said.
It is also important to incorporate feedback from youth themselves, Dr. Edwards added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Calming wall colors, nature-themed murals, and soft nighttime lighting are all part of a unique new state-of-the-art inpatient psychiatric unit that focuses especially on children and adolescents who have experienced significant trauma.
The 16-bed unit, which has been in the works for 3½ years and opened June 30 at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), in Baltimore, Maryland, treats youth aged 5 to 17 years. It has separate wings for younger children and for adolescents.
“We offer a really warm and welcoming environment that we think is going to promote health and healing,” the unit’s head, Sarah Edwards, DO, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at UMMC and assistant professor of psychiatry, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), Baltimore, said in an interview.
Previous research shows that 1 in 4 children experience some kind of maltreatment, whether physical, sexual, or emotional, and that 1 in 5 develop a diagnosable mental health disorder.
, Dr. Edwards noted. Recent data show that the rate of suicidal ideation among youth has increased significantly during the COVID-19 crisis.
“Urban children have unfortunately suffered a lot of what we call traumatic stress, so they might be victims of physical or sexual abuse but also face layers of stressful situations – for example, living in unsafe neighborhoods and attending schools that might not be so welcoming and safe,” said Dr. Edwards.
Safety first
Typical conditions treated at the new unit will include depression, anxiety, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, psychotic spectrum, as well as trauma disorders.
Some of these young patients have been through the foster care system and show signs of trauma and poor attachment, Dr. Edwards noted. As a result, they may have difficulty regulating their thoughts and emotions and at times exhibit dangerous behavior.
The new unit is designed both architecturally and clinically to deliver “trauma-informed” care. This type of approach “recognizes the pervasive nature of trauma” and promotes settings that facilitate recovery, Dr. Edwards added.
The idea is to treat individuals “in a way that doesn’t re-traumatize them or make their condition worse,” she added.
Safety is of the utmost importance in the unit, Jill RachBeisel, MD, chief of psychiatry at UMMC and professor and chair in the department of psychiatry at UMSOM, said in an interview.
“Health care workers must recognize and respond to the effects of trauma – and one very important way is to provide care in settings that emphasize physical and emotional safety, which helps instill a sense of control and empowerment,” Dr. RachBeisel said.
Providing youth with options is an important way to provide that sense of control, Dr. Edwards added. For example, residents can choose their own music in their bedroom, such as sounds of nature, running water, or birds chirping. They can also draw or write personal notes on a large whiteboard in their unit.
Circadian-rhythm lighting
Other unique elements of the new unit include walls painted soothing shades and murals of natural scenery, created by a local artist.
These murals perfectly capture “the kind of overall spirit of what we were trying to induce,” said Dr. Edwards.
A part of the unit dubbed the “front porch” has a large mural depicting “a landscape of beautiful trees and water and animals,” she noted. Kids can gather here to relax or just hang out.
The lighting at the unit mirrors circadian rhythms. It’s brighter during the day to promote wakefulness and participation in activities and gradually dims toward the evening hours to help induce restful nighttime sleep.
Safe and empowering and adopt productive behaviors and coping skills, Dr. Edwards noted.
The staff for the interprofessional unit includes psychiatrists, psychologists, psychiatric nurses, occupational therapists, and others trained in pediatric care.
Advice for other centers
“Our new unit is designed to provide the highest standard in mental health care and incorporates a high-tech approach to create a calming, soothing, and engaging setting,” said Dr. RachBeisel.
School-transition specialists help connect discharged patients and their families to vital services and peer support. These services represent “an essential component of the continuum of care” for youth experiencing mental distress, she added.
Other organizations considering establishing a similar type of psychiatric unit should consult all stakeholders.
“We had staff, no matter what their role, be part of every step of this process, including helping with the design, picking out furniture they thought would make the most sense, and helping choose the artwork,” she said.
It is also important to incorporate feedback from youth themselves, Dr. Edwards added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Enough English” to be at risk
A hectic Friday morning at the hospital seemed less stressful amid morning greetings and humor from colleagues. In a team room full of hospitalists, life and death are often discussed in detail, ranging from medical discussions to joys and frustrations of the day to philosophy, politics, and more. It is almost impossible to miss something interesting.
People breaking into their native languages over the phone call from home always make me smile. The mention of a “complicated Indian patient unable to use interpreter” caught my attention.
My friend and colleague asked if I would be willing to take over the patient since I could speak Hindi. I was doubtful if I would add anything to make a meaningful difference, given the patient wasn’t even participating in a conversation. However, my colleague’s concern for the patient and faith in me was enough to say, “Sure, let me add her to my list.”
At the bedside, it felt like a classic “acute on chronic” hot mess situation. The patient presented with a generalized rash, anasarca, renal failure, multifocal pneumonia, and delirium. All I could gather from the patient were some incomprehensible words that sounded like Hindi. I called the family to obtain some history and to provide updates. Her son was excited to hear from me, and it didn’t take him long to guess that I was from India. But that could still mean that I might speak any of the twenty-two or more Indian languages.
Answering my questions one by one in perfectly understandable English, he was short and sweet. Suspicious of missing out on details, I offered hesitantly, “You could speak in Hindi with me.” Then came a flood of information with the details, concerns, questions, and what was lost in the translation.
We all attend to patients and families with limited English proficiency (LEP), immigrants, and nonimmigrants. LEP is a term used to describe individuals who do not speak English as their primary language and have a limited ability to read, speak, write, or understand English.1 Recent data from the American Community Survey (2005-2009) reports that 8.6% of the population (24 million Americans) have LEP.2 It’s a large and growing population that needs help overcoming language barriers and the appropriate use of professional medical interpreter services – a backbone to safe, quality, and cost-effective patient care.
The following day at bedside rounds, the nurse reported that the patient was looking and responding better. She could cooperate with interpreter services and could speak “some English.” Over the years, one thing that sounds more alarming than “no English” is “some English” or “enough English.” Around noon I received a page that the patient was refusing intravenous Lasix. At the bedside, however, the patient seemed unaware of the perceived refusal. Further discussions with the nurse lead to a familiar culprit, a relatively common gesture in South Asian cultures, a head bobble or shake.
The nurse reported that the patient shook her head side to side, seemed upset, and said “NO” when trying to administer the medication. On the other hand, the patient reported that she was upset to be at the hospital but had “NO” problem with the medicine.
My patient’s “some English” was indeed “enough English” to put her at risk due to medical error, which is highly likely when patients or providers can speak or understand a language to “get by” or to “make do.” Like my patient, the LEP patient population is more likely to experience medical errors, longer hospital stays, hospital-acquired complications, surgical delays, and readmissions. They are also less likely to receive preventive care, have access to regular care, or be satisfied with their care. They are much more likely to have adverse effects from drug complications, poor understanding of diagnoses, a greater risk of being misunderstood by their physicians or ancillary staff, and less likely to follow physician instructions.3-5 One study analyzed over 1,000 adverse-incident reports from six Joint Commission-accredited hospitals for LEP and English-speaking patients and found that 49% of LEP patients experienced physical harm versus 29.5% of English-speaking patients.6
I updated the patient’s LEP status that was missing in the chart, likely due to altered mental status at the time of admission. Reliable language and English proficiency data are usually entered at the patient’s point of entry with documentation of the language services required during the patient-provider encounter. The U.S. Census Bureau’s operational definition for LEP is a patient’s self-assessed ability to speak English less than “very well,” but how well it correlates with a patient’s actual English ability needs more study. Also, one’s self-assessed perception of ability might vary day to day, and language ability, by itself, is not static; it can differ from moment to moment and situation to situation. It may be easier to understand words in English when the situation is simple and less stressful than when things are complicated and stressful.
With a definition of LEP rather vague and the term somewhat derogatory, its meaning is open to interpretation. One study found that though speaking English less than “very well” was the most sensitive measure for identifying all of the patients who reported that they were unable to communicate effectively with their physicians, it was also the least specific.7 This lower specificity could lead to misclassification of some patients as LEP who are, in fact, able to effectively communicate in English with their physicians. This type of misclassification might lead to costly language assistance and carry the potential to cause conflicts between patient and provider. Telling a patient or family that they may have a “limited English proficiency” when they have believed otherwise and feel confident about their skills may come as a challenge. Some patients may also pretend to understand English to avoid being embarrassed about their linguistic abilities or perceive that they might be judged on their abilities in general.
Exiting the room, I gently reminded the RN to use the interpreter services. “Who has never been guilty of using an ad hoc interpreter or rushing through a long interpreter phone call due to time constraints?” I thought. A study from 2011 found that 43% of hospitalized patients with LEP had communicated without an interpreter present during admission, and 40% had communicated without an interpreter present after admission.8 In other words, a system in place does not mean service in use. But, the use of a trained interpreter is not only an obligation for care providers but a right for patients as per legal requirements of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act and the Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS) by the Department of Health and Human Services’ (HSS) Office of Minority Health.9 In January 2010, The Joint Commission released a set of new and revised standards for patient-centered communication as part of an initiative to advance effective communication, cultural competence, and patient- and family-centered care.
Despite the requirements and availability of qualified medical interpreter services, there are multiple perceived and experienced barriers to the use of interpreter services. The most common one is that what comes as a free service for patients is a time commitment for providers. A long list of patients, acuity of the situation, and ease of use/availability of translation aids can change the calculus. One may be able to bill a prolonged service code (99354-99357) in addition to the appropriate E/M code, although a patient cannot be billed for the actual service provided by the interpreter. Longstanding CMS policy also permits reimbursement for translation/interpretation activities, so long as they are not included and paid for as part of the rate for direct service.10
The patient, however, insisted that she would rather have her son as the interpreter on the 3-way over the phone (OPI) conference call for interpretation. “He speaks good English and knows my medical history well,” she said. I counseled the patient on the benefits of using interpreter services and explained how to use the call button light and the visual aids.
Placing emphasis on educating patients about the benefits of using, and risks of not using, interpreter services is as essential as emphasizing that care providers use the services. Some patients may voluntarily choose to provide their own interpreter. Use of family members, friends, or unqualified staff as interpreters is one of the most commonly reported causes of errors by frontline staff. Using in-language collateral may help these patients understand how medical interpretation may create a better patient experience and outcome. A short factsheet, in different languages, on qualified interpreters’ expected benefits: meaning-for-meaning communication, impartiality, medical privacy, and improved patient safety and satisfaction, can also come in handy.
However, if the patient still refuses, providers should document the refusal of the offer of free language services, the name of the interpreter designated by the patient, the interpreter’s relationship to the LEP person, and the time or portions of the patient encounter that the interpreter’s services were used. Yet, language interpretation alone can be inadequate without document translation. According to one study, despite the availability of on-site professional interpreter services, hospitalized patients who do not speak English are less likely to have signed consent forms in their medical records.11 Health care professionals, therefore, need well-translated documents to treat LEP patients. Translated documents of consent forms for medical procedures, post-discharge instructions, prescription and medical device labels, and drug usage information may enhance informed decision making, safety and reduce stress and medical errors.
An unpopular and underused service needs it all: availability, convenience, monitoring, reporting, and team effort. Due to the sheer unpopularity and underuse of interpreter services, institutions should enhance ease of availability, monitor the use and quality of interpreter services, and optimize reporting of language-related errors. Ease of availability goes hand in hand with tapping local resources. Over the years, and even more so during the pandemic, in-person interpretation has transitioned to telephonic or video interpretation due to availability, safety, and cost issues. There are challenges in translating a language, and the absence of a visual channel adds another layer of complexity.
The current body of evidence does not indicate a superior interpreting method. Still, in one study providers and interpreters exposed to all three methods were more critical of remote methods and preferred videoconferencing to the telephone as a remote method. The significantly shorter phone interviews raised questions about the prospects of miscommunication in telephonic interpretation, given the absence of a visual channel.12
One way to bypass language barriers is to recognize the value added by hiring and training bilingual health care providers and fostering cultural competence. International medical graduates in many parts of the country aid in closing language barriers. Language-concordant care enhances trust between patients and physicians, optimizes health outcomes, and advances health equity for diverse populations.13-15 The presence of bilingual providers means more effective and timelier communication and improved patient satisfaction. But, according to a Doximity study, there is a significant “language gap” between those languages spoken by physicians and their patients.16 Hospitals, therefore, should assess, qualify, and incentivize staff who can serve as on-site medical interpreters for patients as a means to facilitate language concordant care for LEP patients.
The Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) also has a guide on how hospitals can better identify, report, monitor, and prevent medical errors in patients with LEP. Included is the TeamSTEPPS LEP module to help develop and deploy a customized plan to train staff in teamwork skills and lead a medical teamwork improvement initiative.17
“Without my family, I was scared that nobody would understand me”
Back to the case. My patient was recovering well, and I was tying up loose ends on the switch day for the hospitalist teams.
“You will likely be discharged in a couple of days,” I said. She and the family were grateful and satisfied with the care. She had used the interpreter services and also received ethnocultural and language concordant and culturally competent care. Reducing language barriers is one of the crucial ways to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in quality of care and health outcomes, and it starts – in many cases – with identifying LEP patients. Proper use and monitoring of interpreter services, reporting language-related errors, hiring and testing bilingual staff’s language proficiency, and educating staff on cultural awareness are essential strategies for caring for LEP patients.
At my weeks’ end, in my handoff note to the incoming providers, I highlighted: “Patient will benefit from a Hindi speaking provider, Limited English Proficiency.”
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Questions and Answers. Limited English Proficiency: A federal interagency website. www.lep.gov/commonly-asked-questions.
2. United States Census Bureau. Percent of people 5 years and over who speak English less than ‘very well’. www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/people-that-speak-english-less-than-very-well.html.
3. Jacobs EA, et al. Overcoming language barriers in health care: Costs and benefits of interpreter services. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(5):866–869. doi: 10.2105/ajph.94.5.866.
4. Gandhi TK, et al. Drug complications in outpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 2000;15(3):149–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2000.04199.x.
5. Karliner LS, et al. Do professional interpreters improve clinical care for patients with limited English proficiency? A systematic review of the literature. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(2):727–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00629.x.
6. Divi C, et al. Language proficiency and adverse events in US hospitals: a pilot study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007 Apr;19(2):60-7. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzl069.
7. Karliner LS, et al. Identification of limited English proficient patients in clinical care. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(10):1555-1560. doi:10.1007/s11606-008-0693-y.
8. Schenker Y, et al. Patterns of interpreter use for hospitalized patients with limited English proficiency. J Gen Intern Med. 2011 Jul;26(7):712-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1619-z.
9. Office of Minority Health, US Department of Health and Human Services. National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health Care: Final Report. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2001. https://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/assets/pdf/checked/finalreport.pdf.
10. www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/financial-management/medicaid-administrative-claiming/translation-and-interpretation-services/index.html
11. Schenker Y, et al. The Impact of Language Barriers on Documentation of Informed Consent at a Hospital with On-Site Interpreter Services. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):294-9. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0359-1.
12. Locatis C, et al. Comparing in-person, video, and telephonic medical interpretation. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(4):345-350. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1236-x.
13. Dunlap JL, et al. The effects of language concordant care on patient satisfaction and clinical understanding for Hispanic pediatric surgery patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1586-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.12.020.
14. Diamond L, et al. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Patient–Physician Non-English Language Concordance on Quality of Care and Outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Aug;34(8):1591-1606. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04847-5.
15. Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Providing high-quality care for limited English proficient patients: the importance of language concordance and interpreter use. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):324-30. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0340-z.
16. https://press.doximity.com/articles/first-ever-national-study-to-examine-different-languages-spoken-by-us-doctors.
17. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Patients with Limited English Proficiency. www.ahrq.gov/teamstepps/lep/index.html.
A hectic Friday morning at the hospital seemed less stressful amid morning greetings and humor from colleagues. In a team room full of hospitalists, life and death are often discussed in detail, ranging from medical discussions to joys and frustrations of the day to philosophy, politics, and more. It is almost impossible to miss something interesting.
People breaking into their native languages over the phone call from home always make me smile. The mention of a “complicated Indian patient unable to use interpreter” caught my attention.
My friend and colleague asked if I would be willing to take over the patient since I could speak Hindi. I was doubtful if I would add anything to make a meaningful difference, given the patient wasn’t even participating in a conversation. However, my colleague’s concern for the patient and faith in me was enough to say, “Sure, let me add her to my list.”
At the bedside, it felt like a classic “acute on chronic” hot mess situation. The patient presented with a generalized rash, anasarca, renal failure, multifocal pneumonia, and delirium. All I could gather from the patient were some incomprehensible words that sounded like Hindi. I called the family to obtain some history and to provide updates. Her son was excited to hear from me, and it didn’t take him long to guess that I was from India. But that could still mean that I might speak any of the twenty-two or more Indian languages.
Answering my questions one by one in perfectly understandable English, he was short and sweet. Suspicious of missing out on details, I offered hesitantly, “You could speak in Hindi with me.” Then came a flood of information with the details, concerns, questions, and what was lost in the translation.
We all attend to patients and families with limited English proficiency (LEP), immigrants, and nonimmigrants. LEP is a term used to describe individuals who do not speak English as their primary language and have a limited ability to read, speak, write, or understand English.1 Recent data from the American Community Survey (2005-2009) reports that 8.6% of the population (24 million Americans) have LEP.2 It’s a large and growing population that needs help overcoming language barriers and the appropriate use of professional medical interpreter services – a backbone to safe, quality, and cost-effective patient care.
The following day at bedside rounds, the nurse reported that the patient was looking and responding better. She could cooperate with interpreter services and could speak “some English.” Over the years, one thing that sounds more alarming than “no English” is “some English” or “enough English.” Around noon I received a page that the patient was refusing intravenous Lasix. At the bedside, however, the patient seemed unaware of the perceived refusal. Further discussions with the nurse lead to a familiar culprit, a relatively common gesture in South Asian cultures, a head bobble or shake.
The nurse reported that the patient shook her head side to side, seemed upset, and said “NO” when trying to administer the medication. On the other hand, the patient reported that she was upset to be at the hospital but had “NO” problem with the medicine.
My patient’s “some English” was indeed “enough English” to put her at risk due to medical error, which is highly likely when patients or providers can speak or understand a language to “get by” or to “make do.” Like my patient, the LEP patient population is more likely to experience medical errors, longer hospital stays, hospital-acquired complications, surgical delays, and readmissions. They are also less likely to receive preventive care, have access to regular care, or be satisfied with their care. They are much more likely to have adverse effects from drug complications, poor understanding of diagnoses, a greater risk of being misunderstood by their physicians or ancillary staff, and less likely to follow physician instructions.3-5 One study analyzed over 1,000 adverse-incident reports from six Joint Commission-accredited hospitals for LEP and English-speaking patients and found that 49% of LEP patients experienced physical harm versus 29.5% of English-speaking patients.6
I updated the patient’s LEP status that was missing in the chart, likely due to altered mental status at the time of admission. Reliable language and English proficiency data are usually entered at the patient’s point of entry with documentation of the language services required during the patient-provider encounter. The U.S. Census Bureau’s operational definition for LEP is a patient’s self-assessed ability to speak English less than “very well,” but how well it correlates with a patient’s actual English ability needs more study. Also, one’s self-assessed perception of ability might vary day to day, and language ability, by itself, is not static; it can differ from moment to moment and situation to situation. It may be easier to understand words in English when the situation is simple and less stressful than when things are complicated and stressful.
With a definition of LEP rather vague and the term somewhat derogatory, its meaning is open to interpretation. One study found that though speaking English less than “very well” was the most sensitive measure for identifying all of the patients who reported that they were unable to communicate effectively with their physicians, it was also the least specific.7 This lower specificity could lead to misclassification of some patients as LEP who are, in fact, able to effectively communicate in English with their physicians. This type of misclassification might lead to costly language assistance and carry the potential to cause conflicts between patient and provider. Telling a patient or family that they may have a “limited English proficiency” when they have believed otherwise and feel confident about their skills may come as a challenge. Some patients may also pretend to understand English to avoid being embarrassed about their linguistic abilities or perceive that they might be judged on their abilities in general.
Exiting the room, I gently reminded the RN to use the interpreter services. “Who has never been guilty of using an ad hoc interpreter or rushing through a long interpreter phone call due to time constraints?” I thought. A study from 2011 found that 43% of hospitalized patients with LEP had communicated without an interpreter present during admission, and 40% had communicated without an interpreter present after admission.8 In other words, a system in place does not mean service in use. But, the use of a trained interpreter is not only an obligation for care providers but a right for patients as per legal requirements of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act and the Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS) by the Department of Health and Human Services’ (HSS) Office of Minority Health.9 In January 2010, The Joint Commission released a set of new and revised standards for patient-centered communication as part of an initiative to advance effective communication, cultural competence, and patient- and family-centered care.
Despite the requirements and availability of qualified medical interpreter services, there are multiple perceived and experienced barriers to the use of interpreter services. The most common one is that what comes as a free service for patients is a time commitment for providers. A long list of patients, acuity of the situation, and ease of use/availability of translation aids can change the calculus. One may be able to bill a prolonged service code (99354-99357) in addition to the appropriate E/M code, although a patient cannot be billed for the actual service provided by the interpreter. Longstanding CMS policy also permits reimbursement for translation/interpretation activities, so long as they are not included and paid for as part of the rate for direct service.10
The patient, however, insisted that she would rather have her son as the interpreter on the 3-way over the phone (OPI) conference call for interpretation. “He speaks good English and knows my medical history well,” she said. I counseled the patient on the benefits of using interpreter services and explained how to use the call button light and the visual aids.
Placing emphasis on educating patients about the benefits of using, and risks of not using, interpreter services is as essential as emphasizing that care providers use the services. Some patients may voluntarily choose to provide their own interpreter. Use of family members, friends, or unqualified staff as interpreters is one of the most commonly reported causes of errors by frontline staff. Using in-language collateral may help these patients understand how medical interpretation may create a better patient experience and outcome. A short factsheet, in different languages, on qualified interpreters’ expected benefits: meaning-for-meaning communication, impartiality, medical privacy, and improved patient safety and satisfaction, can also come in handy.
However, if the patient still refuses, providers should document the refusal of the offer of free language services, the name of the interpreter designated by the patient, the interpreter’s relationship to the LEP person, and the time or portions of the patient encounter that the interpreter’s services were used. Yet, language interpretation alone can be inadequate without document translation. According to one study, despite the availability of on-site professional interpreter services, hospitalized patients who do not speak English are less likely to have signed consent forms in their medical records.11 Health care professionals, therefore, need well-translated documents to treat LEP patients. Translated documents of consent forms for medical procedures, post-discharge instructions, prescription and medical device labels, and drug usage information may enhance informed decision making, safety and reduce stress and medical errors.
An unpopular and underused service needs it all: availability, convenience, monitoring, reporting, and team effort. Due to the sheer unpopularity and underuse of interpreter services, institutions should enhance ease of availability, monitor the use and quality of interpreter services, and optimize reporting of language-related errors. Ease of availability goes hand in hand with tapping local resources. Over the years, and even more so during the pandemic, in-person interpretation has transitioned to telephonic or video interpretation due to availability, safety, and cost issues. There are challenges in translating a language, and the absence of a visual channel adds another layer of complexity.
The current body of evidence does not indicate a superior interpreting method. Still, in one study providers and interpreters exposed to all three methods were more critical of remote methods and preferred videoconferencing to the telephone as a remote method. The significantly shorter phone interviews raised questions about the prospects of miscommunication in telephonic interpretation, given the absence of a visual channel.12
One way to bypass language barriers is to recognize the value added by hiring and training bilingual health care providers and fostering cultural competence. International medical graduates in many parts of the country aid in closing language barriers. Language-concordant care enhances trust between patients and physicians, optimizes health outcomes, and advances health equity for diverse populations.13-15 The presence of bilingual providers means more effective and timelier communication and improved patient satisfaction. But, according to a Doximity study, there is a significant “language gap” between those languages spoken by physicians and their patients.16 Hospitals, therefore, should assess, qualify, and incentivize staff who can serve as on-site medical interpreters for patients as a means to facilitate language concordant care for LEP patients.
The Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) also has a guide on how hospitals can better identify, report, monitor, and prevent medical errors in patients with LEP. Included is the TeamSTEPPS LEP module to help develop and deploy a customized plan to train staff in teamwork skills and lead a medical teamwork improvement initiative.17
“Without my family, I was scared that nobody would understand me”
Back to the case. My patient was recovering well, and I was tying up loose ends on the switch day for the hospitalist teams.
“You will likely be discharged in a couple of days,” I said. She and the family were grateful and satisfied with the care. She had used the interpreter services and also received ethnocultural and language concordant and culturally competent care. Reducing language barriers is one of the crucial ways to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in quality of care and health outcomes, and it starts – in many cases – with identifying LEP patients. Proper use and monitoring of interpreter services, reporting language-related errors, hiring and testing bilingual staff’s language proficiency, and educating staff on cultural awareness are essential strategies for caring for LEP patients.
At my weeks’ end, in my handoff note to the incoming providers, I highlighted: “Patient will benefit from a Hindi speaking provider, Limited English Proficiency.”
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Questions and Answers. Limited English Proficiency: A federal interagency website. www.lep.gov/commonly-asked-questions.
2. United States Census Bureau. Percent of people 5 years and over who speak English less than ‘very well’. www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/people-that-speak-english-less-than-very-well.html.
3. Jacobs EA, et al. Overcoming language barriers in health care: Costs and benefits of interpreter services. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(5):866–869. doi: 10.2105/ajph.94.5.866.
4. Gandhi TK, et al. Drug complications in outpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 2000;15(3):149–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2000.04199.x.
5. Karliner LS, et al. Do professional interpreters improve clinical care for patients with limited English proficiency? A systematic review of the literature. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(2):727–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00629.x.
6. Divi C, et al. Language proficiency and adverse events in US hospitals: a pilot study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007 Apr;19(2):60-7. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzl069.
7. Karliner LS, et al. Identification of limited English proficient patients in clinical care. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(10):1555-1560. doi:10.1007/s11606-008-0693-y.
8. Schenker Y, et al. Patterns of interpreter use for hospitalized patients with limited English proficiency. J Gen Intern Med. 2011 Jul;26(7):712-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1619-z.
9. Office of Minority Health, US Department of Health and Human Services. National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health Care: Final Report. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2001. https://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/assets/pdf/checked/finalreport.pdf.
10. www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/financial-management/medicaid-administrative-claiming/translation-and-interpretation-services/index.html
11. Schenker Y, et al. The Impact of Language Barriers on Documentation of Informed Consent at a Hospital with On-Site Interpreter Services. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):294-9. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0359-1.
12. Locatis C, et al. Comparing in-person, video, and telephonic medical interpretation. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(4):345-350. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1236-x.
13. Dunlap JL, et al. The effects of language concordant care on patient satisfaction and clinical understanding for Hispanic pediatric surgery patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1586-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.12.020.
14. Diamond L, et al. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Patient–Physician Non-English Language Concordance on Quality of Care and Outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Aug;34(8):1591-1606. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04847-5.
15. Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Providing high-quality care for limited English proficient patients: the importance of language concordance and interpreter use. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):324-30. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0340-z.
16. https://press.doximity.com/articles/first-ever-national-study-to-examine-different-languages-spoken-by-us-doctors.
17. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Patients with Limited English Proficiency. www.ahrq.gov/teamstepps/lep/index.html.
A hectic Friday morning at the hospital seemed less stressful amid morning greetings and humor from colleagues. In a team room full of hospitalists, life and death are often discussed in detail, ranging from medical discussions to joys and frustrations of the day to philosophy, politics, and more. It is almost impossible to miss something interesting.
People breaking into their native languages over the phone call from home always make me smile. The mention of a “complicated Indian patient unable to use interpreter” caught my attention.
My friend and colleague asked if I would be willing to take over the patient since I could speak Hindi. I was doubtful if I would add anything to make a meaningful difference, given the patient wasn’t even participating in a conversation. However, my colleague’s concern for the patient and faith in me was enough to say, “Sure, let me add her to my list.”
At the bedside, it felt like a classic “acute on chronic” hot mess situation. The patient presented with a generalized rash, anasarca, renal failure, multifocal pneumonia, and delirium. All I could gather from the patient were some incomprehensible words that sounded like Hindi. I called the family to obtain some history and to provide updates. Her son was excited to hear from me, and it didn’t take him long to guess that I was from India. But that could still mean that I might speak any of the twenty-two or more Indian languages.
Answering my questions one by one in perfectly understandable English, he was short and sweet. Suspicious of missing out on details, I offered hesitantly, “You could speak in Hindi with me.” Then came a flood of information with the details, concerns, questions, and what was lost in the translation.
We all attend to patients and families with limited English proficiency (LEP), immigrants, and nonimmigrants. LEP is a term used to describe individuals who do not speak English as their primary language and have a limited ability to read, speak, write, or understand English.1 Recent data from the American Community Survey (2005-2009) reports that 8.6% of the population (24 million Americans) have LEP.2 It’s a large and growing population that needs help overcoming language barriers and the appropriate use of professional medical interpreter services – a backbone to safe, quality, and cost-effective patient care.
The following day at bedside rounds, the nurse reported that the patient was looking and responding better. She could cooperate with interpreter services and could speak “some English.” Over the years, one thing that sounds more alarming than “no English” is “some English” or “enough English.” Around noon I received a page that the patient was refusing intravenous Lasix. At the bedside, however, the patient seemed unaware of the perceived refusal. Further discussions with the nurse lead to a familiar culprit, a relatively common gesture in South Asian cultures, a head bobble or shake.
The nurse reported that the patient shook her head side to side, seemed upset, and said “NO” when trying to administer the medication. On the other hand, the patient reported that she was upset to be at the hospital but had “NO” problem with the medicine.
My patient’s “some English” was indeed “enough English” to put her at risk due to medical error, which is highly likely when patients or providers can speak or understand a language to “get by” or to “make do.” Like my patient, the LEP patient population is more likely to experience medical errors, longer hospital stays, hospital-acquired complications, surgical delays, and readmissions. They are also less likely to receive preventive care, have access to regular care, or be satisfied with their care. They are much more likely to have adverse effects from drug complications, poor understanding of diagnoses, a greater risk of being misunderstood by their physicians or ancillary staff, and less likely to follow physician instructions.3-5 One study analyzed over 1,000 adverse-incident reports from six Joint Commission-accredited hospitals for LEP and English-speaking patients and found that 49% of LEP patients experienced physical harm versus 29.5% of English-speaking patients.6
I updated the patient’s LEP status that was missing in the chart, likely due to altered mental status at the time of admission. Reliable language and English proficiency data are usually entered at the patient’s point of entry with documentation of the language services required during the patient-provider encounter. The U.S. Census Bureau’s operational definition for LEP is a patient’s self-assessed ability to speak English less than “very well,” but how well it correlates with a patient’s actual English ability needs more study. Also, one’s self-assessed perception of ability might vary day to day, and language ability, by itself, is not static; it can differ from moment to moment and situation to situation. It may be easier to understand words in English when the situation is simple and less stressful than when things are complicated and stressful.
With a definition of LEP rather vague and the term somewhat derogatory, its meaning is open to interpretation. One study found that though speaking English less than “very well” was the most sensitive measure for identifying all of the patients who reported that they were unable to communicate effectively with their physicians, it was also the least specific.7 This lower specificity could lead to misclassification of some patients as LEP who are, in fact, able to effectively communicate in English with their physicians. This type of misclassification might lead to costly language assistance and carry the potential to cause conflicts between patient and provider. Telling a patient or family that they may have a “limited English proficiency” when they have believed otherwise and feel confident about their skills may come as a challenge. Some patients may also pretend to understand English to avoid being embarrassed about their linguistic abilities or perceive that they might be judged on their abilities in general.
Exiting the room, I gently reminded the RN to use the interpreter services. “Who has never been guilty of using an ad hoc interpreter or rushing through a long interpreter phone call due to time constraints?” I thought. A study from 2011 found that 43% of hospitalized patients with LEP had communicated without an interpreter present during admission, and 40% had communicated without an interpreter present after admission.8 In other words, a system in place does not mean service in use. But, the use of a trained interpreter is not only an obligation for care providers but a right for patients as per legal requirements of Title VI of the Civil Rights Act and the Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS) by the Department of Health and Human Services’ (HSS) Office of Minority Health.9 In January 2010, The Joint Commission released a set of new and revised standards for patient-centered communication as part of an initiative to advance effective communication, cultural competence, and patient- and family-centered care.
Despite the requirements and availability of qualified medical interpreter services, there are multiple perceived and experienced barriers to the use of interpreter services. The most common one is that what comes as a free service for patients is a time commitment for providers. A long list of patients, acuity of the situation, and ease of use/availability of translation aids can change the calculus. One may be able to bill a prolonged service code (99354-99357) in addition to the appropriate E/M code, although a patient cannot be billed for the actual service provided by the interpreter. Longstanding CMS policy also permits reimbursement for translation/interpretation activities, so long as they are not included and paid for as part of the rate for direct service.10
The patient, however, insisted that she would rather have her son as the interpreter on the 3-way over the phone (OPI) conference call for interpretation. “He speaks good English and knows my medical history well,” she said. I counseled the patient on the benefits of using interpreter services and explained how to use the call button light and the visual aids.
Placing emphasis on educating patients about the benefits of using, and risks of not using, interpreter services is as essential as emphasizing that care providers use the services. Some patients may voluntarily choose to provide their own interpreter. Use of family members, friends, or unqualified staff as interpreters is one of the most commonly reported causes of errors by frontline staff. Using in-language collateral may help these patients understand how medical interpretation may create a better patient experience and outcome. A short factsheet, in different languages, on qualified interpreters’ expected benefits: meaning-for-meaning communication, impartiality, medical privacy, and improved patient safety and satisfaction, can also come in handy.
However, if the patient still refuses, providers should document the refusal of the offer of free language services, the name of the interpreter designated by the patient, the interpreter’s relationship to the LEP person, and the time or portions of the patient encounter that the interpreter’s services were used. Yet, language interpretation alone can be inadequate without document translation. According to one study, despite the availability of on-site professional interpreter services, hospitalized patients who do not speak English are less likely to have signed consent forms in their medical records.11 Health care professionals, therefore, need well-translated documents to treat LEP patients. Translated documents of consent forms for medical procedures, post-discharge instructions, prescription and medical device labels, and drug usage information may enhance informed decision making, safety and reduce stress and medical errors.
An unpopular and underused service needs it all: availability, convenience, monitoring, reporting, and team effort. Due to the sheer unpopularity and underuse of interpreter services, institutions should enhance ease of availability, monitor the use and quality of interpreter services, and optimize reporting of language-related errors. Ease of availability goes hand in hand with tapping local resources. Over the years, and even more so during the pandemic, in-person interpretation has transitioned to telephonic or video interpretation due to availability, safety, and cost issues. There are challenges in translating a language, and the absence of a visual channel adds another layer of complexity.
The current body of evidence does not indicate a superior interpreting method. Still, in one study providers and interpreters exposed to all three methods were more critical of remote methods and preferred videoconferencing to the telephone as a remote method. The significantly shorter phone interviews raised questions about the prospects of miscommunication in telephonic interpretation, given the absence of a visual channel.12
One way to bypass language barriers is to recognize the value added by hiring and training bilingual health care providers and fostering cultural competence. International medical graduates in many parts of the country aid in closing language barriers. Language-concordant care enhances trust between patients and physicians, optimizes health outcomes, and advances health equity for diverse populations.13-15 The presence of bilingual providers means more effective and timelier communication and improved patient satisfaction. But, according to a Doximity study, there is a significant “language gap” between those languages spoken by physicians and their patients.16 Hospitals, therefore, should assess, qualify, and incentivize staff who can serve as on-site medical interpreters for patients as a means to facilitate language concordant care for LEP patients.
The Agency of Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) also has a guide on how hospitals can better identify, report, monitor, and prevent medical errors in patients with LEP. Included is the TeamSTEPPS LEP module to help develop and deploy a customized plan to train staff in teamwork skills and lead a medical teamwork improvement initiative.17
“Without my family, I was scared that nobody would understand me”
Back to the case. My patient was recovering well, and I was tying up loose ends on the switch day for the hospitalist teams.
“You will likely be discharged in a couple of days,” I said. She and the family were grateful and satisfied with the care. She had used the interpreter services and also received ethnocultural and language concordant and culturally competent care. Reducing language barriers is one of the crucial ways to reduce racial and ethnic disparities in quality of care and health outcomes, and it starts – in many cases – with identifying LEP patients. Proper use and monitoring of interpreter services, reporting language-related errors, hiring and testing bilingual staff’s language proficiency, and educating staff on cultural awareness are essential strategies for caring for LEP patients.
At my weeks’ end, in my handoff note to the incoming providers, I highlighted: “Patient will benefit from a Hindi speaking provider, Limited English Proficiency.”
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Questions and Answers. Limited English Proficiency: A federal interagency website. www.lep.gov/commonly-asked-questions.
2. United States Census Bureau. Percent of people 5 years and over who speak English less than ‘very well’. www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/people-that-speak-english-less-than-very-well.html.
3. Jacobs EA, et al. Overcoming language barriers in health care: Costs and benefits of interpreter services. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(5):866–869. doi: 10.2105/ajph.94.5.866.
4. Gandhi TK, et al. Drug complications in outpatients. J Gen Intern Med. 2000;15(3):149–154. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2000.04199.x.
5. Karliner LS, et al. Do professional interpreters improve clinical care for patients with limited English proficiency? A systematic review of the literature. Health Serv Res. 2007;42(2):727–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2006.00629.x.
6. Divi C, et al. Language proficiency and adverse events in US hospitals: a pilot study. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007 Apr;19(2):60-7. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzl069.
7. Karliner LS, et al. Identification of limited English proficient patients in clinical care. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(10):1555-1560. doi:10.1007/s11606-008-0693-y.
8. Schenker Y, et al. Patterns of interpreter use for hospitalized patients with limited English proficiency. J Gen Intern Med. 2011 Jul;26(7):712-7. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1619-z.
9. Office of Minority Health, US Department of Health and Human Services. National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health Care: Final Report. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2001. https://minorityhealth.hhs.gov/assets/pdf/checked/finalreport.pdf.
10. www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/financial-management/medicaid-administrative-claiming/translation-and-interpretation-services/index.html
11. Schenker Y, et al. The Impact of Language Barriers on Documentation of Informed Consent at a Hospital with On-Site Interpreter Services. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):294-9. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0359-1.
12. Locatis C, et al. Comparing in-person, video, and telephonic medical interpretation. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(4):345-350. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1236-x.
13. Dunlap JL, et al. The effects of language concordant care on patient satisfaction and clinical understanding for Hispanic pediatric surgery patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Sep;50(9):1586-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.12.020.
14. Diamond L, et al. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Patient–Physician Non-English Language Concordance on Quality of Care and Outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Aug;34(8):1591-1606. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04847-5.
15. Ngo-Metzger Q, et al. Providing high-quality care for limited English proficient patients: the importance of language concordance and interpreter use. J Gen Intern Med. 2007 Nov;22 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):324-30. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0340-z.
16. https://press.doximity.com/articles/first-ever-national-study-to-examine-different-languages-spoken-by-us-doctors.
17. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Patients with Limited English Proficiency. www.ahrq.gov/teamstepps/lep/index.html.
Children and COVID: New vaccinations drop as the case count rises
With only a quarter of all children aged 12-15 years fully vaccinated against COVID-19, first vaccinations continued to drop and new cases for all children rose for the second consecutive week.
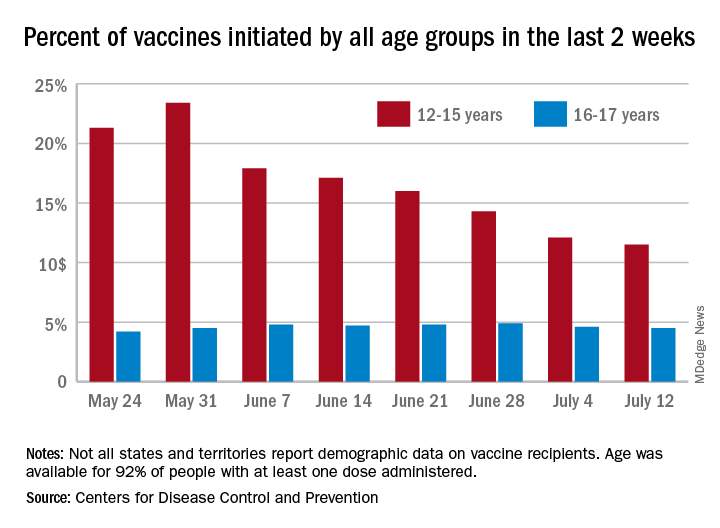
Just under 25% of children aged 12-15 had completed the vaccine regimen as of July 12, and just over one-third (33.5%) had received at least one dose. Meanwhile, that age group represented 11.5% of people who initiated vaccination during the 2 weeks ending July 12, down from 12.1% a week earlier, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said. The total number of new vaccinations for the week ending July 12 was just over 201,000, compared with 307,000 for the previous week.
New cases of COVID-19, however, were on the rise in children. The 19,000 new cases reported for the week ending July 8 were up from 12,000 a week earlier and 8,000 the week before that, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That report also shows that children made up 22.3% of all new cases during the week of July 2-8, compared with 16.8% the previous week, and that there were nine deaths in children that same week, the most since March. COVID-related deaths among children total 344 in the 46 jurisdictions (43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that are reporting such data by age. “It is not possible to standardize more detailed age ranges for children based on what is publicly available from the states,” the two groups noted.
Such data are available from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker, however, and they show that children aged 16-17 years, who became eligible for COVID vaccination before the younger age group, are further ahead in the process. Among the older children, almost 46% had gotten at least one dose and 37% were fully vaccinated by July 12.
With only a quarter of all children aged 12-15 years fully vaccinated against COVID-19, first vaccinations continued to drop and new cases for all children rose for the second consecutive week.

Just under 25% of children aged 12-15 had completed the vaccine regimen as of July 12, and just over one-third (33.5%) had received at least one dose. Meanwhile, that age group represented 11.5% of people who initiated vaccination during the 2 weeks ending July 12, down from 12.1% a week earlier, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said. The total number of new vaccinations for the week ending July 12 was just over 201,000, compared with 307,000 for the previous week.
New cases of COVID-19, however, were on the rise in children. The 19,000 new cases reported for the week ending July 8 were up from 12,000 a week earlier and 8,000 the week before that, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That report also shows that children made up 22.3% of all new cases during the week of July 2-8, compared with 16.8% the previous week, and that there were nine deaths in children that same week, the most since March. COVID-related deaths among children total 344 in the 46 jurisdictions (43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that are reporting such data by age. “It is not possible to standardize more detailed age ranges for children based on what is publicly available from the states,” the two groups noted.
Such data are available from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker, however, and they show that children aged 16-17 years, who became eligible for COVID vaccination before the younger age group, are further ahead in the process. Among the older children, almost 46% had gotten at least one dose and 37% were fully vaccinated by July 12.
With only a quarter of all children aged 12-15 years fully vaccinated against COVID-19, first vaccinations continued to drop and new cases for all children rose for the second consecutive week.

Just under 25% of children aged 12-15 had completed the vaccine regimen as of July 12, and just over one-third (33.5%) had received at least one dose. Meanwhile, that age group represented 11.5% of people who initiated vaccination during the 2 weeks ending July 12, down from 12.1% a week earlier, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said. The total number of new vaccinations for the week ending July 12 was just over 201,000, compared with 307,000 for the previous week.
New cases of COVID-19, however, were on the rise in children. The 19,000 new cases reported for the week ending July 8 were up from 12,000 a week earlier and 8,000 the week before that, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
That report also shows that children made up 22.3% of all new cases during the week of July 2-8, compared with 16.8% the previous week, and that there were nine deaths in children that same week, the most since March. COVID-related deaths among children total 344 in the 46 jurisdictions (43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam) that are reporting such data by age. “It is not possible to standardize more detailed age ranges for children based on what is publicly available from the states,” the two groups noted.
Such data are available from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker, however, and they show that children aged 16-17 years, who became eligible for COVID vaccination before the younger age group, are further ahead in the process. Among the older children, almost 46% had gotten at least one dose and 37% were fully vaccinated by July 12.
FDA to warn J&J that vaccine can increase Guillain-Barré risk: Media
as early as July 13, according to multiple media reports.
Although the FDA is projected to add the new warning to the labeling for the vaccine, the agency still calculates the benefit of vaccination with the J&J product continues to outweigh the risk. Benefits include protection against the Delta variant and serious COVID-19 outcomes.
More than 100 cases of Guillain-Barré reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, a federal program for reporting vaccine issues, spurred the FDA to act.
Men and people older than 50 appear to be at highest risk, according to reports of a July 12 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statement. The CDC also revealed that most cases occur about 2 weeks following immunization.
Guillain-Barré syndrome often causes muscle weakness and sometimes temporary paralysis. Most people who develop the rare syndrome recover.
Such was not the case for a 57-year-old man, the New York Times reported July 12. He had a history of both a heart attack and stroke in the previous 4 years and died in April after vaccination with the J&J vaccine and developing Guillain-Barré.
The new warning comes in the wake of a number of setbacks for the company’s COVID-19 vaccine. On April 13, the FDA and CDC both recommended a 10-day pause on administration of the J&J vaccine after reports of rare blood clot events emerged. In mid-June, the FDA requested that Johnson and Johnson discard millions of vaccine doses produced at a manufacturing facility in Baltimore.
The mRNA vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna are not affected by the new FDA warning.
The Biden administration is expected to make a formal announcement of the new warning for the Johnson and Johnson vaccine as early as July 13, the Times reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as early as July 13, according to multiple media reports.
Although the FDA is projected to add the new warning to the labeling for the vaccine, the agency still calculates the benefit of vaccination with the J&J product continues to outweigh the risk. Benefits include protection against the Delta variant and serious COVID-19 outcomes.
More than 100 cases of Guillain-Barré reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, a federal program for reporting vaccine issues, spurred the FDA to act.
Men and people older than 50 appear to be at highest risk, according to reports of a July 12 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statement. The CDC also revealed that most cases occur about 2 weeks following immunization.
Guillain-Barré syndrome often causes muscle weakness and sometimes temporary paralysis. Most people who develop the rare syndrome recover.
Such was not the case for a 57-year-old man, the New York Times reported July 12. He had a history of both a heart attack and stroke in the previous 4 years and died in April after vaccination with the J&J vaccine and developing Guillain-Barré.
The new warning comes in the wake of a number of setbacks for the company’s COVID-19 vaccine. On April 13, the FDA and CDC both recommended a 10-day pause on administration of the J&J vaccine after reports of rare blood clot events emerged. In mid-June, the FDA requested that Johnson and Johnson discard millions of vaccine doses produced at a manufacturing facility in Baltimore.
The mRNA vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna are not affected by the new FDA warning.
The Biden administration is expected to make a formal announcement of the new warning for the Johnson and Johnson vaccine as early as July 13, the Times reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
as early as July 13, according to multiple media reports.
Although the FDA is projected to add the new warning to the labeling for the vaccine, the agency still calculates the benefit of vaccination with the J&J product continues to outweigh the risk. Benefits include protection against the Delta variant and serious COVID-19 outcomes.
More than 100 cases of Guillain-Barré reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, a federal program for reporting vaccine issues, spurred the FDA to act.
Men and people older than 50 appear to be at highest risk, according to reports of a July 12 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention statement. The CDC also revealed that most cases occur about 2 weeks following immunization.
Guillain-Barré syndrome often causes muscle weakness and sometimes temporary paralysis. Most people who develop the rare syndrome recover.
Such was not the case for a 57-year-old man, the New York Times reported July 12. He had a history of both a heart attack and stroke in the previous 4 years and died in April after vaccination with the J&J vaccine and developing Guillain-Barré.
The new warning comes in the wake of a number of setbacks for the company’s COVID-19 vaccine. On April 13, the FDA and CDC both recommended a 10-day pause on administration of the J&J vaccine after reports of rare blood clot events emerged. In mid-June, the FDA requested that Johnson and Johnson discard millions of vaccine doses produced at a manufacturing facility in Baltimore.
The mRNA vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna are not affected by the new FDA warning.
The Biden administration is expected to make a formal announcement of the new warning for the Johnson and Johnson vaccine as early as July 13, the Times reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Standard medical mask can protect wearer from aerosols
A standard medical face mask is more effective at preventing the wearer from inhaling aerosols without causing substantial breathing resistance than various cloth, medical, or respirator masks, new research shows.
“Medical face masks with good filtration efficacies can provide even better protective effects than KN95 respirators,” Christian Sterr, MD, from Philipps University of Marburg (Germany), and colleagues wrote. “FFP2 respirators, on the other hand, could be useful in high-risk situations but require greater breathing effort and therefore physical stress for users.”
Extensive evidence has shown that face masks are an excellent form of source control, preventing infectious people from spreading the SARS-CoV-2 virus into the environment. But evidence has been less clear about how well masks protect the wearer from inhaling particles containing the virus.
The researchers conducted three experiments to test 32 different face masks. The findings were presented at the 31st European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and published online in PLOS One .
First they tested pressure drop, which “relates to how easily air can pass through the material,” said Chris Cappa, PhD, professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of California, Davis, who was not involved with the study.
“Higher pressure drops mean that there is greater resistance to the air passing through. A higher pressure drop will typically mean breathing through the material will be slightly more challenging, compared to a low pressure drop. There is no relationship between pressure drop and the mask effectiveness,” he said in an interview.
Pressure drop was lowest with type II medical face masks, the typical three-ply surgical masks designed to stop large particles expelled by the wearer from entering the environment, was highest with respirators, including KN95 and FFP2 masks, and varied with the different cloth masks tested.
Next the researchers compared filtration efficacy, which “refers to how well the material removes particles from the air that passes through the mask material,” Dr. Cappa explained. They did this by placing each mask over the opening to an air collector that measured how many particles got through. “A mask that has 100% filtration efficacy will remove all particles from the air that passes through it and 0% means that no particles are removed.”
Cloth masks had the lowest filtration efficacy, at 28%. Certified face masks that met European Standards had a relatively high efficacy, at 70%; for uncertified face masks, filtration efficacy was 63%. As expected, KN95 and FFP2 masks had the highest filtration efficacy, at 94% and 98%, respectively.Finally, the researchers tested as-worn filtration efficacies. They placed each mask on a dummy head with an artificial airway that collected airborne particles. They then pumped a mixture of aerosol particles – ranging in size from 0.3 to 2.0 mcm – and particle-free pressurized air into the air-proof acrylic chamber in which the head was placed.
In this experiment, cloth masks and noncertified face masks were least effective, filtering less than 20% of aerosols. Interestingly, the cloth face mask with the highest filtration on its own (84%) had the lowest filtration efficacy (9%), apparently because of its very high pressure drop (breathing resistance). When more effort is required to breathe through a mask, more air can bypass the filtration system.
Type II medical face masks, however, filtered 47% of aerosols, KN95 masks filtered 41%, and FFP2 masks filtered 65%. Face shields did not prevent the inhalation of any aerosols.
“We know that face shields will only be effective in stopping very large droplets, essentially visible spittle,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Most of the particles that we exhale will travel right around a face shield.”
The “optimal mask effect is a combination of high filter performance and low filter resistance,” which applies to most of the FFP2 and medical type II face masks tested, Dr. Sterr and colleagues wrote. “The type II medical masks in our random sample showed very good as-worn filtration performances with a low additional work of breathing at the same time.”
Although this study showed how well different masks filtered out particles, it could not assess how well different masks prevent actual infection.
“Like any virus, SARS-CoV-2 can only infect people as long as it is viable,” the researchers wrote. “Moreover, a certain number of viable virus particles need to be inhaled to trigger an infection. Thus, the assessed filtration efficacy may differ from the provided protection rate against SARS-CoV-2.”
In addition, particles containing the virus could dry out while going through the mask and become less infectious. “Even a small reduction in inhaled particles might prevent infection or at least lead to a less severe infection,” they noted.
In fact, filtration efficacy does not necessarily indicate how well the mask filters out particles while being worn. “This might be due to the combined effects of mask fit and pressure drop of the mask material and therefore tendency for mask leakage,” the team wrote. “High pressure drop results in higher breathing resistance and therefore supports leakage, especially if combined to a loosely fitting mask.”
These findings are “in line with what we already knew,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Even if the mask material filters out nearly all particles that pass through it, as is the case for high-efficiency masks such as N95 and FFP2, if the mask does not fit well, then it will only provide moderate protection for the wearer.”
Although the findings reaffirm the different levels of filtration provided by various cloth masks, they do not “provide any guidance on which types of cloth masks are better or worse,” he said. But they do show that “medical face masks will generally provide more protection to the wearer.”
It’s not surprising that face shields offer little protection from aerosols, Dr. Cappa said, but they can provide added protection when worn with a mask.
“A face shield could prevent large droplets that might shoot out when a person coughs or sneezes from depositing on a person’s eye,” he pointed out. And it can help “redirect the plume of particles that an infected person exhales, which could be useful in close quarters. However, even then those particles will keep moving around and could be inhaled. A mask can really help to decrease the amount inhaled.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors and Dr. Cappa disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A standard medical face mask is more effective at preventing the wearer from inhaling aerosols without causing substantial breathing resistance than various cloth, medical, or respirator masks, new research shows.
“Medical face masks with good filtration efficacies can provide even better protective effects than KN95 respirators,” Christian Sterr, MD, from Philipps University of Marburg (Germany), and colleagues wrote. “FFP2 respirators, on the other hand, could be useful in high-risk situations but require greater breathing effort and therefore physical stress for users.”
Extensive evidence has shown that face masks are an excellent form of source control, preventing infectious people from spreading the SARS-CoV-2 virus into the environment. But evidence has been less clear about how well masks protect the wearer from inhaling particles containing the virus.
The researchers conducted three experiments to test 32 different face masks. The findings were presented at the 31st European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and published online in PLOS One .
First they tested pressure drop, which “relates to how easily air can pass through the material,” said Chris Cappa, PhD, professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of California, Davis, who was not involved with the study.
“Higher pressure drops mean that there is greater resistance to the air passing through. A higher pressure drop will typically mean breathing through the material will be slightly more challenging, compared to a low pressure drop. There is no relationship between pressure drop and the mask effectiveness,” he said in an interview.
Pressure drop was lowest with type II medical face masks, the typical three-ply surgical masks designed to stop large particles expelled by the wearer from entering the environment, was highest with respirators, including KN95 and FFP2 masks, and varied with the different cloth masks tested.
Next the researchers compared filtration efficacy, which “refers to how well the material removes particles from the air that passes through the mask material,” Dr. Cappa explained. They did this by placing each mask over the opening to an air collector that measured how many particles got through. “A mask that has 100% filtration efficacy will remove all particles from the air that passes through it and 0% means that no particles are removed.”
Cloth masks had the lowest filtration efficacy, at 28%. Certified face masks that met European Standards had a relatively high efficacy, at 70%; for uncertified face masks, filtration efficacy was 63%. As expected, KN95 and FFP2 masks had the highest filtration efficacy, at 94% and 98%, respectively.Finally, the researchers tested as-worn filtration efficacies. They placed each mask on a dummy head with an artificial airway that collected airborne particles. They then pumped a mixture of aerosol particles – ranging in size from 0.3 to 2.0 mcm – and particle-free pressurized air into the air-proof acrylic chamber in which the head was placed.
In this experiment, cloth masks and noncertified face masks were least effective, filtering less than 20% of aerosols. Interestingly, the cloth face mask with the highest filtration on its own (84%) had the lowest filtration efficacy (9%), apparently because of its very high pressure drop (breathing resistance). When more effort is required to breathe through a mask, more air can bypass the filtration system.
Type II medical face masks, however, filtered 47% of aerosols, KN95 masks filtered 41%, and FFP2 masks filtered 65%. Face shields did not prevent the inhalation of any aerosols.
“We know that face shields will only be effective in stopping very large droplets, essentially visible spittle,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Most of the particles that we exhale will travel right around a face shield.”
The “optimal mask effect is a combination of high filter performance and low filter resistance,” which applies to most of the FFP2 and medical type II face masks tested, Dr. Sterr and colleagues wrote. “The type II medical masks in our random sample showed very good as-worn filtration performances with a low additional work of breathing at the same time.”
Although this study showed how well different masks filtered out particles, it could not assess how well different masks prevent actual infection.
“Like any virus, SARS-CoV-2 can only infect people as long as it is viable,” the researchers wrote. “Moreover, a certain number of viable virus particles need to be inhaled to trigger an infection. Thus, the assessed filtration efficacy may differ from the provided protection rate against SARS-CoV-2.”
In addition, particles containing the virus could dry out while going through the mask and become less infectious. “Even a small reduction in inhaled particles might prevent infection or at least lead to a less severe infection,” they noted.
In fact, filtration efficacy does not necessarily indicate how well the mask filters out particles while being worn. “This might be due to the combined effects of mask fit and pressure drop of the mask material and therefore tendency for mask leakage,” the team wrote. “High pressure drop results in higher breathing resistance and therefore supports leakage, especially if combined to a loosely fitting mask.”
These findings are “in line with what we already knew,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Even if the mask material filters out nearly all particles that pass through it, as is the case for high-efficiency masks such as N95 and FFP2, if the mask does not fit well, then it will only provide moderate protection for the wearer.”
Although the findings reaffirm the different levels of filtration provided by various cloth masks, they do not “provide any guidance on which types of cloth masks are better or worse,” he said. But they do show that “medical face masks will generally provide more protection to the wearer.”
It’s not surprising that face shields offer little protection from aerosols, Dr. Cappa said, but they can provide added protection when worn with a mask.
“A face shield could prevent large droplets that might shoot out when a person coughs or sneezes from depositing on a person’s eye,” he pointed out. And it can help “redirect the plume of particles that an infected person exhales, which could be useful in close quarters. However, even then those particles will keep moving around and could be inhaled. A mask can really help to decrease the amount inhaled.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors and Dr. Cappa disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A standard medical face mask is more effective at preventing the wearer from inhaling aerosols without causing substantial breathing resistance than various cloth, medical, or respirator masks, new research shows.
“Medical face masks with good filtration efficacies can provide even better protective effects than KN95 respirators,” Christian Sterr, MD, from Philipps University of Marburg (Germany), and colleagues wrote. “FFP2 respirators, on the other hand, could be useful in high-risk situations but require greater breathing effort and therefore physical stress for users.”
Extensive evidence has shown that face masks are an excellent form of source control, preventing infectious people from spreading the SARS-CoV-2 virus into the environment. But evidence has been less clear about how well masks protect the wearer from inhaling particles containing the virus.
The researchers conducted three experiments to test 32 different face masks. The findings were presented at the 31st European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and published online in PLOS One .
First they tested pressure drop, which “relates to how easily air can pass through the material,” said Chris Cappa, PhD, professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of California, Davis, who was not involved with the study.
“Higher pressure drops mean that there is greater resistance to the air passing through. A higher pressure drop will typically mean breathing through the material will be slightly more challenging, compared to a low pressure drop. There is no relationship between pressure drop and the mask effectiveness,” he said in an interview.
Pressure drop was lowest with type II medical face masks, the typical three-ply surgical masks designed to stop large particles expelled by the wearer from entering the environment, was highest with respirators, including KN95 and FFP2 masks, and varied with the different cloth masks tested.
Next the researchers compared filtration efficacy, which “refers to how well the material removes particles from the air that passes through the mask material,” Dr. Cappa explained. They did this by placing each mask over the opening to an air collector that measured how many particles got through. “A mask that has 100% filtration efficacy will remove all particles from the air that passes through it and 0% means that no particles are removed.”
Cloth masks had the lowest filtration efficacy, at 28%. Certified face masks that met European Standards had a relatively high efficacy, at 70%; for uncertified face masks, filtration efficacy was 63%. As expected, KN95 and FFP2 masks had the highest filtration efficacy, at 94% and 98%, respectively.Finally, the researchers tested as-worn filtration efficacies. They placed each mask on a dummy head with an artificial airway that collected airborne particles. They then pumped a mixture of aerosol particles – ranging in size from 0.3 to 2.0 mcm – and particle-free pressurized air into the air-proof acrylic chamber in which the head was placed.
In this experiment, cloth masks and noncertified face masks were least effective, filtering less than 20% of aerosols. Interestingly, the cloth face mask with the highest filtration on its own (84%) had the lowest filtration efficacy (9%), apparently because of its very high pressure drop (breathing resistance). When more effort is required to breathe through a mask, more air can bypass the filtration system.
Type II medical face masks, however, filtered 47% of aerosols, KN95 masks filtered 41%, and FFP2 masks filtered 65%. Face shields did not prevent the inhalation of any aerosols.
“We know that face shields will only be effective in stopping very large droplets, essentially visible spittle,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Most of the particles that we exhale will travel right around a face shield.”
The “optimal mask effect is a combination of high filter performance and low filter resistance,” which applies to most of the FFP2 and medical type II face masks tested, Dr. Sterr and colleagues wrote. “The type II medical masks in our random sample showed very good as-worn filtration performances with a low additional work of breathing at the same time.”
Although this study showed how well different masks filtered out particles, it could not assess how well different masks prevent actual infection.
“Like any virus, SARS-CoV-2 can only infect people as long as it is viable,” the researchers wrote. “Moreover, a certain number of viable virus particles need to be inhaled to trigger an infection. Thus, the assessed filtration efficacy may differ from the provided protection rate against SARS-CoV-2.”
In addition, particles containing the virus could dry out while going through the mask and become less infectious. “Even a small reduction in inhaled particles might prevent infection or at least lead to a less severe infection,” they noted.
In fact, filtration efficacy does not necessarily indicate how well the mask filters out particles while being worn. “This might be due to the combined effects of mask fit and pressure drop of the mask material and therefore tendency for mask leakage,” the team wrote. “High pressure drop results in higher breathing resistance and therefore supports leakage, especially if combined to a loosely fitting mask.”
These findings are “in line with what we already knew,” Dr. Cappa explained. “Even if the mask material filters out nearly all particles that pass through it, as is the case for high-efficiency masks such as N95 and FFP2, if the mask does not fit well, then it will only provide moderate protection for the wearer.”
Although the findings reaffirm the different levels of filtration provided by various cloth masks, they do not “provide any guidance on which types of cloth masks are better or worse,” he said. But they do show that “medical face masks will generally provide more protection to the wearer.”
It’s not surprising that face shields offer little protection from aerosols, Dr. Cappa said, but they can provide added protection when worn with a mask.
“A face shield could prevent large droplets that might shoot out when a person coughs or sneezes from depositing on a person’s eye,” he pointed out. And it can help “redirect the plume of particles that an infected person exhales, which could be useful in close quarters. However, even then those particles will keep moving around and could be inhaled. A mask can really help to decrease the amount inhaled.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors and Dr. Cappa disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Malpractice claims from the COVID-19 pandemic: More questions than answers
Editor’s note: This article has been provided by The Doctors Company, the exclusively endorsed medical malpractice carrier for the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The pandemic has raised pressing questions around preventive measures, vaccines, and safe treatment, but it has also obscured one key lingering uncertainty for medical professionals: Where are all the medical malpractice claims?
A variety of factors create a cloud of uncertainty around when, if ever, we will see the claims we expected from care provided just before the pandemic, much less claims deriving from care during the pandemic of both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 patients.
Malpractice claims take time to surface
We won’t know until 2022 or later whether there will be an increase in claims related to the pandemic. When a medical error occurs, it’s not like an automobile accident. Everybody nearby knows when there’s been an automobile accident because they hear screeching tires, a loud crash, and then sirens. But when a medical error occurs, generally speaking, neither the doctor nor the patient immediately knows that something is amiss. It can take months or years for people to realize that something untoward has occurred.
Claims from medical errors that occurred before the pandemic bring additional uncertainties. In 2020, we saw fewer than expected overall claims filed from events occurring 18-24 months before the pandemic. In total, 20% fewer claims were filed than in 2019. This may have had to do with courts shutting down, people being reluctant to meet with attorneys to discuss a claim, and/or lawyers working from home. We may see these claims filed later than expected, or maybe we won’t see them at all.
But without a doubt, pandemic-related claims will be filed. The pandemic’s impact on physicians increases the risk of claims. Burnout is a major cause of medical errors, and a recent study found that out of 60 countries, U.S. health care providers showed the highest rates of burnout. We’re concerned about the stress affecting physicians’ performance – not just the physical stress of the demands put on them while treating COVID-19 patients, but all of the worry. For instance, a lot of doctors at the start of this pandemic stayed at hotels because they didn’t want to bring the virus home to their families – if they got exposed. Those sorts of stressors from life disruptions, on top of the stress of treating COVID-19 patients and the stress of treating non–COVID-19 patients within overtaxed health care systems, contribute to the possibilities for error.
Immunity protections are not fail-safe
And while health care providers have medical liability protections during the pandemic, these protections may not prevent claims. Health care provider pandemic-related liability laws vary from state to state, and they will be tested in the courts as to whether they’re constitutional. For example, there is pending legislation in New York state that would repeal the provider protections created there at the start of the pandemic. Further, some expert witnesses will couch their statements in terms of what it takes to get around one of these statutes. Therefore, physicians do have reason for concern, even in states with strong liability protections.
The following case example, which is one of about 40 COVID-19–related claims made against our members so far, is a poster child for why these protections are necessary: A quadriplegic patient with COVID-19 had reached the point of organ failure before he reached the ED. There was really nothing medical science could do for him at that point, in terms of a chance at recovery. Therefore, the patient’s physician and conservator placed him in assisted living for palliative care. This was a sad but reasonable decision during a pandemic, with hospital beds needed for patients with a shot at surviving. Following that patient’s death, the physician is being sued.
Defending claims regarding treatment vs. regarding infection control
We are very confident in our ability to protect our members against claims where they are being sued over the treatment of the disease. Claims arising out of treatment are not concerning to us because there is no cure for COVID-19 – one can only treat the symptoms as the virus runs its course.
On the other hand, suits harder to defend would be those that revolve around transmitting the disease because providers didn’t follow guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or there wasn’t enough personal protective equipment. That’s why we stress the importance of following CDC guidelines, and why we’ve taken proactive steps to communicate with the entire medical community throughout the pandemic as part of our commitment to serve those who provide care.
Mr. White is chief operating officer at The Doctors Company. The guidelines suggested here are not rules, do not constitute legal advice, and do not ensure a successful outcome. The ultimate decision regarding the appropriateness of any treatment must be made by each health care provider considering the circumstances of the individual situation and in accordance with the laws of the jurisdiction in which the care is rendered.
Editor’s note: This article has been provided by The Doctors Company, the exclusively endorsed medical malpractice carrier for the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The pandemic has raised pressing questions around preventive measures, vaccines, and safe treatment, but it has also obscured one key lingering uncertainty for medical professionals: Where are all the medical malpractice claims?
A variety of factors create a cloud of uncertainty around when, if ever, we will see the claims we expected from care provided just before the pandemic, much less claims deriving from care during the pandemic of both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 patients.
Malpractice claims take time to surface
We won’t know until 2022 or later whether there will be an increase in claims related to the pandemic. When a medical error occurs, it’s not like an automobile accident. Everybody nearby knows when there’s been an automobile accident because they hear screeching tires, a loud crash, and then sirens. But when a medical error occurs, generally speaking, neither the doctor nor the patient immediately knows that something is amiss. It can take months or years for people to realize that something untoward has occurred.
Claims from medical errors that occurred before the pandemic bring additional uncertainties. In 2020, we saw fewer than expected overall claims filed from events occurring 18-24 months before the pandemic. In total, 20% fewer claims were filed than in 2019. This may have had to do with courts shutting down, people being reluctant to meet with attorneys to discuss a claim, and/or lawyers working from home. We may see these claims filed later than expected, or maybe we won’t see them at all.
But without a doubt, pandemic-related claims will be filed. The pandemic’s impact on physicians increases the risk of claims. Burnout is a major cause of medical errors, and a recent study found that out of 60 countries, U.S. health care providers showed the highest rates of burnout. We’re concerned about the stress affecting physicians’ performance – not just the physical stress of the demands put on them while treating COVID-19 patients, but all of the worry. For instance, a lot of doctors at the start of this pandemic stayed at hotels because they didn’t want to bring the virus home to their families – if they got exposed. Those sorts of stressors from life disruptions, on top of the stress of treating COVID-19 patients and the stress of treating non–COVID-19 patients within overtaxed health care systems, contribute to the possibilities for error.
Immunity protections are not fail-safe
And while health care providers have medical liability protections during the pandemic, these protections may not prevent claims. Health care provider pandemic-related liability laws vary from state to state, and they will be tested in the courts as to whether they’re constitutional. For example, there is pending legislation in New York state that would repeal the provider protections created there at the start of the pandemic. Further, some expert witnesses will couch their statements in terms of what it takes to get around one of these statutes. Therefore, physicians do have reason for concern, even in states with strong liability protections.
The following case example, which is one of about 40 COVID-19–related claims made against our members so far, is a poster child for why these protections are necessary: A quadriplegic patient with COVID-19 had reached the point of organ failure before he reached the ED. There was really nothing medical science could do for him at that point, in terms of a chance at recovery. Therefore, the patient’s physician and conservator placed him in assisted living for palliative care. This was a sad but reasonable decision during a pandemic, with hospital beds needed for patients with a shot at surviving. Following that patient’s death, the physician is being sued.
Defending claims regarding treatment vs. regarding infection control
We are very confident in our ability to protect our members against claims where they are being sued over the treatment of the disease. Claims arising out of treatment are not concerning to us because there is no cure for COVID-19 – one can only treat the symptoms as the virus runs its course.
On the other hand, suits harder to defend would be those that revolve around transmitting the disease because providers didn’t follow guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or there wasn’t enough personal protective equipment. That’s why we stress the importance of following CDC guidelines, and why we’ve taken proactive steps to communicate with the entire medical community throughout the pandemic as part of our commitment to serve those who provide care.
Mr. White is chief operating officer at The Doctors Company. The guidelines suggested here are not rules, do not constitute legal advice, and do not ensure a successful outcome. The ultimate decision regarding the appropriateness of any treatment must be made by each health care provider considering the circumstances of the individual situation and in accordance with the laws of the jurisdiction in which the care is rendered.
Editor’s note: This article has been provided by The Doctors Company, the exclusively endorsed medical malpractice carrier for the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The pandemic has raised pressing questions around preventive measures, vaccines, and safe treatment, but it has also obscured one key lingering uncertainty for medical professionals: Where are all the medical malpractice claims?
A variety of factors create a cloud of uncertainty around when, if ever, we will see the claims we expected from care provided just before the pandemic, much less claims deriving from care during the pandemic of both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 patients.
Malpractice claims take time to surface
We won’t know until 2022 or later whether there will be an increase in claims related to the pandemic. When a medical error occurs, it’s not like an automobile accident. Everybody nearby knows when there’s been an automobile accident because they hear screeching tires, a loud crash, and then sirens. But when a medical error occurs, generally speaking, neither the doctor nor the patient immediately knows that something is amiss. It can take months or years for people to realize that something untoward has occurred.
Claims from medical errors that occurred before the pandemic bring additional uncertainties. In 2020, we saw fewer than expected overall claims filed from events occurring 18-24 months before the pandemic. In total, 20% fewer claims were filed than in 2019. This may have had to do with courts shutting down, people being reluctant to meet with attorneys to discuss a claim, and/or lawyers working from home. We may see these claims filed later than expected, or maybe we won’t see them at all.
But without a doubt, pandemic-related claims will be filed. The pandemic’s impact on physicians increases the risk of claims. Burnout is a major cause of medical errors, and a recent study found that out of 60 countries, U.S. health care providers showed the highest rates of burnout. We’re concerned about the stress affecting physicians’ performance – not just the physical stress of the demands put on them while treating COVID-19 patients, but all of the worry. For instance, a lot of doctors at the start of this pandemic stayed at hotels because they didn’t want to bring the virus home to their families – if they got exposed. Those sorts of stressors from life disruptions, on top of the stress of treating COVID-19 patients and the stress of treating non–COVID-19 patients within overtaxed health care systems, contribute to the possibilities for error.
Immunity protections are not fail-safe
And while health care providers have medical liability protections during the pandemic, these protections may not prevent claims. Health care provider pandemic-related liability laws vary from state to state, and they will be tested in the courts as to whether they’re constitutional. For example, there is pending legislation in New York state that would repeal the provider protections created there at the start of the pandemic. Further, some expert witnesses will couch their statements in terms of what it takes to get around one of these statutes. Therefore, physicians do have reason for concern, even in states with strong liability protections.
The following case example, which is one of about 40 COVID-19–related claims made against our members so far, is a poster child for why these protections are necessary: A quadriplegic patient with COVID-19 had reached the point of organ failure before he reached the ED. There was really nothing medical science could do for him at that point, in terms of a chance at recovery. Therefore, the patient’s physician and conservator placed him in assisted living for palliative care. This was a sad but reasonable decision during a pandemic, with hospital beds needed for patients with a shot at surviving. Following that patient’s death, the physician is being sued.
Defending claims regarding treatment vs. regarding infection control
We are very confident in our ability to protect our members against claims where they are being sued over the treatment of the disease. Claims arising out of treatment are not concerning to us because there is no cure for COVID-19 – one can only treat the symptoms as the virus runs its course.
On the other hand, suits harder to defend would be those that revolve around transmitting the disease because providers didn’t follow guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or there wasn’t enough personal protective equipment. That’s why we stress the importance of following CDC guidelines, and why we’ve taken proactive steps to communicate with the entire medical community throughout the pandemic as part of our commitment to serve those who provide care.
Mr. White is chief operating officer at The Doctors Company. The guidelines suggested here are not rules, do not constitute legal advice, and do not ensure a successful outcome. The ultimate decision regarding the appropriateness of any treatment must be made by each health care provider considering the circumstances of the individual situation and in accordance with the laws of the jurisdiction in which the care is rendered.
Delta variant key to breakthrough infections in vaccinated Israelis
Israeli officials are reporting a 30% decrease in the effectiveness of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild to moderate cases of COVID-19. At the same time, protection against hospitalization and severe illness remains robust.
The country’s Ministry of Health data cited high levels of circulating Delta variant and a relaxation of public health measures in early June for the drop in the vaccine’s prevention of “breakthrough” cases from 94% to 64% in recent weeks.
However, it is important to consider the findings in context, experts cautioned.
“My overall take on this that the vaccine is highly protective against the endpoints that matter – hospitalization and severe disease,” Anna Durbin, MD, told this news organization.
“I was very pleasantly surprised with the very high efficacy against hospitalization and severe disease – even against the Delta variant,” added Dr. Durbin, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Ali Mokdad, PhD, of the Institute for Health Metrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, agreed that the high degree of protection against severe outcomes should be the focus.
“That’s the whole idea. You want to defend against COVID-19. So even if someone is infected, they don’t end up in the hospital or in the morgue,” he said in an interview.
Compared with an earlier report, the efficacy of the Pfizer vaccine against hospitalization fell slightly from 98% to 93%.
“For me, the fact that there is increased infection from the Delta variant after the vaccines such as Pfizer is of course a concern. But the positive news is that there is 93% prevention against severe disease or mortality,” added Dr. Mokdad, who is also professor of global health at University of Washington.
In addition, the absolute numbers remain relatively small. The Ministry of Health data show that, of the 63 Israelis hospitalized with COVID-19 nationwide on July 3, 34 were in critical condition.
Unrealistic expectations?
People may have unrealistic expectations regarding breakthrough infections, Dr. Durbin said. “It seems that people are almost expecting ‘sterilizing immunity’ from these vaccines,” she said, explaining that would mean complete protection from infection.
Expectations may be high “because these vaccines have been so effective,” added Dr. Durbin, who is also affiliated with the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health.
The higher the number of vaccinated residents, the more breakthrough cases will be reported, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences at the University of Texas Science Center at Houston, wrote in her “Your Local Epidemiologist” blog.
This could apply to Israel, with an estimated 60% of adults in Israel fully vaccinated and 65% receiving at least one dose as of July 5, Our World in Data figures show.
How the updated figures were reported could be confusing, Dr. Jetelina said. Israel’s Health Minister Chezy Levy noted that “55% of the newly infected had been vaccinated” in a radio interview announcing the results.
“This language is important because it’s very different than ‘half of vaccinated people were infected,’ ” Dr. Jetelina noted.
Israel had a 7-day rolling average of 324 new confirmed COVID-19 cases as of July 5. Assuming 55% of these cases were among vaccinated people, that would mean 178 people experienced breakthrough infections.
In contrast, almost 6 million people in Israel are fully vaccinated. If 55% of them experienced breakthrough infections, the number would be much higher – more than 3 million.
Dr. Jetelina added that more details about the new Israel figures would be helpful, including the severity of COVID-19 among the vaccinated cases and breakdown of infections between adults and children.
Next steps
Israeli health officials are weighing the necessity of a third or booster dose of the vaccine. Whether they will reinstate public health measures to prevent spread of COVID-19 also remains unknown.
Going forward, Israel intends to study whether factors such as age, comorbidities, or time since immunization affect risk for breakthrough infections among people vaccinated against COVID-19.
“We want to prevent people from getting hospitalized, seriously ill, and of course, dying. It’s encouraging these vaccines will be able to have a high impact on those outcomes,” Dr. Durbin said. “We just need to get people vaccinated.”
A call for better global surveillance
A global surveillance system is a potential solution to track and respond to the growing threat of the Delta variant and other variants of concern, Scott P. Layne, MD, and Jeffery K. Taubenberger, MD, PhD, wrote in a July 7, 2021, editorial in Science Translational Medicine.
One goal, Dr. Layne said in an interview, is to highlight “the compelling need for a new global COVID-19 program of surveillance and offer a blueprint for building it.” A second aim is to promote global cooperation among key advisers and leaders in the G7, G20, and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation nations.
“It’s an uphill struggle with superpower discords, global warming, cybersecurity, and pandemics all competing for finite attention,” Dr. Layne said. “However, what other options do we have for taming the so-called forever virus?”
Dr. Mokdad and Dr. Jetelina had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Durban disclosed she was the site primary investigator for the phase 3 AstraZeneca vaccine trial and an investigator on the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Israeli officials are reporting a 30% decrease in the effectiveness of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild to moderate cases of COVID-19. At the same time, protection against hospitalization and severe illness remains robust.
The country’s Ministry of Health data cited high levels of circulating Delta variant and a relaxation of public health measures in early June for the drop in the vaccine’s prevention of “breakthrough” cases from 94% to 64% in recent weeks.
However, it is important to consider the findings in context, experts cautioned.
“My overall take on this that the vaccine is highly protective against the endpoints that matter – hospitalization and severe disease,” Anna Durbin, MD, told this news organization.
“I was very pleasantly surprised with the very high efficacy against hospitalization and severe disease – even against the Delta variant,” added Dr. Durbin, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Ali Mokdad, PhD, of the Institute for Health Metrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, agreed that the high degree of protection against severe outcomes should be the focus.
“That’s the whole idea. You want to defend against COVID-19. So even if someone is infected, they don’t end up in the hospital or in the morgue,” he said in an interview.
Compared with an earlier report, the efficacy of the Pfizer vaccine against hospitalization fell slightly from 98% to 93%.
“For me, the fact that there is increased infection from the Delta variant after the vaccines such as Pfizer is of course a concern. But the positive news is that there is 93% prevention against severe disease or mortality,” added Dr. Mokdad, who is also professor of global health at University of Washington.
In addition, the absolute numbers remain relatively small. The Ministry of Health data show that, of the 63 Israelis hospitalized with COVID-19 nationwide on July 3, 34 were in critical condition.
Unrealistic expectations?
People may have unrealistic expectations regarding breakthrough infections, Dr. Durbin said. “It seems that people are almost expecting ‘sterilizing immunity’ from these vaccines,” she said, explaining that would mean complete protection from infection.
Expectations may be high “because these vaccines have been so effective,” added Dr. Durbin, who is also affiliated with the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health.
The higher the number of vaccinated residents, the more breakthrough cases will be reported, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences at the University of Texas Science Center at Houston, wrote in her “Your Local Epidemiologist” blog.
This could apply to Israel, with an estimated 60% of adults in Israel fully vaccinated and 65% receiving at least one dose as of July 5, Our World in Data figures show.
How the updated figures were reported could be confusing, Dr. Jetelina said. Israel’s Health Minister Chezy Levy noted that “55% of the newly infected had been vaccinated” in a radio interview announcing the results.
“This language is important because it’s very different than ‘half of vaccinated people were infected,’ ” Dr. Jetelina noted.
Israel had a 7-day rolling average of 324 new confirmed COVID-19 cases as of July 5. Assuming 55% of these cases were among vaccinated people, that would mean 178 people experienced breakthrough infections.
In contrast, almost 6 million people in Israel are fully vaccinated. If 55% of them experienced breakthrough infections, the number would be much higher – more than 3 million.
Dr. Jetelina added that more details about the new Israel figures would be helpful, including the severity of COVID-19 among the vaccinated cases and breakdown of infections between adults and children.
Next steps
Israeli health officials are weighing the necessity of a third or booster dose of the vaccine. Whether they will reinstate public health measures to prevent spread of COVID-19 also remains unknown.
Going forward, Israel intends to study whether factors such as age, comorbidities, or time since immunization affect risk for breakthrough infections among people vaccinated against COVID-19.
“We want to prevent people from getting hospitalized, seriously ill, and of course, dying. It’s encouraging these vaccines will be able to have a high impact on those outcomes,” Dr. Durbin said. “We just need to get people vaccinated.”
A call for better global surveillance
A global surveillance system is a potential solution to track and respond to the growing threat of the Delta variant and other variants of concern, Scott P. Layne, MD, and Jeffery K. Taubenberger, MD, PhD, wrote in a July 7, 2021, editorial in Science Translational Medicine.
One goal, Dr. Layne said in an interview, is to highlight “the compelling need for a new global COVID-19 program of surveillance and offer a blueprint for building it.” A second aim is to promote global cooperation among key advisers and leaders in the G7, G20, and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation nations.
“It’s an uphill struggle with superpower discords, global warming, cybersecurity, and pandemics all competing for finite attention,” Dr. Layne said. “However, what other options do we have for taming the so-called forever virus?”
Dr. Mokdad and Dr. Jetelina had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Durban disclosed she was the site primary investigator for the phase 3 AstraZeneca vaccine trial and an investigator on the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Israeli officials are reporting a 30% decrease in the effectiveness of the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild to moderate cases of COVID-19. At the same time, protection against hospitalization and severe illness remains robust.
The country’s Ministry of Health data cited high levels of circulating Delta variant and a relaxation of public health measures in early June for the drop in the vaccine’s prevention of “breakthrough” cases from 94% to 64% in recent weeks.
However, it is important to consider the findings in context, experts cautioned.
“My overall take on this that the vaccine is highly protective against the endpoints that matter – hospitalization and severe disease,” Anna Durbin, MD, told this news organization.
“I was very pleasantly surprised with the very high efficacy against hospitalization and severe disease – even against the Delta variant,” added Dr. Durbin, professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Ali Mokdad, PhD, of the Institute for Health Metrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, agreed that the high degree of protection against severe outcomes should be the focus.
“That’s the whole idea. You want to defend against COVID-19. So even if someone is infected, they don’t end up in the hospital or in the morgue,” he said in an interview.
Compared with an earlier report, the efficacy of the Pfizer vaccine against hospitalization fell slightly from 98% to 93%.
“For me, the fact that there is increased infection from the Delta variant after the vaccines such as Pfizer is of course a concern. But the positive news is that there is 93% prevention against severe disease or mortality,” added Dr. Mokdad, who is also professor of global health at University of Washington.
In addition, the absolute numbers remain relatively small. The Ministry of Health data show that, of the 63 Israelis hospitalized with COVID-19 nationwide on July 3, 34 were in critical condition.
Unrealistic expectations?
People may have unrealistic expectations regarding breakthrough infections, Dr. Durbin said. “It seems that people are almost expecting ‘sterilizing immunity’ from these vaccines,” she said, explaining that would mean complete protection from infection.
Expectations may be high “because these vaccines have been so effective,” added Dr. Durbin, who is also affiliated with the Johns Hopkins Center for Global Health.
The higher the number of vaccinated residents, the more breakthrough cases will be reported, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of epidemiology, human genetics, and environmental sciences at the University of Texas Science Center at Houston, wrote in her “Your Local Epidemiologist” blog.
This could apply to Israel, with an estimated 60% of adults in Israel fully vaccinated and 65% receiving at least one dose as of July 5, Our World in Data figures show.
How the updated figures were reported could be confusing, Dr. Jetelina said. Israel’s Health Minister Chezy Levy noted that “55% of the newly infected had been vaccinated” in a radio interview announcing the results.
“This language is important because it’s very different than ‘half of vaccinated people were infected,’ ” Dr. Jetelina noted.
Israel had a 7-day rolling average of 324 new confirmed COVID-19 cases as of July 5. Assuming 55% of these cases were among vaccinated people, that would mean 178 people experienced breakthrough infections.
In contrast, almost 6 million people in Israel are fully vaccinated. If 55% of them experienced breakthrough infections, the number would be much higher – more than 3 million.
Dr. Jetelina added that more details about the new Israel figures would be helpful, including the severity of COVID-19 among the vaccinated cases and breakdown of infections between adults and children.
Next steps
Israeli health officials are weighing the necessity of a third or booster dose of the vaccine. Whether they will reinstate public health measures to prevent spread of COVID-19 also remains unknown.
Going forward, Israel intends to study whether factors such as age, comorbidities, or time since immunization affect risk for breakthrough infections among people vaccinated against COVID-19.
“We want to prevent people from getting hospitalized, seriously ill, and of course, dying. It’s encouraging these vaccines will be able to have a high impact on those outcomes,” Dr. Durbin said. “We just need to get people vaccinated.”
A call for better global surveillance
A global surveillance system is a potential solution to track and respond to the growing threat of the Delta variant and other variants of concern, Scott P. Layne, MD, and Jeffery K. Taubenberger, MD, PhD, wrote in a July 7, 2021, editorial in Science Translational Medicine.
One goal, Dr. Layne said in an interview, is to highlight “the compelling need for a new global COVID-19 program of surveillance and offer a blueprint for building it.” A second aim is to promote global cooperation among key advisers and leaders in the G7, G20, and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation nations.
“It’s an uphill struggle with superpower discords, global warming, cybersecurity, and pandemics all competing for finite attention,” Dr. Layne said. “However, what other options do we have for taming the so-called forever virus?”
Dr. Mokdad and Dr. Jetelina had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Durban disclosed she was the site primary investigator for the phase 3 AstraZeneca vaccine trial and an investigator on the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine trial.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clostridioides difficile: Two sets of guidelines disagree
With two sets of Clostridioides difficile recommendations being published within a month of each other, clinicians may find themselves trying to reconcile some of the conflicts between the two guidelines.
The first set, published June 1 by the American College of Gastroenterology, focuses on fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and the antibiotic vancomycin. The second, published June 24 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, drives a shift in treatment for initial episodes and short-term recurrence from vancomycin to fidaxomicin and, in some cases, adding on the monoclonal antibody bezlotoxumab, both made by Merck.
The updates are timely because researchers are now recognizing that C. difficile can colonize people without causing symptoms, David Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine, Norfolk, said in an interview. He was not involved in writing either set of guidelines. “C. diff infection was a hospital-type infection, but we’re now seeing it in up to approximately 35%-50% of patients coming from the community, so it’s a big concern.”
Although the guidelines agree on which treatments are effective, the recommendations give the options a different emphasis.
Infectious disease specialist Stuart Johnson, MD, professor of medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Maywood, Ill., and a physician researcher at Edward Hines Jr. Veterans Affairs Hospital in Hines, Ill., is the first author in the IDSA/SHEA guidelines. He told this news organization that one reason the two sets of recommendations may diverge in emphasis for initial and recurrent C. difficile is that “everyone has a different way of looking at things.” Compared with infectious disease specialists like him, he said, gastroenterologists “for the most part see the world a little different and have their own bent on things.”
The differences between the two guidelines relate to the first-line therapy for people with an initial or recurrent C. difficile episode. For an initial episode, the IDSA/SHEA authors conditionally recommend fidaxomicin as first preferred choice over vancomycin, with a moderate certainty of evidence. They noted that implementing this recommendation depends on “available resources,” a reference to the higher cost and difficulty of access associated with fidaxomicin.
Gastroenterologist Monika Fischer, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, is one of the authors of the ACG guidelines. She told this news organization that the cost difference between fidaxomicin and vancomycin is considerable and finds the choice to foreground fidaxomicin puzzling. “They did not reference any new data compared to those we have published.” Their recommendation may make sense in terms of efficacy, but real-world demands require attention to cost and reimbursement. “They themselves state this in their recommendations,” she noted.
Dr. Fischer cited a ballpark of about $100 for a course of vancomycin, compared with about $3,000 for a course of fidaxomicin. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines do cite vancomycin as an acceptable alternative. According to Dr. Fischer, the ACG guidelines authors discussed fidaxomicin and concluded that there just wasn’t enough evidence to justify favoring this antibiotic over vancomycin, given the cost-benefit imbalance. The ACG guidelines call for a standard course of oral vancomycin for a first, nonsevere C. difficile episode, listing oral fidaxomicin or oral metronidazole as alternatives.
For a recurrence, the IDSA/SHEA authors also favor fidaxomicin in a conditional recommendation over a standard course of vancomycin. For multiple recurrences, a tapered and pulsed vancomycin regimen, vancomycin followed by rifaximin, or FMT are also options.
Dr. David Johnson said that these recommendations favoring fidaxomicin are “surprising,” and that lower costs of vancomycin outweigh the benefit of fidaxomicin, given more-or-less comparable data on cure rates.
In contrast, the ACG guidelines recommend that an initial recurrence be treated with a tapering dose of vancomycin, and call for FMT for patients who are eligible and who experience a second or more C. difficile recurrences after a round of pulsed vancomycin.
Dr. Stuart Johnson said that FMT carries its own special set of issues. “If you don’t have a donor program set up, you have to rely on a stool bank,” noting that one widely used stool bank “basically had to stop making the product because of the coronavirus.” Costs for FMT products have doubled in recent years, and because Food and Drug Administration approval of the therapy is lacking, insurance does not cover it.
Dr. David Johnson also said that he is not “terribly happy” about the ACG recommendation for vancomycin prophylaxis. “It may help, but it also can have off-target effects against colonic bacterial flora, so we would not agree with that recommendation.”
The IDSA/SHEA authors also conditionally recommend bezlotoxumab, on very low certainty of evidence, as a cotherapy with standard of care antibiotics for recurrence prevention in patients with an episode in the last 6 months, particularly for patients at high recurrence risk “where logistics is not an issue.” The FDA has warned that this monoclonal antibody should be used with great care in patients with heart failure and only when benefits outweigh risks.
The ACG guidelines conditionally recommend considering bezlotoxumab to prevent recurrence in patients with specific risk factors, including age over 65 years and severe presentation. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines expand this population to anyone with a recurrence within 6 months, Dr. Fischer pointed out.
The antibody treatment “does offer another 10% absolute reduction in recurrent C. diff disease,” said Dr. Stuart Johnson, which is a “helpful option and primarily for people who have had recurrent C. diff already.” In general, he said, for both drugs, “access is still something we have to work with.”
In a commentary on the ACG guidelines, Dr. David Johnson wrote that there is good evidence that bezlotoxumab prevents relapse, especially in patients with specific risk factors. The hitch is the $4,500 price tag for a 1,000-mg vial, with a recommended dose of 10 mg/kg.
Dr. Stuart Johnson agreed that the costs of the fidaxomicin and bezlotoxumab are important considerations. In addition, there are logistical issues with using the antibody because most hospitals don’t offer infusions, which pushes patients to infusion centers.
Regardless, he added, “we’re happy that we have new options.”
Dr. Fischer, Dr. Stuart Johnson, and Dr. David Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With two sets of Clostridioides difficile recommendations being published within a month of each other, clinicians may find themselves trying to reconcile some of the conflicts between the two guidelines.
The first set, published June 1 by the American College of Gastroenterology, focuses on fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and the antibiotic vancomycin. The second, published June 24 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, drives a shift in treatment for initial episodes and short-term recurrence from vancomycin to fidaxomicin and, in some cases, adding on the monoclonal antibody bezlotoxumab, both made by Merck.
The updates are timely because researchers are now recognizing that C. difficile can colonize people without causing symptoms, David Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine, Norfolk, said in an interview. He was not involved in writing either set of guidelines. “C. diff infection was a hospital-type infection, but we’re now seeing it in up to approximately 35%-50% of patients coming from the community, so it’s a big concern.”
Although the guidelines agree on which treatments are effective, the recommendations give the options a different emphasis.
Infectious disease specialist Stuart Johnson, MD, professor of medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Maywood, Ill., and a physician researcher at Edward Hines Jr. Veterans Affairs Hospital in Hines, Ill., is the first author in the IDSA/SHEA guidelines. He told this news organization that one reason the two sets of recommendations may diverge in emphasis for initial and recurrent C. difficile is that “everyone has a different way of looking at things.” Compared with infectious disease specialists like him, he said, gastroenterologists “for the most part see the world a little different and have their own bent on things.”
The differences between the two guidelines relate to the first-line therapy for people with an initial or recurrent C. difficile episode. For an initial episode, the IDSA/SHEA authors conditionally recommend fidaxomicin as first preferred choice over vancomycin, with a moderate certainty of evidence. They noted that implementing this recommendation depends on “available resources,” a reference to the higher cost and difficulty of access associated with fidaxomicin.
Gastroenterologist Monika Fischer, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, is one of the authors of the ACG guidelines. She told this news organization that the cost difference between fidaxomicin and vancomycin is considerable and finds the choice to foreground fidaxomicin puzzling. “They did not reference any new data compared to those we have published.” Their recommendation may make sense in terms of efficacy, but real-world demands require attention to cost and reimbursement. “They themselves state this in their recommendations,” she noted.
Dr. Fischer cited a ballpark of about $100 for a course of vancomycin, compared with about $3,000 for a course of fidaxomicin. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines do cite vancomycin as an acceptable alternative. According to Dr. Fischer, the ACG guidelines authors discussed fidaxomicin and concluded that there just wasn’t enough evidence to justify favoring this antibiotic over vancomycin, given the cost-benefit imbalance. The ACG guidelines call for a standard course of oral vancomycin for a first, nonsevere C. difficile episode, listing oral fidaxomicin or oral metronidazole as alternatives.
For a recurrence, the IDSA/SHEA authors also favor fidaxomicin in a conditional recommendation over a standard course of vancomycin. For multiple recurrences, a tapered and pulsed vancomycin regimen, vancomycin followed by rifaximin, or FMT are also options.
Dr. David Johnson said that these recommendations favoring fidaxomicin are “surprising,” and that lower costs of vancomycin outweigh the benefit of fidaxomicin, given more-or-less comparable data on cure rates.
In contrast, the ACG guidelines recommend that an initial recurrence be treated with a tapering dose of vancomycin, and call for FMT for patients who are eligible and who experience a second or more C. difficile recurrences after a round of pulsed vancomycin.
Dr. Stuart Johnson said that FMT carries its own special set of issues. “If you don’t have a donor program set up, you have to rely on a stool bank,” noting that one widely used stool bank “basically had to stop making the product because of the coronavirus.” Costs for FMT products have doubled in recent years, and because Food and Drug Administration approval of the therapy is lacking, insurance does not cover it.
Dr. David Johnson also said that he is not “terribly happy” about the ACG recommendation for vancomycin prophylaxis. “It may help, but it also can have off-target effects against colonic bacterial flora, so we would not agree with that recommendation.”
The IDSA/SHEA authors also conditionally recommend bezlotoxumab, on very low certainty of evidence, as a cotherapy with standard of care antibiotics for recurrence prevention in patients with an episode in the last 6 months, particularly for patients at high recurrence risk “where logistics is not an issue.” The FDA has warned that this monoclonal antibody should be used with great care in patients with heart failure and only when benefits outweigh risks.
The ACG guidelines conditionally recommend considering bezlotoxumab to prevent recurrence in patients with specific risk factors, including age over 65 years and severe presentation. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines expand this population to anyone with a recurrence within 6 months, Dr. Fischer pointed out.
The antibody treatment “does offer another 10% absolute reduction in recurrent C. diff disease,” said Dr. Stuart Johnson, which is a “helpful option and primarily for people who have had recurrent C. diff already.” In general, he said, for both drugs, “access is still something we have to work with.”
In a commentary on the ACG guidelines, Dr. David Johnson wrote that there is good evidence that bezlotoxumab prevents relapse, especially in patients with specific risk factors. The hitch is the $4,500 price tag for a 1,000-mg vial, with a recommended dose of 10 mg/kg.
Dr. Stuart Johnson agreed that the costs of the fidaxomicin and bezlotoxumab are important considerations. In addition, there are logistical issues with using the antibody because most hospitals don’t offer infusions, which pushes patients to infusion centers.
Regardless, he added, “we’re happy that we have new options.”
Dr. Fischer, Dr. Stuart Johnson, and Dr. David Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With two sets of Clostridioides difficile recommendations being published within a month of each other, clinicians may find themselves trying to reconcile some of the conflicts between the two guidelines.
The first set, published June 1 by the American College of Gastroenterology, focuses on fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and the antibiotic vancomycin. The second, published June 24 by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America, drives a shift in treatment for initial episodes and short-term recurrence from vancomycin to fidaxomicin and, in some cases, adding on the monoclonal antibody bezlotoxumab, both made by Merck.
The updates are timely because researchers are now recognizing that C. difficile can colonize people without causing symptoms, David Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine, Norfolk, said in an interview. He was not involved in writing either set of guidelines. “C. diff infection was a hospital-type infection, but we’re now seeing it in up to approximately 35%-50% of patients coming from the community, so it’s a big concern.”
Although the guidelines agree on which treatments are effective, the recommendations give the options a different emphasis.
Infectious disease specialist Stuart Johnson, MD, professor of medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Maywood, Ill., and a physician researcher at Edward Hines Jr. Veterans Affairs Hospital in Hines, Ill., is the first author in the IDSA/SHEA guidelines. He told this news organization that one reason the two sets of recommendations may diverge in emphasis for initial and recurrent C. difficile is that “everyone has a different way of looking at things.” Compared with infectious disease specialists like him, he said, gastroenterologists “for the most part see the world a little different and have their own bent on things.”
The differences between the two guidelines relate to the first-line therapy for people with an initial or recurrent C. difficile episode. For an initial episode, the IDSA/SHEA authors conditionally recommend fidaxomicin as first preferred choice over vancomycin, with a moderate certainty of evidence. They noted that implementing this recommendation depends on “available resources,” a reference to the higher cost and difficulty of access associated with fidaxomicin.
Gastroenterologist Monika Fischer, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Indiana University, Indianapolis, is one of the authors of the ACG guidelines. She told this news organization that the cost difference between fidaxomicin and vancomycin is considerable and finds the choice to foreground fidaxomicin puzzling. “They did not reference any new data compared to those we have published.” Their recommendation may make sense in terms of efficacy, but real-world demands require attention to cost and reimbursement. “They themselves state this in their recommendations,” she noted.
Dr. Fischer cited a ballpark of about $100 for a course of vancomycin, compared with about $3,000 for a course of fidaxomicin. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines do cite vancomycin as an acceptable alternative. According to Dr. Fischer, the ACG guidelines authors discussed fidaxomicin and concluded that there just wasn’t enough evidence to justify favoring this antibiotic over vancomycin, given the cost-benefit imbalance. The ACG guidelines call for a standard course of oral vancomycin for a first, nonsevere C. difficile episode, listing oral fidaxomicin or oral metronidazole as alternatives.
For a recurrence, the IDSA/SHEA authors also favor fidaxomicin in a conditional recommendation over a standard course of vancomycin. For multiple recurrences, a tapered and pulsed vancomycin regimen, vancomycin followed by rifaximin, or FMT are also options.
Dr. David Johnson said that these recommendations favoring fidaxomicin are “surprising,” and that lower costs of vancomycin outweigh the benefit of fidaxomicin, given more-or-less comparable data on cure rates.
In contrast, the ACG guidelines recommend that an initial recurrence be treated with a tapering dose of vancomycin, and call for FMT for patients who are eligible and who experience a second or more C. difficile recurrences after a round of pulsed vancomycin.
Dr. Stuart Johnson said that FMT carries its own special set of issues. “If you don’t have a donor program set up, you have to rely on a stool bank,” noting that one widely used stool bank “basically had to stop making the product because of the coronavirus.” Costs for FMT products have doubled in recent years, and because Food and Drug Administration approval of the therapy is lacking, insurance does not cover it.
Dr. David Johnson also said that he is not “terribly happy” about the ACG recommendation for vancomycin prophylaxis. “It may help, but it also can have off-target effects against colonic bacterial flora, so we would not agree with that recommendation.”
The IDSA/SHEA authors also conditionally recommend bezlotoxumab, on very low certainty of evidence, as a cotherapy with standard of care antibiotics for recurrence prevention in patients with an episode in the last 6 months, particularly for patients at high recurrence risk “where logistics is not an issue.” The FDA has warned that this monoclonal antibody should be used with great care in patients with heart failure and only when benefits outweigh risks.
The ACG guidelines conditionally recommend considering bezlotoxumab to prevent recurrence in patients with specific risk factors, including age over 65 years and severe presentation. The IDSA/SHEA guidelines expand this population to anyone with a recurrence within 6 months, Dr. Fischer pointed out.
The antibody treatment “does offer another 10% absolute reduction in recurrent C. diff disease,” said Dr. Stuart Johnson, which is a “helpful option and primarily for people who have had recurrent C. diff already.” In general, he said, for both drugs, “access is still something we have to work with.”
In a commentary on the ACG guidelines, Dr. David Johnson wrote that there is good evidence that bezlotoxumab prevents relapse, especially in patients with specific risk factors. The hitch is the $4,500 price tag for a 1,000-mg vial, with a recommended dose of 10 mg/kg.
Dr. Stuart Johnson agreed that the costs of the fidaxomicin and bezlotoxumab are important considerations. In addition, there are logistical issues with using the antibody because most hospitals don’t offer infusions, which pushes patients to infusion centers.
Regardless, he added, “we’re happy that we have new options.”
Dr. Fischer, Dr. Stuart Johnson, and Dr. David Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalist movers and shakers – July 2021
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, has been appointed dean of medical education for the University of Chicago’s biological sciences division. She began her assignment on July 1, 2021, taking over for the retiring Halina Brukner, MD, a 36-year veteran in medicine.
Dr. Arora will take charge of undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education for the University of Chicago’s medical education program, with a focus on simulation-based training. She also will represent the medical school within the university proper, as well as with outside organizations such as the Association of American Colleges, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Dr. Arora has been a faculty member at Chicago Medicine since 2005. She is a professor of medicine, assistant dean for scholarship and discovery, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning, and Master of the Academy of Distinguished Medical Educators. Dr. Arora is a member of the National Academy of Medicine and is on the board of directors for the American Board of Internal Medicine.
Zeshan Anwar, MD, SFHM, was named new chief of the section of inpatient internal medicine and director of hospitalist services at Reading Hospital–Tower Health (West Reading, Pa.) in January 2021. He provides support to hospitalists, nurses, pharmacists, care managers, support service professionals and others.
Previously, Dr. Anwar worked as vice chair of the department of medicine and medical director of the hospitalist program at Evangelical Community Hospital (Lewisburg, Pa.). He has a background in education, having taught as an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine (Scranton, Pa.) since 2014.
Katherine Hochman, MD, FHM, has been appointed the first director of the newly established division of hospital medicine at NYU Langone Health in New York. Dr. Hochman is the founder of NYU Langone’s hospitalist program (2004), and the new division was established this year in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hochman will be charged with expanding on the hospitalist program, analyzing best practices, and educating residents, clinicians, and other health care professionals. She plans to emphasize mentorship and creating career pathways for the program’s students.
Dr. Hochman was NYU Langone’s first hospitalist and later became associate program director of medicine at Langone’s Tisch Hospital. She helped grow the hospitalist program to 40 professionals in 2020.
Daniel Asher, MD, recently was named a Top Hospitalist by Continental Who’s Who. Dr. Asher is a night hospitalist at Piedmont Columbus Regional (Columbus, Ga.), where he works with residents and consults with other physicians regarding patients at the facility.
Dr. Asher has spent his entire post–medical school career at Piedmont, serving as a family medicine resident from 2018 to 2020. He was named chief resident in 2019-20, and has continued his efforts at the hospital since then, including front-line work with COVID-19 patients.
Nicholas O’Dell, MD, has been selected as medical director of the Murray Medical Associates hospitalist program at Murray-Calloway County Hospital (Murray, Ky.). Dr. O’Dell, who has been a hospitalist at the facility since 2014, has served as chief medical officer at the hospital since February 2020. He will continue in his role as CMO, but will no longer see clinical patients.
Brad Tate, MD, has been elevated to associate chief medical officer at Children’s Medical Center Plano (Texas), starting in the new leadership role in June 2021.
Dr. Tate has been affiliated with Children’s Health since 2010, when he was a hospitalist in Plano, as well as medical director of the Children’s Health Medical Group Hospitalist Group. He advanced that program from Plano to the network’s Dallas campus.
Touchette Regional Hospital (Centreville, Ill.) has contracted with MEDS Emergency Physician Staffing and Management (O’Fallon, Ill.) to provide inpatient physician and nurse practitioner staffing. The move is an extension of the existing relationship between the two entities, as MEDS has provided emergency room staffing services at Touchette since 2019.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, has been appointed dean of medical education for the University of Chicago’s biological sciences division. She began her assignment on July 1, 2021, taking over for the retiring Halina Brukner, MD, a 36-year veteran in medicine.
Dr. Arora will take charge of undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education for the University of Chicago’s medical education program, with a focus on simulation-based training. She also will represent the medical school within the university proper, as well as with outside organizations such as the Association of American Colleges, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Dr. Arora has been a faculty member at Chicago Medicine since 2005. She is a professor of medicine, assistant dean for scholarship and discovery, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning, and Master of the Academy of Distinguished Medical Educators. Dr. Arora is a member of the National Academy of Medicine and is on the board of directors for the American Board of Internal Medicine.
Zeshan Anwar, MD, SFHM, was named new chief of the section of inpatient internal medicine and director of hospitalist services at Reading Hospital–Tower Health (West Reading, Pa.) in January 2021. He provides support to hospitalists, nurses, pharmacists, care managers, support service professionals and others.
Previously, Dr. Anwar worked as vice chair of the department of medicine and medical director of the hospitalist program at Evangelical Community Hospital (Lewisburg, Pa.). He has a background in education, having taught as an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine (Scranton, Pa.) since 2014.
Katherine Hochman, MD, FHM, has been appointed the first director of the newly established division of hospital medicine at NYU Langone Health in New York. Dr. Hochman is the founder of NYU Langone’s hospitalist program (2004), and the new division was established this year in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hochman will be charged with expanding on the hospitalist program, analyzing best practices, and educating residents, clinicians, and other health care professionals. She plans to emphasize mentorship and creating career pathways for the program’s students.
Dr. Hochman was NYU Langone’s first hospitalist and later became associate program director of medicine at Langone’s Tisch Hospital. She helped grow the hospitalist program to 40 professionals in 2020.
Daniel Asher, MD, recently was named a Top Hospitalist by Continental Who’s Who. Dr. Asher is a night hospitalist at Piedmont Columbus Regional (Columbus, Ga.), where he works with residents and consults with other physicians regarding patients at the facility.
Dr. Asher has spent his entire post–medical school career at Piedmont, serving as a family medicine resident from 2018 to 2020. He was named chief resident in 2019-20, and has continued his efforts at the hospital since then, including front-line work with COVID-19 patients.
Nicholas O’Dell, MD, has been selected as medical director of the Murray Medical Associates hospitalist program at Murray-Calloway County Hospital (Murray, Ky.). Dr. O’Dell, who has been a hospitalist at the facility since 2014, has served as chief medical officer at the hospital since February 2020. He will continue in his role as CMO, but will no longer see clinical patients.
Brad Tate, MD, has been elevated to associate chief medical officer at Children’s Medical Center Plano (Texas), starting in the new leadership role in June 2021.
Dr. Tate has been affiliated with Children’s Health since 2010, when he was a hospitalist in Plano, as well as medical director of the Children’s Health Medical Group Hospitalist Group. He advanced that program from Plano to the network’s Dallas campus.
Touchette Regional Hospital (Centreville, Ill.) has contracted with MEDS Emergency Physician Staffing and Management (O’Fallon, Ill.) to provide inpatient physician and nurse practitioner staffing. The move is an extension of the existing relationship between the two entities, as MEDS has provided emergency room staffing services at Touchette since 2019.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, has been appointed dean of medical education for the University of Chicago’s biological sciences division. She began her assignment on July 1, 2021, taking over for the retiring Halina Brukner, MD, a 36-year veteran in medicine.
Dr. Arora will take charge of undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education for the University of Chicago’s medical education program, with a focus on simulation-based training. She also will represent the medical school within the university proper, as well as with outside organizations such as the Association of American Colleges, the Liaison Committee on Medical Education, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education.
Dr. Arora has been a faculty member at Chicago Medicine since 2005. She is a professor of medicine, assistant dean for scholarship and discovery, associate chief medical officer for clinical learning, and Master of the Academy of Distinguished Medical Educators. Dr. Arora is a member of the National Academy of Medicine and is on the board of directors for the American Board of Internal Medicine.
Zeshan Anwar, MD, SFHM, was named new chief of the section of inpatient internal medicine and director of hospitalist services at Reading Hospital–Tower Health (West Reading, Pa.) in January 2021. He provides support to hospitalists, nurses, pharmacists, care managers, support service professionals and others.
Previously, Dr. Anwar worked as vice chair of the department of medicine and medical director of the hospitalist program at Evangelical Community Hospital (Lewisburg, Pa.). He has a background in education, having taught as an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine (Scranton, Pa.) since 2014.
Katherine Hochman, MD, FHM, has been appointed the first director of the newly established division of hospital medicine at NYU Langone Health in New York. Dr. Hochman is the founder of NYU Langone’s hospitalist program (2004), and the new division was established this year in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hochman will be charged with expanding on the hospitalist program, analyzing best practices, and educating residents, clinicians, and other health care professionals. She plans to emphasize mentorship and creating career pathways for the program’s students.
Dr. Hochman was NYU Langone’s first hospitalist and later became associate program director of medicine at Langone’s Tisch Hospital. She helped grow the hospitalist program to 40 professionals in 2020.
Daniel Asher, MD, recently was named a Top Hospitalist by Continental Who’s Who. Dr. Asher is a night hospitalist at Piedmont Columbus Regional (Columbus, Ga.), where he works with residents and consults with other physicians regarding patients at the facility.
Dr. Asher has spent his entire post–medical school career at Piedmont, serving as a family medicine resident from 2018 to 2020. He was named chief resident in 2019-20, and has continued his efforts at the hospital since then, including front-line work with COVID-19 patients.
Nicholas O’Dell, MD, has been selected as medical director of the Murray Medical Associates hospitalist program at Murray-Calloway County Hospital (Murray, Ky.). Dr. O’Dell, who has been a hospitalist at the facility since 2014, has served as chief medical officer at the hospital since February 2020. He will continue in his role as CMO, but will no longer see clinical patients.
Brad Tate, MD, has been elevated to associate chief medical officer at Children’s Medical Center Plano (Texas), starting in the new leadership role in June 2021.
Dr. Tate has been affiliated with Children’s Health since 2010, when he was a hospitalist in Plano, as well as medical director of the Children’s Health Medical Group Hospitalist Group. He advanced that program from Plano to the network’s Dallas campus.
Touchette Regional Hospital (Centreville, Ill.) has contracted with MEDS Emergency Physician Staffing and Management (O’Fallon, Ill.) to provide inpatient physician and nurse practitioner staffing. The move is an extension of the existing relationship between the two entities, as MEDS has provided emergency room staffing services at Touchette since 2019.










