User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Lifestyle changes may explain skin lesions in pandemic-era patients
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
such as lockdown conditions, which may be clarified with additional research.
Lindy P. Fox, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who was not an author of either study, urged caution in interpreting these results. Data from the American Academy of Dermatology and a recent paper from the British Journal of Dermatology suggest a real association exists, at in least some patients. “It’s going to be true that most patients with toe lesions are PCR [polymerase chain reaction]-negative because it tends to be a late phenomenon when patients are no longer shedding virus,” Dr. Fox said in an interview.
Reports about chickenpox-like vesicles, urticaria, and other skin lesions in SARS-CoV-2 patients have circulated in the clinical literature and the media. Acute acro-ischemia has been cited as a potential sign of infection in adolescents and children.
One of the European studies, which was published in JAMA Dermatology, explored this association in 20 patients aged 1-18 years (mean age, 12.3 years), who presented with new-onset acral inflammatory lesions in their hands and feet at La Fe University Hospital, in Valencia, during the country’s peak quarantine period in April. Investigators conducted blood tests and reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) for SARS-CoV-2, and six patients had skin biopsies.
Juncal Roca-Ginés, MD, of the department of dermatology, at the Hospital Universitario y Politécnico in La Fe, and coauthors, identified acral erythema in 6 (30%) of the cases, dactylitis in 4 (20%), purpuric maculopapules in 7 (35%), and a mixed pattern in 3 (15%). Serologic and viral testing yielded no positive results for SARS-CoV-2 or other viruses, and none of the patients exhibited COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, myalgia, or taste or smell disorders. In other findings, 45% of the patients had a history of vascular reactive disease of the hands, and 75% reported walking barefoot in their homes while staying at home. Only two patients reported taking medications.
In the six patients who had a biopsy, the findings were characteristic of chillblains, “confirming the clinical impression,” the authors wrote. Concluding that they could not show a relationship between acute acral skin changes and COVID-19, they noted that “other studies with improved microbiologic tests or molecular techniques aimed at demonstrating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in the skin may help to clarify this problem.”
The other case series, which was also published in JAMA Dermatology and included 31 adults at a hospital in Brussels, who had recently developed chillblains, also looked for a connection between SARS-CoV-2 and chilblains, in April. Most of the participants were in their teens or 20s. Lesions had appeared on hands, feet, or on both extremities within 1-30 days of consultation, presenting as erythematous or purplish erythematous macules, occasionally with central vesicular or bullous lesions or necrotic areas. Patients reported pain, burning, and itching.
Skin biopsies were obtained in 22 patients and confirmed the diagnosis of chilblains; of the 15 with immunofluorescence analyses, 7 patients were found to have vasculitis of small-diameter vessels.
Of the 31 patients, 20 (64%) reported mild symptoms consistent with SARS-CoV-2, yet none of the RT-PCR or serologic test results showed signs of the virus in all 31 patients. “Because some patients had experienced chilblains for more than 15 days [under 30 days or less] at the time of inclusion, we can reasonably exclude the possibility that serologic testing was done too soon,” observed the authors. They also didn’t find eosinopenia, lymphopenia, and hyperferritinemia, which have been associated with COVID-19, they added.
Changes in lifestyle conditions during the pandemic may explain the appearance of these lesions, according to the authors of both studies, who mentioned that walking around in socks or bare feet and reduced physical activity could have indirectly led to the development of skin lesions.
It’s also possible that young people have less severe disease and a delayed reaction to the virus, Ignacio Torres-Navarro, MD, a dermatologist with La Fe University and the Spanish study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Their feet may lack maturity in neurovascular regulation and/or the eccrine glands, which can happen in other diseases such as neutrophilic idiopathic eccrine hidradenitis. “In this context, perhaps there was an observational bias of the parents to the children when this manifestation was reported in the media. However, nothing has been demonstrated,” he said.
In an accompanying editor’s note, Claudia Hernandez, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, and Anna L. Bruckner, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Colorado, Aurora, wrote that “it is still unclear whether a viral cytopathic process vs a viral reaction pattern or other mechanism is responsible for ‘COVID toes.’ ” Lack of confirmatory testing and reliance on indirect evidence of infection complicates this further, they noted, adding that “dermatologists must be aware of the protean cutaneous findings that are possibly associated with COVID-19, even if our understanding of their origins remains incomplete.”
In an interview, Dr. Fox, a member of the AAD’s’s COVID-19 Registry task force, offered other possible reasons for the negative antibody tests in the studies. The assay might not have been testing the correct antigen, or the timing of the test might not have been optimal. “More studies will help this become less controversial,” she said.
The authors of the two case series acknowledged potential limitations of their studies. Neither was large in scope: Both took place over a week’s time and included small cohorts. The Belgian study had no control group or long-term follow-up. Little is still known about the clinical manifestations and detection methods for SARS-CoV-2, noted the authors of the Spanish study.
The Spanish study received funding La Fe University Hospital’s department of dermatology, and the authors had no disclosures. The Belgian study received support from the Fondation Saint-Luc, which provided academic funding for its lead author, Marie Baeck, MD, PhD. Another author of this study received personal fees from the Fondation Saint-Luc and personal fees and nonfinancial support from Bioderma. The authors of the editor’s note had no disclosures.
SOURCES: Roca-Ginés J et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2340; Herman A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Jun 25. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368.
Once again, no survival benefit with PCI, surgery in stable CAD
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary revascularization does not confer a survival advantage over initial medical therapy in patients with stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) but reduces unstable angina, according to a new study-level meta-analysis.
Routine upfront revascularization is also associated with less spontaneous myocardial infarction but this is at the cost of increased procedural infarctions, reported lead investigator Sripal Bangalore, MD, of New York University.
“These relationships should be taken into consideration for shared decision-making for the management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease,” he said in a late-breaking trial session at PCR e-Course 2020, the virtual meeting of the Congress of European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EuroPCR).
The results, simultaneously published in Circulation, are consistent with last year’s ISCHEMIA trial and other contemporary trials, such as COURAGE, FAME 2, and BARI 2D, that have failed to show a reduction in mortality with revascularization alone in SIHD. Guidelines continue, however, to recommend revascularization to improve survival in SIHD based on trials performed in the 1980s when medical therapy was limited, Dr. Bangalore observed.
The updated meta-analysis included 14 randomized controlled trials, including the aforementioned, and 14,877 patients followed for a weighted mean of 4.5 years. Most trials enrolled patients who had preserved left ventricular function and low symptom burden (Canadian Cardiovascular Society Class I/II).
In the revascularization group, 87.5% of patients underwent any revascularization. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was the first procedure in 71.3% and bypass surgery the first choice in 16.2%. In eight trials, stents were used in at least 50% of PCI patients; drug-eluting stents were mainly used in FAME 2, ISCHEMIA, and ISCHEMIA-CKD.
In eight trials, statins were used in at least 50% of patients. Nearly 1 in 3 patients (31.9%) treated initially with medical therapy underwent revascularization during follow-up.
Results show no reduction in mortality risk with routine revascularization in the overall analysis (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.09) or when analyzed by whether studies did or did not use stents (P for interaction = .85).
Trial sequential analysis also showed that the cumulative z-curve crossed the futility boundary, “suggesting we have great data to show that there is lack of even a 10% reduction in death with revascularization,” Dr. Bangalore said.
Results were very similar for cardiovascular death (RR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.80-1.06), including when analyzed by study stent status (P for interaction = .60).
There was no significant reduction in overall MI risk with revascularization, although a borderline significant 11% decrease in MIs was found in the contemporary stent era trials (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80-0.998).
Revascularization was associated with a 148% increase in the risk of procedural MI (RR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.86-3.31) but reduced risk of spontaneous MI (RR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.67-0.85).
Unstable angina was reduced in patients undergoing revascularization (RR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.45-0.92), driven by a 55% reduction in the contemporary stent era trials. Freedom from angina was also greater with routine revascularization but the difference was modest, Dr. Bangalore said. There was no difference between the two strategies in heart failure or stroke.
“This meta-analysis is well done but really doesn’t change what we already know,” Rasha Al-Lamee, MBBS, of Imperial College, London, said in an interview. “The most important message is that intervention in stable CAD does not change survival. We don’t need to rush to intervene: We have time to plan the best strategy for each patient and to modify our plans based on their response.”
The analysis addresses some of the issues with previous meta-analyses that have included trials that were not strictly stable CAD trials such as SWISSI-2, COMPARE-ACUTE, and DANAMI-3-PRIMULTI, she noted. “However a study like this is only as good as the trials that are included. We must remember that unblinded trials really cannot be used to accurately assess endpoints that are prone to bias such as unstable angina and freedom from angina.”
Following the presentation, dedicated discussant Davide Capodanno, MD, PhD, of the University of Catania (Italy) said, “We have seen beyond any doubt that there is no difference in mortality. For cardiovascular death, it’s pretty much the same. It’s a little bit more mixed and nuanced, the story of myocardial infarction.”
“Additional science is needed to understand the prognostic implications,” he said. “Of course we know that spontaneous myocardial infarction is bad, but I’m not so sure about periprocedural MI. Is this something that is as important as spontaneous myocardial infarction?”
The meta-analysis is the largest ever performed, but there was clinical heterogeneity in the individual studies, especially in the definition of MI, Dr. Capodanno observed. Because of the use of trial-level data rather than patient-level data, the analysis also could not account for adherence to treatment or the effect of stent type or medication dosage.
The MI issue really depends on the trial definition of MI, Dr. Al-Lamee said. “We need long-term follow-up from ISCHEMIA to understand what it means for our patients. While revascularization clearly increases procedural MI rates, it also results in lower spontaneous MI rates with no impact on overall MI or death,” she said. “We will only know if these MIs are important if we see what impact they have in the long term.”
Although the meta-analysis combined data from several decades, it’s likely that the outdated revascularization techniques in the older trials are balanced out by the outdated medical therapy in the same trials, Dr. Al-Lamee observed.
The new findings can certainly be used in patient-physician discussions, with more follow-up from ISCHEMIA to provide additional insights, she said.
“We will of course hear more about the placebo-controlled efficacy of PCI in the blinded ORBITA-2 trial. And I would really like to see some of the older studies of patients and perceptions of the effect of PCI repeated,” Dr. Al-Lamee said. “Now we have more data, are we informing our patients and referrers correctly of the impact of our procedures, and do they truly choose revascularization with a true awareness of what it does and does not do?”
Dr. Bangalore reported grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Abbott Vascular; and serving on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Meril, SMT, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata. Dr. Al-Lamee reported speaker’s honorarium from Philips Volcano and Menarini Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Capodanno has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap: Hospitalized COVID patients need MRIs; Americans vote for face masks
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
A new review outlined a three-stage classification of the impact of COVID-19 on the central nervous system and recommended all hospitalized patients with the virus undergo MRI to flag potential neurologic damage and inform postdischarge monitoring.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” said lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD. The review was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Read more.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release. Read more.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that such testing was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Read more.
Weight loss failures drive bariatric surgery regrets
Not all weight loss surgery patients “live happily ever after,” according to Daniel B. Jones, MD.
A 2014 study of 22 women who underwent weight loss surgery reported lower energy, worse quality of life, and persistent eating disorders.
Of gastric band patients, “almost 20% did not think they made the right decision,” he said. As for RYGP patients, 13% of patients at 1 year and 4 years reported that weight loss surgery caused “some” or “a lot” of negative effects. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Sepsis readmissions risk linked to residence in a poor neighborhoods
according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
The association between living in a disadvantaged neighborhood and 30-day readmission remained significant even after adjustment for “individual demographic variables, active tobacco use, length of index hospitalization, severity of acute and chronic morbidity, and place of initial discharge,” wrote Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Our findings suggest the need for interventions that emphasize neighborhood-level socioeconomic variables in addition to individual-level efforts in an effort to promote and achieve health equity for patients who survive a hospitalization due to sepsis,” the authors wrote. “With a third of our cohort rehospitalized with infections, and other studies emphasizing that the most common readmission diagnosis was infection, attention toward both anticipating and attenuating the risk of infection in sepsis survivors, especially among those who live in higher risk neighborhoods, must be a priority for the prevention of readmissions.”
Although she did not find the study results surprising, Eva DuGoff, PhD, a senior managing consultant with the Berkeley Research Group and a visiting assistant professor at University of Maryland School of Public Health, College Park, said in an interview that she was impressed with how clinically rigorous the analysis was, both in confirming an accurate sepsis diagnosis and in using the more refined measure of the Area Deprivation Index (ADI) to assess neighborhood disadvantage.
“I think it makes sense that people who have less means and are in neighborhoods with fewer resources would run into more issues and would need to return to the hospital, above and beyond the clinical risk factors, such as smoking and chronic conditions,” said Dr. DuGoff, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study.
Shayla N.M. Durfey MD, ScM, a pediatric resident at Hasbro Children’s Hospital in Providence, R.I., said in an interview she was similarly unsurprised by the findings.
“People who live in disadvantaged neighborhoods may have less access to walking spaces, healthy food, and safe housing and more exposure to poor air quality, toxic stress, and violence – any of which can negatively impact health or recovery from illness through stress responses, nutritional deficiencies, or comorbidities, such as reactive airway disease, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes,” said Dr. Durfey, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study. “Our research has found these neighborhood-level factors often matter above and beyond individual social determinants of health.”
Dr. Galiatsatos and associates conducted a retrospective study in Baltimore that compared readmission rates in 2017 at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center among patients discharged after a hospitalization for sepsis, coded via ICD-10. They relied on the ADI to categorize the neighborhoods of patients’ residential addresses. The ADI rates various socioeconomic components, including income, education, employment, and housing characteristics, on a scale of 1-100 in geographic blocks, with higher score indicating a greater level of disadvantage.
Among 647 hospitalized patients with an ICD-10 code of sepsis who also met criteria for sepsis or septic shock per the Sepsis-3 definition, 17.9% were excluded from the analysis because they died or were transferred to hospice care. The other 531 patients had an average age of 61, and just under one-third (30.9%) were active smokers. Their average length of stay was 6.9 days, with a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 4.2 and a mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score of 4.9.
The average ADI for all the patients was 54.2, but the average score was 63 for the 22% of patients who were readmitted within 30 days of initial discharge, compared with an average 51.8 for patients not readmitted (P < .001).
Among those 117 readmitted, “39 patients had a reinfection, 68 had an exacerbation of their chronic conditions, and 10 were admitted for ‘concerning symptoms’ without a primary admitting diagnosis,” the investigators reported. Because “a third of our cohort was readmitted with an infection, it is possible that more disadvantaged neighborhoods created more challenges for a person’s immune system, which may be compromised after recovering from sepsis.”
Dr. DuGoff further noted that health literacy may be lower among people living in less advantaged neighborhoods.
“A number of studies suggest when patients leave the hospital, they’re not sure what they need to do. The language is complicated, and it’s hard to know what kind of medication to take when, and when you’re supposed to return to the doctor or the hospital,” Dr. DuGoff said. “Managing all of that can be pretty scary for people, particularly after a traumatic experience with sepsis at the hospital.”
Most patients had been discharged home (67.3%), but the 31.6% discharged to a skilled nursing facility had a greater likelihood of readmission, compared with those discharged home (P < .01); 1% were discharged to acute rehabilitation. The average length of stay during the index hospitalization was also greater for those readmitted (8.7 days) than for those not readmitted (6.4 days). The groups did not differ in terms of their acute organ dysfunction or severity of their comorbidities.
However, even after adjustment for these factors, “neighborhood disadvantage remained significantly associated with 30-day rehospitalization in patients who were discharged with sepsis,” the authors said. Specifically, each additional standard deviation greater in patients’ ADI was associated with increased risk of 30-day readmission (P < .001).
“Given that the ADI is a composite score, we cannot identify which component is the predominant driver of rehospitalizations for patients who survive sepsis,” the authors wrote. “However, all components that make up the index are intertwined, and policy efforts targeting one (i.e., unemployment) will likely impact others (i.e., housing).”
Dr. Durfey said that medical schools have not traditionally provided training related to management of social risk factors, although this is changing in more recent curricula. But the findings still have clinical relevance for practitioners.
“Certainly, the first step is awareness of where and how patients live and being mindful of how treatment plans may be impacted by social factors at both the individual and community levels,” Dr. Durfey said. “An important part of this is working in partnership with social workers and case managers. Importantly, clinicians can also partner with disadvantaged communities to advocate for improved conditions through policy change and act as expert witnesses to how neighborhood level factors impact health.”
Dr. DuGoff also wondered what implications these findings might have currently, with regards to COVID-19.
“People living in disadvantaged neighborhoods are already at higher risk for getting the disease, and this study raises really good questions about how we should be monitoring discharge now in anticipation of these types of issues,” she said.
The authors noted that their study is cross-sectional and cannot indicate causation, and the findings of a single urban institution may not be generalizable elsewhere. They also did not consider what interventions individual patients had during their index hospitalization that could have increased frailty.
The study did not note external funding. One coauthor of the study, Suchi Saria, PhD, reported receiving honoraria and travel reimbursement from two dozen biotechnology companies for keynotes and advisory board service; she also holds equity in Patient Ping and Bayesian Health. The other authors reported no industry disclosures. In addition to consulting for Berkeley Research Group, Dr. DuGoff has received a past honorarium from Zimmer Biomet. Dr. Durfey has no disclosures.
SOURCE: Galiatsatos P et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 Jun;48(6):808-14.
according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
The association between living in a disadvantaged neighborhood and 30-day readmission remained significant even after adjustment for “individual demographic variables, active tobacco use, length of index hospitalization, severity of acute and chronic morbidity, and place of initial discharge,” wrote Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Our findings suggest the need for interventions that emphasize neighborhood-level socioeconomic variables in addition to individual-level efforts in an effort to promote and achieve health equity for patients who survive a hospitalization due to sepsis,” the authors wrote. “With a third of our cohort rehospitalized with infections, and other studies emphasizing that the most common readmission diagnosis was infection, attention toward both anticipating and attenuating the risk of infection in sepsis survivors, especially among those who live in higher risk neighborhoods, must be a priority for the prevention of readmissions.”
Although she did not find the study results surprising, Eva DuGoff, PhD, a senior managing consultant with the Berkeley Research Group and a visiting assistant professor at University of Maryland School of Public Health, College Park, said in an interview that she was impressed with how clinically rigorous the analysis was, both in confirming an accurate sepsis diagnosis and in using the more refined measure of the Area Deprivation Index (ADI) to assess neighborhood disadvantage.
“I think it makes sense that people who have less means and are in neighborhoods with fewer resources would run into more issues and would need to return to the hospital, above and beyond the clinical risk factors, such as smoking and chronic conditions,” said Dr. DuGoff, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study.
Shayla N.M. Durfey MD, ScM, a pediatric resident at Hasbro Children’s Hospital in Providence, R.I., said in an interview she was similarly unsurprised by the findings.
“People who live in disadvantaged neighborhoods may have less access to walking spaces, healthy food, and safe housing and more exposure to poor air quality, toxic stress, and violence – any of which can negatively impact health or recovery from illness through stress responses, nutritional deficiencies, or comorbidities, such as reactive airway disease, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes,” said Dr. Durfey, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study. “Our research has found these neighborhood-level factors often matter above and beyond individual social determinants of health.”
Dr. Galiatsatos and associates conducted a retrospective study in Baltimore that compared readmission rates in 2017 at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center among patients discharged after a hospitalization for sepsis, coded via ICD-10. They relied on the ADI to categorize the neighborhoods of patients’ residential addresses. The ADI rates various socioeconomic components, including income, education, employment, and housing characteristics, on a scale of 1-100 in geographic blocks, with higher score indicating a greater level of disadvantage.
Among 647 hospitalized patients with an ICD-10 code of sepsis who also met criteria for sepsis or septic shock per the Sepsis-3 definition, 17.9% were excluded from the analysis because they died or were transferred to hospice care. The other 531 patients had an average age of 61, and just under one-third (30.9%) were active smokers. Their average length of stay was 6.9 days, with a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 4.2 and a mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score of 4.9.
The average ADI for all the patients was 54.2, but the average score was 63 for the 22% of patients who were readmitted within 30 days of initial discharge, compared with an average 51.8 for patients not readmitted (P < .001).
Among those 117 readmitted, “39 patients had a reinfection, 68 had an exacerbation of their chronic conditions, and 10 were admitted for ‘concerning symptoms’ without a primary admitting diagnosis,” the investigators reported. Because “a third of our cohort was readmitted with an infection, it is possible that more disadvantaged neighborhoods created more challenges for a person’s immune system, which may be compromised after recovering from sepsis.”
Dr. DuGoff further noted that health literacy may be lower among people living in less advantaged neighborhoods.
“A number of studies suggest when patients leave the hospital, they’re not sure what they need to do. The language is complicated, and it’s hard to know what kind of medication to take when, and when you’re supposed to return to the doctor or the hospital,” Dr. DuGoff said. “Managing all of that can be pretty scary for people, particularly after a traumatic experience with sepsis at the hospital.”
Most patients had been discharged home (67.3%), but the 31.6% discharged to a skilled nursing facility had a greater likelihood of readmission, compared with those discharged home (P < .01); 1% were discharged to acute rehabilitation. The average length of stay during the index hospitalization was also greater for those readmitted (8.7 days) than for those not readmitted (6.4 days). The groups did not differ in terms of their acute organ dysfunction or severity of their comorbidities.
However, even after adjustment for these factors, “neighborhood disadvantage remained significantly associated with 30-day rehospitalization in patients who were discharged with sepsis,” the authors said. Specifically, each additional standard deviation greater in patients’ ADI was associated with increased risk of 30-day readmission (P < .001).
“Given that the ADI is a composite score, we cannot identify which component is the predominant driver of rehospitalizations for patients who survive sepsis,” the authors wrote. “However, all components that make up the index are intertwined, and policy efforts targeting one (i.e., unemployment) will likely impact others (i.e., housing).”
Dr. Durfey said that medical schools have not traditionally provided training related to management of social risk factors, although this is changing in more recent curricula. But the findings still have clinical relevance for practitioners.
“Certainly, the first step is awareness of where and how patients live and being mindful of how treatment plans may be impacted by social factors at both the individual and community levels,” Dr. Durfey said. “An important part of this is working in partnership with social workers and case managers. Importantly, clinicians can also partner with disadvantaged communities to advocate for improved conditions through policy change and act as expert witnesses to how neighborhood level factors impact health.”
Dr. DuGoff also wondered what implications these findings might have currently, with regards to COVID-19.
“People living in disadvantaged neighborhoods are already at higher risk for getting the disease, and this study raises really good questions about how we should be monitoring discharge now in anticipation of these types of issues,” she said.
The authors noted that their study is cross-sectional and cannot indicate causation, and the findings of a single urban institution may not be generalizable elsewhere. They also did not consider what interventions individual patients had during their index hospitalization that could have increased frailty.
The study did not note external funding. One coauthor of the study, Suchi Saria, PhD, reported receiving honoraria and travel reimbursement from two dozen biotechnology companies for keynotes and advisory board service; she also holds equity in Patient Ping and Bayesian Health. The other authors reported no industry disclosures. In addition to consulting for Berkeley Research Group, Dr. DuGoff has received a past honorarium from Zimmer Biomet. Dr. Durfey has no disclosures.
SOURCE: Galiatsatos P et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 Jun;48(6):808-14.
according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
The association between living in a disadvantaged neighborhood and 30-day readmission remained significant even after adjustment for “individual demographic variables, active tobacco use, length of index hospitalization, severity of acute and chronic morbidity, and place of initial discharge,” wrote Panagis Galiatsatos, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Our findings suggest the need for interventions that emphasize neighborhood-level socioeconomic variables in addition to individual-level efforts in an effort to promote and achieve health equity for patients who survive a hospitalization due to sepsis,” the authors wrote. “With a third of our cohort rehospitalized with infections, and other studies emphasizing that the most common readmission diagnosis was infection, attention toward both anticipating and attenuating the risk of infection in sepsis survivors, especially among those who live in higher risk neighborhoods, must be a priority for the prevention of readmissions.”
Although she did not find the study results surprising, Eva DuGoff, PhD, a senior managing consultant with the Berkeley Research Group and a visiting assistant professor at University of Maryland School of Public Health, College Park, said in an interview that she was impressed with how clinically rigorous the analysis was, both in confirming an accurate sepsis diagnosis and in using the more refined measure of the Area Deprivation Index (ADI) to assess neighborhood disadvantage.
“I think it makes sense that people who have less means and are in neighborhoods with fewer resources would run into more issues and would need to return to the hospital, above and beyond the clinical risk factors, such as smoking and chronic conditions,” said Dr. DuGoff, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study.
Shayla N.M. Durfey MD, ScM, a pediatric resident at Hasbro Children’s Hospital in Providence, R.I., said in an interview she was similarly unsurprised by the findings.
“People who live in disadvantaged neighborhoods may have less access to walking spaces, healthy food, and safe housing and more exposure to poor air quality, toxic stress, and violence – any of which can negatively impact health or recovery from illness through stress responses, nutritional deficiencies, or comorbidities, such as reactive airway disease, obesity, hypertension, and diabetes,” said Dr. Durfey, who studies health disparities but was not involved in this study. “Our research has found these neighborhood-level factors often matter above and beyond individual social determinants of health.”
Dr. Galiatsatos and associates conducted a retrospective study in Baltimore that compared readmission rates in 2017 at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center among patients discharged after a hospitalization for sepsis, coded via ICD-10. They relied on the ADI to categorize the neighborhoods of patients’ residential addresses. The ADI rates various socioeconomic components, including income, education, employment, and housing characteristics, on a scale of 1-100 in geographic blocks, with higher score indicating a greater level of disadvantage.
Among 647 hospitalized patients with an ICD-10 code of sepsis who also met criteria for sepsis or septic shock per the Sepsis-3 definition, 17.9% were excluded from the analysis because they died or were transferred to hospice care. The other 531 patients had an average age of 61, and just under one-third (30.9%) were active smokers. Their average length of stay was 6.9 days, with a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 4.2 and a mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score of 4.9.
The average ADI for all the patients was 54.2, but the average score was 63 for the 22% of patients who were readmitted within 30 days of initial discharge, compared with an average 51.8 for patients not readmitted (P < .001).
Among those 117 readmitted, “39 patients had a reinfection, 68 had an exacerbation of their chronic conditions, and 10 were admitted for ‘concerning symptoms’ without a primary admitting diagnosis,” the investigators reported. Because “a third of our cohort was readmitted with an infection, it is possible that more disadvantaged neighborhoods created more challenges for a person’s immune system, which may be compromised after recovering from sepsis.”
Dr. DuGoff further noted that health literacy may be lower among people living in less advantaged neighborhoods.
“A number of studies suggest when patients leave the hospital, they’re not sure what they need to do. The language is complicated, and it’s hard to know what kind of medication to take when, and when you’re supposed to return to the doctor or the hospital,” Dr. DuGoff said. “Managing all of that can be pretty scary for people, particularly after a traumatic experience with sepsis at the hospital.”
Most patients had been discharged home (67.3%), but the 31.6% discharged to a skilled nursing facility had a greater likelihood of readmission, compared with those discharged home (P < .01); 1% were discharged to acute rehabilitation. The average length of stay during the index hospitalization was also greater for those readmitted (8.7 days) than for those not readmitted (6.4 days). The groups did not differ in terms of their acute organ dysfunction or severity of their comorbidities.
However, even after adjustment for these factors, “neighborhood disadvantage remained significantly associated with 30-day rehospitalization in patients who were discharged with sepsis,” the authors said. Specifically, each additional standard deviation greater in patients’ ADI was associated with increased risk of 30-day readmission (P < .001).
“Given that the ADI is a composite score, we cannot identify which component is the predominant driver of rehospitalizations for patients who survive sepsis,” the authors wrote. “However, all components that make up the index are intertwined, and policy efforts targeting one (i.e., unemployment) will likely impact others (i.e., housing).”
Dr. Durfey said that medical schools have not traditionally provided training related to management of social risk factors, although this is changing in more recent curricula. But the findings still have clinical relevance for practitioners.
“Certainly, the first step is awareness of where and how patients live and being mindful of how treatment plans may be impacted by social factors at both the individual and community levels,” Dr. Durfey said. “An important part of this is working in partnership with social workers and case managers. Importantly, clinicians can also partner with disadvantaged communities to advocate for improved conditions through policy change and act as expert witnesses to how neighborhood level factors impact health.”
Dr. DuGoff also wondered what implications these findings might have currently, with regards to COVID-19.
“People living in disadvantaged neighborhoods are already at higher risk for getting the disease, and this study raises really good questions about how we should be monitoring discharge now in anticipation of these types of issues,” she said.
The authors noted that their study is cross-sectional and cannot indicate causation, and the findings of a single urban institution may not be generalizable elsewhere. They also did not consider what interventions individual patients had during their index hospitalization that could have increased frailty.
The study did not note external funding. One coauthor of the study, Suchi Saria, PhD, reported receiving honoraria and travel reimbursement from two dozen biotechnology companies for keynotes and advisory board service; she also holds equity in Patient Ping and Bayesian Health. The other authors reported no industry disclosures. In addition to consulting for Berkeley Research Group, Dr. DuGoff has received a past honorarium from Zimmer Biomet. Dr. Durfey has no disclosures.
SOURCE: Galiatsatos P et al. Crit Care Med. 2020 Jun;48(6):808-14.
FROM CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE
COVID-19: Haiti is vulnerable, but the international community can help
Doctors Without Borders, other groups urged to mobilize
Do you want to know what keeps us up at night? As 4th-year medical students born, raised, and living in Haiti, we worry about the impact of COVID-19 on our patients.
The pandemic has shaken the world, and Haiti is no exception.
It has taken several months for the disease to spread, and it began with two confirmed cases, one from France and the other from Belgium, on March 19.1 Much of the spread of COVID-19 in Haiti has been tied to workers returning from the Dominican Republic. As of June 29, Haiti had 5,975 confirmed cases and 105 deaths.2 Of course, those numbers sound minuscule, compared with those in the United States, where the number of deaths from COVID-19 surpassed 100,000 several weeks ago. But the population of Haiti is 30 times smaller than that of the United States, and Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere. We have watched in horror as the virus has ravaged marginalized groups in the United States and worry that it will do the same in our own country.
Just as the Haitian Ministry of Health worked with various groups to reach the 1-year free of cholera mark in Haiti, groups such as Doctors Without Borders must mobilize to rein in COVID-19.
Community transmission rapid
After the first two cases were confirmed, a state of health emergency was immediately declared. Haitian President Jovenel Moïse and other government officials called for the implementation of several measures aimed at limiting the spread of COVID-19.
Schools, universities, clinical training programs, vocational centers, factories, airports, and ports, except for the transport of goods, were all ordered to close until further notice. Gatherings of larger than 10 people were banned. A curfew from 8 p.m. EST time to 5 a.m. EST was imposed. Measures such as those encouraged by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as hand washing, physical distancing, and staying at home were also encouraged by the Haitian Ministry of Health. Mask wearing in public places was deemed mandatory.
The latest testing data show that community spread has been occurring among the Haitian population at a rapid rate. According to Jean William Pape, MD, Haiti’s top infectious diseases expert and founder of GHESKIO, an iconic infectious disease center that cares for people with HIV-AIDS and tuberculosis, a COVID-19 simulation from Cornell University in New York shows that about 35% of the Haitian population will be infected by the end of August 2020. A simulation by the University of Oxford (England) paints an even more dire picture. That simulation shows that 86% of the population could be infected, More than 9,000 additional hospital beds would be needed, and 20,000 people would be likely to die from COVID-19, Dr. Pape said in an interview with Haiti’s Nouvelliste newspaper.3
Medical response
We know that there is a global shortage of health care workers,4 and Haiti is no exception. According to a 2018 report from the Haitian Ministry of Health, the country has 11,775 health care professionals, including about 3,354 medical doctors, to care for more than 11 million people. That translates to about 23.4 physicians per 100,000.5
The pandemic has led some members of this already anemic health care workforce to stay home because of a lack of personal protective equipment. Others, because of reduced hospital or clinic budgets, have been furloughed, making the COVID-19 national health emergency even harder to manage.
But a severe health care shortage is not the only challenge facing Haiti. It spends about $131 U.S. per capita, which makes Haiti one of most vulnerable among low- and middle-income countries in the world. As a poor country,7 its health care infrastructure is among the most inadequate and weakest. Prior to COVID-19, medical advocacy groups already had started movements and strikes demanding that the government improve the health care system. The country’s precarious health care infrastructure includes a lack of hospital beds, and basic medical supplies and equipment, such as oxygen and ventilators.8 The emergence of COVID-19 has only exacerbated the situation.
Clinical training programs have been suspended, many doctors and nurses are on quarantine, and some hospitals and clinics are closing. We have witnessed makeshift voodoo clinics built by Haitian voodoo leaders to receive, hospitalize, and treat COVID-19 patients through rituals and herbal remedies. In some areas of the country, residents have protested against the opening of several COVID-19 treatment and management centers.
Unique cultural challenges
Public health officials around the world are facing challenges persuading citizens to engage in behaviors that could protect them from the virus.
Just as in America, where many people opt to not wear face coverings9,10 despite the public health risks, deep distrust of the Haitian government has undermined the messages of President Moïse and public health officials about the role of masks in limiting the spread of COVID. We see large numbers of unmasked people on the streets in the informal markets every day. Crammed tap-taps and overloaded motorcycles are moving everywhere. This also could be tied to cultural attitudes about COVID that persist among some Haitians. For example, many people with signs and symptoms of COVID-19 are afraid of going to the hospital to get tested and receive care, and resort to going to the voodoo clinics. Along with rituals, voodoo priests have been serving up teas with ingredients, including moringa, eucalyptus, ginger, and honey to those seeking COVID-19 care in the centers. The voodoo priests claim that the teas they serve strengthen the immune system.
In addition, it is difficult for poor people who live in small quarters with several other people to adhere to physical distancing.11
Stigma and violence
Other barriers in the fight against COVID-19 in Haiti are stigma and violence. If widespread testing were available, some Haitians would opt not to do so – despite clear signs and symptoms of the infection. Some people who would get tested if they could are afraid to do so because of fears tied to being attacked by neighbors.
When Haitian University professor Bellamy Nelson and his girlfriend returned to Haiti from the United States in March and began experiencing some pain and fever, he experienced attacks from neighbors, he said in an interview. He said neighbors threatened to burn down his house. When an ambulance arrived at his house to transport him to a hospital, it had to drive through back roads to avoid people armed with rocks, fire, and machetes, he told us. No hospital wanted to admit him. Eventually, Professor Nelson self-quarantined at home, he said.
In another incident, a national ambulance center in Gonaïves, a town toward the northern region of Haiti, reportedly was vandalized, because COVID-19 equipment and supplies used to treat people had been stored there. Hospital Bernard Mevs, along with many other hospitals, was forced by the area’s residents to suspend the plan to open a center for COVID-19 management. Threats to burn down the hospitals caused the leaders of the hospitals to back down and give up a plan to build a 20-bed COVID-19 response center.
Maternal health
Another concern we have about the pandemic is the risk it could be to pregnant women. On average, 94,000 deaths occur annually in Haiti. Out of this number, maternal mortality accounts for 1,000. In 2017, for every 100,000 live births for women of reproductive age from 15 to 49 years old, 480 women died. In contrast, in the Dominican Republic, 95 women died per 100,000 that same year. In the United States, 19 died, and in Norway, no more than 2 died that year.12
Some of the primary factors contributing to the crisis are limited accessibility, inadequate health care facilities, and an inadequate number of trained health care practitioners; low percentages of skilled attendants at deliveries and of prenatal and postnatal visits; and high numbers of high-risk deliveries in nonqualified health facilities.
During the COVID-19 national health emergency, with most hospitals reducing their health care personnel either because of budget-related reasons or because they are on quarantine, this maternal-fetal health crisis has escalated.
One of the biggest hospitals in Jacmel, a town in the southern region of Haiti, has stopped its prenatal care program. In Delmas, the city with the highest incidence and prevalence of COVID-19, Hôpital Universitaire de la Paix has reduced this program to 50% of its capacity and gynecologic care has been completely suspended. Hôpital St. Luc, one of the first hospitals in the western region of Haiti to open its doors to care for COVID-19 patients, has recently shut down the entire maternal-fetal department.
So, access to prenatal and postnatal care, including the ability to deliver babies in health care institutions, is significantly reduced because of COVID-19. This leaves thousands of already vulnerable pregnant women at risk and having to deliver domestically with little to no health care professional assistance. We worry that, in light of the data, more women and babies will die because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A call to action
Despite these conditions, there are reasons for hope. Various groups, both from the international community and locally have mobilized to respond to the pandemic.
International health care organizations such as Doctors Without Borders and Partners in Health, and local groups such as GHESKIO, the St. Luke Foundation for Haiti, and others have been collaborating with the Haitian Ministry of Health to devise and strategic plans and deploy valuable resources with the common goal of saving lives from COVID-19.
GHESKIO, for example, under Dr. Pape’s leadership, currently has one of the three COVID-19 testing centers in the country. It also has two COVID-19 treatment centers in full operation, in Port-au-Prince, the capital city, managing and treating 520 patients with confirmed COVID-19. GHESKIO, which has been in the front lines of previous major infectious disease outbreaks,13 has trained about 200 clinicians from both public and private health care institutions to care for COVID-19 patients.
Doctors Without Borders has been investing in efforts to support the Ministry of Health by converting and renovating its Burn Center in Drouillard, a small section of the city of Cité Soleil, one of the country’s biggest slums. In May, as part of its COVID-19 response, it launched a 20-bed capacity center that can accommodate up to 45 beds to care for patients who have tested positive for COVID-19.
Partners in Health, the Boston-based nonprofit health care organization cofounded in 1987 by American anthropologist and infectious disease specialist, Paul Farmer, MD, and the largest nonprofit health care provider in Haiti, also joined the Ministry of Health through its national and public health efforts to tackle COVID-19 in Haiti. Partners in Health, through its sister organization, Zanmi Lasante, has pioneered the movement of diagnosing and treating people with HIV-AIDS and TB. Since the late 1990s, its efforts against both infectious diseases have helped 15,000 HIV-positive patients begin and remain on treatment. And every year, 1,500 TB patients have started treatment on the path to a cure.
Early in the pandemic in Haiti, Partners in Health, through its state-of-the-art 300-bed university hospital (Hôpital Universitaire de Mirebalais de Mirebalais), was the first to open a COVID-19 center with a 20-bed capacity and has been caring for COVID-19 patients since then. In June, Partners in Health supported and inaugurated the renovation of the internal medicine department at one of its affiliated community hospitals, Hôpital Saint-Nicolas de Saint Marc. That department will have a 24-bed capacity that can extend up to 36 beds to manage and treat COVID-19 patients.
In total, currently, 26 COVID-19 centers with a capacity of 1,011 beds are available to serve, manage, and treat Haitian patients affected with COVID-19. But are those efforts enough? No.
Haiti, as a weak state even before COVID-19, continues to need funding from the international community so it can strengthen its health care infrastructure to be effective and strong in fighting against COVID-19.
In addition, we would like to see preventive initiatives implemented on the local level. Our family has taken on a role that, we think, could help conquer COVID-19 if others followed suit on a large scale.
As part of our contribution in tackling COVID-19, the two of us have launched a small-scale community experiment. We have educated our family in Delmas about COVID-19 and subsequently launched an awareness campaign in the community. We dispatched small groups that go door to door in the community to educate neighbors about the disease in an effort to help them understand that COVID-19 is real and it is normal for people that feel they may have the disease to seek medical care. This approach helps suppress the transmission of the virus. This pilot project could be reproduced in several other communities. It is easy to operate, rapid, effective, and cost-free. The community has been very receptive to and grateful for our efforts.
Like other countries across the world, Haiti was not ready for COVID-19. But we are confident that, with help from the international community, organizations such as GHESKIO,14 and with due diligence on the local level, we are strong and resilient enough to beat COVID. We must act together – quickly.
References
1. Sénat JD. Coronavirus: 2 cas confirmés en Haïti, Jovenel Moïse décrète l’état d’ur-gence sanitaire. 2020 Le Nouvelliste.
2. Haitian Ministry of Health.
3. “Entre appel a la solidarite et de sombres previsions, le Dr William Pape fait le point.” Le Nouvelliste.
4. Darzi A and Evans T. Lancet. 2016 Nov-Dec 26. 388;10060:2576-7.
5. Rapport Statistique 2018. 2019 Republic of Haiti.
6. Sentlinger K. “Water Crisis in Haiti.” The Water Project.
7. The World Bank in Haiti. worldbank.org.
8. Cenat JM. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1016/jtmaid.2020.101684.
9. Block D. “Why some Americans resist wearing face masks.” voanews.com. 2020 May 31.
10. Panceski B and Douglas J. “Masks could help stop coronavirus. So why are they still controversial?” wsj.com. Updated 29 Jun 2020.
11. Bojarski S. “Social distancing: A luxury Haiti’s poor cannot afford. The Haitian Times. 2020 Apr.
12. World Health Organization, UNICEF, World Bank Group, and the U.N. Population Division. Maternal mortality ratio, Haiti.
13. Feliciano I and Kargbo C. “As COVID cases surge, Haiti’s Dr. Pape is on the front line again.” PBS NewsHour Weekend. 2020 Jun 13.
14. Liautaud B and Deschamps MM. New Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 16.
Mr. Dorcela is a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince, Haiti. He also is a medical intern at Unité de Médecine Familiale Hôpital Saint Nicolas in Saint-Marc. Mr. Dorcela has no disclosures. Mr. St. Jean, who is Mr. Dorcela’s brother, is also a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince. He has no disclosures.
Doctors Without Borders, other groups urged to mobilize
Doctors Without Borders, other groups urged to mobilize
Do you want to know what keeps us up at night? As 4th-year medical students born, raised, and living in Haiti, we worry about the impact of COVID-19 on our patients.
The pandemic has shaken the world, and Haiti is no exception.
It has taken several months for the disease to spread, and it began with two confirmed cases, one from France and the other from Belgium, on March 19.1 Much of the spread of COVID-19 in Haiti has been tied to workers returning from the Dominican Republic. As of June 29, Haiti had 5,975 confirmed cases and 105 deaths.2 Of course, those numbers sound minuscule, compared with those in the United States, where the number of deaths from COVID-19 surpassed 100,000 several weeks ago. But the population of Haiti is 30 times smaller than that of the United States, and Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere. We have watched in horror as the virus has ravaged marginalized groups in the United States and worry that it will do the same in our own country.
Just as the Haitian Ministry of Health worked with various groups to reach the 1-year free of cholera mark in Haiti, groups such as Doctors Without Borders must mobilize to rein in COVID-19.
Community transmission rapid
After the first two cases were confirmed, a state of health emergency was immediately declared. Haitian President Jovenel Moïse and other government officials called for the implementation of several measures aimed at limiting the spread of COVID-19.
Schools, universities, clinical training programs, vocational centers, factories, airports, and ports, except for the transport of goods, were all ordered to close until further notice. Gatherings of larger than 10 people were banned. A curfew from 8 p.m. EST time to 5 a.m. EST was imposed. Measures such as those encouraged by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as hand washing, physical distancing, and staying at home were also encouraged by the Haitian Ministry of Health. Mask wearing in public places was deemed mandatory.
The latest testing data show that community spread has been occurring among the Haitian population at a rapid rate. According to Jean William Pape, MD, Haiti’s top infectious diseases expert and founder of GHESKIO, an iconic infectious disease center that cares for people with HIV-AIDS and tuberculosis, a COVID-19 simulation from Cornell University in New York shows that about 35% of the Haitian population will be infected by the end of August 2020. A simulation by the University of Oxford (England) paints an even more dire picture. That simulation shows that 86% of the population could be infected, More than 9,000 additional hospital beds would be needed, and 20,000 people would be likely to die from COVID-19, Dr. Pape said in an interview with Haiti’s Nouvelliste newspaper.3
Medical response
We know that there is a global shortage of health care workers,4 and Haiti is no exception. According to a 2018 report from the Haitian Ministry of Health, the country has 11,775 health care professionals, including about 3,354 medical doctors, to care for more than 11 million people. That translates to about 23.4 physicians per 100,000.5
The pandemic has led some members of this already anemic health care workforce to stay home because of a lack of personal protective equipment. Others, because of reduced hospital or clinic budgets, have been furloughed, making the COVID-19 national health emergency even harder to manage.
But a severe health care shortage is not the only challenge facing Haiti. It spends about $131 U.S. per capita, which makes Haiti one of most vulnerable among low- and middle-income countries in the world. As a poor country,7 its health care infrastructure is among the most inadequate and weakest. Prior to COVID-19, medical advocacy groups already had started movements and strikes demanding that the government improve the health care system. The country’s precarious health care infrastructure includes a lack of hospital beds, and basic medical supplies and equipment, such as oxygen and ventilators.8 The emergence of COVID-19 has only exacerbated the situation.
Clinical training programs have been suspended, many doctors and nurses are on quarantine, and some hospitals and clinics are closing. We have witnessed makeshift voodoo clinics built by Haitian voodoo leaders to receive, hospitalize, and treat COVID-19 patients through rituals and herbal remedies. In some areas of the country, residents have protested against the opening of several COVID-19 treatment and management centers.
Unique cultural challenges
Public health officials around the world are facing challenges persuading citizens to engage in behaviors that could protect them from the virus.
Just as in America, where many people opt to not wear face coverings9,10 despite the public health risks, deep distrust of the Haitian government has undermined the messages of President Moïse and public health officials about the role of masks in limiting the spread of COVID. We see large numbers of unmasked people on the streets in the informal markets every day. Crammed tap-taps and overloaded motorcycles are moving everywhere. This also could be tied to cultural attitudes about COVID that persist among some Haitians. For example, many people with signs and symptoms of COVID-19 are afraid of going to the hospital to get tested and receive care, and resort to going to the voodoo clinics. Along with rituals, voodoo priests have been serving up teas with ingredients, including moringa, eucalyptus, ginger, and honey to those seeking COVID-19 care in the centers. The voodoo priests claim that the teas they serve strengthen the immune system.
In addition, it is difficult for poor people who live in small quarters with several other people to adhere to physical distancing.11
Stigma and violence
Other barriers in the fight against COVID-19 in Haiti are stigma and violence. If widespread testing were available, some Haitians would opt not to do so – despite clear signs and symptoms of the infection. Some people who would get tested if they could are afraid to do so because of fears tied to being attacked by neighbors.
When Haitian University professor Bellamy Nelson and his girlfriend returned to Haiti from the United States in March and began experiencing some pain and fever, he experienced attacks from neighbors, he said in an interview. He said neighbors threatened to burn down his house. When an ambulance arrived at his house to transport him to a hospital, it had to drive through back roads to avoid people armed with rocks, fire, and machetes, he told us. No hospital wanted to admit him. Eventually, Professor Nelson self-quarantined at home, he said.
In another incident, a national ambulance center in Gonaïves, a town toward the northern region of Haiti, reportedly was vandalized, because COVID-19 equipment and supplies used to treat people had been stored there. Hospital Bernard Mevs, along with many other hospitals, was forced by the area’s residents to suspend the plan to open a center for COVID-19 management. Threats to burn down the hospitals caused the leaders of the hospitals to back down and give up a plan to build a 20-bed COVID-19 response center.
Maternal health
Another concern we have about the pandemic is the risk it could be to pregnant women. On average, 94,000 deaths occur annually in Haiti. Out of this number, maternal mortality accounts for 1,000. In 2017, for every 100,000 live births for women of reproductive age from 15 to 49 years old, 480 women died. In contrast, in the Dominican Republic, 95 women died per 100,000 that same year. In the United States, 19 died, and in Norway, no more than 2 died that year.12
Some of the primary factors contributing to the crisis are limited accessibility, inadequate health care facilities, and an inadequate number of trained health care practitioners; low percentages of skilled attendants at deliveries and of prenatal and postnatal visits; and high numbers of high-risk deliveries in nonqualified health facilities.
During the COVID-19 national health emergency, with most hospitals reducing their health care personnel either because of budget-related reasons or because they are on quarantine, this maternal-fetal health crisis has escalated.
One of the biggest hospitals in Jacmel, a town in the southern region of Haiti, has stopped its prenatal care program. In Delmas, the city with the highest incidence and prevalence of COVID-19, Hôpital Universitaire de la Paix has reduced this program to 50% of its capacity and gynecologic care has been completely suspended. Hôpital St. Luc, one of the first hospitals in the western region of Haiti to open its doors to care for COVID-19 patients, has recently shut down the entire maternal-fetal department.
So, access to prenatal and postnatal care, including the ability to deliver babies in health care institutions, is significantly reduced because of COVID-19. This leaves thousands of already vulnerable pregnant women at risk and having to deliver domestically with little to no health care professional assistance. We worry that, in light of the data, more women and babies will die because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A call to action
Despite these conditions, there are reasons for hope. Various groups, both from the international community and locally have mobilized to respond to the pandemic.
International health care organizations such as Doctors Without Borders and Partners in Health, and local groups such as GHESKIO, the St. Luke Foundation for Haiti, and others have been collaborating with the Haitian Ministry of Health to devise and strategic plans and deploy valuable resources with the common goal of saving lives from COVID-19.
GHESKIO, for example, under Dr. Pape’s leadership, currently has one of the three COVID-19 testing centers in the country. It also has two COVID-19 treatment centers in full operation, in Port-au-Prince, the capital city, managing and treating 520 patients with confirmed COVID-19. GHESKIO, which has been in the front lines of previous major infectious disease outbreaks,13 has trained about 200 clinicians from both public and private health care institutions to care for COVID-19 patients.
Doctors Without Borders has been investing in efforts to support the Ministry of Health by converting and renovating its Burn Center in Drouillard, a small section of the city of Cité Soleil, one of the country’s biggest slums. In May, as part of its COVID-19 response, it launched a 20-bed capacity center that can accommodate up to 45 beds to care for patients who have tested positive for COVID-19.
Partners in Health, the Boston-based nonprofit health care organization cofounded in 1987 by American anthropologist and infectious disease specialist, Paul Farmer, MD, and the largest nonprofit health care provider in Haiti, also joined the Ministry of Health through its national and public health efforts to tackle COVID-19 in Haiti. Partners in Health, through its sister organization, Zanmi Lasante, has pioneered the movement of diagnosing and treating people with HIV-AIDS and TB. Since the late 1990s, its efforts against both infectious diseases have helped 15,000 HIV-positive patients begin and remain on treatment. And every year, 1,500 TB patients have started treatment on the path to a cure.
Early in the pandemic in Haiti, Partners in Health, through its state-of-the-art 300-bed university hospital (Hôpital Universitaire de Mirebalais de Mirebalais), was the first to open a COVID-19 center with a 20-bed capacity and has been caring for COVID-19 patients since then. In June, Partners in Health supported and inaugurated the renovation of the internal medicine department at one of its affiliated community hospitals, Hôpital Saint-Nicolas de Saint Marc. That department will have a 24-bed capacity that can extend up to 36 beds to manage and treat COVID-19 patients.
In total, currently, 26 COVID-19 centers with a capacity of 1,011 beds are available to serve, manage, and treat Haitian patients affected with COVID-19. But are those efforts enough? No.
Haiti, as a weak state even before COVID-19, continues to need funding from the international community so it can strengthen its health care infrastructure to be effective and strong in fighting against COVID-19.
In addition, we would like to see preventive initiatives implemented on the local level. Our family has taken on a role that, we think, could help conquer COVID-19 if others followed suit on a large scale.
As part of our contribution in tackling COVID-19, the two of us have launched a small-scale community experiment. We have educated our family in Delmas about COVID-19 and subsequently launched an awareness campaign in the community. We dispatched small groups that go door to door in the community to educate neighbors about the disease in an effort to help them understand that COVID-19 is real and it is normal for people that feel they may have the disease to seek medical care. This approach helps suppress the transmission of the virus. This pilot project could be reproduced in several other communities. It is easy to operate, rapid, effective, and cost-free. The community has been very receptive to and grateful for our efforts.
Like other countries across the world, Haiti was not ready for COVID-19. But we are confident that, with help from the international community, organizations such as GHESKIO,14 and with due diligence on the local level, we are strong and resilient enough to beat COVID. We must act together – quickly.
References
1. Sénat JD. Coronavirus: 2 cas confirmés en Haïti, Jovenel Moïse décrète l’état d’ur-gence sanitaire. 2020 Le Nouvelliste.
2. Haitian Ministry of Health.
3. “Entre appel a la solidarite et de sombres previsions, le Dr William Pape fait le point.” Le Nouvelliste.
4. Darzi A and Evans T. Lancet. 2016 Nov-Dec 26. 388;10060:2576-7.
5. Rapport Statistique 2018. 2019 Republic of Haiti.
6. Sentlinger K. “Water Crisis in Haiti.” The Water Project.
7. The World Bank in Haiti. worldbank.org.
8. Cenat JM. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1016/jtmaid.2020.101684.
9. Block D. “Why some Americans resist wearing face masks.” voanews.com. 2020 May 31.
10. Panceski B and Douglas J. “Masks could help stop coronavirus. So why are they still controversial?” wsj.com. Updated 29 Jun 2020.
11. Bojarski S. “Social distancing: A luxury Haiti’s poor cannot afford. The Haitian Times. 2020 Apr.
12. World Health Organization, UNICEF, World Bank Group, and the U.N. Population Division. Maternal mortality ratio, Haiti.
13. Feliciano I and Kargbo C. “As COVID cases surge, Haiti’s Dr. Pape is on the front line again.” PBS NewsHour Weekend. 2020 Jun 13.
14. Liautaud B and Deschamps MM. New Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 16.
Mr. Dorcela is a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince, Haiti. He also is a medical intern at Unité de Médecine Familiale Hôpital Saint Nicolas in Saint-Marc. Mr. Dorcela has no disclosures. Mr. St. Jean, who is Mr. Dorcela’s brother, is also a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince. He has no disclosures.
Do you want to know what keeps us up at night? As 4th-year medical students born, raised, and living in Haiti, we worry about the impact of COVID-19 on our patients.
The pandemic has shaken the world, and Haiti is no exception.
It has taken several months for the disease to spread, and it began with two confirmed cases, one from France and the other from Belgium, on March 19.1 Much of the spread of COVID-19 in Haiti has been tied to workers returning from the Dominican Republic. As of June 29, Haiti had 5,975 confirmed cases and 105 deaths.2 Of course, those numbers sound minuscule, compared with those in the United States, where the number of deaths from COVID-19 surpassed 100,000 several weeks ago. But the population of Haiti is 30 times smaller than that of the United States, and Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere. We have watched in horror as the virus has ravaged marginalized groups in the United States and worry that it will do the same in our own country.
Just as the Haitian Ministry of Health worked with various groups to reach the 1-year free of cholera mark in Haiti, groups such as Doctors Without Borders must mobilize to rein in COVID-19.
Community transmission rapid
After the first two cases were confirmed, a state of health emergency was immediately declared. Haitian President Jovenel Moïse and other government officials called for the implementation of several measures aimed at limiting the spread of COVID-19.
Schools, universities, clinical training programs, vocational centers, factories, airports, and ports, except for the transport of goods, were all ordered to close until further notice. Gatherings of larger than 10 people were banned. A curfew from 8 p.m. EST time to 5 a.m. EST was imposed. Measures such as those encouraged by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, such as hand washing, physical distancing, and staying at home were also encouraged by the Haitian Ministry of Health. Mask wearing in public places was deemed mandatory.
The latest testing data show that community spread has been occurring among the Haitian population at a rapid rate. According to Jean William Pape, MD, Haiti’s top infectious diseases expert and founder of GHESKIO, an iconic infectious disease center that cares for people with HIV-AIDS and tuberculosis, a COVID-19 simulation from Cornell University in New York shows that about 35% of the Haitian population will be infected by the end of August 2020. A simulation by the University of Oxford (England) paints an even more dire picture. That simulation shows that 86% of the population could be infected, More than 9,000 additional hospital beds would be needed, and 20,000 people would be likely to die from COVID-19, Dr. Pape said in an interview with Haiti’s Nouvelliste newspaper.3
Medical response
We know that there is a global shortage of health care workers,4 and Haiti is no exception. According to a 2018 report from the Haitian Ministry of Health, the country has 11,775 health care professionals, including about 3,354 medical doctors, to care for more than 11 million people. That translates to about 23.4 physicians per 100,000.5
The pandemic has led some members of this already anemic health care workforce to stay home because of a lack of personal protective equipment. Others, because of reduced hospital or clinic budgets, have been furloughed, making the COVID-19 national health emergency even harder to manage.
But a severe health care shortage is not the only challenge facing Haiti. It spends about $131 U.S. per capita, which makes Haiti one of most vulnerable among low- and middle-income countries in the world. As a poor country,7 its health care infrastructure is among the most inadequate and weakest. Prior to COVID-19, medical advocacy groups already had started movements and strikes demanding that the government improve the health care system. The country’s precarious health care infrastructure includes a lack of hospital beds, and basic medical supplies and equipment, such as oxygen and ventilators.8 The emergence of COVID-19 has only exacerbated the situation.
Clinical training programs have been suspended, many doctors and nurses are on quarantine, and some hospitals and clinics are closing. We have witnessed makeshift voodoo clinics built by Haitian voodoo leaders to receive, hospitalize, and treat COVID-19 patients through rituals and herbal remedies. In some areas of the country, residents have protested against the opening of several COVID-19 treatment and management centers.
Unique cultural challenges
Public health officials around the world are facing challenges persuading citizens to engage in behaviors that could protect them from the virus.
Just as in America, where many people opt to not wear face coverings9,10 despite the public health risks, deep distrust of the Haitian government has undermined the messages of President Moïse and public health officials about the role of masks in limiting the spread of COVID. We see large numbers of unmasked people on the streets in the informal markets every day. Crammed tap-taps and overloaded motorcycles are moving everywhere. This also could be tied to cultural attitudes about COVID that persist among some Haitians. For example, many people with signs and symptoms of COVID-19 are afraid of going to the hospital to get tested and receive care, and resort to going to the voodoo clinics. Along with rituals, voodoo priests have been serving up teas with ingredients, including moringa, eucalyptus, ginger, and honey to those seeking COVID-19 care in the centers. The voodoo priests claim that the teas they serve strengthen the immune system.
In addition, it is difficult for poor people who live in small quarters with several other people to adhere to physical distancing.11
Stigma and violence
Other barriers in the fight against COVID-19 in Haiti are stigma and violence. If widespread testing were available, some Haitians would opt not to do so – despite clear signs and symptoms of the infection. Some people who would get tested if they could are afraid to do so because of fears tied to being attacked by neighbors.
When Haitian University professor Bellamy Nelson and his girlfriend returned to Haiti from the United States in March and began experiencing some pain and fever, he experienced attacks from neighbors, he said in an interview. He said neighbors threatened to burn down his house. When an ambulance arrived at his house to transport him to a hospital, it had to drive through back roads to avoid people armed with rocks, fire, and machetes, he told us. No hospital wanted to admit him. Eventually, Professor Nelson self-quarantined at home, he said.
In another incident, a national ambulance center in Gonaïves, a town toward the northern region of Haiti, reportedly was vandalized, because COVID-19 equipment and supplies used to treat people had been stored there. Hospital Bernard Mevs, along with many other hospitals, was forced by the area’s residents to suspend the plan to open a center for COVID-19 management. Threats to burn down the hospitals caused the leaders of the hospitals to back down and give up a plan to build a 20-bed COVID-19 response center.
Maternal health
Another concern we have about the pandemic is the risk it could be to pregnant women. On average, 94,000 deaths occur annually in Haiti. Out of this number, maternal mortality accounts for 1,000. In 2017, for every 100,000 live births for women of reproductive age from 15 to 49 years old, 480 women died. In contrast, in the Dominican Republic, 95 women died per 100,000 that same year. In the United States, 19 died, and in Norway, no more than 2 died that year.12
Some of the primary factors contributing to the crisis are limited accessibility, inadequate health care facilities, and an inadequate number of trained health care practitioners; low percentages of skilled attendants at deliveries and of prenatal and postnatal visits; and high numbers of high-risk deliveries in nonqualified health facilities.
During the COVID-19 national health emergency, with most hospitals reducing their health care personnel either because of budget-related reasons or because they are on quarantine, this maternal-fetal health crisis has escalated.
One of the biggest hospitals in Jacmel, a town in the southern region of Haiti, has stopped its prenatal care program. In Delmas, the city with the highest incidence and prevalence of COVID-19, Hôpital Universitaire de la Paix has reduced this program to 50% of its capacity and gynecologic care has been completely suspended. Hôpital St. Luc, one of the first hospitals in the western region of Haiti to open its doors to care for COVID-19 patients, has recently shut down the entire maternal-fetal department.
So, access to prenatal and postnatal care, including the ability to deliver babies in health care institutions, is significantly reduced because of COVID-19. This leaves thousands of already vulnerable pregnant women at risk and having to deliver domestically with little to no health care professional assistance. We worry that, in light of the data, more women and babies will die because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A call to action
Despite these conditions, there are reasons for hope. Various groups, both from the international community and locally have mobilized to respond to the pandemic.
International health care organizations such as Doctors Without Borders and Partners in Health, and local groups such as GHESKIO, the St. Luke Foundation for Haiti, and others have been collaborating with the Haitian Ministry of Health to devise and strategic plans and deploy valuable resources with the common goal of saving lives from COVID-19.
GHESKIO, for example, under Dr. Pape’s leadership, currently has one of the three COVID-19 testing centers in the country. It also has two COVID-19 treatment centers in full operation, in Port-au-Prince, the capital city, managing and treating 520 patients with confirmed COVID-19. GHESKIO, which has been in the front lines of previous major infectious disease outbreaks,13 has trained about 200 clinicians from both public and private health care institutions to care for COVID-19 patients.
Doctors Without Borders has been investing in efforts to support the Ministry of Health by converting and renovating its Burn Center in Drouillard, a small section of the city of Cité Soleil, one of the country’s biggest slums. In May, as part of its COVID-19 response, it launched a 20-bed capacity center that can accommodate up to 45 beds to care for patients who have tested positive for COVID-19.
Partners in Health, the Boston-based nonprofit health care organization cofounded in 1987 by American anthropologist and infectious disease specialist, Paul Farmer, MD, and the largest nonprofit health care provider in Haiti, also joined the Ministry of Health through its national and public health efforts to tackle COVID-19 in Haiti. Partners in Health, through its sister organization, Zanmi Lasante, has pioneered the movement of diagnosing and treating people with HIV-AIDS and TB. Since the late 1990s, its efforts against both infectious diseases have helped 15,000 HIV-positive patients begin and remain on treatment. And every year, 1,500 TB patients have started treatment on the path to a cure.
Early in the pandemic in Haiti, Partners in Health, through its state-of-the-art 300-bed university hospital (Hôpital Universitaire de Mirebalais de Mirebalais), was the first to open a COVID-19 center with a 20-bed capacity and has been caring for COVID-19 patients since then. In June, Partners in Health supported and inaugurated the renovation of the internal medicine department at one of its affiliated community hospitals, Hôpital Saint-Nicolas de Saint Marc. That department will have a 24-bed capacity that can extend up to 36 beds to manage and treat COVID-19 patients.
In total, currently, 26 COVID-19 centers with a capacity of 1,011 beds are available to serve, manage, and treat Haitian patients affected with COVID-19. But are those efforts enough? No.
Haiti, as a weak state even before COVID-19, continues to need funding from the international community so it can strengthen its health care infrastructure to be effective and strong in fighting against COVID-19.
In addition, we would like to see preventive initiatives implemented on the local level. Our family has taken on a role that, we think, could help conquer COVID-19 if others followed suit on a large scale.
As part of our contribution in tackling COVID-19, the two of us have launched a small-scale community experiment. We have educated our family in Delmas about COVID-19 and subsequently launched an awareness campaign in the community. We dispatched small groups that go door to door in the community to educate neighbors about the disease in an effort to help them understand that COVID-19 is real and it is normal for people that feel they may have the disease to seek medical care. This approach helps suppress the transmission of the virus. This pilot project could be reproduced in several other communities. It is easy to operate, rapid, effective, and cost-free. The community has been very receptive to and grateful for our efforts.
Like other countries across the world, Haiti was not ready for COVID-19. But we are confident that, with help from the international community, organizations such as GHESKIO,14 and with due diligence on the local level, we are strong and resilient enough to beat COVID. We must act together – quickly.
References
1. Sénat JD. Coronavirus: 2 cas confirmés en Haïti, Jovenel Moïse décrète l’état d’ur-gence sanitaire. 2020 Le Nouvelliste.
2. Haitian Ministry of Health.
3. “Entre appel a la solidarite et de sombres previsions, le Dr William Pape fait le point.” Le Nouvelliste.
4. Darzi A and Evans T. Lancet. 2016 Nov-Dec 26. 388;10060:2576-7.
5. Rapport Statistique 2018. 2019 Republic of Haiti.
6. Sentlinger K. “Water Crisis in Haiti.” The Water Project.
7. The World Bank in Haiti. worldbank.org.
8. Cenat JM. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1016/jtmaid.2020.101684.
9. Block D. “Why some Americans resist wearing face masks.” voanews.com. 2020 May 31.
10. Panceski B and Douglas J. “Masks could help stop coronavirus. So why are they still controversial?” wsj.com. Updated 29 Jun 2020.
11. Bojarski S. “Social distancing: A luxury Haiti’s poor cannot afford. The Haitian Times. 2020 Apr.
12. World Health Organization, UNICEF, World Bank Group, and the U.N. Population Division. Maternal mortality ratio, Haiti.
13. Feliciano I and Kargbo C. “As COVID cases surge, Haiti’s Dr. Pape is on the front line again.” PBS NewsHour Weekend. 2020 Jun 13.
14. Liautaud B and Deschamps MM. New Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 16.
Mr. Dorcela is a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince, Haiti. He also is a medical intern at Unité de Médecine Familiale Hôpital Saint Nicolas in Saint-Marc. Mr. Dorcela has no disclosures. Mr. St. Jean, who is Mr. Dorcela’s brother, is also a senior medical student at Faculté des Sciences de la Santé Université Quisqueya in Port-au-Prince. He has no disclosures.
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
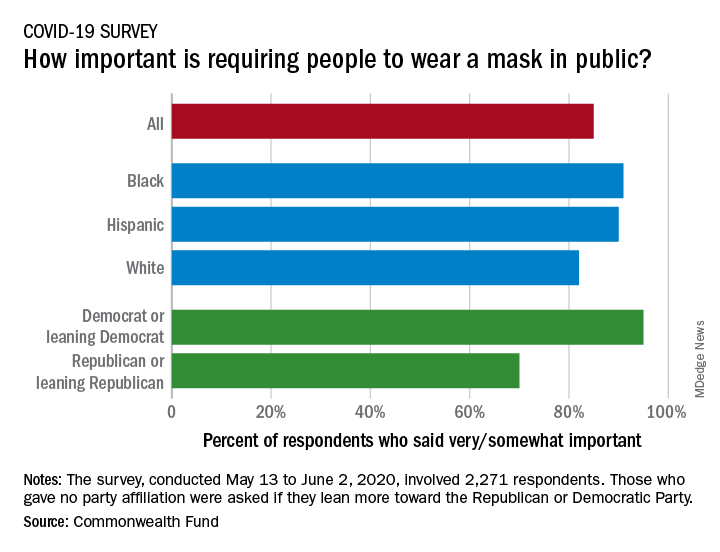
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Triple inhaler combo quells COPD exacerbations
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
FROM ATS 2020
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Daily Recap: Docs are good at saving money; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine trials advance
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Many physicians live within their means and save
Although about two of five physicians report a net worth of between $1 million and $5 million, about half report that they are living at or below their means, according to the latest Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Net worth figures varied greatly by specialty. Among specialists, orthopedists were most likely (at 19%) to top the $5 million level, followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%). Conversely, 46% of family physicians and 44% of pediatricians reported that their net worth was under $500,000. Gender gaps were also apparent in the data, especially at the highest levels. Twice as many male physicians (10%) as their female counterparts (5%) had a net worth of more than $5 million.
Asked about saving habits, 43% of physicians reported they live below their means. Just 7% said they live above their means. How do they save money? Survey respondents reported putting bonus money into an investment account, putting extra money toward paying down the mortgage, and bringing lunch to work everyday.
The survey responses on salary, debt, and net worth from more than 17,000 physicians spanning 30 specialties were collected prior to Feb. 11, before COVID-19 was declared a pandemic. Read more.
Phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials launching in July
There are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine, according to Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.” Read more.
FDA approves in-home breast cancer treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a combination of subcutaneous breast cancer treatments that could be administered at home, following completion of chemotherapy.
The agency gave the green light to pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche), administered subcutaneously rather than intravenously, for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete. Read more.
Could a visual tool aid migraine management?
A new visual tool aims to streamline patient-clinician communication about risk factors for progression from episodic to chronic migraines.
The tool is still just a prototype, but it could eventually synthesize patient responses to an integrated questionnaire and produce a chart illustrating where the patient stands with respect to a range of modifiable risk factors from depression to insomnia.
Physicians must see patients in short appointment periods, making it difficult to communicate all of the risk factors and behavioral characteristics that can contribute to risk of progression. “If you have a patient and you’re able to look at a visualization tool quickly and say: ‘Okay, my patient really is having insomnia and sleep issues,’ you can focus the session talking about sleep, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, and all the things we can help patients with,” lead researcher Ami Cuneo, MD, who is a headache fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Dr. Cuneo presented a poster describing the concept at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Many physicians live within their means and save
Although about two of five physicians report a net worth of between $1 million and $5 million, about half report that they are living at or below their means, according to the latest Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Net worth figures varied greatly by specialty. Among specialists, orthopedists were most likely (at 19%) to top the $5 million level, followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%). Conversely, 46% of family physicians and 44% of pediatricians reported that their net worth was under $500,000. Gender gaps were also apparent in the data, especially at the highest levels. Twice as many male physicians (10%) as their female counterparts (5%) had a net worth of more than $5 million.
Asked about saving habits, 43% of physicians reported they live below their means. Just 7% said they live above their means. How do they save money? Survey respondents reported putting bonus money into an investment account, putting extra money toward paying down the mortgage, and bringing lunch to work everyday.
The survey responses on salary, debt, and net worth from more than 17,000 physicians spanning 30 specialties were collected prior to Feb. 11, before COVID-19 was declared a pandemic. Read more.
Phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials launching in July
There are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine, according to Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.” Read more.
FDA approves in-home breast cancer treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a combination of subcutaneous breast cancer treatments that could be administered at home, following completion of chemotherapy.
The agency gave the green light to pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche), administered subcutaneously rather than intravenously, for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete. Read more.
Could a visual tool aid migraine management?
A new visual tool aims to streamline patient-clinician communication about risk factors for progression from episodic to chronic migraines.
The tool is still just a prototype, but it could eventually synthesize patient responses to an integrated questionnaire and produce a chart illustrating where the patient stands with respect to a range of modifiable risk factors from depression to insomnia.
Physicians must see patients in short appointment periods, making it difficult to communicate all of the risk factors and behavioral characteristics that can contribute to risk of progression. “If you have a patient and you’re able to look at a visualization tool quickly and say: ‘Okay, my patient really is having insomnia and sleep issues,’ you can focus the session talking about sleep, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, and all the things we can help patients with,” lead researcher Ami Cuneo, MD, who is a headache fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Dr. Cuneo presented a poster describing the concept at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Many physicians live within their means and save
Although about two of five physicians report a net worth of between $1 million and $5 million, about half report that they are living at or below their means, according to the latest Medscape Physician Debt and Net Worth Report 2020.
Net worth figures varied greatly by specialty. Among specialists, orthopedists were most likely (at 19%) to top the $5 million level, followed by plastic surgeons and gastroenterologists (both at 16%). Conversely, 46% of family physicians and 44% of pediatricians reported that their net worth was under $500,000. Gender gaps were also apparent in the data, especially at the highest levels. Twice as many male physicians (10%) as their female counterparts (5%) had a net worth of more than $5 million.
Asked about saving habits, 43% of physicians reported they live below their means. Just 7% said they live above their means. How do they save money? Survey respondents reported putting bonus money into an investment account, putting extra money toward paying down the mortgage, and bringing lunch to work everyday.
The survey responses on salary, debt, and net worth from more than 17,000 physicians spanning 30 specialties were collected prior to Feb. 11, before COVID-19 was declared a pandemic. Read more.
Phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials launching in July
There are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine, according to Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.” Read more.
FDA approves in-home breast cancer treatment
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a combination of subcutaneous breast cancer treatments that could be administered at home, following completion of chemotherapy.
The agency gave the green light to pertuzumab (Perjeta, Genentech/Roche), trastuzumab (Herceptin, Genentech/Roche) and hyaluronidase (Phesgo, Genentech/Roche), administered subcutaneously rather than intravenously, for the treatment of early and metastatic HER2-positive breast cancers.
Phesgo is initially used in combination with chemotherapy at an infusion center but could continue to be administered in a patient’s home by a qualified health care professional once chemotherapy is complete. Read more.
Could a visual tool aid migraine management?
A new visual tool aims to streamline patient-clinician communication about risk factors for progression from episodic to chronic migraines.
The tool is still just a prototype, but it could eventually synthesize patient responses to an integrated questionnaire and produce a chart illustrating where the patient stands with respect to a range of modifiable risk factors from depression to insomnia.
Physicians must see patients in short appointment periods, making it difficult to communicate all of the risk factors and behavioral characteristics that can contribute to risk of progression. “If you have a patient and you’re able to look at a visualization tool quickly and say: ‘Okay, my patient really is having insomnia and sleep issues,’ you can focus the session talking about sleep, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, and all the things we can help patients with,” lead researcher Ami Cuneo, MD, who is a headache fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Dr. Cuneo presented a poster describing the concept at the virtual annual meeting of the American Headache Society. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials launching in July, expert says
The race to develop a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is unlike any other global research and development effort in modern medicine.
According to Paul A. Offit, MD, there are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for these vaccines, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine. The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) has awarded $2.5 billion to five different pharmaceutical companies to make a vaccine.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.”
Some research groups are interested in developing a whole, killed virus like those used in the inactivated polio vaccine, and vaccines for hepatitis A virus and rabies, said Dr. Offit, who is a member of Accelerating COVID-19 Technical Innovations And Vaccines, a public-private partnership formed by the National Institutes of Health. Other groups are interested in making a live-attenuated vaccine like those for measles, mumps, and rubella. “Some are interested in using a vectored vaccine, where you take a virus that is relatively weak and doesn’t cause disease in people, like vesicular stomatitis virus, and then clone into that the gene that codes for this coronavirus spike protein, which is the way that we made the Ebola virus vaccine,” Dr. Offit said. “Those approaches have all been used before, with success.”
Novel approaches are also being employed to make this vaccine, including using a replication-defective adenovirus. “That means that the virus can’t reproduce itself, but it can make proteins,” he explained. “There are some proteins that are made, but most aren’t. Therefore, the virus can’t reproduce itself. We’ll see whether or not that [approach] works, but it’s never been used before.”
Another approach is to inject messenger RNA that codes for the coronavirus spike protein, where that genetic material is translated into the spike protein. The other platform being evaluated is a DNA vaccine, in which “you give DNA which is coded for that spike protein, which is transcribed to messenger RNA and then is translated to other proteins.”
Typical vaccine development involves animal models to prove the concept, dose-ranging studies in humans, and progressively larger safety and immunogenicity studies in hundreds of thousands of people. Next come phase 3 studies, “where the proof is in the pudding,” he said. “These are large, prospective placebo-controlled trials to prove that the vaccine is safe. This is the only way whether you can prove or not a vaccine is effective.”
“Some companies may branch out on their own and do smaller studies than that,” he said. “We’ll see how this plays out. Keep your eyes open for that, because you really want to make sure you have a fairly large phase 3 trial. That’s the best way to show whether something works and whether it’s safe.”
The tried and true vaccines that emerge from the effort will not be FDA-licensed products. Rather, they will be approved products under the Emergency Use Authorization program. “Ever since the 1950s, every vaccine that has been used in the U.S. has been under the auspices of FDA licensure,” said Dr. Offit, who is also professor of pediatrics and the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s not going to be true here. The FDA is involved every step of the way but here they have a somewhat lighter touch.”
A few candidate vaccines are being mass-produced at risk, “meaning they’re being produced not knowing whether these vaccines are safe and effective yet or not,” he said. “But when they’re shown in a phase 3 trial to be safe and effective, you will have already produced it, and then it’s much easier to roll it out to the general public the minute you’ve shown that it works. This is what we did for the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. We mass-produced that vaccine at risk.”
Dr. Offit emphasized the importance of managing expectations once a COVID-19 vaccine gets approved for use. “Regarding safety, these vaccines will be tested in tens of thousands of people, not tens of millions of people, so although you can disprove a relatively uncommon side effect preapproval, you’re not going to disprove a rare side effect preapproval. You’re only going to know that post approval. I think we need to make people aware of that and to let them know that through groups like the Vaccine Safety Datalink, we’re going to be monitoring these vaccines once they’re approved.”
Regarding efficacy, he continued, “we’re not going know about the rates of immunity initially; we’re only going to know about that after the vaccine [has been administered]. My guess is the protection is going to be short lived and incomplete. By short lived, I mean that protection would last for years but not decades. By incomplete, I mean that protection will be against moderate to severe disease, which is fine. You don’t need protection against all of the disease; it’s hard to do that with respiratory viruses. That means you can keep people out of the hospital, and you can keep them from dying. That’s the main goal.”
Dr. Offit closed his remarks by noting that much is at stake in this effort to develop a vaccine so quickly and that it “could go one of two ways. We could find that the vaccine is a lifesaver, and [that] we can finally end this awful pandemic. Or, if we cut corners and don’t prove that the vaccines are safe and effective as we should before they’re released, we could shake what is a fragile vaccine confidence in this country. Hopefully, it doesn’t play out that way.”
The race to develop a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is unlike any other global research and development effort in modern medicine.
According to Paul A. Offit, MD, there are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for these vaccines, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine. The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) has awarded $2.5 billion to five different pharmaceutical companies to make a vaccine.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.”
Some research groups are interested in developing a whole, killed virus like those used in the inactivated polio vaccine, and vaccines for hepatitis A virus and rabies, said Dr. Offit, who is a member of Accelerating COVID-19 Technical Innovations And Vaccines, a public-private partnership formed by the National Institutes of Health. Other groups are interested in making a live-attenuated vaccine like those for measles, mumps, and rubella. “Some are interested in using a vectored vaccine, where you take a virus that is relatively weak and doesn’t cause disease in people, like vesicular stomatitis virus, and then clone into that the gene that codes for this coronavirus spike protein, which is the way that we made the Ebola virus vaccine,” Dr. Offit said. “Those approaches have all been used before, with success.”
Novel approaches are also being employed to make this vaccine, including using a replication-defective adenovirus. “That means that the virus can’t reproduce itself, but it can make proteins,” he explained. “There are some proteins that are made, but most aren’t. Therefore, the virus can’t reproduce itself. We’ll see whether or not that [approach] works, but it’s never been used before.”
Another approach is to inject messenger RNA that codes for the coronavirus spike protein, where that genetic material is translated into the spike protein. The other platform being evaluated is a DNA vaccine, in which “you give DNA which is coded for that spike protein, which is transcribed to messenger RNA and then is translated to other proteins.”
Typical vaccine development involves animal models to prove the concept, dose-ranging studies in humans, and progressively larger safety and immunogenicity studies in hundreds of thousands of people. Next come phase 3 studies, “where the proof is in the pudding,” he said. “These are large, prospective placebo-controlled trials to prove that the vaccine is safe. This is the only way whether you can prove or not a vaccine is effective.”
“Some companies may branch out on their own and do smaller studies than that,” he said. “We’ll see how this plays out. Keep your eyes open for that, because you really want to make sure you have a fairly large phase 3 trial. That’s the best way to show whether something works and whether it’s safe.”
The tried and true vaccines that emerge from the effort will not be FDA-licensed products. Rather, they will be approved products under the Emergency Use Authorization program. “Ever since the 1950s, every vaccine that has been used in the U.S. has been under the auspices of FDA licensure,” said Dr. Offit, who is also professor of pediatrics and the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s not going to be true here. The FDA is involved every step of the way but here they have a somewhat lighter touch.”
A few candidate vaccines are being mass-produced at risk, “meaning they’re being produced not knowing whether these vaccines are safe and effective yet or not,” he said. “But when they’re shown in a phase 3 trial to be safe and effective, you will have already produced it, and then it’s much easier to roll it out to the general public the minute you’ve shown that it works. This is what we did for the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. We mass-produced that vaccine at risk.”
Dr. Offit emphasized the importance of managing expectations once a COVID-19 vaccine gets approved for use. “Regarding safety, these vaccines will be tested in tens of thousands of people, not tens of millions of people, so although you can disprove a relatively uncommon side effect preapproval, you’re not going to disprove a rare side effect preapproval. You’re only going to know that post approval. I think we need to make people aware of that and to let them know that through groups like the Vaccine Safety Datalink, we’re going to be monitoring these vaccines once they’re approved.”
Regarding efficacy, he continued, “we’re not going know about the rates of immunity initially; we’re only going to know about that after the vaccine [has been administered]. My guess is the protection is going to be short lived and incomplete. By short lived, I mean that protection would last for years but not decades. By incomplete, I mean that protection will be against moderate to severe disease, which is fine. You don’t need protection against all of the disease; it’s hard to do that with respiratory viruses. That means you can keep people out of the hospital, and you can keep them from dying. That’s the main goal.”
Dr. Offit closed his remarks by noting that much is at stake in this effort to develop a vaccine so quickly and that it “could go one of two ways. We could find that the vaccine is a lifesaver, and [that] we can finally end this awful pandemic. Or, if we cut corners and don’t prove that the vaccines are safe and effective as we should before they’re released, we could shake what is a fragile vaccine confidence in this country. Hopefully, it doesn’t play out that way.”
The race to develop a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is unlike any other global research and development effort in modern medicine.
According to Paul A. Offit, MD, there are now 120 Investigational New Drug applications to the Food and Drug Administration for these vaccines, and researchers at more than 70 companies across the globe are interested in making a vaccine. The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) has awarded $2.5 billion to five different pharmaceutical companies to make a vaccine.
“The good news is that the new coronavirus is relatively stable,” Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said during the virtual Pediatric Dermatology 2020: Best Practices and Innovations Conference. “Although it is a single-stranded RNA virus, it does mutate to some extent, but it doesn’t look like it’s going to mutate away from the vaccine. So, this is not going to be like influenza virus, where you must give a vaccine every year. I think we can make a vaccine that will last for several years. And we know the protein we’re interested in. We’re interested in antibodies directed against the spike glycoprotein, which is abundantly present on the surface of the virus. We know that if we make an antibody response to that protein, we can therefore prevent infection.”
Some research groups are interested in developing a whole, killed virus like those used in the inactivated polio vaccine, and vaccines for hepatitis A virus and rabies, said Dr. Offit, who is a member of Accelerating COVID-19 Technical Innovations And Vaccines, a public-private partnership formed by the National Institutes of Health. Other groups are interested in making a live-attenuated vaccine like those for measles, mumps, and rubella. “Some are interested in using a vectored vaccine, where you take a virus that is relatively weak and doesn’t cause disease in people, like vesicular stomatitis virus, and then clone into that the gene that codes for this coronavirus spike protein, which is the way that we made the Ebola virus vaccine,” Dr. Offit said. “Those approaches have all been used before, with success.”
Novel approaches are also being employed to make this vaccine, including using a replication-defective adenovirus. “That means that the virus can’t reproduce itself, but it can make proteins,” he explained. “There are some proteins that are made, but most aren’t. Therefore, the virus can’t reproduce itself. We’ll see whether or not that [approach] works, but it’s never been used before.”
Another approach is to inject messenger RNA that codes for the coronavirus spike protein, where that genetic material is translated into the spike protein. The other platform being evaluated is a DNA vaccine, in which “you give DNA which is coded for that spike protein, which is transcribed to messenger RNA and then is translated to other proteins.”
Typical vaccine development involves animal models to prove the concept, dose-ranging studies in humans, and progressively larger safety and immunogenicity studies in hundreds of thousands of people. Next come phase 3 studies, “where the proof is in the pudding,” he said. “These are large, prospective placebo-controlled trials to prove that the vaccine is safe. This is the only way whether you can prove or not a vaccine is effective.”
“Some companies may branch out on their own and do smaller studies than that,” he said. “We’ll see how this plays out. Keep your eyes open for that, because you really want to make sure you have a fairly large phase 3 trial. That’s the best way to show whether something works and whether it’s safe.”
The tried and true vaccines that emerge from the effort will not be FDA-licensed products. Rather, they will be approved products under the Emergency Use Authorization program. “Ever since the 1950s, every vaccine that has been used in the U.S. has been under the auspices of FDA licensure,” said Dr. Offit, who is also professor of pediatrics and the Maurice R. Hilleman professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “That’s not going to be true here. The FDA is involved every step of the way but here they have a somewhat lighter touch.”
A few candidate vaccines are being mass-produced at risk, “meaning they’re being produced not knowing whether these vaccines are safe and effective yet or not,” he said. “But when they’re shown in a phase 3 trial to be safe and effective, you will have already produced it, and then it’s much easier to roll it out to the general public the minute you’ve shown that it works. This is what we did for the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. We mass-produced that vaccine at risk.”
Dr. Offit emphasized the importance of managing expectations once a COVID-19 vaccine gets approved for use. “Regarding safety, these vaccines will be tested in tens of thousands of people, not tens of millions of people, so although you can disprove a relatively uncommon side effect preapproval, you’re not going to disprove a rare side effect preapproval. You’re only going to know that post approval. I think we need to make people aware of that and to let them know that through groups like the Vaccine Safety Datalink, we’re going to be monitoring these vaccines once they’re approved.”
Regarding efficacy, he continued, “we’re not going know about the rates of immunity initially; we’re only going to know about that after the vaccine [has been administered]. My guess is the protection is going to be short lived and incomplete. By short lived, I mean that protection would last for years but not decades. By incomplete, I mean that protection will be against moderate to severe disease, which is fine. You don’t need protection against all of the disease; it’s hard to do that with respiratory viruses. That means you can keep people out of the hospital, and you can keep them from dying. That’s the main goal.”
Dr. Offit closed his remarks by noting that much is at stake in this effort to develop a vaccine so quickly and that it “could go one of two ways. We could find that the vaccine is a lifesaver, and [that] we can finally end this awful pandemic. Or, if we cut corners and don’t prove that the vaccines are safe and effective as we should before they’re released, we could shake what is a fragile vaccine confidence in this country. Hopefully, it doesn’t play out that way.”
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY 2020









