User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


RATE-AF trial boosts digoxin for rate control in permanent AFib
Digoxin now deserves to be considered first-line therapy for long-term heart rate control in older patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and symptoms of heart failure, Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, MSc, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
He presented the 12-month results of RATE-AF (Rate Control Therapy Evaluation in Permanent Atrial Fibrillation), in which 160 seniors (mean age, 76 years) with moderate or severe symptoms caused by permanent atrial fibrillation (AFib) as well as heart failure symptoms were randomized to low-dose digoxin or the beta-blocker bisoprolol for rate control.
The open-label trial was designed to address a centuries-old unmet need: “Although digoxin has been in use since 1785, we have no longer-term clinical trials of digoxin in patients with AFib or AFib with heart failure,” noted Dr. Kotecha, professor of cardiology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Not only is digoxin greatly understudied in AFib, but permanent AFib – the most common form of the arrhythmia – has received only a tiny fraction of the research attention that’s been devoted to paroxysmal or persistent AFib, he added.
In RATE-AF, digoxin and bisoprolol proved similarly effective at reducing heart rate, from about 100 bpm at baseline to the mid-70s at 6 and 12 months. Notably, only a handful of study participants required an additional rate control drug during the 12-month study. Nor did the two drugs differ in terms of their impact on patient-reported quality of life at 6 months as reflected by their Short Form–36 physical component score, the primary study endpoint. And both drugs were well tolerated, with 96% of patients in the digoxin group still on the drug at a mean of 161 mcg/day at 6 months, and 89% still on their beta-blocker.
But that’s pretty much where the similarities in outcomes ended.
For example, at 12 months, the digoxin group scored significantly higher than the beta-blocker group on several domains of the Short Form–36 physical component score, including vitality, physical function, and global health. More than half of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement in modified European Heart Rhythm Association AFib-related symptoms at 6 months, compared with 10% of the beta-blocker group. At 12 months, nearly 70% of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement, as did 30% on bisoprolol.
Heart failure symptoms in the digoxin group improved from a mean baseline New York Heart Association class of 2.4 to 1.5 at both 6 and 12 months; the improvement was more modest in the beta-blocker group, going from NYHA 2.4 at baseline to 2.0 at both 6 and 12 months. And while N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels improved in the digoxin group from a baseline of 1,095 pg/mL to 1,058 at 6 months and 960 at 12 months, NT-proBNP actually went up in the beta-blocker group, from 1,041 to 1,209-1,250 pg/mL at 12 months.
Moreover, Dr. Kotecha continued, while RATE-AF was underpowered to assess clinical events, it’s nevertheless noteworthy that a total of 29 adverse events occurred in 12 months in the digoxin group, compared with 142 with beta-blocker therapy. There were 12 unplanned hospital admissions in the digoxin group and 28 in the beta-blocker group, and 22 primary care visits for either AFib or cardiovascular symptoms in patients on digoxin versus 64 in the beta-blocker group.
“Our results suggest a wider use of digoxin for stable patients with permanent AFib,” Dr. Kotecha concluded. However, in an interview, Jonathan Piccini, MD, had a different take on the study results.
“I don’t think this study should widely impact clinical practice in the U.S.,” according to Dr. Piccini, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
His reservations included RATE-AF’s modest sample size as well as uncertainty as to the trial’s generalizability, given that bisoprolol isn’t much used in the United States. Also, these were elderly patients with shortness of breath, and it’s unclear how effective digoxin would be for rate control in patients with permanent AFib who are more active.
“The classic teaching is that digoxin is great for rate control at rest, but when people are active it’s not nearly as good as beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” the cardiologist said.
“A beta-blocker is still going to be my first-line rate control agent. But the results of RATE-AF do open my mind that for an older sedentary patient I may very well think twice now about using digoxin, because in that situation it looks like it achieves similar goals as a beta-blocker,” Dr. Piccini added.
On the plus side for RATE-AF: “I am very pleased to see that we have a randomized controlled trial focused on rate control in permanent AFib. It also tickles me pink to see a randomized, controlled study of digoxin. And I’m really excited to see a clinical trial that focuses on quality of life. It should give some confidence to know that from a quality of life perspective clinicians can consider using either digoxin or a beta-blocker for rate control,” he said.
American College of Cardiology vice president Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, said she’d need to see a much larger randomized trial including a calcium-channel blocker as a third-rate control arm before she’d consider digoxin as first-line rate control therapy in patients with AFib with or without heart failure. Also, she has reservations about drawing definitive conclusions from an open, unblinded study in which patient-reported outcomes are the primary endpoint.
“I think these were surprising findings given what we all think about digoxin in this country. In general, digoxin fell out of favor for rate control, mainly because of observational studies showing increased mortality. So most of us choose a beta-blocker,” she observed in an interview.
But of course, a randomized trial, even a 160-patient randomized trial, constitutes a higher level of evidence.
“I don’t think I’m going to convert tomorrow and make digoxin my first-line rate control therapy without more data. But RATE-AF does makes me stop and think about using it more than I did before in some of my permanent AFib patients,” said Dr. Itchhaporia, director of disease management at Hoag Memorial Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif.
Dr. Kotecha reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, the British Heart Foundation, and the European Union.
Digoxin now deserves to be considered first-line therapy for long-term heart rate control in older patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and symptoms of heart failure, Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, MSc, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
He presented the 12-month results of RATE-AF (Rate Control Therapy Evaluation in Permanent Atrial Fibrillation), in which 160 seniors (mean age, 76 years) with moderate or severe symptoms caused by permanent atrial fibrillation (AFib) as well as heart failure symptoms were randomized to low-dose digoxin or the beta-blocker bisoprolol for rate control.
The open-label trial was designed to address a centuries-old unmet need: “Although digoxin has been in use since 1785, we have no longer-term clinical trials of digoxin in patients with AFib or AFib with heart failure,” noted Dr. Kotecha, professor of cardiology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Not only is digoxin greatly understudied in AFib, but permanent AFib – the most common form of the arrhythmia – has received only a tiny fraction of the research attention that’s been devoted to paroxysmal or persistent AFib, he added.
In RATE-AF, digoxin and bisoprolol proved similarly effective at reducing heart rate, from about 100 bpm at baseline to the mid-70s at 6 and 12 months. Notably, only a handful of study participants required an additional rate control drug during the 12-month study. Nor did the two drugs differ in terms of their impact on patient-reported quality of life at 6 months as reflected by their Short Form–36 physical component score, the primary study endpoint. And both drugs were well tolerated, with 96% of patients in the digoxin group still on the drug at a mean of 161 mcg/day at 6 months, and 89% still on their beta-blocker.
But that’s pretty much where the similarities in outcomes ended.
For example, at 12 months, the digoxin group scored significantly higher than the beta-blocker group on several domains of the Short Form–36 physical component score, including vitality, physical function, and global health. More than half of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement in modified European Heart Rhythm Association AFib-related symptoms at 6 months, compared with 10% of the beta-blocker group. At 12 months, nearly 70% of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement, as did 30% on bisoprolol.
Heart failure symptoms in the digoxin group improved from a mean baseline New York Heart Association class of 2.4 to 1.5 at both 6 and 12 months; the improvement was more modest in the beta-blocker group, going from NYHA 2.4 at baseline to 2.0 at both 6 and 12 months. And while N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels improved in the digoxin group from a baseline of 1,095 pg/mL to 1,058 at 6 months and 960 at 12 months, NT-proBNP actually went up in the beta-blocker group, from 1,041 to 1,209-1,250 pg/mL at 12 months.
Moreover, Dr. Kotecha continued, while RATE-AF was underpowered to assess clinical events, it’s nevertheless noteworthy that a total of 29 adverse events occurred in 12 months in the digoxin group, compared with 142 with beta-blocker therapy. There were 12 unplanned hospital admissions in the digoxin group and 28 in the beta-blocker group, and 22 primary care visits for either AFib or cardiovascular symptoms in patients on digoxin versus 64 in the beta-blocker group.
“Our results suggest a wider use of digoxin for stable patients with permanent AFib,” Dr. Kotecha concluded. However, in an interview, Jonathan Piccini, MD, had a different take on the study results.
“I don’t think this study should widely impact clinical practice in the U.S.,” according to Dr. Piccini, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
His reservations included RATE-AF’s modest sample size as well as uncertainty as to the trial’s generalizability, given that bisoprolol isn’t much used in the United States. Also, these were elderly patients with shortness of breath, and it’s unclear how effective digoxin would be for rate control in patients with permanent AFib who are more active.
“The classic teaching is that digoxin is great for rate control at rest, but when people are active it’s not nearly as good as beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” the cardiologist said.
“A beta-blocker is still going to be my first-line rate control agent. But the results of RATE-AF do open my mind that for an older sedentary patient I may very well think twice now about using digoxin, because in that situation it looks like it achieves similar goals as a beta-blocker,” Dr. Piccini added.
On the plus side for RATE-AF: “I am very pleased to see that we have a randomized controlled trial focused on rate control in permanent AFib. It also tickles me pink to see a randomized, controlled study of digoxin. And I’m really excited to see a clinical trial that focuses on quality of life. It should give some confidence to know that from a quality of life perspective clinicians can consider using either digoxin or a beta-blocker for rate control,” he said.
American College of Cardiology vice president Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, said she’d need to see a much larger randomized trial including a calcium-channel blocker as a third-rate control arm before she’d consider digoxin as first-line rate control therapy in patients with AFib with or without heart failure. Also, she has reservations about drawing definitive conclusions from an open, unblinded study in which patient-reported outcomes are the primary endpoint.
“I think these were surprising findings given what we all think about digoxin in this country. In general, digoxin fell out of favor for rate control, mainly because of observational studies showing increased mortality. So most of us choose a beta-blocker,” she observed in an interview.
But of course, a randomized trial, even a 160-patient randomized trial, constitutes a higher level of evidence.
“I don’t think I’m going to convert tomorrow and make digoxin my first-line rate control therapy without more data. But RATE-AF does makes me stop and think about using it more than I did before in some of my permanent AFib patients,” said Dr. Itchhaporia, director of disease management at Hoag Memorial Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif.
Dr. Kotecha reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, the British Heart Foundation, and the European Union.
Digoxin now deserves to be considered first-line therapy for long-term heart rate control in older patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and symptoms of heart failure, Dipak Kotecha, MBChB, PhD, MSc, declared at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
He presented the 12-month results of RATE-AF (Rate Control Therapy Evaluation in Permanent Atrial Fibrillation), in which 160 seniors (mean age, 76 years) with moderate or severe symptoms caused by permanent atrial fibrillation (AFib) as well as heart failure symptoms were randomized to low-dose digoxin or the beta-blocker bisoprolol for rate control.
The open-label trial was designed to address a centuries-old unmet need: “Although digoxin has been in use since 1785, we have no longer-term clinical trials of digoxin in patients with AFib or AFib with heart failure,” noted Dr. Kotecha, professor of cardiology at the University of Birmingham (England).
Not only is digoxin greatly understudied in AFib, but permanent AFib – the most common form of the arrhythmia – has received only a tiny fraction of the research attention that’s been devoted to paroxysmal or persistent AFib, he added.
In RATE-AF, digoxin and bisoprolol proved similarly effective at reducing heart rate, from about 100 bpm at baseline to the mid-70s at 6 and 12 months. Notably, only a handful of study participants required an additional rate control drug during the 12-month study. Nor did the two drugs differ in terms of their impact on patient-reported quality of life at 6 months as reflected by their Short Form–36 physical component score, the primary study endpoint. And both drugs were well tolerated, with 96% of patients in the digoxin group still on the drug at a mean of 161 mcg/day at 6 months, and 89% still on their beta-blocker.
But that’s pretty much where the similarities in outcomes ended.
For example, at 12 months, the digoxin group scored significantly higher than the beta-blocker group on several domains of the Short Form–36 physical component score, including vitality, physical function, and global health. More than half of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement in modified European Heart Rhythm Association AFib-related symptoms at 6 months, compared with 10% of the beta-blocker group. At 12 months, nearly 70% of the digoxin group had a two-class improvement, as did 30% on bisoprolol.
Heart failure symptoms in the digoxin group improved from a mean baseline New York Heart Association class of 2.4 to 1.5 at both 6 and 12 months; the improvement was more modest in the beta-blocker group, going from NYHA 2.4 at baseline to 2.0 at both 6 and 12 months. And while N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide levels improved in the digoxin group from a baseline of 1,095 pg/mL to 1,058 at 6 months and 960 at 12 months, NT-proBNP actually went up in the beta-blocker group, from 1,041 to 1,209-1,250 pg/mL at 12 months.
Moreover, Dr. Kotecha continued, while RATE-AF was underpowered to assess clinical events, it’s nevertheless noteworthy that a total of 29 adverse events occurred in 12 months in the digoxin group, compared with 142 with beta-blocker therapy. There were 12 unplanned hospital admissions in the digoxin group and 28 in the beta-blocker group, and 22 primary care visits for either AFib or cardiovascular symptoms in patients on digoxin versus 64 in the beta-blocker group.
“Our results suggest a wider use of digoxin for stable patients with permanent AFib,” Dr. Kotecha concluded. However, in an interview, Jonathan Piccini, MD, had a different take on the study results.
“I don’t think this study should widely impact clinical practice in the U.S.,” according to Dr. Piccini, director of cardiac electrophysiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
His reservations included RATE-AF’s modest sample size as well as uncertainty as to the trial’s generalizability, given that bisoprolol isn’t much used in the United States. Also, these were elderly patients with shortness of breath, and it’s unclear how effective digoxin would be for rate control in patients with permanent AFib who are more active.
“The classic teaching is that digoxin is great for rate control at rest, but when people are active it’s not nearly as good as beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” the cardiologist said.
“A beta-blocker is still going to be my first-line rate control agent. But the results of RATE-AF do open my mind that for an older sedentary patient I may very well think twice now about using digoxin, because in that situation it looks like it achieves similar goals as a beta-blocker,” Dr. Piccini added.
On the plus side for RATE-AF: “I am very pleased to see that we have a randomized controlled trial focused on rate control in permanent AFib. It also tickles me pink to see a randomized, controlled study of digoxin. And I’m really excited to see a clinical trial that focuses on quality of life. It should give some confidence to know that from a quality of life perspective clinicians can consider using either digoxin or a beta-blocker for rate control,” he said.
American College of Cardiology vice president Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, said she’d need to see a much larger randomized trial including a calcium-channel blocker as a third-rate control arm before she’d consider digoxin as first-line rate control therapy in patients with AFib with or without heart failure. Also, she has reservations about drawing definitive conclusions from an open, unblinded study in which patient-reported outcomes are the primary endpoint.
“I think these were surprising findings given what we all think about digoxin in this country. In general, digoxin fell out of favor for rate control, mainly because of observational studies showing increased mortality. So most of us choose a beta-blocker,” she observed in an interview.
But of course, a randomized trial, even a 160-patient randomized trial, constitutes a higher level of evidence.
“I don’t think I’m going to convert tomorrow and make digoxin my first-line rate control therapy without more data. But RATE-AF does makes me stop and think about using it more than I did before in some of my permanent AFib patients,” said Dr. Itchhaporia, director of disease management at Hoag Memorial Hospital in Newport Beach, Calif.
Dr. Kotecha reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, which was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research, the British Heart Foundation, and the European Union.
REPORTING FROM ESC CONGRESS 2020
COVID-19 at home: What does optimal care look like?
Marilyn Stebbins, PharmD, fell ill at the end of February 2020. Initially diagnosed with multifocal pneumonia and treated with antibiotics, she later developed severe gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, and shortness of breath. She was hospitalized in early March and was diagnosed with COVID-19.
It was still early in the pandemic, and testing was not available for her husband. After she was discharged, her husband isolated himself as much as possible. But that limited the amount of care he could offer.
“When I came home after 8 days in the ICU, I felt completely alone and terrified of not being able to care for myself and not knowing how much care my husband could provide,” said Dr. Stebbins, professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco.
“I can’t even imagine what it would have been like if I had been home alone without my husband in the house,” she said. “I think about the people who died at home and understand how that might happen.”
Dr. Stebbins is one of tens of thousands of people who, whether hospitalized and discharged or never admitted for inpatient care, needed to find ways to convalesce at home. Data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services show that, of 326,674 beneficiaries who tested positive for COVID-19 between May 16 and June 11, 2020, 109,607 were hospitalized, suggesting that two-thirds were outpatients.
Most attention has focused on the sickest patients, leaving less severe cases to fall through the cracks. Despite fever, cough, difficulty breathing, and a surfeit of other symptoms, there are few available resources and all too little support to help patients navigate the physical and emotional struggles of contending with COVID-19 at home.
No ‘cookie-cutter’ approach
The speed with which the pandemic progressed caught public health systems off guard, but now, “it is essential to put into place the infrastructure to care for the physical and mental health needs of patients at home because most are in the community and many, if not most, still aren’t receiving sufficient support at home,” said Dr. Stebbins.
said Gary LeRoy, MD, a family physician in Dayton, Ohio. He emphasized that there is “no cookie-cutter formula” for home care, because every patient’s situation is different.
“I begin by having a detailed conversation with each patient to ascertain whether their home environment is safe and to paint a picture of their circumstances,” Dr. LeRoy, who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview.
Dr. LeRoy suggested questions that constitute “not just a ‘medical’ checklist but a ‘whole life’ checklist.”
- Do you have access to food, water, medications, sanitation/cleaning supplies, a thermometer, and other necessities? If not, who might assist in providing those?
- Do you need help with activities of daily living and self-care?
- Who else lives in your household? Do they have signs and symptoms of the virus? Have they been tested?
- Do you have enough physical space between you and other household members?
- Do you have children? How are they being cared for?
- What type of work do you do? What are the implications for your employment if you are unable to work for an extended period?
- Do you have an emotional, social, and spiritual support system (e.g., family, friends, community, church)?
- Do you have concerns I haven’t mentioned?
Patients’ responses will inform the management plan and determine what medical and social resources are needed, he said.
Daily check-in
Dr. Stebbins said the nurse case manager from her insurance company called her daily after she came home from the hospital. She was told that a public health nurse would also call, but no one from the health department called for days – a situation she hopes has improved.
One way or another, she said, “health care providers [or their staff] should check in with patients daily, either telephonically or via video.” She noted that video is superior, because “someone who isn’t a family member needs to put eyes on a patient and might be able to detect warning signs that a family member without healthcare training might not notice.”
Dr. LeRoy, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, said that, given his time constraints, a nurse or medical assistant in his practice conducts the daily check-ins and notifies him if the patient has fever or other symptoms.
“Under ordinary circumstances, when a patient comes to see me for some type of medical condition, I get to meet the patient, consider what might be going on, then order a test, wait for the results, and suggest a treatment plan. But these are anything but ordinary circumstances,” said Matthew Exline, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“That traditional structure broke down with COVID-19, when we may have test results without even seeing the patient. And without this interaction, it is harder to know as a physician what course of action to take,” he said in an interview.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the physician has at least some data to help guide next steps, even if there has been no prior meeting with the patient.
For example, a positive test raises a host of issues, not the least of which is the risk of spreading the infection to other household members and questions about whether to go the hospital. Moreover, for patients, positive tests can have serious ramifications.
“Severe shortness of breath at rest is not typical of the flu, nor is loss of taste or smell,” said Dr. Exline. Practitioners must educate patients and families about specific symptoms of COVID-19, including shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, and gastrointestinal or neurologic symptoms, and when to seek emergency care.
Dr. LeRoy suggests buying a pulse oximeter to gauge blood oxygen levels and pulse rate. Together with a thermometer, a portable blood pressure monitor, and, if indicated, a blood glucose monitor, these devices provide a comprehensive and accurate assessment of vital signs.
Dr. LeRoy also educates patients and their families about when to seek medical attention.
Dr. Stebbins takes a similar approach. “Family members are part of, not apart from, the care of patients with COVID-19, and it’s our responsibility as healthcare providers to consider them in the patient’s care plan.”
Keeping family safe
Beyond care, family members need a plan to keep themselves healthy, too.
“A patient with COVID-19 at home should self-quarantine as much as possible to keep other family members safe, if they continue to live in the same house,” Dr. Exline said.
Ideally, uninfected family members should stay with relatives or friends. When that’s not possible, everyone in the household should wear a mask, be vigilant about hand washing, and wipe down all surfaces – including doorknobs, light switches, faucet handles, cellphones, and utensils – regularly with bleach or an alcohol solution.
Caregivers should also minimize the amount of time they are exposed to the patient.
“Set food, water, and medication on the night table and leave the room rather than spending hours at the bedside, since limiting exposure to viral load reduces the chances of contagion,” said Dr. Exline.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers guidance for household members caring for COVID-19 patients at home. It provides tips on how to help patients follow the doctor’s instructions and ways to ensure adequate hydration and rest, among others.
Patients with COVID-19 who live alone face more formidable challenges.
Dr. LeRoy says physicians can help patients by educating themselves about available social services in their community so they can provide appropriate referrals and connections. Such initiatives can include meal programs, friendly visit and financial assistance programs, as well as childcare and home health agencies.
He noted that Aunt Bertha, a social care network, provides a guide to social services throughout the United States. Additional resources are available on USA.gov.
Comfort and support
Patients with COVID-19 need to be as comfortable and as supported as possible, both physically and emotionally.
“While I was sick, my dogs curled up next to me and didn’t leave my side, and they were my saving grace. There’s not enough to be said about emotional support,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Although important, emotional support is not enough. For patients with respiratory disorders, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, heart failure, or pneumonia, their subjective symptoms of shortness of breath, air hunger, or cough may improve with supplemental oxygen at home. Other measures include repositioning of the patient to lessen the body weight over the lungs or the use of lung percussion, Leroy said.
He added that improvement may also come from drainage of sputum from the airway passages, the use of agents to liquefy thick sputum (mucolytics), or aerosolized bronchodilator medications.
However, Dr. LeRoy cautioned, “one remedy does not work for everyone – an individual can improve gradually by using these home support interventions, or their respiratory status can deteriorate rapidly despite all these interventions.”
For this reason, he says patients should consult their personal physician to determine which, if any, of these home treatments would be best for their particular situation.
Patients who need emotional support, psychotherapy, or psychotropic medications may find teletherapy helpful. Guidance for psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers regarding the treatment of COVID-19 patients via teletherapy can be found on the American Psychiatric Association, the American Psychological Association, and the National Association of Social Workers websites.
Pharmacists can also help ensure patient safety, Dr. Stebbins said.
If a patient has not picked up their usual medications, Dr. Stebbins said, “they may need a check-in call. Some may be ill and alone and may need encouragement to seek medical attention, and some may have no means of getting to the pharmacy and may need medications delivered.”
A home healthcare agency may also be helpful for homebound patients. David Bersson, director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, N.J., has arranged in-home caregivers for patients with COVID-19.
The amount of care that professional caregivers provide can range from several hours per week to full-time, depending on the patient’s needs and budget, and can include companionship, Mr. Bersson said in an interview.
Because patient and caregiver safety are paramount, caregivers are thoroughly trained in protection and decontamination procedures and are regularly tested for COVID-19 prior to being sent into a client’s home.
Health insurance companies do not cover this service, Mr. Bersson noted, but the VetAssist program covers home care for veterans and their spouses who meet income requirements.
Caregiving and companionship are both vital pieces of the at-home care puzzle. “It was the virtual emotional support I got from friends, family, coworkers, and healthcare professionals that meant so much to me, and I know they played an important part in my recovery,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Dr. LeRoy agreed, noting that he calls patients, even if they only have mild symptoms and his nurse has already spoken to them. “The call doesn’t take much time – maybe just a 5-minute conversation – but it makes patients aware that I care.”
Dr. Stebbins, Dr. Exline, and Dr. LeRoy report no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Bersson is the director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, New Jersey.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Marilyn Stebbins, PharmD, fell ill at the end of February 2020. Initially diagnosed with multifocal pneumonia and treated with antibiotics, she later developed severe gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, and shortness of breath. She was hospitalized in early March and was diagnosed with COVID-19.
It was still early in the pandemic, and testing was not available for her husband. After she was discharged, her husband isolated himself as much as possible. But that limited the amount of care he could offer.
“When I came home after 8 days in the ICU, I felt completely alone and terrified of not being able to care for myself and not knowing how much care my husband could provide,” said Dr. Stebbins, professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco.
“I can’t even imagine what it would have been like if I had been home alone without my husband in the house,” she said. “I think about the people who died at home and understand how that might happen.”
Dr. Stebbins is one of tens of thousands of people who, whether hospitalized and discharged or never admitted for inpatient care, needed to find ways to convalesce at home. Data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services show that, of 326,674 beneficiaries who tested positive for COVID-19 between May 16 and June 11, 2020, 109,607 were hospitalized, suggesting that two-thirds were outpatients.
Most attention has focused on the sickest patients, leaving less severe cases to fall through the cracks. Despite fever, cough, difficulty breathing, and a surfeit of other symptoms, there are few available resources and all too little support to help patients navigate the physical and emotional struggles of contending with COVID-19 at home.
No ‘cookie-cutter’ approach
The speed with which the pandemic progressed caught public health systems off guard, but now, “it is essential to put into place the infrastructure to care for the physical and mental health needs of patients at home because most are in the community and many, if not most, still aren’t receiving sufficient support at home,” said Dr. Stebbins.
said Gary LeRoy, MD, a family physician in Dayton, Ohio. He emphasized that there is “no cookie-cutter formula” for home care, because every patient’s situation is different.
“I begin by having a detailed conversation with each patient to ascertain whether their home environment is safe and to paint a picture of their circumstances,” Dr. LeRoy, who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview.
Dr. LeRoy suggested questions that constitute “not just a ‘medical’ checklist but a ‘whole life’ checklist.”
- Do you have access to food, water, medications, sanitation/cleaning supplies, a thermometer, and other necessities? If not, who might assist in providing those?
- Do you need help with activities of daily living and self-care?
- Who else lives in your household? Do they have signs and symptoms of the virus? Have they been tested?
- Do you have enough physical space between you and other household members?
- Do you have children? How are they being cared for?
- What type of work do you do? What are the implications for your employment if you are unable to work for an extended period?
- Do you have an emotional, social, and spiritual support system (e.g., family, friends, community, church)?
- Do you have concerns I haven’t mentioned?
Patients’ responses will inform the management plan and determine what medical and social resources are needed, he said.
Daily check-in
Dr. Stebbins said the nurse case manager from her insurance company called her daily after she came home from the hospital. She was told that a public health nurse would also call, but no one from the health department called for days – a situation she hopes has improved.
One way or another, she said, “health care providers [or their staff] should check in with patients daily, either telephonically or via video.” She noted that video is superior, because “someone who isn’t a family member needs to put eyes on a patient and might be able to detect warning signs that a family member without healthcare training might not notice.”
Dr. LeRoy, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, said that, given his time constraints, a nurse or medical assistant in his practice conducts the daily check-ins and notifies him if the patient has fever or other symptoms.
“Under ordinary circumstances, when a patient comes to see me for some type of medical condition, I get to meet the patient, consider what might be going on, then order a test, wait for the results, and suggest a treatment plan. But these are anything but ordinary circumstances,” said Matthew Exline, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“That traditional structure broke down with COVID-19, when we may have test results without even seeing the patient. And without this interaction, it is harder to know as a physician what course of action to take,” he said in an interview.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the physician has at least some data to help guide next steps, even if there has been no prior meeting with the patient.
For example, a positive test raises a host of issues, not the least of which is the risk of spreading the infection to other household members and questions about whether to go the hospital. Moreover, for patients, positive tests can have serious ramifications.
“Severe shortness of breath at rest is not typical of the flu, nor is loss of taste or smell,” said Dr. Exline. Practitioners must educate patients and families about specific symptoms of COVID-19, including shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, and gastrointestinal or neurologic symptoms, and when to seek emergency care.
Dr. LeRoy suggests buying a pulse oximeter to gauge blood oxygen levels and pulse rate. Together with a thermometer, a portable blood pressure monitor, and, if indicated, a blood glucose monitor, these devices provide a comprehensive and accurate assessment of vital signs.
Dr. LeRoy also educates patients and their families about when to seek medical attention.
Dr. Stebbins takes a similar approach. “Family members are part of, not apart from, the care of patients with COVID-19, and it’s our responsibility as healthcare providers to consider them in the patient’s care plan.”
Keeping family safe
Beyond care, family members need a plan to keep themselves healthy, too.
“A patient with COVID-19 at home should self-quarantine as much as possible to keep other family members safe, if they continue to live in the same house,” Dr. Exline said.
Ideally, uninfected family members should stay with relatives or friends. When that’s not possible, everyone in the household should wear a mask, be vigilant about hand washing, and wipe down all surfaces – including doorknobs, light switches, faucet handles, cellphones, and utensils – regularly with bleach or an alcohol solution.
Caregivers should also minimize the amount of time they are exposed to the patient.
“Set food, water, and medication on the night table and leave the room rather than spending hours at the bedside, since limiting exposure to viral load reduces the chances of contagion,” said Dr. Exline.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers guidance for household members caring for COVID-19 patients at home. It provides tips on how to help patients follow the doctor’s instructions and ways to ensure adequate hydration and rest, among others.
Patients with COVID-19 who live alone face more formidable challenges.
Dr. LeRoy says physicians can help patients by educating themselves about available social services in their community so they can provide appropriate referrals and connections. Such initiatives can include meal programs, friendly visit and financial assistance programs, as well as childcare and home health agencies.
He noted that Aunt Bertha, a social care network, provides a guide to social services throughout the United States. Additional resources are available on USA.gov.
Comfort and support
Patients with COVID-19 need to be as comfortable and as supported as possible, both physically and emotionally.
“While I was sick, my dogs curled up next to me and didn’t leave my side, and they were my saving grace. There’s not enough to be said about emotional support,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Although important, emotional support is not enough. For patients with respiratory disorders, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, heart failure, or pneumonia, their subjective symptoms of shortness of breath, air hunger, or cough may improve with supplemental oxygen at home. Other measures include repositioning of the patient to lessen the body weight over the lungs or the use of lung percussion, Leroy said.
He added that improvement may also come from drainage of sputum from the airway passages, the use of agents to liquefy thick sputum (mucolytics), or aerosolized bronchodilator medications.
However, Dr. LeRoy cautioned, “one remedy does not work for everyone – an individual can improve gradually by using these home support interventions, or their respiratory status can deteriorate rapidly despite all these interventions.”
For this reason, he says patients should consult their personal physician to determine which, if any, of these home treatments would be best for their particular situation.
Patients who need emotional support, psychotherapy, or psychotropic medications may find teletherapy helpful. Guidance for psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers regarding the treatment of COVID-19 patients via teletherapy can be found on the American Psychiatric Association, the American Psychological Association, and the National Association of Social Workers websites.
Pharmacists can also help ensure patient safety, Dr. Stebbins said.
If a patient has not picked up their usual medications, Dr. Stebbins said, “they may need a check-in call. Some may be ill and alone and may need encouragement to seek medical attention, and some may have no means of getting to the pharmacy and may need medications delivered.”
A home healthcare agency may also be helpful for homebound patients. David Bersson, director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, N.J., has arranged in-home caregivers for patients with COVID-19.
The amount of care that professional caregivers provide can range from several hours per week to full-time, depending on the patient’s needs and budget, and can include companionship, Mr. Bersson said in an interview.
Because patient and caregiver safety are paramount, caregivers are thoroughly trained in protection and decontamination procedures and are regularly tested for COVID-19 prior to being sent into a client’s home.
Health insurance companies do not cover this service, Mr. Bersson noted, but the VetAssist program covers home care for veterans and their spouses who meet income requirements.
Caregiving and companionship are both vital pieces of the at-home care puzzle. “It was the virtual emotional support I got from friends, family, coworkers, and healthcare professionals that meant so much to me, and I know they played an important part in my recovery,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Dr. LeRoy agreed, noting that he calls patients, even if they only have mild symptoms and his nurse has already spoken to them. “The call doesn’t take much time – maybe just a 5-minute conversation – but it makes patients aware that I care.”
Dr. Stebbins, Dr. Exline, and Dr. LeRoy report no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Bersson is the director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, New Jersey.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Marilyn Stebbins, PharmD, fell ill at the end of February 2020. Initially diagnosed with multifocal pneumonia and treated with antibiotics, she later developed severe gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, and shortness of breath. She was hospitalized in early March and was diagnosed with COVID-19.
It was still early in the pandemic, and testing was not available for her husband. After she was discharged, her husband isolated himself as much as possible. But that limited the amount of care he could offer.
“When I came home after 8 days in the ICU, I felt completely alone and terrified of not being able to care for myself and not knowing how much care my husband could provide,” said Dr. Stebbins, professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco.
“I can’t even imagine what it would have been like if I had been home alone without my husband in the house,” she said. “I think about the people who died at home and understand how that might happen.”
Dr. Stebbins is one of tens of thousands of people who, whether hospitalized and discharged or never admitted for inpatient care, needed to find ways to convalesce at home. Data from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services show that, of 326,674 beneficiaries who tested positive for COVID-19 between May 16 and June 11, 2020, 109,607 were hospitalized, suggesting that two-thirds were outpatients.
Most attention has focused on the sickest patients, leaving less severe cases to fall through the cracks. Despite fever, cough, difficulty breathing, and a surfeit of other symptoms, there are few available resources and all too little support to help patients navigate the physical and emotional struggles of contending with COVID-19 at home.
No ‘cookie-cutter’ approach
The speed with which the pandemic progressed caught public health systems off guard, but now, “it is essential to put into place the infrastructure to care for the physical and mental health needs of patients at home because most are in the community and many, if not most, still aren’t receiving sufficient support at home,” said Dr. Stebbins.
said Gary LeRoy, MD, a family physician in Dayton, Ohio. He emphasized that there is “no cookie-cutter formula” for home care, because every patient’s situation is different.
“I begin by having a detailed conversation with each patient to ascertain whether their home environment is safe and to paint a picture of their circumstances,” Dr. LeRoy, who is the president of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said in an interview.
Dr. LeRoy suggested questions that constitute “not just a ‘medical’ checklist but a ‘whole life’ checklist.”
- Do you have access to food, water, medications, sanitation/cleaning supplies, a thermometer, and other necessities? If not, who might assist in providing those?
- Do you need help with activities of daily living and self-care?
- Who else lives in your household? Do they have signs and symptoms of the virus? Have they been tested?
- Do you have enough physical space between you and other household members?
- Do you have children? How are they being cared for?
- What type of work do you do? What are the implications for your employment if you are unable to work for an extended period?
- Do you have an emotional, social, and spiritual support system (e.g., family, friends, community, church)?
- Do you have concerns I haven’t mentioned?
Patients’ responses will inform the management plan and determine what medical and social resources are needed, he said.
Daily check-in
Dr. Stebbins said the nurse case manager from her insurance company called her daily after she came home from the hospital. She was told that a public health nurse would also call, but no one from the health department called for days – a situation she hopes has improved.
One way or another, she said, “health care providers [or their staff] should check in with patients daily, either telephonically or via video.” She noted that video is superior, because “someone who isn’t a family member needs to put eyes on a patient and might be able to detect warning signs that a family member without healthcare training might not notice.”
Dr. LeRoy, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio, said that, given his time constraints, a nurse or medical assistant in his practice conducts the daily check-ins and notifies him if the patient has fever or other symptoms.
“Under ordinary circumstances, when a patient comes to see me for some type of medical condition, I get to meet the patient, consider what might be going on, then order a test, wait for the results, and suggest a treatment plan. But these are anything but ordinary circumstances,” said Matthew Exline, MD, a pulmonary and critical care specialist at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“That traditional structure broke down with COVID-19, when we may have test results without even seeing the patient. And without this interaction, it is harder to know as a physician what course of action to take,” he said in an interview.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the physician has at least some data to help guide next steps, even if there has been no prior meeting with the patient.
For example, a positive test raises a host of issues, not the least of which is the risk of spreading the infection to other household members and questions about whether to go the hospital. Moreover, for patients, positive tests can have serious ramifications.
“Severe shortness of breath at rest is not typical of the flu, nor is loss of taste or smell,” said Dr. Exline. Practitioners must educate patients and families about specific symptoms of COVID-19, including shortness of breath, loss of taste or smell, and gastrointestinal or neurologic symptoms, and when to seek emergency care.
Dr. LeRoy suggests buying a pulse oximeter to gauge blood oxygen levels and pulse rate. Together with a thermometer, a portable blood pressure monitor, and, if indicated, a blood glucose monitor, these devices provide a comprehensive and accurate assessment of vital signs.
Dr. LeRoy also educates patients and their families about when to seek medical attention.
Dr. Stebbins takes a similar approach. “Family members are part of, not apart from, the care of patients with COVID-19, and it’s our responsibility as healthcare providers to consider them in the patient’s care plan.”
Keeping family safe
Beyond care, family members need a plan to keep themselves healthy, too.
“A patient with COVID-19 at home should self-quarantine as much as possible to keep other family members safe, if they continue to live in the same house,” Dr. Exline said.
Ideally, uninfected family members should stay with relatives or friends. When that’s not possible, everyone in the household should wear a mask, be vigilant about hand washing, and wipe down all surfaces – including doorknobs, light switches, faucet handles, cellphones, and utensils – regularly with bleach or an alcohol solution.
Caregivers should also minimize the amount of time they are exposed to the patient.
“Set food, water, and medication on the night table and leave the room rather than spending hours at the bedside, since limiting exposure to viral load reduces the chances of contagion,” said Dr. Exline.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers guidance for household members caring for COVID-19 patients at home. It provides tips on how to help patients follow the doctor’s instructions and ways to ensure adequate hydration and rest, among others.
Patients with COVID-19 who live alone face more formidable challenges.
Dr. LeRoy says physicians can help patients by educating themselves about available social services in their community so they can provide appropriate referrals and connections. Such initiatives can include meal programs, friendly visit and financial assistance programs, as well as childcare and home health agencies.
He noted that Aunt Bertha, a social care network, provides a guide to social services throughout the United States. Additional resources are available on USA.gov.
Comfort and support
Patients with COVID-19 need to be as comfortable and as supported as possible, both physically and emotionally.
“While I was sick, my dogs curled up next to me and didn’t leave my side, and they were my saving grace. There’s not enough to be said about emotional support,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Although important, emotional support is not enough. For patients with respiratory disorders, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, heart failure, or pneumonia, their subjective symptoms of shortness of breath, air hunger, or cough may improve with supplemental oxygen at home. Other measures include repositioning of the patient to lessen the body weight over the lungs or the use of lung percussion, Leroy said.
He added that improvement may also come from drainage of sputum from the airway passages, the use of agents to liquefy thick sputum (mucolytics), or aerosolized bronchodilator medications.
However, Dr. LeRoy cautioned, “one remedy does not work for everyone – an individual can improve gradually by using these home support interventions, or their respiratory status can deteriorate rapidly despite all these interventions.”
For this reason, he says patients should consult their personal physician to determine which, if any, of these home treatments would be best for their particular situation.
Patients who need emotional support, psychotherapy, or psychotropic medications may find teletherapy helpful. Guidance for psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers regarding the treatment of COVID-19 patients via teletherapy can be found on the American Psychiatric Association, the American Psychological Association, and the National Association of Social Workers websites.
Pharmacists can also help ensure patient safety, Dr. Stebbins said.
If a patient has not picked up their usual medications, Dr. Stebbins said, “they may need a check-in call. Some may be ill and alone and may need encouragement to seek medical attention, and some may have no means of getting to the pharmacy and may need medications delivered.”
A home healthcare agency may also be helpful for homebound patients. David Bersson, director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, N.J., has arranged in-home caregivers for patients with COVID-19.
The amount of care that professional caregivers provide can range from several hours per week to full-time, depending on the patient’s needs and budget, and can include companionship, Mr. Bersson said in an interview.
Because patient and caregiver safety are paramount, caregivers are thoroughly trained in protection and decontamination procedures and are regularly tested for COVID-19 prior to being sent into a client’s home.
Health insurance companies do not cover this service, Mr. Bersson noted, but the VetAssist program covers home care for veterans and their spouses who meet income requirements.
Caregiving and companionship are both vital pieces of the at-home care puzzle. “It was the virtual emotional support I got from friends, family, coworkers, and healthcare professionals that meant so much to me, and I know they played an important part in my recovery,” Dr. Stebbins said.
Dr. LeRoy agreed, noting that he calls patients, even if they only have mild symptoms and his nurse has already spoken to them. “The call doesn’t take much time – maybe just a 5-minute conversation – but it makes patients aware that I care.”
Dr. Stebbins, Dr. Exline, and Dr. LeRoy report no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Bersson is the director of operations at Synergy Home Care of Bergen County, New Jersey.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
New ESC/EACTS guideline on atrial fibrillation
New atrial fibrillation (AFib) management guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) call for diagnostic confirmation and structured characterization of AFib and the need to streamline integrated care with the Atrial fibrillation Better Care (ABC) pathway.
“It’s as simple as CC to ABC,” quipped one task force member during the virtual unveiling of the guidelines at the ESC Congress 2020.
The guidelines were developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and published simultaneously August 29 in the European Heart Journal.
Acknowledging the slew of novel screening tools now available and their reported sensitivity and specificity rates, the document supports opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse taking or electrocardiogram (ECG) rhythm strip in patients at least 65 years of age, with a class 1 recommendation, evidence level B.
Systematic ECG screening should also be considered to detect AFib in individuals at least 75 years of age or in those at high risk for stroke (class IIa, level B).
Other new class I screening recommendations are to inform individuals undergoing screening about the significance and treatment implications of detecting AFib and to have a structured referral platform in place for further physician-led evaluation.
A definite diagnosis of clinical AFib is established only after confirmation by a conventional 12-lead ECG or single-lead ECG strip with at least 30 seconds of AFib.
In line with ESC’s 2016 AFib guidelines, the new iteration classifies AFib as first diagnosed, paroxysmal, persistent, long-standing persistent, and permanent. But it’s also important to classify the clinical profile of AFib, task force member Giuseppe Boriani, MD, PhD, University of Modena, Italy, said in the first of five presentations.
“So the novelty of the 2020 guidelines is related to the proposal of the 4S-AF scheme for a structured characterization of atrial fibrillation that takes into account Stroke risk, severity of Symptoms, Severity of atrial fibrillation burden, and Substrate severity,” he said.
This represents a paradigm shift from a single-domain conventional classification of AFib toward a structured characterization that streamlines assessment, informs treatment decision-making, and facilitates communication among physicians of various specialties, said Tatjana Potpara, MD, PhD, guideline co-chair and head of the Department for Intensive Arrhythmia Care, Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade.
“The beauty of this approach is that, at present, the assessment of the ‘S’ components are performed using available tools, but in the future, the 4S-AF has a great potential to incorporate whatever becomes available for a more precision assessment of substrate or symptoms or arrhythmia burden and so forth,” she said.
ABC pathway
The guidelines advocate the previously described ABC pathway for integrated care management, which includes ‘A’ for Anticoagulation/Avoid stroke, ‘B’ for Better symptom control, and ‘C’ for Comorbidity/Cardiovascular risk factor optimization.
The document strengthens support for formal risk score–based assessment of bleeding risk in all patients, including use of the HAS-BLED score to help address modifiable bleeding risk factors and to identify patients at high bleeding risk (HAS-BLED score ≥3) for early and more frequent follow-up.
These assessments should be done regularly, given that both stroke and bleeding risk are dynamic and change over time with aging and comorbidities, Dr. Potpara stressed. In patients with AFib initially at low risk for stroke, the next assessment should be optimally performed at 4-6 months.
The guideline also targets weight loss in patients who are obese and have AFib, particularly those being evaluated for ablation, and good blood pressure control in patients with AFib and hypertension to reduce AFib recurrences and risk for stroke and bleeding (both class I, up from IIa).
It’s particularly important that these risk factors are addressed, and that modifiable risk factors that go along with increased AFib occurrence and persistence are addressed and communicated to patients, said Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, guideline cochair and medical director of the Rhythmology Department, Heart Centre Leipzig (Germany).
“I have to confess, as an interventional electrophysiologist, there has been a time where I have not appreciated these risk factors intensely enough,” he said. “But we have learned, also in the field of catheter ablation, that weight loss is an essential basis for a good procedure. If we can motivate patients to lose weight and then come to the intervention with better outcome, it’s a true benefit for the patient and addresses patient values. So I’m particularly happy we have introduced that with such intensity in the guidelines.”
Rate and rhythm control
The guidelines make no recommendation of one novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) over another. However, in patients already receiving vitamin K antagonists with low time in the therapeutic range, they recommend switching to a different NOAC but ensuring good adherence and persistence with therapy (class I recommendation) or efforts to improve time in therapeutic range (class IIa).
Catheter ablation takes on a more prominent role for rhythm control and is now recommended after one antiarrhythmic drug therapy fails to improve symptoms of AF recurrence in patients with paroxysmal AFib, or persistent AFib with or without major risk factors for recurrence. The class I recommendation is based on results from the CAPTAF and CABANA trials, said task force member Carina Blomström-Lundqvist, MD, PhD, Uppsala University, Sweden.
Catheter ablation is also now a first-line therapy for patients with AFib who have a high likelihood of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, independent of symptom status. “In this subset of patients, catheter ablation may offer a lot with respect to restoration of left ventricular function,” observed Dr. Hindricks.
Complete electrical isolation of the pulmonary veins is recommended during all AFib catheter ablation procedures (class I).
“Even as a medical conservative, I think it is totally reasonable to move to catheter ablation after a failed drug trial,” commented John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Ky., who was not a part of the guideline development.
Although the chance of a second drug working after one failure is low, he noted that operators in the United States have dofetilide, which is not used much in Europe, and sometimes works surprisingly well.
“That said, the caveat is that moving to catheter ablation after drug failure is only appropriate if we have addressed all the pertinent risk factors: sleep apnea, weight loss, lack of fitness, blood pressure control, and alcohol excess,” he said.
As for tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy, this too can be reasonable, Dr. Mandrola said. “I often get people ‘out of a hole’ with amiodarone plus cardioversion for a few months and then proceed to ablation.”
Notably, the 2020 iteration sharpens its recommendation that amiodarone not be used first-line for long-term rhythm control in all patients with AFib, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, given its extracardiac toxicity (class I, up from IIa).
Quality counts
In response to growing evidence that guideline-adherence is associated with significantly better outcomes in AFib, the 2020 ESC/EACTS guidelines explicitly included a recommendation on the need to measure quality of care to identify opportunities for improvement.
With this framework in mind, a task force with 23 people – including members from ESC and heart rhythm societies in the United States, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, along with patient representatives – was created to develop a list of quality indicators (QIs), ultimately settling on 17 main QIs and 17 secondary ones, said Elena Arbelo, MD, PhD, MSc, University of Barcelona.
The QIs are classified into six domains: patient assessment, anticoagulation, rate control, rhythm control, risk factor modification, and, importantly, outcome measures. A full list is accessible in a paper, simultaneously published in EP EuroPace.
Five patient-reported outcomes fall under the outcomes domain but only one – health-related quality of life – is a main quality indicator. The remaining outcomes are still important but are listed as secondary because of the lack of evidence to sustain or defend their systematic implementation, particularly evidence on how to measure them appropriately, Dr. Arbelo said.
“Hopefully, following the [class I] recommendation by the 2020 ESC guidelines to routinely collect patient-reported outcomes will allow us to collect further evidence and in the future have sufficient evidence to include these as a main outcome,” she said.
The QI work was driven in parallel with the guidelines and had a huge impact on its development, including inclusion of clear recommendations on how to measure quality, Dr. Hindricks said. “I believe that the whole issue of quality management in the treatment of patients with a focus on patient values cannot be overestimated.”
Disclosure information for all writing committee members is in the report. Dr. Mandrola is a writer and podcaster for Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New atrial fibrillation (AFib) management guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) call for diagnostic confirmation and structured characterization of AFib and the need to streamline integrated care with the Atrial fibrillation Better Care (ABC) pathway.
“It’s as simple as CC to ABC,” quipped one task force member during the virtual unveiling of the guidelines at the ESC Congress 2020.
The guidelines were developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and published simultaneously August 29 in the European Heart Journal.
Acknowledging the slew of novel screening tools now available and their reported sensitivity and specificity rates, the document supports opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse taking or electrocardiogram (ECG) rhythm strip in patients at least 65 years of age, with a class 1 recommendation, evidence level B.
Systematic ECG screening should also be considered to detect AFib in individuals at least 75 years of age or in those at high risk for stroke (class IIa, level B).
Other new class I screening recommendations are to inform individuals undergoing screening about the significance and treatment implications of detecting AFib and to have a structured referral platform in place for further physician-led evaluation.
A definite diagnosis of clinical AFib is established only after confirmation by a conventional 12-lead ECG or single-lead ECG strip with at least 30 seconds of AFib.
In line with ESC’s 2016 AFib guidelines, the new iteration classifies AFib as first diagnosed, paroxysmal, persistent, long-standing persistent, and permanent. But it’s also important to classify the clinical profile of AFib, task force member Giuseppe Boriani, MD, PhD, University of Modena, Italy, said in the first of five presentations.
“So the novelty of the 2020 guidelines is related to the proposal of the 4S-AF scheme for a structured characterization of atrial fibrillation that takes into account Stroke risk, severity of Symptoms, Severity of atrial fibrillation burden, and Substrate severity,” he said.
This represents a paradigm shift from a single-domain conventional classification of AFib toward a structured characterization that streamlines assessment, informs treatment decision-making, and facilitates communication among physicians of various specialties, said Tatjana Potpara, MD, PhD, guideline co-chair and head of the Department for Intensive Arrhythmia Care, Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade.
“The beauty of this approach is that, at present, the assessment of the ‘S’ components are performed using available tools, but in the future, the 4S-AF has a great potential to incorporate whatever becomes available for a more precision assessment of substrate or symptoms or arrhythmia burden and so forth,” she said.
ABC pathway
The guidelines advocate the previously described ABC pathway for integrated care management, which includes ‘A’ for Anticoagulation/Avoid stroke, ‘B’ for Better symptom control, and ‘C’ for Comorbidity/Cardiovascular risk factor optimization.
The document strengthens support for formal risk score–based assessment of bleeding risk in all patients, including use of the HAS-BLED score to help address modifiable bleeding risk factors and to identify patients at high bleeding risk (HAS-BLED score ≥3) for early and more frequent follow-up.
These assessments should be done regularly, given that both stroke and bleeding risk are dynamic and change over time with aging and comorbidities, Dr. Potpara stressed. In patients with AFib initially at low risk for stroke, the next assessment should be optimally performed at 4-6 months.
The guideline also targets weight loss in patients who are obese and have AFib, particularly those being evaluated for ablation, and good blood pressure control in patients with AFib and hypertension to reduce AFib recurrences and risk for stroke and bleeding (both class I, up from IIa).
It’s particularly important that these risk factors are addressed, and that modifiable risk factors that go along with increased AFib occurrence and persistence are addressed and communicated to patients, said Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, guideline cochair and medical director of the Rhythmology Department, Heart Centre Leipzig (Germany).
“I have to confess, as an interventional electrophysiologist, there has been a time where I have not appreciated these risk factors intensely enough,” he said. “But we have learned, also in the field of catheter ablation, that weight loss is an essential basis for a good procedure. If we can motivate patients to lose weight and then come to the intervention with better outcome, it’s a true benefit for the patient and addresses patient values. So I’m particularly happy we have introduced that with such intensity in the guidelines.”
Rate and rhythm control
The guidelines make no recommendation of one novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) over another. However, in patients already receiving vitamin K antagonists with low time in the therapeutic range, they recommend switching to a different NOAC but ensuring good adherence and persistence with therapy (class I recommendation) or efforts to improve time in therapeutic range (class IIa).
Catheter ablation takes on a more prominent role for rhythm control and is now recommended after one antiarrhythmic drug therapy fails to improve symptoms of AF recurrence in patients with paroxysmal AFib, or persistent AFib with or without major risk factors for recurrence. The class I recommendation is based on results from the CAPTAF and CABANA trials, said task force member Carina Blomström-Lundqvist, MD, PhD, Uppsala University, Sweden.
Catheter ablation is also now a first-line therapy for patients with AFib who have a high likelihood of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, independent of symptom status. “In this subset of patients, catheter ablation may offer a lot with respect to restoration of left ventricular function,” observed Dr. Hindricks.
Complete electrical isolation of the pulmonary veins is recommended during all AFib catheter ablation procedures (class I).
“Even as a medical conservative, I think it is totally reasonable to move to catheter ablation after a failed drug trial,” commented John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Ky., who was not a part of the guideline development.
Although the chance of a second drug working after one failure is low, he noted that operators in the United States have dofetilide, which is not used much in Europe, and sometimes works surprisingly well.
“That said, the caveat is that moving to catheter ablation after drug failure is only appropriate if we have addressed all the pertinent risk factors: sleep apnea, weight loss, lack of fitness, blood pressure control, and alcohol excess,” he said.
As for tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy, this too can be reasonable, Dr. Mandrola said. “I often get people ‘out of a hole’ with amiodarone plus cardioversion for a few months and then proceed to ablation.”
Notably, the 2020 iteration sharpens its recommendation that amiodarone not be used first-line for long-term rhythm control in all patients with AFib, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, given its extracardiac toxicity (class I, up from IIa).
Quality counts
In response to growing evidence that guideline-adherence is associated with significantly better outcomes in AFib, the 2020 ESC/EACTS guidelines explicitly included a recommendation on the need to measure quality of care to identify opportunities for improvement.
With this framework in mind, a task force with 23 people – including members from ESC and heart rhythm societies in the United States, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, along with patient representatives – was created to develop a list of quality indicators (QIs), ultimately settling on 17 main QIs and 17 secondary ones, said Elena Arbelo, MD, PhD, MSc, University of Barcelona.
The QIs are classified into six domains: patient assessment, anticoagulation, rate control, rhythm control, risk factor modification, and, importantly, outcome measures. A full list is accessible in a paper, simultaneously published in EP EuroPace.
Five patient-reported outcomes fall under the outcomes domain but only one – health-related quality of life – is a main quality indicator. The remaining outcomes are still important but are listed as secondary because of the lack of evidence to sustain or defend their systematic implementation, particularly evidence on how to measure them appropriately, Dr. Arbelo said.
“Hopefully, following the [class I] recommendation by the 2020 ESC guidelines to routinely collect patient-reported outcomes will allow us to collect further evidence and in the future have sufficient evidence to include these as a main outcome,” she said.
The QI work was driven in parallel with the guidelines and had a huge impact on its development, including inclusion of clear recommendations on how to measure quality, Dr. Hindricks said. “I believe that the whole issue of quality management in the treatment of patients with a focus on patient values cannot be overestimated.”
Disclosure information for all writing committee members is in the report. Dr. Mandrola is a writer and podcaster for Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New atrial fibrillation (AFib) management guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) call for diagnostic confirmation and structured characterization of AFib and the need to streamline integrated care with the Atrial fibrillation Better Care (ABC) pathway.
“It’s as simple as CC to ABC,” quipped one task force member during the virtual unveiling of the guidelines at the ESC Congress 2020.
The guidelines were developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and published simultaneously August 29 in the European Heart Journal.
Acknowledging the slew of novel screening tools now available and their reported sensitivity and specificity rates, the document supports opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse taking or electrocardiogram (ECG) rhythm strip in patients at least 65 years of age, with a class 1 recommendation, evidence level B.
Systematic ECG screening should also be considered to detect AFib in individuals at least 75 years of age or in those at high risk for stroke (class IIa, level B).
Other new class I screening recommendations are to inform individuals undergoing screening about the significance and treatment implications of detecting AFib and to have a structured referral platform in place for further physician-led evaluation.
A definite diagnosis of clinical AFib is established only after confirmation by a conventional 12-lead ECG or single-lead ECG strip with at least 30 seconds of AFib.
In line with ESC’s 2016 AFib guidelines, the new iteration classifies AFib as first diagnosed, paroxysmal, persistent, long-standing persistent, and permanent. But it’s also important to classify the clinical profile of AFib, task force member Giuseppe Boriani, MD, PhD, University of Modena, Italy, said in the first of five presentations.
“So the novelty of the 2020 guidelines is related to the proposal of the 4S-AF scheme for a structured characterization of atrial fibrillation that takes into account Stroke risk, severity of Symptoms, Severity of atrial fibrillation burden, and Substrate severity,” he said.
This represents a paradigm shift from a single-domain conventional classification of AFib toward a structured characterization that streamlines assessment, informs treatment decision-making, and facilitates communication among physicians of various specialties, said Tatjana Potpara, MD, PhD, guideline co-chair and head of the Department for Intensive Arrhythmia Care, Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade.
“The beauty of this approach is that, at present, the assessment of the ‘S’ components are performed using available tools, but in the future, the 4S-AF has a great potential to incorporate whatever becomes available for a more precision assessment of substrate or symptoms or arrhythmia burden and so forth,” she said.
ABC pathway
The guidelines advocate the previously described ABC pathway for integrated care management, which includes ‘A’ for Anticoagulation/Avoid stroke, ‘B’ for Better symptom control, and ‘C’ for Comorbidity/Cardiovascular risk factor optimization.
The document strengthens support for formal risk score–based assessment of bleeding risk in all patients, including use of the HAS-BLED score to help address modifiable bleeding risk factors and to identify patients at high bleeding risk (HAS-BLED score ≥3) for early and more frequent follow-up.
These assessments should be done regularly, given that both stroke and bleeding risk are dynamic and change over time with aging and comorbidities, Dr. Potpara stressed. In patients with AFib initially at low risk for stroke, the next assessment should be optimally performed at 4-6 months.
The guideline also targets weight loss in patients who are obese and have AFib, particularly those being evaluated for ablation, and good blood pressure control in patients with AFib and hypertension to reduce AFib recurrences and risk for stroke and bleeding (both class I, up from IIa).
It’s particularly important that these risk factors are addressed, and that modifiable risk factors that go along with increased AFib occurrence and persistence are addressed and communicated to patients, said Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, guideline cochair and medical director of the Rhythmology Department, Heart Centre Leipzig (Germany).
“I have to confess, as an interventional electrophysiologist, there has been a time where I have not appreciated these risk factors intensely enough,” he said. “But we have learned, also in the field of catheter ablation, that weight loss is an essential basis for a good procedure. If we can motivate patients to lose weight and then come to the intervention with better outcome, it’s a true benefit for the patient and addresses patient values. So I’m particularly happy we have introduced that with such intensity in the guidelines.”
Rate and rhythm control
The guidelines make no recommendation of one novel oral anticoagulant (NOAC) over another. However, in patients already receiving vitamin K antagonists with low time in the therapeutic range, they recommend switching to a different NOAC but ensuring good adherence and persistence with therapy (class I recommendation) or efforts to improve time in therapeutic range (class IIa).
Catheter ablation takes on a more prominent role for rhythm control and is now recommended after one antiarrhythmic drug therapy fails to improve symptoms of AF recurrence in patients with paroxysmal AFib, or persistent AFib with or without major risk factors for recurrence. The class I recommendation is based on results from the CAPTAF and CABANA trials, said task force member Carina Blomström-Lundqvist, MD, PhD, Uppsala University, Sweden.
Catheter ablation is also now a first-line therapy for patients with AFib who have a high likelihood of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, independent of symptom status. “In this subset of patients, catheter ablation may offer a lot with respect to restoration of left ventricular function,” observed Dr. Hindricks.
Complete electrical isolation of the pulmonary veins is recommended during all AFib catheter ablation procedures (class I).
“Even as a medical conservative, I think it is totally reasonable to move to catheter ablation after a failed drug trial,” commented John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Ky., who was not a part of the guideline development.
Although the chance of a second drug working after one failure is low, he noted that operators in the United States have dofetilide, which is not used much in Europe, and sometimes works surprisingly well.
“That said, the caveat is that moving to catheter ablation after drug failure is only appropriate if we have addressed all the pertinent risk factors: sleep apnea, weight loss, lack of fitness, blood pressure control, and alcohol excess,” he said.
As for tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy, this too can be reasonable, Dr. Mandrola said. “I often get people ‘out of a hole’ with amiodarone plus cardioversion for a few months and then proceed to ablation.”
Notably, the 2020 iteration sharpens its recommendation that amiodarone not be used first-line for long-term rhythm control in all patients with AFib, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, given its extracardiac toxicity (class I, up from IIa).
Quality counts
In response to growing evidence that guideline-adherence is associated with significantly better outcomes in AFib, the 2020 ESC/EACTS guidelines explicitly included a recommendation on the need to measure quality of care to identify opportunities for improvement.
With this framework in mind, a task force with 23 people – including members from ESC and heart rhythm societies in the United States, Asia Pacific, and Latin America, along with patient representatives – was created to develop a list of quality indicators (QIs), ultimately settling on 17 main QIs and 17 secondary ones, said Elena Arbelo, MD, PhD, MSc, University of Barcelona.
The QIs are classified into six domains: patient assessment, anticoagulation, rate control, rhythm control, risk factor modification, and, importantly, outcome measures. A full list is accessible in a paper, simultaneously published in EP EuroPace.
Five patient-reported outcomes fall under the outcomes domain but only one – health-related quality of life – is a main quality indicator. The remaining outcomes are still important but are listed as secondary because of the lack of evidence to sustain or defend their systematic implementation, particularly evidence on how to measure them appropriately, Dr. Arbelo said.
“Hopefully, following the [class I] recommendation by the 2020 ESC guidelines to routinely collect patient-reported outcomes will allow us to collect further evidence and in the future have sufficient evidence to include these as a main outcome,” she said.
The QI work was driven in parallel with the guidelines and had a huge impact on its development, including inclusion of clear recommendations on how to measure quality, Dr. Hindricks said. “I believe that the whole issue of quality management in the treatment of patients with a focus on patient values cannot be overestimated.”
Disclosure information for all writing committee members is in the report. Dr. Mandrola is a writer and podcaster for Medscape.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
EXPLORER trial hints at potential new drug option in obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
An investigational drug that targets part of the molecular machinery underlying obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) can improve both symptoms and functional status in patients with the genetic disorder, suggests a placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.
Treatment with mavacamten (MyoKardia) worked partly by alleviating high-pressure gradients in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), a key characteristic of obstructive HCM. Its effects appeared consistent across a wide range of objective and patient-assessed endpoints.
Mavacamten is “the first potential medical therapy addressing the underlying biology of symptoms in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” observed Iacopo Olivotto, MD, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy.
Patients in the EXPLORER-HCM trial who took the new drug showed improvements in “every aspect of objective performance and subjective well-being,” Dr. Olivotto said at a preview for journalists before his formal online presentation of the results during the virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2020, staged in lieu of the traditional annual meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Olivotto, also lead author on the study’s same-day publication in The Lancet, was exuberant about the findings. “It is really hard to convey what this actually means for a scientific and clinical community that has spent over 60 years trying to understand and cure hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.”
MyoKardia released abbreviated top-line results of EXPLORER-HCM in May, which were reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology at the time.
“I think it’s pretty exciting. We certainly need more and better drugs for this patient population,” Arnon Adler, MD, who is not associated with the trial but follows HCM at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, Toronto General Hospital, said in an interview.
The trial compared the new drug to placebo rather than full contemporary drug therapy for obstructive HCM, Adler cautioned, and had a fairly short follow-up time. But he was impressed that mavacamten’s apparent benefits seemed consistent not only for endpoints like change in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class and quality of life but also for more objective measures like peak VO2 and LVOT gradients.
“I think the results were promising across the board,” he told.
Unique mechanism of action
Mavacamten is described as a first-in-class, small-molecule, selective allosteric inhibitor of cardiac myosin adenosine triphosphatase that addresses the underlying pathophysiology of HCM by reducing actin–myosin cross-bridge formation. It thereby inhibits the excessive myocyte contractility that is a key mechanism of the disorder’s tell-tale hypertrophy, something the available HCM drug therapies don’t do.
Almost three-fourths of patients in the trial were initially in NYHA class 2. Such patients in practice tend to be treated pharmacologically, with more invasive but generally effective surgical myectomy and alcohol septal ablation performed more often for patients in NYHA class 3.
“In the EXPLORER-HCM trial, patients enrolled did not have any immediate indication for surgery,” although many of them in NYHA class 2 would likely progress to NYHA 3, Dr. Olivotto said in an interview.
Based on the trial, he said, it’s possible that mavacamten could lead to “earlier and broader treatment of obstruction symptoms in patients who would never have qualified for surgery in the first place because their symptoms may not be severe enough, but they are still limited.”
Notably, the published report notes, 27% of patients taking mavacamten achieved what was defined as a complete response – that is, a reduction of all LVOT gradients to less than 30 mm Hg in the total absence of symptoms.
Only 1% of patients in the placebo-treated control group met that goal, “showing that mavacamten might be capable of achieving marked relief of symptoms and LVOT obstruction,” the report states.
In the trial, “treatment with mavacamten led to clinically meaningful improvements in hemodynamic status, functional capacity, and subjective well-being in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” agrees an editorial accompanying the EXPLORER-HCM publication.
Mavacamten might even compare favorably to surgery and ablative therapy, speculated the editorialists, Michael Papadakis, MBBS, MD, and colleagues of St. George’s University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London. The drug appeared to reduce the peak LVOT gradient “to less than the guideline-based threshold for septal reduction therapy, 50 mm Hg, in 74% of patients, compared with 21% in the placebo group, indicating that mavacamten could represent a valid alternative to highly specialized invasive therapy,” they wrote.
Standard drug therapy
“There are approved drugs for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, but they are ancient and were developed for other diseases,” observed Dr. Olivotto at the media briefing. Those drug options – primarily beta-blockers, nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers, and the sodium-channel blocker disopyramide – are often ineffective or cause onerous side effects, he said.
Notably in EXPLORER-HCM, patients in both the mavacamten and placebo groups could also be receiving beta-blockers and calcium-channel blockers, but no one in the trial could be receiving disopyramide, which can prolong the QT interval.
“By design,” mavacamten wasn’t compared to disopyramide, “a much more potent drug for lowering gradient and improving symptoms than beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” said Martin S. Maron, MD, medical director at the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Center and Research Institute, Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
Therefore, the trial’s results can’t be extrapolated to conclude that the new drug is superior to disopyramide “or the gold standard, surgical myectomy,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Adler agreed that observational studies suggest a benefit from disopyramide that may rival the apparent effect of mavacamten. “But of course, you can’t make direct comparisons because we never had a study like this for disopyramide.” Because it has many side effects and limitations, “it’s not a drug that I like using, but it is beneficial for some patients and I do use it quite a bit.”
What EXPLORER-HCM does seem to show, Dr. Maron said, “is that the mechanism of action of the drug does seem to play out. It lowers gradients in a pretty reliable and powerful way, and that translates into clinical improvement in many patients. So it starts to support the idea that this drug and the class of drugs, myosin inhibitors, may represent another medical therapy option for symptomatic obstructive HCM.”
And, he pointed out, about one-fifth of patients with obstructive HCM don’t respond to disopyramide with fewer symptoms, and in others the drug “starts to lose efficacy over time.” So disopyramide has limitations, and EXPLORER-HCM “provides the possibility of an additional drug option.”
EXPLORER-HCM randomly assigned 251 adults with obstructive HCM in 13 countries to receive mavacamten, titrated from a starting dosage of 5 mg/day to a possible 15 mg/day or to placebo for 30 weeks.
The patients were required to have a peak LVOT gradient at least 50 mm Hg, a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 55%, and symptoms indicating NYHA class 2 or 3; ultimately, 73% started the trial in NYHA class 2.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 36.6% of patients receiving mavacamten and 17.2% of control patients met the composite primary endpoint (P = .0005), which consisted of either a 1.5–mL/kg per minute or greater improvement in peak oxygen consumption (pVO2) and at least a one-step reduction in NYHA functional class or at least a 3.0–mL/kg per minute pVO2 increase without deterioration in NYHA class, by week 30.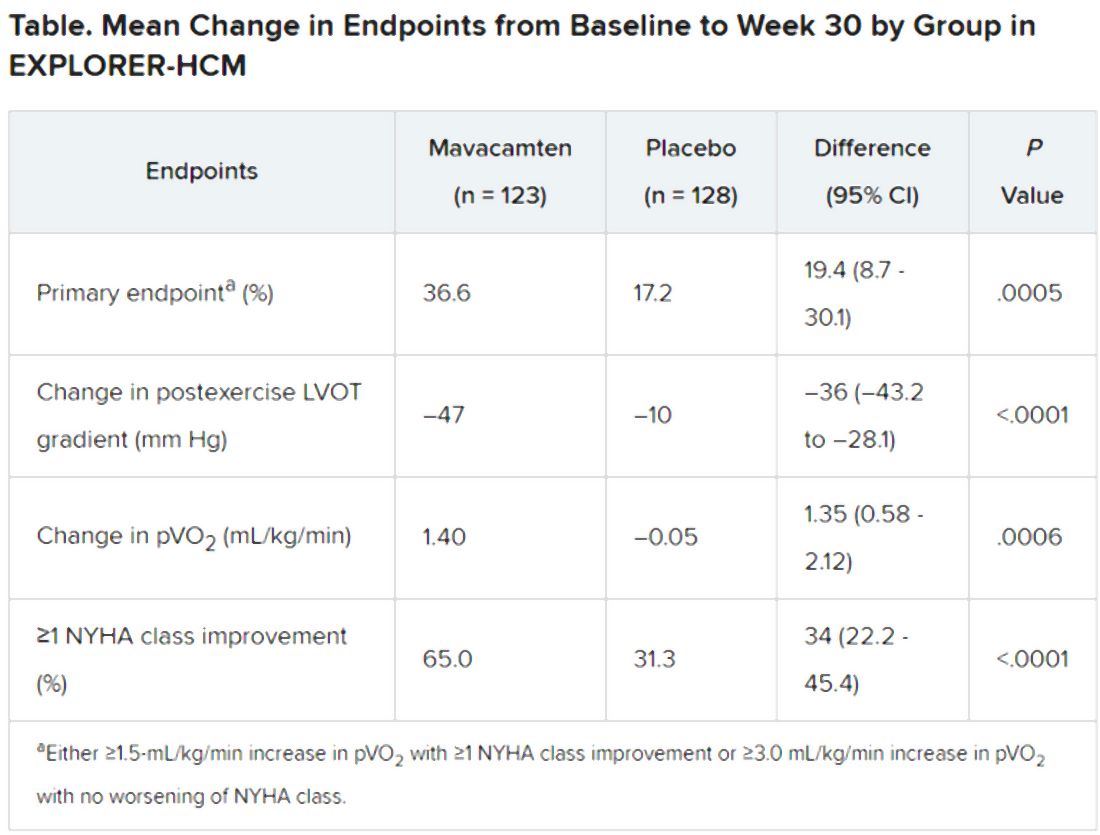
Patients receiving mavacamten also showed greater improvement in the individual endpoints of postexercise LVOT gradient, NYHA class, and two score-based symptom assessments – the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Clinical Summary and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Symptom Questionnaire Shortness-of-Breath domain – compared with control patients.
Safety and tolerability issues were similar in both groups, the reports notes. Ten patients in the mavacamten group reported 11 serious adverse events, compared with 20 such events reported by 11 patients in the control group.
“We can say from these results that mavacamten is a promising drug for symptom relief and functional class improvement associated with outflow gradient reduction in selected patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” and that, on the basis of this trial, it has potential as a drug of first choice, Franco Cecchi, MD, University of Florence (Italy), said as an invited discussant following Dr. Olivotto’s formal presentation of the trial.
Although serious adverse events were few, it was noteworthy that seven patients receiving mavacamten but only two patients receiving placebo showed LVEF reductions to below the 50% threshold during the trial, Dr. Cecchi observed. The LVEFs normalized once the drug was discontinued, but still, it may mean that mavacamten should be carefully uptitrated according to LVEF, he said.
Those LVEF reductions raise questions about “the reliability of being able to dose patients safely in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Maron said. “You have to ask, ‘Can this be extrapolated to the general practicing community without patients dropping their ejection fractions too much?’ ”
In addition, “we don’t have any idea about long-term efficacy for this drug, and we can draw very limited information about long-term safety here as well. That’s another other question mark,” Dr. Maron said.
“If I could have patients really become asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic without any surgery on a drug that is safe and can be taken for a prolonged period of time, that would be great,” Dr. Adler added. He noted that long-term follow-up of patients taking mavacamten in various trials has been underway and should help answer safety and efficacy questions about chronic therapy.
“Should mavacamten prove to be clinically effective and safe following long-term therapy in a larger and more diverse population, it would represent a much anticipated development in the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” the accompanying editorial states.
“Were the drug to realise its potential as a disease-modifying therapy in younger individuals, it would represent a great milestone in the area of inherited cardiomyopathies.”
MyoKardia funded EXPLORER-HCM. Dr. Olivotto discloses receiving grants from MyoKardia, Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, Amicus, and Bayer; honoraria from Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, and Bayer; and payments for consulting from MyoKardia. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Papadakis and the other editorialists report that they have no competing interests. Dr. Adler had no disclosures. Dr. Maron discloses consulting for and serving on a trial steering committee for Cytokinetics, sponsor of the 60-patient phase 2 placebo-controlled trial REDWOOD-HCM of patients with obstructive HCM treated with CK-3773274, a drug that works by a mechanism similar to that of mavacamten.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An investigational drug that targets part of the molecular machinery underlying obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) can improve both symptoms and functional status in patients with the genetic disorder, suggests a placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.
Treatment with mavacamten (MyoKardia) worked partly by alleviating high-pressure gradients in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), a key characteristic of obstructive HCM. Its effects appeared consistent across a wide range of objective and patient-assessed endpoints.
Mavacamten is “the first potential medical therapy addressing the underlying biology of symptoms in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” observed Iacopo Olivotto, MD, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy.
Patients in the EXPLORER-HCM trial who took the new drug showed improvements in “every aspect of objective performance and subjective well-being,” Dr. Olivotto said at a preview for journalists before his formal online presentation of the results during the virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2020, staged in lieu of the traditional annual meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Olivotto, also lead author on the study’s same-day publication in The Lancet, was exuberant about the findings. “It is really hard to convey what this actually means for a scientific and clinical community that has spent over 60 years trying to understand and cure hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.”
MyoKardia released abbreviated top-line results of EXPLORER-HCM in May, which were reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology at the time.
“I think it’s pretty exciting. We certainly need more and better drugs for this patient population,” Arnon Adler, MD, who is not associated with the trial but follows HCM at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, Toronto General Hospital, said in an interview.
The trial compared the new drug to placebo rather than full contemporary drug therapy for obstructive HCM, Adler cautioned, and had a fairly short follow-up time. But he was impressed that mavacamten’s apparent benefits seemed consistent not only for endpoints like change in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class and quality of life but also for more objective measures like peak VO2 and LVOT gradients.
“I think the results were promising across the board,” he told.
Unique mechanism of action
Mavacamten is described as a first-in-class, small-molecule, selective allosteric inhibitor of cardiac myosin adenosine triphosphatase that addresses the underlying pathophysiology of HCM by reducing actin–myosin cross-bridge formation. It thereby inhibits the excessive myocyte contractility that is a key mechanism of the disorder’s tell-tale hypertrophy, something the available HCM drug therapies don’t do.
Almost three-fourths of patients in the trial were initially in NYHA class 2. Such patients in practice tend to be treated pharmacologically, with more invasive but generally effective surgical myectomy and alcohol septal ablation performed more often for patients in NYHA class 3.
“In the EXPLORER-HCM trial, patients enrolled did not have any immediate indication for surgery,” although many of them in NYHA class 2 would likely progress to NYHA 3, Dr. Olivotto said in an interview.
Based on the trial, he said, it’s possible that mavacamten could lead to “earlier and broader treatment of obstruction symptoms in patients who would never have qualified for surgery in the first place because their symptoms may not be severe enough, but they are still limited.”
Notably, the published report notes, 27% of patients taking mavacamten achieved what was defined as a complete response – that is, a reduction of all LVOT gradients to less than 30 mm Hg in the total absence of symptoms.
Only 1% of patients in the placebo-treated control group met that goal, “showing that mavacamten might be capable of achieving marked relief of symptoms and LVOT obstruction,” the report states.
In the trial, “treatment with mavacamten led to clinically meaningful improvements in hemodynamic status, functional capacity, and subjective well-being in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” agrees an editorial accompanying the EXPLORER-HCM publication.
Mavacamten might even compare favorably to surgery and ablative therapy, speculated the editorialists, Michael Papadakis, MBBS, MD, and colleagues of St. George’s University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London. The drug appeared to reduce the peak LVOT gradient “to less than the guideline-based threshold for septal reduction therapy, 50 mm Hg, in 74% of patients, compared with 21% in the placebo group, indicating that mavacamten could represent a valid alternative to highly specialized invasive therapy,” they wrote.
Standard drug therapy
“There are approved drugs for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, but they are ancient and were developed for other diseases,” observed Dr. Olivotto at the media briefing. Those drug options – primarily beta-blockers, nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers, and the sodium-channel blocker disopyramide – are often ineffective or cause onerous side effects, he said.
Notably in EXPLORER-HCM, patients in both the mavacamten and placebo groups could also be receiving beta-blockers and calcium-channel blockers, but no one in the trial could be receiving disopyramide, which can prolong the QT interval.
“By design,” mavacamten wasn’t compared to disopyramide, “a much more potent drug for lowering gradient and improving symptoms than beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” said Martin S. Maron, MD, medical director at the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Center and Research Institute, Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
Therefore, the trial’s results can’t be extrapolated to conclude that the new drug is superior to disopyramide “or the gold standard, surgical myectomy,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Adler agreed that observational studies suggest a benefit from disopyramide that may rival the apparent effect of mavacamten. “But of course, you can’t make direct comparisons because we never had a study like this for disopyramide.” Because it has many side effects and limitations, “it’s not a drug that I like using, but it is beneficial for some patients and I do use it quite a bit.”
What EXPLORER-HCM does seem to show, Dr. Maron said, “is that the mechanism of action of the drug does seem to play out. It lowers gradients in a pretty reliable and powerful way, and that translates into clinical improvement in many patients. So it starts to support the idea that this drug and the class of drugs, myosin inhibitors, may represent another medical therapy option for symptomatic obstructive HCM.”
And, he pointed out, about one-fifth of patients with obstructive HCM don’t respond to disopyramide with fewer symptoms, and in others the drug “starts to lose efficacy over time.” So disopyramide has limitations, and EXPLORER-HCM “provides the possibility of an additional drug option.”
EXPLORER-HCM randomly assigned 251 adults with obstructive HCM in 13 countries to receive mavacamten, titrated from a starting dosage of 5 mg/day to a possible 15 mg/day or to placebo for 30 weeks.
The patients were required to have a peak LVOT gradient at least 50 mm Hg, a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 55%, and symptoms indicating NYHA class 2 or 3; ultimately, 73% started the trial in NYHA class 2.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 36.6% of patients receiving mavacamten and 17.2% of control patients met the composite primary endpoint (P = .0005), which consisted of either a 1.5–mL/kg per minute or greater improvement in peak oxygen consumption (pVO2) and at least a one-step reduction in NYHA functional class or at least a 3.0–mL/kg per minute pVO2 increase without deterioration in NYHA class, by week 30.
Patients receiving mavacamten also showed greater improvement in the individual endpoints of postexercise LVOT gradient, NYHA class, and two score-based symptom assessments – the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Clinical Summary and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Symptom Questionnaire Shortness-of-Breath domain – compared with control patients.
Safety and tolerability issues were similar in both groups, the reports notes. Ten patients in the mavacamten group reported 11 serious adverse events, compared with 20 such events reported by 11 patients in the control group.
“We can say from these results that mavacamten is a promising drug for symptom relief and functional class improvement associated with outflow gradient reduction in selected patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” and that, on the basis of this trial, it has potential as a drug of first choice, Franco Cecchi, MD, University of Florence (Italy), said as an invited discussant following Dr. Olivotto’s formal presentation of the trial.
Although serious adverse events were few, it was noteworthy that seven patients receiving mavacamten but only two patients receiving placebo showed LVEF reductions to below the 50% threshold during the trial, Dr. Cecchi observed. The LVEFs normalized once the drug was discontinued, but still, it may mean that mavacamten should be carefully uptitrated according to LVEF, he said.
Those LVEF reductions raise questions about “the reliability of being able to dose patients safely in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Maron said. “You have to ask, ‘Can this be extrapolated to the general practicing community without patients dropping their ejection fractions too much?’ ”
In addition, “we don’t have any idea about long-term efficacy for this drug, and we can draw very limited information about long-term safety here as well. That’s another other question mark,” Dr. Maron said.
“If I could have patients really become asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic without any surgery on a drug that is safe and can be taken for a prolonged period of time, that would be great,” Dr. Adler added. He noted that long-term follow-up of patients taking mavacamten in various trials has been underway and should help answer safety and efficacy questions about chronic therapy.
“Should mavacamten prove to be clinically effective and safe following long-term therapy in a larger and more diverse population, it would represent a much anticipated development in the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” the accompanying editorial states.
“Were the drug to realise its potential as a disease-modifying therapy in younger individuals, it would represent a great milestone in the area of inherited cardiomyopathies.”
MyoKardia funded EXPLORER-HCM. Dr. Olivotto discloses receiving grants from MyoKardia, Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, Amicus, and Bayer; honoraria from Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, and Bayer; and payments for consulting from MyoKardia. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Papadakis and the other editorialists report that they have no competing interests. Dr. Adler had no disclosures. Dr. Maron discloses consulting for and serving on a trial steering committee for Cytokinetics, sponsor of the 60-patient phase 2 placebo-controlled trial REDWOOD-HCM of patients with obstructive HCM treated with CK-3773274, a drug that works by a mechanism similar to that of mavacamten.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An investigational drug that targets part of the molecular machinery underlying obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) can improve both symptoms and functional status in patients with the genetic disorder, suggests a placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.
Treatment with mavacamten (MyoKardia) worked partly by alleviating high-pressure gradients in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT), a key characteristic of obstructive HCM. Its effects appeared consistent across a wide range of objective and patient-assessed endpoints.
Mavacamten is “the first potential medical therapy addressing the underlying biology of symptoms in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” observed Iacopo Olivotto, MD, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy.
Patients in the EXPLORER-HCM trial who took the new drug showed improvements in “every aspect of objective performance and subjective well-being,” Dr. Olivotto said at a preview for journalists before his formal online presentation of the results during the virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2020, staged in lieu of the traditional annual meeting because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Olivotto, also lead author on the study’s same-day publication in The Lancet, was exuberant about the findings. “It is really hard to convey what this actually means for a scientific and clinical community that has spent over 60 years trying to understand and cure hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.”
MyoKardia released abbreviated top-line results of EXPLORER-HCM in May, which were reported by theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology at the time.
“I think it’s pretty exciting. We certainly need more and better drugs for this patient population,” Arnon Adler, MD, who is not associated with the trial but follows HCM at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, Toronto General Hospital, said in an interview.
The trial compared the new drug to placebo rather than full contemporary drug therapy for obstructive HCM, Adler cautioned, and had a fairly short follow-up time. But he was impressed that mavacamten’s apparent benefits seemed consistent not only for endpoints like change in New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class and quality of life but also for more objective measures like peak VO2 and LVOT gradients.
“I think the results were promising across the board,” he told.
Unique mechanism of action
Mavacamten is described as a first-in-class, small-molecule, selective allosteric inhibitor of cardiac myosin adenosine triphosphatase that addresses the underlying pathophysiology of HCM by reducing actin–myosin cross-bridge formation. It thereby inhibits the excessive myocyte contractility that is a key mechanism of the disorder’s tell-tale hypertrophy, something the available HCM drug therapies don’t do.
Almost three-fourths of patients in the trial were initially in NYHA class 2. Such patients in practice tend to be treated pharmacologically, with more invasive but generally effective surgical myectomy and alcohol septal ablation performed more often for patients in NYHA class 3.
“In the EXPLORER-HCM trial, patients enrolled did not have any immediate indication for surgery,” although many of them in NYHA class 2 would likely progress to NYHA 3, Dr. Olivotto said in an interview.
Based on the trial, he said, it’s possible that mavacamten could lead to “earlier and broader treatment of obstruction symptoms in patients who would never have qualified for surgery in the first place because their symptoms may not be severe enough, but they are still limited.”
Notably, the published report notes, 27% of patients taking mavacamten achieved what was defined as a complete response – that is, a reduction of all LVOT gradients to less than 30 mm Hg in the total absence of symptoms.
Only 1% of patients in the placebo-treated control group met that goal, “showing that mavacamten might be capable of achieving marked relief of symptoms and LVOT obstruction,” the report states.
In the trial, “treatment with mavacamten led to clinically meaningful improvements in hemodynamic status, functional capacity, and subjective well-being in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” agrees an editorial accompanying the EXPLORER-HCM publication.
Mavacamten might even compare favorably to surgery and ablative therapy, speculated the editorialists, Michael Papadakis, MBBS, MD, and colleagues of St. George’s University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London. The drug appeared to reduce the peak LVOT gradient “to less than the guideline-based threshold for septal reduction therapy, 50 mm Hg, in 74% of patients, compared with 21% in the placebo group, indicating that mavacamten could represent a valid alternative to highly specialized invasive therapy,” they wrote.
Standard drug therapy
“There are approved drugs for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, but they are ancient and were developed for other diseases,” observed Dr. Olivotto at the media briefing. Those drug options – primarily beta-blockers, nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers, and the sodium-channel blocker disopyramide – are often ineffective or cause onerous side effects, he said.
Notably in EXPLORER-HCM, patients in both the mavacamten and placebo groups could also be receiving beta-blockers and calcium-channel blockers, but no one in the trial could be receiving disopyramide, which can prolong the QT interval.
“By design,” mavacamten wasn’t compared to disopyramide, “a much more potent drug for lowering gradient and improving symptoms than beta-blockers or calcium-channel blockers,” said Martin S. Maron, MD, medical director at the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Center and Research Institute, Tufts Medical Center, Boston.
Therefore, the trial’s results can’t be extrapolated to conclude that the new drug is superior to disopyramide “or the gold standard, surgical myectomy,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Adler agreed that observational studies suggest a benefit from disopyramide that may rival the apparent effect of mavacamten. “But of course, you can’t make direct comparisons because we never had a study like this for disopyramide.” Because it has many side effects and limitations, “it’s not a drug that I like using, but it is beneficial for some patients and I do use it quite a bit.”
What EXPLORER-HCM does seem to show, Dr. Maron said, “is that the mechanism of action of the drug does seem to play out. It lowers gradients in a pretty reliable and powerful way, and that translates into clinical improvement in many patients. So it starts to support the idea that this drug and the class of drugs, myosin inhibitors, may represent another medical therapy option for symptomatic obstructive HCM.”
And, he pointed out, about one-fifth of patients with obstructive HCM don’t respond to disopyramide with fewer symptoms, and in others the drug “starts to lose efficacy over time.” So disopyramide has limitations, and EXPLORER-HCM “provides the possibility of an additional drug option.”
EXPLORER-HCM randomly assigned 251 adults with obstructive HCM in 13 countries to receive mavacamten, titrated from a starting dosage of 5 mg/day to a possible 15 mg/day or to placebo for 30 weeks.
The patients were required to have a peak LVOT gradient at least 50 mm Hg, a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 55%, and symptoms indicating NYHA class 2 or 3; ultimately, 73% started the trial in NYHA class 2.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, 36.6% of patients receiving mavacamten and 17.2% of control patients met the composite primary endpoint (P = .0005), which consisted of either a 1.5–mL/kg per minute or greater improvement in peak oxygen consumption (pVO2) and at least a one-step reduction in NYHA functional class or at least a 3.0–mL/kg per minute pVO2 increase without deterioration in NYHA class, by week 30.
Patients receiving mavacamten also showed greater improvement in the individual endpoints of postexercise LVOT gradient, NYHA class, and two score-based symptom assessments – the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Clinical Summary and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Symptom Questionnaire Shortness-of-Breath domain – compared with control patients.
Safety and tolerability issues were similar in both groups, the reports notes. Ten patients in the mavacamten group reported 11 serious adverse events, compared with 20 such events reported by 11 patients in the control group.
“We can say from these results that mavacamten is a promising drug for symptom relief and functional class improvement associated with outflow gradient reduction in selected patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,” and that, on the basis of this trial, it has potential as a drug of first choice, Franco Cecchi, MD, University of Florence (Italy), said as an invited discussant following Dr. Olivotto’s formal presentation of the trial.
Although serious adverse events were few, it was noteworthy that seven patients receiving mavacamten but only two patients receiving placebo showed LVEF reductions to below the 50% threshold during the trial, Dr. Cecchi observed. The LVEFs normalized once the drug was discontinued, but still, it may mean that mavacamten should be carefully uptitrated according to LVEF, he said.
Those LVEF reductions raise questions about “the reliability of being able to dose patients safely in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Maron said. “You have to ask, ‘Can this be extrapolated to the general practicing community without patients dropping their ejection fractions too much?’ ”
In addition, “we don’t have any idea about long-term efficacy for this drug, and we can draw very limited information about long-term safety here as well. That’s another other question mark,” Dr. Maron said.
“If I could have patients really become asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic without any surgery on a drug that is safe and can be taken for a prolonged period of time, that would be great,” Dr. Adler added. He noted that long-term follow-up of patients taking mavacamten in various trials has been underway and should help answer safety and efficacy questions about chronic therapy.
“Should mavacamten prove to be clinically effective and safe following long-term therapy in a larger and more diverse population, it would represent a much anticipated development in the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,” the accompanying editorial states.
“Were the drug to realise its potential as a disease-modifying therapy in younger individuals, it would represent a great milestone in the area of inherited cardiomyopathies.”
MyoKardia funded EXPLORER-HCM. Dr. Olivotto discloses receiving grants from MyoKardia, Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, Amicus, and Bayer; honoraria from Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire, and Bayer; and payments for consulting from MyoKardia. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Papadakis and the other editorialists report that they have no competing interests. Dr. Adler had no disclosures. Dr. Maron discloses consulting for and serving on a trial steering committee for Cytokinetics, sponsor of the 60-patient phase 2 placebo-controlled trial REDWOOD-HCM of patients with obstructive HCM treated with CK-3773274, a drug that works by a mechanism similar to that of mavacamten.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
EMPEROR-Reduced: Empagliflozin’s HFrEF benefit solidifies class effects
The SGLT2 inhibitor drug class solidified its role as a major, new treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and no diabetes, with results from a second large, controlled trial showing clear efficacy and safety in this population.
Patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) treated with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) had a statistically significant 25% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization, compared with placebo-treated controls when added on top of standard HFrEF treatment, and this benefit was consistent regardless of whether the treated patients also had type 2 diabetes, Milton Packer, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
This 25% drop in the primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial exactly matched the cut in incidence of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization produced by treatment with a another SGLT2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), in the DAPA-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
The performance of these two SGLT2 inhibitors was “incredibly consistent” across the their respective trials run in HFrEF patients with and without type 2 diabetes, and the combined evidence base of the two trials makes for “really compelling evidence” of both safety and efficacy that should prompt a change to U.S. practice, with both of these drugs forming a new cornerstone of HFrEF treatment, Dr. Packer said.
Results plant drug class firmly as HFrEF treatment
Dr. Packer stressed in his presentation that optimal treatment of patients with HFrEF now demands use of one of these two SGLT2 inhibitors, as well as sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, plus a diuretic as a fifth drug class for the many HFrEF patients who also need treatment for fluid overload. He further advocated for rapid introduction of these four cornerstone agents with proven survival benefits once a patient receives a HFrEF diagnosis, suggesting that sacubitril plus valsartan, an SGLT2 inhibitor, a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist could all be initiated within 6 weeks or less while acknowledging that optimal up-titration of the beta-blocker would likely take longer.
The order in which a patient starts these drugs shouldn’t matter, and there currently seems to be no evidence that clearly points toward using either dapagliflozin or empagliflozin over the other, Dr. Packer added.
In recognition of the importance of sending a message to heart failure clinicians about the newly proven efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in HFrEF patients, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association are now drafting an “expert decision pathway” to help clinicians as they enter this new prescribing space. This interim guidance should come out before the end of 2020, prior to release of fully revised HFrEF management guidelines in 2021, said Athena Poppas, MD, president of the ACC, in an interview.
“There is clearly need for education” that can help guide physicians who care for HFrEF patients on how to introduce an SGLT2 inhibitor along with the additional, lengthy list of drug classes proven to benefit these patients, noted Dr. Poppas, who is also a professor and chief of cardiology at the Brown University in Providence, R.I. Physicians may find that they need extra backup for successfully starting both sacubitril plus valsartan and an SGLT2 inhibitor in HFrEF patients because recent history has shown substantial pushback from third-party payers in reimbursing for these relatively expensive drugs, Dr. Poppas noted. She added that this is a problem that may be compounded when patients should ideally get both drug classes.
Physicians who care for heart failure patients have their own history of dragging their feet when adding new drugs to the regimens HFrEF patients receive. The angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers took about 17 years each to start reaching a majority of U.S. HFrEF patients, and sacubitril plus valsartan is now used on perhaps a quarter to a third of HFrEF patients despite receiving Food and Drug Administration approval for these patients in mid 2015, noted Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Fairfax, Va.
Despite dapagliflozin receiving FDA approval in May 2020 for treating HFrEF in patients without diabetes, early uptake in U.S. practice has been very slow, with findings from large U.S. patient registries suggesting that perhaps 1% of suitable HFrEF patients currently get the drug, estimated Dr. O’Connor in an interview.
Given how strong the evidence now is for benefit and safety from dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, it may take as little as 5 years to reach greater than 50% penetration of one of these drugs into U.S. HFrEF patient populations, suggested Dr. Packer, a distinguished scholar in cardiovascular science at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
EMPEROR-Reduced outcomes
The road to routine use of these SGLT2 inhibitor drugs should be hastened by empagliflozin’s impressive performance in EMPEROR-Reduced, in which the drug scored highly significant benefits over placebo for the prespecified primary and two major secondary endpoints, one of which was a measure of preserved renal function.
The trial randomized 3,730 patients at 520 sites in 20 countries during 2017-2019 and followed them on treatment for a median of 16 months. All patients had a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and roughly three-quarters had New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II function, nearly one-quarter had class III function, and fewer than 1% of patients fell into the class IV category.
The primary endpoint occurred in 19% of the empagliflozin-treated patients and in 25% of those who received placebo. Among the half of patients with diabetes in the trial, the relative risk reduction by empagliflozin compared with placebo was a statistically significant 28%; among those without diabetes, it was a statistically significant 22%. Concurrently with Dr. Packer’s report, the results appeared in an article posted online (N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190).
The study also had two main prespecified secondary endpoints: the incidence of total hospitalizations for heart failure, both first and recurrent, which fell by 30% in the empagliflozin-treated patients, compared with placebo, and the rate of declining renal function during the 16 months of the study as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, which dropped by roughly 1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 among the empagliflozin recipients and by about 4 mL/min/ per 1.73 m2 in the placebo patients.
Treatment with empagliflozin also achieved a notable, statistically significant 50% drop in major adverse renal events, consistent with the performance of other drugs in the class.
“Renal protection is a big plus” of empagliflozin in this trial and from the other SGLT2 inhibitors in prior studies, noted Dr. O’Connor.
The EMPEROR-Reduced results also showed an important benefit for HFrEF patients from empagliflozin not previously seen as quickly with any other drug class, noted Dr. Packer. The SGLT2 inhibitor led to statistically a significant slowing in the progression of patients from NYHA class II function to class III, compared with placebo, and it also significantly promoted the recovery of patients from NYHA class III to class II, an effect that became apparent within the first month on treatment and a benefit that is a “big deal” for patients because it represents a “significant change in functional capacity.” This additional dimension of empagliflozin’s benefit “really impressed me,” Dr. Packer said.
EMPEROR-Reduced was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that market empagliflozin. Dr. Packer has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly and from several other companies. Dr. Poppas and Dr. O’Connor had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Packer M. ESC 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190.
The SGLT2 inhibitor drug class solidified its role as a major, new treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and no diabetes, with results from a second large, controlled trial showing clear efficacy and safety in this population.
Patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) treated with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) had a statistically significant 25% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization, compared with placebo-treated controls when added on top of standard HFrEF treatment, and this benefit was consistent regardless of whether the treated patients also had type 2 diabetes, Milton Packer, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
This 25% drop in the primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial exactly matched the cut in incidence of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization produced by treatment with a another SGLT2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), in the DAPA-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
The performance of these two SGLT2 inhibitors was “incredibly consistent” across the their respective trials run in HFrEF patients with and without type 2 diabetes, and the combined evidence base of the two trials makes for “really compelling evidence” of both safety and efficacy that should prompt a change to U.S. practice, with both of these drugs forming a new cornerstone of HFrEF treatment, Dr. Packer said.
Results plant drug class firmly as HFrEF treatment
Dr. Packer stressed in his presentation that optimal treatment of patients with HFrEF now demands use of one of these two SGLT2 inhibitors, as well as sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, plus a diuretic as a fifth drug class for the many HFrEF patients who also need treatment for fluid overload. He further advocated for rapid introduction of these four cornerstone agents with proven survival benefits once a patient receives a HFrEF diagnosis, suggesting that sacubitril plus valsartan, an SGLT2 inhibitor, a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist could all be initiated within 6 weeks or less while acknowledging that optimal up-titration of the beta-blocker would likely take longer.
The order in which a patient starts these drugs shouldn’t matter, and there currently seems to be no evidence that clearly points toward using either dapagliflozin or empagliflozin over the other, Dr. Packer added.
In recognition of the importance of sending a message to heart failure clinicians about the newly proven efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in HFrEF patients, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association are now drafting an “expert decision pathway” to help clinicians as they enter this new prescribing space. This interim guidance should come out before the end of 2020, prior to release of fully revised HFrEF management guidelines in 2021, said Athena Poppas, MD, president of the ACC, in an interview.
“There is clearly need for education” that can help guide physicians who care for HFrEF patients on how to introduce an SGLT2 inhibitor along with the additional, lengthy list of drug classes proven to benefit these patients, noted Dr. Poppas, who is also a professor and chief of cardiology at the Brown University in Providence, R.I. Physicians may find that they need extra backup for successfully starting both sacubitril plus valsartan and an SGLT2 inhibitor in HFrEF patients because recent history has shown substantial pushback from third-party payers in reimbursing for these relatively expensive drugs, Dr. Poppas noted. She added that this is a problem that may be compounded when patients should ideally get both drug classes.
Physicians who care for heart failure patients have their own history of dragging their feet when adding new drugs to the regimens HFrEF patients receive. The angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers took about 17 years each to start reaching a majority of U.S. HFrEF patients, and sacubitril plus valsartan is now used on perhaps a quarter to a third of HFrEF patients despite receiving Food and Drug Administration approval for these patients in mid 2015, noted Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Fairfax, Va.
Despite dapagliflozin receiving FDA approval in May 2020 for treating HFrEF in patients without diabetes, early uptake in U.S. practice has been very slow, with findings from large U.S. patient registries suggesting that perhaps 1% of suitable HFrEF patients currently get the drug, estimated Dr. O’Connor in an interview.
Given how strong the evidence now is for benefit and safety from dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, it may take as little as 5 years to reach greater than 50% penetration of one of these drugs into U.S. HFrEF patient populations, suggested Dr. Packer, a distinguished scholar in cardiovascular science at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
EMPEROR-Reduced outcomes
The road to routine use of these SGLT2 inhibitor drugs should be hastened by empagliflozin’s impressive performance in EMPEROR-Reduced, in which the drug scored highly significant benefits over placebo for the prespecified primary and two major secondary endpoints, one of which was a measure of preserved renal function.
The trial randomized 3,730 patients at 520 sites in 20 countries during 2017-2019 and followed them on treatment for a median of 16 months. All patients had a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and roughly three-quarters had New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II function, nearly one-quarter had class III function, and fewer than 1% of patients fell into the class IV category.
The primary endpoint occurred in 19% of the empagliflozin-treated patients and in 25% of those who received placebo. Among the half of patients with diabetes in the trial, the relative risk reduction by empagliflozin compared with placebo was a statistically significant 28%; among those without diabetes, it was a statistically significant 22%. Concurrently with Dr. Packer’s report, the results appeared in an article posted online (N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190).
The study also had two main prespecified secondary endpoints: the incidence of total hospitalizations for heart failure, both first and recurrent, which fell by 30% in the empagliflozin-treated patients, compared with placebo, and the rate of declining renal function during the 16 months of the study as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, which dropped by roughly 1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 among the empagliflozin recipients and by about 4 mL/min/ per 1.73 m2 in the placebo patients.
Treatment with empagliflozin also achieved a notable, statistically significant 50% drop in major adverse renal events, consistent with the performance of other drugs in the class.
“Renal protection is a big plus” of empagliflozin in this trial and from the other SGLT2 inhibitors in prior studies, noted Dr. O’Connor.
The EMPEROR-Reduced results also showed an important benefit for HFrEF patients from empagliflozin not previously seen as quickly with any other drug class, noted Dr. Packer. The SGLT2 inhibitor led to statistically a significant slowing in the progression of patients from NYHA class II function to class III, compared with placebo, and it also significantly promoted the recovery of patients from NYHA class III to class II, an effect that became apparent within the first month on treatment and a benefit that is a “big deal” for patients because it represents a “significant change in functional capacity.” This additional dimension of empagliflozin’s benefit “really impressed me,” Dr. Packer said.
EMPEROR-Reduced was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that market empagliflozin. Dr. Packer has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly and from several other companies. Dr. Poppas and Dr. O’Connor had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Packer M. ESC 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190.
The SGLT2 inhibitor drug class solidified its role as a major, new treatment for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and no diabetes, with results from a second large, controlled trial showing clear efficacy and safety in this population.
Patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) treated with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance) had a statistically significant 25% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular death or first heart failure hospitalization, compared with placebo-treated controls when added on top of standard HFrEF treatment, and this benefit was consistent regardless of whether the treated patients also had type 2 diabetes, Milton Packer, MD, reported at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
This 25% drop in the primary endpoint with empagliflozin treatment in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial exactly matched the cut in incidence of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization produced by treatment with a another SGLT2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin (Farxiga), in the DAPA-HF trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
The performance of these two SGLT2 inhibitors was “incredibly consistent” across the their respective trials run in HFrEF patients with and without type 2 diabetes, and the combined evidence base of the two trials makes for “really compelling evidence” of both safety and efficacy that should prompt a change to U.S. practice, with both of these drugs forming a new cornerstone of HFrEF treatment, Dr. Packer said.
Results plant drug class firmly as HFrEF treatment
Dr. Packer stressed in his presentation that optimal treatment of patients with HFrEF now demands use of one of these two SGLT2 inhibitors, as well as sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto), a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, plus a diuretic as a fifth drug class for the many HFrEF patients who also need treatment for fluid overload. He further advocated for rapid introduction of these four cornerstone agents with proven survival benefits once a patient receives a HFrEF diagnosis, suggesting that sacubitril plus valsartan, an SGLT2 inhibitor, a beta-blocker, and a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist could all be initiated within 6 weeks or less while acknowledging that optimal up-titration of the beta-blocker would likely take longer.
The order in which a patient starts these drugs shouldn’t matter, and there currently seems to be no evidence that clearly points toward using either dapagliflozin or empagliflozin over the other, Dr. Packer added.
In recognition of the importance of sending a message to heart failure clinicians about the newly proven efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in HFrEF patients, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association are now drafting an “expert decision pathway” to help clinicians as they enter this new prescribing space. This interim guidance should come out before the end of 2020, prior to release of fully revised HFrEF management guidelines in 2021, said Athena Poppas, MD, president of the ACC, in an interview.
“There is clearly need for education” that can help guide physicians who care for HFrEF patients on how to introduce an SGLT2 inhibitor along with the additional, lengthy list of drug classes proven to benefit these patients, noted Dr. Poppas, who is also a professor and chief of cardiology at the Brown University in Providence, R.I. Physicians may find that they need extra backup for successfully starting both sacubitril plus valsartan and an SGLT2 inhibitor in HFrEF patients because recent history has shown substantial pushback from third-party payers in reimbursing for these relatively expensive drugs, Dr. Poppas noted. She added that this is a problem that may be compounded when patients should ideally get both drug classes.
Physicians who care for heart failure patients have their own history of dragging their feet when adding new drugs to the regimens HFrEF patients receive. The angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers took about 17 years each to start reaching a majority of U.S. HFrEF patients, and sacubitril plus valsartan is now used on perhaps a quarter to a third of HFrEF patients despite receiving Food and Drug Administration approval for these patients in mid 2015, noted Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Fairfax, Va.
Despite dapagliflozin receiving FDA approval in May 2020 for treating HFrEF in patients without diabetes, early uptake in U.S. practice has been very slow, with findings from large U.S. patient registries suggesting that perhaps 1% of suitable HFrEF patients currently get the drug, estimated Dr. O’Connor in an interview.
Given how strong the evidence now is for benefit and safety from dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, it may take as little as 5 years to reach greater than 50% penetration of one of these drugs into U.S. HFrEF patient populations, suggested Dr. Packer, a distinguished scholar in cardiovascular science at Baylor University Medical Center in Dallas.
EMPEROR-Reduced outcomes
The road to routine use of these SGLT2 inhibitor drugs should be hastened by empagliflozin’s impressive performance in EMPEROR-Reduced, in which the drug scored highly significant benefits over placebo for the prespecified primary and two major secondary endpoints, one of which was a measure of preserved renal function.
The trial randomized 3,730 patients at 520 sites in 20 countries during 2017-2019 and followed them on treatment for a median of 16 months. All patients had a left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% or less, and roughly three-quarters had New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II function, nearly one-quarter had class III function, and fewer than 1% of patients fell into the class IV category.
The primary endpoint occurred in 19% of the empagliflozin-treated patients and in 25% of those who received placebo. Among the half of patients with diabetes in the trial, the relative risk reduction by empagliflozin compared with placebo was a statistically significant 28%; among those without diabetes, it was a statistically significant 22%. Concurrently with Dr. Packer’s report, the results appeared in an article posted online (N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190).
The study also had two main prespecified secondary endpoints: the incidence of total hospitalizations for heart failure, both first and recurrent, which fell by 30% in the empagliflozin-treated patients, compared with placebo, and the rate of declining renal function during the 16 months of the study as measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate, which dropped by roughly 1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 among the empagliflozin recipients and by about 4 mL/min/ per 1.73 m2 in the placebo patients.
Treatment with empagliflozin also achieved a notable, statistically significant 50% drop in major adverse renal events, consistent with the performance of other drugs in the class.
“Renal protection is a big plus” of empagliflozin in this trial and from the other SGLT2 inhibitors in prior studies, noted Dr. O’Connor.
The EMPEROR-Reduced results also showed an important benefit for HFrEF patients from empagliflozin not previously seen as quickly with any other drug class, noted Dr. Packer. The SGLT2 inhibitor led to statistically a significant slowing in the progression of patients from NYHA class II function to class III, compared with placebo, and it also significantly promoted the recovery of patients from NYHA class III to class II, an effect that became apparent within the first month on treatment and a benefit that is a “big deal” for patients because it represents a “significant change in functional capacity.” This additional dimension of empagliflozin’s benefit “really impressed me,” Dr. Packer said.
EMPEROR-Reduced was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, the companies that market empagliflozin. Dr. Packer has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly and from several other companies. Dr. Poppas and Dr. O’Connor had no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Packer M. ESC 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022190.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2020
Early rhythm control in AFib gains new life
Initiation of rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs and/or ablation in patients with early, recently diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) led to a significantly lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes, compared with a rate-control strategy, during more than 5 years of follow-up in the large randomized EAST-AFNET 4 trial, Paulus Kirchhof, MD, said at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Previous trials of rate versus rhythm control in AFib, such as AFFIRM (Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management), failed to show an advantage for rhythm over rate control in terms of clinical outcomes. Why was EAST-AFNET 4 different? Dr. Kirchhof offered two major reasons: The study incorporated AFib ablation as an option in the rhythm control strategy, and treatment started soon after diagnosis of the arrhythmia. Indeed, nearly 40% of patients had their first-ever AFib episode at the time of randomization, and the median time from diagnosis to randomization was just 36 days.
“Once you are in AFib for a few months, the atrium suffers severe damage, some of it irreversible, so it becomes more difficult to restore and maintain sinus rhythm when you wait longer,” explained Dr. Kirchhof, director of the department of cardiology at the University Heart and Vascular Center in Hamburg (Ger.) and professor of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Birmingham, England.
Also, epidemiologic studies show that the risk of cardiovascular complications is heightened in the first year following diagnosis of AFib. “So there’s a window of opportunity to prevent complications,” he added.
The impetus for conducting EAST-AFNET 4 (Early Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation for Stroke Prevention Trial ) was straightforward, according to the cardiologist: “The question of whether rhythm control is beneficial or not has been in the field for several decades. Most people, like me, always believed that maintaining sinus rhythm would help, but we didn’t have the data to show it.”
Early rhythm control shows sustained benefits
EAST-AFNET 4 was a prospective, open, blinded-outcome-assessement trial. It included 2,789 patients with early AFib and an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3.4 who were randomized at 135 sites in 11 European countries to early rhythm control or guideline-recommended rate control. At a median 5.1 years of follow-up, the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, or hospitalization for worsening heart failure – occurred at a pace of 3.9% per year in the rhythm control group and 5% per year with rate control. This translated to a statistically significant and clinically meaningful 21% relative risk reduction favoring early rhythm control.
The 28% reduction in cardiovascular death with rhythm control was statistically significant, as was the 35% reduction in stroke. However, the 19% reduction in heart failure hospitalizations and 17% decrease in hospitalizations for acute coronary syndrome were not.
The co–primary endpoint – the mean number of nights spent in the hospital per year, which served as a proxy for the cost of treatment to a health care system – didn’t differ between the two treatment arms, at roughly 5 nights per year.
The clinical benefit of early rhythm control was consistent across all 19 prespecified patient subgroups, including those who were asymptomatic and patients with or without heart failure.
Serious adverse events related to rhythm control therapy – most often drug-related bradycardia – occurred in 4.9% of patients over the course of 5.1 years, compared to a 1.4% serious event rate in patients assigned to rate control. Dr. Kirchhof called the roughly 1% per year serious event rate in the rhythm control group quite acceptable.
“To put that in perspective, the annualized rate of severe bleeds on oral anticoagulation – a very beneficial therapy used by more than 90% of participants at 2 years – is about 2%,” the cardiologist noted.
Only 8% of patients randomized to rhythm control received AFib ablation as initial therapy, consistent with current clinical practice. By 2 years, 19.4% of the rhythm control group had undergone AFib ablation. Also at that time, 15% of the rate control group was receiving rhythm control therapy to help manage AFib-related symptoms.
One of the big surprises in the study, he said, was that nearly three-quarters of patients in both groups were asymptomatic at 2 years.
“I think that shows how well we control symptoms, even without rhythm control,” he observed.
Results ‘move the field forward’
Dr. Kirchhof stressed that this was a trial of two different treatment strategies, and it’s not yet possible to single out any specific component of the rhythm control strategy as being responsible for the improved outcomes.
“I cannot tell you whether the outcome difference was due to AFib ablation or early treatment or the fact that we’re now better at using antiarrhythmic drugs than we were 20 years ago,” he said.
Asked if the EAST-AFNET 4 findings warrant more aggressive screening for AFib in order to detect and intervene early in the arrhythmia, Dr. Kirchhof replied with an unambiguous yes.
“My conclusion is that every patient with newly diagnosed AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or more should not only receive anticoagulation and rate control, but should also be offered rhythm control therapy at the time of diagnosis, which also means that all of these people have to be seen by a cardiologist who has expertise in the domain of AFib management. It’s a big clinical challenge, but it leads to a 21% improvement in outcomes, and I think we have to do what’s best for our patients,” he said.
In an interview, Kalyanam Shivkumar, MD, PhD, called EAST-AFNET 4 “a very important study.”
“It moves the field forward, for sure. I think it will change clinical practice, and it should,” commented Dr. Shivkumar, who was not involved in the study.
“Now there are so many wearable technologies out there – the Apple Watch and others – which will enable rhythm abnormalities to be detected early on. This bodes well for the field,” said Dr. Shivkumar, who is editor-in-chief of JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. He is also professor of medicine, radiology, and bioengineering at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center.
Dr. Kirchhof reported receiving research grants to conduct the EAST-AFNET 4 trial from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, the Atrial Fibrillation Network, the European Heart Rhythm Association, St. Jude Medical, Abbott, Sanofi, the German Heart Foundation, the European Union, the British Heart Foundation, and the Leducq Foundation.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ESC Congress 2020, the study results were published online at NEJM.org.
SOURCE: Kirchhof P. ESC Congress 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2019422.
Initiation of rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs and/or ablation in patients with early, recently diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) led to a significantly lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes, compared with a rate-control strategy, during more than 5 years of follow-up in the large randomized EAST-AFNET 4 trial, Paulus Kirchhof, MD, said at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Previous trials of rate versus rhythm control in AFib, such as AFFIRM (Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management), failed to show an advantage for rhythm over rate control in terms of clinical outcomes. Why was EAST-AFNET 4 different? Dr. Kirchhof offered two major reasons: The study incorporated AFib ablation as an option in the rhythm control strategy, and treatment started soon after diagnosis of the arrhythmia. Indeed, nearly 40% of patients had their first-ever AFib episode at the time of randomization, and the median time from diagnosis to randomization was just 36 days.
“Once you are in AFib for a few months, the atrium suffers severe damage, some of it irreversible, so it becomes more difficult to restore and maintain sinus rhythm when you wait longer,” explained Dr. Kirchhof, director of the department of cardiology at the University Heart and Vascular Center in Hamburg (Ger.) and professor of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Birmingham, England.
Also, epidemiologic studies show that the risk of cardiovascular complications is heightened in the first year following diagnosis of AFib. “So there’s a window of opportunity to prevent complications,” he added.
The impetus for conducting EAST-AFNET 4 (Early Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation for Stroke Prevention Trial ) was straightforward, according to the cardiologist: “The question of whether rhythm control is beneficial or not has been in the field for several decades. Most people, like me, always believed that maintaining sinus rhythm would help, but we didn’t have the data to show it.”
Early rhythm control shows sustained benefits
EAST-AFNET 4 was a prospective, open, blinded-outcome-assessement trial. It included 2,789 patients with early AFib and an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3.4 who were randomized at 135 sites in 11 European countries to early rhythm control or guideline-recommended rate control. At a median 5.1 years of follow-up, the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, or hospitalization for worsening heart failure – occurred at a pace of 3.9% per year in the rhythm control group and 5% per year with rate control. This translated to a statistically significant and clinically meaningful 21% relative risk reduction favoring early rhythm control.
The 28% reduction in cardiovascular death with rhythm control was statistically significant, as was the 35% reduction in stroke. However, the 19% reduction in heart failure hospitalizations and 17% decrease in hospitalizations for acute coronary syndrome were not.
The co–primary endpoint – the mean number of nights spent in the hospital per year, which served as a proxy for the cost of treatment to a health care system – didn’t differ between the two treatment arms, at roughly 5 nights per year.
The clinical benefit of early rhythm control was consistent across all 19 prespecified patient subgroups, including those who were asymptomatic and patients with or without heart failure.
Serious adverse events related to rhythm control therapy – most often drug-related bradycardia – occurred in 4.9% of patients over the course of 5.1 years, compared to a 1.4% serious event rate in patients assigned to rate control. Dr. Kirchhof called the roughly 1% per year serious event rate in the rhythm control group quite acceptable.
“To put that in perspective, the annualized rate of severe bleeds on oral anticoagulation – a very beneficial therapy used by more than 90% of participants at 2 years – is about 2%,” the cardiologist noted.
Only 8% of patients randomized to rhythm control received AFib ablation as initial therapy, consistent with current clinical practice. By 2 years, 19.4% of the rhythm control group had undergone AFib ablation. Also at that time, 15% of the rate control group was receiving rhythm control therapy to help manage AFib-related symptoms.
One of the big surprises in the study, he said, was that nearly three-quarters of patients in both groups were asymptomatic at 2 years.
“I think that shows how well we control symptoms, even without rhythm control,” he observed.
Results ‘move the field forward’
Dr. Kirchhof stressed that this was a trial of two different treatment strategies, and it’s not yet possible to single out any specific component of the rhythm control strategy as being responsible for the improved outcomes.
“I cannot tell you whether the outcome difference was due to AFib ablation or early treatment or the fact that we’re now better at using antiarrhythmic drugs than we were 20 years ago,” he said.
Asked if the EAST-AFNET 4 findings warrant more aggressive screening for AFib in order to detect and intervene early in the arrhythmia, Dr. Kirchhof replied with an unambiguous yes.
“My conclusion is that every patient with newly diagnosed AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or more should not only receive anticoagulation and rate control, but should also be offered rhythm control therapy at the time of diagnosis, which also means that all of these people have to be seen by a cardiologist who has expertise in the domain of AFib management. It’s a big clinical challenge, but it leads to a 21% improvement in outcomes, and I think we have to do what’s best for our patients,” he said.
In an interview, Kalyanam Shivkumar, MD, PhD, called EAST-AFNET 4 “a very important study.”
“It moves the field forward, for sure. I think it will change clinical practice, and it should,” commented Dr. Shivkumar, who was not involved in the study.
“Now there are so many wearable technologies out there – the Apple Watch and others – which will enable rhythm abnormalities to be detected early on. This bodes well for the field,” said Dr. Shivkumar, who is editor-in-chief of JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. He is also professor of medicine, radiology, and bioengineering at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center.
Dr. Kirchhof reported receiving research grants to conduct the EAST-AFNET 4 trial from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, the Atrial Fibrillation Network, the European Heart Rhythm Association, St. Jude Medical, Abbott, Sanofi, the German Heart Foundation, the European Union, the British Heart Foundation, and the Leducq Foundation.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ESC Congress 2020, the study results were published online at NEJM.org.
SOURCE: Kirchhof P. ESC Congress 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2019422.
Initiation of rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs and/or ablation in patients with early, recently diagnosed atrial fibrillation (AFib) led to a significantly lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes, compared with a rate-control strategy, during more than 5 years of follow-up in the large randomized EAST-AFNET 4 trial, Paulus Kirchhof, MD, said at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
Previous trials of rate versus rhythm control in AFib, such as AFFIRM (Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management), failed to show an advantage for rhythm over rate control in terms of clinical outcomes. Why was EAST-AFNET 4 different? Dr. Kirchhof offered two major reasons: The study incorporated AFib ablation as an option in the rhythm control strategy, and treatment started soon after diagnosis of the arrhythmia. Indeed, nearly 40% of patients had their first-ever AFib episode at the time of randomization, and the median time from diagnosis to randomization was just 36 days.
“Once you are in AFib for a few months, the atrium suffers severe damage, some of it irreversible, so it becomes more difficult to restore and maintain sinus rhythm when you wait longer,” explained Dr. Kirchhof, director of the department of cardiology at the University Heart and Vascular Center in Hamburg (Ger.) and professor of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Birmingham, England.
Also, epidemiologic studies show that the risk of cardiovascular complications is heightened in the first year following diagnosis of AFib. “So there’s a window of opportunity to prevent complications,” he added.
The impetus for conducting EAST-AFNET 4 (Early Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation for Stroke Prevention Trial ) was straightforward, according to the cardiologist: “The question of whether rhythm control is beneficial or not has been in the field for several decades. Most people, like me, always believed that maintaining sinus rhythm would help, but we didn’t have the data to show it.”
Early rhythm control shows sustained benefits
EAST-AFNET 4 was a prospective, open, blinded-outcome-assessement trial. It included 2,789 patients with early AFib and an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3.4 who were randomized at 135 sites in 11 European countries to early rhythm control or guideline-recommended rate control. At a median 5.1 years of follow-up, the primary outcome – a composite of cardiovascular death, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, or hospitalization for worsening heart failure – occurred at a pace of 3.9% per year in the rhythm control group and 5% per year with rate control. This translated to a statistically significant and clinically meaningful 21% relative risk reduction favoring early rhythm control.
The 28% reduction in cardiovascular death with rhythm control was statistically significant, as was the 35% reduction in stroke. However, the 19% reduction in heart failure hospitalizations and 17% decrease in hospitalizations for acute coronary syndrome were not.
The co–primary endpoint – the mean number of nights spent in the hospital per year, which served as a proxy for the cost of treatment to a health care system – didn’t differ between the two treatment arms, at roughly 5 nights per year.
The clinical benefit of early rhythm control was consistent across all 19 prespecified patient subgroups, including those who were asymptomatic and patients with or without heart failure.
Serious adverse events related to rhythm control therapy – most often drug-related bradycardia – occurred in 4.9% of patients over the course of 5.1 years, compared to a 1.4% serious event rate in patients assigned to rate control. Dr. Kirchhof called the roughly 1% per year serious event rate in the rhythm control group quite acceptable.
“To put that in perspective, the annualized rate of severe bleeds on oral anticoagulation – a very beneficial therapy used by more than 90% of participants at 2 years – is about 2%,” the cardiologist noted.
Only 8% of patients randomized to rhythm control received AFib ablation as initial therapy, consistent with current clinical practice. By 2 years, 19.4% of the rhythm control group had undergone AFib ablation. Also at that time, 15% of the rate control group was receiving rhythm control therapy to help manage AFib-related symptoms.
One of the big surprises in the study, he said, was that nearly three-quarters of patients in both groups were asymptomatic at 2 years.
“I think that shows how well we control symptoms, even without rhythm control,” he observed.
Results ‘move the field forward’
Dr. Kirchhof stressed that this was a trial of two different treatment strategies, and it’s not yet possible to single out any specific component of the rhythm control strategy as being responsible for the improved outcomes.
“I cannot tell you whether the outcome difference was due to AFib ablation or early treatment or the fact that we’re now better at using antiarrhythmic drugs than we were 20 years ago,” he said.
Asked if the EAST-AFNET 4 findings warrant more aggressive screening for AFib in order to detect and intervene early in the arrhythmia, Dr. Kirchhof replied with an unambiguous yes.
“My conclusion is that every patient with newly diagnosed AFib and a CHA2DS2-VASc score of 2 or more should not only receive anticoagulation and rate control, but should also be offered rhythm control therapy at the time of diagnosis, which also means that all of these people have to be seen by a cardiologist who has expertise in the domain of AFib management. It’s a big clinical challenge, but it leads to a 21% improvement in outcomes, and I think we have to do what’s best for our patients,” he said.
In an interview, Kalyanam Shivkumar, MD, PhD, called EAST-AFNET 4 “a very important study.”
“It moves the field forward, for sure. I think it will change clinical practice, and it should,” commented Dr. Shivkumar, who was not involved in the study.
“Now there are so many wearable technologies out there – the Apple Watch and others – which will enable rhythm abnormalities to be detected early on. This bodes well for the field,” said Dr. Shivkumar, who is editor-in-chief of JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. He is also professor of medicine, radiology, and bioengineering at the University of California, Los Angeles, and director of the UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center.
Dr. Kirchhof reported receiving research grants to conduct the EAST-AFNET 4 trial from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the German Center for Cardiovascular Research, the Atrial Fibrillation Network, the European Heart Rhythm Association, St. Jude Medical, Abbott, Sanofi, the German Heart Foundation, the European Union, the British Heart Foundation, and the Leducq Foundation.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ESC Congress 2020, the study results were published online at NEJM.org.
SOURCE: Kirchhof P. ESC Congress 2020. N Engl J Med. 2020 Aug 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2019422.
REPORTING FROM ESC CONGRESS 2020
SARS-CoV-2 appears unlikely to pass through breast milk
Breast milk is an unlikely source of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from mothers to infants, according to data from case reports and breast milk samples from 18 women.
“To date, SARS-CoV-2 has not been isolated from breast milk, and there are no documented cases of transmission of infectious virus to the infant through breast milk,” but the potential for transmission remains a concern among women who want to breastfeed, wrote Christina Chambers, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators identified 18 women with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections (all but 1 of the women had symptomatic COVID-19 disease) and infants aged 0-19 months between March 27 and May 6, 2020. The average age of the mothers was 34 years, and 78% were non-Hispanic White. The women provided 1-12 samples of breast milk for a total of 64 samples collected before and after positive COVID-19 tests.
One sample yielded detectable RNA from SARS-CoV-2 and was collected on the day of the woman’s symptom onset. However, one sample taken 2 days prior to symptom onset and two samples collected 12 and 41 days later tested negative for viral RNA, the researchers said. In addition, no replication-competent virus was identified in the positive sample or any of the other samples.
The researchers spiked two stored milk samples collected prior to the pandemic with replication-competent SARS-CoV-2. Virus was not detected by culture in the samples after Holder pasteurization, but was detected by culture in nonpasteurized aliquots of the same samples.
“These data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 RNA does not represent replication-competent virus and that breast milk may not be a source of infection for the infant,” Dr. Chambers and associates said.
The results were limited by several factors including the small sample size and potential for selection bias, as well as the use of self-reports of positive tests and self-collection of breast milk, the researchers noted. However, the findings are reassuring in light of the known benefits of breastfeeding and the use of milk banks.
“This research is important because the pandemic is ongoing and has far-reaching consequences: as the authors indicate, the potential for viral transmission through breast milk remains a critical question for women infected with SARS-CoV-2 who wish to breastfeed,” Janet R. Hardy, PhD, MPH, MSc, a consultant on global maternal-child health and pharmacoepidemiology, said in an interview.
“This virus has everyone on a rapid learning track, and all information that helps build evidence to support women’s decision-making in the care of their children is valuable,” she said. “These findings suggest that breast milk may not be a source of SARS-CoV-2 infection for the infant. They provide some reassurance given the recognized benefits of breastfeeding and human milk.”
However, “This study is very specific to breast milk,” she emphasized. “In advising women infected with SARS-CoV-2, clinicians may want to include a discussion of protection methods to prevent maternal transmission of the virus through respiratory droplets.”
Although the data are preliminary, “the investigators established and validated an RT-PCR [reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction] assay and developed tissue culture methods for replication-competent SARS-CoV-2 in breast milk, both valuable tools for further studies. Next steps will include controlled studies of greater sample size with independent verification of RT-PCR positivity,” said Dr. Hardy, a consultant to Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, Conn.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Institute of Mental Health. Medela Corporation provided milk sample collection materials. The Family Larsson-Rosenquist Foundation provided an unrestricted COVID19 emergency gift fund. The Mothers’ Milk Bank at Austin paid for shipping costs.
SOURCE: Chambers C et al. JAMA. 2020 Aug 19. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.15580.
Breast milk is an unlikely source of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from mothers to infants, according to data from case reports and breast milk samples from 18 women.
“To date, SARS-CoV-2 has not been isolated from breast milk, and there are no documented cases of transmission of infectious virus to the infant through breast milk,” but the potential for transmission remains a concern among women who want to breastfeed, wrote Christina Chambers, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators identified 18 women with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections (all but 1 of the women had symptomatic COVID-19 disease) and infants aged 0-19 months between March 27 and May 6, 2020. The average age of the mothers was 34 years, and 78% were non-Hispanic White. The women provided 1-12 samples of breast milk for a total of 64 samples collected before and after positive COVID-19 tests.
One sample yielded detectable RNA from SARS-CoV-2 and was collected on the day of the woman’s symptom onset. However, one sample taken 2 days prior to symptom onset and two samples collected 12 and 41 days later tested negative for viral RNA, the researchers said. In addition, no replication-competent virus was identified in the positive sample or any of the other samples.
The researchers spiked two stored milk samples collected prior to the pandemic with replication-competent SARS-CoV-2. Virus was not detected by culture in the samples after Holder pasteurization, but was detected by culture in nonpasteurized aliquots of the same samples.
“These data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 RNA does not represent replication-competent virus and that breast milk may not be a source of infection for the infant,” Dr. Chambers and associates said.
The results were limited by several factors including the small sample size and potential for selection bias, as well as the use of self-reports of positive tests and self-collection of breast milk, the researchers noted. However, the findings are reassuring in light of the known benefits of breastfeeding and the use of milk banks.
“This research is important because the pandemic is ongoing and has far-reaching consequences: as the authors indicate, the potential for viral transmission through breast milk remains a critical question for women infected with SARS-CoV-2 who wish to breastfeed,” Janet R. Hardy, PhD, MPH, MSc, a consultant on global maternal-child health and pharmacoepidemiology, said in an interview.
“This virus has everyone on a rapid learning track, and all information that helps build evidence to support women’s decision-making in the care of their children is valuable,” she said. “These findings suggest that breast milk may not be a source of SARS-CoV-2 infection for the infant. They provide some reassurance given the recognized benefits of breastfeeding and human milk.”
However, “This study is very specific to breast milk,” she emphasized. “In advising women infected with SARS-CoV-2, clinicians may want to include a discussion of protection methods to prevent maternal transmission of the virus through respiratory droplets.”
Although the data are preliminary, “the investigators established and validated an RT-PCR [reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction] assay and developed tissue culture methods for replication-competent SARS-CoV-2 in breast milk, both valuable tools for further studies. Next steps will include controlled studies of greater sample size with independent verification of RT-PCR positivity,” said Dr. Hardy, a consultant to Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, Conn.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Institute of Mental Health. Medela Corporation provided milk sample collection materials. The Family Larsson-Rosenquist Foundation provided an unrestricted COVID19 emergency gift fund. The Mothers’ Milk Bank at Austin paid for shipping costs.
SOURCE: Chambers C et al. JAMA. 2020 Aug 19. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.15580.
Breast milk is an unlikely source of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from mothers to infants, according to data from case reports and breast milk samples from 18 women.
“To date, SARS-CoV-2 has not been isolated from breast milk, and there are no documented cases of transmission of infectious virus to the infant through breast milk,” but the potential for transmission remains a concern among women who want to breastfeed, wrote Christina Chambers, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues.
In a research letter published in JAMA, the investigators identified 18 women with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infections (all but 1 of the women had symptomatic COVID-19 disease) and infants aged 0-19 months between March 27 and May 6, 2020. The average age of the mothers was 34 years, and 78% were non-Hispanic White. The women provided 1-12 samples of breast milk for a total of 64 samples collected before and after positive COVID-19 tests.
One sample yielded detectable RNA from SARS-CoV-2 and was collected on the day of the woman’s symptom onset. However, one sample taken 2 days prior to symptom onset and two samples collected 12 and 41 days later tested negative for viral RNA, the researchers said. In addition, no replication-competent virus was identified in the positive sample or any of the other samples.
The researchers spiked two stored milk samples collected prior to the pandemic with replication-competent SARS-CoV-2. Virus was not detected by culture in the samples after Holder pasteurization, but was detected by culture in nonpasteurized aliquots of the same samples.
“These data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 RNA does not represent replication-competent virus and that breast milk may not be a source of infection for the infant,” Dr. Chambers and associates said.
The results were limited by several factors including the small sample size and potential for selection bias, as well as the use of self-reports of positive tests and self-collection of breast milk, the researchers noted. However, the findings are reassuring in light of the known benefits of breastfeeding and the use of milk banks.
“This research is important because the pandemic is ongoing and has far-reaching consequences: as the authors indicate, the potential for viral transmission through breast milk remains a critical question for women infected with SARS-CoV-2 who wish to breastfeed,” Janet R. Hardy, PhD, MPH, MSc, a consultant on global maternal-child health and pharmacoepidemiology, said in an interview.
“This virus has everyone on a rapid learning track, and all information that helps build evidence to support women’s decision-making in the care of their children is valuable,” she said. “These findings suggest that breast milk may not be a source of SARS-CoV-2 infection for the infant. They provide some reassurance given the recognized benefits of breastfeeding and human milk.”
However, “This study is very specific to breast milk,” she emphasized. “In advising women infected with SARS-CoV-2, clinicians may want to include a discussion of protection methods to prevent maternal transmission of the virus through respiratory droplets.”
Although the data are preliminary, “the investigators established and validated an RT-PCR [reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction] assay and developed tissue culture methods for replication-competent SARS-CoV-2 in breast milk, both valuable tools for further studies. Next steps will include controlled studies of greater sample size with independent verification of RT-PCR positivity,” said Dr. Hardy, a consultant to Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, Conn.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Institute of Mental Health. Medela Corporation provided milk sample collection materials. The Family Larsson-Rosenquist Foundation provided an unrestricted COVID19 emergency gift fund. The Mothers’ Milk Bank at Austin paid for shipping costs.
SOURCE: Chambers C et al. JAMA. 2020 Aug 19. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.15580.
FROM JAMA
First guideline on NGS testing in cancer, from ESMO
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Recommendations on the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) tests for patients with metastatic cancer have been issued by the European Society for Medical Oncology, the first recommendations of their kind to be published by any medical society.
“Until now, there were no recommendations from scientific societies on how to use this technique in daily clinical practice to profile metastatic cancers,” Fernanda Mosele, MD, medical oncologist, Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, said in a statement.
NGS testing is already used extensively in oncology, particularly in metastatic cancer, she noted. The technology is used to assess the sequence of DNA in genes from a tumor tissue sample. Numerous genes can be quickly sequenced at the same time at relatively low cost. The results provide information on mutations that are present, which, in turn, helps with deciding which treatments to use, including drugs targeting the identified mutations.
“Our intent is that they [the guidelines] will unify decision-making about how NGS should be used for patients with metastatic cancer,” Dr. Mosele said.
The recommendations were published online August 25 in Annals of Oncology.
Overall, ESMO recommends the use of tumor multigene NGS for non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and cholangiocarcinoma.
For other cancers, the authors said that NGS is not recommended in clinical practice but could be used for research purposes.
However, patients should be informed that it is unlikely that test results would benefit them much personally.
Physicians and patients may decide together to subject the tumor to mutational testing using a large panel of genes, provided testing doesn’t burden the health care system with additional costs.
“This recommendation acknowledges that a small number of patients could benefit from a drug because they have a rare mutation,” Joaquin Mateo, MD, chair of the ESMO working group, said in a statement.
“So beyond the cancers in which everyone should receive NGS, there is room for physicians and patients to discuss the pros and cons of ordering these tests,” he added.
ESMO also does not recommend the use of off-label drugs matched to any genomic alteration detected by NGS unless an access program and a decisional procedure have been developed, either regionally or nationally.
No need for NGS testing of other cancers
In contrast to NSCLC, “there is currently no need to perform tumor multigene NGS for patients with mBC [metastatic breast cancer] in the context of daily practice,” ESMO stated.
This is largely because somatic sequencing cannot fully substitute for germline testing for BRCA status, and other mutations, such as HER2, can be detected using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
The same can be said for patients with metastatic gastric cancer, inasmuch as detection of alterations can and should be done using cheaper testing methods, ESMO pointed out.
However, ESMO members still emphasized that it’s important to include patients with metastatic breast cancer in molecular screening programs as well as in clinical trials testing targeted agents.
Similarly, there is no need to test metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) using multigene NGS in daily practice, inasmuch as most level 1 alterations in mCRC can be determined by IHC or PCR.
However, NGS can be considered as an alternative to PCR-based tests in mCRC, provided NGS is not associated with additional cost.
ESMO again recommended that research centers include mCRC patients in molecular screening programs in order for them to have access to innovative clinical trial agents.
As for advanced prostate cancer, ESMO does recommend that clinicians perform NGS on tissue samples to assess the tumor’s mutational status, at least for the presence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, when patients have access to the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors for treatment.
The authors cautioned, however, that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should be used only when there are specific agreements with payers.
Multigene NGS is also not recommended for patients with advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), although ESMO points out that it is the role of research centers to propose multigene sequencing for these patients in the context of molecular screening programs.
This is again to facilitate access to innovative drugs for these patients.
Similar to recommendations for patients with advanced PDAC, patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) do not need to have tumor multigene NGS either.
Considering the high unmet needs of HCC patients, ESMO feels that research centers should propose multigene sequencing to patients with advanced HCC in the context of molecular screening programs.
In contrast, ESMO recommended that tumor multigene NGS be used to detect actionable alterations in patients with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Again, they predict that this strategy is unlikely to be cost-effective, so larger panels should only be used if a specific agreement is in place with payers.
ESMO also assessed the frequency of level 1 alterations in less frequent tumor types, including ovarian cancers. Because BRCA1 and BRCA2 somatic mutations in ovarian tumors have been associated with increased response to the PARP inhibitors, the use of multigene NGS is justified with this malignancy, ESMO states.
The authors also recommend that tumor mutational burden be determined in cervical cancer, moderately differentiated neuroendocrine tumors, salivary cancers, vulvar cancer, and thyroid cancers.
Dr. Mosele has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Many coauthors have relationships with the pharmaceutical industry, as listed in the article.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mitigating psychiatric disorder relapse in pregnancy during pandemic
In a previous column, I addressed some of the issues that quickly arose in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and their implications for reproductive psychiatry. These issues ranged from the importance of sustaining well-being in pregnant and postpartum women during the pandemic, to temporary restrictions that were in place during the early part of the pandemic with respect to performing infertility procedures, to the practical issues of limiting the number of people who could attend to women during labor and delivery in the hospital.
Five months later, we’ve learned a great deal about trying to sustain emotional well-being among pregnant women during COVID-19. There is a high rate of anxiety among women who are pregnant and women who have particularly young children around the various issues of juggling activities of daily living during the pandemic, including switching to remote work and homeschooling children. There is fear of contracting COVID-19 during pregnancy, the exact effects of which are still somewhat unknown. We have seen a shift to telemedicine for prenatal and postpartum obstetrics visits, and a change with respect to visitors and even in-home nurses that would help during the first weeks of life for some couples.
We wondered whether we would see a falloff in the numbers of women presenting to our clinic with questions about the reproductive safety of taking psychiatric medications during pregnancy. We were unclear as to whether women would defer plans to get pregnant given some of the uncertainties that have come with COVID-19. What we’ve seen, at least early on in the pandemic in Massachusetts, has been the opposite. More women during the first 4 months of the pandemic have been seen in our center compared with the same corresponding period over the last 5 years. The precise reasons for this are unclear, but one reason may be that shifting the practice of reproductive psychiatry and pregnancy planning for reproductive-age women to full virtual care has dropped the number of missed appointments to essentially zero. Women perhaps feel an urgency to have a plan for using psychiatric medication during pregnancy. They may also see the benefit of being able to have extended telemedicine consultations that frequently involve their partners, a practice we have always supported, but posed logistical challenges for some.
As our colleagues learned that we had shifted our clinical rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health, which we’ve been doing for 25 years, to a virtual format, we began offering a free 1-hour forum to discuss relevant issues around caring for psychiatrically ill women, with a focus on some of the issues that were particularly relevant during the pandemic. The most common reasons for consultation on our service are the appropriate, safest use of antidepressants and mood stabilizers during pregnancy, and that continues to be the case.
If there has been one guiding principle in treating perinatal depression during pregnancy, it has been our long-standing, laser-like focus on keeping women emotionally well during pregnancy, and to highlight the importance of this with women during consultations prior to and during pregnancy. Relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy is one the strongest predictors of postpartum depression, and the impact of untreated depression during pregnancy has been described in the literature and over the years in this column. However, where we want to minimize, if possible, severe onset of illness requiring hospitalization or emergent attention considering it may make social distancing and some of the other mitigating factors vis-à-vis COVID-19 more challenging.
Despite the accumulated data over the last 2 decades on the reproductive safety of antidepressants, women continue to have questions about the safety of these medications during pregnancy. Studies show now that many women would prefer, if at all possible, to defer treatment with antidepressants, and so they come to us with questions about their reproductive safety, the potential of switching to nonpharmacologic interventions, and the use of alternative interventions that might be used to treat their underlying mood disorder.
Investigators at the University of British Columbia recently have tried to inform the field with still another look, not at reproductive safety per se, but at risk of relapse of depression if women discontinue those medicines during pregnancy.1 There is a timeliness to this investigation, which was a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies that met a priori criteria for inclusion. Since some of our own group’s early work over 15 years ago on relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy,2 which indicated a substantial difference in risk of relapse between women who continued versus who discontinued antidepressants, other investigators have showed the difference in risk for relapse is not as substantial, and that continuation of medication did not appear to mitigate risk for relapse. In fact, in the systematic review, the investigators demonstrated that as a group, maintaining medicine did not appear to confer particular benefit to patients relative to risk for relapse compared to discontinuation of antidepressants.
However, looking more closely, Bayrampour and colleagues note for women with histories of more severe recurrent, major depression, relapse did in fact appear to be greater in women who discontinued compared with those with cases of mild to moderate depression. It is noteworthy that in both our early and later work, and certainly dovetailing with our clinical practice, we have noted severity of illness does not appear to correlate with the actual decisions women ultimately make regarding what they will do with antidepressants. Specifically, some women with very severe illness histories will discontinue antidepressants regardless of their risk for relapse. Alternatively, women with mild to moderate illness will sometimes elect to stay on antidepressant therapy. With all the information that we have about fetal exposure to antidepressants on one hand, the “unknown unknowns” are an understandable concern to both patients and clinicians. Clinicians are faced with the dilemma of how to best counsel women on continuing or discontinuing antidepressants as they plan to conceive or during pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
The literature cited and clinical experience over the last 3 decades suggests rather strongly that there is a relatively low likelihood women with histories of severe recurrent disease will be able to successfully discontinue antidepressants in the absence of relapse. A greater question is, what is the best way to proceed for women who have been on maintenance therapy and had more moderate symptoms?
I am inspired by some of the more recent literature that has tried to elucidate the role of nonpharmacologic interventions such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in an effort to mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who are well with histories of depression. To date, data do not inform the question as to whether MBCT can be used to mitigate risk of depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressants. That research question is actively being studied by several investigators, including ourselves.
Of particular interest is whether the addition of mindfulness practices such as MBCT in treatment could mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressant treatment, as that would certainly be a no-harm intervention that could mitigate risk even in a lower risk sample of patients. The question of how to “thread the needle” during the pandemic and best approach woman with a history of recurrent major depression on antidepressants is particularly timely and critical.
Regardless, we make clinical decisions collaboratively with patients based on their histories and individual wishes, and perhaps what we have learned over the last 5 months is the use of telemedicine does afford us the opportunity, regardless of the decisions that patients make, to more closely follow the clinical trajectory of women during pregnancy and the postpartum period so that regardless of treatment, we have an opportunity to intervene early when needed and to ascertain changes in clinical status early to mitigate the risk of frank relapse. From a reproductive psychiatric point of view, that is a silver lining with respect to the associated challenges that have come along with the pandemic.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
References
1. J Clin Psychiatry 2020;81(4):19r13134.
2. JAMA. 2006 Feb 1;295(5):499-507.
In a previous column, I addressed some of the issues that quickly arose in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and their implications for reproductive psychiatry. These issues ranged from the importance of sustaining well-being in pregnant and postpartum women during the pandemic, to temporary restrictions that were in place during the early part of the pandemic with respect to performing infertility procedures, to the practical issues of limiting the number of people who could attend to women during labor and delivery in the hospital.
Five months later, we’ve learned a great deal about trying to sustain emotional well-being among pregnant women during COVID-19. There is a high rate of anxiety among women who are pregnant and women who have particularly young children around the various issues of juggling activities of daily living during the pandemic, including switching to remote work and homeschooling children. There is fear of contracting COVID-19 during pregnancy, the exact effects of which are still somewhat unknown. We have seen a shift to telemedicine for prenatal and postpartum obstetrics visits, and a change with respect to visitors and even in-home nurses that would help during the first weeks of life for some couples.
We wondered whether we would see a falloff in the numbers of women presenting to our clinic with questions about the reproductive safety of taking psychiatric medications during pregnancy. We were unclear as to whether women would defer plans to get pregnant given some of the uncertainties that have come with COVID-19. What we’ve seen, at least early on in the pandemic in Massachusetts, has been the opposite. More women during the first 4 months of the pandemic have been seen in our center compared with the same corresponding period over the last 5 years. The precise reasons for this are unclear, but one reason may be that shifting the practice of reproductive psychiatry and pregnancy planning for reproductive-age women to full virtual care has dropped the number of missed appointments to essentially zero. Women perhaps feel an urgency to have a plan for using psychiatric medication during pregnancy. They may also see the benefit of being able to have extended telemedicine consultations that frequently involve their partners, a practice we have always supported, but posed logistical challenges for some.
As our colleagues learned that we had shifted our clinical rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health, which we’ve been doing for 25 years, to a virtual format, we began offering a free 1-hour forum to discuss relevant issues around caring for psychiatrically ill women, with a focus on some of the issues that were particularly relevant during the pandemic. The most common reasons for consultation on our service are the appropriate, safest use of antidepressants and mood stabilizers during pregnancy, and that continues to be the case.
If there has been one guiding principle in treating perinatal depression during pregnancy, it has been our long-standing, laser-like focus on keeping women emotionally well during pregnancy, and to highlight the importance of this with women during consultations prior to and during pregnancy. Relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy is one the strongest predictors of postpartum depression, and the impact of untreated depression during pregnancy has been described in the literature and over the years in this column. However, where we want to minimize, if possible, severe onset of illness requiring hospitalization or emergent attention considering it may make social distancing and some of the other mitigating factors vis-à-vis COVID-19 more challenging.
Despite the accumulated data over the last 2 decades on the reproductive safety of antidepressants, women continue to have questions about the safety of these medications during pregnancy. Studies show now that many women would prefer, if at all possible, to defer treatment with antidepressants, and so they come to us with questions about their reproductive safety, the potential of switching to nonpharmacologic interventions, and the use of alternative interventions that might be used to treat their underlying mood disorder.
Investigators at the University of British Columbia recently have tried to inform the field with still another look, not at reproductive safety per se, but at risk of relapse of depression if women discontinue those medicines during pregnancy.1 There is a timeliness to this investigation, which was a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies that met a priori criteria for inclusion. Since some of our own group’s early work over 15 years ago on relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy,2 which indicated a substantial difference in risk of relapse between women who continued versus who discontinued antidepressants, other investigators have showed the difference in risk for relapse is not as substantial, and that continuation of medication did not appear to mitigate risk for relapse. In fact, in the systematic review, the investigators demonstrated that as a group, maintaining medicine did not appear to confer particular benefit to patients relative to risk for relapse compared to discontinuation of antidepressants.
However, looking more closely, Bayrampour and colleagues note for women with histories of more severe recurrent, major depression, relapse did in fact appear to be greater in women who discontinued compared with those with cases of mild to moderate depression. It is noteworthy that in both our early and later work, and certainly dovetailing with our clinical practice, we have noted severity of illness does not appear to correlate with the actual decisions women ultimately make regarding what they will do with antidepressants. Specifically, some women with very severe illness histories will discontinue antidepressants regardless of their risk for relapse. Alternatively, women with mild to moderate illness will sometimes elect to stay on antidepressant therapy. With all the information that we have about fetal exposure to antidepressants on one hand, the “unknown unknowns” are an understandable concern to both patients and clinicians. Clinicians are faced with the dilemma of how to best counsel women on continuing or discontinuing antidepressants as they plan to conceive or during pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
The literature cited and clinical experience over the last 3 decades suggests rather strongly that there is a relatively low likelihood women with histories of severe recurrent disease will be able to successfully discontinue antidepressants in the absence of relapse. A greater question is, what is the best way to proceed for women who have been on maintenance therapy and had more moderate symptoms?
I am inspired by some of the more recent literature that has tried to elucidate the role of nonpharmacologic interventions such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in an effort to mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who are well with histories of depression. To date, data do not inform the question as to whether MBCT can be used to mitigate risk of depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressants. That research question is actively being studied by several investigators, including ourselves.
Of particular interest is whether the addition of mindfulness practices such as MBCT in treatment could mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressant treatment, as that would certainly be a no-harm intervention that could mitigate risk even in a lower risk sample of patients. The question of how to “thread the needle” during the pandemic and best approach woman with a history of recurrent major depression on antidepressants is particularly timely and critical.
Regardless, we make clinical decisions collaboratively with patients based on their histories and individual wishes, and perhaps what we have learned over the last 5 months is the use of telemedicine does afford us the opportunity, regardless of the decisions that patients make, to more closely follow the clinical trajectory of women during pregnancy and the postpartum period so that regardless of treatment, we have an opportunity to intervene early when needed and to ascertain changes in clinical status early to mitigate the risk of frank relapse. From a reproductive psychiatric point of view, that is a silver lining with respect to the associated challenges that have come along with the pandemic.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
References
1. J Clin Psychiatry 2020;81(4):19r13134.
2. JAMA. 2006 Feb 1;295(5):499-507.
In a previous column, I addressed some of the issues that quickly arose in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and their implications for reproductive psychiatry. These issues ranged from the importance of sustaining well-being in pregnant and postpartum women during the pandemic, to temporary restrictions that were in place during the early part of the pandemic with respect to performing infertility procedures, to the practical issues of limiting the number of people who could attend to women during labor and delivery in the hospital.
Five months later, we’ve learned a great deal about trying to sustain emotional well-being among pregnant women during COVID-19. There is a high rate of anxiety among women who are pregnant and women who have particularly young children around the various issues of juggling activities of daily living during the pandemic, including switching to remote work and homeschooling children. There is fear of contracting COVID-19 during pregnancy, the exact effects of which are still somewhat unknown. We have seen a shift to telemedicine for prenatal and postpartum obstetrics visits, and a change with respect to visitors and even in-home nurses that would help during the first weeks of life for some couples.
We wondered whether we would see a falloff in the numbers of women presenting to our clinic with questions about the reproductive safety of taking psychiatric medications during pregnancy. We were unclear as to whether women would defer plans to get pregnant given some of the uncertainties that have come with COVID-19. What we’ve seen, at least early on in the pandemic in Massachusetts, has been the opposite. More women during the first 4 months of the pandemic have been seen in our center compared with the same corresponding period over the last 5 years. The precise reasons for this are unclear, but one reason may be that shifting the practice of reproductive psychiatry and pregnancy planning for reproductive-age women to full virtual care has dropped the number of missed appointments to essentially zero. Women perhaps feel an urgency to have a plan for using psychiatric medication during pregnancy. They may also see the benefit of being able to have extended telemedicine consultations that frequently involve their partners, a practice we have always supported, but posed logistical challenges for some.
As our colleagues learned that we had shifted our clinical rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health, which we’ve been doing for 25 years, to a virtual format, we began offering a free 1-hour forum to discuss relevant issues around caring for psychiatrically ill women, with a focus on some of the issues that were particularly relevant during the pandemic. The most common reasons for consultation on our service are the appropriate, safest use of antidepressants and mood stabilizers during pregnancy, and that continues to be the case.
If there has been one guiding principle in treating perinatal depression during pregnancy, it has been our long-standing, laser-like focus on keeping women emotionally well during pregnancy, and to highlight the importance of this with women during consultations prior to and during pregnancy. Relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy is one the strongest predictors of postpartum depression, and the impact of untreated depression during pregnancy has been described in the literature and over the years in this column. However, where we want to minimize, if possible, severe onset of illness requiring hospitalization or emergent attention considering it may make social distancing and some of the other mitigating factors vis-à-vis COVID-19 more challenging.
Despite the accumulated data over the last 2 decades on the reproductive safety of antidepressants, women continue to have questions about the safety of these medications during pregnancy. Studies show now that many women would prefer, if at all possible, to defer treatment with antidepressants, and so they come to us with questions about their reproductive safety, the potential of switching to nonpharmacologic interventions, and the use of alternative interventions that might be used to treat their underlying mood disorder.
Investigators at the University of British Columbia recently have tried to inform the field with still another look, not at reproductive safety per se, but at risk of relapse of depression if women discontinue those medicines during pregnancy.1 There is a timeliness to this investigation, which was a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies that met a priori criteria for inclusion. Since some of our own group’s early work over 15 years ago on relapse of psychiatric disorder during pregnancy,2 which indicated a substantial difference in risk of relapse between women who continued versus who discontinued antidepressants, other investigators have showed the difference in risk for relapse is not as substantial, and that continuation of medication did not appear to mitigate risk for relapse. In fact, in the systematic review, the investigators demonstrated that as a group, maintaining medicine did not appear to confer particular benefit to patients relative to risk for relapse compared to discontinuation of antidepressants.
However, looking more closely, Bayrampour and colleagues note for women with histories of more severe recurrent, major depression, relapse did in fact appear to be greater in women who discontinued compared with those with cases of mild to moderate depression. It is noteworthy that in both our early and later work, and certainly dovetailing with our clinical practice, we have noted severity of illness does not appear to correlate with the actual decisions women ultimately make regarding what they will do with antidepressants. Specifically, some women with very severe illness histories will discontinue antidepressants regardless of their risk for relapse. Alternatively, women with mild to moderate illness will sometimes elect to stay on antidepressant therapy. With all the information that we have about fetal exposure to antidepressants on one hand, the “unknown unknowns” are an understandable concern to both patients and clinicians. Clinicians are faced with the dilemma of how to best counsel women on continuing or discontinuing antidepressants as they plan to conceive or during pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
The literature cited and clinical experience over the last 3 decades suggests rather strongly that there is a relatively low likelihood women with histories of severe recurrent disease will be able to successfully discontinue antidepressants in the absence of relapse. A greater question is, what is the best way to proceed for women who have been on maintenance therapy and had more moderate symptoms?
I am inspired by some of the more recent literature that has tried to elucidate the role of nonpharmacologic interventions such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) in an effort to mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who are well with histories of depression. To date, data do not inform the question as to whether MBCT can be used to mitigate risk of depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressants. That research question is actively being studied by several investigators, including ourselves.
Of particular interest is whether the addition of mindfulness practices such as MBCT in treatment could mitigate risk for depressive relapse in pregnant women who continue or discontinue antidepressant treatment, as that would certainly be a no-harm intervention that could mitigate risk even in a lower risk sample of patients. The question of how to “thread the needle” during the pandemic and best approach woman with a history of recurrent major depression on antidepressants is particularly timely and critical.
Regardless, we make clinical decisions collaboratively with patients based on their histories and individual wishes, and perhaps what we have learned over the last 5 months is the use of telemedicine does afford us the opportunity, regardless of the decisions that patients make, to more closely follow the clinical trajectory of women during pregnancy and the postpartum period so that regardless of treatment, we have an opportunity to intervene early when needed and to ascertain changes in clinical status early to mitigate the risk of frank relapse. From a reproductive psychiatric point of view, that is a silver lining with respect to the associated challenges that have come along with the pandemic.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
References
1. J Clin Psychiatry 2020;81(4):19r13134.
2. JAMA. 2006 Feb 1;295(5):499-507.
FDA approves point-of-care COVID-19 antigen test
The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.

The BinaxNOW COVID-19 Ag Card (Abbott) is similar in some ways to a home pregnancy test. Clinicians read results on a card – one line for a negative result, two lines for positive.
A health care provider swabs a symptomatic patient’s nose, twirls the sample on a test card with a reagent, and waits approximately 15 minutes for results. No additional equipment is required.
Abbott expects the test to cost about $5.00, the company announced.
Office-based physicians, ED physicians, and school nurses could potentially use the product as a point-of-care test. The FDA granted the test emergency use authorization. It is approved for people suspected of having COVID-19 who are within 7 days of symptom onset.
“This new COVID-19 antigen test is an important addition to available tests because the results can be read in minutes, right off the testing card,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, wrote in a news release. “This means people will know if they have the virus in almost real time.”
“This fits into the testing landscape as a simple, inexpensive test that does not require additional equipment,” Marcus Lynch, PhD, assistant manager of the Health Care Horizon Scanning program at ECRI, told Medscape Medical News when asked to comment. ECRI is an independent, nonprofit organization that reviews and analyses COVID-19 therapeutics and diagnostics.
The test could help with early triage of patients who test positive, perhaps alerting physicians to the need to start COVID-19 therapy, added Lynch, who specializes in immunology and vaccine development. The test also could be useful in low-resource settings.
The FDA included a caveat: antigen tests are generally less sensitive than molecular assays. “Due to the potential for decreased sensitivity compared to molecular assays, negative results from an antigen test may need to be confirmed with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions,” the agency noted.
Lynch agreed and said that when a patient tests negative, physicians still need to use their clinical judgment on the basis of symptoms and other factors. The test is not designed for population-based screening of asymptomatic people, he added.
Abbott announced plans to make up to 50 million tests available per month in the United States starting in October. The product comes with a free smartphone app that people can use to share results with an employer or with others as needed.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.





















