User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Large vessel stroke linked to AstraZeneca COVID vaccine
The three cases (one of which was fatal) occurred in two women and one man in their 30s or 40s and involved blockages of the carotid and middle cerebral artery. Two of the three patients also had venous thrombosis involving the portal and cerebral venous system. All three also had extremely low platelet counts, confirmed antibodies to platelet factor 4, and raised D-dimer levels, all characteristic of the vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) reaction associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They are described in detail in a letter published online on May 25 in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
“These are [the] first detailed reports of arterial stroke believed to be caused by VITT after the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, although stroke has been mentioned previously in the VITT data,” said senior author David Werring, PhD, FRCP.
“VITT has more commonly presented as CVST [Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis] which is stroke caused by a venous thrombosis; these cases are showing that it can also cause stroke caused by an arterial thrombosis,” explained Dr. Werring, professor of clinical neurology at the Stroke Research Centre, University College London.
“In patients who present with ischemic stroke, especially younger patients, and who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine within the past month, clinicians need to consider VITT as a possible cause, as there is a specific treatment needed for this syndrome,” he said.
Young patients presenting with ischemic stroke after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine should urgently be evaluated for VITT with laboratory tests, including platelet count, D-dimers, fibrinogen, and anti-PF4 antibodies, the authors wrote, and then managed by a multidisciplinary team, including hematology, neurology, stroke, neurosurgery, and neuroradiology, for rapid access to treatments including intravenous immune globulin, methylprednisolone, plasmapheresis, and nonheparin anticoagulants such as fondaparinux, argatroban, or direct oral anticoagulants.
Dr. Werring noted that these reports do not add anything to the overall risk/benefit of the vaccine, as they are only describing three cases. “While VITT is very serious, the benefit of the vaccine still outweighs its risks,” he said. “Around 40% of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 experience some sort of thrombosis and about 1.5% have an ischemic stroke. Whereas latest figures from the U.K. estimate the incidence of VITT with the AstraZeneca vaccine of 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 100,000.
“Our report doesn’t suggest that VITT is more common than these latest figures estimate, but we are just drawing attention to an alternative presentation,” he added.
Three cases
The first patient in the current case series, a woman in her 30s, experienced an intermittent headache on the right side and around her eyes 6 days after the vaccine. Five days later, she awoke feeling drowsy and with weakness to her left face, arm, and leg.
Imaging revealed a blocked right middle cerebral artery with brain infarction and clots in the right portal vein. She underwent brain surgery to reduce the pressure in her skull, plasma removal and replacement, and received the anticoagulant fondaparinux, but she still unfortunately died.
The second patient, a woman in her late 30s, presented with headache, confusion, weakness in her left arm, and loss of vision on the left side 12 days after having received the vaccine. Imaging showed occlusion of both carotid arteries, as well as pulmonary embolism and a left cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Her platelet count increased following plasma removal and replacement and intravenous corticosteroids, and her condition improved after fondaparinux treatment.
The third patient, a man in his early 40s, presented 3 weeks after receiving his vaccination with problems speaking. Imaging showed a clot in the left middle cerebral artery, but there was no evidence of clots in the cerebral venous sinuses. He received a platelet and plasma transfusion, and fondaparinux, and remains stable.
High index of suspicion required
In a linked commentary, Hugh Markus, PhD, FRCP, professor of stroke medicine at the University of Cambridge, United Kingdom, wrote: “This report emphasizes that the immune mediated coagulopathy can also cause arterial thrombosis, including ischemic stroke, although venous thrombosis and especially cerebral venous sinus thrombosis appear more frequent.
“During the current period of COVID vaccination, a high index of suspicion is required to identify thrombotic episodes following vaccination,” he added. “However, it is important to remember that these side effects are rare and much less common than both cerebral venous thrombosis and ischemic stroke associated with COVID-19 infection itself.”
Risk/benefit unaltered
Several experts who commented on these reports for the Science Media Centre all agreed with Dr. Werring and Dr. Markus that these reports do not alter the current risk/benefit estimates with the vaccine.
Ian Douglas, PhD, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who sits on the U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency’s Pharmacovigilance Expert Advisory Group, said: “The picture regarding the rare syndrome of blood clots combined with low platelet counts associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine is becoming clearer. Until now, the cases described have tended to involve clots in veins such as cerebral vein thrombosis. In this series of three case reports, we now have some evidence that the types of blood vessels affected include arteries as well as veins.”
“It’s important to stress that such cases remain very rare, and it’s certainly much rarer in people who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine than it is in people affected by COVID-19 itself,” Dr. Douglas emphasized.
“The description of the cases suggests the patients involved presented with the same kind of symptoms as already described in cases involving cerebral vein thrombosis, and they don’t suggest patients need to be on the alert for anything different,” he added.
“However, the emergence of details like this will help guide health professionals who may be faced with similar cases in future; the sooner such cases are recognized, the more chance they will quickly receive the right kind of treatment, hopefully leading to better outcomes.”
Will Lester, MBChB, PhD, consultant hematologist, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, said: “VITT remains a rare complication, and patients with a history of thrombosis, including stroke, should not consider themselves to be at any higher risk of this type of rare thrombosis after vaccination, and COVID infection itself is a significant risk for stroke and other types of thrombosis.”
Many countries have paused use of the AstraZeneca vaccine because of its link to the VITT syndrome or restricted its use to older people as the VITT reaction appears to be slightly more common in younger people. In the United Kingdom, the current recommendation is that individuals under 40 years of age should be offered an alternative to the AstraZeneca vaccine where possible.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The three cases (one of which was fatal) occurred in two women and one man in their 30s or 40s and involved blockages of the carotid and middle cerebral artery. Two of the three patients also had venous thrombosis involving the portal and cerebral venous system. All three also had extremely low platelet counts, confirmed antibodies to platelet factor 4, and raised D-dimer levels, all characteristic of the vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) reaction associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They are described in detail in a letter published online on May 25 in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
“These are [the] first detailed reports of arterial stroke believed to be caused by VITT after the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, although stroke has been mentioned previously in the VITT data,” said senior author David Werring, PhD, FRCP.
“VITT has more commonly presented as CVST [Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis] which is stroke caused by a venous thrombosis; these cases are showing that it can also cause stroke caused by an arterial thrombosis,” explained Dr. Werring, professor of clinical neurology at the Stroke Research Centre, University College London.
“In patients who present with ischemic stroke, especially younger patients, and who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine within the past month, clinicians need to consider VITT as a possible cause, as there is a specific treatment needed for this syndrome,” he said.
Young patients presenting with ischemic stroke after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine should urgently be evaluated for VITT with laboratory tests, including platelet count, D-dimers, fibrinogen, and anti-PF4 antibodies, the authors wrote, and then managed by a multidisciplinary team, including hematology, neurology, stroke, neurosurgery, and neuroradiology, for rapid access to treatments including intravenous immune globulin, methylprednisolone, plasmapheresis, and nonheparin anticoagulants such as fondaparinux, argatroban, or direct oral anticoagulants.
Dr. Werring noted that these reports do not add anything to the overall risk/benefit of the vaccine, as they are only describing three cases. “While VITT is very serious, the benefit of the vaccine still outweighs its risks,” he said. “Around 40% of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 experience some sort of thrombosis and about 1.5% have an ischemic stroke. Whereas latest figures from the U.K. estimate the incidence of VITT with the AstraZeneca vaccine of 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 100,000.
“Our report doesn’t suggest that VITT is more common than these latest figures estimate, but we are just drawing attention to an alternative presentation,” he added.
Three cases
The first patient in the current case series, a woman in her 30s, experienced an intermittent headache on the right side and around her eyes 6 days after the vaccine. Five days later, she awoke feeling drowsy and with weakness to her left face, arm, and leg.
Imaging revealed a blocked right middle cerebral artery with brain infarction and clots in the right portal vein. She underwent brain surgery to reduce the pressure in her skull, plasma removal and replacement, and received the anticoagulant fondaparinux, but she still unfortunately died.
The second patient, a woman in her late 30s, presented with headache, confusion, weakness in her left arm, and loss of vision on the left side 12 days after having received the vaccine. Imaging showed occlusion of both carotid arteries, as well as pulmonary embolism and a left cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Her platelet count increased following plasma removal and replacement and intravenous corticosteroids, and her condition improved after fondaparinux treatment.
The third patient, a man in his early 40s, presented 3 weeks after receiving his vaccination with problems speaking. Imaging showed a clot in the left middle cerebral artery, but there was no evidence of clots in the cerebral venous sinuses. He received a platelet and plasma transfusion, and fondaparinux, and remains stable.
High index of suspicion required
In a linked commentary, Hugh Markus, PhD, FRCP, professor of stroke medicine at the University of Cambridge, United Kingdom, wrote: “This report emphasizes that the immune mediated coagulopathy can also cause arterial thrombosis, including ischemic stroke, although venous thrombosis and especially cerebral venous sinus thrombosis appear more frequent.
“During the current period of COVID vaccination, a high index of suspicion is required to identify thrombotic episodes following vaccination,” he added. “However, it is important to remember that these side effects are rare and much less common than both cerebral venous thrombosis and ischemic stroke associated with COVID-19 infection itself.”
Risk/benefit unaltered
Several experts who commented on these reports for the Science Media Centre all agreed with Dr. Werring and Dr. Markus that these reports do not alter the current risk/benefit estimates with the vaccine.
Ian Douglas, PhD, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who sits on the U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency’s Pharmacovigilance Expert Advisory Group, said: “The picture regarding the rare syndrome of blood clots combined with low platelet counts associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine is becoming clearer. Until now, the cases described have tended to involve clots in veins such as cerebral vein thrombosis. In this series of three case reports, we now have some evidence that the types of blood vessels affected include arteries as well as veins.”
“It’s important to stress that such cases remain very rare, and it’s certainly much rarer in people who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine than it is in people affected by COVID-19 itself,” Dr. Douglas emphasized.
“The description of the cases suggests the patients involved presented with the same kind of symptoms as already described in cases involving cerebral vein thrombosis, and they don’t suggest patients need to be on the alert for anything different,” he added.
“However, the emergence of details like this will help guide health professionals who may be faced with similar cases in future; the sooner such cases are recognized, the more chance they will quickly receive the right kind of treatment, hopefully leading to better outcomes.”
Will Lester, MBChB, PhD, consultant hematologist, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, said: “VITT remains a rare complication, and patients with a history of thrombosis, including stroke, should not consider themselves to be at any higher risk of this type of rare thrombosis after vaccination, and COVID infection itself is a significant risk for stroke and other types of thrombosis.”
Many countries have paused use of the AstraZeneca vaccine because of its link to the VITT syndrome or restricted its use to older people as the VITT reaction appears to be slightly more common in younger people. In the United Kingdom, the current recommendation is that individuals under 40 years of age should be offered an alternative to the AstraZeneca vaccine where possible.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The three cases (one of which was fatal) occurred in two women and one man in their 30s or 40s and involved blockages of the carotid and middle cerebral artery. Two of the three patients also had venous thrombosis involving the portal and cerebral venous system. All three also had extremely low platelet counts, confirmed antibodies to platelet factor 4, and raised D-dimer levels, all characteristic of the vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) reaction associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine.
They are described in detail in a letter published online on May 25 in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
“These are [the] first detailed reports of arterial stroke believed to be caused by VITT after the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine, although stroke has been mentioned previously in the VITT data,” said senior author David Werring, PhD, FRCP.
“VITT has more commonly presented as CVST [Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis] which is stroke caused by a venous thrombosis; these cases are showing that it can also cause stroke caused by an arterial thrombosis,” explained Dr. Werring, professor of clinical neurology at the Stroke Research Centre, University College London.
“In patients who present with ischemic stroke, especially younger patients, and who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine within the past month, clinicians need to consider VITT as a possible cause, as there is a specific treatment needed for this syndrome,” he said.
Young patients presenting with ischemic stroke after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine should urgently be evaluated for VITT with laboratory tests, including platelet count, D-dimers, fibrinogen, and anti-PF4 antibodies, the authors wrote, and then managed by a multidisciplinary team, including hematology, neurology, stroke, neurosurgery, and neuroradiology, for rapid access to treatments including intravenous immune globulin, methylprednisolone, plasmapheresis, and nonheparin anticoagulants such as fondaparinux, argatroban, or direct oral anticoagulants.
Dr. Werring noted that these reports do not add anything to the overall risk/benefit of the vaccine, as they are only describing three cases. “While VITT is very serious, the benefit of the vaccine still outweighs its risks,” he said. “Around 40% of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 experience some sort of thrombosis and about 1.5% have an ischemic stroke. Whereas latest figures from the U.K. estimate the incidence of VITT with the AstraZeneca vaccine of 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 100,000.
“Our report doesn’t suggest that VITT is more common than these latest figures estimate, but we are just drawing attention to an alternative presentation,” he added.
Three cases
The first patient in the current case series, a woman in her 30s, experienced an intermittent headache on the right side and around her eyes 6 days after the vaccine. Five days later, she awoke feeling drowsy and with weakness to her left face, arm, and leg.
Imaging revealed a blocked right middle cerebral artery with brain infarction and clots in the right portal vein. She underwent brain surgery to reduce the pressure in her skull, plasma removal and replacement, and received the anticoagulant fondaparinux, but she still unfortunately died.
The second patient, a woman in her late 30s, presented with headache, confusion, weakness in her left arm, and loss of vision on the left side 12 days after having received the vaccine. Imaging showed occlusion of both carotid arteries, as well as pulmonary embolism and a left cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Her platelet count increased following plasma removal and replacement and intravenous corticosteroids, and her condition improved after fondaparinux treatment.
The third patient, a man in his early 40s, presented 3 weeks after receiving his vaccination with problems speaking. Imaging showed a clot in the left middle cerebral artery, but there was no evidence of clots in the cerebral venous sinuses. He received a platelet and plasma transfusion, and fondaparinux, and remains stable.
High index of suspicion required
In a linked commentary, Hugh Markus, PhD, FRCP, professor of stroke medicine at the University of Cambridge, United Kingdom, wrote: “This report emphasizes that the immune mediated coagulopathy can also cause arterial thrombosis, including ischemic stroke, although venous thrombosis and especially cerebral venous sinus thrombosis appear more frequent.
“During the current period of COVID vaccination, a high index of suspicion is required to identify thrombotic episodes following vaccination,” he added. “However, it is important to remember that these side effects are rare and much less common than both cerebral venous thrombosis and ischemic stroke associated with COVID-19 infection itself.”
Risk/benefit unaltered
Several experts who commented on these reports for the Science Media Centre all agreed with Dr. Werring and Dr. Markus that these reports do not alter the current risk/benefit estimates with the vaccine.
Ian Douglas, PhD, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who sits on the U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency’s Pharmacovigilance Expert Advisory Group, said: “The picture regarding the rare syndrome of blood clots combined with low platelet counts associated with the AstraZeneca vaccine is becoming clearer. Until now, the cases described have tended to involve clots in veins such as cerebral vein thrombosis. In this series of three case reports, we now have some evidence that the types of blood vessels affected include arteries as well as veins.”
“It’s important to stress that such cases remain very rare, and it’s certainly much rarer in people who have had the AstraZeneca vaccine than it is in people affected by COVID-19 itself,” Dr. Douglas emphasized.
“The description of the cases suggests the patients involved presented with the same kind of symptoms as already described in cases involving cerebral vein thrombosis, and they don’t suggest patients need to be on the alert for anything different,” he added.
“However, the emergence of details like this will help guide health professionals who may be faced with similar cases in future; the sooner such cases are recognized, the more chance they will quickly receive the right kind of treatment, hopefully leading to better outcomes.”
Will Lester, MBChB, PhD, consultant hematologist, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, said: “VITT remains a rare complication, and patients with a history of thrombosis, including stroke, should not consider themselves to be at any higher risk of this type of rare thrombosis after vaccination, and COVID infection itself is a significant risk for stroke and other types of thrombosis.”
Many countries have paused use of the AstraZeneca vaccine because of its link to the VITT syndrome or restricted its use to older people as the VITT reaction appears to be slightly more common in younger people. In the United Kingdom, the current recommendation is that individuals under 40 years of age should be offered an alternative to the AstraZeneca vaccine where possible.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
OSA: Heart rate change may signal CPAP benefit
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
Some nonsleepy patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) may receive cardiovascular benefit from continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, according to a post hoc analysis of the RICCADSA clinical trial. That study found no benefit among patients overall, but the new analysis found that patients whose heart rate increases (delta heart rate, or dHR) more than average during apnea or hypopnea experienced fewer cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events during apnea or hypopnea when treated with CPAP.
Although RICCADSA showed no benefit, an analysis of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) cohorts found that elevated pulse rate response to respiratory events was associated with greater risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) morbidity and mortality. But the effect was seen only in nonsleepy patients. “We hypothesized that pulse rate response to apneas would predict which patients with OSA may most benefit from CPAP treatment. Now, our study suggests that there is, in fact, a subgroup of nonsleepy patients with OSA for whom CPAP could provide a reduction in risk, specifically those with a higher pulse rate response to their respiratory events,” Ali Azarbarzin, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Azarbarzin presented the study at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1103). He is in the division of sleep and circadian disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and is assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The study is in line with recent efforts to subgroup OSA patients to determine which are at higher risk of cardiovascular events and other complications, and which are most likely to respond to treatment, according to Esra Tasali, MD, of the University of Chicago, who moderated the session where the study was presented. “The field is really urgently in need of coming up with new methods, and I think this study is getting a handle on that,” said Dr. Tasali in an interview.
“I think that this is really pointing toward a new area that the whole (sleep field) is moving toward, which is better phenotyping of sleep apnea so that we can come up with more personalized treatments,” said Dr. Tasali.
The patients who appeared to gain a cardiovascular benefit from CPAP represented about 16% of trial participants. Dr. Azarbarzin refrained from making clinical recommendations, citing the need for more data. The team next plans to reproduce the findings in additional, larger trials such as the SAVE and ISAACC trials. “Ultimately, our goal is to confirm our findings in a future randomized controlled trial of CPAP by enrolling participants based on their pulse rate response,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
The RICCADSA study was a single center randomized, controlled trial with 226 patients with coronary artery disease and OSA who were randomized to CPAP or no CPAP treatment. In the overall population, CPAP treatment was not associated with a statistically significant change in repeat revascularization, myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P = .435). That study assumed that the effect of OSA on CVD is similar across all subgroups of dHR.
The mean increase in heart rate was 7.1 beats per minute (BPM; standard deviation, 3.7). Each standard deviation increase in dHR was linked to greater CVD risk (HR, 1.45; P = .029). For each standard deviation decrease in dHR, treatment with CPAP decreased the CVD risk (HR, 0.54; P = .043).
For patients with a low dHR of 4 BPM, the hazard ratio for CVD was 0.8 with no CPAP treatment and 1.2 for CPAP treatment. For those at the mean value of 7 BPM, the HRs were 1.1 and 0.9 respectively. For those with a high dHR, (10 BPM), the hazard ratio was 1.6 without treatment and 0.7 with CPAP.
“We modeled delta heart rate interaction with CPAP, which was significant. What this means is that for someone with a mean delta heart rate of 7 beats per minute, the risk reduction (with CPAP) is similar to what RICCADSA reported. But if you look at those with high delta heart rate, the risk reduction was significantly larger. It was actually a more than 50% reduction of risk with CPAP treatment,” said Dr. Azarbarzin.
Dr. Azarbarzin has consulted for Somnifix and Apnimed and has received grants from Somnifix. Dr. Tasali has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ATS 2021
COVID-19 vaccination rate rising quickly among adolescents
With nearly half of all Americans having received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, the youngest eligible group is beginning to overcome its late start, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
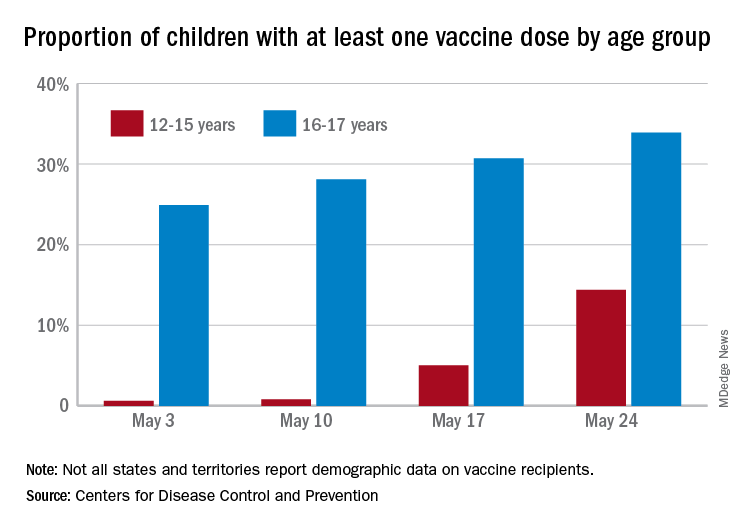
As of May 24, 49.4% of the U.S. population – that’s almost 164 million people – has received at least one dose of vaccine. The corresponding figure for children aged 12-15 years is 14.4%, but that’s up from only 0.6% just 3 weeks before. Among children aged 16-17, who’ve been getting vaccinated since early April in some states, the proportion receiving at least one dose went from 24.9% to 33.9% over those same 3 weeks, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
The comparatively rapid increase among the younger group of eligible children can be seen over the last 14 days. To put that into perspective, only those aged 25-39 years were higher at 21.9%, while 18-24 (12.1%), 40-49 (13.4%), 50-64 (18.2%), 65-74 (5.3%), and ≥75 (2.9%) were all lower.
The 12- to 15-year-olds are further behind when it comes to full vaccination status, however, with just 0.6% having received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 21.6% for those aged 16-17 years. Children aged 12-15 make up 5% of the total U.S. population but just 0.1% of all those who have been fully vaccinated versus 2.5% and 1.4%, respectively, for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
With nearly half of all Americans having received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, the youngest eligible group is beginning to overcome its late start, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

As of May 24, 49.4% of the U.S. population – that’s almost 164 million people – has received at least one dose of vaccine. The corresponding figure for children aged 12-15 years is 14.4%, but that’s up from only 0.6% just 3 weeks before. Among children aged 16-17, who’ve been getting vaccinated since early April in some states, the proportion receiving at least one dose went from 24.9% to 33.9% over those same 3 weeks, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
The comparatively rapid increase among the younger group of eligible children can be seen over the last 14 days. To put that into perspective, only those aged 25-39 years were higher at 21.9%, while 18-24 (12.1%), 40-49 (13.4%), 50-64 (18.2%), 65-74 (5.3%), and ≥75 (2.9%) were all lower.
The 12- to 15-year-olds are further behind when it comes to full vaccination status, however, with just 0.6% having received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 21.6% for those aged 16-17 years. Children aged 12-15 make up 5% of the total U.S. population but just 0.1% of all those who have been fully vaccinated versus 2.5% and 1.4%, respectively, for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
With nearly half of all Americans having received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine, the youngest eligible group is beginning to overcome its late start, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

As of May 24, 49.4% of the U.S. population – that’s almost 164 million people – has received at least one dose of vaccine. The corresponding figure for children aged 12-15 years is 14.4%, but that’s up from only 0.6% just 3 weeks before. Among children aged 16-17, who’ve been getting vaccinated since early April in some states, the proportion receiving at least one dose went from 24.9% to 33.9% over those same 3 weeks, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
The comparatively rapid increase among the younger group of eligible children can be seen over the last 14 days. To put that into perspective, only those aged 25-39 years were higher at 21.9%, while 18-24 (12.1%), 40-49 (13.4%), 50-64 (18.2%), 65-74 (5.3%), and ≥75 (2.9%) were all lower.
The 12- to 15-year-olds are further behind when it comes to full vaccination status, however, with just 0.6% having received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 21.6% for those aged 16-17 years. Children aged 12-15 make up 5% of the total U.S. population but just 0.1% of all those who have been fully vaccinated versus 2.5% and 1.4%, respectively, for those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
Tezepelumab reduces serious exacerbations in severe asthma
Results from the NAVIGATOR study of tezepelumab showed that treatment of adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma with the new biologic led to a large reduction in exacerbations requiring hospital stays and ED visits.
Tezepelumab, codeveloped by Amgen and AstraZeneca, has a novel mechanism of action. It blocks thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), which is a cytokine produced by epithelial cells. TSLP levels correlate with airway obstruction, severity of disease, and glucocorticoid resistance. TSLP is involved in T2 inflammation within the airway, but also plays a role in the interactions between airway cells and immune cells, which doesn’t rely only solely on T2 inflammation. That broad mechanism of action distinguishes tezepelumab from most other biologics for the treatment of asthma, which are more targeted.
“By working at the top of the cascade, tezepelumab helps stop inflammation at a key source. Clinical trials with tezepelumab showed a clinical benefit in patients irrespective of their baseline biomarker level, including patients with low eosinophil levels at baseline,” said Jean-Pierre Llanos-Ackert, MD, who is executive medical director and global medical affairs lead for tezepelumab at Amgen.
The primary endpoint data look robust, according to Praveen Akuthota, MD, who is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and comoderated the session at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, where the research was presented. The study was also published on May 13, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine. The conference session included updated results.
The drug holds promise, but more study is needed. “The question really will be, how is this drug different from the existing biologics? How much better is this drug in patients who have borderline T2 biomarkers, or even low T2. The study does show some efficacy in patients whose T2 signals may not be as robust. We’ll have to see with ongoing longitudinal data, how this drug positions, compared to the other agents. It’s obviously exciting, though, to have another option, given that we know what our current armamentarium of agents there are still nonresponders,” said Dr. Akuthota in an interview.
The other comoderator in the session, Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, commented: “It seems like it might work possibly even better than some that are directly covering one pathway only. Hopefully, this agent will be efficacious in a broader population than some of the more targeted biologics.” Dr. Alexander is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of pulmonary critical care at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System.
She pointed out that physicians often think of asthma patients in broad brush terms, as high or low T2, or T2 high and Th1 or neutrophilic or obese, but many patients present a more complicated picture. “There is some overlap across those phenotypes, such that an agent that works really well for one group doesn’t mean that it won’t have an impact, especially clinically, on some of these other phenotypes,” said Dr. Alexander.
Dr. Akuthota agreed. “Having options for patients whose biomarkers are not maybe as clear is, I think, important.”
Promising results
The study included 1,059 patients aged 12-80 who received 210 mg tezepelumab or placebo. Over 52 weeks, the treatment group had a 79% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization or an ED visit, compared with placebo (rate ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.37), and an 85% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization (RR, 0.15; 95% CI, 0.07-0.33). The drug increased the time to first exacerbation requiring hospitalization that required hospitalization or an ED visit, reducing risk by 65% (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.22-0.56).
Fewer patients in the treatment group than placebo used asthma-related health care resources, including: ED visits (32 vs. 94), unscheduled visit to a specialist (285 vs. 406), telephone calls to a health care provider (234 vs. 599), ambulance transport (5 vs. 22), and home visits from a health care provider (18 vs. 22). Fewer patients in the tezepelumab group had hospital stays (3.2% vs. 7.0%), and they had a lower total number of hospital days (108 vs. 497) and days in the ICU (0 vs. 31).
The study was funded by Amgen and AstraZeneca. Dr. Llanos-Ackert is an employee of Amgen. Dr. Alexander has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Akuthota has consulted for AstraZeneca and participated in their clinical trials.
Results from the NAVIGATOR study of tezepelumab showed that treatment of adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma with the new biologic led to a large reduction in exacerbations requiring hospital stays and ED visits.
Tezepelumab, codeveloped by Amgen and AstraZeneca, has a novel mechanism of action. It blocks thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), which is a cytokine produced by epithelial cells. TSLP levels correlate with airway obstruction, severity of disease, and glucocorticoid resistance. TSLP is involved in T2 inflammation within the airway, but also plays a role in the interactions between airway cells and immune cells, which doesn’t rely only solely on T2 inflammation. That broad mechanism of action distinguishes tezepelumab from most other biologics for the treatment of asthma, which are more targeted.
“By working at the top of the cascade, tezepelumab helps stop inflammation at a key source. Clinical trials with tezepelumab showed a clinical benefit in patients irrespective of their baseline biomarker level, including patients with low eosinophil levels at baseline,” said Jean-Pierre Llanos-Ackert, MD, who is executive medical director and global medical affairs lead for tezepelumab at Amgen.
The primary endpoint data look robust, according to Praveen Akuthota, MD, who is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and comoderated the session at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, where the research was presented. The study was also published on May 13, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine. The conference session included updated results.
The drug holds promise, but more study is needed. “The question really will be, how is this drug different from the existing biologics? How much better is this drug in patients who have borderline T2 biomarkers, or even low T2. The study does show some efficacy in patients whose T2 signals may not be as robust. We’ll have to see with ongoing longitudinal data, how this drug positions, compared to the other agents. It’s obviously exciting, though, to have another option, given that we know what our current armamentarium of agents there are still nonresponders,” said Dr. Akuthota in an interview.
The other comoderator in the session, Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, commented: “It seems like it might work possibly even better than some that are directly covering one pathway only. Hopefully, this agent will be efficacious in a broader population than some of the more targeted biologics.” Dr. Alexander is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of pulmonary critical care at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System.
She pointed out that physicians often think of asthma patients in broad brush terms, as high or low T2, or T2 high and Th1 or neutrophilic or obese, but many patients present a more complicated picture. “There is some overlap across those phenotypes, such that an agent that works really well for one group doesn’t mean that it won’t have an impact, especially clinically, on some of these other phenotypes,” said Dr. Alexander.
Dr. Akuthota agreed. “Having options for patients whose biomarkers are not maybe as clear is, I think, important.”
Promising results
The study included 1,059 patients aged 12-80 who received 210 mg tezepelumab or placebo. Over 52 weeks, the treatment group had a 79% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization or an ED visit, compared with placebo (rate ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.37), and an 85% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization (RR, 0.15; 95% CI, 0.07-0.33). The drug increased the time to first exacerbation requiring hospitalization that required hospitalization or an ED visit, reducing risk by 65% (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.22-0.56).
Fewer patients in the treatment group than placebo used asthma-related health care resources, including: ED visits (32 vs. 94), unscheduled visit to a specialist (285 vs. 406), telephone calls to a health care provider (234 vs. 599), ambulance transport (5 vs. 22), and home visits from a health care provider (18 vs. 22). Fewer patients in the tezepelumab group had hospital stays (3.2% vs. 7.0%), and they had a lower total number of hospital days (108 vs. 497) and days in the ICU (0 vs. 31).
The study was funded by Amgen and AstraZeneca. Dr. Llanos-Ackert is an employee of Amgen. Dr. Alexander has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Akuthota has consulted for AstraZeneca and participated in their clinical trials.
Results from the NAVIGATOR study of tezepelumab showed that treatment of adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma with the new biologic led to a large reduction in exacerbations requiring hospital stays and ED visits.
Tezepelumab, codeveloped by Amgen and AstraZeneca, has a novel mechanism of action. It blocks thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), which is a cytokine produced by epithelial cells. TSLP levels correlate with airway obstruction, severity of disease, and glucocorticoid resistance. TSLP is involved in T2 inflammation within the airway, but also plays a role in the interactions between airway cells and immune cells, which doesn’t rely only solely on T2 inflammation. That broad mechanism of action distinguishes tezepelumab from most other biologics for the treatment of asthma, which are more targeted.
“By working at the top of the cascade, tezepelumab helps stop inflammation at a key source. Clinical trials with tezepelumab showed a clinical benefit in patients irrespective of their baseline biomarker level, including patients with low eosinophil levels at baseline,” said Jean-Pierre Llanos-Ackert, MD, who is executive medical director and global medical affairs lead for tezepelumab at Amgen.
The primary endpoint data look robust, according to Praveen Akuthota, MD, who is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and comoderated the session at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference, where the research was presented. The study was also published on May 13, 2021, in the New England Journal of Medicine. The conference session included updated results.
The drug holds promise, but more study is needed. “The question really will be, how is this drug different from the existing biologics? How much better is this drug in patients who have borderline T2 biomarkers, or even low T2. The study does show some efficacy in patients whose T2 signals may not be as robust. We’ll have to see with ongoing longitudinal data, how this drug positions, compared to the other agents. It’s obviously exciting, though, to have another option, given that we know what our current armamentarium of agents there are still nonresponders,” said Dr. Akuthota in an interview.
The other comoderator in the session, Laura Crotty Alexander, MD, commented: “It seems like it might work possibly even better than some that are directly covering one pathway only. Hopefully, this agent will be efficacious in a broader population than some of the more targeted biologics.” Dr. Alexander is an associate professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of pulmonary critical care at the Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System.
She pointed out that physicians often think of asthma patients in broad brush terms, as high or low T2, or T2 high and Th1 or neutrophilic or obese, but many patients present a more complicated picture. “There is some overlap across those phenotypes, such that an agent that works really well for one group doesn’t mean that it won’t have an impact, especially clinically, on some of these other phenotypes,” said Dr. Alexander.
Dr. Akuthota agreed. “Having options for patients whose biomarkers are not maybe as clear is, I think, important.”
Promising results
The study included 1,059 patients aged 12-80 who received 210 mg tezepelumab or placebo. Over 52 weeks, the treatment group had a 79% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization or an ED visit, compared with placebo (rate ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.37), and an 85% reduction in exacerbations requiring hospitalization (RR, 0.15; 95% CI, 0.07-0.33). The drug increased the time to first exacerbation requiring hospitalization that required hospitalization or an ED visit, reducing risk by 65% (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.22-0.56).
Fewer patients in the treatment group than placebo used asthma-related health care resources, including: ED visits (32 vs. 94), unscheduled visit to a specialist (285 vs. 406), telephone calls to a health care provider (234 vs. 599), ambulance transport (5 vs. 22), and home visits from a health care provider (18 vs. 22). Fewer patients in the tezepelumab group had hospital stays (3.2% vs. 7.0%), and they had a lower total number of hospital days (108 vs. 497) and days in the ICU (0 vs. 31).
The study was funded by Amgen and AstraZeneca. Dr. Llanos-Ackert is an employee of Amgen. Dr. Alexander has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Akuthota has consulted for AstraZeneca and participated in their clinical trials.
FROM ATS 2021
COPD in younger adults deadlier than expected
Adults in their 30s, 40s and 50s with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experience significant morbidity and excess mortality from the disease, results of a population-based study show.
Among adults aged 35-55 years with COPD in Ontario in a longitudinal population cohort study, the overall mortality rate was fivefold higher, compared with other adults in the same age range without COPD.
In contrast, the mortality rate among adults 65 years and older with COPD was 2.5-fold higher than that of their peers without COPD, reported Alina J. Blazer, MSc, MD, a clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
“Overall, our study has shown that younger adults with COPD experience significant morbidity, as evidence by their elevated rates of health care use and excess mortality from their disease. This study provides further evidence that so-called ‘early’ COPD is not a benign disease, and suggests that we should focus clinical efforts on identifying COPD in younger patients, in the hopes that earlier intervention may improve their current health, reduce resource utilization, and prevent further disease progression,” she said during a minisymposium at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1131).
COPD is widely regarded as a disease affecting only older adults, but it can also occur in those younger than 65, and although it is commonly assumed that COPD diagnosed earlier in life will be milder in severity, this assumption has not been fully explored in real-world settings, Dr. Blazer said.
She and her colleagues conducted a study to examine disease burden as measured by health services utilization and mortality among younger adults with COPD, and compared the rates with those of older adults with COPD.
The sample for this study included 194,759 adults with COPD aged 35-55 years in Ontario in 2016. COPD was identified from health administrative data for three or more outpatient claims or one or more hospitalization claims for COPD over a 2-year period.
For context, the data were compared with those for 496,2113 COPD patients aged 65 years and older.
They found that, compared with their peers without the disease, younger adults had a 3.1-fold higher rate of hospitalization for any cause, a 2.2-fold higher rate of all-cause ED visits, and a 1.7-fold higher rate of outpatient visits for any cause.
In contrast, the comparative rates for seniors with versus without COPD were 2.1-fold, 1.8-fold, and 1.4-fold, respectively.
As noted before, the mortality rate for younger adults with COPD was 5-fold higher than for those without COPD, compared with 2.5-fold among older adults with COPD versus those without.
Earlier diagnosis, follow-up
“A very important talk,” commented session comoderator Valerie Press, MD, MPH, from the University of Chicago. “I know that there’s a lot of work to be done in earlier diagnosis in general, and I think starting with the younger population is a really important area.”
She asked Dr. Blazer about the possibility of asthma codiagnosis or misdiagnosis in the younger patients.
“We use a very specific, validated case definition in the study that our group has used before, and the specificity is over 96% for physician-diagnosed COPD, at the expense of sensitivity, so if anything we probably underestimated the rate of COPD in our study,” Dr. Blazer said.
Audience member Sherry Rogers, MD, an allergist and immunologist in private practice in Syracuse, N.Y., asked whether the investigators could determine what proportion of the excess mortality they saw was attributable to COPD.
“This was looking at all-cause mortality, so we don’t know that it’s necessarily all attributable to COPD per se but perhaps also to COPD-attributable comorbidities,” Dr. Blazer said. “It would be important to piece out the actual causes of mortality that are contributing to that elevated [morality] in that population.”
She added that the next step could include examining rates of specialty referrals and pharmacotherapy to see whether younger patients with COPD are receiving appropriate care, and to ascertain how they are being followed.
The study was supported by the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Research Institute. Dr. Blazer reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Adults in their 30s, 40s and 50s with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experience significant morbidity and excess mortality from the disease, results of a population-based study show.
Among adults aged 35-55 years with COPD in Ontario in a longitudinal population cohort study, the overall mortality rate was fivefold higher, compared with other adults in the same age range without COPD.
In contrast, the mortality rate among adults 65 years and older with COPD was 2.5-fold higher than that of their peers without COPD, reported Alina J. Blazer, MSc, MD, a clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
“Overall, our study has shown that younger adults with COPD experience significant morbidity, as evidence by their elevated rates of health care use and excess mortality from their disease. This study provides further evidence that so-called ‘early’ COPD is not a benign disease, and suggests that we should focus clinical efforts on identifying COPD in younger patients, in the hopes that earlier intervention may improve their current health, reduce resource utilization, and prevent further disease progression,” she said during a minisymposium at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1131).
COPD is widely regarded as a disease affecting only older adults, but it can also occur in those younger than 65, and although it is commonly assumed that COPD diagnosed earlier in life will be milder in severity, this assumption has not been fully explored in real-world settings, Dr. Blazer said.
She and her colleagues conducted a study to examine disease burden as measured by health services utilization and mortality among younger adults with COPD, and compared the rates with those of older adults with COPD.
The sample for this study included 194,759 adults with COPD aged 35-55 years in Ontario in 2016. COPD was identified from health administrative data for three or more outpatient claims or one or more hospitalization claims for COPD over a 2-year period.
For context, the data were compared with those for 496,2113 COPD patients aged 65 years and older.
They found that, compared with their peers without the disease, younger adults had a 3.1-fold higher rate of hospitalization for any cause, a 2.2-fold higher rate of all-cause ED visits, and a 1.7-fold higher rate of outpatient visits for any cause.
In contrast, the comparative rates for seniors with versus without COPD were 2.1-fold, 1.8-fold, and 1.4-fold, respectively.
As noted before, the mortality rate for younger adults with COPD was 5-fold higher than for those without COPD, compared with 2.5-fold among older adults with COPD versus those without.
Earlier diagnosis, follow-up
“A very important talk,” commented session comoderator Valerie Press, MD, MPH, from the University of Chicago. “I know that there’s a lot of work to be done in earlier diagnosis in general, and I think starting with the younger population is a really important area.”
She asked Dr. Blazer about the possibility of asthma codiagnosis or misdiagnosis in the younger patients.
“We use a very specific, validated case definition in the study that our group has used before, and the specificity is over 96% for physician-diagnosed COPD, at the expense of sensitivity, so if anything we probably underestimated the rate of COPD in our study,” Dr. Blazer said.
Audience member Sherry Rogers, MD, an allergist and immunologist in private practice in Syracuse, N.Y., asked whether the investigators could determine what proportion of the excess mortality they saw was attributable to COPD.
“This was looking at all-cause mortality, so we don’t know that it’s necessarily all attributable to COPD per se but perhaps also to COPD-attributable comorbidities,” Dr. Blazer said. “It would be important to piece out the actual causes of mortality that are contributing to that elevated [morality] in that population.”
She added that the next step could include examining rates of specialty referrals and pharmacotherapy to see whether younger patients with COPD are receiving appropriate care, and to ascertain how they are being followed.
The study was supported by the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Research Institute. Dr. Blazer reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Adults in their 30s, 40s and 50s with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experience significant morbidity and excess mortality from the disease, results of a population-based study show.
Among adults aged 35-55 years with COPD in Ontario in a longitudinal population cohort study, the overall mortality rate was fivefold higher, compared with other adults in the same age range without COPD.
In contrast, the mortality rate among adults 65 years and older with COPD was 2.5-fold higher than that of their peers without COPD, reported Alina J. Blazer, MSc, MD, a clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
“Overall, our study has shown that younger adults with COPD experience significant morbidity, as evidence by their elevated rates of health care use and excess mortality from their disease. This study provides further evidence that so-called ‘early’ COPD is not a benign disease, and suggests that we should focus clinical efforts on identifying COPD in younger patients, in the hopes that earlier intervention may improve their current health, reduce resource utilization, and prevent further disease progression,” she said during a minisymposium at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference (Abstract A1131).
COPD is widely regarded as a disease affecting only older adults, but it can also occur in those younger than 65, and although it is commonly assumed that COPD diagnosed earlier in life will be milder in severity, this assumption has not been fully explored in real-world settings, Dr. Blazer said.
She and her colleagues conducted a study to examine disease burden as measured by health services utilization and mortality among younger adults with COPD, and compared the rates with those of older adults with COPD.
The sample for this study included 194,759 adults with COPD aged 35-55 years in Ontario in 2016. COPD was identified from health administrative data for three or more outpatient claims or one or more hospitalization claims for COPD over a 2-year period.
For context, the data were compared with those for 496,2113 COPD patients aged 65 years and older.
They found that, compared with their peers without the disease, younger adults had a 3.1-fold higher rate of hospitalization for any cause, a 2.2-fold higher rate of all-cause ED visits, and a 1.7-fold higher rate of outpatient visits for any cause.
In contrast, the comparative rates for seniors with versus without COPD were 2.1-fold, 1.8-fold, and 1.4-fold, respectively.
As noted before, the mortality rate for younger adults with COPD was 5-fold higher than for those without COPD, compared with 2.5-fold among older adults with COPD versus those without.
Earlier diagnosis, follow-up
“A very important talk,” commented session comoderator Valerie Press, MD, MPH, from the University of Chicago. “I know that there’s a lot of work to be done in earlier diagnosis in general, and I think starting with the younger population is a really important area.”
She asked Dr. Blazer about the possibility of asthma codiagnosis or misdiagnosis in the younger patients.
“We use a very specific, validated case definition in the study that our group has used before, and the specificity is over 96% for physician-diagnosed COPD, at the expense of sensitivity, so if anything we probably underestimated the rate of COPD in our study,” Dr. Blazer said.
Audience member Sherry Rogers, MD, an allergist and immunologist in private practice in Syracuse, N.Y., asked whether the investigators could determine what proportion of the excess mortality they saw was attributable to COPD.
“This was looking at all-cause mortality, so we don’t know that it’s necessarily all attributable to COPD per se but perhaps also to COPD-attributable comorbidities,” Dr. Blazer said. “It would be important to piece out the actual causes of mortality that are contributing to that elevated [morality] in that population.”
She added that the next step could include examining rates of specialty referrals and pharmacotherapy to see whether younger patients with COPD are receiving appropriate care, and to ascertain how they are being followed.
The study was supported by the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Research Institute. Dr. Blazer reported no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM ATS 2021
Patients with moderate COPD also benefit from triple therapy
The benefits of a triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist combination extend to patients with moderate as well as severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
That’s according to investigators in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
In a subanalysis of data on patients with moderate COPD who were enrolled in the comparison trial, the single-inhaler combination of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol fumarate (BGF) showed benefits in terms of COPD exacerbations, lung function, symptoms, and quality-of-life compared with either of two dual therapy combinations (glycopyrrolate or budesonide with formoterol [GFF/BFF]).
“A moderate benefit:risk ratio was demonstrated in patients with moderate COPD, consistent with the results of the overall ETHOS population, indicating the results of the ETHOS study were not driven by patients with severe or very severe COPD,” wrote Gary T. Ferguson, MD, from the Pulmonary Research Institute of Southeast Michigan in Farmington Hills, and colleagues. Their poster was presented during the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference. (Abstract A2244).
As reported at ATS 2020, in the overall ETHOS population of 8,509 patients with moderate to very severe COPD the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320-mcg and 160-mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
, Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, of LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues found.
Subanalysis details
At the 2021 iteration of ATS, ETHOS investigator Dr. Ferguson and colleagues reported results for 613 patients with moderate COPD assigned to BGF 320 mcg, 604 assigned to BGF 160 mcg, 596 assigned to GFF, and 614 randomized to BFF.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar among the groups, including age, sex, smoking status, mean COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score, mean blood eosinophil count, ICS use at screening, exacerbations in the previous year, mean postbronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) percentage of predicted, and mean postbronchodilator percentage reversibility.
A modified intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis showed that the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations over 52 weeks with BGF 320 mcg was 21% lower than with GFF (P = .0123), but only 4% lower than with BFF, a difference that was not statistically significant.
The BGF 160-mg dose was associated with a 30% reduction in exacerbations vs. GFF (P = .0002), and with a nonsignificant reduction of 15% compared with BFF.
There was a numerical but not statistically significant improvement from baseline at week 24 in morning pre-dose trough FEV1 between the BGF 320-mcg dose and GFF (difference 47 mL), and a significant improvement (90 mL) with BGF compared with BFF (P = .0006). The BGF 160-mcg dose was associated with a larger improvement (89 mL) compared with BFF (P = .0004) but not with GFF.
The FEV1 area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristics from 0 to 4 hours was superior with BGF at both doses compared with both GFF and BFF.
Patients who used BGF 320 mcg also used significantly less rescue medication over 24 weeks compared with patients who used GFF (P < .0001) or BFF (P = .0001). There were no significant differences in rescue medication use between the BGF 160-mg dose and either of the dual therapy combinations.
Time to clinically important deterioration – defined as a greater than 100 mL decrease in trough FEV1, or a 4 units increase in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire total score, or a treatment-emergent moderate/severe COPD exacerbation occurring up to week 52 – was significantly longer with the 320-mcg but not 160-mcg BGF dose compared with GFF (P = .0295) or BFF (P = .0172).
Safety
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in about two-thirds of patients in each trial arm, although TEAEs related to study treatment were more common with the two triple-therapy combinations and with BFF than with GFF.
TEAEs leading to study discontinuation occurred in 5.5% of patients on BGF 320 mcg, 4% on BGF 160 mcg, 4.5% on GFF, and 3.2% on BFF.
Confirmed major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 0.8% and 1.5% in the BGF 320- and 160-mcg groups, respectively, in 1.8% of patients in the GFF arm, and 1.5% in the BFF arm.
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 2.6% of patients in each BGF arm, 2.2% in the GFF arm, and 3.6% in the BFF arm.
Selected population
In a comment, David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, noted that the enrollment criteria for ETHOS tended to skew the population toward patients with severe disease.
In the trial, all patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
“The question was whether they would see the same results in people with more moderate impairment, and the answer in this subanalysis is ‘yes.’ The findings weren’t identical between patients with severe and moderate disease, but there were similarities with what was seen in the overall ETHOS study,” he said.
The ETHOS Trial was supported by Pearl Therapeutics. Dr. Ferguson reported grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca during the conduct of the study; and grants, fees, and nonfinancial support from Pearl and others. Dr. Mannino reports recruitment to an advisory board for AstraZeneca.
The benefits of a triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist combination extend to patients with moderate as well as severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
That’s according to investigators in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
In a subanalysis of data on patients with moderate COPD who were enrolled in the comparison trial, the single-inhaler combination of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol fumarate (BGF) showed benefits in terms of COPD exacerbations, lung function, symptoms, and quality-of-life compared with either of two dual therapy combinations (glycopyrrolate or budesonide with formoterol [GFF/BFF]).
“A moderate benefit:risk ratio was demonstrated in patients with moderate COPD, consistent with the results of the overall ETHOS population, indicating the results of the ETHOS study were not driven by patients with severe or very severe COPD,” wrote Gary T. Ferguson, MD, from the Pulmonary Research Institute of Southeast Michigan in Farmington Hills, and colleagues. Their poster was presented during the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference. (Abstract A2244).
As reported at ATS 2020, in the overall ETHOS population of 8,509 patients with moderate to very severe COPD the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320-mcg and 160-mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
, Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, of LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues found.
Subanalysis details
At the 2021 iteration of ATS, ETHOS investigator Dr. Ferguson and colleagues reported results for 613 patients with moderate COPD assigned to BGF 320 mcg, 604 assigned to BGF 160 mcg, 596 assigned to GFF, and 614 randomized to BFF.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar among the groups, including age, sex, smoking status, mean COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score, mean blood eosinophil count, ICS use at screening, exacerbations in the previous year, mean postbronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) percentage of predicted, and mean postbronchodilator percentage reversibility.
A modified intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis showed that the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations over 52 weeks with BGF 320 mcg was 21% lower than with GFF (P = .0123), but only 4% lower than with BFF, a difference that was not statistically significant.
The BGF 160-mg dose was associated with a 30% reduction in exacerbations vs. GFF (P = .0002), and with a nonsignificant reduction of 15% compared with BFF.
There was a numerical but not statistically significant improvement from baseline at week 24 in morning pre-dose trough FEV1 between the BGF 320-mcg dose and GFF (difference 47 mL), and a significant improvement (90 mL) with BGF compared with BFF (P = .0006). The BGF 160-mcg dose was associated with a larger improvement (89 mL) compared with BFF (P = .0004) but not with GFF.
The FEV1 area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristics from 0 to 4 hours was superior with BGF at both doses compared with both GFF and BFF.
Patients who used BGF 320 mcg also used significantly less rescue medication over 24 weeks compared with patients who used GFF (P < .0001) or BFF (P = .0001). There were no significant differences in rescue medication use between the BGF 160-mg dose and either of the dual therapy combinations.
Time to clinically important deterioration – defined as a greater than 100 mL decrease in trough FEV1, or a 4 units increase in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire total score, or a treatment-emergent moderate/severe COPD exacerbation occurring up to week 52 – was significantly longer with the 320-mcg but not 160-mcg BGF dose compared with GFF (P = .0295) or BFF (P = .0172).
Safety
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in about two-thirds of patients in each trial arm, although TEAEs related to study treatment were more common with the two triple-therapy combinations and with BFF than with GFF.
TEAEs leading to study discontinuation occurred in 5.5% of patients on BGF 320 mcg, 4% on BGF 160 mcg, 4.5% on GFF, and 3.2% on BFF.
Confirmed major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 0.8% and 1.5% in the BGF 320- and 160-mcg groups, respectively, in 1.8% of patients in the GFF arm, and 1.5% in the BFF arm.
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 2.6% of patients in each BGF arm, 2.2% in the GFF arm, and 3.6% in the BFF arm.
Selected population
In a comment, David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, noted that the enrollment criteria for ETHOS tended to skew the population toward patients with severe disease.
In the trial, all patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
“The question was whether they would see the same results in people with more moderate impairment, and the answer in this subanalysis is ‘yes.’ The findings weren’t identical between patients with severe and moderate disease, but there were similarities with what was seen in the overall ETHOS study,” he said.
The ETHOS Trial was supported by Pearl Therapeutics. Dr. Ferguson reported grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca during the conduct of the study; and grants, fees, and nonfinancial support from Pearl and others. Dr. Mannino reports recruitment to an advisory board for AstraZeneca.
The benefits of a triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist combination extend to patients with moderate as well as severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
That’s according to investigators in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
In a subanalysis of data on patients with moderate COPD who were enrolled in the comparison trial, the single-inhaler combination of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol fumarate (BGF) showed benefits in terms of COPD exacerbations, lung function, symptoms, and quality-of-life compared with either of two dual therapy combinations (glycopyrrolate or budesonide with formoterol [GFF/BFF]).
“A moderate benefit:risk ratio was demonstrated in patients with moderate COPD, consistent with the results of the overall ETHOS population, indicating the results of the ETHOS study were not driven by patients with severe or very severe COPD,” wrote Gary T. Ferguson, MD, from the Pulmonary Research Institute of Southeast Michigan in Farmington Hills, and colleagues. Their poster was presented during the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference. (Abstract A2244).
As reported at ATS 2020, in the overall ETHOS population of 8,509 patients with moderate to very severe COPD the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320-mcg and 160-mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
, Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, of LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues found.
Subanalysis details
At the 2021 iteration of ATS, ETHOS investigator Dr. Ferguson and colleagues reported results for 613 patients with moderate COPD assigned to BGF 320 mcg, 604 assigned to BGF 160 mcg, 596 assigned to GFF, and 614 randomized to BFF.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar among the groups, including age, sex, smoking status, mean COPD Assessment Test (CAT) score, mean blood eosinophil count, ICS use at screening, exacerbations in the previous year, mean postbronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) percentage of predicted, and mean postbronchodilator percentage reversibility.
A modified intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis showed that the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations over 52 weeks with BGF 320 mcg was 21% lower than with GFF (P = .0123), but only 4% lower than with BFF, a difference that was not statistically significant.
The BGF 160-mg dose was associated with a 30% reduction in exacerbations vs. GFF (P = .0002), and with a nonsignificant reduction of 15% compared with BFF.
There was a numerical but not statistically significant improvement from baseline at week 24 in morning pre-dose trough FEV1 between the BGF 320-mcg dose and GFF (difference 47 mL), and a significant improvement (90 mL) with BGF compared with BFF (P = .0006). The BGF 160-mcg dose was associated with a larger improvement (89 mL) compared with BFF (P = .0004) but not with GFF.
The FEV1 area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristics from 0 to 4 hours was superior with BGF at both doses compared with both GFF and BFF.
Patients who used BGF 320 mcg also used significantly less rescue medication over 24 weeks compared with patients who used GFF (P < .0001) or BFF (P = .0001). There were no significant differences in rescue medication use between the BGF 160-mg dose and either of the dual therapy combinations.
Time to clinically important deterioration – defined as a greater than 100 mL decrease in trough FEV1, or a 4 units increase in St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire total score, or a treatment-emergent moderate/severe COPD exacerbation occurring up to week 52 – was significantly longer with the 320-mcg but not 160-mcg BGF dose compared with GFF (P = .0295) or BFF (P = .0172).
Safety
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in about two-thirds of patients in each trial arm, although TEAEs related to study treatment were more common with the two triple-therapy combinations and with BFF than with GFF.
TEAEs leading to study discontinuation occurred in 5.5% of patients on BGF 320 mcg, 4% on BGF 160 mcg, 4.5% on GFF, and 3.2% on BFF.
Confirmed major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 0.8% and 1.5% in the BGF 320- and 160-mcg groups, respectively, in 1.8% of patients in the GFF arm, and 1.5% in the BFF arm.
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 2.6% of patients in each BGF arm, 2.2% in the GFF arm, and 3.6% in the BFF arm.
Selected population
In a comment, David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, noted that the enrollment criteria for ETHOS tended to skew the population toward patients with severe disease.
In the trial, all patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
“The question was whether they would see the same results in people with more moderate impairment, and the answer in this subanalysis is ‘yes.’ The findings weren’t identical between patients with severe and moderate disease, but there were similarities with what was seen in the overall ETHOS study,” he said.
The ETHOS Trial was supported by Pearl Therapeutics. Dr. Ferguson reported grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca during the conduct of the study; and grants, fees, and nonfinancial support from Pearl and others. Dr. Mannino reports recruitment to an advisory board for AstraZeneca.
FROM ATS 2021
Benefit from cooling temps for cardiac arrest does not differ in randomized trial
The first randomized controlled trial to compare specific temperatures for therapeutic hypothermia in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest showed no differences in major outcomes, according to a single-center, double-blind study.
In the CAPITAL-CHILL trial, cooling temperatures of 31° C and 34° C were compared to explore the hypothesis that a lower temperature would improve major outcomes, explained Michel Le May, MD.
No differences for the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or poor neurologic outcome at 180 days were observed, he reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The study was completed over a period of almost 7 years in patients presumed to have had an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and who were unconscious when they reached a center affiliated with the Ottawa Heart Institute, where Dr. Le May directs the regional STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) program. The initial rhythm at the time of the cardiac arrest was not an entry criterion.
Of 389 patients enrolled, the intention-to-treat analysis included 184 randomized to a cooling temperature of 31° C group and 183 to a temperature of 34° C. The assigned target temperature, reached with an endovascular device, was known only by the managing nurses.
31° C and 34° C are equivalent
There was a small numerical disadvantage for the lower temperature assignment, but none reached statistical significance. This was true of the primary outcome (48.4% vs. 45.4% for the higher temperature) and its components of mortality (43.5% vs. 41.0%) and poor neurologic outcome (4.9% vs. 4.4%). Poor neurologic outcome was defined as a Disability Rating Scale score of greater than 5.
Deaths were most common in the early part of the 180-day follow-up in both arms. On a Kaplan-Meier survival graph, Dr. Le May showed curves that he characterized as “almost superimposable.”
There were no significant differences for any subgroup stratifications, such as age 75 years or older versus younger, males versus females, presence versus absence or an initial shockable rhythm, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) within 24 hours versus later, and STEMI versus non-STEMI. In these analyses, the higher temperature was associated with a potential trend for benefit among females and those with a shockable rhythm.
There was no signal for a difference in neurologic outcomes on the Disability Rating Scale or the Modified Rankin Scale. On the latter, for example, 46% of those in the 31° C group and 44% of these in the 34° C group had a score of four or greater at the end of follow-up.
The baseline characteristics of the two groups were similar. About 80% were male; the average age was roughly 62 years. More than 80% of the cardiac arrests were witnessed with CPR being administered by bystanders in nearly 70%. Nearly 40% had a STEMI.
Interventions were similar. Almost all patients underwent coronary angiography, of which nearly 60% received a percutaneous coronary intervention. More than 50% received a stent. The time from arrest to randomization was slightly longer in the 31° C group (228 vs. 204 minutes). The time to balloon inflation from arrival at the cardiac center was also slightly longer (73 vs. 60 minutes).
There was a trend for an increased rate of seizures in the 31° C group (12.5% vs. 7.1%; P = .08), but other secondary outcomes, including pneumonia (67.8% vs. 63.4%), renal replacement therapy (9.2% vs. 9.3%), and stroke (4.4% vs. 1.6%), were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively.
Bleeding, whether measured by transfusion (19.6% vs. 22.4%) or TIMI major bleed (23.4% vs. 19.7%) were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively. Thrombosis, whether measured by stent thrombosis (1.2% vs. 2.2%) or deep venous thrombosis (11.4% vs. 10.9%) were similar in these two groups, respectively.
The length of stay in the cardiac intensive care unit was significantly greater in the 31° C group (10 vs. 7 days; P = .004). Some of this increased length of stay can be attributed to the longer rewarming process required for the greater cooling, according to Dr. Le May, but he acknowledged that it is not clear this provides a full explanation.
More trials like CAPITAL-CHILL needed
The validity of these findings is supported by several strengths of the methodology, according to Jeanne E. Poole, MD, director of the arrhythmia service and electrophysiology laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle. This includes the reliance of an endovascular device, which can accelerate the time to the target temperature and assure the precision with which it is reached and maintained.
Dr. Poole did note that many of the primary and secondary measures, including the rates of stroke, seizures, and major bleeds, even though not significantly different, favored the higher temperature. The slightly longer door-to-balloon times might have been a factor. For the higher rate of pneumonia in the 31° C group, she questioned whether the longer period of ventilation linked to a longer period of rewarming might have been a factor.
However, Dr. Poole praised the CAPITAL-CHILL trial for drawing attention to a group of patients for whom survival rates remain “dismally low.” She indicated that these types of high-level trials are needed to look for strategies to improve outcomes.
Dr. Le May and Dr. Poole report no potential conflicts of interest.
The first randomized controlled trial to compare specific temperatures for therapeutic hypothermia in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest showed no differences in major outcomes, according to a single-center, double-blind study.
In the CAPITAL-CHILL trial, cooling temperatures of 31° C and 34° C were compared to explore the hypothesis that a lower temperature would improve major outcomes, explained Michel Le May, MD.
No differences for the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or poor neurologic outcome at 180 days were observed, he reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The study was completed over a period of almost 7 years in patients presumed to have had an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and who were unconscious when they reached a center affiliated with the Ottawa Heart Institute, where Dr. Le May directs the regional STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) program. The initial rhythm at the time of the cardiac arrest was not an entry criterion.
Of 389 patients enrolled, the intention-to-treat analysis included 184 randomized to a cooling temperature of 31° C group and 183 to a temperature of 34° C. The assigned target temperature, reached with an endovascular device, was known only by the managing nurses.
31° C and 34° C are equivalent
There was a small numerical disadvantage for the lower temperature assignment, but none reached statistical significance. This was true of the primary outcome (48.4% vs. 45.4% for the higher temperature) and its components of mortality (43.5% vs. 41.0%) and poor neurologic outcome (4.9% vs. 4.4%). Poor neurologic outcome was defined as a Disability Rating Scale score of greater than 5.
Deaths were most common in the early part of the 180-day follow-up in both arms. On a Kaplan-Meier survival graph, Dr. Le May showed curves that he characterized as “almost superimposable.”
There were no significant differences for any subgroup stratifications, such as age 75 years or older versus younger, males versus females, presence versus absence or an initial shockable rhythm, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) within 24 hours versus later, and STEMI versus non-STEMI. In these analyses, the higher temperature was associated with a potential trend for benefit among females and those with a shockable rhythm.
There was no signal for a difference in neurologic outcomes on the Disability Rating Scale or the Modified Rankin Scale. On the latter, for example, 46% of those in the 31° C group and 44% of these in the 34° C group had a score of four or greater at the end of follow-up.
The baseline characteristics of the two groups were similar. About 80% were male; the average age was roughly 62 years. More than 80% of the cardiac arrests were witnessed with CPR being administered by bystanders in nearly 70%. Nearly 40% had a STEMI.
Interventions were similar. Almost all patients underwent coronary angiography, of which nearly 60% received a percutaneous coronary intervention. More than 50% received a stent. The time from arrest to randomization was slightly longer in the 31° C group (228 vs. 204 minutes). The time to balloon inflation from arrival at the cardiac center was also slightly longer (73 vs. 60 minutes).
There was a trend for an increased rate of seizures in the 31° C group (12.5% vs. 7.1%; P = .08), but other secondary outcomes, including pneumonia (67.8% vs. 63.4%), renal replacement therapy (9.2% vs. 9.3%), and stroke (4.4% vs. 1.6%), were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively.
Bleeding, whether measured by transfusion (19.6% vs. 22.4%) or TIMI major bleed (23.4% vs. 19.7%) were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively. Thrombosis, whether measured by stent thrombosis (1.2% vs. 2.2%) or deep venous thrombosis (11.4% vs. 10.9%) were similar in these two groups, respectively.
The length of stay in the cardiac intensive care unit was significantly greater in the 31° C group (10 vs. 7 days; P = .004). Some of this increased length of stay can be attributed to the longer rewarming process required for the greater cooling, according to Dr. Le May, but he acknowledged that it is not clear this provides a full explanation.
More trials like CAPITAL-CHILL needed
The validity of these findings is supported by several strengths of the methodology, according to Jeanne E. Poole, MD, director of the arrhythmia service and electrophysiology laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle. This includes the reliance of an endovascular device, which can accelerate the time to the target temperature and assure the precision with which it is reached and maintained.
Dr. Poole did note that many of the primary and secondary measures, including the rates of stroke, seizures, and major bleeds, even though not significantly different, favored the higher temperature. The slightly longer door-to-balloon times might have been a factor. For the higher rate of pneumonia in the 31° C group, she questioned whether the longer period of ventilation linked to a longer period of rewarming might have been a factor.
However, Dr. Poole praised the CAPITAL-CHILL trial for drawing attention to a group of patients for whom survival rates remain “dismally low.” She indicated that these types of high-level trials are needed to look for strategies to improve outcomes.
Dr. Le May and Dr. Poole report no potential conflicts of interest.
The first randomized controlled trial to compare specific temperatures for therapeutic hypothermia in comatose survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest showed no differences in major outcomes, according to a single-center, double-blind study.
In the CAPITAL-CHILL trial, cooling temperatures of 31° C and 34° C were compared to explore the hypothesis that a lower temperature would improve major outcomes, explained Michel Le May, MD.
No differences for the primary composite outcome of all-cause mortality or poor neurologic outcome at 180 days were observed, he reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The study was completed over a period of almost 7 years in patients presumed to have had an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and who were unconscious when they reached a center affiliated with the Ottawa Heart Institute, where Dr. Le May directs the regional STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) program. The initial rhythm at the time of the cardiac arrest was not an entry criterion.
Of 389 patients enrolled, the intention-to-treat analysis included 184 randomized to a cooling temperature of 31° C group and 183 to a temperature of 34° C. The assigned target temperature, reached with an endovascular device, was known only by the managing nurses.
31° C and 34° C are equivalent
There was a small numerical disadvantage for the lower temperature assignment, but none reached statistical significance. This was true of the primary outcome (48.4% vs. 45.4% for the higher temperature) and its components of mortality (43.5% vs. 41.0%) and poor neurologic outcome (4.9% vs. 4.4%). Poor neurologic outcome was defined as a Disability Rating Scale score of greater than 5.
Deaths were most common in the early part of the 180-day follow-up in both arms. On a Kaplan-Meier survival graph, Dr. Le May showed curves that he characterized as “almost superimposable.”
There were no significant differences for any subgroup stratifications, such as age 75 years or older versus younger, males versus females, presence versus absence or an initial shockable rhythm, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) within 24 hours versus later, and STEMI versus non-STEMI. In these analyses, the higher temperature was associated with a potential trend for benefit among females and those with a shockable rhythm.
There was no signal for a difference in neurologic outcomes on the Disability Rating Scale or the Modified Rankin Scale. On the latter, for example, 46% of those in the 31° C group and 44% of these in the 34° C group had a score of four or greater at the end of follow-up.
The baseline characteristics of the two groups were similar. About 80% were male; the average age was roughly 62 years. More than 80% of the cardiac arrests were witnessed with CPR being administered by bystanders in nearly 70%. Nearly 40% had a STEMI.
Interventions were similar. Almost all patients underwent coronary angiography, of which nearly 60% received a percutaneous coronary intervention. More than 50% received a stent. The time from arrest to randomization was slightly longer in the 31° C group (228 vs. 204 minutes). The time to balloon inflation from arrival at the cardiac center was also slightly longer (73 vs. 60 minutes).
There was a trend for an increased rate of seizures in the 31° C group (12.5% vs. 7.1%; P = .08), but other secondary outcomes, including pneumonia (67.8% vs. 63.4%), renal replacement therapy (9.2% vs. 9.3%), and stroke (4.4% vs. 1.6%), were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively.
Bleeding, whether measured by transfusion (19.6% vs. 22.4%) or TIMI major bleed (23.4% vs. 19.7%) were similar in the 31° C and 34° C groups, respectively. Thrombosis, whether measured by stent thrombosis (1.2% vs. 2.2%) or deep venous thrombosis (11.4% vs. 10.9%) were similar in these two groups, respectively.
The length of stay in the cardiac intensive care unit was significantly greater in the 31° C group (10 vs. 7 days; P = .004). Some of this increased length of stay can be attributed to the longer rewarming process required for the greater cooling, according to Dr. Le May, but he acknowledged that it is not clear this provides a full explanation.
More trials like CAPITAL-CHILL needed
The validity of these findings is supported by several strengths of the methodology, according to Jeanne E. Poole, MD, director of the arrhythmia service and electrophysiology laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle. This includes the reliance of an endovascular device, which can accelerate the time to the target temperature and assure the precision with which it is reached and maintained.
Dr. Poole did note that many of the primary and secondary measures, including the rates of stroke, seizures, and major bleeds, even though not significantly different, favored the higher temperature. The slightly longer door-to-balloon times might have been a factor. For the higher rate of pneumonia in the 31° C group, she questioned whether the longer period of ventilation linked to a longer period of rewarming might have been a factor.
However, Dr. Poole praised the CAPITAL-CHILL trial for drawing attention to a group of patients for whom survival rates remain “dismally low.” She indicated that these types of high-level trials are needed to look for strategies to improve outcomes.
Dr. Le May and Dr. Poole report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM ACC 2021
AHA reassures myocarditis rare after COVID vaccination, benefits overwhelm risks
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination “enormously outweigh” the rare possible risk for heart-related complications, including myocarditis, the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (ASA) says in new statement.
The message follows a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report that the agency is monitoring the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) and the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD) for cases of myocarditis that have been associated with the mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 from Pfizer and Moderna.
The “relatively few” reported cases myocarditis in adolescents or young adults have involved males more often than females, more often followed the second dose rather than the first, and were usually seen in the 4 days after vaccination, the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Technical Work Group (VaST) found.
“Most cases appear to be mild, and follow-up of cases is ongoing,” the CDC says. “Within CDC safety monitoring systems, rates of myocarditis reports in the window following COVID-19 vaccination have not differed from expected baseline rates.”
In their statement, the AHA/ASA “strongly urge” all adults and children 12 years and older to receive a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as possible.
“The evidence continues to indicate that the COVID-19 vaccines are nearly 100% effective at preventing death and hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection,” the groups say.
Although the investigation of cases of myocarditis related to COVID-19 vaccination is ongoing, the AHA/ASA notes that myocarditis is typically the result of an actual viral infection, “and it is yet to be determined if these cases have any correlation to receiving a COVID-19 vaccine.”
“We’ve lost hundreds of children, and there have been thousands who have been hospitalized, thousands who developed an inflammatory syndrome, and one of the pieces of that can be myocarditis,” Richard Besser, MD, president and CEO of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), said today on ABC’s Good Morning America.
Still, “from my perspective, the risk of COVID is so much greater than any theoretical risk from the vaccine,” said Dr. Besser, former acting director of the CDC.
The symptoms that can occur after COVID-19 vaccination include tiredness, headache, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea, reminds the AHA/ASA statement. Such symptoms would “typically appear within 24-48 hours and usually pass within 36-48 hours after receiving the vaccine.”
All health care providers should be aware of the “very rare” adverse events that could be related to a COVID-19 vaccine, including myocarditis, blood clots, low platelets, and symptoms of severe inflammation, it says.
“Health care professionals should strongly consider inquiring about the timing of any recent COVID vaccination among patients presenting with these conditions, as needed, in order to provide appropriate treatment quickly,” the statement advises.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians’ trust in health care leadership drops in pandemic
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy takes first major step into earlier NSCLC
Immunotherapy has already had a huge impact on treatment of patients with later stages of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): new clinical data are now showing benefits in patients with earlier stage disease.
Patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC showed a markedly improved disease-free survival (DFS) when atezolizumab (Tecentriq) was added onto adjuvant chemotherapy following resection, according to results from an interim analysis of the IMpower010 study.
Notably, the benefit with atezolizumab versus best supportive care was greatest in patients with expression of programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) on their tumor, in whom the DFS improvement was a significant 34%.
This is the “first global phase 3 trial using an immune checkpoint inhibitor to show a disease-free survival outcome in early-stage NSCLC,” said lead researcher Heather Wakelee, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center.
She was speaking at a press briefing ahead of the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, where the results will be presented on June 6.
Dr. Wakelee added that the “planned analysis for disease-free survival and overall survival in the intention-to-treat populations will continue with longer-term follow-up.”
Asked whether the drug could be recommended for these patients based on the current results, Dr. Wakelee said that “obviously we need approval” for this use from the Food and Drug Administration, but she added that “the FDA has approved other agents, particularly most recently osimertinib [Tagrisso], based on a disease-free survival endpoint.”
These new results show that the benefit with atezolizumab plus chemotherapy is “more profound” than with chemotherapy plus best supportive care, “and therefore, to me, it would be something I would want to offer my patients in that setting.”
Dr. Wakelee also emphasized the importance of screening for lung cancer, so that the disease is detected at earlier stages “when it is potentially curable.”
She also stressed the importance of biomarker testing for patients with resected disease “to look for EGFR mutations, which can be treated with EGFR [tyrosine kinase inhibitors] and also, at some point, to check for PD-L1 ... because, in this trial, the vast majority of benefit” appeared to be in those with PD-L1 expression on their tumors.
Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, said that “immune checkpoint inhibitors have certainly changed the treatment landscape for many types of cancers” and the current study “is the first time we’ve seen an immunotherapy that’s effective in treating early-stage NSCLC.”
“This is an important advance in understanding the role of immunotherapy in earlier stage lung cancer” and “potentially a step forward for many patients.”
Study details
The standard of care for many stage IB-IIIA NSCLC patients “has not changed for many years,” despite “significant progress” having been made in the treatment of more advanced disease, Dr. Wakelee commented.
Consequently, the majority of patients with resected NSCLC continue to receive adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy, which has been shown to reduce the risk of disease recurrence by 16% in those with completely resected disease.
The new study set out to examine the benefit of adding atezolizumab to adjuvant chemotherapy in the global phase 3 IMpower010 study.
Patients had to have stage IB-IIIA NSCLC, with stage IB tumors at least 4 cm in size, and tumor tissue available for PD-L1 analysis. Following complete resection, 1,280 patients were given up to four cycles of adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy.
Of those, 1,005 patients were then randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either 16 cycles of atezolizumab 1,200 mg IV every 3 weeks or best supportive care.
The interim results show that, after a median follow-up of 32.8 months, the addition of atezolizumab significantly reduced the risk of recurrence or death versus best supportive care in patients whose tumors had PD-L1 expression of at least 1%, at a hazard ratio of 0.66 (P = .004).
At 24 months, the DFS rate was 74.6% among patients given atezolizumab versus 61% in those receiving best supportive care, reducing to 60% and 48.2%, respectively, at 36 months.
When looking across all randomized patients, the addition of atezolizumab was associated with a smaller reduction in the risk of recurrence of death versus best supportive care, at a hazard ratio of 0.79 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .02).
On the intention to treat analysis, the reduction in the risk of recurrence or death with atezolizumab was of borderline significance, at a hazard ratio of 0.81 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .04).
Dr. Wakelee pointed out that patients with stage IB disease, who represented around 12% of those in the trial, “tend to do better and we require longer time to see some of the disease recurrence outcomes,” and so these results are “preliminary.”
She also emphasized that the overall survival data are not yet mature and survival was not formally tested in the current analysis.
In terms of safety, the adverse event profile with atezolizumab was consistent with previous reports, the investigators noted in the abstract. However, Dr. Wakelee said at the briefing that “we had to stop treatment with atezolizumab in 18% of patients because of toxicity.”
All-grade adverse events were reported in 70.7% of the best supportive care group versus 92.7% among those given atezolizumab, while grade 3-4 adverse events were reported in 11.5% and 21.8% of patients, respectively.
The study was funded by Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Wakelee reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines, Daiichi Sankyo, Helsinn Therapeutics, Janssen Oncology, Mirati Therapeutics, Xcovery, ACEA Biosciences, Arrys Therapeutics, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Clovis Oncology, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Xcovery. She also reports uncompensated relationships with Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Takeda. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech, Sandoz, and Immunomedics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy has already had a huge impact on treatment of patients with later stages of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): new clinical data are now showing benefits in patients with earlier stage disease.
Patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC showed a markedly improved disease-free survival (DFS) when atezolizumab (Tecentriq) was added onto adjuvant chemotherapy following resection, according to results from an interim analysis of the IMpower010 study.
Notably, the benefit with atezolizumab versus best supportive care was greatest in patients with expression of programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) on their tumor, in whom the DFS improvement was a significant 34%.
This is the “first global phase 3 trial using an immune checkpoint inhibitor to show a disease-free survival outcome in early-stage NSCLC,” said lead researcher Heather Wakelee, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center.
She was speaking at a press briefing ahead of the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, where the results will be presented on June 6.
Dr. Wakelee added that the “planned analysis for disease-free survival and overall survival in the intention-to-treat populations will continue with longer-term follow-up.”
Asked whether the drug could be recommended for these patients based on the current results, Dr. Wakelee said that “obviously we need approval” for this use from the Food and Drug Administration, but she added that “the FDA has approved other agents, particularly most recently osimertinib [Tagrisso], based on a disease-free survival endpoint.”
These new results show that the benefit with atezolizumab plus chemotherapy is “more profound” than with chemotherapy plus best supportive care, “and therefore, to me, it would be something I would want to offer my patients in that setting.”
Dr. Wakelee also emphasized the importance of screening for lung cancer, so that the disease is detected at earlier stages “when it is potentially curable.”
She also stressed the importance of biomarker testing for patients with resected disease “to look for EGFR mutations, which can be treated with EGFR [tyrosine kinase inhibitors] and also, at some point, to check for PD-L1 ... because, in this trial, the vast majority of benefit” appeared to be in those with PD-L1 expression on their tumors.
Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, said that “immune checkpoint inhibitors have certainly changed the treatment landscape for many types of cancers” and the current study “is the first time we’ve seen an immunotherapy that’s effective in treating early-stage NSCLC.”
“This is an important advance in understanding the role of immunotherapy in earlier stage lung cancer” and “potentially a step forward for many patients.”
Study details
The standard of care for many stage IB-IIIA NSCLC patients “has not changed for many years,” despite “significant progress” having been made in the treatment of more advanced disease, Dr. Wakelee commented.
Consequently, the majority of patients with resected NSCLC continue to receive adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy, which has been shown to reduce the risk of disease recurrence by 16% in those with completely resected disease.
The new study set out to examine the benefit of adding atezolizumab to adjuvant chemotherapy in the global phase 3 IMpower010 study.
Patients had to have stage IB-IIIA NSCLC, with stage IB tumors at least 4 cm in size, and tumor tissue available for PD-L1 analysis. Following complete resection, 1,280 patients were given up to four cycles of adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy.
Of those, 1,005 patients were then randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either 16 cycles of atezolizumab 1,200 mg IV every 3 weeks or best supportive care.
The interim results show that, after a median follow-up of 32.8 months, the addition of atezolizumab significantly reduced the risk of recurrence or death versus best supportive care in patients whose tumors had PD-L1 expression of at least 1%, at a hazard ratio of 0.66 (P = .004).
At 24 months, the DFS rate was 74.6% among patients given atezolizumab versus 61% in those receiving best supportive care, reducing to 60% and 48.2%, respectively, at 36 months.
When looking across all randomized patients, the addition of atezolizumab was associated with a smaller reduction in the risk of recurrence of death versus best supportive care, at a hazard ratio of 0.79 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .02).
On the intention to treat analysis, the reduction in the risk of recurrence or death with atezolizumab was of borderline significance, at a hazard ratio of 0.81 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .04).
Dr. Wakelee pointed out that patients with stage IB disease, who represented around 12% of those in the trial, “tend to do better and we require longer time to see some of the disease recurrence outcomes,” and so these results are “preliminary.”
She also emphasized that the overall survival data are not yet mature and survival was not formally tested in the current analysis.
In terms of safety, the adverse event profile with atezolizumab was consistent with previous reports, the investigators noted in the abstract. However, Dr. Wakelee said at the briefing that “we had to stop treatment with atezolizumab in 18% of patients because of toxicity.”
All-grade adverse events were reported in 70.7% of the best supportive care group versus 92.7% among those given atezolizumab, while grade 3-4 adverse events were reported in 11.5% and 21.8% of patients, respectively.
The study was funded by Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Wakelee reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines, Daiichi Sankyo, Helsinn Therapeutics, Janssen Oncology, Mirati Therapeutics, Xcovery, ACEA Biosciences, Arrys Therapeutics, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Clovis Oncology, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Xcovery. She also reports uncompensated relationships with Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Takeda. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech, Sandoz, and Immunomedics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy has already had a huge impact on treatment of patients with later stages of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): new clinical data are now showing benefits in patients with earlier stage disease.
Patients with stage IB-IIIA NSCLC showed a markedly improved disease-free survival (DFS) when atezolizumab (Tecentriq) was added onto adjuvant chemotherapy following resection, according to results from an interim analysis of the IMpower010 study.
Notably, the benefit with atezolizumab versus best supportive care was greatest in patients with expression of programmed death–ligand 1 (PD-L1) on their tumor, in whom the DFS improvement was a significant 34%.
This is the “first global phase 3 trial using an immune checkpoint inhibitor to show a disease-free survival outcome in early-stage NSCLC,” said lead researcher Heather Wakelee, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical Center.
She was speaking at a press briefing ahead of the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting, where the results will be presented on June 6.
Dr. Wakelee added that the “planned analysis for disease-free survival and overall survival in the intention-to-treat populations will continue with longer-term follow-up.”
Asked whether the drug could be recommended for these patients based on the current results, Dr. Wakelee said that “obviously we need approval” for this use from the Food and Drug Administration, but she added that “the FDA has approved other agents, particularly most recently osimertinib [Tagrisso], based on a disease-free survival endpoint.”
These new results show that the benefit with atezolizumab plus chemotherapy is “more profound” than with chemotherapy plus best supportive care, “and therefore, to me, it would be something I would want to offer my patients in that setting.”
Dr. Wakelee also emphasized the importance of screening for lung cancer, so that the disease is detected at earlier stages “when it is potentially curable.”
She also stressed the importance of biomarker testing for patients with resected disease “to look for EGFR mutations, which can be treated with EGFR [tyrosine kinase inhibitors] and also, at some point, to check for PD-L1 ... because, in this trial, the vast majority of benefit” appeared to be in those with PD-L1 expression on their tumors.
Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president, said that “immune checkpoint inhibitors have certainly changed the treatment landscape for many types of cancers” and the current study “is the first time we’ve seen an immunotherapy that’s effective in treating early-stage NSCLC.”
“This is an important advance in understanding the role of immunotherapy in earlier stage lung cancer” and “potentially a step forward for many patients.”
Study details
The standard of care for many stage IB-IIIA NSCLC patients “has not changed for many years,” despite “significant progress” having been made in the treatment of more advanced disease, Dr. Wakelee commented.
Consequently, the majority of patients with resected NSCLC continue to receive adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy, which has been shown to reduce the risk of disease recurrence by 16% in those with completely resected disease.
The new study set out to examine the benefit of adding atezolizumab to adjuvant chemotherapy in the global phase 3 IMpower010 study.
Patients had to have stage IB-IIIA NSCLC, with stage IB tumors at least 4 cm in size, and tumor tissue available for PD-L1 analysis. Following complete resection, 1,280 patients were given up to four cycles of adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy.
Of those, 1,005 patients were then randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either 16 cycles of atezolizumab 1,200 mg IV every 3 weeks or best supportive care.
The interim results show that, after a median follow-up of 32.8 months, the addition of atezolizumab significantly reduced the risk of recurrence or death versus best supportive care in patients whose tumors had PD-L1 expression of at least 1%, at a hazard ratio of 0.66 (P = .004).
At 24 months, the DFS rate was 74.6% among patients given atezolizumab versus 61% in those receiving best supportive care, reducing to 60% and 48.2%, respectively, at 36 months.
When looking across all randomized patients, the addition of atezolizumab was associated with a smaller reduction in the risk of recurrence of death versus best supportive care, at a hazard ratio of 0.79 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .02).
On the intention to treat analysis, the reduction in the risk of recurrence or death with atezolizumab was of borderline significance, at a hazard ratio of 0.81 after a median follow-up of 32.2 months (P = .04).
Dr. Wakelee pointed out that patients with stage IB disease, who represented around 12% of those in the trial, “tend to do better and we require longer time to see some of the disease recurrence outcomes,” and so these results are “preliminary.”
She also emphasized that the overall survival data are not yet mature and survival was not formally tested in the current analysis.
In terms of safety, the adverse event profile with atezolizumab was consistent with previous reports, the investigators noted in the abstract. However, Dr. Wakelee said at the briefing that “we had to stop treatment with atezolizumab in 18% of patients because of toxicity.”
All-grade adverse events were reported in 70.7% of the best supportive care group versus 92.7% among those given atezolizumab, while grade 3-4 adverse events were reported in 11.5% and 21.8% of patients, respectively.
The study was funded by Hoffmann–La Roche. Dr. Wakelee reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines, Daiichi Sankyo, Helsinn Therapeutics, Janssen Oncology, Mirati Therapeutics, Xcovery, ACEA Biosciences, Arrys Therapeutics, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Clovis Oncology, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Gilead Sciences, Merck, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Xcovery. She also reports uncompensated relationships with Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Takeda. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with AstraZeneca, Genentech, Sandoz, and Immunomedics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.





