User login
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.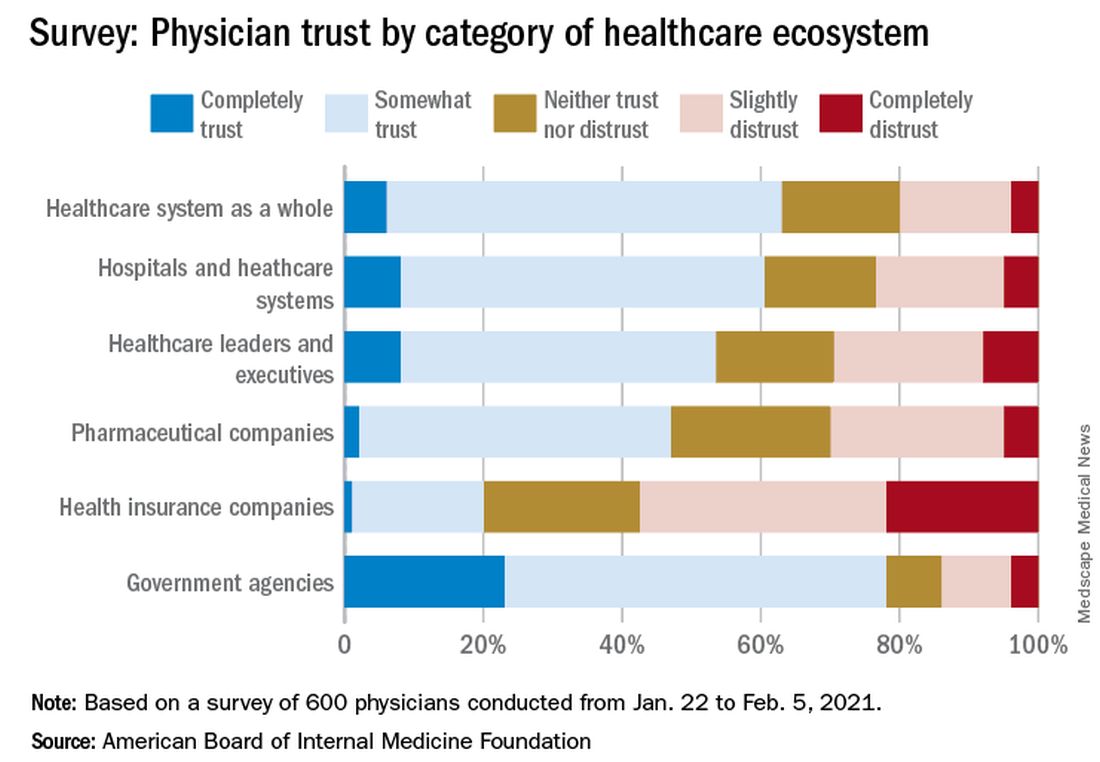
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a survey conducted by NORC at the University of Chicago on behalf of the American Board of Internal Medicine Foundation.
Survey results, released May 21, indicate that 30% of physicians say their trust in the U.S. health care system and health care leadership has decreased during the pandemic. Only 18% reported an increase in trust.
Physicians, however, have great trust in their fellow clinicians.
In the survey of 600 physicians, 94% said they trust doctors within their practice; 85% trusted doctors outside of their practice; and 89% trusted nurses. That trust increased during the pandemic, with 41% saying their trust in fellow physicians rose and 37% saying their trust in nurses did.
In a separate survey, NORC asked patients about their trust in various aspects of health care. Among 2,069 respondents, a wide majority reported that they trust doctors (84%) and nurses (85%), but only 64% trusted the health care system as a whole. One in three consumers (32%) said their trust in the health care system decreased during the pandemic, compared with 11% who said their trust increased.
The ABIM Foundation released the research findings on May 21 as part of Building Trust, a national campaign that aims to boost trust among patients, clinicians, system leaders, researchers, and others.
Richard J. Baron, MD, president and chief executive officer of the ABIM Foundation, said in an interview, “Clearly there’s lower trust in health care organization leaders and executives, and that’s troubling.
“Science by itself is not enough,” he said. “Becoming trustworthy has to be a core project of everybody in health care.”
Deterioration in physicians’ trust during the pandemic comes in part from failed promises of adequate personal protective equipment and some physicians’ loss of income as a result of the crisis, Dr. Baron said.
He added that the vaccine rollout was very uneven and that policies as to which elective procedures could be performed were handled differently in different parts of the country.
He also noted that, early on, transparency was lacking as to how many COVID patients hospitals were treating, which may have contributed to the decrease in trust in the system.
Fear of being known as ‘the COVID hospital’
Hospitals were afraid of being known as “the COVID hospital” and losing patients who were afraid to come there, Dr. Baron said.
He said the COVID-19 epidemic exacerbated problems regarding trust, but that trust has been declining for some time. The Building Trust campaign will focus on solutions in breaches of trust as physicians move increasingly toward being employees of huge systems, according to Dr. Baron.
However, trust works both ways, Dr. Baron notes. Physicians can be champions for their health care system or “throw the system under the bus,” he said.
For example, if a patient complains about the appointment system, clinicians who trust their institutions may say the system usually works and that they will try to make sure the patient has a better experience next time. Clinicians without trust may say they agree that the health care system doesn’t know what it is doing, and patients may further lose confidence when physicians validate their complaint, and patients may then go elsewhere.
78% of patients trust primary care doctor
When asked whether they trust their primary care physician, 78% of patients said yes. However, trust in doctors was higher among people who were older (90%), White (82%), or had high income (89%). Among people reporting lower trust, 25% said their physician spends too little time with them, and 14% said their doctor does not know or listen to them.
The survey shows that government agencies have work to do to earn trust. Responses indicate that 43% of physicians said they have “complete trust” in government health care agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is substantially higher than other parts of the health care system. However, trust in agencies declined for 43% of physician respondents and increased for 21%.
Dhruv Khullar, MD, MPP, of the department of health policy and economics at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, told this news organization the survey results match what he sees anecdotally in medicine – that physicians have been losing trust in the system but not in their colleagues.
He said the sample size of 600 is enough to be influential, though he said he would like to know the response rate, which was not calculated for this survey.
He added that, in large part, physicians’ lack of trust in their systems may come from generally being asked to see more patients and to meet more metrics during the same or shorter periods.
Physicians’ lack of trust in the system can have significant consequences, he said. It can lead to burnout, which has been linked with poorer quality of care and physician turnover, he noted.
COVID-19 led some physicians to wonder whether their system had their best interests at heart, insofar as access to adequate medicines and supplies as well as emotional support were inconsistent, Dr. Khullar said.
He said that to regain trust health care systems need to ask themselves questions in three areas. The first is whether their goals are focused on the best interest of the organization or the best interest of the patient.
“Next is competency,” Dr. Khullar said. “Maybe your motives are right, but are you able to deliver? Are you delivering a good product, whether clinical services or something else?”
The third area is transparency, he said. “Are you going to be honest and forthright in what we’re doing and where we’re going?”
Caroline Pearson, senior vice president of health care strategy for NORC, said the emailed survey was conducted between Dec. 29, 2020, and Feb. 5, 2021, with a health care survey partner that maintains a nationwide panel of physicians across specialties.
She said this report is fairly novel insofar as surveys are more typically conducted regarding patients’ trust of their doctors or of the health care system.
Ms. Pearson said because health care is delivered in teams, understanding the level of trust among the entities helps ensure that care will be delivered effectively and seamlessly with high quality.
“We want our patients to trust our doctors, but we really want doctors to trust each other and trust the hospitals and systems in which they’re working,” she said.
Dr. Baron, Ms. Pearson, and Dr. Khullar report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.