User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


GALACTIC-HF: Novel drug most effective in sickest HFrEF patients
The greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil, a member of the novel myotropic drug class that improves cardiac performance, is produced in heart failure patients with the lowest left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), a new analysis of the recently published phase 3 GALACTIC-HF trial has found.
The findings reinforce the potential for this drug to be helpful in the management of the most advanced stages of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), reported John R. Teerlink, MD, director of heart failure at San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The phase 3 multinational GALACTIC-HF trial, published earlier this year, linked omecamtiv mecarbil with an 8% reduction in the risk of a heart failure–related events or cardiovascular death, relative to placebo, which was the primary outcome. For entry, HFrEF patients were required to have a LVEF of 35% or less.
Drilling down on ejection fraction
The new analysis divided participants into quartiles of baseline LVEF and then compared relative outcomes and safety.
In the lowest quartile, defined by a LVEF of 22% or lower, the reduction in risk of events reached 17% (hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.95) for omecamtiv mecarbil relative to placebo. In the highest, defined by a LVEF of 33% or greater, the benefit fell short of significance (HR 0.99; 95% CI, 0.84-1.16). Across quartiles, LVEF was the “strongest modifier of the treatment effect,” emerging in this analysis as a statistically significant (P = .004) continuous variable.
The comparison by LVEF quartiles also provided an opportunity to show that omecamtiv mecarbil was as safe and well tolerated in those with the most advanced disease as in those less sick. At the lowest levels of LVEF, like the higher levels, omecamtiv mecarbil did not produce any adverse effects on blood pressure, heart rate, potassium homeostasis, or renal function.
In GALACTIC-HF, 8,256 HFrEF patients with LVEF 35% or less were randomized to omecamtiv mecarbil or placebo. The primary composite outcome of hospitalization or urgent visit for heart failure or death from cardiovascular causes was evaluated after a median of 21.8 months on therapy.
When incidence rate per 100 patient years was graphed against the range of LVEF, the relative advantage of omecamtiv mecarbil became visible just below an LVEF of 30%, climbing steadily even to the lowest LVEF, which reached 10%.
Perhaps relevant to the reduction in events, there were also greater relative reductions in NT-proBNP (NT-proB-type natriuretic peptide) for omecamtiv mecarbil at lower relative to higher LVEF. Although omecamtiv mecarbil is not associated with any direct vascular, electrophysiologic, or neurohormonal effects, according to Dr. Teerlink, the indirect effects of selective binding to cardiac myosin has been associated with lower NT-proBNP and other biomarkers of cardiac remodeling in prior clinical studies.
Although Dr. Teerlink acknowledged that relatively few patients in GALACTIC-HF received an angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) or a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, he said there is “every reason to believe that omecamtiv mecarbil would be complementary to these therapies.” He said the mechanism of action of omecamtiv mecarbil, which improves systolic function, has no overlap with these drugs.
Importantly, there is a particular need for new treatment options in patients with advanced LVEF, according to Dr. Teerlink, who cited evidence, for example, that “the beneficial effect of [the ARNI] sacubitril valsartan, while still significant, decreases in patients with LVEF less than 35%.”
Overall, based on these results, “we believe that omecamtiv mecarbil represents a novel therapy that holds the promise of improving clinical outcomes in patients with severely reduced ejection fraction, which are the very patients that are most challenging for us to treat,” Dr. Teerlink said.
Omecamtiv mecarbil may ‘buy you some time’
Ileana Piña, MD, clinical professor of medicine, Central Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, Mich., agreed. She said that omecamtiv mecarbil, if approved, will be an option for the type of HFrEF patients who are being considered for heart transplant or mechanical-assist devices.
“We are very loath to use inotropes in this population, because we know that ultimately the inotrope is not going to do well,” said Dr. Piña, calling these therapies a “Band-Aid.” Based on the evidence from GALACTIC-HF, she thinks that omecamtiv mecarbil will be more versatile.
“This drug does not increase myocardial oxygen demand as do the inotropes, and it can be given in the outpatient setting if need be, so I see this as a real advance,” Dr. Piña said. Although Dr. Piña acknowledged that omecamtiv mecarbil did not reduce mortality in the GALACTIC-HF trial, “at least it will buy you some time.”
Dr. Teerlink has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Amgen, Cytogenetics, and Servier, which provided funding for the GALACTIC-HF trial. Dr. Piña reports no potential conflicts of interest.
The greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil, a member of the novel myotropic drug class that improves cardiac performance, is produced in heart failure patients with the lowest left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), a new analysis of the recently published phase 3 GALACTIC-HF trial has found.
The findings reinforce the potential for this drug to be helpful in the management of the most advanced stages of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), reported John R. Teerlink, MD, director of heart failure at San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The phase 3 multinational GALACTIC-HF trial, published earlier this year, linked omecamtiv mecarbil with an 8% reduction in the risk of a heart failure–related events or cardiovascular death, relative to placebo, which was the primary outcome. For entry, HFrEF patients were required to have a LVEF of 35% or less.
Drilling down on ejection fraction
The new analysis divided participants into quartiles of baseline LVEF and then compared relative outcomes and safety.
In the lowest quartile, defined by a LVEF of 22% or lower, the reduction in risk of events reached 17% (hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.95) for omecamtiv mecarbil relative to placebo. In the highest, defined by a LVEF of 33% or greater, the benefit fell short of significance (HR 0.99; 95% CI, 0.84-1.16). Across quartiles, LVEF was the “strongest modifier of the treatment effect,” emerging in this analysis as a statistically significant (P = .004) continuous variable.
The comparison by LVEF quartiles also provided an opportunity to show that omecamtiv mecarbil was as safe and well tolerated in those with the most advanced disease as in those less sick. At the lowest levels of LVEF, like the higher levels, omecamtiv mecarbil did not produce any adverse effects on blood pressure, heart rate, potassium homeostasis, or renal function.
In GALACTIC-HF, 8,256 HFrEF patients with LVEF 35% or less were randomized to omecamtiv mecarbil or placebo. The primary composite outcome of hospitalization or urgent visit for heart failure or death from cardiovascular causes was evaluated after a median of 21.8 months on therapy.
When incidence rate per 100 patient years was graphed against the range of LVEF, the relative advantage of omecamtiv mecarbil became visible just below an LVEF of 30%, climbing steadily even to the lowest LVEF, which reached 10%.
Perhaps relevant to the reduction in events, there were also greater relative reductions in NT-proBNP (NT-proB-type natriuretic peptide) for omecamtiv mecarbil at lower relative to higher LVEF. Although omecamtiv mecarbil is not associated with any direct vascular, electrophysiologic, or neurohormonal effects, according to Dr. Teerlink, the indirect effects of selective binding to cardiac myosin has been associated with lower NT-proBNP and other biomarkers of cardiac remodeling in prior clinical studies.
Although Dr. Teerlink acknowledged that relatively few patients in GALACTIC-HF received an angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) or a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, he said there is “every reason to believe that omecamtiv mecarbil would be complementary to these therapies.” He said the mechanism of action of omecamtiv mecarbil, which improves systolic function, has no overlap with these drugs.
Importantly, there is a particular need for new treatment options in patients with advanced LVEF, according to Dr. Teerlink, who cited evidence, for example, that “the beneficial effect of [the ARNI] sacubitril valsartan, while still significant, decreases in patients with LVEF less than 35%.”
Overall, based on these results, “we believe that omecamtiv mecarbil represents a novel therapy that holds the promise of improving clinical outcomes in patients with severely reduced ejection fraction, which are the very patients that are most challenging for us to treat,” Dr. Teerlink said.
Omecamtiv mecarbil may ‘buy you some time’
Ileana Piña, MD, clinical professor of medicine, Central Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, Mich., agreed. She said that omecamtiv mecarbil, if approved, will be an option for the type of HFrEF patients who are being considered for heart transplant or mechanical-assist devices.
“We are very loath to use inotropes in this population, because we know that ultimately the inotrope is not going to do well,” said Dr. Piña, calling these therapies a “Band-Aid.” Based on the evidence from GALACTIC-HF, she thinks that omecamtiv mecarbil will be more versatile.
“This drug does not increase myocardial oxygen demand as do the inotropes, and it can be given in the outpatient setting if need be, so I see this as a real advance,” Dr. Piña said. Although Dr. Piña acknowledged that omecamtiv mecarbil did not reduce mortality in the GALACTIC-HF trial, “at least it will buy you some time.”
Dr. Teerlink has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Amgen, Cytogenetics, and Servier, which provided funding for the GALACTIC-HF trial. Dr. Piña reports no potential conflicts of interest.
The greatest relative benefit from omecamtiv mecarbil, a member of the novel myotropic drug class that improves cardiac performance, is produced in heart failure patients with the lowest left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), a new analysis of the recently published phase 3 GALACTIC-HF trial has found.
The findings reinforce the potential for this drug to be helpful in the management of the most advanced stages of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), reported John R. Teerlink, MD, director of heart failure at San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The phase 3 multinational GALACTIC-HF trial, published earlier this year, linked omecamtiv mecarbil with an 8% reduction in the risk of a heart failure–related events or cardiovascular death, relative to placebo, which was the primary outcome. For entry, HFrEF patients were required to have a LVEF of 35% or less.
Drilling down on ejection fraction
The new analysis divided participants into quartiles of baseline LVEF and then compared relative outcomes and safety.
In the lowest quartile, defined by a LVEF of 22% or lower, the reduction in risk of events reached 17% (hazard ratio, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.95) for omecamtiv mecarbil relative to placebo. In the highest, defined by a LVEF of 33% or greater, the benefit fell short of significance (HR 0.99; 95% CI, 0.84-1.16). Across quartiles, LVEF was the “strongest modifier of the treatment effect,” emerging in this analysis as a statistically significant (P = .004) continuous variable.
The comparison by LVEF quartiles also provided an opportunity to show that omecamtiv mecarbil was as safe and well tolerated in those with the most advanced disease as in those less sick. At the lowest levels of LVEF, like the higher levels, omecamtiv mecarbil did not produce any adverse effects on blood pressure, heart rate, potassium homeostasis, or renal function.
In GALACTIC-HF, 8,256 HFrEF patients with LVEF 35% or less were randomized to omecamtiv mecarbil or placebo. The primary composite outcome of hospitalization or urgent visit for heart failure or death from cardiovascular causes was evaluated after a median of 21.8 months on therapy.
When incidence rate per 100 patient years was graphed against the range of LVEF, the relative advantage of omecamtiv mecarbil became visible just below an LVEF of 30%, climbing steadily even to the lowest LVEF, which reached 10%.
Perhaps relevant to the reduction in events, there were also greater relative reductions in NT-proBNP (NT-proB-type natriuretic peptide) for omecamtiv mecarbil at lower relative to higher LVEF. Although omecamtiv mecarbil is not associated with any direct vascular, electrophysiologic, or neurohormonal effects, according to Dr. Teerlink, the indirect effects of selective binding to cardiac myosin has been associated with lower NT-proBNP and other biomarkers of cardiac remodeling in prior clinical studies.
Although Dr. Teerlink acknowledged that relatively few patients in GALACTIC-HF received an angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) or a sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, he said there is “every reason to believe that omecamtiv mecarbil would be complementary to these therapies.” He said the mechanism of action of omecamtiv mecarbil, which improves systolic function, has no overlap with these drugs.
Importantly, there is a particular need for new treatment options in patients with advanced LVEF, according to Dr. Teerlink, who cited evidence, for example, that “the beneficial effect of [the ARNI] sacubitril valsartan, while still significant, decreases in patients with LVEF less than 35%.”
Overall, based on these results, “we believe that omecamtiv mecarbil represents a novel therapy that holds the promise of improving clinical outcomes in patients with severely reduced ejection fraction, which are the very patients that are most challenging for us to treat,” Dr. Teerlink said.
Omecamtiv mecarbil may ‘buy you some time’
Ileana Piña, MD, clinical professor of medicine, Central Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, Mich., agreed. She said that omecamtiv mecarbil, if approved, will be an option for the type of HFrEF patients who are being considered for heart transplant or mechanical-assist devices.
“We are very loath to use inotropes in this population, because we know that ultimately the inotrope is not going to do well,” said Dr. Piña, calling these therapies a “Band-Aid.” Based on the evidence from GALACTIC-HF, she thinks that omecamtiv mecarbil will be more versatile.
“This drug does not increase myocardial oxygen demand as do the inotropes, and it can be given in the outpatient setting if need be, so I see this as a real advance,” Dr. Piña said. Although Dr. Piña acknowledged that omecamtiv mecarbil did not reduce mortality in the GALACTIC-HF trial, “at least it will buy you some time.”
Dr. Teerlink has financial relationships with multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Amgen, Cytogenetics, and Servier, which provided funding for the GALACTIC-HF trial. Dr. Piña reports no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM ACC 2021
Sotagliflozin’s HFpEF benefit confirmed by new analyses
It’s now official: The investigational sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 1/2 inhibitor sotagliflozin is the first agent clearly shown in a prespecified analysis of randomized trials to improve clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Researchers who ran the SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF pivotal trials for sotagliflozin first made that claim in November 2020 when reporting top-line results from a prespecified meta-analysis of the two trials during the American Heart Association annual scientific sessions. A follow-up report during the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology fleshed out the evidence and firmed up their landmark conclusion.
The meta-analysis (Abstract 410-08) included 4,500 patients with type 2 diabetes and diagnosed heart failure at entry; its primary endpoint, which was the same in both trials, was the combined incidence of cardiovascular death and the total number of either hospitalization for heart failure or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure.
Compared with placebo, treatment with sotagliflozin for a median of about 15 months dropped this composite endpoint by a relative 33% among the 1,931 who began the study with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 50% (HFpEF), by a relative 22% in the 1,758 patients who entered with an LVEF of less than 40% (patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction), and by a relative 43% among the 811 patients who began with an LVEF of 40%-49% (patients with heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction). The relative risk reductions were significant for all three subgroups, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, reported at the meeting.
Equally effective ‘across the full range of LVEFs.’
Perhaps as notable and unprecedented was the further finding that the clinical benefits seen with treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes with sotagliflozin was consistent regardless of the ejection fraction they had at entry. Enrolled patients with baseline LVEFs in the range of 25% received a relative benefit from sotagliflozin treatment that was statistically no different from the benefit seen in patients who entered with an LVEF in the neighborhood of 45%, 65%, or at any other level across the LVEF spectrum, a finding that Dr. Bhatt called “remarkable” during a press briefing. “The results show the benefit of sotagliflozin across the full range of LVEFs.”
“We are very excited in the heart failure world by the SGLT2 inhibitors; we’ve been impressed by their reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but we wonder about the patients with HFpEF, where we haven’t had a blockbuster drug to give,” said Ileana L. Piña, MD, a heart failure specialist and medical officer with the Food and Drug Administration.
The new findings “look like they could pose a regulatory indication [for sotagliflozin] for patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure across the entire spectrum of heart failure,” said Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart & Vascular institute in Falls Church, Va., and designated discussant for Dr. Bhatt’s report.
SCORED randomized 10,584 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease to treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo on top of guideline-directed medical therapy. During a median 16 months of treatment, the combined primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 5.6 events/100 patient years on sotagliflozin and 7.5 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 26% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:129-39). Nearly a third of the enrolled patients had heart failure, with representation across the range of LVEF.
SOLOIST-WHF randomized 1,222 patients with type 2 diabetes who were recently hospitalized for worsening heart failure. During a median 9 months of follow-up, the primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 51 events/100 patient years in the sotagliflozin-treated patients and a rate of 76 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 33% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:117-28). Both trials stopped prematurely because of sponsorship issues.
In addition to the 4,500 patients with heart failure at entry in both trials, SCORED included a total of more than 6,700 without diagnosed heart failure at baseline, and in this subgroup treatment with sotagliflozin cut the incidence of the primary endpoint by a significant 27% compared with control patients.
A significant on-treatment reduction in CV death
Other new, notable findings from the meta-analysis included the observation that while treatment with sotagliflozin failed to produce a significant reduction in cardiovascular death, compared with placebo, in the intent-to-treat analysis of all patients and of those with heart failure at baseline (it produced nonsignificant point-estimate reductions of 11% compared with placebo for all patients, and of 23% for patients who began the study with heart failure), it did result in a significant 23% relative risk reduction when the researchers focused on patients while they remained adherent to their sotagliflozin regimen (the on-treatment analysis). This 23% relative reduction appeared among all enrolled patients, as well as in the subgroup that started with diagnosed heart failure.
“Given the totality of data from the SGLT2 inhibitors, I think this is a real finding,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Additional analyses also showed that, among women, treatment with sotagliflozin was linked with significant relative reductions in the primary endpoint of roughly 30% compared with placebo among all patients, and also among those with heart failure at baseline. “HFpEF is a problem particularly in older women, and we showed that the benefit was consistent in men and women,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He acknowledged that results are expected soon from two pivotal trials that are examining two different SGLT2 inhibitors, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in patients with HFpEF. “I think there will be a class effect for both SGLT2 inhibitors and sotagliflozin for reducing heart failure events in patients with HFpEF, and I predict that the dapagliflozin and empagliflozin trials will have positive results,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Sotagliflozin differs from the SGLT2 inhibitors by also inhibiting SGLT1, an enzyme found in the gastrointestinal system that, when inhibited, results in increased glucose excretion from the gut and a cut in bloodstream levels of postprandial glucose levels. The Food and Drug Administration accepted data from SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF as part of the evidence the agency is now considering for granting a new drug approval to sotagliflozin.
SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF were initially sponsored by Sanofi, and later by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bhatt’s institution, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, has received funding from Sanofi and Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an adviser to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies. Dr. Piña has no relevant disclosures. Dr. O’Connor has been a consultant to Arena, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Windtree, and he has an ownership interest in Biscardia.
It’s now official: The investigational sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 1/2 inhibitor sotagliflozin is the first agent clearly shown in a prespecified analysis of randomized trials to improve clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Researchers who ran the SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF pivotal trials for sotagliflozin first made that claim in November 2020 when reporting top-line results from a prespecified meta-analysis of the two trials during the American Heart Association annual scientific sessions. A follow-up report during the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology fleshed out the evidence and firmed up their landmark conclusion.
The meta-analysis (Abstract 410-08) included 4,500 patients with type 2 diabetes and diagnosed heart failure at entry; its primary endpoint, which was the same in both trials, was the combined incidence of cardiovascular death and the total number of either hospitalization for heart failure or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure.
Compared with placebo, treatment with sotagliflozin for a median of about 15 months dropped this composite endpoint by a relative 33% among the 1,931 who began the study with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 50% (HFpEF), by a relative 22% in the 1,758 patients who entered with an LVEF of less than 40% (patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction), and by a relative 43% among the 811 patients who began with an LVEF of 40%-49% (patients with heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction). The relative risk reductions were significant for all three subgroups, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, reported at the meeting.
Equally effective ‘across the full range of LVEFs.’
Perhaps as notable and unprecedented was the further finding that the clinical benefits seen with treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes with sotagliflozin was consistent regardless of the ejection fraction they had at entry. Enrolled patients with baseline LVEFs in the range of 25% received a relative benefit from sotagliflozin treatment that was statistically no different from the benefit seen in patients who entered with an LVEF in the neighborhood of 45%, 65%, or at any other level across the LVEF spectrum, a finding that Dr. Bhatt called “remarkable” during a press briefing. “The results show the benefit of sotagliflozin across the full range of LVEFs.”
“We are very excited in the heart failure world by the SGLT2 inhibitors; we’ve been impressed by their reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but we wonder about the patients with HFpEF, where we haven’t had a blockbuster drug to give,” said Ileana L. Piña, MD, a heart failure specialist and medical officer with the Food and Drug Administration.
The new findings “look like they could pose a regulatory indication [for sotagliflozin] for patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure across the entire spectrum of heart failure,” said Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart & Vascular institute in Falls Church, Va., and designated discussant for Dr. Bhatt’s report.
SCORED randomized 10,584 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease to treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo on top of guideline-directed medical therapy. During a median 16 months of treatment, the combined primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 5.6 events/100 patient years on sotagliflozin and 7.5 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 26% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:129-39). Nearly a third of the enrolled patients had heart failure, with representation across the range of LVEF.
SOLOIST-WHF randomized 1,222 patients with type 2 diabetes who were recently hospitalized for worsening heart failure. During a median 9 months of follow-up, the primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 51 events/100 patient years in the sotagliflozin-treated patients and a rate of 76 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 33% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:117-28). Both trials stopped prematurely because of sponsorship issues.
In addition to the 4,500 patients with heart failure at entry in both trials, SCORED included a total of more than 6,700 without diagnosed heart failure at baseline, and in this subgroup treatment with sotagliflozin cut the incidence of the primary endpoint by a significant 27% compared with control patients.
A significant on-treatment reduction in CV death
Other new, notable findings from the meta-analysis included the observation that while treatment with sotagliflozin failed to produce a significant reduction in cardiovascular death, compared with placebo, in the intent-to-treat analysis of all patients and of those with heart failure at baseline (it produced nonsignificant point-estimate reductions of 11% compared with placebo for all patients, and of 23% for patients who began the study with heart failure), it did result in a significant 23% relative risk reduction when the researchers focused on patients while they remained adherent to their sotagliflozin regimen (the on-treatment analysis). This 23% relative reduction appeared among all enrolled patients, as well as in the subgroup that started with diagnosed heart failure.
“Given the totality of data from the SGLT2 inhibitors, I think this is a real finding,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Additional analyses also showed that, among women, treatment with sotagliflozin was linked with significant relative reductions in the primary endpoint of roughly 30% compared with placebo among all patients, and also among those with heart failure at baseline. “HFpEF is a problem particularly in older women, and we showed that the benefit was consistent in men and women,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He acknowledged that results are expected soon from two pivotal trials that are examining two different SGLT2 inhibitors, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in patients with HFpEF. “I think there will be a class effect for both SGLT2 inhibitors and sotagliflozin for reducing heart failure events in patients with HFpEF, and I predict that the dapagliflozin and empagliflozin trials will have positive results,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Sotagliflozin differs from the SGLT2 inhibitors by also inhibiting SGLT1, an enzyme found in the gastrointestinal system that, when inhibited, results in increased glucose excretion from the gut and a cut in bloodstream levels of postprandial glucose levels. The Food and Drug Administration accepted data from SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF as part of the evidence the agency is now considering for granting a new drug approval to sotagliflozin.
SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF were initially sponsored by Sanofi, and later by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bhatt’s institution, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, has received funding from Sanofi and Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an adviser to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies. Dr. Piña has no relevant disclosures. Dr. O’Connor has been a consultant to Arena, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Windtree, and he has an ownership interest in Biscardia.
It’s now official: The investigational sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 1/2 inhibitor sotagliflozin is the first agent clearly shown in a prespecified analysis of randomized trials to improve clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Researchers who ran the SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF pivotal trials for sotagliflozin first made that claim in November 2020 when reporting top-line results from a prespecified meta-analysis of the two trials during the American Heart Association annual scientific sessions. A follow-up report during the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology fleshed out the evidence and firmed up their landmark conclusion.
The meta-analysis (Abstract 410-08) included 4,500 patients with type 2 diabetes and diagnosed heart failure at entry; its primary endpoint, which was the same in both trials, was the combined incidence of cardiovascular death and the total number of either hospitalization for heart failure or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure.
Compared with placebo, treatment with sotagliflozin for a median of about 15 months dropped this composite endpoint by a relative 33% among the 1,931 who began the study with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 50% (HFpEF), by a relative 22% in the 1,758 patients who entered with an LVEF of less than 40% (patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction), and by a relative 43% among the 811 patients who began with an LVEF of 40%-49% (patients with heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction). The relative risk reductions were significant for all three subgroups, Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, reported at the meeting.
Equally effective ‘across the full range of LVEFs.’
Perhaps as notable and unprecedented was the further finding that the clinical benefits seen with treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes with sotagliflozin was consistent regardless of the ejection fraction they had at entry. Enrolled patients with baseline LVEFs in the range of 25% received a relative benefit from sotagliflozin treatment that was statistically no different from the benefit seen in patients who entered with an LVEF in the neighborhood of 45%, 65%, or at any other level across the LVEF spectrum, a finding that Dr. Bhatt called “remarkable” during a press briefing. “The results show the benefit of sotagliflozin across the full range of LVEFs.”
“We are very excited in the heart failure world by the SGLT2 inhibitors; we’ve been impressed by their reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but we wonder about the patients with HFpEF, where we haven’t had a blockbuster drug to give,” said Ileana L. Piña, MD, a heart failure specialist and medical officer with the Food and Drug Administration.
The new findings “look like they could pose a regulatory indication [for sotagliflozin] for patients with type 2 diabetes and heart failure across the entire spectrum of heart failure,” said Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, a heart failure specialist and president of the Inova Heart & Vascular institute in Falls Church, Va., and designated discussant for Dr. Bhatt’s report.
SCORED randomized 10,584 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease to treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo on top of guideline-directed medical therapy. During a median 16 months of treatment, the combined primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 5.6 events/100 patient years on sotagliflozin and 7.5 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 26% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:129-39). Nearly a third of the enrolled patients had heart failure, with representation across the range of LVEF.
SOLOIST-WHF randomized 1,222 patients with type 2 diabetes who were recently hospitalized for worsening heart failure. During a median 9 months of follow-up, the primary endpoint occurred at a rate of 51 events/100 patient years in the sotagliflozin-treated patients and a rate of 76 events/100 patient years in the controls, a significant 33% relative reduction with sotagliflozin (N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 14;384[2]:117-28). Both trials stopped prematurely because of sponsorship issues.
In addition to the 4,500 patients with heart failure at entry in both trials, SCORED included a total of more than 6,700 without diagnosed heart failure at baseline, and in this subgroup treatment with sotagliflozin cut the incidence of the primary endpoint by a significant 27% compared with control patients.
A significant on-treatment reduction in CV death
Other new, notable findings from the meta-analysis included the observation that while treatment with sotagliflozin failed to produce a significant reduction in cardiovascular death, compared with placebo, in the intent-to-treat analysis of all patients and of those with heart failure at baseline (it produced nonsignificant point-estimate reductions of 11% compared with placebo for all patients, and of 23% for patients who began the study with heart failure), it did result in a significant 23% relative risk reduction when the researchers focused on patients while they remained adherent to their sotagliflozin regimen (the on-treatment analysis). This 23% relative reduction appeared among all enrolled patients, as well as in the subgroup that started with diagnosed heart failure.
“Given the totality of data from the SGLT2 inhibitors, I think this is a real finding,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Additional analyses also showed that, among women, treatment with sotagliflozin was linked with significant relative reductions in the primary endpoint of roughly 30% compared with placebo among all patients, and also among those with heart failure at baseline. “HFpEF is a problem particularly in older women, and we showed that the benefit was consistent in men and women,” Dr. Bhatt said.
He acknowledged that results are expected soon from two pivotal trials that are examining two different SGLT2 inhibitors, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin, in patients with HFpEF. “I think there will be a class effect for both SGLT2 inhibitors and sotagliflozin for reducing heart failure events in patients with HFpEF, and I predict that the dapagliflozin and empagliflozin trials will have positive results,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Sotagliflozin differs from the SGLT2 inhibitors by also inhibiting SGLT1, an enzyme found in the gastrointestinal system that, when inhibited, results in increased glucose excretion from the gut and a cut in bloodstream levels of postprandial glucose levels. The Food and Drug Administration accepted data from SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF as part of the evidence the agency is now considering for granting a new drug approval to sotagliflozin.
SCORED and SOLOIST-WHF were initially sponsored by Sanofi, and later by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Bhatt’s institution, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, has received funding from Sanofi and Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. He has been a consultant to and received honoraria from K2P, Level Ex, and MJH Life Sciences; he has been an adviser to Cardax, Cereno Scientific, Myokardia, Novo Nordisk, Phase Bio, and PLx Pharma; and he has received research funding from numerous companies. Dr. Piña has no relevant disclosures. Dr. O’Connor has been a consultant to Arena, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, and Windtree, and he has an ownership interest in Biscardia.
FROM ACC 2021
ID experts dole out practical advice to help with mask confusion
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest guidance on what fully vaccinated people can do safely – including not socially distancing and not wearing a mask indoors or outdoors unless other regulations require it – has been widely misinterpreted and caused confusion, two infectious disease experts said at a briefing on May 20 hosted by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The CDC did not ‘’lift” the mask mandate, but rather supplied guidance for those who are fully vaccinated. However, many questions and gray areas remain, and the experts addressed those. ‘’The CDC guidance is really directed at people who are fully vaccinated and who we know are likely to have a really solid response to the vaccine,” said Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of infectious diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and an IDSA board member.
That message was largely lost, said Dr. Marrazzo and Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer of public health for Seattle and King County, Washington, and also an IDSA board member. Dr. Duchin said many people mistakenly regarded the new guidance as a message that the pandemic is over.
Among their practical tips on how to interpret the guidance:
To mask or not?
To make the decision, people need to think about not only the numbers of vaccinated versus unvaccinated individuals in their community but the local rates of disease, the experts said. And they need to know that the CDC guidance doesn’t apply if regulations by federal or state authorities or businesses and workplace are in conflict.
Deciding on mask use sometimes depends on where you are going. What about going into grocery stores or large bin stores without a mask? “If you are fully vaccinated and have no other conditions that compromise your immune system, and the rates of COVID are relatively low where you live, and the vaccination rates are high, I would be 100% fine” without a mask, Dr. Marrazzo said. But it’s important to think of all these factors in calculating your risk.
“I’m still wearing a mask when I go anywhere in public,” she said, citing vaccination rates that have not yet reached 50% in her area.
If that rate reached 80%, the typical percentage talked about for herd immunity, and new cases were low, Dr. Marrazzo said she might shed the mask.
The CDC also continues to recommend masks on mass transit for all.
One population that also must be considered, and who must evaluate their risk, even if vaccinated, are the immunocompromised, Dr. Marrazzo said. While people think of the immunocompromised as those with HIV or organ transplants, the numbers are actually much larger.
“A study a couple of years ago indicated up to 3% of Americans may actually have been told by their physician they have some of level of being immunocompromised,” she said. Among the examples are those who are on dialysis, on chemotherapy, or those taking any of the medications that modify the immune system.
“Millions of people fit this bill, and we have [very] little data on whether the vaccine works in them. We think it does,” Dr. Marrazzo said.
Still, she said, it’s a reason for these people to be cautious. For some other vaccines, the dose is modified for those who are immunocompromised. What’s not known yet is whether additional doses of the COVID vaccines might boost protection for those who are immunocompromised.
Many people, even after vaccination, may choose to keep wearing a mask especially in indoor, crowded settings, Dr. Duchin said. “We need to expect, accept, and respect continued mask wearing by anyone at any time.”
In most outdoor settings, he said, “I think masks are probably not necessary, vaccinated or not, regardless of age.” One exception: close face-to-face contact, such as in certain sports.
How to protect toddlers and infants
With masks not practical or recommended for infants and toddlers under 2 years old, Dr. Marrazzo said adults should remember that ‘’those very little kids don’t do poorly at all [even if infected], although there is not a ton of data.”
Adults should still treat young children as vulnerable, especially newborns. Adults not yet vaccinated should wear a mask when around them, she said.
J & J vaccine recipients
With less ‘’real world” data on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, should those who got it think of themselves in a different risk group than those who got Moderna or Pfizer and adjust their behavior accordingly?
“The J&J vaccine, based on everything we know, does provide a great deal of protection,” Dr. Marrazzo said. ‘’We don’t know as much about prevention of transmission in the asymptomatic cases in the J&J.”
Most of that data, she said, is from the mRNA vaccines Pfizer and Moderna. “I think it’s an important area to study and learn about.” But all three vaccines, overall, provide a high level of protection, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest guidance on what fully vaccinated people can do safely – including not socially distancing and not wearing a mask indoors or outdoors unless other regulations require it – has been widely misinterpreted and caused confusion, two infectious disease experts said at a briefing on May 20 hosted by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The CDC did not ‘’lift” the mask mandate, but rather supplied guidance for those who are fully vaccinated. However, many questions and gray areas remain, and the experts addressed those. ‘’The CDC guidance is really directed at people who are fully vaccinated and who we know are likely to have a really solid response to the vaccine,” said Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of infectious diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and an IDSA board member.
That message was largely lost, said Dr. Marrazzo and Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer of public health for Seattle and King County, Washington, and also an IDSA board member. Dr. Duchin said many people mistakenly regarded the new guidance as a message that the pandemic is over.
Among their practical tips on how to interpret the guidance:
To mask or not?
To make the decision, people need to think about not only the numbers of vaccinated versus unvaccinated individuals in their community but the local rates of disease, the experts said. And they need to know that the CDC guidance doesn’t apply if regulations by federal or state authorities or businesses and workplace are in conflict.
Deciding on mask use sometimes depends on where you are going. What about going into grocery stores or large bin stores without a mask? “If you are fully vaccinated and have no other conditions that compromise your immune system, and the rates of COVID are relatively low where you live, and the vaccination rates are high, I would be 100% fine” without a mask, Dr. Marrazzo said. But it’s important to think of all these factors in calculating your risk.
“I’m still wearing a mask when I go anywhere in public,” she said, citing vaccination rates that have not yet reached 50% in her area.
If that rate reached 80%, the typical percentage talked about for herd immunity, and new cases were low, Dr. Marrazzo said she might shed the mask.
The CDC also continues to recommend masks on mass transit for all.
One population that also must be considered, and who must evaluate their risk, even if vaccinated, are the immunocompromised, Dr. Marrazzo said. While people think of the immunocompromised as those with HIV or organ transplants, the numbers are actually much larger.
“A study a couple of years ago indicated up to 3% of Americans may actually have been told by their physician they have some of level of being immunocompromised,” she said. Among the examples are those who are on dialysis, on chemotherapy, or those taking any of the medications that modify the immune system.
“Millions of people fit this bill, and we have [very] little data on whether the vaccine works in them. We think it does,” Dr. Marrazzo said.
Still, she said, it’s a reason for these people to be cautious. For some other vaccines, the dose is modified for those who are immunocompromised. What’s not known yet is whether additional doses of the COVID vaccines might boost protection for those who are immunocompromised.
Many people, even after vaccination, may choose to keep wearing a mask especially in indoor, crowded settings, Dr. Duchin said. “We need to expect, accept, and respect continued mask wearing by anyone at any time.”
In most outdoor settings, he said, “I think masks are probably not necessary, vaccinated or not, regardless of age.” One exception: close face-to-face contact, such as in certain sports.
How to protect toddlers and infants
With masks not practical or recommended for infants and toddlers under 2 years old, Dr. Marrazzo said adults should remember that ‘’those very little kids don’t do poorly at all [even if infected], although there is not a ton of data.”
Adults should still treat young children as vulnerable, especially newborns. Adults not yet vaccinated should wear a mask when around them, she said.
J & J vaccine recipients
With less ‘’real world” data on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, should those who got it think of themselves in a different risk group than those who got Moderna or Pfizer and adjust their behavior accordingly?
“The J&J vaccine, based on everything we know, does provide a great deal of protection,” Dr. Marrazzo said. ‘’We don’t know as much about prevention of transmission in the asymptomatic cases in the J&J.”
Most of that data, she said, is from the mRNA vaccines Pfizer and Moderna. “I think it’s an important area to study and learn about.” But all three vaccines, overall, provide a high level of protection, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s latest guidance on what fully vaccinated people can do safely – including not socially distancing and not wearing a mask indoors or outdoors unless other regulations require it – has been widely misinterpreted and caused confusion, two infectious disease experts said at a briefing on May 20 hosted by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
The CDC did not ‘’lift” the mask mandate, but rather supplied guidance for those who are fully vaccinated. However, many questions and gray areas remain, and the experts addressed those. ‘’The CDC guidance is really directed at people who are fully vaccinated and who we know are likely to have a really solid response to the vaccine,” said Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of infectious diseases at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and an IDSA board member.
That message was largely lost, said Dr. Marrazzo and Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer of public health for Seattle and King County, Washington, and also an IDSA board member. Dr. Duchin said many people mistakenly regarded the new guidance as a message that the pandemic is over.
Among their practical tips on how to interpret the guidance:
To mask or not?
To make the decision, people need to think about not only the numbers of vaccinated versus unvaccinated individuals in their community but the local rates of disease, the experts said. And they need to know that the CDC guidance doesn’t apply if regulations by federal or state authorities or businesses and workplace are in conflict.
Deciding on mask use sometimes depends on where you are going. What about going into grocery stores or large bin stores without a mask? “If you are fully vaccinated and have no other conditions that compromise your immune system, and the rates of COVID are relatively low where you live, and the vaccination rates are high, I would be 100% fine” without a mask, Dr. Marrazzo said. But it’s important to think of all these factors in calculating your risk.
“I’m still wearing a mask when I go anywhere in public,” she said, citing vaccination rates that have not yet reached 50% in her area.
If that rate reached 80%, the typical percentage talked about for herd immunity, and new cases were low, Dr. Marrazzo said she might shed the mask.
The CDC also continues to recommend masks on mass transit for all.
One population that also must be considered, and who must evaluate their risk, even if vaccinated, are the immunocompromised, Dr. Marrazzo said. While people think of the immunocompromised as those with HIV or organ transplants, the numbers are actually much larger.
“A study a couple of years ago indicated up to 3% of Americans may actually have been told by their physician they have some of level of being immunocompromised,” she said. Among the examples are those who are on dialysis, on chemotherapy, or those taking any of the medications that modify the immune system.
“Millions of people fit this bill, and we have [very] little data on whether the vaccine works in them. We think it does,” Dr. Marrazzo said.
Still, she said, it’s a reason for these people to be cautious. For some other vaccines, the dose is modified for those who are immunocompromised. What’s not known yet is whether additional doses of the COVID vaccines might boost protection for those who are immunocompromised.
Many people, even after vaccination, may choose to keep wearing a mask especially in indoor, crowded settings, Dr. Duchin said. “We need to expect, accept, and respect continued mask wearing by anyone at any time.”
In most outdoor settings, he said, “I think masks are probably not necessary, vaccinated or not, regardless of age.” One exception: close face-to-face contact, such as in certain sports.
How to protect toddlers and infants
With masks not practical or recommended for infants and toddlers under 2 years old, Dr. Marrazzo said adults should remember that ‘’those very little kids don’t do poorly at all [even if infected], although there is not a ton of data.”
Adults should still treat young children as vulnerable, especially newborns. Adults not yet vaccinated should wear a mask when around them, she said.
J & J vaccine recipients
With less ‘’real world” data on the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, should those who got it think of themselves in a different risk group than those who got Moderna or Pfizer and adjust their behavior accordingly?
“The J&J vaccine, based on everything we know, does provide a great deal of protection,” Dr. Marrazzo said. ‘’We don’t know as much about prevention of transmission in the asymptomatic cases in the J&J.”
Most of that data, she said, is from the mRNA vaccines Pfizer and Moderna. “I think it’s an important area to study and learn about.” But all three vaccines, overall, provide a high level of protection, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Care of post–acute COVID-19 patients requires multidisciplinary collaboration
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, a population of patients has arisen with a range of symptoms and complications after surviving the acute phase of illness, according to Mezgebe Berhe, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas.
Different terms have been used to describe this condition, including post COVID, long COVID, chronic COVID, and long-haulers, Dr. Berhe said in a presentation at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. However, the current medical consensus for a definition is post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.
Acute COVID-19 generally lasts for about 4 weeks after the onset of symptoms, and post–acute COVID-19 is generally defined as “persistent symptoms and/or delayed or long-term complications beyond 4 weeks from the onset of symptoms,” he said. The postacute period may be broken into a subacute phase with symptoms and abnormalities present from 4-12 weeks beyond the acute phase, and then a chronic or post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, with symptoms and abnormalities present beyond 12 weeks after the onset of acute COVID-19.
Patients in the subacute or post–COVID-19 phase of illness are polymerase chain reaction negative and may have multiorgan symptomatology, said Dr. Berhe. Physical symptoms include fatigue, decline in quality of life, joint pain, and muscle weakness; reported mental symptoms include anxiety and depression; sleep disturbance; PTSD; cognitive disturbance (described by patients as “brain fog”); and headaches.
Pulmonary symptoms in post–acute COVID-19 patients include dyspnea, cough, and persistent oxygen requirements; patients also have reported palpitations and chest pain. Thromboembolism, chronic kidney disease, and hair loss also have been reported in COVID-19 patients in the postacute period.
What studies show
Early reports on postacute consequences of COVID-19 have been reported in published studies from the United States, Europe, and China, and the current treatment recommendations are based on findings from these studies, Dr. Berhe said.
In an observational cohort study from 38 hospitals in Michigan, researchers assessed 60-day outcomes for 1,250 COVID-19 patients who were discharged alive from the hospital. The researchers used medical record abstraction and telephone surveys to assess long-term symptoms. Overall, 6.7% of the patients died and 15.1% required hospital readmission. A total of 488 patients completed the telephone survey. Of these, 32.6% reported persistent symptoms, 18.9% reported new or worsening symptoms, 22.9% reported dyspnea while walking up stairs, 15.4% reported a cough, and 13.1% reported a persistent loss of taste or smell.
Data from multiple countries in Europe have shown similar prevalence of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, but Dr. Berhe highlighted an Italian study in which 87% of 143 patients discharged from hospitals after acute COVID-19 reported at least one symptom at 60 day. “A decline in quality of life, as measured by the EuroQol visual analog scale, was reported by 44.1% of patients” in the Italian study, Dr. Berhe noted.
In a prospective cohort study conducted in Wuhan, China, researchers conducted a comprehensive in-person evaluation of symptoms in 1,733 COVID-19 patients at 6 months from symptom onset, and found that 76% reported at least one symptom, said Dr. Berhe. “Similar to other studies, muscle weakness and fatigue were the most common symptoms, followed by sleep problems and anxiety/depression.
Dr. Berhe also cited a literature review published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that addressed COVID-19 in children; in one study of postacute COVID-19, approximately 12% of children had 5 weeks’ prevalence of persistent symptoms, compared with 22% of adults. This finding should remind clinicians that “Children can have devastating persistent symptoms following acute COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Berhe said.
In the post–acute COVID clinic
“Multidisciplinary collaboration is essential to provide integrated outpatient care to survivors of acute COVID-19,” Dr. Berhe said. Such collaboration includes pulmonary and cardiovascular symptom assessment through virtual or in-person follow-up at 4-6 weeks and at 12 weeks after hospital discharge. For those with dyspnea and persistent oxygen requirements at 12 weeks, consider the 6-minute walk test, pulmonary function test, chest x-ray, pulmonary embolism work-up, echocardiogram, and high-resolution CT of the chest as indicated.
With regard to neuropsychiatry, patients should be screened for anxiety, depression, PTSD, sleep disturbance, and cognitive impairment, said Dr. Berhe.
For hematology, “consider extended thromboprophylaxis for high-risk survivors based on shared decision-making,” he said. The incidence of thrombotic events post COVID is less than 5% so you have to be very selective and they should be in the highest-risk category.
COVID-19 patients with acute kidney infections should have a follow-up with a nephrologist soon after hospital discharge, he added.
From a primary care standpoint, early rehabilitation and patient education are important for managing symptoms; also consider recommending patient enrollment in research studies, Dr. Berhe said.
Dr. Berhe has been involved in multiple clinical trials of treating acute COVID-19 patients, but had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, a population of patients has arisen with a range of symptoms and complications after surviving the acute phase of illness, according to Mezgebe Berhe, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas.
Different terms have been used to describe this condition, including post COVID, long COVID, chronic COVID, and long-haulers, Dr. Berhe said in a presentation at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. However, the current medical consensus for a definition is post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.
Acute COVID-19 generally lasts for about 4 weeks after the onset of symptoms, and post–acute COVID-19 is generally defined as “persistent symptoms and/or delayed or long-term complications beyond 4 weeks from the onset of symptoms,” he said. The postacute period may be broken into a subacute phase with symptoms and abnormalities present from 4-12 weeks beyond the acute phase, and then a chronic or post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, with symptoms and abnormalities present beyond 12 weeks after the onset of acute COVID-19.
Patients in the subacute or post–COVID-19 phase of illness are polymerase chain reaction negative and may have multiorgan symptomatology, said Dr. Berhe. Physical symptoms include fatigue, decline in quality of life, joint pain, and muscle weakness; reported mental symptoms include anxiety and depression; sleep disturbance; PTSD; cognitive disturbance (described by patients as “brain fog”); and headaches.
Pulmonary symptoms in post–acute COVID-19 patients include dyspnea, cough, and persistent oxygen requirements; patients also have reported palpitations and chest pain. Thromboembolism, chronic kidney disease, and hair loss also have been reported in COVID-19 patients in the postacute period.
What studies show
Early reports on postacute consequences of COVID-19 have been reported in published studies from the United States, Europe, and China, and the current treatment recommendations are based on findings from these studies, Dr. Berhe said.
In an observational cohort study from 38 hospitals in Michigan, researchers assessed 60-day outcomes for 1,250 COVID-19 patients who were discharged alive from the hospital. The researchers used medical record abstraction and telephone surveys to assess long-term symptoms. Overall, 6.7% of the patients died and 15.1% required hospital readmission. A total of 488 patients completed the telephone survey. Of these, 32.6% reported persistent symptoms, 18.9% reported new or worsening symptoms, 22.9% reported dyspnea while walking up stairs, 15.4% reported a cough, and 13.1% reported a persistent loss of taste or smell.
Data from multiple countries in Europe have shown similar prevalence of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, but Dr. Berhe highlighted an Italian study in which 87% of 143 patients discharged from hospitals after acute COVID-19 reported at least one symptom at 60 day. “A decline in quality of life, as measured by the EuroQol visual analog scale, was reported by 44.1% of patients” in the Italian study, Dr. Berhe noted.
In a prospective cohort study conducted in Wuhan, China, researchers conducted a comprehensive in-person evaluation of symptoms in 1,733 COVID-19 patients at 6 months from symptom onset, and found that 76% reported at least one symptom, said Dr. Berhe. “Similar to other studies, muscle weakness and fatigue were the most common symptoms, followed by sleep problems and anxiety/depression.
Dr. Berhe also cited a literature review published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that addressed COVID-19 in children; in one study of postacute COVID-19, approximately 12% of children had 5 weeks’ prevalence of persistent symptoms, compared with 22% of adults. This finding should remind clinicians that “Children can have devastating persistent symptoms following acute COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Berhe said.
In the post–acute COVID clinic
“Multidisciplinary collaboration is essential to provide integrated outpatient care to survivors of acute COVID-19,” Dr. Berhe said. Such collaboration includes pulmonary and cardiovascular symptom assessment through virtual or in-person follow-up at 4-6 weeks and at 12 weeks after hospital discharge. For those with dyspnea and persistent oxygen requirements at 12 weeks, consider the 6-minute walk test, pulmonary function test, chest x-ray, pulmonary embolism work-up, echocardiogram, and high-resolution CT of the chest as indicated.
With regard to neuropsychiatry, patients should be screened for anxiety, depression, PTSD, sleep disturbance, and cognitive impairment, said Dr. Berhe.
For hematology, “consider extended thromboprophylaxis for high-risk survivors based on shared decision-making,” he said. The incidence of thrombotic events post COVID is less than 5% so you have to be very selective and they should be in the highest-risk category.
COVID-19 patients with acute kidney infections should have a follow-up with a nephrologist soon after hospital discharge, he added.
From a primary care standpoint, early rehabilitation and patient education are important for managing symptoms; also consider recommending patient enrollment in research studies, Dr. Berhe said.
Dr. Berhe has been involved in multiple clinical trials of treating acute COVID-19 patients, but had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, a population of patients has arisen with a range of symptoms and complications after surviving the acute phase of illness, according to Mezgebe Berhe, MD, of Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas.
Different terms have been used to describe this condition, including post COVID, long COVID, chronic COVID, and long-haulers, Dr. Berhe said in a presentation at SHM Converge, the annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. However, the current medical consensus for a definition is post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.
Acute COVID-19 generally lasts for about 4 weeks after the onset of symptoms, and post–acute COVID-19 is generally defined as “persistent symptoms and/or delayed or long-term complications beyond 4 weeks from the onset of symptoms,” he said. The postacute period may be broken into a subacute phase with symptoms and abnormalities present from 4-12 weeks beyond the acute phase, and then a chronic or post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, with symptoms and abnormalities present beyond 12 weeks after the onset of acute COVID-19.
Patients in the subacute or post–COVID-19 phase of illness are polymerase chain reaction negative and may have multiorgan symptomatology, said Dr. Berhe. Physical symptoms include fatigue, decline in quality of life, joint pain, and muscle weakness; reported mental symptoms include anxiety and depression; sleep disturbance; PTSD; cognitive disturbance (described by patients as “brain fog”); and headaches.
Pulmonary symptoms in post–acute COVID-19 patients include dyspnea, cough, and persistent oxygen requirements; patients also have reported palpitations and chest pain. Thromboembolism, chronic kidney disease, and hair loss also have been reported in COVID-19 patients in the postacute period.
What studies show
Early reports on postacute consequences of COVID-19 have been reported in published studies from the United States, Europe, and China, and the current treatment recommendations are based on findings from these studies, Dr. Berhe said.
In an observational cohort study from 38 hospitals in Michigan, researchers assessed 60-day outcomes for 1,250 COVID-19 patients who were discharged alive from the hospital. The researchers used medical record abstraction and telephone surveys to assess long-term symptoms. Overall, 6.7% of the patients died and 15.1% required hospital readmission. A total of 488 patients completed the telephone survey. Of these, 32.6% reported persistent symptoms, 18.9% reported new or worsening symptoms, 22.9% reported dyspnea while walking up stairs, 15.4% reported a cough, and 13.1% reported a persistent loss of taste or smell.
Data from multiple countries in Europe have shown similar prevalence of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome, but Dr. Berhe highlighted an Italian study in which 87% of 143 patients discharged from hospitals after acute COVID-19 reported at least one symptom at 60 day. “A decline in quality of life, as measured by the EuroQol visual analog scale, was reported by 44.1% of patients” in the Italian study, Dr. Berhe noted.
In a prospective cohort study conducted in Wuhan, China, researchers conducted a comprehensive in-person evaluation of symptoms in 1,733 COVID-19 patients at 6 months from symptom onset, and found that 76% reported at least one symptom, said Dr. Berhe. “Similar to other studies, muscle weakness and fatigue were the most common symptoms, followed by sleep problems and anxiety/depression.
Dr. Berhe also cited a literature review published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that addressed COVID-19 in children; in one study of postacute COVID-19, approximately 12% of children had 5 weeks’ prevalence of persistent symptoms, compared with 22% of adults. This finding should remind clinicians that “Children can have devastating persistent symptoms following acute COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Berhe said.
In the post–acute COVID clinic
“Multidisciplinary collaboration is essential to provide integrated outpatient care to survivors of acute COVID-19,” Dr. Berhe said. Such collaboration includes pulmonary and cardiovascular symptom assessment through virtual or in-person follow-up at 4-6 weeks and at 12 weeks after hospital discharge. For those with dyspnea and persistent oxygen requirements at 12 weeks, consider the 6-minute walk test, pulmonary function test, chest x-ray, pulmonary embolism work-up, echocardiogram, and high-resolution CT of the chest as indicated.
With regard to neuropsychiatry, patients should be screened for anxiety, depression, PTSD, sleep disturbance, and cognitive impairment, said Dr. Berhe.
For hematology, “consider extended thromboprophylaxis for high-risk survivors based on shared decision-making,” he said. The incidence of thrombotic events post COVID is less than 5% so you have to be very selective and they should be in the highest-risk category.
COVID-19 patients with acute kidney infections should have a follow-up with a nephrologist soon after hospital discharge, he added.
From a primary care standpoint, early rehabilitation and patient education are important for managing symptoms; also consider recommending patient enrollment in research studies, Dr. Berhe said.
Dr. Berhe has been involved in multiple clinical trials of treating acute COVID-19 patients, but had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SHM CONVERGE 2021
Hospital outcomes for children with MIS-C unaffected by initial presentation site
Length of hospital stay and the need for intensive care for pediatric COVID-19 patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children was not significantly different for those who presented first as outpatients or emergency patients, based on data from 34 children.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) can be challenging to diagnose, as the key characteristics of fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and involvement of at least two organ systems often overlap with other illnesses, said Erin B. Treemarcki, DO, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“Primary care and urgent care providers are often the first point of health care for children with symptoms of MIS-C,” the researchers wrote. In a study (Poster 142) presented at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies, held virtually, the researchers conducted a retrospective review of 34 patients younger than 21 years who were hospitalized with MIS-C at a single center between April 2020 and December 2020. The average age of the patients was 7.9 years, 68% were male, 82% were White, and 53% first presented to an outpatient clinic.
Sixteen patients presented to an emergency department and 18 presented to an ambulatory setting. The length of hospitalization ranged from 3 to 16 days with a median of 6 days, and the PICU stay ranged from 1 to 10 days with a median of 2 days.
Overall, the length of hospital stay and rate of PICU admission were not significantly different between the emergency presentation and outpatient presentation groups. Twenty-four patients entered the PICU, 13 at admission and 11 as transfers. However, the median number of days of symptoms prior to admission was significantly higher for outpatient cases (6 days vs. 4 days, P = .03).
One patient was readmitted to the hospital within 30 days for aseptic meningitis, and none of the patients died.
Initial symptoms were not significantly different for outpatient vs. emergency department patients. The most common initial manifestations of MIS-C included fever (100%), gastrointestinal symptoms (85%), and mucocutaneous symptoms (88%). Mucocutaneous symptoms included rash, oral mucosal changes, conjunctivitis, and hand/foot edema. In addition, 65% of the patients met at least 3 criteria for Kawasaki disease, the researchers noted.
The most common elevated labs at presentation regardless of setting were D-dimer (100%), C-reactive protein (97%), ferritin (97%), procalcitonin (97%), and serum IL-6 (94%).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and focus on data from a single center. However, the results emphasize the varied presentations of MIS-C and the importance that both primary care and urgent care providers know the signs, as they are often the first point of health care for children with MIS-C, the researchers noted.
Keep looking for factors that put children at risk
“MIS-C is probably the most serious complication of COVID in children, so we as pediatricians on the front line need to know what it looks like,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
Dr. Kinsella said she was surprised by the study finding that children’s length of hospital stay was not affected by presentation setting.
“I would have thought the kids presenting in an outpatient setting would take longer to diagnose, and therefore have a longer hospital stay,” she noted. Instead, the take-home message is that whether the MIS-C diagnosis occurs in the outpatient or emergency setting, the length of stay is the same, and that the most common symptoms are fever, gastrointestinal, mucocutaneous, and cardiac symptoms regardless of initial presentation setting, she said.
More research is needed, and future studies should examine “any potential underlying factors making these particular kids susceptible to MIS-C,” Dr. Kinsella added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Length of hospital stay and the need for intensive care for pediatric COVID-19 patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children was not significantly different for those who presented first as outpatients or emergency patients, based on data from 34 children.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) can be challenging to diagnose, as the key characteristics of fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and involvement of at least two organ systems often overlap with other illnesses, said Erin B. Treemarcki, DO, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“Primary care and urgent care providers are often the first point of health care for children with symptoms of MIS-C,” the researchers wrote. In a study (Poster 142) presented at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies, held virtually, the researchers conducted a retrospective review of 34 patients younger than 21 years who were hospitalized with MIS-C at a single center between April 2020 and December 2020. The average age of the patients was 7.9 years, 68% were male, 82% were White, and 53% first presented to an outpatient clinic.
Sixteen patients presented to an emergency department and 18 presented to an ambulatory setting. The length of hospitalization ranged from 3 to 16 days with a median of 6 days, and the PICU stay ranged from 1 to 10 days with a median of 2 days.
Overall, the length of hospital stay and rate of PICU admission were not significantly different between the emergency presentation and outpatient presentation groups. Twenty-four patients entered the PICU, 13 at admission and 11 as transfers. However, the median number of days of symptoms prior to admission was significantly higher for outpatient cases (6 days vs. 4 days, P = .03).
One patient was readmitted to the hospital within 30 days for aseptic meningitis, and none of the patients died.
Initial symptoms were not significantly different for outpatient vs. emergency department patients. The most common initial manifestations of MIS-C included fever (100%), gastrointestinal symptoms (85%), and mucocutaneous symptoms (88%). Mucocutaneous symptoms included rash, oral mucosal changes, conjunctivitis, and hand/foot edema. In addition, 65% of the patients met at least 3 criteria for Kawasaki disease, the researchers noted.
The most common elevated labs at presentation regardless of setting were D-dimer (100%), C-reactive protein (97%), ferritin (97%), procalcitonin (97%), and serum IL-6 (94%).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and focus on data from a single center. However, the results emphasize the varied presentations of MIS-C and the importance that both primary care and urgent care providers know the signs, as they are often the first point of health care for children with MIS-C, the researchers noted.
Keep looking for factors that put children at risk
“MIS-C is probably the most serious complication of COVID in children, so we as pediatricians on the front line need to know what it looks like,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
Dr. Kinsella said she was surprised by the study finding that children’s length of hospital stay was not affected by presentation setting.
“I would have thought the kids presenting in an outpatient setting would take longer to diagnose, and therefore have a longer hospital stay,” she noted. Instead, the take-home message is that whether the MIS-C diagnosis occurs in the outpatient or emergency setting, the length of stay is the same, and that the most common symptoms are fever, gastrointestinal, mucocutaneous, and cardiac symptoms regardless of initial presentation setting, she said.
More research is needed, and future studies should examine “any potential underlying factors making these particular kids susceptible to MIS-C,” Dr. Kinsella added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Length of hospital stay and the need for intensive care for pediatric COVID-19 patients with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children was not significantly different for those who presented first as outpatients or emergency patients, based on data from 34 children.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) can be challenging to diagnose, as the key characteristics of fever, elevated inflammatory markers, and involvement of at least two organ systems often overlap with other illnesses, said Erin B. Treemarcki, DO, of the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
“Primary care and urgent care providers are often the first point of health care for children with symptoms of MIS-C,” the researchers wrote. In a study (Poster 142) presented at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies, held virtually, the researchers conducted a retrospective review of 34 patients younger than 21 years who were hospitalized with MIS-C at a single center between April 2020 and December 2020. The average age of the patients was 7.9 years, 68% were male, 82% were White, and 53% first presented to an outpatient clinic.
Sixteen patients presented to an emergency department and 18 presented to an ambulatory setting. The length of hospitalization ranged from 3 to 16 days with a median of 6 days, and the PICU stay ranged from 1 to 10 days with a median of 2 days.
Overall, the length of hospital stay and rate of PICU admission were not significantly different between the emergency presentation and outpatient presentation groups. Twenty-four patients entered the PICU, 13 at admission and 11 as transfers. However, the median number of days of symptoms prior to admission was significantly higher for outpatient cases (6 days vs. 4 days, P = .03).
One patient was readmitted to the hospital within 30 days for aseptic meningitis, and none of the patients died.
Initial symptoms were not significantly different for outpatient vs. emergency department patients. The most common initial manifestations of MIS-C included fever (100%), gastrointestinal symptoms (85%), and mucocutaneous symptoms (88%). Mucocutaneous symptoms included rash, oral mucosal changes, conjunctivitis, and hand/foot edema. In addition, 65% of the patients met at least 3 criteria for Kawasaki disease, the researchers noted.
The most common elevated labs at presentation regardless of setting were D-dimer (100%), C-reactive protein (97%), ferritin (97%), procalcitonin (97%), and serum IL-6 (94%).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and focus on data from a single center. However, the results emphasize the varied presentations of MIS-C and the importance that both primary care and urgent care providers know the signs, as they are often the first point of health care for children with MIS-C, the researchers noted.
Keep looking for factors that put children at risk
“MIS-C is probably the most serious complication of COVID in children, so we as pediatricians on the front line need to know what it looks like,” Karalyn Kinsella, MD, a pediatrician in Cheshire, Conn., said in an interview.
Dr. Kinsella said she was surprised by the study finding that children’s length of hospital stay was not affected by presentation setting.
“I would have thought the kids presenting in an outpatient setting would take longer to diagnose, and therefore have a longer hospital stay,” she noted. Instead, the take-home message is that whether the MIS-C diagnosis occurs in the outpatient or emergency setting, the length of stay is the same, and that the most common symptoms are fever, gastrointestinal, mucocutaneous, and cardiac symptoms regardless of initial presentation setting, she said.
More research is needed, and future studies should examine “any potential underlying factors making these particular kids susceptible to MIS-C,” Dr. Kinsella added.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Kinsella had no financial conflicts, but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
FROM PAS 2021
Sex differences in COPD symptoms predict cardiac comorbidity
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sex-specific differences in the severity of symptoms and prevalence of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may point to different criteria for diagnosing cardiac comorbidities in women and men, a retrospective analysis suggests.
Among 2,046 patients in the German COSYCONET (COPD and Systemic Consequences–Comorbidities Net) cohort, most functional parameters and comorbidities and several items on the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) differed significantly between men and women.
In addition, there were sex-specific differences in the association between symptoms and cardiac disease, Franziska C. Trudzinski, MD, from the University of Heidelberg (Germany), and colleagues reported.
(Note: Although the authors used the term “gender” to distinguish male from female, this news organization has used the term “sex” in this article to refer to biological attributes of individual patients rather than personal identity.)
“[Sex]-specific differences in COPD comprised not only differences in the level of symptoms, comorbidities, and functional alterations but also differences in their mutual relationships. This was reflected in different sets of predictors for cardiac disease,” they wrote in a thematic poster presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual international conference.
GOLD standard
The investigators conducted an analysis of data on 795 women and 1,251 men with GOLD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease) class 1-3 disease from the COSYCONET COPD cohort.
They looked at the patients’ clinical history, comorbidities, lung function, CAT scores, and modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea score.
The authors used multivariate regression analysis to model potential sex-related differences in the relationship between symptoms in general and CAT items in particular, and the pattern of comorbidities and functional alterations.
They also performed logistic regression analyses to identify predictors for cardiac disease, defined as myocardial infarction, heart failure, or coronary artery disease. The analyses were controlled for age, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, mMRC, CAT items, and z scores of forced expiratory volume in 1 second/forced vital capacity ratio.
and for CAT items of cough (item 1), phlegm (item 2), and energy (item 8; P < .05 for all comparisons).
In logistic regression analysis, predictors for cardiac disease in men were energy (CAT item 8), mMRC score, smoking status, BMI, age, and spirometric lung function.
In women, however, only age was significantly predictive for cardiac disease.
“Our findings give hints how diagnostic information might be used differently in men and women,” Dr. Trudzinski and colleagues wrote.
Reassuring data
David Mannino, MD, medical director of the COPD Foundation, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview that sex differences in COPD presentation and severity are common.
“In general, men and women report symptoms differently. For example, women don’t report a whole lot of chronic bronchitis and phlegm, although they may have it,” he said, “whereas men may report less dyspnea. It varies, but in general we know that men and women, even with the same type of disease, report symptoms differently.”
Comorbidities also differ between the sexes, he noted. Women more frequently have osteoporosis, and men more frequently have heart disease, as borne out in the study. The prevalence of heart disease among patients in the study was approximately 2.5 times higher in men than women.
“It’s reassuring, because what we’re seeing is similar to what we’ve seen in other [studies] with regards to comorbidities,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Philipps University Marburg Medical Center, Germany. The authors and Dr. Mannino have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of the article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Worse outcomes for patients with COPD and COVID-19
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study of COVID-19 outcomes across the United States bolsters reports from China and Europe that indicate that patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and SARS-CoV-2 infection have worse outcomes than those of patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD.
Investigators at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Texas, combed through electronic health records from four geographic regions of the United States and identified a cohort of 6,056 patients with COPD among 150,775 patients whose records indicate either a diagnostic code or a positive laboratory test result for COVID-19.
Their findings indicate that patients with both COPD and COVID-19 “have worse outcomes compared to non-COPD COVID-19 patients, including 14-day hospitalization, length of stay, ICU admission, 30-day mortality, and use of mechanical ventilation,” Daniel Puebla Neira, MD, and colleagues from the University of Texas Medical Branch reported in a thematic poster presented during the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2021 virtual international conference.
A critical care specialist who was not involved in the study said that the results are concerning but not surprising.
“If you already have a lung disease and you develop an additional lung disease on top of that, you don’t have as much reserve and you’re not going to tolerate the acute COVID infection,” said ATS expert Marc Moss, MD, Roger S. Mitchell Professor of Medicine in the division of pulmonary sciences and critical care medicine at the University of Colorado, Aurora.
The evidence shows that “patients with COPD should be even more cautious, because if they get sick and develop, they could do worse,” he said in an interview.
Retrospective analysis
Dr. Neira and colleagues assessed the characteristics and outcomes of patients with COPD who were treated for COVID-19 in the United States from March through August 2020.
Baseline demographics of the patients with and those without COPD were similar except that the mean age was higher among patients with COPD (68.62 vs. 47.08 years).
In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients with COPD had comorbidities compared with those without COPD. Comorbidities included diabetes, hypertension, asthma, chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease, stroke, heart failure, cancer, coronary artery disease, and liver disease (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
Among patients with COPD, percentages were higher with respect to the following parameters: 14-day hospitalization for any cause (28.7% vs. 10.4%), COVID-19-related 14-day hospitalization (28.1% vs. 9.9%), ICU use (26.3% vs. 17.9%), mechanical ventilation use (26.3% vs. 16.1%), and 30-day mortality (13.6% vs. 7.2%; P < .0001 for all comparisons).
‘Mechanisms unclear’
“It is unclear what mechanisms drive the association between COPD and mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the investigators wrote. “Several biological factors have been proposed, including chronic lung inflammation, oxidative stress, protease-antiprotease imbalance, and increased airway mediators.”
They recommend use of multivariable logistic regression to tease out the effects of covariates among patients with COPD and COVID-19 and call for research into long-term outcomes for these patients, “as survivors of critical illness are increasingly recognized to have cognitive, psychological, and physical consequences.”
Dr. Moss said that in general, the management of patients with COPD and COVID-19 is similar to that for patients with COVID-19 who do not have COPD, although there may be “subtle” differences, such as ventilator settings for patients with COPD.
No source of funding for the study has been disclosed. The investigators and Dr. Moss have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No survival dip with neoadjuvant letrozole-palbociclib in NeoPAL study
Three-year survival rates were similarly high among postmenopausal women with high-risk early luminal breast cancer who were treated with either the neoadjuvant combination of letrozole and palbociclib (Ibrance) or standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the phase 2 NeoPAL study.
Progression-free survival (PFS) was a respective 86.7% and 87.2%, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.01 (P = .98) comparing the endocrine therapy and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor combination versus FEC/taxane chemotherapy.
There were also no differences between the two treatment arms in terms of invasive disease-free survival (iDFS, HR = 0.83, P = .71) or breast cancer–specific survival (BCSS), although the latter was an exploratory endpoint alongside overall survival (OS).
“The lack of difference is impressive,” said Hope S. Rugo, MD, FASCO, who commented independently on the study’s findings after their presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology: Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
“Overall survival in patients who received chemotherapy appears to be better, but the very small numbers here make interpretation of this difference impossible,” observed Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine at the University of California San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Unfortunately, this study is underpowered for definitive conclusions,” acknowledged study investigator Suzette Delaloge, MD, associate professor of medical oncology at Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
However, “it shows that the nonchemotherapy, preoperative letrozole/palbociclib approach deserves further exploration and could be an option for a chemotherapy-free regimen in some specific cases.”
Primary data already reported
The NeoPAL study was an open-label, randomized study conducted in 27 centers throughout France that compared the preoperative use of letrozole plus palbociclib to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 106 postmenopausal patients with either luminal A or B node-positive disease.
Patients were considered for inclusion in the trial if they had been newly diagnosed with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-negative stage I-III breast cancer and were not candidates for breast conservation. Genetic testing was used to confirm that only those with luminal B, or luminal A and who were node positive were recruited.
Neoadjuvant treatment consisted of either letrozole (2.5 mg/day) and palbociclib (125 mg daily for 3 weeks out of 4 weeks) for 19 weeks or three 21-day cycles of 5-fluorouracil (500 mg/m2), epirubicin (100 mg/m2), and cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2), followed by three 21-day cycles of docetaxel (100 mg/m2).
The primary endpoint was the pathological complete response (pCR), defined as a residual cancer burden (RCB) of 0 to 1. Results, which have already been reported, showed equivalent, but perhaps disappointingly low, pathological responses in both the letrozole/palbociclib and chemotherapy arms (3.8% and 5.9%, respectively).
There were, however, identical clinical responses (at around 75%) and “encouraging biomarker responses in the Prosigna-defined high risk luminal breast cancer population,” Dr. Delaloge said.
The NeoPAL findings were on par with those of the CORALLEEN study, Dr. Delaloge suggested. That trial, as Dr. Rugo has also pointed out, was conducted in 106 patients with luminal B early breast cancer and used a combination of letrozole and the CDK 4/6 inhibitor ribociclib (Kisquali).
Future studies needed
NeoPAL “is a small study with relatively short follow-up even for hormone receptor-positive, high-risk disease,” Dr. Rugo observed. However, she qualified “this short follow-up can be very meaningful in high-risk disease.” as shown by other CDK 4/6 inhibitor trials.
Dr. Rugo also noted: “Short-term biologic endpoints are clearly more informative following and during neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than pCR and this trial, as well as the data from previous studies, indicates that this is the case.”
Further, Dr. Rugo said: “Antiproliferative response is enhanced with CDK 4/6 inhibitors, but this doesn’t seem to translate into a difference in pCR. The lack of impact on longer term, outcome to date, provides support for ongoing trials.”
Two such trials are already underway. The 200-patient CARABELA trial started recruitment in March last year and is comparing endocrine therapy with letrozole plus the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) to standard chemotherapy in patients with hormone receptor–positive, high-risk Ki67 disease.
Then there is the ADAPTcycle trial, a large open-label, phase 3 trial that is randomizing patients based on Ki67 and recurrence score after a short preoperative induction with endocrine therapy to postoperative chemotherapy or to 2 years of endocrine therapy plus ribociclib, with both arms receiving a standard course of 5 years of endocrine therapy.
“These two studies have provided interesting information that will help us design studies in the future,” said Dr. Rugo.
Not only that, but they will also help “investigate the subgroups of patients that benefit the most from CDK 4/6 inhibitors and better study neoadjuvant endocrine therapy which is an important option for patients that can be evaluated in terms of its efficacy by short term measures of antiproliferative response.”
NeoPAL was sponsored by UNICANCER with funding from Pfizer and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Delaloge disclosed receiving research grants or funding via her institution from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche, Merck, Sanofi, Lilly, Novartis, BMS, Orion, Daiichi, Puma, and Pierre Fabre. Dr. Rugo reported receipt of grants via her institution to perform clinical trials from Pfizer and multiple other companies. She disclosed receiving honoraria from PUMA, Samsung, and Mylan.
Three-year survival rates were similarly high among postmenopausal women with high-risk early luminal breast cancer who were treated with either the neoadjuvant combination of letrozole and palbociclib (Ibrance) or standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the phase 2 NeoPAL study.
Progression-free survival (PFS) was a respective 86.7% and 87.2%, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.01 (P = .98) comparing the endocrine therapy and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor combination versus FEC/taxane chemotherapy.
There were also no differences between the two treatment arms in terms of invasive disease-free survival (iDFS, HR = 0.83, P = .71) or breast cancer–specific survival (BCSS), although the latter was an exploratory endpoint alongside overall survival (OS).
“The lack of difference is impressive,” said Hope S. Rugo, MD, FASCO, who commented independently on the study’s findings after their presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology: Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
“Overall survival in patients who received chemotherapy appears to be better, but the very small numbers here make interpretation of this difference impossible,” observed Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine at the University of California San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Unfortunately, this study is underpowered for definitive conclusions,” acknowledged study investigator Suzette Delaloge, MD, associate professor of medical oncology at Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
However, “it shows that the nonchemotherapy, preoperative letrozole/palbociclib approach deserves further exploration and could be an option for a chemotherapy-free regimen in some specific cases.”
Primary data already reported
The NeoPAL study was an open-label, randomized study conducted in 27 centers throughout France that compared the preoperative use of letrozole plus palbociclib to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 106 postmenopausal patients with either luminal A or B node-positive disease.
Patients were considered for inclusion in the trial if they had been newly diagnosed with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-negative stage I-III breast cancer and were not candidates for breast conservation. Genetic testing was used to confirm that only those with luminal B, or luminal A and who were node positive were recruited.
Neoadjuvant treatment consisted of either letrozole (2.5 mg/day) and palbociclib (125 mg daily for 3 weeks out of 4 weeks) for 19 weeks or three 21-day cycles of 5-fluorouracil (500 mg/m2), epirubicin (100 mg/m2), and cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2), followed by three 21-day cycles of docetaxel (100 mg/m2).
The primary endpoint was the pathological complete response (pCR), defined as a residual cancer burden (RCB) of 0 to 1. Results, which have already been reported, showed equivalent, but perhaps disappointingly low, pathological responses in both the letrozole/palbociclib and chemotherapy arms (3.8% and 5.9%, respectively).
There were, however, identical clinical responses (at around 75%) and “encouraging biomarker responses in the Prosigna-defined high risk luminal breast cancer population,” Dr. Delaloge said.
The NeoPAL findings were on par with those of the CORALLEEN study, Dr. Delaloge suggested. That trial, as Dr. Rugo has also pointed out, was conducted in 106 patients with luminal B early breast cancer and used a combination of letrozole and the CDK 4/6 inhibitor ribociclib (Kisquali).
Future studies needed
NeoPAL “is a small study with relatively short follow-up even for hormone receptor-positive, high-risk disease,” Dr. Rugo observed. However, she qualified “this short follow-up can be very meaningful in high-risk disease.” as shown by other CDK 4/6 inhibitor trials.
Dr. Rugo also noted: “Short-term biologic endpoints are clearly more informative following and during neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than pCR and this trial, as well as the data from previous studies, indicates that this is the case.”
Further, Dr. Rugo said: “Antiproliferative response is enhanced with CDK 4/6 inhibitors, but this doesn’t seem to translate into a difference in pCR. The lack of impact on longer term, outcome to date, provides support for ongoing trials.”
Two such trials are already underway. The 200-patient CARABELA trial started recruitment in March last year and is comparing endocrine therapy with letrozole plus the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) to standard chemotherapy in patients with hormone receptor–positive, high-risk Ki67 disease.
Then there is the ADAPTcycle trial, a large open-label, phase 3 trial that is randomizing patients based on Ki67 and recurrence score after a short preoperative induction with endocrine therapy to postoperative chemotherapy or to 2 years of endocrine therapy plus ribociclib, with both arms receiving a standard course of 5 years of endocrine therapy.
“These two studies have provided interesting information that will help us design studies in the future,” said Dr. Rugo.
Not only that, but they will also help “investigate the subgroups of patients that benefit the most from CDK 4/6 inhibitors and better study neoadjuvant endocrine therapy which is an important option for patients that can be evaluated in terms of its efficacy by short term measures of antiproliferative response.”
NeoPAL was sponsored by UNICANCER with funding from Pfizer and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Delaloge disclosed receiving research grants or funding via her institution from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche, Merck, Sanofi, Lilly, Novartis, BMS, Orion, Daiichi, Puma, and Pierre Fabre. Dr. Rugo reported receipt of grants via her institution to perform clinical trials from Pfizer and multiple other companies. She disclosed receiving honoraria from PUMA, Samsung, and Mylan.
Three-year survival rates were similarly high among postmenopausal women with high-risk early luminal breast cancer who were treated with either the neoadjuvant combination of letrozole and palbociclib (Ibrance) or standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the phase 2 NeoPAL study.
Progression-free survival (PFS) was a respective 86.7% and 87.2%, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.01 (P = .98) comparing the endocrine therapy and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor combination versus FEC/taxane chemotherapy.
There were also no differences between the two treatment arms in terms of invasive disease-free survival (iDFS, HR = 0.83, P = .71) or breast cancer–specific survival (BCSS), although the latter was an exploratory endpoint alongside overall survival (OS).
“The lack of difference is impressive,” said Hope S. Rugo, MD, FASCO, who commented independently on the study’s findings after their presentation at the European Society for Medical Oncology: Breast Cancer virtual meeting.
“Overall survival in patients who received chemotherapy appears to be better, but the very small numbers here make interpretation of this difference impossible,” observed Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine at the University of California San Francisco’s Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center.
“Unfortunately, this study is underpowered for definitive conclusions,” acknowledged study investigator Suzette Delaloge, MD, associate professor of medical oncology at Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
However, “it shows that the nonchemotherapy, preoperative letrozole/palbociclib approach deserves further exploration and could be an option for a chemotherapy-free regimen in some specific cases.”
Primary data already reported
The NeoPAL study was an open-label, randomized study conducted in 27 centers throughout France that compared the preoperative use of letrozole plus palbociclib to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 106 postmenopausal patients with either luminal A or B node-positive disease.
Patients were considered for inclusion in the trial if they had been newly diagnosed with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-negative stage I-III breast cancer and were not candidates for breast conservation. Genetic testing was used to confirm that only those with luminal B, or luminal A and who were node positive were recruited.
Neoadjuvant treatment consisted of either letrozole (2.5 mg/day) and palbociclib (125 mg daily for 3 weeks out of 4 weeks) for 19 weeks or three 21-day cycles of 5-fluorouracil (500 mg/m2), epirubicin (100 mg/m2), and cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2), followed by three 21-day cycles of docetaxel (100 mg/m2).
The primary endpoint was the pathological complete response (pCR), defined as a residual cancer burden (RCB) of 0 to 1. Results, which have already been reported, showed equivalent, but perhaps disappointingly low, pathological responses in both the letrozole/palbociclib and chemotherapy arms (3.8% and 5.9%, respectively).
There were, however, identical clinical responses (at around 75%) and “encouraging biomarker responses in the Prosigna-defined high risk luminal breast cancer population,” Dr. Delaloge said.
The NeoPAL findings were on par with those of the CORALLEEN study, Dr. Delaloge suggested. That trial, as Dr. Rugo has also pointed out, was conducted in 106 patients with luminal B early breast cancer and used a combination of letrozole and the CDK 4/6 inhibitor ribociclib (Kisquali).
Future studies needed
NeoPAL “is a small study with relatively short follow-up even for hormone receptor-positive, high-risk disease,” Dr. Rugo observed. However, she qualified “this short follow-up can be very meaningful in high-risk disease.” as shown by other CDK 4/6 inhibitor trials.
Dr. Rugo also noted: “Short-term biologic endpoints are clearly more informative following and during neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than pCR and this trial, as well as the data from previous studies, indicates that this is the case.”
Further, Dr. Rugo said: “Antiproliferative response is enhanced with CDK 4/6 inhibitors, but this doesn’t seem to translate into a difference in pCR. The lack of impact on longer term, outcome to date, provides support for ongoing trials.”
Two such trials are already underway. The 200-patient CARABELA trial started recruitment in March last year and is comparing endocrine therapy with letrozole plus the CDK 4/6 inhibitor abemaciclib (Verzenio) to standard chemotherapy in patients with hormone receptor–positive, high-risk Ki67 disease.
Then there is the ADAPTcycle trial, a large open-label, phase 3 trial that is randomizing patients based on Ki67 and recurrence score after a short preoperative induction with endocrine therapy to postoperative chemotherapy or to 2 years of endocrine therapy plus ribociclib, with both arms receiving a standard course of 5 years of endocrine therapy.
“These two studies have provided interesting information that will help us design studies in the future,” said Dr. Rugo.
Not only that, but they will also help “investigate the subgroups of patients that benefit the most from CDK 4/6 inhibitors and better study neoadjuvant endocrine therapy which is an important option for patients that can be evaluated in terms of its efficacy by short term measures of antiproliferative response.”
NeoPAL was sponsored by UNICANCER with funding from Pfizer and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Delaloge disclosed receiving research grants or funding via her institution from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche, Merck, Sanofi, Lilly, Novartis, BMS, Orion, Daiichi, Puma, and Pierre Fabre. Dr. Rugo reported receipt of grants via her institution to perform clinical trials from Pfizer and multiple other companies. She disclosed receiving honoraria from PUMA, Samsung, and Mylan.
FROM ESMO BREAST CANCER 2021
New guidance for those fully vaccinated against COVID-19
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
As has been dominating the headlines, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released updated public health guidance for those who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
This new guidance applies to those who are fully vaccinated as indicated by 2 weeks after the second dose in a 2-dose series or 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine. Those who meet these criteria no longer need to wear a mask or physically distance themselves from others in both indoor and outdoor settings. For those not fully vaccinated, masking and social distancing should continue to be practiced.
The new guidance indicates that quarantine after a known exposure is no longer necessary.
Unless required by local, state, or territorial health authorities, testing is no longer required following domestic travel for fully vaccinated individuals. A negative test is still required prior to boarding an international flight to the United States and testing 3-5 days after arrival is still recommended. Self-quarantine is no longer required after international travel for fully vaccinated individuals.
The new guidance recommends that individuals who are fully vaccinated not participate in routine screening programs when feasible. Finally, if an individual has tested positive for COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, that person should isolate and not visit public or private settings for a minimum of ten days.1
Updated guidance for health care facilities
In addition to changes for the general public in all settings, the CDC updated guidance for health care facilities on April 27, 2021. These updated guidelines allow for communal dining and visitation for fully vaccinated patients and their visitors. The guidelines indicate that fully vaccinated health care personnel (HCP) do not require quarantine after exposure to patients who have tested positive for COVID-19 as long as the HCP remains asymptomatic. They should, however, continue to utilize personal protective equipment as previously recommended. HCPs are able to be in break and meeting rooms unmasked if all HCPs are vaccinated.2
There are some important caveats to these updated guidelines. They do not apply to those who have immunocompromising conditions, including those using immunosuppressant agents. They also do not apply to locations subject to federal, state, local, tribal, or territorial laws, rules, and regulations, including local business and workplace guidance.
Those who work or reside in correction or detention facilities and homeless shelters are also still required to test after known exposures. Masking is still required by all travelers on all forms of public transportation into and within the United States.
Most importantly, the guidelines apply only to those who are fully vaccinated. Finally, no vaccine is perfect. As such, anyone who experiences symptoms indicative of COVID-19, regardless of vaccination status, should obtain viral testing and isolate themselves from others.1,2
Pros and cons to new guidance
Both sets of updated guidelines are a great example of public health guidance that is changing as the evidence is gathered and changes. This guidance is also a welcome encouragement that the vaccines are effective at decreasing transmission of this virus that has upended our world.
These guidelines leave room for change as evidence is gathered on emerging novel variants. There are, however, a few remaining concerns.
My first concern is for those who are not yet able to be vaccinated, including children under the age of 12. For families with members who are not fully vaccinated, they may have first heard the headlines of “you do not have to mask” to then read the fine print that remains. When truly following these guidelines, many social situations in both the public and private setting should still include both masking and social distancing.
There is no clarity on how these guidelines are enforced. Within the guidance, it is clear that individuals’ privacy is of utmost importance. In the absence of knowledge, that means that the assumption should be that all are not yet vaccinated. Unless there is a way to reliably demonstrate vaccination status, it would likely still be safer to assume that there are individuals who are not fully vaccinated within the setting.
Finally, although this is great news surrounding the efficacy of the vaccine, some are concerned that local mask mandates that have already started to be lifted will be completely removed. As there is still a large portion of the population not yet fully vaccinated, it seems premature for local, state, and territorial authorities to lift these mandates.
How to continue exercising caution
With the outstanding concerns, I will continue to mask in settings, particularly indoors, where I do not definitely know that everyone is vaccinated. I will continue to do this to protect my children and my patients who are not yet vaccinated, and my patients who are immunosuppressed for whom we do not yet have enough information.
I will continue to advise my patients to be thoughtful about the risk for themselves and their families as well.
There has been more benefit to these public health measures then just decreased transmission of COVID-19. I hope that this year has reinforced within us the benefits of masking and self-isolation in the cases of any contagious illnesses.
Although I am looking forward to the opportunities to interact in person with more colleagues and friends, I think we should continue to do this with caution and thoughtfulness. We must be prepared for the possibility of vaccines having decreased efficacy against novel variants as well as eventually the possibility of waning immunity. If these should occur, we need to be prepared for additional recommendation changes and tightening of restrictions.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. She is program director of Northwestern’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program at Humboldt Park, Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, May 13, 2021.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated Healthcare Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations in Response to COVID-19 Vaccination. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, April 27, 2021.
COVID-19 in children: Weekly cases drop to 6-month low
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
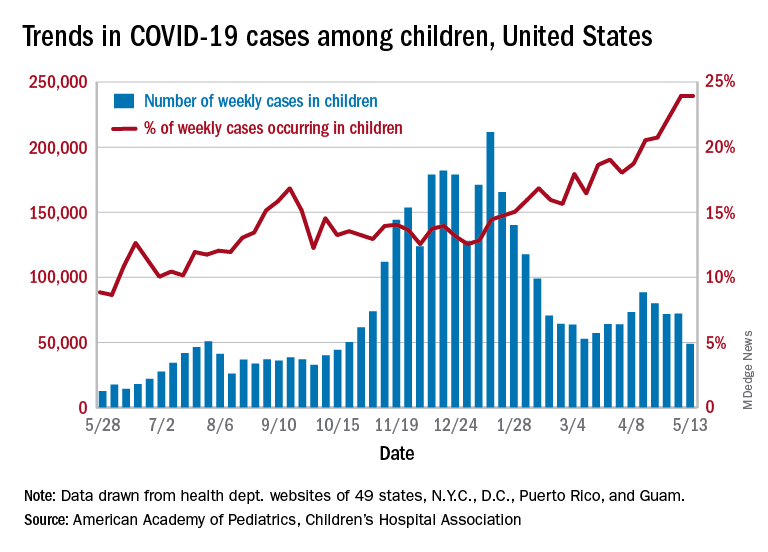
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.









