User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


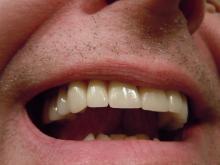
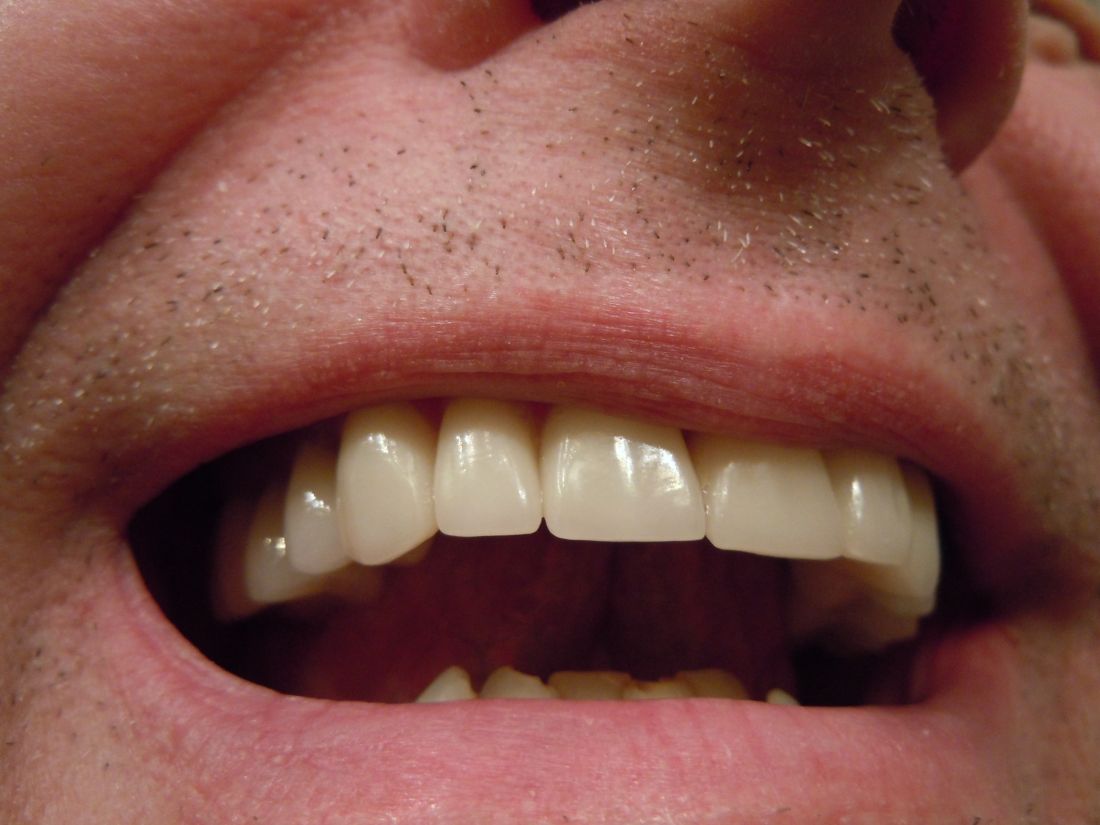
A very strange place to find a tooth
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
A nose for the tooth
Have you ever had a stuffy nose that just wouldn’t go away? Those irritating head colds have nothing on the stuffy nose a man in New York recently had to go through. A stuffy nose to top all stuffy noses. One stuffy nose to rule them all, as it were.
This man went to a Mount Sinai clinic with difficulty breathing through his right nostril, a problem that had been going on for years. Let us repeat that: A stuffy nose that lasted for years. The exam revealed a white mass jutting through the back of the septum and a CT scan confirmed the diagnosis. Perhaps you’ve already guessed, since the headline does give things away. Yes, this man had a tooth growing into his nose.
The problem was a half-inch-long ectopic tooth. Ectopic teeth are rare, occurring in less than 1% of people, but an ectopic tooth growing backward into the nasal cavity? Well, that’s so uncommon that this man got a case report in the New England Journal of Medicine.
This story does have a happy ending. Not all ectopic teeth need to be treated, but this one really did have to go. The offending tooth was surgically removed and, at a 3-month follow-up, the stuffy nose issue was completely resolved. So our friend gets the best of both worlds: His issue gets cured and he gets a case report in a major medical publication. If that’s not living the dream, we don’t know what is, and that’s the tooth.
Lettuce recommend you a sleep aid
Lettuce is great for many things. The star in a salad? Of course. The fresh element in a BLT? Yep. A sleep aid? According to a TikTok hack with almost 5 million views, the pinch hitter in a sandwich is switching leagues to be used like a tea for faster sleep. But, does it really work? Researchers say yes and no, according to a recent report at Tyla.com.
Studies conducted in 2013 and 2017 pointed toward a compound called lactucin, which is found in the plant’s n-butanol fraction. In the 2013 study, mice that received n-butanol fraction fell asleep faster and stayed asleep longer. In 2017, researchers found that lettuce made mice sleep longer and helped protect against cell inflammation and damage.
OK, so it works on mice. But what about humans? In the TikTok video, user Shapla Hoque pours hot water on a few lettuce leaves in a mug with a peppermint tea bag (for flavor). After 10 minutes, when the leaves are soaked and soggy, she removes them and drinks the lettuce tea. By the end of the video she’s visibly drowsy and ready to crash. Does this hold water?
Here’s the no. Dr. Charlotte Norton of the Slimming Clinic told Tyla.com that yeah, there are some properties in lettuce that will help you fall asleep, such as lactucarium, which is prominent in romaine. But you would need a massive amount of lettuce to get any effect. The TikTok video, she said, is an example of the placebo effect.
Brains get a rise out of Viagra
A lot of medications are used off label. Antidepressants for COVID have taken the cake recently, but here’s a new one: Viagra for Alzheimer’s disease.
Although there’s no definite link yet between the two, neuron models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Alzheimer’s suggest that sildenafil increases neurite growth and decreases phospho-tau expression, Jiansong Fang, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and associates said in Nature Aging.
Their research is an attempt to find untapped sources of new treatments among existing drugs. They began the search with 1,600 approved drugs and focused on those that target the buildup of beta amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, according to the Daily Beast.
Since sildenafil is obviously for men, more research will need to be done on how this drug affects women. Don’t start stocking up just yet.
Omicron is not a social-distancing robot
COVID, safe to say, has not been your typical, run-of-the-mill pandemic. People have protested social distancing. People have protested lockdowns. People have protested mask mandates. People have protested vaccine mandates. People have protested people protesting vaccine mandates.
Someone used a fake arm to get a COVID vaccine card. People have tried to reverse their COVID vaccinations. People had COVID contamination parties.
The common denominator? People. Humans. Maybe what we need is a nonhuman intervention. To fight COVID, we need a hero. A robotic hero.
And where can we find such a hero? The University of Maryland, of course, where computer scientists and engineers are working on an autonomous mobile robot to enforce indoor social-distancing rules.
Their robot can detect lapses in social distancing using cameras, both thermal and visual, along with a LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor. It then sorts the offenders into various groups depending on whether they are standing still or moving and predicts their future movement using a state-of-the-art hybrid collision avoidance method known as Frozone, Adarsh Jagan Sathyamoorthy and associates explained in PLOS One.
“Once it reaches the breach, the robot encourages people to move apart via text that appears on a mounted display,” ScienceDaily said.
Maybe you were expecting a Terminator-type robot coming to enforce social distancing requirements rather than a simple text message. Let’s just hope that all COVID guidelines are followed, including social distancing, so the pandemic will finally end and won’t “be back.”
Vaccine protection drops against Omicron, making boosters crucial
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A raft of new
The new studies, from teams of researchers in Germany, South Africa, Sweden, and the drug company Pfizer, showed 25 to 40-fold drops in the ability of antibodies created by two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to neutralize the virus.
But there seemed to be a bright spot in the studies too. The virus didn’t completely escape the immunity from the vaccines, and giving a third, booster dose appeared to restore antibodies to a level that’s been associated with protection against variants in the past.
“One of the silver linings of this pandemic so far is that mRNA vaccines manufactured based on the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 continue to work in the laboratory and, importantly, in real life against variant strains,” said Hana El Sahly, MD, professor of molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. “The strains so far vary by their degree of being neutralized by the antibodies from these vaccines, but they are being neutralized nonetheless.”
Dr. El Sahly points out that the Beta variant was associated with a 10-fold drop in antibodies, but two doses of the vaccines still protected against it.
President Biden hailed the study results as good news.
“That Pfizer lab report came back saying that the expectation is that the existing vaccines protect against Omicron. But if you get the booster, you’re really in good shape. And so that’s very encouraging,” he said in a press briefing Dec. 8.
More research needed
Other scientists, however, stressed that these studies are from lab tests, and don’t necessarily reflect what will happen with Omicron in the real world. They cautioned about a worldwide push for boosters with so many countries still struggling to give first doses of vaccines.
Soumya Swaminathan, MD, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, stressed in a press briefing Dec. 8 that the results from the four studies varied widely, showing dips in neutralizing activity with Omicron that ranged from 5-fold to 40-fold.
The types of lab tests that were run were different, too, and involved small numbers of blood samples from patients.
She stressed that immunity depends not just on neutralizing antibodies, which act as a first line of defense when a virus invades, but also on B cells and T cells, and so far, tests show that these crucial components — which are important for preventing severe disease and death — had been less impacted than antibodies.
“So, I think it’s premature to conclude that this reduction in neutralizing activity would result in a significant reduction in vaccine effectiveness,” she said.
Whether or not these first-generation vaccines will be enough to stop Omicron, though, remains to be seen. A study of the Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca vaccines, led by German physician Sandra Ciesek, MD, who directs the Institute of Medical Virology at the University of Frankfurt, shows a booster didn’t appear to hold up well over time.
Dr. Ciesek and her team exposed Omicron viruses to the antibodies of volunteers who had been boosted with the Pfizer vaccine 3 months prior.
She also compared the results to what happened to those same 3-month antibody levels against Delta variant viruses. She found only a 25% neutralization of Omicron compared with a 95% neutralization of Delta. That represented about a 37-fold reduction in the ability of the antibodies to neutralize Omicron vs Delta.
“The data confirm that developing a vaccine adapted for Omicron makes sense,” she tweeted as part of a long thread she posted on her results.
Retool the vaccines?
Both Pfizer and Moderna are retooling their vaccines to better match them to the changes in the Omicron variant. In a press release, Pfizer said it could start deliveries of that updated vaccine by March, pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorization.
“What the booster really does in neutralizing Omicron right now, they don’t know, they have no idea,” said Peter Palese, PhD, chair of the department of microbiology at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City.
Dr. Palese said he was definitely concerned about a possible Omicron wave.
“There are four major sites on the spike protein targeted by antibodies from the vaccines, and all four sites have mutations,” he said. “All these important antigenic sites are changed.
“If Omicron becomes the new Delta, and the old vaccines really aren’t good enough, then we have to make new Omicron vaccines. Then we have to revaccinate everybody twice,” he said, and the costs could be staggering. “I am worried.”
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, director general of the WHO, urged countries to move quickly.
“Don’t wait. Act now,” he said, even before all the science is in hand. “All of us, every government, every individual should use all the tools we have right now,” to drive down transmission, increase testing and surveillance, and share scientific findings.
“We can prevent Omicron [from] becoming a global crisis right now,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Female patients fare worse with male surgeons, study finds
, according to a new analysis of over 1.3 million surgery patients. The study found no difference in adverse outcomes in male patients treated by surgeons of either sex.
While the effect of patient and provider sex discordance (female patient/male physician or male patient/female physician) on care has been explored before, “to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to assess this in patients undergoing surgery,” Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the division of urology at the University of Toronto, said in an email. The study was published online December 8 in JAMA Surgery.
Past studies in primary care settings have found that sex discordance between a physician and patient can result in “worse rapport, lower certainty of diagnosis, lower likelihood of assessing patient’s conditions as being of high severity, concerns of a hidden agenda, and disagreements regarding advice provided,” the authors write in the paper. Gender discordance has also been shown to negatively affect cancer screening rates and survival after heart attack. Given these past findings, Dr. Wallis and colleagues postulated that gender match between patients and surgeons could affect postoperative outcomes.
To find out, researchers analyzed data from over 1,320,100 patients undergoing one of 21 common elective and emergent surgical procedures in Ontario, Canada, from January 1, 2007, through December 31, 2019. Procedures were performed across the following specialties: cardiothoracic surgery, general surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, otolaryngology, plastic surgery, thoracic surgery, urology, and vascular surgery. The investigators compared adverse postoperative outcomes — death, readmission, or complications within 30 days after surgery — in patients of both sexes when treated by male or female surgeons.
The study included 2,937 surgeons, and nearly 46% of patients included in the study were the same sex as their surgeon. Of the remaining 717,548 sex-discordant pairings, 93% were female patients with male surgeons, and 7% were male patients with female surgeons.
Among all patients, 14.9% experienced at least one adverse outcome. The researchers found that sex discordance between patient and surgeon was associated with higher odds of complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07 – 1.11) and death (aOR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02 – 1.13). There was no statistically significant relationship between sex discordance and readmission in the study.
Using multivariable modeling, the researchers then teased out how patient sex affected this association. They found that female patients treated by male surgeons, compared to those treated by female surgeons, were more likely to have worse outcomes (aOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.10 – 1.20); however, there was no difference in outcomes in male patients treated by female surgeons compared with those with male surgeons (aOR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.95 – 1.03).
While the study did not look at the underlying reasons for this disparity, communication differences between surgeons and patients could be one factor, Dr. Wallis noted. “Prior research has suggested differences in communication style between male and female physicians. Further, there is evidence that female physicians, including surgeons, spend more time with patients,” he wrote in an email. “This, coupled with evidence that female patients may have disparities in the management of their pain, suggest that communication differences may underpin the observed disparity.”
The finding “sounds the alarm for urgent action,” write Andrea Riner, MD, MPH, and Amalia Cochran, MD, both from the department of surgery at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, in an accompanying commentary. While recruiting more women into surgical specialties is one way to address this disparity, both Dr. Riner and Dr. Cochran note the importance of identifying unconscious biases in patient care. “Surgeons likely believe they provide the same quality of care to patients irrespective of identity,” they write. “However, these data underscore an underappreciated phenomenon and highlight a measurable repercussion of implicit bias.”
Training programs that work with surgeons to improve communication and care with diverse patients may help counter these biases, they suggest, and incorporating patient identity in surgical outcome metrics could help identify biases. “Female patients with surgical disease should not be disadvantaged because there simply are not enough female surgeons or surgeons who are competent in the care of female patients,” they note. “We owe it to patients to provide them with the best outcomes, regardless of how their identities may align with ours.”
Dr. Riner reports grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute and the National Cancer Institute.Dr. Cochran is a section editor for UpToDate. Dr. Wallis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new analysis of over 1.3 million surgery patients. The study found no difference in adverse outcomes in male patients treated by surgeons of either sex.
While the effect of patient and provider sex discordance (female patient/male physician or male patient/female physician) on care has been explored before, “to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to assess this in patients undergoing surgery,” Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the division of urology at the University of Toronto, said in an email. The study was published online December 8 in JAMA Surgery.
Past studies in primary care settings have found that sex discordance between a physician and patient can result in “worse rapport, lower certainty of diagnosis, lower likelihood of assessing patient’s conditions as being of high severity, concerns of a hidden agenda, and disagreements regarding advice provided,” the authors write in the paper. Gender discordance has also been shown to negatively affect cancer screening rates and survival after heart attack. Given these past findings, Dr. Wallis and colleagues postulated that gender match between patients and surgeons could affect postoperative outcomes.
To find out, researchers analyzed data from over 1,320,100 patients undergoing one of 21 common elective and emergent surgical procedures in Ontario, Canada, from January 1, 2007, through December 31, 2019. Procedures were performed across the following specialties: cardiothoracic surgery, general surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, otolaryngology, plastic surgery, thoracic surgery, urology, and vascular surgery. The investigators compared adverse postoperative outcomes — death, readmission, or complications within 30 days after surgery — in patients of both sexes when treated by male or female surgeons.
The study included 2,937 surgeons, and nearly 46% of patients included in the study were the same sex as their surgeon. Of the remaining 717,548 sex-discordant pairings, 93% were female patients with male surgeons, and 7% were male patients with female surgeons.
Among all patients, 14.9% experienced at least one adverse outcome. The researchers found that sex discordance between patient and surgeon was associated with higher odds of complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07 – 1.11) and death (aOR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02 – 1.13). There was no statistically significant relationship between sex discordance and readmission in the study.
Using multivariable modeling, the researchers then teased out how patient sex affected this association. They found that female patients treated by male surgeons, compared to those treated by female surgeons, were more likely to have worse outcomes (aOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.10 – 1.20); however, there was no difference in outcomes in male patients treated by female surgeons compared with those with male surgeons (aOR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.95 – 1.03).
While the study did not look at the underlying reasons for this disparity, communication differences between surgeons and patients could be one factor, Dr. Wallis noted. “Prior research has suggested differences in communication style between male and female physicians. Further, there is evidence that female physicians, including surgeons, spend more time with patients,” he wrote in an email. “This, coupled with evidence that female patients may have disparities in the management of their pain, suggest that communication differences may underpin the observed disparity.”
The finding “sounds the alarm for urgent action,” write Andrea Riner, MD, MPH, and Amalia Cochran, MD, both from the department of surgery at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, in an accompanying commentary. While recruiting more women into surgical specialties is one way to address this disparity, both Dr. Riner and Dr. Cochran note the importance of identifying unconscious biases in patient care. “Surgeons likely believe they provide the same quality of care to patients irrespective of identity,” they write. “However, these data underscore an underappreciated phenomenon and highlight a measurable repercussion of implicit bias.”
Training programs that work with surgeons to improve communication and care with diverse patients may help counter these biases, they suggest, and incorporating patient identity in surgical outcome metrics could help identify biases. “Female patients with surgical disease should not be disadvantaged because there simply are not enough female surgeons or surgeons who are competent in the care of female patients,” they note. “We owe it to patients to provide them with the best outcomes, regardless of how their identities may align with ours.”
Dr. Riner reports grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute and the National Cancer Institute.Dr. Cochran is a section editor for UpToDate. Dr. Wallis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new analysis of over 1.3 million surgery patients. The study found no difference in adverse outcomes in male patients treated by surgeons of either sex.
While the effect of patient and provider sex discordance (female patient/male physician or male patient/female physician) on care has been explored before, “to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to assess this in patients undergoing surgery,” Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the division of urology at the University of Toronto, said in an email. The study was published online December 8 in JAMA Surgery.
Past studies in primary care settings have found that sex discordance between a physician and patient can result in “worse rapport, lower certainty of diagnosis, lower likelihood of assessing patient’s conditions as being of high severity, concerns of a hidden agenda, and disagreements regarding advice provided,” the authors write in the paper. Gender discordance has also been shown to negatively affect cancer screening rates and survival after heart attack. Given these past findings, Dr. Wallis and colleagues postulated that gender match between patients and surgeons could affect postoperative outcomes.
To find out, researchers analyzed data from over 1,320,100 patients undergoing one of 21 common elective and emergent surgical procedures in Ontario, Canada, from January 1, 2007, through December 31, 2019. Procedures were performed across the following specialties: cardiothoracic surgery, general surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, otolaryngology, plastic surgery, thoracic surgery, urology, and vascular surgery. The investigators compared adverse postoperative outcomes — death, readmission, or complications within 30 days after surgery — in patients of both sexes when treated by male or female surgeons.
The study included 2,937 surgeons, and nearly 46% of patients included in the study were the same sex as their surgeon. Of the remaining 717,548 sex-discordant pairings, 93% were female patients with male surgeons, and 7% were male patients with female surgeons.
Among all patients, 14.9% experienced at least one adverse outcome. The researchers found that sex discordance between patient and surgeon was associated with higher odds of complications (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.09; 95% CI, 1.07 – 1.11) and death (aOR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02 – 1.13). There was no statistically significant relationship between sex discordance and readmission in the study.
Using multivariable modeling, the researchers then teased out how patient sex affected this association. They found that female patients treated by male surgeons, compared to those treated by female surgeons, were more likely to have worse outcomes (aOR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.10 – 1.20); however, there was no difference in outcomes in male patients treated by female surgeons compared with those with male surgeons (aOR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.95 – 1.03).
While the study did not look at the underlying reasons for this disparity, communication differences between surgeons and patients could be one factor, Dr. Wallis noted. “Prior research has suggested differences in communication style between male and female physicians. Further, there is evidence that female physicians, including surgeons, spend more time with patients,” he wrote in an email. “This, coupled with evidence that female patients may have disparities in the management of their pain, suggest that communication differences may underpin the observed disparity.”
The finding “sounds the alarm for urgent action,” write Andrea Riner, MD, MPH, and Amalia Cochran, MD, both from the department of surgery at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, in an accompanying commentary. While recruiting more women into surgical specialties is one way to address this disparity, both Dr. Riner and Dr. Cochran note the importance of identifying unconscious biases in patient care. “Surgeons likely believe they provide the same quality of care to patients irrespective of identity,” they write. “However, these data underscore an underappreciated phenomenon and highlight a measurable repercussion of implicit bias.”
Training programs that work with surgeons to improve communication and care with diverse patients may help counter these biases, they suggest, and incorporating patient identity in surgical outcome metrics could help identify biases. “Female patients with surgical disease should not be disadvantaged because there simply are not enough female surgeons or surgeons who are competent in the care of female patients,” they note. “We owe it to patients to provide them with the best outcomes, regardless of how their identities may align with ours.”
Dr. Riner reports grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute and the National Cancer Institute.Dr. Cochran is a section editor for UpToDate. Dr. Wallis reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA SURGERY
New data on rare myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA challenges diet doctor’s study alleging COVID vax risks
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An abstract and poster presentation questioning the safety of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, embraced by some and lambasted by others, has drawn an “expression of concern” from the American Heart Association, along with a bid for correction.
The abstract in question concludes that COVID vaccines “dramatically increase” levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, and therefore, the 5-year risk of acute coronary syndromes (ACS), based on pre- and post-vaccination results of an obscure blood panel called the PULS Cardiac Test (GD Biosciences). The findings were presented at the AHA’s 2021 Scientific Sessionsas, an uncontrolled observational study of 566 patients in a preventive cardiology practice.
Some on social media have seized on the abstract as evidence of serious potential harm from the two available mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and mRNA-1273 (Moderna). But others contend that the study’s described design and findings are specious and its conclusions overstated.
They also point to the notoriety of its one listed author, Steven R. Gundry, MD, who promotes his diet books and supplements as well as fringe, highly criticized theories about diet and disease on several websites, including drgundry.com. Dr. Gundry has not responded to requests for an interview.
Dr. Gundry’s abstract from the AHA Scientific Sessions 2021, available on the meeting’s program planner, was marked with an “expression of concern” by the AHA that is to stand “until a suitable correction is published, to indicate that the abstract in its current version may not be reliable.”
The expression of concern statement, also published online Nov. 24 in Circulation, says “potential errors in the abstract” were brought to the attention of the meeting planners. “Specifically, there are several typographical errors, there is no data in the abstract regarding myocardial T-cell infiltration, there are no statistical analyses for significance provided, and the author is not clear that only anecdotal data was used.”
The biomarker elevations on which the abstract’s conclusions are based included hepatocyte growth factor, “which serves as a marker for chemotaxis of T-cells into epithelium and cardiac tissue,” it states.
“The expression of concern about the abstract will remain in place until a correction is accepted and published” in Circulation, AHA spokesperson Suzanne Grant told this news organization by email.
“The specific data needed will be up to the abstract author to determine and supply,” she said, noting that Dr. Gundry “has been in communication with the journal throughout this process.”
Submitting researchers “must always attest to the validity of the abstract,” Ms. Grant said. “Abstracts are then curated by independent review panels, blinded to the identities of the abstract authors, and are considered based on the potential to add to the diversity of scientific issues and views discussed at the meeting.”
Regarding the AHA’s system for vetting abstracts vying for acceptance to the scientific sessions, she said it is not primarily intended to “evaluate scientific validity” and that the organization is “currently reviewing its existing abstract submission processes.”
A recent Reuters report reviews the controversy and provides links to criticisms of the study on social media.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is mindfulness key to helping physicians with mental health?
In 2011, the Mayo Clinic began surveying physicians about burnout and found 45% of physicians experienced at least one symptom, such as emotional exhaustion, finding work no longer meaningful, feelings of ineffectiveness, and depersonalizing patients. Associated manifestations can range from headache and insomnia to impaired memory and decreased attention.
Fast forward 10 years to the Medscape National Physician Burnout and Suicide Report, which found that a similar number of physicians (42%) feel burned out. The COVID-19 pandemic only added insult to injury. A Medscape survey that included nearly 5,000 U.S. physicians revealed that about two-thirds (64%) of them reported burnout had intensified during the crisis.
These elevated numbers are being labeled as “a public health crisis” for the impact widespread physician burnout could have on the health of the doctor and patient safety. The relatively consistent levels across the decade seem to suggest that, if health organizations are attempting to improve physician well-being, it doesn’t appear to be working, forcing doctors to find solutions for themselves.
Jill Wener, MD, considers herself part of the 45% burned out 10 years ago. She was working as an internist at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, but the “existential reality of being a doctor in this world” was wearing on her. “Staying up with the literature, knowing that every day you’re going to go into work without knowing what you’re going to find, threats of lawsuits, the pressure of perfectionism,” Dr. Wener told this news organization. “By the time I hit burnout, everything made me feel like the world was crashing down on me.”
When Dr. Wener encountered someone who meditated twice a day, she was intrigued, even though the self-described “most Type-A, inside-the-box, nonspiritual type, anxious, linear-path doctor” didn’t think people like her could meditate. Dr. Wener is not alone in her hesitation to explore meditation as a means to help prevent burnout because the causes of burnout are primarily linked to external rather than internal factors. Issues including a loss of autonomy, the burden and distraction of electronic health records, and the intense pressure to comply with rules from the government are not things mindfulness can fix.
And because the sources of burnout are primarily environmental and inherent to the current medical system, the suggestion that physicians need to fix themselves with meditation can come as a slap in the face. However, when up against a system slow to change, mindfulness can provide physicians access to the one thing they can control: How they perceive and react to what’s in front of them.
At the recommendation of an acquaintance, Dr. Wener enrolled in a Vedic Meditation (also known as Conscious Health Meditation) course taught by Light Watkins, a well-known traveling instructor, author, and speaker. By the second meeting she was successfully practicing 20 minutes twice a day. This form of mediation traces its roots to the Vedas, ancient Indian texts (also the foundation for yoga), and uses a mantra to settle the mind, transitioning to an awake state of inner contentment.
Three weeks later, Dr. Wener’s daily crying jags ended as did her propensity for road rage. “I felt like I was on the cusp of something life-changing, I just didn’t understand it,” she recalled. “But I knew I was never going to give it up.”
Defining mindfulness
“Mindfulness is being able to be present in the moment that you’re in with acceptance of what it is and without judging it,” said Donna Rockwell, PsyD, a leading mindfulness meditation teacher. The practice of mindfulness is really meditation. Dr. Rockwell explained that the noise of our mind is most often focused on either the past or the future. “We’re either bemoaning something that happened earlier or we’re catastrophizing the future,” she said, which prevents us from being present in the moment.
Meditation allows you to notice when your mind has drifted from the present moment into the past or future. “You gently notice it, label it with a lot of self-compassion, and then bring your mind back by focusing on your breath – going out, going in – and the incoming stimuli through your five senses,” said Dr. Rockwell. “When you’re doing that, you can’t be in the past or future.”
Dr. Rockwell also pointed out that we constantly categorize incoming data of the moment as either “good for me or bad for me,” which gets in the way of simply being present for what you’re facing. “When you’re more fully present, you become more skillful and able to do what this moment is asking of you,” she said. Being mindful allows us to better navigate incoming stimuli, which could be a “code blue” in the ED or a patient who needs another 2 minutes during an office visit.
When Dr. Wener was burned out, she felt unable to adapt whenever something unexpected happened. “When you have no emotional reserves, everything feels like a big deal,” she said. “The meditation gave me what we call adaptation energy; it filled up my tank and kept me from feeling like I was going to lose it at 10 o’clock in the morning.”
Dr. Rockwell explained burnout as an overactive fight or flight response activated by the amygdala. It starts pumping cortisol, our pupils dilate, and our pores open. The prefrontal cortex is offline when we’re experiencing this physiological response because they both can’t be operational at the same time. “When we’re constantly in a ‘fight or flight’ response and don’t have any access to our prefrontal cortex, we are coming from a brain that is pumping cortisol and that leads to burnout,” said Dr. Rockwell.
“Any fight or flight response leaves a mark on your body,” Dr. Wener echoed. “When we go into our state of deep rest in the meditation practice, which is two to five times more restful than sleep, it heals those stress scars.”
Making time for mindfulness
Prescribing mindfulness for physicians is not new. Molecular biologist Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD, developed Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) in 1979, a practice that incorporates mindfulness exercises to help people become familiar with their behavior patterns in stressful situations. Thus, instead of reacting, they can respond with a clearer understanding of the circumstance. Dr. Kabat-Zinn initially targeted people with chronic health problems to help them cope with the effects of pain and the condition of their illness, but it has expanded to anyone experiencing challenges in their life, including physicians. A standard MBSR course runs 8 weeks, making it a commitment for most people.
Mindfulness training requires that physicians use what they already have so little of: time.
Dr. Wener was able to take a sabbatical, embarking on a 3-month trip to India to immerse herself in the study of Vedic Meditation. Upon her return, Dr. Wener took a position at Emory University, Atlanta, and has launched a number of CME-accredited meditation courses and retreats. Unlike Dr. Kabat-Zinn, her programs are by physicians and for physicians. She also created an online version of the meditation course to make it more accessible.
For these reasons, Kara Pepper, MD, an internist in outpatient primary care in Atlanta, was drawn to the meditation course. Dr. Pepper was 7 years into practice when she burned out. “The program dovetailed into my burnout recovery,” she said. “It allowed me space to separate myself from the thoughts I was having about work and just recognize them as just that – as thoughts.”
In the course, Dr. Wener teaches the REST Technique, which she says is different than mindfulness in that she encourages the mind to run rampant. “Trying to control the mind can feel very uncomfortable because we always have thoughts,” she says. “We can’t tell the mind to stop thinking just like we can’t tell the heart to stop beating.” Dr. Wener said the REST Technique lets “the mind swim downstream,” allowing the brain to go into a deep state of rest and start to heal from the scars caused by stress.
Dr. Pepper said the self-paced online course gave her all the tools she needed, and it was pragmatic and evidence based. “I didn’t feel ‘woo’ or like another gimmick,” she said. Pepper, who continues to practice medicine, became a life coach in 2019 to teach others the skills she uses daily.
An integrated strategy
In a review published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2019, Scott Yates, MD, MBA, from the Center for Executive Medicine in Plano, Tex., found that physicians who had adopted mediation and mindfulness training to decrease anxiety and perceived work stress only experienced modest benefits. In fact, Dr. Yates claims that there’s little data to suggest the long-term benefit of any particular stress management intervention in the prevention of burnout symptoms.
“The often-repeated goals of the Triple Aim [enhancing patient experience, improving population health, and reducing costs] may be unreachable until we recognize and address burnout in health care providers,” Dr. Yates wrote. He recommends adding a fourth goal to specifically address physician wellness, which certainly could include mindfulness training and meditation.
Burnout coach, trainer, and consultant Dike Drummond, MD, also professes that physician wellness must be added as the key fourth ingredient to improving health care. “Burnout is a dilemma, a balancing act,” he said. “It takes an integrated strategy.” The CEO and founder of TheHappyMD.com, Dr. Drummond’s integrated strategy to stop physician burnout has been taught to more than 40,000 physicians in 175 organizations, and one element of that strategy can be mindfulness training.
Dr. Drummond said he doesn’t use the word meditation “because that scares most people”; it takes a commitment and isn’t accessible for a lot of doctors. Instead, he coaches doctors to use a ‘single-breath’ technique to help them reset multiple times throughout the day. “I teach people how to breathe up to the top of their head and then down to the bottom of their feet,” Dr. Drummond said. He calls it the Squeegee Breath Technique because when they exhale, they “wipe away” anything that doesn’t need to be there right now. “If you happen to have a mindfulness practice like meditation, they work synergistically because the calmness you feel in your mediation is available to you at the bottom of these releasing breaths.”
Various studies and surveys provide great detail as to the “why” of physician burnout. And while mindfulness is not the sole answer, it’s something physicians can explore for themselves while health care as an industry looks for a more comprehensive solution.
“It’s not rocket science,” Dr. Drummond insisted. “You want a different result? You’re not satisfied with the way things are now and you want to feel different? You absolutely must do something different.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2011, the Mayo Clinic began surveying physicians about burnout and found 45% of physicians experienced at least one symptom, such as emotional exhaustion, finding work no longer meaningful, feelings of ineffectiveness, and depersonalizing patients. Associated manifestations can range from headache and insomnia to impaired memory and decreased attention.
Fast forward 10 years to the Medscape National Physician Burnout and Suicide Report, which found that a similar number of physicians (42%) feel burned out. The COVID-19 pandemic only added insult to injury. A Medscape survey that included nearly 5,000 U.S. physicians revealed that about two-thirds (64%) of them reported burnout had intensified during the crisis.
These elevated numbers are being labeled as “a public health crisis” for the impact widespread physician burnout could have on the health of the doctor and patient safety. The relatively consistent levels across the decade seem to suggest that, if health organizations are attempting to improve physician well-being, it doesn’t appear to be working, forcing doctors to find solutions for themselves.
Jill Wener, MD, considers herself part of the 45% burned out 10 years ago. She was working as an internist at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, but the “existential reality of being a doctor in this world” was wearing on her. “Staying up with the literature, knowing that every day you’re going to go into work without knowing what you’re going to find, threats of lawsuits, the pressure of perfectionism,” Dr. Wener told this news organization. “By the time I hit burnout, everything made me feel like the world was crashing down on me.”
When Dr. Wener encountered someone who meditated twice a day, she was intrigued, even though the self-described “most Type-A, inside-the-box, nonspiritual type, anxious, linear-path doctor” didn’t think people like her could meditate. Dr. Wener is not alone in her hesitation to explore meditation as a means to help prevent burnout because the causes of burnout are primarily linked to external rather than internal factors. Issues including a loss of autonomy, the burden and distraction of electronic health records, and the intense pressure to comply with rules from the government are not things mindfulness can fix.
And because the sources of burnout are primarily environmental and inherent to the current medical system, the suggestion that physicians need to fix themselves with meditation can come as a slap in the face. However, when up against a system slow to change, mindfulness can provide physicians access to the one thing they can control: How they perceive and react to what’s in front of them.
At the recommendation of an acquaintance, Dr. Wener enrolled in a Vedic Meditation (also known as Conscious Health Meditation) course taught by Light Watkins, a well-known traveling instructor, author, and speaker. By the second meeting she was successfully practicing 20 minutes twice a day. This form of mediation traces its roots to the Vedas, ancient Indian texts (also the foundation for yoga), and uses a mantra to settle the mind, transitioning to an awake state of inner contentment.
Three weeks later, Dr. Wener’s daily crying jags ended as did her propensity for road rage. “I felt like I was on the cusp of something life-changing, I just didn’t understand it,” she recalled. “But I knew I was never going to give it up.”
Defining mindfulness
“Mindfulness is being able to be present in the moment that you’re in with acceptance of what it is and without judging it,” said Donna Rockwell, PsyD, a leading mindfulness meditation teacher. The practice of mindfulness is really meditation. Dr. Rockwell explained that the noise of our mind is most often focused on either the past or the future. “We’re either bemoaning something that happened earlier or we’re catastrophizing the future,” she said, which prevents us from being present in the moment.
Meditation allows you to notice when your mind has drifted from the present moment into the past or future. “You gently notice it, label it with a lot of self-compassion, and then bring your mind back by focusing on your breath – going out, going in – and the incoming stimuli through your five senses,” said Dr. Rockwell. “When you’re doing that, you can’t be in the past or future.”
Dr. Rockwell also pointed out that we constantly categorize incoming data of the moment as either “good for me or bad for me,” which gets in the way of simply being present for what you’re facing. “When you’re more fully present, you become more skillful and able to do what this moment is asking of you,” she said. Being mindful allows us to better navigate incoming stimuli, which could be a “code blue” in the ED or a patient who needs another 2 minutes during an office visit.
When Dr. Wener was burned out, she felt unable to adapt whenever something unexpected happened. “When you have no emotional reserves, everything feels like a big deal,” she said. “The meditation gave me what we call adaptation energy; it filled up my tank and kept me from feeling like I was going to lose it at 10 o’clock in the morning.”
Dr. Rockwell explained burnout as an overactive fight or flight response activated by the amygdala. It starts pumping cortisol, our pupils dilate, and our pores open. The prefrontal cortex is offline when we’re experiencing this physiological response because they both can’t be operational at the same time. “When we’re constantly in a ‘fight or flight’ response and don’t have any access to our prefrontal cortex, we are coming from a brain that is pumping cortisol and that leads to burnout,” said Dr. Rockwell.
“Any fight or flight response leaves a mark on your body,” Dr. Wener echoed. “When we go into our state of deep rest in the meditation practice, which is two to five times more restful than sleep, it heals those stress scars.”
Making time for mindfulness
Prescribing mindfulness for physicians is not new. Molecular biologist Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD, developed Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) in 1979, a practice that incorporates mindfulness exercises to help people become familiar with their behavior patterns in stressful situations. Thus, instead of reacting, they can respond with a clearer understanding of the circumstance. Dr. Kabat-Zinn initially targeted people with chronic health problems to help them cope with the effects of pain and the condition of their illness, but it has expanded to anyone experiencing challenges in their life, including physicians. A standard MBSR course runs 8 weeks, making it a commitment for most people.
Mindfulness training requires that physicians use what they already have so little of: time.
Dr. Wener was able to take a sabbatical, embarking on a 3-month trip to India to immerse herself in the study of Vedic Meditation. Upon her return, Dr. Wener took a position at Emory University, Atlanta, and has launched a number of CME-accredited meditation courses and retreats. Unlike Dr. Kabat-Zinn, her programs are by physicians and for physicians. She also created an online version of the meditation course to make it more accessible.
For these reasons, Kara Pepper, MD, an internist in outpatient primary care in Atlanta, was drawn to the meditation course. Dr. Pepper was 7 years into practice when she burned out. “The program dovetailed into my burnout recovery,” she said. “It allowed me space to separate myself from the thoughts I was having about work and just recognize them as just that – as thoughts.”
In the course, Dr. Wener teaches the REST Technique, which she says is different than mindfulness in that she encourages the mind to run rampant. “Trying to control the mind can feel very uncomfortable because we always have thoughts,” she says. “We can’t tell the mind to stop thinking just like we can’t tell the heart to stop beating.” Dr. Wener said the REST Technique lets “the mind swim downstream,” allowing the brain to go into a deep state of rest and start to heal from the scars caused by stress.
Dr. Pepper said the self-paced online course gave her all the tools she needed, and it was pragmatic and evidence based. “I didn’t feel ‘woo’ or like another gimmick,” she said. Pepper, who continues to practice medicine, became a life coach in 2019 to teach others the skills she uses daily.
An integrated strategy
In a review published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2019, Scott Yates, MD, MBA, from the Center for Executive Medicine in Plano, Tex., found that physicians who had adopted mediation and mindfulness training to decrease anxiety and perceived work stress only experienced modest benefits. In fact, Dr. Yates claims that there’s little data to suggest the long-term benefit of any particular stress management intervention in the prevention of burnout symptoms.
“The often-repeated goals of the Triple Aim [enhancing patient experience, improving population health, and reducing costs] may be unreachable until we recognize and address burnout in health care providers,” Dr. Yates wrote. He recommends adding a fourth goal to specifically address physician wellness, which certainly could include mindfulness training and meditation.
Burnout coach, trainer, and consultant Dike Drummond, MD, also professes that physician wellness must be added as the key fourth ingredient to improving health care. “Burnout is a dilemma, a balancing act,” he said. “It takes an integrated strategy.” The CEO and founder of TheHappyMD.com, Dr. Drummond’s integrated strategy to stop physician burnout has been taught to more than 40,000 physicians in 175 organizations, and one element of that strategy can be mindfulness training.
Dr. Drummond said he doesn’t use the word meditation “because that scares most people”; it takes a commitment and isn’t accessible for a lot of doctors. Instead, he coaches doctors to use a ‘single-breath’ technique to help them reset multiple times throughout the day. “I teach people how to breathe up to the top of their head and then down to the bottom of their feet,” Dr. Drummond said. He calls it the Squeegee Breath Technique because when they exhale, they “wipe away” anything that doesn’t need to be there right now. “If you happen to have a mindfulness practice like meditation, they work synergistically because the calmness you feel in your mediation is available to you at the bottom of these releasing breaths.”
Various studies and surveys provide great detail as to the “why” of physician burnout. And while mindfulness is not the sole answer, it’s something physicians can explore for themselves while health care as an industry looks for a more comprehensive solution.
“It’s not rocket science,” Dr. Drummond insisted. “You want a different result? You’re not satisfied with the way things are now and you want to feel different? You absolutely must do something different.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2011, the Mayo Clinic began surveying physicians about burnout and found 45% of physicians experienced at least one symptom, such as emotional exhaustion, finding work no longer meaningful, feelings of ineffectiveness, and depersonalizing patients. Associated manifestations can range from headache and insomnia to impaired memory and decreased attention.
Fast forward 10 years to the Medscape National Physician Burnout and Suicide Report, which found that a similar number of physicians (42%) feel burned out. The COVID-19 pandemic only added insult to injury. A Medscape survey that included nearly 5,000 U.S. physicians revealed that about two-thirds (64%) of them reported burnout had intensified during the crisis.
These elevated numbers are being labeled as “a public health crisis” for the impact widespread physician burnout could have on the health of the doctor and patient safety. The relatively consistent levels across the decade seem to suggest that, if health organizations are attempting to improve physician well-being, it doesn’t appear to be working, forcing doctors to find solutions for themselves.
Jill Wener, MD, considers herself part of the 45% burned out 10 years ago. She was working as an internist at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, but the “existential reality of being a doctor in this world” was wearing on her. “Staying up with the literature, knowing that every day you’re going to go into work without knowing what you’re going to find, threats of lawsuits, the pressure of perfectionism,” Dr. Wener told this news organization. “By the time I hit burnout, everything made me feel like the world was crashing down on me.”
When Dr. Wener encountered someone who meditated twice a day, she was intrigued, even though the self-described “most Type-A, inside-the-box, nonspiritual type, anxious, linear-path doctor” didn’t think people like her could meditate. Dr. Wener is not alone in her hesitation to explore meditation as a means to help prevent burnout because the causes of burnout are primarily linked to external rather than internal factors. Issues including a loss of autonomy, the burden and distraction of electronic health records, and the intense pressure to comply with rules from the government are not things mindfulness can fix.
And because the sources of burnout are primarily environmental and inherent to the current medical system, the suggestion that physicians need to fix themselves with meditation can come as a slap in the face. However, when up against a system slow to change, mindfulness can provide physicians access to the one thing they can control: How they perceive and react to what’s in front of them.
At the recommendation of an acquaintance, Dr. Wener enrolled in a Vedic Meditation (also known as Conscious Health Meditation) course taught by Light Watkins, a well-known traveling instructor, author, and speaker. By the second meeting she was successfully practicing 20 minutes twice a day. This form of mediation traces its roots to the Vedas, ancient Indian texts (also the foundation for yoga), and uses a mantra to settle the mind, transitioning to an awake state of inner contentment.
Three weeks later, Dr. Wener’s daily crying jags ended as did her propensity for road rage. “I felt like I was on the cusp of something life-changing, I just didn’t understand it,” she recalled. “But I knew I was never going to give it up.”
Defining mindfulness
“Mindfulness is being able to be present in the moment that you’re in with acceptance of what it is and without judging it,” said Donna Rockwell, PsyD, a leading mindfulness meditation teacher. The practice of mindfulness is really meditation. Dr. Rockwell explained that the noise of our mind is most often focused on either the past or the future. “We’re either bemoaning something that happened earlier or we’re catastrophizing the future,” she said, which prevents us from being present in the moment.
Meditation allows you to notice when your mind has drifted from the present moment into the past or future. “You gently notice it, label it with a lot of self-compassion, and then bring your mind back by focusing on your breath – going out, going in – and the incoming stimuli through your five senses,” said Dr. Rockwell. “When you’re doing that, you can’t be in the past or future.”
Dr. Rockwell also pointed out that we constantly categorize incoming data of the moment as either “good for me or bad for me,” which gets in the way of simply being present for what you’re facing. “When you’re more fully present, you become more skillful and able to do what this moment is asking of you,” she said. Being mindful allows us to better navigate incoming stimuli, which could be a “code blue” in the ED or a patient who needs another 2 minutes during an office visit.
When Dr. Wener was burned out, she felt unable to adapt whenever something unexpected happened. “When you have no emotional reserves, everything feels like a big deal,” she said. “The meditation gave me what we call adaptation energy; it filled up my tank and kept me from feeling like I was going to lose it at 10 o’clock in the morning.”
Dr. Rockwell explained burnout as an overactive fight or flight response activated by the amygdala. It starts pumping cortisol, our pupils dilate, and our pores open. The prefrontal cortex is offline when we’re experiencing this physiological response because they both can’t be operational at the same time. “When we’re constantly in a ‘fight or flight’ response and don’t have any access to our prefrontal cortex, we are coming from a brain that is pumping cortisol and that leads to burnout,” said Dr. Rockwell.
“Any fight or flight response leaves a mark on your body,” Dr. Wener echoed. “When we go into our state of deep rest in the meditation practice, which is two to five times more restful than sleep, it heals those stress scars.”
Making time for mindfulness
Prescribing mindfulness for physicians is not new. Molecular biologist Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD, developed Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) in 1979, a practice that incorporates mindfulness exercises to help people become familiar with their behavior patterns in stressful situations. Thus, instead of reacting, they can respond with a clearer understanding of the circumstance. Dr. Kabat-Zinn initially targeted people with chronic health problems to help them cope with the effects of pain and the condition of their illness, but it has expanded to anyone experiencing challenges in their life, including physicians. A standard MBSR course runs 8 weeks, making it a commitment for most people.
Mindfulness training requires that physicians use what they already have so little of: time.
Dr. Wener was able to take a sabbatical, embarking on a 3-month trip to India to immerse herself in the study of Vedic Meditation. Upon her return, Dr. Wener took a position at Emory University, Atlanta, and has launched a number of CME-accredited meditation courses and retreats. Unlike Dr. Kabat-Zinn, her programs are by physicians and for physicians. She also created an online version of the meditation course to make it more accessible.
For these reasons, Kara Pepper, MD, an internist in outpatient primary care in Atlanta, was drawn to the meditation course. Dr. Pepper was 7 years into practice when she burned out. “The program dovetailed into my burnout recovery,” she said. “It allowed me space to separate myself from the thoughts I was having about work and just recognize them as just that – as thoughts.”
In the course, Dr. Wener teaches the REST Technique, which she says is different than mindfulness in that she encourages the mind to run rampant. “Trying to control the mind can feel very uncomfortable because we always have thoughts,” she says. “We can’t tell the mind to stop thinking just like we can’t tell the heart to stop beating.” Dr. Wener said the REST Technique lets “the mind swim downstream,” allowing the brain to go into a deep state of rest and start to heal from the scars caused by stress.
Dr. Pepper said the self-paced online course gave her all the tools she needed, and it was pragmatic and evidence based. “I didn’t feel ‘woo’ or like another gimmick,” she said. Pepper, who continues to practice medicine, became a life coach in 2019 to teach others the skills she uses daily.
An integrated strategy
In a review published in The American Journal of Medicine in 2019, Scott Yates, MD, MBA, from the Center for Executive Medicine in Plano, Tex., found that physicians who had adopted mediation and mindfulness training to decrease anxiety and perceived work stress only experienced modest benefits. In fact, Dr. Yates claims that there’s little data to suggest the long-term benefit of any particular stress management intervention in the prevention of burnout symptoms.
“The often-repeated goals of the Triple Aim [enhancing patient experience, improving population health, and reducing costs] may be unreachable until we recognize and address burnout in health care providers,” Dr. Yates wrote. He recommends adding a fourth goal to specifically address physician wellness, which certainly could include mindfulness training and meditation.
Burnout coach, trainer, and consultant Dike Drummond, MD, also professes that physician wellness must be added as the key fourth ingredient to improving health care. “Burnout is a dilemma, a balancing act,” he said. “It takes an integrated strategy.” The CEO and founder of TheHappyMD.com, Dr. Drummond’s integrated strategy to stop physician burnout has been taught to more than 40,000 physicians in 175 organizations, and one element of that strategy can be mindfulness training.
Dr. Drummond said he doesn’t use the word meditation “because that scares most people”; it takes a commitment and isn’t accessible for a lot of doctors. Instead, he coaches doctors to use a ‘single-breath’ technique to help them reset multiple times throughout the day. “I teach people how to breathe up to the top of their head and then down to the bottom of their feet,” Dr. Drummond said. He calls it the Squeegee Breath Technique because when they exhale, they “wipe away” anything that doesn’t need to be there right now. “If you happen to have a mindfulness practice like meditation, they work synergistically because the calmness you feel in your mediation is available to you at the bottom of these releasing breaths.”
Various studies and surveys provide great detail as to the “why” of physician burnout. And while mindfulness is not the sole answer, it’s something physicians can explore for themselves while health care as an industry looks for a more comprehensive solution.
“It’s not rocket science,” Dr. Drummond insisted. “You want a different result? You’re not satisfied with the way things are now and you want to feel different? You absolutely must do something different.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Intent to vaccinate kids against COVID higher among vaccinated parents
“Parental vaccine hesitancy is a major issue for schools resuming in-person instruction, potentially requiring regular testing, strict mask wearing, and physical distancing for safe operation,” wrote lead author Madhura S. Rane, PhD, from the City University of New York in New York City, and colleagues in their paper, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
The survey was conducted in June 2021 of 1,162 parents with children ranging in age from 2 to 17 years. The majority of parents (74.4%) were already vaccinated/vaccine-willing ,while 25.6% were vaccine hesitant. The study cohort, including both 1,652 children and their parents, was part of the nationwide CHASING COVID.
Vaccinated parents overall were more willing to vaccinate or had already vaccinated their eligible children when compared with vaccine-hesitant parents: 64.9% vs. 8.3% for children 2-4 years of age; 77.6% vs. 12.1% for children 5-11 years of age; 81.3% vs. 13.9% for children 12-15 years of age; and 86.4% vs. 12.7% for children 16-17 years of age; P < .001.
The researchers found greater hesitancy among Black and Hispanic parents, compared with parents who were non-Hispanic White, women, younger, and did not have a college education. Parents of children who were currently attending school remotely or only partially, were found to be more willing to vaccinate their children when compared to parents of children who were attending school fully in person.
The authors also found that parents who knew someone who had died of COVID-19 or had experienced a prior COVID-19 infection, were more willing to vaccinate their children.
Hesitance in vaccinated parents
Interestingly, 10% of COVID-vaccinated parents said they were still hesitant to vaccinate their kids because of concern for long-term adverse effects of the vaccine.
“These data point out that vaccine concerns may exist even among vaccinated or vaccine-favorable parents, so we should ask any parent who has not vaccinated their child whether we can discuss their concerns and perhaps move their opinions,” said William T. Basco Jr, MD, MS, a professor of pediatrics at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and director of the division of general pediatrics.
In an interview, when asked whether recent approval of the vaccine for children aged 5-11 will likely aid in overcoming parental hesitancy, Dr. Basco replied: “Absolutely. As more children get the vaccine and people know a neighbor or nephew or cousin, etc., who received the vaccine and did fine, it will engender greater comfort and allow parents to feel better about having their own child receive the vaccine.”
Advice for clinicians from outside expert
“We can always start by asking parents if we can help them understand the vaccine and the need for it. The tidal wave of disinformation is huge, but we can, on a daily basis, offer to help families navigate this decision,” concluded Dr. Basco, who was not involved with the new paper.
Funding for this study was provided through grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the CUNY Institute of Implementation Science in Population Health, and the COVID-19 Grant Program of the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy. The authors and Dr. Basco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
“Parental vaccine hesitancy is a major issue for schools resuming in-person instruction, potentially requiring regular testing, strict mask wearing, and physical distancing for safe operation,” wrote lead author Madhura S. Rane, PhD, from the City University of New York in New York City, and colleagues in their paper, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
The survey was conducted in June 2021 of 1,162 parents with children ranging in age from 2 to 17 years. The majority of parents (74.4%) were already vaccinated/vaccine-willing ,while 25.6% were vaccine hesitant. The study cohort, including both 1,652 children and their parents, was part of the nationwide CHASING COVID.
Vaccinated parents overall were more willing to vaccinate or had already vaccinated their eligible children when compared with vaccine-hesitant parents: 64.9% vs. 8.3% for children 2-4 years of age; 77.6% vs. 12.1% for children 5-11 years of age; 81.3% vs. 13.9% for children 12-15 years of age; and 86.4% vs. 12.7% for children 16-17 years of age; P < .001.
The researchers found greater hesitancy among Black and Hispanic parents, compared with parents who were non-Hispanic White, women, younger, and did not have a college education. Parents of children who were currently attending school remotely or only partially, were found to be more willing to vaccinate their children when compared to parents of children who were attending school fully in person.
The authors also found that parents who knew someone who had died of COVID-19 or had experienced a prior COVID-19 infection, were more willing to vaccinate their children.
Hesitance in vaccinated parents
Interestingly, 10% of COVID-vaccinated parents said they were still hesitant to vaccinate their kids because of concern for long-term adverse effects of the vaccine.
“These data point out that vaccine concerns may exist even among vaccinated or vaccine-favorable parents, so we should ask any parent who has not vaccinated their child whether we can discuss their concerns and perhaps move their opinions,” said William T. Basco Jr, MD, MS, a professor of pediatrics at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and director of the division of general pediatrics.
In an interview, when asked whether recent approval of the vaccine for children aged 5-11 will likely aid in overcoming parental hesitancy, Dr. Basco replied: “Absolutely. As more children get the vaccine and people know a neighbor or nephew or cousin, etc., who received the vaccine and did fine, it will engender greater comfort and allow parents to feel better about having their own child receive the vaccine.”
Advice for clinicians from outside expert
“We can always start by asking parents if we can help them understand the vaccine and the need for it. The tidal wave of disinformation is huge, but we can, on a daily basis, offer to help families navigate this decision,” concluded Dr. Basco, who was not involved with the new paper.
Funding for this study was provided through grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the CUNY Institute of Implementation Science in Population Health, and the COVID-19 Grant Program of the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy. The authors and Dr. Basco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
“Parental vaccine hesitancy is a major issue for schools resuming in-person instruction, potentially requiring regular testing, strict mask wearing, and physical distancing for safe operation,” wrote lead author Madhura S. Rane, PhD, from the City University of New York in New York City, and colleagues in their paper, published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
The survey was conducted in June 2021 of 1,162 parents with children ranging in age from 2 to 17 years. The majority of parents (74.4%) were already vaccinated/vaccine-willing ,while 25.6% were vaccine hesitant. The study cohort, including both 1,652 children and their parents, was part of the nationwide CHASING COVID.
Vaccinated parents overall were more willing to vaccinate or had already vaccinated their eligible children when compared with vaccine-hesitant parents: 64.9% vs. 8.3% for children 2-4 years of age; 77.6% vs. 12.1% for children 5-11 years of age; 81.3% vs. 13.9% for children 12-15 years of age; and 86.4% vs. 12.7% for children 16-17 years of age; P < .001.
The researchers found greater hesitancy among Black and Hispanic parents, compared with parents who were non-Hispanic White, women, younger, and did not have a college education. Parents of children who were currently attending school remotely or only partially, were found to be more willing to vaccinate their children when compared to parents of children who were attending school fully in person.
The authors also found that parents who knew someone who had died of COVID-19 or had experienced a prior COVID-19 infection, were more willing to vaccinate their children.
Hesitance in vaccinated parents
Interestingly, 10% of COVID-vaccinated parents said they were still hesitant to vaccinate their kids because of concern for long-term adverse effects of the vaccine.
“These data point out that vaccine concerns may exist even among vaccinated or vaccine-favorable parents, so we should ask any parent who has not vaccinated their child whether we can discuss their concerns and perhaps move their opinions,” said William T. Basco Jr, MD, MS, a professor of pediatrics at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and director of the division of general pediatrics.
In an interview, when asked whether recent approval of the vaccine for children aged 5-11 will likely aid in overcoming parental hesitancy, Dr. Basco replied: “Absolutely. As more children get the vaccine and people know a neighbor or nephew or cousin, etc., who received the vaccine and did fine, it will engender greater comfort and allow parents to feel better about having their own child receive the vaccine.”
Advice for clinicians from outside expert
“We can always start by asking parents if we can help them understand the vaccine and the need for it. The tidal wave of disinformation is huge, but we can, on a daily basis, offer to help families navigate this decision,” concluded Dr. Basco, who was not involved with the new paper.
Funding for this study was provided through grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the CUNY Institute of Implementation Science in Population Health, and the COVID-19 Grant Program of the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy. The authors and Dr. Basco have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Are physician-owned large groups better than flying solo?
Large, physician-owned group practices are gaining ground as a popular form of practice, even as the number of physicians in solo and small practices declines, and employment maintains its appeal.
As physicians shift from owning private practices to employment in hospital systems, this countertrend is also taking place. Large group practices are growing in number, even as solo and small practices are in decline.
Do large, physician-owned groups bring benefits that beat employment? And how do large groups compare with smaller practices and new opportunities, such as private equity? You’ll find some answers here.
Working in large group practices
Large group practices with 50 or more physicians are enjoying a renaissance, even though physicians are still streaming into hospital systems. The share of physicians in large practices increased from 14.7% in 2018 to 17.2% in 2020, the largest 2-year change for this group, according to the American Medical Association.
“Physicians expect that large groups will treat them better than hospitals do,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of Permanente Medical Group, the nation’s largest physicians’ group.
Compared with hospitals, “doctors would prefer working in a group practice, if all other things are equal,” says Dr. Pearl, who is now a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical School.
Large group practices can include both multispecialty groups and single-specialty groups. Groups in specialties like urology, orthopedics, and oncology have been growing in recent years, according to Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group in Virginia Beach, Va.
A group practice could also be an independent physicians association – a federation of small practices that share functions like negotiations with insurers and management. Physicians can also form larger groups for single purposes like running an accountable care organization.
Some large group practices can have a mix of partners and employees. In these groups, “some doctors either don’t want a partnership or aren’t offered one,” says Nathan Miller, CEO of the Medicus Firm, a physician recruitment company in Dallas. The AMA reports that about 10% of physicians are employees of large practices.
“Large groups like the Permanente Medical Group are not partnerships,” Dr. Pearl says. “They tend to be a corporation with a board of directors, and all the physicians are employees, but it’s a physician-led organization.”
Doctors in these groups can enjoy a great deal of control. While Permanente Medical Group is exclusively affiliated with Kaiser, which runs hospitals and an HMO, the group is an independent corporation run by its doctors, who are both shareholders and employees, Dr. Pearl says.
The Cleveland Clinic and Mayo Clinic are not medical groups in the strict sense of the word. They describe themselves as academic medical centers, but Dr. Pearl says, “Doctors have a tremendous amount of control there, particularly those in the most remunerative specialties.”
Pros of large groups
Group practices are able to focus more on the physician participants’ needs and priorities, says Mr. Mertz. “In a hospital-based organization, physicians’ needs have to compete with the needs of the hospital. … In a large group, it can be easier to get policies changed and order equipment.”
However, for many physicians, their primary reason for joining a large group is having negotiating leverage with health insurance plans, and this leverage seems even more important today. It typically results in higher reimbursements, which could translate into higher pay. The higher practice income, however, could be negated by higher administrative overhead, which is endemic in large organizations.
Mr. Mertz says large groups also have the resources to recruit new doctors. Small practices, in contrast, often decide not to grow. The practice would at first need to guarantee the salary of a new partner, which could require existing partners to take a pay cut, which they often don’t want to do. “They’ll decide to ride the practice into the ground,” which means closing it down when they retire, he says.
Cons of large groups
One individual doctor may have relatively little input in decision-making in a large group, and strong leadership may be lacking. One study examining the pros and cons of large group practices found that lack of physician cooperation, investment, and leadership were the most frequently cited barriers in large groups.
Physicians in large groups can also divide into competing factions. Mr. Mertz says rifts are more likely to take place in multispecialty groups, where higher-reimbursed proceduralists resent having to financially support lower-reimbursed primary care physicians. But it’s rare that such rifts actually break up the practice, he says.
Private practice vs. employment
Even as more physicians enter large groups, physicians continue to flee private practice in general. In 2020, the AMA found that the number of physicians in private practices had dropped nearly 5 percentage points since 2018, the largest 2-year drop recorded by the AMA.
The hardest hit are small groups of 10 physicians or fewer, once the backbone of U.S. medicine. A 2020 survey found that 53.7% of physicians still work in small practices of 10 or fewer physicians, compared with 61.4% in 2012.
Private practices tend to be partnerships, but younger physicians, for their part, often don’t want to become a partner. In a 2016 survey, only 22% of medical residents surveyed said they anticipate owning a stake in a practice someday.
What’s good about private practice?
The obvious advantage of private practice is having control. Physician-owners can choose staff, oversee finances, and decide on the direction the practice should take. They don’t have to worry about being fired, because the partnership agreement virtually guarantees each doctor’s place in the group.
The atmosphere in a small practice is often more relaxed. “Private practices tend to offer a family-like environment,” Mr. Miller says. Owners of small practices tend to have lower burnout than large practices, a 2018 study found.
Unlike hospital-employed doctors, private practitioners get to keep their ancillary income. “Physicians own the equipment and receive income generated from ancillary services, not just professional fees,” says Mr. Miller.
What’s negative about private practice?
Since small groups have little negotiating power with private payers, they can’t get favorable reimbursement rates. And while partners are protected from being fired, the practice could still go bankrupt.
Running a private practice means putting on an entrepreneurial hat. To develop a strong practice, you need to learn about marketing, finance, IT, contract negotiations, and facility management. “Most young doctors have no interest in this work,” Mr. Mertz says.
Value-based contracting has added another disadvantage for small practices. “It can be harder for small, independent groups to compete,” says Mike Belkin, JD, a divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician recruitment company based in Dallas. “They don’t have the data and integration of services that are necessary for this.”
Employment in hospital systems
More than one-third of all physicians worked for hospitals in 2018, and hospitals’ share has been growing since then. In 2020, for the first time, the AMA found that more than half of all physicians were employed, and employment is mainly a hospital phenomenon.
The trend shows no signs of stopping. In 2019 and 2020, hospitals and other corporate entities acquired 20,900 physician practices, representing 29,800 doctors. “This trend will continue,” Dr. Pearl says. “The bigger will get bigger. It’s all about market control. Everyone wants to be wider, more vertical, and more powerful.”
Pros of hospital employment
“The advantages of hospital employment are mostly financial,” Mr. Mertz says. Unlike a private practice, “there’s no financial risk to hospital employment because you don’t own it. You won’t be on the tab for any losses.”
“Hospitals usually offer a highly competitive salary with less emphasis on production than in a private practice,” he says. New physicians are typically paid a guaranteed salary in the first 1-3 years of employment.
“You don’t have any management responsibilities, as you would in a practice,” Mr. Mertz says. “The hospital has a professional management team to handle the business side. Most young doctors have no interest in this work.”
“Employed physicians have a built-in referral network at a hospital,” Mr. Miller says. This is especially an advantage for new physicians, who don’t yet have a referral network of their own.”
Cons of hospital employment
Physicians employed by a hospital lack control. “You don’t decide the hours you work, the schedules you follow, and the physical facility you work in, and, for the most part, you don’t pick your staff,” Mr. Mertz says.
Like any big organization, hospitals are bureaucratic. “If you want to purchase a new piece of equipment, your request goes up the chain of command,” Mr. Mertz says. “Your purchase has to fit into the budget.” (This can be the case with large groups, too.)
Many employed doctors chafe under this lack of control. In an earlier survey by Medscape, 45% of employed respondents didn’t like having limited influence in decision-making, and 32% said they had less control over their work or schedule.
It’s no wonder that a large percentage of physicians would rather work in practices than hospitals. According to a 2021 Medicus Firm survey, 23% of physicians are interested in working in hospitals, while 40% would rather work either in multispecialty or single-specialty groups, Mr. Miller reports.
Doctors have differing views of hospital employment
New physicians are apt to dismiss any negatives about hospitals. “Lack of autonomy often matters less to younger physicians, who were trained in team-based models,” Mr. Belkin says.
Many young doctors actually like working in a large organization. “Young doctors out of residency are used to having everything at their fingertips – labs and testing is in-house,” Mr. Mertz says.
On the other hand, doctors who were previously self-employed – a group that makes up almost one-third of all hospital-employed doctors – can often be dissatisfied with employment. In a 2014 Medscape survey, 26% of previously self-employed doctors said job satisfaction had not improved with employment.
Mr. Mertz says these doctors remember what it was like to be in charge of a practice. “If you once owned a practice, you can always compare what’s going on now with that experience, and that can make you frustrated.”
Hospitals have higher turnover
It’s much easier to leave an organization when you don’t have an ownership stake. The annual physician turnover rate at hospitals is 28%, compared with 7% at medical groups, according to a 2019 report.
Mr. Belkin says changing jobs has become a way of life for many doctors. “Staying at a job for only a few years is no longer a red flag,” he says. “Physicians are exploring different options. They might try group practice and switch to hospitals or vice versa.”
Physicians are now part of a high-turnover culture: Once in a new job, many are already thinking about the next one. A 2018 survey found that 46% of doctors planned to leave their position within 3 years.
Private equity ownership of practice
Selling majority control of your practice to a private equity firm is a relatively new phenomenon and accounts for a small share of physicians – just 4% in 2020. This trend was originally limited to certain specialties, such as anesthesiology, emergency medicine, and dermatology, but now many others are courted.
The deals work like this: Physicians sell majority control of their practice to investors in return for shares in the private equity practice, and they become employees of that practice. The private equity firm then adds more physicians to the practice and invests in infrastructure with the intention of selling the practice at a large profit, which is then shared with the original physicians.
Pros of private equity
The original owners of the practice stand to make a substantial profit if they are willing to wait several years for the practice to be built up and sold. “If they are patient, they could earn a bonanza,” Mr. Belkin says.
Private equity investment helps the practice expand. “It’s an alternative to going to the bank and borrowing money,” Mr. Mertz says.
Cons of private equity
Physicians lose control of their practice. A client of Mr. Mertz’s briefly considered a private equity offer and turned it down. “The private equity firm would have veto power over what the doctors wanted to do,” he says.
Mr. Belkin says the selling physicians typically lose income after the sale. “Money they earned from ancillary services now goes to the practice,” Mr. Belkin says. The selling doctors could potentially take up to a 30% cut in their compensation, according to Coker Capital Advisors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Large, physician-owned group practices are gaining ground as a popular form of practice, even as the number of physicians in solo and small practices declines, and employment maintains its appeal.
As physicians shift from owning private practices to employment in hospital systems, this countertrend is also taking place. Large group practices are growing in number, even as solo and small practices are in decline.
Do large, physician-owned groups bring benefits that beat employment? And how do large groups compare with smaller practices and new opportunities, such as private equity? You’ll find some answers here.
Working in large group practices
Large group practices with 50 or more physicians are enjoying a renaissance, even though physicians are still streaming into hospital systems. The share of physicians in large practices increased from 14.7% in 2018 to 17.2% in 2020, the largest 2-year change for this group, according to the American Medical Association.
“Physicians expect that large groups will treat them better than hospitals do,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of Permanente Medical Group, the nation’s largest physicians’ group.
Compared with hospitals, “doctors would prefer working in a group practice, if all other things are equal,” says Dr. Pearl, who is now a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical School.
Large group practices can include both multispecialty groups and single-specialty groups. Groups in specialties like urology, orthopedics, and oncology have been growing in recent years, according to Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group in Virginia Beach, Va.
A group practice could also be an independent physicians association – a federation of small practices that share functions like negotiations with insurers and management. Physicians can also form larger groups for single purposes like running an accountable care organization.
Some large group practices can have a mix of partners and employees. In these groups, “some doctors either don’t want a partnership or aren’t offered one,” says Nathan Miller, CEO of the Medicus Firm, a physician recruitment company in Dallas. The AMA reports that about 10% of physicians are employees of large practices.
“Large groups like the Permanente Medical Group are not partnerships,” Dr. Pearl says. “They tend to be a corporation with a board of directors, and all the physicians are employees, but it’s a physician-led organization.”
Doctors in these groups can enjoy a great deal of control. While Permanente Medical Group is exclusively affiliated with Kaiser, which runs hospitals and an HMO, the group is an independent corporation run by its doctors, who are both shareholders and employees, Dr. Pearl says.
The Cleveland Clinic and Mayo Clinic are not medical groups in the strict sense of the word. They describe themselves as academic medical centers, but Dr. Pearl says, “Doctors have a tremendous amount of control there, particularly those in the most remunerative specialties.”
Pros of large groups
Group practices are able to focus more on the physician participants’ needs and priorities, says Mr. Mertz. “In a hospital-based organization, physicians’ needs have to compete with the needs of the hospital. … In a large group, it can be easier to get policies changed and order equipment.”
However, for many physicians, their primary reason for joining a large group is having negotiating leverage with health insurance plans, and this leverage seems even more important today. It typically results in higher reimbursements, which could translate into higher pay. The higher practice income, however, could be negated by higher administrative overhead, which is endemic in large organizations.
Mr. Mertz says large groups also have the resources to recruit new doctors. Small practices, in contrast, often decide not to grow. The practice would at first need to guarantee the salary of a new partner, which could require existing partners to take a pay cut, which they often don’t want to do. “They’ll decide to ride the practice into the ground,” which means closing it down when they retire, he says.
Cons of large groups
One individual doctor may have relatively little input in decision-making in a large group, and strong leadership may be lacking. One study examining the pros and cons of large group practices found that lack of physician cooperation, investment, and leadership were the most frequently cited barriers in large groups.
Physicians in large groups can also divide into competing factions. Mr. Mertz says rifts are more likely to take place in multispecialty groups, where higher-reimbursed proceduralists resent having to financially support lower-reimbursed primary care physicians. But it’s rare that such rifts actually break up the practice, he says.
Private practice vs. employment
Even as more physicians enter large groups, physicians continue to flee private practice in general. In 2020, the AMA found that the number of physicians in private practices had dropped nearly 5 percentage points since 2018, the largest 2-year drop recorded by the AMA.
The hardest hit are small groups of 10 physicians or fewer, once the backbone of U.S. medicine. A 2020 survey found that 53.7% of physicians still work in small practices of 10 or fewer physicians, compared with 61.4% in 2012.
Private practices tend to be partnerships, but younger physicians, for their part, often don’t want to become a partner. In a 2016 survey, only 22% of medical residents surveyed said they anticipate owning a stake in a practice someday.
What’s good about private practice?
The obvious advantage of private practice is having control. Physician-owners can choose staff, oversee finances, and decide on the direction the practice should take. They don’t have to worry about being fired, because the partnership agreement virtually guarantees each doctor’s place in the group.
The atmosphere in a small practice is often more relaxed. “Private practices tend to offer a family-like environment,” Mr. Miller says. Owners of small practices tend to have lower burnout than large practices, a 2018 study found.
Unlike hospital-employed doctors, private practitioners get to keep their ancillary income. “Physicians own the equipment and receive income generated from ancillary services, not just professional fees,” says Mr. Miller.
What’s negative about private practice?
Since small groups have little negotiating power with private payers, they can’t get favorable reimbursement rates. And while partners are protected from being fired, the practice could still go bankrupt.
Running a private practice means putting on an entrepreneurial hat. To develop a strong practice, you need to learn about marketing, finance, IT, contract negotiations, and facility management. “Most young doctors have no interest in this work,” Mr. Mertz says.
Value-based contracting has added another disadvantage for small practices. “It can be harder for small, independent groups to compete,” says Mike Belkin, JD, a divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician recruitment company based in Dallas. “They don’t have the data and integration of services that are necessary for this.”
Employment in hospital systems
More than one-third of all physicians worked for hospitals in 2018, and hospitals’ share has been growing since then. In 2020, for the first time, the AMA found that more than half of all physicians were employed, and employment is mainly a hospital phenomenon.
The trend shows no signs of stopping. In 2019 and 2020, hospitals and other corporate entities acquired 20,900 physician practices, representing 29,800 doctors. “This trend will continue,” Dr. Pearl says. “The bigger will get bigger. It’s all about market control. Everyone wants to be wider, more vertical, and more powerful.”
Pros of hospital employment
“The advantages of hospital employment are mostly financial,” Mr. Mertz says. Unlike a private practice, “there’s no financial risk to hospital employment because you don’t own it. You won’t be on the tab for any losses.”
“Hospitals usually offer a highly competitive salary with less emphasis on production than in a private practice,” he says. New physicians are typically paid a guaranteed salary in the first 1-3 years of employment.
“You don’t have any management responsibilities, as you would in a practice,” Mr. Mertz says. “The hospital has a professional management team to handle the business side. Most young doctors have no interest in this work.”
“Employed physicians have a built-in referral network at a hospital,” Mr. Miller says. This is especially an advantage for new physicians, who don’t yet have a referral network of their own.”
Cons of hospital employment
Physicians employed by a hospital lack control. “You don’t decide the hours you work, the schedules you follow, and the physical facility you work in, and, for the most part, you don’t pick your staff,” Mr. Mertz says.
Like any big organization, hospitals are bureaucratic. “If you want to purchase a new piece of equipment, your request goes up the chain of command,” Mr. Mertz says. “Your purchase has to fit into the budget.” (This can be the case with large groups, too.)
Many employed doctors chafe under this lack of control. In an earlier survey by Medscape, 45% of employed respondents didn’t like having limited influence in decision-making, and 32% said they had less control over their work or schedule.
It’s no wonder that a large percentage of physicians would rather work in practices than hospitals. According to a 2021 Medicus Firm survey, 23% of physicians are interested in working in hospitals, while 40% would rather work either in multispecialty or single-specialty groups, Mr. Miller reports.
Doctors have differing views of hospital employment
New physicians are apt to dismiss any negatives about hospitals. “Lack of autonomy often matters less to younger physicians, who were trained in team-based models,” Mr. Belkin says.
Many young doctors actually like working in a large organization. “Young doctors out of residency are used to having everything at their fingertips – labs and testing is in-house,” Mr. Mertz says.
On the other hand, doctors who were previously self-employed – a group that makes up almost one-third of all hospital-employed doctors – can often be dissatisfied with employment. In a 2014 Medscape survey, 26% of previously self-employed doctors said job satisfaction had not improved with employment.
Mr. Mertz says these doctors remember what it was like to be in charge of a practice. “If you once owned a practice, you can always compare what’s going on now with that experience, and that can make you frustrated.”
Hospitals have higher turnover
It’s much easier to leave an organization when you don’t have an ownership stake. The annual physician turnover rate at hospitals is 28%, compared with 7% at medical groups, according to a 2019 report.
Mr. Belkin says changing jobs has become a way of life for many doctors. “Staying at a job for only a few years is no longer a red flag,” he says. “Physicians are exploring different options. They might try group practice and switch to hospitals or vice versa.”
Physicians are now part of a high-turnover culture: Once in a new job, many are already thinking about the next one. A 2018 survey found that 46% of doctors planned to leave their position within 3 years.
Private equity ownership of practice
Selling majority control of your practice to a private equity firm is a relatively new phenomenon and accounts for a small share of physicians – just 4% in 2020. This trend was originally limited to certain specialties, such as anesthesiology, emergency medicine, and dermatology, but now many others are courted.
The deals work like this: Physicians sell majority control of their practice to investors in return for shares in the private equity practice, and they become employees of that practice. The private equity firm then adds more physicians to the practice and invests in infrastructure with the intention of selling the practice at a large profit, which is then shared with the original physicians.
Pros of private equity
The original owners of the practice stand to make a substantial profit if they are willing to wait several years for the practice to be built up and sold. “If they are patient, they could earn a bonanza,” Mr. Belkin says.
Private equity investment helps the practice expand. “It’s an alternative to going to the bank and borrowing money,” Mr. Mertz says.
Cons of private equity
Physicians lose control of their practice. A client of Mr. Mertz’s briefly considered a private equity offer and turned it down. “The private equity firm would have veto power over what the doctors wanted to do,” he says.
Mr. Belkin says the selling physicians typically lose income after the sale. “Money they earned from ancillary services now goes to the practice,” Mr. Belkin says. The selling doctors could potentially take up to a 30% cut in their compensation, according to Coker Capital Advisors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Large, physician-owned group practices are gaining ground as a popular form of practice, even as the number of physicians in solo and small practices declines, and employment maintains its appeal.
As physicians shift from owning private practices to employment in hospital systems, this countertrend is also taking place. Large group practices are growing in number, even as solo and small practices are in decline.
Do large, physician-owned groups bring benefits that beat employment? And how do large groups compare with smaller practices and new opportunities, such as private equity? You’ll find some answers here.
Working in large group practices
Large group practices with 50 or more physicians are enjoying a renaissance, even though physicians are still streaming into hospital systems. The share of physicians in large practices increased from 14.7% in 2018 to 17.2% in 2020, the largest 2-year change for this group, according to the American Medical Association.
“Physicians expect that large groups will treat them better than hospitals do,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of Permanente Medical Group, the nation’s largest physicians’ group.
Compared with hospitals, “doctors would prefer working in a group practice, if all other things are equal,” says Dr. Pearl, who is now a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University Medical School.
Large group practices can include both multispecialty groups and single-specialty groups. Groups in specialties like urology, orthopedics, and oncology have been growing in recent years, according to Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group in Virginia Beach, Va.
A group practice could also be an independent physicians association – a federation of small practices that share functions like negotiations with insurers and management. Physicians can also form larger groups for single purposes like running an accountable care organization.
Some large group practices can have a mix of partners and employees. In these groups, “some doctors either don’t want a partnership or aren’t offered one,” says Nathan Miller, CEO of the Medicus Firm, a physician recruitment company in Dallas. The AMA reports that about 10% of physicians are employees of large practices.
“Large groups like the Permanente Medical Group are not partnerships,” Dr. Pearl says. “They tend to be a corporation with a board of directors, and all the physicians are employees, but it’s a physician-led organization.”
Doctors in these groups can enjoy a great deal of control. While Permanente Medical Group is exclusively affiliated with Kaiser, which runs hospitals and an HMO, the group is an independent corporation run by its doctors, who are both shareholders and employees, Dr. Pearl says.
The Cleveland Clinic and Mayo Clinic are not medical groups in the strict sense of the word. They describe themselves as academic medical centers, but Dr. Pearl says, “Doctors have a tremendous amount of control there, particularly those in the most remunerative specialties.”
Pros of large groups
Group practices are able to focus more on the physician participants’ needs and priorities, says Mr. Mertz. “In a hospital-based organization, physicians’ needs have to compete with the needs of the hospital. … In a large group, it can be easier to get policies changed and order equipment.”
However, for many physicians, their primary reason for joining a large group is having negotiating leverage with health insurance plans, and this leverage seems even more important today. It typically results in higher reimbursements, which could translate into higher pay. The higher practice income, however, could be negated by higher administrative overhead, which is endemic in large organizations.
Mr. Mertz says large groups also have the resources to recruit new doctors. Small practices, in contrast, often decide not to grow. The practice would at first need to guarantee the salary of a new partner, which could require existing partners to take a pay cut, which they often don’t want to do. “They’ll decide to ride the practice into the ground,” which means closing it down when they retire, he says.
Cons of large groups
One individual doctor may have relatively little input in decision-making in a large group, and strong leadership may be lacking. One study examining the pros and cons of large group practices found that lack of physician cooperation, investment, and leadership were the most frequently cited barriers in large groups.
Physicians in large groups can also divide into competing factions. Mr. Mertz says rifts are more likely to take place in multispecialty groups, where higher-reimbursed proceduralists resent having to financially support lower-reimbursed primary care physicians. But it’s rare that such rifts actually break up the practice, he says.
Private practice vs. employment
Even as more physicians enter large groups, physicians continue to flee private practice in general. In 2020, the AMA found that the number of physicians in private practices had dropped nearly 5 percentage points since 2018, the largest 2-year drop recorded by the AMA.
The hardest hit are small groups of 10 physicians or fewer, once the backbone of U.S. medicine. A 2020 survey found that 53.7% of physicians still work in small practices of 10 or fewer physicians, compared with 61.4% in 2012.
Private practices tend to be partnerships, but younger physicians, for their part, often don’t want to become a partner. In a 2016 survey, only 22% of medical residents surveyed said they anticipate owning a stake in a practice someday.
What’s good about private practice?
The obvious advantage of private practice is having control. Physician-owners can choose staff, oversee finances, and decide on the direction the practice should take. They don’t have to worry about being fired, because the partnership agreement virtually guarantees each doctor’s place in the group.
The atmosphere in a small practice is often more relaxed. “Private practices tend to offer a family-like environment,” Mr. Miller says. Owners of small practices tend to have lower burnout than large practices, a 2018 study found.
Unlike hospital-employed doctors, private practitioners get to keep their ancillary income. “Physicians own the equipment and receive income generated from ancillary services, not just professional fees,” says Mr. Miller.
What’s negative about private practice?
Since small groups have little negotiating power with private payers, they can’t get favorable reimbursement rates. And while partners are protected from being fired, the practice could still go bankrupt.
Running a private practice means putting on an entrepreneurial hat. To develop a strong practice, you need to learn about marketing, finance, IT, contract negotiations, and facility management. “Most young doctors have no interest in this work,” Mr. Mertz says.
Value-based contracting has added another disadvantage for small practices. “It can be harder for small, independent groups to compete,” says Mike Belkin, JD, a divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins, a physician recruitment company based in Dallas. “They don’t have the data and integration of services that are necessary for this.”
Employment in hospital systems
More than one-third of all physicians worked for hospitals in 2018, and hospitals’ share has been growing since then. In 2020, for the first time, the AMA found that more than half of all physicians were employed, and employment is mainly a hospital phenomenon.
The trend shows no signs of stopping. In 2019 and 2020, hospitals and other corporate entities acquired 20,900 physician practices, representing 29,800 doctors. “This trend will continue,” Dr. Pearl says. “The bigger will get bigger. It’s all about market control. Everyone wants to be wider, more vertical, and more powerful.”
Pros of hospital employment
“The advantages of hospital employment are mostly financial,” Mr. Mertz says. Unlike a private practice, “there’s no financial risk to hospital employment because you don’t own it. You won’t be on the tab for any losses.”
“Hospitals usually offer a highly competitive salary with less emphasis on production than in a private practice,” he says. New physicians are typically paid a guaranteed salary in the first 1-3 years of employment.
“You don’t have any management responsibilities, as you would in a practice,” Mr. Mertz says. “The hospital has a professional management team to handle the business side. Most young doctors have no interest in this work.”
“Employed physicians have a built-in referral network at a hospital,” Mr. Miller says. This is especially an advantage for new physicians, who don’t yet have a referral network of their own.”
Cons of hospital employment
Physicians employed by a hospital lack control. “You don’t decide the hours you work, the schedules you follow, and the physical facility you work in, and, for the most part, you don’t pick your staff,” Mr. Mertz says.
Like any big organization, hospitals are bureaucratic. “If you want to purchase a new piece of equipment, your request goes up the chain of command,” Mr. Mertz says. “Your purchase has to fit into the budget.” (This can be the case with large groups, too.)
Many employed doctors chafe under this lack of control. In an earlier survey by Medscape, 45% of employed respondents didn’t like having limited influence in decision-making, and 32% said they had less control over their work or schedule.
It’s no wonder that a large percentage of physicians would rather work in practices than hospitals. According to a 2021 Medicus Firm survey, 23% of physicians are interested in working in hospitals, while 40% would rather work either in multispecialty or single-specialty groups, Mr. Miller reports.
Doctors have differing views of hospital employment
New physicians are apt to dismiss any negatives about hospitals. “Lack of autonomy often matters less to younger physicians, who were trained in team-based models,” Mr. Belkin says.
Many young doctors actually like working in a large organization. “Young doctors out of residency are used to having everything at their fingertips – labs and testing is in-house,” Mr. Mertz says.
On the other hand, doctors who were previously self-employed – a group that makes up almost one-third of all hospital-employed doctors – can often be dissatisfied with employment. In a 2014 Medscape survey, 26% of previously self-employed doctors said job satisfaction had not improved with employment.
Mr. Mertz says these doctors remember what it was like to be in charge of a practice. “If you once owned a practice, you can always compare what’s going on now with that experience, and that can make you frustrated.”
Hospitals have higher turnover
It’s much easier to leave an organization when you don’t have an ownership stake. The annual physician turnover rate at hospitals is 28%, compared with 7% at medical groups, according to a 2019 report.
Mr. Belkin says changing jobs has become a way of life for many doctors. “Staying at a job for only a few years is no longer a red flag,” he says. “Physicians are exploring different options. They might try group practice and switch to hospitals or vice versa.”
Physicians are now part of a high-turnover culture: Once in a new job, many are already thinking about the next one. A 2018 survey found that 46% of doctors planned to leave their position within 3 years.
Private equity ownership of practice
Selling majority control of your practice to a private equity firm is a relatively new phenomenon and accounts for a small share of physicians – just 4% in 2020. This trend was originally limited to certain specialties, such as anesthesiology, emergency medicine, and dermatology, but now many others are courted.
The deals work like this: Physicians sell majority control of their practice to investors in return for shares in the private equity practice, and they become employees of that practice. The private equity firm then adds more physicians to the practice and invests in infrastructure with the intention of selling the practice at a large profit, which is then shared with the original physicians.
Pros of private equity
The original owners of the practice stand to make a substantial profit if they are willing to wait several years for the practice to be built up and sold. “If they are patient, they could earn a bonanza,” Mr. Belkin says.
Private equity investment helps the practice expand. “It’s an alternative to going to the bank and borrowing money,” Mr. Mertz says.
Cons of private equity
Physicians lose control of their practice. A client of Mr. Mertz’s briefly considered a private equity offer and turned it down. “The private equity firm would have veto power over what the doctors wanted to do,” he says.
Mr. Belkin says the selling physicians typically lose income after the sale. “Money they earned from ancillary services now goes to the practice,” Mr. Belkin says. The selling doctors could potentially take up to a 30% cut in their compensation, according to Coker Capital Advisors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AMA president calls on Congress to stabilize Medicare payments to physicians
Physician practices around the country took an unprecedented financial hit with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020. Recent research from the American Medical Association reveals an estimated pandemic-related shortfall in Medicare physician fee spending of $13.9 billion, or a 14% reduction, across all states and all major specialties in 2020.
While the report pointed to a “strong recovery” in May and June, that recovery stalled in the second half of 2020, and spending never returned to pre–COVID-19 levels.
“Physicians experienced a significant and sustained drop in Medicare revenue during the first 10 months of the pandemic,” said AMA President Gerald Harmon, MD, in a statement. “Medical practices that have not buckled under financial strain continue to be stretched clinically, emotionally, and fiscally as the pandemic persists. Yet physicians face an array of planned cuts that would reduce Medicare physician payments by nearly 10% for 2022.”
The reduction in the Medicare physician fee schedule payments means providers may face payment cuts of more than 9% starting Jan. 1, 2022, when the cuts take effect. That is, unless Congress makes changes.
Medicare physician fee schedule spending on telehealth stood at $4.1 billion, or 5% of the total Medicare spent in 2020. From March 16 to June 30, $1.8 billion of this amount was on telehealth, while $1.1 billion came in during third and fourth quarters of 2020, respectively, per the report.
According to AMA’s research:
- Medicare physician fee schedule spending for 2020, relative to expected 2020 spending, dipped 32% between March 16 and June 30; spending was down during the last 6 months of the year by between 9% and 10%.
- The care settings hit the worst were ambulatory surgical centers, outpatient hospitals, and physician offices; the next worst off were hospital emergency departments, inpatient hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities.
- The specialties that fared worst included physical therapists (-28%), opthamologists (-19%), podiatrists (-18%), and dermatologists (-18%).
- Cumulative spending was down the most in Minnesota (-22%), Maine (-19%), and New York (-19%); less affected states included Idaho (-9%), Oklahoma (-9%), and South Carolina (9%).
AMA: Budget neutrality hurting physicians’ financial stability
Dr. Harmon is calling for financial stability in Medicare spending. In particular, the AMA is “strongly urging Congress to avert the planned payment cuts,” he said in a statement.
The challenge: The Medicare physician fee schedule is currently “budget neutral,” meaning that the budget is fixed, Dr. Harmon, a family medicine specialist in South Carolina, told this news organization.
“If you rob from Peter to pay Paul, Paul is going to be less efficient or less rewarded. It continues to be that there’s always a ‘pay for’ in these things. So budget neutrality is probably one of the first things we need to address,” he said.
Lack of routine care expected to affect health outcomes
The result of reduced screening and treatment during the pandemic could be as many as 10,000 excess deaths due to cancers of the breast and colon during the next 10 years, wrote Norman Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, in Science in June. Combined, breast cancer and colon cancer account for one-sixth of all cancers in the U.S., he wrote.
In addition, blood pressure control has gotten worse since the start of the pandemic, said Michael Rakotz, MD, FAHA, FAAFP, vice president of improving health outcomes at the AMA, in an AMA blog post.
Dr. Harmon’s advice for physician practices on getting patients in for routine care:
- Educate the area’s largest employers to encourage their employees.
- Engage with hospital employees, since hospitals are often the largest employers in many communities.
- Partner with health insurers.
- Show up at athletic events, which is a particularly good fit for “small town America,” said Dr. Harmon.
The AMA’s research doesn’t consider reimbursement from other public and private payers. It also doesn’t account for funding sources such as Provider Relief Fund grants, Paycheck Protection Program loans, and the temporary suspension of the Medicare sequester, per the report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician practices around the country took an unprecedented financial hit with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020. Recent research from the American Medical Association reveals an estimated pandemic-related shortfall in Medicare physician fee spending of $13.9 billion, or a 14% reduction, across all states and all major specialties in 2020.
While the report pointed to a “strong recovery” in May and June, that recovery stalled in the second half of 2020, and spending never returned to pre–COVID-19 levels.
“Physicians experienced a significant and sustained drop in Medicare revenue during the first 10 months of the pandemic,” said AMA President Gerald Harmon, MD, in a statement. “Medical practices that have not buckled under financial strain continue to be stretched clinically, emotionally, and fiscally as the pandemic persists. Yet physicians face an array of planned cuts that would reduce Medicare physician payments by nearly 10% for 2022.”
The reduction in the Medicare physician fee schedule payments means providers may face payment cuts of more than 9% starting Jan. 1, 2022, when the cuts take effect. That is, unless Congress makes changes.
Medicare physician fee schedule spending on telehealth stood at $4.1 billion, or 5% of the total Medicare spent in 2020. From March 16 to June 30, $1.8 billion of this amount was on telehealth, while $1.1 billion came in during third and fourth quarters of 2020, respectively, per the report.
According to AMA’s research:
- Medicare physician fee schedule spending for 2020, relative to expected 2020 spending, dipped 32% between March 16 and June 30; spending was down during the last 6 months of the year by between 9% and 10%.
- The care settings hit the worst were ambulatory surgical centers, outpatient hospitals, and physician offices; the next worst off were hospital emergency departments, inpatient hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities.
- The specialties that fared worst included physical therapists (-28%), opthamologists (-19%), podiatrists (-18%), and dermatologists (-18%).
- Cumulative spending was down the most in Minnesota (-22%), Maine (-19%), and New York (-19%); less affected states included Idaho (-9%), Oklahoma (-9%), and South Carolina (9%).
AMA: Budget neutrality hurting physicians’ financial stability
Dr. Harmon is calling for financial stability in Medicare spending. In particular, the AMA is “strongly urging Congress to avert the planned payment cuts,” he said in a statement.
The challenge: The Medicare physician fee schedule is currently “budget neutral,” meaning that the budget is fixed, Dr. Harmon, a family medicine specialist in South Carolina, told this news organization.
“If you rob from Peter to pay Paul, Paul is going to be less efficient or less rewarded. It continues to be that there’s always a ‘pay for’ in these things. So budget neutrality is probably one of the first things we need to address,” he said.
Lack of routine care expected to affect health outcomes
The result of reduced screening and treatment during the pandemic could be as many as 10,000 excess deaths due to cancers of the breast and colon during the next 10 years, wrote Norman Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, in Science in June. Combined, breast cancer and colon cancer account for one-sixth of all cancers in the U.S., he wrote.
In addition, blood pressure control has gotten worse since the start of the pandemic, said Michael Rakotz, MD, FAHA, FAAFP, vice president of improving health outcomes at the AMA, in an AMA blog post.
Dr. Harmon’s advice for physician practices on getting patients in for routine care:
- Educate the area’s largest employers to encourage their employees.
- Engage with hospital employees, since hospitals are often the largest employers in many communities.
- Partner with health insurers.
- Show up at athletic events, which is a particularly good fit for “small town America,” said Dr. Harmon.
The AMA’s research doesn’t consider reimbursement from other public and private payers. It also doesn’t account for funding sources such as Provider Relief Fund grants, Paycheck Protection Program loans, and the temporary suspension of the Medicare sequester, per the report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician practices around the country took an unprecedented financial hit with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020. Recent research from the American Medical Association reveals an estimated pandemic-related shortfall in Medicare physician fee spending of $13.9 billion, or a 14% reduction, across all states and all major specialties in 2020.
While the report pointed to a “strong recovery” in May and June, that recovery stalled in the second half of 2020, and spending never returned to pre–COVID-19 levels.
“Physicians experienced a significant and sustained drop in Medicare revenue during the first 10 months of the pandemic,” said AMA President Gerald Harmon, MD, in a statement. “Medical practices that have not buckled under financial strain continue to be stretched clinically, emotionally, and fiscally as the pandemic persists. Yet physicians face an array of planned cuts that would reduce Medicare physician payments by nearly 10% for 2022.”
The reduction in the Medicare physician fee schedule payments means providers may face payment cuts of more than 9% starting Jan. 1, 2022, when the cuts take effect. That is, unless Congress makes changes.
Medicare physician fee schedule spending on telehealth stood at $4.1 billion, or 5% of the total Medicare spent in 2020. From March 16 to June 30, $1.8 billion of this amount was on telehealth, while $1.1 billion came in during third and fourth quarters of 2020, respectively, per the report.
According to AMA’s research:
- Medicare physician fee schedule spending for 2020, relative to expected 2020 spending, dipped 32% between March 16 and June 30; spending was down during the last 6 months of the year by between 9% and 10%.
- The care settings hit the worst were ambulatory surgical centers, outpatient hospitals, and physician offices; the next worst off were hospital emergency departments, inpatient hospitals, and skilled nursing facilities.
- The specialties that fared worst included physical therapists (-28%), opthamologists (-19%), podiatrists (-18%), and dermatologists (-18%).
- Cumulative spending was down the most in Minnesota (-22%), Maine (-19%), and New York (-19%); less affected states included Idaho (-9%), Oklahoma (-9%), and South Carolina (9%).
AMA: Budget neutrality hurting physicians’ financial stability
Dr. Harmon is calling for financial stability in Medicare spending. In particular, the AMA is “strongly urging Congress to avert the planned payment cuts,” he said in a statement.
The challenge: The Medicare physician fee schedule is currently “budget neutral,” meaning that the budget is fixed, Dr. Harmon, a family medicine specialist in South Carolina, told this news organization.
“If you rob from Peter to pay Paul, Paul is going to be less efficient or less rewarded. It continues to be that there’s always a ‘pay for’ in these things. So budget neutrality is probably one of the first things we need to address,” he said.
Lack of routine care expected to affect health outcomes
The result of reduced screening and treatment during the pandemic could be as many as 10,000 excess deaths due to cancers of the breast and colon during the next 10 years, wrote Norman Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, in Science in June. Combined, breast cancer and colon cancer account for one-sixth of all cancers in the U.S., he wrote.
In addition, blood pressure control has gotten worse since the start of the pandemic, said Michael Rakotz, MD, FAHA, FAAFP, vice president of improving health outcomes at the AMA, in an AMA blog post.
Dr. Harmon’s advice for physician practices on getting patients in for routine care:
- Educate the area’s largest employers to encourage their employees.
- Engage with hospital employees, since hospitals are often the largest employers in many communities.
- Partner with health insurers.
- Show up at athletic events, which is a particularly good fit for “small town America,” said Dr. Harmon.
The AMA’s research doesn’t consider reimbursement from other public and private payers. It also doesn’t account for funding sources such as Provider Relief Fund grants, Paycheck Protection Program loans, and the temporary suspension of the Medicare sequester, per the report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians may be overprescribing immunotherapy for unfit cancer patients
.
The study, by Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor of medical ethics and health policy and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, is an analysis of patient data from 280 U.S.-based community oncology practices. It included 34,131 patients who received first-line systemic therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), or other treatment, between January 2014 and December 2019 for newly diagnosed metastatic or recurrent non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), urothelial cell cancer (UCC), renal cell cancer (RCC), or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers examined survival outcomes between patients who were eligible to participate in clinical trials with those who were deemed ineligible but may have still received ICIs.
For patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction, participating in randomized clinical trials for immune checkpoint inhibitors is largely out of reach because of advanced disease, but it is not unusual for these patients to be accepted into clinical trials, a decision sometimes referred to as “desperation oncology,” the authors wrote.
In this study of 34,131 patients, 9,318 were considered ineligible to participate in ICI clinical trials because of advanced disease or organ dysfunction, yet up to 30% of these patients were treated with ICIs by their physician outside of a clinical trial. Dr. Parikh and colleagues found no overall survival differences between patients deemed ineligible for clinical trials, but were ultimately treated with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy, or other treatments at 12 and 36 months. In fact, ICI monotherapy appeared to be harmful within 6 months of starting treatment.
“Clinicians who care for patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction should be cautious about ICI use and carefully weigh expected survival gains against the potential for early mortality and adverse effects,” the authors wrote. They found the efficacy of ICI treatment alone, or in combination with other treatment, can be worse among trial-ineligible patients than patients who met the criteria for clinical trials.
No survival benefit was found for trial-ineligible patients who were treated with ICI monotherapy or combination therapy. Overall survival rates were similar at 12 and 36 months for both treatment groups. The overall median survival was less than 10 months, but 40% of trial ineligible patients treated with ICIs died within 6 months.
The use of ICIs for patients with poor performance status was found to be associated with lower hospice enrollment, more inpatient deaths, and more treatment during the last month of life. “It is critical to ensure that vulnerable, trial-ineligible patients are not exposed to non–evidence-based therapies that could cause harm and contradict patient goals,” the authors wrote.
The harms of treating unfit patients
The use of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in trial-ineligible patients is concerning, the authors said, because for patients with UCC and NSCLC, the standard of care is platinum-based chemotherapy. For patients with HCC and RCC, the standard of care is oral anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Immune checkpoint inhibitors may be prescribed in these cases to avoid side effects associated with other therapies, despite the lack of evidence showing that ICIs are effective in these cases.
“Individuals with poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction are vulnerable to receiving treatments that may not benefit them or cause disproportionately high side effects,” Dr. Parikh said in an interview. “Immunotherapy causes fewer side effects overall and is an attractive option, but there is no good phase 3 evidence that immunotherapy has benefits in this population.
“Physicians are preferentially using immunotherapy for unfit patients despite the fact that these individuals are usually excluded from clinical trials. Trial-ineligible patients – despite making up 30% of the cancer population – are different from patients studied in clinical trials. They are generally sicker, older and more prone to treatment adverse effects (including death), However, excluding these groups means that we don’t have good data on what treatments could benefit this vulnerable group. Thus, we are usually left to extrapolating results from healthier patients to unhealthy patients which risks giving them the wrong treatment,” he said.
A review that looked at immunotherapy in older adults suggested that, while those aged 65 or older represent most cancer patients, they are under-represented in clinical trials, including studies that led to approval of immunotherapy agents. A 2019 report suggested that, while 11 pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials have estimated the activity of ICIs in locally advanced and advanced NSCLC, each trial excluded patients with poor performance status.
Phase 3 trials needed for patients with poor performance
This retrospective study included 34,131 patients (median age, 70 years; 42% women) of which 27.3% had poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction and were classed as trial ineligible. The researchers assessed the use and overall survival outcomes following first-line ICI and non-ICI therapy that was initiated from January 2014 through December 2019.
Over the course of the study, the proportion of patients receiving ICI monotherapy increased from 0%-30.2% among trial-ineligible patients and from 0.1%-19.4% among eligible patients. However, among trial-ineligible patients, there were no overall survival differences between treatment with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy and non-ICI therapy at 12 and 36 months.
Among trial-ineligible patients, ICI use was linked to a 14%-19% greater risk of death during the first 6 months after ICI initiation, but a 20% lower risk of death among those who survived 6 months after ICI initiation. Further, ICI combination therapy was associated with potential early harm among trial-ineligible patients.
“Phase 3 trials are sorely needed in patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction so that we can adequately counsel patients who are unfit about expectations with novel cancer therapies,” Dr. Parikh said.
The cohort only included patients who received systemic therapy, which is a limitation of the study, so conclusions cannot be made about the efficacy of systemic therapy versus no systemic therapy in trial-ineligible patients.
Dr. Parikh reported nonfinancial support from Flatiron Health, grants from Humana, personal fees and equity from GNS Healthcare and Onc.AI, along with personal fees from the Cancer Study Group and Nanology outside the submitted work.
.
The study, by Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor of medical ethics and health policy and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, is an analysis of patient data from 280 U.S.-based community oncology practices. It included 34,131 patients who received first-line systemic therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), or other treatment, between January 2014 and December 2019 for newly diagnosed metastatic or recurrent non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), urothelial cell cancer (UCC), renal cell cancer (RCC), or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers examined survival outcomes between patients who were eligible to participate in clinical trials with those who were deemed ineligible but may have still received ICIs.
For patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction, participating in randomized clinical trials for immune checkpoint inhibitors is largely out of reach because of advanced disease, but it is not unusual for these patients to be accepted into clinical trials, a decision sometimes referred to as “desperation oncology,” the authors wrote.
In this study of 34,131 patients, 9,318 were considered ineligible to participate in ICI clinical trials because of advanced disease or organ dysfunction, yet up to 30% of these patients were treated with ICIs by their physician outside of a clinical trial. Dr. Parikh and colleagues found no overall survival differences between patients deemed ineligible for clinical trials, but were ultimately treated with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy, or other treatments at 12 and 36 months. In fact, ICI monotherapy appeared to be harmful within 6 months of starting treatment.
“Clinicians who care for patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction should be cautious about ICI use and carefully weigh expected survival gains against the potential for early mortality and adverse effects,” the authors wrote. They found the efficacy of ICI treatment alone, or in combination with other treatment, can be worse among trial-ineligible patients than patients who met the criteria for clinical trials.
No survival benefit was found for trial-ineligible patients who were treated with ICI monotherapy or combination therapy. Overall survival rates were similar at 12 and 36 months for both treatment groups. The overall median survival was less than 10 months, but 40% of trial ineligible patients treated with ICIs died within 6 months.
The use of ICIs for patients with poor performance status was found to be associated with lower hospice enrollment, more inpatient deaths, and more treatment during the last month of life. “It is critical to ensure that vulnerable, trial-ineligible patients are not exposed to non–evidence-based therapies that could cause harm and contradict patient goals,” the authors wrote.
The harms of treating unfit patients
The use of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in trial-ineligible patients is concerning, the authors said, because for patients with UCC and NSCLC, the standard of care is platinum-based chemotherapy. For patients with HCC and RCC, the standard of care is oral anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Immune checkpoint inhibitors may be prescribed in these cases to avoid side effects associated with other therapies, despite the lack of evidence showing that ICIs are effective in these cases.
“Individuals with poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction are vulnerable to receiving treatments that may not benefit them or cause disproportionately high side effects,” Dr. Parikh said in an interview. “Immunotherapy causes fewer side effects overall and is an attractive option, but there is no good phase 3 evidence that immunotherapy has benefits in this population.
“Physicians are preferentially using immunotherapy for unfit patients despite the fact that these individuals are usually excluded from clinical trials. Trial-ineligible patients – despite making up 30% of the cancer population – are different from patients studied in clinical trials. They are generally sicker, older and more prone to treatment adverse effects (including death), However, excluding these groups means that we don’t have good data on what treatments could benefit this vulnerable group. Thus, we are usually left to extrapolating results from healthier patients to unhealthy patients which risks giving them the wrong treatment,” he said.
A review that looked at immunotherapy in older adults suggested that, while those aged 65 or older represent most cancer patients, they are under-represented in clinical trials, including studies that led to approval of immunotherapy agents. A 2019 report suggested that, while 11 pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials have estimated the activity of ICIs in locally advanced and advanced NSCLC, each trial excluded patients with poor performance status.
Phase 3 trials needed for patients with poor performance
This retrospective study included 34,131 patients (median age, 70 years; 42% women) of which 27.3% had poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction and were classed as trial ineligible. The researchers assessed the use and overall survival outcomes following first-line ICI and non-ICI therapy that was initiated from January 2014 through December 2019.
Over the course of the study, the proportion of patients receiving ICI monotherapy increased from 0%-30.2% among trial-ineligible patients and from 0.1%-19.4% among eligible patients. However, among trial-ineligible patients, there were no overall survival differences between treatment with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy and non-ICI therapy at 12 and 36 months.
Among trial-ineligible patients, ICI use was linked to a 14%-19% greater risk of death during the first 6 months after ICI initiation, but a 20% lower risk of death among those who survived 6 months after ICI initiation. Further, ICI combination therapy was associated with potential early harm among trial-ineligible patients.
“Phase 3 trials are sorely needed in patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction so that we can adequately counsel patients who are unfit about expectations with novel cancer therapies,” Dr. Parikh said.
The cohort only included patients who received systemic therapy, which is a limitation of the study, so conclusions cannot be made about the efficacy of systemic therapy versus no systemic therapy in trial-ineligible patients.
Dr. Parikh reported nonfinancial support from Flatiron Health, grants from Humana, personal fees and equity from GNS Healthcare and Onc.AI, along with personal fees from the Cancer Study Group and Nanology outside the submitted work.
.
The study, by Ravi B. Parikh, MD, an assistant professor of medical ethics and health policy and medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, is an analysis of patient data from 280 U.S.-based community oncology practices. It included 34,131 patients who received first-line systemic therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), or other treatment, between January 2014 and December 2019 for newly diagnosed metastatic or recurrent non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), urothelial cell cancer (UCC), renal cell cancer (RCC), or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers examined survival outcomes between patients who were eligible to participate in clinical trials with those who were deemed ineligible but may have still received ICIs.
For patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction, participating in randomized clinical trials for immune checkpoint inhibitors is largely out of reach because of advanced disease, but it is not unusual for these patients to be accepted into clinical trials, a decision sometimes referred to as “desperation oncology,” the authors wrote.
In this study of 34,131 patients, 9,318 were considered ineligible to participate in ICI clinical trials because of advanced disease or organ dysfunction, yet up to 30% of these patients were treated with ICIs by their physician outside of a clinical trial. Dr. Parikh and colleagues found no overall survival differences between patients deemed ineligible for clinical trials, but were ultimately treated with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy, or other treatments at 12 and 36 months. In fact, ICI monotherapy appeared to be harmful within 6 months of starting treatment.
“Clinicians who care for patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction should be cautious about ICI use and carefully weigh expected survival gains against the potential for early mortality and adverse effects,” the authors wrote. They found the efficacy of ICI treatment alone, or in combination with other treatment, can be worse among trial-ineligible patients than patients who met the criteria for clinical trials.
No survival benefit was found for trial-ineligible patients who were treated with ICI monotherapy or combination therapy. Overall survival rates were similar at 12 and 36 months for both treatment groups. The overall median survival was less than 10 months, but 40% of trial ineligible patients treated with ICIs died within 6 months.
The use of ICIs for patients with poor performance status was found to be associated with lower hospice enrollment, more inpatient deaths, and more treatment during the last month of life. “It is critical to ensure that vulnerable, trial-ineligible patients are not exposed to non–evidence-based therapies that could cause harm and contradict patient goals,” the authors wrote.
The harms of treating unfit patients
The use of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in trial-ineligible patients is concerning, the authors said, because for patients with UCC and NSCLC, the standard of care is platinum-based chemotherapy. For patients with HCC and RCC, the standard of care is oral anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Immune checkpoint inhibitors may be prescribed in these cases to avoid side effects associated with other therapies, despite the lack of evidence showing that ICIs are effective in these cases.
“Individuals with poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction are vulnerable to receiving treatments that may not benefit them or cause disproportionately high side effects,” Dr. Parikh said in an interview. “Immunotherapy causes fewer side effects overall and is an attractive option, but there is no good phase 3 evidence that immunotherapy has benefits in this population.
“Physicians are preferentially using immunotherapy for unfit patients despite the fact that these individuals are usually excluded from clinical trials. Trial-ineligible patients – despite making up 30% of the cancer population – are different from patients studied in clinical trials. They are generally sicker, older and more prone to treatment adverse effects (including death), However, excluding these groups means that we don’t have good data on what treatments could benefit this vulnerable group. Thus, we are usually left to extrapolating results from healthier patients to unhealthy patients which risks giving them the wrong treatment,” he said.
A review that looked at immunotherapy in older adults suggested that, while those aged 65 or older represent most cancer patients, they are under-represented in clinical trials, including studies that led to approval of immunotherapy agents. A 2019 report suggested that, while 11 pivotal phase 3, randomized clinical trials have estimated the activity of ICIs in locally advanced and advanced NSCLC, each trial excluded patients with poor performance status.
Phase 3 trials needed for patients with poor performance
This retrospective study included 34,131 patients (median age, 70 years; 42% women) of which 27.3% had poor performance status and/or organ dysfunction and were classed as trial ineligible. The researchers assessed the use and overall survival outcomes following first-line ICI and non-ICI therapy that was initiated from January 2014 through December 2019.
Over the course of the study, the proportion of patients receiving ICI monotherapy increased from 0%-30.2% among trial-ineligible patients and from 0.1%-19.4% among eligible patients. However, among trial-ineligible patients, there were no overall survival differences between treatment with ICI monotherapy, ICI combination therapy and non-ICI therapy at 12 and 36 months.
Among trial-ineligible patients, ICI use was linked to a 14%-19% greater risk of death during the first 6 months after ICI initiation, but a 20% lower risk of death among those who survived 6 months after ICI initiation. Further, ICI combination therapy was associated with potential early harm among trial-ineligible patients.
“Phase 3 trials are sorely needed in patients with poor performance status or organ dysfunction so that we can adequately counsel patients who are unfit about expectations with novel cancer therapies,” Dr. Parikh said.
The cohort only included patients who received systemic therapy, which is a limitation of the study, so conclusions cannot be made about the efficacy of systemic therapy versus no systemic therapy in trial-ineligible patients.
Dr. Parikh reported nonfinancial support from Flatiron Health, grants from Humana, personal fees and equity from GNS Healthcare and Onc.AI, along with personal fees from the Cancer Study Group and Nanology outside the submitted work.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY