User login
Burnout among surgeons: Lessons for psychiatrists
Burnout is an occupational phenomenon and a syndrome resulting from unsuccessfully managed chronic workplace stress. The characteristic features of burnout include feelings of exhaustion, cynicism, and reduced professional efficacy.1 A career in surgery is associated with demanding and unpredictable work hours in a high-stress environment.2-8 Research indicates that surgeons are at an elevated risk for developing burnout and mental health problems that can compromise patient care. A survey of the fellows of the American College of Surgeons found that 40% of surgeons experience burnout, 30% experience symptoms of depression, and 28% have a mental quality of life (QOL) score greater than one-half an SD below the population norm.9,10 Surgeon burnout was also found to compromise the delivery of medical care.9,10
To prevent serious harm to surgeons and patients, it is critical to understand the causative factors of burnout among surgeons and how they can be addressed. We conducted this systematic review to identify factors linked to burnout across surgical specialties and to suggest ways to mitigate these risk factors.
Methods
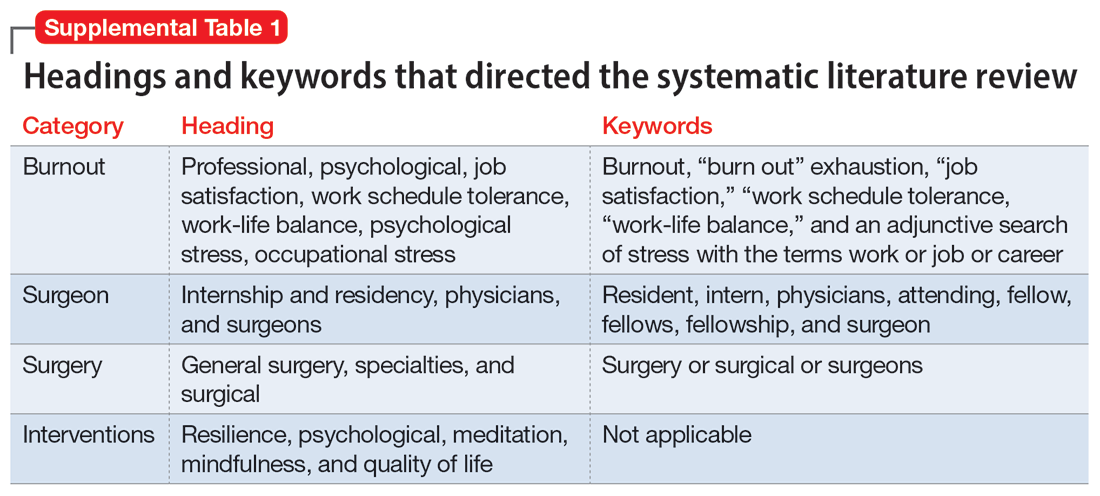
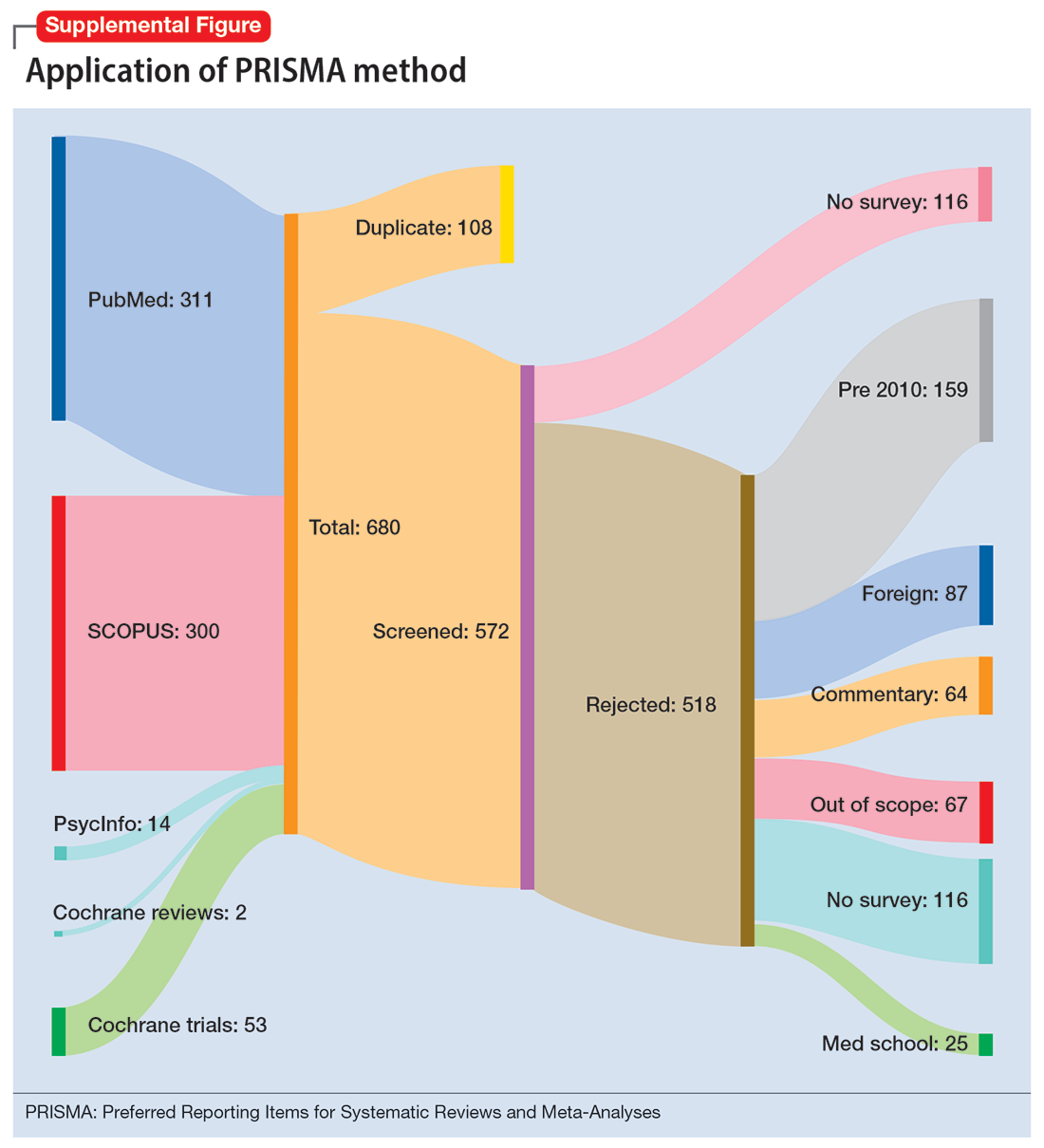
To identify studies of burnout among surgeons, we conducted an electronic search of Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid PsycInfo, SCOPUS, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. The headings and keywords used are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Studies met the inclusion criteria if they evaluated residents or attendings, used a tool to measure burnout, and examined any surgical specialty. Studies were excluded if they were published before 2010; were conducted outside the United States; were review articles, commentaries, or abstracts without full text articles; evaluated medical school students; were published in a language other than English; did not use a tool to measure burnout; or examined a nonsurgical specialty. Our analysis was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)11 and is outlined in the Supplemental Figure.
Results
Surgical specialties and burnout
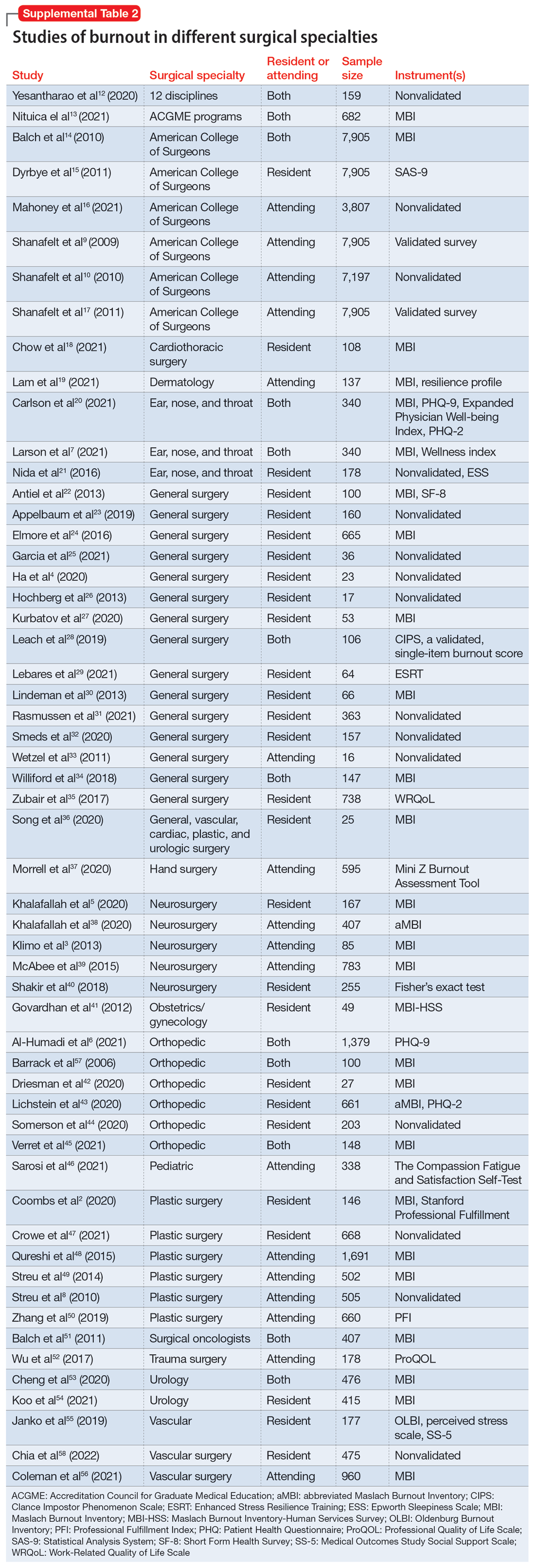
We identified 56 studies2-10,12-58 that focused on specific surgical specialties in relation to burnout. Supplemental Table 22-10,12-58 lists these studies and the surgical specialties they evaluated.
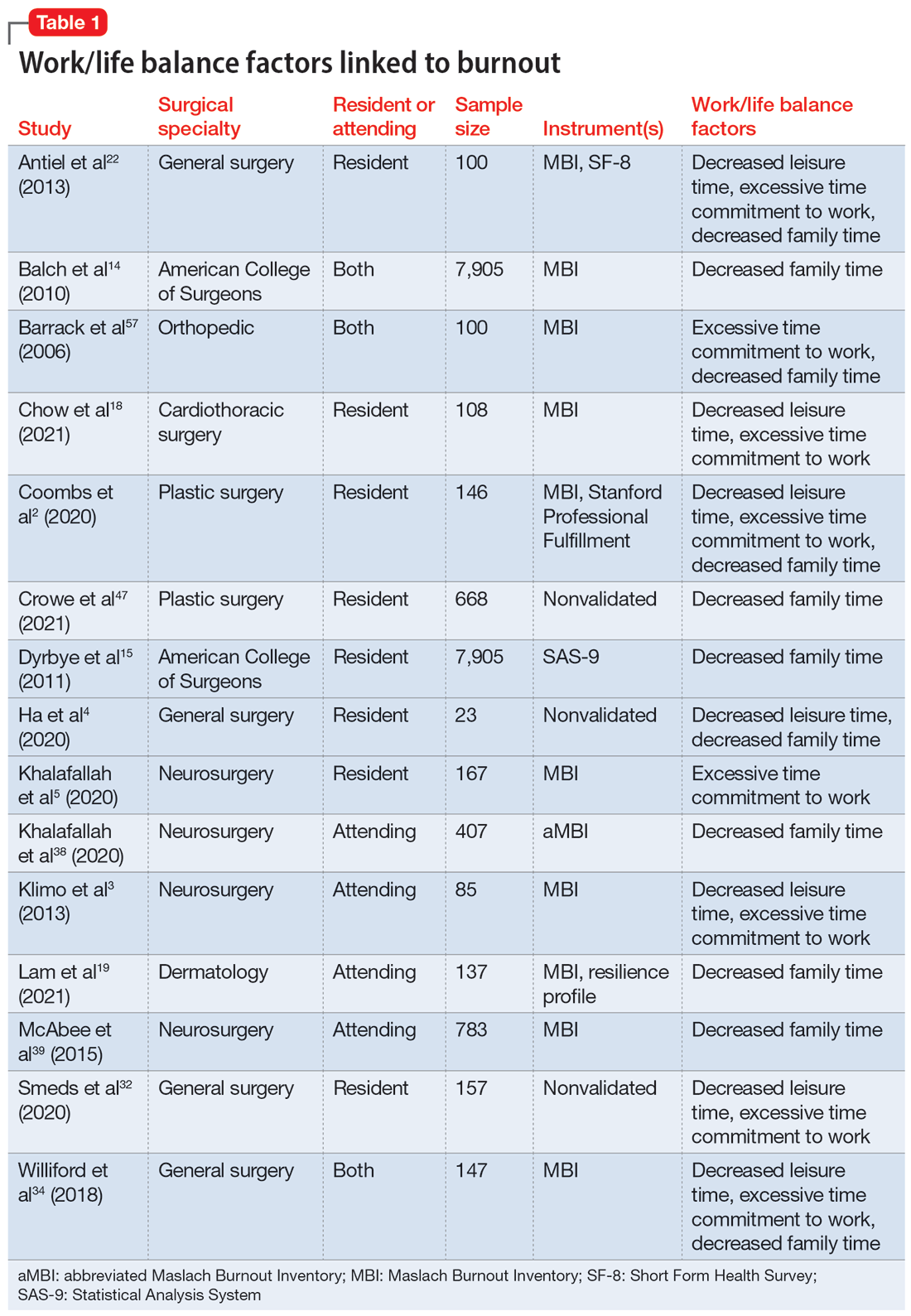
Work/life balance factors
Fifteen studies
Work hours
Fifteen studies2,7,14,20,21,30,34,41,42,44-46,50,52,56 examined work hours and burnout. Of these, 142,7,14,20,21,30,34,42,44-46,50,52,56 found a correlation between increased work hours and burnout, while only 1 study41 found no correlation between these factors.
Medical errors
Six studies2,14,18,43,49,52 discussed the role of burnout in medical errors. Of these, 52,14,43,49,52 reported a correlation between burnout and medical errors, while 1 study18 found no link between burnout and medical errors. The medical errors were self-reported.14,49 They included actions that resulted in patient harm, sample collection error, and errors in medication orders and laboratory test orders.2
Continue to: Institutional and organizational factors
Institutional and organizational factors
Eighteen studies3,13,14,18,20,22,23,29,30,36-38,44,45,47,54,56,57 examined how different organizational factors play a role in burnout. Four studies3,13,20,37 discussed administrative/bureaucratic work, 420,45,54,57 mentioned electronic medical documentation, 222,30 covered duty hour regulations, 318,45,57 discussed mistreatment of physicians, and 613,18,23,44,47,56 described the importance of workplace support in addressing burnout.
Physical and mental health factors
Eighteen studies6,7,14,15,17,20,26,27,29,34,43,44,48,52,54,57-59 discussed aspects of physical and mental health linked to burnout. Among these, 334,43,59 discussed the importance of physical health and focused on how improving physical health can reduce stress and burnout. Three studies6,17,58 noted the prevalence of suicidal ideation in both residents and attendings experiencing prolonged burnout. Five studies26,29,43,44,48 described the systematic barriers that inhibit physicians from getting professional help. Two studies7,27 reported marital status as a factor for burnout; participants who were single reported higher levels of depression and suicidal ideation. Five studies6,14,15,54,57 outlined how depression is associated with burnout.
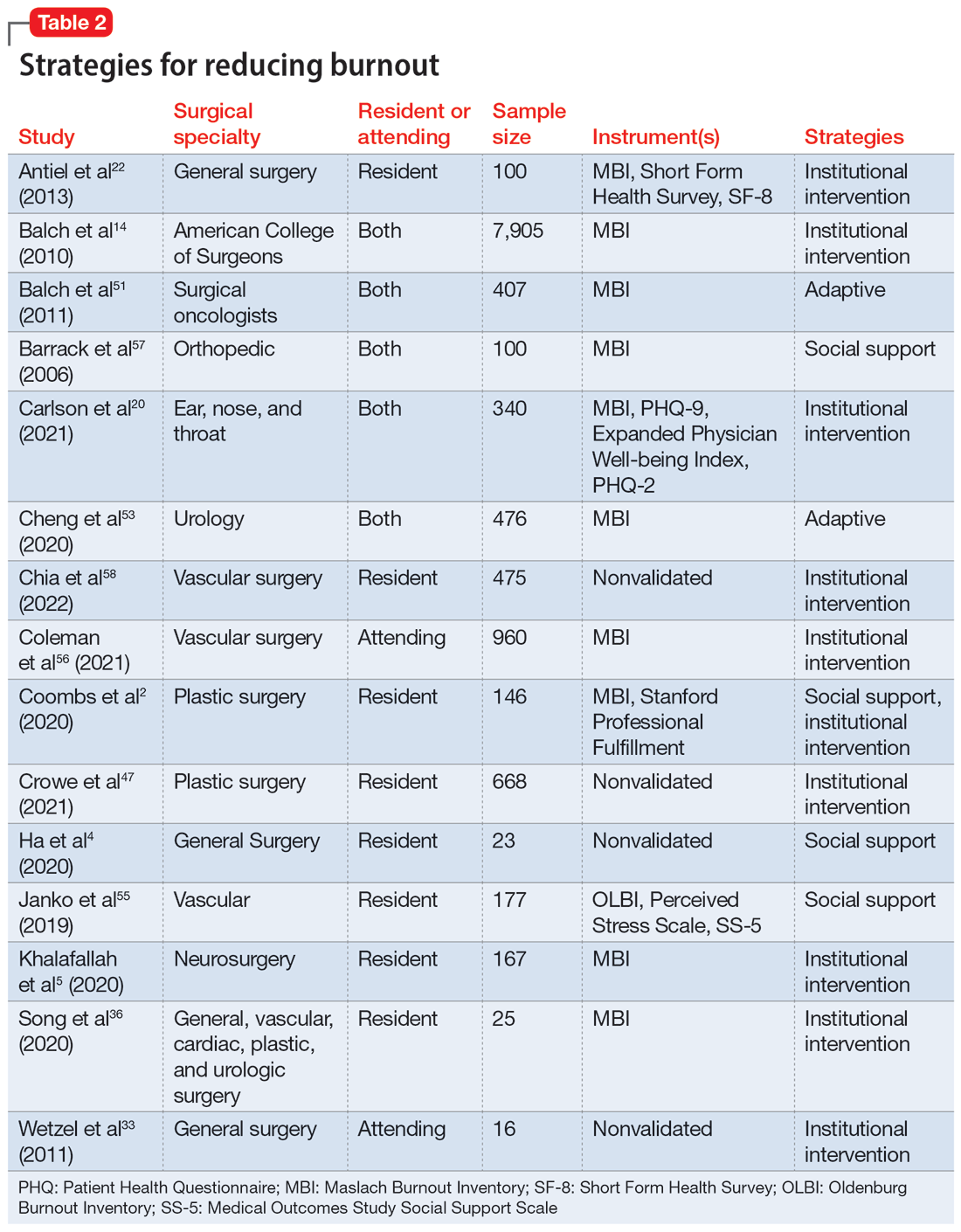
Strategies to mitigate burnout
Fifteen studies
Take-home points
Research that focused on work/life balance and burnout found excessive time commitment to work is a major factor associated with poor work/life balance. Residents who worked >80 hours a week had a significantly higher burnout rate.56 One study found that 70% of residents reported not getting enough sleep, 30% reported not having enough energy for relationships, and 39% reported that they were not eating or exercising due to time constraints.4 A high correlation was found between the number of hours worked per week and rates of burnout, emotional exhaustion, and depersonalization. Emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are aspects of burnout measured by the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI).24 The excessive time commitment to work not only contributes to burnout but also prevents physicians from getting professional help. In 1 study, both residents (56%) and attendings (24%) reported that 1 of the biggest barriers to getting help for their burnout symptoms was the inability to take time off.34 Research indicates that the hours worked per week and work/home conflicts were independently associated with burnout and career satisfaction.15 A decrease of weekly work hours may give physicians time to meet their responsibilities at work and home, allowing for a decrease in burnout and an increase in career satisfaction.
Increased work hours have also been found to be correlated with medical errors. One study found that those who worked 60 hours per week were significantly less likely to report any major medical errors in the previous 3 months compared with those who worked 80 hours per week.9 The risk for the number of medical errors has been reported as being 2-fold if surgeons are unable to combat the burnout.49 On the other hand, a positive and supportive environment with easy access to resources to combat burnout and burnout prevention programs can reduce the frequency of medical errors, which also can reduce the risk of malpractice, thus further reducing stress and burnout.43
Continue to: In response to resident complaints...
In response to resident complaints about long duty hours, a new rule has been implemented that states residents cannot work >16 hours per shift.30 This rule has been found to increase quality of life and prevent burnout.30
The amount of time spent on electronic medical records and documentation has been a major complaint from doctors and was identified as a factor contributing to burnout.45 It can act as a time drain that impedes the physician from providing optimal patient care and cause additional stress. This suggests the need for organizations to find solutions to minimize this strain.
A concerning issue reported as an institutional factor and associated with burnout is mistreatment through discrimination, harassment, and physical or verbal abuse. A recent study found 45% of general and vascular surgeons reported being mistreated in some fashion.57 The strategies reported as helpful for institutions to combat mistreatment include resilience training, improved mentorship, and implicit bias training.57
Burnout has been positively correlated with anxiety and depression.6 A recent study reported that 13% of orthopedic surgery residents screened positive for depression.44 Higher levels of burnout and depersonalization have been found to be closely associated with increased rates of suicidal ideation.17 In a study of vascular surgeons, 8% were found to report suicidal ideation, and this increased to 15% among vascular surgeons who had higher levels of depersonalization and emotional exhaustion,58 both of which are associated with burnout. In another study, surgery residents and fellows were found to have lower levels of personal achievement and higher levels of depersonalization, depressive symptoms, alcohol abuse, and suicidal ideation compared to attending physicians and the general population.54 These findings spell out the association between burnout and depressive symptoms among surgeons and emphasize the need for institutions to create a culture that supports the mental health needs of their physicians. Without access to supportive resources, residents resort to alternative methods that may be detrimental in the long run. In a recent study, 17% of residents admitted to using alcohol, including binge drinking, to cope with their stress.4
Burnout and depression are linked to physical health risks such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, substance abuse, and male infertility.6 Exercise has been shown to be beneficial for stress reduction, which can lead to changes in metabolism, inflammation, coagulation, and autonomic function.6 One study of surgeons found aerobic exercise and strength training were associated with lower rates of burnout and a higher quality of life.59
Continue to: The amount of burnout physicians...
The amount of burnout physicians experience can be determined by how they respond to adversities. Adaptive behaviors such as socializing, mindfulness, volunteering, and exercising have been found to be protective against burnout.6,37,54 Resilience training and maintaining low stress at work can decrease burnout.37 These findings highlight the need for physicians to be trained in the appropriate ways to combat their burnout symptoms.
Unfortunately, seeking help by health care professionals to improve mental health has been stigmatized, causing physicians to not seek help and instead resort to other ways to cope with their distress.26,34 While some of these coping methods may be positive, others—such as substance abuse or stress eating—can be maladaptive, leading to a poor quality of life, and in some cases, suicide.54 It is vital that effective mental health services become more accessible and for health care professionals to become aware of their maladaptive behaviors.34
Institutions finding ways to ease the path for their physicians to seek professional help to combat burnout may mitigate its negative impact. One strategy is to embed access to mental health services within regular wellness checks. Institutions can use wellness checks to provide resources to physicians who need it. These interventions have been found to be effective because they give physicians a safe space to seek help and become aware of any factors that could lead to burnout.18 Apart from these direct attempts to combat burnout, program-sponsored social events would also promote social connectedness with colleagues and contribute to a sense of well-being that could help decrease levels of burnout and depression.13 Mentorship has been shown to play a crucial role in decreasing burnout among residents. One study that examined the role of mentorship reported that 55% of residents felt supported, and of these, 96% felt mentorship was critical to their success.18 The role of institutions in helping to improve the well-being of surgeons is highlighted by the finding that increasing workplace support results in psychological resilience that can mitigate burnout at its roots.29
Bottom Line
Surgeons are at risk for burnout, which can impact their mental health and reduce their professional efficacy. Both institutions and surgeons themselves can take action to prevent burnout and treat burnout early when it occurs.
Related Resources
- Pahal P, Lippmann S. Building a better work/life balance. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):e1-e2. doi:10.12788/cp.0158
- Gibson R, Hategan A. Physician burnout vs depression: recognize the signs. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(10):41-42.
1. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
2. Coombs DM, Lanni MA, Fosnot J, et al. Professional burnout in United States plastic surgery residents: is it a legitimate concern? Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(7):802-810.
3. Klimo P Jr, DeCuypere M, Ragel BT, et al. Career satisfaction and burnout among U.S. neurosurgeons: a feasibility and pilot study. World Neurosurg. 2013;80(5):e59-e68.
4. Ha GQ, Go JT, Murayama KM, et al. Identifying sources of stress across years of general surgery residency. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2020;79(3):75-81.
5. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. A national survey on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon burnout and career satisfaction among neurosurgery residents. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;80:137-142.
6. Al-Humadi SM, Cáceda R, Bronson B, et al. Orthopaedic surgeon mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Geriatric Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2021;12:21514593211035230.
7. Larson DP, Carlson ML, Lohse CM, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part I, trainees. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1019-1029.
8. Streu R, Hawley S, Gay A, et al. Satisfaction with career choice among U.S. plastic surgeons: results from a national survey. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):636-642.
9. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps GJ, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2009;250(3):463-471.
10. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps G, et al. Burnout and medical errors among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2010;251(6):995-1000.
11. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336-341.
12. Yesantharao P, Lee E, Kraenzlin F, et al. Surgical block time satisfaction: a multi-institutional experience across twelve surgical disciplines. Perioperative Care Operating Room Manage. 2020;21:100128.
13. Nituica C, Bota OA, Blebea J. Specialty differences in resident resilience and burnout - a national survey. Am J Surg. 2021;222(2):319-328.
14. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye L, et al. Surgeon distress as calibrated by hours worked and nights on call. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211(5):609-619.
15. Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Satele D, Sloan J, Freischlag J. Relationship between work-home conflicts and burnout among American surgeons: a comparison by sex. Arch Surg. 2011;146(2):211-217.
16. Mahoney ST, Irish W, Strassle PD, et al. Practice characteristics and job satisfaction of private practice and academic surgeons. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(3):247-254.
17. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Dyrbye L, et al. Special report: suicidal ideation among American surgeons. Arch Surg. 2011;146(1):54-62.
18. Chow OS, Sudarshan M, Maxfield MW, et al. National survey of burnout and distress among cardiothoracic surgery trainees. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;111(6):2066-2071.
19. Lam C, Kim Y, Cruz M, et al. Burnout and resiliency in Mohs surgeons: a survey study. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7(3):319-322.
20. Carlson ML, Larson DP, O’Brien EK, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part II, attending physicians. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1030-1039.
21. Nida AM, Googe BJ, Lewis AF, et al. Resident fatigue in otolaryngology residents: a Web based survey. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016;37(3):210-216.
22. Antiel RM, Reed DA, Van Arendonk KJ, et al. Effects of duty hour restrictions on core competencies, education, quality of life, and burnout among general surgery interns. JAMA Surg. 2013;148(5):448-455.
23. Appelbaum NP, Lee N, Amendola M, et al. Surgical resident burnout and job satisfaction: the role of workplace climate and perceived support. J Surg Res. 2019;234:20-25.
24. Elmore LC, Jeffe DB, Jin L, et al. National survey of burnout among US general surgery residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;223(3):440-451.
25. Garcia DI, Pannuccio A, Gallegos J, et al. Resident-driven wellness initiatives improve resident wellness and perception of work environment. J Surg Res. 2021;258:8-16.
26. Hochberg MS, Berman RS, Kalet AL, et al. The stress of residency: recognizing the signs of depression and suicide in you and your fellow residents. Am J Surg. 2013;205(2):141-146.
27. Kurbatov V, Shaughnessy M, Baratta V, et al. Application of advanced bioinformatics to understand and predict burnout among surgical trainees. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(3):499-507.
28. Leach PK, Nygaard RM, Chipman JG, et al. Impostor phenomenon and burnout in general surgeons and general surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2019;76(1):99-106.
29. Lebares CC, Greenberg AL, Ascher NL, et al. Exploration of individual and system-level well-being initiatives at an academic surgical residency program: a mixed-methods study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2032676.
30. Lindeman BM, Sacks BC, Hirose K, et al. Multifaceted longitudinal study of surgical resident education, quality of life, and patient care before and after July 2011. J Surg Educ. 2013;70(6):769-776.
31. Rasmussen JM, Najarian MM, Ties JS, et al. Career satisfaction, gender bias, and work-life balance: a contemporary assessment of general surgeons. J Surg Educ. 2021;78(1):119-125.
32. Smeds MR, Janko MR, Allen S, et al. Burnout and its relationship with perceived stress, self-efficacy, depression, social support, and programmatic factors in general surgery residents. Am J Surg. 2020;219(6):907-912.
33. Wetzel CM, George A, Hanna GB, et al. Stress management training for surgeons--a randomized, controlled, intervention study. Ann Surg. 2011;253(3):488-494.
34. Williford ML, Scarlet S, Meyers MO, et al. Multiple-institution comparison of resident and faculty perceptions of burnout and depression during surgical training. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(8):705-711.
35. Zubair MH, Hussain LR, Williams KN, et al. Work-related quality of life of US general surgery residents: is it really so bad? J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):e138-e146.
36. Song Y, Swendiman RA, Shannon AB, et al. Can we coach resilience? An evaluation of professional resilience coaching as a well-being initiative for surgical interns. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(6):1481-1489.
37. Morrell NT, Sears ED, Desai MJ, et al. A survey of burnout among members of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. J Hand Surg Am. 2020;45(7):573-581.e516.
38. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among attending neurosurgeons during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;198:106193.
39. McAbee JH, Ragel BT, McCartney S, et al. Factors associated with career satisfaction and burnout among US neurosurgeons: results of a nationwide survey. J Neurosurg. 2015;123(1):161-173.
40. Shakir HJ, McPheeters MJ, Shallwani H, et al. The prevalence of burnout among US neurosurgery residents. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(3):582-590.
41. Govardhan LM, Pinelli V, Schnatz PF. Burnout, depression and job satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology residents. Conn Med. 2012;76(7):389-395.
42. Driesman AS, Strauss EJ, Konda SR, et al. Factors associated with orthopaedic resident burnout: a pilot study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(21):900-906.
43. Lichstein PM, He JK, Estok D, et al. What is the prevalence of burnout, depression, and substance use among orthopaedic surgery residents and what are the risk factors? A collaborative orthopaedic educational research group survey study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(8):1709-1718.
44. Somerson JS, Patton A, Ahmed AA, et al. Burnout among United States orthopaedic surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(4):961-968.
45. Verret CI, Nguyen J, Verret C, et al. How do areas of work life drive burnout in orthopaedic attending surgeons, fellows, and residents? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(2):251-262.
46. Sarosi A, Coakley BA, Berman L, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction in pediatric surgeons in the U.S. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56(8):1276-1284.
47. Crowe CS, Lopez J, Morrison SD, et al. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on resident education and wellness: a national survey of plastic surgery residents. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(3):462e-474e.
48. Qureshi HA, Rawlani R, Mioton LM, et al. Burnout phenomenon in U.S. plastic surgeons: risk factors and impact on quality of life. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2):619-626.
49. Streu R, Hansen J, Abrahamse P, et al. Professional burnout among US plastic surgeons: results of a national survey. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;72(3):346-350.
50. Zhang JQ, Riba L, Magrini L, ET AL. Assessing burnout and professional fulfillment in breast surgery: results from a national survey of the American Society of Breast Surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(10):3089-3098.
51. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Sloan J, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among surgical oncologists compared with other surgical specialties. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(1):16-25.
52. Wu D, Gross B, Rittenhouse K, et al. A preliminary analysis of compassion fatigue in a surgeon population: are female surgeons at heightened risk? Am Surg. 2017;83(11):1302-1307.
53. Cheng JW, Wagner H, Hernandez BC, et al. Stressors and coping mechanisms related to burnout within urology. Urology. 2020;139:27-36.
54. Koo K, Javier-DesLoges JF, Fang R, ET AL. Professional burnout, career choice regret, and unmet needs for well-being among urology residents. Urology. 2021;157:57-63.
55. Janko MR, Smeds MR. Burnout, depression, perceived stress, and self-efficacy in vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69(4):1233-1242.
56. Coleman DM, Money SR, Meltzer AJ, et al. Vascular surgeon wellness and burnout: a report from the Society for Vascular Surgery Wellness Task Force. J Vasc Surg. 2021;73(6):1841-1850.e3.
57. Barrack RL, Miller LS, Sotile WM, et al. Effect of duty hour standards on burnout among orthopaedic surgery residents. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:134-137.
58. Chia MC, Hu YY, Li RD, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for burnout in U.S. vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2022;75(1):308-315.e4.
59. Shanafelt TD, Oreskovich MR, Dyrbye LN, et al. Avoiding burnout: the personal health habits and wellness practices of US surgeons. Ann Surg. 2012;255(4):625-633.
Burnout is an occupational phenomenon and a syndrome resulting from unsuccessfully managed chronic workplace stress. The characteristic features of burnout include feelings of exhaustion, cynicism, and reduced professional efficacy.1 A career in surgery is associated with demanding and unpredictable work hours in a high-stress environment.2-8 Research indicates that surgeons are at an elevated risk for developing burnout and mental health problems that can compromise patient care. A survey of the fellows of the American College of Surgeons found that 40% of surgeons experience burnout, 30% experience symptoms of depression, and 28% have a mental quality of life (QOL) score greater than one-half an SD below the population norm.9,10 Surgeon burnout was also found to compromise the delivery of medical care.9,10
To prevent serious harm to surgeons and patients, it is critical to understand the causative factors of burnout among surgeons and how they can be addressed. We conducted this systematic review to identify factors linked to burnout across surgical specialties and to suggest ways to mitigate these risk factors.

Methods
To identify studies of burnout among surgeons, we conducted an electronic search of Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid PsycInfo, SCOPUS, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. The headings and keywords used are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Studies met the inclusion criteria if they evaluated residents or attendings, used a tool to measure burnout, and examined any surgical specialty. Studies were excluded if they were published before 2010; were conducted outside the United States; were review articles, commentaries, or abstracts without full text articles; evaluated medical school students; were published in a language other than English; did not use a tool to measure burnout; or examined a nonsurgical specialty. Our analysis was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)11 and is outlined in the Supplemental Figure.

Results
Surgical specialties and burnout
We identified 56 studies2-10,12-58 that focused on specific surgical specialties in relation to burnout. Supplemental Table 22-10,12-58 lists these studies and the surgical specialties they evaluated.

Work/life balance factors
Fifteen studies

Work hours
Fifteen studies2,7,14,20,21,30,34,41,42,44-46,50,52,56 examined work hours and burnout. Of these, 142,7,14,20,21,30,34,42,44-46,50,52,56 found a correlation between increased work hours and burnout, while only 1 study41 found no correlation between these factors.
Medical errors
Six studies2,14,18,43,49,52 discussed the role of burnout in medical errors. Of these, 52,14,43,49,52 reported a correlation between burnout and medical errors, while 1 study18 found no link between burnout and medical errors. The medical errors were self-reported.14,49 They included actions that resulted in patient harm, sample collection error, and errors in medication orders and laboratory test orders.2
Continue to: Institutional and organizational factors
Institutional and organizational factors
Eighteen studies3,13,14,18,20,22,23,29,30,36-38,44,45,47,54,56,57 examined how different organizational factors play a role in burnout. Four studies3,13,20,37 discussed administrative/bureaucratic work, 420,45,54,57 mentioned electronic medical documentation, 222,30 covered duty hour regulations, 318,45,57 discussed mistreatment of physicians, and 613,18,23,44,47,56 described the importance of workplace support in addressing burnout.
Physical and mental health factors
Eighteen studies6,7,14,15,17,20,26,27,29,34,43,44,48,52,54,57-59 discussed aspects of physical and mental health linked to burnout. Among these, 334,43,59 discussed the importance of physical health and focused on how improving physical health can reduce stress and burnout. Three studies6,17,58 noted the prevalence of suicidal ideation in both residents and attendings experiencing prolonged burnout. Five studies26,29,43,44,48 described the systematic barriers that inhibit physicians from getting professional help. Two studies7,27 reported marital status as a factor for burnout; participants who were single reported higher levels of depression and suicidal ideation. Five studies6,14,15,54,57 outlined how depression is associated with burnout.
Strategies to mitigate burnout
Fifteen studies

Take-home points
Research that focused on work/life balance and burnout found excessive time commitment to work is a major factor associated with poor work/life balance. Residents who worked >80 hours a week had a significantly higher burnout rate.56 One study found that 70% of residents reported not getting enough sleep, 30% reported not having enough energy for relationships, and 39% reported that they were not eating or exercising due to time constraints.4 A high correlation was found between the number of hours worked per week and rates of burnout, emotional exhaustion, and depersonalization. Emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are aspects of burnout measured by the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI).24 The excessive time commitment to work not only contributes to burnout but also prevents physicians from getting professional help. In 1 study, both residents (56%) and attendings (24%) reported that 1 of the biggest barriers to getting help for their burnout symptoms was the inability to take time off.34 Research indicates that the hours worked per week and work/home conflicts were independently associated with burnout and career satisfaction.15 A decrease of weekly work hours may give physicians time to meet their responsibilities at work and home, allowing for a decrease in burnout and an increase in career satisfaction.
Increased work hours have also been found to be correlated with medical errors. One study found that those who worked 60 hours per week were significantly less likely to report any major medical errors in the previous 3 months compared with those who worked 80 hours per week.9 The risk for the number of medical errors has been reported as being 2-fold if surgeons are unable to combat the burnout.49 On the other hand, a positive and supportive environment with easy access to resources to combat burnout and burnout prevention programs can reduce the frequency of medical errors, which also can reduce the risk of malpractice, thus further reducing stress and burnout.43
Continue to: In response to resident complaints...
In response to resident complaints about long duty hours, a new rule has been implemented that states residents cannot work >16 hours per shift.30 This rule has been found to increase quality of life and prevent burnout.30
The amount of time spent on electronic medical records and documentation has been a major complaint from doctors and was identified as a factor contributing to burnout.45 It can act as a time drain that impedes the physician from providing optimal patient care and cause additional stress. This suggests the need for organizations to find solutions to minimize this strain.
A concerning issue reported as an institutional factor and associated with burnout is mistreatment through discrimination, harassment, and physical or verbal abuse. A recent study found 45% of general and vascular surgeons reported being mistreated in some fashion.57 The strategies reported as helpful for institutions to combat mistreatment include resilience training, improved mentorship, and implicit bias training.57
Burnout has been positively correlated with anxiety and depression.6 A recent study reported that 13% of orthopedic surgery residents screened positive for depression.44 Higher levels of burnout and depersonalization have been found to be closely associated with increased rates of suicidal ideation.17 In a study of vascular surgeons, 8% were found to report suicidal ideation, and this increased to 15% among vascular surgeons who had higher levels of depersonalization and emotional exhaustion,58 both of which are associated with burnout. In another study, surgery residents and fellows were found to have lower levels of personal achievement and higher levels of depersonalization, depressive symptoms, alcohol abuse, and suicidal ideation compared to attending physicians and the general population.54 These findings spell out the association between burnout and depressive symptoms among surgeons and emphasize the need for institutions to create a culture that supports the mental health needs of their physicians. Without access to supportive resources, residents resort to alternative methods that may be detrimental in the long run. In a recent study, 17% of residents admitted to using alcohol, including binge drinking, to cope with their stress.4
Burnout and depression are linked to physical health risks such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, substance abuse, and male infertility.6 Exercise has been shown to be beneficial for stress reduction, which can lead to changes in metabolism, inflammation, coagulation, and autonomic function.6 One study of surgeons found aerobic exercise and strength training were associated with lower rates of burnout and a higher quality of life.59
Continue to: The amount of burnout physicians...
The amount of burnout physicians experience can be determined by how they respond to adversities. Adaptive behaviors such as socializing, mindfulness, volunteering, and exercising have been found to be protective against burnout.6,37,54 Resilience training and maintaining low stress at work can decrease burnout.37 These findings highlight the need for physicians to be trained in the appropriate ways to combat their burnout symptoms.
Unfortunately, seeking help by health care professionals to improve mental health has been stigmatized, causing physicians to not seek help and instead resort to other ways to cope with their distress.26,34 While some of these coping methods may be positive, others—such as substance abuse or stress eating—can be maladaptive, leading to a poor quality of life, and in some cases, suicide.54 It is vital that effective mental health services become more accessible and for health care professionals to become aware of their maladaptive behaviors.34
Institutions finding ways to ease the path for their physicians to seek professional help to combat burnout may mitigate its negative impact. One strategy is to embed access to mental health services within regular wellness checks. Institutions can use wellness checks to provide resources to physicians who need it. These interventions have been found to be effective because they give physicians a safe space to seek help and become aware of any factors that could lead to burnout.18 Apart from these direct attempts to combat burnout, program-sponsored social events would also promote social connectedness with colleagues and contribute to a sense of well-being that could help decrease levels of burnout and depression.13 Mentorship has been shown to play a crucial role in decreasing burnout among residents. One study that examined the role of mentorship reported that 55% of residents felt supported, and of these, 96% felt mentorship was critical to their success.18 The role of institutions in helping to improve the well-being of surgeons is highlighted by the finding that increasing workplace support results in psychological resilience that can mitigate burnout at its roots.29
Bottom Line
Surgeons are at risk for burnout, which can impact their mental health and reduce their professional efficacy. Both institutions and surgeons themselves can take action to prevent burnout and treat burnout early when it occurs.
Related Resources
- Pahal P, Lippmann S. Building a better work/life balance. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):e1-e2. doi:10.12788/cp.0158
- Gibson R, Hategan A. Physician burnout vs depression: recognize the signs. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(10):41-42.
Burnout is an occupational phenomenon and a syndrome resulting from unsuccessfully managed chronic workplace stress. The characteristic features of burnout include feelings of exhaustion, cynicism, and reduced professional efficacy.1 A career in surgery is associated with demanding and unpredictable work hours in a high-stress environment.2-8 Research indicates that surgeons are at an elevated risk for developing burnout and mental health problems that can compromise patient care. A survey of the fellows of the American College of Surgeons found that 40% of surgeons experience burnout, 30% experience symptoms of depression, and 28% have a mental quality of life (QOL) score greater than one-half an SD below the population norm.9,10 Surgeon burnout was also found to compromise the delivery of medical care.9,10
To prevent serious harm to surgeons and patients, it is critical to understand the causative factors of burnout among surgeons and how they can be addressed. We conducted this systematic review to identify factors linked to burnout across surgical specialties and to suggest ways to mitigate these risk factors.

Methods
To identify studies of burnout among surgeons, we conducted an electronic search of Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid PsycInfo, SCOPUS, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. The headings and keywords used are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Studies met the inclusion criteria if they evaluated residents or attendings, used a tool to measure burnout, and examined any surgical specialty. Studies were excluded if they were published before 2010; were conducted outside the United States; were review articles, commentaries, or abstracts without full text articles; evaluated medical school students; were published in a language other than English; did not use a tool to measure burnout; or examined a nonsurgical specialty. Our analysis was guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)11 and is outlined in the Supplemental Figure.

Results
Surgical specialties and burnout
We identified 56 studies2-10,12-58 that focused on specific surgical specialties in relation to burnout. Supplemental Table 22-10,12-58 lists these studies and the surgical specialties they evaluated.

Work/life balance factors
Fifteen studies

Work hours
Fifteen studies2,7,14,20,21,30,34,41,42,44-46,50,52,56 examined work hours and burnout. Of these, 142,7,14,20,21,30,34,42,44-46,50,52,56 found a correlation between increased work hours and burnout, while only 1 study41 found no correlation between these factors.
Medical errors
Six studies2,14,18,43,49,52 discussed the role of burnout in medical errors. Of these, 52,14,43,49,52 reported a correlation between burnout and medical errors, while 1 study18 found no link between burnout and medical errors. The medical errors were self-reported.14,49 They included actions that resulted in patient harm, sample collection error, and errors in medication orders and laboratory test orders.2
Continue to: Institutional and organizational factors
Institutional and organizational factors
Eighteen studies3,13,14,18,20,22,23,29,30,36-38,44,45,47,54,56,57 examined how different organizational factors play a role in burnout. Four studies3,13,20,37 discussed administrative/bureaucratic work, 420,45,54,57 mentioned electronic medical documentation, 222,30 covered duty hour regulations, 318,45,57 discussed mistreatment of physicians, and 613,18,23,44,47,56 described the importance of workplace support in addressing burnout.
Physical and mental health factors
Eighteen studies6,7,14,15,17,20,26,27,29,34,43,44,48,52,54,57-59 discussed aspects of physical and mental health linked to burnout. Among these, 334,43,59 discussed the importance of physical health and focused on how improving physical health can reduce stress and burnout. Three studies6,17,58 noted the prevalence of suicidal ideation in both residents and attendings experiencing prolonged burnout. Five studies26,29,43,44,48 described the systematic barriers that inhibit physicians from getting professional help. Two studies7,27 reported marital status as a factor for burnout; participants who were single reported higher levels of depression and suicidal ideation. Five studies6,14,15,54,57 outlined how depression is associated with burnout.
Strategies to mitigate burnout
Fifteen studies

Take-home points
Research that focused on work/life balance and burnout found excessive time commitment to work is a major factor associated with poor work/life balance. Residents who worked >80 hours a week had a significantly higher burnout rate.56 One study found that 70% of residents reported not getting enough sleep, 30% reported not having enough energy for relationships, and 39% reported that they were not eating or exercising due to time constraints.4 A high correlation was found between the number of hours worked per week and rates of burnout, emotional exhaustion, and depersonalization. Emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are aspects of burnout measured by the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI).24 The excessive time commitment to work not only contributes to burnout but also prevents physicians from getting professional help. In 1 study, both residents (56%) and attendings (24%) reported that 1 of the biggest barriers to getting help for their burnout symptoms was the inability to take time off.34 Research indicates that the hours worked per week and work/home conflicts were independently associated with burnout and career satisfaction.15 A decrease of weekly work hours may give physicians time to meet their responsibilities at work and home, allowing for a decrease in burnout and an increase in career satisfaction.
Increased work hours have also been found to be correlated with medical errors. One study found that those who worked 60 hours per week were significantly less likely to report any major medical errors in the previous 3 months compared with those who worked 80 hours per week.9 The risk for the number of medical errors has been reported as being 2-fold if surgeons are unable to combat the burnout.49 On the other hand, a positive and supportive environment with easy access to resources to combat burnout and burnout prevention programs can reduce the frequency of medical errors, which also can reduce the risk of malpractice, thus further reducing stress and burnout.43
Continue to: In response to resident complaints...
In response to resident complaints about long duty hours, a new rule has been implemented that states residents cannot work >16 hours per shift.30 This rule has been found to increase quality of life and prevent burnout.30
The amount of time spent on electronic medical records and documentation has been a major complaint from doctors and was identified as a factor contributing to burnout.45 It can act as a time drain that impedes the physician from providing optimal patient care and cause additional stress. This suggests the need for organizations to find solutions to minimize this strain.
A concerning issue reported as an institutional factor and associated with burnout is mistreatment through discrimination, harassment, and physical or verbal abuse. A recent study found 45% of general and vascular surgeons reported being mistreated in some fashion.57 The strategies reported as helpful for institutions to combat mistreatment include resilience training, improved mentorship, and implicit bias training.57
Burnout has been positively correlated with anxiety and depression.6 A recent study reported that 13% of orthopedic surgery residents screened positive for depression.44 Higher levels of burnout and depersonalization have been found to be closely associated with increased rates of suicidal ideation.17 In a study of vascular surgeons, 8% were found to report suicidal ideation, and this increased to 15% among vascular surgeons who had higher levels of depersonalization and emotional exhaustion,58 both of which are associated with burnout. In another study, surgery residents and fellows were found to have lower levels of personal achievement and higher levels of depersonalization, depressive symptoms, alcohol abuse, and suicidal ideation compared to attending physicians and the general population.54 These findings spell out the association between burnout and depressive symptoms among surgeons and emphasize the need for institutions to create a culture that supports the mental health needs of their physicians. Without access to supportive resources, residents resort to alternative methods that may be detrimental in the long run. In a recent study, 17% of residents admitted to using alcohol, including binge drinking, to cope with their stress.4
Burnout and depression are linked to physical health risks such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, substance abuse, and male infertility.6 Exercise has been shown to be beneficial for stress reduction, which can lead to changes in metabolism, inflammation, coagulation, and autonomic function.6 One study of surgeons found aerobic exercise and strength training were associated with lower rates of burnout and a higher quality of life.59
Continue to: The amount of burnout physicians...
The amount of burnout physicians experience can be determined by how they respond to adversities. Adaptive behaviors such as socializing, mindfulness, volunteering, and exercising have been found to be protective against burnout.6,37,54 Resilience training and maintaining low stress at work can decrease burnout.37 These findings highlight the need for physicians to be trained in the appropriate ways to combat their burnout symptoms.
Unfortunately, seeking help by health care professionals to improve mental health has been stigmatized, causing physicians to not seek help and instead resort to other ways to cope with their distress.26,34 While some of these coping methods may be positive, others—such as substance abuse or stress eating—can be maladaptive, leading to a poor quality of life, and in some cases, suicide.54 It is vital that effective mental health services become more accessible and for health care professionals to become aware of their maladaptive behaviors.34
Institutions finding ways to ease the path for their physicians to seek professional help to combat burnout may mitigate its negative impact. One strategy is to embed access to mental health services within regular wellness checks. Institutions can use wellness checks to provide resources to physicians who need it. These interventions have been found to be effective because they give physicians a safe space to seek help and become aware of any factors that could lead to burnout.18 Apart from these direct attempts to combat burnout, program-sponsored social events would also promote social connectedness with colleagues and contribute to a sense of well-being that could help decrease levels of burnout and depression.13 Mentorship has been shown to play a crucial role in decreasing burnout among residents. One study that examined the role of mentorship reported that 55% of residents felt supported, and of these, 96% felt mentorship was critical to their success.18 The role of institutions in helping to improve the well-being of surgeons is highlighted by the finding that increasing workplace support results in psychological resilience that can mitigate burnout at its roots.29
Bottom Line
Surgeons are at risk for burnout, which can impact their mental health and reduce their professional efficacy. Both institutions and surgeons themselves can take action to prevent burnout and treat burnout early when it occurs.
Related Resources
- Pahal P, Lippmann S. Building a better work/life balance. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(8):e1-e2. doi:10.12788/cp.0158
- Gibson R, Hategan A. Physician burnout vs depression: recognize the signs. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(10):41-42.
1. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
2. Coombs DM, Lanni MA, Fosnot J, et al. Professional burnout in United States plastic surgery residents: is it a legitimate concern? Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(7):802-810.
3. Klimo P Jr, DeCuypere M, Ragel BT, et al. Career satisfaction and burnout among U.S. neurosurgeons: a feasibility and pilot study. World Neurosurg. 2013;80(5):e59-e68.
4. Ha GQ, Go JT, Murayama KM, et al. Identifying sources of stress across years of general surgery residency. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2020;79(3):75-81.
5. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. A national survey on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon burnout and career satisfaction among neurosurgery residents. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;80:137-142.
6. Al-Humadi SM, Cáceda R, Bronson B, et al. Orthopaedic surgeon mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Geriatric Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2021;12:21514593211035230.
7. Larson DP, Carlson ML, Lohse CM, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part I, trainees. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1019-1029.
8. Streu R, Hawley S, Gay A, et al. Satisfaction with career choice among U.S. plastic surgeons: results from a national survey. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):636-642.
9. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps GJ, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2009;250(3):463-471.
10. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps G, et al. Burnout and medical errors among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2010;251(6):995-1000.
11. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336-341.
12. Yesantharao P, Lee E, Kraenzlin F, et al. Surgical block time satisfaction: a multi-institutional experience across twelve surgical disciplines. Perioperative Care Operating Room Manage. 2020;21:100128.
13. Nituica C, Bota OA, Blebea J. Specialty differences in resident resilience and burnout - a national survey. Am J Surg. 2021;222(2):319-328.
14. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye L, et al. Surgeon distress as calibrated by hours worked and nights on call. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211(5):609-619.
15. Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Satele D, Sloan J, Freischlag J. Relationship between work-home conflicts and burnout among American surgeons: a comparison by sex. Arch Surg. 2011;146(2):211-217.
16. Mahoney ST, Irish W, Strassle PD, et al. Practice characteristics and job satisfaction of private practice and academic surgeons. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(3):247-254.
17. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Dyrbye L, et al. Special report: suicidal ideation among American surgeons. Arch Surg. 2011;146(1):54-62.
18. Chow OS, Sudarshan M, Maxfield MW, et al. National survey of burnout and distress among cardiothoracic surgery trainees. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;111(6):2066-2071.
19. Lam C, Kim Y, Cruz M, et al. Burnout and resiliency in Mohs surgeons: a survey study. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7(3):319-322.
20. Carlson ML, Larson DP, O’Brien EK, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part II, attending physicians. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1030-1039.
21. Nida AM, Googe BJ, Lewis AF, et al. Resident fatigue in otolaryngology residents: a Web based survey. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016;37(3):210-216.
22. Antiel RM, Reed DA, Van Arendonk KJ, et al. Effects of duty hour restrictions on core competencies, education, quality of life, and burnout among general surgery interns. JAMA Surg. 2013;148(5):448-455.
23. Appelbaum NP, Lee N, Amendola M, et al. Surgical resident burnout and job satisfaction: the role of workplace climate and perceived support. J Surg Res. 2019;234:20-25.
24. Elmore LC, Jeffe DB, Jin L, et al. National survey of burnout among US general surgery residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;223(3):440-451.
25. Garcia DI, Pannuccio A, Gallegos J, et al. Resident-driven wellness initiatives improve resident wellness and perception of work environment. J Surg Res. 2021;258:8-16.
26. Hochberg MS, Berman RS, Kalet AL, et al. The stress of residency: recognizing the signs of depression and suicide in you and your fellow residents. Am J Surg. 2013;205(2):141-146.
27. Kurbatov V, Shaughnessy M, Baratta V, et al. Application of advanced bioinformatics to understand and predict burnout among surgical trainees. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(3):499-507.
28. Leach PK, Nygaard RM, Chipman JG, et al. Impostor phenomenon and burnout in general surgeons and general surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2019;76(1):99-106.
29. Lebares CC, Greenberg AL, Ascher NL, et al. Exploration of individual and system-level well-being initiatives at an academic surgical residency program: a mixed-methods study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2032676.
30. Lindeman BM, Sacks BC, Hirose K, et al. Multifaceted longitudinal study of surgical resident education, quality of life, and patient care before and after July 2011. J Surg Educ. 2013;70(6):769-776.
31. Rasmussen JM, Najarian MM, Ties JS, et al. Career satisfaction, gender bias, and work-life balance: a contemporary assessment of general surgeons. J Surg Educ. 2021;78(1):119-125.
32. Smeds MR, Janko MR, Allen S, et al. Burnout and its relationship with perceived stress, self-efficacy, depression, social support, and programmatic factors in general surgery residents. Am J Surg. 2020;219(6):907-912.
33. Wetzel CM, George A, Hanna GB, et al. Stress management training for surgeons--a randomized, controlled, intervention study. Ann Surg. 2011;253(3):488-494.
34. Williford ML, Scarlet S, Meyers MO, et al. Multiple-institution comparison of resident and faculty perceptions of burnout and depression during surgical training. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(8):705-711.
35. Zubair MH, Hussain LR, Williams KN, et al. Work-related quality of life of US general surgery residents: is it really so bad? J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):e138-e146.
36. Song Y, Swendiman RA, Shannon AB, et al. Can we coach resilience? An evaluation of professional resilience coaching as a well-being initiative for surgical interns. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(6):1481-1489.
37. Morrell NT, Sears ED, Desai MJ, et al. A survey of burnout among members of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. J Hand Surg Am. 2020;45(7):573-581.e516.
38. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among attending neurosurgeons during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;198:106193.
39. McAbee JH, Ragel BT, McCartney S, et al. Factors associated with career satisfaction and burnout among US neurosurgeons: results of a nationwide survey. J Neurosurg. 2015;123(1):161-173.
40. Shakir HJ, McPheeters MJ, Shallwani H, et al. The prevalence of burnout among US neurosurgery residents. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(3):582-590.
41. Govardhan LM, Pinelli V, Schnatz PF. Burnout, depression and job satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology residents. Conn Med. 2012;76(7):389-395.
42. Driesman AS, Strauss EJ, Konda SR, et al. Factors associated with orthopaedic resident burnout: a pilot study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(21):900-906.
43. Lichstein PM, He JK, Estok D, et al. What is the prevalence of burnout, depression, and substance use among orthopaedic surgery residents and what are the risk factors? A collaborative orthopaedic educational research group survey study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(8):1709-1718.
44. Somerson JS, Patton A, Ahmed AA, et al. Burnout among United States orthopaedic surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(4):961-968.
45. Verret CI, Nguyen J, Verret C, et al. How do areas of work life drive burnout in orthopaedic attending surgeons, fellows, and residents? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(2):251-262.
46. Sarosi A, Coakley BA, Berman L, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction in pediatric surgeons in the U.S. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56(8):1276-1284.
47. Crowe CS, Lopez J, Morrison SD, et al. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on resident education and wellness: a national survey of plastic surgery residents. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(3):462e-474e.
48. Qureshi HA, Rawlani R, Mioton LM, et al. Burnout phenomenon in U.S. plastic surgeons: risk factors and impact on quality of life. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2):619-626.
49. Streu R, Hansen J, Abrahamse P, et al. Professional burnout among US plastic surgeons: results of a national survey. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;72(3):346-350.
50. Zhang JQ, Riba L, Magrini L, ET AL. Assessing burnout and professional fulfillment in breast surgery: results from a national survey of the American Society of Breast Surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(10):3089-3098.
51. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Sloan J, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among surgical oncologists compared with other surgical specialties. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(1):16-25.
52. Wu D, Gross B, Rittenhouse K, et al. A preliminary analysis of compassion fatigue in a surgeon population: are female surgeons at heightened risk? Am Surg. 2017;83(11):1302-1307.
53. Cheng JW, Wagner H, Hernandez BC, et al. Stressors and coping mechanisms related to burnout within urology. Urology. 2020;139:27-36.
54. Koo K, Javier-DesLoges JF, Fang R, ET AL. Professional burnout, career choice regret, and unmet needs for well-being among urology residents. Urology. 2021;157:57-63.
55. Janko MR, Smeds MR. Burnout, depression, perceived stress, and self-efficacy in vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69(4):1233-1242.
56. Coleman DM, Money SR, Meltzer AJ, et al. Vascular surgeon wellness and burnout: a report from the Society for Vascular Surgery Wellness Task Force. J Vasc Surg. 2021;73(6):1841-1850.e3.
57. Barrack RL, Miller LS, Sotile WM, et al. Effect of duty hour standards on burnout among orthopaedic surgery residents. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:134-137.
58. Chia MC, Hu YY, Li RD, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for burnout in U.S. vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2022;75(1):308-315.e4.
59. Shanafelt TD, Oreskovich MR, Dyrbye LN, et al. Avoiding burnout: the personal health habits and wellness practices of US surgeons. Ann Surg. 2012;255(4):625-633.
1. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD). 11th ed. World Health Organization; 2019.
2. Coombs DM, Lanni MA, Fosnot J, et al. Professional burnout in United States plastic surgery residents: is it a legitimate concern? Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(7):802-810.
3. Klimo P Jr, DeCuypere M, Ragel BT, et al. Career satisfaction and burnout among U.S. neurosurgeons: a feasibility and pilot study. World Neurosurg. 2013;80(5):e59-e68.
4. Ha GQ, Go JT, Murayama KM, et al. Identifying sources of stress across years of general surgery residency. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2020;79(3):75-81.
5. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. A national survey on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon burnout and career satisfaction among neurosurgery residents. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;80:137-142.
6. Al-Humadi SM, Cáceda R, Bronson B, et al. Orthopaedic surgeon mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Geriatric Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2021;12:21514593211035230.
7. Larson DP, Carlson ML, Lohse CM, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part I, trainees. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1019-1029.
8. Streu R, Hawley S, Gay A, et al. Satisfaction with career choice among U.S. plastic surgeons: results from a national survey. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):636-642.
9. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps GJ, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2009;250(3):463-471.
10. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Bechamps G, et al. Burnout and medical errors among American surgeons. Ann Surg. 2010;251(6):995-1000.
11. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336-341.
12. Yesantharao P, Lee E, Kraenzlin F, et al. Surgical block time satisfaction: a multi-institutional experience across twelve surgical disciplines. Perioperative Care Operating Room Manage. 2020;21:100128.
13. Nituica C, Bota OA, Blebea J. Specialty differences in resident resilience and burnout - a national survey. Am J Surg. 2021;222(2):319-328.
14. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Dyrbye L, et al. Surgeon distress as calibrated by hours worked and nights on call. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211(5):609-619.
15. Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Satele D, Sloan J, Freischlag J. Relationship between work-home conflicts and burnout among American surgeons: a comparison by sex. Arch Surg. 2011;146(2):211-217.
16. Mahoney ST, Irish W, Strassle PD, et al. Practice characteristics and job satisfaction of private practice and academic surgeons. JAMA Surg. 2021;156(3):247-254.
17. Shanafelt TD, Balch CM, Dyrbye L, et al. Special report: suicidal ideation among American surgeons. Arch Surg. 2011;146(1):54-62.
18. Chow OS, Sudarshan M, Maxfield MW, et al. National survey of burnout and distress among cardiothoracic surgery trainees. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;111(6):2066-2071.
19. Lam C, Kim Y, Cruz M, et al. Burnout and resiliency in Mohs surgeons: a survey study. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7(3):319-322.
20. Carlson ML, Larson DP, O’Brien EK, et al. Prevalence of and associations with distress and professional burnout among otolaryngologists: part II, attending physicians. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;164(5):1030-1039.
21. Nida AM, Googe BJ, Lewis AF, et al. Resident fatigue in otolaryngology residents: a Web based survey. Am J Otolaryngol. 2016;37(3):210-216.
22. Antiel RM, Reed DA, Van Arendonk KJ, et al. Effects of duty hour restrictions on core competencies, education, quality of life, and burnout among general surgery interns. JAMA Surg. 2013;148(5):448-455.
23. Appelbaum NP, Lee N, Amendola M, et al. Surgical resident burnout and job satisfaction: the role of workplace climate and perceived support. J Surg Res. 2019;234:20-25.
24. Elmore LC, Jeffe DB, Jin L, et al. National survey of burnout among US general surgery residents. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;223(3):440-451.
25. Garcia DI, Pannuccio A, Gallegos J, et al. Resident-driven wellness initiatives improve resident wellness and perception of work environment. J Surg Res. 2021;258:8-16.
26. Hochberg MS, Berman RS, Kalet AL, et al. The stress of residency: recognizing the signs of depression and suicide in you and your fellow residents. Am J Surg. 2013;205(2):141-146.
27. Kurbatov V, Shaughnessy M, Baratta V, et al. Application of advanced bioinformatics to understand and predict burnout among surgical trainees. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(3):499-507.
28. Leach PK, Nygaard RM, Chipman JG, et al. Impostor phenomenon and burnout in general surgeons and general surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2019;76(1):99-106.
29. Lebares CC, Greenberg AL, Ascher NL, et al. Exploration of individual and system-level well-being initiatives at an academic surgical residency program: a mixed-methods study. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2032676.
30. Lindeman BM, Sacks BC, Hirose K, et al. Multifaceted longitudinal study of surgical resident education, quality of life, and patient care before and after July 2011. J Surg Educ. 2013;70(6):769-776.
31. Rasmussen JM, Najarian MM, Ties JS, et al. Career satisfaction, gender bias, and work-life balance: a contemporary assessment of general surgeons. J Surg Educ. 2021;78(1):119-125.
32. Smeds MR, Janko MR, Allen S, et al. Burnout and its relationship with perceived stress, self-efficacy, depression, social support, and programmatic factors in general surgery residents. Am J Surg. 2020;219(6):907-912.
33. Wetzel CM, George A, Hanna GB, et al. Stress management training for surgeons--a randomized, controlled, intervention study. Ann Surg. 2011;253(3):488-494.
34. Williford ML, Scarlet S, Meyers MO, et al. Multiple-institution comparison of resident and faculty perceptions of burnout and depression during surgical training. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(8):705-711.
35. Zubair MH, Hussain LR, Williams KN, et al. Work-related quality of life of US general surgery residents: is it really so bad? J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):e138-e146.
36. Song Y, Swendiman RA, Shannon AB, et al. Can we coach resilience? An evaluation of professional resilience coaching as a well-being initiative for surgical interns. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(6):1481-1489.
37. Morrell NT, Sears ED, Desai MJ, et al. A survey of burnout among members of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. J Hand Surg Am. 2020;45(7):573-581.e516.
38. Khalafallah AM, Lam S, Gami A, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among attending neurosurgeons during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;198:106193.
39. McAbee JH, Ragel BT, McCartney S, et al. Factors associated with career satisfaction and burnout among US neurosurgeons: results of a nationwide survey. J Neurosurg. 2015;123(1):161-173.
40. Shakir HJ, McPheeters MJ, Shallwani H, et al. The prevalence of burnout among US neurosurgery residents. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(3):582-590.
41. Govardhan LM, Pinelli V, Schnatz PF. Burnout, depression and job satisfaction in obstetrics and gynecology residents. Conn Med. 2012;76(7):389-395.
42. Driesman AS, Strauss EJ, Konda SR, et al. Factors associated with orthopaedic resident burnout: a pilot study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(21):900-906.
43. Lichstein PM, He JK, Estok D, et al. What is the prevalence of burnout, depression, and substance use among orthopaedic surgery residents and what are the risk factors? A collaborative orthopaedic educational research group survey study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(8):1709-1718.
44. Somerson JS, Patton A, Ahmed AA, et al. Burnout among United States orthopaedic surgery residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77(4):961-968.
45. Verret CI, Nguyen J, Verret C, et al. How do areas of work life drive burnout in orthopaedic attending surgeons, fellows, and residents? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021;479(2):251-262.
46. Sarosi A, Coakley BA, Berman L, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction in pediatric surgeons in the U.S. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56(8):1276-1284.
47. Crowe CS, Lopez J, Morrison SD, et al. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on resident education and wellness: a national survey of plastic surgery residents. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(3):462e-474e.
48. Qureshi HA, Rawlani R, Mioton LM, et al. Burnout phenomenon in U.S. plastic surgeons: risk factors and impact on quality of life. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2):619-626.
49. Streu R, Hansen J, Abrahamse P, et al. Professional burnout among US plastic surgeons: results of a national survey. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;72(3):346-350.
50. Zhang JQ, Riba L, Magrini L, ET AL. Assessing burnout and professional fulfillment in breast surgery: results from a national survey of the American Society of Breast Surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(10):3089-3098.
51. Balch CM, Shanafelt TD, Sloan J, et al. Burnout and career satisfaction among surgical oncologists compared with other surgical specialties. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(1):16-25.
52. Wu D, Gross B, Rittenhouse K, et al. A preliminary analysis of compassion fatigue in a surgeon population: are female surgeons at heightened risk? Am Surg. 2017;83(11):1302-1307.
53. Cheng JW, Wagner H, Hernandez BC, et al. Stressors and coping mechanisms related to burnout within urology. Urology. 2020;139:27-36.
54. Koo K, Javier-DesLoges JF, Fang R, ET AL. Professional burnout, career choice regret, and unmet needs for well-being among urology residents. Urology. 2021;157:57-63.
55. Janko MR, Smeds MR. Burnout, depression, perceived stress, and self-efficacy in vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2019;69(4):1233-1242.
56. Coleman DM, Money SR, Meltzer AJ, et al. Vascular surgeon wellness and burnout: a report from the Society for Vascular Surgery Wellness Task Force. J Vasc Surg. 2021;73(6):1841-1850.e3.
57. Barrack RL, Miller LS, Sotile WM, et al. Effect of duty hour standards on burnout among orthopaedic surgery residents. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;449:134-137.
58. Chia MC, Hu YY, Li RD, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for burnout in U.S. vascular surgery trainees. J Vasc Surg. 2022;75(1):308-315.e4.
59. Shanafelt TD, Oreskovich MR, Dyrbye LN, et al. Avoiding burnout: the personal health habits and wellness practices of US surgeons. Ann Surg. 2012;255(4):625-633.
Brain damage from recurrent relapses of bipolar mania: A call for early LAI use
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a psychotic mood disorder. Like schizophrenia, it has been shown to be associated with significant degeneration and structural brain abnormalities with multiple relapses.1,2
Just as I have always advocated preventing recurrences in schizophrenia by using long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotic formulations immediately after the first episode to prevent psychotic relapses and progressive brain damage,3 I strongly recommend using LAIs right after hospital discharge from the first manic episode. It is the most rational management approach for bipolar mania given the grave consequences of multiple episodes, which are so common in this psychotic mood disorder due to poor medication adherence.
In contrast to the depressive episodes of BD I, where patients have insight into their depression and seek psychiatric treatment, during a manic episode patients often have no insight (anosognosia) that they suffer from a serious brain disorder, and refuse treatment.4 In addition, young patients with BD I frequently discontinue their oral mood stabilizer or second-generation antipsychotic (which are approved for mania) because they miss the blissful euphoria and the buoyant physical and mental energy of their manic episodes. They are completely oblivious to (and uninformed about) the grave neurobiological damage of further manic episodes, which can condemn them to clinical, functional, and cognitive deterioration. These patients are also likely to become treatment-resistant, which has been labeled as “the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder.”5
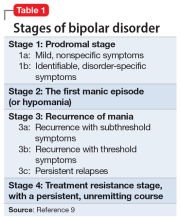
The evidence for progressive brain tissue loss, clinical deterioration, functional decline, and treatment resistance is abundant.6 I was the lead investigator of the first study to report ventricular dilatation (which is a proxy for cortical atrophy) in bipolar mania,7 a discovery that was subsequently replicated by 2 dozen researchers. This was followed by numerous neuroimaging studies reporting a loss of volume across multiple brain regions, including the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, cerebellum, thalamus, hippocampus, and basal ganglia. BD is heterogeneous8 with 4 stages (Table 19), and patients experience progressively worse brain structure and function with each stage.
Many patients with bipolar mania end up with poor clinical and functional outcomes, even when they respond well to initial treatment with lithium, anticonvulsant mood stabilizers, or second-generation antipsychotics. With their intentional nonadherence to oral medications leading to multiple recurrent relapses, these patients are at serious risk for neuroprogression and brain atrophic changes driven by multiple factors: inflammatory cytokines, increased cortical steroids, decreased neurotrophins, deceased neurogenesis, increased oxidative stress, and mitochondrial energy dysfunction. The consequences include progressive shortening of the interval between episodes with every relapse and loss of responsiveness to pharmacotherapy as the illness progresses.6,10 Predictors of a downhill progression include genetic vulnerability, perinatal complication during fetal life, childhood trauma (physical, sexual, emotional, or neglect), substance use, stress, psychiatric/medial comorbidities, and especially the number of episodes.9,11
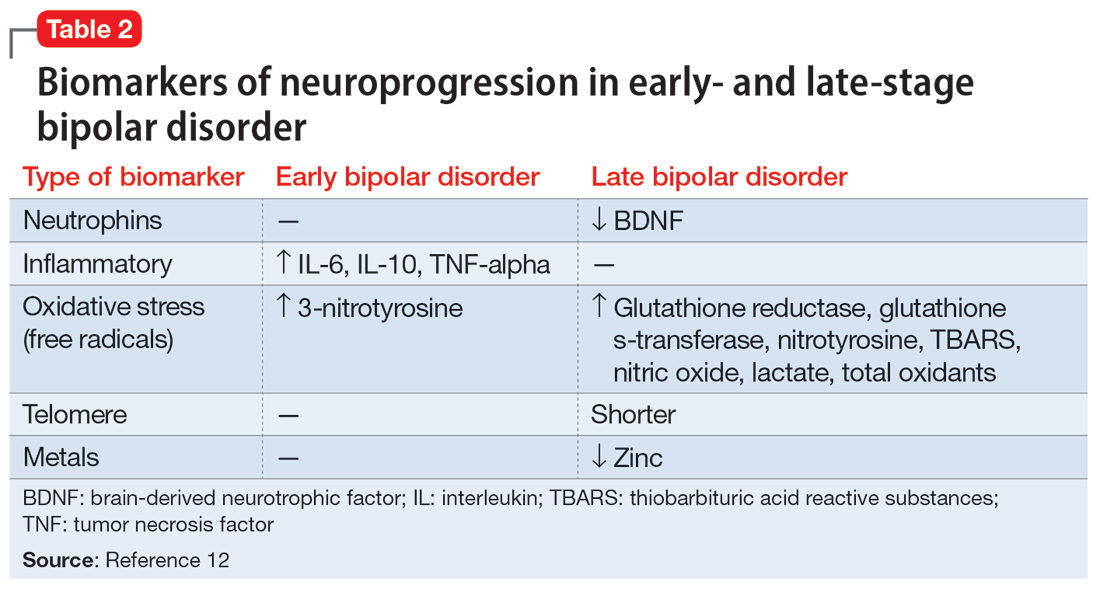
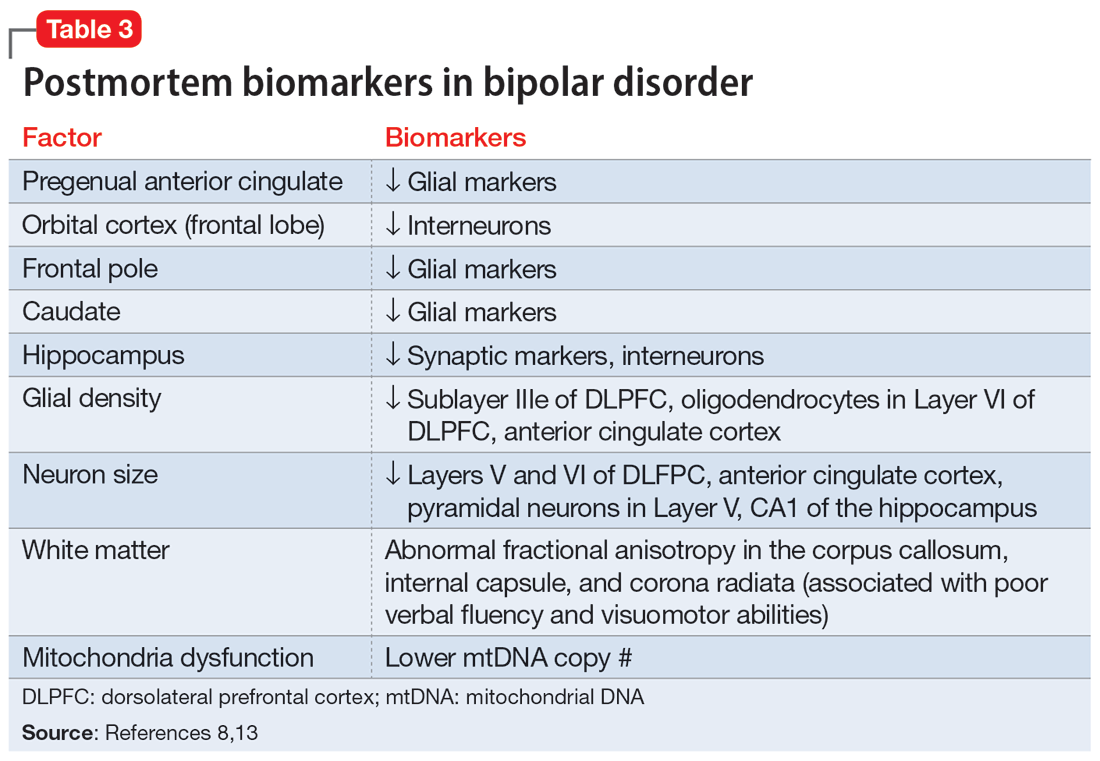
Biomarkers have been reported in both the early and late stages of BD (Table 212) as well as in postmortem studies (Table 38,13). They reflect the progressive neurodegenerative nature of recurrent BD I episodes as the disorder moves to the advanced stages. I summarize these stages in Table 19 and Table 212 for the benefit of psychiatric clinicians who do not have access to the neuroscience journals where such findings are usually published.
BD I is also believed to be associated with accelerated aging14,15 and an increased risk for dementia16 or cognitive deterioration.17 There is also an emerging hypothesis that neuroprogression and treatment resistance in BD is frequently associated with insulin resistance,18 peripheral inflammation,19 and blood-brain barrier permeability dysfunction.20
The bottom line is that like patients with schizophrenia, where relapses lead to devastating consequences,21 those with BD are at a similar high risk for neuroprogression, which includes atrophy in several brain regions, treatment resistance, and functional disability. This underscores the urgency for implementing LAI therapy early in the illness, when the first manic episode (Stage 2) emerges after the prodrome (Stage 1). This is the best strategy to preserve brain health in persons with BD22 and to allow them to remain functional with their many intellectual gifts, such as eloquence, poetry, artistic talents, humor, and social skills. It is unfortunate that the combination of patients’ and clinicians’ reluctance to use an LAI early in the illness dooms many patients with BD to a potentially avoidable malignant outcome.
1. Strakowski SM, DelBello MP, Adler CM. The functional neuroanatomy of bipolar disorder: a review of neuroimaging findings. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(1):105-106.
2. Kapezinski NS, Mwangi B, Cassidy RM, et al. Neuroprogression and illness trajectories in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2017;17(3):277-285.
3. Nasrallah HA. Errors of omission and commission in psychiatric practice. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(11):4,6,8.
4. Nasrallah HA. Is anosognosia a delusion, a negative symptom, or a cognitive deficit? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(1):6-8,14.
5. Post RM. Preventing the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder. JAMA. 2018;319(12):1197-1198.
6. Berk M, Kapczinski F, Andreazza AC, et al. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35(3):804-817.
7. Nasrallah HA, McCalley-Whitters M, Jacoby CG. Cerebral ventricular enlargement in young manic males. A controlled CT study. J Affective Dis. 1982;4(1):15-19.
8. Maletic V, Raison C. Integrated neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2014;5:98.
9. Berk M. Neuroprogression: pathways to progressive brain changes in bipolar disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;12(4):441-445.
10. Berk M, Conus P, Kapczinski F, et al. From neuroprogression to neuroprotection: implications for clinical care. Med J Aust. 2010;193(S4):S36-S40.
11. Passos IC, Mwangi B, Vieta E, et al. Areas of controversy in neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2016;134(2):91-103.
12. Fries GR, Pfaffenseller B, Stertz L, et al. Staging and neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012;14(6):667-675.
13. Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS. The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat Med. 2001;7(5):541-547.
14. Fries GR, Zamzow MJ, Andrews T, et al. Accelerated aging in bipolar disorder: a comprehensive review of molecular findings and their clinical implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;112:107-116.
15. Fries GR, Bauer IE, Scaini G, et al. Accelerated hippocampal biological aging in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Dis. 2020;22(5):498-507.
16. Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Cao F, et al. History of bipolar disorder and the risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017;25(4):357-362.
17. Bauer IE, Ouyang A, Mwangi B, et al. Reduced white matter integrity and verbal fluency impairment in young adults with bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;62:115-122.
18. Calkin CV. Insulin resistance takes center stage: a new paradigm in the progression of bipolar disorder. Ann Med. 2019;51(5-6):281-293.
19. Grewal S, McKinlay S, Kapczinski F, et al. Biomarkers of neuroprogression and late staging in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2023;57(3):328-343.
20. Calkin C, McClelland C, Cairns K, et al. Insulin resistance and blood-brain barrier dysfunction underlie neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:636174.
21. Nasrallah HA. 10 devastating consequences of psychotic relapses. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(5):9-12.
22. Berk M, Hallam K, Malhi GS, et al. Evidence and implications for early intervention in bipolar disorder. J Ment Health. 2010;19(2):113-126.
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a psychotic mood disorder. Like schizophrenia, it has been shown to be associated with significant degeneration and structural brain abnormalities with multiple relapses.1,2
Just as I have always advocated preventing recurrences in schizophrenia by using long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotic formulations immediately after the first episode to prevent psychotic relapses and progressive brain damage,3 I strongly recommend using LAIs right after hospital discharge from the first manic episode. It is the most rational management approach for bipolar mania given the grave consequences of multiple episodes, which are so common in this psychotic mood disorder due to poor medication adherence.
In contrast to the depressive episodes of BD I, where patients have insight into their depression and seek psychiatric treatment, during a manic episode patients often have no insight (anosognosia) that they suffer from a serious brain disorder, and refuse treatment.4 In addition, young patients with BD I frequently discontinue their oral mood stabilizer or second-generation antipsychotic (which are approved for mania) because they miss the blissful euphoria and the buoyant physical and mental energy of their manic episodes. They are completely oblivious to (and uninformed about) the grave neurobiological damage of further manic episodes, which can condemn them to clinical, functional, and cognitive deterioration. These patients are also likely to become treatment-resistant, which has been labeled as “the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder.”5
The evidence for progressive brain tissue loss, clinical deterioration, functional decline, and treatment resistance is abundant.6 I was the lead investigator of the first study to report ventricular dilatation (which is a proxy for cortical atrophy) in bipolar mania,7 a discovery that was subsequently replicated by 2 dozen researchers. This was followed by numerous neuroimaging studies reporting a loss of volume across multiple brain regions, including the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, cerebellum, thalamus, hippocampus, and basal ganglia. BD is heterogeneous8 with 4 stages (Table 19), and patients experience progressively worse brain structure and function with each stage.
Many patients with bipolar mania end up with poor clinical and functional outcomes, even when they respond well to initial treatment with lithium, anticonvulsant mood stabilizers, or second-generation antipsychotics. With their intentional nonadherence to oral medications leading to multiple recurrent relapses, these patients are at serious risk for neuroprogression and brain atrophic changes driven by multiple factors: inflammatory cytokines, increased cortical steroids, decreased neurotrophins, deceased neurogenesis, increased oxidative stress, and mitochondrial energy dysfunction. The consequences include progressive shortening of the interval between episodes with every relapse and loss of responsiveness to pharmacotherapy as the illness progresses.6,10 Predictors of a downhill progression include genetic vulnerability, perinatal complication during fetal life, childhood trauma (physical, sexual, emotional, or neglect), substance use, stress, psychiatric/medial comorbidities, and especially the number of episodes.9,11

Biomarkers have been reported in both the early and late stages of BD (Table 212) as well as in postmortem studies (Table 38,13). They reflect the progressive neurodegenerative nature of recurrent BD I episodes as the disorder moves to the advanced stages. I summarize these stages in Table 19 and Table 212 for the benefit of psychiatric clinicians who do not have access to the neuroscience journals where such findings are usually published.

BD I is also believed to be associated with accelerated aging14,15 and an increased risk for dementia16 or cognitive deterioration.17 There is also an emerging hypothesis that neuroprogression and treatment resistance in BD is frequently associated with insulin resistance,18 peripheral inflammation,19 and blood-brain barrier permeability dysfunction.20
The bottom line is that like patients with schizophrenia, where relapses lead to devastating consequences,21 those with BD are at a similar high risk for neuroprogression, which includes atrophy in several brain regions, treatment resistance, and functional disability. This underscores the urgency for implementing LAI therapy early in the illness, when the first manic episode (Stage 2) emerges after the prodrome (Stage 1). This is the best strategy to preserve brain health in persons with BD22 and to allow them to remain functional with their many intellectual gifts, such as eloquence, poetry, artistic talents, humor, and social skills. It is unfortunate that the combination of patients’ and clinicians’ reluctance to use an LAI early in the illness dooms many patients with BD to a potentially avoidable malignant outcome.
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a psychotic mood disorder. Like schizophrenia, it has been shown to be associated with significant degeneration and structural brain abnormalities with multiple relapses.1,2
Just as I have always advocated preventing recurrences in schizophrenia by using long-acting injectable (LAI) antipsychotic formulations immediately after the first episode to prevent psychotic relapses and progressive brain damage,3 I strongly recommend using LAIs right after hospital discharge from the first manic episode. It is the most rational management approach for bipolar mania given the grave consequences of multiple episodes, which are so common in this psychotic mood disorder due to poor medication adherence.
In contrast to the depressive episodes of BD I, where patients have insight into their depression and seek psychiatric treatment, during a manic episode patients often have no insight (anosognosia) that they suffer from a serious brain disorder, and refuse treatment.4 In addition, young patients with BD I frequently discontinue their oral mood stabilizer or second-generation antipsychotic (which are approved for mania) because they miss the blissful euphoria and the buoyant physical and mental energy of their manic episodes. They are completely oblivious to (and uninformed about) the grave neurobiological damage of further manic episodes, which can condemn them to clinical, functional, and cognitive deterioration. These patients are also likely to become treatment-resistant, which has been labeled as “the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder.”5
The evidence for progressive brain tissue loss, clinical deterioration, functional decline, and treatment resistance is abundant.6 I was the lead investigator of the first study to report ventricular dilatation (which is a proxy for cortical atrophy) in bipolar mania,7 a discovery that was subsequently replicated by 2 dozen researchers. This was followed by numerous neuroimaging studies reporting a loss of volume across multiple brain regions, including the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, cerebellum, thalamus, hippocampus, and basal ganglia. BD is heterogeneous8 with 4 stages (Table 19), and patients experience progressively worse brain structure and function with each stage.
Many patients with bipolar mania end up with poor clinical and functional outcomes, even when they respond well to initial treatment with lithium, anticonvulsant mood stabilizers, or second-generation antipsychotics. With their intentional nonadherence to oral medications leading to multiple recurrent relapses, these patients are at serious risk for neuroprogression and brain atrophic changes driven by multiple factors: inflammatory cytokines, increased cortical steroids, decreased neurotrophins, deceased neurogenesis, increased oxidative stress, and mitochondrial energy dysfunction. The consequences include progressive shortening of the interval between episodes with every relapse and loss of responsiveness to pharmacotherapy as the illness progresses.6,10 Predictors of a downhill progression include genetic vulnerability, perinatal complication during fetal life, childhood trauma (physical, sexual, emotional, or neglect), substance use, stress, psychiatric/medial comorbidities, and especially the number of episodes.9,11

Biomarkers have been reported in both the early and late stages of BD (Table 212) as well as in postmortem studies (Table 38,13). They reflect the progressive neurodegenerative nature of recurrent BD I episodes as the disorder moves to the advanced stages. I summarize these stages in Table 19 and Table 212 for the benefit of psychiatric clinicians who do not have access to the neuroscience journals where such findings are usually published.

BD I is also believed to be associated with accelerated aging14,15 and an increased risk for dementia16 or cognitive deterioration.17 There is also an emerging hypothesis that neuroprogression and treatment resistance in BD is frequently associated with insulin resistance,18 peripheral inflammation,19 and blood-brain barrier permeability dysfunction.20
The bottom line is that like patients with schizophrenia, where relapses lead to devastating consequences,21 those with BD are at a similar high risk for neuroprogression, which includes atrophy in several brain regions, treatment resistance, and functional disability. This underscores the urgency for implementing LAI therapy early in the illness, when the first manic episode (Stage 2) emerges after the prodrome (Stage 1). This is the best strategy to preserve brain health in persons with BD22 and to allow them to remain functional with their many intellectual gifts, such as eloquence, poetry, artistic talents, humor, and social skills. It is unfortunate that the combination of patients’ and clinicians’ reluctance to use an LAI early in the illness dooms many patients with BD to a potentially avoidable malignant outcome.
1. Strakowski SM, DelBello MP, Adler CM. The functional neuroanatomy of bipolar disorder: a review of neuroimaging findings. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(1):105-106.
2. Kapezinski NS, Mwangi B, Cassidy RM, et al. Neuroprogression and illness trajectories in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2017;17(3):277-285.
3. Nasrallah HA. Errors of omission and commission in psychiatric practice. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(11):4,6,8.
4. Nasrallah HA. Is anosognosia a delusion, a negative symptom, or a cognitive deficit? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(1):6-8,14.
5. Post RM. Preventing the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder. JAMA. 2018;319(12):1197-1198.
6. Berk M, Kapczinski F, Andreazza AC, et al. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35(3):804-817.
7. Nasrallah HA, McCalley-Whitters M, Jacoby CG. Cerebral ventricular enlargement in young manic males. A controlled CT study. J Affective Dis. 1982;4(1):15-19.
8. Maletic V, Raison C. Integrated neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2014;5:98.
9. Berk M. Neuroprogression: pathways to progressive brain changes in bipolar disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;12(4):441-445.
10. Berk M, Conus P, Kapczinski F, et al. From neuroprogression to neuroprotection: implications for clinical care. Med J Aust. 2010;193(S4):S36-S40.
11. Passos IC, Mwangi B, Vieta E, et al. Areas of controversy in neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2016;134(2):91-103.
12. Fries GR, Pfaffenseller B, Stertz L, et al. Staging and neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012;14(6):667-675.
13. Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS. The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat Med. 2001;7(5):541-547.
14. Fries GR, Zamzow MJ, Andrews T, et al. Accelerated aging in bipolar disorder: a comprehensive review of molecular findings and their clinical implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;112:107-116.
15. Fries GR, Bauer IE, Scaini G, et al. Accelerated hippocampal biological aging in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Dis. 2020;22(5):498-507.
16. Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Cao F, et al. History of bipolar disorder and the risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017;25(4):357-362.
17. Bauer IE, Ouyang A, Mwangi B, et al. Reduced white matter integrity and verbal fluency impairment in young adults with bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;62:115-122.
18. Calkin CV. Insulin resistance takes center stage: a new paradigm in the progression of bipolar disorder. Ann Med. 2019;51(5-6):281-293.
19. Grewal S, McKinlay S, Kapczinski F, et al. Biomarkers of neuroprogression and late staging in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2023;57(3):328-343.
20. Calkin C, McClelland C, Cairns K, et al. Insulin resistance and blood-brain barrier dysfunction underlie neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:636174.
21. Nasrallah HA. 10 devastating consequences of psychotic relapses. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(5):9-12.
22. Berk M, Hallam K, Malhi GS, et al. Evidence and implications for early intervention in bipolar disorder. J Ment Health. 2010;19(2):113-126.
1. Strakowski SM, DelBello MP, Adler CM. The functional neuroanatomy of bipolar disorder: a review of neuroimaging findings. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(1):105-106.
2. Kapezinski NS, Mwangi B, Cassidy RM, et al. Neuroprogression and illness trajectories in bipolar disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2017;17(3):277-285.
3. Nasrallah HA. Errors of omission and commission in psychiatric practice. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(11):4,6,8.
4. Nasrallah HA. Is anosognosia a delusion, a negative symptom, or a cognitive deficit? Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(1):6-8,14.
5. Post RM. Preventing the malignant transformation of bipolar disorder. JAMA. 2018;319(12):1197-1198.
6. Berk M, Kapczinski F, Andreazza AC, et al. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011;35(3):804-817.
7. Nasrallah HA, McCalley-Whitters M, Jacoby CG. Cerebral ventricular enlargement in young manic males. A controlled CT study. J Affective Dis. 1982;4(1):15-19.
8. Maletic V, Raison C. Integrated neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2014;5:98.
9. Berk M. Neuroprogression: pathways to progressive brain changes in bipolar disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;12(4):441-445.
10. Berk M, Conus P, Kapczinski F, et al. From neuroprogression to neuroprotection: implications for clinical care. Med J Aust. 2010;193(S4):S36-S40.
11. Passos IC, Mwangi B, Vieta E, et al. Areas of controversy in neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2016;134(2):91-103.
12. Fries GR, Pfaffenseller B, Stertz L, et al. Staging and neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2012;14(6):667-675.
13. Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS. The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat Med. 2001;7(5):541-547.
14. Fries GR, Zamzow MJ, Andrews T, et al. Accelerated aging in bipolar disorder: a comprehensive review of molecular findings and their clinical implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;112:107-116.
15. Fries GR, Bauer IE, Scaini G, et al. Accelerated hippocampal biological aging in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Dis. 2020;22(5):498-507.
16. Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Cao F, et al. History of bipolar disorder and the risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2017;25(4):357-362.
17. Bauer IE, Ouyang A, Mwangi B, et al. Reduced white matter integrity and verbal fluency impairment in young adults with bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;62:115-122.
18. Calkin CV. Insulin resistance takes center stage: a new paradigm in the progression of bipolar disorder. Ann Med. 2019;51(5-6):281-293.
19. Grewal S, McKinlay S, Kapczinski F, et al. Biomarkers of neuroprogression and late staging in bipolar disorder: a systematic review. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2023;57(3):328-343.
20. Calkin C, McClelland C, Cairns K, et al. Insulin resistance and blood-brain barrier dysfunction underlie neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:636174.
21. Nasrallah HA. 10 devastating consequences of psychotic relapses. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(5):9-12.
22. Berk M, Hallam K, Malhi GS, et al. Evidence and implications for early intervention in bipolar disorder. J Ment Health. 2010;19(2):113-126.
Infested with worms, but are they really there?
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
CASE Detoxification and preoccupation with parasites
Mr. H, age 51, has an extensive history of alcohol and methamphetamine use. He presents to the emergency department (ED) requesting inpatient detoxification. He says he had been drinking alcohol but is unable to say how much. His blood ethanol level is 61 mg/dL (unintoxicated level: <50 mg/dL), and a urine drug screen is positive for methamphetamine; Mr. H also admits to using fentanyl. The ED team treats Mr. H’s electrolyte abnormalities, initiates thiamine supplementation, and transfers him to a unit for inpatient withdrawal management.
On the detoxification unit, Mr. H receives a total of 1,950 mg of phenobarbital for alcohol withdrawal and stabilizes on a buprenorphine/naloxone maintenance dose of 8 mg/2 mg twice daily for methamphetamine and fentanyl use. Though he was not taking any psychiatric medications prior to his arrival at the ED, Mr. H agrees to restart quetiapine
During Mr. H’s 3-day detoxification, the psychiatry team evaluates him. Mr. H says he believes he is infested with worms. He describes a prior sensation of “meth mites,” or the feeling of bugs crawling under his skin, while using methamphetamines. However, Mr. H says his current infestation feels distinctively different, and he had continued to experience these
The psychiatry team expresses concern over his preoccupation with infestations, disheveled appearance, poor hygiene, and healed scars from excoriation. Mr. H also reports poor sleep and appetite and was observed writing an incomprehensible “experiment” on a paper towel. Due to his bizarre behavior, delusional thoughts, and concerns about his inability to care for himself, the team admits Mr. H to the acute inpatient psychiatric unit on a voluntary commitment.
HISTORY Long-standing drug use and repeated hospital visits
Mr. H reports a history of drug use. His first documented ED visit was >5 years before his current admission. He has a family history of substance abuse and reports previously using methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol. Mr. H was never diagnosed with a psychiatric illness, but when he was younger, there were suspicions of bipolar depression, with no contributing family psychiatric history. Though he took quetiapine at an unspecified younger age, Mr. H did not follow through with any outpatient mental health services or medications.
Mr. H first reported infestation
In the 6 months prior to his current admission, Mr. H came to the hospital >20 times for various reasons, including methamphetamine abuse, alcohol withdrawal, opiate overdose, cellulitis, wound checks, and 3 visits for hallucinations for which he requested physical evaluation and medical care. His substance use was the suspected cause of his tactile and visual hallucinations of infestation because formication
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also known as delusional infestation or Ekbom Syndrome, is a condition characterized by the fixed, false belief of an infestation without any objective evidence. This condition was previously defined in DSM-IV, but was removed from DSM-5-TR. In DSM-5-TR, DP is most closely associated with delusional disorder
DP is rare, affecting approximately 1.9 per 100,000 people. There has not been consistent data supporting differences in prevalence between sexes, but there is evidence for increasing incidence with age, with a mean age of diagnosis of 61.4.2,3 DP can be divided into 2 types based on the history and etiology of the symptoms: primary DP and secondary DP. Primary DP occurs when there is a failure to identify an organic cause for the occurrence of the symptoms. Therefore, primary DP requires an extensive investigation by a multidisciplinary team that commonly includes medical specialists for a nonpsychiatric workup. Secondary DP occurs when the patient has delusional symptoms associated with a primary diagnosis of schizophrenia, depression, stroke, diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or substance use.4
Though Mr. H initially presented to the ED, patients with DP commonly present to a primary care physician or dermatologist with the complaint of itching or feelings of insects, worms, or unclear organisms inside them. Patients with DP may often develop poor working relationships with physicians while obtaining multiple negative results. They may seek opinions from multiple specialists; however, patients typically do not consider psychiatrists as a source of help. When patients seek psychiatric care, often after a recommendation from a primary care physician or dermatologist, mental health clinicians should listen to and evaluate the patient holistically, continuing to rule out other possible etiologies.
[polldaddy:12570072]
TREATMENT Finding the right antipsychotic
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. H says he believes worms are exiting his ears, mouth, toenail, and self-inflicted scratch wounds. He believes he has been dealing with the parasites for >1 year and they are slowly draining his energy. Mr. H insists he contracted the “infection” from his home carpet, which was wet due to a flood in his house, and after he had fallen asleep following drug use. He also believes he acquired the parasites while walking barefoot along the beach and collecting rocks, and that there are multiple species living inside him, all intelligent enough to hide, making it difficult to prove their existence. He notes they vary in size, and some have red eyes.
During admission, Mr. H voices his frustration that clinicians had not found the worms he has been seeing. He continuously requests to review imaging performed during his visit and wants a multidisciplinary team to evaluate his case. He demands to test a cup with spit-up “samples,” believing the parasites would be visible under a microscope. Throughout his admission, Mr. H continues to take buprenorphine/naloxone and does not experience withdrawal symptoms. The treatment team titrates his quetiapine to 400 mg/d. Due to the lack of improvement, the team initiates olanzapine 5 mg/d at bedtime. However, Mr. H reports significant tinnitus and requests a medication change. He is started on haloperidol 5 mg twice daily.
Continue to: Mr. H begins to see improvements...
Mr. H begins to see improvements on Day 7 of taking haloperidol. He no longer brings up infestation but still acknowledges having worms inside him when directly asked. He says the worms cause him less distress than before and he is hopeful to live without discomfort. He also demonstrates an ability to conduct activities of daily living. Because Mr. H is being monitored on an acute inpatient psychiatric basis, he is deemed appropriate for discharge even though his symptoms have not yet fully resolved. After a 19-day hospital stay, Mr. H is discharged on haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d.
[polldaddy:12570074]
The authors’ observations
Mr. H asked to have his sputum examined. The “specimen sign,” also called “matchbox sign” or “Ziploc bag sign,” in which patients collect what they believe to be infected tissue or organisms in a container, is a well-studied part of DP.5 Such samples should be considered during initial encounters and can be examined for formal evaluation, but cautiously. Overtesting may incur a financial burden or reinforce deleterious beliefs and behaviors.
It can be difficult to identify triggers of DP. Research shows DP may arise from nonorganic and stressful life events, home floods, or contact with people infected with parasites.6,7 Organic causes have also been found, such as patients taking multiple medications for Parkinson disease who developed delusional symptoms.8 Buscarino et al9 reported the case of a woman who started to develop symptoms of delusions and hallucinations after being on high-dose amphetamines for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Research shows that stopping the suspected medication commonly improves such symptoms.9,10 Although methamphetamine can remain detectable in urine for up to 4 days after use and potentially a few days longer for chronic users due to circulating levels,11 Mr. H’s symptoms continued for weeks after all substances of abuse should have been cleared from his system. This suggests he was experiencing a psychiatric illness and was accurate in distinguishing methamphetamine-induced from psychiatric-induced sensations. Regardless, polysubstance use has been shown to potentially increase the risk and play a role in the onset and progression of delusional illness, as seen in prior cases as well as in this case.9
It has been hypothesized that the pathophysiology of DP is associated with the deterioration of the striatal dopaminergic pathway, leading to an increase in extracellular dopamine levels. The striatum is responsible for most dopamine reuptake in the brain; therefore, certain drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate may precipitate symptoms of DP due to their blockade of presynaptic dopamine reuptake.12 Additionally, conditions that decrease the functioning of striatal dopamine transporters, such as schizophrenia or depression, may be underlying causes of DP.13
Treatment of DP remains a topic of debate. Most current recommendations appear to be based on a small, nonrandomized placebo-controlled trial.14 The first-generation antipsychotic pimozide had been a first-line treatment for DP, but its adverse effect profile, which includes QTc prolongation and extrapyramidal symptoms, led to the exploration of second-generation antipsychotics such as olanzapine and risperidone.15,16 There is a dearth of literature about the use of haloperidol, quetiapine, or a combination of both as treatment options for DP, though the combination of these 2 medications proved effective for Mr. H. Further research is necessary to justify changes to current treatment standards, but this finding highlights a successful symptom reduction achieved with this combination.
Continue to: Patients may experience genuine symptoms...
Patients may experience genuine symptoms despite the delusional nature of DP, and it is important for clinicians to recognize the potential burden and anxiety these individuals face. Patients may present with self-inflicted bruises, cuts, and erosions to gain access to infected areas, which may be confused with skin picking disorder. Excessive cleansing or use of irritant products can also cause skin damage, leading to other dermatological conditions that reinforce the patient’s belief that something is medically wrong. During treatment, consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain. Focus on offering patients the opportunity to express their concerns, treat them with empathy, avoid stigmatizing language such as “delusions” or “psychosis,” and refrain from contradicting them until a strong rapport has been established (Table 217).
Symptoms of DP can persist for months to years. Patients who fully recovered experienced a median duration of 0.5 years until symptom resolution, compared to incompletely recovered patients, who took approximately 1 year.18 Primary DP has slower improvement rates compared to secondary DP, with the median onset of effects occurring at Week 1.5 and peak improvements occurring at Week 6.16
OUTCOME Continued ED visits
Unfortunately, Mr. H does not follow through with his outpatient psychiatry appointments. In the 7 months following discharge, he visits the ED 8 times for alcohol intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and methamphetamine abuse, in addition to 2 admissions for inpatient detoxification, during which he was still receiving the same scheduled medications (haloperidol 15 mg/d and quetiapine 200 mg/d). At each of his ED visits, there was no documentation of DP symptoms, which suggests his symptoms may have resolved.
Bottom Line
Because delusional parasitosis symptoms feel real to patients, it is crucial to build rapport to recommend and successfully initiate treatment. After ruling out nonpsychiatric etiologies, consider traditional treatment with antipsychotics, and consider medications for relief of pruritus or pain.
Related Resources
- Sellman D, Phan SV, Inyang M. Bugs on her skin—but nobody else sees them. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(8):48,50-53.
- Campbell EH, Elston DM, Hawthorne JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of delusional parasitosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(5):1428-1434. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.12.012
Drug Brand Names
Buprenorphine/naloxone • Suboxone
Haloperidol • Haldol
Hydroxyzine • Vistaril
Lithium • Eskalith, Lithobid
Methylphenidate • Concerta
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Permethrin • Elimite
Phenobarbital • Solfoton, Tedral, Luminal
Pimozide • Orap
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Risperidone • Risperdal
Sertraline • Zoloft
Valproic acid • Depakote
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
2. Bailey CH, Andersen LK, Lowe GC, et al. A population-based study of the incidence of delusional infestation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1976-2010. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170(5):1130-1135. doi:10.1111/bjd.12848
3. Kohorst JJ, Bailey CH, Andersen LK, et al. Prevalence of delusional infestation-a population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154(5):615-617. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.0004
4. Freinhar JP. Delusions of parasitosis. Psychosomatics. 1984;25(1):47-53. doi:10.1016/S0033-3182(84)73096-9
5. Reich A, Kwiatkowska D, Pacan P. Delusions of parasitosis: an update. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(4):631-638. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00324-3
6. Berrios GE. Delusional parasitosis and physical disease. Compr Psychiatry. 1985;26(5):395-403. doi:10.1016/0010-440x(85)90077-x
7. Aizenberg D, Schwartz B, Zemishlany Z. Delusional parasitosis associated with phenelzine. Br J Psychiatry. 1991;159:716-717. doi:10.1192/bjp.159.5.716
8. Flann S, Shotbolt J, Kessel B, et al. Three cases of delusional parasitosis caused by dopamine agonists. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35(7):740-742. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03810.x
9. Buscarino M, Saal J, Young JL. Delusional parasitosis in a female treated with mixed amphetamine salts: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2012;2012:624235. doi:10.1155/2012/624235
10. Elpern DJ. Cocaine abuse and delusions of parasitosis. Cutis. 1988;42(4):273-274.
11. Richards JR, Laurin EG. Methamphetamine toxicity. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Updated January 8, 2023. Accessed May 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430895/
12. Huber M, Kirchler E, Karner M, et al. Delusional parasitosis and the dopamine transporter. A new insight of etiology? Med Hypotheses. 2007;68(6):1351-1358. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2006.07.061
13. Lipman ZM, Yosipovitch G. Substance use disorders and chronic itch. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(1):148-155. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.117
14. Kenchaiah BK, Kumar S, Tharyan P. Atypical anti-psychotics in delusional parasitosis: a retrospective case series of 20 patients. Int J Dermatol. 2010;49(1):95-100. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04312.x
15. Laidler N. Delusions of parasitosis: a brief review of the literature and pathway for diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24(1):13030/qt1fh739nx.
16. Freudenmann RW, Lepping P. Second-generation antipsychotics in primary and secondary delusional parasitosis: outcome and efficacy. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(5):500-508. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e318185e774
17. Mumcuoglu KY, Leibovici V, Reuveni I, et al. Delusional parasitosis: diagnosis and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 2018;20(7):456-460.
18. Trabert W. 100 years of delusional parasitosis. Meta-analysis of 1,223 case reports. Psychopathology. 1995;28(5):238-246. doi:10.1159/000284934
Perinatal psychiatry: 5 key principles
Perinatal mood and anxiety disorders are the most common complication of pregnancy and childbirth.1 Mental health concerns are a leading cause of maternal mortality in the United States, which has rising maternal mortality rates and glaring racial and socioeconomic disparities.2 Inconsistent perinatal psychiatry training likely contributes to perceived discomfort of patients who are pregnant.3 This is why it is critical for all psychiatrists to understand the principles of perinatal psychiatry. Here is a brief description of 5 key principles.
1. Discuss preconception planning
Reproductive life planning should occur with all patients who are capable of becoming pregnant. This planning should include not just a risks/benefits analysis and anticipatory planning regarding medications but also a discussion of prior perinatal symptoms, pregnancy intentions and contraception (especially in light of increasingly limited access to abortion), and the bidirectional nature of pregnancy and mental health conditions.
The acronym PATH provides a framework for these conversations:
- Pregnancy Attitudes: “Do you think you might like to have (more) children at some point?”
- Timing: “If considering future parenthood, when do you think that might be?”
- How important is prevention: “How important is it to you to prevent pregnancy (until then)?”4
2. Focus on perinatal mental health
Discussion often centers on medication risks to the fetus at the expense of considering risks of under- or nontreatment for both members of the dyad. Undertreating perinatal mental health conditions results in dual exposures (medication and illness), and untreated illness is associated with negative effects on obstetric and neonatal outcomes and the well-being of the parent and offspring.1
3. Resist experimentation
It is common for clinicians to reflexively switch patients who are pregnant from an effective medication to one viewed as the “safest” or “best” because it has more data. This exposes the fetus to 2 medications and the dyad to potential symptoms of the illness. Decisions about medication changes should instead be made on an individual basis considering the risks and benefits of all exposures as well as the patient’s current symptoms, previous treatment, and family history.
4. Collaborate and communicate
Despite effective interventions, many perinatal mental health conditions go untreated.1 Normalize perinatal mental health symptoms with patients to reduce stigma and barriers to disclosure, and respect their decisions regarding perinatal medication use. Proper communication with the obstetric team ensures appropriate perinatal mental health screening and fetal monitoring (eg, possible fetal growth ultrasounds for a patient taking prazosin, or assessing for neonatal adaptation syndrome if there is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure in utero).
5. Recognize your limitations
Our understanding of psychotropics’ teratogenicity is constantly evolving, and we must recognize when we don’t know something. In addition to medication databases such as Reprotox (https://reprotox.org/) and LactMed (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), several perinatal psychiatry resources are available for both patients and clinicians (Table). Additionally, Postpartum Support International maintains a National Perinatal Consult Line (1-877-499-4773) as well as a list of state perinatal psychiatry access lines (https://www.postpartum.net/professionals/state-perinatal-psychiatry-access-lines/) for clinicians. The Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health (https://womensmentalhealth.org) is also a helpful resource for clinicians.
1. Luca DL, Garlow N, Staatz C, et al. Societal costs of untreated perinatal mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Mathematica Policy Research. April 29, 2019. Accessed July 13, 2023. https://www.mathematica.org/publications/societal-costs-of-untreated-perinatal-mood-and-anxiety-disorders-in-the-united-states
2. Singh GK. Trends and social inequalities in maternal mortality in the United States, 1969-2018. Int J MCH AIDS. 2021;10(1):29-42. doi:10.21106/ijma.444
3. Weinreb L, Byatt N, Moore Simas TA, et al. What happens to mental health treatment during pregnancy? Women’s experience with prescribing providers. Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):349-355. doi:10.1007/s11126-014-9293-7
4. Callegari LS, Aiken AR, Dehlendorf C, et al. Addressing potential pitfalls of reproductive life planning with patient-centered counseling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216(2):129-134. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.10.004
Perinatal mood and anxiety disorders are the most common complication of pregnancy and childbirth.1 Mental health concerns are a leading cause of maternal mortality in the United States, which has rising maternal mortality rates and glaring racial and socioeconomic disparities.2 Inconsistent perinatal psychiatry training likely contributes to perceived discomfort of patients who are pregnant.3 This is why it is critical for all psychiatrists to understand the principles of perinatal psychiatry. Here is a brief description of 5 key principles.
1. Discuss preconception planning
Reproductive life planning should occur with all patients who are capable of becoming pregnant. This planning should include not just a risks/benefits analysis and anticipatory planning regarding medications but also a discussion of prior perinatal symptoms, pregnancy intentions and contraception (especially in light of increasingly limited access to abortion), and the bidirectional nature of pregnancy and mental health conditions.
The acronym PATH provides a framework for these conversations:
- Pregnancy Attitudes: “Do you think you might like to have (more) children at some point?”
- Timing: “If considering future parenthood, when do you think that might be?”
- How important is prevention: “How important is it to you to prevent pregnancy (until then)?”4
2. Focus on perinatal mental health
Discussion often centers on medication risks to the fetus at the expense of considering risks of under- or nontreatment for both members of the dyad. Undertreating perinatal mental health conditions results in dual exposures (medication and illness), and untreated illness is associated with negative effects on obstetric and neonatal outcomes and the well-being of the parent and offspring.1
3. Resist experimentation
It is common for clinicians to reflexively switch patients who are pregnant from an effective medication to one viewed as the “safest” or “best” because it has more data. This exposes the fetus to 2 medications and the dyad to potential symptoms of the illness. Decisions about medication changes should instead be made on an individual basis considering the risks and benefits of all exposures as well as the patient’s current symptoms, previous treatment, and family history.
4. Collaborate and communicate
Despite effective interventions, many perinatal mental health conditions go untreated.1 Normalize perinatal mental health symptoms with patients to reduce stigma and barriers to disclosure, and respect their decisions regarding perinatal medication use. Proper communication with the obstetric team ensures appropriate perinatal mental health screening and fetal monitoring (eg, possible fetal growth ultrasounds for a patient taking prazosin, or assessing for neonatal adaptation syndrome if there is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure in utero).
5. Recognize your limitations
Our understanding of psychotropics’ teratogenicity is constantly evolving, and we must recognize when we don’t know something. In addition to medication databases such as Reprotox (https://reprotox.org/) and LactMed (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), several perinatal psychiatry resources are available for both patients and clinicians (Table). Additionally, Postpartum Support International maintains a National Perinatal Consult Line (1-877-499-4773) as well as a list of state perinatal psychiatry access lines (https://www.postpartum.net/professionals/state-perinatal-psychiatry-access-lines/) for clinicians. The Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health (https://womensmentalhealth.org) is also a helpful resource for clinicians.

Perinatal mood and anxiety disorders are the most common complication of pregnancy and childbirth.1 Mental health concerns are a leading cause of maternal mortality in the United States, which has rising maternal mortality rates and glaring racial and socioeconomic disparities.2 Inconsistent perinatal psychiatry training likely contributes to perceived discomfort of patients who are pregnant.3 This is why it is critical for all psychiatrists to understand the principles of perinatal psychiatry. Here is a brief description of 5 key principles.
1. Discuss preconception planning
Reproductive life planning should occur with all patients who are capable of becoming pregnant. This planning should include not just a risks/benefits analysis and anticipatory planning regarding medications but also a discussion of prior perinatal symptoms, pregnancy intentions and contraception (especially in light of increasingly limited access to abortion), and the bidirectional nature of pregnancy and mental health conditions.
The acronym PATH provides a framework for these conversations:
- Pregnancy Attitudes: “Do you think you might like to have (more) children at some point?”
- Timing: “If considering future parenthood, when do you think that might be?”
- How important is prevention: “How important is it to you to prevent pregnancy (until then)?”4
2. Focus on perinatal mental health
Discussion often centers on medication risks to the fetus at the expense of considering risks of under- or nontreatment for both members of the dyad. Undertreating perinatal mental health conditions results in dual exposures (medication and illness), and untreated illness is associated with negative effects on obstetric and neonatal outcomes and the well-being of the parent and offspring.1
3. Resist experimentation
It is common for clinicians to reflexively switch patients who are pregnant from an effective medication to one viewed as the “safest” or “best” because it has more data. This exposes the fetus to 2 medications and the dyad to potential symptoms of the illness. Decisions about medication changes should instead be made on an individual basis considering the risks and benefits of all exposures as well as the patient’s current symptoms, previous treatment, and family history.
4. Collaborate and communicate
Despite effective interventions, many perinatal mental health conditions go untreated.1 Normalize perinatal mental health symptoms with patients to reduce stigma and barriers to disclosure, and respect their decisions regarding perinatal medication use. Proper communication with the obstetric team ensures appropriate perinatal mental health screening and fetal monitoring (eg, possible fetal growth ultrasounds for a patient taking prazosin, or assessing for neonatal adaptation syndrome if there is selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure in utero).
5. Recognize your limitations
Our understanding of psychotropics’ teratogenicity is constantly evolving, and we must recognize when we don’t know something. In addition to medication databases such as Reprotox (https://reprotox.org/) and LactMed (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501922/), several perinatal psychiatry resources are available for both patients and clinicians (Table). Additionally, Postpartum Support International maintains a National Perinatal Consult Line (1-877-499-4773) as well as a list of state perinatal psychiatry access lines (https://www.postpartum.net/professionals/state-perinatal-psychiatry-access-lines/) for clinicians. The Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health (https://womensmentalhealth.org) is also a helpful resource for clinicians.

1. Luca DL, Garlow N, Staatz C, et al. Societal costs of untreated perinatal mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Mathematica Policy Research. April 29, 2019. Accessed July 13, 2023. https://www.mathematica.org/publications/societal-costs-of-untreated-perinatal-mood-and-anxiety-disorders-in-the-united-states
2. Singh GK. Trends and social inequalities in maternal mortality in the United States, 1969-2018. Int J MCH AIDS. 2021;10(1):29-42. doi:10.21106/ijma.444
3. Weinreb L, Byatt N, Moore Simas TA, et al. What happens to mental health treatment during pregnancy? Women’s experience with prescribing providers. Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):349-355. doi:10.1007/s11126-014-9293-7
4. Callegari LS, Aiken AR, Dehlendorf C, et al. Addressing potential pitfalls of reproductive life planning with patient-centered counseling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216(2):129-134. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.10.004
1. Luca DL, Garlow N, Staatz C, et al. Societal costs of untreated perinatal mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Mathematica Policy Research. April 29, 2019. Accessed July 13, 2023. https://www.mathematica.org/publications/societal-costs-of-untreated-perinatal-mood-and-anxiety-disorders-in-the-united-states
2. Singh GK. Trends and social inequalities in maternal mortality in the United States, 1969-2018. Int J MCH AIDS. 2021;10(1):29-42. doi:10.21106/ijma.444
3. Weinreb L, Byatt N, Moore Simas TA, et al. What happens to mental health treatment during pregnancy? Women’s experience with prescribing providers. Psychiatr Q. 2014;85(3):349-355. doi:10.1007/s11126-014-9293-7
4. Callegari LS, Aiken AR, Dehlendorf C, et al. Addressing potential pitfalls of reproductive life planning with patient-centered counseling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216(2):129-134. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.10.004
Diagnosing borderline personality disorder: Avoid these pitfalls
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with impaired psychosocial functioning, reduced quality of life, increased use of health care services, and excess mortality.1 Unfortunately, this disorder is often underrecognized and underdiagnosed, and patients with BPD may not receive an accurate diagnosis for years after first seeking treatment.1 Problems in diagnosing BPD include:
Stigma. Some patients may view the term “borderline” as stigmatizing, as if we are calling these patients borderline human beings. One of the symptoms of BPD is a “markedly and persistently unstable self-image.”2 Such patients do not need a stigmatizing label to worsen their self-image.
Terminology. The word borderline may also imply relatively mild psychiatric symptoms. However, “borderline personality disorder” does not refer to a mild personality disorder. DSM-5 describes potential BPD symptoms as “intense,” “marked,” or “severe,” and 1 of the symptoms is suicidal behavior.2
Symptoms. To meet the criteria for a BPD diagnosis, a patient must exhibit ≥5 of 9 severe symptoms2:
- frantic efforts to avoid abandonment
- unstable and intense interpersonal relationships
- unstable self-image
- impulsivity in ≥2 areas that are potentially self-damaging
- suicidal behavior
- affective instability
- chronic feelings of emptiness
- inappropriate anger
- transient paranoid ideation or dissociative symptoms.
Asking about all 9 of these criteria and their severity is not part of a routine psychiatric evaluation. A patient might not volunteer any of this information because they are concerned about potential stigma. Additionally, perhaps most of the general population has had a “BPD-like” symptom at least once during their lives. This symptom might not have been severe enough to qualify as a true BPD symptom. Clinicians might have difficulty discerning BPD-like symptoms from true BPD symptoms.
Comorbidities. Many patients with BPD also have a comorbid mood disorder or substance use disorder.1,3 Clinicians might focus on a comorbid diagnosis and not recognize BPD.
Stress. BPD symptoms may become more severe when the patient faces a stressful situation. The BPD symptoms might seem more severe than the stress would warrant.2 However, clinicians might blame the BPD symptoms solely on stress and not acknowledge the underlying BPD diagnosis.
Awareness of these factors can help clinicians keep BPD in the differential diagnosis when conducting a psychiatric evaluation, thus reducing the chances of overlooking this serious disorder.
1. Zimmerman M. Improving the recognition of borderline personality disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):13-19.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:663-666.
3. Grant BF, Chou SP, Goldstein RB, et al. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV borderline personality disorder: results from the Wave 2 National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008:69(4)533-545.
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with impaired psychosocial functioning, reduced quality of life, increased use of health care services, and excess mortality.1 Unfortunately, this disorder is often underrecognized and underdiagnosed, and patients with BPD may not receive an accurate diagnosis for years after first seeking treatment.1 Problems in diagnosing BPD include:
Stigma. Some patients may view the term “borderline” as stigmatizing, as if we are calling these patients borderline human beings. One of the symptoms of BPD is a “markedly and persistently unstable self-image.”2 Such patients do not need a stigmatizing label to worsen their self-image.
Terminology. The word borderline may also imply relatively mild psychiatric symptoms. However, “borderline personality disorder” does not refer to a mild personality disorder. DSM-5 describes potential BPD symptoms as “intense,” “marked,” or “severe,” and 1 of the symptoms is suicidal behavior.2
Symptoms. To meet the criteria for a BPD diagnosis, a patient must exhibit ≥5 of 9 severe symptoms2:
- frantic efforts to avoid abandonment
- unstable and intense interpersonal relationships
- unstable self-image
- impulsivity in ≥2 areas that are potentially self-damaging
- suicidal behavior
- affective instability
- chronic feelings of emptiness
- inappropriate anger
- transient paranoid ideation or dissociative symptoms.
Asking about all 9 of these criteria and their severity is not part of a routine psychiatric evaluation. A patient might not volunteer any of this information because they are concerned about potential stigma. Additionally, perhaps most of the general population has had a “BPD-like” symptom at least once during their lives. This symptom might not have been severe enough to qualify as a true BPD symptom. Clinicians might have difficulty discerning BPD-like symptoms from true BPD symptoms.
Comorbidities. Many patients with BPD also have a comorbid mood disorder or substance use disorder.1,3 Clinicians might focus on a comorbid diagnosis and not recognize BPD.
Stress. BPD symptoms may become more severe when the patient faces a stressful situation. The BPD symptoms might seem more severe than the stress would warrant.2 However, clinicians might blame the BPD symptoms solely on stress and not acknowledge the underlying BPD diagnosis.
Awareness of these factors can help clinicians keep BPD in the differential diagnosis when conducting a psychiatric evaluation, thus reducing the chances of overlooking this serious disorder.
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is associated with impaired psychosocial functioning, reduced quality of life, increased use of health care services, and excess mortality.1 Unfortunately, this disorder is often underrecognized and underdiagnosed, and patients with BPD may not receive an accurate diagnosis for years after first seeking treatment.1 Problems in diagnosing BPD include:
Stigma. Some patients may view the term “borderline” as stigmatizing, as if we are calling these patients borderline human beings. One of the symptoms of BPD is a “markedly and persistently unstable self-image.”2 Such patients do not need a stigmatizing label to worsen their self-image.
Terminology. The word borderline may also imply relatively mild psychiatric symptoms. However, “borderline personality disorder” does not refer to a mild personality disorder. DSM-5 describes potential BPD symptoms as “intense,” “marked,” or “severe,” and 1 of the symptoms is suicidal behavior.2
Symptoms. To meet the criteria for a BPD diagnosis, a patient must exhibit ≥5 of 9 severe symptoms2:
- frantic efforts to avoid abandonment
- unstable and intense interpersonal relationships
- unstable self-image
- impulsivity in ≥2 areas that are potentially self-damaging
- suicidal behavior
- affective instability
- chronic feelings of emptiness
- inappropriate anger
- transient paranoid ideation or dissociative symptoms.
Asking about all 9 of these criteria and their severity is not part of a routine psychiatric evaluation. A patient might not volunteer any of this information because they are concerned about potential stigma. Additionally, perhaps most of the general population has had a “BPD-like” symptom at least once during their lives. This symptom might not have been severe enough to qualify as a true BPD symptom. Clinicians might have difficulty discerning BPD-like symptoms from true BPD symptoms.
Comorbidities. Many patients with BPD also have a comorbid mood disorder or substance use disorder.1,3 Clinicians might focus on a comorbid diagnosis and not recognize BPD.
Stress. BPD symptoms may become more severe when the patient faces a stressful situation. The BPD symptoms might seem more severe than the stress would warrant.2 However, clinicians might blame the BPD symptoms solely on stress and not acknowledge the underlying BPD diagnosis.
Awareness of these factors can help clinicians keep BPD in the differential diagnosis when conducting a psychiatric evaluation, thus reducing the chances of overlooking this serious disorder.
1. Zimmerman M. Improving the recognition of borderline personality disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):13-19.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:663-666.
3. Grant BF, Chou SP, Goldstein RB, et al. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV borderline personality disorder: results from the Wave 2 National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008:69(4)533-545.
1. Zimmerman M. Improving the recognition of borderline personality disorder. Current Psychiatry. 2017;16(10):13-19.
2. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013:663-666.
3. Grant BF, Chou SP, Goldstein RB, et al. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV borderline personality disorder: results from the Wave 2 National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008:69(4)533-545.
Extended-release injectable naltrexone for opioid use disorder
We appreciate the important review by Gluck et al (“Managing patients with comorbid opioid and alcohol use disorders,”
XR-NTX should be considered an equal OUD treatment alternative to buprenorphine-naloxone, especially for patients who prefer an opioid-free option.1,2 It has the added advantage of being FDA-approved for both AUD and OUD.
One obstacle to the success of XR-NTX is the induction period. The National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network X:BOT trial found that once the induction hurdle was surmounted, XR-NTX and buprenorphine were equally effective in a population of approximately 80% heroin users and two-thirds injection drug users.2 Patient variables that predict successful induction include young age, baseline preference for XR-NTX, fewer drug complications, and fewer family/social complications.3 If the length of the induction (usually 7 to 10 days) is a deterrent, a study supported the feasibility of a 5-day outpatient XR-NTX induction.4 Further research is needed to improve successful induction for XR-NTX.
Ashmeer Ogbuchi, MD
Karen Drexler, MD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif Z, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(12):1197-1205. doi:10.1001/ jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
2. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
3. Murphy SM, Jeng PJ, McCollister KE, et al. Cost‐effectiveness implications of increasing the efficiency of the extended‐release naltrexone induction process for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a secondary analysis. Addiction. 2021;116(12)3444-3453. doi:10.1111/add.15531
4. Sibai M, Mishlen K, Nunes EV, et al. A week-long outpatient induction onto XR-naltrexone in patients with opioid use disorder. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2020;46(3):289-296. doi:10.1080/00952990.2019.1700265
Continue to: The authors respond
The authors respond
We appreciate Drs. Ogbuchi and Drexler for their thoughtful attention to our review. They proposed amending our original algorithm, recommending that XR-NTX be considered as another first-line option for patients with OUD. We agree with this suggestion, particularly for inpatients. However, we have some reservations about applying this suggestion to outpatient treatment. Though research evidence from Lee et al1 indicates that once initiation is completed, both medications are equally safe and effective, the initial attrition rate in the XR-NTX group was much higher (28% vs 6%, P < .0001), which suggests lower acceptability/tolerability compared with buprenorphine. Notably, the initiation of both medications in Lee et al1 was done in an inpatient setting. Moreover, although some medications are endorsed as “first-line,” the actual utilization rate is often influenced by many factors, including the ease of treatment initiation. Wakeman et al2 found the most common treatment modality received by patients with OUD was nonintensive behavioral health (59.5%), followed by inpatient withdrawal management and residential treatment (15.2%). Among all patients in the Wakeman study,2 only 12.5% received buprenorphine or methadone, and 2.4% received naltrexone.
Data from our clinic corroborate this trend. Currently, in our clinic approximately 300 patients with OUD are receiving medications, including approximately 250 on buprenorphine (including 5 to 10 on the long-acting injectable formulation), 50 on methadone, and only 1 or 2 on XR-NTX. Though this disparity may reflect bias in our clinicians’ prescribing practices, in the past few years we have had many unsuccessful attempts at initiating XR-NTX. To our disappointment, a theoretically excellent medication has not translated clinically. The recent surge in fentanyl use further complicates XR-NTX initiation for OUD, because the length of induction may be longer.
In conclusion, we agree that XR-NTX is a potential treatment option for patients with OUD, but clinicians should be cognizant of the potential barriers; inform patients of the advantages, expectations, and challenges; and respect patients’ informed decisions.
Rachel Gluck, MD
Karen Hochman, MD
Yi-lang Tang, MD, PhD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
2. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622
We appreciate the important review by Gluck et al (“Managing patients with comorbid opioid and alcohol use disorders,”
XR-NTX should be considered an equal OUD treatment alternative to buprenorphine-naloxone, especially for patients who prefer an opioid-free option.1,2 It has the added advantage of being FDA-approved for both AUD and OUD.
One obstacle to the success of XR-NTX is the induction period. The National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network X:BOT trial found that once the induction hurdle was surmounted, XR-NTX and buprenorphine were equally effective in a population of approximately 80% heroin users and two-thirds injection drug users.2 Patient variables that predict successful induction include young age, baseline preference for XR-NTX, fewer drug complications, and fewer family/social complications.3 If the length of the induction (usually 7 to 10 days) is a deterrent, a study supported the feasibility of a 5-day outpatient XR-NTX induction.4 Further research is needed to improve successful induction for XR-NTX.
Ashmeer Ogbuchi, MD
Karen Drexler, MD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif Z, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(12):1197-1205. doi:10.1001/ jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
2. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
3. Murphy SM, Jeng PJ, McCollister KE, et al. Cost‐effectiveness implications of increasing the efficiency of the extended‐release naltrexone induction process for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a secondary analysis. Addiction. 2021;116(12)3444-3453. doi:10.1111/add.15531
4. Sibai M, Mishlen K, Nunes EV, et al. A week-long outpatient induction onto XR-naltrexone in patients with opioid use disorder. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2020;46(3):289-296. doi:10.1080/00952990.2019.1700265
Continue to: The authors respond
The authors respond
We appreciate Drs. Ogbuchi and Drexler for their thoughtful attention to our review. They proposed amending our original algorithm, recommending that XR-NTX be considered as another first-line option for patients with OUD. We agree with this suggestion, particularly for inpatients. However, we have some reservations about applying this suggestion to outpatient treatment. Though research evidence from Lee et al1 indicates that once initiation is completed, both medications are equally safe and effective, the initial attrition rate in the XR-NTX group was much higher (28% vs 6%, P < .0001), which suggests lower acceptability/tolerability compared with buprenorphine. Notably, the initiation of both medications in Lee et al1 was done in an inpatient setting. Moreover, although some medications are endorsed as “first-line,” the actual utilization rate is often influenced by many factors, including the ease of treatment initiation. Wakeman et al2 found the most common treatment modality received by patients with OUD was nonintensive behavioral health (59.5%), followed by inpatient withdrawal management and residential treatment (15.2%). Among all patients in the Wakeman study,2 only 12.5% received buprenorphine or methadone, and 2.4% received naltrexone.
Data from our clinic corroborate this trend. Currently, in our clinic approximately 300 patients with OUD are receiving medications, including approximately 250 on buprenorphine (including 5 to 10 on the long-acting injectable formulation), 50 on methadone, and only 1 or 2 on XR-NTX. Though this disparity may reflect bias in our clinicians’ prescribing practices, in the past few years we have had many unsuccessful attempts at initiating XR-NTX. To our disappointment, a theoretically excellent medication has not translated clinically. The recent surge in fentanyl use further complicates XR-NTX initiation for OUD, because the length of induction may be longer.
In conclusion, we agree that XR-NTX is a potential treatment option for patients with OUD, but clinicians should be cognizant of the potential barriers; inform patients of the advantages, expectations, and challenges; and respect patients’ informed decisions.
Rachel Gluck, MD
Karen Hochman, MD
Yi-lang Tang, MD, PhD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
2. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622
We appreciate the important review by Gluck et al (“Managing patients with comorbid opioid and alcohol use disorders,”
XR-NTX should be considered an equal OUD treatment alternative to buprenorphine-naloxone, especially for patients who prefer an opioid-free option.1,2 It has the added advantage of being FDA-approved for both AUD and OUD.
One obstacle to the success of XR-NTX is the induction period. The National Institute on Drug Abuse Clinical Trials Network X:BOT trial found that once the induction hurdle was surmounted, XR-NTX and buprenorphine were equally effective in a population of approximately 80% heroin users and two-thirds injection drug users.2 Patient variables that predict successful induction include young age, baseline preference for XR-NTX, fewer drug complications, and fewer family/social complications.3 If the length of the induction (usually 7 to 10 days) is a deterrent, a study supported the feasibility of a 5-day outpatient XR-NTX induction.4 Further research is needed to improve successful induction for XR-NTX.
Ashmeer Ogbuchi, MD
Karen Drexler, MD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Tanum L, Solli KK, Latif Z, et al. Effectiveness of injectable extended-release naltrexone vs daily buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid dependence. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(12):1197-1205. doi:10.1001/ jamapsychiatry.2017.3206
2. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
3. Murphy SM, Jeng PJ, McCollister KE, et al. Cost‐effectiveness implications of increasing the efficiency of the extended‐release naltrexone induction process for the treatment of opioid use disorder: a secondary analysis. Addiction. 2021;116(12)3444-3453. doi:10.1111/add.15531
4. Sibai M, Mishlen K, Nunes EV, et al. A week-long outpatient induction onto XR-naltrexone in patients with opioid use disorder. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2020;46(3):289-296. doi:10.1080/00952990.2019.1700265
Continue to: The authors respond
The authors respond
We appreciate Drs. Ogbuchi and Drexler for their thoughtful attention to our review. They proposed amending our original algorithm, recommending that XR-NTX be considered as another first-line option for patients with OUD. We agree with this suggestion, particularly for inpatients. However, we have some reservations about applying this suggestion to outpatient treatment. Though research evidence from Lee et al1 indicates that once initiation is completed, both medications are equally safe and effective, the initial attrition rate in the XR-NTX group was much higher (28% vs 6%, P < .0001), which suggests lower acceptability/tolerability compared with buprenorphine. Notably, the initiation of both medications in Lee et al1 was done in an inpatient setting. Moreover, although some medications are endorsed as “first-line,” the actual utilization rate is often influenced by many factors, including the ease of treatment initiation. Wakeman et al2 found the most common treatment modality received by patients with OUD was nonintensive behavioral health (59.5%), followed by inpatient withdrawal management and residential treatment (15.2%). Among all patients in the Wakeman study,2 only 12.5% received buprenorphine or methadone, and 2.4% received naltrexone.
Data from our clinic corroborate this trend. Currently, in our clinic approximately 300 patients with OUD are receiving medications, including approximately 250 on buprenorphine (including 5 to 10 on the long-acting injectable formulation), 50 on methadone, and only 1 or 2 on XR-NTX. Though this disparity may reflect bias in our clinicians’ prescribing practices, in the past few years we have had many unsuccessful attempts at initiating XR-NTX. To our disappointment, a theoretically excellent medication has not translated clinically. The recent surge in fentanyl use further complicates XR-NTX initiation for OUD, because the length of induction may be longer.
In conclusion, we agree that XR-NTX is a potential treatment option for patients with OUD, but clinicians should be cognizant of the potential barriers; inform patients of the advantages, expectations, and challenges; and respect patients’ informed decisions.
Rachel Gluck, MD
Karen Hochman, MD
Yi-lang Tang, MD, PhD
Atlanta, Georgia
References
1. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32812-x
2. Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(2):e1920622. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622
Foot rash during self-treatment
The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.

The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
Commentary: PsA domains and analysis of various biologics in PsA, August 2023
Although there are several treatment options for PsA, there have been few head-to-head studies conducted to determine comparative efficacy. Ustekinumab, a biologic agent targeting IL-p40, and therefore both IL-12 and IL-23, has proven efficacy in PsA, but the impression is that this drug is less effective than are TNF inhibitors for the treatment of the peripheral arthritis domain. However, in a prospective, observational study, Gossec and colleagues report that the improvements in patient-reported outcomes were generally comparable between ustekinumab and TNF inhibitor treatments. This study evaluated 437 patients with PsA from the PsABio study who initiated first- to third-line ustekinumab (n = 219) or TNF inhibitors (n = 218) and continued the initial treatment for 3 years. At 3 years, ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors were associated with comparable improvements in the EuroQol-5 dimensions health state visual analog scale scores, Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease 12-item scores, and work productivity, although the improvements were generally greater in the TNF inhibitor–treated group. A randomized trial comparing ustekinumab to TNF inhibitors in PsA is warranted to confirm these findings and inform treatment decisions.
Targeted therapies, such as biologics, are proven to be more efficacious than are conventional therapies; however, only about 60% of patients initiating targeted therapies demonstrate treatment response. Identifying the predictors of treatment response is an active area of research. Linde and colleagues looked at data from 13,369 biologic-naive patients registered with a PsA diagnosis from 13 European registries who initiated a first TNF inhibitor treatment. The study demonstrated that sex, disease duration, C-reactive protein level, age at treatment initiation, and fatigue predicted the achievement of the Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis in 28 joints remission at 6 months.
Could biomarkers help predict response beyond clinical predictors? An interesting study indicates that beta–defensin 2 (BD-2) may serve as a predictive biomarker for clinical response to secukinumab in PsA. BD-2 is an antimicrobial peptide and an important protein in innate immune response. Cardner and colleagues analyzed protein expression data in serum samples from the phase 3 FUTURE 1-5 trials that included 1989 patients with PsA who received secukinumab or placebo. Baseline BD-2 levels were associated with early as well as sustained PsA treatment response to secukinumab, independent of psoriasis severity. BD-2 levels did not predict response to adalimumab in PsA nor was it associated with treatment response to secukinumab in RA. The addition of BD-2 to the clinical prediction model significantly improved the prediction of the 16-week American College of Rheumatology 20 response. Thus, BD-2 seems to be a secukinumab treatment response biomarker and requires further evaluation.
Although there are several treatment options for PsA, there have been few head-to-head studies conducted to determine comparative efficacy. Ustekinumab, a biologic agent targeting IL-p40, and therefore both IL-12 and IL-23, has proven efficacy in PsA, but the impression is that this drug is less effective than are TNF inhibitors for the treatment of the peripheral arthritis domain. However, in a prospective, observational study, Gossec and colleagues report that the improvements in patient-reported outcomes were generally comparable between ustekinumab and TNF inhibitor treatments. This study evaluated 437 patients with PsA from the PsABio study who initiated first- to third-line ustekinumab (n = 219) or TNF inhibitors (n = 218) and continued the initial treatment for 3 years. At 3 years, ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors were associated with comparable improvements in the EuroQol-5 dimensions health state visual analog scale scores, Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease 12-item scores, and work productivity, although the improvements were generally greater in the TNF inhibitor–treated group. A randomized trial comparing ustekinumab to TNF inhibitors in PsA is warranted to confirm these findings and inform treatment decisions.
Targeted therapies, such as biologics, are proven to be more efficacious than are conventional therapies; however, only about 60% of patients initiating targeted therapies demonstrate treatment response. Identifying the predictors of treatment response is an active area of research. Linde and colleagues looked at data from 13,369 biologic-naive patients registered with a PsA diagnosis from 13 European registries who initiated a first TNF inhibitor treatment. The study demonstrated that sex, disease duration, C-reactive protein level, age at treatment initiation, and fatigue predicted the achievement of the Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis in 28 joints remission at 6 months.
Could biomarkers help predict response beyond clinical predictors? An interesting study indicates that beta–defensin 2 (BD-2) may serve as a predictive biomarker for clinical response to secukinumab in PsA. BD-2 is an antimicrobial peptide and an important protein in innate immune response. Cardner and colleagues analyzed protein expression data in serum samples from the phase 3 FUTURE 1-5 trials that included 1989 patients with PsA who received secukinumab or placebo. Baseline BD-2 levels were associated with early as well as sustained PsA treatment response to secukinumab, independent of psoriasis severity. BD-2 levels did not predict response to adalimumab in PsA nor was it associated with treatment response to secukinumab in RA. The addition of BD-2 to the clinical prediction model significantly improved the prediction of the 16-week American College of Rheumatology 20 response. Thus, BD-2 seems to be a secukinumab treatment response biomarker and requires further evaluation.
Although there are several treatment options for PsA, there have been few head-to-head studies conducted to determine comparative efficacy. Ustekinumab, a biologic agent targeting IL-p40, and therefore both IL-12 and IL-23, has proven efficacy in PsA, but the impression is that this drug is less effective than are TNF inhibitors for the treatment of the peripheral arthritis domain. However, in a prospective, observational study, Gossec and colleagues report that the improvements in patient-reported outcomes were generally comparable between ustekinumab and TNF inhibitor treatments. This study evaluated 437 patients with PsA from the PsABio study who initiated first- to third-line ustekinumab (n = 219) or TNF inhibitors (n = 218) and continued the initial treatment for 3 years. At 3 years, ustekinumab and TNF inhibitors were associated with comparable improvements in the EuroQol-5 dimensions health state visual analog scale scores, Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease 12-item scores, and work productivity, although the improvements were generally greater in the TNF inhibitor–treated group. A randomized trial comparing ustekinumab to TNF inhibitors in PsA is warranted to confirm these findings and inform treatment decisions.
Targeted therapies, such as biologics, are proven to be more efficacious than are conventional therapies; however, only about 60% of patients initiating targeted therapies demonstrate treatment response. Identifying the predictors of treatment response is an active area of research. Linde and colleagues looked at data from 13,369 biologic-naive patients registered with a PsA diagnosis from 13 European registries who initiated a first TNF inhibitor treatment. The study demonstrated that sex, disease duration, C-reactive protein level, age at treatment initiation, and fatigue predicted the achievement of the Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis in 28 joints remission at 6 months.
Could biomarkers help predict response beyond clinical predictors? An interesting study indicates that beta–defensin 2 (BD-2) may serve as a predictive biomarker for clinical response to secukinumab in PsA. BD-2 is an antimicrobial peptide and an important protein in innate immune response. Cardner and colleagues analyzed protein expression data in serum samples from the phase 3 FUTURE 1-5 trials that included 1989 patients with PsA who received secukinumab or placebo. Baseline BD-2 levels were associated with early as well as sustained PsA treatment response to secukinumab, independent of psoriasis severity. BD-2 levels did not predict response to adalimumab in PsA nor was it associated with treatment response to secukinumab in RA. The addition of BD-2 to the clinical prediction model significantly improved the prediction of the 16-week American College of Rheumatology 20 response. Thus, BD-2 seems to be a secukinumab treatment response biomarker and requires further evaluation.
Commentary: Abrocitinib, Malignancy Risk, and S aureus in AD, August 2023
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
The excellent short-term efficacy of the drug was well maintained up to 48 weeks, with only a slight loss of efficacy over time. Abrocitinib is a small molecule. We wouldn't expect a loss of efficacy due to the anti-drug antibodies that we see for large-molecule biologic drugs. I suspect that the slight loss of efficacy over time is a form of tachyphylaxis that is, to my thinking, probably due to poor adherence. Shocking, I know! Patients may not be fully adherent to treatment, even in a clinical trial. I think we should encourage patients to use 7-day pill boxes to aid better long-term adherence and outcomes.
Long-term safety is a critical issue with any new drug, certainly with a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Reich and colleagues concluded, "The long-term safety profile was manageable and consistent with previous reports." That conclusion seems reasonable to me. The most common side effects were upper respiratory tract infections. There may be a slight signal for increased risk for oral herpes infection, particularly at the higher dose. If this safety profile endures with longer-term data in larger numbers of people, it will be very reassuring.
The study by Wan and colleagues is another extremely well-done, important study by the premier dermatoepidemiology research team at the University of Pennsylvania. The study used an outstanding database from the United Kingdom that encompassed the clinical care experience of hundreds of thousands of children and adults with atopic dermatitis and millions of control patients without atopic dermatitis. With this many patients, the study has tremendous power to detect risk differences between groups.
With all that power, this study’s findings are very reassuring that there is no meaningful overall increased risk for malignancy in children or adults with atopic dermatitis. And while there was a statistically significant increased risk for lymphoma in children with severe atopic dermatitis, that risk is small … very small. Similarly, adults with severe AD had a twofold higher risk for noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but since non-CTCL is rare, patients with severe AD shouldn't lose any sleep over it..
Simpson and colleagues' study of the effect of dupilumab on Staphylococcus aureus surprised me. Of course, we could expect that S aureus counts would be reduced with dupilumab; as barrier function is restored, surely S aureus counts would go down too. But, fascinatingly, with dupilumab treatment, S aureus counts decreased almost immediately, at both 3 and 7 days, before there was apparent clinical improvement in the skin rash. Simpson and colleagues suggest that the drop in S aureus counts could be due to improvement in immune function when interleukins 4 and 13 are blocked. Whether or not that is true, it is striking how fast S aureus counts improved, long before normal skin barrier function is restored.
Here's a fun fact: Atopic dermatitis is a little less common, about 10% less common, in people born second or later in the birth order. Lisik and colleagues did a meta-analysis of 114 studies and found this marginally lower rate in those born second or later compared with those born first. I'm not sure that there is any clinically meaningful significance to this, but I found it interesting (even though I was born first, and my younger brother had atopic dermatitis).
Polio in the US? Yes, and it prompted ACIP to update its recs
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recently issued new recommendations on polio vaccine for adults. The ACIP decided to update its previous recommendations (from 2000) in response to a case in New York that demonstrated the United States is at risk for poliovirus importation as long as the disease has not been eliminated worldwide.1
What happened in New York? In July 2022, a case of paralytic polio was confirmed in an unvaccinated adult in Rockland County, New York, an area that has low polio vaccine coverage. Subsequent testing of wastewater systems detected poliovirus in a total of 5 New York counties (including 2 in New York City).1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that this region of the state probably experienced 1000 to 2000 nonparalytic, mostly asymptomatic poliovirus infections. The virus detected in wastewater in New York is genetically linked to polioviruses collected in wastewater in Israel, the United Kingdom, and Canada. No poliovirus has been detected in these wastewater systems since late 2022.1,2
Why there’s reason for concern. Routine immunization against polio has been part of the immunization schedule for infants and children since the mid-1950s. As a result, endemic polio was eliminated in the United States in 1979 and in the Western Hemisphere in 1994.
However, adult vaccination until now has been recommended only for those at risk for exposure to poliovirus by way of travel or occupation. And while most adults in the United States are immune to polio due to childhood vaccination, unvaccinated adults remain susceptible if exposed to poliovirus—as demonstrated in the New York case.
What does the ACIP now recommend? Two recommendations were adopted by the ACIP this June to address this problem2:
- Adults who are known or suspected to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated against polio should complete a primary vaccination series with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV).
- Adults who have received a primary series of oral polio vaccine (OPV) or IPV in any combination and who are at increased risk for poliovirus exposure may receive another dose of IPV. Available data do not indicate a need for > 1 lifetime booster.
A few details: To be considered fully vaccinated, a patient must have received a primary series of ≥ 3 doses of OPV or IPV (in any combination) given at least 4 weeks apart, with the last dose given on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 months from the previous dose. Most adults who were born and raised in the United States can assume they were vaccinated against polio as children, unless there are specific reasons to suspect otherwise.2
Individuals considered to be at increased risk include: travelers who are going to countries where polio is epidemic or endemic; laboratory and health care workers who handle specimens that might contain polioviruses; and health care workers or other caregivers who have close contact with a person who could be infected with poliovirus.2
Take-home message. Be prepared to discuss and offer IPV (the only form of the vaccine currently in use in the United States) to adults, as either a one-time booster for those at increased risk for exposure to poliovirus or a complete series for those you know or suspect to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated.
1. Ryerson AB, Lang D, Alazawi MA, et al; US Poliovirus Response Team. Wastewater testing and detection of poliovirus type 2 genetically linked to virus isolated from a paralytic polio case—New York, March 9-October 11, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1418-1424. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7144e2
2. Kidd S. Adult polio vaccination. Presented to the ACIP on June 21, 2023. Accessed July 24, 2023. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2023-06-21-23/02-POLIO-Kidd-Jun-2023.pdf
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recently issued new recommendations on polio vaccine for adults. The ACIP decided to update its previous recommendations (from 2000) in response to a case in New York that demonstrated the United States is at risk for poliovirus importation as long as the disease has not been eliminated worldwide.1
What happened in New York? In July 2022, a case of paralytic polio was confirmed in an unvaccinated adult in Rockland County, New York, an area that has low polio vaccine coverage. Subsequent testing of wastewater systems detected poliovirus in a total of 5 New York counties (including 2 in New York City).1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that this region of the state probably experienced 1000 to 2000 nonparalytic, mostly asymptomatic poliovirus infections. The virus detected in wastewater in New York is genetically linked to polioviruses collected in wastewater in Israel, the United Kingdom, and Canada. No poliovirus has been detected in these wastewater systems since late 2022.1,2
Why there’s reason for concern. Routine immunization against polio has been part of the immunization schedule for infants and children since the mid-1950s. As a result, endemic polio was eliminated in the United States in 1979 and in the Western Hemisphere in 1994.
However, adult vaccination until now has been recommended only for those at risk for exposure to poliovirus by way of travel or occupation. And while most adults in the United States are immune to polio due to childhood vaccination, unvaccinated adults remain susceptible if exposed to poliovirus—as demonstrated in the New York case.
What does the ACIP now recommend? Two recommendations were adopted by the ACIP this June to address this problem2:
- Adults who are known or suspected to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated against polio should complete a primary vaccination series with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV).
- Adults who have received a primary series of oral polio vaccine (OPV) or IPV in any combination and who are at increased risk for poliovirus exposure may receive another dose of IPV. Available data do not indicate a need for > 1 lifetime booster.
A few details: To be considered fully vaccinated, a patient must have received a primary series of ≥ 3 doses of OPV or IPV (in any combination) given at least 4 weeks apart, with the last dose given on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 months from the previous dose. Most adults who were born and raised in the United States can assume they were vaccinated against polio as children, unless there are specific reasons to suspect otherwise.2
Individuals considered to be at increased risk include: travelers who are going to countries where polio is epidemic or endemic; laboratory and health care workers who handle specimens that might contain polioviruses; and health care workers or other caregivers who have close contact with a person who could be infected with poliovirus.2
Take-home message. Be prepared to discuss and offer IPV (the only form of the vaccine currently in use in the United States) to adults, as either a one-time booster for those at increased risk for exposure to poliovirus or a complete series for those you know or suspect to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recently issued new recommendations on polio vaccine for adults. The ACIP decided to update its previous recommendations (from 2000) in response to a case in New York that demonstrated the United States is at risk for poliovirus importation as long as the disease has not been eliminated worldwide.1
What happened in New York? In July 2022, a case of paralytic polio was confirmed in an unvaccinated adult in Rockland County, New York, an area that has low polio vaccine coverage. Subsequent testing of wastewater systems detected poliovirus in a total of 5 New York counties (including 2 in New York City).1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that this region of the state probably experienced 1000 to 2000 nonparalytic, mostly asymptomatic poliovirus infections. The virus detected in wastewater in New York is genetically linked to polioviruses collected in wastewater in Israel, the United Kingdom, and Canada. No poliovirus has been detected in these wastewater systems since late 2022.1,2
Why there’s reason for concern. Routine immunization against polio has been part of the immunization schedule for infants and children since the mid-1950s. As a result, endemic polio was eliminated in the United States in 1979 and in the Western Hemisphere in 1994.
However, adult vaccination until now has been recommended only for those at risk for exposure to poliovirus by way of travel or occupation. And while most adults in the United States are immune to polio due to childhood vaccination, unvaccinated adults remain susceptible if exposed to poliovirus—as demonstrated in the New York case.
What does the ACIP now recommend? Two recommendations were adopted by the ACIP this June to address this problem2:
- Adults who are known or suspected to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated against polio should complete a primary vaccination series with inactivated polio vaccine (IPV).
- Adults who have received a primary series of oral polio vaccine (OPV) or IPV in any combination and who are at increased risk for poliovirus exposure may receive another dose of IPV. Available data do not indicate a need for > 1 lifetime booster.
A few details: To be considered fully vaccinated, a patient must have received a primary series of ≥ 3 doses of OPV or IPV (in any combination) given at least 4 weeks apart, with the last dose given on or after the 4th birthday and at least 6 months from the previous dose. Most adults who were born and raised in the United States can assume they were vaccinated against polio as children, unless there are specific reasons to suspect otherwise.2
Individuals considered to be at increased risk include: travelers who are going to countries where polio is epidemic or endemic; laboratory and health care workers who handle specimens that might contain polioviruses; and health care workers or other caregivers who have close contact with a person who could be infected with poliovirus.2
Take-home message. Be prepared to discuss and offer IPV (the only form of the vaccine currently in use in the United States) to adults, as either a one-time booster for those at increased risk for exposure to poliovirus or a complete series for those you know or suspect to be unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated.
1. Ryerson AB, Lang D, Alazawi MA, et al; US Poliovirus Response Team. Wastewater testing and detection of poliovirus type 2 genetically linked to virus isolated from a paralytic polio case—New York, March 9-October 11, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1418-1424. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7144e2
2. Kidd S. Adult polio vaccination. Presented to the ACIP on June 21, 2023. Accessed July 24, 2023. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2023-06-21-23/02-POLIO-Kidd-Jun-2023.pdf
1. Ryerson AB, Lang D, Alazawi MA, et al; US Poliovirus Response Team. Wastewater testing and detection of poliovirus type 2 genetically linked to virus isolated from a paralytic polio case—New York, March 9-October 11, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1418-1424. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7144e2
2. Kidd S. Adult polio vaccination. Presented to the ACIP on June 21, 2023. Accessed July 24, 2023. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/acip/meetings/downloads/slides-2023-06-21-23/02-POLIO-Kidd-Jun-2023.pdf