User login
Cancer Risk: Are Pesticides the New Smoking?
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pesticides have transformed modern agriculture by boosting production yields and helping alleviate food insecurity amid rapid global population growth. However, from a public health perspective, exposure to pesticides has been linked to numerous harmful effects, including neurologic disorders like Parkinson’s disease, weakened immune function, and an increased risk for cancer.
thus offering a limited perspective.
A comprehensive assessment of how pesticide use affects cancer risk across a broader population has yet to be conducted.
A recent population-level study aimed to address this gap by evaluating cancer risks in the US population using a model that accounts for pesticide use and adjusts for various factors. The goal was to identify regional disparities in exposure and contribute to the development of public health policies that protect populations from potential harm.
Calculating Cancer Risk
Researchers developed a model using several data sources to estimate the additional cancer risk from agricultural pesticide use. Key data included:
- Pesticide use data from the US Geological Survey in 2019, which covered 69 agricultural pesticides across 3143 counties
- Cancer incidence rates per 100,000 people, which were collected between 2015 and 2019 by the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; these data covered various cancers, including bladder, colorectal, leukemia, lung, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and pancreatic cancers
- Covariates, including smoking prevalence, the Social Vulnerability Index, agricultural land use, and total US population in 2019
Pesticide use profile patterns were developed using latent class analysis, a statistical method used to identify homogeneous subgroups within a heterogeneous population. A generalized linear model then estimated how these pesticide use patterns and the covariates affected cancer incidence.
The model highlighted regions with the highest and lowest “additional” cancer risks linked to pesticide exposure, calculating the estimated increase in cancer cases per year that resulted from variations in agricultural pesticide use.
Midwest Most Affected
While this model doesn’t establish causality or assess individual risk, it reveals regional trends in the association between pesticide use patterns and cancer incidence from a population-based perspective.
The Midwest, known for its high corn production, emerged as the region most affected by pesticide use. Compared with regions with the lowest risk, the Midwest faced an additional 154,541 cancer cases annually across all types. For colorectal and pancreatic cancers, the yearly increases were 20,927 and 3835 cases, respectively. Similar trends were observed for leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Pesticides vs Smoking
The researchers also estimated the additional cancer risk related to smoking, using the same model. They found that pesticides contributed to a higher risk for cancer than smoking in several cases.
The most significant difference was observed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, where pesticides were linked to 154.1% more cases than smoking. For all cancers combined, as well as bladder cancer and leukemia, the increases were moderate: 18.7%, 19.3%, and 21.0%, respectively.
This result highlights the importance of considering pesticide exposure alongside smoking when studying cancer risks.
Expanding Scope of Research
Some limitations of this study should be noted. Certain counties lacked complete data, and there was heterogeneity in the size and population of the counties studied. The research also did not account for seasonal and migrant workers, who are likely to be heavily exposed. In addition, the data used in the study were not independently validated, and they could not be used to assess individual risk.
The effect of pesticides on human health is a vast and critical field of research, often focusing on a limited range of pesticides or specific cancers. This study stands out by taking a broader, more holistic approach, aiming to highlight regional inequalities and identify less-studied pesticides that could be future research priorities.
Given the significant public health impact, the authors encouraged the authorities to share these findings with the most vulnerable communities to raise awareness.
This story was translated from JIM using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs Subcutaneous Atezolizumab Formulation for Multiple Cancer Indications
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approved indications include non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), SCLC, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. Specific indications are available with the full prescribing information at Drugs@FDA.
This is the first programmed death–ligand 1 inhibitor to gain approval for subcutaneous administration.
“This approval represents a significant option to improve the patient experience,” Ann Fish-Steagall, RN, Senior Vice President of Patient Services at the LUNGevity Foundation stated in a Genentech press release.
Subcutaneous atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs was evaluated in the open-label, randomized IMscin001 trial of 371 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who were not previously exposed to cancer immunotherapy and who had disease progression following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive subcutaneous or IV administration until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Atezolizumab exposure, the primary outcome measure of the study, met the lower limit of geometric mean ratio above the prespecified threshold of 0.8 (cycle 1C trough, 1.05; area under the curve for days 0-21, 0.87).
No notable differences were observed in overall response rate, progression-free survival, or overall survival between the two formulations, according to the FDA approval notice.
The confirmed overall response rate was 9% in the subcutaneous arm and 8% intravenous arm.
Adverse events of any grade occurring in at least 10% of patients were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
The recommended dose for subcutaneous injection is one 15 mL injection, which contains 1875 mg of atezolizumab and 30,000 units of hyaluronidase.
Injections should be administered in the thigh over approximately 7 minutes every 3 weeks. By contrast, IV administration generally takes 30-60 minutes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Clonal Hematopoiesis and Mosaic Chromosomal Alterations Increase Solid Tumor Risk?
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) and mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCAs) are associated with an increased risk for breast cancer, and CHIP is associated with increased mortality in patients with colon cancer, according to the authors of new research.
These findings, drawn from almost 11,000 patients in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, add further evidence that CHIP and mCA drive solid tumor risk, alongside known associations with hematologic malignancies, reported lead author Pinkal Desai, MD, associate professor of medicine and clinical director of molecular aging at Englander Institute for Precision Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and colleagues.
How This Study Differs From Others of Breast Cancer Risk Factors
“The independent effect of CHIP and mCA on risk and mortality from solid tumors has not been elucidated due to lack of detailed data on mortality outcomes and risk factors,” the investigators wrote in Cancer, although some previous studies have suggested a link.
In particular, the investigators highlighted a 2022 UK Biobank study, which reported an association between CHIP and lung cancer and a borderline association with breast cancer that did not quite reach statistical significance.
But the UK Biobank study was confined to a UK population, Dr. Desai noted in an interview, and the data were less detailed than those in the present investigation.
“In terms of risk, the part that was lacking in previous studies was a comprehensive assessment of risk factors that increase risk for all these cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “For example, for breast cancer, we had very detailed data on [participants’] Gail risk score, which is known to impact breast cancer risk. We also had mammogram data and colonoscopy data.”
In an accompanying editorial, Koichi Takahashi, MD, PhD , and Nehali Shah, BS, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, pointed out the same UK Biobank findings, then noted that CHIP has also been linked with worse overall survival in unselected cancer patients. Still, they wrote, “the impact of CH on cancer risk and mortality remains controversial due to conflicting data and context‐dependent effects,” necessitating studies like this one by Dr. Desai and colleagues.
How Was the Relationship Between CHIP, MCA, and Solid Tumor Risk Assessed?
To explore possible associations between CHIP, mCA, and solid tumors, the investigators analyzed whole genome sequencing data from 10,866 women in the WHI, a multi-study program that began in 1992 and involved 161,808 women in both observational and clinical trial cohorts.
In 2002, the first big data release from the WHI suggested that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) increased breast cancer risk, leading to widespread reduction in HRT use.
More recent reports continue to shape our understanding of these risks, suggesting differences across cancer types. For breast cancer, the WHI data suggested that HRT-associated risk was largely driven by formulations involving progesterone and estrogen, whereas estrogen-only formulations, now more common, are generally considered to present an acceptable risk profile for suitable patients.
The new study accounted for this potential HRT-associated risk, including by adjusting for patients who received HRT, type of HRT received, and duration of HRT received. According to Desai, this approach is commonly used when analyzing data from the WHI, nullifying concerns about the potentially deleterious effects of the hormones used in the study.
“Our question was not ‘does HRT cause cancer?’ ” Dr. Desai said in an interview. “But HRT can be linked to breast cancer risk and has a potential to be a confounder, and hence the above methodology.
“So I can say that the confounding/effect modification that HRT would have contributed to in the relationship between exposure (CH and mCA) and outcome (cancer) is well adjusted for as described above. This is standard in WHI analyses,” she continued.
“Every Women’s Health Initiative analysis that comes out — not just for our study — uses a standard method ... where you account for hormonal therapy,” Dr. Desai added, again noting that many other potential risk factors were considered, enabling a “detailed, robust” analysis.
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah agreed. “A notable strength of this study is its adjustment for many confounding factors,” they wrote. “The cohort’s well‐annotated data on other known cancer risk factors allowed for a robust assessment of CH’s independent risk.”
How Do Findings Compare With Those of the UK Biobank Study?
CHIP was associated with a 30% increased risk for breast cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 1.30; 95% CI, 1.03-1.64; P = .02), strengthening the borderline association reported by the UK Biobank study.
In contrast with the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with lung cancer risk, although this may have been caused by fewer cases of lung cancer and a lack of male patients, Dr. Desai suggested.
“The discrepancy between the studies lies in the risk of lung cancer, although the point estimate in the current study suggested a positive association,” wrote Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah.
As in the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Mortality analysis, however, which was not conducted in the UK Biobank study, offered a new insight: Patients with existing colorectal cancer and CHIP had a significantly higher mortality risk than those without CHIP. Before stage adjustment, risk for mortality among those with colorectal cancer and CHIP was fourfold higher than those without CHIP (HR, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.41-6.62; P < .001). After stage adjustment, CHIP was still associated with a twofold higher mortality risk (HR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.32-4.72; P = .004).
The investigators’ first mCA analyses, which employed a cell fraction cutoff greater than 3%, were unfruitful. But raising the cell fraction threshold to 5% in an exploratory analysis showed that autosomal mCA was associated with a 39% increased risk for breast cancer (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.06-1.83; P = .01). No such associations were found between mCA and colorectal or lung cancer, regardless of cell fraction threshold.
The original 3% cell fraction threshold was selected on the basis of previous studies reporting a link between mCA and hematologic malignancies at this cutoff, Dr. Desai said.
She and her colleagues said a higher 5% cutoff might be needed, as they suspected that the link between mCA and solid tumors may not be causal, requiring a higher mutation rate.
Why Do Results Differ Between These Types of Studies?
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah suggested that one possible limitation of the new study, and an obstacle to comparing results with the UK Biobank study and others like it, goes beyond population heterogeneity; incongruent findings could also be explained by differences in whole genome sequencing (WGS) technique.
“Although WGS allows sensitive detection of mCA through broad genomic coverage, it is less effective at detecting CHIP with low variant allele frequency (VAF) due to its relatively shallow depth (30x),” they wrote. “Consequently, the prevalence of mCA (18.8%) was much higher than that of CHIP (8.3%) in this cohort, contrasting with other studies using deeper sequencing.” As a result, the present study may have underestimated CHIP prevalence because of shallow sequencing depth.
“This inconsistency is a common challenge in CH population studies due to the lack of standardized methodologies and the frequent reliance on preexisting data not originally intended for CH detection,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said.
Even so, despite the “heavily context-dependent” nature of these reported risks, the body of evidence to date now offers a convincing biological rationale linking CH with cancer development and outcomes, they added.
How Do the CHIP- and mCA-associated Risks Differ Between Solid Tumors and Blood Cancers?
“[These solid tumor risks are] not causal in the way CHIP mutations are causal for blood cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “Here we are talking about solid tumor risk, and it’s kind of scattered. It’s not just breast cancer ... there’s also increased colon cancer mortality. So I feel these mutations are doing something different ... they are sort of an added factor.”
Specific mechanisms remain unclear, Dr. Desai said, although she speculated about possible impacts on the inflammatory state or alterations to the tumor microenvironment.
“These are blood cells, right?” Dr. Desai asked. “They’re everywhere, and they’re changing something inherently in these tumors.”
Future research and therapeutic development
Siddhartha Jaiswal, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Pathology at Stanford University in California, whose lab focuses on clonal hematopoiesis, said the causality question is central to future research.
“The key question is, are these mutations acting because they alter the function of blood cells in some way to promote cancer risk, or is it reflective of some sort of shared etiology that’s not causal?” Dr. Jaiswal said in an interview.
Available data support both possibilities.
On one side, “reasonable evidence” supports the noncausal view, Dr. Jaiswal noted, because telomere length is one of the most common genetic risk factors for clonal hematopoiesis and also for solid tumors, suggesting a shared genetic factor. On the other hand, CHIP and mCA could be directly protumorigenic via conferred disturbances of immune cell function.
When asked if both causal and noncausal factors could be at play, Dr. Jaiswal said, “yeah, absolutely.”
The presence of a causal association could be promising from a therapeutic standpoint.
“If it turns out that this association is driven by a direct causal effect of the mutations, perhaps related to immune cell function or dysfunction, then targeting that dysfunction could be a therapeutic path to improve outcomes in people, and there’s a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Jaiswal said. He went on to explain how a trial exploring this approach via interleukin-8 inhibition in lung cancer fell short.
Yet earlier intervention may still hold promise, according to experts.
“[This study] provokes the hypothesis that CH‐targeted interventions could potentially reduce cancer risk in the future,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said in their editorial.
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institutes of Health; and the Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Celgene, and others. Dr. Jaiswal reported stock equity in a company that has an interest in clonal hematopoiesis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) and mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCAs) are associated with an increased risk for breast cancer, and CHIP is associated with increased mortality in patients with colon cancer, according to the authors of new research.
These findings, drawn from almost 11,000 patients in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, add further evidence that CHIP and mCA drive solid tumor risk, alongside known associations with hematologic malignancies, reported lead author Pinkal Desai, MD, associate professor of medicine and clinical director of molecular aging at Englander Institute for Precision Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and colleagues.
How This Study Differs From Others of Breast Cancer Risk Factors
“The independent effect of CHIP and mCA on risk and mortality from solid tumors has not been elucidated due to lack of detailed data on mortality outcomes and risk factors,” the investigators wrote in Cancer, although some previous studies have suggested a link.
In particular, the investigators highlighted a 2022 UK Biobank study, which reported an association between CHIP and lung cancer and a borderline association with breast cancer that did not quite reach statistical significance.
But the UK Biobank study was confined to a UK population, Dr. Desai noted in an interview, and the data were less detailed than those in the present investigation.
“In terms of risk, the part that was lacking in previous studies was a comprehensive assessment of risk factors that increase risk for all these cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “For example, for breast cancer, we had very detailed data on [participants’] Gail risk score, which is known to impact breast cancer risk. We also had mammogram data and colonoscopy data.”
In an accompanying editorial, Koichi Takahashi, MD, PhD , and Nehali Shah, BS, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, pointed out the same UK Biobank findings, then noted that CHIP has also been linked with worse overall survival in unselected cancer patients. Still, they wrote, “the impact of CH on cancer risk and mortality remains controversial due to conflicting data and context‐dependent effects,” necessitating studies like this one by Dr. Desai and colleagues.
How Was the Relationship Between CHIP, MCA, and Solid Tumor Risk Assessed?
To explore possible associations between CHIP, mCA, and solid tumors, the investigators analyzed whole genome sequencing data from 10,866 women in the WHI, a multi-study program that began in 1992 and involved 161,808 women in both observational and clinical trial cohorts.
In 2002, the first big data release from the WHI suggested that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) increased breast cancer risk, leading to widespread reduction in HRT use.
More recent reports continue to shape our understanding of these risks, suggesting differences across cancer types. For breast cancer, the WHI data suggested that HRT-associated risk was largely driven by formulations involving progesterone and estrogen, whereas estrogen-only formulations, now more common, are generally considered to present an acceptable risk profile for suitable patients.
The new study accounted for this potential HRT-associated risk, including by adjusting for patients who received HRT, type of HRT received, and duration of HRT received. According to Desai, this approach is commonly used when analyzing data from the WHI, nullifying concerns about the potentially deleterious effects of the hormones used in the study.
“Our question was not ‘does HRT cause cancer?’ ” Dr. Desai said in an interview. “But HRT can be linked to breast cancer risk and has a potential to be a confounder, and hence the above methodology.
“So I can say that the confounding/effect modification that HRT would have contributed to in the relationship between exposure (CH and mCA) and outcome (cancer) is well adjusted for as described above. This is standard in WHI analyses,” she continued.
“Every Women’s Health Initiative analysis that comes out — not just for our study — uses a standard method ... where you account for hormonal therapy,” Dr. Desai added, again noting that many other potential risk factors were considered, enabling a “detailed, robust” analysis.
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah agreed. “A notable strength of this study is its adjustment for many confounding factors,” they wrote. “The cohort’s well‐annotated data on other known cancer risk factors allowed for a robust assessment of CH’s independent risk.”
How Do Findings Compare With Those of the UK Biobank Study?
CHIP was associated with a 30% increased risk for breast cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 1.30; 95% CI, 1.03-1.64; P = .02), strengthening the borderline association reported by the UK Biobank study.
In contrast with the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with lung cancer risk, although this may have been caused by fewer cases of lung cancer and a lack of male patients, Dr. Desai suggested.
“The discrepancy between the studies lies in the risk of lung cancer, although the point estimate in the current study suggested a positive association,” wrote Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah.
As in the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Mortality analysis, however, which was not conducted in the UK Biobank study, offered a new insight: Patients with existing colorectal cancer and CHIP had a significantly higher mortality risk than those without CHIP. Before stage adjustment, risk for mortality among those with colorectal cancer and CHIP was fourfold higher than those without CHIP (HR, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.41-6.62; P < .001). After stage adjustment, CHIP was still associated with a twofold higher mortality risk (HR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.32-4.72; P = .004).
The investigators’ first mCA analyses, which employed a cell fraction cutoff greater than 3%, were unfruitful. But raising the cell fraction threshold to 5% in an exploratory analysis showed that autosomal mCA was associated with a 39% increased risk for breast cancer (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.06-1.83; P = .01). No such associations were found between mCA and colorectal or lung cancer, regardless of cell fraction threshold.
The original 3% cell fraction threshold was selected on the basis of previous studies reporting a link between mCA and hematologic malignancies at this cutoff, Dr. Desai said.
She and her colleagues said a higher 5% cutoff might be needed, as they suspected that the link between mCA and solid tumors may not be causal, requiring a higher mutation rate.
Why Do Results Differ Between These Types of Studies?
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah suggested that one possible limitation of the new study, and an obstacle to comparing results with the UK Biobank study and others like it, goes beyond population heterogeneity; incongruent findings could also be explained by differences in whole genome sequencing (WGS) technique.
“Although WGS allows sensitive detection of mCA through broad genomic coverage, it is less effective at detecting CHIP with low variant allele frequency (VAF) due to its relatively shallow depth (30x),” they wrote. “Consequently, the prevalence of mCA (18.8%) was much higher than that of CHIP (8.3%) in this cohort, contrasting with other studies using deeper sequencing.” As a result, the present study may have underestimated CHIP prevalence because of shallow sequencing depth.
“This inconsistency is a common challenge in CH population studies due to the lack of standardized methodologies and the frequent reliance on preexisting data not originally intended for CH detection,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said.
Even so, despite the “heavily context-dependent” nature of these reported risks, the body of evidence to date now offers a convincing biological rationale linking CH with cancer development and outcomes, they added.
How Do the CHIP- and mCA-associated Risks Differ Between Solid Tumors and Blood Cancers?
“[These solid tumor risks are] not causal in the way CHIP mutations are causal for blood cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “Here we are talking about solid tumor risk, and it’s kind of scattered. It’s not just breast cancer ... there’s also increased colon cancer mortality. So I feel these mutations are doing something different ... they are sort of an added factor.”
Specific mechanisms remain unclear, Dr. Desai said, although she speculated about possible impacts on the inflammatory state or alterations to the tumor microenvironment.
“These are blood cells, right?” Dr. Desai asked. “They’re everywhere, and they’re changing something inherently in these tumors.”
Future research and therapeutic development
Siddhartha Jaiswal, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Pathology at Stanford University in California, whose lab focuses on clonal hematopoiesis, said the causality question is central to future research.
“The key question is, are these mutations acting because they alter the function of blood cells in some way to promote cancer risk, or is it reflective of some sort of shared etiology that’s not causal?” Dr. Jaiswal said in an interview.
Available data support both possibilities.
On one side, “reasonable evidence” supports the noncausal view, Dr. Jaiswal noted, because telomere length is one of the most common genetic risk factors for clonal hematopoiesis and also for solid tumors, suggesting a shared genetic factor. On the other hand, CHIP and mCA could be directly protumorigenic via conferred disturbances of immune cell function.
When asked if both causal and noncausal factors could be at play, Dr. Jaiswal said, “yeah, absolutely.”
The presence of a causal association could be promising from a therapeutic standpoint.
“If it turns out that this association is driven by a direct causal effect of the mutations, perhaps related to immune cell function or dysfunction, then targeting that dysfunction could be a therapeutic path to improve outcomes in people, and there’s a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Jaiswal said. He went on to explain how a trial exploring this approach via interleukin-8 inhibition in lung cancer fell short.
Yet earlier intervention may still hold promise, according to experts.
“[This study] provokes the hypothesis that CH‐targeted interventions could potentially reduce cancer risk in the future,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said in their editorial.
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institutes of Health; and the Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Celgene, and others. Dr. Jaiswal reported stock equity in a company that has an interest in clonal hematopoiesis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) and mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCAs) are associated with an increased risk for breast cancer, and CHIP is associated with increased mortality in patients with colon cancer, according to the authors of new research.
These findings, drawn from almost 11,000 patients in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study, add further evidence that CHIP and mCA drive solid tumor risk, alongside known associations with hematologic malignancies, reported lead author Pinkal Desai, MD, associate professor of medicine and clinical director of molecular aging at Englander Institute for Precision Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and colleagues.
How This Study Differs From Others of Breast Cancer Risk Factors
“The independent effect of CHIP and mCA on risk and mortality from solid tumors has not been elucidated due to lack of detailed data on mortality outcomes and risk factors,” the investigators wrote in Cancer, although some previous studies have suggested a link.
In particular, the investigators highlighted a 2022 UK Biobank study, which reported an association between CHIP and lung cancer and a borderline association with breast cancer that did not quite reach statistical significance.
But the UK Biobank study was confined to a UK population, Dr. Desai noted in an interview, and the data were less detailed than those in the present investigation.
“In terms of risk, the part that was lacking in previous studies was a comprehensive assessment of risk factors that increase risk for all these cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “For example, for breast cancer, we had very detailed data on [participants’] Gail risk score, which is known to impact breast cancer risk. We also had mammogram data and colonoscopy data.”
In an accompanying editorial, Koichi Takahashi, MD, PhD , and Nehali Shah, BS, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, pointed out the same UK Biobank findings, then noted that CHIP has also been linked with worse overall survival in unselected cancer patients. Still, they wrote, “the impact of CH on cancer risk and mortality remains controversial due to conflicting data and context‐dependent effects,” necessitating studies like this one by Dr. Desai and colleagues.
How Was the Relationship Between CHIP, MCA, and Solid Tumor Risk Assessed?
To explore possible associations between CHIP, mCA, and solid tumors, the investigators analyzed whole genome sequencing data from 10,866 women in the WHI, a multi-study program that began in 1992 and involved 161,808 women in both observational and clinical trial cohorts.
In 2002, the first big data release from the WHI suggested that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) increased breast cancer risk, leading to widespread reduction in HRT use.
More recent reports continue to shape our understanding of these risks, suggesting differences across cancer types. For breast cancer, the WHI data suggested that HRT-associated risk was largely driven by formulations involving progesterone and estrogen, whereas estrogen-only formulations, now more common, are generally considered to present an acceptable risk profile for suitable patients.
The new study accounted for this potential HRT-associated risk, including by adjusting for patients who received HRT, type of HRT received, and duration of HRT received. According to Desai, this approach is commonly used when analyzing data from the WHI, nullifying concerns about the potentially deleterious effects of the hormones used in the study.
“Our question was not ‘does HRT cause cancer?’ ” Dr. Desai said in an interview. “But HRT can be linked to breast cancer risk and has a potential to be a confounder, and hence the above methodology.
“So I can say that the confounding/effect modification that HRT would have contributed to in the relationship between exposure (CH and mCA) and outcome (cancer) is well adjusted for as described above. This is standard in WHI analyses,” she continued.
“Every Women’s Health Initiative analysis that comes out — not just for our study — uses a standard method ... where you account for hormonal therapy,” Dr. Desai added, again noting that many other potential risk factors were considered, enabling a “detailed, robust” analysis.
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah agreed. “A notable strength of this study is its adjustment for many confounding factors,” they wrote. “The cohort’s well‐annotated data on other known cancer risk factors allowed for a robust assessment of CH’s independent risk.”
How Do Findings Compare With Those of the UK Biobank Study?
CHIP was associated with a 30% increased risk for breast cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 1.30; 95% CI, 1.03-1.64; P = .02), strengthening the borderline association reported by the UK Biobank study.
In contrast with the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with lung cancer risk, although this may have been caused by fewer cases of lung cancer and a lack of male patients, Dr. Desai suggested.
“The discrepancy between the studies lies in the risk of lung cancer, although the point estimate in the current study suggested a positive association,” wrote Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah.
As in the UK Biobank study, CHIP was not associated with increased risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Mortality analysis, however, which was not conducted in the UK Biobank study, offered a new insight: Patients with existing colorectal cancer and CHIP had a significantly higher mortality risk than those without CHIP. Before stage adjustment, risk for mortality among those with colorectal cancer and CHIP was fourfold higher than those without CHIP (HR, 3.99; 95% CI, 2.41-6.62; P < .001). After stage adjustment, CHIP was still associated with a twofold higher mortality risk (HR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.32-4.72; P = .004).
The investigators’ first mCA analyses, which employed a cell fraction cutoff greater than 3%, were unfruitful. But raising the cell fraction threshold to 5% in an exploratory analysis showed that autosomal mCA was associated with a 39% increased risk for breast cancer (HR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.06-1.83; P = .01). No such associations were found between mCA and colorectal or lung cancer, regardless of cell fraction threshold.
The original 3% cell fraction threshold was selected on the basis of previous studies reporting a link between mCA and hematologic malignancies at this cutoff, Dr. Desai said.
She and her colleagues said a higher 5% cutoff might be needed, as they suspected that the link between mCA and solid tumors may not be causal, requiring a higher mutation rate.
Why Do Results Differ Between These Types of Studies?
Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah suggested that one possible limitation of the new study, and an obstacle to comparing results with the UK Biobank study and others like it, goes beyond population heterogeneity; incongruent findings could also be explained by differences in whole genome sequencing (WGS) technique.
“Although WGS allows sensitive detection of mCA through broad genomic coverage, it is less effective at detecting CHIP with low variant allele frequency (VAF) due to its relatively shallow depth (30x),” they wrote. “Consequently, the prevalence of mCA (18.8%) was much higher than that of CHIP (8.3%) in this cohort, contrasting with other studies using deeper sequencing.” As a result, the present study may have underestimated CHIP prevalence because of shallow sequencing depth.
“This inconsistency is a common challenge in CH population studies due to the lack of standardized methodologies and the frequent reliance on preexisting data not originally intended for CH detection,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said.
Even so, despite the “heavily context-dependent” nature of these reported risks, the body of evidence to date now offers a convincing biological rationale linking CH with cancer development and outcomes, they added.
How Do the CHIP- and mCA-associated Risks Differ Between Solid Tumors and Blood Cancers?
“[These solid tumor risks are] not causal in the way CHIP mutations are causal for blood cancers,” Dr. Desai said. “Here we are talking about solid tumor risk, and it’s kind of scattered. It’s not just breast cancer ... there’s also increased colon cancer mortality. So I feel these mutations are doing something different ... they are sort of an added factor.”
Specific mechanisms remain unclear, Dr. Desai said, although she speculated about possible impacts on the inflammatory state or alterations to the tumor microenvironment.
“These are blood cells, right?” Dr. Desai asked. “They’re everywhere, and they’re changing something inherently in these tumors.”
Future research and therapeutic development
Siddhartha Jaiswal, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Pathology at Stanford University in California, whose lab focuses on clonal hematopoiesis, said the causality question is central to future research.
“The key question is, are these mutations acting because they alter the function of blood cells in some way to promote cancer risk, or is it reflective of some sort of shared etiology that’s not causal?” Dr. Jaiswal said in an interview.
Available data support both possibilities.
On one side, “reasonable evidence” supports the noncausal view, Dr. Jaiswal noted, because telomere length is one of the most common genetic risk factors for clonal hematopoiesis and also for solid tumors, suggesting a shared genetic factor. On the other hand, CHIP and mCA could be directly protumorigenic via conferred disturbances of immune cell function.
When asked if both causal and noncausal factors could be at play, Dr. Jaiswal said, “yeah, absolutely.”
The presence of a causal association could be promising from a therapeutic standpoint.
“If it turns out that this association is driven by a direct causal effect of the mutations, perhaps related to immune cell function or dysfunction, then targeting that dysfunction could be a therapeutic path to improve outcomes in people, and there’s a lot of interest in this,” Dr. Jaiswal said. He went on to explain how a trial exploring this approach via interleukin-8 inhibition in lung cancer fell short.
Yet earlier intervention may still hold promise, according to experts.
“[This study] provokes the hypothesis that CH‐targeted interventions could potentially reduce cancer risk in the future,” Dr. Takahashi and Ms. Shah said in their editorial.
The WHI program is funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institutes of Health; and the Department of Health & Human Services. The investigators disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Celgene, and others. Dr. Jaiswal reported stock equity in a company that has an interest in clonal hematopoiesis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER
Cancer Cases, Deaths in Men Predicted to Surge by 2050
TOPLINE:
— with substantial disparities in cancer cases and deaths by age and region of the world, a recent analysis found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Overall, men have higher cancer incidence and mortality rates, which can be largely attributed to a higher prevalence of modifiable risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and occupational carcinogens, as well as the underuse of cancer prevention, screening, and treatment services.
- To assess the burden of cancer in men of different ages and from different regions of the world, researchers analyzed data from the 2022 Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN), which provides national-level estimates for cancer cases and deaths.
- Study outcomes included the incidence, mortality, and prevalence of cancer among men in 2022, along with projections for 2050. Estimates were stratified by several factors, including age; region; and Human Development Index (HDI), a composite score for health, education, and standard of living.
- Researchers also calculated mortality-to-incidence ratios (MIRs) for various cancer types, where higher values indicate worse survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers reported an estimated 10.3 million cancer cases and 5.4 million deaths globally in 2022, with almost two thirds of cases and deaths occurring in men aged 65 years or older.
- By 2050, cancer cases and deaths were projected to increase by 84.3% (to 19 million) and 93.2% (to 10.5 million), respectively. The increase from 2022 to 2050 was more than twofold higher for older men and countries with low and medium HDI.
- In 2022, the estimated global cancer MIR among men was nearly 55%, with variations by cancer types, age, and HDI. The MIR was lowest for thyroid cancer (7.6%) and highest for pancreatic cancer (90.9%); among World Health Organization regions, Africa had the highest MIR (72.6%), while the Americas had the lowest MIR (39.1%); countries with the lowest HDI had the highest MIR (73.5% vs 41.1% for very high HDI).
- Lung cancer was the leading cause for cases and deaths in 2022 and was projected to remain the leading cause in 2050.
IN PRACTICE:
“Disparities in cancer incidence and mortality among men were observed across age groups, countries/territories, and HDI in 2022, with these disparities projected to widen further by 2050,” according to the authors, who called for efforts to “reduce disparities in cancer burden and ensure equity in cancer prevention and care for men across the globe.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Habtamu Mellie Bizuayehu, PhD, School of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be influenced by the quality of GLOBOCAN data. Interpretation should be cautious as MIR may not fully reflect cancer outcome inequalities. The study did not include other measures of cancer burden, such as years of life lost or years lived with disability, which were unavailable from the data source.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
— with substantial disparities in cancer cases and deaths by age and region of the world, a recent analysis found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Overall, men have higher cancer incidence and mortality rates, which can be largely attributed to a higher prevalence of modifiable risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and occupational carcinogens, as well as the underuse of cancer prevention, screening, and treatment services.
- To assess the burden of cancer in men of different ages and from different regions of the world, researchers analyzed data from the 2022 Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN), which provides national-level estimates for cancer cases and deaths.
- Study outcomes included the incidence, mortality, and prevalence of cancer among men in 2022, along with projections for 2050. Estimates were stratified by several factors, including age; region; and Human Development Index (HDI), a composite score for health, education, and standard of living.
- Researchers also calculated mortality-to-incidence ratios (MIRs) for various cancer types, where higher values indicate worse survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers reported an estimated 10.3 million cancer cases and 5.4 million deaths globally in 2022, with almost two thirds of cases and deaths occurring in men aged 65 years or older.
- By 2050, cancer cases and deaths were projected to increase by 84.3% (to 19 million) and 93.2% (to 10.5 million), respectively. The increase from 2022 to 2050 was more than twofold higher for older men and countries with low and medium HDI.
- In 2022, the estimated global cancer MIR among men was nearly 55%, with variations by cancer types, age, and HDI. The MIR was lowest for thyroid cancer (7.6%) and highest for pancreatic cancer (90.9%); among World Health Organization regions, Africa had the highest MIR (72.6%), while the Americas had the lowest MIR (39.1%); countries with the lowest HDI had the highest MIR (73.5% vs 41.1% for very high HDI).
- Lung cancer was the leading cause for cases and deaths in 2022 and was projected to remain the leading cause in 2050.
IN PRACTICE:
“Disparities in cancer incidence and mortality among men were observed across age groups, countries/territories, and HDI in 2022, with these disparities projected to widen further by 2050,” according to the authors, who called for efforts to “reduce disparities in cancer burden and ensure equity in cancer prevention and care for men across the globe.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Habtamu Mellie Bizuayehu, PhD, School of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be influenced by the quality of GLOBOCAN data. Interpretation should be cautious as MIR may not fully reflect cancer outcome inequalities. The study did not include other measures of cancer burden, such as years of life lost or years lived with disability, which were unavailable from the data source.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
— with substantial disparities in cancer cases and deaths by age and region of the world, a recent analysis found.
METHODOLOGY:
- Overall, men have higher cancer incidence and mortality rates, which can be largely attributed to a higher prevalence of modifiable risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and occupational carcinogens, as well as the underuse of cancer prevention, screening, and treatment services.
- To assess the burden of cancer in men of different ages and from different regions of the world, researchers analyzed data from the 2022 Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN), which provides national-level estimates for cancer cases and deaths.
- Study outcomes included the incidence, mortality, and prevalence of cancer among men in 2022, along with projections for 2050. Estimates were stratified by several factors, including age; region; and Human Development Index (HDI), a composite score for health, education, and standard of living.
- Researchers also calculated mortality-to-incidence ratios (MIRs) for various cancer types, where higher values indicate worse survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- The researchers reported an estimated 10.3 million cancer cases and 5.4 million deaths globally in 2022, with almost two thirds of cases and deaths occurring in men aged 65 years or older.
- By 2050, cancer cases and deaths were projected to increase by 84.3% (to 19 million) and 93.2% (to 10.5 million), respectively. The increase from 2022 to 2050 was more than twofold higher for older men and countries with low and medium HDI.
- In 2022, the estimated global cancer MIR among men was nearly 55%, with variations by cancer types, age, and HDI. The MIR was lowest for thyroid cancer (7.6%) and highest for pancreatic cancer (90.9%); among World Health Organization regions, Africa had the highest MIR (72.6%), while the Americas had the lowest MIR (39.1%); countries with the lowest HDI had the highest MIR (73.5% vs 41.1% for very high HDI).
- Lung cancer was the leading cause for cases and deaths in 2022 and was projected to remain the leading cause in 2050.
IN PRACTICE:
“Disparities in cancer incidence and mortality among men were observed across age groups, countries/territories, and HDI in 2022, with these disparities projected to widen further by 2050,” according to the authors, who called for efforts to “reduce disparities in cancer burden and ensure equity in cancer prevention and care for men across the globe.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Habtamu Mellie Bizuayehu, PhD, School of Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings may be influenced by the quality of GLOBOCAN data. Interpretation should be cautious as MIR may not fully reflect cancer outcome inequalities. The study did not include other measures of cancer burden, such as years of life lost or years lived with disability, which were unavailable from the data source.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose any funding information. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Treatment 101: A Primer for Non-Oncologists
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
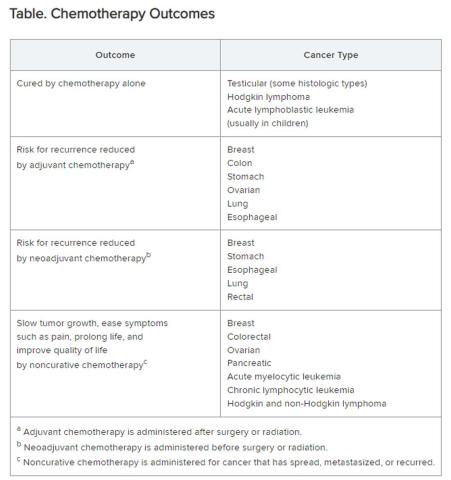
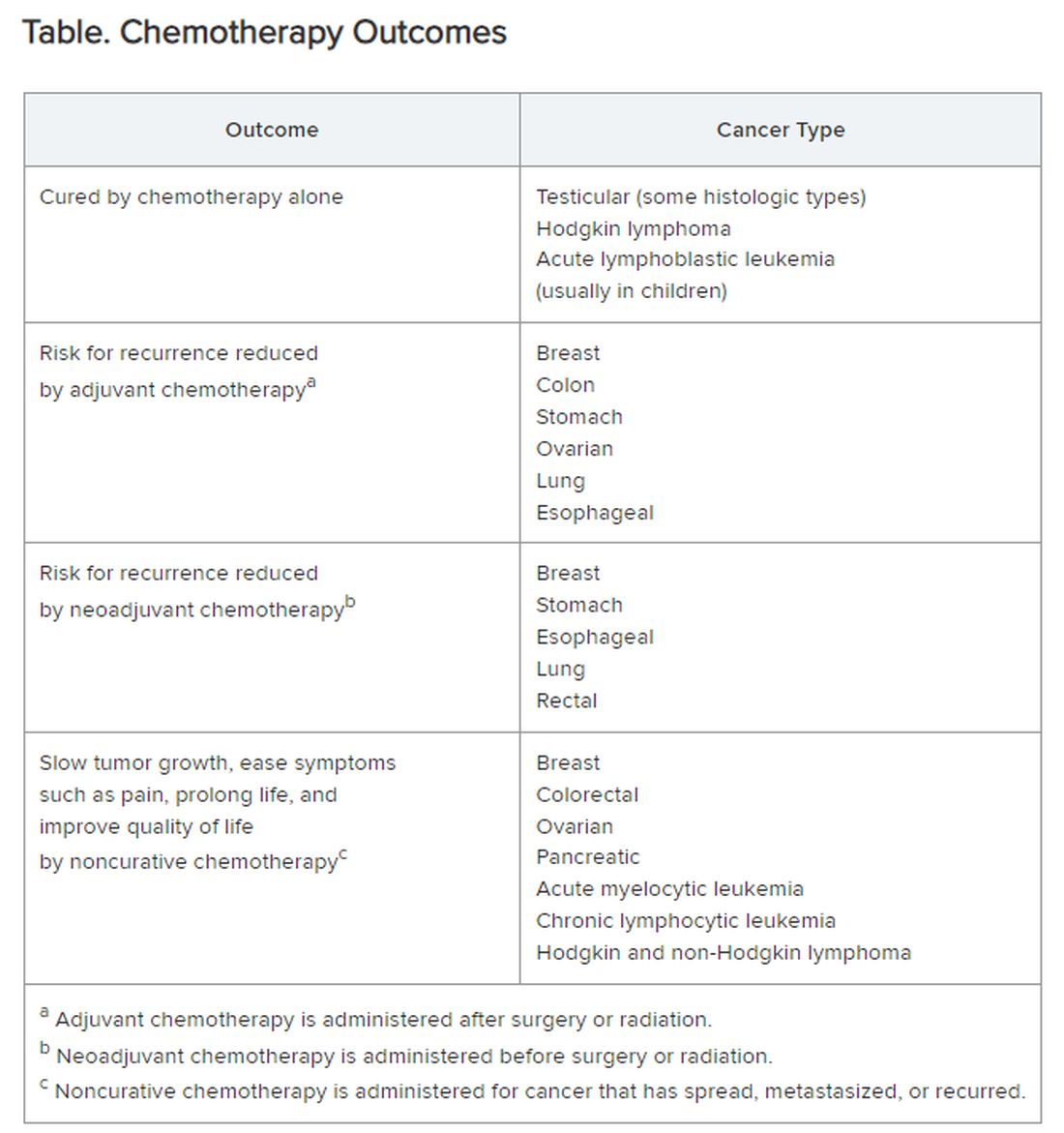
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The remaining 700,000 or so often proceed to chemotherapy either immediately or upon cancer recurrence, spread, or newly recognized metastases. “Cures” after that point are rare.
I’m speaking in generalities, understanding that each cancer and each patient is unique.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy alone can cure a small number of cancer types. When added to radiation or surgery, chemotherapy can help to cure a wider range of cancer types. As an add-on, chemotherapy can extend the length and quality of life for many patients with cancer. Since chemotherapy is by definition “toxic,” it can also shorten the duration or harm the quality of life and provide false hope. The Table summarizes what chemotherapy can and cannot achieve in selected cancer types.
Careful, compassionate communication between patient and physician is key. Goals and expectations must be clearly understood.
Organized chemotherapeutic efforts are further categorized as first line, second line, and third line.
First-line treatment. The initial round of recommended chemotherapy for a specific cancer. It is typically considered the most effective treatment for that type and stage of cancer on the basis of current research and clinical trials.
Second-line treatment. This is the treatment used if the first-line chemotherapy doesn’t work as desired. Reasons to switch to second-line chemo include:
- Lack of response (the tumor failed to shrink).
- Progression (the cancer may have grown or spread further).
- Adverse side effects were too severe to continue.
The drugs used in second-line chemo will typically be different from those used in first line, sometimes because cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time. Moreover, the goal of second-line chemo may differ from that of first-line therapy. Rather than chiefly aiming for a cure, second-line treatment might focus on slowing cancer growth, managing symptoms, or improving quality of life. Unfortunately, not every type of cancer has a readily available second-line option.
Third-line treatment. Third-line options come into play when both the initial course of chemo (first line) and the subsequent treatment (second line) have failed to achieve remission or control the cancer’s spread. Owing to the progressive nature of advanced cancers, patients might not be eligible or healthy enough for third-line therapy. Depending on cancer type, the patient’s general health, and response to previous treatments, third-line options could include:
- New or different chemotherapy drugs compared with prior lines.
- Surgery to debulk the tumor.
- Radiation for symptom control.
- Targeted therapy: drugs designed to target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: agents that help the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
- Clinical trials testing new or investigational treatments, which may be applicable at any time, depending on the questions being addressed.
The goals of third-line therapy may shift from aiming for a cure to managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and potentially slowing cancer growth. The decision to pursue third-line therapy involves careful consideration by the doctor and patient, weighing the potential benefits and risks of treatment considering the individual’s overall health and specific situation.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of third-line therapy. Although remission may be unlikely, third-line therapy can still play a role in managing the disease.
Navigating advanced cancer treatment is very complex. The patient and physician must together consider detailed explanations and clarifications to set expectations and make informed decisions about care.
Interventions to Consider Earlier
In traditional clinical oncology practice, other interventions are possible, but these may not be offered until treatment has reached the third line:
- Molecular testing.
- Palliation.
- Clinical trials.
- Innovative testing to guide targeted therapy by ascertaining which agents are most likely (or not likely at all) to be effective.
I would argue that the patient’s interests are better served by considering and offering these other interventions much earlier, even before starting first-line chemotherapy.
Molecular testing. The best time for molecular testing of a new malignant tumor is typically at the time of diagnosis. Here’s why:
- Molecular testing helps identify specific genetic mutations in the cancer cells. This information can be crucial for selecting targeted therapies that are most effective against those specific mutations. Early detection allows for the most treatment options. For example, for non–small cell lung cancer, early is best because treatment and outcomes may well be changed by test results.
- Knowing the tumor’s molecular makeup can help determine whether a patient qualifies for clinical trials of new drugs designed for specific mutations.
- Some molecular markers can offer information about the tumor’s aggressiveness and potential for metastasis so that prognosis can be informed.
Molecular testing can be a valuable tool throughout a cancer patient’s journey. With genetically diverse tumors, the initial biopsy might not capture the full picture. Molecular testing of circulating tumor DNA can be used to monitor a patient’s response to treatment and detect potential mutations that might arise during treatment resistance. Retesting after metastasis can provide additional information that can aid in treatment decisions.
Palliative care. The ideal time to discuss palliative care with a patient with cancer is early in the diagnosis and treatment process. Palliative care is not the same as hospice care; it isn’t just about end-of-life. Palliative care focuses on improving a patient’s quality of life throughout cancer treatment. Palliative care specialists can address a wide range of symptoms a patient might experience from cancer or its treatment, including pain, fatigue, nausea, and anxiety.
Early discussions allow for a more comprehensive care plan. Open communication about all treatment options, including palliative care, empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care goals and preferences.
Specific situations where discussing palliative care might be appropriate are:
- Soon after a cancer diagnosis.
- If the patient experiences significant side effects from cancer treatment.
- When considering different treatment options, palliative care can complement those treatments.
- In advanced stages of cancer, to focus on comfort and quality of life.
Clinical trials. Participation in a clinical trial to explore new or investigational treatments should always be considered.
In theory, clinical trials should be an option at any time in the patient’s course. But the organized clinical trial experience may not be available or appropriate. Then, the individual becomes a de facto “clinical trial with an n of 1.” Read this brief open-access blog post at Cancer Commons to learn more about that circumstance.
Innovative testing. The best choice of chemotherapeutic or targeted therapies is often unclear. The clinician is likely to follow published guidelines, often from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
These are evidence based and driven by consensus of experts. But guideline-recommended therapy is not always effective, and weeks or months can pass before this ineffectiveness becomes apparent. Thus, many researchers and companies are seeking methods of testing each patient’s specific cancer to determine in advance, or very quickly, whether a particular drug is likely to be effective.
Read more about these leading innovations:
SAGE Oncotest: Entering the Next Generation of Tailored Cancer Treatment
Alibrex: A New Blood Test to Reveal Whether a Cancer Treatment is Working
PARIS Test Uses Lab-Grown Mini-Tumors to Find a Patient’s Best Treatment
Using Live Cells from Patients to Find the Right Cancer Drug
Other innovative therapies under investigation could even be agnostic to cancer type:
Treating Pancreatic Cancer: Could Metabolism — Not Genomics — Be the Key?
High-Energy Blue Light Powers a Promising New Treatment to Destroy Cancer Cells
All-Clear Follow-Up: Hydrogen Peroxide Appears to Treat Oral and Skin Lesions
Cancer is a tough nut to crack. Many people and organizations are trying very hard. So much is being learned. Some approaches will be effective. We can all hope.
Dr. Lundberg, editor in chief, Cancer Commons, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Immunotherapy May Be Overused in Dying Patients With Cancer
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chemotherapy has fallen out of favor for treating cancer toward the end of life. The toxicity is too high, and the benefit, if any, is often too low.
Immunotherapy, however, has been taking its place.
This means “there are patients who are getting immunotherapy who shouldn’t,” said Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, surgical oncologist Sajid Khan, MD, senior investigator on a recent study that highlighted the growing use of these agents in patients’ last month of life.
What’s driving this trend, and how can oncologists avoid overtreatment with immunotherapy at the end of life?
The N-of-1 Patient
With immunotherapy at the end of life, “each of us has had our N-of-1” where a patient bounces back with a remarkable and durable response, said Don Dizon, MD, a gynecologic oncologist at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island.
He recalled a patient with sarcoma who did not respond to chemotherapy. But after Dr. Dizon started her on immunotherapy, everything turned around. She has now been in remission for 8 years and counting.
The possibility of an unexpected or remarkable responder is seductive. And the improved safety of immunotherapy over chemotherapy adds to the allure.
Meanwhile, patients are often desperate. It’s rare for someone to be ready to stop treatment, Dr. Dizon said. Everybody “hopes that they’re going to be the exceptional responder.”
At the end of the day, the question often becomes: “Why not try immunotherapy? What’s there to lose?”
This thinking may be prompting broader use of immunotherapy in late-stage disease, even in instances with no Food and Drug Administration indication and virtually no supportive data, such as for metastatic ovarian cancer, Dr. Dizon said.
Back to Earth
The problem with the hopeful approach is that end-of-life turnarounds with immunotherapy are rare, and there’s no way at the moment to predict who will have one, said Laura Petrillo, MD, a palliative care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Even though immunotherapy generally comes with fewer adverse events than chemotherapy, catastrophic side effects are still possible.
Dr. Petrillo recalled a 95-year-old woman with metastatic cancer who was largely asymptomatic.
She had a qualifying mutation for a checkpoint inhibitor, so her oncologist started her on one. The patient never bounced back from the severe colitis the agent caused, and she died of complications in the hospital.
Although such reactions with immunotherapy are uncommon, less serious problems caused by the agents can still have a major impact on a person’s quality of life. Low-grade diarrhea, for instance, may not sound too bad, but in a patient’s daily life, it can translate to six or more episodes a day.
Even with no side effects, prescribing immunotherapy can mean that patients with limited time left spend a good portion of it at an infusion clinic instead of at home. These patients are also less likely to be referred to hospice and more likely to be admitted to and die in the hospital.
And with treatments that can cost $20,000 per dose, financial toxicity becomes a big concern.
In short, some of the reasons why chemotherapy is not recommended at the end of life also apply to immunotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said.
Prescribing Decisions
Recent research highlights the growing use of immunotherapy at the end of life.
Dr. Khan’s retrospective study found, for instance, that the percentage of patients starting immunotherapy in the last 30 days of life increased by about fourfold to fivefold over the study period for the three cancers analyzed — stage IV melanoma, lung, and kidney cancers.
Among the population that died within 30 days, the percentage receiving immunotherapy increased over the study periods — 0.8%-4.3% for melanoma, 0.9%-3.2% for NSCLC, and 0.5%-2.6% for kidney cell carcinoma — prompting the conclusion that immunotherapy prescriptions in the last month of life are on the rise.
Prescribing immunotherapy in patients who ultimately died within 1 month occurred more frequently at low-volume, nonacademic centers than at academic or high-volume centers, and outcomes varied by practice setting.
Patients had better survival outcomes overall when receiving immunotherapy at academic or high-volume centers — a finding Dr. Khan said is worth investigating further. Possible explanations include better management of severe immune-related side effects at larger centers and more caution when prescribing immunotherapy to “borderline” candidates, such as those with several comorbidities.
Importantly, given the retrospective design, Dr. Khan and colleagues already knew which patients prescribed immunotherapy died within 30 days of initiating treatment.
More specifically, 5192 of 71,204 patients who received immunotherapy (7.3%) died within a month of initiating therapy, while 66,012 (92.7%) lived beyond that point.
The study, however, did not assess how the remaining 92.7% who lived beyond 30 days fared on immunotherapy and the differences between those who lived less than 30 days and those who survived longer.
Knowing the outcome of patients at the outset of the analysis still leaves open the question of when immunotherapy can extend life and when it can’t for the patient in front of you.
To avoid overtreating at the end of life, it’s important to have “the same standard that you have for giving chemotherapy. You have to treat it with the same respect,” said Moshe Chasky, MD, a community medical oncologist with Alliance Cancer Specialists in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. “You can’t just be throwing” immunotherapy around “at the end of life.”
While there are no clear predictors of risk and benefit, there are some factors to help guide decisions.
As with chemotherapy, Dr. Petrillo said performance status is key. Dr. Petrillo and colleagues found that median overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non–small cell lung cancer was 14.3 months in patients with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score of 0-1 but only 4.5 months with scores of ≥ 2.
Dr. Khan also found that immunotherapy survival is, unsurprisingly, worse in patients with high metastatic burdens and more comorbidities.
“You should still consider immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma,” Dr. Khan said. The message here is to “think twice before using” it, especially in comorbid patients with widespread metastases.
“Just because something can be done doesn’t always mean it should be done,” he said.
At Yale, when Dr. Khan works, immunotherapy decisions are considered by a multidisciplinary tumor board. At Mass General, immunotherapy has generally moved to the frontline setting, and the hospital no longer prescribes checkpoint inhibitors to hospitalized patients because the cost is too high relative to the potential benefit, Dr. Petrillo explained.
Still, with all the uncertainties about risk and benefit, counseling patients is a challenge. Dr. Dizon called it “the epitome of shared decision-making.”
Dr. Petrillo noted that it’s critical not to counsel patients based solely on the anecdotal patients who do surprisingly well.
“It’s hard to mention that and not have that be what somebody anchors on,” she said. But that speaks to “how desperate people can feel, how hopeful they can be.”
Dr. Khan, Dr. Petrillo, and Dr. Chasky all reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves First Engineered Cell Therapy for a Solid Tumor
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Afami-cel — the first engineered cell therapy for a solid tumor — is indicated specifically for adults with unresectable or metastatic synovial sarcoma who have received prior chemotherapy, are positive for several human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), and whose tumors express melanoma-associated antigen A4, as determined by FDA-authorized companion diagnostic devices.
The single-dose treatment targets solid tumors expressing melanoma-associated antigen A4, a protein highly expressed in synovial sarcoma.
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer, which affects about 1000 people in the US each year. Malignant cells develop and form a tumor in soft tissues, often in the extremities.
“Adults with metastatic synovial sarcoma, a life-threatening form of cancer, often face limited treatment options in addition to the risk of cancer spread or recurrence,” Nicole Verdun, MD, director of the Office of Therapeutic Products in the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in the agency press release announcing the approval. “Today’s approval represents a significant milestone in the development of an innovative, safe and effective therapy for patients with this rare but potentially fatal disease.”
T-cell receptor therapy, like chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, involves altering patient T cells to fight cancer. While CAR-T therapy inserts an artificial receptor to target a specific surface protein on cancer cells, the T-cell receptor therapy modifies existing receptors to recognize an array of antigens on the surface of cancer cells — a promising strategy for targeting solid tumors.
The accelerated approval of afami-cel was based on the phase 2 SPEARHEAD-1 trial in 44 patients with synovial sarcoma who received a single infusion of the therapy. The trial had enrolled 52 patients, but 8 did not receive afami-cel, including 3 who died and 1 who withdrew.
According to the FDA announcement, the overall response rate was 43.2%, with a median time to response of 4.9 weeks. The median duration of response was 6 months (95% CI, 4.6 months to not reached). Among patients who responded, 39% had a duration of response of 12 months or longer.
“These results suggest that a one-time treatment with afami-cel has the potential to extend life while allowing responders to go off chemotherapy,” said lead investigator Sandra D’Angelo, MD, a sarcoma specialist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, in a company press release.
The prescribing information includes a boxed warning for serious or fatal cytokine release syndrome.
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included cytokine release syndrome, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, infections, pyrexia, constipation, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and edema. The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, occurring in at least 20% of patients, included decreased lymphocyte count, neutrophil count, white cell blood count, red blood cell, and platelet count.
The recommended dose is between 2.68x109 to 10x109 MAGE-A4 T-cell receptor–positive T-cells. The FDA notice specifies not using a leukodepleting filter or prophylactic systemic corticosteroids.
The list price for the one-time therapy is $727,000, according to Fierce Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Last 30 Days: How Oncologists’ Choices Affect End-of-Life Cancer Care
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients treated by oncologists in the top quartile for end-of-life prescribing behavior were almost four and a half times more likely to receive end-of-life therapy than those treated by these specialists in the bottom quartile.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER)-Medicare database, focusing on patients who died of cancer between 2012 and 2017.
- A total of 17,609 patients with breast, lung, colorectal, or prostate cancer were included, treated by 960 oncologists across 388 practices.
- Patients were required to have had at least one systemic cancer therapy claim in the last 180 days of life, with the treating oncologist identified on the basis of the therapy claim closest to the time of death.
- The study used multilevel models to estimate oncologists’ rates of providing cancer therapy in the last 30 days of life, adjusting for patient characteristics and practice variation.
- Functional status was assessed on the basis of paid claims for durable medical equipment in the last 60 months of life, with scores categorized as 0, 1, ≥ 2, or unknown.
TAKEAWAY:
- Oncologists in the 95th percentile for high end-of-life prescribing behavior had a 45% adjusted rate of treating patients in the last 30 days of life, compared with 17% among those in the 5th percentile.
- Patients treated by high end-of-life prescribing oncologists had over four times higher odds of receiving systemic therapy in the last 30 days of life (odds ratio [OR], 4.42; 95% CI, 4.00-4.89).
- Higher end-of-life prescribing oncologists also had a higher proportion of patients hospitalized in the last 30 days of life than low prescribers (58% vs 51.9%).
- No significant association was found between oncologist prescribing behavior and patient race or ethnicity, except for Black patients who had lower odds of receiving treatment (OR, 0.77; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Given calls to rein in overutilization of end-of-life six to eight cancer therapies, our findings highlight an underappreciated area for further research: How treatment discontinuation before death is shaped by oncologists’ unique treatment propensities. Elucidating the reasons for this remarkable variability in oncologist treatment behavior could inform efforts to reduce end-of-life cancer treatment overutilization,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Login S. George, PhD, Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, Rutgers University in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s reliance on SEER-Medicare data may limit the generalizability of the findings to patients with Medicare Advantage, private insurance, or Medicaid, as well as younger patients. The lack of data on patient preferences and other health characteristics could confound the results. The study focused on systemic therapies and may not be generalizable to other treatments such as clinical trial drugs, oral therapies, surgery, or radiation. The data from 2012 to 2017 may not reflect more recent trends in cancer treatment.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey. George disclosed receiving grants from these organizations. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.