User login
Best Practice Implementation and Clinical Inertia
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.
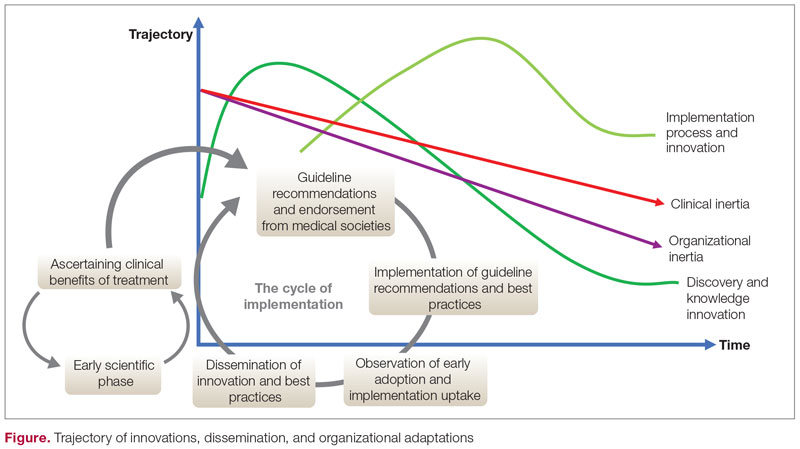
Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.

Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
From the Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Clinical inertia is defined as the failure of clinicians to initiate or escalate guideline-directed medical therapy to achieve treatment goals for well-defined clinical conditions.1,2 Evidence-based guidelines recommend optimal disease management with readily available medical therapies throughout the phases of clinical care. Unfortunately, the care provided to individual patients undergoes multiple modifications throughout the disease course, resulting in divergent pathways, significant deviations from treatment guidelines, and failure of “safeguard” checkpoints to reinstate, initiate, optimize, or stop treatments. Clinical inertia generally describes rigidity or resistance to change around implementing evidence-based guidelines. Furthermore, this term describes treatment behavior on the part of an individual clinician, not organizational inertia, which generally encompasses both internal (immediate clinical practice settings) and external factors (national and international guidelines and recommendations), eventually leading to resistance to optimizing disease treatment and therapeutic regimens. Individual clinicians’ clinical inertia in the form of resistance to guideline implementation and evidence-based principles can be one factor that drives organizational inertia. In turn, such individual behavior can be dictated by personal beliefs, knowledge, interpretation, skills, management principles, and biases. The terms therapeutic inertia or clinical inertia should not be confused with nonadherence from the patient’s standpoint when the clinician follows the best practice guidelines.3
Clinical inertia has been described in several clinical domains, including diabetes,4,5 hypertension,6,7 heart failure,8 depression,9 pulmonary medicine,10 and complex disease management.11 Clinicians can set suboptimal treatment goals due to specific beliefs and attitudes around optimal therapeutic goals. For example, when treating a patient with a chronic disease that is presently stable, a clinician could elect to initiate suboptimal treatment, as escalation of treatment might not be the priority in stable disease; they also may have concerns about overtreatment. Other factors that can contribute to clinical inertia (ie, undertreatment in the presence of indications for treatment) include those related to the patient, the clinical setting, and the organization, along with the importance of individualizing therapies in specific patients. Organizational inertia is the initial global resistance by the system to implementation, which can slow the dissemination and adaptation of best practices but eventually declines over time. Individual clinical inertia, on the other hand, will likely persist after the system-level rollout of guideline-based approaches.
The trajectory of dissemination, implementation, and adaptation of innovations and best practices is illustrated in the Figure. When the guidelines and medical societies endorse the adaptation of innovations or practice change after the benefits of such innovations/change have been established by the regulatory bodies, uptake can be hindered by both organizational and clinical inertia. Overcoming inertia to system-level changes requires addressing individual clinicians, along with practice and organizational factors, in order to ensure systematic adaptations. From the clinicians’ view, training and cognitive interventions to improve the adaptation and coping skills can improve understanding of treatment options through standardized educational and behavioral modification tools, direct and indirect feedback around performance, and decision support through a continuous improvement approach on both individual and system levels.

Addressing inertia in clinical practice requires a deep understanding of the individual and organizational elements that foster resistance to adapting best practice models. Research that explores tools and approaches to overcome inertia in managing complex diseases is a key step in advancing clinical innovation and disseminating best practices.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
1. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, et al. Clinical inertia. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(9):825-834. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
2. Allen JD, Curtiss FR, Fairman KA. Nonadherence, clinical inertia, or therapeutic inertia? J Manag Care Pharm. 2009;15(8):690-695. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2009.15.8.690
3. Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K. Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes. 2010;4(4):203-207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
4. Khunti K, Davies MJ. Clinical inertia—time to reappraise the terminology? Prim Care Diabetes. 2017;11(2):105-106. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2017.01.007
5. O’Connor PJ. Overcome clinical inertia to control systolic blood pressure. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(22):2677-2678. doi:10.1001/archinte.163.22.2677
6. Faria C, Wenzel M, Lee KW, et al. A narrative review of clinical inertia: focus on hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2009;3(4):267-276. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2009.03.001
7. Jarjour M, Henri C, de Denus S, et al. Care gaps in adherence to heart failure guidelines: clinical inertia or physiological limitations? JACC Heart Fail. 2020;8(9):725-738. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2020.04.019
8. Henke RM, Zaslavsky AM, McGuire TG, et al. Clinical inertia in depression treatment. Med Care. 2009;47(9):959-67. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31819a5da0
9. Cooke CE, Sidel M, Belletti DA, Fuhlbrigge AL. Clinical inertia in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2012;9(1):73-80. doi:10.3109/15412555.2011.631957
10. Whitford DL, Al-Anjawi HA, Al-Baharna MM. Impact of clinical inertia on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with diabetes. Prim Care Diabetes. 2014;8(2):133-138. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.10.007
A plane crash interrupts a doctor’s vacation
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a doctor on the plane? Tips for providing in-flight assistance
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.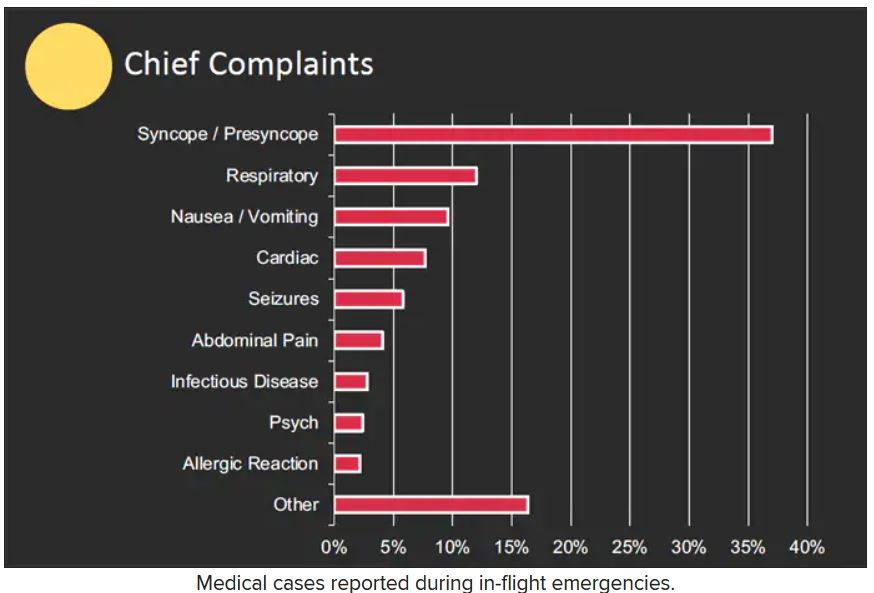
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
Downward trend in Medicare payments for GI services
“When Medicare reimbursements decrease, health outcomes, health care access, and patient satisfaction may be affected, particularly in light of high inflation and increased costs due to staffing shortages, increased staffing salaries, and additional equipment necessary for COVID-19 safety,” researchers wrote in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Samir A. Shah, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues evaluated trends from 2007 to 2022 in Medicare reimbursement for the top 10 common GI procedures.
These procedures, which included colonoscopies, endoscopies, and gastrostomy tube placement, were identified through a joint list published by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA).
From 2007 to 2022, unadjusted and adjusted reimbursement for GI procedures declined by 7% and 33%, respectively, on average.
The adjusted change in physician reimbursement ranged from a decrease of roughly 29% for esophagus endoscopy to 38% for colonoscopy and biopsy, the study team found.
They found that the decline in reimbursement of GI procedures was significantly larger after 2015 (P < .001).
From 2007 to 2014, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement for GI services was 6.7%, and the annual growth rate in reimbursement was –1.0%.
In comparison, from 2015 to 2022, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement was 28.2%, and the mean annual growth rate in reimbursement was –4.7%.
To examine trends in reimbursement for office and inpatient visits from 2007 to 2022, the researchers identified the top five current procedural terminology (CPT) codes from outpatient office and inpatient consult visits provided to Medicare Part B beneficiaries by gastroenterologists.
In contrast to the reimbursement trends for GI procedures, the unadjusted physician reimbursement for inpatient and outpatient visits showed an average increase of 32%.
However, after adjustment for inflation, physician reimbursement for patient visits showed an average decline of 4.9%.
Overall, reimbursement for outpatient visits increased by 4.3%, while reimbursement for inpatient visits decreased by 18.8%.
Dr. Shah and colleagues said their findings are important, given that Medicare patients make up a substantial and growing proportion of patients with GI problems and because fewer than 1% of gastroenterologists have opted out of Medicare.
They noted that the trends in GI reimbursement they observed mirror trends in other specialties, which have also noted a decrease in adjusted reimbursement for care.
Physicians are once again facing cuts of at least 4.5% on Jan. 1, 2023, unless Congress acts. AGA and the entire medical community continue to call on Congress to make statutory changes to the Medicare payment system to address these payment challenges. Specifically, AGA and the physician community have recommended that payment rates include an inflationary adjustment similar to what other providers, such as hospitals, nursing homes, and ambulatory surgery centers, receive to account for practice, equipment, labor, and other costs associated with running a clinical practice.
AGA continues to urge physicians to write federal lawmakers to educate Congress about the detrimental effects of payment cuts, noting that the cuts, when coupled with rising inflation, increased administrative burdens, and staffing shortages, will negatively impact patients’ access to care.
The study had no financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
--From Staff Reports
“When Medicare reimbursements decrease, health outcomes, health care access, and patient satisfaction may be affected, particularly in light of high inflation and increased costs due to staffing shortages, increased staffing salaries, and additional equipment necessary for COVID-19 safety,” researchers wrote in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Samir A. Shah, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues evaluated trends from 2007 to 2022 in Medicare reimbursement for the top 10 common GI procedures.
These procedures, which included colonoscopies, endoscopies, and gastrostomy tube placement, were identified through a joint list published by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA).
From 2007 to 2022, unadjusted and adjusted reimbursement for GI procedures declined by 7% and 33%, respectively, on average.
The adjusted change in physician reimbursement ranged from a decrease of roughly 29% for esophagus endoscopy to 38% for colonoscopy and biopsy, the study team found.
They found that the decline in reimbursement of GI procedures was significantly larger after 2015 (P < .001).
From 2007 to 2014, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement for GI services was 6.7%, and the annual growth rate in reimbursement was –1.0%.
In comparison, from 2015 to 2022, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement was 28.2%, and the mean annual growth rate in reimbursement was –4.7%.
To examine trends in reimbursement for office and inpatient visits from 2007 to 2022, the researchers identified the top five current procedural terminology (CPT) codes from outpatient office and inpatient consult visits provided to Medicare Part B beneficiaries by gastroenterologists.
In contrast to the reimbursement trends for GI procedures, the unadjusted physician reimbursement for inpatient and outpatient visits showed an average increase of 32%.
However, after adjustment for inflation, physician reimbursement for patient visits showed an average decline of 4.9%.
Overall, reimbursement for outpatient visits increased by 4.3%, while reimbursement for inpatient visits decreased by 18.8%.
Dr. Shah and colleagues said their findings are important, given that Medicare patients make up a substantial and growing proportion of patients with GI problems and because fewer than 1% of gastroenterologists have opted out of Medicare.
They noted that the trends in GI reimbursement they observed mirror trends in other specialties, which have also noted a decrease in adjusted reimbursement for care.
Physicians are once again facing cuts of at least 4.5% on Jan. 1, 2023, unless Congress acts. AGA and the entire medical community continue to call on Congress to make statutory changes to the Medicare payment system to address these payment challenges. Specifically, AGA and the physician community have recommended that payment rates include an inflationary adjustment similar to what other providers, such as hospitals, nursing homes, and ambulatory surgery centers, receive to account for practice, equipment, labor, and other costs associated with running a clinical practice.
AGA continues to urge physicians to write federal lawmakers to educate Congress about the detrimental effects of payment cuts, noting that the cuts, when coupled with rising inflation, increased administrative burdens, and staffing shortages, will negatively impact patients’ access to care.
The study had no financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
--From Staff Reports
“When Medicare reimbursements decrease, health outcomes, health care access, and patient satisfaction may be affected, particularly in light of high inflation and increased costs due to staffing shortages, increased staffing salaries, and additional equipment necessary for COVID-19 safety,” researchers wrote in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Samir A. Shah, MD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues evaluated trends from 2007 to 2022 in Medicare reimbursement for the top 10 common GI procedures.
These procedures, which included colonoscopies, endoscopies, and gastrostomy tube placement, were identified through a joint list published by the American College of Gastroenterology, the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA).
From 2007 to 2022, unadjusted and adjusted reimbursement for GI procedures declined by 7% and 33%, respectively, on average.
The adjusted change in physician reimbursement ranged from a decrease of roughly 29% for esophagus endoscopy to 38% for colonoscopy and biopsy, the study team found.
They found that the decline in reimbursement of GI procedures was significantly larger after 2015 (P < .001).
From 2007 to 2014, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement for GI services was 6.7%, and the annual growth rate in reimbursement was –1.0%.
In comparison, from 2015 to 2022, the mean decrease in physician reimbursement was 28.2%, and the mean annual growth rate in reimbursement was –4.7%.
To examine trends in reimbursement for office and inpatient visits from 2007 to 2022, the researchers identified the top five current procedural terminology (CPT) codes from outpatient office and inpatient consult visits provided to Medicare Part B beneficiaries by gastroenterologists.
In contrast to the reimbursement trends for GI procedures, the unadjusted physician reimbursement for inpatient and outpatient visits showed an average increase of 32%.
However, after adjustment for inflation, physician reimbursement for patient visits showed an average decline of 4.9%.
Overall, reimbursement for outpatient visits increased by 4.3%, while reimbursement for inpatient visits decreased by 18.8%.
Dr. Shah and colleagues said their findings are important, given that Medicare patients make up a substantial and growing proportion of patients with GI problems and because fewer than 1% of gastroenterologists have opted out of Medicare.
They noted that the trends in GI reimbursement they observed mirror trends in other specialties, which have also noted a decrease in adjusted reimbursement for care.
Physicians are once again facing cuts of at least 4.5% on Jan. 1, 2023, unless Congress acts. AGA and the entire medical community continue to call on Congress to make statutory changes to the Medicare payment system to address these payment challenges. Specifically, AGA and the physician community have recommended that payment rates include an inflationary adjustment similar to what other providers, such as hospitals, nursing homes, and ambulatory surgery centers, receive to account for practice, equipment, labor, and other costs associated with running a clinical practice.
AGA continues to urge physicians to write federal lawmakers to educate Congress about the detrimental effects of payment cuts, noting that the cuts, when coupled with rising inflation, increased administrative burdens, and staffing shortages, will negatively impact patients’ access to care.
The study had no financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
--From Staff Reports
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Physicians react: Climate change and other social issues
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Med students dismayed that residency match process won’t change
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Switching to Disposable Duodenoscopes: Risks and Rewards
- US Food and Drug Administration. Infections associated with reprocessed duodenoscopes. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/reprocessing-reusable-medical-devices/infections-associated-reprocessed-duodenoscopes
- Heuvelmans M, Wunderink HF, van der Mei HC, Monkelbaan JF. A narrative review on current duodenoscope reprocessing techniques and novel developments. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021;10(1):171. doi:10.1186/s13756-021-01037-z
- US Food and Drug Administration. Use duodenoscopes with innovative designs to enhance safety: FDA safety communication. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/use-duodenoscopes-innovative-designs-enhance-safety-fda-safety-communication
- Pass W. Weighing the pros and cons of disposable duodenoscopes. MDedge News. Published May 19, 2021. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/240339/endoscopy
- Le NNT, Hernandez L, Vakil N, Guda N, Patnode C, Jolliet O. Environmental and health outcomes of single-use versus reusable duodenoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01765-5. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.014
- Ridtitid W, Thummongkol T, Chatsuwan T, et al. Bacterial contamination and organic residue after reprocessing in duodenoscopes with disposable distal caps compared to duodenoscopes with fixed distal caps: a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01766-7. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.015
- Naryzhny I, Silas D, Chi K. Impact of ethylene oxide gas sterilization of duodenoscopes after a carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae outbreak. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):259-262. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.01.055
- Muthusamy VR, Bruno MJ, Kozarek RA, et al. Clinical evaluation of a single-use duodenoscope for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):2108-2117.e3. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052
- Bang JY, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Equivalent performance of single-use and reusable duodenoscopes in a randomised trial. Gut. 2021;70(5):838-844. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321836
- Bhatt A, Thosani N, Patil P. ID: 3527241. Ergonomic study analyzing differences in endoscopy styles between female and male gastroenterologists [abstract]. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(6 Suppl):AB42-AB43. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.03.148
- Trindade AJ, Copland A, Bhatt A, et al. Single-use duodenoscopes and duodenoscopes with disposable end caps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):997-1005. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.12.033
- Namburar S, von Renteln D, Damianos J, et al. Estimating the environmental impact of disposable endoscopic equipment and endoscopes. Gut. 2022;71(7):1326-1331. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324729
- Kröner PT, Bilal M, Samuel R, et al. Use of ERCP in the United States over the past decade. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8(6):E761-E769. doi:10.1055/a-1134-4873
- Patel K, Lad M, Siddiqui E, Ahlawat S. National trends in reimbursement and utilization of advanced endoscopic procedures in the Medicare population [abstract S0904]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S465-S466. doi:10.14309/01.ajg.0000705664.35696.6e
- Bang JY, Sutton B, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Concept of disposable duodenoscope: at what cost? Gut. 2019;68(11):1915-1917. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318227
- US Food and Drug Administration. Infections associated with reprocessed duodenoscopes. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/reprocessing-reusable-medical-devices/infections-associated-reprocessed-duodenoscopes
- Heuvelmans M, Wunderink HF, van der Mei HC, Monkelbaan JF. A narrative review on current duodenoscope reprocessing techniques and novel developments. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021;10(1):171. doi:10.1186/s13756-021-01037-z
- US Food and Drug Administration. Use duodenoscopes with innovative designs to enhance safety: FDA safety communication. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/use-duodenoscopes-innovative-designs-enhance-safety-fda-safety-communication
- Pass W. Weighing the pros and cons of disposable duodenoscopes. MDedge News. Published May 19, 2021. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/240339/endoscopy
- Le NNT, Hernandez L, Vakil N, Guda N, Patnode C, Jolliet O. Environmental and health outcomes of single-use versus reusable duodenoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01765-5. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.014
- Ridtitid W, Thummongkol T, Chatsuwan T, et al. Bacterial contamination and organic residue after reprocessing in duodenoscopes with disposable distal caps compared to duodenoscopes with fixed distal caps: a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01766-7. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.015
- Naryzhny I, Silas D, Chi K. Impact of ethylene oxide gas sterilization of duodenoscopes after a carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae outbreak. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):259-262. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.01.055
- Muthusamy VR, Bruno MJ, Kozarek RA, et al. Clinical evaluation of a single-use duodenoscope for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):2108-2117.e3. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052
- Bang JY, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Equivalent performance of single-use and reusable duodenoscopes in a randomised trial. Gut. 2021;70(5):838-844. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321836
- Bhatt A, Thosani N, Patil P. ID: 3527241. Ergonomic study analyzing differences in endoscopy styles between female and male gastroenterologists [abstract]. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(6 Suppl):AB42-AB43. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.03.148
- Trindade AJ, Copland A, Bhatt A, et al. Single-use duodenoscopes and duodenoscopes with disposable end caps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):997-1005. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.12.033
- Namburar S, von Renteln D, Damianos J, et al. Estimating the environmental impact of disposable endoscopic equipment and endoscopes. Gut. 2022;71(7):1326-1331. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324729
- Kröner PT, Bilal M, Samuel R, et al. Use of ERCP in the United States over the past decade. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8(6):E761-E769. doi:10.1055/a-1134-4873
- Patel K, Lad M, Siddiqui E, Ahlawat S. National trends in reimbursement and utilization of advanced endoscopic procedures in the Medicare population [abstract S0904]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S465-S466. doi:10.14309/01.ajg.0000705664.35696.6e
- Bang JY, Sutton B, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Concept of disposable duodenoscope: at what cost? Gut. 2019;68(11):1915-1917. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318227
- US Food and Drug Administration. Infections associated with reprocessed duodenoscopes. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/reprocessing-reusable-medical-devices/infections-associated-reprocessed-duodenoscopes
- Heuvelmans M, Wunderink HF, van der Mei HC, Monkelbaan JF. A narrative review on current duodenoscope reprocessing techniques and novel developments. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021;10(1):171. doi:10.1186/s13756-021-01037-z
- US Food and Drug Administration. Use duodenoscopes with innovative designs to enhance safety: FDA safety communication. Updated June 30, 2022. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/use-duodenoscopes-innovative-designs-enhance-safety-fda-safety-communication
- Pass W. Weighing the pros and cons of disposable duodenoscopes. MDedge News. Published May 19, 2021. Accessed July 28, 2022. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/240339/endoscopy
- Le NNT, Hernandez L, Vakil N, Guda N, Patnode C, Jolliet O. Environmental and health outcomes of single-use versus reusable duodenoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01765-5. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.014
- Ridtitid W, Thummongkol T, Chatsuwan T, et al. Bacterial contamination and organic residue after reprocessing in duodenoscopes with disposable distal caps compared to duodenoscopes with fixed distal caps: a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;S0016-5107(22)01766-7. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.06.015
- Naryzhny I, Silas D, Chi K. Impact of ethylene oxide gas sterilization of duodenoscopes after a carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae outbreak. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):259-262. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.01.055
- Muthusamy VR, Bruno MJ, Kozarek RA, et al. Clinical evaluation of a single-use duodenoscope for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(9):2108-2117.e3. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.052
- Bang JY, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Equivalent performance of single-use and reusable duodenoscopes in a randomised trial. Gut. 2021;70(5):838-844. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321836
- Bhatt A, Thosani N, Patil P. ID: 3527241. Ergonomic study analyzing differences in endoscopy styles between female and male gastroenterologists [abstract]. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(6 Suppl):AB42-AB43. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.03.148
- Trindade AJ, Copland A, Bhatt A, et al. Single-use duodenoscopes and duodenoscopes with disposable end caps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):997-1005. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.12.033
- Namburar S, von Renteln D, Damianos J, et al. Estimating the environmental impact of disposable endoscopic equipment and endoscopes. Gut. 2022;71(7):1326-1331. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324729
- Kröner PT, Bilal M, Samuel R, et al. Use of ERCP in the United States over the past decade. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8(6):E761-E769. doi:10.1055/a-1134-4873
- Patel K, Lad M, Siddiqui E, Ahlawat S. National trends in reimbursement and utilization of advanced endoscopic procedures in the Medicare population [abstract S0904]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S465-S466. doi:10.14309/01.ajg.0000705664.35696.6e
- Bang JY, Sutton B, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Concept of disposable duodenoscope: at what cost? Gut. 2019;68(11):1915-1917. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318227
Diversity in the Gastroenterology Workforce and its Implications for Patients
- Welch M. Required curricula in diversity and cross-cultural medicine: the time is now. J Am Med Womens Assoc (1972). 1998;53(3 Suppl):121-3, 130. PMID:17598289.
- Carethers JM. Toward realizing diversity in academic medicine. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(11):5626-5628. doi:10.1172/JCI144527
- Guevara JP, Adanga E, Avakame E, Carthon MB. Minority faculty development programs and underrepresented minority faculty representation at US medical schools. JAMA. 2013;310(21):2297-2304. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282116
- Guevara JP, Wade R, Aysola J. Racial and ethnic diversity at medical schools – why aren’t we there yet? N Engl J Med. 2021;385(19):1732-1734. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2105578
- Dill J, Akosionu O, Karbeah JM, Henning-Smith C. Addressing systemic racial inequity in the health care workforce. Health Affairs. September 10, 2020. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/forefront.20200908.133196/full/
- Carr RM, Quezada SM, Gangarosa LM, et al; Governing Board of the American Gastroenterological Association. From intention to action: operationalizing AGA diversity policy to combat racism and health disparities in gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(5):1637-1647. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.044
- American Gastroenterological Association. AGA equity project. Accessed July 11, 2022. https://gastro.org/aga-leadership/initiatives-and-programs/aga-equity-project/
- Barnes EL, Loftus EV Jr, Kappelman MD. Effects of race and ethnicity on diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(3):677-689. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.064
- White PM, Iroku U, Carr RM, May FP; Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists Board of Directors. Advancing health equity: The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(7):449-450. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00464-y
- Ogunyemi D, Okekpe CC, Barrientos DR, Bui T, Au MN, Lamba S. United States medical school academic faculty workforce diversity, institutional characteristics, and geographical distributions from 2014-2018. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e22292. doi:10.7759/cureus.22292
- Weiss J, Balasuriya L, Cramer LD, et al. Medical students’ demographic characteristics and their perceptions of faculty role modeling of respect for diversity. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(6):e2112795. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12795
- Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Medical school enrollment more diverse in 2021. December 8, 2021. Accessed June 29, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/press-releases/medical-school-enrollment-more-diverse-2021
- Silvernale C, Kuo B, Staller K. Racial disparity in healthcare utilization among patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a multicenter cohort. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;33(5):e14039. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14039
- Robinett K, Kareem R, Reavis K, Quezada S. A multi-pronged, antiracist approach to optimize equity in medical school admissions. Med Educ. 2021;55(12):1376-1382. doi:10.1111/medu.14589
- Welch M. Required curricula in diversity and cross-cultural medicine: the time is now. J Am Med Womens Assoc (1972). 1998;53(3 Suppl):121-3, 130. PMID:17598289.
- Carethers JM. Toward realizing diversity in academic medicine. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(11):5626-5628. doi:10.1172/JCI144527
- Guevara JP, Adanga E, Avakame E, Carthon MB. Minority faculty development programs and underrepresented minority faculty representation at US medical schools. JAMA. 2013;310(21):2297-2304. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282116
- Guevara JP, Wade R, Aysola J. Racial and ethnic diversity at medical schools – why aren’t we there yet? N Engl J Med. 2021;385(19):1732-1734. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2105578
- Dill J, Akosionu O, Karbeah JM, Henning-Smith C. Addressing systemic racial inequity in the health care workforce. Health Affairs. September 10, 2020. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/forefront.20200908.133196/full/
- Carr RM, Quezada SM, Gangarosa LM, et al; Governing Board of the American Gastroenterological Association. From intention to action: operationalizing AGA diversity policy to combat racism and health disparities in gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(5):1637-1647. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.044
- American Gastroenterological Association. AGA equity project. Accessed July 11, 2022. https://gastro.org/aga-leadership/initiatives-and-programs/aga-equity-project/
- Barnes EL, Loftus EV Jr, Kappelman MD. Effects of race and ethnicity on diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(3):677-689. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.064
- White PM, Iroku U, Carr RM, May FP; Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists Board of Directors. Advancing health equity: The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(7):449-450. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00464-y
- Ogunyemi D, Okekpe CC, Barrientos DR, Bui T, Au MN, Lamba S. United States medical school academic faculty workforce diversity, institutional characteristics, and geographical distributions from 2014-2018. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e22292. doi:10.7759/cureus.22292
- Weiss J, Balasuriya L, Cramer LD, et al. Medical students’ demographic characteristics and their perceptions of faculty role modeling of respect for diversity. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(6):e2112795. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12795
- Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Medical school enrollment more diverse in 2021. December 8, 2021. Accessed June 29, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/press-releases/medical-school-enrollment-more-diverse-2021
- Silvernale C, Kuo B, Staller K. Racial disparity in healthcare utilization among patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a multicenter cohort. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;33(5):e14039. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14039
- Robinett K, Kareem R, Reavis K, Quezada S. A multi-pronged, antiracist approach to optimize equity in medical school admissions. Med Educ. 2021;55(12):1376-1382. doi:10.1111/medu.14589
- Welch M. Required curricula in diversity and cross-cultural medicine: the time is now. J Am Med Womens Assoc (1972). 1998;53(3 Suppl):121-3, 130. PMID:17598289.
- Carethers JM. Toward realizing diversity in academic medicine. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(11):5626-5628. doi:10.1172/JCI144527
- Guevara JP, Adanga E, Avakame E, Carthon MB. Minority faculty development programs and underrepresented minority faculty representation at US medical schools. JAMA. 2013;310(21):2297-2304. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282116
- Guevara JP, Wade R, Aysola J. Racial and ethnic diversity at medical schools – why aren’t we there yet? N Engl J Med. 2021;385(19):1732-1734. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2105578
- Dill J, Akosionu O, Karbeah JM, Henning-Smith C. Addressing systemic racial inequity in the health care workforce. Health Affairs. September 10, 2020. Accessed July 12, 2022. https://www.healthaffairs.org/do/10.1377/forefront.20200908.133196/full/
- Carr RM, Quezada SM, Gangarosa LM, et al; Governing Board of the American Gastroenterological Association. From intention to action: operationalizing AGA diversity policy to combat racism and health disparities in gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(5):1637-1647. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.044
- American Gastroenterological Association. AGA equity project. Accessed July 11, 2022. https://gastro.org/aga-leadership/initiatives-and-programs/aga-equity-project/
- Barnes EL, Loftus EV Jr, Kappelman MD. Effects of race and ethnicity on diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(3):677-689. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.064
- White PM, Iroku U, Carr RM, May FP; Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists Board of Directors. Advancing health equity: The Association of Black Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(7):449-450. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00464-y
- Ogunyemi D, Okekpe CC, Barrientos DR, Bui T, Au MN, Lamba S. United States medical school academic faculty workforce diversity, institutional characteristics, and geographical distributions from 2014-2018. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e22292. doi:10.7759/cureus.22292
- Weiss J, Balasuriya L, Cramer LD, et al. Medical students’ demographic characteristics and their perceptions of faculty role modeling of respect for diversity. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(6):e2112795. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.12795
- Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). Medical school enrollment more diverse in 2021. December 8, 2021. Accessed June 29, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/news-insights/press-releases/medical-school-enrollment-more-diverse-2021
- Silvernale C, Kuo B, Staller K. Racial disparity in healthcare utilization among patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a multicenter cohort. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;33(5):e14039. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14039
- Robinett K, Kareem R, Reavis K, Quezada S. A multi-pronged, antiracist approach to optimize equity in medical school admissions. Med Educ. 2021;55(12):1376-1382. doi:10.1111/medu.14589
New Medicare physician fee schedule leaves docs fuming over pay cuts
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The rule also seeks to ease financial and administrative burdens on accountable care organizations (ACOs).
But physician groups’ initial reactions centered on what the American Medical Association describes as a “damaging across-the-board reduction” of 4.4% in a base calculation, known as a conversion factor.
The reduction is only one of the current threats to physician’s finances, Jack Resneck Jr, MD, AMA’s president, said in a statement. Medicare payment rates also fail to account for inflation in practice costs and COVID-related challenges. Physician’s Medicare payments could be cut by nearly 8.5% in 2023, factoring in other budget cuts, Dr. Resneck said in the statement.
That “would severely impede patient access to care due to the forced closure of physician practices and put further strain on those that remained open during the pandemic,” he said.
A key driver of these cuts is a law that was intended to resolve budget battles between Congress and physicians, while also transitioning Medicare away from fee-for-service payments and pegging reimbursement to judgments about value of care provided. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services thus had little choice about cuts mandated by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) of 2015.
For AMA and other physician groups, the finalization of the Medicare rule served as a rallying point to build support for pending legislation intended to stave off at least some payment cuts.
Federal officials should act soon to block the expected cuts before this season of Congress ends in January, said Anders Gilberg, senior vice president for government affairs at the Medical Group Management Association, in a statement.
“This cannot wait until next Congress – there are claims-processing implications for retroactively applying these policies,” Mr. Gilberg said.
He said MGMA would work with Congress and CMS “to mitigate these cuts and develop sustainable payment policies to allow physician practices to focus on treating patients instead of scrambling to keep their doors open.”
Chronic budget battles
Once seen as a promising resolution to chronic annual budget battles between physicians and Medicare, MACRA has proven a near-universal disappointment. A federal advisory commission in 2018 recommended that Congress scrap MACRA’s Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and replace it with a new approach for attempting to tie reimbursement to judgments about the quality of medical care.
MACRA replaced an earlier budgeting approach on Medicare physician pay, known as the sustainable growth rate (SGR). Physician groups successfully lobbied Congress for many years to block threatened Medicare payment cuts. Between 2003 and April 2014, Congress passed 17 laws overriding the cuts to physician pay that the lawmakers earlier mandated through the SGR.
A similar pattern has emerged as Congress now acts on short-term fixes to stave off MACRA-mandated cuts. A law passed last December postponed cuts in physician pay from MACRA and federal budget laws.
And more than 70 members of the House support a bill (HR 8800) intended to block a slated 4.4% MACRA-related cut in physician pay for 2023. Two physicians, Rep. Ami Bera, MD, (D-CA) and Rep. Larry Bucshon (R-IN) sponsored the bill.
Among the groups backing the bill are the AMA, American Academy of Family Physicians, and American College of Physicians. The lawmakers may try to attach this bill to a large spending measure, known as an omnibus, that Congress will try to clear in December to avoid a partial government shutdown.
In a statement, Tochi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, the president of AAFP, urged Congress to factor in inflation in setting physician reimbursement and to reconsider Medicare’s approach to paying physicians.
“It’s past time to end the untenable physician payment cuts – which have now become an annual threat to the stability of physician practices – caused by Medicare budget neutrality requirements and the ongoing freeze in annual payment updates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
Congress also needs to retool its approach to alternative payment models (APMs) intended to improve the quality of patient care, Dr. Iroku-Malize said.
“Physicians in APMs are better equipped to address unmet social needs and provide other enhanced services that are not supported by fee-for-service payment rates,” Dr. Iroku-Malize said. “However, insufficient Medicare fee-for-service payment rates, inadequate support, and burdensome timelines are undermining the move to value-based care and exacerbating our nation’s underinvestment in primary care.”
Policy changes
But the new rule did have some good news for family physicians, Dr. Iroku-Malize told this news organization in an email.
CMS said it will pay psychologists and social workers to help manage behavioral health needs as part of the primary care team, in addition to their own services. This change will give primary care practices more flexibility to coordinate with behavioral health professionals, Dr. Iroku-Malize noted.
“We know that primary care physicians are the first point of contact for many patients, and behavioral health integration increases critical access to mental health care, decreases stigma for patients, and can prevent more severe medical and behavioral health events,” she wrote.
CMS also eased a supervision requirement for nonphysicians providing behavioral health services.
It intends to allow certain health professionals to provide this care without requiring that a supervising physician or nurse practitioner be physically on site. This shift from direct supervision to what’s called general supervision applies to marriage and family therapists, licensed professional counselors, addiction counselors, certified peer recovery specialists, and behavioral health specialists, CMS said.
Other major policy changes include:
Medicare will pay for telehealth opioid treatment programs allowing patients to initiate treatment with buprenorphine. CMS also clarified that certain programs can bill for opioid use disorder treatment services provided through mobile units, such as vans.
Medicare enrollees may see audiologists for nonacute hearing conditions without an order from a physician or nurse practitioner. The policy is meant to allow audiologists to examine patients to prescribe, fit, or change hearing aids, or to provide hearing tests unrelated to disequilibrium.
CMS created new reimbursement codes for chronic pain management and treatment services to encourage clinicians to see patients with this condition. The codes also are meant to encourage practitioners already treating Medicare patients with chronic pain to spend more time helping them manage their condition “within a trusting, supportive, and ongoing care partnership,” CMS said.
CMS also made changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP) intended to reduce administrative burdens and offer more financial support to practices involved in ACOs. These steps include expanding opportunities for certain low-revenue ACOs to share in savings even if they do not meet a target rate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Working while sick: Why doctors don’t stay home when ill
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The reasons are likely as varied as, “you weren’t feeling bad enough to miss work,” “you couldn’t afford to miss pay,” “you had too many patients to see,” or “too much work to do.”
In Medscape’s Employed Physicians Report: Loving the Focus, Hating the Bureaucracy, 61% of physicians reported that they sometimes or often come to work sick. Only 2% of respondents said they never come to work unwell.
Medscape wanted to know more about how often you call in sick, how often you come to work feeling unwell, what symptoms you have, and the dogma of your workplace culture regarding sick days. Not to mention the brutal ethos that starts in medical school, in which calling in sick shows weakness or is unacceptable.
So, we polled 2,347 physicians in the United States and abroad and asked them about their sniffling, sneezing, cold, flu, and fever symptoms, and, of course, COVID. Results were split about 50-50 among male and female physicians. The poll ran from Sept. 28 through Oct. 11.
Coming to work sick
It’s no surprise that the majority of physicians who were polled (85%) have come to work sick in 2022. In the last prepandemic year (2019), about 70% came to work feeling sick one to five times, and 13% worked while sick six to ten times.
When asked about the symptoms that they’ve previously come to work with, 48% of U.S. physicians said multiple symptoms. They gave high marks for runny nose, cough, congestion, and sore throat. Only 27% have worked with a fever, 22% have worked with other symptoms, and 7% have worked with both strep throat and COVID.
“My workplace, especially in the COVID years, accommodates persons who honestly do not feel well enough to report. Sooner or later, everyone covers for someone else who has to be out,” says Kenneth Abbott, MD, an oncologist in Maryland.
The culture of working while sick
Why doctors come to work when they’re sick is complicated. The overwhelming majority of U.S. respondents cited professional obligations; 73% noted that they feel a professional obligation to their patients, and 72% feel a professional obligation to their co-workers. Half of the polled U.S. physicians said they didn’t feel bad enough to stay home, while 48% said they had too much work to do to stay home.
Some 45% said the expectation at their workplace is to come to work unless seriously ill; 43% had too many patients to see; and 18% didn’t think they were contagious when they headed to work sick. Unfortunately, 15% chose to work while sick because otherwise they would lose pay.
In light of these responses, it’s not surprising that 93% reported they’d seen other medical professionals working when sick.
“My schedule is almost always booked weeks in advance. If someone misses or has to cancel their appointment, they typically have 2-4 weeks to wait to get back in. If I was sick and a full day of patients (or God forbid more than a day) had to be canceled because I called in, it’s so much more work when I return,” says Caitlin Briggs, MD, a psychiatrist in Lexington, Ky.
Doctors’ workplace sick day policy
Most employees’ benefits allow at least a few sick days, but doctors who treat society’s ill patients don’t seem to stay home from work when they’re suffering. So, we asked physicians, official policy aside, whether they thought going to work sick was expected in their workplace. The majority (76%) said yes, while 24% said no.
“Unless I’m dying or extremely contagious, I usually work. At least now, I have the telehealth option. Not saying any of this is right, but it’s the reality we deal with and the choice we must make,” says Dr. Briggs.
Additionally, 58% of polled physicians said their workplace did not have a clearly defined policy against coming to work sick, while 20% said theirs did, and 22% weren’t sure.
“The first thing I heard on the subject as a medical student was that sick people come to the hospital, so if you’re sick, then you come to the hospital too ... to work. If you can’t work, then you will be admitted. Another aphorism was from Churchill, that ‘most of the world’s work is done by people who don’t feel very well,’ ” says Paul Andreason, MD, a psychiatrist in Bethesda, Md.
Working in the time of COVID
Working while ill during ordinary times is one thing, but what about working in the time of COVID? Has the pandemic changed the culture of coming to work sick because medical facilities, such as doctor’s offices and hospitals, don’t want their staff coming in when they have COVID?
Surprisingly, when we asked physicians whether the pandemic has made it more or less acceptable to come to work sick, only 61% thought COVID has made it less acceptable to work while sick, while 16% thought it made it more acceptable, and 23% said there’s no change.
“I draw the line at fevers/chills, feeling like you’ve just been run over, or significant enteritis,” says Dr. Abbott. “Also, if I have to take palliative meds that interfere with alertness, I’m not doing my patients any favors.”
While a minority of physicians may call in sick, most still suffer through their sneezing, coughing, chills, and fever while seeing patients as usual.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.