User login
Unleashing Our Immune Response to Quash Cancer
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was originally published on February 10 in Eric Topol’s substack “Ground Truths.”
It’s astounding how devious cancer cells and tumor tissue can be. This week in Science we learned how certain lung cancer cells can function like “Catch Me If You Can” — changing their driver mutation and cell identity to escape targeted therapy. This histologic transformation, as seen in an experimental model, is just one of so many cancer tricks that we are learning about.
Recently, as shown by single-cell sequencing, cancer cells can steal the mitochondria from T cells, a double whammy that turbocharges cancer cells with the hijacked fuel supply and, at the same time, dismantles the immune response.
Last week, we saw how tumor cells can release a virus-like protein that unleashes a vicious autoimmune response.
And then there’s the finding that cancer cell spread predominantly is occurring while we sleep.
As I previously reviewed, the ability for cancer cells to hijack neurons and neural circuits is now well established, no less their ability to reprogram neurons to become adrenergic and stimulate tumor progression, and interfere with the immune response. Stay tuned on that for a new Ground Truths podcast with Prof Michelle Monje, a leader in cancer neuroscience, which will post soon.
Add advancing age’s immunosenescence as yet another challenge to the long and growing list of formidable ways that cancer cells, and the tumor microenvironment, evade our immune response.
An Ever-Expanding Armamentarium
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
The field of immunotherapies took off with the immune checkpoint inhibitors, first approved by the FDA in 2011, that take the brakes off of T cells, with the programmed death-1 (PD-1), PD-ligand1, and anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies.
But we’re clearly learning they are not enough to prevail over cancer with common recurrences, only short term success in most patients, with some notable exceptions. Adding other immune response strategies, such as a vaccine, or antibody-drug conjugates, or engineered T cells, are showing improved chances for success.
Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines
There are many therapeutic cancer vaccines in the works, as reviewed in depth here.
Here’s a list of ongoing clinical trials of cancer vaccines. You’ll note most of these are on top of a checkpoint inhibitor and use personalized neoantigens (cancer cell surface proteins) derived from sequencing (whole-exome or whole genome, RNA-sequencing and HLA-profiling) the patient’s tumor.
An example of positive findings is with the combination of an mRNA-nanoparticle vaccine with up to 34 personalized neoantigens and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) vs pembrolizumab alone in advanced melanoma after resection, with improved outcomes at 3-year follow-up, cutting death or relapse rate in half.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADC)
There is considerable excitement about antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) whereby a linker is used to attach a chemotherapy agent to the checkpoint inhibitor antibody, specifically targeting the cancer cell and facilitating entry of the chemotherapy into the cell. Akin to these are bispecific antibodies (BiTEs, binding to a tumor antigen and T cell receptor simultaneously), both of these conjugates acting as “biologic” or “guided” missiles.
A very good example of the potency of an ADC was seen in a “HER2-low” breast cancer randomized trial. The absence or very low expression or amplification of the HER2 receptor is common in breast cancer and successful treatment has been elusive. A randomized trial of an ADC (trastuzumab deruxtecan) compared to physician’s choice therapy demonstrated a marked success for progression-free survival in HER2-low patients, which was characterized as “unheard-of success” by media coverage.
This strategy is being used to target some of the most difficult cancer driver mutations such as TP53 and KRAS.
Oncolytic Viruses
Modifying viruses to infect the tumor and make it more visible to the immune system, potentiating anti-tumor responses, known as oncolytic viruses, have been proposed as a way to rev up the immune response for a long time but without positive Phase 3 clinical trials.
After decades of failure, a recent trial in refractory bladder cancer showed marked success, along with others, summarized here, now providing very encouraging results. It looks like oncolytic viruses are on a comeback path.
Engineering T Cells (Chimeric Antigen Receptor [CAR-T])
As I recently reviewed, there are over 500 ongoing clinical trials to build on the success of the first CAR-T approval for leukemia 7 years ago. I won’t go through that all again here, but to reiterate most of the success to date has been in “liquid” blood (leukemia and lymphoma) cancer tumors. This week in Nature is the discovery of a T cell cancer mutation, a gene fusion CARD11-PIK3R3, from a T cell lymphoma that can potentially be used to augment CAR-T efficacy. It has pronounced and prolonged effects in the experimental model. Instead of 1 million cells needed for treatment, even 20,000 were enough to melt the tumor. This is a noteworthy discovery since CAR-T work to date has largely not exploited such naturally occurring mutations, while instead concentrating on those seen in the patient’s set of key tumor mutations.
As currently conceived, CAR-T, and what is being referred to more broadly as adoptive cell therapies, involves removing T cells from the patient’s body and engineering their activation, then reintroducing them back to the patient. This is laborious, technically difficult, and very expensive. Recently, the idea of achieving all of this via an injection of virus that specifically infects T cells and inserts the genes needed, was advanced by two biotech companies with preclinical results, one in non-human primates.
Gearing up to meet the challenge of solid tumor CAR-T intervention, there’s more work using CRISPR genome editing of T cell receptors. A.I. is increasingly being exploited to process the data from sequencing and identify optimal neoantigens.
Instead of just CAR-T, we’re seeing the emergence of CAR-macrophage and CAR-natural killer (NK) cells strategies, and rapidly expanding potential combinations of all the strategies I’ve mentioned. No less, there’s been maturation of on-off suicide switches programmed in, to limit cytokine release and promote safety of these interventions. Overall, major side effects of immunotherapies are not only cytokine release syndromes, but also include interstitial pneumonitis and neurotoxicity.
Summary
Given the multitude of ways cancer cells and tumor tissue can evade our immune response, durably successful treatment remains a daunting challenge. But the ingenuity of so many different approaches to unleash our immune response, and their combinations, provides considerable hope that we’ll increasingly meet the challenge in the years ahead. We have clearly learned that combining different immunotherapy strategies will be essential for many patients with the most resilient solid tumors.
Of concern, as noted by a recent editorial in The Lancet, entitled “Cancer Research Equity: Innovations For The Many, Not The Few,” is that these individualized, sophisticated strategies are not scalable; they will have limited reach and benefit. The movement towards “off the shelf” CAR-T and inexpensive, orally active checkpoint inhibitors may help mitigate this issue.
Notwithstanding this important concern, we’re seeing an array of diverse and potent immunotherapy strategies that are providing highly encouraging results, engendering more excitement than we’ve seen in this space for some time. These should propel substantial improvements in outcomes for patients in the years ahead. It can’t happen soon enough.
Thanks for reading this edition of Ground Truths. If you found it informative, please share it with your colleagues.
Dr. Topol has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Dexcom; Illumina; Molecular Stethoscope; Quest Diagnostics; Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Received research grant from National Institutes of Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Most Sudden Infant Deaths Occur in Shared Sleep Space
, according to new data published online in Pediatrics.
SUID occur in infants less than 1 year old. The deaths happen without an obvious cause before investigation and account for 3,400 deaths per year in the United States.
Alexa B. Erck Lambert, MPH, Maternal and Infant Health Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), led the study that examined 7,595 such deaths in 23 US jurisdictions from 2011 to 2020, using data from the CDC’s SUID Case Registry.
The researchers reported that the prevalence of surface sharing ranges from 34% to 64% among living infants and about 50% among SUID.
Common Factors
They found common factors when infants share sleep space compared with infants who did not. Those who shared space, for example, were often 0-3 months old; publicly insured; non-Hispanic Black; found in an adult bed, couch, or chair; exposed to maternal cigarette smoking prenatally; and supervised by a parent when they died or had a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol at the time of death.
Having a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol was much more common among sharing (16.3%) than nonsharing infants (4.7%).
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidance says a safe sleep environment for infants includes a place to sleep on a nonshared sleep surface (in a crib or bassinet) without soft bedding, and lying on the back facing up.
Most Who Died had Multiple Unsafe Sleep Factors
At least 76% of all SUID had multiple unsafe sleep factors present, regardless of whether the infants shared sleep space. Unsafe sleep factors include an inclined or soft sleep surface, sleeping on the side or stomach, sleeping with soft or loose bedding or objects, not breastfeeding, prenatal or environmental exposure to cigarette smoke, and overheating.
Sharing sleep space combined with parents’ smoking and maternal alcohol or drug use greatly increases risk of sudden infant death, the authors noted.
Sharing More Common With Multiples
Among SUID, surface sharing was more common among multiples than singletons and more common in an adult bed than in the same crib. The authors noted that parents often cite financial reasons for such arrangements.
However, AAP recommends multiples sleep on separate surfaces. The authors say pediatricians and other healthcare providers should be aware of free crib distribution programs. A study by Hauck et al. found “crib distribution and safe sleep education positively influence knowledge and practices about safe sleep.”
Robin Haynes, PhD, who studies causes underlying the pathology of SIDS at Boston Children’s Hospital, pointed to the Cribs for Kids website as a place for parents and clinicians to start for help with providing separate sleeping surfaces.
Dr. Haynes said the large number of infants included is a strength of the study. The findings help confirm the risk of sharing a sleep surface, she said, but the details on characteristics of sleep-sharing environments provide “novel insight into this problem,” she said.
“For basic researchers,” Dr. Haynes said, “it reiterates that most cases of sudden and unexpected infant deaths are exposed to multiple risk factors. It also highlights the role that young infant age and maternal smoking have as risk factors that contribute to biological vulnerabilities in infants.”
The results also give clinicians more information on characteristics of bedsharing families and some of the factors related to bedsharing, including socioeconomic and behavioral factors, she said. She highlighted the higher risk of SUID when drug or alcohol impairment is involved while bedsharing.
“All of this information is really important and helps clinicians shape the safe sleep messages to families,” she said.
The study authors and Dr. Haynes report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to new data published online in Pediatrics.
SUID occur in infants less than 1 year old. The deaths happen without an obvious cause before investigation and account for 3,400 deaths per year in the United States.
Alexa B. Erck Lambert, MPH, Maternal and Infant Health Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), led the study that examined 7,595 such deaths in 23 US jurisdictions from 2011 to 2020, using data from the CDC’s SUID Case Registry.
The researchers reported that the prevalence of surface sharing ranges from 34% to 64% among living infants and about 50% among SUID.
Common Factors
They found common factors when infants share sleep space compared with infants who did not. Those who shared space, for example, were often 0-3 months old; publicly insured; non-Hispanic Black; found in an adult bed, couch, or chair; exposed to maternal cigarette smoking prenatally; and supervised by a parent when they died or had a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol at the time of death.
Having a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol was much more common among sharing (16.3%) than nonsharing infants (4.7%).
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidance says a safe sleep environment for infants includes a place to sleep on a nonshared sleep surface (in a crib or bassinet) without soft bedding, and lying on the back facing up.
Most Who Died had Multiple Unsafe Sleep Factors
At least 76% of all SUID had multiple unsafe sleep factors present, regardless of whether the infants shared sleep space. Unsafe sleep factors include an inclined or soft sleep surface, sleeping on the side or stomach, sleeping with soft or loose bedding or objects, not breastfeeding, prenatal or environmental exposure to cigarette smoke, and overheating.
Sharing sleep space combined with parents’ smoking and maternal alcohol or drug use greatly increases risk of sudden infant death, the authors noted.
Sharing More Common With Multiples
Among SUID, surface sharing was more common among multiples than singletons and more common in an adult bed than in the same crib. The authors noted that parents often cite financial reasons for such arrangements.
However, AAP recommends multiples sleep on separate surfaces. The authors say pediatricians and other healthcare providers should be aware of free crib distribution programs. A study by Hauck et al. found “crib distribution and safe sleep education positively influence knowledge and practices about safe sleep.”
Robin Haynes, PhD, who studies causes underlying the pathology of SIDS at Boston Children’s Hospital, pointed to the Cribs for Kids website as a place for parents and clinicians to start for help with providing separate sleeping surfaces.
Dr. Haynes said the large number of infants included is a strength of the study. The findings help confirm the risk of sharing a sleep surface, she said, but the details on characteristics of sleep-sharing environments provide “novel insight into this problem,” she said.
“For basic researchers,” Dr. Haynes said, “it reiterates that most cases of sudden and unexpected infant deaths are exposed to multiple risk factors. It also highlights the role that young infant age and maternal smoking have as risk factors that contribute to biological vulnerabilities in infants.”
The results also give clinicians more information on characteristics of bedsharing families and some of the factors related to bedsharing, including socioeconomic and behavioral factors, she said. She highlighted the higher risk of SUID when drug or alcohol impairment is involved while bedsharing.
“All of this information is really important and helps clinicians shape the safe sleep messages to families,” she said.
The study authors and Dr. Haynes report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to new data published online in Pediatrics.
SUID occur in infants less than 1 year old. The deaths happen without an obvious cause before investigation and account for 3,400 deaths per year in the United States.
Alexa B. Erck Lambert, MPH, Maternal and Infant Health Branch of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), led the study that examined 7,595 such deaths in 23 US jurisdictions from 2011 to 2020, using data from the CDC’s SUID Case Registry.
The researchers reported that the prevalence of surface sharing ranges from 34% to 64% among living infants and about 50% among SUID.
Common Factors
They found common factors when infants share sleep space compared with infants who did not. Those who shared space, for example, were often 0-3 months old; publicly insured; non-Hispanic Black; found in an adult bed, couch, or chair; exposed to maternal cigarette smoking prenatally; and supervised by a parent when they died or had a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol at the time of death.
Having a supervisor who was impaired by drugs or alcohol was much more common among sharing (16.3%) than nonsharing infants (4.7%).
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidance says a safe sleep environment for infants includes a place to sleep on a nonshared sleep surface (in a crib or bassinet) without soft bedding, and lying on the back facing up.
Most Who Died had Multiple Unsafe Sleep Factors
At least 76% of all SUID had multiple unsafe sleep factors present, regardless of whether the infants shared sleep space. Unsafe sleep factors include an inclined or soft sleep surface, sleeping on the side or stomach, sleeping with soft or loose bedding or objects, not breastfeeding, prenatal or environmental exposure to cigarette smoke, and overheating.
Sharing sleep space combined with parents’ smoking and maternal alcohol or drug use greatly increases risk of sudden infant death, the authors noted.
Sharing More Common With Multiples
Among SUID, surface sharing was more common among multiples than singletons and more common in an adult bed than in the same crib. The authors noted that parents often cite financial reasons for such arrangements.
However, AAP recommends multiples sleep on separate surfaces. The authors say pediatricians and other healthcare providers should be aware of free crib distribution programs. A study by Hauck et al. found “crib distribution and safe sleep education positively influence knowledge and practices about safe sleep.”
Robin Haynes, PhD, who studies causes underlying the pathology of SIDS at Boston Children’s Hospital, pointed to the Cribs for Kids website as a place for parents and clinicians to start for help with providing separate sleeping surfaces.
Dr. Haynes said the large number of infants included is a strength of the study. The findings help confirm the risk of sharing a sleep surface, she said, but the details on characteristics of sleep-sharing environments provide “novel insight into this problem,” she said.
“For basic researchers,” Dr. Haynes said, “it reiterates that most cases of sudden and unexpected infant deaths are exposed to multiple risk factors. It also highlights the role that young infant age and maternal smoking have as risk factors that contribute to biological vulnerabilities in infants.”
The results also give clinicians more information on characteristics of bedsharing families and some of the factors related to bedsharing, including socioeconomic and behavioral factors, she said. She highlighted the higher risk of SUID when drug or alcohol impairment is involved while bedsharing.
“All of this information is really important and helps clinicians shape the safe sleep messages to families,” she said.
The study authors and Dr. Haynes report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
What Skin Manifestations Are Associated With Pediatric IBD?
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Skin conditions burden many children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), according to the authors of a single-center study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with (CD) or ulcerative (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed the medical charts of 425 children and adolescents with Crohn’s disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) at one or more dermatologic diagnoses who were seen at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, between 1999 and 2017.
- Of the children studied, 53% were male, 64.9% had CD, and 42.8% had one or more cutaneous infections.
- They used the chi-square/Fischer’s exact test to compare categorical outcomes between patients with CD and UC and to detect differences in IBD/CD/UC disease severity and skin conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- The most common noninfectious dermatologic condition among the 425 children and adolescents was (30.8%), followed by eczema (15.8%) and perianal skin tags (14.6%).
- Angular cheilitis was more common among those with CD than those with UC (7.2% vs 2%, respectively; P = .024) as was keratosis pilaris (6.9% vs 0.7%; P = .003), and perianal skin complications such as skin tags (20.3% vs 4%), fistulas (13.4% vs 2.7%), and abscesses (13.4% vs 2%; P < .001 for all associations).
- Fungal skin infections were more frequently diagnosed in children with UC than those with CD (15.4% vs 8%; P = .017).
- The researchers observed that the severity of IBD correlated with a higher prevalence of perianal fistula (P = .003), perianal region abscess (P = .041), psoriasis (P < .001), and pyoderma gangrenosum (P = .003).
IN PRACTICE:
“Early identification of common dermatologic conditions in children and adolescents with IBD and recognizing their characteristic associations may alter management and improve skin-related outcomes in this patient population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Corresponding author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, and colleagues conducted the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The single-center design and the fact that database studies are subject to extraction error. There was no age- and sex-matched cohort to determine whether the prevalence of cutaneous infections, acne, eczema, and other inflammatory disorders was truly increased in IBD.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Company Announces Regulatory Filing for Nemolizumab for Two Indications
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
On February 14, 2024, Galderma announced that .
A first-in-class investigational monoclonal antibody specifically designed to inhibit interleukin (IL) IL-31 signaling, nemolizumab has also been granted FDA Priority Review for prurigo nodularis, according to a press release from the company. The European Medicines Agency has also accepted Galderma’s Marketing Authorization Applications for nemolizumab for both prurigo nodularis and atopic dermatitis.
The regulatory developments follow data from the phase III OLYMPIA clinical trial program, which evaluated the efficacy and safety of nemolizumab administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks in patients with prurigo nodularis (NCT04501679 and NCT04501666). According to the press release, in OLYMPIA 1 and 2, 58% and 56% of patients, respectively, achieved at least a least four-point reduction in itch intensity as measured by the peak-pruritus numerical rating scale (PP-NRS), compared with 17% and 21% in the placebo groups (P < .0001). At the same time, 26% and 38% of nemolizumab-treated patients reached clearance or almost-clearance of skin lesions on the investigator’s global assessment (IGA) score, compared with 7% and 11% in the placebo groups (P < .0001).
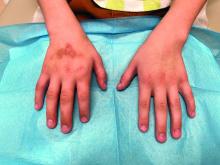
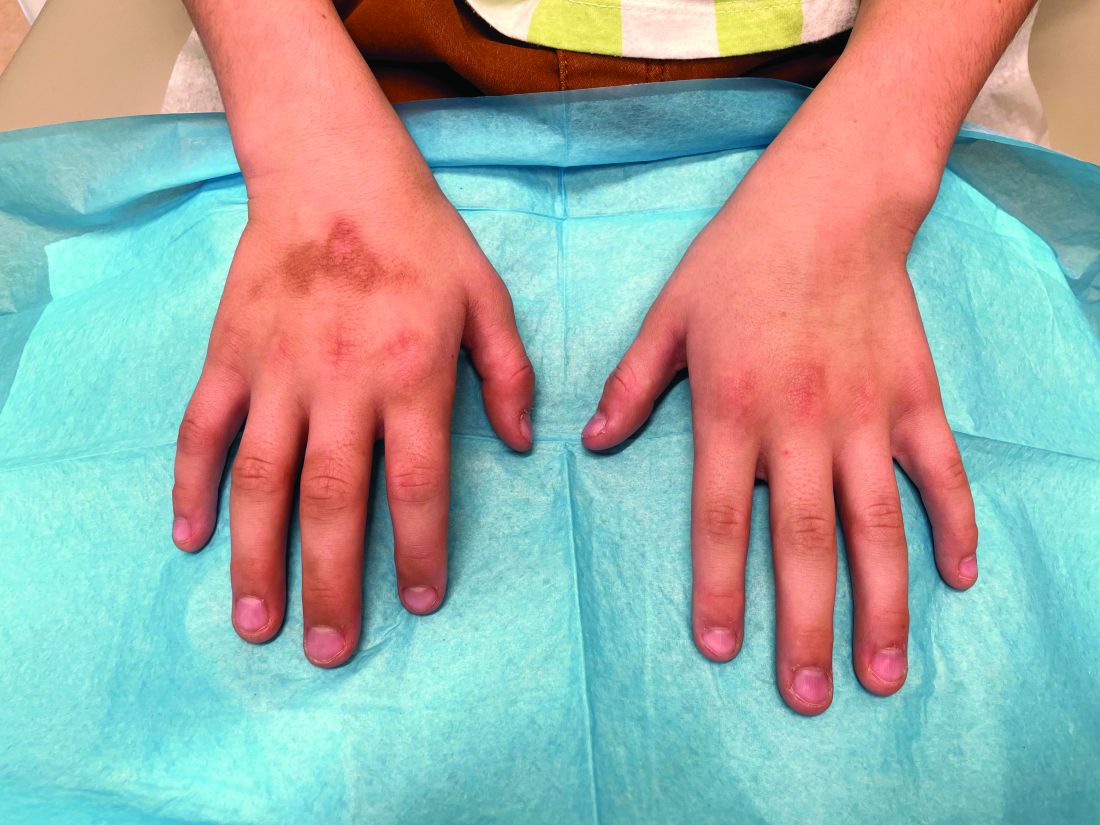
An 8-Year-Old Male With Asymptomatic Brown Rough Plaques on the Dorsum of the Right Hand and Fingers, Accompanied by Widening of the Knuckles
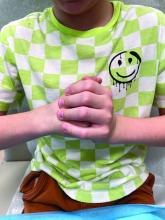
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
During examination, the patient was observed repetitively cracking his knuckles, making a fist with the right hand, placing the left hand on top, and rubbing the hand, a behavior he routinely did multiple times daily. The observed pattern of finger involvement on the dorsum of the right hand corresponded to areas subjected to significant pressure during the described activity. Consequently, a diagnosis of lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) secondary to mechanical rubbing, along with associated pachydermodactyly on the fingers of the right hand, was established.
Lichen simplex chronicus and pachydermodactyly are both attributed to microtrauma inflicted upon the skin. Lichen simplex chronicus often constitutes a diagnosis of exclusion and is characterized by repetitive trauma-induced keratinocyte proliferation and melanocyte activation, resulting in hyperpigmentation and skin thickening. Although typically observed in women between the fourth and fifth decades of life, LSC is rarely reported in children. In adults, LSC-related rubbing or scratching frequently arises from chronic pruritic dermatitis such as eczema or psoriasis, neurodermatitis from dysesthesia, or habitual movements, as exhibited by this young patient. While generally benign, LSC may become infected. In rare instances, malignant transformation may occur.
The association with pachydermodactyly implicates microtrauma, necessitating careful observation and questioning to elucidate the cause, as demonstrated in this case. Lesions are typically hyperpigmented, though cases of associated hypopigmentation or depigmentation have been documented. Affected areas typically fall within the patient’s hand and finger reach, with lesion improvement over several months achievable through trigger avoidance.
Pachydermodactyly, a rare but benign fibromatosis around the proximal interphalangeal joints, is often misdiagnosed as juvenile idiopathic arthritis, potentially leading to unnecessary treatments and patient anxiety. Microtrauma history due to digit manipulation is prevalent among affected individuals, with most also exhibiting neuropsychiatric disorders. Histological examination of pachydermodactyly reveals hypergranulosis and dermal thickening, accompanied by increased fibroblasts and collagen types I, III, and V, differing from the epidermal changes seen in LSC.
The differential diagnosis also included phytophotodermatitis, a phototoxic dermatologic reaction following exposure to ultraviolet light subsequent to contact with furocoumarin-containing plant chemicals. However, the persistence of the patient’s lesions for over a year precluded this diagnosis. Secondary hyperpigmentation was also contemplated but excluded due to the absence of preceding inflammatory dermatitis.
Treatment of LSC primarily involves identifying and addressing any underlying conditions, repairing the skin barrier, reducing inflammation, and modifying behaviors contributing to chronic microtrauma, as observed in this patient. Topical corticosteroids may aid in decreasing epidermal thickening and discoloration, though lesion resolution necessitates behavior cessation.
It’s important to identify these types of skin changes in children to avoid unnecessary medical treatments for these benign conditions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Seier JA, Dissemond J. Lichen Simplex Chronicus Due to Mechanical Irritation. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022 Nov 18;119(46):802. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0213.
Small S et al. A 12-Year-Old Boy Presenting With Unilateral Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Swelling. BMJ Case Rep. 2011 Apr 13:2011:bcr0120113719. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3719.
Voicu C et al Lichen Simplex Chronicus as an Essential Part of the Dermatologic Masquerade. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Jul 24;5(4):556-557. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.133.
The patient was otherwise healthy, with no current medication intake, and he engaged in baseball and soccer activities. Upon physical examination, a hyperpigmented lichenified irregular plaque was observed on the dorsum of the right hand, along with irregular hyperpigmented macules and plaques on the fingers. Fusiform widening of the interphalangeal joints on the second, third, and fourth fingers of the right hand was noted, without associated pain, edema, or erythema.
Obesity’s Effect on Neonatal Outcomes Is Dose Dependent
TOPLINE:
Higher body mass index (BMI) at the start of pregnancy is associated with increased risk for adverse maternal outcomes, including preeclampsia, and neonatal complications, such as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), in a dose-dependent manner, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 58,497 singleton pregnancies delivered at an urban hospital between 2013 and 2021.
- They focused on pregnancies delivered between 24 and 42 weeks of gestation, for which information about BMI at the first prenatal visit was available.
- 21.1% of mothers had class I , 9.3% had class II obesity, and 6% had class III obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Obesity was associated with a dose-dependent increase in cesarean deliveries (27% of deliveries without obesity vs 46% of deliveries with class III obesity).
- Severe preeclampsia occurred in 8% of mothers without obesity and in 19% of mothers with class III obesity.
- Infants born to mothers with class III obesity were more likely than were infants born to mothers without obesity to have RDS, with a relative risk (RR) of 2.66.
- With class II obesity, the RR was 1.77. With class I obesity, the RR was 1.3.
- Obesity also was associated with increased risk for grade III-IV (RR), 4.58 for class III obesity) and (RR, 3.76).
IN PRACTICE:
“Infants born to patients with higher classes of obesity have significant associated morbidity including a 2 to 4 times increased risk of neonatal acidosis, grades III-IV intraventricular hemorrhage, sepsis, and RDS,” the researchers reported.
SOURCE:
Sara I. Jones, MD, with University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, presented the study on February 14 at the 2024 Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, in National Harbor, Maryland.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher body mass index (BMI) at the start of pregnancy is associated with increased risk for adverse maternal outcomes, including preeclampsia, and neonatal complications, such as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), in a dose-dependent manner, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 58,497 singleton pregnancies delivered at an urban hospital between 2013 and 2021.
- They focused on pregnancies delivered between 24 and 42 weeks of gestation, for which information about BMI at the first prenatal visit was available.
- 21.1% of mothers had class I , 9.3% had class II obesity, and 6% had class III obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Obesity was associated with a dose-dependent increase in cesarean deliveries (27% of deliveries without obesity vs 46% of deliveries with class III obesity).
- Severe preeclampsia occurred in 8% of mothers without obesity and in 19% of mothers with class III obesity.
- Infants born to mothers with class III obesity were more likely than were infants born to mothers without obesity to have RDS, with a relative risk (RR) of 2.66.
- With class II obesity, the RR was 1.77. With class I obesity, the RR was 1.3.
- Obesity also was associated with increased risk for grade III-IV (RR), 4.58 for class III obesity) and (RR, 3.76).
IN PRACTICE:
“Infants born to patients with higher classes of obesity have significant associated morbidity including a 2 to 4 times increased risk of neonatal acidosis, grades III-IV intraventricular hemorrhage, sepsis, and RDS,” the researchers reported.
SOURCE:
Sara I. Jones, MD, with University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, presented the study on February 14 at the 2024 Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, in National Harbor, Maryland.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher body mass index (BMI) at the start of pregnancy is associated with increased risk for adverse maternal outcomes, including preeclampsia, and neonatal complications, such as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), in a dose-dependent manner, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective study of 58,497 singleton pregnancies delivered at an urban hospital between 2013 and 2021.
- They focused on pregnancies delivered between 24 and 42 weeks of gestation, for which information about BMI at the first prenatal visit was available.
- 21.1% of mothers had class I , 9.3% had class II obesity, and 6% had class III obesity.
TAKEAWAY:
- Obesity was associated with a dose-dependent increase in cesarean deliveries (27% of deliveries without obesity vs 46% of deliveries with class III obesity).
- Severe preeclampsia occurred in 8% of mothers without obesity and in 19% of mothers with class III obesity.
- Infants born to mothers with class III obesity were more likely than were infants born to mothers without obesity to have RDS, with a relative risk (RR) of 2.66.
- With class II obesity, the RR was 1.77. With class I obesity, the RR was 1.3.
- Obesity also was associated with increased risk for grade III-IV (RR), 4.58 for class III obesity) and (RR, 3.76).
IN PRACTICE:
“Infants born to patients with higher classes of obesity have significant associated morbidity including a 2 to 4 times increased risk of neonatal acidosis, grades III-IV intraventricular hemorrhage, sepsis, and RDS,” the researchers reported.
SOURCE:
Sara I. Jones, MD, with University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, presented the study on February 14 at the 2024 Pregnancy Meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, in National Harbor, Maryland.
DISCLOSURES:
The researchers had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Parent-Led Digital CBT Effective for Childhood Anxiety
while substantially reducing cost and therapist time, new research showed.
In a randomized controlled trial, children participating in the program Online Support and Intervention (OSI) for Child Anxiety showed similar reductions in anxiety and improvements in daily functioning as peers receiving standard CBT.
“This study shows that by making the most of digital tools, we can deliver effective treatments more efficiently, helping services to better meet the growing demand for mental health services for children in ways that can also be more accessible for many families,” lead investigator Cathy Creswell, PhD, Departments of Experimental Psychology and Psychiatry, Oxford University, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
“I believe by incorporating this approach into standard care, we could address some of the major challenges faced by services and families,” Dr. Creswell added. “We are now moving the work out of the research environment into routine practice.”
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry
Care Gaps for Common Problem
Anxiety is common in children, yet gaps exist between needed and available care, which investigators say could be filled by digitally augmented psychological treatments.
OSI, the digital platform used in the current study, was designed with therapists and families to aid parents in helping their children overcome problems with anxiety with remote therapist support.
The program provides parents with the core CBT content in accessible forms, including information in text, audio, and video and exercises supported by worksheets and quizzes.
There is also an optional child game app to help motivate the child to engage with the intervention. Parents are supported with weekly brief telephone or video call sessions with the therapist.
The two-arm randomized controlled non-inferiority trial included 444 families from 34 participating Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) sites in England and Northern Ireland. Half received OSI plus therapist support and half CAMHS treatment as usual. The children were between 5 and 12 years old.
A total of 176 (79%) participants in the OSI plus therapist support group and 164 (74%) in the treatment as usual group completed the 26-week assessment.
‘Compelling’ Evidence
The primary clinical outcome was parent-reported interference caused by child anxiety at 26 weeks, using the Child Anxiety Impact Scale-Parent report.
On this measure, OSI plus therapist support was non-inferior to usual treatment, with a standardized mean difference of only 0.01 (95% CI, −0.15 to 0.17; P < .0001).
The intervention was also significantly non-inferior to usual treatment across all secondary outcomes, including total anxiety and depression scores, overall functioning, peer relationship problems, and prosocial behavior.
In addition, OSI plus therapist support was associated with nearly 60% less therapist time (182 min on average vs 307 min) and with lower costs than standard treatment. The OSI program was “likely to be cost-effective under several scenarios,” the researchers reported. Qualitative interviews showed “good” acceptability of the online program.
“This trial presents compelling clinical evidence and promising cost-effectiveness evidence that digitally augmented psychological therapies with therapist support can increase efficiencies in and access to child mental health services without compromising patient outcomes,” Dr. Creswell and colleagues concluded.
“Efforts are now needed to take full advantage of the opportunity that digitally augmented psychological treatments can bring to drive a step change in children’s mental health services, learning from successful examples of digital implementation elsewhere in health services,” they added.
‘Call to Action’
“We desperately need more trials” like this one, which showed the “clear value of a digitally augmented intervention over the usual face-to-face treatment” for child anxiety, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“Moreover, with the intervention delivered across 34 CAMHS settings in England and Northern Ireland, this study gives us confidence that the new intervention is effective in a range of clinical contexts at least in high-income countries and offers invaluable information about barriers and facilitators to future implementation,” wrote Sam Cartwright-Hatton, PhD, with the University of Sussex, Brighton and Hove, and Abby Dunn, PhD, with the University of Surrey, Guilford, England. “The potential benefits to overburdened services are clear.”
“That regular CAMHS clinicians, with minimal training and support from researchers, delivered the intervention within their standard caseload shows that it can be embedded within routine practice without a requirement for highly prepared and supervised clinicians,” they added.
However, more information is needed on the content and quality of the traditional CBT provided in the control group. It’s also important to determine if the program would be as effective with even less clinical support and in all types of childhood anxiety.
In addition, most clinicians in the OSI group only treated one patient with the new program and didn’t take advantage of the additional support offered by the research team, “which means we have not seen the true effectiveness of this intervention in the hands of well-practiced and well-trained staff,” Drs. Cartwright-Hatton and Dunn wrote.
Analyses included recruitment at the lower target amount, and one fifth of children were not offered treatment within the 12-week window recommended in the trial, they added.
“Although these issues place limits on the conclusions that can be drawn, they should also be seen as a call to action,” they wrote, adding that real-world clinical trials with greater clinician participation are needed. “All credit to this exceptional team for making this trial happen and for making it work as well as it did.”
The study was funded by the Department for Health and Social Care, UK Research and Innovation Research Grant, National Institute for Health and Care (NIHR) Research Policy Research Programme, Oxford and Thames Valley NIHR Applied Research Collaboration, and Oxford Health NIHR Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Creswell is co-developer of the OSI platform and the author of a book for parents that is used in many of the participating clinical teams to augment treatment as usual for child anxiety problems and receives royalties from sales. Dr. Cartwright-Hatton and Dr. Dunn had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
while substantially reducing cost and therapist time, new research showed.
In a randomized controlled trial, children participating in the program Online Support and Intervention (OSI) for Child Anxiety showed similar reductions in anxiety and improvements in daily functioning as peers receiving standard CBT.
“This study shows that by making the most of digital tools, we can deliver effective treatments more efficiently, helping services to better meet the growing demand for mental health services for children in ways that can also be more accessible for many families,” lead investigator Cathy Creswell, PhD, Departments of Experimental Psychology and Psychiatry, Oxford University, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
“I believe by incorporating this approach into standard care, we could address some of the major challenges faced by services and families,” Dr. Creswell added. “We are now moving the work out of the research environment into routine practice.”
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry
Care Gaps for Common Problem
Anxiety is common in children, yet gaps exist between needed and available care, which investigators say could be filled by digitally augmented psychological treatments.
OSI, the digital platform used in the current study, was designed with therapists and families to aid parents in helping their children overcome problems with anxiety with remote therapist support.
The program provides parents with the core CBT content in accessible forms, including information in text, audio, and video and exercises supported by worksheets and quizzes.
There is also an optional child game app to help motivate the child to engage with the intervention. Parents are supported with weekly brief telephone or video call sessions with the therapist.
The two-arm randomized controlled non-inferiority trial included 444 families from 34 participating Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) sites in England and Northern Ireland. Half received OSI plus therapist support and half CAMHS treatment as usual. The children were between 5 and 12 years old.
A total of 176 (79%) participants in the OSI plus therapist support group and 164 (74%) in the treatment as usual group completed the 26-week assessment.
‘Compelling’ Evidence
The primary clinical outcome was parent-reported interference caused by child anxiety at 26 weeks, using the Child Anxiety Impact Scale-Parent report.
On this measure, OSI plus therapist support was non-inferior to usual treatment, with a standardized mean difference of only 0.01 (95% CI, −0.15 to 0.17; P < .0001).
The intervention was also significantly non-inferior to usual treatment across all secondary outcomes, including total anxiety and depression scores, overall functioning, peer relationship problems, and prosocial behavior.
In addition, OSI plus therapist support was associated with nearly 60% less therapist time (182 min on average vs 307 min) and with lower costs than standard treatment. The OSI program was “likely to be cost-effective under several scenarios,” the researchers reported. Qualitative interviews showed “good” acceptability of the online program.
“This trial presents compelling clinical evidence and promising cost-effectiveness evidence that digitally augmented psychological therapies with therapist support can increase efficiencies in and access to child mental health services without compromising patient outcomes,” Dr. Creswell and colleagues concluded.
“Efforts are now needed to take full advantage of the opportunity that digitally augmented psychological treatments can bring to drive a step change in children’s mental health services, learning from successful examples of digital implementation elsewhere in health services,” they added.
‘Call to Action’
“We desperately need more trials” like this one, which showed the “clear value of a digitally augmented intervention over the usual face-to-face treatment” for child anxiety, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“Moreover, with the intervention delivered across 34 CAMHS settings in England and Northern Ireland, this study gives us confidence that the new intervention is effective in a range of clinical contexts at least in high-income countries and offers invaluable information about barriers and facilitators to future implementation,” wrote Sam Cartwright-Hatton, PhD, with the University of Sussex, Brighton and Hove, and Abby Dunn, PhD, with the University of Surrey, Guilford, England. “The potential benefits to overburdened services are clear.”
“That regular CAMHS clinicians, with minimal training and support from researchers, delivered the intervention within their standard caseload shows that it can be embedded within routine practice without a requirement for highly prepared and supervised clinicians,” they added.
However, more information is needed on the content and quality of the traditional CBT provided in the control group. It’s also important to determine if the program would be as effective with even less clinical support and in all types of childhood anxiety.
In addition, most clinicians in the OSI group only treated one patient with the new program and didn’t take advantage of the additional support offered by the research team, “which means we have not seen the true effectiveness of this intervention in the hands of well-practiced and well-trained staff,” Drs. Cartwright-Hatton and Dunn wrote.
Analyses included recruitment at the lower target amount, and one fifth of children were not offered treatment within the 12-week window recommended in the trial, they added.
“Although these issues place limits on the conclusions that can be drawn, they should also be seen as a call to action,” they wrote, adding that real-world clinical trials with greater clinician participation are needed. “All credit to this exceptional team for making this trial happen and for making it work as well as it did.”
The study was funded by the Department for Health and Social Care, UK Research and Innovation Research Grant, National Institute for Health and Care (NIHR) Research Policy Research Programme, Oxford and Thames Valley NIHR Applied Research Collaboration, and Oxford Health NIHR Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Creswell is co-developer of the OSI platform and the author of a book for parents that is used in many of the participating clinical teams to augment treatment as usual for child anxiety problems and receives royalties from sales. Dr. Cartwright-Hatton and Dr. Dunn had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
while substantially reducing cost and therapist time, new research showed.
In a randomized controlled trial, children participating in the program Online Support and Intervention (OSI) for Child Anxiety showed similar reductions in anxiety and improvements in daily functioning as peers receiving standard CBT.
“This study shows that by making the most of digital tools, we can deliver effective treatments more efficiently, helping services to better meet the growing demand for mental health services for children in ways that can also be more accessible for many families,” lead investigator Cathy Creswell, PhD, Departments of Experimental Psychology and Psychiatry, Oxford University, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
“I believe by incorporating this approach into standard care, we could address some of the major challenges faced by services and families,” Dr. Creswell added. “We are now moving the work out of the research environment into routine practice.”
The study was published online in The Lancet Psychiatry
Care Gaps for Common Problem
Anxiety is common in children, yet gaps exist between needed and available care, which investigators say could be filled by digitally augmented psychological treatments.
OSI, the digital platform used in the current study, was designed with therapists and families to aid parents in helping their children overcome problems with anxiety with remote therapist support.
The program provides parents with the core CBT content in accessible forms, including information in text, audio, and video and exercises supported by worksheets and quizzes.
There is also an optional child game app to help motivate the child to engage with the intervention. Parents are supported with weekly brief telephone or video call sessions with the therapist.
The two-arm randomized controlled non-inferiority trial included 444 families from 34 participating Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) sites in England and Northern Ireland. Half received OSI plus therapist support and half CAMHS treatment as usual. The children were between 5 and 12 years old.
A total of 176 (79%) participants in the OSI plus therapist support group and 164 (74%) in the treatment as usual group completed the 26-week assessment.
‘Compelling’ Evidence
The primary clinical outcome was parent-reported interference caused by child anxiety at 26 weeks, using the Child Anxiety Impact Scale-Parent report.
On this measure, OSI plus therapist support was non-inferior to usual treatment, with a standardized mean difference of only 0.01 (95% CI, −0.15 to 0.17; P < .0001).
The intervention was also significantly non-inferior to usual treatment across all secondary outcomes, including total anxiety and depression scores, overall functioning, peer relationship problems, and prosocial behavior.
In addition, OSI plus therapist support was associated with nearly 60% less therapist time (182 min on average vs 307 min) and with lower costs than standard treatment. The OSI program was “likely to be cost-effective under several scenarios,” the researchers reported. Qualitative interviews showed “good” acceptability of the online program.
“This trial presents compelling clinical evidence and promising cost-effectiveness evidence that digitally augmented psychological therapies with therapist support can increase efficiencies in and access to child mental health services without compromising patient outcomes,” Dr. Creswell and colleagues concluded.
“Efforts are now needed to take full advantage of the opportunity that digitally augmented psychological treatments can bring to drive a step change in children’s mental health services, learning from successful examples of digital implementation elsewhere in health services,” they added.
‘Call to Action’
“We desperately need more trials” like this one, which showed the “clear value of a digitally augmented intervention over the usual face-to-face treatment” for child anxiety, wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
“Moreover, with the intervention delivered across 34 CAMHS settings in England and Northern Ireland, this study gives us confidence that the new intervention is effective in a range of clinical contexts at least in high-income countries and offers invaluable information about barriers and facilitators to future implementation,” wrote Sam Cartwright-Hatton, PhD, with the University of Sussex, Brighton and Hove, and Abby Dunn, PhD, with the University of Surrey, Guilford, England. “The potential benefits to overburdened services are clear.”
“That regular CAMHS clinicians, with minimal training and support from researchers, delivered the intervention within their standard caseload shows that it can be embedded within routine practice without a requirement for highly prepared and supervised clinicians,” they added.
However, more information is needed on the content and quality of the traditional CBT provided in the control group. It’s also important to determine if the program would be as effective with even less clinical support and in all types of childhood anxiety.
In addition, most clinicians in the OSI group only treated one patient with the new program and didn’t take advantage of the additional support offered by the research team, “which means we have not seen the true effectiveness of this intervention in the hands of well-practiced and well-trained staff,” Drs. Cartwright-Hatton and Dunn wrote.
Analyses included recruitment at the lower target amount, and one fifth of children were not offered treatment within the 12-week window recommended in the trial, they added.
“Although these issues place limits on the conclusions that can be drawn, they should also be seen as a call to action,” they wrote, adding that real-world clinical trials with greater clinician participation are needed. “All credit to this exceptional team for making this trial happen and for making it work as well as it did.”
The study was funded by the Department for Health and Social Care, UK Research and Innovation Research Grant, National Institute for Health and Care (NIHR) Research Policy Research Programme, Oxford and Thames Valley NIHR Applied Research Collaboration, and Oxford Health NIHR Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Creswell is co-developer of the OSI platform and the author of a book for parents that is used in many of the participating clinical teams to augment treatment as usual for child anxiety problems and receives royalties from sales. Dr. Cartwright-Hatton and Dr. Dunn had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET PSYCHIATRY
Stimulant Medications for ADHD — the Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
Children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are mainly cared for in primary care settings by us. Management of this chronic neurodevelopmental condition that affects 5+% of children worldwide should include proper diagnosis, assessment for contributing and comorbid conditions, behavioral intervention (the primary treatment for preschoolers), ensuring good sleep and nutrition, and usually medication.
Because stimulants are very effective for reducing ADHD symptoms, we may readily begin these first-line medications even on the initial visit when the diagnosis is determined. But are we really thoughtful about knowing and explaining the potential short- and long-term side effects of these medications that may then be used for many years? Considerable discussion with the child and parents may be needed to address their concerns, balanced with benefits, and to make a plan for their access and use of stimulants (and other medications for ADHD not the topic here).
Consider the Side Effects
In children older than 6 years, some form of either a methylphenidate (MPH) or a dextroamphetamine (DA) class of stimulant have been shown to be equally effective in reducing symptoms of ADHD in about 77% of cases, but side effects are common, mostly mild, and mostly in the first months of use. These include reduced appetite, abdominal pain, headache, weight loss, tics, jitteriness, and delays in falling asleep. About half of all children treated will have one of these adverse effects over 5 years, with reduced appetite the most common. There is no difference in effectiveness or side effects by presentation type, i.e. hyperactive, inattentive, or combined, but the DA forms are associated with more side effects than MPH (10% vs. 6%). Medicated preschoolers have more and different side effects which, in addition to those above, may include listlessness, social withdrawal, and repetitive movements. Fortunately, we can reassure families that side effects can usually be readily managed by slower ramp up of dose, spacing to ensure appetite for meals, extra snacks, attention to bowel patterns and bedtime routines, or change in medication class.
Rates of tics while on stimulants are low irrespective of whether DA or MPH is used, and are usually transient, but difficult cases may occur, sometimes as part of Tourette’s, although not a contraindication. Additional side effects of concern are anxiety, irritability, sadness, and overfocusing that may require a change in class of stimulant or to a nonstimulant. Keep in mind that these symptoms may represent comorbid conditions to ADHD, warranting counseling intervention rather than being a medication side effect. Both initial assessment for ADHD and monitoring should look for comorbidities whether medication is used or not.
Measuring height, weight, pulse, and blood pressure should be part of ADHD care. How concerned should you and the family be about variations? Growth rate declines are more common in preschool children; in the PATS study height varied by 20.3%, and weight by 55.2%, more in heavier children. Growth can be protected by providing favored food for school, encouraging eating when hungry, and an evening fourth meal. You can reassure families that, even with continual use of stimulant medicines for years and initial deficits of 2 cm and 2.7 kg compared to expected, no significant differences remain in adulthood.
This longitudinal growth data was collected when short-acting stimulants were the usual, rather than the now common long-acting stimulants given 7 days per week, however. Children on transdermal MPH with 12-hour release over 3 years showed a small but significant delay in growth with the mean deficit rates 1.3 kg/year mainly in the first year, and 0.68 cm/year in height in the second year. If we see growth not recovering as it is expected to after the first year of treatment, we can advise shorter-acting forms, and medication “holidays” on weekends or vacations, that reduce but do not end the deficits. When concerned, a nonstimulant can be selected.
Blood pressure and pulse rate are predictably slightly increased on stimulants (about 2-4 mm Hg and about 3-6 bpm) but not clinically significantly. Although ECGs are not routinely recommended, careful consideration and consultation is warranted before starting stimulants for any patient with structural cardiac abnormalities, unexplained syncope, exertional chest pain, or a family history of sudden death in children or young adults. Neither current nor former users of stimulants for ADHD were found to have greater rates of cardiac events than the general population, however.
Misuse and abuse
Misuse and diversion of stimulants is common (e.g. 26% diverted MPH in the past month; 14% of 12th graders divert DA), often undetected, and potentially dangerous. And the problem is not limited to just the kids. Sixteen percent of parents reported diversion of stimulant medication to another household member, mainly to themselves. Stimulant overdose can occur, especially taken parenterally, and presents with dilated pupils, tremor, agitation, hyperreflexia, combative behavior, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, anxiety, paranoia, movement disorders, and/or seizures. Fortunately, overdose of prescribed stimulants is rarely fatal if medically managed, but recent “fake” Adderall (not from pharmacies) has been circulating. These fake drugs may contain lethal amounts of fentanyl or methamphetamine. Point out to families that a peer-provided stimulant not prescribed for them may have underlying medical or psychiatric issues that increase adverse events. Selling stimulants can have serious legal implications, with punishments ranging from fines to incarceration. A record of arrest during adolescence increases the likelihood of high school dropout, lack of 4-year college education, and later employment barriers. Besides these serious outcomes, it is useful to remind patients that if they deviate from your recommended dosing that you, and others, will not prescribe for them in the future the medication that has been supporting their successful functioning.
You can be fooled about being able to tell if your patients are misusing or diverting the stimulants you prescribe. Most (59%) physicians suspect that more than one of their patients with ADHD has diverted or feigned symptoms (66%) to get a prescription. Women were less likely to suspect their patients than are men, though, so be vigilant! Child psychiatrists had the highest suspicion with their greater proportion of patients with ADHD plus conduct or substance use disorder, who account for 83% of misusers/diverters. We can use education about misuse, pill counts, contracts on dosing, or switching to long-acting or nonstimulants to curb this.
Additional concerns
With more ADHD diagnosis and stimulants used for many years should we worry about longer-term issues? There have been reports in rodent models and a few children of chromosomal changes with stimulant exposure, but reviewers do not interpret these as an individual cancer risk. Record review of patients who received stimulants showed lower numbers of cancer than expected. Nor is there evidence of reproductive effects of stimulants, although use during pregnancy is not cleared.
Stimulants carry a boxed warning as having high potential for abuse and psychological or physical dependence, which is unsurprising given their effects on brain reward pathways. However, neither past nor present use of stimulants for ADHD has been associated with greater substance use long term.
To top off these issues, recent shortages of stimulants complicate ADHD management. Most states require electronic prescribing, US rules only allowing one transfer of such e-prescriptions. With many pharmacies refusing to tell families about availability, we must make multiple calls to locate a source. Pharmacists could help us by looking up patient names of abusers on the registry and identifying sites with adequate supplies.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are mainly cared for in primary care settings by us. Management of this chronic neurodevelopmental condition that affects 5+% of children worldwide should include proper diagnosis, assessment for contributing and comorbid conditions, behavioral intervention (the primary treatment for preschoolers), ensuring good sleep and nutrition, and usually medication.
Because stimulants are very effective for reducing ADHD symptoms, we may readily begin these first-line medications even on the initial visit when the diagnosis is determined. But are we really thoughtful about knowing and explaining the potential short- and long-term side effects of these medications that may then be used for many years? Considerable discussion with the child and parents may be needed to address their concerns, balanced with benefits, and to make a plan for their access and use of stimulants (and other medications for ADHD not the topic here).
Consider the Side Effects
In children older than 6 years, some form of either a methylphenidate (MPH) or a dextroamphetamine (DA) class of stimulant have been shown to be equally effective in reducing symptoms of ADHD in about 77% of cases, but side effects are common, mostly mild, and mostly in the first months of use. These include reduced appetite, abdominal pain, headache, weight loss, tics, jitteriness, and delays in falling asleep. About half of all children treated will have one of these adverse effects over 5 years, with reduced appetite the most common. There is no difference in effectiveness or side effects by presentation type, i.e. hyperactive, inattentive, or combined, but the DA forms are associated with more side effects than MPH (10% vs. 6%). Medicated preschoolers have more and different side effects which, in addition to those above, may include listlessness, social withdrawal, and repetitive movements. Fortunately, we can reassure families that side effects can usually be readily managed by slower ramp up of dose, spacing to ensure appetite for meals, extra snacks, attention to bowel patterns and bedtime routines, or change in medication class.
Rates of tics while on stimulants are low irrespective of whether DA or MPH is used, and are usually transient, but difficult cases may occur, sometimes as part of Tourette’s, although not a contraindication. Additional side effects of concern are anxiety, irritability, sadness, and overfocusing that may require a change in class of stimulant or to a nonstimulant. Keep in mind that these symptoms may represent comorbid conditions to ADHD, warranting counseling intervention rather than being a medication side effect. Both initial assessment for ADHD and monitoring should look for comorbidities whether medication is used or not.
Measuring height, weight, pulse, and blood pressure should be part of ADHD care. How concerned should you and the family be about variations? Growth rate declines are more common in preschool children; in the PATS study height varied by 20.3%, and weight by 55.2%, more in heavier children. Growth can be protected by providing favored food for school, encouraging eating when hungry, and an evening fourth meal. You can reassure families that, even with continual use of stimulant medicines for years and initial deficits of 2 cm and 2.7 kg compared to expected, no significant differences remain in adulthood.
This longitudinal growth data was collected when short-acting stimulants were the usual, rather than the now common long-acting stimulants given 7 days per week, however. Children on transdermal MPH with 12-hour release over 3 years showed a small but significant delay in growth with the mean deficit rates 1.3 kg/year mainly in the first year, and 0.68 cm/year in height in the second year. If we see growth not recovering as it is expected to after the first year of treatment, we can advise shorter-acting forms, and medication “holidays” on weekends or vacations, that reduce but do not end the deficits. When concerned, a nonstimulant can be selected.
Blood pressure and pulse rate are predictably slightly increased on stimulants (about 2-4 mm Hg and about 3-6 bpm) but not clinically significantly. Although ECGs are not routinely recommended, careful consideration and consultation is warranted before starting stimulants for any patient with structural cardiac abnormalities, unexplained syncope, exertional chest pain, or a family history of sudden death in children or young adults. Neither current nor former users of stimulants for ADHD were found to have greater rates of cardiac events than the general population, however.
Misuse and abuse
Misuse and diversion of stimulants is common (e.g. 26% diverted MPH in the past month; 14% of 12th graders divert DA), often undetected, and potentially dangerous. And the problem is not limited to just the kids. Sixteen percent of parents reported diversion of stimulant medication to another household member, mainly to themselves. Stimulant overdose can occur, especially taken parenterally, and presents with dilated pupils, tremor, agitation, hyperreflexia, combative behavior, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, anxiety, paranoia, movement disorders, and/or seizures. Fortunately, overdose of prescribed stimulants is rarely fatal if medically managed, but recent “fake” Adderall (not from pharmacies) has been circulating. These fake drugs may contain lethal amounts of fentanyl or methamphetamine. Point out to families that a peer-provided stimulant not prescribed for them may have underlying medical or psychiatric issues that increase adverse events. Selling stimulants can have serious legal implications, with punishments ranging from fines to incarceration. A record of arrest during adolescence increases the likelihood of high school dropout, lack of 4-year college education, and later employment barriers. Besides these serious outcomes, it is useful to remind patients that if they deviate from your recommended dosing that you, and others, will not prescribe for them in the future the medication that has been supporting their successful functioning.
You can be fooled about being able to tell if your patients are misusing or diverting the stimulants you prescribe. Most (59%) physicians suspect that more than one of their patients with ADHD has diverted or feigned symptoms (66%) to get a prescription. Women were less likely to suspect their patients than are men, though, so be vigilant! Child psychiatrists had the highest suspicion with their greater proportion of patients with ADHD plus conduct or substance use disorder, who account for 83% of misusers/diverters. We can use education about misuse, pill counts, contracts on dosing, or switching to long-acting or nonstimulants to curb this.
Additional concerns
With more ADHD diagnosis and stimulants used for many years should we worry about longer-term issues? There have been reports in rodent models and a few children of chromosomal changes with stimulant exposure, but reviewers do not interpret these as an individual cancer risk. Record review of patients who received stimulants showed lower numbers of cancer than expected. Nor is there evidence of reproductive effects of stimulants, although use during pregnancy is not cleared.
Stimulants carry a boxed warning as having high potential for abuse and psychological or physical dependence, which is unsurprising given their effects on brain reward pathways. However, neither past nor present use of stimulants for ADHD has been associated with greater substance use long term.
To top off these issues, recent shortages of stimulants complicate ADHD management. Most states require electronic prescribing, US rules only allowing one transfer of such e-prescriptions. With many pharmacies refusing to tell families about availability, we must make multiple calls to locate a source. Pharmacists could help us by looking up patient names of abusers on the registry and identifying sites with adequate supplies.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are mainly cared for in primary care settings by us. Management of this chronic neurodevelopmental condition that affects 5+% of children worldwide should include proper diagnosis, assessment for contributing and comorbid conditions, behavioral intervention (the primary treatment for preschoolers), ensuring good sleep and nutrition, and usually medication.
Because stimulants are very effective for reducing ADHD symptoms, we may readily begin these first-line medications even on the initial visit when the diagnosis is determined. But are we really thoughtful about knowing and explaining the potential short- and long-term side effects of these medications that may then be used for many years? Considerable discussion with the child and parents may be needed to address their concerns, balanced with benefits, and to make a plan for their access and use of stimulants (and other medications for ADHD not the topic here).
Consider the Side Effects
In children older than 6 years, some form of either a methylphenidate (MPH) or a dextroamphetamine (DA) class of stimulant have been shown to be equally effective in reducing symptoms of ADHD in about 77% of cases, but side effects are common, mostly mild, and mostly in the first months of use. These include reduced appetite, abdominal pain, headache, weight loss, tics, jitteriness, and delays in falling asleep. About half of all children treated will have one of these adverse effects over 5 years, with reduced appetite the most common. There is no difference in effectiveness or side effects by presentation type, i.e. hyperactive, inattentive, or combined, but the DA forms are associated with more side effects than MPH (10% vs. 6%). Medicated preschoolers have more and different side effects which, in addition to those above, may include listlessness, social withdrawal, and repetitive movements. Fortunately, we can reassure families that side effects can usually be readily managed by slower ramp up of dose, spacing to ensure appetite for meals, extra snacks, attention to bowel patterns and bedtime routines, or change in medication class.
Rates of tics while on stimulants are low irrespective of whether DA or MPH is used, and are usually transient, but difficult cases may occur, sometimes as part of Tourette’s, although not a contraindication. Additional side effects of concern are anxiety, irritability, sadness, and overfocusing that may require a change in class of stimulant or to a nonstimulant. Keep in mind that these symptoms may represent comorbid conditions to ADHD, warranting counseling intervention rather than being a medication side effect. Both initial assessment for ADHD and monitoring should look for comorbidities whether medication is used or not.
Measuring height, weight, pulse, and blood pressure should be part of ADHD care. How concerned should you and the family be about variations? Growth rate declines are more common in preschool children; in the PATS study height varied by 20.3%, and weight by 55.2%, more in heavier children. Growth can be protected by providing favored food for school, encouraging eating when hungry, and an evening fourth meal. You can reassure families that, even with continual use of stimulant medicines for years and initial deficits of 2 cm and 2.7 kg compared to expected, no significant differences remain in adulthood.
This longitudinal growth data was collected when short-acting stimulants were the usual, rather than the now common long-acting stimulants given 7 days per week, however. Children on transdermal MPH with 12-hour release over 3 years showed a small but significant delay in growth with the mean deficit rates 1.3 kg/year mainly in the first year, and 0.68 cm/year in height in the second year. If we see growth not recovering as it is expected to after the first year of treatment, we can advise shorter-acting forms, and medication “holidays” on weekends or vacations, that reduce but do not end the deficits. When concerned, a nonstimulant can be selected.
Blood pressure and pulse rate are predictably slightly increased on stimulants (about 2-4 mm Hg and about 3-6 bpm) but not clinically significantly. Although ECGs are not routinely recommended, careful consideration and consultation is warranted before starting stimulants for any patient with structural cardiac abnormalities, unexplained syncope, exertional chest pain, or a family history of sudden death in children or young adults. Neither current nor former users of stimulants for ADHD were found to have greater rates of cardiac events than the general population, however.
Misuse and abuse
Misuse and diversion of stimulants is common (e.g. 26% diverted MPH in the past month; 14% of 12th graders divert DA), often undetected, and potentially dangerous. And the problem is not limited to just the kids. Sixteen percent of parents reported diversion of stimulant medication to another household member, mainly to themselves. Stimulant overdose can occur, especially taken parenterally, and presents with dilated pupils, tremor, agitation, hyperreflexia, combative behavior, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, anxiety, paranoia, movement disorders, and/or seizures. Fortunately, overdose of prescribed stimulants is rarely fatal if medically managed, but recent “fake” Adderall (not from pharmacies) has been circulating. These fake drugs may contain lethal amounts of fentanyl or methamphetamine. Point out to families that a peer-provided stimulant not prescribed for them may have underlying medical or psychiatric issues that increase adverse events. Selling stimulants can have serious legal implications, with punishments ranging from fines to incarceration. A record of arrest during adolescence increases the likelihood of high school dropout, lack of 4-year college education, and later employment barriers. Besides these serious outcomes, it is useful to remind patients that if they deviate from your recommended dosing that you, and others, will not prescribe for them in the future the medication that has been supporting their successful functioning.
You can be fooled about being able to tell if your patients are misusing or diverting the stimulants you prescribe. Most (59%) physicians suspect that more than one of their patients with ADHD has diverted or feigned symptoms (66%) to get a prescription. Women were less likely to suspect their patients than are men, though, so be vigilant! Child psychiatrists had the highest suspicion with their greater proportion of patients with ADHD plus conduct or substance use disorder, who account for 83% of misusers/diverters. We can use education about misuse, pill counts, contracts on dosing, or switching to long-acting or nonstimulants to curb this.
Additional concerns
With more ADHD diagnosis and stimulants used for many years should we worry about longer-term issues? There have been reports in rodent models and a few children of chromosomal changes with stimulant exposure, but reviewers do not interpret these as an individual cancer risk. Record review of patients who received stimulants showed lower numbers of cancer than expected. Nor is there evidence of reproductive effects of stimulants, although use during pregnancy is not cleared.
Stimulants carry a boxed warning as having high potential for abuse and psychological or physical dependence, which is unsurprising given their effects on brain reward pathways. However, neither past nor present use of stimulants for ADHD has been associated with greater substance use long term.
To top off these issues, recent shortages of stimulants complicate ADHD management. Most states require electronic prescribing, US rules only allowing one transfer of such e-prescriptions. With many pharmacies refusing to tell families about availability, we must make multiple calls to locate a source. Pharmacists could help us by looking up patient names of abusers on the registry and identifying sites with adequate supplies.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Long-Term Follow-Up Emphasizes HPV Vaccination Importance
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to briefly discuss a critically important topic that cannot be overly emphasized. It is the relevance, the importance, the benefits, and the outcome of HPV vaccination.
The paper I’m referring to was published in Pediatrics in October 2023. It’s titled, “Ten-Year Follow-up of 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: Immunogenicity, Effectiveness, and Safety.”
Let me emphasize that we’re talking about a 10-year follow-up. In this particular paper and analysis, 301 boys — I emphasize boys — were included and 971 girls at 40 different sites in 13 countries, who received the 9-valent vaccine, which includes HPV 16, 18, and seven other types.
Most importantly, there was not a single case. Not one. Let me repeat this: There was not a single case of high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, or worse, or condyloma in either males or females. There was not a single case in over 1000 individuals with a follow-up of more than 10 years.
It is difficult to overstate the magnitude of the benefit associated with HPV vaccination for our children and young adults on their risk of developing highly relevant, life-changing, potentially deadly cancers.
For those of you who are interested in this topic — which should include almost all of you, if not all of you — I encourage you to read this very important follow-up paper, again, demonstrating the simple, overwhelming magnitude of the benefit of HPV vaccination. I thank you for your attention.
Dr. Markman is a professor in the department of medical oncology and therapeutics research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of medicine and science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix. He disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline; AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to briefly discuss a critically important topic that cannot be overly emphasized. It is the relevance, the importance, the benefits, and the outcome of HPV vaccination.
The paper I’m referring to was published in Pediatrics in October 2023. It’s titled, “Ten-Year Follow-up of 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: Immunogenicity, Effectiveness, and Safety.”
Let me emphasize that we’re talking about a 10-year follow-up. In this particular paper and analysis, 301 boys — I emphasize boys — were included and 971 girls at 40 different sites in 13 countries, who received the 9-valent vaccine, which includes HPV 16, 18, and seven other types.
Most importantly, there was not a single case. Not one. Let me repeat this: There was not a single case of high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, or worse, or condyloma in either males or females. There was not a single case in over 1000 individuals with a follow-up of more than 10 years.
It is difficult to overstate the magnitude of the benefit associated with HPV vaccination for our children and young adults on their risk of developing highly relevant, life-changing, potentially deadly cancers.
For those of you who are interested in this topic — which should include almost all of you, if not all of you — I encourage you to read this very important follow-up paper, again, demonstrating the simple, overwhelming magnitude of the benefit of HPV vaccination. I thank you for your attention.
Dr. Markman is a professor in the department of medical oncology and therapeutics research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of medicine and science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix. He disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline; AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I want to briefly discuss a critically important topic that cannot be overly emphasized. It is the relevance, the importance, the benefits, and the outcome of HPV vaccination.
The paper I’m referring to was published in Pediatrics in October 2023. It’s titled, “Ten-Year Follow-up of 9-Valent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: Immunogenicity, Effectiveness, and Safety.”
Let me emphasize that we’re talking about a 10-year follow-up. In this particular paper and analysis, 301 boys — I emphasize boys — were included and 971 girls at 40 different sites in 13 countries, who received the 9-valent vaccine, which includes HPV 16, 18, and seven other types.
Most importantly, there was not a single case. Not one. Let me repeat this: There was not a single case of high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, or worse, or condyloma in either males or females. There was not a single case in over 1000 individuals with a follow-up of more than 10 years.
It is difficult to overstate the magnitude of the benefit associated with HPV vaccination for our children and young adults on their risk of developing highly relevant, life-changing, potentially deadly cancers.
For those of you who are interested in this topic — which should include almost all of you, if not all of you — I encourage you to read this very important follow-up paper, again, demonstrating the simple, overwhelming magnitude of the benefit of HPV vaccination. I thank you for your attention.
Dr. Markman is a professor in the department of medical oncology and therapeutics research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of medicine and science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix. He disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline; AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tapinarof Cream Under FDA Review for Atopic Dermatitis Indication
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.