User login
Silent Epidemic: Loneliness a Serious Threat to Both Brain and Body
In a world that is more connected than ever, a silent epidemic is taking its toll. Overall, one in three US adults report chronic loneliness — a condition so detrimental that it rivals smoking and obesity with respect to its negative effect on health and well-being. From anxiety and depression to life-threatening conditions like cardiovascular disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, loneliness is more than an emotion — it’s a serious threat to both the brain and body.
In 2023, a US Surgeon General advisory raised the alarm about the national problem of loneliness and isolation, describing it as an epidemic.
“Given the significant health consequences of loneliness and isolation, we must prioritize building social connection in the same way we have prioritized other critical public health issues such as tobacco, obesity, and substance use disorders. Together, we can build a country that’s healthier, more resilient, less lonely, and more connected,” the report concluded.
But how, exactly, does chronic loneliness affect the physiology and function of the brain? What does the latest research reveal about the link between loneliness and neurologic and psychiatric illness, and what can clinicians do to address the issue?
This news organization spoke to multiple experts in the field to explore these issues.
A Major Risk Factor
Anna Finley, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at North Dakota State University, Fargo, explained that loneliness and social isolation are different entities. Social isolation is an objective measure of the number of people someone interacts with on a regular basis, whereas loneliness is a subjective feeling that occurs when close connections are lacking.
“These two things are not actually as related as you think they would be. People can feel lonely in a crowd or feel well connected with only a few friendships. It’s more about the quality of the connection and the quality of your perception of it. So someone could be in some very supportive relationships but still feel that there’s something missing,” she said in an interview.
So what do we know about how loneliness affects health? Evidence supporting the hypothesis that loneliness is an emerging risk factor for many diseases is steadily building.
Recently, the American Heart Association published a statement summarizing the evidence for a direct association between social isolation and loneliness and coronary heart disease and stroke mortality.
In addition, many studies have shown that individuals experiencing social isolation or loneliness have an increased risk for anxiety and depression, dementia, infectious disease, hospitalization, and all-cause death, even after adjusting for age and many other traditional risk factors.
One study revealed that eliminating loneliness has the potential to prevent nearly 20% of cases of depression in adults aged 50 years or older.
Indu Subramanian, MD, professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues conducted a study involving patients with Parkinson’s disease, which showed that the negative impact of loneliness on disease severity was as significant as the positive effects of 30 minutes of daily exercise.
“The importance of loneliness is under-recognized and undervalued, and it poses a major risk for health outcomes and quality of life,” said Subramanian.
Subramanian noted that loneliness is stigmatizing, causing people to feel unlikable and blame themselves, which prevents them from opening up to doctors or loved ones about their struggle. At the same time, healthcare providers may not think to ask about loneliness or know about potential interventions. She emphasized that much more work is needed to address this issue.
Early Mortality Risk
Julianne Holt-Lunstad, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah, is the author of two large meta-analyses that suggest loneliness, social isolation, or living alone are independent risk factors for early mortality, increasing this risk by about a third — the equivalent to the risk of smoking 15 cigarettes per day.
“We have quite robust evidence across a number of health outcomes implicating the harmful effects of loneliness and social isolation. While these are observational studies and show mainly associations, we do have evidence from longitudinal studies that show lacking social connection, whether that be loneliness or social isolation, predicts subsequent worse outcomes, and most of these studies have adjusted for alternative kinds of explanations, like age, initial health status, lifestyle factors,” Holt-Lunstad said.
There is some evidence to suggest that isolation is more predictive of physical health outcomes, whereas loneliness is more predictive of mental health outcomes. That said, both isolation and loneliness have significant effects on mental and physical health outcomes, she noted.
There is also the question of whether loneliness is causing poor health or whether people who are in poor health feel lonely because poor health can lead to social isolation.
Finley said there’s probably a bit of both going on, but longitudinal studies, where loneliness is measured at a fixed timepoint then health outcomes are reported a few years later, suggest that loneliness is contributing to these adverse outcomes.
She added that there is also some evidence in animal models to suggest that loneliness is a causal risk factor for adverse health outcomes. “But you can’t ask a mouse or rat how lonely they’re feeling. All you can do is house them individually — removing them from social connection. This isn’t necessarily the same thing as loneliness in humans.”
Finley is studying mechanisms in the brain that may be involved in mediating the adverse health consequences of loneliness.
“What I’ve been seeing in the data so far is that it tends to be the self-report of how lonely folks are feeling that has the associations with differences in the brain, as opposed to the number of social connections people have. It does seem to be the more subjective, emotional perception of loneliness that is important.”
In a review of potential mechanisms involved, she concluded that it is dysregulated emotions and altered perceptions of social interactions that has profound impacts on the brain, suggesting that people who are lonely may have a tendency to interpret social cues in a negative way, preventing them from forming productive positive relationships.
Lack of Trust
One researcher who has studied this phenomenon is Dirk Scheele, PhD, professor of social neuroscience at Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
“We were interested to find out why people remained lonely,” he said in an interview. “Loneliness is an unpleasant experience, and there are so many opportunities for social contacts nowadays, it’s not really clear at first sight why people are chronically lonely.”
To examine this question, Scheele and his team conducted a study in which functional MRI was used to examine the brain in otherwise healthy individuals with high or low loneliness scores while they played a trust game.
They also simulated a positive social interaction between participants and researchers, in which they talked about plans for a fictitious lottery win, and about their hobbies and interests, during which mood was measured with questionnaires, and saliva samples were collected to measure hormone levels.
Results showed that the high-lonely individuals had reduced activation in the insula cortex during the trust decisions. “This area of the brain is involved in the processing of bodily signals, such as ‘gut feelings.’ So reduced activity here could be interpreted as fewer gut feelings on who can be trusted,” Scheele explained.
The high-lonely individuals also had reduced responsiveness to the positive social interaction with a lower release of oxytocin and a smaller elevation in mood compared with the control individuals.
Scheele pointed out that there is some evidence that oxytocin might increase trust, and there is reduced release of endogenous oxytocin in high loneliness.
“Our results are consistent with the idea that loneliness is associated with negative biases about other people. So if we expect negative things from other people — for instance, that they cannot be trusted — then that would hamper further social interactions and could lead to loneliness,” he added.
A Role for Oxytocin?
In another study, the same researchers tested short-term (five weekly sessions) group psychotherapy to reduce loneliness using established techniques to target these negative biases. They also investigated whether the effects of this group psychotherapy could be augmented by administering intranasal oxytocin (vs placebo) before the group psychotherapy sessions.
Results showed that the group psychotherapy intervention reduced trait loneliness (loneliness experienced over a prolonged period). The oxytocin did not show a significant effect on trait loneliness, but there was a suggestion that it may enhance the reduction in state loneliness (how someone is feeling at a specific time) brought about by the psychotherapy sessions.
“We found that bonding within the groups was experienced as more positive in the oxytocin treated groups. It is possible that a longer intervention would be helpful for longer-term results,” Scheele concluded. “It’s not going to be a quick fix for loneliness, but there may be a role for oxytocin as an adjunct to psychotherapy.”
A Basic Human Need
Another loneliness researcher, Livia Tomova, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at Cardiff University in Wales, has used social isolation to induce loneliness in young people and found that this intervention was linked to brain patterns similar to those associated with hunger.
“We know that the drive to eat food is a very basic human need. We know quite well how it is represented in the brain,” she explained.
The researchers tested how the brains of the participants responded to seeing pictures of social interactions after they underwent a prolonged period of social isolation. In a subsequent session, the same people were asked to undergo food fasting and then underwent brain scans when looking at pictures of food. Results showed that the neural patterns were similar in the two situations with increased activity in the substantia nigra area within the midbrain.
“This area of the brain processes rewards and motivation. It consists primarily of dopamine neurons and increased activity corresponds to a feeling of craving something. So this area of the brain that controls essential homeostatic needs is activated when people feel lonely, suggesting that our need for social contact with others is potentially a very basic need similar to eating,” Tomova said.
Lower Gray Matter Volumes in Key Brain Areas
And another group from Germany has found that higher loneliness scores are negatively associated with specific brain regions responsible for memory, emotion regulation, and social processing.
Sandra Düzel, PhD, and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development and the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, both in Berlin, Germany, reported a study in which individuals who reported higher loneliness had smaller gray matter volumes in brain regions such as the left amygdala, anterior hippocampus, and cerebellum, regions which are crucial for both emotional regulation and higher-order cognitive processes, such as self-reflection and executive function.
Düzel believes that possible mechanisms behind the link between loneliness and brain volume differences could include stress-related damage, with prolonged loneliness associated with elevated levels of stress hormones, which can damage the hippocampus over time, and reduced cognitive and social stimulation, which may contribute to brain volume reductions in regions critical for memory and emotional processing.
“Loneliness is often characterized by reduced social and environmental diversity, leading to less engagement with novel experiences and potentially lower hippocampal-striatal connectivity.
Since novelty-seeking and environmental diversity are associated with positive emotional states, individuals experiencing loneliness might benefit from increased exposure to new environments which could stimulate the brain’s reward circuits, fostering positive affect and potentially mitigating the emotional burden of loneliness,” she said.
Is Social Prescribing the Answer?
So are there enough data now to act and attempt to develop interventions to reduce loneliness? Most of these researchers believe so.
“I think we have enough information to act on this now. There are a number of national academies consensus reports, which suggest that, while certainly there are still gaps in our evidence and more to be learned, there is sufficient evidence that a concerning portion of the population seems to lack connection, and that the consequences are serious enough that we need to do something about it,” said Holt-Lunstad.
Some countries have introduced social prescribing where doctors can prescribe a group activity or a regular visit or telephone conversation with a supportive person.
Subramanian pointed out that it’s easier to implement in countries with national health services and may be more difficult to embrace in the US healthcare system.
“We are not so encouraged from a financial perspective to think about preventive care in the US. We don’t have an easy way to recognize in any tangible way the downstream of such activities in terms of preventing future problems. That is something we need to work on,” she said.
Finley cautioned that to work well, social prescribing will require an understanding of each person’s individual situation.
“Some people may only receive benefit of interacting with others if they are also getting some sort of support to address the social and emotional concerns that are tagging along with loneliness. I’m not sure that just telling people to go join their local gardening club or whatever will be the correct answer for everyone.”
She pointed out that many people will have issues in their life that are making it hard for them to be social. These could be mobility or financial challenges, care responsibilities, or concerns about illnesses or life events. “We need to figure out what would have the most bang for the person’s buck, so to speak, as an intervention. That could mean connecting them to a group relevant to their individual situation.”
Opportunity to Connect Not Enough?
Tomova believes that training people in social skills may be a better option. “It appears that some people who are chronically lonely seem to struggle to make relationships with others. So just encouraging them to interact with others more will not necessarily help. We need to better understand the pathways involved and who are the people who become ill. We can then develop and target better interventions and teach people coping strategies for that situation.”
Scheele agreed. “While just giving people the opportunity to connect may work for some, others who are experiencing really chronic loneliness may not benefit very much from this unless their negative belief systems are addressed.” He suggested some sort of psychotherapy may be helpful in this situation.
But at least all seem to agree that healthcare providers need to be more aware of loneliness as a health risk factor, try to identify people at risk, and to think about how best to support them.
Holt-Lunstad noted that one of the recommendations in the US Surgeon General’s advisory was to increase the education, training, and resources on loneliness for healthcare providers.
“If we want this to be addressed, we need to give healthcare providers the time, resources, and training in order to do that, otherwise, we are adding one more thing to an already overburdened system. They need to understand how important it is, and how it might help them take care of the patient.”
“Our hope is that we can start to reverse some of the trends that we are seeing, both in terms of the prevalence rates of loneliness, but also that we could start seeing improvements in health and other kinds of outcomes,” she concluded.
Progress is being made in increasing awareness about the dangers of chronic loneliness. It’s now recognized as a serious health risk, but there are actionable steps that can help. Loneliness doesn’t have to be a permanent condition for anyone, said Scheele.
Holt-Lunstad served as an adviser for Foundation for Social Connection, Global Initiative on Loneliness and Connection, and Nextdoor Neighborhood Vitality Board and received research grants/income from Templeton Foundation, Eventbrite, Foundation for Social Connection, and Triple-S Foundation. Subramanian served as a speaker bureau for Acorda Pharma. The other researchers reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a world that is more connected than ever, a silent epidemic is taking its toll. Overall, one in three US adults report chronic loneliness — a condition so detrimental that it rivals smoking and obesity with respect to its negative effect on health and well-being. From anxiety and depression to life-threatening conditions like cardiovascular disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, loneliness is more than an emotion — it’s a serious threat to both the brain and body.
In 2023, a US Surgeon General advisory raised the alarm about the national problem of loneliness and isolation, describing it as an epidemic.
“Given the significant health consequences of loneliness and isolation, we must prioritize building social connection in the same way we have prioritized other critical public health issues such as tobacco, obesity, and substance use disorders. Together, we can build a country that’s healthier, more resilient, less lonely, and more connected,” the report concluded.
But how, exactly, does chronic loneliness affect the physiology and function of the brain? What does the latest research reveal about the link between loneliness and neurologic and psychiatric illness, and what can clinicians do to address the issue?
This news organization spoke to multiple experts in the field to explore these issues.
A Major Risk Factor
Anna Finley, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at North Dakota State University, Fargo, explained that loneliness and social isolation are different entities. Social isolation is an objective measure of the number of people someone interacts with on a regular basis, whereas loneliness is a subjective feeling that occurs when close connections are lacking.
“These two things are not actually as related as you think they would be. People can feel lonely in a crowd or feel well connected with only a few friendships. It’s more about the quality of the connection and the quality of your perception of it. So someone could be in some very supportive relationships but still feel that there’s something missing,” she said in an interview.
So what do we know about how loneliness affects health? Evidence supporting the hypothesis that loneliness is an emerging risk factor for many diseases is steadily building.
Recently, the American Heart Association published a statement summarizing the evidence for a direct association between social isolation and loneliness and coronary heart disease and stroke mortality.
In addition, many studies have shown that individuals experiencing social isolation or loneliness have an increased risk for anxiety and depression, dementia, infectious disease, hospitalization, and all-cause death, even after adjusting for age and many other traditional risk factors.
One study revealed that eliminating loneliness has the potential to prevent nearly 20% of cases of depression in adults aged 50 years or older.
Indu Subramanian, MD, professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues conducted a study involving patients with Parkinson’s disease, which showed that the negative impact of loneliness on disease severity was as significant as the positive effects of 30 minutes of daily exercise.
“The importance of loneliness is under-recognized and undervalued, and it poses a major risk for health outcomes and quality of life,” said Subramanian.
Subramanian noted that loneliness is stigmatizing, causing people to feel unlikable and blame themselves, which prevents them from opening up to doctors or loved ones about their struggle. At the same time, healthcare providers may not think to ask about loneliness or know about potential interventions. She emphasized that much more work is needed to address this issue.
Early Mortality Risk
Julianne Holt-Lunstad, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah, is the author of two large meta-analyses that suggest loneliness, social isolation, or living alone are independent risk factors for early mortality, increasing this risk by about a third — the equivalent to the risk of smoking 15 cigarettes per day.
“We have quite robust evidence across a number of health outcomes implicating the harmful effects of loneliness and social isolation. While these are observational studies and show mainly associations, we do have evidence from longitudinal studies that show lacking social connection, whether that be loneliness or social isolation, predicts subsequent worse outcomes, and most of these studies have adjusted for alternative kinds of explanations, like age, initial health status, lifestyle factors,” Holt-Lunstad said.
There is some evidence to suggest that isolation is more predictive of physical health outcomes, whereas loneliness is more predictive of mental health outcomes. That said, both isolation and loneliness have significant effects on mental and physical health outcomes, she noted.
There is also the question of whether loneliness is causing poor health or whether people who are in poor health feel lonely because poor health can lead to social isolation.
Finley said there’s probably a bit of both going on, but longitudinal studies, where loneliness is measured at a fixed timepoint then health outcomes are reported a few years later, suggest that loneliness is contributing to these adverse outcomes.
She added that there is also some evidence in animal models to suggest that loneliness is a causal risk factor for adverse health outcomes. “But you can’t ask a mouse or rat how lonely they’re feeling. All you can do is house them individually — removing them from social connection. This isn’t necessarily the same thing as loneliness in humans.”
Finley is studying mechanisms in the brain that may be involved in mediating the adverse health consequences of loneliness.
“What I’ve been seeing in the data so far is that it tends to be the self-report of how lonely folks are feeling that has the associations with differences in the brain, as opposed to the number of social connections people have. It does seem to be the more subjective, emotional perception of loneliness that is important.”
In a review of potential mechanisms involved, she concluded that it is dysregulated emotions and altered perceptions of social interactions that has profound impacts on the brain, suggesting that people who are lonely may have a tendency to interpret social cues in a negative way, preventing them from forming productive positive relationships.
Lack of Trust
One researcher who has studied this phenomenon is Dirk Scheele, PhD, professor of social neuroscience at Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
“We were interested to find out why people remained lonely,” he said in an interview. “Loneliness is an unpleasant experience, and there are so many opportunities for social contacts nowadays, it’s not really clear at first sight why people are chronically lonely.”
To examine this question, Scheele and his team conducted a study in which functional MRI was used to examine the brain in otherwise healthy individuals with high or low loneliness scores while they played a trust game.
They also simulated a positive social interaction between participants and researchers, in which they talked about plans for a fictitious lottery win, and about their hobbies and interests, during which mood was measured with questionnaires, and saliva samples were collected to measure hormone levels.
Results showed that the high-lonely individuals had reduced activation in the insula cortex during the trust decisions. “This area of the brain is involved in the processing of bodily signals, such as ‘gut feelings.’ So reduced activity here could be interpreted as fewer gut feelings on who can be trusted,” Scheele explained.
The high-lonely individuals also had reduced responsiveness to the positive social interaction with a lower release of oxytocin and a smaller elevation in mood compared with the control individuals.
Scheele pointed out that there is some evidence that oxytocin might increase trust, and there is reduced release of endogenous oxytocin in high loneliness.
“Our results are consistent with the idea that loneliness is associated with negative biases about other people. So if we expect negative things from other people — for instance, that they cannot be trusted — then that would hamper further social interactions and could lead to loneliness,” he added.
A Role for Oxytocin?
In another study, the same researchers tested short-term (five weekly sessions) group psychotherapy to reduce loneliness using established techniques to target these negative biases. They also investigated whether the effects of this group psychotherapy could be augmented by administering intranasal oxytocin (vs placebo) before the group psychotherapy sessions.
Results showed that the group psychotherapy intervention reduced trait loneliness (loneliness experienced over a prolonged period). The oxytocin did not show a significant effect on trait loneliness, but there was a suggestion that it may enhance the reduction in state loneliness (how someone is feeling at a specific time) brought about by the psychotherapy sessions.
“We found that bonding within the groups was experienced as more positive in the oxytocin treated groups. It is possible that a longer intervention would be helpful for longer-term results,” Scheele concluded. “It’s not going to be a quick fix for loneliness, but there may be a role for oxytocin as an adjunct to psychotherapy.”
A Basic Human Need
Another loneliness researcher, Livia Tomova, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at Cardiff University in Wales, has used social isolation to induce loneliness in young people and found that this intervention was linked to brain patterns similar to those associated with hunger.
“We know that the drive to eat food is a very basic human need. We know quite well how it is represented in the brain,” she explained.
The researchers tested how the brains of the participants responded to seeing pictures of social interactions after they underwent a prolonged period of social isolation. In a subsequent session, the same people were asked to undergo food fasting and then underwent brain scans when looking at pictures of food. Results showed that the neural patterns were similar in the two situations with increased activity in the substantia nigra area within the midbrain.
“This area of the brain processes rewards and motivation. It consists primarily of dopamine neurons and increased activity corresponds to a feeling of craving something. So this area of the brain that controls essential homeostatic needs is activated when people feel lonely, suggesting that our need for social contact with others is potentially a very basic need similar to eating,” Tomova said.
Lower Gray Matter Volumes in Key Brain Areas
And another group from Germany has found that higher loneliness scores are negatively associated with specific brain regions responsible for memory, emotion regulation, and social processing.
Sandra Düzel, PhD, and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development and the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, both in Berlin, Germany, reported a study in which individuals who reported higher loneliness had smaller gray matter volumes in brain regions such as the left amygdala, anterior hippocampus, and cerebellum, regions which are crucial for both emotional regulation and higher-order cognitive processes, such as self-reflection and executive function.
Düzel believes that possible mechanisms behind the link between loneliness and brain volume differences could include stress-related damage, with prolonged loneliness associated with elevated levels of stress hormones, which can damage the hippocampus over time, and reduced cognitive and social stimulation, which may contribute to brain volume reductions in regions critical for memory and emotional processing.
“Loneliness is often characterized by reduced social and environmental diversity, leading to less engagement with novel experiences and potentially lower hippocampal-striatal connectivity.
Since novelty-seeking and environmental diversity are associated with positive emotional states, individuals experiencing loneliness might benefit from increased exposure to new environments which could stimulate the brain’s reward circuits, fostering positive affect and potentially mitigating the emotional burden of loneliness,” she said.
Is Social Prescribing the Answer?
So are there enough data now to act and attempt to develop interventions to reduce loneliness? Most of these researchers believe so.
“I think we have enough information to act on this now. There are a number of national academies consensus reports, which suggest that, while certainly there are still gaps in our evidence and more to be learned, there is sufficient evidence that a concerning portion of the population seems to lack connection, and that the consequences are serious enough that we need to do something about it,” said Holt-Lunstad.
Some countries have introduced social prescribing where doctors can prescribe a group activity or a regular visit or telephone conversation with a supportive person.
Subramanian pointed out that it’s easier to implement in countries with national health services and may be more difficult to embrace in the US healthcare system.
“We are not so encouraged from a financial perspective to think about preventive care in the US. We don’t have an easy way to recognize in any tangible way the downstream of such activities in terms of preventing future problems. That is something we need to work on,” she said.
Finley cautioned that to work well, social prescribing will require an understanding of each person’s individual situation.
“Some people may only receive benefit of interacting with others if they are also getting some sort of support to address the social and emotional concerns that are tagging along with loneliness. I’m not sure that just telling people to go join their local gardening club or whatever will be the correct answer for everyone.”
She pointed out that many people will have issues in their life that are making it hard for them to be social. These could be mobility or financial challenges, care responsibilities, or concerns about illnesses or life events. “We need to figure out what would have the most bang for the person’s buck, so to speak, as an intervention. That could mean connecting them to a group relevant to their individual situation.”
Opportunity to Connect Not Enough?
Tomova believes that training people in social skills may be a better option. “It appears that some people who are chronically lonely seem to struggle to make relationships with others. So just encouraging them to interact with others more will not necessarily help. We need to better understand the pathways involved and who are the people who become ill. We can then develop and target better interventions and teach people coping strategies for that situation.”
Scheele agreed. “While just giving people the opportunity to connect may work for some, others who are experiencing really chronic loneliness may not benefit very much from this unless their negative belief systems are addressed.” He suggested some sort of psychotherapy may be helpful in this situation.
But at least all seem to agree that healthcare providers need to be more aware of loneliness as a health risk factor, try to identify people at risk, and to think about how best to support them.
Holt-Lunstad noted that one of the recommendations in the US Surgeon General’s advisory was to increase the education, training, and resources on loneliness for healthcare providers.
“If we want this to be addressed, we need to give healthcare providers the time, resources, and training in order to do that, otherwise, we are adding one more thing to an already overburdened system. They need to understand how important it is, and how it might help them take care of the patient.”
“Our hope is that we can start to reverse some of the trends that we are seeing, both in terms of the prevalence rates of loneliness, but also that we could start seeing improvements in health and other kinds of outcomes,” she concluded.
Progress is being made in increasing awareness about the dangers of chronic loneliness. It’s now recognized as a serious health risk, but there are actionable steps that can help. Loneliness doesn’t have to be a permanent condition for anyone, said Scheele.
Holt-Lunstad served as an adviser for Foundation for Social Connection, Global Initiative on Loneliness and Connection, and Nextdoor Neighborhood Vitality Board and received research grants/income from Templeton Foundation, Eventbrite, Foundation for Social Connection, and Triple-S Foundation. Subramanian served as a speaker bureau for Acorda Pharma. The other researchers reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a world that is more connected than ever, a silent epidemic is taking its toll. Overall, one in three US adults report chronic loneliness — a condition so detrimental that it rivals smoking and obesity with respect to its negative effect on health and well-being. From anxiety and depression to life-threatening conditions like cardiovascular disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, loneliness is more than an emotion — it’s a serious threat to both the brain and body.
In 2023, a US Surgeon General advisory raised the alarm about the national problem of loneliness and isolation, describing it as an epidemic.
“Given the significant health consequences of loneliness and isolation, we must prioritize building social connection in the same way we have prioritized other critical public health issues such as tobacco, obesity, and substance use disorders. Together, we can build a country that’s healthier, more resilient, less lonely, and more connected,” the report concluded.
But how, exactly, does chronic loneliness affect the physiology and function of the brain? What does the latest research reveal about the link between loneliness and neurologic and psychiatric illness, and what can clinicians do to address the issue?
This news organization spoke to multiple experts in the field to explore these issues.
A Major Risk Factor
Anna Finley, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at North Dakota State University, Fargo, explained that loneliness and social isolation are different entities. Social isolation is an objective measure of the number of people someone interacts with on a regular basis, whereas loneliness is a subjective feeling that occurs when close connections are lacking.
“These two things are not actually as related as you think they would be. People can feel lonely in a crowd or feel well connected with only a few friendships. It’s more about the quality of the connection and the quality of your perception of it. So someone could be in some very supportive relationships but still feel that there’s something missing,” she said in an interview.
So what do we know about how loneliness affects health? Evidence supporting the hypothesis that loneliness is an emerging risk factor for many diseases is steadily building.
Recently, the American Heart Association published a statement summarizing the evidence for a direct association between social isolation and loneliness and coronary heart disease and stroke mortality.
In addition, many studies have shown that individuals experiencing social isolation or loneliness have an increased risk for anxiety and depression, dementia, infectious disease, hospitalization, and all-cause death, even after adjusting for age and many other traditional risk factors.
One study revealed that eliminating loneliness has the potential to prevent nearly 20% of cases of depression in adults aged 50 years or older.
Indu Subramanian, MD, professor of neurology at the University of California, Los Angeles, and colleagues conducted a study involving patients with Parkinson’s disease, which showed that the negative impact of loneliness on disease severity was as significant as the positive effects of 30 minutes of daily exercise.
“The importance of loneliness is under-recognized and undervalued, and it poses a major risk for health outcomes and quality of life,” said Subramanian.
Subramanian noted that loneliness is stigmatizing, causing people to feel unlikable and blame themselves, which prevents them from opening up to doctors or loved ones about their struggle. At the same time, healthcare providers may not think to ask about loneliness or know about potential interventions. She emphasized that much more work is needed to address this issue.
Early Mortality Risk
Julianne Holt-Lunstad, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah, is the author of two large meta-analyses that suggest loneliness, social isolation, or living alone are independent risk factors for early mortality, increasing this risk by about a third — the equivalent to the risk of smoking 15 cigarettes per day.
“We have quite robust evidence across a number of health outcomes implicating the harmful effects of loneliness and social isolation. While these are observational studies and show mainly associations, we do have evidence from longitudinal studies that show lacking social connection, whether that be loneliness or social isolation, predicts subsequent worse outcomes, and most of these studies have adjusted for alternative kinds of explanations, like age, initial health status, lifestyle factors,” Holt-Lunstad said.
There is some evidence to suggest that isolation is more predictive of physical health outcomes, whereas loneliness is more predictive of mental health outcomes. That said, both isolation and loneliness have significant effects on mental and physical health outcomes, she noted.
There is also the question of whether loneliness is causing poor health or whether people who are in poor health feel lonely because poor health can lead to social isolation.
Finley said there’s probably a bit of both going on, but longitudinal studies, where loneliness is measured at a fixed timepoint then health outcomes are reported a few years later, suggest that loneliness is contributing to these adverse outcomes.
She added that there is also some evidence in animal models to suggest that loneliness is a causal risk factor for adverse health outcomes. “But you can’t ask a mouse or rat how lonely they’re feeling. All you can do is house them individually — removing them from social connection. This isn’t necessarily the same thing as loneliness in humans.”
Finley is studying mechanisms in the brain that may be involved in mediating the adverse health consequences of loneliness.
“What I’ve been seeing in the data so far is that it tends to be the self-report of how lonely folks are feeling that has the associations with differences in the brain, as opposed to the number of social connections people have. It does seem to be the more subjective, emotional perception of loneliness that is important.”
In a review of potential mechanisms involved, she concluded that it is dysregulated emotions and altered perceptions of social interactions that has profound impacts on the brain, suggesting that people who are lonely may have a tendency to interpret social cues in a negative way, preventing them from forming productive positive relationships.
Lack of Trust
One researcher who has studied this phenomenon is Dirk Scheele, PhD, professor of social neuroscience at Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
“We were interested to find out why people remained lonely,” he said in an interview. “Loneliness is an unpleasant experience, and there are so many opportunities for social contacts nowadays, it’s not really clear at first sight why people are chronically lonely.”
To examine this question, Scheele and his team conducted a study in which functional MRI was used to examine the brain in otherwise healthy individuals with high or low loneliness scores while they played a trust game.
They also simulated a positive social interaction between participants and researchers, in which they talked about plans for a fictitious lottery win, and about their hobbies and interests, during which mood was measured with questionnaires, and saliva samples were collected to measure hormone levels.
Results showed that the high-lonely individuals had reduced activation in the insula cortex during the trust decisions. “This area of the brain is involved in the processing of bodily signals, such as ‘gut feelings.’ So reduced activity here could be interpreted as fewer gut feelings on who can be trusted,” Scheele explained.
The high-lonely individuals also had reduced responsiveness to the positive social interaction with a lower release of oxytocin and a smaller elevation in mood compared with the control individuals.
Scheele pointed out that there is some evidence that oxytocin might increase trust, and there is reduced release of endogenous oxytocin in high loneliness.
“Our results are consistent with the idea that loneliness is associated with negative biases about other people. So if we expect negative things from other people — for instance, that they cannot be trusted — then that would hamper further social interactions and could lead to loneliness,” he added.
A Role for Oxytocin?
In another study, the same researchers tested short-term (five weekly sessions) group psychotherapy to reduce loneliness using established techniques to target these negative biases. They also investigated whether the effects of this group psychotherapy could be augmented by administering intranasal oxytocin (vs placebo) before the group psychotherapy sessions.
Results showed that the group psychotherapy intervention reduced trait loneliness (loneliness experienced over a prolonged period). The oxytocin did not show a significant effect on trait loneliness, but there was a suggestion that it may enhance the reduction in state loneliness (how someone is feeling at a specific time) brought about by the psychotherapy sessions.
“We found that bonding within the groups was experienced as more positive in the oxytocin treated groups. It is possible that a longer intervention would be helpful for longer-term results,” Scheele concluded. “It’s not going to be a quick fix for loneliness, but there may be a role for oxytocin as an adjunct to psychotherapy.”
A Basic Human Need
Another loneliness researcher, Livia Tomova, PhD, assistant professor of psychology at Cardiff University in Wales, has used social isolation to induce loneliness in young people and found that this intervention was linked to brain patterns similar to those associated with hunger.
“We know that the drive to eat food is a very basic human need. We know quite well how it is represented in the brain,” she explained.
The researchers tested how the brains of the participants responded to seeing pictures of social interactions after they underwent a prolonged period of social isolation. In a subsequent session, the same people were asked to undergo food fasting and then underwent brain scans when looking at pictures of food. Results showed that the neural patterns were similar in the two situations with increased activity in the substantia nigra area within the midbrain.
“This area of the brain processes rewards and motivation. It consists primarily of dopamine neurons and increased activity corresponds to a feeling of craving something. So this area of the brain that controls essential homeostatic needs is activated when people feel lonely, suggesting that our need for social contact with others is potentially a very basic need similar to eating,” Tomova said.
Lower Gray Matter Volumes in Key Brain Areas
And another group from Germany has found that higher loneliness scores are negatively associated with specific brain regions responsible for memory, emotion regulation, and social processing.
Sandra Düzel, PhD, and colleagues from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development and the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, both in Berlin, Germany, reported a study in which individuals who reported higher loneliness had smaller gray matter volumes in brain regions such as the left amygdala, anterior hippocampus, and cerebellum, regions which are crucial for both emotional regulation and higher-order cognitive processes, such as self-reflection and executive function.
Düzel believes that possible mechanisms behind the link between loneliness and brain volume differences could include stress-related damage, with prolonged loneliness associated with elevated levels of stress hormones, which can damage the hippocampus over time, and reduced cognitive and social stimulation, which may contribute to brain volume reductions in regions critical for memory and emotional processing.
“Loneliness is often characterized by reduced social and environmental diversity, leading to less engagement with novel experiences and potentially lower hippocampal-striatal connectivity.
Since novelty-seeking and environmental diversity are associated with positive emotional states, individuals experiencing loneliness might benefit from increased exposure to new environments which could stimulate the brain’s reward circuits, fostering positive affect and potentially mitigating the emotional burden of loneliness,” she said.
Is Social Prescribing the Answer?
So are there enough data now to act and attempt to develop interventions to reduce loneliness? Most of these researchers believe so.
“I think we have enough information to act on this now. There are a number of national academies consensus reports, which suggest that, while certainly there are still gaps in our evidence and more to be learned, there is sufficient evidence that a concerning portion of the population seems to lack connection, and that the consequences are serious enough that we need to do something about it,” said Holt-Lunstad.
Some countries have introduced social prescribing where doctors can prescribe a group activity or a regular visit or telephone conversation with a supportive person.
Subramanian pointed out that it’s easier to implement in countries with national health services and may be more difficult to embrace in the US healthcare system.
“We are not so encouraged from a financial perspective to think about preventive care in the US. We don’t have an easy way to recognize in any tangible way the downstream of such activities in terms of preventing future problems. That is something we need to work on,” she said.
Finley cautioned that to work well, social prescribing will require an understanding of each person’s individual situation.
“Some people may only receive benefit of interacting with others if they are also getting some sort of support to address the social and emotional concerns that are tagging along with loneliness. I’m not sure that just telling people to go join their local gardening club or whatever will be the correct answer for everyone.”
She pointed out that many people will have issues in their life that are making it hard for them to be social. These could be mobility or financial challenges, care responsibilities, or concerns about illnesses or life events. “We need to figure out what would have the most bang for the person’s buck, so to speak, as an intervention. That could mean connecting them to a group relevant to their individual situation.”
Opportunity to Connect Not Enough?
Tomova believes that training people in social skills may be a better option. “It appears that some people who are chronically lonely seem to struggle to make relationships with others. So just encouraging them to interact with others more will not necessarily help. We need to better understand the pathways involved and who are the people who become ill. We can then develop and target better interventions and teach people coping strategies for that situation.”
Scheele agreed. “While just giving people the opportunity to connect may work for some, others who are experiencing really chronic loneliness may not benefit very much from this unless their negative belief systems are addressed.” He suggested some sort of psychotherapy may be helpful in this situation.
But at least all seem to agree that healthcare providers need to be more aware of loneliness as a health risk factor, try to identify people at risk, and to think about how best to support them.
Holt-Lunstad noted that one of the recommendations in the US Surgeon General’s advisory was to increase the education, training, and resources on loneliness for healthcare providers.
“If we want this to be addressed, we need to give healthcare providers the time, resources, and training in order to do that, otherwise, we are adding one more thing to an already overburdened system. They need to understand how important it is, and how it might help them take care of the patient.”
“Our hope is that we can start to reverse some of the trends that we are seeing, both in terms of the prevalence rates of loneliness, but also that we could start seeing improvements in health and other kinds of outcomes,” she concluded.
Progress is being made in increasing awareness about the dangers of chronic loneliness. It’s now recognized as a serious health risk, but there are actionable steps that can help. Loneliness doesn’t have to be a permanent condition for anyone, said Scheele.
Holt-Lunstad served as an adviser for Foundation for Social Connection, Global Initiative on Loneliness and Connection, and Nextdoor Neighborhood Vitality Board and received research grants/income from Templeton Foundation, Eventbrite, Foundation for Social Connection, and Triple-S Foundation. Subramanian served as a speaker bureau for Acorda Pharma. The other researchers reported no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lichenoid Drug Eruption Secondary to Apalutamide Treatment
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
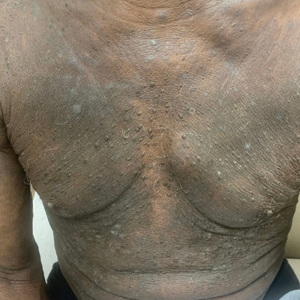
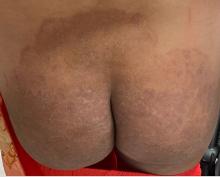
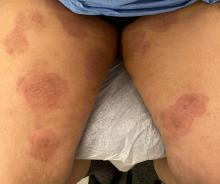
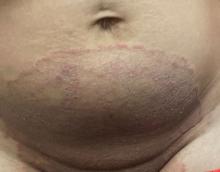
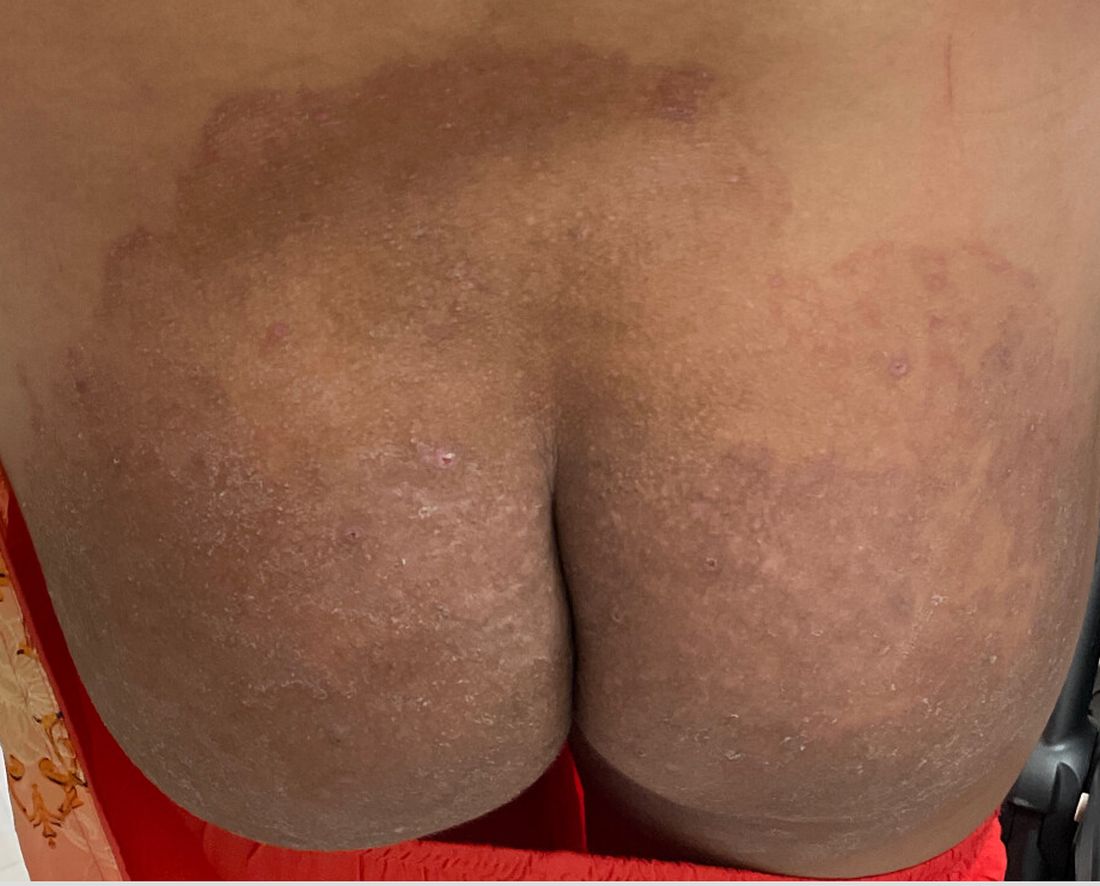
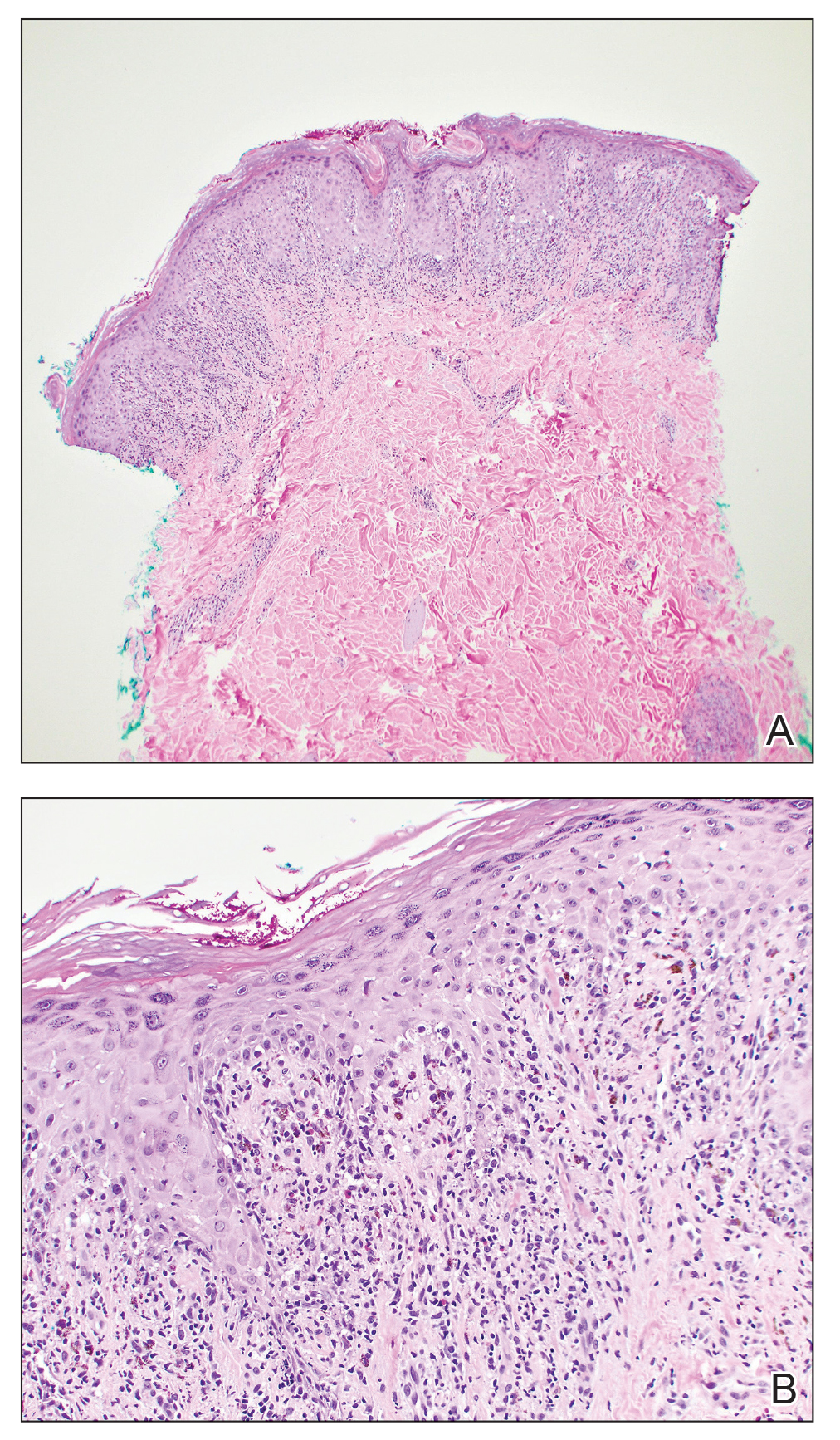
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.
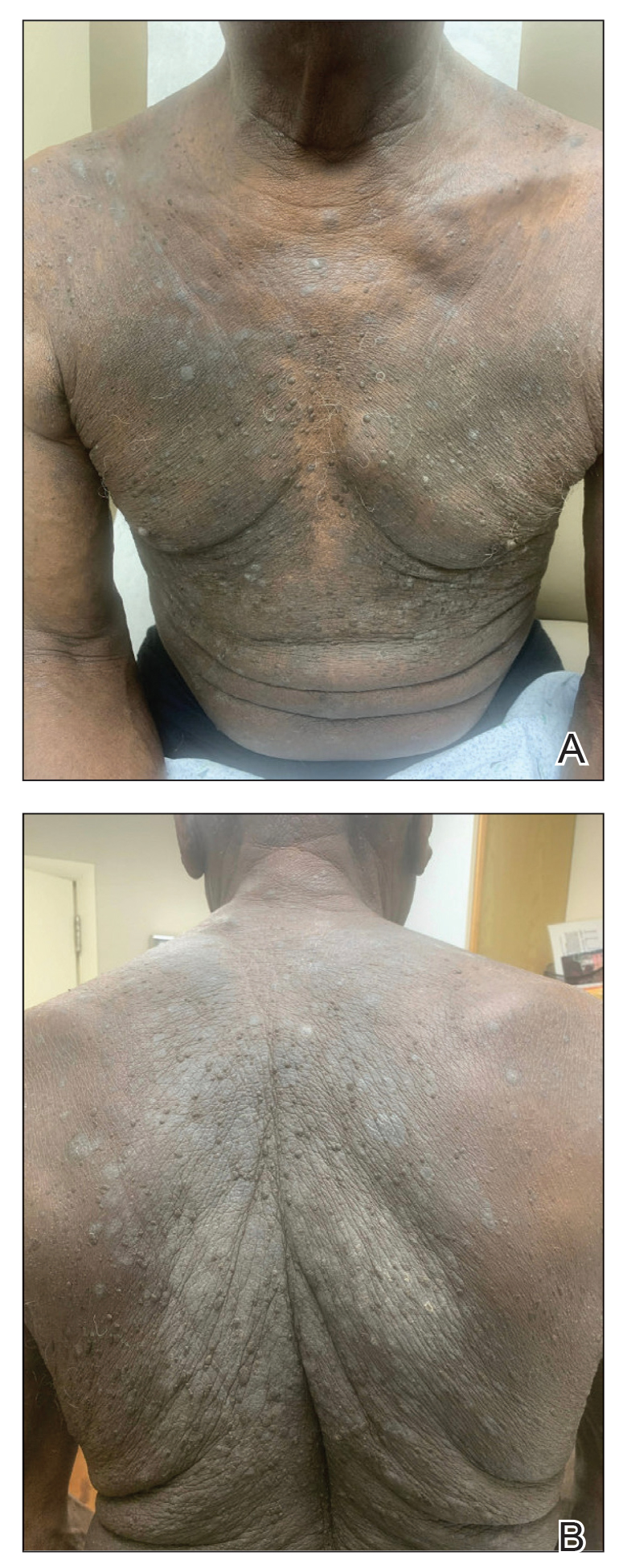
Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.


Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.


Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
Practice Points
- Although it is rare, patients can develop lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to treatment with second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide.
- If a patient develops a lichenoid drug eruption while taking a specific second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist, the entire class of medications should not be ruled out, as some patients can tolerate other drugs from that class.
Social Adversity Increases Mortality Risk in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON — Social adversity is associated with worse survival among patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH), according to a new retrospective study of a New York City population.
A sub-analysis of both HIV+ and HIV– patients showed worse mortality outcomes with social adversity in both groups.
“Almost the majority of patients that we treat have either some social adversity or no insurance or are undocumented, so as a group of residents, we decided to study the impact of these factors on their health and the care that can be provided. We started using the two cohorts and now we keep it going with every new resident,” said Luca Biavati, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting.
“The presence of any form of socioeconomic disadvantage is negatively impacting care and for a large part of the population, there are some factors that could probably be addressed by either an institutional or hospital policy,” said Dr. Biavati, who is an internal medicine resident at Jacobi Medical Center, New York.
Other factors are more difficult to address, such as lack of education. “[Some patients] don’t understand the gravity of their issue and medical condition until it’s too late, and then they’re not fit enough for the treatment, or just because of the social situation, they cannot qualify for advanced therapies,” said Dr. Biavati.
The researchers established two cohorts: One consisting of patients with HIV and heart failure who may or may not have had PH and one comprising patients with PH with or without HIV and heart failure. In the HIV/heart failure group, PH without social adversity was associated with a nearly threefold increase in all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.83; P = .004), whereas PH with social adversity was linked to a more than sevenfold increase in all-cause mortality (HR, 7.14; P < .001). Social adversity without PA was associated with a more than fourfold increase (HR, 4.47; P < .001).
Within the PH cohort, social adversity was associated with lower survival (P < .001). When the researchers broke down the results by types of social adversity, they found statistically significant relationships between greater mortality risk and economic instability within the HIV+ population (HR, 2.59; P = .040), transportation issues within the HIV– population (HR, 12.8; P < .001), and lack of social or family support within both the HIV– (HR, 5.49; P < .001) and the HIV+ population (HR, 2.03; P = .028).
The research has prompted interventions, which are now being studied at the institution, according to Dr. Biavati. “We have a policy of giving medications in bags when we discharge a patient with a social adversity. We literally go to the pharmacy, bring up the bag of medication, and we [put it] in their hands before they leave the hospital. They get a 1- or 3-month supply, depending on the medication, and then we usually discharge them with a clinical appointment already scheduled with either a pulmonary or primary care provider, and we usually call them before every appointment to confirm that they’re coming. That increases the chances of some success, but there’s still a very long way to go,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati was blinded to the results of the intervention, so he could not report on whether it was working. “But I can tell you that I’ve had busier clinics, so hopefully that means that they’re showing up more,” he said.
The problem is complex, according to Sandeep Jain, MD, who moderated the session. “Social adversity means lack of education. Lack of education means lack of compliance. Lack of compliance means what can you do if people are not taking medications? So it’s all matched together. It’s all lack of education and lack of money, lack of family support. And these drugs they have to take every single day. It’s not that easy. It’s very easy for us to say I had antiretroviral treatment for 6 months. It is almost impossible to continue regular treatment for that long [for a patient with social adversity]. You can’t blame them if they aren’t taking treatments. It’s very difficult for them,” said Dr. Jain.
That underscores the need for interventions that can address the needs of patients with social adversity. “We have to [practice] medicine considering the social situation of the patient and not just the medicine that we study in books. That’s kind of what we are faced with every day. We have therapies, and then life happens. It’s much harder to care for those patients,” said Dr. Biavati.
Dr. Biavati and Dr. Jain reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Digital Twin Model Predicts Sepsis Mortality
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A “digital twin” model successfully predicted adverse outcomes in intensive care unit (ICU) patients treated for sepsis.
The digital twin could reduce the risk for some interventions, according to Amos Lal, MD, who presented the study at the CHEST Annual Meeting. That’s because the model can predict the outcome. “You don’t actually have to make an intervention to the patient, which might be risky. By doing that, you can actually prevent a lot of harm,” said Dr. Lal, assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
The researchers used a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN), similar to two-dimensional CNNs that are used to classify images, substituting the color channels used in imaging with 38 time-dependent variables. They applied it to predicting outcomes in the ICU, focusing on data generated within the first 24 hours of admission. The team made the model dynamic by adding time-sensitive data like vitals, laboratory values, and interventions every 15 minutes. That contrasts with existing models that are usually static, relying on values at admission or at 24 hours, for example. It also takes into account time-insensitive data like age, gender, and comorbidities. “Combining these two and coming up with the prediction model in real time can give you a more informed decision about how these patients are going to perform over a period of 2 weeks or 4 weeks of their stay within the ICU. And of course, as we get more and more data within the first 24 hours, the performance of the model improves as well,” said Dr. Lal.
The researchers tested the model by creating a virtual model of the patient and then performing an intervention on the patient and a simulated intervention on the virtual patient. “Then we advance the clock and the patient either improved or deteriorated, and we compared how the digital twin performed, whether the changes were concordant or discordant [between the virtual and real-world patients],” said Dr. Lal.
The model was designed to predict which patients with sepsis would be at greater risk for death or ICU stays longer than 14 days. It was created using data from 28,617 patients with critical care sepsis at a single hospital who were treated between 2011 and 2018, with 70% used as a training set, 20% as a test set, and 10% as a validation set. The researchers conducted an external validation using MIMIC-IV data on 30,903 patients from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. The model included 31 time-independent variables and 38 time-dependent variables that were collected every 15 minutes at the Mayo Clinic and every 60 minutes at Beth Israel Deaconess. Surgical patients represented 24% of the Mayo dataset and 58% of the MIMIC-IV dataset, but otherwise the two groups were demographically similar.
At 24 hours, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for predicting 14-day mortality was −0.82 in the Mayo validation cohort and −0.78 in the MIMIC validation cohort. The model improved in accuracy over time as more data were accumulated.
The session’s co-moderators, Sandeep Jain, MD, and Casey Cable, MD, praised the work. Dr. Cable, associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at VCU Health, Richmond, Virginia, noted that the model used both surgical patients and medical patients with sepsis, and the two groups can present quite differently. Another variable was the COVID pandemic, where some patients presented at the hospital when they were quite sick. “I’m curious how different starting points would play into it,” she said.
She called for institutions to develop such models on their own rather than relying on companies that might develop software solutions. “I think that this needs to be clinician-led, from the ground up,” said Dr. Cable.
Dr. Jain, an associate professor of pulmonary care medicine at Broward Health, suggested that such models might need to be individualized for each institution, but “my fear is it could become too expensive, so I think a group like CHEST could come together and [create] an open source system to have their researchers jumpstart the research on this,” he said.
Dr. Lal, Dr. Jain, and Dr. Cable reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
COVID on the Floor Linked to Outbreaks on Two Hospital Wards
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The viral burden of SARS-CoV-2 on floors, even in healthcare worker–only areas, was strongly associated with COVID-19 outbreaks in two acute-care hospitals, according to a new study from Ontario, Canada.
With every 10-fold increase in viral copies, the chance of an impending outbreak of COVID-19 rose 22-fold.
“These data add to the mounting evidence that built environment detection for SARS-CoV-2 may provide an additional layer of monitoring and could help inform local infection prevention and control measures,” they wrote.
The study was published online in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
Preventing Future Suffering
The current study builds on the researchers’ previous work, which found the same correlation between viral load on floors and COVID outbreaks in long-term care homes.
Currently, the best-known method of environmental surveillance for COVID is wastewater detection. “Swabbing the floors would be another approach to surveillance,” senior author Caroline Nott, MD, infectious disease physician at the Ottawa Hospital, said in an interview.
“We do have environmental surveillance with wastewater, but while this may tell you what’s going on in the city, it doesn’t tell you what is going on in a particular ward of a hospital, for instance,” she added.
Nott and her colleagues believe that swabbing, which is easy and relatively inexpensive, will become another tool to examine the built environment. “Instead of having to close a whole hospital, for example, we could just close one room instead of an entire ward if swabbing showed a high concentration of COVID,” Nott said.
The current study was conducted at two hospitals in Ontario between July 2022 and March 2023. The floors of healthcare worker–only areas on four inpatient adult wards were swabbed. These areas included changing rooms, meeting rooms, staff washrooms, nursing stations, and interdisciplinary team rooms.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 537 of 760 floor swabs (71%). The overall positivity rate in the first hospital was 90% (n = 280). In the second hospital, the rate was 60% (n = 480).
Four COVID-19 outbreaks occurred in the first acute care hospital, and seven outbreaks occurred at the second hospital. Outbreaks occurred mostly among hospitalized patients (140 cases), but also in four hospital workers.
COVID-19 still requires vigilance, said Nott. “We weren’t prepared for COVID, and so as a result, many people died or have suffered long-term effects, especially vulnerable people like those being treated in hospital or in long-term care facilities. We want to develop methods to prevent similar suffering in the future, whether it’s a new COVID variant or a different pathogen altogether.”
Changing Surveillance Practice?
“This is a good study,” Steven Rogak, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC) in Vancouver, Canada, said in an interivew. “The fundamental idea is that respiratory droplets and aerosols will deposit on the floor, and polymerase chain reaction [PCR] tests of swabs will provide a surrogate measurement of what might have been inhaled. There are solid statistics that it worked for the hospitals studied,” said Rogak, who studies aerosols at UBC’s Energy and Aerosols Laboratory. Rogak did not participate in the study.
“The authors note several limitations, including that increased healthcare worker testing may have been triggered by the higher values of PCR counts from the floor swabs. But this doesn’t seem to be a problem to me, because if the floor swabs motivate the hospital to test workers more, and that results in identifying outbreaks sooner, then great,” he said.
“Another limitation is that if the hospital has better HVAC or uses air purifiers, it could remove the most infectious aerosols, but the large droplets that fall quickly to the ground would remain, and this would still result in high PCR counts from floor swabs. In this case, perhaps the floor swabs would be a poorer indication of impending outbreaks,” said Rogak.
Determining the best timing and location for floor swabbing might be challenging and specific to the particular hospital, he added. ”For example, you would not want to take swabs from floors right after they are cleaned. Overall, I think this method deserves further development, and it could become a standard technique, but the details might require refinement for widespread application.”
Adrian Popp, MD, chair of the Infectious Disease Service at Huntington Hospital–Northwell Health in New York, said that, although interesting, the study would not change his current practice.
“I’m going to start testing the environment in different rooms in the hospital, and yes, I might find different amounts of COVID, but what does that mean? If pieces of RNA from COVID are on the floor, the likelihood is that they’re not infectious,” Popp said in an interview.
“Hospital workers do get sick with COVID, and sometimes they are asymptomatic and come to work. Patients may come into the hospital for another reason and be sick with COVID. There are many ways people who work in the hospital, as well as the patients, can get COVID. To me, it means that in that hospital and community there is a lot of COVID, but I can’t tell if there is causation here. Who is giving COVID to whom? What am I supposed to do with the information?”
The study was supported by the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association Clinical Innovation Opportunities Fund, the Ottawa Hospital Academic Medical Organization Innovation Fund, and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant. One author was a consultant for ProofDx, a startup company creating a point-of-care diagnostic test for COVID-19, and is an advisor for SIGNAL1, a startup company deploying machine-learning models to improve inpatient care. Nott, Rogak, and Popp reported having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM INFECTION CONTROL & HOSPITAL EPIDEMIOLOGY
FDA OKs New Drug for Urinary Tract Infections
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Orlynvah, a new oral treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women who have limited options for effective antibiotic therapy.
Uncomplicated UTIs are bladder infections that typically affect women who don’t have other issues like kidney disease or urinary tract abnormalities. These infections are common, affecting around half of all women at least once in their lives.
Treating UTIs can be difficult when standard antibiotics don’t work well, often because of antibiotic resistance or certain health conditions. Orlynvah offers a promising new option by combining two drugs, sulopenem etzadroxil and probenecid, in one oral tablet. This combination helps keep the antibiotic in the body longer, making it work better, especially against bacteria that resist traditional treatments. Orlynvah is specifically approved to target infections from bacteria like Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis, which can be harder to treat.
Marjorie Golden, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Yale New Haven Hospital in Connecticut, described Orlynvah as a much-needed alternative for women struggling with difficult-to-treat UTIs.
“Orlynvah has the potential to be an important treatment option for those who need it,” she said in a news release from Iterum Therapeutics, the drug’s maker.
The FDA approved Orlynvah based on two large clinical trials involving over 3,800 women. In these studies, Orlynvah worked as well as or better than antibiotics like ciprofloxacin and Augmentin. It was generally well-tolerated, though common side effects included diarrhea, nausea, yeast infections, and headaches.
The FDA advises people to discuss their medical history with their doctor before taking Orlynvah, especially if they have conditions like gout, kidney stones, or allergies to other antibiotics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Orlynvah, a new oral treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women who have limited options for effective antibiotic therapy.
Uncomplicated UTIs are bladder infections that typically affect women who don’t have other issues like kidney disease or urinary tract abnormalities. These infections are common, affecting around half of all women at least once in their lives.
Treating UTIs can be difficult when standard antibiotics don’t work well, often because of antibiotic resistance or certain health conditions. Orlynvah offers a promising new option by combining two drugs, sulopenem etzadroxil and probenecid, in one oral tablet. This combination helps keep the antibiotic in the body longer, making it work better, especially against bacteria that resist traditional treatments. Orlynvah is specifically approved to target infections from bacteria like Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis, which can be harder to treat.
Marjorie Golden, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Yale New Haven Hospital in Connecticut, described Orlynvah as a much-needed alternative for women struggling with difficult-to-treat UTIs.
“Orlynvah has the potential to be an important treatment option for those who need it,” she said in a news release from Iterum Therapeutics, the drug’s maker.
The FDA approved Orlynvah based on two large clinical trials involving over 3,800 women. In these studies, Orlynvah worked as well as or better than antibiotics like ciprofloxacin and Augmentin. It was generally well-tolerated, though common side effects included diarrhea, nausea, yeast infections, and headaches.
The FDA advises people to discuss their medical history with their doctor before taking Orlynvah, especially if they have conditions like gout, kidney stones, or allergies to other antibiotics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Orlynvah, a new oral treatment for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) in women who have limited options for effective antibiotic therapy.
Uncomplicated UTIs are bladder infections that typically affect women who don’t have other issues like kidney disease or urinary tract abnormalities. These infections are common, affecting around half of all women at least once in their lives.
Treating UTIs can be difficult when standard antibiotics don’t work well, often because of antibiotic resistance or certain health conditions. Orlynvah offers a promising new option by combining two drugs, sulopenem etzadroxil and probenecid, in one oral tablet. This combination helps keep the antibiotic in the body longer, making it work better, especially against bacteria that resist traditional treatments. Orlynvah is specifically approved to target infections from bacteria like Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis, which can be harder to treat.
Marjorie Golden, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Yale New Haven Hospital in Connecticut, described Orlynvah as a much-needed alternative for women struggling with difficult-to-treat UTIs.
“Orlynvah has the potential to be an important treatment option for those who need it,” she said in a news release from Iterum Therapeutics, the drug’s maker.
The FDA approved Orlynvah based on two large clinical trials involving over 3,800 women. In these studies, Orlynvah worked as well as or better than antibiotics like ciprofloxacin and Augmentin. It was generally well-tolerated, though common side effects included diarrhea, nausea, yeast infections, and headaches.
The FDA advises people to discuss their medical history with their doctor before taking Orlynvah, especially if they have conditions like gout, kidney stones, or allergies to other antibiotics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Increase in Troublesome Fungal Infections Requires All-Out Approach
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
H pylori: ACG Guideline Advises New Approaches to Treatment
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ACIP Recommends Pneumococcal Vaccine for Adults 50 Years or Older
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) now recommends a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) for all PCV-naive adults aged 50 years or older. The new recommendation, which passed with an ACIP member vote of 14 for and one against, expands the current age-based recommendations, which include children younger than 5 years and adults older than 65 years, as well as adults aged 19-64 years with underlying conditions or risk factors who have not received a PCV and certain adults who have received PCV13 but not PCV20.
The decision was based in part on economic analyses of the use of PCV in adults aged 50-64 years in the United States. Miwako Kobayashi, MD, presented the summary of the Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group’s interpretation of the evidence and the proposed recommendation in a meeting of the ACIP on October 23, 2024, when the ACIP voting occurred.
Data from the CDC show an increase in the relative burden of pneumococcal disease in adults aged 50-64 years based in part on the success of the pediatric PCV program, she said.
Health equity was another main factor in the Work Group’s decision to recommend vaccination for adults aged 50 years or older. “Disparities in pneumococcal vaccine coverage by race and ethnicity exist for both age-based and risk-based indications,” Kobayashi noted in her presentation. The Work Group acknowledged that the overall effect of a vaccine recommendation on health equity is complex, but the majority agreed that the update would improve health equity by increasing vaccine coverage for those with known or unknown risk factors and providing protection at an earlier age when some populations already experience elevated disease rates, she said.
As for safety, the Work Group concluded that the undesirable anticipated effects of PCVs are minimal, despite the potential signal for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, and the CDC and US Food and Drug Administration will continue to monitor post-licensure safety of PCVs.
Support Not Universal
A majority of the ACIP Pneumococcal Vaccines Work Group supported the approved option, but agreed that a future booster dose may be needed, Work Group Chair James Loehr, MD, said in his introductory presentation.
Overall, key uncertainties remain, including indirect effects of new pediatric pneumococcal vaccines on adults, data on the duration of protection with adult vaccinations, and the impact new higher-valency vaccines have on adults, several of which are in development, Loehr said.
A new 21-valent PCV, known as PCV 21, was approved by the FDA for adults aged 18 years or older in June 2024, said Loehr. “PCV21 is not PCV20 with one additional serotype” and provides additional protection, he emphasized. The Work Group examined models involving PCV21 and the existing PCV20. However, a majority of the Work Group agreed that having age-based recommendations based on vaccine product would be more challenging to implement and that insurance coverage may be a factor given the recent approval of PCV21. Therefore, the proposal submitted to the full ACIP was not for a specific PCV.
Notably, Loehr said that, although as Work Group Chair he was tasked with making the motion in favor of the recommendation, he voted against it as a voting member because of his strong opinion that only the PCV21 vaccine is needed for vaccine-naive adults aged 50 or older. “I think that PCV21 is a better vaccine that targets more serotypes,” he said during the discussion. Data presented at the February 2024 ACIP meeting showed more than 80% coverage vs less than 60% coverage for invasive pneumococcal disease with PCV21 vs PCV20 among adults aged 65 years or older and those aged 19-64 years with a risk-based indication, Loehr said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Groups With Highest Unmet Need for PrEP Highlighted in Analysis
LOS ANGELES — Use of preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV is increasing overall, but both the rate of increase for starting PrEP and the rate of unmet need differ widely by demographic group, according to new data from a large study.
An analysis by Li Tao, MD, MS, PhD, director of real-world evidence at Gilead Sciences, and colleagues looked at statistical trends from 2019 to 2023 and found that Black, Hispanic, and Medicaid-insured populations continue to lack equitable access to PrEP.
Among the findings were that most new PrEP users were men with HIV risk factors who are commercially insured and live in predominantly non-Hispanic White areas (53% in 2019 and 43% in 2023). For comparison, men living in predominantly Black or Hispanic neighborhoods, or who are insured by Medicaid, saw lower proportions of PrEP use (16% in 2019 and 17% in 2023) despite higher annual increases in PrEP use (11% per year) and higher unmet needs.
Half a Million Real-World Participants
Tao presented her team’s findings at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting. The study included “more than half a million real-world PrEP users over the past 5 years,” she said.
The group with the lowest growth in initiation of PrEP in the study period (an annual percentage increase of 2%) and the lowest unmet need included men with HIV risk factors, who were using commercial insurance and living in White-dominant neighborhoods.
HIV risk factors included diagnosis of any sexually transmitted disease, contact with and exposure to communicable diseases, high-risk sexual behavior, contact with a hypodermic needle, long-term prophylaxis, HIV prevention counseling, and HIV screening.
Other men with HIV risk factors (those who were commercially insured, living in Black/Hispanic neighborhoods, or those on Medicaid across all neighborhoods) had a moderate increase in PrEP initiation (an annual percentage increase of 11%-16%) and higher unmet needs.
Researchers gathered data on PrEP prescriptions and new HIV diagnoses (from 2019 to 2023) through the IQVIA pharmacy claims database. PrEP-to-need ratio (PNR) is the number of individuals using PrEP in a year divided by new HIV diagnoses in the previous year. It was calculated for subgroups defined by five PNR-associated factors: Sex, insurance, recorded HIV risk factors (identified by diagnosis or procedure codes), “Ending the HIV Epidemic” jurisdictions, and neighborhood race/ethnicity mix.
Disparities Persist
While PrEP use improved across all the groups studied in the 5 years, “disparities still persist and the need remains very significant,” Tao said. “It’s very crucial for guiding the future HIV prevention options.”
“Long-acting PrEP options may help to address some social determinants structural factors in HIV acquisition,” she added.
What Programs Are Helping?
Some guidelines and programs are helping increase uptake, Tao said.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines “reinforce more accessible PrEP programs to individuals like zero-cost sharing or same-day dispensing,” Tao said in a press briefing. “Those kinds of policies are really effective. We can see that after the implementation of the USPSTF guidelines, the copay sharing is really decreasing and is coinciding with the HIV rates declining.”
The Medicaid coverage expansion in 40 states “has been really effective” in PrEP uptake, she added.
Colleen Kelley, MD, MPH, with the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, in Atlanta, who was not part of the research, said there has been a slow but improving uptake of PrEP across the board in the United States, “but the issue is that the uptake has been inequitable.”
Large Study With Recent Data
“This is an extremely large study with very recent data,” Kelley said. “Additionally, they were able to couple (the uptake) with unmet need. People who are at higher risk of acquiring HIV or who live in high-risk areas for HIV should have greater access to PrEP. They have a greater need for PrEP. What we really need to do from an equity perspective is match the PrEP use with the PrEP need and we have not been successful in doing that.”
Kelley added that the finding that the group that had the highest unmet need for PrEP in the study also had no recorded HIV risk factors. “It’s an interesting time to start thinking about beyond risk factor coverage for PrEP,” she said.
Another issue, Kelley said, is that “people are using (PrEP) but they’re also stopping it. People will need to take PrEP many years for protection, but about half discontinue in the first 6-12 months.
“We need to look at how people will persist on PrEP over the long term. That’s the next frontier,” she said. “We hope the long-acting injectables will help overcome some of the PrEP fatigue. But some may just tire of taking medication repeatedly for an infection they don’t have,” she said.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Tao is employed by and is a shareholder of Gilead Sciences. All relevant financial disclosures have been mitigated, according to the paper. Kelley has research grants to her institution from Gilead, Moderna, Novavax, ViiV, and Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — Use of preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV is increasing overall, but both the rate of increase for starting PrEP and the rate of unmet need differ widely by demographic group, according to new data from a large study.
An analysis by Li Tao, MD, MS, PhD, director of real-world evidence at Gilead Sciences, and colleagues looked at statistical trends from 2019 to 2023 and found that Black, Hispanic, and Medicaid-insured populations continue to lack equitable access to PrEP.
Among the findings were that most new PrEP users were men with HIV risk factors who are commercially insured and live in predominantly non-Hispanic White areas (53% in 2019 and 43% in 2023). For comparison, men living in predominantly Black or Hispanic neighborhoods, or who are insured by Medicaid, saw lower proportions of PrEP use (16% in 2019 and 17% in 2023) despite higher annual increases in PrEP use (11% per year) and higher unmet needs.
Half a Million Real-World Participants
Tao presented her team’s findings at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting. The study included “more than half a million real-world PrEP users over the past 5 years,” she said.
The group with the lowest growth in initiation of PrEP in the study period (an annual percentage increase of 2%) and the lowest unmet need included men with HIV risk factors, who were using commercial insurance and living in White-dominant neighborhoods.
HIV risk factors included diagnosis of any sexually transmitted disease, contact with and exposure to communicable diseases, high-risk sexual behavior, contact with a hypodermic needle, long-term prophylaxis, HIV prevention counseling, and HIV screening.
Other men with HIV risk factors (those who were commercially insured, living in Black/Hispanic neighborhoods, or those on Medicaid across all neighborhoods) had a moderate increase in PrEP initiation (an annual percentage increase of 11%-16%) and higher unmet needs.
Researchers gathered data on PrEP prescriptions and new HIV diagnoses (from 2019 to 2023) through the IQVIA pharmacy claims database. PrEP-to-need ratio (PNR) is the number of individuals using PrEP in a year divided by new HIV diagnoses in the previous year. It was calculated for subgroups defined by five PNR-associated factors: Sex, insurance, recorded HIV risk factors (identified by diagnosis or procedure codes), “Ending the HIV Epidemic” jurisdictions, and neighborhood race/ethnicity mix.
Disparities Persist
While PrEP use improved across all the groups studied in the 5 years, “disparities still persist and the need remains very significant,” Tao said. “It’s very crucial for guiding the future HIV prevention options.”
“Long-acting PrEP options may help to address some social determinants structural factors in HIV acquisition,” she added.
What Programs Are Helping?
Some guidelines and programs are helping increase uptake, Tao said.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines “reinforce more accessible PrEP programs to individuals like zero-cost sharing or same-day dispensing,” Tao said in a press briefing. “Those kinds of policies are really effective. We can see that after the implementation of the USPSTF guidelines, the copay sharing is really decreasing and is coinciding with the HIV rates declining.”
The Medicaid coverage expansion in 40 states “has been really effective” in PrEP uptake, she added.
Colleen Kelley, MD, MPH, with the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, in Atlanta, who was not part of the research, said there has been a slow but improving uptake of PrEP across the board in the United States, “but the issue is that the uptake has been inequitable.”
Large Study With Recent Data
“This is an extremely large study with very recent data,” Kelley said. “Additionally, they were able to couple (the uptake) with unmet need. People who are at higher risk of acquiring HIV or who live in high-risk areas for HIV should have greater access to PrEP. They have a greater need for PrEP. What we really need to do from an equity perspective is match the PrEP use with the PrEP need and we have not been successful in doing that.”
Kelley added that the finding that the group that had the highest unmet need for PrEP in the study also had no recorded HIV risk factors. “It’s an interesting time to start thinking about beyond risk factor coverage for PrEP,” she said.
Another issue, Kelley said, is that “people are using (PrEP) but they’re also stopping it. People will need to take PrEP many years for protection, but about half discontinue in the first 6-12 months.
“We need to look at how people will persist on PrEP over the long term. That’s the next frontier,” she said. “We hope the long-acting injectables will help overcome some of the PrEP fatigue. But some may just tire of taking medication repeatedly for an infection they don’t have,” she said.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Tao is employed by and is a shareholder of Gilead Sciences. All relevant financial disclosures have been mitigated, according to the paper. Kelley has research grants to her institution from Gilead, Moderna, Novavax, ViiV, and Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — Use of preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV is increasing overall, but both the rate of increase for starting PrEP and the rate of unmet need differ widely by demographic group, according to new data from a large study.
An analysis by Li Tao, MD, MS, PhD, director of real-world evidence at Gilead Sciences, and colleagues looked at statistical trends from 2019 to 2023 and found that Black, Hispanic, and Medicaid-insured populations continue to lack equitable access to PrEP.
Among the findings were that most new PrEP users were men with HIV risk factors who are commercially insured and live in predominantly non-Hispanic White areas (53% in 2019 and 43% in 2023). For comparison, men living in predominantly Black or Hispanic neighborhoods, or who are insured by Medicaid, saw lower proportions of PrEP use (16% in 2019 and 17% in 2023) despite higher annual increases in PrEP use (11% per year) and higher unmet needs.
Half a Million Real-World Participants
Tao presented her team’s findings at the Infectious Disease Week (IDWeek) 2024 Annual Meeting. The study included “more than half a million real-world PrEP users over the past 5 years,” she said.
The group with the lowest growth in initiation of PrEP in the study period (an annual percentage increase of 2%) and the lowest unmet need included men with HIV risk factors, who were using commercial insurance and living in White-dominant neighborhoods.
HIV risk factors included diagnosis of any sexually transmitted disease, contact with and exposure to communicable diseases, high-risk sexual behavior, contact with a hypodermic needle, long-term prophylaxis, HIV prevention counseling, and HIV screening.
Other men with HIV risk factors (those who were commercially insured, living in Black/Hispanic neighborhoods, or those on Medicaid across all neighborhoods) had a moderate increase in PrEP initiation (an annual percentage increase of 11%-16%) and higher unmet needs.
Researchers gathered data on PrEP prescriptions and new HIV diagnoses (from 2019 to 2023) through the IQVIA pharmacy claims database. PrEP-to-need ratio (PNR) is the number of individuals using PrEP in a year divided by new HIV diagnoses in the previous year. It was calculated for subgroups defined by five PNR-associated factors: Sex, insurance, recorded HIV risk factors (identified by diagnosis or procedure codes), “Ending the HIV Epidemic” jurisdictions, and neighborhood race/ethnicity mix.
Disparities Persist
While PrEP use improved across all the groups studied in the 5 years, “disparities still persist and the need remains very significant,” Tao said. “It’s very crucial for guiding the future HIV prevention options.”
“Long-acting PrEP options may help to address some social determinants structural factors in HIV acquisition,” she added.
What Programs Are Helping?
Some guidelines and programs are helping increase uptake, Tao said.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines “reinforce more accessible PrEP programs to individuals like zero-cost sharing or same-day dispensing,” Tao said in a press briefing. “Those kinds of policies are really effective. We can see that after the implementation of the USPSTF guidelines, the copay sharing is really decreasing and is coinciding with the HIV rates declining.”
The Medicaid coverage expansion in 40 states “has been really effective” in PrEP uptake, she added.
Colleen Kelley, MD, MPH, with the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, in Atlanta, who was not part of the research, said there has been a slow but improving uptake of PrEP across the board in the United States, “but the issue is that the uptake has been inequitable.”
Large Study With Recent Data
“This is an extremely large study with very recent data,” Kelley said. “Additionally, they were able to couple (the uptake) with unmet need. People who are at higher risk of acquiring HIV or who live in high-risk areas for HIV should have greater access to PrEP. They have a greater need for PrEP. What we really need to do from an equity perspective is match the PrEP use with the PrEP need and we have not been successful in doing that.”
Kelley added that the finding that the group that had the highest unmet need for PrEP in the study also had no recorded HIV risk factors. “It’s an interesting time to start thinking about beyond risk factor coverage for PrEP,” she said.
Another issue, Kelley said, is that “people are using (PrEP) but they’re also stopping it. People will need to take PrEP many years for protection, but about half discontinue in the first 6-12 months.
“We need to look at how people will persist on PrEP over the long term. That’s the next frontier,” she said. “We hope the long-acting injectables will help overcome some of the PrEP fatigue. But some may just tire of taking medication repeatedly for an infection they don’t have,” she said.
The study was funded by Gilead Sciences. Tao is employed by and is a shareholder of Gilead Sciences. All relevant financial disclosures have been mitigated, according to the paper. Kelley has research grants to her institution from Gilead, Moderna, Novavax, ViiV, and Humanigen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM IDWEEK 2024