User login
FDA approvals permit double-immunoassay approach to Lyme disease diagnosis
Concurrent or sequential enzyme immunoassays can now be conducted to diagnose Lyme disease, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Four previously cleared tests are now approved by the agency for marketing with new indications as part of the revised diagnostic approach. Previously, the two-step diagnostic process consisted of an initial enzyme immunoassay followed by a Western blot test.
“With today’s action, clinicians have a new option to test for Lyme that is easier to interpret by a clinical laboratory due to the streamlined method of conducting the test. These tests may improve confidence in diagnosing a patient for a condition that requires the earliest possible treatment to ensure the best outcome for patients,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiologic Health, said in a press release announcing the newly approved approach.
The modified two-tier enzyme immunoassay approach was found to be as accurate for assessing exposure to Borrelia burgdorferi as the standard immunoassay followed by Western blot test in an FDA review of data from clinical studies using the following ZEUS Scientific ELISA Test Systems: Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgM; and Borrelia burgdorferi IgG.
The recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention should be followed for the diagnosis of Lyme disease and for determining when laboratory tests are appropriate, the FDA statement said. In 2017, the last year for which the CDC published data, a total of 42,743 confirmed and probable cases of Lyme disease were reported, an increase of 17% from 2016.
The FDA granted clearance of the ZEUS ELISA enzyme immunoassay tests to ZEUS Scientific.
Concurrent or sequential enzyme immunoassays can now be conducted to diagnose Lyme disease, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Four previously cleared tests are now approved by the agency for marketing with new indications as part of the revised diagnostic approach. Previously, the two-step diagnostic process consisted of an initial enzyme immunoassay followed by a Western blot test.
“With today’s action, clinicians have a new option to test for Lyme that is easier to interpret by a clinical laboratory due to the streamlined method of conducting the test. These tests may improve confidence in diagnosing a patient for a condition that requires the earliest possible treatment to ensure the best outcome for patients,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiologic Health, said in a press release announcing the newly approved approach.
The modified two-tier enzyme immunoassay approach was found to be as accurate for assessing exposure to Borrelia burgdorferi as the standard immunoassay followed by Western blot test in an FDA review of data from clinical studies using the following ZEUS Scientific ELISA Test Systems: Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgM; and Borrelia burgdorferi IgG.
The recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention should be followed for the diagnosis of Lyme disease and for determining when laboratory tests are appropriate, the FDA statement said. In 2017, the last year for which the CDC published data, a total of 42,743 confirmed and probable cases of Lyme disease were reported, an increase of 17% from 2016.
The FDA granted clearance of the ZEUS ELISA enzyme immunoassay tests to ZEUS Scientific.
Concurrent or sequential enzyme immunoassays can now be conducted to diagnose Lyme disease, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Four previously cleared tests are now approved by the agency for marketing with new indications as part of the revised diagnostic approach. Previously, the two-step diagnostic process consisted of an initial enzyme immunoassay followed by a Western blot test.
“With today’s action, clinicians have a new option to test for Lyme that is easier to interpret by a clinical laboratory due to the streamlined method of conducting the test. These tests may improve confidence in diagnosing a patient for a condition that requires the earliest possible treatment to ensure the best outcome for patients,” Tim Stenzel, MD, PhD, director of the Office of In Vitro Diagnostics and Radiological Health in the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiologic Health, said in a press release announcing the newly approved approach.
The modified two-tier enzyme immunoassay approach was found to be as accurate for assessing exposure to Borrelia burgdorferi as the standard immunoassay followed by Western blot test in an FDA review of data from clinical studies using the following ZEUS Scientific ELISA Test Systems: Borrelia VlsE1/pepC10 IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgG/IgM; Borrelia burgdorferi IgM; and Borrelia burgdorferi IgG.
The recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention should be followed for the diagnosis of Lyme disease and for determining when laboratory tests are appropriate, the FDA statement said. In 2017, the last year for which the CDC published data, a total of 42,743 confirmed and probable cases of Lyme disease were reported, an increase of 17% from 2016.
The FDA granted clearance of the ZEUS ELISA enzyme immunoassay tests to ZEUS Scientific.
Gram-negative bacteremia: Cultures, drugs, and duration
Are we doing it right?
Case
A 42-year-old woman with uncontrolled diabetes presents to the ED with fever, chills, dysuria, and flank pain for 3 days. On exam, she is febrile and tachycardic. Lab results show leukocytosis and urinalysis is consistent with infection. CT scan shows acute pyelonephritis without complication. She is admitted to the hospital and started on ceftriaxone 2 g/24 hrs. On hospital day 2, her blood cultures show gram-negative bacteria.
Brief overview
Management of gram-negative (GN) bacteremia remains a challenging clinical situation for inpatient providers. With the push for high-value care and reductions in length of stay, recent literature has focused on reviewing current practices and attempting to standardize care. Despite this, no overarching guidelines exist to direct practice and clinicians are left to make decisions based on prior experience and expert opinion. Three key clinical questions exist when caring for a hospitalized patient with GN bacteremia: Should blood cultures be repeated? When is transition to oral antibiotics appropriate? And for what duration should antibiotics be given?
Overview of the data
When considering repeating blood cultures, it is important to understand that current literature does not support the practice for all GN bacteremias.
Canzoneri et al. retrospectively studied GN bacteremia and found that it took 17 repeat blood cultures being drawn to yield 1 positive result, which suggests that they are not necessary in all cases.1 Furthermore, repeat blood cultures increase cost of hospitalization, length of stay, and inconvenience to patients.2
However, Mushtaq et al. noted that repeating blood cultures can provide valuable information to confirm the response to treatment in patients with endovascular infection. Furthermore, they found that repeated blood cultures are also reasonable when the following scenarios are suspected: endocarditis or central line–associated infection, concern for multidrug resistant GN bacilli, and ongoing evidence of sepsis or patient decompensation.3
Consideration of a transition from intravenous to oral antibiotics is a key decision point in the care of GN bacteremia. Without guidelines, clinicians are left to evaluate patients on a case-by-case basis.4 Studies have suggested that the transition should be guided by the condition of the patient, the type of infection, and the culture-derived sensitivities.5 Additionally, bioavailability of antibiotics (see Table 1) is an important consideration and a recent examination of oral antibiotic failure rates demonstrated that lower bioavailability antibiotics have an increased risk of failure (2% vs. 16%).6
In their study, Kutob et al. highlighted the importance of choosing not only an antibiotic of high bioavailability, but also an antibiotic dose which will support a high concentration of the antibiotic in the bloodstream.6 For example, they identify ciprofloxacin as a moderate bioavailability medication, but note that most cases they examined utilized 500 mg b.i.d., where the concentration-dependent killing and dose-dependent bioavailability would advocate for the use of 750 mg b.i.d. or 500 mg every 8 hours.
The heterogeneity of GN bloodstream infections also creates difficulty in standardization of care. The literature suggests that infection source plays a significant role in the type of GN bacteria isolated.6,7 The best data for the transition to oral antibiotics exists with urologic sources and it remains unclear whether bacteria from other sources have higher risks of oral antibiotic failure.8
One recent study of 66 patients examined bacteremia in the setting of cholangitis and found that, once patients had stabilized, a switch from intravenous to oral antibiotics was noninferior, but randomized, prospective trials have not been performed. Notably, patients were transitioned to orals only after they were found to have a fluoroquinolone-sensitive infection, allowing the study authors to use higher-bioavailability agents for the transition to orals.9 Multiple studies have highlighted the unique care required for certain infections, such as pseudomonal infections, which most experts agree requires a more conservative approach.5,6
Fluoroquinolones are the bedrock of therapy for GN bacteremia because of historic in vivo experience and in vitro findings about bioavailability and dose-dependent killing, but they are also the antibiotic class associated with the highest hospitalization rates for antibiotic-associated adverse events.8 A recent noninferiority trial comparing the use of beta-lactams with fluoroquinolones found that beta-lactams were noninferior, though the study was flawed by the limited number of beta-lactam–using patients identified.8 It is clear that more investigation is needed before recommendations can be made regarding ideal oral antibiotics for GN bacteremia.
The transition to oral is reasonable given the following criteria: the patient has improved on intravenous antibiotics and source control has been achieved; the culture data have demonstrated sensitivity to the oral antibiotic of choice, with special care given to higher-risk bacteria such as Pseudomonas; the patient is able to take the oral antibiotic; and the oral antibiotic of choice has the highest bioavailability possible and is given at an appropriate dose to reach its highest killing and bioavailability concentrations.7
After evaluating the appropriateness of transition to oral antibiotics, the final decision is about duration of antibiotic therapy. Current Infectious Disease Society of America guidelines are based on expert opinion and recommend 7-14 days of therapy. As with many common infections, recent studies have focused on evaluating reduction in antibiotic durations.
Chotiprasitsakul et al. demonstrated no difference in mortality or morbidity in 385 propensity-matched pairs with treatment of Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia for 8 versus 15 days.10 A mixed meta-analysis performed in 2011 evaluated 24 randomized, controlled trials and found shorter durations (5-7 days) had similar outcomes to prolonged durations (7-21 days).11 Recently, Yahav et al. performed a randomized control trial comparing 7- and 14-day regimens for uncomplicated GN bacteremia and found a 7-day course to be noninferior if patients were clinically stable by day 5 and had source control.12
It should be noted that not all studies have found that reduced durations are without harm. Nelson et al. performed a retrospective cohort analysis and found that reduced durations of antibiotics (7-10 days) increased mortality and recurrent infection when compared with a longer course (greater than 10 days).13 These contrary findings highlight the need for provider discretion in selecting a course of antibiotics as well as the need for further studies about optimal duration of antibiotics.
Application of the data
Returning to our case, on day 3, the patient’s fever had resolved and leukocytosis improved. In the absence of concern for persistent infection, repeat blood cultures were not performed. On day 4 initial blood cultures showed pan-sensitive Escherichia coli. The patient was transitioned to 750 mg oral ciprofloxacin b.i.d. to complete a 10-day course from first dose of ceftriaxone and was discharged from the hospital.
Bottom line
Management of GN bacteremia requires individualized care based on clinical presentation, but the data presented above can be used as broad guidelines to help reduce excess blood cultures, avoid prolonged use of intravenous antibiotics, and limit the duration of antibiotic exposure.
Dr. Imber is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and director of the Internal Medicine Simulation Education and Hospitalist Procedural Certification. Dr. Burns is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico. Dr. Chan is currently a chief resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of New Mexico.
References
1. Canzoneri CN et al. Follow-up blood cultures in gram-negative bacteremia: Are they needed? Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1776-9. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix648.
2. Kang CK et al. Can a routine follow-up blood culture be justified in Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia? A retrospective case-control study. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:365. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-365.
3. Mushtaq A et al. Repeating blood cultures after an initial bacteremia: When and how often? Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86(2):89-92. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.86a.18001.
4. Nimmich EB et al. Development of institutional guidelines for management of gram-negative bloodstream infections: Incorporating local evidence. Hosp Pharm. 2017;52(10):691-7. doi: 10.1177/0018578717720506.
5. Hale AJ et al. When are oral antibiotics a safe and effective choice for bacterial bloodstream infections? An evidence-based narrative review. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2949.
6. Kutob LF et al. Effectiveness of oral antibiotics for definitive therapy of gram-negative bloodstream infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.013.
7. Tamma PD et al. Association of 30-day mortality with oral step-down vs. continued intravenous therapy in patients hospitalized with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia. JAMA Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.6226.
8. Mercuro NJ et al. Retrospective analysis comparing oral stepdown therapy for enterobacteriaceae bloodstream infections: fluoroquinolones vs. B-lactams. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.12.007.
9. Park TY et al. Early oral antibiotic switch compared with conventional intravenous antibiotic therapy for acute cholangitis with bacteremia. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2790-6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3233-0.
10. Chotiprasitsakul D et al. Comparing the outcomes of adults with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia receiving short-course versus prolonged-course antibiotic therapy in a multicenter, propensity score-matched cohort. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(2):172-7. doi:10.1093/cid/cix767.
11. Havey TC et al. Duration of antibiotic therapy for bacteremia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2011;15(6):R267. doi:10.1186/cc10545.
12. Yahav D et al. Seven versus fourteen days of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: A noninferiority randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Dec. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy1054.
13. Nelson AN et al. Optimal duration of antimicrobial therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bloodstream infections. Infection. 2017;45(5):613-20. doi:10.1007/s15010-017-1020-5.
Are we doing it right?
Are we doing it right?
Case
A 42-year-old woman with uncontrolled diabetes presents to the ED with fever, chills, dysuria, and flank pain for 3 days. On exam, she is febrile and tachycardic. Lab results show leukocytosis and urinalysis is consistent with infection. CT scan shows acute pyelonephritis without complication. She is admitted to the hospital and started on ceftriaxone 2 g/24 hrs. On hospital day 2, her blood cultures show gram-negative bacteria.
Brief overview
Management of gram-negative (GN) bacteremia remains a challenging clinical situation for inpatient providers. With the push for high-value care and reductions in length of stay, recent literature has focused on reviewing current practices and attempting to standardize care. Despite this, no overarching guidelines exist to direct practice and clinicians are left to make decisions based on prior experience and expert opinion. Three key clinical questions exist when caring for a hospitalized patient with GN bacteremia: Should blood cultures be repeated? When is transition to oral antibiotics appropriate? And for what duration should antibiotics be given?
Overview of the data
When considering repeating blood cultures, it is important to understand that current literature does not support the practice for all GN bacteremias.
Canzoneri et al. retrospectively studied GN bacteremia and found that it took 17 repeat blood cultures being drawn to yield 1 positive result, which suggests that they are not necessary in all cases.1 Furthermore, repeat blood cultures increase cost of hospitalization, length of stay, and inconvenience to patients.2
However, Mushtaq et al. noted that repeating blood cultures can provide valuable information to confirm the response to treatment in patients with endovascular infection. Furthermore, they found that repeated blood cultures are also reasonable when the following scenarios are suspected: endocarditis or central line–associated infection, concern for multidrug resistant GN bacilli, and ongoing evidence of sepsis or patient decompensation.3
Consideration of a transition from intravenous to oral antibiotics is a key decision point in the care of GN bacteremia. Without guidelines, clinicians are left to evaluate patients on a case-by-case basis.4 Studies have suggested that the transition should be guided by the condition of the patient, the type of infection, and the culture-derived sensitivities.5 Additionally, bioavailability of antibiotics (see Table 1) is an important consideration and a recent examination of oral antibiotic failure rates demonstrated that lower bioavailability antibiotics have an increased risk of failure (2% vs. 16%).6
In their study, Kutob et al. highlighted the importance of choosing not only an antibiotic of high bioavailability, but also an antibiotic dose which will support a high concentration of the antibiotic in the bloodstream.6 For example, they identify ciprofloxacin as a moderate bioavailability medication, but note that most cases they examined utilized 500 mg b.i.d., where the concentration-dependent killing and dose-dependent bioavailability would advocate for the use of 750 mg b.i.d. or 500 mg every 8 hours.
The heterogeneity of GN bloodstream infections also creates difficulty in standardization of care. The literature suggests that infection source plays a significant role in the type of GN bacteria isolated.6,7 The best data for the transition to oral antibiotics exists with urologic sources and it remains unclear whether bacteria from other sources have higher risks of oral antibiotic failure.8
One recent study of 66 patients examined bacteremia in the setting of cholangitis and found that, once patients had stabilized, a switch from intravenous to oral antibiotics was noninferior, but randomized, prospective trials have not been performed. Notably, patients were transitioned to orals only after they were found to have a fluoroquinolone-sensitive infection, allowing the study authors to use higher-bioavailability agents for the transition to orals.9 Multiple studies have highlighted the unique care required for certain infections, such as pseudomonal infections, which most experts agree requires a more conservative approach.5,6
Fluoroquinolones are the bedrock of therapy for GN bacteremia because of historic in vivo experience and in vitro findings about bioavailability and dose-dependent killing, but they are also the antibiotic class associated with the highest hospitalization rates for antibiotic-associated adverse events.8 A recent noninferiority trial comparing the use of beta-lactams with fluoroquinolones found that beta-lactams were noninferior, though the study was flawed by the limited number of beta-lactam–using patients identified.8 It is clear that more investigation is needed before recommendations can be made regarding ideal oral antibiotics for GN bacteremia.
The transition to oral is reasonable given the following criteria: the patient has improved on intravenous antibiotics and source control has been achieved; the culture data have demonstrated sensitivity to the oral antibiotic of choice, with special care given to higher-risk bacteria such as Pseudomonas; the patient is able to take the oral antibiotic; and the oral antibiotic of choice has the highest bioavailability possible and is given at an appropriate dose to reach its highest killing and bioavailability concentrations.7
After evaluating the appropriateness of transition to oral antibiotics, the final decision is about duration of antibiotic therapy. Current Infectious Disease Society of America guidelines are based on expert opinion and recommend 7-14 days of therapy. As with many common infections, recent studies have focused on evaluating reduction in antibiotic durations.
Chotiprasitsakul et al. demonstrated no difference in mortality or morbidity in 385 propensity-matched pairs with treatment of Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia for 8 versus 15 days.10 A mixed meta-analysis performed in 2011 evaluated 24 randomized, controlled trials and found shorter durations (5-7 days) had similar outcomes to prolonged durations (7-21 days).11 Recently, Yahav et al. performed a randomized control trial comparing 7- and 14-day regimens for uncomplicated GN bacteremia and found a 7-day course to be noninferior if patients were clinically stable by day 5 and had source control.12
It should be noted that not all studies have found that reduced durations are without harm. Nelson et al. performed a retrospective cohort analysis and found that reduced durations of antibiotics (7-10 days) increased mortality and recurrent infection when compared with a longer course (greater than 10 days).13 These contrary findings highlight the need for provider discretion in selecting a course of antibiotics as well as the need for further studies about optimal duration of antibiotics.
Application of the data
Returning to our case, on day 3, the patient’s fever had resolved and leukocytosis improved. In the absence of concern for persistent infection, repeat blood cultures were not performed. On day 4 initial blood cultures showed pan-sensitive Escherichia coli. The patient was transitioned to 750 mg oral ciprofloxacin b.i.d. to complete a 10-day course from first dose of ceftriaxone and was discharged from the hospital.
Bottom line
Management of GN bacteremia requires individualized care based on clinical presentation, but the data presented above can be used as broad guidelines to help reduce excess blood cultures, avoid prolonged use of intravenous antibiotics, and limit the duration of antibiotic exposure.
Dr. Imber is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and director of the Internal Medicine Simulation Education and Hospitalist Procedural Certification. Dr. Burns is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico. Dr. Chan is currently a chief resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of New Mexico.
References
1. Canzoneri CN et al. Follow-up blood cultures in gram-negative bacteremia: Are they needed? Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1776-9. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix648.
2. Kang CK et al. Can a routine follow-up blood culture be justified in Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia? A retrospective case-control study. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:365. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-365.
3. Mushtaq A et al. Repeating blood cultures after an initial bacteremia: When and how often? Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86(2):89-92. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.86a.18001.
4. Nimmich EB et al. Development of institutional guidelines for management of gram-negative bloodstream infections: Incorporating local evidence. Hosp Pharm. 2017;52(10):691-7. doi: 10.1177/0018578717720506.
5. Hale AJ et al. When are oral antibiotics a safe and effective choice for bacterial bloodstream infections? An evidence-based narrative review. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2949.
6. Kutob LF et al. Effectiveness of oral antibiotics for definitive therapy of gram-negative bloodstream infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.013.
7. Tamma PD et al. Association of 30-day mortality with oral step-down vs. continued intravenous therapy in patients hospitalized with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia. JAMA Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.6226.
8. Mercuro NJ et al. Retrospective analysis comparing oral stepdown therapy for enterobacteriaceae bloodstream infections: fluoroquinolones vs. B-lactams. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.12.007.
9. Park TY et al. Early oral antibiotic switch compared with conventional intravenous antibiotic therapy for acute cholangitis with bacteremia. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2790-6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3233-0.
10. Chotiprasitsakul D et al. Comparing the outcomes of adults with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia receiving short-course versus prolonged-course antibiotic therapy in a multicenter, propensity score-matched cohort. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(2):172-7. doi:10.1093/cid/cix767.
11. Havey TC et al. Duration of antibiotic therapy for bacteremia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2011;15(6):R267. doi:10.1186/cc10545.
12. Yahav D et al. Seven versus fourteen days of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: A noninferiority randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Dec. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy1054.
13. Nelson AN et al. Optimal duration of antimicrobial therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bloodstream infections. Infection. 2017;45(5):613-20. doi:10.1007/s15010-017-1020-5.
Case
A 42-year-old woman with uncontrolled diabetes presents to the ED with fever, chills, dysuria, and flank pain for 3 days. On exam, she is febrile and tachycardic. Lab results show leukocytosis and urinalysis is consistent with infection. CT scan shows acute pyelonephritis without complication. She is admitted to the hospital and started on ceftriaxone 2 g/24 hrs. On hospital day 2, her blood cultures show gram-negative bacteria.
Brief overview
Management of gram-negative (GN) bacteremia remains a challenging clinical situation for inpatient providers. With the push for high-value care and reductions in length of stay, recent literature has focused on reviewing current practices and attempting to standardize care. Despite this, no overarching guidelines exist to direct practice and clinicians are left to make decisions based on prior experience and expert opinion. Three key clinical questions exist when caring for a hospitalized patient with GN bacteremia: Should blood cultures be repeated? When is transition to oral antibiotics appropriate? And for what duration should antibiotics be given?
Overview of the data
When considering repeating blood cultures, it is important to understand that current literature does not support the practice for all GN bacteremias.
Canzoneri et al. retrospectively studied GN bacteremia and found that it took 17 repeat blood cultures being drawn to yield 1 positive result, which suggests that they are not necessary in all cases.1 Furthermore, repeat blood cultures increase cost of hospitalization, length of stay, and inconvenience to patients.2
However, Mushtaq et al. noted that repeating blood cultures can provide valuable information to confirm the response to treatment in patients with endovascular infection. Furthermore, they found that repeated blood cultures are also reasonable when the following scenarios are suspected: endocarditis or central line–associated infection, concern for multidrug resistant GN bacilli, and ongoing evidence of sepsis or patient decompensation.3
Consideration of a transition from intravenous to oral antibiotics is a key decision point in the care of GN bacteremia. Without guidelines, clinicians are left to evaluate patients on a case-by-case basis.4 Studies have suggested that the transition should be guided by the condition of the patient, the type of infection, and the culture-derived sensitivities.5 Additionally, bioavailability of antibiotics (see Table 1) is an important consideration and a recent examination of oral antibiotic failure rates demonstrated that lower bioavailability antibiotics have an increased risk of failure (2% vs. 16%).6
In their study, Kutob et al. highlighted the importance of choosing not only an antibiotic of high bioavailability, but also an antibiotic dose which will support a high concentration of the antibiotic in the bloodstream.6 For example, they identify ciprofloxacin as a moderate bioavailability medication, but note that most cases they examined utilized 500 mg b.i.d., where the concentration-dependent killing and dose-dependent bioavailability would advocate for the use of 750 mg b.i.d. or 500 mg every 8 hours.
The heterogeneity of GN bloodstream infections also creates difficulty in standardization of care. The literature suggests that infection source plays a significant role in the type of GN bacteria isolated.6,7 The best data for the transition to oral antibiotics exists with urologic sources and it remains unclear whether bacteria from other sources have higher risks of oral antibiotic failure.8
One recent study of 66 patients examined bacteremia in the setting of cholangitis and found that, once patients had stabilized, a switch from intravenous to oral antibiotics was noninferior, but randomized, prospective trials have not been performed. Notably, patients were transitioned to orals only after they were found to have a fluoroquinolone-sensitive infection, allowing the study authors to use higher-bioavailability agents for the transition to orals.9 Multiple studies have highlighted the unique care required for certain infections, such as pseudomonal infections, which most experts agree requires a more conservative approach.5,6
Fluoroquinolones are the bedrock of therapy for GN bacteremia because of historic in vivo experience and in vitro findings about bioavailability and dose-dependent killing, but they are also the antibiotic class associated with the highest hospitalization rates for antibiotic-associated adverse events.8 A recent noninferiority trial comparing the use of beta-lactams with fluoroquinolones found that beta-lactams were noninferior, though the study was flawed by the limited number of beta-lactam–using patients identified.8 It is clear that more investigation is needed before recommendations can be made regarding ideal oral antibiotics for GN bacteremia.
The transition to oral is reasonable given the following criteria: the patient has improved on intravenous antibiotics and source control has been achieved; the culture data have demonstrated sensitivity to the oral antibiotic of choice, with special care given to higher-risk bacteria such as Pseudomonas; the patient is able to take the oral antibiotic; and the oral antibiotic of choice has the highest bioavailability possible and is given at an appropriate dose to reach its highest killing and bioavailability concentrations.7
After evaluating the appropriateness of transition to oral antibiotics, the final decision is about duration of antibiotic therapy. Current Infectious Disease Society of America guidelines are based on expert opinion and recommend 7-14 days of therapy. As with many common infections, recent studies have focused on evaluating reduction in antibiotic durations.
Chotiprasitsakul et al. demonstrated no difference in mortality or morbidity in 385 propensity-matched pairs with treatment of Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia for 8 versus 15 days.10 A mixed meta-analysis performed in 2011 evaluated 24 randomized, controlled trials and found shorter durations (5-7 days) had similar outcomes to prolonged durations (7-21 days).11 Recently, Yahav et al. performed a randomized control trial comparing 7- and 14-day regimens for uncomplicated GN bacteremia and found a 7-day course to be noninferior if patients were clinically stable by day 5 and had source control.12
It should be noted that not all studies have found that reduced durations are without harm. Nelson et al. performed a retrospective cohort analysis and found that reduced durations of antibiotics (7-10 days) increased mortality and recurrent infection when compared with a longer course (greater than 10 days).13 These contrary findings highlight the need for provider discretion in selecting a course of antibiotics as well as the need for further studies about optimal duration of antibiotics.
Application of the data
Returning to our case, on day 3, the patient’s fever had resolved and leukocytosis improved. In the absence of concern for persistent infection, repeat blood cultures were not performed. On day 4 initial blood cultures showed pan-sensitive Escherichia coli. The patient was transitioned to 750 mg oral ciprofloxacin b.i.d. to complete a 10-day course from first dose of ceftriaxone and was discharged from the hospital.
Bottom line
Management of GN bacteremia requires individualized care based on clinical presentation, but the data presented above can be used as broad guidelines to help reduce excess blood cultures, avoid prolonged use of intravenous antibiotics, and limit the duration of antibiotic exposure.
Dr. Imber is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, and director of the Internal Medicine Simulation Education and Hospitalist Procedural Certification. Dr. Burns is an assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of New Mexico. Dr. Chan is currently a chief resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of New Mexico.
References
1. Canzoneri CN et al. Follow-up blood cultures in gram-negative bacteremia: Are they needed? Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(11):1776-9. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix648.
2. Kang CK et al. Can a routine follow-up blood culture be justified in Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia? A retrospective case-control study. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:365. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-365.
3. Mushtaq A et al. Repeating blood cultures after an initial bacteremia: When and how often? Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86(2):89-92. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.86a.18001.
4. Nimmich EB et al. Development of institutional guidelines for management of gram-negative bloodstream infections: Incorporating local evidence. Hosp Pharm. 2017;52(10):691-7. doi: 10.1177/0018578717720506.
5. Hale AJ et al. When are oral antibiotics a safe and effective choice for bacterial bloodstream infections? An evidence-based narrative review. J Hosp Med. 2018 May. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2949.
6. Kutob LF et al. Effectiveness of oral antibiotics for definitive therapy of gram-negative bloodstream infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.07.013.
7. Tamma PD et al. Association of 30-day mortality with oral step-down vs. continued intravenous therapy in patients hospitalized with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia. JAMA Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.6226.
8. Mercuro NJ et al. Retrospective analysis comparing oral stepdown therapy for enterobacteriaceae bloodstream infections: fluoroquinolones vs. B-lactams. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.12.007.
9. Park TY et al. Early oral antibiotic switch compared with conventional intravenous antibiotic therapy for acute cholangitis with bacteremia. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:2790-6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3233-0.
10. Chotiprasitsakul D et al. Comparing the outcomes of adults with Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia receiving short-course versus prolonged-course antibiotic therapy in a multicenter, propensity score-matched cohort. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(2):172-7. doi:10.1093/cid/cix767.
11. Havey TC et al. Duration of antibiotic therapy for bacteremia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2011;15(6):R267. doi:10.1186/cc10545.
12. Yahav D et al. Seven versus fourteen days of antibiotic therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: A noninferiority randomized controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2018 Dec. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy1054.
13. Nelson AN et al. Optimal duration of antimicrobial therapy for uncomplicated gram-negative bloodstream infections. Infection. 2017;45(5):613-20. doi:10.1007/s15010-017-1020-5.
Prescriptions for cough, cold medicine dropping for children
with evidence suggesting replacement by off-label antihistamines, according to analysis of two national databases.
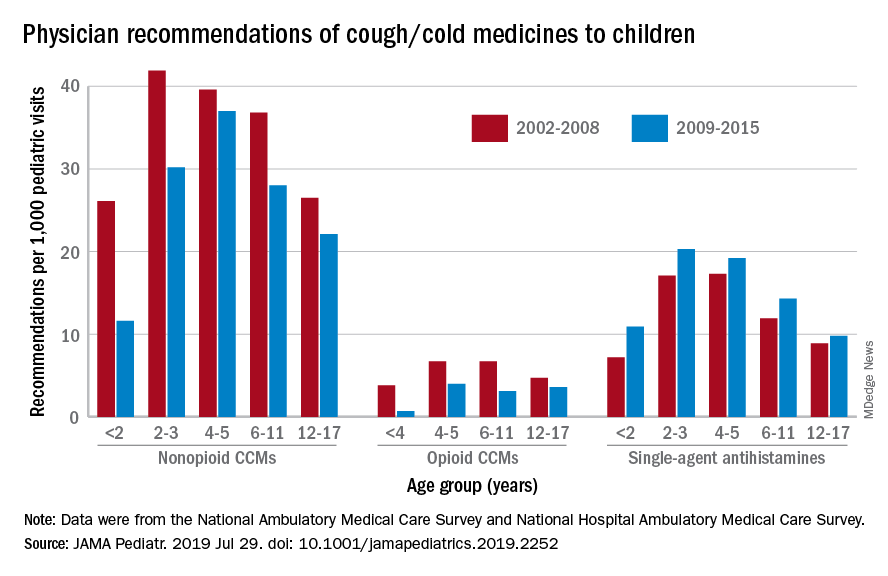
Compared with older children, declines in both opioid and nonopioid cold and cough medicine (CCM) use “appeared to accelerate in children younger than 2 years … and among children younger than 6 years for opioid-containing CCM” after the Food and Drug Administration’s 2008 public health advisory on use of OTC forms of CCM, Daniel B. Horton, MD, of the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., and his associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
Meanwhile, recommendations for single-agent antihistamines rose – for some age groups significantly – over the 14-year study period, which was divided into two eras: 2002-2008 and 2009-2015.
When the two eras were compared, trends for decreased use of CCM in children under 2 years of age (nonopioid) and under 4 years (opioid) approached – both were P = .05 – but did not quite reach the less than .05 considered statistically significant. Adjusted odds ratios for the other age groups were further off the mark. For antihistamines, the upward trend between the two eras was significant for children aged under 2 years, 2-3 years, and 6-11 years, Dr. Horton and associates reported.
The two youngest groups, under 2 years and 2-3, were combined for the opioid CCM analyses to avoid a population under 30, which would have yielded unreliable estimates. The investigators used data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, with the sample representing 3.1 billion pediatric visits from 2002 to 2015.
Dr. Horton is supported by an award from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study.
SOURCE: Horton DB et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Jul 29. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.2252.
with evidence suggesting replacement by off-label antihistamines, according to analysis of two national databases.

Compared with older children, declines in both opioid and nonopioid cold and cough medicine (CCM) use “appeared to accelerate in children younger than 2 years … and among children younger than 6 years for opioid-containing CCM” after the Food and Drug Administration’s 2008 public health advisory on use of OTC forms of CCM, Daniel B. Horton, MD, of the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., and his associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
Meanwhile, recommendations for single-agent antihistamines rose – for some age groups significantly – over the 14-year study period, which was divided into two eras: 2002-2008 and 2009-2015.
When the two eras were compared, trends for decreased use of CCM in children under 2 years of age (nonopioid) and under 4 years (opioid) approached – both were P = .05 – but did not quite reach the less than .05 considered statistically significant. Adjusted odds ratios for the other age groups were further off the mark. For antihistamines, the upward trend between the two eras was significant for children aged under 2 years, 2-3 years, and 6-11 years, Dr. Horton and associates reported.
The two youngest groups, under 2 years and 2-3, were combined for the opioid CCM analyses to avoid a population under 30, which would have yielded unreliable estimates. The investigators used data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, with the sample representing 3.1 billion pediatric visits from 2002 to 2015.
Dr. Horton is supported by an award from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study.
SOURCE: Horton DB et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Jul 29. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.2252.
with evidence suggesting replacement by off-label antihistamines, according to analysis of two national databases.

Compared with older children, declines in both opioid and nonopioid cold and cough medicine (CCM) use “appeared to accelerate in children younger than 2 years … and among children younger than 6 years for opioid-containing CCM” after the Food and Drug Administration’s 2008 public health advisory on use of OTC forms of CCM, Daniel B. Horton, MD, of the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., and his associates wrote in JAMA Pediatrics.
Meanwhile, recommendations for single-agent antihistamines rose – for some age groups significantly – over the 14-year study period, which was divided into two eras: 2002-2008 and 2009-2015.
When the two eras were compared, trends for decreased use of CCM in children under 2 years of age (nonopioid) and under 4 years (opioid) approached – both were P = .05 – but did not quite reach the less than .05 considered statistically significant. Adjusted odds ratios for the other age groups were further off the mark. For antihistamines, the upward trend between the two eras was significant for children aged under 2 years, 2-3 years, and 6-11 years, Dr. Horton and associates reported.
The two youngest groups, under 2 years and 2-3, were combined for the opioid CCM analyses to avoid a population under 30, which would have yielded unreliable estimates. The investigators used data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, with the sample representing 3.1 billion pediatric visits from 2002 to 2015.
Dr. Horton is supported by an award from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The investigators reported no disclosures relevant to this study.
SOURCE: Horton DB et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019 Jul 29. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.2252.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Novel translocation inhibitor shows efficacy in treatment-naive HIV-1–infected adults
The first-in-class antiretroviral therapy islatravir (Merck) was well tolerated and had promising efficacy in a phase 2B study including treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, supporting plans to initiate a phase 3 trial, an investigator said at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The proportion of patients achieving viral suppression at week 48 with combinations including the nucleoside transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) was comparable to what was achieved with a standard triple regimen, said investigator Jean-Michel Molina, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris Diderot, and head of the infectious diseases department at the Saint-Louis Hospital in Paris
The treatment was effective not only as part of a three-drug combination of islatravir, doravirine, and lamivudine over 24 weeks, but also over an additional 24 weeks in patients who achieved viral suppression and were switched to dual therapy with islatravir and doravirine, according to Dr. Molina.
“These are promising data that will encourage the company to move to a phase 3 trial to see how these results can be confirmed in a larger study set, and also to assess the potency of the dual combination for maintenance therapy in the future, providing also novel options for people with a drug that has a high genetic barrier to resistance and efficacy that seems to be quite interesting,” Dr. Molina said in an IAS press conference in Mexico City.
This drug has very potent activity not only against wild-type HIV-1 viruses, but also multiresistant viruses, according to Dr. Molina.
“It has a high inhibitory quotient at a very low dose, so you give people a tiny amount of drug – in the range of 1 milligram per day, instead of a few hundred milligrams with other, regular drugs,” he said.
Another attribute of islatravir is its long half-life of approximately 120 hours, allowing not only for once-daily dosing, but potentially for evaluation as once-weekly or once-monthly dosing in the future, he said, adding that a subdermal islatravir-eluting implant under investigation for preexposure prophylaxis has potential as a once-yearly option.
The international, multicenter, 121-patient clinical trial that Dr. Molina described included adults with HIV-1 infection naive to antiretroviral therapy randomized to islatravir (in one of three doses) plus doravirine and lamivudine, or to the combination of doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir (Delstrigo, Merck).
After at least 24 weeks of treatment, subjects in the islatravir treatment groups were transitioned to the two-drug combination of islatravir and doravirine if they had HIV-1 RNA levels less than 50 copies/mL and did not meet any protocol-defined criteria for virologic failure.
Those participants in the islatravir arms who received 48 weeks of treatment had “very good response” and safety that was comparable to the control arm, according to Dr. Molina.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL were 89.7%, 90%, and 77.4% for regimens containing islatravir 0.25 mg, 0.75 mg, and 2.25 mg, respectively, and 83.9% for those receiving the standard triple therapy, according to reported data.
All patients with protocol-defined virologic failure (greater than or equal to 50 copies/mL) in the study actually had very low viral load, below 80 copies/mL, Dr. Molina said.
The study was supported by Merck. Dr. Molina has been on the Merck advisory board and speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Molina J-M et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0402LB.
The first-in-class antiretroviral therapy islatravir (Merck) was well tolerated and had promising efficacy in a phase 2B study including treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, supporting plans to initiate a phase 3 trial, an investigator said at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The proportion of patients achieving viral suppression at week 48 with combinations including the nucleoside transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) was comparable to what was achieved with a standard triple regimen, said investigator Jean-Michel Molina, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris Diderot, and head of the infectious diseases department at the Saint-Louis Hospital in Paris
The treatment was effective not only as part of a three-drug combination of islatravir, doravirine, and lamivudine over 24 weeks, but also over an additional 24 weeks in patients who achieved viral suppression and were switched to dual therapy with islatravir and doravirine, according to Dr. Molina.
“These are promising data that will encourage the company to move to a phase 3 trial to see how these results can be confirmed in a larger study set, and also to assess the potency of the dual combination for maintenance therapy in the future, providing also novel options for people with a drug that has a high genetic barrier to resistance and efficacy that seems to be quite interesting,” Dr. Molina said in an IAS press conference in Mexico City.
This drug has very potent activity not only against wild-type HIV-1 viruses, but also multiresistant viruses, according to Dr. Molina.
“It has a high inhibitory quotient at a very low dose, so you give people a tiny amount of drug – in the range of 1 milligram per day, instead of a few hundred milligrams with other, regular drugs,” he said.
Another attribute of islatravir is its long half-life of approximately 120 hours, allowing not only for once-daily dosing, but potentially for evaluation as once-weekly or once-monthly dosing in the future, he said, adding that a subdermal islatravir-eluting implant under investigation for preexposure prophylaxis has potential as a once-yearly option.
The international, multicenter, 121-patient clinical trial that Dr. Molina described included adults with HIV-1 infection naive to antiretroviral therapy randomized to islatravir (in one of three doses) plus doravirine and lamivudine, or to the combination of doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir (Delstrigo, Merck).
After at least 24 weeks of treatment, subjects in the islatravir treatment groups were transitioned to the two-drug combination of islatravir and doravirine if they had HIV-1 RNA levels less than 50 copies/mL and did not meet any protocol-defined criteria for virologic failure.
Those participants in the islatravir arms who received 48 weeks of treatment had “very good response” and safety that was comparable to the control arm, according to Dr. Molina.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL were 89.7%, 90%, and 77.4% for regimens containing islatravir 0.25 mg, 0.75 mg, and 2.25 mg, respectively, and 83.9% for those receiving the standard triple therapy, according to reported data.
All patients with protocol-defined virologic failure (greater than or equal to 50 copies/mL) in the study actually had very low viral load, below 80 copies/mL, Dr. Molina said.
The study was supported by Merck. Dr. Molina has been on the Merck advisory board and speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Molina J-M et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0402LB.
The first-in-class antiretroviral therapy islatravir (Merck) was well tolerated and had promising efficacy in a phase 2B study including treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, supporting plans to initiate a phase 3 trial, an investigator said at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The proportion of patients achieving viral suppression at week 48 with combinations including the nucleoside transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) was comparable to what was achieved with a standard triple regimen, said investigator Jean-Michel Molina, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Paris Diderot, and head of the infectious diseases department at the Saint-Louis Hospital in Paris
The treatment was effective not only as part of a three-drug combination of islatravir, doravirine, and lamivudine over 24 weeks, but also over an additional 24 weeks in patients who achieved viral suppression and were switched to dual therapy with islatravir and doravirine, according to Dr. Molina.
“These are promising data that will encourage the company to move to a phase 3 trial to see how these results can be confirmed in a larger study set, and also to assess the potency of the dual combination for maintenance therapy in the future, providing also novel options for people with a drug that has a high genetic barrier to resistance and efficacy that seems to be quite interesting,” Dr. Molina said in an IAS press conference in Mexico City.
This drug has very potent activity not only against wild-type HIV-1 viruses, but also multiresistant viruses, according to Dr. Molina.
“It has a high inhibitory quotient at a very low dose, so you give people a tiny amount of drug – in the range of 1 milligram per day, instead of a few hundred milligrams with other, regular drugs,” he said.
Another attribute of islatravir is its long half-life of approximately 120 hours, allowing not only for once-daily dosing, but potentially for evaluation as once-weekly or once-monthly dosing in the future, he said, adding that a subdermal islatravir-eluting implant under investigation for preexposure prophylaxis has potential as a once-yearly option.
The international, multicenter, 121-patient clinical trial that Dr. Molina described included adults with HIV-1 infection naive to antiretroviral therapy randomized to islatravir (in one of three doses) plus doravirine and lamivudine, or to the combination of doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir (Delstrigo, Merck).
After at least 24 weeks of treatment, subjects in the islatravir treatment groups were transitioned to the two-drug combination of islatravir and doravirine if they had HIV-1 RNA levels less than 50 copies/mL and did not meet any protocol-defined criteria for virologic failure.
Those participants in the islatravir arms who received 48 weeks of treatment had “very good response” and safety that was comparable to the control arm, according to Dr. Molina.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL were 89.7%, 90%, and 77.4% for regimens containing islatravir 0.25 mg, 0.75 mg, and 2.25 mg, respectively, and 83.9% for those receiving the standard triple therapy, according to reported data.
All patients with protocol-defined virologic failure (greater than or equal to 50 copies/mL) in the study actually had very low viral load, below 80 copies/mL, Dr. Molina said.
The study was supported by Merck. Dr. Molina has been on the Merck advisory board and speaker’s bureau.
SOURCE: Molina J-M et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0402LB.
FROM IAS 2019
Antiretroviral-eluting implant could provide HIV prophylaxis for a year or more
An implant that elutes an investigational antiretroviral agent provided drug release that should be sufficient for HIV prophylaxis for 12 months or more, according to results of a phase 1 clinical trial just presented here at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The islatravir-eluting arm implant was safe and generally well tolerated, with drug concentrations that remained above the target level needed for protection throughout the randomized, placebo-controlled study, said investigator Randolph P. Matthews, MD, PhD, senior principal scientist at Merck, Kenilworth, N.J.
“Based on this study, the islatravir-eluting implant appears to be a potentially important option for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) as an agent that could be effective with yearly dosing,” Dr. Matthews said in an IAS press conference.
This drug-eluting implant, inserted subdermally in the skin of the upper arm, could represent a “meaningful option” for many individuals at high risk of HIV infection, particularly those who have adherence challenges, said Dr. Matthews.
“Many at-risk individuals face adherence challenges with the existing daily oral PrEP therapy,” he added. “A high degree of adherence is required for it to be effective, and daily adherence is challenging for many, particularly for women.”
Islatravir, formerly known as MK-8591, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) being evaluated in clinical trials not only for PrEP, but also for treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with other antiretrovirals.
In preclinical trials, islatravir demonstrated high potency, a high barrier to resistance, and a long half-life, according to Dr. Matthews.
The phase 1, single-site, double-blind study included a total of 16 healthy adult volunteers who received implants of islatravir at one of two doses (54 mg and 62 mg) or placebo for 12 weeks.
Both active doses of islatravir led to concentrations above the target level at 12 weeks, and based on data modeling, the higher-dose implant would still be above the target level for at least a year, Dr. Matthews said in the press conference.
The projected duration above the target ranged from 12 to 16 months for the 62-mg dose of islatravir, and from 8 to 10 months for the 54-mg dose, according to the reported data.
All drug-related adverse events were mild or moderate in severity, and none of the volunteers discontinued the study because of an adverse event, Dr. Matthews said.
Taken together, these data support the continued progression of the implant clinical development program, said Dr. Matthews, who is an employee of Merck, which sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Matthews RP et al. IAS 2019, Abstract TUAC0401LB.
An implant that elutes an investigational antiretroviral agent provided drug release that should be sufficient for HIV prophylaxis for 12 months or more, according to results of a phase 1 clinical trial just presented here at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The islatravir-eluting arm implant was safe and generally well tolerated, with drug concentrations that remained above the target level needed for protection throughout the randomized, placebo-controlled study, said investigator Randolph P. Matthews, MD, PhD, senior principal scientist at Merck, Kenilworth, N.J.
“Based on this study, the islatravir-eluting implant appears to be a potentially important option for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) as an agent that could be effective with yearly dosing,” Dr. Matthews said in an IAS press conference.
This drug-eluting implant, inserted subdermally in the skin of the upper arm, could represent a “meaningful option” for many individuals at high risk of HIV infection, particularly those who have adherence challenges, said Dr. Matthews.
“Many at-risk individuals face adherence challenges with the existing daily oral PrEP therapy,” he added. “A high degree of adherence is required for it to be effective, and daily adherence is challenging for many, particularly for women.”
Islatravir, formerly known as MK-8591, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) being evaluated in clinical trials not only for PrEP, but also for treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with other antiretrovirals.
In preclinical trials, islatravir demonstrated high potency, a high barrier to resistance, and a long half-life, according to Dr. Matthews.
The phase 1, single-site, double-blind study included a total of 16 healthy adult volunteers who received implants of islatravir at one of two doses (54 mg and 62 mg) or placebo for 12 weeks.
Both active doses of islatravir led to concentrations above the target level at 12 weeks, and based on data modeling, the higher-dose implant would still be above the target level for at least a year, Dr. Matthews said in the press conference.
The projected duration above the target ranged from 12 to 16 months for the 62-mg dose of islatravir, and from 8 to 10 months for the 54-mg dose, according to the reported data.
All drug-related adverse events were mild or moderate in severity, and none of the volunteers discontinued the study because of an adverse event, Dr. Matthews said.
Taken together, these data support the continued progression of the implant clinical development program, said Dr. Matthews, who is an employee of Merck, which sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Matthews RP et al. IAS 2019, Abstract TUAC0401LB.
An implant that elutes an investigational antiretroviral agent provided drug release that should be sufficient for HIV prophylaxis for 12 months or more, according to results of a phase 1 clinical trial just presented here at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
The islatravir-eluting arm implant was safe and generally well tolerated, with drug concentrations that remained above the target level needed for protection throughout the randomized, placebo-controlled study, said investigator Randolph P. Matthews, MD, PhD, senior principal scientist at Merck, Kenilworth, N.J.
“Based on this study, the islatravir-eluting implant appears to be a potentially important option for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) as an agent that could be effective with yearly dosing,” Dr. Matthews said in an IAS press conference.
This drug-eluting implant, inserted subdermally in the skin of the upper arm, could represent a “meaningful option” for many individuals at high risk of HIV infection, particularly those who have adherence challenges, said Dr. Matthews.
“Many at-risk individuals face adherence challenges with the existing daily oral PrEP therapy,” he added. “A high degree of adherence is required for it to be effective, and daily adherence is challenging for many, particularly for women.”
Islatravir, formerly known as MK-8591, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase translocation inhibitor (NRTTI) being evaluated in clinical trials not only for PrEP, but also for treatment of HIV-1 infection in combination with other antiretrovirals.
In preclinical trials, islatravir demonstrated high potency, a high barrier to resistance, and a long half-life, according to Dr. Matthews.
The phase 1, single-site, double-blind study included a total of 16 healthy adult volunteers who received implants of islatravir at one of two doses (54 mg and 62 mg) or placebo for 12 weeks.
Both active doses of islatravir led to concentrations above the target level at 12 weeks, and based on data modeling, the higher-dose implant would still be above the target level for at least a year, Dr. Matthews said in the press conference.
The projected duration above the target ranged from 12 to 16 months for the 62-mg dose of islatravir, and from 8 to 10 months for the 54-mg dose, according to the reported data.
All drug-related adverse events were mild or moderate in severity, and none of the volunteers discontinued the study because of an adverse event, Dr. Matthews said.
Taken together, these data support the continued progression of the implant clinical development program, said Dr. Matthews, who is an employee of Merck, which sponsored the study.
SOURCE: Matthews RP et al. IAS 2019, Abstract TUAC0401LB.
FROM IAS 2019
Two-drug integrase inhibitor–based regimen noninferior to standard in HIV-infected adults
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
New studies of a two-drug, integrase inhibitor–based regimen, presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, provide additional data to challenge the three-drug HIV treatment paradigm.
In the results of one study, known as TANGO (NCT03446573), switching to the fixed-dose combination of dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) from a tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)–based three- or four-drug regimen maintained virologic suppression at 48 weeks in HIV-1 infected adults, an investigator said, and was noninferior to continuing TAF-based therapy.
In another presentation, updating results of the GEMINI-1 (NCT02831673) and GEMINI-2 studies (NCT02831764), a researcher said the DTG+3TC combination remained noninferior to DTG plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) at week 96 in antiretroviral (ART) treatment-naive adults with HIV-1 infection, with no treatment-emergent resistance and no increase in risk of virologic failure.
,” according to IAS Past President Pedro Cahn, MD, PhD, of Fundación Huésped, Buenos Aires, who presented the updated GEMINI study results.
“We don’t mean to say now everything should be dual therapy, and we are going to wipe out all other options, but I think we have another strong option for initiating therapy, and probably also for switch therapy,” Dr. Cahn said in a press conference.
Dr. Cahn presented an updated analysis of GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2, two identically designed phase 3 randomized clinical trials including a total of 1,400 patients.
The 48-week results from those trials, presented in 2018, showed for the first time that a dual-therapy combination of an integrase inhibitor with 3TC was noninferior to the triple-drug regimen of DTG+TDF/FTC, Dr. Cahn said.
In the updated analysis, including 96 weeks of data, the two-drug regimen remained noninferior to the three-drug regimen, according to the investigator.
A total of 11 patients on DTG+3TC and 7 on DTG+TDF/FTC met virologic withdrawal criteria through week 96, with no treatment-emergent resistance mutations seen in either arm, according to results reported in the study abstract.
The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA below 50 c/mL at week 96 was 86% for the two-drug regimen and 90% for the three-drug regimen (adjusted difference, –3.4; 95% confidence interval, –6.7 to 0.0), the reported data showed.
Drug-related adverse events were numerically more common in the three-drug arm, though rates of adverse event–related withdrawal were low in both arms, according to investigators.
The strategy of switching to DTG+3TC was evaluated in the randomized, phase 3 TANGO trial, which included 741 subjects who were already virally suppressed on a TAF-based three- or four-drug regimen. After 48 weeks of therapy, the two-drug regimen was noninferior to remaining on TAF-based therapy in terms of achieving and maintaining viral suppression, according to investigator Jean van Wyk, MB, ChB, Global Medical Lead for dolutegravir at ViiV Healthcare.
Safety outcomes were similar between the arms, though the absolute number of treatment-related adverse events was higher in the DTG+3TC arm “as expected in a switch study,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The percentage of subjects withdrawing from the study because of adverse events was 4% in the DTG+3TC arm and less than 1% in the TAF-based treatment arm, according to reported data.
And with regard to safety there were similar outcomes between the two arms, with regard to overall adverse events, “but as expected in a switch study, we did see more treatment-related adverse events in the dolutegravir plus lamivudine arm, and that’s because the majority of patients were on two new agents in the form of dolutegravir plus lamivudine, so it’s completely expected,” Dr. van Wyk said.
The study met its primary endpoint for noninferiority at week 48, based on the Food and Drug Administration snapshot algorithm. Results showed that switching to DTG+3TC was noninferior to continuing the TAF-containing regimen at week 48, with virologic failure per snapshot criteria seen in less than 1% of subjects in either arm, according to reported data. The proportion of subjects with plasma HIV-1 RNA less than 50 c/mL was 93.2% and 93.0% for the DTG+3TC and TAF-based treatment arms, respectively.
Longer-term follow-up will be important to confirm the noninferiority of the two-drug approach, Dr. van Wyk and Dr. Cahn said in the press conference. The TANGO study of the switch strategy will continue through 148 weeks, while an additional year of follow-up is ongoing for the GEMINI studies of the initial therapy approach.
TANGO and both GEMINI 1 and GEMINI 2 were sponsored by ViiV Healthcare. Dr. van Wyk is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. Dr. Cahn has received research support grants, and fees as consultant and speaker from ViiV Healthcare.
SOURCE: Cahn P et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0404LB; van Wyk J et al. IAS 2019, Abstract WEAB0403LB.
REPORTING FROM IAS 2019
PHiD-CV with 4CMenB safe, effective for infants
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines is not only safe but also offers the potential to improve vaccine uptake and reduce the number of doctors’ visits required for routine vaccination, advised Marco Aurelio P. Safadi, MD, PhD, of Santa Casa de São Paulo School of Medical Sciences, Brazil, and associates.
In a post hoc analysis of a phase 3b open-label study, Dr. Safadi and associates sought to evaluate immune response in pneumococcal non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae protein D conjugate vaccine (PHiD-CV) administered concomitantly with either meningococcal serogroup B (4CMenB) vaccine and CRM-conjugated meningococcal serogroup C vaccine (MenC-CRM) or with MenC-CRM alone using reduced schedules in 213 healthy infants aged 83-104 days. Study participants were enrolled and randomized to one of two groups between April 2011 and December 2014 at four sites in Brazil (Vaccine. 2019 Jul 18. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.07.021).
Similar immune response was seen with vaccine serotypes and vaccine-related pneumococcal serotypes 6A and 19A in children who had received concomitant administration of PHiD-CV, 4CMenB, and MenC-CRM without 4CMenB.
Dr. Safadi and associates pointed out that PHiD-CV was given in accordance with a 3+1 dosing schedule, while 4CMenB used a reduced 2+1 schedule, which was observed to produce an immune response and provide an acceptable safety profile.
The findings yielded valuable information for the 2+1 PHiD-CV vaccination schedule, which was recently introduced in Brazil, the researchers said. The post-booster results further reflect the “immunogenicity following 3-dose priming.”
The post hoc nature of this study design effectively demonstrated that or with MenC-CRM alone, they explained.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Biologicals. Three authors are employees of the GSK group of companies, and three others received a grant from the GSK companies, two of whom received compensation from other pharmaceutical companies. The institution of one of the authors received clinical trial fees from the GSK companies, and received personal fees/nonfinancial support/grants/other from the GSK companies and many other pharmaceutical companies.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines is not only safe but also offers the potential to improve vaccine uptake and reduce the number of doctors’ visits required for routine vaccination, advised Marco Aurelio P. Safadi, MD, PhD, of Santa Casa de São Paulo School of Medical Sciences, Brazil, and associates.
In a post hoc analysis of a phase 3b open-label study, Dr. Safadi and associates sought to evaluate immune response in pneumococcal non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae protein D conjugate vaccine (PHiD-CV) administered concomitantly with either meningococcal serogroup B (4CMenB) vaccine and CRM-conjugated meningococcal serogroup C vaccine (MenC-CRM) or with MenC-CRM alone using reduced schedules in 213 healthy infants aged 83-104 days. Study participants were enrolled and randomized to one of two groups between April 2011 and December 2014 at four sites in Brazil (Vaccine. 2019 Jul 18. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.07.021).
Similar immune response was seen with vaccine serotypes and vaccine-related pneumococcal serotypes 6A and 19A in children who had received concomitant administration of PHiD-CV, 4CMenB, and MenC-CRM without 4CMenB.
Dr. Safadi and associates pointed out that PHiD-CV was given in accordance with a 3+1 dosing schedule, while 4CMenB used a reduced 2+1 schedule, which was observed to produce an immune response and provide an acceptable safety profile.
The findings yielded valuable information for the 2+1 PHiD-CV vaccination schedule, which was recently introduced in Brazil, the researchers said. The post-booster results further reflect the “immunogenicity following 3-dose priming.”
The post hoc nature of this study design effectively demonstrated that or with MenC-CRM alone, they explained.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Biologicals. Three authors are employees of the GSK group of companies, and three others received a grant from the GSK companies, two of whom received compensation from other pharmaceutical companies. The institution of one of the authors received clinical trial fees from the GSK companies, and received personal fees/nonfinancial support/grants/other from the GSK companies and many other pharmaceutical companies.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal and meningococcal vaccines is not only safe but also offers the potential to improve vaccine uptake and reduce the number of doctors’ visits required for routine vaccination, advised Marco Aurelio P. Safadi, MD, PhD, of Santa Casa de São Paulo School of Medical Sciences, Brazil, and associates.
In a post hoc analysis of a phase 3b open-label study, Dr. Safadi and associates sought to evaluate immune response in pneumococcal non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae protein D conjugate vaccine (PHiD-CV) administered concomitantly with either meningococcal serogroup B (4CMenB) vaccine and CRM-conjugated meningococcal serogroup C vaccine (MenC-CRM) or with MenC-CRM alone using reduced schedules in 213 healthy infants aged 83-104 days. Study participants were enrolled and randomized to one of two groups between April 2011 and December 2014 at four sites in Brazil (Vaccine. 2019 Jul 18. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.07.021).
Similar immune response was seen with vaccine serotypes and vaccine-related pneumococcal serotypes 6A and 19A in children who had received concomitant administration of PHiD-CV, 4CMenB, and MenC-CRM without 4CMenB.
Dr. Safadi and associates pointed out that PHiD-CV was given in accordance with a 3+1 dosing schedule, while 4CMenB used a reduced 2+1 schedule, which was observed to produce an immune response and provide an acceptable safety profile.
The findings yielded valuable information for the 2+1 PHiD-CV vaccination schedule, which was recently introduced in Brazil, the researchers said. The post-booster results further reflect the “immunogenicity following 3-dose priming.”
The post hoc nature of this study design effectively demonstrated that or with MenC-CRM alone, they explained.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Biologicals. Three authors are employees of the GSK group of companies, and three others received a grant from the GSK companies, two of whom received compensation from other pharmaceutical companies. The institution of one of the authors received clinical trial fees from the GSK companies, and received personal fees/nonfinancial support/grants/other from the GSK companies and many other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM VACCINE
Spleen/liver stiffness ratio differentiates HCV, ALD
The spleen stiffness (SS) to liver stiffness (LS) ratio was significantly higher in patients with hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) than in patients with alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), according to the results of a multicenter prospective study. In addition, long-term outcome and complications differed dramatically between HCV and ALD. Variceal bleeding was the most common sign of decompensation and cause of death in patients with HCV, while jaundice was the most common sign of decompensation in patients with ALD.
Omar Elshaarawy, MSc, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and colleagues reported on their prospective study of 411 patients with HCV (220 patients) or ALD (191 patients) that were assessed for both LS and SS using the Fibroscan device. They also discussed their retrospective analysis of LS and spleen length (SL) from a separate, retrospective cohort of 449 patients (267 with HCV, 182 with ALD) for whom long-term data on decompensation/death were available.
The researchers found that SS was significantly higher in HCV patients, compared with those with ALD (42.0 vs. 32.6 kPa; P less than .0001), as was SL (15.6 vs. 11.9 cm, P less than .0001); this was despite a lower mean LS in HCV. As a result, the SS/LS ratio and the SL/LS ratio were both significantly higher in HCV (3.8 vs. 1.72 and 1.46 vs. 0.86, P less than .0001) through all fibrosis stages.
They also found that patients with ALD had higher LS values (30.5 vs. 21.3 kPa) and predominantly presented with jaundice (65.2%), with liver failure as the major cause of death (P less than .01). In contrast, in HCV, spleens were larger (17.6 vs. 12.1 cm) while variceal bleeding was the major cause of decompensation (73.2%) and death (P less than .001).
“We have demonstrated the disease-specific differences in SS/LS and SL/LS ratio between HCV and ALD. They underscore the role of the intrahepatic histological site of inflammation/fibrosis. We suggest that the SS/LS ratio could be used to confirm the disease etiology and predict disease-specific complications,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the Dietmar Hopp Foundation. The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Elshaarawy O et al. J Hepatol Reports. 2019 Jun 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.05.003.
The spleen stiffness (SS) to liver stiffness (LS) ratio was significantly higher in patients with hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) than in patients with alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), according to the results of a multicenter prospective study. In addition, long-term outcome and complications differed dramatically between HCV and ALD. Variceal bleeding was the most common sign of decompensation and cause of death in patients with HCV, while jaundice was the most common sign of decompensation in patients with ALD.
Omar Elshaarawy, MSc, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and colleagues reported on their prospective study of 411 patients with HCV (220 patients) or ALD (191 patients) that were assessed for both LS and SS using the Fibroscan device. They also discussed their retrospective analysis of LS and spleen length (SL) from a separate, retrospective cohort of 449 patients (267 with HCV, 182 with ALD) for whom long-term data on decompensation/death were available.
The researchers found that SS was significantly higher in HCV patients, compared with those with ALD (42.0 vs. 32.6 kPa; P less than .0001), as was SL (15.6 vs. 11.9 cm, P less than .0001); this was despite a lower mean LS in HCV. As a result, the SS/LS ratio and the SL/LS ratio were both significantly higher in HCV (3.8 vs. 1.72 and 1.46 vs. 0.86, P less than .0001) through all fibrosis stages.
They also found that patients with ALD had higher LS values (30.5 vs. 21.3 kPa) and predominantly presented with jaundice (65.2%), with liver failure as the major cause of death (P less than .01). In contrast, in HCV, spleens were larger (17.6 vs. 12.1 cm) while variceal bleeding was the major cause of decompensation (73.2%) and death (P less than .001).
“We have demonstrated the disease-specific differences in SS/LS and SL/LS ratio between HCV and ALD. They underscore the role of the intrahepatic histological site of inflammation/fibrosis. We suggest that the SS/LS ratio could be used to confirm the disease etiology and predict disease-specific complications,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the Dietmar Hopp Foundation. The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Elshaarawy O et al. J Hepatol Reports. 2019 Jun 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.05.003.
The spleen stiffness (SS) to liver stiffness (LS) ratio was significantly higher in patients with hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) than in patients with alcohol-related liver disease (ALD), according to the results of a multicenter prospective study. In addition, long-term outcome and complications differed dramatically between HCV and ALD. Variceal bleeding was the most common sign of decompensation and cause of death in patients with HCV, while jaundice was the most common sign of decompensation in patients with ALD.
Omar Elshaarawy, MSc, of the University of Heidelberg (Germany) and colleagues reported on their prospective study of 411 patients with HCV (220 patients) or ALD (191 patients) that were assessed for both LS and SS using the Fibroscan device. They also discussed their retrospective analysis of LS and spleen length (SL) from a separate, retrospective cohort of 449 patients (267 with HCV, 182 with ALD) for whom long-term data on decompensation/death were available.
The researchers found that SS was significantly higher in HCV patients, compared with those with ALD (42.0 vs. 32.6 kPa; P less than .0001), as was SL (15.6 vs. 11.9 cm, P less than .0001); this was despite a lower mean LS in HCV. As a result, the SS/LS ratio and the SL/LS ratio were both significantly higher in HCV (3.8 vs. 1.72 and 1.46 vs. 0.86, P less than .0001) through all fibrosis stages.
They also found that patients with ALD had higher LS values (30.5 vs. 21.3 kPa) and predominantly presented with jaundice (65.2%), with liver failure as the major cause of death (P less than .01). In contrast, in HCV, spleens were larger (17.6 vs. 12.1 cm) while variceal bleeding was the major cause of decompensation (73.2%) and death (P less than .001).
“We have demonstrated the disease-specific differences in SS/LS and SL/LS ratio between HCV and ALD. They underscore the role of the intrahepatic histological site of inflammation/fibrosis. We suggest that the SS/LS ratio could be used to confirm the disease etiology and predict disease-specific complications,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported by the Dietmar Hopp Foundation. The authors reported they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Elshaarawy O et al. J Hepatol Reports. 2019 Jun 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.05.003.
FROM JHEP REPORTS
USPSTF updates, reaffirms recommendation for HBV screening in pregnant women
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
FROM JAMA
New WHO recommendations promote dolutegravir benefits in the face of lowered risk signal for neural tube defects
The risk of neural tube defects linked to dolutegravir exposure during pregnancy is lower than previously signaled, according to new reports that have prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to confirm that this antiviral medication should be the preferred option across all populations.
The use of dolutegravir (DTG) during pregnancy has been a pressing global health question since May 2018, when an unplanned interim analysis of the Tsepamo surveillance study of birth outcomes in Botswana showed four neural tube defects associated with dolutegravir exposure among 426 infants born to HIV-positive women (0.94%).
With follow-up for additional births, however, just one more neural tube defect was identified out of 1,683 deliveries among women who had taken DTG around the time of conception (0.30%), according to a report just presented here at the at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
By comparison, prevalence rates of neural tube defects were 0.10% for mothers taking other antiretroviral therapies at conception, 0.04% for those specifically taking efavirenz at conception, and 0.08% in HIV-uninfected mothers, according to the report, which was simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“While there may be a risk for neural tube defects, this risk is small, and really importantly, needs to be weighed against the large potential benefits of dolutegravir,” investigator Rebecca M. Zash, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said here in Mexico City during an IAS 2019 video press conference.
The WHO had previously sounded a note of caution, saying that DTG could be “considered” in women of childbearing age if other first‐line antiretroviral agents such as efavirenz could not be used.
However, following release of new evidence, including the study by Dr. Zash and colleagues, the WHO has come out with a clear recommendation for HIV drug as “the preferred first-line and second-line treatment for all populations, including pregnant women and those of childbearing potential.”
The updated scientific reports and guidelines have important implications for global health. “Many countries have been working to make dolutegravir-based treatment their preferred first-line regimen, as it’s got several advantages over efavirenz, which people have been using for many years now, including its tolerability and resistance profiles, and its impact on morbidity and mortality,” IAS president Anton Pozniak, MD, said in the press conference.
Some countries paused their plans to roll out dolutegravir-based regimens after the preliminary safety signal from the Tsepamo study was reported, Dr. Pozniak added.
In another study presented at IAS looking at dolutegravir use at conception, investigators described an additional surveillance study in Botswana, conducted independently from the Tsepamo study. One neural tube defect was found among 152 deliveries in mothers who had been taking DTG at conception (0.66%), and two neural tube defects among 2,326 deliveries to HIV-negative mothers (0.09%).
Although the number of deliveries are small in this study, the results suggest a risk of neural tube defects with DTG exposure at conception of less than 1%, said Mmakgomo Mimi Raesima, MD, MPH, public health specialist, Ministry of Health and Wellness, Botswana.
Because neural-tube defects might be related to low folate levels, Dr. Raesima said “conversations are continuing” with regard to folate food fortification in Botswana, a country that does not mandate folate-fortified grains.
“We want to capitalize on the momentum from these results,” Dr. Raesima said in the press conference.
The Tsepamo study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zash reported grants during the conduct of the study from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
SOURCE: Zash R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905230.
The risk of neural tube defects linked to dolutegravir exposure during pregnancy is lower than previously signaled, according to new reports that have prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to confirm that this antiviral medication should be the preferred option across all populations.
The use of dolutegravir (DTG) during pregnancy has been a pressing global health question since May 2018, when an unplanned interim analysis of the Tsepamo surveillance study of birth outcomes in Botswana showed four neural tube defects associated with dolutegravir exposure among 426 infants born to HIV-positive women (0.94%).
With follow-up for additional births, however, just one more neural tube defect was identified out of 1,683 deliveries among women who had taken DTG around the time of conception (0.30%), according to a report just presented here at the at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
By comparison, prevalence rates of neural tube defects were 0.10% for mothers taking other antiretroviral therapies at conception, 0.04% for those specifically taking efavirenz at conception, and 0.08% in HIV-uninfected mothers, according to the report, which was simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“While there may be a risk for neural tube defects, this risk is small, and really importantly, needs to be weighed against the large potential benefits of dolutegravir,” investigator Rebecca M. Zash, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said here in Mexico City during an IAS 2019 video press conference.
The WHO had previously sounded a note of caution, saying that DTG could be “considered” in women of childbearing age if other first‐line antiretroviral agents such as efavirenz could not be used.
However, following release of new evidence, including the study by Dr. Zash and colleagues, the WHO has come out with a clear recommendation for HIV drug as “the preferred first-line and second-line treatment for all populations, including pregnant women and those of childbearing potential.”
The updated scientific reports and guidelines have important implications for global health. “Many countries have been working to make dolutegravir-based treatment their preferred first-line regimen, as it’s got several advantages over efavirenz, which people have been using for many years now, including its tolerability and resistance profiles, and its impact on morbidity and mortality,” IAS president Anton Pozniak, MD, said in the press conference.
Some countries paused their plans to roll out dolutegravir-based regimens after the preliminary safety signal from the Tsepamo study was reported, Dr. Pozniak added.
In another study presented at IAS looking at dolutegravir use at conception, investigators described an additional surveillance study in Botswana, conducted independently from the Tsepamo study. One neural tube defect was found among 152 deliveries in mothers who had been taking DTG at conception (0.66%), and two neural tube defects among 2,326 deliveries to HIV-negative mothers (0.09%).
Although the number of deliveries are small in this study, the results suggest a risk of neural tube defects with DTG exposure at conception of less than 1%, said Mmakgomo Mimi Raesima, MD, MPH, public health specialist, Ministry of Health and Wellness, Botswana.
Because neural-tube defects might be related to low folate levels, Dr. Raesima said “conversations are continuing” with regard to folate food fortification in Botswana, a country that does not mandate folate-fortified grains.
“We want to capitalize on the momentum from these results,” Dr. Raesima said in the press conference.
The Tsepamo study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zash reported grants during the conduct of the study from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
SOURCE: Zash R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905230.
The risk of neural tube defects linked to dolutegravir exposure during pregnancy is lower than previously signaled, according to new reports that have prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to confirm that this antiviral medication should be the preferred option across all populations.
The use of dolutegravir (DTG) during pregnancy has been a pressing global health question since May 2018, when an unplanned interim analysis of the Tsepamo surveillance study of birth outcomes in Botswana showed four neural tube defects associated with dolutegravir exposure among 426 infants born to HIV-positive women (0.94%).
With follow-up for additional births, however, just one more neural tube defect was identified out of 1,683 deliveries among women who had taken DTG around the time of conception (0.30%), according to a report just presented here at the at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
By comparison, prevalence rates of neural tube defects were 0.10% for mothers taking other antiretroviral therapies at conception, 0.04% for those specifically taking efavirenz at conception, and 0.08% in HIV-uninfected mothers, according to the report, which was simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“While there may be a risk for neural tube defects, this risk is small, and really importantly, needs to be weighed against the large potential benefits of dolutegravir,” investigator Rebecca M. Zash, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said here in Mexico City during an IAS 2019 video press conference.
The WHO had previously sounded a note of caution, saying that DTG could be “considered” in women of childbearing age if other first‐line antiretroviral agents such as efavirenz could not be used.
However, following release of new evidence, including the study by Dr. Zash and colleagues, the WHO has come out with a clear recommendation for HIV drug as “the preferred first-line and second-line treatment for all populations, including pregnant women and those of childbearing potential.”
The updated scientific reports and guidelines have important implications for global health. “Many countries have been working to make dolutegravir-based treatment their preferred first-line regimen, as it’s got several advantages over efavirenz, which people have been using for many years now, including its tolerability and resistance profiles, and its impact on morbidity and mortality,” IAS president Anton Pozniak, MD, said in the press conference.
Some countries paused their plans to roll out dolutegravir-based regimens after the preliminary safety signal from the Tsepamo study was reported, Dr. Pozniak added.
In another study presented at IAS looking at dolutegravir use at conception, investigators described an additional surveillance study in Botswana, conducted independently from the Tsepamo study. One neural tube defect was found among 152 deliveries in mothers who had been taking DTG at conception (0.66%), and two neural tube defects among 2,326 deliveries to HIV-negative mothers (0.09%).
Although the number of deliveries are small in this study, the results suggest a risk of neural tube defects with DTG exposure at conception of less than 1%, said Mmakgomo Mimi Raesima, MD, MPH, public health specialist, Ministry of Health and Wellness, Botswana.
Because neural-tube defects might be related to low folate levels, Dr. Raesima said “conversations are continuing” with regard to folate food fortification in Botswana, a country that does not mandate folate-fortified grains.
“We want to capitalize on the momentum from these results,” Dr. Raesima said in the press conference.
The Tsepamo study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zash reported grants during the conduct of the study from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
SOURCE: Zash R et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905230.
FROM IAS 2019