User login
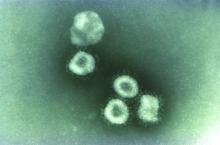
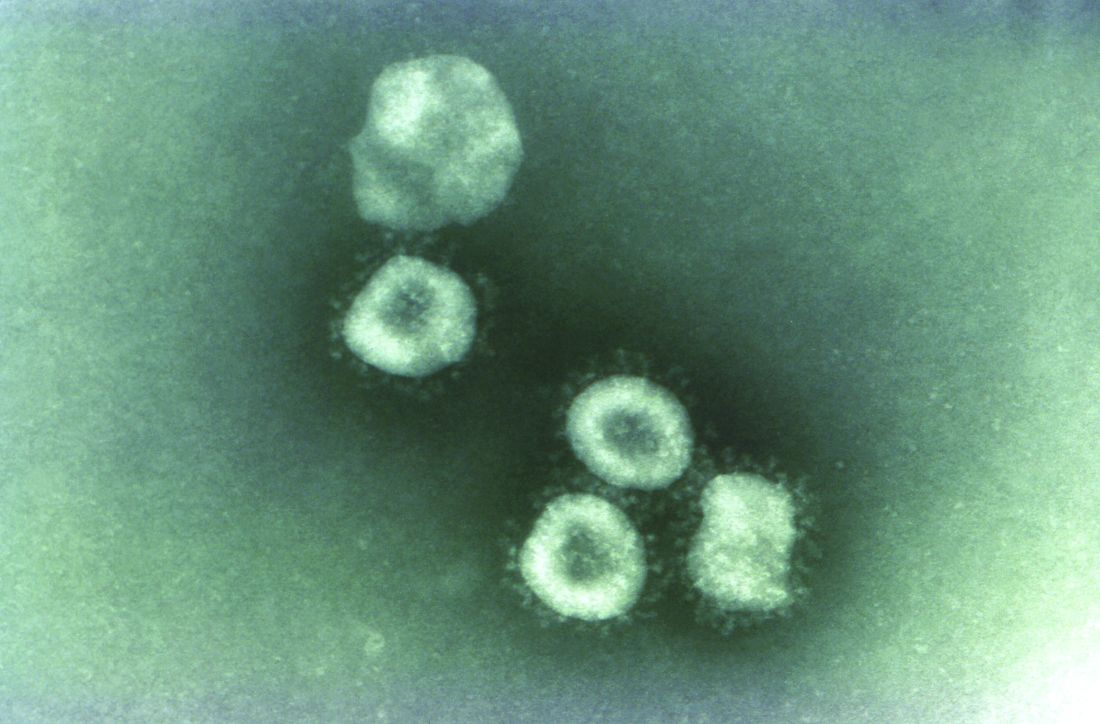
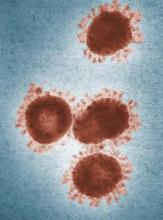
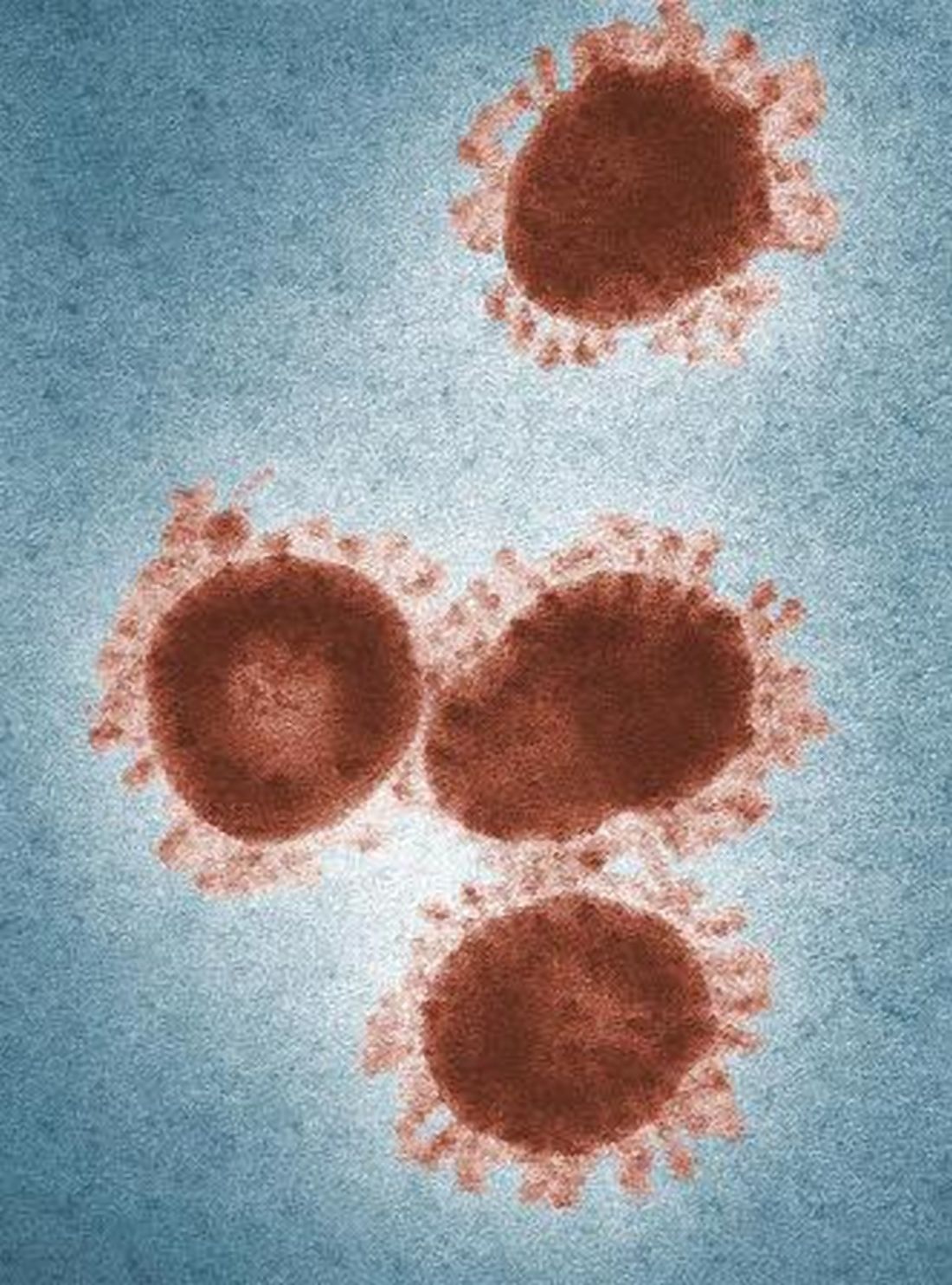
Travelers to three U.S. airports to be screened for novel coronavirus
according to an announcement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Starting today, Jan. 17, 2020, people traveling from Wuhan to New York (JFK), San Francisco (SFO), and Los Angeles (LAX) airports will be screened for symptoms associated with 2019-nCoV, which include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
“Based on the information that CDC has today, we believe the current risk for this virus to the general public is low,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a CDC telebriefing.
To date, 45 cases of 2019-nCoV have been reported in Wuhan, according to the CDC. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission said 15 patients have been cured and discharged, 5 severe cases are still being treated, and 2 patients have died. Both deaths occurred in older patients, one of whom was aged 69 years and one aged 61 years. One of the patients was known to have underlying health conditions.
Three cases of 2019-nCoV have been confirmed outside of Wuhan, one in Japan and two in Thailand. All three were travelers from Wuhan.
The virus is believed to have originated at Wuhan South China Seafood City, a market that sold seafood, chickens, bats, cats, marmots, and other wild animals. (The market has since been closed and disinfected.) The origin suggests animal-to-human transmission of 2019-nCoV, but it appears that human-to-human transmission can occur as well.
“While most of these infections seem to be happening from animals to people, there is some indication that limited person-to-person spread is happening,” Dr. Messonnier said.
Because of this potential risk, the CDC is working with the Department of Homeland Security’s Customs and Border Protection to screen travelers from Wuhan to the United States. The CDC is deploying about 100 additional staff to JFK, SFO, and LAX, where direct flights (JFK and SFO) or connecting flights (LAX) from Wuhan land.
The CDC could not confirm if exit screening is planned for people traveling abroad from Wuhan.
At the U.S. airports, travelers from Wuhan will be given a questionnaire asking about symptoms of 2019-nCoV (fever, cough, and difficulty breathing). People who exhibit symptoms will be assessed and questioned further. If they are believed to have 2019-nCoV, they will be sent to designated hospitals, where they will be examined, and samples will be collected.
Samples from patients with suspected 2019-nCoV will be sent to the CDC for analysis. Chinese health authorities made the full genome of 2019-nCoV publicly available, which will allow the CDC to confirm any cases that may arise in the United States. The CDC is currently working on a test to detect 2019-nCoV, which can be distributed to state health departments.
Earlier this month, the CDC issued a Level 1 Travel Health Notice for travelers to Wuhan and a Health Alert on 2019-nCoV. The latest information on 2019-nCoV can be found on the CDC’s Novel Coronavirus 2019 webpage.
according to an announcement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Starting today, Jan. 17, 2020, people traveling from Wuhan to New York (JFK), San Francisco (SFO), and Los Angeles (LAX) airports will be screened for symptoms associated with 2019-nCoV, which include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
“Based on the information that CDC has today, we believe the current risk for this virus to the general public is low,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a CDC telebriefing.
To date, 45 cases of 2019-nCoV have been reported in Wuhan, according to the CDC. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission said 15 patients have been cured and discharged, 5 severe cases are still being treated, and 2 patients have died. Both deaths occurred in older patients, one of whom was aged 69 years and one aged 61 years. One of the patients was known to have underlying health conditions.
Three cases of 2019-nCoV have been confirmed outside of Wuhan, one in Japan and two in Thailand. All three were travelers from Wuhan.
The virus is believed to have originated at Wuhan South China Seafood City, a market that sold seafood, chickens, bats, cats, marmots, and other wild animals. (The market has since been closed and disinfected.) The origin suggests animal-to-human transmission of 2019-nCoV, but it appears that human-to-human transmission can occur as well.
“While most of these infections seem to be happening from animals to people, there is some indication that limited person-to-person spread is happening,” Dr. Messonnier said.
Because of this potential risk, the CDC is working with the Department of Homeland Security’s Customs and Border Protection to screen travelers from Wuhan to the United States. The CDC is deploying about 100 additional staff to JFK, SFO, and LAX, where direct flights (JFK and SFO) or connecting flights (LAX) from Wuhan land.
The CDC could not confirm if exit screening is planned for people traveling abroad from Wuhan.
At the U.S. airports, travelers from Wuhan will be given a questionnaire asking about symptoms of 2019-nCoV (fever, cough, and difficulty breathing). People who exhibit symptoms will be assessed and questioned further. If they are believed to have 2019-nCoV, they will be sent to designated hospitals, where they will be examined, and samples will be collected.
Samples from patients with suspected 2019-nCoV will be sent to the CDC for analysis. Chinese health authorities made the full genome of 2019-nCoV publicly available, which will allow the CDC to confirm any cases that may arise in the United States. The CDC is currently working on a test to detect 2019-nCoV, which can be distributed to state health departments.
Earlier this month, the CDC issued a Level 1 Travel Health Notice for travelers to Wuhan and a Health Alert on 2019-nCoV. The latest information on 2019-nCoV can be found on the CDC’s Novel Coronavirus 2019 webpage.
according to an announcement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Starting today, Jan. 17, 2020, people traveling from Wuhan to New York (JFK), San Francisco (SFO), and Los Angeles (LAX) airports will be screened for symptoms associated with 2019-nCoV, which include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
“Based on the information that CDC has today, we believe the current risk for this virus to the general public is low,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said during a CDC telebriefing.
To date, 45 cases of 2019-nCoV have been reported in Wuhan, according to the CDC. The Wuhan Municipal Health Commission said 15 patients have been cured and discharged, 5 severe cases are still being treated, and 2 patients have died. Both deaths occurred in older patients, one of whom was aged 69 years and one aged 61 years. One of the patients was known to have underlying health conditions.
Three cases of 2019-nCoV have been confirmed outside of Wuhan, one in Japan and two in Thailand. All three were travelers from Wuhan.
The virus is believed to have originated at Wuhan South China Seafood City, a market that sold seafood, chickens, bats, cats, marmots, and other wild animals. (The market has since been closed and disinfected.) The origin suggests animal-to-human transmission of 2019-nCoV, but it appears that human-to-human transmission can occur as well.
“While most of these infections seem to be happening from animals to people, there is some indication that limited person-to-person spread is happening,” Dr. Messonnier said.
Because of this potential risk, the CDC is working with the Department of Homeland Security’s Customs and Border Protection to screen travelers from Wuhan to the United States. The CDC is deploying about 100 additional staff to JFK, SFO, and LAX, where direct flights (JFK and SFO) or connecting flights (LAX) from Wuhan land.
The CDC could not confirm if exit screening is planned for people traveling abroad from Wuhan.
At the U.S. airports, travelers from Wuhan will be given a questionnaire asking about symptoms of 2019-nCoV (fever, cough, and difficulty breathing). People who exhibit symptoms will be assessed and questioned further. If they are believed to have 2019-nCoV, they will be sent to designated hospitals, where they will be examined, and samples will be collected.
Samples from patients with suspected 2019-nCoV will be sent to the CDC for analysis. Chinese health authorities made the full genome of 2019-nCoV publicly available, which will allow the CDC to confirm any cases that may arise in the United States. The CDC is currently working on a test to detect 2019-nCoV, which can be distributed to state health departments.
Earlier this month, the CDC issued a Level 1 Travel Health Notice for travelers to Wuhan and a Health Alert on 2019-nCoV. The latest information on 2019-nCoV can be found on the CDC’s Novel Coronavirus 2019 webpage.
Flu activity declines for second straight week
Flu activity dropped nationally for a second consecutive week, but the changing predominance in type from influenza B to A suggests that “it is too early to know whether the season has peaked,” the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said Jan. 17.
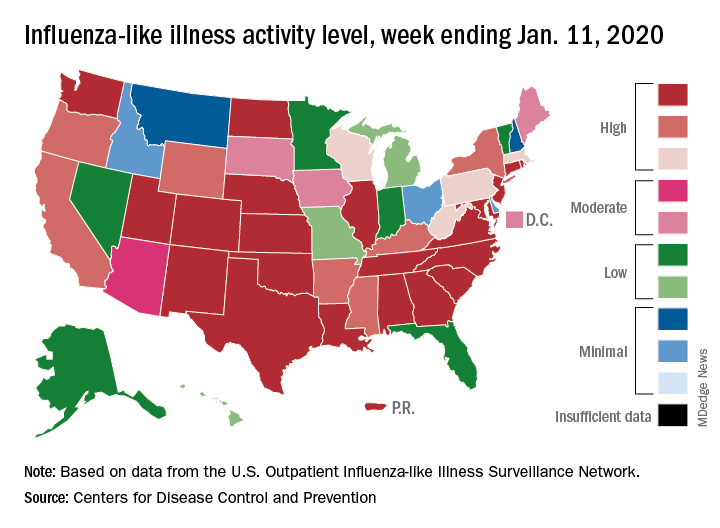
Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) dropped from 5.7% to 4.7% of all visits to outpatient providers for the week ending Jan. 11, and the proportion of respiratory specimens positive for influenza decreased from 23.6% the week before to 22.9%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Despite that overall drop in positive specimens, however, “the percent positive for influenza A viruses increased and some regions are seeing increases in the proportion of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses compared to other influenza viruses,” the influenza division noted.
Outpatient activity on the state level also was down for the week. There were 23 jurisdictions – 21 states, New York City, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity for the week ending Jan. 11, compared with 33 the previous week, data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network show.
Indicators of ILI severity have not risen to high levels. “The percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased from 6.0% to 6.9% but remains below the epidemic threshold” of 7.0% for the week, and the hospitalization rate remains at a fairly typical level for this time of year, the influenza division said.
For the week ending Jan. 11, 7 new ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported, which brings the total to 39 for the 2019-2020 season. Children aged 0-4 years are the second-most likely age group to be hospitalized with the flu (34.4/100,000 population) after adults aged 65 years and older, who have a cumulative rate of 47.6/100,000 for the season, the CDC reported.
Flu activity dropped nationally for a second consecutive week, but the changing predominance in type from influenza B to A suggests that “it is too early to know whether the season has peaked,” the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said Jan. 17.

Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) dropped from 5.7% to 4.7% of all visits to outpatient providers for the week ending Jan. 11, and the proportion of respiratory specimens positive for influenza decreased from 23.6% the week before to 22.9%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Despite that overall drop in positive specimens, however, “the percent positive for influenza A viruses increased and some regions are seeing increases in the proportion of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses compared to other influenza viruses,” the influenza division noted.
Outpatient activity on the state level also was down for the week. There were 23 jurisdictions – 21 states, New York City, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity for the week ending Jan. 11, compared with 33 the previous week, data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network show.
Indicators of ILI severity have not risen to high levels. “The percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased from 6.0% to 6.9% but remains below the epidemic threshold” of 7.0% for the week, and the hospitalization rate remains at a fairly typical level for this time of year, the influenza division said.
For the week ending Jan. 11, 7 new ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported, which brings the total to 39 for the 2019-2020 season. Children aged 0-4 years are the second-most likely age group to be hospitalized with the flu (34.4/100,000 population) after adults aged 65 years and older, who have a cumulative rate of 47.6/100,000 for the season, the CDC reported.
Flu activity dropped nationally for a second consecutive week, but the changing predominance in type from influenza B to A suggests that “it is too early to know whether the season has peaked,” the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said Jan. 17.

Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) dropped from 5.7% to 4.7% of all visits to outpatient providers for the week ending Jan. 11, and the proportion of respiratory specimens positive for influenza decreased from 23.6% the week before to 22.9%, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
Despite that overall drop in positive specimens, however, “the percent positive for influenza A viruses increased and some regions are seeing increases in the proportion of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses compared to other influenza viruses,” the influenza division noted.
Outpatient activity on the state level also was down for the week. There were 23 jurisdictions – 21 states, New York City, and Puerto Rico – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale of ILI activity for the week ending Jan. 11, compared with 33 the previous week, data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network show.
Indicators of ILI severity have not risen to high levels. “The percentage of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza increased from 6.0% to 6.9% but remains below the epidemic threshold” of 7.0% for the week, and the hospitalization rate remains at a fairly typical level for this time of year, the influenza division said.
For the week ending Jan. 11, 7 new ILI-related pediatric deaths were reported, which brings the total to 39 for the 2019-2020 season. Children aged 0-4 years are the second-most likely age group to be hospitalized with the flu (34.4/100,000 population) after adults aged 65 years and older, who have a cumulative rate of 47.6/100,000 for the season, the CDC reported.
Children with resistant UTIs unexpectedly may respond to discordant antibiotics
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Two new cases of coronavirus pneumonia in Thailand, Japan
Health authorities in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, identified the novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, responsible for the outbreak of a mysterious pneumonia that resulted in hospitalization of more than 40 patients and one death, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in a statement on the CDC website.
On Jan. 13, the Thailand’s Ministry of Public Health reported the first imported case of lab-confirmed 2019-nCoV from Wuhan. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated: “The traveler with febrile illness was detected on the same day by thermal surveillance at Suvarnabhumi Airport, Thailand, and was hospitalized the same day. After temperature check and initial assessment, she was transferred to the hospital for further investigations and treatment.”
Samples from this patient tested positive for coronaviruses by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The genomic sequencing analysis was performed by Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Center, the Thai Red Cross Society, and the Thai National Institute of Health. The patient is reported to be in stable condition.
The New York Times has reported a case of 2019-nCoV in Japan in a traveler returning from Wuhan. That patient is reported to have recovered and been discharged.
Chinese health authorities transmitted the full genome of “2019 novel coronavirus,” or “2019-nCoV,” to GenBank, the genetic sequence database managed by the National Institutes of Health, and in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data portal.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses. Most known human coronaviruses only cause mild respiratory disease, such as the common cold. But several coronaviruses have emerged to infect people and cause severe disease, such as has been seen with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). The cases in the Wuhan pneumonia outbreak have tested negative for both SARS and MERS.
The outbreak in Wuhan appears to be contained. The World Health Organization reported that the Wuhan health authorities identified and followed 763 close contacts, including health care workers. No additional cases of infection with the novel coronavirus have been identified. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert and recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”
Health authorities in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, identified the novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, responsible for the outbreak of a mysterious pneumonia that resulted in hospitalization of more than 40 patients and one death, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in a statement on the CDC website.
On Jan. 13, the Thailand’s Ministry of Public Health reported the first imported case of lab-confirmed 2019-nCoV from Wuhan. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated: “The traveler with febrile illness was detected on the same day by thermal surveillance at Suvarnabhumi Airport, Thailand, and was hospitalized the same day. After temperature check and initial assessment, she was transferred to the hospital for further investigations and treatment.”
Samples from this patient tested positive for coronaviruses by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The genomic sequencing analysis was performed by Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Center, the Thai Red Cross Society, and the Thai National Institute of Health. The patient is reported to be in stable condition.
The New York Times has reported a case of 2019-nCoV in Japan in a traveler returning from Wuhan. That patient is reported to have recovered and been discharged.
Chinese health authorities transmitted the full genome of “2019 novel coronavirus,” or “2019-nCoV,” to GenBank, the genetic sequence database managed by the National Institutes of Health, and in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data portal.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses. Most known human coronaviruses only cause mild respiratory disease, such as the common cold. But several coronaviruses have emerged to infect people and cause severe disease, such as has been seen with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). The cases in the Wuhan pneumonia outbreak have tested negative for both SARS and MERS.
The outbreak in Wuhan appears to be contained. The World Health Organization reported that the Wuhan health authorities identified and followed 763 close contacts, including health care workers. No additional cases of infection with the novel coronavirus have been identified. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert and recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”
Health authorities in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, identified the novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV, responsible for the outbreak of a mysterious pneumonia that resulted in hospitalization of more than 40 patients and one death, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in a statement on the CDC website.
On Jan. 13, the Thailand’s Ministry of Public Health reported the first imported case of lab-confirmed 2019-nCoV from Wuhan. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention stated: “The traveler with febrile illness was detected on the same day by thermal surveillance at Suvarnabhumi Airport, Thailand, and was hospitalized the same day. After temperature check and initial assessment, she was transferred to the hospital for further investigations and treatment.”
Samples from this patient tested positive for coronaviruses by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The genomic sequencing analysis was performed by Emerging Infectious Diseases Health Science Center, the Thai Red Cross Society, and the Thai National Institute of Health. The patient is reported to be in stable condition.
The New York Times has reported a case of 2019-nCoV in Japan in a traveler returning from Wuhan. That patient is reported to have recovered and been discharged.
Chinese health authorities transmitted the full genome of “2019 novel coronavirus,” or “2019-nCoV,” to GenBank, the genetic sequence database managed by the National Institutes of Health, and in the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data portal.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses. Most known human coronaviruses only cause mild respiratory disease, such as the common cold. But several coronaviruses have emerged to infect people and cause severe disease, such as has been seen with severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). The cases in the Wuhan pneumonia outbreak have tested negative for both SARS and MERS.
The outbreak in Wuhan appears to be contained. The World Health Organization reported that the Wuhan health authorities identified and followed 763 close contacts, including health care workers. No additional cases of infection with the novel coronavirus have been identified. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert and recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”
Drop in flu activity may not signal seasonal peak
A key indicator of flu activity dropped but remains high, but measures of severity have not yet shown any unusual increases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
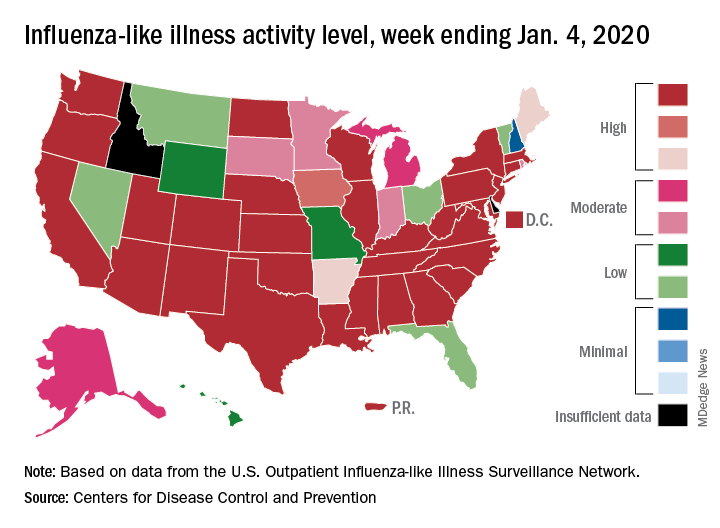
Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) made up an estimated 5.8% of the visits to outpatient providers during the week ending Jan. 4, and that’s a decline from 7.0% for the last full week of 2019, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That 7.0% outpatient ILI visit rate was the highest seen in December since 2003, but “hospitalization rates and percent of deaths due to pneumonia and influenza remain low,” the influenza division said in its weekly report.
Influenza B/Victoria and influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have been the predominant strains so far this season, and they “are more likely to affect children and younger adults than the elderly. Because the majority of hospitalizations and deaths occur among people age 65 and older, with fewer illnesses among that group, we expect, on a population level, to see less impact in flu-related hospitalizations and deaths,” the CDC said.
Last year, there was a similar drop in the outpatient ILI rate in early January after visits rose through December. The rate then increased for another 5 weeks before peaking at 5.0% in February. A similar pattern also occurred during the 2016-2017 and 2015-2016 seasons, CDC data show.
The nationwide ILI hospitalization rate, which is cumulative through the season, was up to 14.6 per 100,000 population for the week ending Jan. 4, the CDC said. Here are the corresponding rates for each of the last five seasons:
- 11.6 (2018-2019).
- 30.5 (2017-2018).
- 12.2 (2016-2017).
- 1.8 (2015-2016).
- 38.3 (2014-2015).
There were five new ILI-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 4, two of which occurred the week before. The total is now up to 32 for the 2019-2020 season, the CDC said in the weekly report. Last season, there were 21 pediatric deaths through the first January report, compared with 42 during the 2017-2018 season and 13 in 2016-2017.
A key indicator of flu activity dropped but remains high, but measures of severity have not yet shown any unusual increases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) made up an estimated 5.8% of the visits to outpatient providers during the week ending Jan. 4, and that’s a decline from 7.0% for the last full week of 2019, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That 7.0% outpatient ILI visit rate was the highest seen in December since 2003, but “hospitalization rates and percent of deaths due to pneumonia and influenza remain low,” the influenza division said in its weekly report.
Influenza B/Victoria and influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have been the predominant strains so far this season, and they “are more likely to affect children and younger adults than the elderly. Because the majority of hospitalizations and deaths occur among people age 65 and older, with fewer illnesses among that group, we expect, on a population level, to see less impact in flu-related hospitalizations and deaths,” the CDC said.
Last year, there was a similar drop in the outpatient ILI rate in early January after visits rose through December. The rate then increased for another 5 weeks before peaking at 5.0% in February. A similar pattern also occurred during the 2016-2017 and 2015-2016 seasons, CDC data show.
The nationwide ILI hospitalization rate, which is cumulative through the season, was up to 14.6 per 100,000 population for the week ending Jan. 4, the CDC said. Here are the corresponding rates for each of the last five seasons:
- 11.6 (2018-2019).
- 30.5 (2017-2018).
- 12.2 (2016-2017).
- 1.8 (2015-2016).
- 38.3 (2014-2015).
There were five new ILI-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 4, two of which occurred the week before. The total is now up to 32 for the 2019-2020 season, the CDC said in the weekly report. Last season, there were 21 pediatric deaths through the first January report, compared with 42 during the 2017-2018 season and 13 in 2016-2017.
A key indicator of flu activity dropped but remains high, but measures of severity have not yet shown any unusual increases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Patients with influenza-like illness (ILI) made up an estimated 5.8% of the visits to outpatient providers during the week ending Jan. 4, and that’s a decline from 7.0% for the last full week of 2019, the CDC’s influenza division reported.
That 7.0% outpatient ILI visit rate was the highest seen in December since 2003, but “hospitalization rates and percent of deaths due to pneumonia and influenza remain low,” the influenza division said in its weekly report.
Influenza B/Victoria and influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have been the predominant strains so far this season, and they “are more likely to affect children and younger adults than the elderly. Because the majority of hospitalizations and deaths occur among people age 65 and older, with fewer illnesses among that group, we expect, on a population level, to see less impact in flu-related hospitalizations and deaths,” the CDC said.
Last year, there was a similar drop in the outpatient ILI rate in early January after visits rose through December. The rate then increased for another 5 weeks before peaking at 5.0% in February. A similar pattern also occurred during the 2016-2017 and 2015-2016 seasons, CDC data show.
The nationwide ILI hospitalization rate, which is cumulative through the season, was up to 14.6 per 100,000 population for the week ending Jan. 4, the CDC said. Here are the corresponding rates for each of the last five seasons:
- 11.6 (2018-2019).
- 30.5 (2017-2018).
- 12.2 (2016-2017).
- 1.8 (2015-2016).
- 38.3 (2014-2015).
There were five new ILI-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 4, two of which occurred the week before. The total is now up to 32 for the 2019-2020 season, the CDC said in the weekly report. Last season, there were 21 pediatric deaths through the first January report, compared with 42 during the 2017-2018 season and 13 in 2016-2017.
Unnecessary pelvic exams, Pap tests common in young women
according to estimates from a study published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Approximately 2.6 million young women – about a quarter of those in this age group – reported receiving a pelvic exam in the previous year even though fewer than 10% were pregnant or receiving treatment for a sexually transmitted infection (STI) at the time.
Similarly, an estimated three in four Pap tests given to women aged 15-20 years likely were unnecessary. Based on Medicare payments for screening Pap tests and pelvic exams, the unnecessary procedures represented an estimated $123 million in a year.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recognizes that no evidence supports routine speculum examination or BPE in healthy, asymptomatic women younger than 21 years and recommends that these examinations be performed only when medically indicated,” said Jin Qin, ScD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues.
“Our results showed that, despite the recommendation, many young women without discernible medical indication received potentially unnecessary BPE or Pap tests, which may be a reflection of a long-standing clinical practice in the United States.”
These findings “demonstrate what happens to vulnerable populations (in this case, girls and young women) when clinicians do not keep up with or do not adhere to new guidelines,” Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, wrote in an invited commentary. She acknowledged the challenges of keeping up with new guidelines but noted the potential for harm from unnecessary screening. Dr. Simon is vice chair for clinical research in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The researchers analyzed responses from 3,410 young women aged 15-20 years in the National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) during 2011-2017 and extrapolated the results to estimate nationwide statistics. The researchers found that 23% of young women – 2.6 million in the United States – had received a bimanual pelvic exam during the previous year.
“This analysis focused on the bimanual component of the pelvic examination because it is the most invasive of the pelvic examination components and less likely to be confused with a speculum examination for cervical cancer or STI screening,” the authors note.
More than half of these pelvic exams (54%) – an estimated 1.4 million exams – potentially were unnecessary. The authors classified these pelvic exams as potentially unnecessary if it was not indicated for pregnancy, intrauterine device (IUD) use, or STI treatment in the past 12 months or for another medical problem.
Among the respondents, 5% were pregnant, 22% had been tested for an STI, and 5% had been treated for an STI during the previous year. About a third of respondents (33%) had used at least one type of hormonal contraception besides an IUD in the past year, but only 2% had used an IUD.
Dr. Simon said that some have advocated for routine bimanual pelvic exams to prompt women to see their provider every year, but without evidence to support the practice.
“In fact, many women (younger and older) associate the bimanual pelvic and speculum examinations with fear, anxiety, embarrassment, discomfort, and pain,” Dr. Simon emphasized. “Girls and women with a history of sexual violence may be more vulnerable to these harms. In addition, adolescent girls may delay starting contraception use or obtaining screening for sexually transmitted infections because of fear of pelvic examination, which thus creates unnecessary barriers to obtaining important screening and family-planning methods.”
The researchers also found that 19% of young women, about 2.2 million, had received a Pap test in the previous year. The majority of these (72%) likely were unnecessary, they wrote, explaining that cervical cancer screening is not recommended for those younger than 21 years unless they are HIV positive and sexually active.
“Because HIV infection status is not available in the NSFG, we estimated prevalence of Pap tests performed as part of a routine examination and considered them potentially unnecessary,” the authors explained.
Young women were seven times more likely to have undergone a bimanual pelvic exam if they received a Pap test (adjusted prevalence ratio [aPR], 7.12). In fact, the authors reported that nearly all potentially unnecessary bimanual pelvic exams (98%) occurred during the same visit as a Pap test that was potentially unnecessary as well.
Young women also were more likely to receive a bimanual pelvic exam if they underwent STI testing or used any hormonal contraception besides an IUD (aPR, 1.6 and 1.31, respectively). Those with public insurance or no insurance were less likely to receive a pelvic exam compared with those who had private insurance, although no associations were found with race/ethnicity.
Young women were about four times more likely to have a Pap test if they had STI testing (aPR, 3.77). Odds of a Pap test also were greater among those aged 18-20 years (aPR, 1.54), those with a pregnancy (aPR, 2.31), those with an IUD (aPR, 1.54), and those using any non-IUD hormonal contraception (aPR, 1.75).
Staying up to date on current guidelines and consistently delivering evidence-based care according to those guidelines “is not easy,” Dr. Simon commented. It involves building and maintaining a trusting clinician-patient relationship that centers on shared decision making, keeping up with research, and “unlearn[ing] deeply ingrained practices,” which is difficult.
“Clinicians are not well instructed on how to pivot or unlearn a practice,” Dr. Simon continued. “The science of deimplementation, especially with respect to guideline-concordant care, is in its infancy.” She also noted the value of annual visits, even without routine pelvic exams.
“Rethinking the goals of the annual health examination for young women and learning to unlearn will not put anyone out of business,” Dr. Simon concluded. “Rather, change can increase patients’ connectivity, trust, and engagement with primary care clinicians and, most importantly, avoid harms, especially to those who are most vulnerable.”
No external funding was used. The study authors and Dr. Simon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Qin J et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2019 Jan 6. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.5727.
An earlier version of this story appeared on Medscape.com.
A call for shared decision making
The experts who wrote American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ clinical guideline on the pelvic exam (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Oct;132[4]:e174-80) reviewed available evidence and found insufficient evidence to support routine screening for asymptomatic nonpregnant women who have no increased risk for specific gynecologic conditions (e.g., history of gynecologic cancer). Hence, ACOG recommends routine screening based on a shared decision between the asymptomatic woman and her doctor keeping in mind her medical and family history and her preference. This decision should be made after reviewing the limitations of the exam with regard to insufficient evidence to support its accuracy in screening for ovarian cancer, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes, plus lack of evidence for other gynecologic conditions.
In addition, we physicians must educate women, especially vulnerable populations, that deferring a pelvic exam for asymptomatic women entails judicious care. Deferring an exam does not mean that we are withholding medical care. If she wants an exam, understanding its limitations, then this preference is an indication itself for the exam as stated in our guideline.
It is important to emphasize to patients that we are deferring Pap smears until age 21 years per ACOG and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and that there is no need for a pelvic exam for sexually transmitted infection screening per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Likewise, there is no need for a pelvic exam prior initiation of contraception except for intrauterine device insertion also according to the CDC.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH , is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Qin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is a coauthor of the ACOG 2018 guideline on the utility of pelvic exam. She also is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A call for shared decision making
The experts who wrote American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ clinical guideline on the pelvic exam (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Oct;132[4]:e174-80) reviewed available evidence and found insufficient evidence to support routine screening for asymptomatic nonpregnant women who have no increased risk for specific gynecologic conditions (e.g., history of gynecologic cancer). Hence, ACOG recommends routine screening based on a shared decision between the asymptomatic woman and her doctor keeping in mind her medical and family history and her preference. This decision should be made after reviewing the limitations of the exam with regard to insufficient evidence to support its accuracy in screening for ovarian cancer, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes, plus lack of evidence for other gynecologic conditions.
In addition, we physicians must educate women, especially vulnerable populations, that deferring a pelvic exam for asymptomatic women entails judicious care. Deferring an exam does not mean that we are withholding medical care. If she wants an exam, understanding its limitations, then this preference is an indication itself for the exam as stated in our guideline.
It is important to emphasize to patients that we are deferring Pap smears until age 21 years per ACOG and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and that there is no need for a pelvic exam for sexually transmitted infection screening per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Likewise, there is no need for a pelvic exam prior initiation of contraception except for intrauterine device insertion also according to the CDC.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH , is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Qin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is a coauthor of the ACOG 2018 guideline on the utility of pelvic exam. She also is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A call for shared decision making
The experts who wrote American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ clinical guideline on the pelvic exam (Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Oct;132[4]:e174-80) reviewed available evidence and found insufficient evidence to support routine screening for asymptomatic nonpregnant women who have no increased risk for specific gynecologic conditions (e.g., history of gynecologic cancer). Hence, ACOG recommends routine screening based on a shared decision between the asymptomatic woman and her doctor keeping in mind her medical and family history and her preference. This decision should be made after reviewing the limitations of the exam with regard to insufficient evidence to support its accuracy in screening for ovarian cancer, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes, plus lack of evidence for other gynecologic conditions.
In addition, we physicians must educate women, especially vulnerable populations, that deferring a pelvic exam for asymptomatic women entails judicious care. Deferring an exam does not mean that we are withholding medical care. If she wants an exam, understanding its limitations, then this preference is an indication itself for the exam as stated in our guideline.
It is important to emphasize to patients that we are deferring Pap smears until age 21 years per ACOG and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and that there is no need for a pelvic exam for sexually transmitted infection screening per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Likewise, there is no need for a pelvic exam prior initiation of contraception except for intrauterine device insertion also according to the CDC.
Catherine Cansino, MD, MPH , is associate clinical professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of California, Davis. She was asked to comment on the Qin et al. article. Dr. Cansino is a coauthor of the ACOG 2018 guideline on the utility of pelvic exam. She also is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
according to estimates from a study published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Approximately 2.6 million young women – about a quarter of those in this age group – reported receiving a pelvic exam in the previous year even though fewer than 10% were pregnant or receiving treatment for a sexually transmitted infection (STI) at the time.
Similarly, an estimated three in four Pap tests given to women aged 15-20 years likely were unnecessary. Based on Medicare payments for screening Pap tests and pelvic exams, the unnecessary procedures represented an estimated $123 million in a year.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recognizes that no evidence supports routine speculum examination or BPE in healthy, asymptomatic women younger than 21 years and recommends that these examinations be performed only when medically indicated,” said Jin Qin, ScD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues.
“Our results showed that, despite the recommendation, many young women without discernible medical indication received potentially unnecessary BPE or Pap tests, which may be a reflection of a long-standing clinical practice in the United States.”
These findings “demonstrate what happens to vulnerable populations (in this case, girls and young women) when clinicians do not keep up with or do not adhere to new guidelines,” Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, wrote in an invited commentary. She acknowledged the challenges of keeping up with new guidelines but noted the potential for harm from unnecessary screening. Dr. Simon is vice chair for clinical research in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The researchers analyzed responses from 3,410 young women aged 15-20 years in the National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) during 2011-2017 and extrapolated the results to estimate nationwide statistics. The researchers found that 23% of young women – 2.6 million in the United States – had received a bimanual pelvic exam during the previous year.
“This analysis focused on the bimanual component of the pelvic examination because it is the most invasive of the pelvic examination components and less likely to be confused with a speculum examination for cervical cancer or STI screening,” the authors note.
More than half of these pelvic exams (54%) – an estimated 1.4 million exams – potentially were unnecessary. The authors classified these pelvic exams as potentially unnecessary if it was not indicated for pregnancy, intrauterine device (IUD) use, or STI treatment in the past 12 months or for another medical problem.
Among the respondents, 5% were pregnant, 22% had been tested for an STI, and 5% had been treated for an STI during the previous year. About a third of respondents (33%) had used at least one type of hormonal contraception besides an IUD in the past year, but only 2% had used an IUD.
Dr. Simon said that some have advocated for routine bimanual pelvic exams to prompt women to see their provider every year, but without evidence to support the practice.
“In fact, many women (younger and older) associate the bimanual pelvic and speculum examinations with fear, anxiety, embarrassment, discomfort, and pain,” Dr. Simon emphasized. “Girls and women with a history of sexual violence may be more vulnerable to these harms. In addition, adolescent girls may delay starting contraception use or obtaining screening for sexually transmitted infections because of fear of pelvic examination, which thus creates unnecessary barriers to obtaining important screening and family-planning methods.”
The researchers also found that 19% of young women, about 2.2 million, had received a Pap test in the previous year. The majority of these (72%) likely were unnecessary, they wrote, explaining that cervical cancer screening is not recommended for those younger than 21 years unless they are HIV positive and sexually active.
“Because HIV infection status is not available in the NSFG, we estimated prevalence of Pap tests performed as part of a routine examination and considered them potentially unnecessary,” the authors explained.
Young women were seven times more likely to have undergone a bimanual pelvic exam if they received a Pap test (adjusted prevalence ratio [aPR], 7.12). In fact, the authors reported that nearly all potentially unnecessary bimanual pelvic exams (98%) occurred during the same visit as a Pap test that was potentially unnecessary as well.
Young women also were more likely to receive a bimanual pelvic exam if they underwent STI testing or used any hormonal contraception besides an IUD (aPR, 1.6 and 1.31, respectively). Those with public insurance or no insurance were less likely to receive a pelvic exam compared with those who had private insurance, although no associations were found with race/ethnicity.
Young women were about four times more likely to have a Pap test if they had STI testing (aPR, 3.77). Odds of a Pap test also were greater among those aged 18-20 years (aPR, 1.54), those with a pregnancy (aPR, 2.31), those with an IUD (aPR, 1.54), and those using any non-IUD hormonal contraception (aPR, 1.75).
Staying up to date on current guidelines and consistently delivering evidence-based care according to those guidelines “is not easy,” Dr. Simon commented. It involves building and maintaining a trusting clinician-patient relationship that centers on shared decision making, keeping up with research, and “unlearn[ing] deeply ingrained practices,” which is difficult.
“Clinicians are not well instructed on how to pivot or unlearn a practice,” Dr. Simon continued. “The science of deimplementation, especially with respect to guideline-concordant care, is in its infancy.” She also noted the value of annual visits, even without routine pelvic exams.
“Rethinking the goals of the annual health examination for young women and learning to unlearn will not put anyone out of business,” Dr. Simon concluded. “Rather, change can increase patients’ connectivity, trust, and engagement with primary care clinicians and, most importantly, avoid harms, especially to those who are most vulnerable.”
No external funding was used. The study authors and Dr. Simon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Qin J et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2019 Jan 6. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.5727.
An earlier version of this story appeared on Medscape.com.
according to estimates from a study published online in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Approximately 2.6 million young women – about a quarter of those in this age group – reported receiving a pelvic exam in the previous year even though fewer than 10% were pregnant or receiving treatment for a sexually transmitted infection (STI) at the time.
Similarly, an estimated three in four Pap tests given to women aged 15-20 years likely were unnecessary. Based on Medicare payments for screening Pap tests and pelvic exams, the unnecessary procedures represented an estimated $123 million in a year.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recognizes that no evidence supports routine speculum examination or BPE in healthy, asymptomatic women younger than 21 years and recommends that these examinations be performed only when medically indicated,” said Jin Qin, ScD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and colleagues.
“Our results showed that, despite the recommendation, many young women without discernible medical indication received potentially unnecessary BPE or Pap tests, which may be a reflection of a long-standing clinical practice in the United States.”
These findings “demonstrate what happens to vulnerable populations (in this case, girls and young women) when clinicians do not keep up with or do not adhere to new guidelines,” Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, wrote in an invited commentary. She acknowledged the challenges of keeping up with new guidelines but noted the potential for harm from unnecessary screening. Dr. Simon is vice chair for clinical research in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The researchers analyzed responses from 3,410 young women aged 15-20 years in the National Survey of Family Growth (NSFG) during 2011-2017 and extrapolated the results to estimate nationwide statistics. The researchers found that 23% of young women – 2.6 million in the United States – had received a bimanual pelvic exam during the previous year.
“This analysis focused on the bimanual component of the pelvic examination because it is the most invasive of the pelvic examination components and less likely to be confused with a speculum examination for cervical cancer or STI screening,” the authors note.
More than half of these pelvic exams (54%) – an estimated 1.4 million exams – potentially were unnecessary. The authors classified these pelvic exams as potentially unnecessary if it was not indicated for pregnancy, intrauterine device (IUD) use, or STI treatment in the past 12 months or for another medical problem.
Among the respondents, 5% were pregnant, 22% had been tested for an STI, and 5% had been treated for an STI during the previous year. About a third of respondents (33%) had used at least one type of hormonal contraception besides an IUD in the past year, but only 2% had used an IUD.
Dr. Simon said that some have advocated for routine bimanual pelvic exams to prompt women to see their provider every year, but without evidence to support the practice.
“In fact, many women (younger and older) associate the bimanual pelvic and speculum examinations with fear, anxiety, embarrassment, discomfort, and pain,” Dr. Simon emphasized. “Girls and women with a history of sexual violence may be more vulnerable to these harms. In addition, adolescent girls may delay starting contraception use or obtaining screening for sexually transmitted infections because of fear of pelvic examination, which thus creates unnecessary barriers to obtaining important screening and family-planning methods.”
The researchers also found that 19% of young women, about 2.2 million, had received a Pap test in the previous year. The majority of these (72%) likely were unnecessary, they wrote, explaining that cervical cancer screening is not recommended for those younger than 21 years unless they are HIV positive and sexually active.
“Because HIV infection status is not available in the NSFG, we estimated prevalence of Pap tests performed as part of a routine examination and considered them potentially unnecessary,” the authors explained.
Young women were seven times more likely to have undergone a bimanual pelvic exam if they received a Pap test (adjusted prevalence ratio [aPR], 7.12). In fact, the authors reported that nearly all potentially unnecessary bimanual pelvic exams (98%) occurred during the same visit as a Pap test that was potentially unnecessary as well.
Young women also were more likely to receive a bimanual pelvic exam if they underwent STI testing or used any hormonal contraception besides an IUD (aPR, 1.6 and 1.31, respectively). Those with public insurance or no insurance were less likely to receive a pelvic exam compared with those who had private insurance, although no associations were found with race/ethnicity.
Young women were about four times more likely to have a Pap test if they had STI testing (aPR, 3.77). Odds of a Pap test also were greater among those aged 18-20 years (aPR, 1.54), those with a pregnancy (aPR, 2.31), those with an IUD (aPR, 1.54), and those using any non-IUD hormonal contraception (aPR, 1.75).
Staying up to date on current guidelines and consistently delivering evidence-based care according to those guidelines “is not easy,” Dr. Simon commented. It involves building and maintaining a trusting clinician-patient relationship that centers on shared decision making, keeping up with research, and “unlearn[ing] deeply ingrained practices,” which is difficult.
“Clinicians are not well instructed on how to pivot or unlearn a practice,” Dr. Simon continued. “The science of deimplementation, especially with respect to guideline-concordant care, is in its infancy.” She also noted the value of annual visits, even without routine pelvic exams.
“Rethinking the goals of the annual health examination for young women and learning to unlearn will not put anyone out of business,” Dr. Simon concluded. “Rather, change can increase patients’ connectivity, trust, and engagement with primary care clinicians and, most importantly, avoid harms, especially to those who are most vulnerable.”
No external funding was used. The study authors and Dr. Simon have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
SOURCE: Qin J et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2019 Jan 6. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.5727.
An earlier version of this story appeared on Medscape.com.
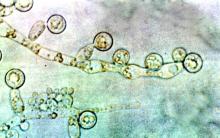
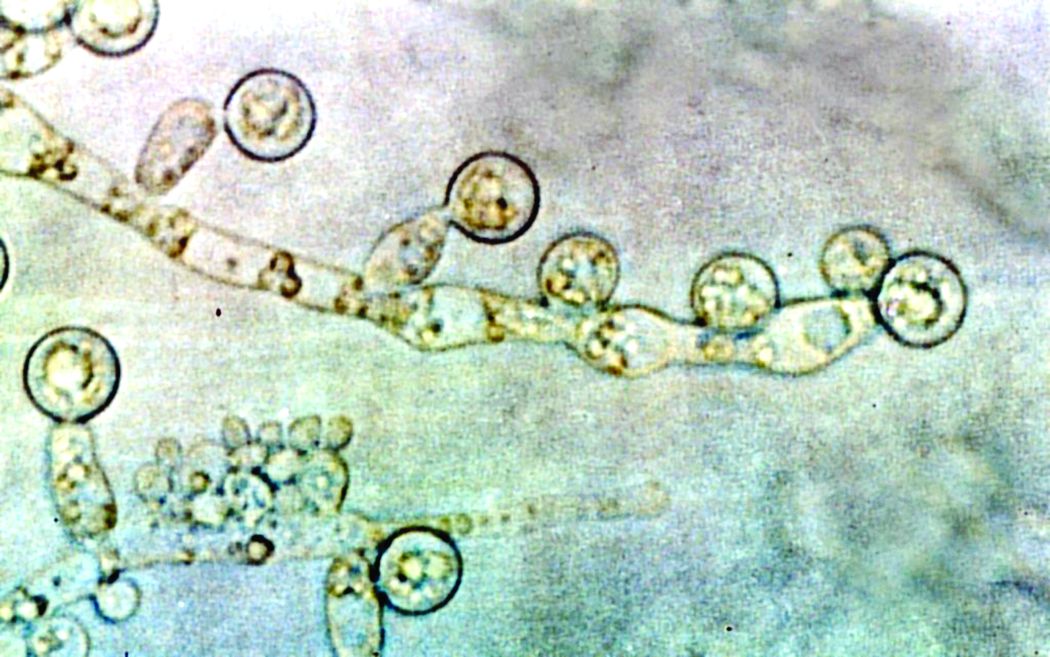
ID consult for Candida bloodstream infections can reduce mortality risk
findings from a large retrospective study suggest.
Mortality attributable to Candida bloodstream infection ranges between 15% and 47%, and delay in initiation of appropriate treatment has been associated with increased mortality. Previous small studies showed that ID consultation has conferred benefits to patients with Candida bloodstream infections. Carlos Mejia-Chew, MD, and colleagues from Washington University, St. Louis, sought to explore this further by performing a retrospective, single-center cohort study of 1,691 patients aged 18 years or older with Candida bloodstream infection from 2002 to 2015. They analyzed demographics, comorbidities, predisposing factors, all-cause mortality, antifungal use, central-line removal, and ophthalmological and echocardiographic evaluation in order to compare 90-day all-cause mortality between individuals with and without an ID consultation.
They found that those patients who received an ID consult for a Candida bloodstream infection had a significantly lower 90-day mortality rate than did those who did not (29% vs. 51%).
With a model using inverse weighting by the propensity score, they found that ID consultation was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.81 for mortality (95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.91; P less than .0001). In the ID consultation group, the median duration of antifungal therapy was significantly longer (18 vs. 14 days; P less than .0001); central-line removal was significantly more common (76% vs. 59%; P less than .0001); echocardiography use was more frequent (57% vs. 33%; P less than .0001); and ophthalmological examinations were performed more often (53% vs. 17%; P less than .0001). Importantly, fewer patients in the ID consultation group were untreated (2% vs. 14%; P less than .0001).
In an accompanying commentary, Katrien Lagrou, MD, and Eric Van Wijngaerden, MD, of the department of microbiology, immunology and transplantation, University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) stated: “We think that the high proportion of patients (14%) with a Candida bloodstream infection who did not receive any antifungal treatment and did not have an infectious disease consultation is a particularly alarming finding. ... Ninety-day mortality in these untreated patients was high (67%).”
“We believe every hospital should have an expert management strategy addressing all individual cases of candidaemia. The need for such expert management should be incorporated in all future candidaemia management guidelines,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Astellas Global Development Pharma, the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences, and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Several of the authors had financial connections to Astellas Global Development or other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Lagrou and Dr. Van Wijngaerden both reported receiving personal fees and nonfinancial support from a number of pharmaceutical companies, but all outside the scope of the study.
SOURCE: Mejia-Chew C et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19:1336-44.
findings from a large retrospective study suggest.
Mortality attributable to Candida bloodstream infection ranges between 15% and 47%, and delay in initiation of appropriate treatment has been associated with increased mortality. Previous small studies showed that ID consultation has conferred benefits to patients with Candida bloodstream infections. Carlos Mejia-Chew, MD, and colleagues from Washington University, St. Louis, sought to explore this further by performing a retrospective, single-center cohort study of 1,691 patients aged 18 years or older with Candida bloodstream infection from 2002 to 2015. They analyzed demographics, comorbidities, predisposing factors, all-cause mortality, antifungal use, central-line removal, and ophthalmological and echocardiographic evaluation in order to compare 90-day all-cause mortality between individuals with and without an ID consultation.
They found that those patients who received an ID consult for a Candida bloodstream infection had a significantly lower 90-day mortality rate than did those who did not (29% vs. 51%).
With a model using inverse weighting by the propensity score, they found that ID consultation was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.81 for mortality (95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.91; P less than .0001). In the ID consultation group, the median duration of antifungal therapy was significantly longer (18 vs. 14 days; P less than .0001); central-line removal was significantly more common (76% vs. 59%; P less than .0001); echocardiography use was more frequent (57% vs. 33%; P less than .0001); and ophthalmological examinations were performed more often (53% vs. 17%; P less than .0001). Importantly, fewer patients in the ID consultation group were untreated (2% vs. 14%; P less than .0001).
In an accompanying commentary, Katrien Lagrou, MD, and Eric Van Wijngaerden, MD, of the department of microbiology, immunology and transplantation, University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) stated: “We think that the high proportion of patients (14%) with a Candida bloodstream infection who did not receive any antifungal treatment and did not have an infectious disease consultation is a particularly alarming finding. ... Ninety-day mortality in these untreated patients was high (67%).”
“We believe every hospital should have an expert management strategy addressing all individual cases of candidaemia. The need for such expert management should be incorporated in all future candidaemia management guidelines,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Astellas Global Development Pharma, the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences, and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Several of the authors had financial connections to Astellas Global Development or other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Lagrou and Dr. Van Wijngaerden both reported receiving personal fees and nonfinancial support from a number of pharmaceutical companies, but all outside the scope of the study.
SOURCE: Mejia-Chew C et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19:1336-44.
findings from a large retrospective study suggest.
Mortality attributable to Candida bloodstream infection ranges between 15% and 47%, and delay in initiation of appropriate treatment has been associated with increased mortality. Previous small studies showed that ID consultation has conferred benefits to patients with Candida bloodstream infections. Carlos Mejia-Chew, MD, and colleagues from Washington University, St. Louis, sought to explore this further by performing a retrospective, single-center cohort study of 1,691 patients aged 18 years or older with Candida bloodstream infection from 2002 to 2015. They analyzed demographics, comorbidities, predisposing factors, all-cause mortality, antifungal use, central-line removal, and ophthalmological and echocardiographic evaluation in order to compare 90-day all-cause mortality between individuals with and without an ID consultation.
They found that those patients who received an ID consult for a Candida bloodstream infection had a significantly lower 90-day mortality rate than did those who did not (29% vs. 51%).
With a model using inverse weighting by the propensity score, they found that ID consultation was associated with a hazard ratio of 0.81 for mortality (95% confidence interval, 0.73-0.91; P less than .0001). In the ID consultation group, the median duration of antifungal therapy was significantly longer (18 vs. 14 days; P less than .0001); central-line removal was significantly more common (76% vs. 59%; P less than .0001); echocardiography use was more frequent (57% vs. 33%; P less than .0001); and ophthalmological examinations were performed more often (53% vs. 17%; P less than .0001). Importantly, fewer patients in the ID consultation group were untreated (2% vs. 14%; P less than .0001).
In an accompanying commentary, Katrien Lagrou, MD, and Eric Van Wijngaerden, MD, of the department of microbiology, immunology and transplantation, University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) stated: “We think that the high proportion of patients (14%) with a Candida bloodstream infection who did not receive any antifungal treatment and did not have an infectious disease consultation is a particularly alarming finding. ... Ninety-day mortality in these untreated patients was high (67%).”
“We believe every hospital should have an expert management strategy addressing all individual cases of candidaemia. The need for such expert management should be incorporated in all future candidaemia management guidelines,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the Astellas Global Development Pharma, the Washington University Institute of Clinical and Translational Sciences, and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Several of the authors had financial connections to Astellas Global Development or other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Lagrou and Dr. Van Wijngaerden both reported receiving personal fees and nonfinancial support from a number of pharmaceutical companies, but all outside the scope of the study.
SOURCE: Mejia-Chew C et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19:1336-44.
FROM LANCET: INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Why is AOM frequency decreasing in the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine era?
In 2000, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine 7 (PCV7) was introduced in the United States, and in 2010, PCV13 was introduced. When each of those vaccines were used, they reduced acute otitis media (AOM) incidence caused by the pneumococcal types included in the vaccines. In the time frame of those vaccine introductions, about one-third of AOM cases occurred because of pneumococci and half of those cases occurred because of strains expressing the serotypes in the two formulations of the vaccines. Efficacy is about 70% for AOM prevention for PCVs. The math matches clinical trial results that have shown about an 11%-12% reduction of all AOM attributable to PCVs. However, our group continues to do tympanocentesis to track the etiology of AOM, and we have reported that elimination of strains of pneumococci expressing capsular types included in the PCVs has been followed by emergence of replacement strains of pneumococci that express non-PCV capsules. We also have shown that Haemophilus influenzae has increased proportionally as a cause of AOM and is the most frequent cause of recurrent AOM. So what else is going on?
My colleague, Stephen I. Pelton, MD, – another ID Consult columnist – is a coauthor of a paper along with Ron Dagan, MD; Lauren Bakaletz, PhD; and Robert Cohen, MD, (all major figures in pneumococcal disease or AOM) that was published in Lancet Infectious Diseases (Dagan R et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Apr;16[4]:480-92.). They gathered evidence suggesting that prevention of early AOM episodes caused by pneumococci expressing PCV serotypes resulted in a reduction of subsequent complex cases caused by nonvaccine serotypes and other otopathogens. Thus, PCVs may have an impact on AOM indirectly attributable to vaccination.
However, the American Academy of Pediatrics made several recommendations in the 2004 and 2013 guidelines for diagnosis and management of AOM that had a remarkable impact in reducing the frequency that this infection is diagnosed and treated as well. The recommendations included:
- Stricter diagnostic criteria in 2004 that became more strict in 2013 requiring bulging of the eardrum.
- Introduction of “watchful waiting” as an option in management that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Introduction of delayed prescription of antibiotic when diagnosis was uncertain that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Endorsement of specific antibiotics with the greatest anticipated efficacy taking into consideration spectrum of activity, safety, and costs.
In the same general time frame, a second development occurred: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched a national campaign to reduce unnecessary and inappropriate antibiotic use in an effort to reduce rising antibiotic resistance among bacteria. The public media and professional communication campaign emphasized that antibiotic treatment carried with it risks that should be considered by patients and clinicians.
Because of the AAP and CDC recommendations, clinicians diagnosed AOM less frequently, and they treated it less frequently. Parents of children took note of the fact that their children with viral upper respiratory infections suspected to have AOM were diagnosed with AOM less often; even when a diagnosis was made, an antibiotic was prescribed less often. Therefore, parents brought their children to clinicians less often when their child had a viral upper respiratory infections or when they suspected AOM.
In addition, guidelines endorsed specific antibiotics that had better efficacy in treatment of AOM. Therefore, when clinicians did treat the infection with antibiotics, they used more effective drugs resulting in fewer treatment failures. This gives the impression of less-frequent AOM as well.
Both universal PCV use and universal influenza vaccine use have been endorsed in recent years, and uptake of that recommendation has increased over time. Clinical trials have shown that influenza is a common virus associated with secondary bacterial AOM.
Lastly, returning to antibiotic use, we now increasingly appreciate the adverse effect on the natural microbiome of the nasopharynx and gut when antibiotics are given. Natural resistance provided by commensals is disrupted when antibiotics are given. This may allow otopathogens to colonize the nasopharynx more readily, an effect that may last for months after a single antibiotic course. We also appreciate more that the microbiome modulates our immune system favorably, so antibiotics that disrupt the microbiome may have an adverse effect on innate or adaptive immunity as well. These adverse consequences of antibiotic use on microbiome and immunity are reduced when less antibiotics are given to children, as has been occurring over the past 2 decades.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he had no relevent financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
In 2000, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine 7 (PCV7) was introduced in the United States, and in 2010, PCV13 was introduced. When each of those vaccines were used, they reduced acute otitis media (AOM) incidence caused by the pneumococcal types included in the vaccines. In the time frame of those vaccine introductions, about one-third of AOM cases occurred because of pneumococci and half of those cases occurred because of strains expressing the serotypes in the two formulations of the vaccines. Efficacy is about 70% for AOM prevention for PCVs. The math matches clinical trial results that have shown about an 11%-12% reduction of all AOM attributable to PCVs. However, our group continues to do tympanocentesis to track the etiology of AOM, and we have reported that elimination of strains of pneumococci expressing capsular types included in the PCVs has been followed by emergence of replacement strains of pneumococci that express non-PCV capsules. We also have shown that Haemophilus influenzae has increased proportionally as a cause of AOM and is the most frequent cause of recurrent AOM. So what else is going on?
My colleague, Stephen I. Pelton, MD, – another ID Consult columnist – is a coauthor of a paper along with Ron Dagan, MD; Lauren Bakaletz, PhD; and Robert Cohen, MD, (all major figures in pneumococcal disease or AOM) that was published in Lancet Infectious Diseases (Dagan R et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Apr;16[4]:480-92.). They gathered evidence suggesting that prevention of early AOM episodes caused by pneumococci expressing PCV serotypes resulted in a reduction of subsequent complex cases caused by nonvaccine serotypes and other otopathogens. Thus, PCVs may have an impact on AOM indirectly attributable to vaccination.
However, the American Academy of Pediatrics made several recommendations in the 2004 and 2013 guidelines for diagnosis and management of AOM that had a remarkable impact in reducing the frequency that this infection is diagnosed and treated as well. The recommendations included:
- Stricter diagnostic criteria in 2004 that became more strict in 2013 requiring bulging of the eardrum.
- Introduction of “watchful waiting” as an option in management that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Introduction of delayed prescription of antibiotic when diagnosis was uncertain that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Endorsement of specific antibiotics with the greatest anticipated efficacy taking into consideration spectrum of activity, safety, and costs.
In the same general time frame, a second development occurred: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched a national campaign to reduce unnecessary and inappropriate antibiotic use in an effort to reduce rising antibiotic resistance among bacteria. The public media and professional communication campaign emphasized that antibiotic treatment carried with it risks that should be considered by patients and clinicians.
Because of the AAP and CDC recommendations, clinicians diagnosed AOM less frequently, and they treated it less frequently. Parents of children took note of the fact that their children with viral upper respiratory infections suspected to have AOM were diagnosed with AOM less often; even when a diagnosis was made, an antibiotic was prescribed less often. Therefore, parents brought their children to clinicians less often when their child had a viral upper respiratory infections or when they suspected AOM.
In addition, guidelines endorsed specific antibiotics that had better efficacy in treatment of AOM. Therefore, when clinicians did treat the infection with antibiotics, they used more effective drugs resulting in fewer treatment failures. This gives the impression of less-frequent AOM as well.
Both universal PCV use and universal influenza vaccine use have been endorsed in recent years, and uptake of that recommendation has increased over time. Clinical trials have shown that influenza is a common virus associated with secondary bacterial AOM.
Lastly, returning to antibiotic use, we now increasingly appreciate the adverse effect on the natural microbiome of the nasopharynx and gut when antibiotics are given. Natural resistance provided by commensals is disrupted when antibiotics are given. This may allow otopathogens to colonize the nasopharynx more readily, an effect that may last for months after a single antibiotic course. We also appreciate more that the microbiome modulates our immune system favorably, so antibiotics that disrupt the microbiome may have an adverse effect on innate or adaptive immunity as well. These adverse consequences of antibiotic use on microbiome and immunity are reduced when less antibiotics are given to children, as has been occurring over the past 2 decades.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he had no relevent financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
In 2000, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine 7 (PCV7) was introduced in the United States, and in 2010, PCV13 was introduced. When each of those vaccines were used, they reduced acute otitis media (AOM) incidence caused by the pneumococcal types included in the vaccines. In the time frame of those vaccine introductions, about one-third of AOM cases occurred because of pneumococci and half of those cases occurred because of strains expressing the serotypes in the two formulations of the vaccines. Efficacy is about 70% for AOM prevention for PCVs. The math matches clinical trial results that have shown about an 11%-12% reduction of all AOM attributable to PCVs. However, our group continues to do tympanocentesis to track the etiology of AOM, and we have reported that elimination of strains of pneumococci expressing capsular types included in the PCVs has been followed by emergence of replacement strains of pneumococci that express non-PCV capsules. We also have shown that Haemophilus influenzae has increased proportionally as a cause of AOM and is the most frequent cause of recurrent AOM. So what else is going on?
My colleague, Stephen I. Pelton, MD, – another ID Consult columnist – is a coauthor of a paper along with Ron Dagan, MD; Lauren Bakaletz, PhD; and Robert Cohen, MD, (all major figures in pneumococcal disease or AOM) that was published in Lancet Infectious Diseases (Dagan R et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Apr;16[4]:480-92.). They gathered evidence suggesting that prevention of early AOM episodes caused by pneumococci expressing PCV serotypes resulted in a reduction of subsequent complex cases caused by nonvaccine serotypes and other otopathogens. Thus, PCVs may have an impact on AOM indirectly attributable to vaccination.
However, the American Academy of Pediatrics made several recommendations in the 2004 and 2013 guidelines for diagnosis and management of AOM that had a remarkable impact in reducing the frequency that this infection is diagnosed and treated as well. The recommendations included:
- Stricter diagnostic criteria in 2004 that became more strict in 2013 requiring bulging of the eardrum.
- Introduction of “watchful waiting” as an option in management that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Introduction of delayed prescription of antibiotic when diagnosis was uncertain that possibly led to no antibiotic treatment.
- Endorsement of specific antibiotics with the greatest anticipated efficacy taking into consideration spectrum of activity, safety, and costs.
In the same general time frame, a second development occurred: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched a national campaign to reduce unnecessary and inappropriate antibiotic use in an effort to reduce rising antibiotic resistance among bacteria. The public media and professional communication campaign emphasized that antibiotic treatment carried with it risks that should be considered by patients and clinicians.
Because of the AAP and CDC recommendations, clinicians diagnosed AOM less frequently, and they treated it less frequently. Parents of children took note of the fact that their children with viral upper respiratory infections suspected to have AOM were diagnosed with AOM less often; even when a diagnosis was made, an antibiotic was prescribed less often. Therefore, parents brought their children to clinicians less often when their child had a viral upper respiratory infections or when they suspected AOM.
In addition, guidelines endorsed specific antibiotics that had better efficacy in treatment of AOM. Therefore, when clinicians did treat the infection with antibiotics, they used more effective drugs resulting in fewer treatment failures. This gives the impression of less-frequent AOM as well.
Both universal PCV use and universal influenza vaccine use have been endorsed in recent years, and uptake of that recommendation has increased over time. Clinical trials have shown that influenza is a common virus associated with secondary bacterial AOM.
Lastly, returning to antibiotic use, we now increasingly appreciate the adverse effect on the natural microbiome of the nasopharynx and gut when antibiotics are given. Natural resistance provided by commensals is disrupted when antibiotics are given. This may allow otopathogens to colonize the nasopharynx more readily, an effect that may last for months after a single antibiotic course. We also appreciate more that the microbiome modulates our immune system favorably, so antibiotics that disrupt the microbiome may have an adverse effect on innate or adaptive immunity as well. These adverse consequences of antibiotic use on microbiome and immunity are reduced when less antibiotics are given to children, as has been occurring over the past 2 decades.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he had no relevent financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Long-term entecavir looks safe, effective in HBV
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
For patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, up to 10 years of treatment with entecavir was safe and produced a superior rate of sustained virologic response, compared with other HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogues in a global randomized clinical trial.
Virologic responses were confirmed and maintained in 80% of entecavir patients and 61% of patients who received other therapies, said Jin-Lin Hou, MD, of Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China, and associates. Regardless of which treatment patients received, a sustained virologic response was associated with a significantly lower rate of liver-related hepatitis B virus (HBV) disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Rates of serious treatment-related adverse events were 0.2% in the entecavir arm and 0.8% in the nonentecavir arm. Moreover, the primary outcome of time-to-adjudicated clinical outcome events “showed that entecavir treatment, compared with nonentecavir, was not associated with an increased risk of malignant neoplasms, including hepatocellular carcinoma, nonhepatocellular carcinoma malignancies, and overall malignancies,” they wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Entecavir is approved for the treatment of adults with chronic HBV infection, and its long-term use has been linked to the regression of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. In treatment-naive patients, genotypic resistance and virologic breakthrough are rare even after up to 5 years of entecavir therapy. Although human studies have not linked this treatment duration with an increased risk of adverse events, murine studies have identified benign and malignant tumors of the brain, lung, and liver in entecavir-treated mice and rats. “With the exception of lung tumors, which were limited to male mice, rodent tumors occurred only at entecavir exposures [that were] significantly higher than those achieved in human beings with standard approved doses,” the researchers wrote.
For the trial, they assigned more than 12,000 patients with chronic HBV infection to receive long-term treatment with entecavir or investigators’ choice of another HBV nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. Patients were from 229 centers in Asia, Europe, and North and South America, and a total of 6,216 received entecavir, while 6,162 received another therapy.
Compared with other HBV nucleoside and nucleotide analogues, long-term treatment with entecavir “provided a high margin of safety” and was not tied to higher rates of liver or nonliver malignancies, the researchers found. The carcinogenicity of entecavir in rodents did not appear to extend to humans. Furthermore, among 5,305 trial participants in China, a sustained virologic response was associated with a clinically and statistically significant reduction in the risk of liver-related HBV disease progression (hazard ratio, 0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.22) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.009-0.113).
The results confirm the appropriateness of long-term entecavir therapy for chronic HBV infection, as recommended by current guidelines, Dr. Hou and associates concluded. However, patients in this trial were relatively young, with a median age of only 39 years. Therefore, the risk of entecavir-associated malignancies in older age cohorts could not be evaluated.
Bristol-Myers Squibb designed the study, performed statistical analyses, and funded the study and manuscript preparation. The Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program provided partial support. Dr. Hou disclosed grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. Several coinvestigators also disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and to several other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Hou J-L et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.010.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Mystery pneumonia in China has health officials on alert
An according to a statement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As of Jan. 5, 2020, 59 cases of the disease have been reported by the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
Wuhan health authorities are closely monitoring over 150 contacts for symptoms. Laboratory results have been negative for influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, and the viruses that caused SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome). So far, there are no reports of person-to-person transmission or health care worker infection of this pneumonia.
The World Health Organization reported that, as of Dec. 31, 2019, about one-quarter of patients were severely ill with the pneumonia and the rest were stable. Symptoms reported include fever, difficulty breathing, and chest radiographs showing invasive lesions in both lungs. All patients are being treated in isolation and efforts to identify the pathogen are ongoing.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately. In addition, the CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert, which recommends travelers observe usual precautions against infectious disease.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”
An according to a statement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As of Jan. 5, 2020, 59 cases of the disease have been reported by the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
Wuhan health authorities are closely monitoring over 150 contacts for symptoms. Laboratory results have been negative for influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, and the viruses that caused SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome). So far, there are no reports of person-to-person transmission or health care worker infection of this pneumonia.
The World Health Organization reported that, as of Dec. 31, 2019, about one-quarter of patients were severely ill with the pneumonia and the rest were stable. Symptoms reported include fever, difficulty breathing, and chest radiographs showing invasive lesions in both lungs. All patients are being treated in isolation and efforts to identify the pathogen are ongoing.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately. In addition, the CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert, which recommends travelers observe usual precautions against infectious disease.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”
An according to a statement from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As of Jan. 5, 2020, 59 cases of the disease have been reported by the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. The cluster of cases is linked to the Wuhan South China Seafood City market where – in addition to seafood – chickens, bats, marmots, and other animals were sold. That market has been closed since Jan. 1, 2020, for cleaning and disinfection.
Wuhan health authorities are closely monitoring over 150 contacts for symptoms. Laboratory results have been negative for influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, and the viruses that caused SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome). So far, there are no reports of person-to-person transmission or health care worker infection of this pneumonia.
The World Health Organization reported that, as of Dec. 31, 2019, about one-quarter of patients were severely ill with the pneumonia and the rest were stable. Symptoms reported include fever, difficulty breathing, and chest radiographs showing invasive lesions in both lungs. All patients are being treated in isolation and efforts to identify the pathogen are ongoing.
The WHO is monitoring the situation closely and is in close contact with Chinese health authorities.
The CDC has recommended that travelers to Wuhan, a city of over 19 million people, avoid animal and meat markets, avoid contact with sick people, and wash hands often with soap and water. Travelers who have been in Wuhan recently and who experience respiratory symptoms should notify the local health department immediately. In addition, the CDC has issued a Level 1 travel alert, which recommends travelers observe usual precautions against infectious disease.
In addition, the CDC recommends that, for symptomatic patients with a history of travel to Wuhan, caution should be exercised in the health care setting. “Ask such patients to don a surgical mask as soon as they are identified. Conduct their evaluation in a private room with the door closed. Personnel entering the room to evaluate the patient should use contact precautions and wear an N95 disposable facepiece respirator. For patients admitted for inpatient care, implement contact and airborne isolation precautions, in addition to standard precautions, until further information becomes available. For additional infection control guidance see: www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html.”