User login
Preventable diseases could gain a foothold because of COVID-19
There is a highly infectious virus spreading around the world and it is targeting the most vulnerable among us. It is among the most contagious of human diseases, spreading through the air unseen. No, it isn’t the novel coronavirus, COVID-19. It’s measles.
Remember measles? Outbreaks in recent years have brought the disease, which once was declared eliminated in the United States, back into the news and public awareness, but measles never has really gone away. Every year there are millions of cases worldwide – in 2018 alone there were nearly 10 million estimated cases and 142,300 deaths, according to the World Health Organization. The good news is that measles vaccination is highly effective, at about 97% after the recommended two doses. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “because of vaccination, more than 21 million lives have been saved and measles deaths have been reduced by 80% since 2000.” This is a tremendous public health success and a cause for celebration. But our work is not done. The recent increases in vaccine hesitancy and refusal in many countries has contributed to the resurgence of measles worldwide.
Influenza still is in full swing with the CDC reporting high activity in 1 states for the week ending April 4th. Seasonal influenza, according to currently available data, has a lower fatality rate than COVID-19, but that doesn’t mean it is harmless. Thus far in the 2019-2020 flu season, there have been at least 24,000 deaths because of influenza in the United States alone, 166 of which were among pediatric patients.*
Like many pediatricians, I have seen firsthand the impact of vaccine-preventable illnesses like influenza, pertussis, and varicella. I have personally cared for an infant with pertussis who had to be intubated and on a ventilator for nearly a week. I have told the family of a child with cancer that they would have to be admitted to the hospital yet again for intravenous antiviral medication because that little rash turned out to be varicella. I have performed CPR on a previously healthy teenager with the flu whose heart was failing despite maximum ventilator support. All these illnesses might have been prevented had these patients or those around them been appropriately vaccinated.
Right now, the United States and governments around the world are taking unprecedented public health measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, directing the public to stay home, avoid unnecessary contact with other people, practice good hand-washing and infection-control techniques. In order to promote social distancing, many primary care clinics are canceling nonurgent appointments or converting them to virtual visits, including some visits for routine vaccinations for older children, teens, and adults. This is a responsible choice to keep potentially asymptomatic people from spreading COVID-19, but once restrictions begin to lift, we all will need to act to help our patients catch up on these missing vaccinations.
This pandemic has made it more apparent than ever that we all rely upon each other to stay healthy. While this pandemic has disrupted nearly every aspect of daily life, we can’t let it disrupt one of the great successes in health care today: the prevention of serious illnesses. As soon as it is safe to do so, we must help and encourage patients to catch up on missing vaccinations. It’s rare that preventative public health measures and vaccine developments are in the nightly news, so we should use this increased public awareness to ensure patients are well educated and protected from every disease. As part of this, we must continue our efforts to share accurate information on the safety and efficacy of routine vaccination. And when there is a vaccine for COVID-19? Let’s make sure everyone gets that too.
Dr. Leighton is a pediatrician in the ED at Children’s National Hospital and currently is completing her MPH in health policy at George Washington University, both in Washington. She had no relevant financial disclosures.*
* This article was updated 4/10/2020.
There is a highly infectious virus spreading around the world and it is targeting the most vulnerable among us. It is among the most contagious of human diseases, spreading through the air unseen. No, it isn’t the novel coronavirus, COVID-19. It’s measles.
Remember measles? Outbreaks in recent years have brought the disease, which once was declared eliminated in the United States, back into the news and public awareness, but measles never has really gone away. Every year there are millions of cases worldwide – in 2018 alone there were nearly 10 million estimated cases and 142,300 deaths, according to the World Health Organization. The good news is that measles vaccination is highly effective, at about 97% after the recommended two doses. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “because of vaccination, more than 21 million lives have been saved and measles deaths have been reduced by 80% since 2000.” This is a tremendous public health success and a cause for celebration. But our work is not done. The recent increases in vaccine hesitancy and refusal in many countries has contributed to the resurgence of measles worldwide.
Influenza still is in full swing with the CDC reporting high activity in 1 states for the week ending April 4th. Seasonal influenza, according to currently available data, has a lower fatality rate than COVID-19, but that doesn’t mean it is harmless. Thus far in the 2019-2020 flu season, there have been at least 24,000 deaths because of influenza in the United States alone, 166 of which were among pediatric patients.*
Like many pediatricians, I have seen firsthand the impact of vaccine-preventable illnesses like influenza, pertussis, and varicella. I have personally cared for an infant with pertussis who had to be intubated and on a ventilator for nearly a week. I have told the family of a child with cancer that they would have to be admitted to the hospital yet again for intravenous antiviral medication because that little rash turned out to be varicella. I have performed CPR on a previously healthy teenager with the flu whose heart was failing despite maximum ventilator support. All these illnesses might have been prevented had these patients or those around them been appropriately vaccinated.
Right now, the United States and governments around the world are taking unprecedented public health measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, directing the public to stay home, avoid unnecessary contact with other people, practice good hand-washing and infection-control techniques. In order to promote social distancing, many primary care clinics are canceling nonurgent appointments or converting them to virtual visits, including some visits for routine vaccinations for older children, teens, and adults. This is a responsible choice to keep potentially asymptomatic people from spreading COVID-19, but once restrictions begin to lift, we all will need to act to help our patients catch up on these missing vaccinations.
This pandemic has made it more apparent than ever that we all rely upon each other to stay healthy. While this pandemic has disrupted nearly every aspect of daily life, we can’t let it disrupt one of the great successes in health care today: the prevention of serious illnesses. As soon as it is safe to do so, we must help and encourage patients to catch up on missing vaccinations. It’s rare that preventative public health measures and vaccine developments are in the nightly news, so we should use this increased public awareness to ensure patients are well educated and protected from every disease. As part of this, we must continue our efforts to share accurate information on the safety and efficacy of routine vaccination. And when there is a vaccine for COVID-19? Let’s make sure everyone gets that too.
Dr. Leighton is a pediatrician in the ED at Children’s National Hospital and currently is completing her MPH in health policy at George Washington University, both in Washington. She had no relevant financial disclosures.*
* This article was updated 4/10/2020.
There is a highly infectious virus spreading around the world and it is targeting the most vulnerable among us. It is among the most contagious of human diseases, spreading through the air unseen. No, it isn’t the novel coronavirus, COVID-19. It’s measles.
Remember measles? Outbreaks in recent years have brought the disease, which once was declared eliminated in the United States, back into the news and public awareness, but measles never has really gone away. Every year there are millions of cases worldwide – in 2018 alone there were nearly 10 million estimated cases and 142,300 deaths, according to the World Health Organization. The good news is that measles vaccination is highly effective, at about 97% after the recommended two doses. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “because of vaccination, more than 21 million lives have been saved and measles deaths have been reduced by 80% since 2000.” This is a tremendous public health success and a cause for celebration. But our work is not done. The recent increases in vaccine hesitancy and refusal in many countries has contributed to the resurgence of measles worldwide.
Influenza still is in full swing with the CDC reporting high activity in 1 states for the week ending April 4th. Seasonal influenza, according to currently available data, has a lower fatality rate than COVID-19, but that doesn’t mean it is harmless. Thus far in the 2019-2020 flu season, there have been at least 24,000 deaths because of influenza in the United States alone, 166 of which were among pediatric patients.*
Like many pediatricians, I have seen firsthand the impact of vaccine-preventable illnesses like influenza, pertussis, and varicella. I have personally cared for an infant with pertussis who had to be intubated and on a ventilator for nearly a week. I have told the family of a child with cancer that they would have to be admitted to the hospital yet again for intravenous antiviral medication because that little rash turned out to be varicella. I have performed CPR on a previously healthy teenager with the flu whose heart was failing despite maximum ventilator support. All these illnesses might have been prevented had these patients or those around them been appropriately vaccinated.
Right now, the United States and governments around the world are taking unprecedented public health measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19, directing the public to stay home, avoid unnecessary contact with other people, practice good hand-washing and infection-control techniques. In order to promote social distancing, many primary care clinics are canceling nonurgent appointments or converting them to virtual visits, including some visits for routine vaccinations for older children, teens, and adults. This is a responsible choice to keep potentially asymptomatic people from spreading COVID-19, but once restrictions begin to lift, we all will need to act to help our patients catch up on these missing vaccinations.
This pandemic has made it more apparent than ever that we all rely upon each other to stay healthy. While this pandemic has disrupted nearly every aspect of daily life, we can’t let it disrupt one of the great successes in health care today: the prevention of serious illnesses. As soon as it is safe to do so, we must help and encourage patients to catch up on missing vaccinations. It’s rare that preventative public health measures and vaccine developments are in the nightly news, so we should use this increased public awareness to ensure patients are well educated and protected from every disease. As part of this, we must continue our efforts to share accurate information on the safety and efficacy of routine vaccination. And when there is a vaccine for COVID-19? Let’s make sure everyone gets that too.
Dr. Leighton is a pediatrician in the ED at Children’s National Hospital and currently is completing her MPH in health policy at George Washington University, both in Washington. She had no relevant financial disclosures.*
* This article was updated 4/10/2020.
Coronavirus resources from AAD target safe office practices, new telemedicine guidance
The American Academy of Dermatology (
The guidance pages are publicly viewable. Additionally, AAD has made a collection of COVID-19 articles from the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology freely available for the next 6 months.
George Hruza, MD, AAD president, detailed regulatory updates and other federal actions as well as guidance regarding telemedicine and clinical practice in a message to AAD members.
“While many questions still need answers, I have appointed an Ad Hoc Task Force to assess dermatology’s needs, share knowledge, and provide ongoing guidance and information throughout the crisis,” Dr. Hruza wrote.
“The situation is changing rapidly, and we are committed to keeping you updated with reliable and practical information to help you adapt to the circumstances,” he noted, referring dermatologists to the AAD’s information hub for the coronavirus outbreak. “We are keeping this page updated frequently, and it will serve as your primary source for what we know now,” he noted.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has recently relaxed key regulations regarding technology to provide telemedicine so that physicians and patients can use existing platforms such as FaceTime and Skype for virtual visits. The usual fines for HIPAA noncompliance have been waived. Additionally, telemedicine visits can now be reimbursed at the same rate as in-person visits.
Private payers are beginning to follow suit, said Dr. Hruza, noting that the AAD Association is working to harmonize private coverage with public reimbursement. The AAD also is tracking which payers are coming in line with federal policies on its teledermatology page.
These changes in regulation around telemedicine apply to patient encounters for any purpose, not just coronavirus-related encounters, noted Dr. Hruza. “The good news is that the government has taken action to make it much easier for us to provide virtual consults to patients. Dermatology has always been a leader in telemedicine, and it will be an important way to offer care to patients who can’t or don’t need to come into the office or clinic,” he added.
Importantly, said Dr. Hruza, CMS is allowing practices to have discretion over whether copays are collected, or collected in full, so that these payments don’t present a barrier to patient care in the current crisis environment.
For dermatologists who are new to telemedicine, AAD has created an online resource that includes information about various telemedicine platforms, updated guidance regarding regulations, and best practices for accurate coding and documentation of telemedicine visits.
The Academy has also been developing dermatology-specific guidance, including how to address the concerns of patients who are receiving biologic therapies and how to conserve personal protective equipment while still protecting physicians, staff, and patients from COVID-19 infection.
For patients on biologic therapy who show no sign of coronavirus infection, the decision to continue or stop biologics should be made on a case-by-case basis. Factors to be considered include patient age, comorbidities, and the severity of the original indication for biologic use.
Initiation of biologics should only be done after a similar risk-benefit analysis, with a recommendation to consider deferring initiation for patients 60 and older and those with comorbidities that may portend a worse course in the event of coronavirus infection. Biologics should be discontinued for patients who test positive for COVID-19.
Dr. Hruza outlined some of the federal measures taken that may affect the business side of dermatology practices. These include a $20 million transfer to the Small Business Administration to offset administrative expenses associated with increased loan volumes related to the coronavirus outbreak. Eligible expenses for loans may include new devices and environmental adjustments to accommodate telehealth services.
Additionally, it is anticipated that as employers are required to provide paid sick and family leave, a payroll tax credit will be issued to employers. Some self-employed individuals will also be able to claim a tax credit for sick and family leave.
A recent news release from the AAD encourages the public to use high-emollient moisturizers after handwashing. The release also provides other tips, such as using petrolatum at bedtime for hands that are particularly dry and focusing on the fingertips when moisturizing, as these areas are prone to cracking. The release also reaffirms that the most effective way to clean hands is soap and water, and that moisturizing after handwashing does not negate the antiviral effects of cleansing, contrary to some social media reports.
[email protected]
The American Academy of Dermatology (
The guidance pages are publicly viewable. Additionally, AAD has made a collection of COVID-19 articles from the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology freely available for the next 6 months.
George Hruza, MD, AAD president, detailed regulatory updates and other federal actions as well as guidance regarding telemedicine and clinical practice in a message to AAD members.
“While many questions still need answers, I have appointed an Ad Hoc Task Force to assess dermatology’s needs, share knowledge, and provide ongoing guidance and information throughout the crisis,” Dr. Hruza wrote.
“The situation is changing rapidly, and we are committed to keeping you updated with reliable and practical information to help you adapt to the circumstances,” he noted, referring dermatologists to the AAD’s information hub for the coronavirus outbreak. “We are keeping this page updated frequently, and it will serve as your primary source for what we know now,” he noted.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has recently relaxed key regulations regarding technology to provide telemedicine so that physicians and patients can use existing platforms such as FaceTime and Skype for virtual visits. The usual fines for HIPAA noncompliance have been waived. Additionally, telemedicine visits can now be reimbursed at the same rate as in-person visits.
Private payers are beginning to follow suit, said Dr. Hruza, noting that the AAD Association is working to harmonize private coverage with public reimbursement. The AAD also is tracking which payers are coming in line with federal policies on its teledermatology page.
These changes in regulation around telemedicine apply to patient encounters for any purpose, not just coronavirus-related encounters, noted Dr. Hruza. “The good news is that the government has taken action to make it much easier for us to provide virtual consults to patients. Dermatology has always been a leader in telemedicine, and it will be an important way to offer care to patients who can’t or don’t need to come into the office or clinic,” he added.
Importantly, said Dr. Hruza, CMS is allowing practices to have discretion over whether copays are collected, or collected in full, so that these payments don’t present a barrier to patient care in the current crisis environment.
For dermatologists who are new to telemedicine, AAD has created an online resource that includes information about various telemedicine platforms, updated guidance regarding regulations, and best practices for accurate coding and documentation of telemedicine visits.
The Academy has also been developing dermatology-specific guidance, including how to address the concerns of patients who are receiving biologic therapies and how to conserve personal protective equipment while still protecting physicians, staff, and patients from COVID-19 infection.
For patients on biologic therapy who show no sign of coronavirus infection, the decision to continue or stop biologics should be made on a case-by-case basis. Factors to be considered include patient age, comorbidities, and the severity of the original indication for biologic use.
Initiation of biologics should only be done after a similar risk-benefit analysis, with a recommendation to consider deferring initiation for patients 60 and older and those with comorbidities that may portend a worse course in the event of coronavirus infection. Biologics should be discontinued for patients who test positive for COVID-19.
Dr. Hruza outlined some of the federal measures taken that may affect the business side of dermatology practices. These include a $20 million transfer to the Small Business Administration to offset administrative expenses associated with increased loan volumes related to the coronavirus outbreak. Eligible expenses for loans may include new devices and environmental adjustments to accommodate telehealth services.
Additionally, it is anticipated that as employers are required to provide paid sick and family leave, a payroll tax credit will be issued to employers. Some self-employed individuals will also be able to claim a tax credit for sick and family leave.
A recent news release from the AAD encourages the public to use high-emollient moisturizers after handwashing. The release also provides other tips, such as using petrolatum at bedtime for hands that are particularly dry and focusing on the fingertips when moisturizing, as these areas are prone to cracking. The release also reaffirms that the most effective way to clean hands is soap and water, and that moisturizing after handwashing does not negate the antiviral effects of cleansing, contrary to some social media reports.
[email protected]
The American Academy of Dermatology (
The guidance pages are publicly viewable. Additionally, AAD has made a collection of COVID-19 articles from the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology freely available for the next 6 months.
George Hruza, MD, AAD president, detailed regulatory updates and other federal actions as well as guidance regarding telemedicine and clinical practice in a message to AAD members.
“While many questions still need answers, I have appointed an Ad Hoc Task Force to assess dermatology’s needs, share knowledge, and provide ongoing guidance and information throughout the crisis,” Dr. Hruza wrote.
“The situation is changing rapidly, and we are committed to keeping you updated with reliable and practical information to help you adapt to the circumstances,” he noted, referring dermatologists to the AAD’s information hub for the coronavirus outbreak. “We are keeping this page updated frequently, and it will serve as your primary source for what we know now,” he noted.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has recently relaxed key regulations regarding technology to provide telemedicine so that physicians and patients can use existing platforms such as FaceTime and Skype for virtual visits. The usual fines for HIPAA noncompliance have been waived. Additionally, telemedicine visits can now be reimbursed at the same rate as in-person visits.
Private payers are beginning to follow suit, said Dr. Hruza, noting that the AAD Association is working to harmonize private coverage with public reimbursement. The AAD also is tracking which payers are coming in line with federal policies on its teledermatology page.
These changes in regulation around telemedicine apply to patient encounters for any purpose, not just coronavirus-related encounters, noted Dr. Hruza. “The good news is that the government has taken action to make it much easier for us to provide virtual consults to patients. Dermatology has always been a leader in telemedicine, and it will be an important way to offer care to patients who can’t or don’t need to come into the office or clinic,” he added.
Importantly, said Dr. Hruza, CMS is allowing practices to have discretion over whether copays are collected, or collected in full, so that these payments don’t present a barrier to patient care in the current crisis environment.
For dermatologists who are new to telemedicine, AAD has created an online resource that includes information about various telemedicine platforms, updated guidance regarding regulations, and best practices for accurate coding and documentation of telemedicine visits.
The Academy has also been developing dermatology-specific guidance, including how to address the concerns of patients who are receiving biologic therapies and how to conserve personal protective equipment while still protecting physicians, staff, and patients from COVID-19 infection.
For patients on biologic therapy who show no sign of coronavirus infection, the decision to continue or stop biologics should be made on a case-by-case basis. Factors to be considered include patient age, comorbidities, and the severity of the original indication for biologic use.
Initiation of biologics should only be done after a similar risk-benefit analysis, with a recommendation to consider deferring initiation for patients 60 and older and those with comorbidities that may portend a worse course in the event of coronavirus infection. Biologics should be discontinued for patients who test positive for COVID-19.
Dr. Hruza outlined some of the federal measures taken that may affect the business side of dermatology practices. These include a $20 million transfer to the Small Business Administration to offset administrative expenses associated with increased loan volumes related to the coronavirus outbreak. Eligible expenses for loans may include new devices and environmental adjustments to accommodate telehealth services.
Additionally, it is anticipated that as employers are required to provide paid sick and family leave, a payroll tax credit will be issued to employers. Some self-employed individuals will also be able to claim a tax credit for sick and family leave.
A recent news release from the AAD encourages the public to use high-emollient moisturizers after handwashing. The release also provides other tips, such as using petrolatum at bedtime for hands that are particularly dry and focusing on the fingertips when moisturizing, as these areas are prone to cracking. The release also reaffirms that the most effective way to clean hands is soap and water, and that moisturizing after handwashing does not negate the antiviral effects of cleansing, contrary to some social media reports.
[email protected]
DIY masks: Worth the risk? Researchers are conflicted
In the midst of the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and clinics are running out of masks. Health care workers are going online to beg for more, the hashtags #GetMePPE and #WeNeedPPE are trending on Twitter, and some hospitals have even put out public calls for mask donations. Health providers are working scared: They know that the moment the masks run out, they’re at increased risk for disease. So instead of waiting for mask shipments that may be weeks off, some people are making their own.
Using a simple template, they cut green surgical sheeting into half-moons, which they pin and sew before attaching elastic straps. Deaconess Health System in Evansville, Indiana, has posted instructions for fabric masks on their website and asked the public to step up and sew.
Elsewhere, health care workers have turned to diapers, maxi pads and other products to create masks. Social media channels are full of tips and sewing patterns. It’s an innovative strategy that is also contentious. Limited evidence suggests that homemade masks can offer some protection. But the DIY approach has also drawn criticism for providing a false sense of security, potentially putting wearers at risk.
The conflict points to an immediate need for more protective equipment, says Christopher Friese, PhD, RN, professor of nursing and public health at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Also needed, he says, are new ideas for reducing strain on limited supplies, like adopting gear from other industries and finding innovative ways to provide care so that less protective gear is needed.
“We don’t want clinicians inventing and ‘MacGyvering’ their own device because we don’t want to put them at risk if we can avoid it,” says Friese, referring to the TV character who could build and assemble a vast array of tools/devices. “We have options that have been tested, and we have experience, maybe not in health care, but in other settings. We want to try that first before that frontline doctor, nurse, respiratory therapist decides to take matters into their own hands.
Increasingly, though, health care workers are finding they have no other choice — something even the CDC has acknowledged. In new guidelines, the agency recommends a bandanna, scarf, or other type of covering in cases where face masks are not available.
N95 respirators or surgical masks?
There are two main types of masks generally used in health care. N95 respirators filter out 95% of airborne particles, including bacteria and viruses. The lighter surgical or medical face masks are made to prevent spit and mucous from getting on patients or equipment.
Both types reduce rates of infection among health care workers, though comparisons (at least for influenza) have yet to show that one is superior to the other. One 2020 review by Chinese researchers, for example, analyzed six randomly controlled trials that included more than 9000 participants and found no added benefits of N95 masks over ordinary surgical masks for health care providers treating patients with the flu.
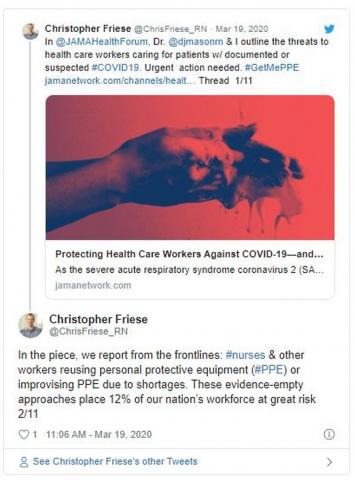
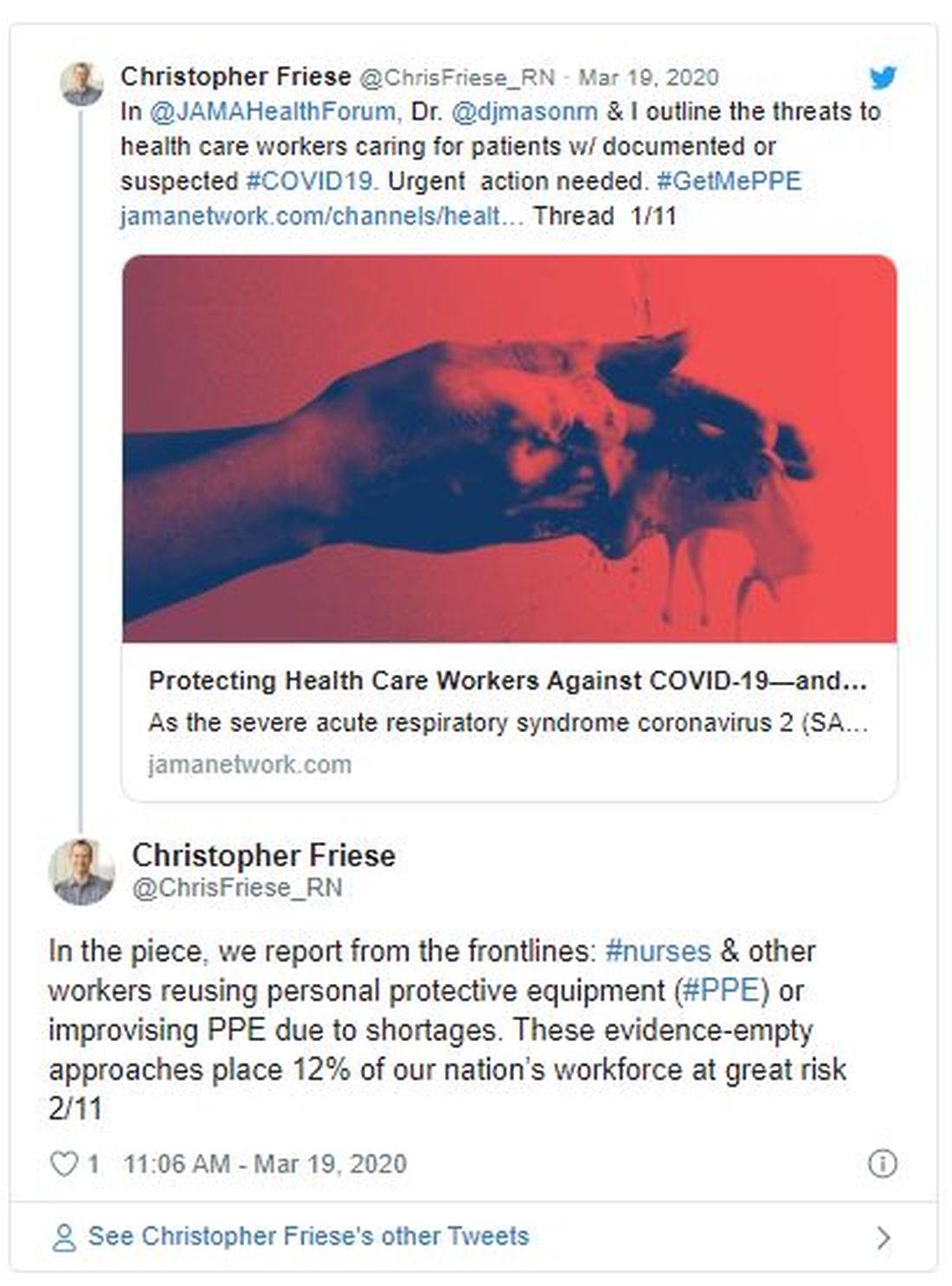
But COVID-19 is not influenza, and evidence suggests it may require more intensive protection, says Friese, who coauthored a blog post for JAMA about the country’s unpreparedness for protecting health care workers during a pandemic. The virus can linger in the air for hours, suggesting that N95 respirators are health care providers’ best option when treating infected patients.
The problem is there’s not enough to go around — of either mask type. In a March 5 survey, National Nurses United reported that just 30% of more than 6500 US respondents said their organizations had enough PPE to respond to a surge in patients. Another 38% did not know if their organizations were prepared. In a tweet, Friese estimated that 12% of nurses and other providers are at risk from reusing equipment or using equipment that is not backed by evidence.
Physicians and providers around the world have been sharing strategies online for how to make their own masks. Techniques vary, as do materials and plans for how to use the homemade equipment. At Phoebe Putney Health, DIY masks are intended to be worn over N95 respirators and then disposed of so that the respirators can be reused more safely, says Amanda Clements, the hospital’s public relations coordinator. Providers might also wear them to greet people at the front door.
Some evidence suggests that homemade masks can help in a pinch, at least for some illnesses. For a 2013 study by researchers in the UK, volunteers made surgical masks from cotton T-shirts, then put them on and coughed into a chamber that measured how much bacterial content got through. The team also assessed the aerosol-filtering ability of a variety of household materials, including scarfs, antimicrobial pillowcases, vacuum-cleaner bags, and tea towels. They tested each material with an aerosol containing two types of bacteria similar in size to influenza.
Commercial surgical masks performed three times better than homemade ones in the filtration test. Surgical masks worked twice as well at blocking droplets on the cough test. But all the makeshift materials — which also included silk, linen, and regular pillowcases — blocked some microbes. Vacuum-cleaner bags blocked the most bacteria, but their stiffness and thickness made them unsuitable for use as masks, the researchers reported. Tea towels showed a similar pattern. But pillowcases and cotton T-shirts were stretchy enough to fit well, thereby reducing the particles that could get through or around them.
Homemade masks should be used only as a last resort if commercial masks become unavailable, the researchers concluded. “Probably something is better than nothing for trained health care workers — for droplet contact avoidance, if nothing else,” says Anna Davies, BSc, a research facilitator at the University of Cambridge, UK, who is a former public health microbiologist and one of the study’s authors.
She recommends that members of the general public donate any stockpiles they have to health care workers, and make their own if they want masks for personal use. She is working with collaborators in the US to develop guidance for how best to do it.
“If people are quarantined and looking for something worthwhile to do, it probably wouldn’t be the worst thing to apply themselves to,” she wrote by email. “My suggestion would be for something soft and cotton, ideally with a bit of stretch (although it’s a pain to sew), and in two layers, marked ‘inside’ and ‘outside.’ ”
The idea that something is better than nothing was also the conclusion of a 2008 study by researchers in the Netherlands and the US. The study enlisted 28 healthy individuals who performed a variety of tasks while wearing N95 masks, surgical masks, or homemade masks sewn from teacloths. Effectiveness varied among individuals, but over a 90-second period, N95 masks worked best, with 25 times more protection than surgical masks and about 50 times more protection than homemade ones. Surgical masks were twice as effective as homemade masks. But the homemade masks offered at least some protection against large droplets.
Researchers emphasize that it’s not yet clear whether those findings are applicable to aerosolized COVID-19. In an influenza pandemic, at least, the authors posit that homemade masks could reduce transmission for the general public enough for some immunity to build. “It is important not to focus on a single intervention in case of a pandemic,” the researchers write, “but to integrate all effective interventions for optimal protection.”
For health care workers on the frontlines of COVID-19, Friese says, homemade masks might do more than nothing but they also might not work. Instead, he would rather see providers using construction or nuclear-engineering masks. And his best suggestion is something many providers are already doing: reducing physical contact with patients through telemedicine and other creative solutions, which is cutting down the overwhelming need for PPE.
Homemade mask production emphasizes the urgent need for more supplies, Friese adds.
“The government needs to step up and do a variety of things to increase production, and that needs to happen now, immediately,” he says. “We don’t we don’t want our clinicians to have to come up with these decisions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the midst of the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and clinics are running out of masks. Health care workers are going online to beg for more, the hashtags #GetMePPE and #WeNeedPPE are trending on Twitter, and some hospitals have even put out public calls for mask donations. Health providers are working scared: They know that the moment the masks run out, they’re at increased risk for disease. So instead of waiting for mask shipments that may be weeks off, some people are making their own.
Using a simple template, they cut green surgical sheeting into half-moons, which they pin and sew before attaching elastic straps. Deaconess Health System in Evansville, Indiana, has posted instructions for fabric masks on their website and asked the public to step up and sew.
Elsewhere, health care workers have turned to diapers, maxi pads and other products to create masks. Social media channels are full of tips and sewing patterns. It’s an innovative strategy that is also contentious. Limited evidence suggests that homemade masks can offer some protection. But the DIY approach has also drawn criticism for providing a false sense of security, potentially putting wearers at risk.
The conflict points to an immediate need for more protective equipment, says Christopher Friese, PhD, RN, professor of nursing and public health at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Also needed, he says, are new ideas for reducing strain on limited supplies, like adopting gear from other industries and finding innovative ways to provide care so that less protective gear is needed.
“We don’t want clinicians inventing and ‘MacGyvering’ their own device because we don’t want to put them at risk if we can avoid it,” says Friese, referring to the TV character who could build and assemble a vast array of tools/devices. “We have options that have been tested, and we have experience, maybe not in health care, but in other settings. We want to try that first before that frontline doctor, nurse, respiratory therapist decides to take matters into their own hands.
Increasingly, though, health care workers are finding they have no other choice — something even the CDC has acknowledged. In new guidelines, the agency recommends a bandanna, scarf, or other type of covering in cases where face masks are not available.
N95 respirators or surgical masks?
There are two main types of masks generally used in health care. N95 respirators filter out 95% of airborne particles, including bacteria and viruses. The lighter surgical or medical face masks are made to prevent spit and mucous from getting on patients or equipment.
Both types reduce rates of infection among health care workers, though comparisons (at least for influenza) have yet to show that one is superior to the other. One 2020 review by Chinese researchers, for example, analyzed six randomly controlled trials that included more than 9000 participants and found no added benefits of N95 masks over ordinary surgical masks for health care providers treating patients with the flu.
But COVID-19 is not influenza, and evidence suggests it may require more intensive protection, says Friese, who coauthored a blog post for JAMA about the country’s unpreparedness for protecting health care workers during a pandemic. The virus can linger in the air for hours, suggesting that N95 respirators are health care providers’ best option when treating infected patients.
The problem is there’s not enough to go around — of either mask type. In a March 5 survey, National Nurses United reported that just 30% of more than 6500 US respondents said their organizations had enough PPE to respond to a surge in patients. Another 38% did not know if their organizations were prepared. In a tweet, Friese estimated that 12% of nurses and other providers are at risk from reusing equipment or using equipment that is not backed by evidence.
Physicians and providers around the world have been sharing strategies online for how to make their own masks. Techniques vary, as do materials and plans for how to use the homemade equipment. At Phoebe Putney Health, DIY masks are intended to be worn over N95 respirators and then disposed of so that the respirators can be reused more safely, says Amanda Clements, the hospital’s public relations coordinator. Providers might also wear them to greet people at the front door.
Some evidence suggests that homemade masks can help in a pinch, at least for some illnesses. For a 2013 study by researchers in the UK, volunteers made surgical masks from cotton T-shirts, then put them on and coughed into a chamber that measured how much bacterial content got through. The team also assessed the aerosol-filtering ability of a variety of household materials, including scarfs, antimicrobial pillowcases, vacuum-cleaner bags, and tea towels. They tested each material with an aerosol containing two types of bacteria similar in size to influenza.
Commercial surgical masks performed three times better than homemade ones in the filtration test. Surgical masks worked twice as well at blocking droplets on the cough test. But all the makeshift materials — which also included silk, linen, and regular pillowcases — blocked some microbes. Vacuum-cleaner bags blocked the most bacteria, but their stiffness and thickness made them unsuitable for use as masks, the researchers reported. Tea towels showed a similar pattern. But pillowcases and cotton T-shirts were stretchy enough to fit well, thereby reducing the particles that could get through or around them.
Homemade masks should be used only as a last resort if commercial masks become unavailable, the researchers concluded. “Probably something is better than nothing for trained health care workers — for droplet contact avoidance, if nothing else,” says Anna Davies, BSc, a research facilitator at the University of Cambridge, UK, who is a former public health microbiologist and one of the study’s authors.
She recommends that members of the general public donate any stockpiles they have to health care workers, and make their own if they want masks for personal use. She is working with collaborators in the US to develop guidance for how best to do it.
“If people are quarantined and looking for something worthwhile to do, it probably wouldn’t be the worst thing to apply themselves to,” she wrote by email. “My suggestion would be for something soft and cotton, ideally with a bit of stretch (although it’s a pain to sew), and in two layers, marked ‘inside’ and ‘outside.’ ”
The idea that something is better than nothing was also the conclusion of a 2008 study by researchers in the Netherlands and the US. The study enlisted 28 healthy individuals who performed a variety of tasks while wearing N95 masks, surgical masks, or homemade masks sewn from teacloths. Effectiveness varied among individuals, but over a 90-second period, N95 masks worked best, with 25 times more protection than surgical masks and about 50 times more protection than homemade ones. Surgical masks were twice as effective as homemade masks. But the homemade masks offered at least some protection against large droplets.
Researchers emphasize that it’s not yet clear whether those findings are applicable to aerosolized COVID-19. In an influenza pandemic, at least, the authors posit that homemade masks could reduce transmission for the general public enough for some immunity to build. “It is important not to focus on a single intervention in case of a pandemic,” the researchers write, “but to integrate all effective interventions for optimal protection.”
For health care workers on the frontlines of COVID-19, Friese says, homemade masks might do more than nothing but they also might not work. Instead, he would rather see providers using construction or nuclear-engineering masks. And his best suggestion is something many providers are already doing: reducing physical contact with patients through telemedicine and other creative solutions, which is cutting down the overwhelming need for PPE.
Homemade mask production emphasizes the urgent need for more supplies, Friese adds.
“The government needs to step up and do a variety of things to increase production, and that needs to happen now, immediately,” he says. “We don’t we don’t want our clinicians to have to come up with these decisions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the midst of the rapidly spreading COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and clinics are running out of masks. Health care workers are going online to beg for more, the hashtags #GetMePPE and #WeNeedPPE are trending on Twitter, and some hospitals have even put out public calls for mask donations. Health providers are working scared: They know that the moment the masks run out, they’re at increased risk for disease. So instead of waiting for mask shipments that may be weeks off, some people are making their own.
Using a simple template, they cut green surgical sheeting into half-moons, which they pin and sew before attaching elastic straps. Deaconess Health System in Evansville, Indiana, has posted instructions for fabric masks on their website and asked the public to step up and sew.
Elsewhere, health care workers have turned to diapers, maxi pads and other products to create masks. Social media channels are full of tips and sewing patterns. It’s an innovative strategy that is also contentious. Limited evidence suggests that homemade masks can offer some protection. But the DIY approach has also drawn criticism for providing a false sense of security, potentially putting wearers at risk.
The conflict points to an immediate need for more protective equipment, says Christopher Friese, PhD, RN, professor of nursing and public health at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Also needed, he says, are new ideas for reducing strain on limited supplies, like adopting gear from other industries and finding innovative ways to provide care so that less protective gear is needed.
“We don’t want clinicians inventing and ‘MacGyvering’ their own device because we don’t want to put them at risk if we can avoid it,” says Friese, referring to the TV character who could build and assemble a vast array of tools/devices. “We have options that have been tested, and we have experience, maybe not in health care, but in other settings. We want to try that first before that frontline doctor, nurse, respiratory therapist decides to take matters into their own hands.
Increasingly, though, health care workers are finding they have no other choice — something even the CDC has acknowledged. In new guidelines, the agency recommends a bandanna, scarf, or other type of covering in cases where face masks are not available.
N95 respirators or surgical masks?
There are two main types of masks generally used in health care. N95 respirators filter out 95% of airborne particles, including bacteria and viruses. The lighter surgical or medical face masks are made to prevent spit and mucous from getting on patients or equipment.
Both types reduce rates of infection among health care workers, though comparisons (at least for influenza) have yet to show that one is superior to the other. One 2020 review by Chinese researchers, for example, analyzed six randomly controlled trials that included more than 9000 participants and found no added benefits of N95 masks over ordinary surgical masks for health care providers treating patients with the flu.
But COVID-19 is not influenza, and evidence suggests it may require more intensive protection, says Friese, who coauthored a blog post for JAMA about the country’s unpreparedness for protecting health care workers during a pandemic. The virus can linger in the air for hours, suggesting that N95 respirators are health care providers’ best option when treating infected patients.
The problem is there’s not enough to go around — of either mask type. In a March 5 survey, National Nurses United reported that just 30% of more than 6500 US respondents said their organizations had enough PPE to respond to a surge in patients. Another 38% did not know if their organizations were prepared. In a tweet, Friese estimated that 12% of nurses and other providers are at risk from reusing equipment or using equipment that is not backed by evidence.
Physicians and providers around the world have been sharing strategies online for how to make their own masks. Techniques vary, as do materials and plans for how to use the homemade equipment. At Phoebe Putney Health, DIY masks are intended to be worn over N95 respirators and then disposed of so that the respirators can be reused more safely, says Amanda Clements, the hospital’s public relations coordinator. Providers might also wear them to greet people at the front door.
Some evidence suggests that homemade masks can help in a pinch, at least for some illnesses. For a 2013 study by researchers in the UK, volunteers made surgical masks from cotton T-shirts, then put them on and coughed into a chamber that measured how much bacterial content got through. The team also assessed the aerosol-filtering ability of a variety of household materials, including scarfs, antimicrobial pillowcases, vacuum-cleaner bags, and tea towels. They tested each material with an aerosol containing two types of bacteria similar in size to influenza.
Commercial surgical masks performed three times better than homemade ones in the filtration test. Surgical masks worked twice as well at blocking droplets on the cough test. But all the makeshift materials — which also included silk, linen, and regular pillowcases — blocked some microbes. Vacuum-cleaner bags blocked the most bacteria, but their stiffness and thickness made them unsuitable for use as masks, the researchers reported. Tea towels showed a similar pattern. But pillowcases and cotton T-shirts were stretchy enough to fit well, thereby reducing the particles that could get through or around them.
Homemade masks should be used only as a last resort if commercial masks become unavailable, the researchers concluded. “Probably something is better than nothing for trained health care workers — for droplet contact avoidance, if nothing else,” says Anna Davies, BSc, a research facilitator at the University of Cambridge, UK, who is a former public health microbiologist and one of the study’s authors.
She recommends that members of the general public donate any stockpiles they have to health care workers, and make their own if they want masks for personal use. She is working with collaborators in the US to develop guidance for how best to do it.
“If people are quarantined and looking for something worthwhile to do, it probably wouldn’t be the worst thing to apply themselves to,” she wrote by email. “My suggestion would be for something soft and cotton, ideally with a bit of stretch (although it’s a pain to sew), and in two layers, marked ‘inside’ and ‘outside.’ ”
The idea that something is better than nothing was also the conclusion of a 2008 study by researchers in the Netherlands and the US. The study enlisted 28 healthy individuals who performed a variety of tasks while wearing N95 masks, surgical masks, or homemade masks sewn from teacloths. Effectiveness varied among individuals, but over a 90-second period, N95 masks worked best, with 25 times more protection than surgical masks and about 50 times more protection than homemade ones. Surgical masks were twice as effective as homemade masks. But the homemade masks offered at least some protection against large droplets.
Researchers emphasize that it’s not yet clear whether those findings are applicable to aerosolized COVID-19. In an influenza pandemic, at least, the authors posit that homemade masks could reduce transmission for the general public enough for some immunity to build. “It is important not to focus on a single intervention in case of a pandemic,” the researchers write, “but to integrate all effective interventions for optimal protection.”
For health care workers on the frontlines of COVID-19, Friese says, homemade masks might do more than nothing but they also might not work. Instead, he would rather see providers using construction or nuclear-engineering masks. And his best suggestion is something many providers are already doing: reducing physical contact with patients through telemedicine and other creative solutions, which is cutting down the overwhelming need for PPE.
Homemade mask production emphasizes the urgent need for more supplies, Friese adds.
“The government needs to step up and do a variety of things to increase production, and that needs to happen now, immediately,” he says. “We don’t we don’t want our clinicians to have to come up with these decisions.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 prompts ‘lifesaving’ policy change for opioid addiction
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feds tout drug candidates to treat COVID-19
Therapeutics could be available in the near term to help treat COVID-19 patients, according to President Donald Trump.
During a March 19 press briefing, the president highlighted two drugs that could be put into play in the battle against the virus.
The first product is hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), a drug used to treat malaria and severe arthritis, is showing promise as a possible treatment for COVID-19.
“The nice part is it’s been around for a long time, so we know that if things go as planned, it’s not going to kill anybody,” President Trump said. “When you go with a brand-new drug, you don’t know that that’s going to happen,” adding that it has shown “very, very encouraging” results as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
He said this drug will be made available “almost immediately.” During the press conference, Food and Drug Administration Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, suggested the drug would be made available in the context of a large pragmatic clinical trial, enabling the FDA to collect data on it and make a long-term decision on its viability to treat COVID-19.
Dr. Hahn also pointed to the Gilead drug remdesivir – a drug originally developed to fight Ebola and currently undergoing clinical trials – as another possible candidate for a near-term therapeutic to help treat patients while vaccine development occurs.
Dr. Hahn noted that, while the agency is striving to provide regulatory flexibility, safety is paramount. “Let me make one thing clear: FDA’s responsibility to the American people is to ensure that products are safe and effective and that we are continuing to do that.”
He noted that if these and other experimental drugs show promise, physicians can request them under “compassionate use” provisions.
“We have criteria for that, and very speedy approval for that,” Dr. Hahn said. “The important thing about compassionate use ... this is even beyond ‘right to try.’ [We] get to collect the information about that.”
He noted that the FDA is looking at other drugs that are approved for other indications. The examinations of existing therapies are meant to be a bridge as companies work to develop new therapeutics as well as vaccines.
Dr. Hahn also highlighted a cross-agency effort on convalescent plasma, which uses the plasma from a patient who has recovered from COVID-19 infection to help patients fight the virus. “This is a possible treatment; this is not a proven treatment, “ Dr. Hahn said.
Takeda is working on an immunoglobulin treatment based on its intravenous immunoglobulin product Gammagard Liquid.
Julie Kim, president of plasma-derived therapies at Takeda, said the company should be able to go straight into testing efficacy of this approach, given the known safety profile of the treatment. She made the comments during a March 18 press briefing hosted by Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). Ms. Kim did caution that this would not be a mass market kind of treatment, as supply would depend on plasma donations from individuals who have fully recovered from a COVID-19 infection. She estimated that the treatment could be available to a targeted group of high-risk patients in 9-18 months.
PhRMA president and CEO Stephen Ubl said the industry is “literally working around the clock” on four key areas: development of new diagnostics, identification of potential existing treatments to make available through trials and compassionate use, development of novel therapies, and development of a vaccine.
There are more than 80 clinical trials underway on existing treatments that could have approval to treat COVID-19 in a matter of months, he said.
Mikael Dolsten, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer at Pfizer, said that the company is working with Germany-based BioNTech SE to develop an mRNA-based vaccine for COVID-19, with testing expected to begin in Germany, China, and the United States by the end of April. The company also is screening antiviral compounds that were previously in development against other coronavirus diseases.
Clement Lewin, PhD, associate vice president of R&D strategy for vaccines at Sanofi, said the company has partnered with Regeneron to launch a trial of sarilumab (Kevzara), a drug approved to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, to help treat COVID-19.
Meanwhile, Lilly Chief Scientific Officer Daniel Skovronsky, MD, PhD, noted that his company is collaborating with AbCellera to develop therapeutics using monoclonal antibodies isolated from one of the first U.S. patients who recovered from COVID-19. He said the goal is to begin testing within the next 4 months.
Separately, World Health Organization Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus announced during a March 18 press conference that it is spearheading a large international study examining a number of different treatments in what has been dubbed the SOLIDARITY trial. Argentina, Bahrain, Canada, France, Iran, Norway, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, and Thailand have signed on to be a part of the trial, with more countries expected to participate.
“I continue to be inspired by the many demonstrations of solidarity from all over the world,” he said. “These and other efforts give me hope that together, we can and will prevail. This virus is presenting us with an unprecedented threat. But it’s also an unprecedented opportunity to come together as one against a common enemy, an enemy against humanity.”
Therapeutics could be available in the near term to help treat COVID-19 patients, according to President Donald Trump.
During a March 19 press briefing, the president highlighted two drugs that could be put into play in the battle against the virus.
The first product is hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), a drug used to treat malaria and severe arthritis, is showing promise as a possible treatment for COVID-19.
“The nice part is it’s been around for a long time, so we know that if things go as planned, it’s not going to kill anybody,” President Trump said. “When you go with a brand-new drug, you don’t know that that’s going to happen,” adding that it has shown “very, very encouraging” results as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
He said this drug will be made available “almost immediately.” During the press conference, Food and Drug Administration Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, suggested the drug would be made available in the context of a large pragmatic clinical trial, enabling the FDA to collect data on it and make a long-term decision on its viability to treat COVID-19.
Dr. Hahn also pointed to the Gilead drug remdesivir – a drug originally developed to fight Ebola and currently undergoing clinical trials – as another possible candidate for a near-term therapeutic to help treat patients while vaccine development occurs.
Dr. Hahn noted that, while the agency is striving to provide regulatory flexibility, safety is paramount. “Let me make one thing clear: FDA’s responsibility to the American people is to ensure that products are safe and effective and that we are continuing to do that.”
He noted that if these and other experimental drugs show promise, physicians can request them under “compassionate use” provisions.
“We have criteria for that, and very speedy approval for that,” Dr. Hahn said. “The important thing about compassionate use ... this is even beyond ‘right to try.’ [We] get to collect the information about that.”
He noted that the FDA is looking at other drugs that are approved for other indications. The examinations of existing therapies are meant to be a bridge as companies work to develop new therapeutics as well as vaccines.
Dr. Hahn also highlighted a cross-agency effort on convalescent plasma, which uses the plasma from a patient who has recovered from COVID-19 infection to help patients fight the virus. “This is a possible treatment; this is not a proven treatment, “ Dr. Hahn said.
Takeda is working on an immunoglobulin treatment based on its intravenous immunoglobulin product Gammagard Liquid.
Julie Kim, president of plasma-derived therapies at Takeda, said the company should be able to go straight into testing efficacy of this approach, given the known safety profile of the treatment. She made the comments during a March 18 press briefing hosted by Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). Ms. Kim did caution that this would not be a mass market kind of treatment, as supply would depend on plasma donations from individuals who have fully recovered from a COVID-19 infection. She estimated that the treatment could be available to a targeted group of high-risk patients in 9-18 months.
PhRMA president and CEO Stephen Ubl said the industry is “literally working around the clock” on four key areas: development of new diagnostics, identification of potential existing treatments to make available through trials and compassionate use, development of novel therapies, and development of a vaccine.
There are more than 80 clinical trials underway on existing treatments that could have approval to treat COVID-19 in a matter of months, he said.
Mikael Dolsten, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer at Pfizer, said that the company is working with Germany-based BioNTech SE to develop an mRNA-based vaccine for COVID-19, with testing expected to begin in Germany, China, and the United States by the end of April. The company also is screening antiviral compounds that were previously in development against other coronavirus diseases.
Clement Lewin, PhD, associate vice president of R&D strategy for vaccines at Sanofi, said the company has partnered with Regeneron to launch a trial of sarilumab (Kevzara), a drug approved to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, to help treat COVID-19.
Meanwhile, Lilly Chief Scientific Officer Daniel Skovronsky, MD, PhD, noted that his company is collaborating with AbCellera to develop therapeutics using monoclonal antibodies isolated from one of the first U.S. patients who recovered from COVID-19. He said the goal is to begin testing within the next 4 months.
Separately, World Health Organization Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus announced during a March 18 press conference that it is spearheading a large international study examining a number of different treatments in what has been dubbed the SOLIDARITY trial. Argentina, Bahrain, Canada, France, Iran, Norway, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, and Thailand have signed on to be a part of the trial, with more countries expected to participate.
“I continue to be inspired by the many demonstrations of solidarity from all over the world,” he said. “These and other efforts give me hope that together, we can and will prevail. This virus is presenting us with an unprecedented threat. But it’s also an unprecedented opportunity to come together as one against a common enemy, an enemy against humanity.”
Therapeutics could be available in the near term to help treat COVID-19 patients, according to President Donald Trump.
During a March 19 press briefing, the president highlighted two drugs that could be put into play in the battle against the virus.
The first product is hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), a drug used to treat malaria and severe arthritis, is showing promise as a possible treatment for COVID-19.
“The nice part is it’s been around for a long time, so we know that if things go as planned, it’s not going to kill anybody,” President Trump said. “When you go with a brand-new drug, you don’t know that that’s going to happen,” adding that it has shown “very, very encouraging” results as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
He said this drug will be made available “almost immediately.” During the press conference, Food and Drug Administration Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, suggested the drug would be made available in the context of a large pragmatic clinical trial, enabling the FDA to collect data on it and make a long-term decision on its viability to treat COVID-19.
Dr. Hahn also pointed to the Gilead drug remdesivir – a drug originally developed to fight Ebola and currently undergoing clinical trials – as another possible candidate for a near-term therapeutic to help treat patients while vaccine development occurs.
Dr. Hahn noted that, while the agency is striving to provide regulatory flexibility, safety is paramount. “Let me make one thing clear: FDA’s responsibility to the American people is to ensure that products are safe and effective and that we are continuing to do that.”
He noted that if these and other experimental drugs show promise, physicians can request them under “compassionate use” provisions.
“We have criteria for that, and very speedy approval for that,” Dr. Hahn said. “The important thing about compassionate use ... this is even beyond ‘right to try.’ [We] get to collect the information about that.”
He noted that the FDA is looking at other drugs that are approved for other indications. The examinations of existing therapies are meant to be a bridge as companies work to develop new therapeutics as well as vaccines.
Dr. Hahn also highlighted a cross-agency effort on convalescent plasma, which uses the plasma from a patient who has recovered from COVID-19 infection to help patients fight the virus. “This is a possible treatment; this is not a proven treatment, “ Dr. Hahn said.
Takeda is working on an immunoglobulin treatment based on its intravenous immunoglobulin product Gammagard Liquid.
Julie Kim, president of plasma-derived therapies at Takeda, said the company should be able to go straight into testing efficacy of this approach, given the known safety profile of the treatment. She made the comments during a March 18 press briefing hosted by Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). Ms. Kim did caution that this would not be a mass market kind of treatment, as supply would depend on plasma donations from individuals who have fully recovered from a COVID-19 infection. She estimated that the treatment could be available to a targeted group of high-risk patients in 9-18 months.
PhRMA president and CEO Stephen Ubl said the industry is “literally working around the clock” on four key areas: development of new diagnostics, identification of potential existing treatments to make available through trials and compassionate use, development of novel therapies, and development of a vaccine.
There are more than 80 clinical trials underway on existing treatments that could have approval to treat COVID-19 in a matter of months, he said.
Mikael Dolsten, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer at Pfizer, said that the company is working with Germany-based BioNTech SE to develop an mRNA-based vaccine for COVID-19, with testing expected to begin in Germany, China, and the United States by the end of April. The company also is screening antiviral compounds that were previously in development against other coronavirus diseases.
Clement Lewin, PhD, associate vice president of R&D strategy for vaccines at Sanofi, said the company has partnered with Regeneron to launch a trial of sarilumab (Kevzara), a drug approved to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, to help treat COVID-19.
Meanwhile, Lilly Chief Scientific Officer Daniel Skovronsky, MD, PhD, noted that his company is collaborating with AbCellera to develop therapeutics using monoclonal antibodies isolated from one of the first U.S. patients who recovered from COVID-19. He said the goal is to begin testing within the next 4 months.
Separately, World Health Organization Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus announced during a March 18 press conference that it is spearheading a large international study examining a number of different treatments in what has been dubbed the SOLIDARITY trial. Argentina, Bahrain, Canada, France, Iran, Norway, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, and Thailand have signed on to be a part of the trial, with more countries expected to participate.
“I continue to be inspired by the many demonstrations of solidarity from all over the world,” he said. “These and other efforts give me hope that together, we can and will prevail. This virus is presenting us with an unprecedented threat. But it’s also an unprecedented opportunity to come together as one against a common enemy, an enemy against humanity.”
20% of U.S. COVID-19 deaths were aged 20-64 years
*Correction, 3/20/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the age range for COVID-19 deaths. The headline of this story was corrected to read "20% of COVID-19 deaths were aged 20-64 years" and the text was adjusted to reflect the correct age range.
A review of more than 4,000 U.S. patients who were diagnosed with novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) shows that an unexpected 20% of deaths occurred among adults aged 20-64 years, and 20% of those hospitalized were aged 20-44 years.
The expectation has been that people over 65 are most vulnerable to COVID-19 infection, but this study indicates that, at least in the United States, a significant number of patients under 45 can land in the hospital and can even die of the disease.
To assess rates of hospitalization, admission to an ICU, and death among patients with COVID-19 by age group, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed 4,226 COVID-19 cases in the United States that were reported between Feb. 12 and March 16.
Overall, older patients in this group were the most likely to be hospitalized, to be admitted to ICU, and to die of COVID-19. A total of 31% of the cases, 45% of hospitalizations, 53% of ICU admissions, and 80% of deaths occurred in patients aged 65 years and older. “Similar to reports from other countries, this finding suggests that the risk for serious disease and death from COVID-19 is higher in older age groups,” said the investigators. “In contrast, persons aged [19 years and younger] appear to have milder COVID-19 illness, with almost no hospitalizations or deaths reported to date in the United States in this age group.”
But compared with the under-19 group, patients aged 20-44 years appeared to be at higher risk for hospitalization and ICU admission, according to the data published March 18 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The researchers excluded from their analysis patients who repatriated to the United States from Wuhan, China, and from Japan, including patients repatriated from cruise ships. Data on serious underlying health conditions were not available, and many cases were missing key data, they noted.
Among 508 patients known to have been hospitalized, 9% were aged 85 years or older, 36% were aged 65-84 years, 17% were aged 55-64 years, 18% were 45-54 years, and 20% were aged 20-44 years.
Among 121 patients admitted to an ICU, 7% were aged 85 years or older, 46% were aged 65-84 years, 36% were aged 45-64 years, and 12% were aged 20-44 years. Between 11% and 31% of patients with COVID-19 aged 75-84 years were admitted to an ICU.
Of 44 deaths, more than a third occurred among adults aged 85 years and older, and 46% occurred among adults aged 65-84 years, and 20% occurred among adults aged 20-64 years.
More follow-up time is needed to determine outcomes among active cases, the researchers said. These results also might overestimate the prevalence of severe disease because the initial approach to testing for COVID-19 focused on people with more severe disease. “These preliminary data also demonstrate that severe illness leading to hospitalization, including ICU admission and death, can occur in adults of any age with COVID-19,” according to the CDC.
SOURCE: CDC COVID-19 Response Team. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2.
*Correction, 3/20/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the age range for COVID-19 deaths. The headline of this story was corrected to read "20% of COVID-19 deaths were aged 20-64 years" and the text was adjusted to reflect the correct age range.
A review of more than 4,000 U.S. patients who were diagnosed with novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) shows that an unexpected 20% of deaths occurred among adults aged 20-64 years, and 20% of those hospitalized were aged 20-44 years.
The expectation has been that people over 65 are most vulnerable to COVID-19 infection, but this study indicates that, at least in the United States, a significant number of patients under 45 can land in the hospital and can even die of the disease.
To assess rates of hospitalization, admission to an ICU, and death among patients with COVID-19 by age group, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed 4,226 COVID-19 cases in the United States that were reported between Feb. 12 and March 16.
Overall, older patients in this group were the most likely to be hospitalized, to be admitted to ICU, and to die of COVID-19. A total of 31% of the cases, 45% of hospitalizations, 53% of ICU admissions, and 80% of deaths occurred in patients aged 65 years and older. “Similar to reports from other countries, this finding suggests that the risk for serious disease and death from COVID-19 is higher in older age groups,” said the investigators. “In contrast, persons aged [19 years and younger] appear to have milder COVID-19 illness, with almost no hospitalizations or deaths reported to date in the United States in this age group.”
But compared with the under-19 group, patients aged 20-44 years appeared to be at higher risk for hospitalization and ICU admission, according to the data published March 18 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The researchers excluded from their analysis patients who repatriated to the United States from Wuhan, China, and from Japan, including patients repatriated from cruise ships. Data on serious underlying health conditions were not available, and many cases were missing key data, they noted.
Among 508 patients known to have been hospitalized, 9% were aged 85 years or older, 36% were aged 65-84 years, 17% were aged 55-64 years, 18% were 45-54 years, and 20% were aged 20-44 years.
Among 121 patients admitted to an ICU, 7% were aged 85 years or older, 46% were aged 65-84 years, 36% were aged 45-64 years, and 12% were aged 20-44 years. Between 11% and 31% of patients with COVID-19 aged 75-84 years were admitted to an ICU.
Of 44 deaths, more than a third occurred among adults aged 85 years and older, and 46% occurred among adults aged 65-84 years, and 20% occurred among adults aged 20-64 years.
More follow-up time is needed to determine outcomes among active cases, the researchers said. These results also might overestimate the prevalence of severe disease because the initial approach to testing for COVID-19 focused on people with more severe disease. “These preliminary data also demonstrate that severe illness leading to hospitalization, including ICU admission and death, can occur in adults of any age with COVID-19,” according to the CDC.
SOURCE: CDC COVID-19 Response Team. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2.
*Correction, 3/20/2020: An earlier version of this story misstated the age range for COVID-19 deaths. The headline of this story was corrected to read "20% of COVID-19 deaths were aged 20-64 years" and the text was adjusted to reflect the correct age range.
A review of more than 4,000 U.S. patients who were diagnosed with novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) shows that an unexpected 20% of deaths occurred among adults aged 20-64 years, and 20% of those hospitalized were aged 20-44 years.
The expectation has been that people over 65 are most vulnerable to COVID-19 infection, but this study indicates that, at least in the United States, a significant number of patients under 45 can land in the hospital and can even die of the disease.
To assess rates of hospitalization, admission to an ICU, and death among patients with COVID-19 by age group, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention analyzed 4,226 COVID-19 cases in the United States that were reported between Feb. 12 and March 16.
Overall, older patients in this group were the most likely to be hospitalized, to be admitted to ICU, and to die of COVID-19. A total of 31% of the cases, 45% of hospitalizations, 53% of ICU admissions, and 80% of deaths occurred in patients aged 65 years and older. “Similar to reports from other countries, this finding suggests that the risk for serious disease and death from COVID-19 is higher in older age groups,” said the investigators. “In contrast, persons aged [19 years and younger] appear to have milder COVID-19 illness, with almost no hospitalizations or deaths reported to date in the United States in this age group.”
But compared with the under-19 group, patients aged 20-44 years appeared to be at higher risk for hospitalization and ICU admission, according to the data published March 18 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The researchers excluded from their analysis patients who repatriated to the United States from Wuhan, China, and from Japan, including patients repatriated from cruise ships. Data on serious underlying health conditions were not available, and many cases were missing key data, they noted.
Among 508 patients known to have been hospitalized, 9% were aged 85 years or older, 36% were aged 65-84 years, 17% were aged 55-64 years, 18% were 45-54 years, and 20% were aged 20-44 years.
Among 121 patients admitted to an ICU, 7% were aged 85 years or older, 46% were aged 65-84 years, 36% were aged 45-64 years, and 12% were aged 20-44 years. Between 11% and 31% of patients with COVID-19 aged 75-84 years were admitted to an ICU.
Of 44 deaths, more than a third occurred among adults aged 85 years and older, and 46% occurred among adults aged 65-84 years, and 20% occurred among adults aged 20-64 years.
More follow-up time is needed to determine outcomes among active cases, the researchers said. These results also might overestimate the prevalence of severe disease because the initial approach to testing for COVID-19 focused on people with more severe disease. “These preliminary data also demonstrate that severe illness leading to hospitalization, including ICU admission and death, can occur in adults of any age with COVID-19,” according to the CDC.
SOURCE: CDC COVID-19 Response Team. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2.
Real-world shortages not addressed in new COVID-19 guidance
Newly updated guidance on treating patients with the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has been published by the World Health Organization.
While it can’t replace clinical judgment or specialist consultation, the new guidance may help strengthen the clinical management of patients when COVID-19 is suspected, according to its authors.
The guidance, adapted from an earlier edition focused on the management of suspected Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), covers best practices for triage, infection prevention and control, and optimized supportive care for mild, severe, or critical coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
“This guidance should serve as a foundation for optimized supportive care to ensure the best possible chance for survival,” the authors wrote in the guidance.
While the WHO guidance does provide solid facts to support best practices for managing COVID-19, providers will also need to look beyond the document to tackle real-world issues, said David M. Ferraro, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary and critical care physician and associate professor of medicine at National Jewish Health in Denver.
For example, while the guidelines address the importance of screening and triage, limited COVID-19 testing may be a barrier to timely diagnoses that might compel more individuals to comply with social distancing recommendations, according to Dr. Ferraro, vice chair of the Fundamental Disaster Management Committee for the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM).
“If we’re not providing people with confirmation that they have the virus, they may potentially continue to be spreaders of the disease, because they don’t have that absolute proof,” Dr. Ferraro said in an interview. “I think that’s where we are limited right now, because often we’re not able to tell the mild symptomatic people – or even the asymptomatic people – that they really need to play a role in preventing further spread.”
Likewise, the guidelines provide sound guidance on management of severe or critical COVID-19, according to Dr. Ferraro, yet they don’t address the potential for shortages of trained health care personnel to handle more severe cases requiring ventilation. That’s clearly an important issue, he said, especially with recent reports that the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed Italian intensive care units (ICUs) to the brink of collapse.
If the pandemic reaches crisis levels in the United States, nearly 1 million people would need ventilatory support, according to a recent report from SCCM on U.S. resource availability for COVID-19. And while there are an estimated 200,000 ventilators available in the United States, it’s estimated in that report that only 135,000 patients could be handled at a time, given the shortage of ICU physicians, advanced practice providers, nurses, and respiratory therapists with training in mechanical ventilation.
“If our ICUs get overwhelmed and swarmed, we may have the technology available, but we may not have enough resources and personnel to safely manage the number of patients,” Dr. Ferraro said.
The solution to that, according to the SCCM report, is to focus on expanding the pool of trained professionals who may be needed, not only to mechanically ventilate patients with COVID-19, but also to care for other critically ill patients routinely cared for in the ICU. They also suggest adopting a “tiered staffing strategy” in which non-ICU trained health care providers augment the capacity of experienced ICU staff.
With the prospect of untrained health care workers in mind, the WHO guidance could be a valuable resource for those who do have to jump into ICU roles, according to Dr. Ferraro.
The WHO also stresses immediate implementation of appropriate measures for infection prevention and control (IPC). According to their guidance, IPC needs to be initiated right at the point where the patient enters the hospital, with screening done at the first point of contact in the emergency department or outpatient clinics.
If patients are suspected to have COVID-19, they should receive a mask, and should be directed to a separate area where they are kept at least 1 meter apart from other individuals with suspected COVID-19, according to the WHO. (The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends maintaining a distance of 6 feet to prevent spread of illness).
Beyond standard precautions such as hand washing and use of personal protective equipment, health care workers should do a point-of-care risk assessment at every patient contact to determine whether additional precautions are required.
Having standard IPC measures in place is “paramount,” according to Dr. Ferraro, for a disease that has no available vaccine, no proven treatments, and a stealthy spread fueled by asymptomatic carriers.
“Those are huge weapons against us, and the only thing we really have to knock this down is really infection prevention control, so that truly is at the cornerstone,” he said. “These are things that we must strictly follow.”
Newly updated guidance on treating patients with the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has been published by the World Health Organization.
While it can’t replace clinical judgment or specialist consultation, the new guidance may help strengthen the clinical management of patients when COVID-19 is suspected, according to its authors.
The guidance, adapted from an earlier edition focused on the management of suspected Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), covers best practices for triage, infection prevention and control, and optimized supportive care for mild, severe, or critical coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
“This guidance should serve as a foundation for optimized supportive care to ensure the best possible chance for survival,” the authors wrote in the guidance.
While the WHO guidance does provide solid facts to support best practices for managing COVID-19, providers will also need to look beyond the document to tackle real-world issues, said David M. Ferraro, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary and critical care physician and associate professor of medicine at National Jewish Health in Denver.
For example, while the guidelines address the importance of screening and triage, limited COVID-19 testing may be a barrier to timely diagnoses that might compel more individuals to comply with social distancing recommendations, according to Dr. Ferraro, vice chair of the Fundamental Disaster Management Committee for the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM).
“If we’re not providing people with confirmation that they have the virus, they may potentially continue to be spreaders of the disease, because they don’t have that absolute proof,” Dr. Ferraro said in an interview. “I think that’s where we are limited right now, because often we’re not able to tell the mild symptomatic people – or even the asymptomatic people – that they really need to play a role in preventing further spread.”
Likewise, the guidelines provide sound guidance on management of severe or critical COVID-19, according to Dr. Ferraro, yet they don’t address the potential for shortages of trained health care personnel to handle more severe cases requiring ventilation. That’s clearly an important issue, he said, especially with recent reports that the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed Italian intensive care units (ICUs) to the brink of collapse.
If the pandemic reaches crisis levels in the United States, nearly 1 million people would need ventilatory support, according to a recent report from SCCM on U.S. resource availability for COVID-19. And while there are an estimated 200,000 ventilators available in the United States, it’s estimated in that report that only 135,000 patients could be handled at a time, given the shortage of ICU physicians, advanced practice providers, nurses, and respiratory therapists with training in mechanical ventilation.
“If our ICUs get overwhelmed and swarmed, we may have the technology available, but we may not have enough resources and personnel to safely manage the number of patients,” Dr. Ferraro said.
The solution to that, according to the SCCM report, is to focus on expanding the pool of trained professionals who may be needed, not only to mechanically ventilate patients with COVID-19, but also to care for other critically ill patients routinely cared for in the ICU. They also suggest adopting a “tiered staffing strategy” in which non-ICU trained health care providers augment the capacity of experienced ICU staff.
With the prospect of untrained health care workers in mind, the WHO guidance could be a valuable resource for those who do have to jump into ICU roles, according to Dr. Ferraro.
The WHO also stresses immediate implementation of appropriate measures for infection prevention and control (IPC). According to their guidance, IPC needs to be initiated right at the point where the patient enters the hospital, with screening done at the first point of contact in the emergency department or outpatient clinics.
If patients are suspected to have COVID-19, they should receive a mask, and should be directed to a separate area where they are kept at least 1 meter apart from other individuals with suspected COVID-19, according to the WHO. (The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends maintaining a distance of 6 feet to prevent spread of illness).
Beyond standard precautions such as hand washing and use of personal protective equipment, health care workers should do a point-of-care risk assessment at every patient contact to determine whether additional precautions are required.
Having standard IPC measures in place is “paramount,” according to Dr. Ferraro, for a disease that has no available vaccine, no proven treatments, and a stealthy spread fueled by asymptomatic carriers.
“Those are huge weapons against us, and the only thing we really have to knock this down is really infection prevention control, so that truly is at the cornerstone,” he said. “These are things that we must strictly follow.”
Newly updated guidance on treating patients with the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has been published by the World Health Organization.
While it can’t replace clinical judgment or specialist consultation, the new guidance may help strengthen the clinical management of patients when COVID-19 is suspected, according to its authors.
The guidance, adapted from an earlier edition focused on the management of suspected Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), covers best practices for triage, infection prevention and control, and optimized supportive care for mild, severe, or critical coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
“This guidance should serve as a foundation for optimized supportive care to ensure the best possible chance for survival,” the authors wrote in the guidance.
While the WHO guidance does provide solid facts to support best practices for managing COVID-19, providers will also need to look beyond the document to tackle real-world issues, said David M. Ferraro, MD, FCCP, a pulmonary and critical care physician and associate professor of medicine at National Jewish Health in Denver.
For example, while the guidelines address the importance of screening and triage, limited COVID-19 testing may be a barrier to timely diagnoses that might compel more individuals to comply with social distancing recommendations, according to Dr. Ferraro, vice chair of the Fundamental Disaster Management Committee for the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM).
“If we’re not providing people with confirmation that they have the virus, they may potentially continue to be spreaders of the disease, because they don’t have that absolute proof,” Dr. Ferraro said in an interview. “I think that’s where we are limited right now, because often we’re not able to tell the mild symptomatic people – or even the asymptomatic people – that they really need to play a role in preventing further spread.”
Likewise, the guidelines provide sound guidance on management of severe or critical COVID-19, according to Dr. Ferraro, yet they don’t address the potential for shortages of trained health care personnel to handle more severe cases requiring ventilation. That’s clearly an important issue, he said, especially with recent reports that the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed Italian intensive care units (ICUs) to the brink of collapse.
If the pandemic reaches crisis levels in the United States, nearly 1 million people would need ventilatory support, according to a recent report from SCCM on U.S. resource availability for COVID-19. And while there are an estimated 200,000 ventilators available in the United States, it’s estimated in that report that only 135,000 patients could be handled at a time, given the shortage of ICU physicians, advanced practice providers, nurses, and respiratory therapists with training in mechanical ventilation.
“If our ICUs get overwhelmed and swarmed, we may have the technology available, but we may not have enough resources and personnel to safely manage the number of patients,” Dr. Ferraro said.
The solution to that, according to the SCCM report, is to focus on expanding the pool of trained professionals who may be needed, not only to mechanically ventilate patients with COVID-19, but also to care for other critically ill patients routinely cared for in the ICU. They also suggest adopting a “tiered staffing strategy” in which non-ICU trained health care providers augment the capacity of experienced ICU staff.
With the prospect of untrained health care workers in mind, the WHO guidance could be a valuable resource for those who do have to jump into ICU roles, according to Dr. Ferraro.
The WHO also stresses immediate implementation of appropriate measures for infection prevention and control (IPC). According to their guidance, IPC needs to be initiated right at the point where the patient enters the hospital, with screening done at the first point of contact in the emergency department or outpatient clinics.
If patients are suspected to have COVID-19, they should receive a mask, and should be directed to a separate area where they are kept at least 1 meter apart from other individuals with suspected COVID-19, according to the WHO. (The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends maintaining a distance of 6 feet to prevent spread of illness).
Beyond standard precautions such as hand washing and use of personal protective equipment, health care workers should do a point-of-care risk assessment at every patient contact to determine whether additional precautions are required.
Having standard IPC measures in place is “paramount,” according to Dr. Ferraro, for a disease that has no available vaccine, no proven treatments, and a stealthy spread fueled by asymptomatic carriers.
“Those are huge weapons against us, and the only thing we really have to knock this down is really infection prevention control, so that truly is at the cornerstone,” he said. “These are things that we must strictly follow.”
FROM THE WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
Lopinavir-ritonavir trial results ‘disappointing’ for severe COVID-19
No difference in the primary endpoint of the time to clinical improvement was seen in an open-label trial of the antiretroviral drug lopinavir-ritonavir versus standard of care in adult patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
The median time to clinical improvement – defined as the time from randomization to either an improvement of two points on a seven-category ordinal scale or discharge from the hospital, whichever was first – was 16 days in both groups (hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval 0.95-1.85; P = .09).
Although a numerically lower number of deaths were recorded at 28 days (19.2% vs. 25%) with the antiretroviral treatment versus standard of care, a similar percentage of patients had detectable levels of viral RNA in throat swabs taken at various time points during the study, Chinese researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bai Cao, M.D, from the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, both in Beijing, and associates, performed a randomized, controlled, trial of 199 adult patients hospitalized at the Jin Yin-Tan Hospital in Wuhan in Hubei Province, China.
For inclusion, patients had to have laboratory confirmed infection with SARS-Cov-2, the virus that causes COVID-19; pneumonia confirmed by chest imaging; and severely reduced oxygen saturation (94% or less while breathing ambient air or a ratio of the partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen of less than 300 mm Hg).
Patients were randomized to receive either a combination of lopinavir (400 mg) and ritonavir (100 mg) twice a day on top of standard care (n = 99) or to standard care alone (n = 100) for 14 days. “Because of the emergency nature of the trial, placebos of lopinavir-ritonavir were not prepared,” Dr. Cao et al. explained, noting that standard care consisted of supplemental oxygen, ventilation, antibiotic treatment, vasopressor support, renal-replacement therapy, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
While the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Cao et al. reported that patients in the lopinavir-ritonavir group had a shorter stay in the intensive care unit than did those in the standard-care group, at a median of 6 versus 11 days. They also reported that the duration from randomization to hospital discharge was numerically shorter, at a median of 12 versus 14 days. Furthermore, there was a higher percentage of patients with clinical improvement at day 14 in the lopinavir-ritonavir group than in the standard-care group (45.5% vs. 30.0%)
“The trial was initiated in rapid response to the COVID-19 public health emergency, at which time there was very limited information about clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the researchers observed. “The question of whether earlier lopinavir-ritonavir treatment in COVID-19 could have clinical benefit is an important one that requires further study,” they wrote.
Among the trial’s limitations are it was not blinded and the researchers do not have data on the lopinavir exposure levels in the trial participants.
“This was a heroic effort” in a “particularly challenging population,” Lindsey R. Baden, MD, and Eric J. Rubin, MD, stated in an editorial accompanying the article (Baden LR and Rubin EJ. New Engl J Med. March 18, 2020. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2005477). “Unfortunately, the trial results were disappointing,” they noted.
“The secondary end points provide both reason for hope and reason for discouragement,” wrote Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin. The lack of effect on viral shedding, however, “strongly [suggests] that it did not have the activity desired” they observed.
Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin commented that one of the important takeaways from the trial is that “the investigators appropriately prioritized speed, designing a trial that could rapidly produce an answer.” They continued that the investigators had shown that “rapidly initiated, high-quality randomized clinical trials are possible in epidemic conditions” and that results of such trials, whether they are positive or negative, “will be central to clinical care as the dangerous coronavirus outbreak continues.”
As it stands, more than 100 trials are listed in the ClinicalTrials.gov database as testing a wide range of different treatment approaches for COVID-19. These include trials investigating if sarilumab, hydroxychloroquine, fingolimod, bevacizumab, and losartan might have a role to play. There are also trials looking at the potential of other antiviral agents, such as Gilead’s investigational drug remdesivir, which has shown to have in vitro and in vivo activity against many emerging viral pathogens that cause Ebola, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome, and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
Dr. Cao’s trial was supported by grants from Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development and from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Emergency Project of Covid-19, and a National Science Grant for Distinguished Young Scholars.
All authors had no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Baden is the director of clinical research in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the director of infectious diseases at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. He is a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine and chair of the FDA’s Antimicrobial Drug Advisory Committee. He is involved in HIV vaccine clinical trials and has received research grants from the Ragon Institute, the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the Gates Foundation.
Dr. Rubin is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as editor-in-chief. He is an associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and is chair and Irene Heinz Given Professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
SOURCE: Cao B et al. New Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.
No difference in the primary endpoint of the time to clinical improvement was seen in an open-label trial of the antiretroviral drug lopinavir-ritonavir versus standard of care in adult patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
The median time to clinical improvement – defined as the time from randomization to either an improvement of two points on a seven-category ordinal scale or discharge from the hospital, whichever was first – was 16 days in both groups (hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval 0.95-1.85; P = .09).
Although a numerically lower number of deaths were recorded at 28 days (19.2% vs. 25%) with the antiretroviral treatment versus standard of care, a similar percentage of patients had detectable levels of viral RNA in throat swabs taken at various time points during the study, Chinese researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bai Cao, M.D, from the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, both in Beijing, and associates, performed a randomized, controlled, trial of 199 adult patients hospitalized at the Jin Yin-Tan Hospital in Wuhan in Hubei Province, China.
For inclusion, patients had to have laboratory confirmed infection with SARS-Cov-2, the virus that causes COVID-19; pneumonia confirmed by chest imaging; and severely reduced oxygen saturation (94% or less while breathing ambient air or a ratio of the partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen of less than 300 mm Hg).
Patients were randomized to receive either a combination of lopinavir (400 mg) and ritonavir (100 mg) twice a day on top of standard care (n = 99) or to standard care alone (n = 100) for 14 days. “Because of the emergency nature of the trial, placebos of lopinavir-ritonavir were not prepared,” Dr. Cao et al. explained, noting that standard care consisted of supplemental oxygen, ventilation, antibiotic treatment, vasopressor support, renal-replacement therapy, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
While the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Cao et al. reported that patients in the lopinavir-ritonavir group had a shorter stay in the intensive care unit than did those in the standard-care group, at a median of 6 versus 11 days. They also reported that the duration from randomization to hospital discharge was numerically shorter, at a median of 12 versus 14 days. Furthermore, there was a higher percentage of patients with clinical improvement at day 14 in the lopinavir-ritonavir group than in the standard-care group (45.5% vs. 30.0%)
“The trial was initiated in rapid response to the COVID-19 public health emergency, at which time there was very limited information about clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the researchers observed. “The question of whether earlier lopinavir-ritonavir treatment in COVID-19 could have clinical benefit is an important one that requires further study,” they wrote.
Among the trial’s limitations are it was not blinded and the researchers do not have data on the lopinavir exposure levels in the trial participants.
“This was a heroic effort” in a “particularly challenging population,” Lindsey R. Baden, MD, and Eric J. Rubin, MD, stated in an editorial accompanying the article (Baden LR and Rubin EJ. New Engl J Med. March 18, 2020. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2005477). “Unfortunately, the trial results were disappointing,” they noted.
“The secondary end points provide both reason for hope and reason for discouragement,” wrote Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin. The lack of effect on viral shedding, however, “strongly [suggests] that it did not have the activity desired” they observed.
Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin commented that one of the important takeaways from the trial is that “the investigators appropriately prioritized speed, designing a trial that could rapidly produce an answer.” They continued that the investigators had shown that “rapidly initiated, high-quality randomized clinical trials are possible in epidemic conditions” and that results of such trials, whether they are positive or negative, “will be central to clinical care as the dangerous coronavirus outbreak continues.”
As it stands, more than 100 trials are listed in the ClinicalTrials.gov database as testing a wide range of different treatment approaches for COVID-19. These include trials investigating if sarilumab, hydroxychloroquine, fingolimod, bevacizumab, and losartan might have a role to play. There are also trials looking at the potential of other antiviral agents, such as Gilead’s investigational drug remdesivir, which has shown to have in vitro and in vivo activity against many emerging viral pathogens that cause Ebola, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome, and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
Dr. Cao’s trial was supported by grants from Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development and from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Emergency Project of Covid-19, and a National Science Grant for Distinguished Young Scholars.
All authors had no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Baden is the director of clinical research in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the director of infectious diseases at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. He is a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine and chair of the FDA’s Antimicrobial Drug Advisory Committee. He is involved in HIV vaccine clinical trials and has received research grants from the Ragon Institute, the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the Gates Foundation.
Dr. Rubin is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as editor-in-chief. He is an associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and is chair and Irene Heinz Given Professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
SOURCE: Cao B et al. New Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.
No difference in the primary endpoint of the time to clinical improvement was seen in an open-label trial of the antiretroviral drug lopinavir-ritonavir versus standard of care in adult patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
The median time to clinical improvement – defined as the time from randomization to either an improvement of two points on a seven-category ordinal scale or discharge from the hospital, whichever was first – was 16 days in both groups (hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval 0.95-1.85; P = .09).
Although a numerically lower number of deaths were recorded at 28 days (19.2% vs. 25%) with the antiretroviral treatment versus standard of care, a similar percentage of patients had detectable levels of viral RNA in throat swabs taken at various time points during the study, Chinese researchers reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bai Cao, M.D, from the China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, both in Beijing, and associates, performed a randomized, controlled, trial of 199 adult patients hospitalized at the Jin Yin-Tan Hospital in Wuhan in Hubei Province, China.
For inclusion, patients had to have laboratory confirmed infection with SARS-Cov-2, the virus that causes COVID-19; pneumonia confirmed by chest imaging; and severely reduced oxygen saturation (94% or less while breathing ambient air or a ratio of the partial pressure of oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen of less than 300 mm Hg).
Patients were randomized to receive either a combination of lopinavir (400 mg) and ritonavir (100 mg) twice a day on top of standard care (n = 99) or to standard care alone (n = 100) for 14 days. “Because of the emergency nature of the trial, placebos of lopinavir-ritonavir were not prepared,” Dr. Cao et al. explained, noting that standard care consisted of supplemental oxygen, ventilation, antibiotic treatment, vasopressor support, renal-replacement therapy, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
While the trial did not meet its primary endpoint, Dr. Cao et al. reported that patients in the lopinavir-ritonavir group had a shorter stay in the intensive care unit than did those in the standard-care group, at a median of 6 versus 11 days. They also reported that the duration from randomization to hospital discharge was numerically shorter, at a median of 12 versus 14 days. Furthermore, there was a higher percentage of patients with clinical improvement at day 14 in the lopinavir-ritonavir group than in the standard-care group (45.5% vs. 30.0%)
“The trial was initiated in rapid response to the COVID-19 public health emergency, at which time there was very limited information about clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” the researchers observed. “The question of whether earlier lopinavir-ritonavir treatment in COVID-19 could have clinical benefit is an important one that requires further study,” they wrote.
Among the trial’s limitations are it was not blinded and the researchers do not have data on the lopinavir exposure levels in the trial participants.
“This was a heroic effort” in a “particularly challenging population,” Lindsey R. Baden, MD, and Eric J. Rubin, MD, stated in an editorial accompanying the article (Baden LR and Rubin EJ. New Engl J Med. March 18, 2020. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2005477). “Unfortunately, the trial results were disappointing,” they noted.
“The secondary end points provide both reason for hope and reason for discouragement,” wrote Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin. The lack of effect on viral shedding, however, “strongly [suggests] that it did not have the activity desired” they observed.
Dr. Baden and Dr. Rubin commented that one of the important takeaways from the trial is that “the investigators appropriately prioritized speed, designing a trial that could rapidly produce an answer.” They continued that the investigators had shown that “rapidly initiated, high-quality randomized clinical trials are possible in epidemic conditions” and that results of such trials, whether they are positive or negative, “will be central to clinical care as the dangerous coronavirus outbreak continues.”
As it stands, more than 100 trials are listed in the ClinicalTrials.gov database as testing a wide range of different treatment approaches for COVID-19. These include trials investigating if sarilumab, hydroxychloroquine, fingolimod, bevacizumab, and losartan might have a role to play. There are also trials looking at the potential of other antiviral agents, such as Gilead’s investigational drug remdesivir, which has shown to have in vitro and in vivo activity against many emerging viral pathogens that cause Ebola, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome, and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
Dr. Cao’s trial was supported by grants from Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development and from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Emergency Project of Covid-19, and a National Science Grant for Distinguished Young Scholars.
All authors had no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Dr. Baden is the director of clinical research in the Division of Infectious Diseases at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the director of infectious diseases at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. He is a deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine and chair of the FDA’s Antimicrobial Drug Advisory Committee. He is involved in HIV vaccine clinical trials and has received research grants from the Ragon Institute, the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and the Gates Foundation.
Dr. Rubin is employed by the New England Journal of Medicine as editor-in-chief. He is an associate physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and is chair and Irene Heinz Given Professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
SOURCE: Cao B et al. New Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
AGA and colleague societies issue clinical insights for COVID-19
Amid the growing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, currently in its expansive growth phase in the United States, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA), the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) have jointly released “COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers,” which can be found on the websites of the various societies.
“The purpose of this communication is to jointly provide you with up to date COVID-19 information in order to maintain the highest level of health and safety for our patients, staff, community, and ourselves,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In particular, the societies point out that there is recent evidence suggesting the potential for coronavirus transmission through droplets and perhaps fecal shedding, which pose potential risks in particular during endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures to other patients, endoscopy personnel, and practitioners.
Relevant clinical factors related to COVID-19 are discussed, including the fact that asymptomatic spread can occur during the prodromal phase (the mean incubation period is approximately 5 days, with a range of 0-14 days), with viral shedding greatest when symptoms begin.
Between 20% and 30% of patients with COVID-19 infection show abnormal liver enzymes. In addition, COVID-19 patients show drops in their leukocyte counts, and elevated white blood cell counts is a poor prognostic sign, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists vulnerable populations at the greatest risk for more serious outcomes; these include the elderly and those with severe chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, decompensated cirrhosis, HIV with low CD4 counts, and immunosuppression (including liver and other solid organ transplant recipients), are at higher risk of developing more serious illness. In addition pregnancy may provide added risk.
Specific advice for the gastroenterology profession
The joint statement urges that practitioners strongly consider rescheduling elective nonurgent endoscopic procedures, although some nonurgent procedures are higher priority and may need to be performed, including cancer evaluations, prosthetic removals, and evaluation of significant symptoms. “Of note, the Surgeon General on 3/14/20 advised hospitals to postpone all elective surgeries,” the document states.
Patient concerns
In all cases, patients should be prescreened for high-risk exposure or symptoms. This includes asking about history of fever or respiratory symptoms, family members or close contacts with similar symptoms, any contact with a confirmed case of COVID-19, and recent travel to a high-risk area. “Avoid bringing patients (or their escorts) into the medical facility who are over age 65 or have one of the CDC recognized risks listed above,” the societies advise.
Check body temperature of the patient upon arrival at endoscopy unit or clinic, and keep all patients at an appropriate distance from each other (6 feet is recommended) throughout the entire time in the endoscopy unit.
“For COVID-19 positive patients, or those awaiting test results, isolation precautions should be taken with procedures performed in negative pressure rooms,” according to the statement.
In addition, use telemedicine where possible in elective cases, and consider phone follow-up after any procedures at 7 and 14 days to ask about new diagnosis of COVID-19 or development of its symptoms, .
Those patients who are on immunosuppressive drugs for inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmune hepatitis should continue taking their medications because the risk of disease flare outweighs the chance of contracting coronavirus, according to the document. In addition, these patients should be advised to follow CDC guidelines for at-risk groups by avoiding crowds and limiting travel.
Protection of practitioners
Key factors in ensuring practitioner safety and maintaining practice functionality are discussed by the joint document. In particular, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn by all members of the endoscopy team: gloves, mask, eye shield/goggles, face shields, and gown, but practitioners should also be aware of how to put on and take off PPE appropriately.
“Conservation of PPE is critical. Only essential personnel should be present in cases. Consider extended use or reuse of surgical masks and eye protection in accordance with hospital policies,” the document recommends.
“It is important to address our collective staff needs and institute policies that protect our workforce.” To that end, the document recommends that centers should strategically assign available personnel in order to minimize concomitant exposure of those with similar or unique skill sets. This includes the use of nonphysician practitioners and fellows that cannot participate in cases for screening and triaging patients, or performing virtual visits.
Coming at a time of pandemic, when gastrointestinal symptoms have been recognized as a more common symptom of COVID-19 than previously expected and liver damage has been noted as a potential repercussion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, these clinical insights provide a template for gastroenterologists and related professionals for dealing with their patients and keeping themselves safe under dramatically changed circumstances.
The partnered organizations, AASLD, ACG, AGA, and ASGE, are committed to providing updated COVID-19 information as appropriate. However: “Given the evolving and fluid nature of the situation, institutions, hospitals and clinics have also been formulating their own local guidelines, so we urge you to follow the evolving CDC recommendations and your local requirements,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In addition to the joint communication, the society websites each offer additional COVID-19 information. The AGA practice updates on the COVID-19 webpage provides information about announcements, such as the cancellation of Digestive Disease Week® in May, a location for AGA members to discuss their COVID-19 experiences and share advice, and links to the CDC COVID-19 updates.
SOURCE: American Gastroenterological Association et al. March 2020, COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers.
Amid the growing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, currently in its expansive growth phase in the United States, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA), the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) have jointly released “COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers,” which can be found on the websites of the various societies.
“The purpose of this communication is to jointly provide you with up to date COVID-19 information in order to maintain the highest level of health and safety for our patients, staff, community, and ourselves,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In particular, the societies point out that there is recent evidence suggesting the potential for coronavirus transmission through droplets and perhaps fecal shedding, which pose potential risks in particular during endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures to other patients, endoscopy personnel, and practitioners.
Relevant clinical factors related to COVID-19 are discussed, including the fact that asymptomatic spread can occur during the prodromal phase (the mean incubation period is approximately 5 days, with a range of 0-14 days), with viral shedding greatest when symptoms begin.
Between 20% and 30% of patients with COVID-19 infection show abnormal liver enzymes. In addition, COVID-19 patients show drops in their leukocyte counts, and elevated white blood cell counts is a poor prognostic sign, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists vulnerable populations at the greatest risk for more serious outcomes; these include the elderly and those with severe chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, decompensated cirrhosis, HIV with low CD4 counts, and immunosuppression (including liver and other solid organ transplant recipients), are at higher risk of developing more serious illness. In addition pregnancy may provide added risk.
Specific advice for the gastroenterology profession
The joint statement urges that practitioners strongly consider rescheduling elective nonurgent endoscopic procedures, although some nonurgent procedures are higher priority and may need to be performed, including cancer evaluations, prosthetic removals, and evaluation of significant symptoms. “Of note, the Surgeon General on 3/14/20 advised hospitals to postpone all elective surgeries,” the document states.
Patient concerns
In all cases, patients should be prescreened for high-risk exposure or symptoms. This includes asking about history of fever or respiratory symptoms, family members or close contacts with similar symptoms, any contact with a confirmed case of COVID-19, and recent travel to a high-risk area. “Avoid bringing patients (or their escorts) into the medical facility who are over age 65 or have one of the CDC recognized risks listed above,” the societies advise.
Check body temperature of the patient upon arrival at endoscopy unit or clinic, and keep all patients at an appropriate distance from each other (6 feet is recommended) throughout the entire time in the endoscopy unit.
“For COVID-19 positive patients, or those awaiting test results, isolation precautions should be taken with procedures performed in negative pressure rooms,” according to the statement.
In addition, use telemedicine where possible in elective cases, and consider phone follow-up after any procedures at 7 and 14 days to ask about new diagnosis of COVID-19 or development of its symptoms, .
Those patients who are on immunosuppressive drugs for inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmune hepatitis should continue taking their medications because the risk of disease flare outweighs the chance of contracting coronavirus, according to the document. In addition, these patients should be advised to follow CDC guidelines for at-risk groups by avoiding crowds and limiting travel.
Protection of practitioners
Key factors in ensuring practitioner safety and maintaining practice functionality are discussed by the joint document. In particular, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn by all members of the endoscopy team: gloves, mask, eye shield/goggles, face shields, and gown, but practitioners should also be aware of how to put on and take off PPE appropriately.
“Conservation of PPE is critical. Only essential personnel should be present in cases. Consider extended use or reuse of surgical masks and eye protection in accordance with hospital policies,” the document recommends.
“It is important to address our collective staff needs and institute policies that protect our workforce.” To that end, the document recommends that centers should strategically assign available personnel in order to minimize concomitant exposure of those with similar or unique skill sets. This includes the use of nonphysician practitioners and fellows that cannot participate in cases for screening and triaging patients, or performing virtual visits.
Coming at a time of pandemic, when gastrointestinal symptoms have been recognized as a more common symptom of COVID-19 than previously expected and liver damage has been noted as a potential repercussion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, these clinical insights provide a template for gastroenterologists and related professionals for dealing with their patients and keeping themselves safe under dramatically changed circumstances.
The partnered organizations, AASLD, ACG, AGA, and ASGE, are committed to providing updated COVID-19 information as appropriate. However: “Given the evolving and fluid nature of the situation, institutions, hospitals and clinics have also been formulating their own local guidelines, so we urge you to follow the evolving CDC recommendations and your local requirements,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In addition to the joint communication, the society websites each offer additional COVID-19 information. The AGA practice updates on the COVID-19 webpage provides information about announcements, such as the cancellation of Digestive Disease Week® in May, a location for AGA members to discuss their COVID-19 experiences and share advice, and links to the CDC COVID-19 updates.
SOURCE: American Gastroenterological Association et al. March 2020, COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers.
Amid the growing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, currently in its expansive growth phase in the United States, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA), the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) have jointly released “COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers,” which can be found on the websites of the various societies.
“The purpose of this communication is to jointly provide you with up to date COVID-19 information in order to maintain the highest level of health and safety for our patients, staff, community, and ourselves,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In particular, the societies point out that there is recent evidence suggesting the potential for coronavirus transmission through droplets and perhaps fecal shedding, which pose potential risks in particular during endoscopy and colonoscopy procedures to other patients, endoscopy personnel, and practitioners.
Relevant clinical factors related to COVID-19 are discussed, including the fact that asymptomatic spread can occur during the prodromal phase (the mean incubation period is approximately 5 days, with a range of 0-14 days), with viral shedding greatest when symptoms begin.
Between 20% and 30% of patients with COVID-19 infection show abnormal liver enzymes. In addition, COVID-19 patients show drops in their leukocyte counts, and elevated white blood cell counts is a poor prognostic sign, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists vulnerable populations at the greatest risk for more serious outcomes; these include the elderly and those with severe chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, decompensated cirrhosis, HIV with low CD4 counts, and immunosuppression (including liver and other solid organ transplant recipients), are at higher risk of developing more serious illness. In addition pregnancy may provide added risk.
Specific advice for the gastroenterology profession
The joint statement urges that practitioners strongly consider rescheduling elective nonurgent endoscopic procedures, although some nonurgent procedures are higher priority and may need to be performed, including cancer evaluations, prosthetic removals, and evaluation of significant symptoms. “Of note, the Surgeon General on 3/14/20 advised hospitals to postpone all elective surgeries,” the document states.
Patient concerns
In all cases, patients should be prescreened for high-risk exposure or symptoms. This includes asking about history of fever or respiratory symptoms, family members or close contacts with similar symptoms, any contact with a confirmed case of COVID-19, and recent travel to a high-risk area. “Avoid bringing patients (or their escorts) into the medical facility who are over age 65 or have one of the CDC recognized risks listed above,” the societies advise.
Check body temperature of the patient upon arrival at endoscopy unit or clinic, and keep all patients at an appropriate distance from each other (6 feet is recommended) throughout the entire time in the endoscopy unit.
“For COVID-19 positive patients, or those awaiting test results, isolation precautions should be taken with procedures performed in negative pressure rooms,” according to the statement.
In addition, use telemedicine where possible in elective cases, and consider phone follow-up after any procedures at 7 and 14 days to ask about new diagnosis of COVID-19 or development of its symptoms, .
Those patients who are on immunosuppressive drugs for inflammatory bowel disease and autoimmune hepatitis should continue taking their medications because the risk of disease flare outweighs the chance of contracting coronavirus, according to the document. In addition, these patients should be advised to follow CDC guidelines for at-risk groups by avoiding crowds and limiting travel.
Protection of practitioners
Key factors in ensuring practitioner safety and maintaining practice functionality are discussed by the joint document. In particular, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn by all members of the endoscopy team: gloves, mask, eye shield/goggles, face shields, and gown, but practitioners should also be aware of how to put on and take off PPE appropriately.
“Conservation of PPE is critical. Only essential personnel should be present in cases. Consider extended use or reuse of surgical masks and eye protection in accordance with hospital policies,” the document recommends.
“It is important to address our collective staff needs and institute policies that protect our workforce.” To that end, the document recommends that centers should strategically assign available personnel in order to minimize concomitant exposure of those with similar or unique skill sets. This includes the use of nonphysician practitioners and fellows that cannot participate in cases for screening and triaging patients, or performing virtual visits.
Coming at a time of pandemic, when gastrointestinal symptoms have been recognized as a more common symptom of COVID-19 than previously expected and liver damage has been noted as a potential repercussion of SARS-CoV-2 infection, these clinical insights provide a template for gastroenterologists and related professionals for dealing with their patients and keeping themselves safe under dramatically changed circumstances.
The partnered organizations, AASLD, ACG, AGA, and ASGE, are committed to providing updated COVID-19 information as appropriate. However: “Given the evolving and fluid nature of the situation, institutions, hospitals and clinics have also been formulating their own local guidelines, so we urge you to follow the evolving CDC recommendations and your local requirements,” according to the AGA website announcement.
In addition to the joint communication, the society websites each offer additional COVID-19 information. The AGA practice updates on the COVID-19 webpage provides information about announcements, such as the cancellation of Digestive Disease Week® in May, a location for AGA members to discuss their COVID-19 experiences and share advice, and links to the CDC COVID-19 updates.
SOURCE: American Gastroenterological Association et al. March 2020, COVID-19 Clinical Insights for Our Community of Gastroenterologists and Gastroenterology Care Providers.
Patients with COVID-19 may face risk for liver injury
Patients with COVID-19 may be at risk for liver injury, but mechanisms of damage remain unclear, according to investigators.
Proposed mechanisms include direct virus-induced effects, immune-induced damage due to excessive inflammatory responses, and drug-induced injury, reported lead author Ling Xu of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
“From a clinical perspective, in addition to actively dealing with the primary disease caused by coronavirus infection, attention should also be paid to monitor the occurrence of liver injury, and to the application of drugs which may induce liver damage,” the investigators wrote in Liver International. “Patients with liver damage are advised to be treated with drugs that could both protect liver functions and inhibit inflammatory responses, such as ammonium glycyrrhizinate, which may, in turn, accelerate the process of disease recovery.”
The review of liver injury associated with major pathogenic coronaviruses included severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the newly emergent SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19.
In cases of COVID-19, reported incidence of liver injury ranges from 15% to 53%, based on elevations of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), along with slightly elevated bilirubin levels. In severe cases, albumin decreases have also been documented.
Liver injury appears to be significantly more common among those with severe infection. In one cohort of 82 patients who died from COVID-19, the incidence of liver injury was 78%, while another study of 36 nonsurvivors reported a rate of 58%.
According to the investigators, both bile duct epithelial cells and liver cells express angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2), which is an entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2; however, expression of ACE2 in bile duct cells is “much higher” than in liver cells, and comparable with alveolar type 2 cells in the lungs.
“Bile duct epithelial cells are known to play important roles in liver regeneration and immune response,” the investigators noted.
Beyond direct- and immune-induced effects of COVID-19, postmortem findings suggest that drug-induced liver injury may also be a possibility, with a number of theoretical culprits, including antibiotics, steroids, and antivirals. Although the investigators emphasized that data are insufficient to pinpoint an exact agent, they highlighted a recent preprint study, which reported a significantly higher rate of lopinavir/ritonavir administration among patients with abnormal liver function, compared with those who had normal liver function (56.1% vs. 25%; P = .009).
“Drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of coronavirus infection should not be ignored and needs to be carefully investigated,” the investigators concluded.
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities supported the work. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Xu L et al. Liver Int. 2020 Mar 14. doi: 10.1111/liv.14435.
Patients with COVID-19 may be at risk for liver injury, but mechanisms of damage remain unclear, according to investigators.
Proposed mechanisms include direct virus-induced effects, immune-induced damage due to excessive inflammatory responses, and drug-induced injury, reported lead author Ling Xu of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
“From a clinical perspective, in addition to actively dealing with the primary disease caused by coronavirus infection, attention should also be paid to monitor the occurrence of liver injury, and to the application of drugs which may induce liver damage,” the investigators wrote in Liver International. “Patients with liver damage are advised to be treated with drugs that could both protect liver functions and inhibit inflammatory responses, such as ammonium glycyrrhizinate, which may, in turn, accelerate the process of disease recovery.”
The review of liver injury associated with major pathogenic coronaviruses included severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the newly emergent SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19.
In cases of COVID-19, reported incidence of liver injury ranges from 15% to 53%, based on elevations of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), along with slightly elevated bilirubin levels. In severe cases, albumin decreases have also been documented.
Liver injury appears to be significantly more common among those with severe infection. In one cohort of 82 patients who died from COVID-19, the incidence of liver injury was 78%, while another study of 36 nonsurvivors reported a rate of 58%.
According to the investigators, both bile duct epithelial cells and liver cells express angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2), which is an entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2; however, expression of ACE2 in bile duct cells is “much higher” than in liver cells, and comparable with alveolar type 2 cells in the lungs.
“Bile duct epithelial cells are known to play important roles in liver regeneration and immune response,” the investigators noted.
Beyond direct- and immune-induced effects of COVID-19, postmortem findings suggest that drug-induced liver injury may also be a possibility, with a number of theoretical culprits, including antibiotics, steroids, and antivirals. Although the investigators emphasized that data are insufficient to pinpoint an exact agent, they highlighted a recent preprint study, which reported a significantly higher rate of lopinavir/ritonavir administration among patients with abnormal liver function, compared with those who had normal liver function (56.1% vs. 25%; P = .009).
“Drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of coronavirus infection should not be ignored and needs to be carefully investigated,” the investigators concluded.
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities supported the work. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Xu L et al. Liver Int. 2020 Mar 14. doi: 10.1111/liv.14435.
Patients with COVID-19 may be at risk for liver injury, but mechanisms of damage remain unclear, according to investigators.
Proposed mechanisms include direct virus-induced effects, immune-induced damage due to excessive inflammatory responses, and drug-induced injury, reported lead author Ling Xu of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, and colleagues.
“From a clinical perspective, in addition to actively dealing with the primary disease caused by coronavirus infection, attention should also be paid to monitor the occurrence of liver injury, and to the application of drugs which may induce liver damage,” the investigators wrote in Liver International. “Patients with liver damage are advised to be treated with drugs that could both protect liver functions and inhibit inflammatory responses, such as ammonium glycyrrhizinate, which may, in turn, accelerate the process of disease recovery.”
The review of liver injury associated with major pathogenic coronaviruses included severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and the newly emergent SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19.
In cases of COVID-19, reported incidence of liver injury ranges from 15% to 53%, based on elevations of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), along with slightly elevated bilirubin levels. In severe cases, albumin decreases have also been documented.
Liver injury appears to be significantly more common among those with severe infection. In one cohort of 82 patients who died from COVID-19, the incidence of liver injury was 78%, while another study of 36 nonsurvivors reported a rate of 58%.
According to the investigators, both bile duct epithelial cells and liver cells express angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2), which is an entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2; however, expression of ACE2 in bile duct cells is “much higher” than in liver cells, and comparable with alveolar type 2 cells in the lungs.
“Bile duct epithelial cells are known to play important roles in liver regeneration and immune response,” the investigators noted.
Beyond direct- and immune-induced effects of COVID-19, postmortem findings suggest that drug-induced liver injury may also be a possibility, with a number of theoretical culprits, including antibiotics, steroids, and antivirals. Although the investigators emphasized that data are insufficient to pinpoint an exact agent, they highlighted a recent preprint study, which reported a significantly higher rate of lopinavir/ritonavir administration among patients with abnormal liver function, compared with those who had normal liver function (56.1% vs. 25%; P = .009).
“Drug-induced liver injury during the treatment of coronavirus infection should not be ignored and needs to be carefully investigated,” the investigators concluded.
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities supported the work. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Xu L et al. Liver Int. 2020 Mar 14. doi: 10.1111/liv.14435.
FROM LIVER INTERNATIONAL