User login
Five rules for evaluating melanonychia
WAIKOLOA, HAWAII – Many dermatologists find melanonychia to be intimidating. The clinical features are ambiguous, and the prospect of doing a painful nail apparatus biopsy can be daunting for the inexperienced. As a result, the biopsy gets delayed and melanoma of the nail is often initially a missed diagnosis, not uncommonly for years, with devastating consequences.
Here are five at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Rule #1: Always look beyond the nail
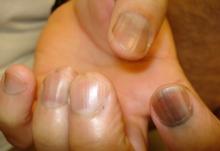
When a light-skinned person presents with more than one nail with pigmentation, the likelihood that one of them is melanoma is much less than if there is only one nail with melanonychia, according to Dr. Jellinek, a dermatologist in private practice in East Greenwich, R.I.
Also, be sure to look at the skin and mucosa. Consider the medications the patients may be taking: For example, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) is notorious for causing nail changes as a side effect. A past medical history of lichen planus, carpal tunnel syndrome, Addison disease, or other conditions may explain the melanonychia.
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is a condition worth getting to know. It’s an acquired disorder characterized longitudinal melanonychia and other pigmentary changes, which may include diffuse hyperpigmentation of the orolabial mucosa, ocular pigment, and/or pigmented palmoplantar lesions. It’s said to be rare, but Dr. Jellinek disagrees.
“Learn this one if you don’t know it. I see a case about every 2 weeks. It’s not heritable and not associated with any other medical condition,” he said.
Rule #2: Your dermatoscope is great for nails
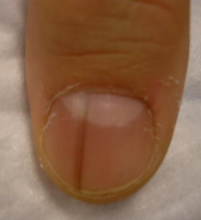
What Dr. Jellinek considers to be among the all-time best papers on the value of dermoscopy for nail pigmentation was authored by French investigators. They analyzed 148 consecutive cases of longitudinal melanonychia and concluded that the dermoscopic combination of a brown background coupled with irregular longitudinal lines in terms of color, spacing, diameter, and/or lack of parallelism strongly suggests melanoma. A micro-Hutchinson’s sign, while a rare finding, occurred only in melanoma, where it represented periungual spread of a radial growth phase malignancy (Arch Dermatol. 2002 Oct;138[10]:1327-33).
“I think nail dermoscopy is most helpful for subungual hemorrhage. I average one referral per week for hemorrhage under the nail. On dermoscopy it’s as if someone took paint and threw it at the nail. Purple to brown blood spots, with no background color. This should be a doorway diagnosis of hemorrhage,” Dr. Jellinek said.
Rule #3: Know when you don’t know
“This is really the key for me,” the dermatologist commented. “There are automatic cases for biopsy, and more commonly routine cases for reassurance. But the gray zone, when you know you don’t know, is the key decision making moment.”
When something just doesn’t feel right, there’s absolutely nothing wrong with getting a second opinion, he stressed.
“It’s worthwhile getting to know people whose opinions you trust. There’s a saying I like to teach our fellows: ‘Never worry alone.’ So if you’re worried about someone, listen to that inner voice. There’s no shame in getting a second opinion. It’s great! Patients are never upset, either. They feel really well taken care of,” he said.
Rule #4: Don’t wimp out when a biopsy is warranted
Many dermatologists hem and haw about doing a biopsy for a concerning lesion on the nail, when they wouldn’t hesitate to biopsy a similarly suspicious lesion on the face.
But it’s essential to biopsy the right area, he added. For longitudinal melanonychia, that’s the matrix. The nail plate is the wrong place; a biopsy obtained there will result in an inappropriate benign diagnosis.
“The starter set is to do a punch biopsy. This is your gateway drug to the world of nail surgery. Lots of dermatologists are intimidated by nail surgery, but if you can do any minor surgery, you can do a punch of the matrix. All it takes is a little practice. And if all you can do is punch biopsies, you’re good for your career. If you can do that, you’re golden. There are people who’ve just done punch biopsies for their whole career and they don’t miss melanomas,” he said.
Step one is to undermine the proximal nail fold using a pediatric elevator, which costs only about $30. “If you’re going to do a lot of nail surgery, they’re really helpful,” he said.
There’s no need at all to evulse the nail. Just make oblique incisions in the proximal nail fold in order to reflect it and look at the matrix. A 3-mm punch is standard, directed right over the origin of the pigment. Resist the temptation to force or squeeze the specimen in order to extract it. Instead, use really fine-tipped scissors to nibble at the base of the specimen, then gently pull it out, making an effort to keep the nail plate attached to the digit and avoid getting it stuck up in the punch.
Rule #5: Have dermatopathologists extensively experienced with nail pathology on your Rolodex
The histopathologic findings present in early subungual melanoma in situ are often too subtle for general dermatopathologists to appreciate, in Dr. Jellinek’s experience. He cited other investigators’ study of 18 cases of subungual melanoma in situ, all marked by longitudinal melanonychia. Only half showed the classic giveaway on the original nail matrix biopsy, consisting of a significantly increased number of atypical melanocytes with marked nuclear atypia. Blatant pagetoid spread was infrequent. However, all 18 cases displayed a novel, more subtle, and previously undescribed finding: haphazard and uneven distribution of atypical solitary melanocytes with variably sized and shaped hyperchromatic nuclei (J Cutan Pathol. 2016 Jan;43[1]:41-52).
Dr. Jellinek reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation. SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
WAIKOLOA, HAWAII – Many dermatologists find melanonychia to be intimidating. The clinical features are ambiguous, and the prospect of doing a painful nail apparatus biopsy can be daunting for the inexperienced. As a result, the biopsy gets delayed and melanoma of the nail is often initially a missed diagnosis, not uncommonly for years, with devastating consequences.
Here are five at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Rule #1: Always look beyond the nail
When a light-skinned person presents with more than one nail with pigmentation, the likelihood that one of them is melanoma is much less than if there is only one nail with melanonychia, according to Dr. Jellinek, a dermatologist in private practice in East Greenwich, R.I.
Also, be sure to look at the skin and mucosa. Consider the medications the patients may be taking: For example, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) is notorious for causing nail changes as a side effect. A past medical history of lichen planus, carpal tunnel syndrome, Addison disease, or other conditions may explain the melanonychia.
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is a condition worth getting to know. It’s an acquired disorder characterized longitudinal melanonychia and other pigmentary changes, which may include diffuse hyperpigmentation of the orolabial mucosa, ocular pigment, and/or pigmented palmoplantar lesions. It’s said to be rare, but Dr. Jellinek disagrees.
“Learn this one if you don’t know it. I see a case about every 2 weeks. It’s not heritable and not associated with any other medical condition,” he said.
Rule #2: Your dermatoscope is great for nails
What Dr. Jellinek considers to be among the all-time best papers on the value of dermoscopy for nail pigmentation was authored by French investigators. They analyzed 148 consecutive cases of longitudinal melanonychia and concluded that the dermoscopic combination of a brown background coupled with irregular longitudinal lines in terms of color, spacing, diameter, and/or lack of parallelism strongly suggests melanoma. A micro-Hutchinson’s sign, while a rare finding, occurred only in melanoma, where it represented periungual spread of a radial growth phase malignancy (Arch Dermatol. 2002 Oct;138[10]:1327-33).
“I think nail dermoscopy is most helpful for subungual hemorrhage. I average one referral per week for hemorrhage under the nail. On dermoscopy it’s as if someone took paint and threw it at the nail. Purple to brown blood spots, with no background color. This should be a doorway diagnosis of hemorrhage,” Dr. Jellinek said.
Rule #3: Know when you don’t know
“This is really the key for me,” the dermatologist commented. “There are automatic cases for biopsy, and more commonly routine cases for reassurance. But the gray zone, when you know you don’t know, is the key decision making moment.”
When something just doesn’t feel right, there’s absolutely nothing wrong with getting a second opinion, he stressed.
“It’s worthwhile getting to know people whose opinions you trust. There’s a saying I like to teach our fellows: ‘Never worry alone.’ So if you’re worried about someone, listen to that inner voice. There’s no shame in getting a second opinion. It’s great! Patients are never upset, either. They feel really well taken care of,” he said.
Rule #4: Don’t wimp out when a biopsy is warranted
Many dermatologists hem and haw about doing a biopsy for a concerning lesion on the nail, when they wouldn’t hesitate to biopsy a similarly suspicious lesion on the face.
But it’s essential to biopsy the right area, he added. For longitudinal melanonychia, that’s the matrix. The nail plate is the wrong place; a biopsy obtained there will result in an inappropriate benign diagnosis.
“The starter set is to do a punch biopsy. This is your gateway drug to the world of nail surgery. Lots of dermatologists are intimidated by nail surgery, but if you can do any minor surgery, you can do a punch of the matrix. All it takes is a little practice. And if all you can do is punch biopsies, you’re good for your career. If you can do that, you’re golden. There are people who’ve just done punch biopsies for their whole career and they don’t miss melanomas,” he said.
Step one is to undermine the proximal nail fold using a pediatric elevator, which costs only about $30. “If you’re going to do a lot of nail surgery, they’re really helpful,” he said.
There’s no need at all to evulse the nail. Just make oblique incisions in the proximal nail fold in order to reflect it and look at the matrix. A 3-mm punch is standard, directed right over the origin of the pigment. Resist the temptation to force or squeeze the specimen in order to extract it. Instead, use really fine-tipped scissors to nibble at the base of the specimen, then gently pull it out, making an effort to keep the nail plate attached to the digit and avoid getting it stuck up in the punch.
Rule #5: Have dermatopathologists extensively experienced with nail pathology on your Rolodex
The histopathologic findings present in early subungual melanoma in situ are often too subtle for general dermatopathologists to appreciate, in Dr. Jellinek’s experience. He cited other investigators’ study of 18 cases of subungual melanoma in situ, all marked by longitudinal melanonychia. Only half showed the classic giveaway on the original nail matrix biopsy, consisting of a significantly increased number of atypical melanocytes with marked nuclear atypia. Blatant pagetoid spread was infrequent. However, all 18 cases displayed a novel, more subtle, and previously undescribed finding: haphazard and uneven distribution of atypical solitary melanocytes with variably sized and shaped hyperchromatic nuclei (J Cutan Pathol. 2016 Jan;43[1]:41-52).
Dr. Jellinek reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation. SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
WAIKOLOA, HAWAII – Many dermatologists find melanonychia to be intimidating. The clinical features are ambiguous, and the prospect of doing a painful nail apparatus biopsy can be daunting for the inexperienced. As a result, the biopsy gets delayed and melanoma of the nail is often initially a missed diagnosis, not uncommonly for years, with devastating consequences.
Here are five at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
Rule #1: Always look beyond the nail
When a light-skinned person presents with more than one nail with pigmentation, the likelihood that one of them is melanoma is much less than if there is only one nail with melanonychia, according to Dr. Jellinek, a dermatologist in private practice in East Greenwich, R.I.
Also, be sure to look at the skin and mucosa. Consider the medications the patients may be taking: For example, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) is notorious for causing nail changes as a side effect. A past medical history of lichen planus, carpal tunnel syndrome, Addison disease, or other conditions may explain the melanonychia.
Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is a condition worth getting to know. It’s an acquired disorder characterized longitudinal melanonychia and other pigmentary changes, which may include diffuse hyperpigmentation of the orolabial mucosa, ocular pigment, and/or pigmented palmoplantar lesions. It’s said to be rare, but Dr. Jellinek disagrees.
“Learn this one if you don’t know it. I see a case about every 2 weeks. It’s not heritable and not associated with any other medical condition,” he said.
Rule #2: Your dermatoscope is great for nails
What Dr. Jellinek considers to be among the all-time best papers on the value of dermoscopy for nail pigmentation was authored by French investigators. They analyzed 148 consecutive cases of longitudinal melanonychia and concluded that the dermoscopic combination of a brown background coupled with irregular longitudinal lines in terms of color, spacing, diameter, and/or lack of parallelism strongly suggests melanoma. A micro-Hutchinson’s sign, while a rare finding, occurred only in melanoma, where it represented periungual spread of a radial growth phase malignancy (Arch Dermatol. 2002 Oct;138[10]:1327-33).
“I think nail dermoscopy is most helpful for subungual hemorrhage. I average one referral per week for hemorrhage under the nail. On dermoscopy it’s as if someone took paint and threw it at the nail. Purple to brown blood spots, with no background color. This should be a doorway diagnosis of hemorrhage,” Dr. Jellinek said.
Rule #3: Know when you don’t know
“This is really the key for me,” the dermatologist commented. “There are automatic cases for biopsy, and more commonly routine cases for reassurance. But the gray zone, when you know you don’t know, is the key decision making moment.”
When something just doesn’t feel right, there’s absolutely nothing wrong with getting a second opinion, he stressed.
“It’s worthwhile getting to know people whose opinions you trust. There’s a saying I like to teach our fellows: ‘Never worry alone.’ So if you’re worried about someone, listen to that inner voice. There’s no shame in getting a second opinion. It’s great! Patients are never upset, either. They feel really well taken care of,” he said.
Rule #4: Don’t wimp out when a biopsy is warranted
Many dermatologists hem and haw about doing a biopsy for a concerning lesion on the nail, when they wouldn’t hesitate to biopsy a similarly suspicious lesion on the face.
But it’s essential to biopsy the right area, he added. For longitudinal melanonychia, that’s the matrix. The nail plate is the wrong place; a biopsy obtained there will result in an inappropriate benign diagnosis.
“The starter set is to do a punch biopsy. This is your gateway drug to the world of nail surgery. Lots of dermatologists are intimidated by nail surgery, but if you can do any minor surgery, you can do a punch of the matrix. All it takes is a little practice. And if all you can do is punch biopsies, you’re good for your career. If you can do that, you’re golden. There are people who’ve just done punch biopsies for their whole career and they don’t miss melanomas,” he said.
Step one is to undermine the proximal nail fold using a pediatric elevator, which costs only about $30. “If you’re going to do a lot of nail surgery, they’re really helpful,” he said.
There’s no need at all to evulse the nail. Just make oblique incisions in the proximal nail fold in order to reflect it and look at the matrix. A 3-mm punch is standard, directed right over the origin of the pigment. Resist the temptation to force or squeeze the specimen in order to extract it. Instead, use really fine-tipped scissors to nibble at the base of the specimen, then gently pull it out, making an effort to keep the nail plate attached to the digit and avoid getting it stuck up in the punch.
Rule #5: Have dermatopathologists extensively experienced with nail pathology on your Rolodex
The histopathologic findings present in early subungual melanoma in situ are often too subtle for general dermatopathologists to appreciate, in Dr. Jellinek’s experience. He cited other investigators’ study of 18 cases of subungual melanoma in situ, all marked by longitudinal melanonychia. Only half showed the classic giveaway on the original nail matrix biopsy, consisting of a significantly increased number of atypical melanocytes with marked nuclear atypia. Blatant pagetoid spread was infrequent. However, all 18 cases displayed a novel, more subtle, and previously undescribed finding: haphazard and uneven distribution of atypical solitary melanocytes with variably sized and shaped hyperchromatic nuclei (J Cutan Pathol. 2016 Jan;43[1]:41-52).
Dr. Jellinek reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation. SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur Syndrome
To the Editor:
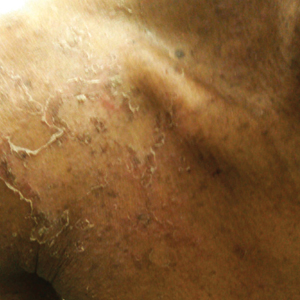
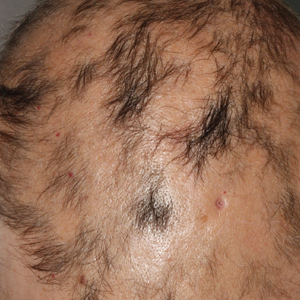
A 56-year-old white woman with a history of melanoma and hypertension presented for evaluation of progressive hair loss of more than 1 year’s duration with associated pruritis. Scalp examination revealed diffuse erythema and scarring alopecia of the bilateral parietal and temporal regions. Physical examination also revealed nonscarring alopecia of the bilateral axillae, with associated thinning of the pubic hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes, as well as keratosis pilaris on the upper arms. Biopsy of the parietal scalp revealed mild scarring alopecia with isthmic fibroplasia consistent with early lichen planopilaris (LPP)(Figure). These histologic features combined with the patient’s clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome (GLPL).
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome was first described by Piccardi in 1913.A second case was then described by Graham-Little in 1915 in a patient referred by Lassueur, resulting in the name it bears today.1,2 The condition presents most commonly in middle-aged white women and is characterized by a triad of cicatricial alopecia of the scalp, nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and/or groin, and a rough follicular eruption on the body and/or scalp. Symptoms may not be present simultaneously. In GLPL, scarring alopecia of the scalp often precedes follicular eruptions of the trunk, arms, and legs by as much as years,2 and the inverse also has been reported.1 The inflammatory lesions of the scalp eventually resolve spontaneously, but the hair loss is by definition irreversible.
This rare condition is considered one of the 3 clinical variants of LPP. Other variants include classic LPP, also known as follicular lichen planus, and frontal fibrosing alopecia.3 More recently, fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution has gained some popularity as a fourth variant of LPP.4 All variants of LPP, including GLPL, result in a scarring alopecia. The classic scalp finding is an erythematous to violaceous, perifollicular, hyperkeratotic scale at the base of the terminal hairs. The population of inflamed follicles spreads outward, leaving behind a round to oval, central, atrophic scar that often is devoid of follicles. Few hairs may persist within zones of alopecia at presentation; however, these hairs are affected by inflammation and also will likely shed. A hair pull test will be positive at the margins during active disease, consisting of mostly anagen hairs on trichogram examination.1,5 Patients may develop only a single foci of hair loss, but much more commonly, a patchy multifocal alopecia is noted.6 Sites often will coalesce. Onset of scalp alopecia may be insidious or fulminant.
The nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and groin may be described as subtle thinning to complete hair loss with no signs of atrophy or inflammation. Although not commonly reported, a case of nonscarring alopecia located on the shoulders has been seen.7
The follicular eruption that can be present on the trunk, arms, or legs in GLPL is most often but not limited to keratosis pilaris, as was seen in our patient. One reported case also described lichen spinulosus as a potential variant.8 Lichen planopilaris is separate from lichen planus (LP) because of its selective follicular involvement vs the nonselective mucocutaneous distribution of LP. The 2 processes also are histologically distinct; however, estimations have shown that more than 50% of patients with GLPL experience at least 1 episode of mucosal or cutaneous LP in their lifetime.9 Rarely, coexistence of GLPL and LP lesions has been described. One reported case of GLPL and concomitant hypertrophic LP could represent a severe form of the disease.9 Additionally, lichen planus pigmentosus, an uncommon variant of LP characterized by hyperpigmented brown macules in sun-exposed areas and flexural folds, was identified in a case report of an Asian woman with GLPL.10
As a general rule, the variants of LPP most commonly are seen in postmenopausal women aged 40 to 60 years; however, rare cases in a child and a teenager have been reported.11 The GLPL variant of LPP is reported up to 4 times more frequently in females.5 Pruritus and pain are inconsistent findings, and there are no systemic signs of illness. A case of androgen insensitivity syndrome associated with GLPL suggested a potential influence of hormones in LPP.12 Stress, vitamin A deficiency, and autoimmunity also have been proposed as triggers of GLPL.13 Furthermore, familial GLPL was described in a mother and daughter, though the association was uncertain.14 Our patient had no relevant family history.
Workups to reveal the etiology of GLPL have been inconclusive. Reports of laboratory testing including complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone levels, and chest radiograph have been normal.2 Additional workup for viral triggers also has been negative.15 A case series of 29 patients with LPP and its variants, including GLPL, revealed positive antinuclear antibodies in 10% of patients and a thyroid disorder in 24% of patients, with Hashimoto thyroiditis being the most prevalent in 7% of cases.16 There may be a strong association between the comorbidities of thyroid dysfunction and GLPL, as documented in other studies.10,17 A case-control study by Mesinkovska et al17 revealed a considerable increase in the prevalence of thyroid gland disease among patients with LPP vs controls. Human leukocyte antigen DR1 was found in a familial case of GLPL,4 and a case of GLPL following hepatitis B vaccination also has been described.18
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome most likely is a T-cell mediated autoimmune condition associated with one or multiple unknown keratinocyte antigens. Autoantibodies to the inner centromere protein were identified in a case that was positive on direct immunofluorescence, which may provide more insight into the disease pathophysiology.13 Interestingly, a study comparing the concentrations of inflammatory cells in LPP and traction alopecia found an elevation in the ratio of Langerhans cells to T lymphocytes within the follicular inflammatory infiltrate of LPP.19
Histologically, cicatricial alopecia of the scalp is characterized by an interface dermatitis and a lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate of the isthmus and infundibulum of the hair follicle sparing the bulb (Figure). A follicular plug is present in the active border. The increased pressure from the keratinous plug from above and the pressure from the infiltrate from the sides has been proposed to decrease the blood supply to the follicle and result in its death.2 Late-stage disease is notable for fibrotic longitudinal tracks of the hair follicle, perifollicular lamellar fibrosis, and adjacent epidermal atrophy.20 Direct immunofluorescence in GLPL generally is negative. A trichogram performed in a 29-year-old woman with GLPL was normal, with 84% anagen, 2% catagen, and 14% telogen hairs. It was noted that 10% of the sampled hairs were classified as dystrophical dysplastic hairs.12 Despite the lack of fibrosis on physical examination in patients with GLPL, nonscarring alopecia of the axilla and groin may show follicular destruction on microscopic examination.1 The pathology of the papules present on the trunk and extremities—whether that of keratosis pilaris or lichen spinulosus—demonstrates similar hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and follicular plugging with a possible superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate.

The differential diagnosis of GLPL includes other variants of LPP as well as discoid lupus erythematous (DLE), pseudopelade of Brocq, pityriasis rubra pilaris, sarcoidosis, acne keloidalis, central centrifugal scarring alopecia, follicular mucinosis, and folliculitis decalvans.14 Differentiation of LPP from DLE is difficult. Clinical clues include lack of central erythema and telangiectases within the lesions. Histologically, the lymphocytic dermatitis and folliculitis can be indistinguishable, but subtle findings suggesting DLE may be present, such as increased mucin in the reticular dermis, a focally thinned epidermis, and less severe dermal sclerosis when compared to cases of LPP.2 Direct immunofluorescence with IgG and C3 revealing linear granular deposits at the dermoepidermal junction is characteristic of DLE.20 Pseudopelade of Brocq is best thought of as an end-stage clinical pattern of hair loss in LPP rather than a separate condition. It is considered to be the end point of GLPL as well as DLE and others when the inflammation has subsided and the cicatricial alopecia is stable. For the duration of active disease, GLPL is classified as an unstable cicatricial alopecia that has a tendency to progress and recur periodically.20 Folliculitis decalvans also can mimic GLPL during a period when the pustules have resolved; however, a neutrophilic infiltrate will be present.
The goal of treatment in GLPL as well as other scarring alopecias is to stop the progression of hair loss. Early diagnosis is imperative if control is to be gained before considerable hair loss has occurred. Once follicular destruction has occurred as a result of the inflammation, there is minimal potential for hair rejuvenation.21 To date, treatment has been mostly fruitless, except in the management of keratosis pilaris that accompanies GLPL. First-line therapy often includes topical corticosteroids with or without intralesional corticosteroids. Systemic corticosteroids, retinoids, and psoralen plus UVA therapy also are frequently employed.1,2 Success in treating GLPL with cyclosporine A at a dosage of 4 mg/kg daily was described in several studies.1,2,15 Treatment resulted in reduction of perifollicular erythema and follicular hyperkeratotic papules as well as mild hair regrowth within the scarring patches.15 Nonetheless, cyclosporine A may prove useful in the initial inflammatory phase of GLPL. Consequently, cyclosporine A also is associated with a high relapse rate.1,2
Because the number of patients with GLPL is so few, therapy should mirror advances being made in treatments for other variants of LPP. More recent studies of LPP treatment with hydroxychloroquine showed opposing results, though the safety profile of this agent makes it an enticing treatment option.22,23 Tetracyclines showed improvement in 4 of 15 (26.7%) patients in a retrospective study by Spencer et al.24 Another retrospective study showed promising results with the potent 5-alpha reductase inhibitor dutasteride with 7 of 10 (70%) postmenopausal patients reporting stabilization over a mean duration of 28 months with no reported side effects.25 Antimalarial medications also have been implemented as adjunct therapies with mixed results.5 A case of a 26-year-old man with GLPL from South India showed systemic disease improvement following treatment with pulsed systemic steroids, isotretinoin, and anxiolytics.7 Chloroquine phosphate at a daily dose of 150 mg for 3 to 9 months yielded a transient response in one postmenopausal patient with frontal fibrosing alopecia.6 Stabilization of hair loss was achieved with a combination of hydroxychloroquine and doxycycline in a woman with GLPL who was previously unresponsive to tacrolimus ointment.10 Thalidomide showed early promise in an isolated report claiming successful treatment of LPP,26 but there is contradictory evidence, as thalidomide showed no benefit in a series of 4 patients with LPP.27
Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), a transcription factor that regulates genes, is downregulated in LPP.28 Deletion of PPAR-γ within follicular stem cells in mice results in a phenotype similar to cicatricial alopecia. Data have supported the role of PPAR-γ in maintaining the pilosebaceous unit. A case report of pioglitazone (PPAR-γ agonist) therapy used at 15 mg daily for 8 months was successful in treating a patient with LPP.28 Further investigation must be conducted to evaluate these treatments since early attenuation of the disease process is crucial to the reduction of permanent hair loss.
Advances in the early recognition and successful treatment of GLPL are dependent on continued research in all variants of LPP. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to establish standard of care. Further studies should target the association of GLPL and other autoimmune phenomena. Moreover, research into the etiology will provide direction in understanding disease progression and outcome.
- Zegarska B, Kallas D, Schwartz RA, et al. Graham-Little syndrome. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2010;19:39-42.
- Assouly P, Reygagne P. Lichen planopilaris: update on diagnosis and treatment. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:3-10.
- Olsen EA, Bergfield WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)–sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110.
- Zinkernagel MS, Trueb RM. Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution: patterned lichen planopilaris or androgenetic alopecia with a lichenoid tissue reaction pattern? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:205-211.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Company; 2016.
- Kossard S, Lee MS, Wilkinson B. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: a frontal variant of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:59-66.
- Pai VV, Kikkeri NN, Sori T, et al. Graham-Little Piccardi Lassueur syndrome: an unusual variant of follicular lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;3:28-30.
- Srivastava M, Mikkilineni R, Konstadt J. Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:12.
- Brar BK, Khanna E, Mahajan BB. Graham Little Piccardi Lasseur syndrome: a rare case report with concomitant hypertrophic lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;5:199-200.
- Vashi N, Newlove T, Chu J, et al. Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:30.
- Chieregato C, Zini A, Barba A, et al. Lichen planopilaris: report of 30 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:342-345.
- Vega Gutierrez J, Miranda-Romera A, Perez Milan F, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:463-466.
- Rodríguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Viglizzo G, Verrini A, Rongioletti F. Familial Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatology. 2004;208:142-144.
- Bianchi L, Paro Vidolin A, Piemonte P, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome: effective treatment with cyclosporin A. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26:518-520.
- Cevasco NC, Bergfeld WF, Remzi BK, et al. A case-series of 29 patients with lichen planopilaris: the Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience on evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:47-53.
- Mesinkovska NA, Brankov N, Piliang M, et al. Association of lichen planopilaris with thyroid disease: a retrospective case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:889-892.
- Bardazzi F, Landi C, Orlandi C, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lasseur syndrome following HBV vaccination. Acta Derm Venereol. 1999;79:93.
- Hutchens KA, Balfour EM, Smoller BR. Comparison between Langerhans cell concentration in lichen planopilaris and traction alopecia with possible immunologic implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:277-280.
- Dogra S, Sarangal R. What’s new in cicatricial alopecia? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:576-590.
- Daoud MS, Pittelkow MR. Lichen planus. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz Si, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 7th ed. New York, NY: Mc Graw Hill; 2008:463-477.
- Donati A, Assouly P, Matard B, et al. Clinical and photographic assessment of lichen planopilaris treatment efficacy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:597-599.
- Samrao A, Chew AL, Price V. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a clinical review of 36 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1296-1300.
- Spencer LA, Hawryluk EB, English JC. Lichen planopilaris: retrospective study and stepwise therapeutic approach. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:333-334.
- Ladizinski B, Bazakas A, Selim MA, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a retrospective review of 19 patients seen at Duke University. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:749-755
- George SJ, Hsu SJ. Lichen planopilaris treated with thalidomide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:965-966.
- Jouanique C, Reygagne P, Bachelez H, et al. Thalidomide is ineffective in the treatment of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:480-481.
- Mirmirani P, Karnik P. Lichen planopilaris treated with a peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ agonist. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1363-1366.
To the Editor:
A 56-year-old white woman with a history of melanoma and hypertension presented for evaluation of progressive hair loss of more than 1 year’s duration with associated pruritis. Scalp examination revealed diffuse erythema and scarring alopecia of the bilateral parietal and temporal regions. Physical examination also revealed nonscarring alopecia of the bilateral axillae, with associated thinning of the pubic hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes, as well as keratosis pilaris on the upper arms. Biopsy of the parietal scalp revealed mild scarring alopecia with isthmic fibroplasia consistent with early lichen planopilaris (LPP)(Figure). These histologic features combined with the patient’s clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome (GLPL).
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome was first described by Piccardi in 1913.A second case was then described by Graham-Little in 1915 in a patient referred by Lassueur, resulting in the name it bears today.1,2 The condition presents most commonly in middle-aged white women and is characterized by a triad of cicatricial alopecia of the scalp, nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and/or groin, and a rough follicular eruption on the body and/or scalp. Symptoms may not be present simultaneously. In GLPL, scarring alopecia of the scalp often precedes follicular eruptions of the trunk, arms, and legs by as much as years,2 and the inverse also has been reported.1 The inflammatory lesions of the scalp eventually resolve spontaneously, but the hair loss is by definition irreversible.
This rare condition is considered one of the 3 clinical variants of LPP. Other variants include classic LPP, also known as follicular lichen planus, and frontal fibrosing alopecia.3 More recently, fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution has gained some popularity as a fourth variant of LPP.4 All variants of LPP, including GLPL, result in a scarring alopecia. The classic scalp finding is an erythematous to violaceous, perifollicular, hyperkeratotic scale at the base of the terminal hairs. The population of inflamed follicles spreads outward, leaving behind a round to oval, central, atrophic scar that often is devoid of follicles. Few hairs may persist within zones of alopecia at presentation; however, these hairs are affected by inflammation and also will likely shed. A hair pull test will be positive at the margins during active disease, consisting of mostly anagen hairs on trichogram examination.1,5 Patients may develop only a single foci of hair loss, but much more commonly, a patchy multifocal alopecia is noted.6 Sites often will coalesce. Onset of scalp alopecia may be insidious or fulminant.
The nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and groin may be described as subtle thinning to complete hair loss with no signs of atrophy or inflammation. Although not commonly reported, a case of nonscarring alopecia located on the shoulders has been seen.7
The follicular eruption that can be present on the trunk, arms, or legs in GLPL is most often but not limited to keratosis pilaris, as was seen in our patient. One reported case also described lichen spinulosus as a potential variant.8 Lichen planopilaris is separate from lichen planus (LP) because of its selective follicular involvement vs the nonselective mucocutaneous distribution of LP. The 2 processes also are histologically distinct; however, estimations have shown that more than 50% of patients with GLPL experience at least 1 episode of mucosal or cutaneous LP in their lifetime.9 Rarely, coexistence of GLPL and LP lesions has been described. One reported case of GLPL and concomitant hypertrophic LP could represent a severe form of the disease.9 Additionally, lichen planus pigmentosus, an uncommon variant of LP characterized by hyperpigmented brown macules in sun-exposed areas and flexural folds, was identified in a case report of an Asian woman with GLPL.10
As a general rule, the variants of LPP most commonly are seen in postmenopausal women aged 40 to 60 years; however, rare cases in a child and a teenager have been reported.11 The GLPL variant of LPP is reported up to 4 times more frequently in females.5 Pruritus and pain are inconsistent findings, and there are no systemic signs of illness. A case of androgen insensitivity syndrome associated with GLPL suggested a potential influence of hormones in LPP.12 Stress, vitamin A deficiency, and autoimmunity also have been proposed as triggers of GLPL.13 Furthermore, familial GLPL was described in a mother and daughter, though the association was uncertain.14 Our patient had no relevant family history.
Workups to reveal the etiology of GLPL have been inconclusive. Reports of laboratory testing including complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone levels, and chest radiograph have been normal.2 Additional workup for viral triggers also has been negative.15 A case series of 29 patients with LPP and its variants, including GLPL, revealed positive antinuclear antibodies in 10% of patients and a thyroid disorder in 24% of patients, with Hashimoto thyroiditis being the most prevalent in 7% of cases.16 There may be a strong association between the comorbidities of thyroid dysfunction and GLPL, as documented in other studies.10,17 A case-control study by Mesinkovska et al17 revealed a considerable increase in the prevalence of thyroid gland disease among patients with LPP vs controls. Human leukocyte antigen DR1 was found in a familial case of GLPL,4 and a case of GLPL following hepatitis B vaccination also has been described.18
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome most likely is a T-cell mediated autoimmune condition associated with one or multiple unknown keratinocyte antigens. Autoantibodies to the inner centromere protein were identified in a case that was positive on direct immunofluorescence, which may provide more insight into the disease pathophysiology.13 Interestingly, a study comparing the concentrations of inflammatory cells in LPP and traction alopecia found an elevation in the ratio of Langerhans cells to T lymphocytes within the follicular inflammatory infiltrate of LPP.19
Histologically, cicatricial alopecia of the scalp is characterized by an interface dermatitis and a lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate of the isthmus and infundibulum of the hair follicle sparing the bulb (Figure). A follicular plug is present in the active border. The increased pressure from the keratinous plug from above and the pressure from the infiltrate from the sides has been proposed to decrease the blood supply to the follicle and result in its death.2 Late-stage disease is notable for fibrotic longitudinal tracks of the hair follicle, perifollicular lamellar fibrosis, and adjacent epidermal atrophy.20 Direct immunofluorescence in GLPL generally is negative. A trichogram performed in a 29-year-old woman with GLPL was normal, with 84% anagen, 2% catagen, and 14% telogen hairs. It was noted that 10% of the sampled hairs were classified as dystrophical dysplastic hairs.12 Despite the lack of fibrosis on physical examination in patients with GLPL, nonscarring alopecia of the axilla and groin may show follicular destruction on microscopic examination.1 The pathology of the papules present on the trunk and extremities—whether that of keratosis pilaris or lichen spinulosus—demonstrates similar hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and follicular plugging with a possible superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate.

The differential diagnosis of GLPL includes other variants of LPP as well as discoid lupus erythematous (DLE), pseudopelade of Brocq, pityriasis rubra pilaris, sarcoidosis, acne keloidalis, central centrifugal scarring alopecia, follicular mucinosis, and folliculitis decalvans.14 Differentiation of LPP from DLE is difficult. Clinical clues include lack of central erythema and telangiectases within the lesions. Histologically, the lymphocytic dermatitis and folliculitis can be indistinguishable, but subtle findings suggesting DLE may be present, such as increased mucin in the reticular dermis, a focally thinned epidermis, and less severe dermal sclerosis when compared to cases of LPP.2 Direct immunofluorescence with IgG and C3 revealing linear granular deposits at the dermoepidermal junction is characteristic of DLE.20 Pseudopelade of Brocq is best thought of as an end-stage clinical pattern of hair loss in LPP rather than a separate condition. It is considered to be the end point of GLPL as well as DLE and others when the inflammation has subsided and the cicatricial alopecia is stable. For the duration of active disease, GLPL is classified as an unstable cicatricial alopecia that has a tendency to progress and recur periodically.20 Folliculitis decalvans also can mimic GLPL during a period when the pustules have resolved; however, a neutrophilic infiltrate will be present.
The goal of treatment in GLPL as well as other scarring alopecias is to stop the progression of hair loss. Early diagnosis is imperative if control is to be gained before considerable hair loss has occurred. Once follicular destruction has occurred as a result of the inflammation, there is minimal potential for hair rejuvenation.21 To date, treatment has been mostly fruitless, except in the management of keratosis pilaris that accompanies GLPL. First-line therapy often includes topical corticosteroids with or without intralesional corticosteroids. Systemic corticosteroids, retinoids, and psoralen plus UVA therapy also are frequently employed.1,2 Success in treating GLPL with cyclosporine A at a dosage of 4 mg/kg daily was described in several studies.1,2,15 Treatment resulted in reduction of perifollicular erythema and follicular hyperkeratotic papules as well as mild hair regrowth within the scarring patches.15 Nonetheless, cyclosporine A may prove useful in the initial inflammatory phase of GLPL. Consequently, cyclosporine A also is associated with a high relapse rate.1,2
Because the number of patients with GLPL is so few, therapy should mirror advances being made in treatments for other variants of LPP. More recent studies of LPP treatment with hydroxychloroquine showed opposing results, though the safety profile of this agent makes it an enticing treatment option.22,23 Tetracyclines showed improvement in 4 of 15 (26.7%) patients in a retrospective study by Spencer et al.24 Another retrospective study showed promising results with the potent 5-alpha reductase inhibitor dutasteride with 7 of 10 (70%) postmenopausal patients reporting stabilization over a mean duration of 28 months with no reported side effects.25 Antimalarial medications also have been implemented as adjunct therapies with mixed results.5 A case of a 26-year-old man with GLPL from South India showed systemic disease improvement following treatment with pulsed systemic steroids, isotretinoin, and anxiolytics.7 Chloroquine phosphate at a daily dose of 150 mg for 3 to 9 months yielded a transient response in one postmenopausal patient with frontal fibrosing alopecia.6 Stabilization of hair loss was achieved with a combination of hydroxychloroquine and doxycycline in a woman with GLPL who was previously unresponsive to tacrolimus ointment.10 Thalidomide showed early promise in an isolated report claiming successful treatment of LPP,26 but there is contradictory evidence, as thalidomide showed no benefit in a series of 4 patients with LPP.27
Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), a transcription factor that regulates genes, is downregulated in LPP.28 Deletion of PPAR-γ within follicular stem cells in mice results in a phenotype similar to cicatricial alopecia. Data have supported the role of PPAR-γ in maintaining the pilosebaceous unit. A case report of pioglitazone (PPAR-γ agonist) therapy used at 15 mg daily for 8 months was successful in treating a patient with LPP.28 Further investigation must be conducted to evaluate these treatments since early attenuation of the disease process is crucial to the reduction of permanent hair loss.
Advances in the early recognition and successful treatment of GLPL are dependent on continued research in all variants of LPP. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to establish standard of care. Further studies should target the association of GLPL and other autoimmune phenomena. Moreover, research into the etiology will provide direction in understanding disease progression and outcome.
To the Editor:
A 56-year-old white woman with a history of melanoma and hypertension presented for evaluation of progressive hair loss of more than 1 year’s duration with associated pruritis. Scalp examination revealed diffuse erythema and scarring alopecia of the bilateral parietal and temporal regions. Physical examination also revealed nonscarring alopecia of the bilateral axillae, with associated thinning of the pubic hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes, as well as keratosis pilaris on the upper arms. Biopsy of the parietal scalp revealed mild scarring alopecia with isthmic fibroplasia consistent with early lichen planopilaris (LPP)(Figure). These histologic features combined with the patient’s clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome (GLPL).
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome was first described by Piccardi in 1913.A second case was then described by Graham-Little in 1915 in a patient referred by Lassueur, resulting in the name it bears today.1,2 The condition presents most commonly in middle-aged white women and is characterized by a triad of cicatricial alopecia of the scalp, nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and/or groin, and a rough follicular eruption on the body and/or scalp. Symptoms may not be present simultaneously. In GLPL, scarring alopecia of the scalp often precedes follicular eruptions of the trunk, arms, and legs by as much as years,2 and the inverse also has been reported.1 The inflammatory lesions of the scalp eventually resolve spontaneously, but the hair loss is by definition irreversible.
This rare condition is considered one of the 3 clinical variants of LPP. Other variants include classic LPP, also known as follicular lichen planus, and frontal fibrosing alopecia.3 More recently, fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution has gained some popularity as a fourth variant of LPP.4 All variants of LPP, including GLPL, result in a scarring alopecia. The classic scalp finding is an erythematous to violaceous, perifollicular, hyperkeratotic scale at the base of the terminal hairs. The population of inflamed follicles spreads outward, leaving behind a round to oval, central, atrophic scar that often is devoid of follicles. Few hairs may persist within zones of alopecia at presentation; however, these hairs are affected by inflammation and also will likely shed. A hair pull test will be positive at the margins during active disease, consisting of mostly anagen hairs on trichogram examination.1,5 Patients may develop only a single foci of hair loss, but much more commonly, a patchy multifocal alopecia is noted.6 Sites often will coalesce. Onset of scalp alopecia may be insidious or fulminant.
The nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and groin may be described as subtle thinning to complete hair loss with no signs of atrophy or inflammation. Although not commonly reported, a case of nonscarring alopecia located on the shoulders has been seen.7
The follicular eruption that can be present on the trunk, arms, or legs in GLPL is most often but not limited to keratosis pilaris, as was seen in our patient. One reported case also described lichen spinulosus as a potential variant.8 Lichen planopilaris is separate from lichen planus (LP) because of its selective follicular involvement vs the nonselective mucocutaneous distribution of LP. The 2 processes also are histologically distinct; however, estimations have shown that more than 50% of patients with GLPL experience at least 1 episode of mucosal or cutaneous LP in their lifetime.9 Rarely, coexistence of GLPL and LP lesions has been described. One reported case of GLPL and concomitant hypertrophic LP could represent a severe form of the disease.9 Additionally, lichen planus pigmentosus, an uncommon variant of LP characterized by hyperpigmented brown macules in sun-exposed areas and flexural folds, was identified in a case report of an Asian woman with GLPL.10
As a general rule, the variants of LPP most commonly are seen in postmenopausal women aged 40 to 60 years; however, rare cases in a child and a teenager have been reported.11 The GLPL variant of LPP is reported up to 4 times more frequently in females.5 Pruritus and pain are inconsistent findings, and there are no systemic signs of illness. A case of androgen insensitivity syndrome associated with GLPL suggested a potential influence of hormones in LPP.12 Stress, vitamin A deficiency, and autoimmunity also have been proposed as triggers of GLPL.13 Furthermore, familial GLPL was described in a mother and daughter, though the association was uncertain.14 Our patient had no relevant family history.
Workups to reveal the etiology of GLPL have been inconclusive. Reports of laboratory testing including complete blood cell count, basic metabolic panel, liver function tests, testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone levels, and chest radiograph have been normal.2 Additional workup for viral triggers also has been negative.15 A case series of 29 patients with LPP and its variants, including GLPL, revealed positive antinuclear antibodies in 10% of patients and a thyroid disorder in 24% of patients, with Hashimoto thyroiditis being the most prevalent in 7% of cases.16 There may be a strong association between the comorbidities of thyroid dysfunction and GLPL, as documented in other studies.10,17 A case-control study by Mesinkovska et al17 revealed a considerable increase in the prevalence of thyroid gland disease among patients with LPP vs controls. Human leukocyte antigen DR1 was found in a familial case of GLPL,4 and a case of GLPL following hepatitis B vaccination also has been described.18
Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome most likely is a T-cell mediated autoimmune condition associated with one or multiple unknown keratinocyte antigens. Autoantibodies to the inner centromere protein were identified in a case that was positive on direct immunofluorescence, which may provide more insight into the disease pathophysiology.13 Interestingly, a study comparing the concentrations of inflammatory cells in LPP and traction alopecia found an elevation in the ratio of Langerhans cells to T lymphocytes within the follicular inflammatory infiltrate of LPP.19
Histologically, cicatricial alopecia of the scalp is characterized by an interface dermatitis and a lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate of the isthmus and infundibulum of the hair follicle sparing the bulb (Figure). A follicular plug is present in the active border. The increased pressure from the keratinous plug from above and the pressure from the infiltrate from the sides has been proposed to decrease the blood supply to the follicle and result in its death.2 Late-stage disease is notable for fibrotic longitudinal tracks of the hair follicle, perifollicular lamellar fibrosis, and adjacent epidermal atrophy.20 Direct immunofluorescence in GLPL generally is negative. A trichogram performed in a 29-year-old woman with GLPL was normal, with 84% anagen, 2% catagen, and 14% telogen hairs. It was noted that 10% of the sampled hairs were classified as dystrophical dysplastic hairs.12 Despite the lack of fibrosis on physical examination in patients with GLPL, nonscarring alopecia of the axilla and groin may show follicular destruction on microscopic examination.1 The pathology of the papules present on the trunk and extremities—whether that of keratosis pilaris or lichen spinulosus—demonstrates similar hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and follicular plugging with a possible superficial, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltrate.

The differential diagnosis of GLPL includes other variants of LPP as well as discoid lupus erythematous (DLE), pseudopelade of Brocq, pityriasis rubra pilaris, sarcoidosis, acne keloidalis, central centrifugal scarring alopecia, follicular mucinosis, and folliculitis decalvans.14 Differentiation of LPP from DLE is difficult. Clinical clues include lack of central erythema and telangiectases within the lesions. Histologically, the lymphocytic dermatitis and folliculitis can be indistinguishable, but subtle findings suggesting DLE may be present, such as increased mucin in the reticular dermis, a focally thinned epidermis, and less severe dermal sclerosis when compared to cases of LPP.2 Direct immunofluorescence with IgG and C3 revealing linear granular deposits at the dermoepidermal junction is characteristic of DLE.20 Pseudopelade of Brocq is best thought of as an end-stage clinical pattern of hair loss in LPP rather than a separate condition. It is considered to be the end point of GLPL as well as DLE and others when the inflammation has subsided and the cicatricial alopecia is stable. For the duration of active disease, GLPL is classified as an unstable cicatricial alopecia that has a tendency to progress and recur periodically.20 Folliculitis decalvans also can mimic GLPL during a period when the pustules have resolved; however, a neutrophilic infiltrate will be present.
The goal of treatment in GLPL as well as other scarring alopecias is to stop the progression of hair loss. Early diagnosis is imperative if control is to be gained before considerable hair loss has occurred. Once follicular destruction has occurred as a result of the inflammation, there is minimal potential for hair rejuvenation.21 To date, treatment has been mostly fruitless, except in the management of keratosis pilaris that accompanies GLPL. First-line therapy often includes topical corticosteroids with or without intralesional corticosteroids. Systemic corticosteroids, retinoids, and psoralen plus UVA therapy also are frequently employed.1,2 Success in treating GLPL with cyclosporine A at a dosage of 4 mg/kg daily was described in several studies.1,2,15 Treatment resulted in reduction of perifollicular erythema and follicular hyperkeratotic papules as well as mild hair regrowth within the scarring patches.15 Nonetheless, cyclosporine A may prove useful in the initial inflammatory phase of GLPL. Consequently, cyclosporine A also is associated with a high relapse rate.1,2
Because the number of patients with GLPL is so few, therapy should mirror advances being made in treatments for other variants of LPP. More recent studies of LPP treatment with hydroxychloroquine showed opposing results, though the safety profile of this agent makes it an enticing treatment option.22,23 Tetracyclines showed improvement in 4 of 15 (26.7%) patients in a retrospective study by Spencer et al.24 Another retrospective study showed promising results with the potent 5-alpha reductase inhibitor dutasteride with 7 of 10 (70%) postmenopausal patients reporting stabilization over a mean duration of 28 months with no reported side effects.25 Antimalarial medications also have been implemented as adjunct therapies with mixed results.5 A case of a 26-year-old man with GLPL from South India showed systemic disease improvement following treatment with pulsed systemic steroids, isotretinoin, and anxiolytics.7 Chloroquine phosphate at a daily dose of 150 mg for 3 to 9 months yielded a transient response in one postmenopausal patient with frontal fibrosing alopecia.6 Stabilization of hair loss was achieved with a combination of hydroxychloroquine and doxycycline in a woman with GLPL who was previously unresponsive to tacrolimus ointment.10 Thalidomide showed early promise in an isolated report claiming successful treatment of LPP,26 but there is contradictory evidence, as thalidomide showed no benefit in a series of 4 patients with LPP.27
Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), a transcription factor that regulates genes, is downregulated in LPP.28 Deletion of PPAR-γ within follicular stem cells in mice results in a phenotype similar to cicatricial alopecia. Data have supported the role of PPAR-γ in maintaining the pilosebaceous unit. A case report of pioglitazone (PPAR-γ agonist) therapy used at 15 mg daily for 8 months was successful in treating a patient with LPP.28 Further investigation must be conducted to evaluate these treatments since early attenuation of the disease process is crucial to the reduction of permanent hair loss.
Advances in the early recognition and successful treatment of GLPL are dependent on continued research in all variants of LPP. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to establish standard of care. Further studies should target the association of GLPL and other autoimmune phenomena. Moreover, research into the etiology will provide direction in understanding disease progression and outcome.
- Zegarska B, Kallas D, Schwartz RA, et al. Graham-Little syndrome. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2010;19:39-42.
- Assouly P, Reygagne P. Lichen planopilaris: update on diagnosis and treatment. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:3-10.
- Olsen EA, Bergfield WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)–sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110.
- Zinkernagel MS, Trueb RM. Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution: patterned lichen planopilaris or androgenetic alopecia with a lichenoid tissue reaction pattern? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:205-211.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Company; 2016.
- Kossard S, Lee MS, Wilkinson B. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: a frontal variant of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:59-66.
- Pai VV, Kikkeri NN, Sori T, et al. Graham-Little Piccardi Lassueur syndrome: an unusual variant of follicular lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;3:28-30.
- Srivastava M, Mikkilineni R, Konstadt J. Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:12.
- Brar BK, Khanna E, Mahajan BB. Graham Little Piccardi Lasseur syndrome: a rare case report with concomitant hypertrophic lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;5:199-200.
- Vashi N, Newlove T, Chu J, et al. Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:30.
- Chieregato C, Zini A, Barba A, et al. Lichen planopilaris: report of 30 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:342-345.
- Vega Gutierrez J, Miranda-Romera A, Perez Milan F, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:463-466.
- Rodríguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Viglizzo G, Verrini A, Rongioletti F. Familial Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatology. 2004;208:142-144.
- Bianchi L, Paro Vidolin A, Piemonte P, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome: effective treatment with cyclosporin A. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26:518-520.
- Cevasco NC, Bergfeld WF, Remzi BK, et al. A case-series of 29 patients with lichen planopilaris: the Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience on evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:47-53.
- Mesinkovska NA, Brankov N, Piliang M, et al. Association of lichen planopilaris with thyroid disease: a retrospective case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:889-892.
- Bardazzi F, Landi C, Orlandi C, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lasseur syndrome following HBV vaccination. Acta Derm Venereol. 1999;79:93.
- Hutchens KA, Balfour EM, Smoller BR. Comparison between Langerhans cell concentration in lichen planopilaris and traction alopecia with possible immunologic implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:277-280.
- Dogra S, Sarangal R. What’s new in cicatricial alopecia? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:576-590.
- Daoud MS, Pittelkow MR. Lichen planus. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz Si, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 7th ed. New York, NY: Mc Graw Hill; 2008:463-477.
- Donati A, Assouly P, Matard B, et al. Clinical and photographic assessment of lichen planopilaris treatment efficacy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:597-599.
- Samrao A, Chew AL, Price V. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a clinical review of 36 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1296-1300.
- Spencer LA, Hawryluk EB, English JC. Lichen planopilaris: retrospective study and stepwise therapeutic approach. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:333-334.
- Ladizinski B, Bazakas A, Selim MA, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a retrospective review of 19 patients seen at Duke University. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:749-755
- George SJ, Hsu SJ. Lichen planopilaris treated with thalidomide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:965-966.
- Jouanique C, Reygagne P, Bachelez H, et al. Thalidomide is ineffective in the treatment of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:480-481.
- Mirmirani P, Karnik P. Lichen planopilaris treated with a peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ agonist. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1363-1366.
- Zegarska B, Kallas D, Schwartz RA, et al. Graham-Little syndrome. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2010;19:39-42.
- Assouly P, Reygagne P. Lichen planopilaris: update on diagnosis and treatment. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28:3-10.
- Olsen EA, Bergfield WF, Cotsarelis G, et al. Summary of North American Hair Research Society (NAHRS)–sponsored Workshop on Cicatricial Alopecia, Duke University Medical Center, February 10 and 11, 2001. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:103-110.
- Zinkernagel MS, Trueb RM. Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution: patterned lichen planopilaris or androgenetic alopecia with a lichenoid tissue reaction pattern? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:205-211.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Company; 2016.
- Kossard S, Lee MS, Wilkinson B. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: a frontal variant of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36:59-66.
- Pai VV, Kikkeri NN, Sori T, et al. Graham-Little Piccardi Lassueur syndrome: an unusual variant of follicular lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;3:28-30.
- Srivastava M, Mikkilineni R, Konstadt J. Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:12.
- Brar BK, Khanna E, Mahajan BB. Graham Little Piccardi Lasseur syndrome: a rare case report with concomitant hypertrophic lichen planus. Int J Trichology. 2011;5:199-200.
- Vashi N, Newlove T, Chu J, et al. Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:30.
- Chieregato C, Zini A, Barba A, et al. Lichen planopilaris: report of 30 cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:342-345.
- Vega Gutierrez J, Miranda-Romera A, Perez Milan F, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:463-466.
- Rodríguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Viglizzo G, Verrini A, Rongioletti F. Familial Lassueur-Graham-Little-Piccardi syndrome. Dermatology. 2004;208:142-144.
- Bianchi L, Paro Vidolin A, Piemonte P, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome: effective treatment with cyclosporin A. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26:518-520.
- Cevasco NC, Bergfeld WF, Remzi BK, et al. A case-series of 29 patients with lichen planopilaris: the Cleveland Clinic Foundation experience on evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:47-53.
- Mesinkovska NA, Brankov N, Piliang M, et al. Association of lichen planopilaris with thyroid disease: a retrospective case-control study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:889-892.
- Bardazzi F, Landi C, Orlandi C, et al. Graham Little-Piccardi-Lasseur syndrome following HBV vaccination. Acta Derm Venereol. 1999;79:93.
- Hutchens KA, Balfour EM, Smoller BR. Comparison between Langerhans cell concentration in lichen planopilaris and traction alopecia with possible immunologic implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:277-280.
- Dogra S, Sarangal R. What’s new in cicatricial alopecia? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:576-590.
- Daoud MS, Pittelkow MR. Lichen planus. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz Si, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 7th ed. New York, NY: Mc Graw Hill; 2008:463-477.
- Donati A, Assouly P, Matard B, et al. Clinical and photographic assessment of lichen planopilaris treatment efficacy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:597-599.
- Samrao A, Chew AL, Price V. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a clinical review of 36 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:1296-1300.
- Spencer LA, Hawryluk EB, English JC. Lichen planopilaris: retrospective study and stepwise therapeutic approach. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:333-334.
- Ladizinski B, Bazakas A, Selim MA, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a retrospective review of 19 patients seen at Duke University. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:749-755
- George SJ, Hsu SJ. Lichen planopilaris treated with thalidomide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:965-966.
- Jouanique C, Reygagne P, Bachelez H, et al. Thalidomide is ineffective in the treatment of lichen planopilaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:480-481.
- Mirmirani P, Karnik P. Lichen planopilaris treated with a peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ agonist. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:1363-1366.
Practice Points
- Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome (GLPL) is characterized by a triad of cicatricial alopecia of the scalp, nonscarring alopecia of the axillae and/or groin, and a rough follicular eruption on the body and/or scalp.
- Graham-Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome is considered one of the 3 clinical variants of lichen planopilaris.
- Potential therapies for GLPL include hydroxychloroquine, cyclosporine, tetracyclines, and pioglitazone.
Hormone use linked to hair loss in transgender adults
Gender-affirming hormone use was significantly associated with reports of androgenetic alopecia in transgender men, based on data from a survey of 991 individuals.
Given the importance of hair in body image and gender identity, hair concerns are important to the quality of life of gender-minority individuals, wrote Dustin Marks, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues.
To explore the impact of hormone use on hair loss in gender-minority patients, the researchers conducted a web-based survey of transgender individuals aged 18 years and older, who self-identified as gender minority. Participants were invited based on profiles on Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram. The findings were published in a research letter in the British Journal of Dermatology.
The 991 survey respondents included 59% transmen, 31% transwomen, and 9% gender nonbinary or gender queer. The average age of the participants was 33 years; 79% were white, 89% had medical insurance, and 91% reported using gender-affirming hormones.
Overall, 65% of transwomen, 43% of transmen, and 35% of nonbinary individuals reported scalp hair loss or thinning. Scalp hair loss was significantly more common among transmen on masculinizing hormones compared to transmen not on hormones (45% vs. 17%). Scalp hair loss was not significantly different between transwomen on feminizing hormones and those not on hormones.
The transwomen who reported scalp hair loss and were on hormones reported significantly less severe Sinclair grades, compared with transwomen with scalp hair loss and were not on hormones. By contrast, transmen and nonbinary individuals on testosterone reported significantly more hair loss (using Hamilton-Norwood and Sinclair scores) between a baseline before hormone use and their present state of hormone use.
The findings support the impact of testosterone use on androgenic alopecia (AGA) in gender-minority patients similar to the established role of testosterone in male pattern hair loss overall, the researchers wrote.
“Some transmen, moreover, may view AGA as a wanted masculine trait, while others seek dermatologic evaluation and treatment for their hair loss,” they noted. By contrast, some transwomen may find AGA especially distressing. In this study, AGA scores were stable for transwomen, which suggests that feminizing hormones may be enough to stabilize hair loss in these patients.
The study was limited by several factors including use of a convenience sample study population without cisgender controls, lack of data on the duration of hormone use, and specific focus on AGE, the researchers noted.
“Mindful of these limitations, clinicians should appreciate the impact of gender-affirming hormones on androgenetic alopecia severity and continue to address the hair concerns of each patient individually,” they wrote.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose, and no sources of study funding were reported.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 May 3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18099.
Gender-affirming hormone use was significantly associated with reports of androgenetic alopecia in transgender men, based on data from a survey of 991 individuals.
Given the importance of hair in body image and gender identity, hair concerns are important to the quality of life of gender-minority individuals, wrote Dustin Marks, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues.
To explore the impact of hormone use on hair loss in gender-minority patients, the researchers conducted a web-based survey of transgender individuals aged 18 years and older, who self-identified as gender minority. Participants were invited based on profiles on Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram. The findings were published in a research letter in the British Journal of Dermatology.
The 991 survey respondents included 59% transmen, 31% transwomen, and 9% gender nonbinary or gender queer. The average age of the participants was 33 years; 79% were white, 89% had medical insurance, and 91% reported using gender-affirming hormones.
Overall, 65% of transwomen, 43% of transmen, and 35% of nonbinary individuals reported scalp hair loss or thinning. Scalp hair loss was significantly more common among transmen on masculinizing hormones compared to transmen not on hormones (45% vs. 17%). Scalp hair loss was not significantly different between transwomen on feminizing hormones and those not on hormones.
The transwomen who reported scalp hair loss and were on hormones reported significantly less severe Sinclair grades, compared with transwomen with scalp hair loss and were not on hormones. By contrast, transmen and nonbinary individuals on testosterone reported significantly more hair loss (using Hamilton-Norwood and Sinclair scores) between a baseline before hormone use and their present state of hormone use.
The findings support the impact of testosterone use on androgenic alopecia (AGA) in gender-minority patients similar to the established role of testosterone in male pattern hair loss overall, the researchers wrote.
“Some transmen, moreover, may view AGA as a wanted masculine trait, while others seek dermatologic evaluation and treatment for their hair loss,” they noted. By contrast, some transwomen may find AGA especially distressing. In this study, AGA scores were stable for transwomen, which suggests that feminizing hormones may be enough to stabilize hair loss in these patients.
The study was limited by several factors including use of a convenience sample study population without cisgender controls, lack of data on the duration of hormone use, and specific focus on AGE, the researchers noted.
“Mindful of these limitations, clinicians should appreciate the impact of gender-affirming hormones on androgenetic alopecia severity and continue to address the hair concerns of each patient individually,” they wrote.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose, and no sources of study funding were reported.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 May 3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18099.
Gender-affirming hormone use was significantly associated with reports of androgenetic alopecia in transgender men, based on data from a survey of 991 individuals.
Given the importance of hair in body image and gender identity, hair concerns are important to the quality of life of gender-minority individuals, wrote Dustin Marks, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and colleagues.
To explore the impact of hormone use on hair loss in gender-minority patients, the researchers conducted a web-based survey of transgender individuals aged 18 years and older, who self-identified as gender minority. Participants were invited based on profiles on Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram. The findings were published in a research letter in the British Journal of Dermatology.
The 991 survey respondents included 59% transmen, 31% transwomen, and 9% gender nonbinary or gender queer. The average age of the participants was 33 years; 79% were white, 89% had medical insurance, and 91% reported using gender-affirming hormones.
Overall, 65% of transwomen, 43% of transmen, and 35% of nonbinary individuals reported scalp hair loss or thinning. Scalp hair loss was significantly more common among transmen on masculinizing hormones compared to transmen not on hormones (45% vs. 17%). Scalp hair loss was not significantly different between transwomen on feminizing hormones and those not on hormones.
The transwomen who reported scalp hair loss and were on hormones reported significantly less severe Sinclair grades, compared with transwomen with scalp hair loss and were not on hormones. By contrast, transmen and nonbinary individuals on testosterone reported significantly more hair loss (using Hamilton-Norwood and Sinclair scores) between a baseline before hormone use and their present state of hormone use.
The findings support the impact of testosterone use on androgenic alopecia (AGA) in gender-minority patients similar to the established role of testosterone in male pattern hair loss overall, the researchers wrote.
“Some transmen, moreover, may view AGA as a wanted masculine trait, while others seek dermatologic evaluation and treatment for their hair loss,” they noted. By contrast, some transwomen may find AGA especially distressing. In this study, AGA scores were stable for transwomen, which suggests that feminizing hormones may be enough to stabilize hair loss in these patients.
The study was limited by several factors including use of a convenience sample study population without cisgender controls, lack of data on the duration of hormone use, and specific focus on AGE, the researchers noted.
“Mindful of these limitations, clinicians should appreciate the impact of gender-affirming hormones on androgenetic alopecia severity and continue to address the hair concerns of each patient individually,” they wrote.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose, and no sources of study funding were reported.
SOURCE: Marks D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 May 3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18099.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Use of hormone therapy had a significant impact on scalp and hair loss in trans men who used masculinizing hormones.
Major finding: Scalp hair loss or hair thinning was reported by 65% of trans women, 43% of trans men, and 35% of nonbinary individuals.
Study details: The data come from a cross-sectional study including 991 adults self-identifying as gender minorities.
Disclosures: The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose, and no sources of study funding were reported.
Source: Marks D et al. Br J Dermatol. 2019 May 3. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18099.
Netherton Syndrome: An Atypical Presentation
To the Editor:
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive ichthyosiform disease.1 The incidence is estimated to be 1 in 200,000 individuals.2 Netherton syndrome presents with generalized erythroderma and scaling, characteristic hair shaft abnormalities, and dysregulation of the immune system. Treatment is largely symptomatic and includes fragrance-free emollients, keratolytics, tretinoin, and corticosteroids, either alone or in combination. We report a case of NS in a man with congenital erythroderma, pili torti, and elevated IgE levels.
A 23-year-old man presented with generalized scaly skin that was present since birth. He was the first child born of nonconsanguineous parents. His medical history was suggestive of atopic diatheses such as allergic rhinitis and recurrent urticaria. The patient was of thin build and had widespread erythematous, annular, and polycyclic scaly lesions (Figure 1A), some with characteristic double-edged scale (Figure 1B). The skin was dry due to anhidrosis that was present since birth. Flexural lichenification was present at the cubital fossa of both arms. Scalp hairs were easily pluckable and had generalized thinning of hair density. Hair mount examination showed characteristic features of both trichorrhexis invaginata (Figure 2A) and pili torti (Figure 2B).
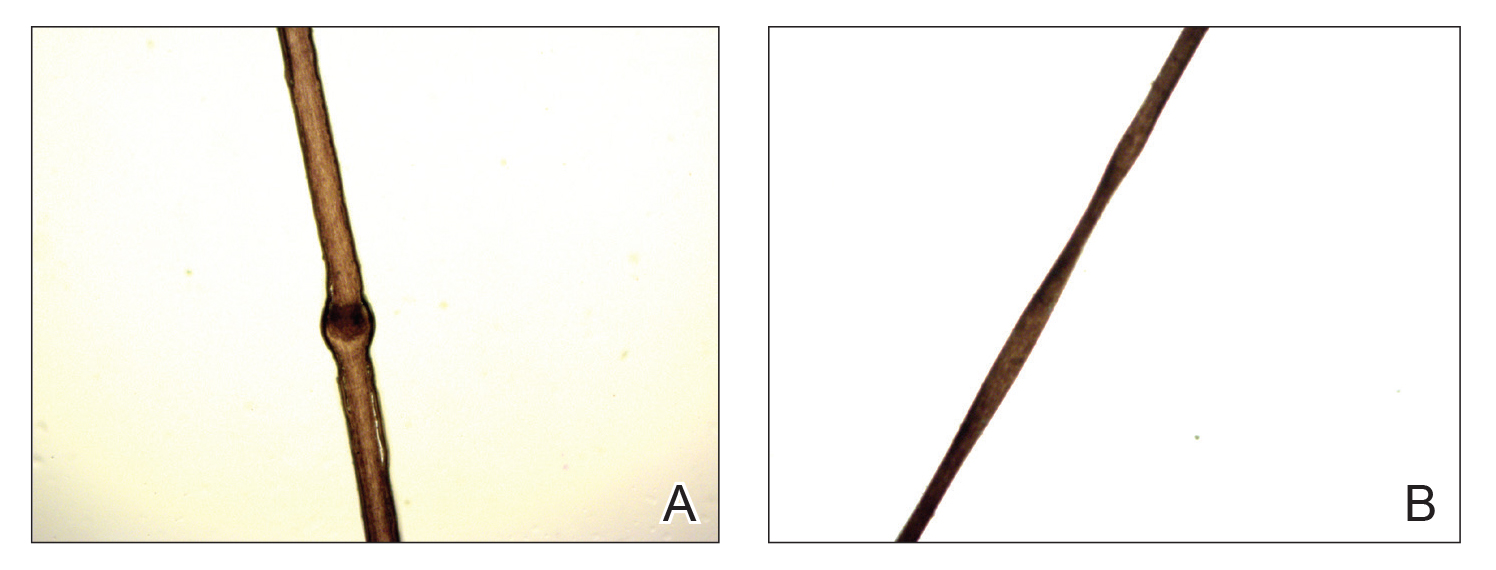
hair shaft known as bamboo hair or trichorrhexis invaginata. B, Features of pili torti; the hair
shaft twisted at irregular intervals.
Potassium hydroxide mount from a lesion was negative for fungal elements. Complete hematologic workup showed moderate anemia at 8.0 g/dL (reference range, 8.0–10.9 g/dL) and peripheral eosinophilia at 12% (reference range, 0%–6%). His IgE level was markedly elevated at6331 IU/mL (reference range, 150–1000 IU/mL) when tested with fully automated bidirectionally interfaced chemiluminescent immunoassay. Histopathologic examination of a lesion biopsy showed psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis, and acanthosis, consistent with ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (ILC)(Figure 3). Clinicopathologic correlation led to a diagnosis of ILC, trichorrhexis invaginata/pili torti, and atopic diathesis, which is a constellation of disorders related to NS.
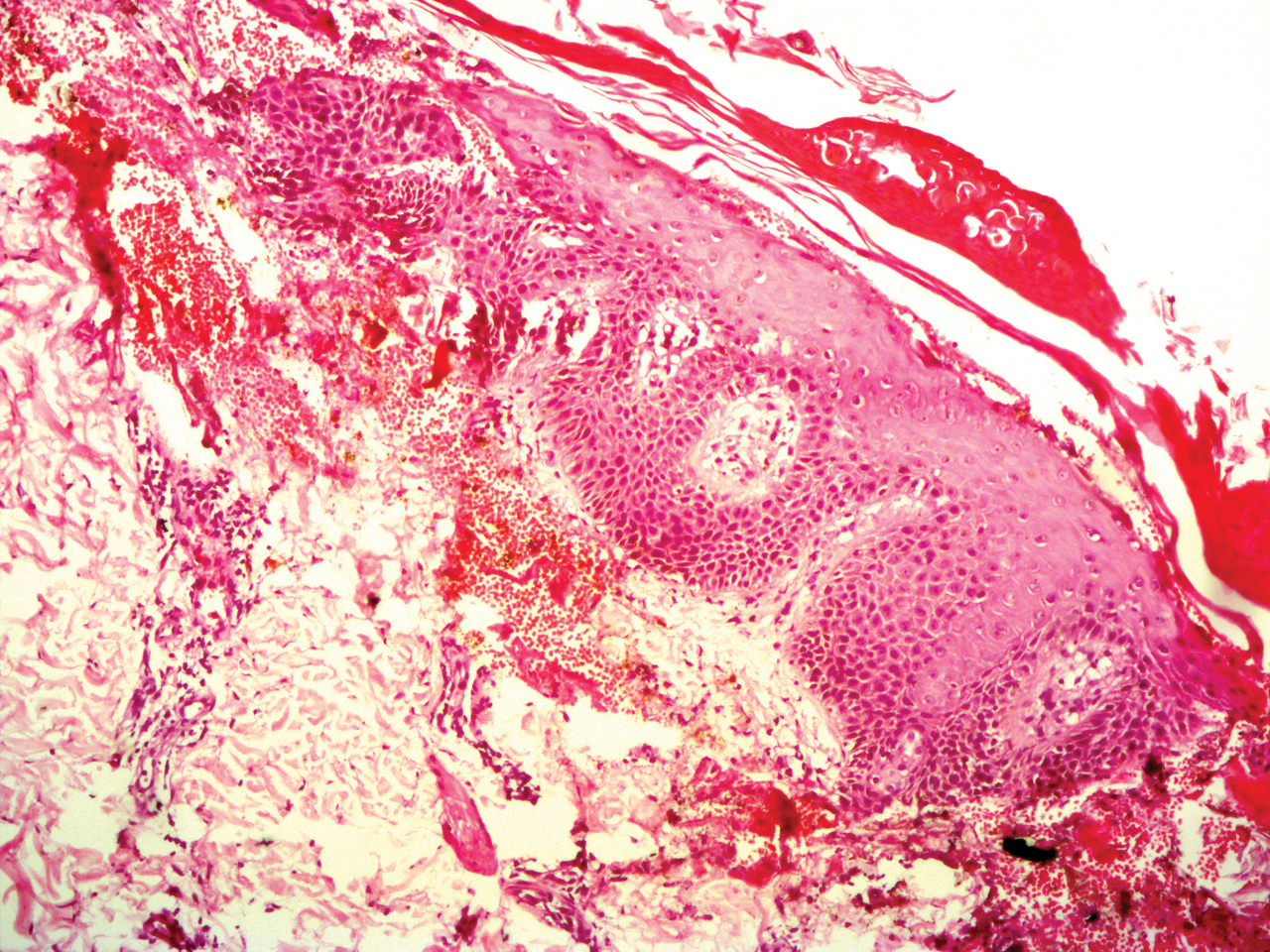
We prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg once daily and instructed the patient to apply petroleum jelly; however, the patient returned after 2 weeks due to aggravation of the skin condition with increased scaling and redness. Because the patient showed signs of acute skin failure and erythroderma, we stopped acitretin treatment and managed his condition conservatively with the application of petroleum jelly.
Netherton syndrome is caused by mutation of the SPINK5 gene, serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5; the corresponding gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5.3 The gene encodes a serine protease inhibitor proprotein LEKTI (lymphoepithelial Kazal type inhibitor).4 The product of the gene is thought to be necessary for epidermal cell growth and differentiation. The classic clinical triad of NS includes ichthyosiform dermatosis with double-edged scale, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopy or elevated IgE levels.5 Generalized (congenital) erythroderma usually becomes evident at birth or shortly thereafter. Half of patients develop lesions of ILC on the trunk and limbs during childhood.6 A typical ILC lesion is characterized by an erythematous scaly patch that may be annular or polycyclic with double-edged scale at the advancing border. The ability to sweat is impaired, which may cause episodes of hyperpyrexia, especially during humid weather. Patients with hyperpyrexia may be incorrectly diagnosed with bacterial infection and treated with antipyretic drugs or a prolonged course of antibiotics. Trichorrhexis invaginata, also referred to as bamboo hair or ball-and-socket defect, is the pathognomonic hair shaft abnormality seen in NS.7 Other hair shaft abnormalities in this syndrome include trichorrhexis nodosa and pili torti.8 Our patient had hair shaft abnormalities of trichorrhexis invaginata and pili torti, which are rare findings. The third component of this syndrome is atopy, which generally manifests as angioedema, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, peripheral eosinophilia, atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions, asthma, and elevated IgE levels.9
Treatment with emollients, topical steroids, tacrolimus, and psoralen plus UVA does not elicit a satisfactory response. The Table highlights the clinical features and management of NS.
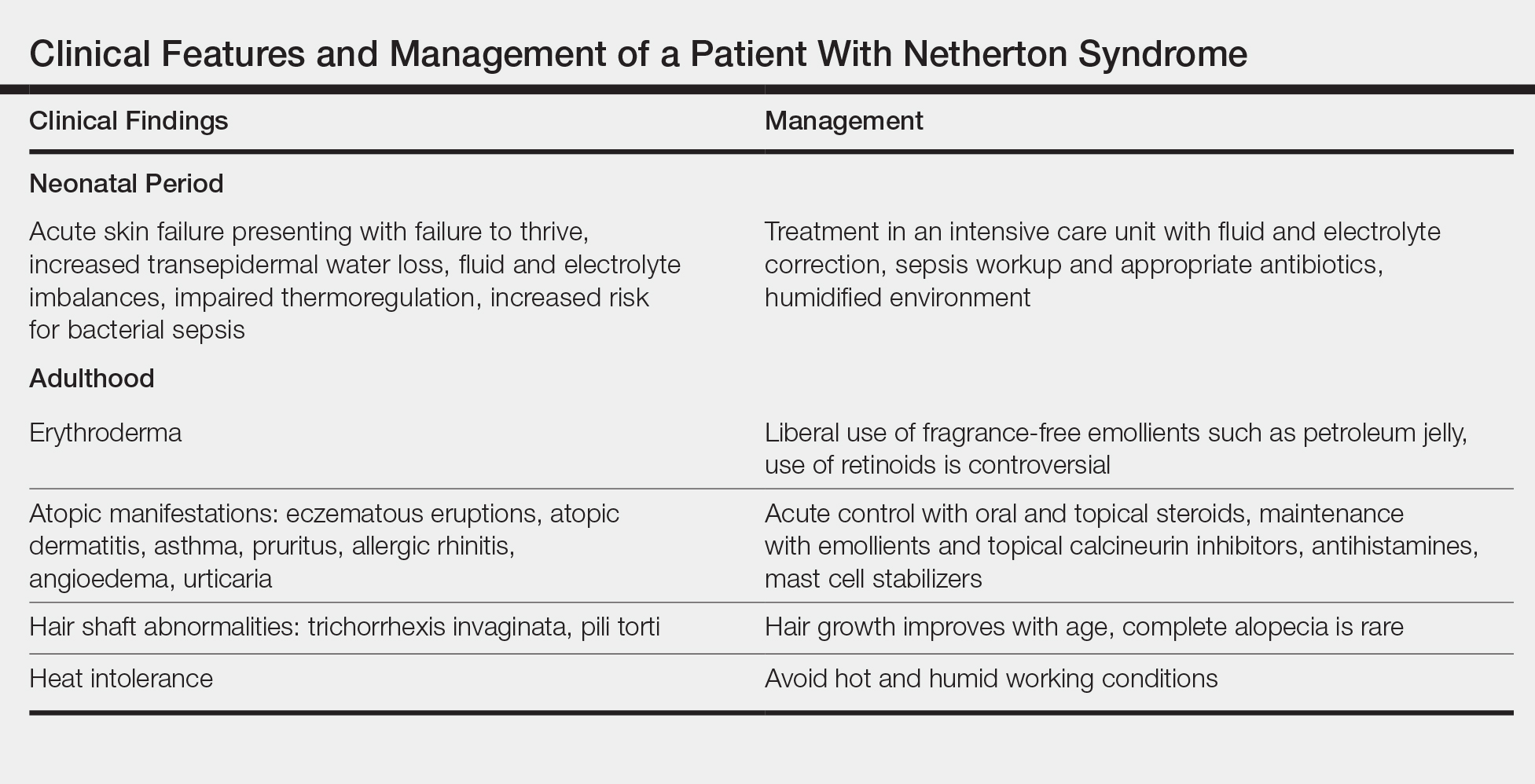
Generally, systemic retinoid therapy is helpful in cases of erythrodermic ichthyosis, but a unique feature of NS is that erythroderma may worsen with systemic retinoid therapy, as retinoids aggravate atopic dermatitis by worsening existing xerosis.4 Our case highlights the rare association of trichorrhexis invaginata with pili torti as well as acitretin treatment worsening our patient’s condition. This paradoxical effect of retinoid therapy further confirmed the diagnosis of NS.
- Suhaila O, Muzhirah A. Netherton syndrome: a case report. Malaysian J Pediatr Child Health. 2010;16:26.
- Emre S, Metin A, Demirseren D, et al. Two siblings with Netherton syndrome. Turk J Med Sci. 2010;40:819-823.
- Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A, et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000;25:141-142.
- Judge MR, Mclean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Singapore: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010:19.1-19.122.
- Greene SL, Muller SA. Netherton’s syndrome. report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13:329-337.
- Khan I-U, Chaudhary R. Netherton’s syndrome, an uncommon genodermatosis. J Pakistan Assoc Dermatol. 2006;16.
- Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Mafinejad S. Netherton syndrome, a case report and review of literature. Iran J Pediatr. 2013;23:611-612.
- Hurwitz S. Hereditary skin disorders: the genodermatoses. In: Hurwitz, ed. Clinical Pediatric Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1993:173.
- Judge MR, McLean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 7th ed. Vol 2. Oxford, England: Blackwell Science; 2004:34.35.
To the Editor:
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive ichthyosiform disease.1 The incidence is estimated to be 1 in 200,000 individuals.2 Netherton syndrome presents with generalized erythroderma and scaling, characteristic hair shaft abnormalities, and dysregulation of the immune system. Treatment is largely symptomatic and includes fragrance-free emollients, keratolytics, tretinoin, and corticosteroids, either alone or in combination. We report a case of NS in a man with congenital erythroderma, pili torti, and elevated IgE levels.
A 23-year-old man presented with generalized scaly skin that was present since birth. He was the first child born of nonconsanguineous parents. His medical history was suggestive of atopic diatheses such as allergic rhinitis and recurrent urticaria. The patient was of thin build and had widespread erythematous, annular, and polycyclic scaly lesions (Figure 1A), some with characteristic double-edged scale (Figure 1B). The skin was dry due to anhidrosis that was present since birth. Flexural lichenification was present at the cubital fossa of both arms. Scalp hairs were easily pluckable and had generalized thinning of hair density. Hair mount examination showed characteristic features of both trichorrhexis invaginata (Figure 2A) and pili torti (Figure 2B).


hair shaft known as bamboo hair or trichorrhexis invaginata. B, Features of pili torti; the hair
shaft twisted at irregular intervals.
Potassium hydroxide mount from a lesion was negative for fungal elements. Complete hematologic workup showed moderate anemia at 8.0 g/dL (reference range, 8.0–10.9 g/dL) and peripheral eosinophilia at 12% (reference range, 0%–6%). His IgE level was markedly elevated at6331 IU/mL (reference range, 150–1000 IU/mL) when tested with fully automated bidirectionally interfaced chemiluminescent immunoassay. Histopathologic examination of a lesion biopsy showed psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis, and acanthosis, consistent with ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (ILC)(Figure 3). Clinicopathologic correlation led to a diagnosis of ILC, trichorrhexis invaginata/pili torti, and atopic diathesis, which is a constellation of disorders related to NS.

We prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg once daily and instructed the patient to apply petroleum jelly; however, the patient returned after 2 weeks due to aggravation of the skin condition with increased scaling and redness. Because the patient showed signs of acute skin failure and erythroderma, we stopped acitretin treatment and managed his condition conservatively with the application of petroleum jelly.
Netherton syndrome is caused by mutation of the SPINK5 gene, serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5; the corresponding gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5.3 The gene encodes a serine protease inhibitor proprotein LEKTI (lymphoepithelial Kazal type inhibitor).4 The product of the gene is thought to be necessary for epidermal cell growth and differentiation. The classic clinical triad of NS includes ichthyosiform dermatosis with double-edged scale, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopy or elevated IgE levels.5 Generalized (congenital) erythroderma usually becomes evident at birth or shortly thereafter. Half of patients develop lesions of ILC on the trunk and limbs during childhood.6 A typical ILC lesion is characterized by an erythematous scaly patch that may be annular or polycyclic with double-edged scale at the advancing border. The ability to sweat is impaired, which may cause episodes of hyperpyrexia, especially during humid weather. Patients with hyperpyrexia may be incorrectly diagnosed with bacterial infection and treated with antipyretic drugs or a prolonged course of antibiotics. Trichorrhexis invaginata, also referred to as bamboo hair or ball-and-socket defect, is the pathognomonic hair shaft abnormality seen in NS.7 Other hair shaft abnormalities in this syndrome include trichorrhexis nodosa and pili torti.8 Our patient had hair shaft abnormalities of trichorrhexis invaginata and pili torti, which are rare findings. The third component of this syndrome is atopy, which generally manifests as angioedema, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, peripheral eosinophilia, atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions, asthma, and elevated IgE levels.9
Treatment with emollients, topical steroids, tacrolimus, and psoralen plus UVA does not elicit a satisfactory response. The Table highlights the clinical features and management of NS.

Generally, systemic retinoid therapy is helpful in cases of erythrodermic ichthyosis, but a unique feature of NS is that erythroderma may worsen with systemic retinoid therapy, as retinoids aggravate atopic dermatitis by worsening existing xerosis.4 Our case highlights the rare association of trichorrhexis invaginata with pili torti as well as acitretin treatment worsening our patient’s condition. This paradoxical effect of retinoid therapy further confirmed the diagnosis of NS.
To the Editor:
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare autosomal-recessive ichthyosiform disease.1 The incidence is estimated to be 1 in 200,000 individuals.2 Netherton syndrome presents with generalized erythroderma and scaling, characteristic hair shaft abnormalities, and dysregulation of the immune system. Treatment is largely symptomatic and includes fragrance-free emollients, keratolytics, tretinoin, and corticosteroids, either alone or in combination. We report a case of NS in a man with congenital erythroderma, pili torti, and elevated IgE levels.
A 23-year-old man presented with generalized scaly skin that was present since birth. He was the first child born of nonconsanguineous parents. His medical history was suggestive of atopic diatheses such as allergic rhinitis and recurrent urticaria. The patient was of thin build and had widespread erythematous, annular, and polycyclic scaly lesions (Figure 1A), some with characteristic double-edged scale (Figure 1B). The skin was dry due to anhidrosis that was present since birth. Flexural lichenification was present at the cubital fossa of both arms. Scalp hairs were easily pluckable and had generalized thinning of hair density. Hair mount examination showed characteristic features of both trichorrhexis invaginata (Figure 2A) and pili torti (Figure 2B).


hair shaft known as bamboo hair or trichorrhexis invaginata. B, Features of pili torti; the hair
shaft twisted at irregular intervals.
Potassium hydroxide mount from a lesion was negative for fungal elements. Complete hematologic workup showed moderate anemia at 8.0 g/dL (reference range, 8.0–10.9 g/dL) and peripheral eosinophilia at 12% (reference range, 0%–6%). His IgE level was markedly elevated at6331 IU/mL (reference range, 150–1000 IU/mL) when tested with fully automated bidirectionally interfaced chemiluminescent immunoassay. Histopathologic examination of a lesion biopsy showed psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia, papillomatosis, and acanthosis, consistent with ichthyosis linearis circumflexa (ILC)(Figure 3). Clinicopathologic correlation led to a diagnosis of ILC, trichorrhexis invaginata/pili torti, and atopic diathesis, which is a constellation of disorders related to NS.

We prescribed oral acitretin 25 mg once daily and instructed the patient to apply petroleum jelly; however, the patient returned after 2 weeks due to aggravation of the skin condition with increased scaling and redness. Because the patient showed signs of acute skin failure and erythroderma, we stopped acitretin treatment and managed his condition conservatively with the application of petroleum jelly.
Netherton syndrome is caused by mutation of the SPINK5 gene, serine protease inhibitor Kazal type 5; the corresponding gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5.3 The gene encodes a serine protease inhibitor proprotein LEKTI (lymphoepithelial Kazal type inhibitor).4 The product of the gene is thought to be necessary for epidermal cell growth and differentiation. The classic clinical triad of NS includes ichthyosiform dermatosis with double-edged scale, hair shaft abnormalities, and atopy or elevated IgE levels.5 Generalized (congenital) erythroderma usually becomes evident at birth or shortly thereafter. Half of patients develop lesions of ILC on the trunk and limbs during childhood.6 A typical ILC lesion is characterized by an erythematous scaly patch that may be annular or polycyclic with double-edged scale at the advancing border. The ability to sweat is impaired, which may cause episodes of hyperpyrexia, especially during humid weather. Patients with hyperpyrexia may be incorrectly diagnosed with bacterial infection and treated with antipyretic drugs or a prolonged course of antibiotics. Trichorrhexis invaginata, also referred to as bamboo hair or ball-and-socket defect, is the pathognomonic hair shaft abnormality seen in NS.7 Other hair shaft abnormalities in this syndrome include trichorrhexis nodosa and pili torti.8 Our patient had hair shaft abnormalities of trichorrhexis invaginata and pili torti, which are rare findings. The third component of this syndrome is atopy, which generally manifests as angioedema, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, peripheral eosinophilia, atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions, asthma, and elevated IgE levels.9
Treatment with emollients, topical steroids, tacrolimus, and psoralen plus UVA does not elicit a satisfactory response. The Table highlights the clinical features and management of NS.

Generally, systemic retinoid therapy is helpful in cases of erythrodermic ichthyosis, but a unique feature of NS is that erythroderma may worsen with systemic retinoid therapy, as retinoids aggravate atopic dermatitis by worsening existing xerosis.4 Our case highlights the rare association of trichorrhexis invaginata with pili torti as well as acitretin treatment worsening our patient’s condition. This paradoxical effect of retinoid therapy further confirmed the diagnosis of NS.
- Suhaila O, Muzhirah A. Netherton syndrome: a case report. Malaysian J Pediatr Child Health. 2010;16:26.
- Emre S, Metin A, Demirseren D, et al. Two siblings with Netherton syndrome. Turk J Med Sci. 2010;40:819-823.
- Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A, et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000;25:141-142.
- Judge MR, Mclean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Singapore: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010:19.1-19.122.
- Greene SL, Muller SA. Netherton’s syndrome. report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13:329-337.
- Khan I-U, Chaudhary R. Netherton’s syndrome, an uncommon genodermatosis. J Pakistan Assoc Dermatol. 2006;16.
- Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Mafinejad S. Netherton syndrome, a case report and review of literature. Iran J Pediatr. 2013;23:611-612.
- Hurwitz S. Hereditary skin disorders: the genodermatoses. In: Hurwitz, ed. Clinical Pediatric Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1993:173.
- Judge MR, McLean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 7th ed. Vol 2. Oxford, England: Blackwell Science; 2004:34.35.
- Suhaila O, Muzhirah A. Netherton syndrome: a case report. Malaysian J Pediatr Child Health. 2010;16:26.
- Emre S, Metin A, Demirseren D, et al. Two siblings with Netherton syndrome. Turk J Med Sci. 2010;40:819-823.
- Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A, et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000;25:141-142.
- Judge MR, Mclean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Singapore: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010:19.1-19.122.
- Greene SL, Muller SA. Netherton’s syndrome. report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13:329-337.
- Khan I-U, Chaudhary R. Netherton’s syndrome, an uncommon genodermatosis. J Pakistan Assoc Dermatol. 2006;16.
- Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Mafinejad S. Netherton syndrome, a case report and review of literature. Iran J Pediatr. 2013;23:611-612.
- Hurwitz S. Hereditary skin disorders: the genodermatoses. In: Hurwitz, ed. Clinical Pediatric Dermatology. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1993:173.
- Judge MR, McLean WH, Munro CS. Disorders of keratinization. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, et al, eds. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 7th ed. Vol 2. Oxford, England: Blackwell Science; 2004:34.35.
Practice Points
- Netherton syndrome is characterized by generalized erythroderma and scaling, hair shaft abnormalities, and dysregulation of the immune system.
- Treatment is largely symptomatic and includes fragrance-free emollients, keratolytics, tretinoin, and corticosteroids, either alone or in combination.
Dermoscopic Patterns of Acral Melanocytic Lesions in Skin of Color
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a rare subtype of melanoma that occurs on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus. Unlike more common types of melanoma, ALM occurs on sun-protected areas of the skin and has distinct clinical, histologic, and genetic features. Acral lentiginous melanoma accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in individuals with skin of color and has a worse prognosis and recurrence rate than other forms of melanoma.
Population Trends in Skin of Color
Much of the literature on malignant melanoma historically has involved non-Hispanic white patients, but the incidence in lighter-skinned populations has been increasing steadily over the last few decades.1 Although ALM can occur in any race, it disproportionately affects skin of color populations; ALM accounts for only 0.8% to 1% of all melanomas in white populations, but it constitutes 4% to 58% of melanomas in ethnic populations and is the most common melanoma subtype among black Americans.2-5 Acral lentiginous melanoma also is associated with a worse prognosis compared to other subtypes, which may indicate a more aggressive biological nature6 but also may point toward socioeconomic and cultural barriers (eg, low income or education levels, lack of insurance, lower health literacy), leading to disparities in access to care and diagnosis at advanced stages.5
Similarly, the distribution of acral melanocytic nevi appears to demonstrate an association with ethnicity and skin pigmentation. Although skin of color patients have fewer nevi than non-Hispanic whites, the proportion of acral melanocytic nevi tends to be greater.6,7 Given its grim prognosis, accurately differentiating ALM from acral nevi is of utmost importance.
Diagnostic Challenges of Acral Lesions
Due to the unique nature of the surfaces of acral sites, melanocytic lesions on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus present many diagnostic challenges. It can be difficult to distinguish acral melanoma from benign lesions using the naked eye alone. Volar surfaces are characterized by the presence of dermatoglyphics, and pigment deposition along ridges and furrows create particular dermoscopic patterns exclusive to these sites.8 Thus, dermoscopy can be useful on acral surfaces, but the dermoscopic features are different from those on the rest of the body and must be learned separately.
In addition, nearly half of patients are unaware of their acral lesions.6 Acral surfaces may not always be examined by clinicians during total-body skin examinations, leading to further possibility of overlooking a lesion. Obtaining biopsies on glabrous skin or nails also is challenging because they can be more painful and hemostasis can be more difficult, especially in the nail. Acral melanomas also may be amelanotic, including those at subungual sites.
Dermoscopic Patterns of Acral Volar Skin
Dermoscopy is a useful noninvasive tool for distinguishing between benign and malignant acral melanocytic lesions, and its efficacy in improving diagnostic accuracy and decreasing unnecessary biopsies is well-established in the literature.13,14 Acral dermoscopy allows for visualization of pigment along the dermatoglyphics that constitute the characteristic dermoscopic patterns.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
The hallmark dermoscopic pattern and most important finding of ALM is the parallel ridge pattern, characterized by parallel linear pigmentation along the ridges of dermatoglyphics. In the early phases of malignancy, the pattern appears light brown and involves most of the lesion; as the tumor develops, increasing melanin production results in focal areas of the parallel ridge pattern with darker bands.15,16 The sensitivity and specificity of a parallel ridge pattern for diagnosing early ALM has been shown to be 86% and 99%, respectively.15,16
A pattern of irregular diffuse pigmentation also can be observed in more advanced ALM. Dermoscopy may reveal a structureless pattern (ie, lack of identifiable structures or patterns) in a background of tan-black coloration due to more exuberant melanocyte proliferation along the epidermis.15 Sensitivity and specificity of this dermoscopic finding for invasive lesions is high at 94% and 97%, respectively.16,17 Interestingly, once ALM lesions have advanced even further, conventional melanoma-associated structures (ie, blue-white veil, polymorphous blood vessels, ulceration, irregular dots/globules or streaks) or atypical forms of typically benign acral dermoscopic patterns may be observed.15
Per a 3-step diagnostic algorithm created by Koga and Saida,18 a suspected acral lesion should first be evaluated for a parallel ridge pattern to determine the need for biopsy, as it is seen in approximately two-thirds of ALMs.19 If no parallel ridge pattern is observed, the lesion should then be checked for any of the typical dermoscopic patterns seen in benign acral nevi (eg, parallel furrow, latticelike, or fibrillar patterns).18 The maximum diameter should be measured only if the lesion does not exhibit any of the typical dermoscopic patterns. If the lesion’s diameter is greater than 7 mm in diameter, it should be biopsied; if the diameter is less than 7 mm, it should have regular clinical and dermoscopic follow-up.18
In 2015, Lallas et al20 developed the BRAAFF checklist, a scoring system of 6 variables: blotches, ridge pattern, asymmetry of structures, asymmetry of colors, parallel furrow pattern, and fibrillar pattern. The checklist also was shown to substantially improve diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for ALM, with sensitivity and specificity at 93.1% and 86.7%, respectively.20
Acquired Acral Nevi
Three classic dermoscopic patterns are associated with acquired acral nevi: parallel furrow pattern, latticelike pattern, and fibrillar pattern.15,21 Approximately three-quarters of all acquired acral nevi exhibit one of these patterns, roughly half exhibiting parallel furrow with tan-brown bandlike pigmentation along dermatoglyphic grooves.16,17
Latticelike patterns also are characterized by brown parallel lines along the sulci of dermatoglyphics but additionally have multiple intersecting lines. Thus, this pattern can be considered a variant of the parallel furrow pattern.15 The crisscross markings can be predominantly found in the plantar arch.22 This dermoscopic pattern comprises 15% to 25% of all acral nevi.21
Fibrillar pattern accounts for 10% to 20% of all acral melanocytic nevi.21 Dermoscopically, these lesions demonstrate parallel filamentous streaks that cross dermatoglyphics obliquely. The fibrillar pattern is predominantly found on weight-bearing areas of the sole,22 which likely is explained by pressure causing slanting of melanin columns in the horny layer.23 The fibrillar pattern has been shown to be the benign acral dermoscopic pattern that is most commonly misdiagnosed, with higher reported rates of biopsy.24
Acral Congenital Melanocytic Nevi
Congenital melanocytic nevi (CMN) present at birth or appear during the first few weeks of life. Congenital melanocytic nevi can vary widely in size, shape, and color, and they are occasionally biopsied in cases of larger diameter or dermoscopic atypia to differentiate from melanoma.25 Congenital melanocytic nevi also can occur on acral volar surfaces. Possible dermoscopic patterns include parallel furrow or fibrillar patterns as well as a crista dotted pattern, defined as evenly spaced dots/globules on the ridges near the openings of eccrine ducts.26 A more commonly observed dermoscopic pattern in acral CMN is a combination of the crista dotted and parallel furrow patterns, known as the peas-in-a-pod pattern. Changes in the clinical appearance and dermoscopic features of an acral CMN are possible over time; some lesions also may fade with age.26
Final Thoughts
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a rare but potentially aggressive melanoma subtype that accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in patients with skin of color than in white patients. Dermoscopy of acral volar skin provides invaluable diagnostic information and allows for better management of acral melanocytic lesions. Dermoscopic patterns such as the parallel ridge, parallel furrow, latticelike, fibrillar, and peas-in-a-pod patterns are unique to acral sites and can be used to differentiate between ALMs, acquired nevi, or CMNs.
- Whiteman DC, Green AC, Olsen CM. The growing burden of invasive melanoma: projections of incidence rates and numbers of new cases in six susceptible populations through 2031. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:1161-1171.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Nakamura Y, Fujisawa Y. Diagnosis and management of acral lentiginous melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018;19:42.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ma S. Racial differences in six major subtypes of melanoma: descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:691.
- Madankumar R, Gumaste PV, Martires K, et al. Acral melanocytic lesions in the United States: prevalence, awareness, and dermoscopic patterns in skin-of-color and non-Hispanic white patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:724.e1-730.e1.
- Palicka GA, Rhodes AR. Acral melanocytic nevi: prevalence and distribution of gross morphologic features in white and black adults. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1085-1094.
- Thomas L, Phan A, Pralong P, et al. Special locations dermoscopy: facial, acral, and nail. Dermatol Clin. 2013;31:615-624.
- Gong HZ, Zheng HY, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma [published online January 21, 2019]. Melanoma Res. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571.
- Ise M, Yasuda F, Konohana I, et al. Acral melanoma with hyperkeratosis mimicking a pigmented wart. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:37-39.
- Serarslan G, Akçaly CM, Atik E. Acral lentiginous melanoma misdiagnosed as tinea pedis: a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:37-38.
- Gumaste P, Penn L, Cohen N, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the foot misdiagnosed as a traumatic ulcer. a cautionary case. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2015;105:189-194.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Chiarugi A, et al. Addition of dermoscopy to conventional naked-eye examination in melanoma screening: a randomized study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:683-689.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Crocetti E, et al. Improvement of malignant/benign ratio in excised melanocytic lesions in the ‘dermoscopy era’: a retrospective study 1997-2001. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:687-692.
- Saida T, Koga H, Uhara H. Key points in dermoscopic differentiation between early acral melanoma and acral nevus. J Dermatol. 2011;38:25-34.
- Ishihara Y, Saida T, Miyazaki A, et al. Early acral melanoma in situ: correlation between the parallel ridge pattern on dermoscopy and microscopic features. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:21-27.
- Saida T, Miyazaki A, Oguchi S, et al. Significance of dermoscopic patterns in detecting malignant melanoma on acral volar skin: results of a multicenter study in Japan. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1233-1238.
- Koga H, Saida T. Revised 3-step dermoscopic algorithm for the management of acral melanocytic lesions. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:741-743.
- Lallas A, Sgouros D, Zalaudek I, et al. Palmar and plantar melanomas differ for sex prevalence and tumor thickness but not for dermoscopic patterns. Melanoma Res. 2014;24:83-87.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Koga H, et al. The BRAAFF checklist: a new dermoscopic algorithm for diagnosing acral melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1041-1049.
- Saida T, Koga H. Dermoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi: their variations, changes, and significance. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1423-1426.
- Miyazaki A, Saida T, Koga H, et al. Anatomical and histopathological correlates of the dermoscopic patterns seen in melanocytic nevi on the sole: a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:230-236.
- Watanabe S, Sawada M, Ishizaki S, et al. Comparison of dermatoscopic images of acral lentiginous melanoma and acral melanocytic nevus occurring on body weight-bearing areas. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:47-50.
- Costello CM, Ghanavatian S, Temkit M, et al. Educational and practice gaps in the management of volar melanocytic lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:1450-1455.
- Alikhan A, Ibrahimi OA, Eisen DB. Congenital melanocytic nevi: where are we now? part I. clinical presentation, epidemiology, pathogenesis, histology, malignant transformation, and neurocutaneous melanosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:495.e1-495.e17; quiz 512-514.
- Minagawa A, Koga H, Saida T. Dermoscopic characteristics of congenital melanocytic nevi affecting acral volar skin. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:809-813.
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a rare subtype of melanoma that occurs on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus. Unlike more common types of melanoma, ALM occurs on sun-protected areas of the skin and has distinct clinical, histologic, and genetic features. Acral lentiginous melanoma accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in individuals with skin of color and has a worse prognosis and recurrence rate than other forms of melanoma.
Population Trends in Skin of Color
Much of the literature on malignant melanoma historically has involved non-Hispanic white patients, but the incidence in lighter-skinned populations has been increasing steadily over the last few decades.1 Although ALM can occur in any race, it disproportionately affects skin of color populations; ALM accounts for only 0.8% to 1% of all melanomas in white populations, but it constitutes 4% to 58% of melanomas in ethnic populations and is the most common melanoma subtype among black Americans.2-5 Acral lentiginous melanoma also is associated with a worse prognosis compared to other subtypes, which may indicate a more aggressive biological nature6 but also may point toward socioeconomic and cultural barriers (eg, low income or education levels, lack of insurance, lower health literacy), leading to disparities in access to care and diagnosis at advanced stages.5
Similarly, the distribution of acral melanocytic nevi appears to demonstrate an association with ethnicity and skin pigmentation. Although skin of color patients have fewer nevi than non-Hispanic whites, the proportion of acral melanocytic nevi tends to be greater.6,7 Given its grim prognosis, accurately differentiating ALM from acral nevi is of utmost importance.
Diagnostic Challenges of Acral Lesions
Due to the unique nature of the surfaces of acral sites, melanocytic lesions on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus present many diagnostic challenges. It can be difficult to distinguish acral melanoma from benign lesions using the naked eye alone. Volar surfaces are characterized by the presence of dermatoglyphics, and pigment deposition along ridges and furrows create particular dermoscopic patterns exclusive to these sites.8 Thus, dermoscopy can be useful on acral surfaces, but the dermoscopic features are different from those on the rest of the body and must be learned separately.
In addition, nearly half of patients are unaware of their acral lesions.6 Acral surfaces may not always be examined by clinicians during total-body skin examinations, leading to further possibility of overlooking a lesion. Obtaining biopsies on glabrous skin or nails also is challenging because they can be more painful and hemostasis can be more difficult, especially in the nail. Acral melanomas also may be amelanotic, including those at subungual sites.
Dermoscopic Patterns of Acral Volar Skin
Dermoscopy is a useful noninvasive tool for distinguishing between benign and malignant acral melanocytic lesions, and its efficacy in improving diagnostic accuracy and decreasing unnecessary biopsies is well-established in the literature.13,14 Acral dermoscopy allows for visualization of pigment along the dermatoglyphics that constitute the characteristic dermoscopic patterns.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
The hallmark dermoscopic pattern and most important finding of ALM is the parallel ridge pattern, characterized by parallel linear pigmentation along the ridges of dermatoglyphics. In the early phases of malignancy, the pattern appears light brown and involves most of the lesion; as the tumor develops, increasing melanin production results in focal areas of the parallel ridge pattern with darker bands.15,16 The sensitivity and specificity of a parallel ridge pattern for diagnosing early ALM has been shown to be 86% and 99%, respectively.15,16
A pattern of irregular diffuse pigmentation also can be observed in more advanced ALM. Dermoscopy may reveal a structureless pattern (ie, lack of identifiable structures or patterns) in a background of tan-black coloration due to more exuberant melanocyte proliferation along the epidermis.15 Sensitivity and specificity of this dermoscopic finding for invasive lesions is high at 94% and 97%, respectively.16,17 Interestingly, once ALM lesions have advanced even further, conventional melanoma-associated structures (ie, blue-white veil, polymorphous blood vessels, ulceration, irregular dots/globules or streaks) or atypical forms of typically benign acral dermoscopic patterns may be observed.15
Per a 3-step diagnostic algorithm created by Koga and Saida,18 a suspected acral lesion should first be evaluated for a parallel ridge pattern to determine the need for biopsy, as it is seen in approximately two-thirds of ALMs.19 If no parallel ridge pattern is observed, the lesion should then be checked for any of the typical dermoscopic patterns seen in benign acral nevi (eg, parallel furrow, latticelike, or fibrillar patterns).18 The maximum diameter should be measured only if the lesion does not exhibit any of the typical dermoscopic patterns. If the lesion’s diameter is greater than 7 mm in diameter, it should be biopsied; if the diameter is less than 7 mm, it should have regular clinical and dermoscopic follow-up.18
In 2015, Lallas et al20 developed the BRAAFF checklist, a scoring system of 6 variables: blotches, ridge pattern, asymmetry of structures, asymmetry of colors, parallel furrow pattern, and fibrillar pattern. The checklist also was shown to substantially improve diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for ALM, with sensitivity and specificity at 93.1% and 86.7%, respectively.20
Acquired Acral Nevi
Three classic dermoscopic patterns are associated with acquired acral nevi: parallel furrow pattern, latticelike pattern, and fibrillar pattern.15,21 Approximately three-quarters of all acquired acral nevi exhibit one of these patterns, roughly half exhibiting parallel furrow with tan-brown bandlike pigmentation along dermatoglyphic grooves.16,17
Latticelike patterns also are characterized by brown parallel lines along the sulci of dermatoglyphics but additionally have multiple intersecting lines. Thus, this pattern can be considered a variant of the parallel furrow pattern.15 The crisscross markings can be predominantly found in the plantar arch.22 This dermoscopic pattern comprises 15% to 25% of all acral nevi.21
Fibrillar pattern accounts for 10% to 20% of all acral melanocytic nevi.21 Dermoscopically, these lesions demonstrate parallel filamentous streaks that cross dermatoglyphics obliquely. The fibrillar pattern is predominantly found on weight-bearing areas of the sole,22 which likely is explained by pressure causing slanting of melanin columns in the horny layer.23 The fibrillar pattern has been shown to be the benign acral dermoscopic pattern that is most commonly misdiagnosed, with higher reported rates of biopsy.24
Acral Congenital Melanocytic Nevi
Congenital melanocytic nevi (CMN) present at birth or appear during the first few weeks of life. Congenital melanocytic nevi can vary widely in size, shape, and color, and they are occasionally biopsied in cases of larger diameter or dermoscopic atypia to differentiate from melanoma.25 Congenital melanocytic nevi also can occur on acral volar surfaces. Possible dermoscopic patterns include parallel furrow or fibrillar patterns as well as a crista dotted pattern, defined as evenly spaced dots/globules on the ridges near the openings of eccrine ducts.26 A more commonly observed dermoscopic pattern in acral CMN is a combination of the crista dotted and parallel furrow patterns, known as the peas-in-a-pod pattern. Changes in the clinical appearance and dermoscopic features of an acral CMN are possible over time; some lesions also may fade with age.26
Final Thoughts
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a rare but potentially aggressive melanoma subtype that accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in patients with skin of color than in white patients. Dermoscopy of acral volar skin provides invaluable diagnostic information and allows for better management of acral melanocytic lesions. Dermoscopic patterns such as the parallel ridge, parallel furrow, latticelike, fibrillar, and peas-in-a-pod patterns are unique to acral sites and can be used to differentiate between ALMs, acquired nevi, or CMNs.
Acral lentiginous melanoma (ALM) is a rare subtype of melanoma that occurs on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus. Unlike more common types of melanoma, ALM occurs on sun-protected areas of the skin and has distinct clinical, histologic, and genetic features. Acral lentiginous melanoma accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in individuals with skin of color and has a worse prognosis and recurrence rate than other forms of melanoma.
Population Trends in Skin of Color
Much of the literature on malignant melanoma historically has involved non-Hispanic white patients, but the incidence in lighter-skinned populations has been increasing steadily over the last few decades.1 Although ALM can occur in any race, it disproportionately affects skin of color populations; ALM accounts for only 0.8% to 1% of all melanomas in white populations, but it constitutes 4% to 58% of melanomas in ethnic populations and is the most common melanoma subtype among black Americans.2-5 Acral lentiginous melanoma also is associated with a worse prognosis compared to other subtypes, which may indicate a more aggressive biological nature6 but also may point toward socioeconomic and cultural barriers (eg, low income or education levels, lack of insurance, lower health literacy), leading to disparities in access to care and diagnosis at advanced stages.5
Similarly, the distribution of acral melanocytic nevi appears to demonstrate an association with ethnicity and skin pigmentation. Although skin of color patients have fewer nevi than non-Hispanic whites, the proportion of acral melanocytic nevi tends to be greater.6,7 Given its grim prognosis, accurately differentiating ALM from acral nevi is of utmost importance.
Diagnostic Challenges of Acral Lesions
Due to the unique nature of the surfaces of acral sites, melanocytic lesions on the palms, soles, and nail apparatus present many diagnostic challenges. It can be difficult to distinguish acral melanoma from benign lesions using the naked eye alone. Volar surfaces are characterized by the presence of dermatoglyphics, and pigment deposition along ridges and furrows create particular dermoscopic patterns exclusive to these sites.8 Thus, dermoscopy can be useful on acral surfaces, but the dermoscopic features are different from those on the rest of the body and must be learned separately.
In addition, nearly half of patients are unaware of their acral lesions.6 Acral surfaces may not always be examined by clinicians during total-body skin examinations, leading to further possibility of overlooking a lesion. Obtaining biopsies on glabrous skin or nails also is challenging because they can be more painful and hemostasis can be more difficult, especially in the nail. Acral melanomas also may be amelanotic, including those at subungual sites.
Dermoscopic Patterns of Acral Volar Skin
Dermoscopy is a useful noninvasive tool for distinguishing between benign and malignant acral melanocytic lesions, and its efficacy in improving diagnostic accuracy and decreasing unnecessary biopsies is well-established in the literature.13,14 Acral dermoscopy allows for visualization of pigment along the dermatoglyphics that constitute the characteristic dermoscopic patterns.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
The hallmark dermoscopic pattern and most important finding of ALM is the parallel ridge pattern, characterized by parallel linear pigmentation along the ridges of dermatoglyphics. In the early phases of malignancy, the pattern appears light brown and involves most of the lesion; as the tumor develops, increasing melanin production results in focal areas of the parallel ridge pattern with darker bands.15,16 The sensitivity and specificity of a parallel ridge pattern for diagnosing early ALM has been shown to be 86% and 99%, respectively.15,16
A pattern of irregular diffuse pigmentation also can be observed in more advanced ALM. Dermoscopy may reveal a structureless pattern (ie, lack of identifiable structures or patterns) in a background of tan-black coloration due to more exuberant melanocyte proliferation along the epidermis.15 Sensitivity and specificity of this dermoscopic finding for invasive lesions is high at 94% and 97%, respectively.16,17 Interestingly, once ALM lesions have advanced even further, conventional melanoma-associated structures (ie, blue-white veil, polymorphous blood vessels, ulceration, irregular dots/globules or streaks) or atypical forms of typically benign acral dermoscopic patterns may be observed.15
Per a 3-step diagnostic algorithm created by Koga and Saida,18 a suspected acral lesion should first be evaluated for a parallel ridge pattern to determine the need for biopsy, as it is seen in approximately two-thirds of ALMs.19 If no parallel ridge pattern is observed, the lesion should then be checked for any of the typical dermoscopic patterns seen in benign acral nevi (eg, parallel furrow, latticelike, or fibrillar patterns).18 The maximum diameter should be measured only if the lesion does not exhibit any of the typical dermoscopic patterns. If the lesion’s diameter is greater than 7 mm in diameter, it should be biopsied; if the diameter is less than 7 mm, it should have regular clinical and dermoscopic follow-up.18
In 2015, Lallas et al20 developed the BRAAFF checklist, a scoring system of 6 variables: blotches, ridge pattern, asymmetry of structures, asymmetry of colors, parallel furrow pattern, and fibrillar pattern. The checklist also was shown to substantially improve diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for ALM, with sensitivity and specificity at 93.1% and 86.7%, respectively.20
Acquired Acral Nevi
Three classic dermoscopic patterns are associated with acquired acral nevi: parallel furrow pattern, latticelike pattern, and fibrillar pattern.15,21 Approximately three-quarters of all acquired acral nevi exhibit one of these patterns, roughly half exhibiting parallel furrow with tan-brown bandlike pigmentation along dermatoglyphic grooves.16,17
Latticelike patterns also are characterized by brown parallel lines along the sulci of dermatoglyphics but additionally have multiple intersecting lines. Thus, this pattern can be considered a variant of the parallel furrow pattern.15 The crisscross markings can be predominantly found in the plantar arch.22 This dermoscopic pattern comprises 15% to 25% of all acral nevi.21
Fibrillar pattern accounts for 10% to 20% of all acral melanocytic nevi.21 Dermoscopically, these lesions demonstrate parallel filamentous streaks that cross dermatoglyphics obliquely. The fibrillar pattern is predominantly found on weight-bearing areas of the sole,22 which likely is explained by pressure causing slanting of melanin columns in the horny layer.23 The fibrillar pattern has been shown to be the benign acral dermoscopic pattern that is most commonly misdiagnosed, with higher reported rates of biopsy.24
Acral Congenital Melanocytic Nevi
Congenital melanocytic nevi (CMN) present at birth or appear during the first few weeks of life. Congenital melanocytic nevi can vary widely in size, shape, and color, and they are occasionally biopsied in cases of larger diameter or dermoscopic atypia to differentiate from melanoma.25 Congenital melanocytic nevi also can occur on acral volar surfaces. Possible dermoscopic patterns include parallel furrow or fibrillar patterns as well as a crista dotted pattern, defined as evenly spaced dots/globules on the ridges near the openings of eccrine ducts.26 A more commonly observed dermoscopic pattern in acral CMN is a combination of the crista dotted and parallel furrow patterns, known as the peas-in-a-pod pattern. Changes in the clinical appearance and dermoscopic features of an acral CMN are possible over time; some lesions also may fade with age.26
Final Thoughts
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a rare but potentially aggressive melanoma subtype that accounts for a larger proportion of melanomas in patients with skin of color than in white patients. Dermoscopy of acral volar skin provides invaluable diagnostic information and allows for better management of acral melanocytic lesions. Dermoscopic patterns such as the parallel ridge, parallel furrow, latticelike, fibrillar, and peas-in-a-pod patterns are unique to acral sites and can be used to differentiate between ALMs, acquired nevi, or CMNs.
- Whiteman DC, Green AC, Olsen CM. The growing burden of invasive melanoma: projections of incidence rates and numbers of new cases in six susceptible populations through 2031. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:1161-1171.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Nakamura Y, Fujisawa Y. Diagnosis and management of acral lentiginous melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018;19:42.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ma S. Racial differences in six major subtypes of melanoma: descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:691.
- Madankumar R, Gumaste PV, Martires K, et al. Acral melanocytic lesions in the United States: prevalence, awareness, and dermoscopic patterns in skin-of-color and non-Hispanic white patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:724.e1-730.e1.
- Palicka GA, Rhodes AR. Acral melanocytic nevi: prevalence and distribution of gross morphologic features in white and black adults. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1085-1094.
- Thomas L, Phan A, Pralong P, et al. Special locations dermoscopy: facial, acral, and nail. Dermatol Clin. 2013;31:615-624.
- Gong HZ, Zheng HY, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma [published online January 21, 2019]. Melanoma Res. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571.
- Ise M, Yasuda F, Konohana I, et al. Acral melanoma with hyperkeratosis mimicking a pigmented wart. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:37-39.
- Serarslan G, Akçaly CM, Atik E. Acral lentiginous melanoma misdiagnosed as tinea pedis: a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:37-38.
- Gumaste P, Penn L, Cohen N, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the foot misdiagnosed as a traumatic ulcer. a cautionary case. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2015;105:189-194.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Chiarugi A, et al. Addition of dermoscopy to conventional naked-eye examination in melanoma screening: a randomized study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:683-689.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Crocetti E, et al. Improvement of malignant/benign ratio in excised melanocytic lesions in the ‘dermoscopy era’: a retrospective study 1997-2001. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:687-692.
- Saida T, Koga H, Uhara H. Key points in dermoscopic differentiation between early acral melanoma and acral nevus. J Dermatol. 2011;38:25-34.
- Ishihara Y, Saida T, Miyazaki A, et al. Early acral melanoma in situ: correlation between the parallel ridge pattern on dermoscopy and microscopic features. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:21-27.
- Saida T, Miyazaki A, Oguchi S, et al. Significance of dermoscopic patterns in detecting malignant melanoma on acral volar skin: results of a multicenter study in Japan. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1233-1238.
- Koga H, Saida T. Revised 3-step dermoscopic algorithm for the management of acral melanocytic lesions. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:741-743.
- Lallas A, Sgouros D, Zalaudek I, et al. Palmar and plantar melanomas differ for sex prevalence and tumor thickness but not for dermoscopic patterns. Melanoma Res. 2014;24:83-87.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Koga H, et al. The BRAAFF checklist: a new dermoscopic algorithm for diagnosing acral melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1041-1049.
- Saida T, Koga H. Dermoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi: their variations, changes, and significance. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1423-1426.
- Miyazaki A, Saida T, Koga H, et al. Anatomical and histopathological correlates of the dermoscopic patterns seen in melanocytic nevi on the sole: a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:230-236.
- Watanabe S, Sawada M, Ishizaki S, et al. Comparison of dermatoscopic images of acral lentiginous melanoma and acral melanocytic nevus occurring on body weight-bearing areas. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:47-50.
- Costello CM, Ghanavatian S, Temkit M, et al. Educational and practice gaps in the management of volar melanocytic lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:1450-1455.
- Alikhan A, Ibrahimi OA, Eisen DB. Congenital melanocytic nevi: where are we now? part I. clinical presentation, epidemiology, pathogenesis, histology, malignant transformation, and neurocutaneous melanosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:495.e1-495.e17; quiz 512-514.
- Minagawa A, Koga H, Saida T. Dermoscopic characteristics of congenital melanocytic nevi affecting acral volar skin. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:809-813.
- Whiteman DC, Green AC, Olsen CM. The growing burden of invasive melanoma: projections of incidence rates and numbers of new cases in six susceptible populations through 2031. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:1161-1171.
- Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, McMaster ML, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:427-434.
- Nakamura Y, Fujisawa Y. Diagnosis and management of acral lentiginous melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018;19:42.
- Cormier JN, Xing Y, Ding M, et al. Ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1907-1914.
- Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ma S. Racial differences in six major subtypes of melanoma: descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:691.
- Madankumar R, Gumaste PV, Martires K, et al. Acral melanocytic lesions in the United States: prevalence, awareness, and dermoscopic patterns in skin-of-color and non-Hispanic white patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:724.e1-730.e1.
- Palicka GA, Rhodes AR. Acral melanocytic nevi: prevalence and distribution of gross morphologic features in white and black adults. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1085-1094.
- Thomas L, Phan A, Pralong P, et al. Special locations dermoscopy: facial, acral, and nail. Dermatol Clin. 2013;31:615-624.
- Gong HZ, Zheng HY, Li J. Amelanotic melanoma [published online January 21, 2019]. Melanoma Res. doi:10.1097/CMR.0000000000000571.
- Ise M, Yasuda F, Konohana I, et al. Acral melanoma with hyperkeratosis mimicking a pigmented wart. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013;3:37-39.
- Serarslan G, Akçaly CM, Atik E. Acral lentiginous melanoma misdiagnosed as tinea pedis: a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:37-38.
- Gumaste P, Penn L, Cohen N, et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma of the foot misdiagnosed as a traumatic ulcer. a cautionary case. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2015;105:189-194.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Chiarugi A, et al. Addition of dermoscopy to conventional naked-eye examination in melanoma screening: a randomized study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:683-689.
- Carli P, de Giorgi V, Crocetti E, et al. Improvement of malignant/benign ratio in excised melanocytic lesions in the ‘dermoscopy era’: a retrospective study 1997-2001. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:687-692.
- Saida T, Koga H, Uhara H. Key points in dermoscopic differentiation between early acral melanoma and acral nevus. J Dermatol. 2011;38:25-34.
- Ishihara Y, Saida T, Miyazaki A, et al. Early acral melanoma in situ: correlation between the parallel ridge pattern on dermoscopy and microscopic features. Am J Dermatopathol. 2006;28:21-27.
- Saida T, Miyazaki A, Oguchi S, et al. Significance of dermoscopic patterns in detecting malignant melanoma on acral volar skin: results of a multicenter study in Japan. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1233-1238.
- Koga H, Saida T. Revised 3-step dermoscopic algorithm for the management of acral melanocytic lesions. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:741-743.
- Lallas A, Sgouros D, Zalaudek I, et al. Palmar and plantar melanomas differ for sex prevalence and tumor thickness but not for dermoscopic patterns. Melanoma Res. 2014;24:83-87.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Koga H, et al. The BRAAFF checklist: a new dermoscopic algorithm for diagnosing acral melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173:1041-1049.
- Saida T, Koga H. Dermoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi: their variations, changes, and significance. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1423-1426.
- Miyazaki A, Saida T, Koga H, et al. Anatomical and histopathological correlates of the dermoscopic patterns seen in melanocytic nevi on the sole: a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:230-236.
- Watanabe S, Sawada M, Ishizaki S, et al. Comparison of dermatoscopic images of acral lentiginous melanoma and acral melanocytic nevus occurring on body weight-bearing areas. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:47-50.
- Costello CM, Ghanavatian S, Temkit M, et al. Educational and practice gaps in the management of volar melanocytic lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:1450-1455.
- Alikhan A, Ibrahimi OA, Eisen DB. Congenital melanocytic nevi: where are we now? part I. clinical presentation, epidemiology, pathogenesis, histology, malignant transformation, and neurocutaneous melanosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:495.e1-495.e17; quiz 512-514.
- Minagawa A, Koga H, Saida T. Dermoscopic characteristics of congenital melanocytic nevi affecting acral volar skin. Arch Dermatol. 2011;147:809-813.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be familiar with common dermoscopic patterns seen at acral sites in patients with skin of color as well as the most up-to-date diagnostic algorithms.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma should be strongly suspected if dermoscopy reveals a parallel ridge pattern or if dermoscopy of volar skin reveals a lack of typical dermoscopic patterns in lesions with a diameter greater than 7 mm.
Acute-Onset Alopecia
The Diagnosis: Thallium-Induced Alopecia
At the time of presentation, a punch biopsy specimen of the scalp revealed nonscarring alopecia with increased catagen hairs; follicular miniaturization; peribulbar lymphoid infiltrates; and fibrous tract remnants containing melanin, lymphocytes, and occasional mast cells (Figure 1). The differential diagnosis included alopecia areata, syphilis, and toxin-mediated anagen effluvium (AE). Given the abrupt onset affecting multiple individuals in an industrial environment, heavy metal poisoning was suspected. Blood and urine testing was negative, but a few months had elapsed since exposure. Several months after his initial presentation, the patient reported problems with his teeth, thin brittle nails, and resolution of the visual changes. Photographs sent by the patient revealed darkening and degeneration of the gingival margin (Figure 2).
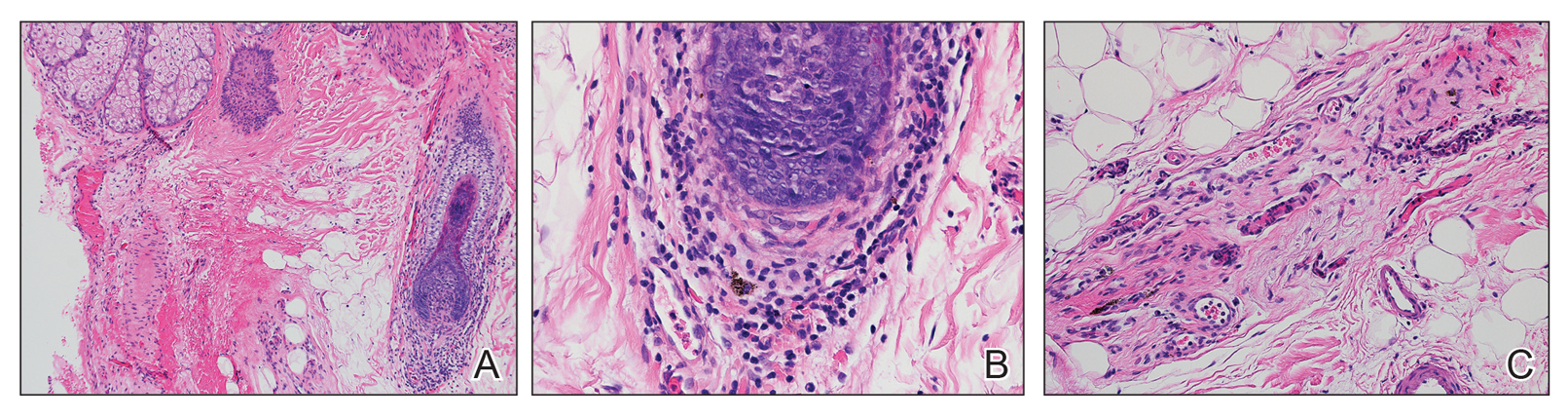
Environmental review revealed the patient was working on a demolition site of a 150-year-old electrical plant near a river. Inundation of rainfall caused a river swell and subsequent flooding of the work site. The patient reported working for more than 2 months in knee-deep muddy water, and he noted that water for consumption and showers was procured on-site from a well-based source that may have been contaminated by the floodwaters.
Acute nonscarring alopecia can be an AE or telogen effluvium (TE), also known as telogen defluvium. The key distinguishing factor is the mode of injury.1 In TE, medications, stress, hormonal shifts, or inflammation induce a synchronized and abrupt transition of hairs from anagen phase to catagen phase, a committed step that then must fully cycle through the telogen phase, culminating in the simultaneous shedding of numerous telogen hairs approximately 3 to 4 months later. Conversely, AE is caused by a sudden insult to the metabolic machinery of the hair matrix. Affected follicles rapidly produce thinner weaker shafts yielding Pohl-Pinkus constrictions or pencil point-shaped fractures that shed approximately 1 to 2 months after injury. The 10% of scalp hairs in the resting telogen phase have no matrix and thus are unaffected. Some etiologies can cause either AE or TE, depending on the dose and intensity of the insult. Common causes of AE include alopecia areata and syphilis, both consisting of abrupt severe bulbar inflammation.1 Other causes include chemotherapy, particularly antimetabolites, alkylating agents, and mitotic inhibitors; radiation; medications (eg, isoniazid); severe protein malnutrition; toxic chemicals (eg, boron/boric acid); and heavy metals (eg, thallium, mercury).
Thallium is one of the most common causes of heavy metal poisoning and is particularly dangerous due to its colorless, tasteless, and odorless characteristics. Although its common use as a rodenticide has dramatically decreased in the United States after it was banned in 1965, it is still used in this fashion in other countries and has a notable industrial presence, particularly in electronics, superconductors, and low-temperature thermometers. Accidental poisoning of a graduate chemistry student during copper research has been reported,2 highlighting that thallium can be inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Thallium is even present in mycoplasma agar plates, the ingestion of which has resulted in poisoning.3
Systemic symptoms of thallium poisoning include somnolence, weakness, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tachycardia, hypertension, and polyneuropathy.4-7 Neuropathy often manifests as painful acral dysesthesia and paresthesia, perioral numbness, optic neuropathy causing visual changes, and encephalopathy. Cutaneous findings include diffuse alopecia of the scalp and eyebrows, perioral dermatitis, glossitis, diffuse hyperpigmentation, oral hyperpigmentation (often as a stippled lead line along the gingival margin with subsequent alveolar damage and resorption), melanonychia, palmoplantar keratoderma, acneform or pustular eruption, and nail changes including Mees lines.2,4,5,7-9 Rarely, major organ failure and death may result.10
Toxin panels may not include thallium, and urine and serum tests may be negative if too much time has transpired since the acute exposure. Hair or nail analysis has proved useful in subacute cases11; however, most laboratories require a pencil-thick segment of hair cut at the roots and bundled, weighing at least 500 mg. Thallium poisoning is treated with activated charcoal, Prussian blue, and blood purification therapies (eg, hemodialysis, hemoperfusion, hemofiltration).4,7 Cutaneous findings typically resolve, but neuropathic changes may persist.
- Sperling LC, Cowper SE, Knopp EA. An Atlas of Hair Pathology With Clinical Correlations. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Campbell C, Bahrami S, Owen C. Anagen effluvium caused by thallium poisoning. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:724-726.
- Puschner B, Basso MM. Graham TW. Thallium toxicosis in a dog consequent to ingestion of Mycoplasma agar plates. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012;24:227-230.
- Sojáková M, Zigrai M, Karaman A, et al. Thallium intoxication: case report. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36:311-315.
- Lu Cl, Huang CC, Chang YC, et al. Short-term thallium intoxication: dermatological findings correlated with thallium concentration. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:93-98.
- Liu EM, Rajagopal R, Grand MG. Optic nerve atrophy and hair loss in a young man. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015;133:1469-1470.
- Zhang HT, Qiao BP, Liu BP, et al. Study on the treatment of acute thallium poisoning. Am J Med Sci. 2014;347:377-381.
- Misra UK, Kalita J, Yadav RK, et al. Thallium poisoning: emphasis on early diagnosis and response to haemodialysis. Postgrad Med J. 2003;79:103-105.
- Tromme I, Van Neste D, Dobbelaere F, et al. Skin signs in the diagnosis of thallium poisoning. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:321-325.
- Li S, Huang W, Duan Y, et al. Human fatality due to thallium poisoning: autopsy, microscopy, and mass spectrometry assays. J Forensic Sci. 2015;60:247-251.
- Daniel CR 3rd, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. The nail and hair in forensic science. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:258-261.
The Diagnosis: Thallium-Induced Alopecia
At the time of presentation, a punch biopsy specimen of the scalp revealed nonscarring alopecia with increased catagen hairs; follicular miniaturization; peribulbar lymphoid infiltrates; and fibrous tract remnants containing melanin, lymphocytes, and occasional mast cells (Figure 1). The differential diagnosis included alopecia areata, syphilis, and toxin-mediated anagen effluvium (AE). Given the abrupt onset affecting multiple individuals in an industrial environment, heavy metal poisoning was suspected. Blood and urine testing was negative, but a few months had elapsed since exposure. Several months after his initial presentation, the patient reported problems with his teeth, thin brittle nails, and resolution of the visual changes. Photographs sent by the patient revealed darkening and degeneration of the gingival margin (Figure 2).


Environmental review revealed the patient was working on a demolition site of a 150-year-old electrical plant near a river. Inundation of rainfall caused a river swell and subsequent flooding of the work site. The patient reported working for more than 2 months in knee-deep muddy water, and he noted that water for consumption and showers was procured on-site from a well-based source that may have been contaminated by the floodwaters.
Acute nonscarring alopecia can be an AE or telogen effluvium (TE), also known as telogen defluvium. The key distinguishing factor is the mode of injury.1 In TE, medications, stress, hormonal shifts, or inflammation induce a synchronized and abrupt transition of hairs from anagen phase to catagen phase, a committed step that then must fully cycle through the telogen phase, culminating in the simultaneous shedding of numerous telogen hairs approximately 3 to 4 months later. Conversely, AE is caused by a sudden insult to the metabolic machinery of the hair matrix. Affected follicles rapidly produce thinner weaker shafts yielding Pohl-Pinkus constrictions or pencil point-shaped fractures that shed approximately 1 to 2 months after injury. The 10% of scalp hairs in the resting telogen phase have no matrix and thus are unaffected. Some etiologies can cause either AE or TE, depending on the dose and intensity of the insult. Common causes of AE include alopecia areata and syphilis, both consisting of abrupt severe bulbar inflammation.1 Other causes include chemotherapy, particularly antimetabolites, alkylating agents, and mitotic inhibitors; radiation; medications (eg, isoniazid); severe protein malnutrition; toxic chemicals (eg, boron/boric acid); and heavy metals (eg, thallium, mercury).
Thallium is one of the most common causes of heavy metal poisoning and is particularly dangerous due to its colorless, tasteless, and odorless characteristics. Although its common use as a rodenticide has dramatically decreased in the United States after it was banned in 1965, it is still used in this fashion in other countries and has a notable industrial presence, particularly in electronics, superconductors, and low-temperature thermometers. Accidental poisoning of a graduate chemistry student during copper research has been reported,2 highlighting that thallium can be inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Thallium is even present in mycoplasma agar plates, the ingestion of which has resulted in poisoning.3
Systemic symptoms of thallium poisoning include somnolence, weakness, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tachycardia, hypertension, and polyneuropathy.4-7 Neuropathy often manifests as painful acral dysesthesia and paresthesia, perioral numbness, optic neuropathy causing visual changes, and encephalopathy. Cutaneous findings include diffuse alopecia of the scalp and eyebrows, perioral dermatitis, glossitis, diffuse hyperpigmentation, oral hyperpigmentation (often as a stippled lead line along the gingival margin with subsequent alveolar damage and resorption), melanonychia, palmoplantar keratoderma, acneform or pustular eruption, and nail changes including Mees lines.2,4,5,7-9 Rarely, major organ failure and death may result.10
Toxin panels may not include thallium, and urine and serum tests may be negative if too much time has transpired since the acute exposure. Hair or nail analysis has proved useful in subacute cases11; however, most laboratories require a pencil-thick segment of hair cut at the roots and bundled, weighing at least 500 mg. Thallium poisoning is treated with activated charcoal, Prussian blue, and blood purification therapies (eg, hemodialysis, hemoperfusion, hemofiltration).4,7 Cutaneous findings typically resolve, but neuropathic changes may persist.
The Diagnosis: Thallium-Induced Alopecia
At the time of presentation, a punch biopsy specimen of the scalp revealed nonscarring alopecia with increased catagen hairs; follicular miniaturization; peribulbar lymphoid infiltrates; and fibrous tract remnants containing melanin, lymphocytes, and occasional mast cells (Figure 1). The differential diagnosis included alopecia areata, syphilis, and toxin-mediated anagen effluvium (AE). Given the abrupt onset affecting multiple individuals in an industrial environment, heavy metal poisoning was suspected. Blood and urine testing was negative, but a few months had elapsed since exposure. Several months after his initial presentation, the patient reported problems with his teeth, thin brittle nails, and resolution of the visual changes. Photographs sent by the patient revealed darkening and degeneration of the gingival margin (Figure 2).


Environmental review revealed the patient was working on a demolition site of a 150-year-old electrical plant near a river. Inundation of rainfall caused a river swell and subsequent flooding of the work site. The patient reported working for more than 2 months in knee-deep muddy water, and he noted that water for consumption and showers was procured on-site from a well-based source that may have been contaminated by the floodwaters.
Acute nonscarring alopecia can be an AE or telogen effluvium (TE), also known as telogen defluvium. The key distinguishing factor is the mode of injury.1 In TE, medications, stress, hormonal shifts, or inflammation induce a synchronized and abrupt transition of hairs from anagen phase to catagen phase, a committed step that then must fully cycle through the telogen phase, culminating in the simultaneous shedding of numerous telogen hairs approximately 3 to 4 months later. Conversely, AE is caused by a sudden insult to the metabolic machinery of the hair matrix. Affected follicles rapidly produce thinner weaker shafts yielding Pohl-Pinkus constrictions or pencil point-shaped fractures that shed approximately 1 to 2 months after injury. The 10% of scalp hairs in the resting telogen phase have no matrix and thus are unaffected. Some etiologies can cause either AE or TE, depending on the dose and intensity of the insult. Common causes of AE include alopecia areata and syphilis, both consisting of abrupt severe bulbar inflammation.1 Other causes include chemotherapy, particularly antimetabolites, alkylating agents, and mitotic inhibitors; radiation; medications (eg, isoniazid); severe protein malnutrition; toxic chemicals (eg, boron/boric acid); and heavy metals (eg, thallium, mercury).
Thallium is one of the most common causes of heavy metal poisoning and is particularly dangerous due to its colorless, tasteless, and odorless characteristics. Although its common use as a rodenticide has dramatically decreased in the United States after it was banned in 1965, it is still used in this fashion in other countries and has a notable industrial presence, particularly in electronics, superconductors, and low-temperature thermometers. Accidental poisoning of a graduate chemistry student during copper research has been reported,2 highlighting that thallium can be inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Thallium is even present in mycoplasma agar plates, the ingestion of which has resulted in poisoning.3
Systemic symptoms of thallium poisoning include somnolence, weakness, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tachycardia, hypertension, and polyneuropathy.4-7 Neuropathy often manifests as painful acral dysesthesia and paresthesia, perioral numbness, optic neuropathy causing visual changes, and encephalopathy. Cutaneous findings include diffuse alopecia of the scalp and eyebrows, perioral dermatitis, glossitis, diffuse hyperpigmentation, oral hyperpigmentation (often as a stippled lead line along the gingival margin with subsequent alveolar damage and resorption), melanonychia, palmoplantar keratoderma, acneform or pustular eruption, and nail changes including Mees lines.2,4,5,7-9 Rarely, major organ failure and death may result.10
Toxin panels may not include thallium, and urine and serum tests may be negative if too much time has transpired since the acute exposure. Hair or nail analysis has proved useful in subacute cases11; however, most laboratories require a pencil-thick segment of hair cut at the roots and bundled, weighing at least 500 mg. Thallium poisoning is treated with activated charcoal, Prussian blue, and blood purification therapies (eg, hemodialysis, hemoperfusion, hemofiltration).4,7 Cutaneous findings typically resolve, but neuropathic changes may persist.
- Sperling LC, Cowper SE, Knopp EA. An Atlas of Hair Pathology With Clinical Correlations. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Campbell C, Bahrami S, Owen C. Anagen effluvium caused by thallium poisoning. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:724-726.
- Puschner B, Basso MM. Graham TW. Thallium toxicosis in a dog consequent to ingestion of Mycoplasma agar plates. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012;24:227-230.
- Sojáková M, Zigrai M, Karaman A, et al. Thallium intoxication: case report. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36:311-315.
- Lu Cl, Huang CC, Chang YC, et al. Short-term thallium intoxication: dermatological findings correlated with thallium concentration. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:93-98.
- Liu EM, Rajagopal R, Grand MG. Optic nerve atrophy and hair loss in a young man. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015;133:1469-1470.
- Zhang HT, Qiao BP, Liu BP, et al. Study on the treatment of acute thallium poisoning. Am J Med Sci. 2014;347:377-381.
- Misra UK, Kalita J, Yadav RK, et al. Thallium poisoning: emphasis on early diagnosis and response to haemodialysis. Postgrad Med J. 2003;79:103-105.
- Tromme I, Van Neste D, Dobbelaere F, et al. Skin signs in the diagnosis of thallium poisoning. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:321-325.
- Li S, Huang W, Duan Y, et al. Human fatality due to thallium poisoning: autopsy, microscopy, and mass spectrometry assays. J Forensic Sci. 2015;60:247-251.
- Daniel CR 3rd, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. The nail and hair in forensic science. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:258-261.
- Sperling LC, Cowper SE, Knopp EA. An Atlas of Hair Pathology With Clinical Correlations. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Campbell C, Bahrami S, Owen C. Anagen effluvium caused by thallium poisoning. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:724-726.
- Puschner B, Basso MM. Graham TW. Thallium toxicosis in a dog consequent to ingestion of Mycoplasma agar plates. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012;24:227-230.
- Sojáková M, Zigrai M, Karaman A, et al. Thallium intoxication: case report. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36:311-315.
- Lu Cl, Huang CC, Chang YC, et al. Short-term thallium intoxication: dermatological findings correlated with thallium concentration. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:93-98.
- Liu EM, Rajagopal R, Grand MG. Optic nerve atrophy and hair loss in a young man. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015;133:1469-1470.
- Zhang HT, Qiao BP, Liu BP, et al. Study on the treatment of acute thallium poisoning. Am J Med Sci. 2014;347:377-381.
- Misra UK, Kalita J, Yadav RK, et al. Thallium poisoning: emphasis on early diagnosis and response to haemodialysis. Postgrad Med J. 2003;79:103-105.
- Tromme I, Van Neste D, Dobbelaere F, et al. Skin signs in the diagnosis of thallium poisoning. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:321-325.
- Li S, Huang W, Duan Y, et al. Human fatality due to thallium poisoning: autopsy, microscopy, and mass spectrometry assays. J Forensic Sci. 2015;60:247-251.
- Daniel CR 3rd, Piraccini BM, Tosti A. The nail and hair in forensic science. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:258-261.

A previously healthy 45-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with abrupt onset of patchy, progressively worsening alopecia of the scalp as well as nausea with emesis and blurry vision of a few weeks' duration. All symptoms were temporally associated with a new demolition job the patient had started at an industrial site. He reported 10 other contractors were similarly affected. The patient denied paresthesia or other skin changes. On physical examination, large patches of smooth alopecia without erythema, scale, scarring, tenderness, or edema that coalesced to involve the majority of the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes (inset) were noted.
Acquired Hypertrichosis of the Periorbital Area and Malar Cheek
The Diagnosis: Bimatoprost-Induced Hypertrichosis
Latanoprost, a prostaglandin analogue, typically is prescribed by ophthalmologists as eye drops to reduce intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma.1 Common adverse reactions of latanoprost drops include blurred vision, ocular irritation, darkening of the eyelid skin, and pigmentation of the iris.
In 1997, Johnstone2 reported hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of the eyelashes of both eyes and adjacent skin after latanoprost drops were used in glaucoma patients. Subsequently, topical latanoprost and bimatoprost, a similar analogue, are now utilized for the cosmetic purpose of thickening and lengthening the eyelashes due to the hypertrichosis effect. Travoprost, another prostaglandin analogue used to treat glaucoma, also has been associated with periocular hypertrichosis.3 Concomitant poliosis of the eyelashes with hypertrichosis from latanoprost also has been reported.4 Our patient specifically purchased the eye drops (marketed as generic bimatoprost) to lengthen her eyelashes and had noticed an increase in length. She denied a family history of increased facial hair in females.
Along with gingival hyperplasia, systemic cyclosporine may cause generalized hypertrichosis consisting of terminal hair growth, particularly on the face and forearms. However, hypertrichosis from cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion 0.05% rarely has been reported5 but would be more likely to occur in a patient reporting a history of chronic dry eye. Oral acetazolamide, not eye drops, is prescribed for glaucoma and typically is not associated with hypertrichosis. Betamethasone and timolol eye drops may cause burning, stinging, redness, or watering of the eyes, but they do not typically cause hypertrichosis.
Other systemic medications (eg, zidovudine, phenytoin, minoxidil, danazol, anabolic steroids) may cause hypertrichosis but not typically localized to the periocular area. Phenytoin usually causes hair growth on the limbs but not on the face and trunk. Oral minoxidil causes hypertrichosis, predominately on the face, lower legs, and forearms.
Systemic conditions such as endocrine abnormalities or porphyria cutanea tarda also may cause hypertrichosis; however, it typically does not present in small focal areas, and other stigmata often are present such as signs of virilization in hirsutism (ie, deepening of voice, pattern alopecia, acne) or liver disease with photosensitive erosions and bullae that leave scars and milia in porphyria cutanea tarda. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa deserves consideration, in part due to its association with lung and colon cancers; however, it consists of softer, downy, nonterminal hairs (malignant down) and is more generalized on the face. Malnutrition from anorexia nervosa may similarly induce hypertrichosis lanuginose.
The molecular mechanism for latanoprost-induced hypertrichosis is unknown; however, it may promote anagen growth as well as hypertrophic changes in the affected follicles.6 Patients should use extreme caution when purchasing unregulated medications due to the risk for impurities, less stable formulation, or inaccurate concentrations. Comparison between brand name and approved generic latanoprost has found notable differences, including variations in active-ingredient concentration, poor stability in warmer temperatures, and higher levels of particulate matter.7 Some cosmetic eyelash enhancers sold over-the-counter or online may contain prostaglandin analogues, but they may not be listed as ingredients.8 One report noted a bimatoprost product with a concentration level double that of brand-name bimatoprost that was discovered using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.9
Treatment options for eliminating the excess hairs include discontinuing the prostaglandin analogue or applying it only to the eyelid margin with an appropriate applicator. Waxing, manual extraction, laser hair removal, electrolysis, and depilatory creams are alternative treatments.
- Alm A. Latanoprost in the treatment of glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:1967-1985.
- Johnstone MA. Hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of eyelashes and adjacent hair in the region of the ipsilateral eyelids of patients treated with unilateral topical latanoprost. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997;124:544-547.
- Ortiz-Perez S, Olver JM. Hypertrichosis of the upper cheek area associated with travoprost treatment of glaucoma. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:376-377.
- Özyurt S, Çetinkaya GS. Hypertrichosis of the malar areas and poliosis of the eyelashes caused by latanoprost. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:74-75.
- Lei HL, Ku WC, Sun MH, et al. Cyclosporine A eye drop-induced elongated eyelashes: a case report. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011;2:398-400.
- Johnstone MA, Albert DM. Prostaglandin-induced hair growth. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002;47(suppl 1):S185-S202.
- Kahook MY, Fechtner RD, Katz LJ, et al. A comparison of active ingredients and preservatives between brand name and generic topical glaucoma medications using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37:101-108.
- Swedish Medical Products Agency. Pharmaceutical ingredients in one out of three eyelash serums. https://www.dr-jetskeultee.nl/jetskeultee/download/common/artikel-wimpers-ingredients.pdf. Published April 15, 2013. Accessed April 11, 2019.
- Marchei E, De Orsi D, Guarino C, et al. High performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bimatoprost, latanoprost and travoprost in eyelash enhancing cosmetic serums. Cosmetics. 2016;3:4.
The Diagnosis: Bimatoprost-Induced Hypertrichosis
Latanoprost, a prostaglandin analogue, typically is prescribed by ophthalmologists as eye drops to reduce intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma.1 Common adverse reactions of latanoprost drops include blurred vision, ocular irritation, darkening of the eyelid skin, and pigmentation of the iris.
In 1997, Johnstone2 reported hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of the eyelashes of both eyes and adjacent skin after latanoprost drops were used in glaucoma patients. Subsequently, topical latanoprost and bimatoprost, a similar analogue, are now utilized for the cosmetic purpose of thickening and lengthening the eyelashes due to the hypertrichosis effect. Travoprost, another prostaglandin analogue used to treat glaucoma, also has been associated with periocular hypertrichosis.3 Concomitant poliosis of the eyelashes with hypertrichosis from latanoprost also has been reported.4 Our patient specifically purchased the eye drops (marketed as generic bimatoprost) to lengthen her eyelashes and had noticed an increase in length. She denied a family history of increased facial hair in females.
Along with gingival hyperplasia, systemic cyclosporine may cause generalized hypertrichosis consisting of terminal hair growth, particularly on the face and forearms. However, hypertrichosis from cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion 0.05% rarely has been reported5 but would be more likely to occur in a patient reporting a history of chronic dry eye. Oral acetazolamide, not eye drops, is prescribed for glaucoma and typically is not associated with hypertrichosis. Betamethasone and timolol eye drops may cause burning, stinging, redness, or watering of the eyes, but they do not typically cause hypertrichosis.
Other systemic medications (eg, zidovudine, phenytoin, minoxidil, danazol, anabolic steroids) may cause hypertrichosis but not typically localized to the periocular area. Phenytoin usually causes hair growth on the limbs but not on the face and trunk. Oral minoxidil causes hypertrichosis, predominately on the face, lower legs, and forearms.
Systemic conditions such as endocrine abnormalities or porphyria cutanea tarda also may cause hypertrichosis; however, it typically does not present in small focal areas, and other stigmata often are present such as signs of virilization in hirsutism (ie, deepening of voice, pattern alopecia, acne) or liver disease with photosensitive erosions and bullae that leave scars and milia in porphyria cutanea tarda. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa deserves consideration, in part due to its association with lung and colon cancers; however, it consists of softer, downy, nonterminal hairs (malignant down) and is more generalized on the face. Malnutrition from anorexia nervosa may similarly induce hypertrichosis lanuginose.
The molecular mechanism for latanoprost-induced hypertrichosis is unknown; however, it may promote anagen growth as well as hypertrophic changes in the affected follicles.6 Patients should use extreme caution when purchasing unregulated medications due to the risk for impurities, less stable formulation, or inaccurate concentrations. Comparison between brand name and approved generic latanoprost has found notable differences, including variations in active-ingredient concentration, poor stability in warmer temperatures, and higher levels of particulate matter.7 Some cosmetic eyelash enhancers sold over-the-counter or online may contain prostaglandin analogues, but they may not be listed as ingredients.8 One report noted a bimatoprost product with a concentration level double that of brand-name bimatoprost that was discovered using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.9
Treatment options for eliminating the excess hairs include discontinuing the prostaglandin analogue or applying it only to the eyelid margin with an appropriate applicator. Waxing, manual extraction, laser hair removal, electrolysis, and depilatory creams are alternative treatments.
The Diagnosis: Bimatoprost-Induced Hypertrichosis
Latanoprost, a prostaglandin analogue, typically is prescribed by ophthalmologists as eye drops to reduce intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma.1 Common adverse reactions of latanoprost drops include blurred vision, ocular irritation, darkening of the eyelid skin, and pigmentation of the iris.
In 1997, Johnstone2 reported hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of the eyelashes of both eyes and adjacent skin after latanoprost drops were used in glaucoma patients. Subsequently, topical latanoprost and bimatoprost, a similar analogue, are now utilized for the cosmetic purpose of thickening and lengthening the eyelashes due to the hypertrichosis effect. Travoprost, another prostaglandin analogue used to treat glaucoma, also has been associated with periocular hypertrichosis.3 Concomitant poliosis of the eyelashes with hypertrichosis from latanoprost also has been reported.4 Our patient specifically purchased the eye drops (marketed as generic bimatoprost) to lengthen her eyelashes and had noticed an increase in length. She denied a family history of increased facial hair in females.
Along with gingival hyperplasia, systemic cyclosporine may cause generalized hypertrichosis consisting of terminal hair growth, particularly on the face and forearms. However, hypertrichosis from cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion 0.05% rarely has been reported5 but would be more likely to occur in a patient reporting a history of chronic dry eye. Oral acetazolamide, not eye drops, is prescribed for glaucoma and typically is not associated with hypertrichosis. Betamethasone and timolol eye drops may cause burning, stinging, redness, or watering of the eyes, but they do not typically cause hypertrichosis.
Other systemic medications (eg, zidovudine, phenytoin, minoxidil, danazol, anabolic steroids) may cause hypertrichosis but not typically localized to the periocular area. Phenytoin usually causes hair growth on the limbs but not on the face and trunk. Oral minoxidil causes hypertrichosis, predominately on the face, lower legs, and forearms.
Systemic conditions such as endocrine abnormalities or porphyria cutanea tarda also may cause hypertrichosis; however, it typically does not present in small focal areas, and other stigmata often are present such as signs of virilization in hirsutism (ie, deepening of voice, pattern alopecia, acne) or liver disease with photosensitive erosions and bullae that leave scars and milia in porphyria cutanea tarda. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa deserves consideration, in part due to its association with lung and colon cancers; however, it consists of softer, downy, nonterminal hairs (malignant down) and is more generalized on the face. Malnutrition from anorexia nervosa may similarly induce hypertrichosis lanuginose.
The molecular mechanism for latanoprost-induced hypertrichosis is unknown; however, it may promote anagen growth as well as hypertrophic changes in the affected follicles.6 Patients should use extreme caution when purchasing unregulated medications due to the risk for impurities, less stable formulation, or inaccurate concentrations. Comparison between brand name and approved generic latanoprost has found notable differences, including variations in active-ingredient concentration, poor stability in warmer temperatures, and higher levels of particulate matter.7 Some cosmetic eyelash enhancers sold over-the-counter or online may contain prostaglandin analogues, but they may not be listed as ingredients.8 One report noted a bimatoprost product with a concentration level double that of brand-name bimatoprost that was discovered using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.9
Treatment options for eliminating the excess hairs include discontinuing the prostaglandin analogue or applying it only to the eyelid margin with an appropriate applicator. Waxing, manual extraction, laser hair removal, electrolysis, and depilatory creams are alternative treatments.
- Alm A. Latanoprost in the treatment of glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:1967-1985.
- Johnstone MA. Hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of eyelashes and adjacent hair in the region of the ipsilateral eyelids of patients treated with unilateral topical latanoprost. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997;124:544-547.
- Ortiz-Perez S, Olver JM. Hypertrichosis of the upper cheek area associated with travoprost treatment of glaucoma. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:376-377.
- Özyurt S, Çetinkaya GS. Hypertrichosis of the malar areas and poliosis of the eyelashes caused by latanoprost. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:74-75.
- Lei HL, Ku WC, Sun MH, et al. Cyclosporine A eye drop-induced elongated eyelashes: a case report. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011;2:398-400.
- Johnstone MA, Albert DM. Prostaglandin-induced hair growth. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002;47(suppl 1):S185-S202.
- Kahook MY, Fechtner RD, Katz LJ, et al. A comparison of active ingredients and preservatives between brand name and generic topical glaucoma medications using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37:101-108.
- Swedish Medical Products Agency. Pharmaceutical ingredients in one out of three eyelash serums. https://www.dr-jetskeultee.nl/jetskeultee/download/common/artikel-wimpers-ingredients.pdf. Published April 15, 2013. Accessed April 11, 2019.
- Marchei E, De Orsi D, Guarino C, et al. High performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bimatoprost, latanoprost and travoprost in eyelash enhancing cosmetic serums. Cosmetics. 2016;3:4.
- Alm A. Latanoprost in the treatment of glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014;8:1967-1985.
- Johnstone MA. Hypertrichosis and increased pigmentation of eyelashes and adjacent hair in the region of the ipsilateral eyelids of patients treated with unilateral topical latanoprost. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997;124:544-547.
- Ortiz-Perez S, Olver JM. Hypertrichosis of the upper cheek area associated with travoprost treatment of glaucoma. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:376-377.
- Özyurt S, Çetinkaya GS. Hypertrichosis of the malar areas and poliosis of the eyelashes caused by latanoprost. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106:74-75.
- Lei HL, Ku WC, Sun MH, et al. Cyclosporine A eye drop-induced elongated eyelashes: a case report. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011;2:398-400.
- Johnstone MA, Albert DM. Prostaglandin-induced hair growth. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002;47(suppl 1):S185-S202.
- Kahook MY, Fechtner RD, Katz LJ, et al. A comparison of active ingredients and preservatives between brand name and generic topical glaucoma medications using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Curr Eye Res. 2012;37:101-108.
- Swedish Medical Products Agency. Pharmaceutical ingredients in one out of three eyelash serums. https://www.dr-jetskeultee.nl/jetskeultee/download/common/artikel-wimpers-ingredients.pdf. Published April 15, 2013. Accessed April 11, 2019.
- Marchei E, De Orsi D, Guarino C, et al. High performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bimatoprost, latanoprost and travoprost in eyelash enhancing cosmetic serums. Cosmetics. 2016;3:4.
An otherwise healthy woman in her late 50s with Fitzpatrick skin type II presented to the dermatology department for a scheduled cosmetic botulinum toxin injection. Her medical history was notable only for periodic nonsurgical cosmetic procedures including botulinum toxin and dermal fillers, and she was not taking any daily systemic medications. During the preoperative assessment, subtle bilateral and symmetric hypertrichosis with darker terminal hair formation was noted on the periorbital skin and zygomatic cheek. Upon inquiry, the patient admitted to purchasing a “special eye drop” from Mexico and using it regularly. After instillation of 2 to 3 drops per eye, she would laterally wipe the resulting excess drops away from the eyes with her hands and then wash her hands. She denied a change in eye color from their natural brown but did report using blue color contact lenses. She denied an increase in hair growth elsewhere including the upper lip, chin, upper chest, forearms, and hands. She denied deepening of her voice, acne, or hair thinning.
Nail Irregularities Associated With Sézary Syndrome
Sézary syndrome (SS) is an advanced leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) that is characterized by generalized erythroderma and T-cell leukemia. Skin changes can include erythroderma, keratosis pilaris–like lesions, keratoderma, ectropion, alopecia, and nail changes.1 Nail changes in SS patients frequently are overlooked and underreported; they vary greatly from patient to patient, and their incidence has not been widely evaluated in the literature.
In this retrospective study, we reviewed medical records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Houston, Texas) and found nail abnormalities in 36 of 83 (43.4%) patients with a diagnosis of SS. Findings for 2 select cases are described in more detail; they were compared to prior case reports from the literature to establish a comprehensive list of nail irregularities that have been associated with SS.
Methods
We examined records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. This database was part of an institutional review board–approved protocol to prospectively collect data from patients with CTCL. Our search yielded 83 patients with SS who were seen between 2007 and 2014.
Results
Of the 83 cases reviewed from the CTCL database, 36 (43.4%) SS patients reported at least 1 nail abnormality on the fingernails or toenails. Patients ranged in age from 59 to 85 years and included 27 (75%) men and 9 (25%) women. Nail irregularities noted on physical examination are summarized in Table 1. More than half of the patients presented with nail thickening (58.3% [21/36]), dystrophy (55.6% [20/36]), or yellowing (55.6% [20/36]) of 1 or more nails. Other findings included 15 (41.7%) patients with subungual hyperkeratosis, 3 (8.3%) with Beau lines, and 1 (2.8%) with multiple oil spots consistent with salmon patches. Five (13.9%) patients had only 1 reported nail irregularity, and 1 (2.8%) patient had 6 irregularities. The average number of nail abnormalities per patient was 2.88 (range, 1–6). We selected 2 patients with extensive nail findings who represent the spectrum of nail findings in patients with SS.
Patient 1
A 71-year-old white man presented with a papular rash of 30 years’ duration. The eruption first occurred on the soles of the feet but progressed to generalized erythroderma. He was found to be colonized with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Over the next 9 months, the patient was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution and was treated with cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, gemcitabine, etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, cisplatin, topical steroids, and intravenous methotrexate with no apparent improvement. At presentation to our institution, physical examination revealed pruritus; alopecia; generalized lymphadenopathy; erythroderma; and irregular nail findings, including yellowing, thickened fingernails and toenails with subungual debris, and splinter hemorrhage (Figure 1). A thick plaque with perioral distribution as well as erosions on the face and feet were noted. The total body surface area (BSA) affected was 100% (patches, 91%; plaques, 9%).
At diagnosis at our institution, the patient’s white blood cell (WBC) count was 17,800/µL (reference range, 4000–11,000/µL), with 11% Sézary cells noted. Biopsy of a lymph node from the inguinal area indicated T-cell lymphoma with clonal T-cell receptor (TCR) β gene rearrangement. Biopsy of lesional skin in the right groin area showed an atypical T-cell lymphocytic infiltrate with a CD4:CD8 ratio of 2.9:1 and partial loss of CD7 expression, consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF)/SS stage IVA. At presentation to our institution, the WBC count was 12,700/µL with a neutrophil count of 47% (reference range, 42%–66%), lymphocyte count of 36% (reference range, 24%–44%), monocyte count of 4% (reference range, 2%–7%), platelet count of 427,000/µL (reference range, 150,000–350,000/µL), hemoglobin of 9.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 733 U/L (reference range, 135–214 U/L). Lymphocytes were positive for CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD25, CD52, TCRα, TCRβ, and TCR VB17; partial for CD26; and negative for CD7, CD8, and CD57. At follow-up 1 month later, the CD4+CD26− T-cell population was 56%, which was consistent with SS T-cell lymphoma.
Skin scrapings from the generalized keratoderma on the patient’s feet were positive for fungal hyphae under potassium hydroxide examination. Nail clippings showed compact keratin with periodic acid–Schiff–positive small yeast forms admixed with bacterial organisms, consistent with onychomycosis. At our institution, the patient received extracorporeal photopheresis, whirlpool therapy (a type of hydrotherapy), steroid wet wraps, and intravenous vancomycin for methicillin-resistant S aureus. He also received bexarotene, levothyroxine sodium, and fenofibrate. After antibiotics and 2 sessions of photopheresis, the total BSA improved from 100% to 33%. The feet and nails were treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, but neither the keratoderma nor the nails improved.
Patient 2
An 84-year-old white man with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia also was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution. One year later, he presented to our institution with mild pruritus and swelling of the lower left leg, which was diagnosed as deep vein thrombosis. There was bilateral scaling of the palms, with fissures present on the left palm. The fingernails showed dystrophy with Beau lines, and the toenails were dystrophic with onycholysis on the bilateral great toes (Figure 2). Patches were noted on most of the body, including the feet, with plaques limited to the hands; the total BSA affected was 80%. Flow cytometry showed an elevated Sézary cell count (CD4+CD26−) of 4700 cells/µL. Complete blood cell count with differential included a hemoglobin level of 11.4 g/dL, hematocrit level of 35.3% (reference range, 37%–47%), a platelet count of 217,000/µL, and a WBC count of 17,7
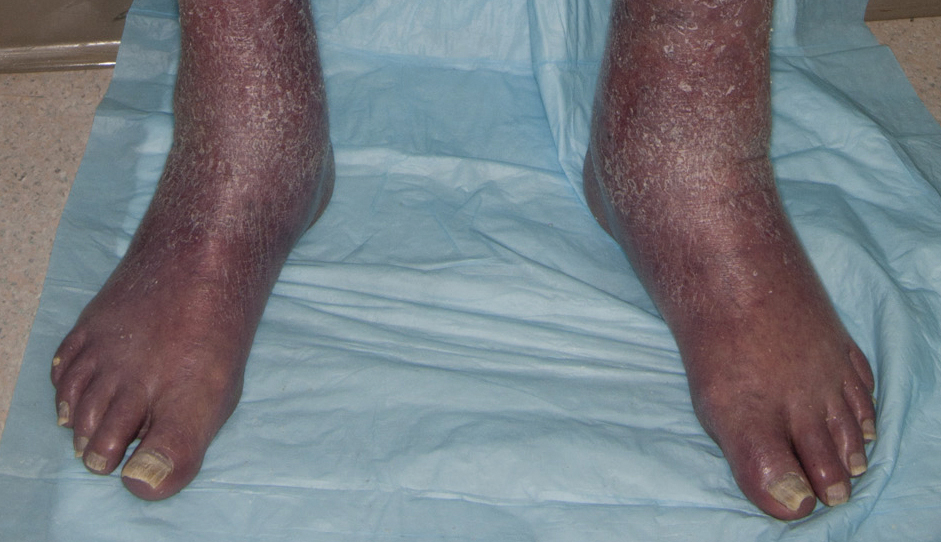
the bilateral great toes.
Comment
Nail changes are found in many cases of advanced-stage SS but rarely have been reported in the literature. A literature review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the search terms Sézary, nail, onychodystrophy, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and CTCL. All results were reviewed for original reported cases of SS with at least 1 reported nail finding. A total of 7 reports2-8 met these requirements with a total of 43 SS patients with reported nail findings, which are summarized in Tables 2 and 3.
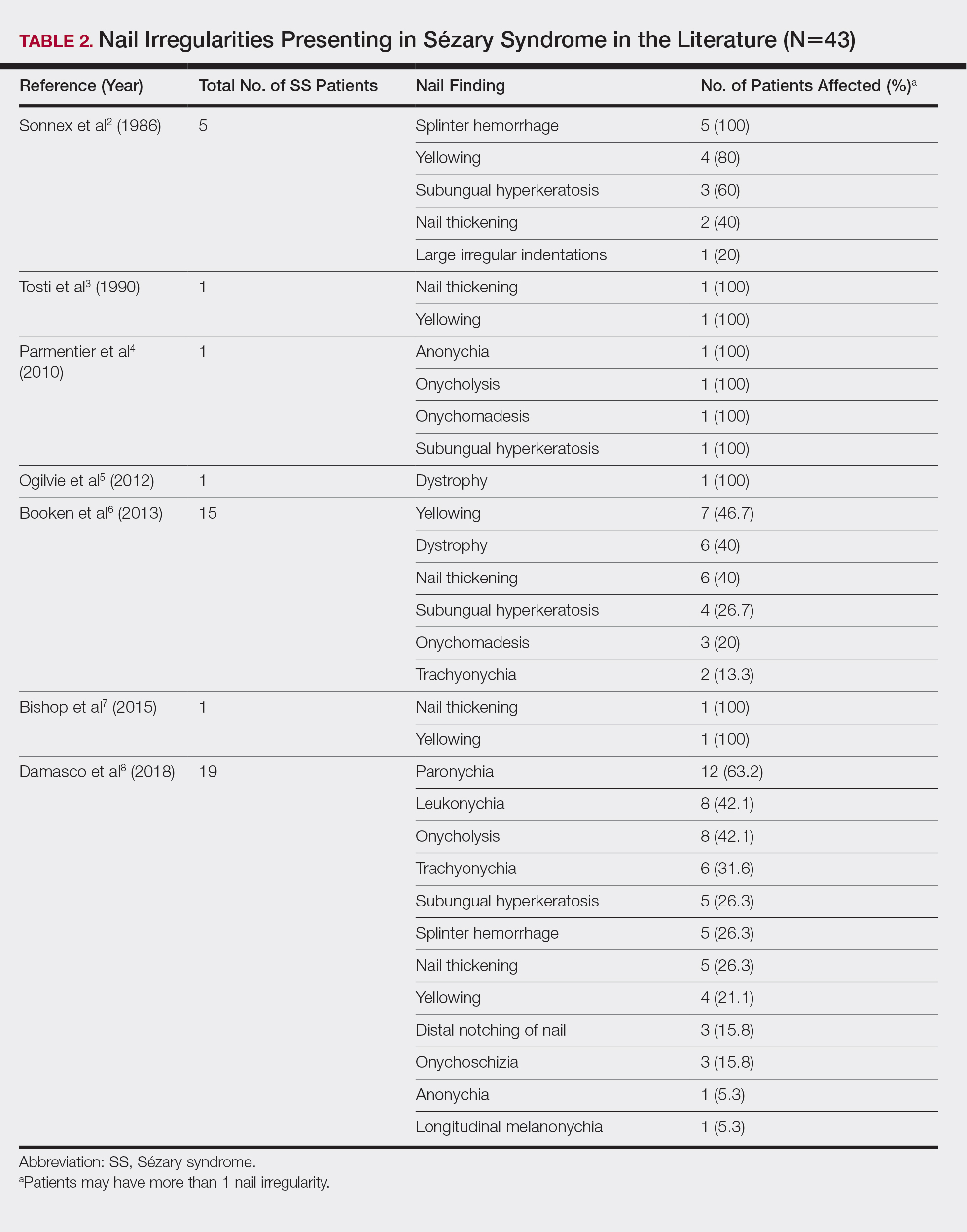

Our findings are generally consistent with those previously described in the literature. Nail thickening, yellowing, subungual hyperkeratosis, dystrophy, and onycholysis are consistently some of the most common nail findings in patients with SS. In 2012, Martin and Duvic9 found that 52.9% (45/85) of SS patients with keratoderma on physical examination were positive for dermatophyte hyphae when skin scrapings were done under potassium hydroxide examination, a considerably greater incidence than in the general population (10%–20%). The nail changes seen in our SS patients were identical to those found in dermatophyte infections, including discoloration, subungual debris, nail thickening, onycholysis, and dystrophy.10 In patient 1, nail clippings were positive for onychomycosis, a common nail condition that is especially prevalent in older or immunocompromised patients.9,10
Interestingly, findings not observed in the literature included salmon patches and Beau lines. Beau lines are horizontal depressions in the nail plate and often are indicative of temporary interruption of nail growth, such as due to an underlying disease process, severe illness, and/or chemotherapy.11,12 In our review, patient 2 had clinical findings of Beau lines. Because the average time for fingernail regrowth is 3 to 6 months,13 it is reasonable to assume that physical findings associated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab chemotherapy treatment would no longer be demonstrated 11 months after completion of therapy. On the other hand, paronychia was frequently observed by Damasco et al8 (63.2% [12/19] of their cases), yet it was not found in our database or the other literature reports we reviewed. Perhaps these differences are due to differences in patient populations and/or available therapies, lack of documentation, or small sample size and limited reports in the literature.
A common question is: Are the nail irregularities caused by the physical symptoms of advanced CTCL or by the underlying disease process in response to the atypical T cells? Erythroderma has been speculated to cause many of the clinical findings of nail abnormalities found in CTCL patients.2,3 However, Fleming et al14 described an MF patient who experienced onychomadesis without erythroderma, which suggests that a different mechanism may cause these nail changes. The wide range of nail abnormalities in CTCL can cause problems with diagnosing the specific cause underlying the nail alteration.
To further complicate the issue, numerous therapies for CTCL also may cause nail changes, such as the previously described Beau lines. In 2010, Parmentier et al4 reported a patient with nail alterations that had been present for more than 1 year, with 9 of 10 fingernails demonstrating anonychia, onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis. In this case report, the authors were able to exclude phototherapy as the cause of onycholysis (visible separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and other clinical nail findings in the SS patient based on the onset of nail changes prior to beginning psoralen plus UVA therapy and complete sparing of 1 finger.4 The findings in our patient 1, who had no history of psoralen plus UVA therapy at the time the irregular nail findings presented, supports this observation. Total skin electron beam therapy for MF also has been reported to cause temporary nail stasis and thus must be taken into account when considering nail changes in patients with MF/SS.15
A nail matrix biopsy may provide clues to the definitive cause of the clinically observed nail changes; however, this procedure typically is not performed due to patient concerns of postoperative complications including pain and nail dystrophy.16 Histopathology features were similar in reported nail biopsies of 2 SS patients.3,4 Tosti et al3 reported that longitudinal biopsy showed a dense lymphocytic infiltrate of atypical lymphocytes with involuted nuclei and notable epidermotropism. Parmentier et al4 reported a longitudinal nail biopsy in an SS patient that presented with atypical lymphocytes, epidermotropism, and Pautrier microabscess formation. Immunostaining showed CD3 positivity within the distal nail matrix, nail bed, and hyponychium. One-third of the cells stained positive for CD4, while the majority stained positive for CD8. Most notably, the skin, nails, and blood showed identical clonal rearrangement of TCRγ.4 Nail matrix biopsies in MF patients rarely have been reported in the literature, but those that are available show similar features to those seen in SS patients. Harland et al17 summarized the findings of 4 case reports of CTCL patients that included nail biopsies by stating, “[a]ll histopathologic findings from nail biopsies showed a dense subepithelial infiltrate of lymphocytes with marked epitheliotropism.” These histopathologic abnormalities are akin to skin biopsies in MF patients, thus providing an essential link to the disease state of MF and the nail abnormalities found within SS patients.
Treatment of the nail problems found within SS is challenging due to limited research. Parmentier et al4 noted an SS patient who was treated with topical mechlorethamine applied directly to the nail. In this case, topical mechlorethamine was effective at treating onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis within 6 months.4 Another SS patient, who presented with thickening and yellowing of the nail, had reported a proximal nail plate that resolved after chemotherapy. The patient did not survive long enough to note complete improvement of the nail.3 In our study, patient 1 was treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, which did not result in nail improvement. Nail treatments in SS patients have yet to show much improvement and thus need more research and focus in the literature.
Conclusion
Sézary syndrome is a rare CTCL that can present with clinical features that may be mistaken for other diseases. Nail abnormalities in SS patients may be related to fungal involvement, medical therapy, or the underlying disease process of SS. We report one of the largest populations of SS patients with specific reported nail abnormalities, thus expanding the possibilities of nail changes that accompany the disease. Continued research and studies involving SS can provide a better understanding of nail involvement and successful treatment of these clinical findings.
- Willemz e R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Sonnex TS, Dawber RP, Zachary CB, et al. The nails in adult type 1 pityriasis rubra pilaris. a comparison with Sézary syndrome and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(5 pt 1):956-960.
- Tosti A, Fanti PA, Varotti C. Massive lymphomatous nail involvement in Sézary syndrome. Dermatologica. 1990;181:162-164.
- Parmentier L, Durr C, Vassella E, et al. Specific nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: successful treatment with topical mechlorethamine. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1287-1291.
- Ogilvie C, Jackson R, Leach M, et al. Sézary syndrome: diagnosis and management. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:317-321.
- Booken N, Nicolay JP, Weiss C, et al. Cutaneous tumor cell load correlates with survival in patients with Sézary syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:67-79.
- Bishop BE, Wulkan A, Kerdel F, et al. Nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a case series and review of nail manifestations. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:82-86.
- Damasco FM, Geskin L, Akilov OE. Onychodystrophy in Sézary syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:972-973.
- Martin SJ, Duvic M. Prevalence and treatment of palmoplantar keratoderma and tinea pedis in patients with Sézary syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1195-1198.
- Mayo TT, Cantrell W. Putting onychomycosis under the microscope. Nurse Pract. 2014;39:8-11.
- Singh M, Kaur S. Chemotherapy-induced multiple Beau’s lines. Int J Dermatol. 1986;25:590-591.
- Tully AS, Trayes KP, Studdiford JS. Evaluation of nail abnormalities. Am Family Physician. 2012;85:779-787.
- Shirwaikar AA, Thomas T, Shirwaikar A, et al. Treatment of onychomycosis: an update. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008;70:710-714.
- Fleming CJ, Hunt MJ, Barnetson RS. Mycosis fungoides with onychomadesis. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:1012-1013.
- Jones GW, Kacinski BM, Wilson LD, et al. Total skin electron radiation in the management of mycosis fungoides: consensus of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Cutaneous Lymphoma Project Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:364-370.
- Haneke E. Advanced nail surgery. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2011;4:167-175.
- Harland E, Dalle S, Balme B, et al. Ungueotropic T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1071-1073.
Sézary syndrome (SS) is an advanced leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) that is characterized by generalized erythroderma and T-cell leukemia. Skin changes can include erythroderma, keratosis pilaris–like lesions, keratoderma, ectropion, alopecia, and nail changes.1 Nail changes in SS patients frequently are overlooked and underreported; they vary greatly from patient to patient, and their incidence has not been widely evaluated in the literature.
In this retrospective study, we reviewed medical records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Houston, Texas) and found nail abnormalities in 36 of 83 (43.4%) patients with a diagnosis of SS. Findings for 2 select cases are described in more detail; they were compared to prior case reports from the literature to establish a comprehensive list of nail irregularities that have been associated with SS.
Methods
We examined records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. This database was part of an institutional review board–approved protocol to prospectively collect data from patients with CTCL. Our search yielded 83 patients with SS who were seen between 2007 and 2014.
Results
Of the 83 cases reviewed from the CTCL database, 36 (43.4%) SS patients reported at least 1 nail abnormality on the fingernails or toenails. Patients ranged in age from 59 to 85 years and included 27 (75%) men and 9 (25%) women. Nail irregularities noted on physical examination are summarized in Table 1. More than half of the patients presented with nail thickening (58.3% [21/36]), dystrophy (55.6% [20/36]), or yellowing (55.6% [20/36]) of 1 or more nails. Other findings included 15 (41.7%) patients with subungual hyperkeratosis, 3 (8.3%) with Beau lines, and 1 (2.8%) with multiple oil spots consistent with salmon patches. Five (13.9%) patients had only 1 reported nail irregularity, and 1 (2.8%) patient had 6 irregularities. The average number of nail abnormalities per patient was 2.88 (range, 1–6). We selected 2 patients with extensive nail findings who represent the spectrum of nail findings in patients with SS.

Patient 1
A 71-year-old white man presented with a papular rash of 30 years’ duration. The eruption first occurred on the soles of the feet but progressed to generalized erythroderma. He was found to be colonized with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Over the next 9 months, the patient was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution and was treated with cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, gemcitabine, etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, cisplatin, topical steroids, and intravenous methotrexate with no apparent improvement. At presentation to our institution, physical examination revealed pruritus; alopecia; generalized lymphadenopathy; erythroderma; and irregular nail findings, including yellowing, thickened fingernails and toenails with subungual debris, and splinter hemorrhage (Figure 1). A thick plaque with perioral distribution as well as erosions on the face and feet were noted. The total body surface area (BSA) affected was 100% (patches, 91%; plaques, 9%).

At diagnosis at our institution, the patient’s white blood cell (WBC) count was 17,800/µL (reference range, 4000–11,000/µL), with 11% Sézary cells noted. Biopsy of a lymph node from the inguinal area indicated T-cell lymphoma with clonal T-cell receptor (TCR) β gene rearrangement. Biopsy of lesional skin in the right groin area showed an atypical T-cell lymphocytic infiltrate with a CD4:CD8 ratio of 2.9:1 and partial loss of CD7 expression, consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF)/SS stage IVA. At presentation to our institution, the WBC count was 12,700/µL with a neutrophil count of 47% (reference range, 42%–66%), lymphocyte count of 36% (reference range, 24%–44%), monocyte count of 4% (reference range, 2%–7%), platelet count of 427,000/µL (reference range, 150,000–350,000/µL), hemoglobin of 9.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 733 U/L (reference range, 135–214 U/L). Lymphocytes were positive for CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD25, CD52, TCRα, TCRβ, and TCR VB17; partial for CD26; and negative for CD7, CD8, and CD57. At follow-up 1 month later, the CD4+CD26− T-cell population was 56%, which was consistent with SS T-cell lymphoma.
Skin scrapings from the generalized keratoderma on the patient’s feet were positive for fungal hyphae under potassium hydroxide examination. Nail clippings showed compact keratin with periodic acid–Schiff–positive small yeast forms admixed with bacterial organisms, consistent with onychomycosis. At our institution, the patient received extracorporeal photopheresis, whirlpool therapy (a type of hydrotherapy), steroid wet wraps, and intravenous vancomycin for methicillin-resistant S aureus. He also received bexarotene, levothyroxine sodium, and fenofibrate. After antibiotics and 2 sessions of photopheresis, the total BSA improved from 100% to 33%. The feet and nails were treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, but neither the keratoderma nor the nails improved.
Patient 2
An 84-year-old white man with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia also was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution. One year later, he presented to our institution with mild pruritus and swelling of the lower left leg, which was diagnosed as deep vein thrombosis. There was bilateral scaling of the palms, with fissures present on the left palm. The fingernails showed dystrophy with Beau lines, and the toenails were dystrophic with onycholysis on the bilateral great toes (Figure 2). Patches were noted on most of the body, including the feet, with plaques limited to the hands; the total BSA affected was 80%. Flow cytometry showed an elevated Sézary cell count (CD4+CD26−) of 4700 cells/µL. Complete blood cell count with differential included a hemoglobin level of 11.4 g/dL, hematocrit level of 35.3% (reference range, 37%–47%), a platelet count of 217,000/µL, and a WBC count of 17,7

the bilateral great toes.
Comment
Nail changes are found in many cases of advanced-stage SS but rarely have been reported in the literature. A literature review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the search terms Sézary, nail, onychodystrophy, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and CTCL. All results were reviewed for original reported cases of SS with at least 1 reported nail finding. A total of 7 reports2-8 met these requirements with a total of 43 SS patients with reported nail findings, which are summarized in Tables 2 and 3.


Our findings are generally consistent with those previously described in the literature. Nail thickening, yellowing, subungual hyperkeratosis, dystrophy, and onycholysis are consistently some of the most common nail findings in patients with SS. In 2012, Martin and Duvic9 found that 52.9% (45/85) of SS patients with keratoderma on physical examination were positive for dermatophyte hyphae when skin scrapings were done under potassium hydroxide examination, a considerably greater incidence than in the general population (10%–20%). The nail changes seen in our SS patients were identical to those found in dermatophyte infections, including discoloration, subungual debris, nail thickening, onycholysis, and dystrophy.10 In patient 1, nail clippings were positive for onychomycosis, a common nail condition that is especially prevalent in older or immunocompromised patients.9,10
Interestingly, findings not observed in the literature included salmon patches and Beau lines. Beau lines are horizontal depressions in the nail plate and often are indicative of temporary interruption of nail growth, such as due to an underlying disease process, severe illness, and/or chemotherapy.11,12 In our review, patient 2 had clinical findings of Beau lines. Because the average time for fingernail regrowth is 3 to 6 months,13 it is reasonable to assume that physical findings associated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab chemotherapy treatment would no longer be demonstrated 11 months after completion of therapy. On the other hand, paronychia was frequently observed by Damasco et al8 (63.2% [12/19] of their cases), yet it was not found in our database or the other literature reports we reviewed. Perhaps these differences are due to differences in patient populations and/or available therapies, lack of documentation, or small sample size and limited reports in the literature.
A common question is: Are the nail irregularities caused by the physical symptoms of advanced CTCL or by the underlying disease process in response to the atypical T cells? Erythroderma has been speculated to cause many of the clinical findings of nail abnormalities found in CTCL patients.2,3 However, Fleming et al14 described an MF patient who experienced onychomadesis without erythroderma, which suggests that a different mechanism may cause these nail changes. The wide range of nail abnormalities in CTCL can cause problems with diagnosing the specific cause underlying the nail alteration.
To further complicate the issue, numerous therapies for CTCL also may cause nail changes, such as the previously described Beau lines. In 2010, Parmentier et al4 reported a patient with nail alterations that had been present for more than 1 year, with 9 of 10 fingernails demonstrating anonychia, onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis. In this case report, the authors were able to exclude phototherapy as the cause of onycholysis (visible separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and other clinical nail findings in the SS patient based on the onset of nail changes prior to beginning psoralen plus UVA therapy and complete sparing of 1 finger.4 The findings in our patient 1, who had no history of psoralen plus UVA therapy at the time the irregular nail findings presented, supports this observation. Total skin electron beam therapy for MF also has been reported to cause temporary nail stasis and thus must be taken into account when considering nail changes in patients with MF/SS.15
A nail matrix biopsy may provide clues to the definitive cause of the clinically observed nail changes; however, this procedure typically is not performed due to patient concerns of postoperative complications including pain and nail dystrophy.16 Histopathology features were similar in reported nail biopsies of 2 SS patients.3,4 Tosti et al3 reported that longitudinal biopsy showed a dense lymphocytic infiltrate of atypical lymphocytes with involuted nuclei and notable epidermotropism. Parmentier et al4 reported a longitudinal nail biopsy in an SS patient that presented with atypical lymphocytes, epidermotropism, and Pautrier microabscess formation. Immunostaining showed CD3 positivity within the distal nail matrix, nail bed, and hyponychium. One-third of the cells stained positive for CD4, while the majority stained positive for CD8. Most notably, the skin, nails, and blood showed identical clonal rearrangement of TCRγ.4 Nail matrix biopsies in MF patients rarely have been reported in the literature, but those that are available show similar features to those seen in SS patients. Harland et al17 summarized the findings of 4 case reports of CTCL patients that included nail biopsies by stating, “[a]ll histopathologic findings from nail biopsies showed a dense subepithelial infiltrate of lymphocytes with marked epitheliotropism.” These histopathologic abnormalities are akin to skin biopsies in MF patients, thus providing an essential link to the disease state of MF and the nail abnormalities found within SS patients.
Treatment of the nail problems found within SS is challenging due to limited research. Parmentier et al4 noted an SS patient who was treated with topical mechlorethamine applied directly to the nail. In this case, topical mechlorethamine was effective at treating onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis within 6 months.4 Another SS patient, who presented with thickening and yellowing of the nail, had reported a proximal nail plate that resolved after chemotherapy. The patient did not survive long enough to note complete improvement of the nail.3 In our study, patient 1 was treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, which did not result in nail improvement. Nail treatments in SS patients have yet to show much improvement and thus need more research and focus in the literature.
Conclusion
Sézary syndrome is a rare CTCL that can present with clinical features that may be mistaken for other diseases. Nail abnormalities in SS patients may be related to fungal involvement, medical therapy, or the underlying disease process of SS. We report one of the largest populations of SS patients with specific reported nail abnormalities, thus expanding the possibilities of nail changes that accompany the disease. Continued research and studies involving SS can provide a better understanding of nail involvement and successful treatment of these clinical findings.
Sézary syndrome (SS) is an advanced leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) that is characterized by generalized erythroderma and T-cell leukemia. Skin changes can include erythroderma, keratosis pilaris–like lesions, keratoderma, ectropion, alopecia, and nail changes.1 Nail changes in SS patients frequently are overlooked and underreported; they vary greatly from patient to patient, and their incidence has not been widely evaluated in the literature.
In this retrospective study, we reviewed medical records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Houston, Texas) and found nail abnormalities in 36 of 83 (43.4%) patients with a diagnosis of SS. Findings for 2 select cases are described in more detail; they were compared to prior case reports from the literature to establish a comprehensive list of nail irregularities that have been associated with SS.
Methods
We examined records from a previously collected CTCL clinic database at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. This database was part of an institutional review board–approved protocol to prospectively collect data from patients with CTCL. Our search yielded 83 patients with SS who were seen between 2007 and 2014.
Results
Of the 83 cases reviewed from the CTCL database, 36 (43.4%) SS patients reported at least 1 nail abnormality on the fingernails or toenails. Patients ranged in age from 59 to 85 years and included 27 (75%) men and 9 (25%) women. Nail irregularities noted on physical examination are summarized in Table 1. More than half of the patients presented with nail thickening (58.3% [21/36]), dystrophy (55.6% [20/36]), or yellowing (55.6% [20/36]) of 1 or more nails. Other findings included 15 (41.7%) patients with subungual hyperkeratosis, 3 (8.3%) with Beau lines, and 1 (2.8%) with multiple oil spots consistent with salmon patches. Five (13.9%) patients had only 1 reported nail irregularity, and 1 (2.8%) patient had 6 irregularities. The average number of nail abnormalities per patient was 2.88 (range, 1–6). We selected 2 patients with extensive nail findings who represent the spectrum of nail findings in patients with SS.

Patient 1
A 71-year-old white man presented with a papular rash of 30 years’ duration. The eruption first occurred on the soles of the feet but progressed to generalized erythroderma. He was found to be colonized with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Over the next 9 months, the patient was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution and was treated with cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, gemcitabine, etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, cisplatin, topical steroids, and intravenous methotrexate with no apparent improvement. At presentation to our institution, physical examination revealed pruritus; alopecia; generalized lymphadenopathy; erythroderma; and irregular nail findings, including yellowing, thickened fingernails and toenails with subungual debris, and splinter hemorrhage (Figure 1). A thick plaque with perioral distribution as well as erosions on the face and feet were noted. The total body surface area (BSA) affected was 100% (patches, 91%; plaques, 9%).

At diagnosis at our institution, the patient’s white blood cell (WBC) count was 17,800/µL (reference range, 4000–11,000/µL), with 11% Sézary cells noted. Biopsy of a lymph node from the inguinal area indicated T-cell lymphoma with clonal T-cell receptor (TCR) β gene rearrangement. Biopsy of lesional skin in the right groin area showed an atypical T-cell lymphocytic infiltrate with a CD4:CD8 ratio of 2.9:1 and partial loss of CD7 expression, consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF)/SS stage IVA. At presentation to our institution, the WBC count was 12,700/µL with a neutrophil count of 47% (reference range, 42%–66%), lymphocyte count of 36% (reference range, 24%–44%), monocyte count of 4% (reference range, 2%–7%), platelet count of 427,000/µL (reference range, 150,000–350,000/µL), hemoglobin of 9.9 g/dL (reference range, 14.0–17.5 g/dL), and lactate dehydrogenase of 733 U/L (reference range, 135–214 U/L). Lymphocytes were positive for CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD25, CD52, TCRα, TCRβ, and TCR VB17; partial for CD26; and negative for CD7, CD8, and CD57. At follow-up 1 month later, the CD4+CD26− T-cell population was 56%, which was consistent with SS T-cell lymphoma.
Skin scrapings from the generalized keratoderma on the patient’s feet were positive for fungal hyphae under potassium hydroxide examination. Nail clippings showed compact keratin with periodic acid–Schiff–positive small yeast forms admixed with bacterial organisms, consistent with onychomycosis. At our institution, the patient received extracorporeal photopheresis, whirlpool therapy (a type of hydrotherapy), steroid wet wraps, and intravenous vancomycin for methicillin-resistant S aureus. He also received bexarotene, levothyroxine sodium, and fenofibrate. After antibiotics and 2 sessions of photopheresis, the total BSA improved from 100% to 33%. The feet and nails were treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, but neither the keratoderma nor the nails improved.
Patient 2
An 84-year-old white man with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia also was diagnosed with SS at an outside institution. One year later, he presented to our institution with mild pruritus and swelling of the lower left leg, which was diagnosed as deep vein thrombosis. There was bilateral scaling of the palms, with fissures present on the left palm. The fingernails showed dystrophy with Beau lines, and the toenails were dystrophic with onycholysis on the bilateral great toes (Figure 2). Patches were noted on most of the body, including the feet, with plaques limited to the hands; the total BSA affected was 80%. Flow cytometry showed an elevated Sézary cell count (CD4+CD26−) of 4700 cells/µL. Complete blood cell count with differential included a hemoglobin level of 11.4 g/dL, hematocrit level of 35.3% (reference range, 37%–47%), a platelet count of 217,000/µL, and a WBC count of 17,7

the bilateral great toes.
Comment
Nail changes are found in many cases of advanced-stage SS but rarely have been reported in the literature. A literature review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the search terms Sézary, nail, onychodystrophy, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and CTCL. All results were reviewed for original reported cases of SS with at least 1 reported nail finding. A total of 7 reports2-8 met these requirements with a total of 43 SS patients with reported nail findings, which are summarized in Tables 2 and 3.


Our findings are generally consistent with those previously described in the literature. Nail thickening, yellowing, subungual hyperkeratosis, dystrophy, and onycholysis are consistently some of the most common nail findings in patients with SS. In 2012, Martin and Duvic9 found that 52.9% (45/85) of SS patients with keratoderma on physical examination were positive for dermatophyte hyphae when skin scrapings were done under potassium hydroxide examination, a considerably greater incidence than in the general population (10%–20%). The nail changes seen in our SS patients were identical to those found in dermatophyte infections, including discoloration, subungual debris, nail thickening, onycholysis, and dystrophy.10 In patient 1, nail clippings were positive for onychomycosis, a common nail condition that is especially prevalent in older or immunocompromised patients.9,10
Interestingly, findings not observed in the literature included salmon patches and Beau lines. Beau lines are horizontal depressions in the nail plate and often are indicative of temporary interruption of nail growth, such as due to an underlying disease process, severe illness, and/or chemotherapy.11,12 In our review, patient 2 had clinical findings of Beau lines. Because the average time for fingernail regrowth is 3 to 6 months,13 it is reasonable to assume that physical findings associated with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab chemotherapy treatment would no longer be demonstrated 11 months after completion of therapy. On the other hand, paronychia was frequently observed by Damasco et al8 (63.2% [12/19] of their cases), yet it was not found in our database or the other literature reports we reviewed. Perhaps these differences are due to differences in patient populations and/or available therapies, lack of documentation, or small sample size and limited reports in the literature.
A common question is: Are the nail irregularities caused by the physical symptoms of advanced CTCL or by the underlying disease process in response to the atypical T cells? Erythroderma has been speculated to cause many of the clinical findings of nail abnormalities found in CTCL patients.2,3 However, Fleming et al14 described an MF patient who experienced onychomadesis without erythroderma, which suggests that a different mechanism may cause these nail changes. The wide range of nail abnormalities in CTCL can cause problems with diagnosing the specific cause underlying the nail alteration.
To further complicate the issue, numerous therapies for CTCL also may cause nail changes, such as the previously described Beau lines. In 2010, Parmentier et al4 reported a patient with nail alterations that had been present for more than 1 year, with 9 of 10 fingernails demonstrating anonychia, onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis. In this case report, the authors were able to exclude phototherapy as the cause of onycholysis (visible separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and other clinical nail findings in the SS patient based on the onset of nail changes prior to beginning psoralen plus UVA therapy and complete sparing of 1 finger.4 The findings in our patient 1, who had no history of psoralen plus UVA therapy at the time the irregular nail findings presented, supports this observation. Total skin electron beam therapy for MF also has been reported to cause temporary nail stasis and thus must be taken into account when considering nail changes in patients with MF/SS.15
A nail matrix biopsy may provide clues to the definitive cause of the clinically observed nail changes; however, this procedure typically is not performed due to patient concerns of postoperative complications including pain and nail dystrophy.16 Histopathology features were similar in reported nail biopsies of 2 SS patients.3,4 Tosti et al3 reported that longitudinal biopsy showed a dense lymphocytic infiltrate of atypical lymphocytes with involuted nuclei and notable epidermotropism. Parmentier et al4 reported a longitudinal nail biopsy in an SS patient that presented with atypical lymphocytes, epidermotropism, and Pautrier microabscess formation. Immunostaining showed CD3 positivity within the distal nail matrix, nail bed, and hyponychium. One-third of the cells stained positive for CD4, while the majority stained positive for CD8. Most notably, the skin, nails, and blood showed identical clonal rearrangement of TCRγ.4 Nail matrix biopsies in MF patients rarely have been reported in the literature, but those that are available show similar features to those seen in SS patients. Harland et al17 summarized the findings of 4 case reports of CTCL patients that included nail biopsies by stating, “[a]ll histopathologic findings from nail biopsies showed a dense subepithelial infiltrate of lymphocytes with marked epitheliotropism.” These histopathologic abnormalities are akin to skin biopsies in MF patients, thus providing an essential link to the disease state of MF and the nail abnormalities found within SS patients.
Treatment of the nail problems found within SS is challenging due to limited research. Parmentier et al4 noted an SS patient who was treated with topical mechlorethamine applied directly to the nail. In this case, topical mechlorethamine was effective at treating onychomadesis, subungual distal hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis within 6 months.4 Another SS patient, who presented with thickening and yellowing of the nail, had reported a proximal nail plate that resolved after chemotherapy. The patient did not survive long enough to note complete improvement of the nail.3 In our study, patient 1 was treated with ciclopirox gel and terbinafine, which did not result in nail improvement. Nail treatments in SS patients have yet to show much improvement and thus need more research and focus in the literature.
Conclusion
Sézary syndrome is a rare CTCL that can present with clinical features that may be mistaken for other diseases. Nail abnormalities in SS patients may be related to fungal involvement, medical therapy, or the underlying disease process of SS. We report one of the largest populations of SS patients with specific reported nail abnormalities, thus expanding the possibilities of nail changes that accompany the disease. Continued research and studies involving SS can provide a better understanding of nail involvement and successful treatment of these clinical findings.
- Willemz e R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Sonnex TS, Dawber RP, Zachary CB, et al. The nails in adult type 1 pityriasis rubra pilaris. a comparison with Sézary syndrome and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(5 pt 1):956-960.
- Tosti A, Fanti PA, Varotti C. Massive lymphomatous nail involvement in Sézary syndrome. Dermatologica. 1990;181:162-164.
- Parmentier L, Durr C, Vassella E, et al. Specific nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: successful treatment with topical mechlorethamine. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1287-1291.
- Ogilvie C, Jackson R, Leach M, et al. Sézary syndrome: diagnosis and management. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:317-321.
- Booken N, Nicolay JP, Weiss C, et al. Cutaneous tumor cell load correlates with survival in patients with Sézary syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:67-79.
- Bishop BE, Wulkan A, Kerdel F, et al. Nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a case series and review of nail manifestations. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:82-86.
- Damasco FM, Geskin L, Akilov OE. Onychodystrophy in Sézary syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:972-973.
- Martin SJ, Duvic M. Prevalence and treatment of palmoplantar keratoderma and tinea pedis in patients with Sézary syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1195-1198.
- Mayo TT, Cantrell W. Putting onychomycosis under the microscope. Nurse Pract. 2014;39:8-11.
- Singh M, Kaur S. Chemotherapy-induced multiple Beau’s lines. Int J Dermatol. 1986;25:590-591.
- Tully AS, Trayes KP, Studdiford JS. Evaluation of nail abnormalities. Am Family Physician. 2012;85:779-787.
- Shirwaikar AA, Thomas T, Shirwaikar A, et al. Treatment of onychomycosis: an update. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008;70:710-714.
- Fleming CJ, Hunt MJ, Barnetson RS. Mycosis fungoides with onychomadesis. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:1012-1013.
- Jones GW, Kacinski BM, Wilson LD, et al. Total skin electron radiation in the management of mycosis fungoides: consensus of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Cutaneous Lymphoma Project Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:364-370.
- Haneke E. Advanced nail surgery. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2011;4:167-175.
- Harland E, Dalle S, Balme B, et al. Ungueotropic T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1071-1073.
- Willemz e R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785.
- Sonnex TS, Dawber RP, Zachary CB, et al. The nails in adult type 1 pityriasis rubra pilaris. a comparison with Sézary syndrome and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15(5 pt 1):956-960.
- Tosti A, Fanti PA, Varotti C. Massive lymphomatous nail involvement in Sézary syndrome. Dermatologica. 1990;181:162-164.
- Parmentier L, Durr C, Vassella E, et al. Specific nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: successful treatment with topical mechlorethamine. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:1287-1291.
- Ogilvie C, Jackson R, Leach M, et al. Sézary syndrome: diagnosis and management. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:317-321.
- Booken N, Nicolay JP, Weiss C, et al. Cutaneous tumor cell load correlates with survival in patients with Sézary syndrome. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:67-79.
- Bishop BE, Wulkan A, Kerdel F, et al. Nail alterations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a case series and review of nail manifestations. Skin Appendage Disord. 2015;1:82-86.
- Damasco FM, Geskin L, Akilov OE. Onychodystrophy in Sézary syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:972-973.
- Martin SJ, Duvic M. Prevalence and treatment of palmoplantar keratoderma and tinea pedis in patients with Sézary syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1195-1198.
- Mayo TT, Cantrell W. Putting onychomycosis under the microscope. Nurse Pract. 2014;39:8-11.
- Singh M, Kaur S. Chemotherapy-induced multiple Beau’s lines. Int J Dermatol. 1986;25:590-591.
- Tully AS, Trayes KP, Studdiford JS. Evaluation of nail abnormalities. Am Family Physician. 2012;85:779-787.
- Shirwaikar AA, Thomas T, Shirwaikar A, et al. Treatment of onychomycosis: an update. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2008;70:710-714.
- Fleming CJ, Hunt MJ, Barnetson RS. Mycosis fungoides with onychomadesis. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:1012-1013.
- Jones GW, Kacinski BM, Wilson LD, et al. Total skin electron radiation in the management of mycosis fungoides: consensus of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Cutaneous Lymphoma Project Group. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:364-370.
- Haneke E. Advanced nail surgery. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2011;4:167-175.
- Harland E, Dalle S, Balme B, et al. Ungueotropic T-cell lymphoma. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:1071-1073.
Practice Points
- Nail changes are frequently observed in patients with Sézary syndrome.
- Nail changes in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma may result from the disease process or physical symptoms of advanced disease, or they may present secondary to treatment.
Papules and Telangiectases on the Distal Fingers of a Child
The Diagnosis: Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory myopathy of childhood that is autoimmune in nature with an annual incidence ranging from 2.5 to 4.1 cases per million children. Its peak incidence is between 5 and 10 years of age, and it affects girls more than boys at a 2-fold to 5-fold greater rate.1 Juvenile dermatomyositis is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness in the presence of distinctive rashes, including Gottron papules and heliotrope erythema. Muscle weakness typically is proximal and symmetrical, and eventually patients may have trouble rising from a seated position or lifting objects overhead. Other skin manifestations include nail fold capillary changes, calcinosis cutis, and less commonly ulcerations signifying vasculopathy of the skin.2 A subset of patients will present with juvenile amyopathic dermatomyositis. These children have the characteristic skin changes without the muscle weakness or elevated muscle enzymes for more than 6 months; however, one-quarter may go on to develop mysositis.3
Diagnosis of JDM traditionally was based on the following 5 diagnostic criteria: characteristic skin rash, proximal muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, myopathic changes on electromyogram, and typical muscle biopsy.1 Current practice shows a broadening of diagnostic criteria using new techniques in the diagnosis of JDM. To make the diagnosis, the patient must have the characteristic skin manifestations with a minimum of 3 other criteria.4 A 2006 international consensus survey expanded the list of criteria to include typical findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nail fold capillaroscopy abnormalities, calcinosis, and
dysphonia.5
To assess muscle disease, MRI is utilized because it is a reliable noninvasive tool to assess muscle inflammation. Muscle biopsy is only recommended if the diagnosis is unclear.5 The results of the MRI in our patient displayed symmetric mild fatty atrophy of the gluteus maximus muscle, as well as edema in the right rectus femoris and left vastus lateralis muscles, suggesting early findings of myositis. Muscle enzymes may not be diagnostic because they are not always elevated at diagnosis. Our patient had a normal creatinine kinase level (92 U/L [reference range, <190 U/L]), and both aldolase and lactate dehydrogenase also were within reference range. Conversely, antinuclear antibodies frequently are positive in patients with JDM, such as in our patient at a 1:320 dilution, but are nonspecific and nondiagnostic. It is recommended to include nail fold capillaroscopy to evaluate periungual capillary changes because nailfold capillary density is a sensitive measure of both skin and muscle disease.5 Using dermoscopy, nail fold capillary dilation was observed in our patient.
Other differential diagnoses can have somewhat similar clinical features to JDM. Infantile papular acrodermatitis, commonly referred to as Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, is a viral exanthem that affects children (median age, 2 years).6 The rash appears as monomorphous, flat-topped, pink to brown papules affecting the face, buttocks, and arms; it typically spontaneously resolves in 10 days.6
Juvenile-onset lupus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can involve any organ system and typically affects children aged 11 to 12 years with a female preponderance. Skin manifestations are similar to adult-onset lupus and include malar rash, discoid rash, oral ulcerations, petechiae, palpable purpura, and digital telangiectasia and ulcers. 7
Juvenile scleroderma is rare connective-tissue disorder that also has multiple organ involvement. Cutaneous involvement can range from isolated morphealike plaques to diffuse sclerotic lesions with growth disturbances, contractures, and facial atrophy.8
Verrucae planae, commonly referred to as flat warts, are papules caused primarily by human papillomavirus types 3, 10, 28, and 41. Children and young adults commonly are affected, and warts can appear on the hands, as in our patient.6
Treatment of JDM depends on disease severity at initial presentation and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The mainstay of treatment is high-dose oral prednisone in combination with disease-modifying drugs such as methotrexate and cyclosporin A. Patients with more severe presentations (eg, ulcerative skin disease) or life-threatening organ involvement are treated with cyclophosphamide, usually in combination with high-dose glucocorticoids.9
Early detection with aggressive treatment is vital to reduce morbidity and mortality from organ damage and disease complications. Mortality rates have dropped to 3%10 in recent decades with the use of systemic glucocorticoids. Delayed treatment is associated with a prolonged disease course and poorer outcomes. Disease complications in children with JDM include osteoporosis, calcinosis, and intestinal perforation; however, with early treatment, children with JDM can expect full recovery and to live a normal life as compared to adults with dermatomyositis.10
Prior to our patient's diagnosis, the family was assigned to move to an overseas location through the US Military with no direct access to advanced medical care. Early detection and diagnosis of JDM through an astute clinical examination allowed the patient and her family to remain in the continental United States to continue receiving specialty care.
- Mendez EP, Lipton R, Ramsey-Goldman R, et al. US incidence of juvenile dermatomyositis,1995-1998: results from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:300-305.
- Shah M, Mamyrova G, Targoff IN, et al. The clinical phenotypes of the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Medicine. 2013;92:25-41.
- Gerami P, Walling HW, Lewis J, et al. A systematic review of juvenile-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;57:637-644.
- Enders FB, Bader-Meunier B, Baildam E, et al. Consensus-based recommendations for the management of juvenile dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:329-340.
- Brown VE, Pilkington CA, Feldman BM, et al. An international consensus survey of the diagnostic criteria for juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45:990-993.
- William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Viral diseases. In: William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th ed. China: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:360-413.
- Levy DM, Kamphuis S. Systemic lupus erythematosus in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2012;59:345-364.
- Li SC, Torok KS, Pope E, et al; Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Localized Scleroderma Workgroup. Development of consensus treatment plans for juvenile localized scleroderma: a roadmap toward comparative effectiveness studies in juvenile localized scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64:1175-1185.
- Stringer E, Ota S, Bohnsack J, et al. Treatment approaches to juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) across North America: the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) JDM treatment study. J Rhematol. 2010;37:S1953-S1961.
- Huber AM, Feldman BM. Long-term outcomes in juvenile dermatomyositis: how did we get here and where are we going? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2005;7:441-446.
The Diagnosis: Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory myopathy of childhood that is autoimmune in nature with an annual incidence ranging from 2.5 to 4.1 cases per million children. Its peak incidence is between 5 and 10 years of age, and it affects girls more than boys at a 2-fold to 5-fold greater rate.1 Juvenile dermatomyositis is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness in the presence of distinctive rashes, including Gottron papules and heliotrope erythema. Muscle weakness typically is proximal and symmetrical, and eventually patients may have trouble rising from a seated position or lifting objects overhead. Other skin manifestations include nail fold capillary changes, calcinosis cutis, and less commonly ulcerations signifying vasculopathy of the skin.2 A subset of patients will present with juvenile amyopathic dermatomyositis. These children have the characteristic skin changes without the muscle weakness or elevated muscle enzymes for more than 6 months; however, one-quarter may go on to develop mysositis.3
Diagnosis of JDM traditionally was based on the following 5 diagnostic criteria: characteristic skin rash, proximal muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, myopathic changes on electromyogram, and typical muscle biopsy.1 Current practice shows a broadening of diagnostic criteria using new techniques in the diagnosis of JDM. To make the diagnosis, the patient must have the characteristic skin manifestations with a minimum of 3 other criteria.4 A 2006 international consensus survey expanded the list of criteria to include typical findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nail fold capillaroscopy abnormalities, calcinosis, and
dysphonia.5
To assess muscle disease, MRI is utilized because it is a reliable noninvasive tool to assess muscle inflammation. Muscle biopsy is only recommended if the diagnosis is unclear.5 The results of the MRI in our patient displayed symmetric mild fatty atrophy of the gluteus maximus muscle, as well as edema in the right rectus femoris and left vastus lateralis muscles, suggesting early findings of myositis. Muscle enzymes may not be diagnostic because they are not always elevated at diagnosis. Our patient had a normal creatinine kinase level (92 U/L [reference range, <190 U/L]), and both aldolase and lactate dehydrogenase also were within reference range. Conversely, antinuclear antibodies frequently are positive in patients with JDM, such as in our patient at a 1:320 dilution, but are nonspecific and nondiagnostic. It is recommended to include nail fold capillaroscopy to evaluate periungual capillary changes because nailfold capillary density is a sensitive measure of both skin and muscle disease.5 Using dermoscopy, nail fold capillary dilation was observed in our patient.
Other differential diagnoses can have somewhat similar clinical features to JDM. Infantile papular acrodermatitis, commonly referred to as Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, is a viral exanthem that affects children (median age, 2 years).6 The rash appears as monomorphous, flat-topped, pink to brown papules affecting the face, buttocks, and arms; it typically spontaneously resolves in 10 days.6
Juvenile-onset lupus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can involve any organ system and typically affects children aged 11 to 12 years with a female preponderance. Skin manifestations are similar to adult-onset lupus and include malar rash, discoid rash, oral ulcerations, petechiae, palpable purpura, and digital telangiectasia and ulcers. 7
Juvenile scleroderma is rare connective-tissue disorder that also has multiple organ involvement. Cutaneous involvement can range from isolated morphealike plaques to diffuse sclerotic lesions with growth disturbances, contractures, and facial atrophy.8
Verrucae planae, commonly referred to as flat warts, are papules caused primarily by human papillomavirus types 3, 10, 28, and 41. Children and young adults commonly are affected, and warts can appear on the hands, as in our patient.6
Treatment of JDM depends on disease severity at initial presentation and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The mainstay of treatment is high-dose oral prednisone in combination with disease-modifying drugs such as methotrexate and cyclosporin A. Patients with more severe presentations (eg, ulcerative skin disease) or life-threatening organ involvement are treated with cyclophosphamide, usually in combination with high-dose glucocorticoids.9
Early detection with aggressive treatment is vital to reduce morbidity and mortality from organ damage and disease complications. Mortality rates have dropped to 3%10 in recent decades with the use of systemic glucocorticoids. Delayed treatment is associated with a prolonged disease course and poorer outcomes. Disease complications in children with JDM include osteoporosis, calcinosis, and intestinal perforation; however, with early treatment, children with JDM can expect full recovery and to live a normal life as compared to adults with dermatomyositis.10
Prior to our patient's diagnosis, the family was assigned to move to an overseas location through the US Military with no direct access to advanced medical care. Early detection and diagnosis of JDM through an astute clinical examination allowed the patient and her family to remain in the continental United States to continue receiving specialty care.
The Diagnosis: Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory myopathy of childhood that is autoimmune in nature with an annual incidence ranging from 2.5 to 4.1 cases per million children. Its peak incidence is between 5 and 10 years of age, and it affects girls more than boys at a 2-fold to 5-fold greater rate.1 Juvenile dermatomyositis is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness in the presence of distinctive rashes, including Gottron papules and heliotrope erythema. Muscle weakness typically is proximal and symmetrical, and eventually patients may have trouble rising from a seated position or lifting objects overhead. Other skin manifestations include nail fold capillary changes, calcinosis cutis, and less commonly ulcerations signifying vasculopathy of the skin.2 A subset of patients will present with juvenile amyopathic dermatomyositis. These children have the characteristic skin changes without the muscle weakness or elevated muscle enzymes for more than 6 months; however, one-quarter may go on to develop mysositis.3
Diagnosis of JDM traditionally was based on the following 5 diagnostic criteria: characteristic skin rash, proximal muscle weakness, elevated muscle enzymes, myopathic changes on electromyogram, and typical muscle biopsy.1 Current practice shows a broadening of diagnostic criteria using new techniques in the diagnosis of JDM. To make the diagnosis, the patient must have the characteristic skin manifestations with a minimum of 3 other criteria.4 A 2006 international consensus survey expanded the list of criteria to include typical findings on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nail fold capillaroscopy abnormalities, calcinosis, and
dysphonia.5
To assess muscle disease, MRI is utilized because it is a reliable noninvasive tool to assess muscle inflammation. Muscle biopsy is only recommended if the diagnosis is unclear.5 The results of the MRI in our patient displayed symmetric mild fatty atrophy of the gluteus maximus muscle, as well as edema in the right rectus femoris and left vastus lateralis muscles, suggesting early findings of myositis. Muscle enzymes may not be diagnostic because they are not always elevated at diagnosis. Our patient had a normal creatinine kinase level (92 U/L [reference range, <190 U/L]), and both aldolase and lactate dehydrogenase also were within reference range. Conversely, antinuclear antibodies frequently are positive in patients with JDM, such as in our patient at a 1:320 dilution, but are nonspecific and nondiagnostic. It is recommended to include nail fold capillaroscopy to evaluate periungual capillary changes because nailfold capillary density is a sensitive measure of both skin and muscle disease.5 Using dermoscopy, nail fold capillary dilation was observed in our patient.
Other differential diagnoses can have somewhat similar clinical features to JDM. Infantile papular acrodermatitis, commonly referred to as Gianotti-Crosti syndrome, is a viral exanthem that affects children (median age, 2 years).6 The rash appears as monomorphous, flat-topped, pink to brown papules affecting the face, buttocks, and arms; it typically spontaneously resolves in 10 days.6
Juvenile-onset lupus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can involve any organ system and typically affects children aged 11 to 12 years with a female preponderance. Skin manifestations are similar to adult-onset lupus and include malar rash, discoid rash, oral ulcerations, petechiae, palpable purpura, and digital telangiectasia and ulcers. 7
Juvenile scleroderma is rare connective-tissue disorder that also has multiple organ involvement. Cutaneous involvement can range from isolated morphealike plaques to diffuse sclerotic lesions with growth disturbances, contractures, and facial atrophy.8
Verrucae planae, commonly referred to as flat warts, are papules caused primarily by human papillomavirus types 3, 10, 28, and 41. Children and young adults commonly are affected, and warts can appear on the hands, as in our patient.6
Treatment of JDM depends on disease severity at initial presentation and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The mainstay of treatment is high-dose oral prednisone in combination with disease-modifying drugs such as methotrexate and cyclosporin A. Patients with more severe presentations (eg, ulcerative skin disease) or life-threatening organ involvement are treated with cyclophosphamide, usually in combination with high-dose glucocorticoids.9
Early detection with aggressive treatment is vital to reduce morbidity and mortality from organ damage and disease complications. Mortality rates have dropped to 3%10 in recent decades with the use of systemic glucocorticoids. Delayed treatment is associated with a prolonged disease course and poorer outcomes. Disease complications in children with JDM include osteoporosis, calcinosis, and intestinal perforation; however, with early treatment, children with JDM can expect full recovery and to live a normal life as compared to adults with dermatomyositis.10
Prior to our patient's diagnosis, the family was assigned to move to an overseas location through the US Military with no direct access to advanced medical care. Early detection and diagnosis of JDM through an astute clinical examination allowed the patient and her family to remain in the continental United States to continue receiving specialty care.
- Mendez EP, Lipton R, Ramsey-Goldman R, et al. US incidence of juvenile dermatomyositis,1995-1998: results from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:300-305.
- Shah M, Mamyrova G, Targoff IN, et al. The clinical phenotypes of the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Medicine. 2013;92:25-41.
- Gerami P, Walling HW, Lewis J, et al. A systematic review of juvenile-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;57:637-644.
- Enders FB, Bader-Meunier B, Baildam E, et al. Consensus-based recommendations for the management of juvenile dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:329-340.
- Brown VE, Pilkington CA, Feldman BM, et al. An international consensus survey of the diagnostic criteria for juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45:990-993.
- William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Viral diseases. In: William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th ed. China: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:360-413.
- Levy DM, Kamphuis S. Systemic lupus erythematosus in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2012;59:345-364.
- Li SC, Torok KS, Pope E, et al; Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Localized Scleroderma Workgroup. Development of consensus treatment plans for juvenile localized scleroderma: a roadmap toward comparative effectiveness studies in juvenile localized scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64:1175-1185.
- Stringer E, Ota S, Bohnsack J, et al. Treatment approaches to juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) across North America: the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) JDM treatment study. J Rhematol. 2010;37:S1953-S1961.
- Huber AM, Feldman BM. Long-term outcomes in juvenile dermatomyositis: how did we get here and where are we going? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2005;7:441-446.
- Mendez EP, Lipton R, Ramsey-Goldman R, et al. US incidence of juvenile dermatomyositis,1995-1998: results from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:300-305.
- Shah M, Mamyrova G, Targoff IN, et al. The clinical phenotypes of the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Medicine. 2013;92:25-41.
- Gerami P, Walling HW, Lewis J, et al. A systematic review of juvenile-onset clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;57:637-644.
- Enders FB, Bader-Meunier B, Baildam E, et al. Consensus-based recommendations for the management of juvenile dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:329-340.
- Brown VE, Pilkington CA, Feldman BM, et al. An international consensus survey of the diagnostic criteria for juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45:990-993.
- William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Viral diseases. In: William JD, Berger TG, Elston DM. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 11th ed. China: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:360-413.
- Levy DM, Kamphuis S. Systemic lupus erythematosus in children and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2012;59:345-364.
- Li SC, Torok KS, Pope E, et al; Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Localized Scleroderma Workgroup. Development of consensus treatment plans for juvenile localized scleroderma: a roadmap toward comparative effectiveness studies in juvenile localized scleroderma. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64:1175-1185.
- Stringer E, Ota S, Bohnsack J, et al. Treatment approaches to juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) across North America: the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) JDM treatment study. J Rhematol. 2010;37:S1953-S1961.
- Huber AM, Feldman BM. Long-term outcomes in juvenile dermatomyositis: how did we get here and where are we going? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2005;7:441-446.
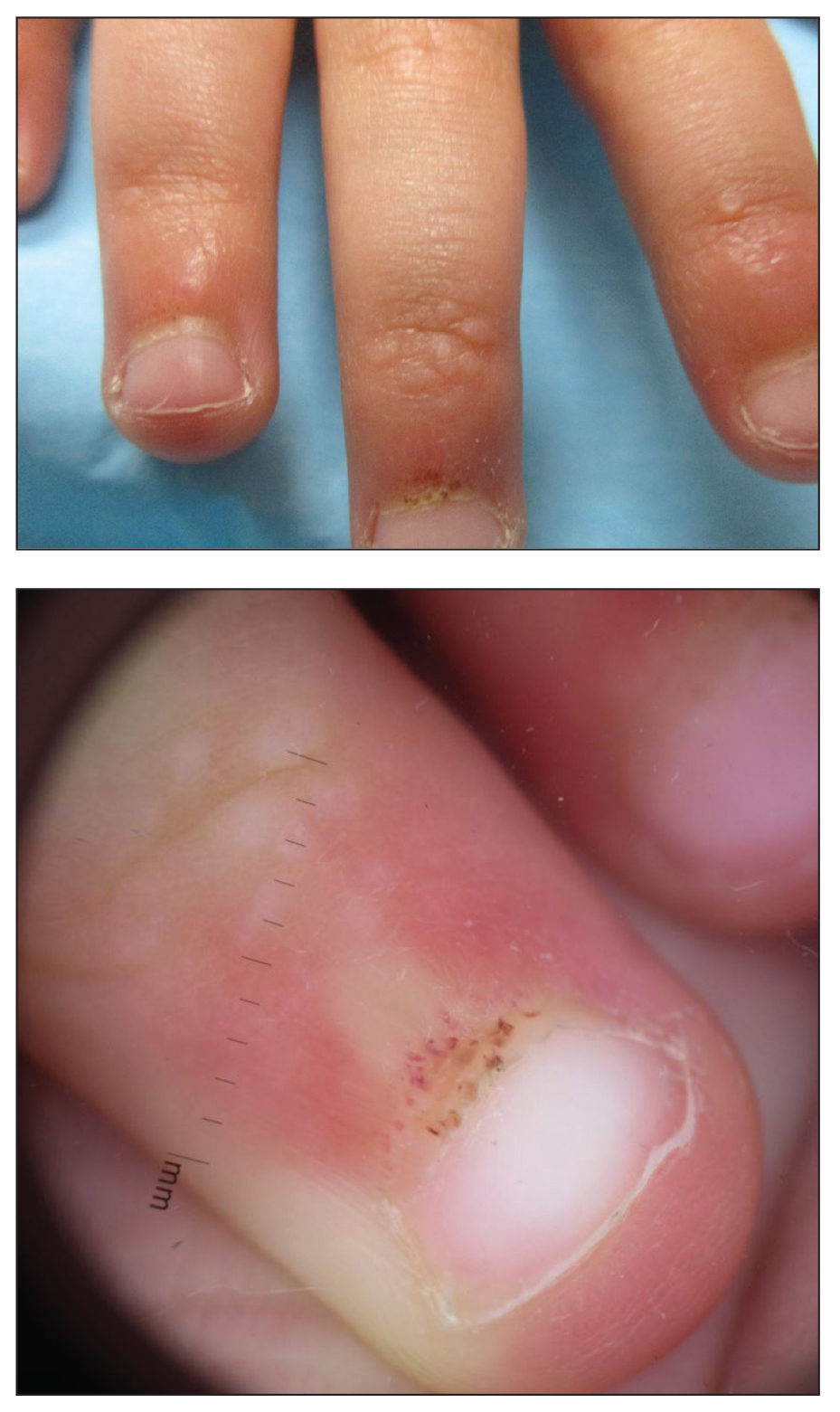
A 4-year-old girl presented to our dermatology clinic with asymptomatic flesh-colored bumps on the fingers of 2 to 3 months’ duration. Prior to presentation the patient was otherwise healthy with normal growth and development. She was referred to dermatology for recommended treatment options for suspected flat warts. On physical examination, grouped 1- to 3-mm, smooth, flat-topped papules were found on the dorsal aspects of the distal interphalangeal joints of all fingers (top). The papules were nonpruritic. Additionally, there were nail findings of ragged cuticles and dilated capillary loops in the proximal nail folds (bottom). The patient did not bite her nails, per the mother’s report, and no other rashes were noted. There were no systemic symptoms or reports of muscle fatigue. She was positive for antinuclear antibodies at 1:320 dilution. Magnetic resonance imaging of the thighs and pelvis was ordered.
Hair Loss in Skin of Color Patients
What does your patient need to know at the first visit?
All patients, regardless of race, gender, or age, are afraid of an alopecia diagnosis. Often, the first thing a patient may say when I enter the examination room is, "Please don't tell me I have alopecia."
The first step to a successful initial visit for hair loss is addressing the angst around the word alopecia, which helps to manage the patient's hair-induced anxiety. The next priority is setting expectations for the journey including what to expect during the diagnosis process, treatment, and beyond.
Next is data collection. An extensive hair care practice investigation can begin with a survey that the patient fills out before the visit. Dive into and expand on hair loss history questions, including medical history as well as hair care practices (eg, history of use, frequency, number of years, maintenance for that particular hairstyle) such as braids (eg, individual braids, cornrow braids, with or without added synthetic or human hair), locs (eg, length of locs), chemical relaxers (eg, number of years, frequency, professionally applied or applied at home), hair color, weaves (eg, glued in, sewn in, combination), and more.1 Include a family history of hair loss, both maternal and paternal.
The hair loss investigation almost always includes a scalp biopsy, hair-pull test, dermoscopy, photographs, and even blood work, if applicable. Scalp biopsies may reveal more than one type of alopecia diagnosis, which may impact the treatment plan.2 Sending the scalp biopsy specimen to a dermatopathologist specializing in alopecia along with clinical information about the patient is preferred.
What are your go-to treatments?
My go-to treatments for patients with skin of color (SOC) and hair loss really depend on the specific diagnosis. Randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials focusing on treatment are lacking in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia and traction alopecia, which holds true for many other types of alopecia.
For black patients with central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, I often address the inflammatory component of the disease with oral doxycycline and either a topical corticosteroid, such as clobetasol, or intralesional triamcinolone. Adding minoxidil-containing products later in the treatment process can be helpful. Various treatment protocols exist but are mainly based on anecdotal evidence.1
For those with traction alopecia, modification of offending hairstyle practices is a must.3 Also, treatment of inflammation is key. Typically, I gravitate to topical or intralesional corticosteroids, followed by minoxidil-containing products. However, a challenge of treating traction alopecia is changing the hair care practices that cause tight pulling, friction, or pressure on the scalp, such as from the band of a tightly fitted wig.
It is important to discuss potential side effects of any treatment with the patient. For the most common side effects, discuss how to best prevent them. For example, because of the photosensitivity potential of doxycycline, I ask patients to wear sunscreen daily. To prevent nausea, I recommend that they avoid taking doxycycline on an empty stomach, drink plenty of fluids, and avoid laying down within a few hours after taking the medication.
How do you keep patients compliant with treatment?
Dermatologists should try to understand their patients' hair. A study of 200 black women demonstrated that 68% of the patients did not think their physician understood their hair,4 which likely impacts patients' perceptions of their physician, confidence in the treatment plan, and even compliance with the plan. Attempting to understand the nuances of tightly coiled hair in those of African descent is the first step in the journey of diagnosing and treating hair loss in partnership with the patient.
Setting the goal is a crucial step toward patient compliance. It may be going out in public without a wig or weave and feeling confident, providing more coverage so affected areas do not show as much, improving scalp tenderness, and/or preventing further progression of the condition. These are all reasonable outcomes and each goal is uniquely tailored to each patient.
Familiarize yourself with various hair types, hairstyles, and preferred medication vehicles by attending continuing medical education lectures on alopecia in patients with SOC and on nuances to diagnosis and treatment, reading textbooks focusing on SOC, or seeking out mentorship from a dermatologist who is a hair expert in the types of alopecia most commonly affecting patients with SOC.
What resources do you recommend to patients for more information
For patients with scarring alopecia, the Cicatricial Alopecia Research Foundation (http://www.carfintl.org/) is a great resource for medical information and support groups. Also, the Skin of Color Society has dermatology patient education information (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/).
For patients who are extremely distressed by hair loss, I encourage them to see a mental health professional. The mental health impact of alopecia, despite the extent of disease, is likely underestimated. Patients sometimes need our permission to seek help, especially in many SOC communities where even seeking mental health care often is frowned upon.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric skin of color patients: bootcamp discussion. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
What does your patient need to know at the first visit?
All patients, regardless of race, gender, or age, are afraid of an alopecia diagnosis. Often, the first thing a patient may say when I enter the examination room is, "Please don't tell me I have alopecia."
The first step to a successful initial visit for hair loss is addressing the angst around the word alopecia, which helps to manage the patient's hair-induced anxiety. The next priority is setting expectations for the journey including what to expect during the diagnosis process, treatment, and beyond.
Next is data collection. An extensive hair care practice investigation can begin with a survey that the patient fills out before the visit. Dive into and expand on hair loss history questions, including medical history as well as hair care practices (eg, history of use, frequency, number of years, maintenance for that particular hairstyle) such as braids (eg, individual braids, cornrow braids, with or without added synthetic or human hair), locs (eg, length of locs), chemical relaxers (eg, number of years, frequency, professionally applied or applied at home), hair color, weaves (eg, glued in, sewn in, combination), and more.1 Include a family history of hair loss, both maternal and paternal.
The hair loss investigation almost always includes a scalp biopsy, hair-pull test, dermoscopy, photographs, and even blood work, if applicable. Scalp biopsies may reveal more than one type of alopecia diagnosis, which may impact the treatment plan.2 Sending the scalp biopsy specimen to a dermatopathologist specializing in alopecia along with clinical information about the patient is preferred.
What are your go-to treatments?
My go-to treatments for patients with skin of color (SOC) and hair loss really depend on the specific diagnosis. Randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials focusing on treatment are lacking in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia and traction alopecia, which holds true for many other types of alopecia.
For black patients with central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, I often address the inflammatory component of the disease with oral doxycycline and either a topical corticosteroid, such as clobetasol, or intralesional triamcinolone. Adding minoxidil-containing products later in the treatment process can be helpful. Various treatment protocols exist but are mainly based on anecdotal evidence.1
For those with traction alopecia, modification of offending hairstyle practices is a must.3 Also, treatment of inflammation is key. Typically, I gravitate to topical or intralesional corticosteroids, followed by minoxidil-containing products. However, a challenge of treating traction alopecia is changing the hair care practices that cause tight pulling, friction, or pressure on the scalp, such as from the band of a tightly fitted wig.
It is important to discuss potential side effects of any treatment with the patient. For the most common side effects, discuss how to best prevent them. For example, because of the photosensitivity potential of doxycycline, I ask patients to wear sunscreen daily. To prevent nausea, I recommend that they avoid taking doxycycline on an empty stomach, drink plenty of fluids, and avoid laying down within a few hours after taking the medication.
How do you keep patients compliant with treatment?
Dermatologists should try to understand their patients' hair. A study of 200 black women demonstrated that 68% of the patients did not think their physician understood their hair,4 which likely impacts patients' perceptions of their physician, confidence in the treatment plan, and even compliance with the plan. Attempting to understand the nuances of tightly coiled hair in those of African descent is the first step in the journey of diagnosing and treating hair loss in partnership with the patient.
Setting the goal is a crucial step toward patient compliance. It may be going out in public without a wig or weave and feeling confident, providing more coverage so affected areas do not show as much, improving scalp tenderness, and/or preventing further progression of the condition. These are all reasonable outcomes and each goal is uniquely tailored to each patient.
Familiarize yourself with various hair types, hairstyles, and preferred medication vehicles by attending continuing medical education lectures on alopecia in patients with SOC and on nuances to diagnosis and treatment, reading textbooks focusing on SOC, or seeking out mentorship from a dermatologist who is a hair expert in the types of alopecia most commonly affecting patients with SOC.
What resources do you recommend to patients for more information
For patients with scarring alopecia, the Cicatricial Alopecia Research Foundation (http://www.carfintl.org/) is a great resource for medical information and support groups. Also, the Skin of Color Society has dermatology patient education information (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/).
For patients who are extremely distressed by hair loss, I encourage them to see a mental health professional. The mental health impact of alopecia, despite the extent of disease, is likely underestimated. Patients sometimes need our permission to seek help, especially in many SOC communities where even seeking mental health care often is frowned upon.
What does your patient need to know at the first visit?
All patients, regardless of race, gender, or age, are afraid of an alopecia diagnosis. Often, the first thing a patient may say when I enter the examination room is, "Please don't tell me I have alopecia."
The first step to a successful initial visit for hair loss is addressing the angst around the word alopecia, which helps to manage the patient's hair-induced anxiety. The next priority is setting expectations for the journey including what to expect during the diagnosis process, treatment, and beyond.
Next is data collection. An extensive hair care practice investigation can begin with a survey that the patient fills out before the visit. Dive into and expand on hair loss history questions, including medical history as well as hair care practices (eg, history of use, frequency, number of years, maintenance for that particular hairstyle) such as braids (eg, individual braids, cornrow braids, with or without added synthetic or human hair), locs (eg, length of locs), chemical relaxers (eg, number of years, frequency, professionally applied or applied at home), hair color, weaves (eg, glued in, sewn in, combination), and more.1 Include a family history of hair loss, both maternal and paternal.
The hair loss investigation almost always includes a scalp biopsy, hair-pull test, dermoscopy, photographs, and even blood work, if applicable. Scalp biopsies may reveal more than one type of alopecia diagnosis, which may impact the treatment plan.2 Sending the scalp biopsy specimen to a dermatopathologist specializing in alopecia along with clinical information about the patient is preferred.
What are your go-to treatments?
My go-to treatments for patients with skin of color (SOC) and hair loss really depend on the specific diagnosis. Randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials focusing on treatment are lacking in central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia and traction alopecia, which holds true for many other types of alopecia.
For black patients with central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia, I often address the inflammatory component of the disease with oral doxycycline and either a topical corticosteroid, such as clobetasol, or intralesional triamcinolone. Adding minoxidil-containing products later in the treatment process can be helpful. Various treatment protocols exist but are mainly based on anecdotal evidence.1
For those with traction alopecia, modification of offending hairstyle practices is a must.3 Also, treatment of inflammation is key. Typically, I gravitate to topical or intralesional corticosteroids, followed by minoxidil-containing products. However, a challenge of treating traction alopecia is changing the hair care practices that cause tight pulling, friction, or pressure on the scalp, such as from the band of a tightly fitted wig.
It is important to discuss potential side effects of any treatment with the patient. For the most common side effects, discuss how to best prevent them. For example, because of the photosensitivity potential of doxycycline, I ask patients to wear sunscreen daily. To prevent nausea, I recommend that they avoid taking doxycycline on an empty stomach, drink plenty of fluids, and avoid laying down within a few hours after taking the medication.
How do you keep patients compliant with treatment?
Dermatologists should try to understand their patients' hair. A study of 200 black women demonstrated that 68% of the patients did not think their physician understood their hair,4 which likely impacts patients' perceptions of their physician, confidence in the treatment plan, and even compliance with the plan. Attempting to understand the nuances of tightly coiled hair in those of African descent is the first step in the journey of diagnosing and treating hair loss in partnership with the patient.
Setting the goal is a crucial step toward patient compliance. It may be going out in public without a wig or weave and feeling confident, providing more coverage so affected areas do not show as much, improving scalp tenderness, and/or preventing further progression of the condition. These are all reasonable outcomes and each goal is uniquely tailored to each patient.
Familiarize yourself with various hair types, hairstyles, and preferred medication vehicles by attending continuing medical education lectures on alopecia in patients with SOC and on nuances to diagnosis and treatment, reading textbooks focusing on SOC, or seeking out mentorship from a dermatologist who is a hair expert in the types of alopecia most commonly affecting patients with SOC.
What resources do you recommend to patients for more information
For patients with scarring alopecia, the Cicatricial Alopecia Research Foundation (http://www.carfintl.org/) is a great resource for medical information and support groups. Also, the Skin of Color Society has dermatology patient education information (http://skinofcolorsociety.org/).
For patients who are extremely distressed by hair loss, I encourage them to see a mental health professional. The mental health impact of alopecia, despite the extent of disease, is likely underestimated. Patients sometimes need our permission to seek help, especially in many SOC communities where even seeking mental health care often is frowned upon.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric skin of color patients: bootcamp discussion. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.
- Taylor SC, Barbosa V, Burgess C, et al. Hair and scalp disorders in adult and pediatric skin of color patients: bootcamp discussion. Cutis. 2017;100:31-35.
- Wohltmann WE, Sperling L. Histopathologic diagnosis of multifactorial alopecia. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:483-491.
- Haskin A, Aguh C. All hairstyles are not created equal: what the dermatologist needs to know about black hairstyling practices and the risk of traction alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:606-611.
- Gathers RC, Mahan MG. African American women, hair care and health barriers. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:26-29.