User login
Physicians react: Should docs lose their licenses for spreading false COVID information?
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The death of expertise
Unless your social circle is packed with medical professionals, I suspect you are the go-to gal/guy when there is a question about the pandemic. Seated around the fire pit trying to stay warm and socially distanced, inevitably the discussion will turn to COVID. Someone will report something they have read about vaccine side effects or the appropriate timing of isolation or quarantine and then turn to me assuming that I have inside information and ask: “But Will you know all about that. Tell us what have you heard.”
By now, well into our second year of the pandemic, my friends and neighbors should have come to expect my usual answer. “I don’t really know any more about this than you have read on the Internet or seen on television.” I am flattered that folks keep asking for my observations. I guess old habits die slowly. Although I usually introduce myself as an ex-pediatrician, the “doctor” descriptor still seems to command some respect, whether it is deserved or not.
It is not just my waning ability to speak authoritatively about the pandemic that has put expertise at death’s door. Although my formal medical education is more than a half-century old, like most physicians I have tried to stay abreast of what’s happening in health care. Keeping up to date with the new developments in pathophysiology and pharmacology does take some work, but the pandemic has shone a spotlight on how quickly these changes can occur.
With the pandemic, a sense of urgency has thrust onto the world stage opinions that in the past might have been quietly held theories based on preliminary studies. However, even the most careful scientists who might otherwise have been content to patiently wait for peer review are sharing their findings prematurely with international news sources and on social media. Not surprisingly, this rush to share has generated confusion and concern and in many cases resulted in retractions or corrections. Even more importantly, it has made us all skeptical about who these “experts” are, making often disproven pronouncements.
While my friends still persist in politely asking my opinion based on the same reports we are all reading on the Internet, I sense the nation as a whole has become wary of claimed expertise. I haven’t done a Google search but I wouldn’t be surprised if “expert” gets far fewer hits than the term “so-called expert.”
Even before we were engulfed by the pandemic, there has been an unfortunate phenomenon in which health care providers and other scientists are parlaying their degrees to promote products with little if any proven efficacy. Of course, this country has a long history of snake oil salesmen making their rounds. However, the electronic media and the Internet have increased the power to persuade so that we are awash in so-called experts. Many good scientists, in an attempt to be helpful, have succumbed to the sin of impatience. And there are a few who had never earned the moniker “expert.”
I hope that expertise returns to the landscape when the pandemic abates. But, I fear it may be a while.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Unless your social circle is packed with medical professionals, I suspect you are the go-to gal/guy when there is a question about the pandemic. Seated around the fire pit trying to stay warm and socially distanced, inevitably the discussion will turn to COVID. Someone will report something they have read about vaccine side effects or the appropriate timing of isolation or quarantine and then turn to me assuming that I have inside information and ask: “But Will you know all about that. Tell us what have you heard.”
By now, well into our second year of the pandemic, my friends and neighbors should have come to expect my usual answer. “I don’t really know any more about this than you have read on the Internet or seen on television.” I am flattered that folks keep asking for my observations. I guess old habits die slowly. Although I usually introduce myself as an ex-pediatrician, the “doctor” descriptor still seems to command some respect, whether it is deserved or not.
It is not just my waning ability to speak authoritatively about the pandemic that has put expertise at death’s door. Although my formal medical education is more than a half-century old, like most physicians I have tried to stay abreast of what’s happening in health care. Keeping up to date with the new developments in pathophysiology and pharmacology does take some work, but the pandemic has shone a spotlight on how quickly these changes can occur.
With the pandemic, a sense of urgency has thrust onto the world stage opinions that in the past might have been quietly held theories based on preliminary studies. However, even the most careful scientists who might otherwise have been content to patiently wait for peer review are sharing their findings prematurely with international news sources and on social media. Not surprisingly, this rush to share has generated confusion and concern and in many cases resulted in retractions or corrections. Even more importantly, it has made us all skeptical about who these “experts” are, making often disproven pronouncements.
While my friends still persist in politely asking my opinion based on the same reports we are all reading on the Internet, I sense the nation as a whole has become wary of claimed expertise. I haven’t done a Google search but I wouldn’t be surprised if “expert” gets far fewer hits than the term “so-called expert.”
Even before we were engulfed by the pandemic, there has been an unfortunate phenomenon in which health care providers and other scientists are parlaying their degrees to promote products with little if any proven efficacy. Of course, this country has a long history of snake oil salesmen making their rounds. However, the electronic media and the Internet have increased the power to persuade so that we are awash in so-called experts. Many good scientists, in an attempt to be helpful, have succumbed to the sin of impatience. And there are a few who had never earned the moniker “expert.”
I hope that expertise returns to the landscape when the pandemic abates. But, I fear it may be a while.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Unless your social circle is packed with medical professionals, I suspect you are the go-to gal/guy when there is a question about the pandemic. Seated around the fire pit trying to stay warm and socially distanced, inevitably the discussion will turn to COVID. Someone will report something they have read about vaccine side effects or the appropriate timing of isolation or quarantine and then turn to me assuming that I have inside information and ask: “But Will you know all about that. Tell us what have you heard.”
By now, well into our second year of the pandemic, my friends and neighbors should have come to expect my usual answer. “I don’t really know any more about this than you have read on the Internet or seen on television.” I am flattered that folks keep asking for my observations. I guess old habits die slowly. Although I usually introduce myself as an ex-pediatrician, the “doctor” descriptor still seems to command some respect, whether it is deserved or not.
It is not just my waning ability to speak authoritatively about the pandemic that has put expertise at death’s door. Although my formal medical education is more than a half-century old, like most physicians I have tried to stay abreast of what’s happening in health care. Keeping up to date with the new developments in pathophysiology and pharmacology does take some work, but the pandemic has shone a spotlight on how quickly these changes can occur.
With the pandemic, a sense of urgency has thrust onto the world stage opinions that in the past might have been quietly held theories based on preliminary studies. However, even the most careful scientists who might otherwise have been content to patiently wait for peer review are sharing their findings prematurely with international news sources and on social media. Not surprisingly, this rush to share has generated confusion and concern and in many cases resulted in retractions or corrections. Even more importantly, it has made us all skeptical about who these “experts” are, making often disproven pronouncements.
While my friends still persist in politely asking my opinion based on the same reports we are all reading on the Internet, I sense the nation as a whole has become wary of claimed expertise. I haven’t done a Google search but I wouldn’t be surprised if “expert” gets far fewer hits than the term “so-called expert.”
Even before we were engulfed by the pandemic, there has been an unfortunate phenomenon in which health care providers and other scientists are parlaying their degrees to promote products with little if any proven efficacy. Of course, this country has a long history of snake oil salesmen making their rounds. However, the electronic media and the Internet have increased the power to persuade so that we are awash in so-called experts. Many good scientists, in an attempt to be helpful, have succumbed to the sin of impatience. And there are a few who had never earned the moniker “expert.”
I hope that expertise returns to the landscape when the pandemic abates. But, I fear it may be a while.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Responding to the Pandemic: How is the VA doing?
The VA’s Coronavirus Disease 2019 Response Report is now in its third iteration as the pandemic continues. On the bright side, as Steven Lieberman, MD, deputy under secretary for health at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), writes in the report’s introduction, “we have learned a great deal about mounting a national response to a public health crisis.”
“Annex B” covers January 1, 2021 to July 31, 2021, building on the 2 previous reports. All 3 have sought to capture and share lessons learned, with updated information on vaccination, elder care, health equity, mental health, health care ethics, preparedness, and other topics.
As the pandemic evolved, so did the VA efforts to cope with it. This iteration, for instance, deals with details of the campaign that vaccinated more than 2.5 million people “while sustaining all other aspects of the pandemic response and veteran health services,” and how the VA implemented a vaccine mandate for all VA employees in health care roles—the first federal agency to do so. In addition to vaccinating veterans, the Strengthening and Amplifying Vaccination Efforts to Locally Immunize All Veterans and Every Spouse (SAVE LIVES) Act led to nearly 80,000 other vaccinations among families, caregivers, and veterans who do not use VHA services.
The VA also conducted extensive COVID-19 testing, processing as many as 70,000 to 90,000 tests per week. It enhanced telehealth services to reach home-based and rural veterans, for an almost 2,500% increase in home-based primary care. Recognizing the added stress the pandemic put on people at risk for suicide, the VHA used predictive analytic tools specific to veterans with COVID-19 and monitored “high-risk flags,” using them to identify veterans for tailored outreach.
The response also included carrying out 158 Federal Emergency Management Agency Fourth Mission assignments. The report highlights the contributions of the more than 1,600 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) employees who volunteered to deploy across the country, often multiple times.
In addition to active response, more than 300 studies on COVID-19 have been published by VA researchers.
The current status report discusses how to expand what worked and to improve what did not. For instance, one unsurprising finding was that “the sustained pandemic response has imposed stress on the workforce, most evident in the nursing workforce.” The recommendation: Develop a comprehensive strategy with metrics and actions to monitor and mitigate stress on the health care workforce, facilitate wellness, and enhance retention.
The finding that VHA has demonstrated that telehealth usage for care to elderly veterans is “beneficial and feasible with the right technical support” led to recommendations for expanded research to identify effective COVID-19 prevention and intervention measures for elderly veterans residing at home or in long-term care facilities.
The research found that VHA processes for protecting community living center (CLC) residents during the pandemic “have succeeded in keeping rates of CLC-onset COVID-19 at the same rate as for the population of enrolled veterans over 65,” the report says. The recommendation based on that finding is to develop an information system to facilitate monitoring of state-run veterans homes for indicators of infectious disease risk, combining periodic assessment results with epidemiologic community data.
However, the report also acknowledges unexpected detours or blocks. “Planning for the mass vaccination campaign was highly effective, but did not anticipate the complexity of interagency support.” And “[t[he inability to access state vaccination data left VHA with an incomplete picture of the vaccination status of enrolled veterans.” In response, the VA recommends incorporating interagency support into planning templates and pursuing legislative action to enable the VA to obtain vaccination data from states.
Overall, the report gives the VA high marks for managing a “well-coordinated response” to an overwhelming crisis. But the lessons are not over.
“As we continue to address the pandemic and as new variants arise,” Dr. Lieberman said in comments, “it is clear that continuous learning and improvement are essential to a successful COVID-19 response. We will continue to update this report to document our efforts so veterans, doctors, and the public can understand and learn from what we’ve discovered to better serve our veterans and communities.” Stay tuned for Annex C.
The VA’s Coronavirus Disease 2019 Response Report is now in its third iteration as the pandemic continues. On the bright side, as Steven Lieberman, MD, deputy under secretary for health at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), writes in the report’s introduction, “we have learned a great deal about mounting a national response to a public health crisis.”
“Annex B” covers January 1, 2021 to July 31, 2021, building on the 2 previous reports. All 3 have sought to capture and share lessons learned, with updated information on vaccination, elder care, health equity, mental health, health care ethics, preparedness, and other topics.
As the pandemic evolved, so did the VA efforts to cope with it. This iteration, for instance, deals with details of the campaign that vaccinated more than 2.5 million people “while sustaining all other aspects of the pandemic response and veteran health services,” and how the VA implemented a vaccine mandate for all VA employees in health care roles—the first federal agency to do so. In addition to vaccinating veterans, the Strengthening and Amplifying Vaccination Efforts to Locally Immunize All Veterans and Every Spouse (SAVE LIVES) Act led to nearly 80,000 other vaccinations among families, caregivers, and veterans who do not use VHA services.
The VA also conducted extensive COVID-19 testing, processing as many as 70,000 to 90,000 tests per week. It enhanced telehealth services to reach home-based and rural veterans, for an almost 2,500% increase in home-based primary care. Recognizing the added stress the pandemic put on people at risk for suicide, the VHA used predictive analytic tools specific to veterans with COVID-19 and monitored “high-risk flags,” using them to identify veterans for tailored outreach.
The response also included carrying out 158 Federal Emergency Management Agency Fourth Mission assignments. The report highlights the contributions of the more than 1,600 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) employees who volunteered to deploy across the country, often multiple times.
In addition to active response, more than 300 studies on COVID-19 have been published by VA researchers.
The current status report discusses how to expand what worked and to improve what did not. For instance, one unsurprising finding was that “the sustained pandemic response has imposed stress on the workforce, most evident in the nursing workforce.” The recommendation: Develop a comprehensive strategy with metrics and actions to monitor and mitigate stress on the health care workforce, facilitate wellness, and enhance retention.
The finding that VHA has demonstrated that telehealth usage for care to elderly veterans is “beneficial and feasible with the right technical support” led to recommendations for expanded research to identify effective COVID-19 prevention and intervention measures for elderly veterans residing at home or in long-term care facilities.
The research found that VHA processes for protecting community living center (CLC) residents during the pandemic “have succeeded in keeping rates of CLC-onset COVID-19 at the same rate as for the population of enrolled veterans over 65,” the report says. The recommendation based on that finding is to develop an information system to facilitate monitoring of state-run veterans homes for indicators of infectious disease risk, combining periodic assessment results with epidemiologic community data.
However, the report also acknowledges unexpected detours or blocks. “Planning for the mass vaccination campaign was highly effective, but did not anticipate the complexity of interagency support.” And “[t[he inability to access state vaccination data left VHA with an incomplete picture of the vaccination status of enrolled veterans.” In response, the VA recommends incorporating interagency support into planning templates and pursuing legislative action to enable the VA to obtain vaccination data from states.
Overall, the report gives the VA high marks for managing a “well-coordinated response” to an overwhelming crisis. But the lessons are not over.
“As we continue to address the pandemic and as new variants arise,” Dr. Lieberman said in comments, “it is clear that continuous learning and improvement are essential to a successful COVID-19 response. We will continue to update this report to document our efforts so veterans, doctors, and the public can understand and learn from what we’ve discovered to better serve our veterans and communities.” Stay tuned for Annex C.
The VA’s Coronavirus Disease 2019 Response Report is now in its third iteration as the pandemic continues. On the bright side, as Steven Lieberman, MD, deputy under secretary for health at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), writes in the report’s introduction, “we have learned a great deal about mounting a national response to a public health crisis.”
“Annex B” covers January 1, 2021 to July 31, 2021, building on the 2 previous reports. All 3 have sought to capture and share lessons learned, with updated information on vaccination, elder care, health equity, mental health, health care ethics, preparedness, and other topics.
As the pandemic evolved, so did the VA efforts to cope with it. This iteration, for instance, deals with details of the campaign that vaccinated more than 2.5 million people “while sustaining all other aspects of the pandemic response and veteran health services,” and how the VA implemented a vaccine mandate for all VA employees in health care roles—the first federal agency to do so. In addition to vaccinating veterans, the Strengthening and Amplifying Vaccination Efforts to Locally Immunize All Veterans and Every Spouse (SAVE LIVES) Act led to nearly 80,000 other vaccinations among families, caregivers, and veterans who do not use VHA services.
The VA also conducted extensive COVID-19 testing, processing as many as 70,000 to 90,000 tests per week. It enhanced telehealth services to reach home-based and rural veterans, for an almost 2,500% increase in home-based primary care. Recognizing the added stress the pandemic put on people at risk for suicide, the VHA used predictive analytic tools specific to veterans with COVID-19 and monitored “high-risk flags,” using them to identify veterans for tailored outreach.
The response also included carrying out 158 Federal Emergency Management Agency Fourth Mission assignments. The report highlights the contributions of the more than 1,600 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) employees who volunteered to deploy across the country, often multiple times.
In addition to active response, more than 300 studies on COVID-19 have been published by VA researchers.
The current status report discusses how to expand what worked and to improve what did not. For instance, one unsurprising finding was that “the sustained pandemic response has imposed stress on the workforce, most evident in the nursing workforce.” The recommendation: Develop a comprehensive strategy with metrics and actions to monitor and mitigate stress on the health care workforce, facilitate wellness, and enhance retention.
The finding that VHA has demonstrated that telehealth usage for care to elderly veterans is “beneficial and feasible with the right technical support” led to recommendations for expanded research to identify effective COVID-19 prevention and intervention measures for elderly veterans residing at home or in long-term care facilities.
The research found that VHA processes for protecting community living center (CLC) residents during the pandemic “have succeeded in keeping rates of CLC-onset COVID-19 at the same rate as for the population of enrolled veterans over 65,” the report says. The recommendation based on that finding is to develop an information system to facilitate monitoring of state-run veterans homes for indicators of infectious disease risk, combining periodic assessment results with epidemiologic community data.
However, the report also acknowledges unexpected detours or blocks. “Planning for the mass vaccination campaign was highly effective, but did not anticipate the complexity of interagency support.” And “[t[he inability to access state vaccination data left VHA with an incomplete picture of the vaccination status of enrolled veterans.” In response, the VA recommends incorporating interagency support into planning templates and pursuing legislative action to enable the VA to obtain vaccination data from states.
Overall, the report gives the VA high marks for managing a “well-coordinated response” to an overwhelming crisis. But the lessons are not over.
“As we continue to address the pandemic and as new variants arise,” Dr. Lieberman said in comments, “it is clear that continuous learning and improvement are essential to a successful COVID-19 response. We will continue to update this report to document our efforts so veterans, doctors, and the public can understand and learn from what we’ve discovered to better serve our veterans and communities.” Stay tuned for Annex C.
Children and COVID: New cases and hospital admissions skyrocket
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.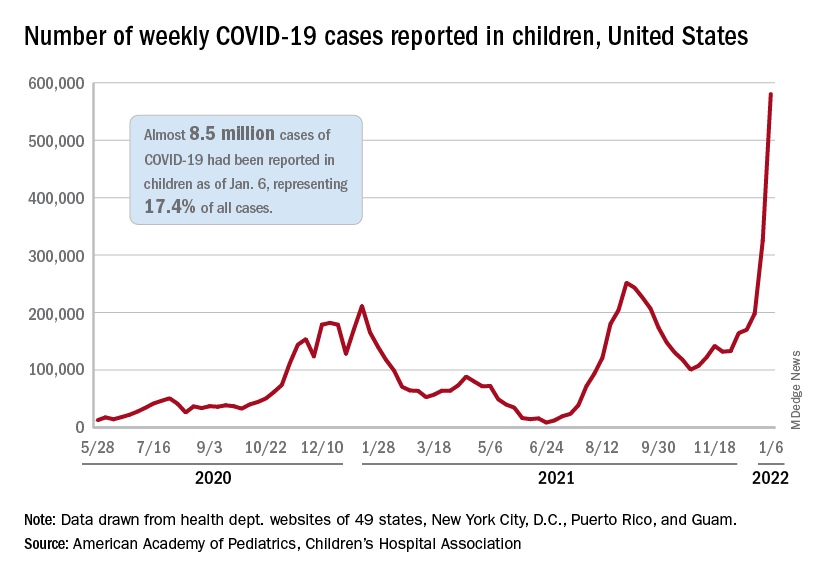
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
U.S. reports record-breaking 1.35 million new COVID cases in a day
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
What if the National Guard Can’t Help?
What if the National Guard Can’t Help?
In early January, Ohio not only set a state record for COVID-19 hospitalizations—it had the fourth highest rate in the country, with 6,747 hospitalized coronavirus patients on January 10, a 40% increase over the previous 21 days. Most were unvaccinated. To help overwhelmed hospitals cope, Ohio Gov. Mike DeWine turned to the National Guard. Unfortunately, nearly half of the Ohio National Guard also were unvaccinated.
By US Department of Defense (DoD) directive, National Guard members must have a COVID-19 vaccination to be deployed on hospital missions. Thus, in COVID hotspots across the nation, governors are on the horns of a dilemma. They want and need to deploy the National Guard to give medical and nonclinical support but aren’t sure whether they will be able to or, indeed, whether they should.
So far, vaccinated teams are already on the ground in a number of states. In Indiana, where hospitalizations jumped 50% over 2 weeks in December, the National Guard sent 6-person teams, all fully vaccinated. In New Hampshire, 70 guards are being deployed to help hospitals with food service, clerical work, and other nonmedical functions. New York Governor Kathy Hochul has deployed guard members for help to ease the strain on nursing homes. Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker has activated up to 500 guard members; some will be supporting 55 acute care hospital and 12 ambulance services. In Maine, where cases have peaked, Governor Janet Mills activated guard members to support nursing facilities and administer monoclonal antibodies. The Louisiana National Guard has administered more than 542,000 COVID-19 tests and 206,300 vaccines. As many as 1,000 Maryland Air and Army National Guardsmen are being activated to help with testing and other missions.
However, as in Ohio, other states are facing problematic scenarios. For instance, about 40% of the more than 20,000 Texas National Guard are refusing to get vaccinated, challenging the Biden Administration vaccine requirement for all military.
And a court showdown over federal vaccine mandates, started by Governor Kevin Stitt of Oklahoma and joined by the Republican governors of Wyoming, Iowa, Alaska, Nebraska, and Mississippi, came to a head in December. Last November, Stitt asked Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin to exempt Oklahoma’s National Guard from the vaccine mandate. He claimed the requirement violated the personal freedoms of many Oklahomans and could cause them to “potentially sacrifice their personal beliefs.” But in a memo to the Joint Chiefs chairmen, the service secretaries and the head of the National Guard Bureau, Austin wrote that Pentagon funds could not be used to pay for duties performed under Title 32 for members of the Guard who do not comply with the military’s vaccine requirement. (Title 32 refers to Guard operations under state orders.) Austin also said National Guard members must be vaccinated to participate in drills, training, and other duty conducted under Title 32.
Stitt, maintaining that he is commander in chief of the Oklahoma National Guard as long as it operates under Title 32 orders, put out his own memo stipulating that no Guard member was required to get vaccinated. He also ordered Brig. Gen. Thomas Mancino, newly appointed commander of the Oklahoma National Guard, to not enforce the mandate. Subsequently, Mancino issued a statement pointing out that current state law is limited in protecting troops who opt out of the shot. Moreover, if the Guard were called up under federal orders, he said, he would enforce the mandate. Training events, schools, and mobilizations were going to “eventually force you out of that safe harbor,” he wrote, “…This is reality.”
In late December, a federal judge denied Oklahoma’s motion to enjoin the mandate. The Oklahoma Attorney General’s office responded, “We will not be surprised if the President’s vaccine mandate actually reduces the nation’s military readiness instead of promoting it.”
In a press briefing, Pentagon press secretary John Kirby said, “The Secretary has the authorities he needs to require this vaccine across the force, including the National Guard. …[E]ven when they’re in a Title 32 status.” He added, “It is a lawful order for National Guardsmen to receive the COVID vaccine. It’s a lawful order, and refusing to do that, absent of an improved exemption, puts them in the same potential [position] as active-duty members who refuse the vaccine.” That could mean, for instance, loss of pay and membership in the National Guard.
A core rationale for the mandate, according to Secretary Austin, is the need for military readiness—meaning Guard members must be healthy and fit for duty. And that extends to being healthy and fit for missions like transporting at-risk patients. Ohio National Guard Adjutant General Major General John Harris Jr. said, “I would never put a soldier or airman in harm’s way without the best protection we could put on them—body armor, helmets. And this medical readiness is the exact same thing. We’re putting folks into harm’s way.” He has moved the deadline from the Pentagon’s June 30 date to March 31—a move that boosted the vaccination rate from 53% to 56% in one week.
Ohio Governor DeWine has expressed frustration that almost half of the Ohio Army National Guard personnel can’t be deployed on this mission because they’re unvaccinated. “In some of our testing places, 40 to 50% of the people are testing positive,” he said. “So this is a high-risk operation. You need to be protected. The best way for you to be protected is to get the vaccination.”
As of December 2021, according to the National Guard Bureau, the National Guard as a whole was 66% fully vaccinated. The percentages vary according to service; for instance, nearly 90% of airmen have been vaccinated, compared with only 40% of Army Guardsmen. Among the states challenging the mandate, the vaccinated rates have been moving upward: In Alaska, about 92% of the Air National Guard have been vaccinated—leaving roughly 11,000 troops who had not met the December 2 deadline. In Iowa, as of Nov. 30, 91% of Air National Guard and 80% of Army National Guard members had been vaccinated, but about 9,000 soldiers had been directed to get the vaccination or risk disciplinary action. Almost 2,200 of the more than 2,800-strong Wyoming National Guard (77%) have received at least 1 dose. Nebraska Air National Guard’s force of 1,000 was 94% fully vaccinated as of December 1. (Maj Scott Ingalsbe, public affairs officer, said, “Vaccinations are tied to individual medical readiness. They provide service members with the best protection available so they can perform missions across the globe.”).
In most states, Army National Guard members have until June 30, 2022, to comply. “Our soldiers …have until [the DoD’s deadline], and some of them are just going to wait close to the deadline,” John Goheen of the National Guard Association of the United States said in a discussion on NPR. “That’s human nature.”
Earlier this month, Texas Governor Greg Abbott told National Guard members they can ignore the Pentagon’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate: “President Biden is not your commander-in-chief.” He has also sued the Biden administration over the requirement.
In the meantime, the hospitals at breaking point must hope for the best and take as much help as they can get.
In early January, Ohio not only set a state record for COVID-19 hospitalizations—it had the fourth highest rate in the country, with 6,747 hospitalized coronavirus patients on January 10, a 40% increase over the previous 21 days. Most were unvaccinated. To help overwhelmed hospitals cope, Ohio Gov. Mike DeWine turned to the National Guard. Unfortunately, nearly half of the Ohio National Guard also were unvaccinated.
By US Department of Defense (DoD) directive, National Guard members must have a COVID-19 vaccination to be deployed on hospital missions. Thus, in COVID hotspots across the nation, governors are on the horns of a dilemma. They want and need to deploy the National Guard to give medical and nonclinical support but aren’t sure whether they will be able to or, indeed, whether they should.
So far, vaccinated teams are already on the ground in a number of states. In Indiana, where hospitalizations jumped 50% over 2 weeks in December, the National Guard sent 6-person teams, all fully vaccinated. In New Hampshire, 70 guards are being deployed to help hospitals with food service, clerical work, and other nonmedical functions. New York Governor Kathy Hochul has deployed guard members for help to ease the strain on nursing homes. Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker has activated up to 500 guard members; some will be supporting 55 acute care hospital and 12 ambulance services. In Maine, where cases have peaked, Governor Janet Mills activated guard members to support nursing facilities and administer monoclonal antibodies. The Louisiana National Guard has administered more than 542,000 COVID-19 tests and 206,300 vaccines. As many as 1,000 Maryland Air and Army National Guardsmen are being activated to help with testing and other missions.
However, as in Ohio, other states are facing problematic scenarios. For instance, about 40% of the more than 20,000 Texas National Guard are refusing to get vaccinated, challenging the Biden Administration vaccine requirement for all military.
And a court showdown over federal vaccine mandates, started by Governor Kevin Stitt of Oklahoma and joined by the Republican governors of Wyoming, Iowa, Alaska, Nebraska, and Mississippi, came to a head in December. Last November, Stitt asked Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin to exempt Oklahoma’s National Guard from the vaccine mandate. He claimed the requirement violated the personal freedoms of many Oklahomans and could cause them to “potentially sacrifice their personal beliefs.” But in a memo to the Joint Chiefs chairmen, the service secretaries and the head of the National Guard Bureau, Austin wrote that Pentagon funds could not be used to pay for duties performed under Title 32 for members of the Guard who do not comply with the military’s vaccine requirement. (Title 32 refers to Guard operations under state orders.) Austin also said National Guard members must be vaccinated to participate in drills, training, and other duty conducted under Title 32.
Stitt, maintaining that he is commander in chief of the Oklahoma National Guard as long as it operates under Title 32 orders, put out his own memo stipulating that no Guard member was required to get vaccinated. He also ordered Brig. Gen. Thomas Mancino, newly appointed commander of the Oklahoma National Guard, to not enforce the mandate. Subsequently, Mancino issued a statement pointing out that current state law is limited in protecting troops who opt out of the shot. Moreover, if the Guard were called up under federal orders, he said, he would enforce the mandate. Training events, schools, and mobilizations were going to “eventually force you out of that safe harbor,” he wrote, “…This is reality.”
In late December, a federal judge denied Oklahoma’s motion to enjoin the mandate. The Oklahoma Attorney General’s office responded, “We will not be surprised if the President’s vaccine mandate actually reduces the nation’s military readiness instead of promoting it.”
In a press briefing, Pentagon press secretary John Kirby said, “The Secretary has the authorities he needs to require this vaccine across the force, including the National Guard. …[E]ven when they’re in a Title 32 status.” He added, “It is a lawful order for National Guardsmen to receive the COVID vaccine. It’s a lawful order, and refusing to do that, absent of an improved exemption, puts them in the same potential [position] as active-duty members who refuse the vaccine.” That could mean, for instance, loss of pay and membership in the National Guard.
A core rationale for the mandate, according to Secretary Austin, is the need for military readiness—meaning Guard members must be healthy and fit for duty. And that extends to being healthy and fit for missions like transporting at-risk patients. Ohio National Guard Adjutant General Major General John Harris Jr. said, “I would never put a soldier or airman in harm’s way without the best protection we could put on them—body armor, helmets. And this medical readiness is the exact same thing. We’re putting folks into harm’s way.” He has moved the deadline from the Pentagon’s June 30 date to March 31—a move that boosted the vaccination rate from 53% to 56% in one week.
Ohio Governor DeWine has expressed frustration that almost half of the Ohio Army National Guard personnel can’t be deployed on this mission because they’re unvaccinated. “In some of our testing places, 40 to 50% of the people are testing positive,” he said. “So this is a high-risk operation. You need to be protected. The best way for you to be protected is to get the vaccination.”
As of December 2021, according to the National Guard Bureau, the National Guard as a whole was 66% fully vaccinated. The percentages vary according to service; for instance, nearly 90% of airmen have been vaccinated, compared with only 40% of Army Guardsmen. Among the states challenging the mandate, the vaccinated rates have been moving upward: In Alaska, about 92% of the Air National Guard have been vaccinated—leaving roughly 11,000 troops who had not met the December 2 deadline. In Iowa, as of Nov. 30, 91% of Air National Guard and 80% of Army National Guard members had been vaccinated, but about 9,000 soldiers had been directed to get the vaccination or risk disciplinary action. Almost 2,200 of the more than 2,800-strong Wyoming National Guard (77%) have received at least 1 dose. Nebraska Air National Guard’s force of 1,000 was 94% fully vaccinated as of December 1. (Maj Scott Ingalsbe, public affairs officer, said, “Vaccinations are tied to individual medical readiness. They provide service members with the best protection available so they can perform missions across the globe.”).
In most states, Army National Guard members have until June 30, 2022, to comply. “Our soldiers …have until [the DoD’s deadline], and some of them are just going to wait close to the deadline,” John Goheen of the National Guard Association of the United States said in a discussion on NPR. “That’s human nature.”
Earlier this month, Texas Governor Greg Abbott told National Guard members they can ignore the Pentagon’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate: “President Biden is not your commander-in-chief.” He has also sued the Biden administration over the requirement.
In the meantime, the hospitals at breaking point must hope for the best and take as much help as they can get.
In early January, Ohio not only set a state record for COVID-19 hospitalizations—it had the fourth highest rate in the country, with 6,747 hospitalized coronavirus patients on January 10, a 40% increase over the previous 21 days. Most were unvaccinated. To help overwhelmed hospitals cope, Ohio Gov. Mike DeWine turned to the National Guard. Unfortunately, nearly half of the Ohio National Guard also were unvaccinated.
By US Department of Defense (DoD) directive, National Guard members must have a COVID-19 vaccination to be deployed on hospital missions. Thus, in COVID hotspots across the nation, governors are on the horns of a dilemma. They want and need to deploy the National Guard to give medical and nonclinical support but aren’t sure whether they will be able to or, indeed, whether they should.
So far, vaccinated teams are already on the ground in a number of states. In Indiana, where hospitalizations jumped 50% over 2 weeks in December, the National Guard sent 6-person teams, all fully vaccinated. In New Hampshire, 70 guards are being deployed to help hospitals with food service, clerical work, and other nonmedical functions. New York Governor Kathy Hochul has deployed guard members for help to ease the strain on nursing homes. Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker has activated up to 500 guard members; some will be supporting 55 acute care hospital and 12 ambulance services. In Maine, where cases have peaked, Governor Janet Mills activated guard members to support nursing facilities and administer monoclonal antibodies. The Louisiana National Guard has administered more than 542,000 COVID-19 tests and 206,300 vaccines. As many as 1,000 Maryland Air and Army National Guardsmen are being activated to help with testing and other missions.
However, as in Ohio, other states are facing problematic scenarios. For instance, about 40% of the more than 20,000 Texas National Guard are refusing to get vaccinated, challenging the Biden Administration vaccine requirement for all military.
And a court showdown over federal vaccine mandates, started by Governor Kevin Stitt of Oklahoma and joined by the Republican governors of Wyoming, Iowa, Alaska, Nebraska, and Mississippi, came to a head in December. Last November, Stitt asked Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin to exempt Oklahoma’s National Guard from the vaccine mandate. He claimed the requirement violated the personal freedoms of many Oklahomans and could cause them to “potentially sacrifice their personal beliefs.” But in a memo to the Joint Chiefs chairmen, the service secretaries and the head of the National Guard Bureau, Austin wrote that Pentagon funds could not be used to pay for duties performed under Title 32 for members of the Guard who do not comply with the military’s vaccine requirement. (Title 32 refers to Guard operations under state orders.) Austin also said National Guard members must be vaccinated to participate in drills, training, and other duty conducted under Title 32.
Stitt, maintaining that he is commander in chief of the Oklahoma National Guard as long as it operates under Title 32 orders, put out his own memo stipulating that no Guard member was required to get vaccinated. He also ordered Brig. Gen. Thomas Mancino, newly appointed commander of the Oklahoma National Guard, to not enforce the mandate. Subsequently, Mancino issued a statement pointing out that current state law is limited in protecting troops who opt out of the shot. Moreover, if the Guard were called up under federal orders, he said, he would enforce the mandate. Training events, schools, and mobilizations were going to “eventually force you out of that safe harbor,” he wrote, “…This is reality.”
In late December, a federal judge denied Oklahoma’s motion to enjoin the mandate. The Oklahoma Attorney General’s office responded, “We will not be surprised if the President’s vaccine mandate actually reduces the nation’s military readiness instead of promoting it.”
In a press briefing, Pentagon press secretary John Kirby said, “The Secretary has the authorities he needs to require this vaccine across the force, including the National Guard. …[E]ven when they’re in a Title 32 status.” He added, “It is a lawful order for National Guardsmen to receive the COVID vaccine. It’s a lawful order, and refusing to do that, absent of an improved exemption, puts them in the same potential [position] as active-duty members who refuse the vaccine.” That could mean, for instance, loss of pay and membership in the National Guard.
A core rationale for the mandate, according to Secretary Austin, is the need for military readiness—meaning Guard members must be healthy and fit for duty. And that extends to being healthy and fit for missions like transporting at-risk patients. Ohio National Guard Adjutant General Major General John Harris Jr. said, “I would never put a soldier or airman in harm’s way without the best protection we could put on them—body armor, helmets. And this medical readiness is the exact same thing. We’re putting folks into harm’s way.” He has moved the deadline from the Pentagon’s June 30 date to March 31—a move that boosted the vaccination rate from 53% to 56% in one week.
Ohio Governor DeWine has expressed frustration that almost half of the Ohio Army National Guard personnel can’t be deployed on this mission because they’re unvaccinated. “In some of our testing places, 40 to 50% of the people are testing positive,” he said. “So this is a high-risk operation. You need to be protected. The best way for you to be protected is to get the vaccination.”
As of December 2021, according to the National Guard Bureau, the National Guard as a whole was 66% fully vaccinated. The percentages vary according to service; for instance, nearly 90% of airmen have been vaccinated, compared with only 40% of Army Guardsmen. Among the states challenging the mandate, the vaccinated rates have been moving upward: In Alaska, about 92% of the Air National Guard have been vaccinated—leaving roughly 11,000 troops who had not met the December 2 deadline. In Iowa, as of Nov. 30, 91% of Air National Guard and 80% of Army National Guard members had been vaccinated, but about 9,000 soldiers had been directed to get the vaccination or risk disciplinary action. Almost 2,200 of the more than 2,800-strong Wyoming National Guard (77%) have received at least 1 dose. Nebraska Air National Guard’s force of 1,000 was 94% fully vaccinated as of December 1. (Maj Scott Ingalsbe, public affairs officer, said, “Vaccinations are tied to individual medical readiness. They provide service members with the best protection available so they can perform missions across the globe.”).
In most states, Army National Guard members have until June 30, 2022, to comply. “Our soldiers …have until [the DoD’s deadline], and some of them are just going to wait close to the deadline,” John Goheen of the National Guard Association of the United States said in a discussion on NPR. “That’s human nature.”
Earlier this month, Texas Governor Greg Abbott told National Guard members they can ignore the Pentagon’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate: “President Biden is not your commander-in-chief.” He has also sued the Biden administration over the requirement.
In the meantime, the hospitals at breaking point must hope for the best and take as much help as they can get.
What if the National Guard Can’t Help?
What if the National Guard Can’t Help?
CDC: More kids hospitalized with COVID since pandemic began
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Increased electronic media use and youth suicidality: What can clinicians do?
Pediatric suicide was an emerging public health crisis prior to COVID-19, and recent data indicate that pediatric suicide attempts continued to increase during the pandemic.1 In October 2021, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and the Children’s Hospital Association declared a national state of emergency for pediatric mental health because of a surge in youth suicide attempts.2 Isolation mediated by the degradation of community and exacerbated by the pandemic, has been identified as a contributor to increasing pediatric suicidality.
It is impossible to understand this current public health crisis and to seek solutions without recognizing the ways in which the degradation of community and consequent social isolation play a central role. While the degradation of community and the isolation epidemic that preceded COVID-19 have been mediated by multiple factors, one factor associated with mental health problems in youth is electronic media use.3 During COVID-19, when physical distancing and virtual learning have been necessary to curb the spread, electronic media use has increased exponentially in the pediatric demographic. Some of this increase in screen time has been attributable to virtual schooling, but electronic devices also have become the only means by which kids can stay in contact with one another. While electronic communication has been viewed as an antidote to isolation, disturbing consequences associated with electronic media use have also been noted in our pediatric population.
In the health care system where I (P.L.L.) work as a pediatrician and a child and adolescent psychiatrist, electronic media use has been implicated in more than 90% of our inpatient admissions for suicidal ideation. Use of electronic devices has contributed to suicidal thoughts and attempts in most patients admitted to our acute crisis stabilization unit over the past year. During the pandemic, and in the absence of meaningful interpersonal interactions, many in our pediatric population have become even more dependent on electronic devices to cope with isolation. This has created an often-devastating irony, where the very devices already associated with mental health problems in youth are now being endorsed as “necessary” by mental health professionals.
So how does electronic media use relate to isolation and the continued degradation of community, and why might electronic media use be exacerbating pediatric suicide? One way we have coped with the deterioration of our communities has been the creation of the synthetic community-substitutes found on electronic devices. Unfortunately, our electronic devices create only an illusion of community, where interpersonal interaction occurs by way of inanimate objects, and by electronic text and ideograms. These become substitutes for genuine intimacy, personal contact, and reciprocity. Instead of engaging with one another, our youth are spending hours daily in isolation engaging with a piece of plastic. The mirage generated by pixels on a plastic screen creates an illusion of connectivity, but in reality, this only increases the isolation of our youth.
Human evolution and connection
Intimate social connectivity, woven together in our communities, was a fundamental mechanism for human survival. Historically, for our hunter-gatherer ancestors, the community provided access to our fundamental needs, such as safety from predators and access to substantive nutrition.4 Community allowed our ancestors to survive and procreate, and facilitated their triumph over predation and disease.5 Our distinction as the dominant species on Earth has been afforded by our social connectivity. Unfortunately, in the virtual worlds of our electronic devices the intimate social connectivity of community is absent. Our children wander in isolation, left to navigate age-old evolutionary pressures in the absence of the fundamental advantage for our survival as a species.
Unlike the living, breathing bears and wolves that threatened our ancestors, in the virtual world of the electronic device children are stalked by invisible predators seeking sexual or monetary exploitation. Children are being consumed by digital advertising and social media platforms that perpetually reinforce the requirement of perfection, and they fall prey to cyberbullies who mercilessly disparage their imperfections. In their virtual worlds, where their value is predicated upon anonymous others’ opinions, they succumb to the idea that they will never be enough.6 Their fundamental needs of competence and relatedness go unmet, and they lose their sense of purpose, belonging, and often their will to live. More importantly, absent from their children’s virtual worlds, and preoccupied within their own, parents cannot protect their children from online predators, deflect the vicious attacks of cyberbullies, or reframe their children’s imperfections as distinctive or empowering. They are unable to provide their children with the substantive interpersonal contact necessary for resilience and that bolsters their self-worth.
Human beings are inherently social creatures, who regardless of era require community to meet their fundamental needs. As the duration of daily screen time steadily increases, our youth are spending more and more of their waking hours living in isolation in an electronic world. Without the protective social connectivity of community, they are hunted by online predators, and they are consumed by the predatory culture of perfectionism that is contradictory to the reciprocal caretaking necessary to support their healthy development. Evolutionary biology informs us that, when children are isolated, they are susceptible to predation and disease. And in the socialized isolation of their electronic worlds, they are succumbing to predation and to the depressive diseases that are exacerbating the pediatric mental health crisis.
Creating and building community amid a pandemic has been challenging at best. However, now that we have better tools to fight COVID, it is important to encourage our young patients to reduce their nonacademic screen time, and to get outside and engage with others. Their mental health depends on it.
Dr. Loper is a pediatrician and child and adolescent psychiatrist at Prisma Health–Midlands in Columbia, S.C. He is an assistant professor in the department of neuropsychiatry and behavioral science at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. Dr. Loper has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaminstein is an adjunct assistant professor at the graduate school of education and affiliated faculty in the organizational dynamics program, School of Arts and Sciences, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. He is a social psychologist who has been studying groups and organizations for more than 40 years. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. MMWR. 2021 Jun 18;70(24):888-94.
2. Ray G. “Pediatricians, Child and Adolescent Psychiatrists and Children’s Hospitals Declare National Emergency in Children’s Mental Health.” Childrenshospitals.org. 2021 Oct 19.
3. JAMA Netw Open. 2020(8):e2011381.
4. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2018 April:165(4):777-800.
5. The influence of predation on primate and early human evolution: Impetus for cooperation, in “Origins of Altruism and Cooperation. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects.” (Basingstoke, England: Springer Nature, 2011, pp. 19-40).
6. Media Psychology. 2020;23(1):52-78.
Pediatric suicide was an emerging public health crisis prior to COVID-19, and recent data indicate that pediatric suicide attempts continued to increase during the pandemic.1 In October 2021, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and the Children’s Hospital Association declared a national state of emergency for pediatric mental health because of a surge in youth suicide attempts.2 Isolation mediated by the degradation of community and exacerbated by the pandemic, has been identified as a contributor to increasing pediatric suicidality.
It is impossible to understand this current public health crisis and to seek solutions without recognizing the ways in which the degradation of community and consequent social isolation play a central role. While the degradation of community and the isolation epidemic that preceded COVID-19 have been mediated by multiple factors, one factor associated with mental health problems in youth is electronic media use.3 During COVID-19, when physical distancing and virtual learning have been necessary to curb the spread, electronic media use has increased exponentially in the pediatric demographic. Some of this increase in screen time has been attributable to virtual schooling, but electronic devices also have become the only means by which kids can stay in contact with one another. While electronic communication has been viewed as an antidote to isolation, disturbing consequences associated with electronic media use have also been noted in our pediatric population.
In the health care system where I (P.L.L.) work as a pediatrician and a child and adolescent psychiatrist, electronic media use has been implicated in more than 90% of our inpatient admissions for suicidal ideation. Use of electronic devices has contributed to suicidal thoughts and attempts in most patients admitted to our acute crisis stabilization unit over the past year. During the pandemic, and in the absence of meaningful interpersonal interactions, many in our pediatric population have become even more dependent on electronic devices to cope with isolation. This has created an often-devastating irony, where the very devices already associated with mental health problems in youth are now being endorsed as “necessary” by mental health professionals.
So how does electronic media use relate to isolation and the continued degradation of community, and why might electronic media use be exacerbating pediatric suicide? One way we have coped with the deterioration of our communities has been the creation of the synthetic community-substitutes found on electronic devices. Unfortunately, our electronic devices create only an illusion of community, where interpersonal interaction occurs by way of inanimate objects, and by electronic text and ideograms. These become substitutes for genuine intimacy, personal contact, and reciprocity. Instead of engaging with one another, our youth are spending hours daily in isolation engaging with a piece of plastic. The mirage generated by pixels on a plastic screen creates an illusion of connectivity, but in reality, this only increases the isolation of our youth.
Human evolution and connection
Intimate social connectivity, woven together in our communities, was a fundamental mechanism for human survival. Historically, for our hunter-gatherer ancestors, the community provided access to our fundamental needs, such as safety from predators and access to substantive nutrition.4 Community allowed our ancestors to survive and procreate, and facilitated their triumph over predation and disease.5 Our distinction as the dominant species on Earth has been afforded by our social connectivity. Unfortunately, in the virtual worlds of our electronic devices the intimate social connectivity of community is absent. Our children wander in isolation, left to navigate age-old evolutionary pressures in the absence of the fundamental advantage for our survival as a species.
Unlike the living, breathing bears and wolves that threatened our ancestors, in the virtual world of the electronic device children are stalked by invisible predators seeking sexual or monetary exploitation. Children are being consumed by digital advertising and social media platforms that perpetually reinforce the requirement of perfection, and they fall prey to cyberbullies who mercilessly disparage their imperfections. In their virtual worlds, where their value is predicated upon anonymous others’ opinions, they succumb to the idea that they will never be enough.6 Their fundamental needs of competence and relatedness go unmet, and they lose their sense of purpose, belonging, and often their will to live. More importantly, absent from their children’s virtual worlds, and preoccupied within their own, parents cannot protect their children from online predators, deflect the vicious attacks of cyberbullies, or reframe their children’s imperfections as distinctive or empowering. They are unable to provide their children with the substantive interpersonal contact necessary for resilience and that bolsters their self-worth.
Human beings are inherently social creatures, who regardless of era require community to meet their fundamental needs. As the duration of daily screen time steadily increases, our youth are spending more and more of their waking hours living in isolation in an electronic world. Without the protective social connectivity of community, they are hunted by online predators, and they are consumed by the predatory culture of perfectionism that is contradictory to the reciprocal caretaking necessary to support their healthy development. Evolutionary biology informs us that, when children are isolated, they are susceptible to predation and disease. And in the socialized isolation of their electronic worlds, they are succumbing to predation and to the depressive diseases that are exacerbating the pediatric mental health crisis.
Creating and building community amid a pandemic has been challenging at best. However, now that we have better tools to fight COVID, it is important to encourage our young patients to reduce their nonacademic screen time, and to get outside and engage with others. Their mental health depends on it.
Dr. Loper is a pediatrician and child and adolescent psychiatrist at Prisma Health–Midlands in Columbia, S.C. He is an assistant professor in the department of neuropsychiatry and behavioral science at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. Dr. Loper has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaminstein is an adjunct assistant professor at the graduate school of education and affiliated faculty in the organizational dynamics program, School of Arts and Sciences, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. He is a social psychologist who has been studying groups and organizations for more than 40 years. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. MMWR. 2021 Jun 18;70(24):888-94.
2. Ray G. “Pediatricians, Child and Adolescent Psychiatrists and Children’s Hospitals Declare National Emergency in Children’s Mental Health.” Childrenshospitals.org. 2021 Oct 19.
3. JAMA Netw Open. 2020(8):e2011381.
4. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2018 April:165(4):777-800.
5. The influence of predation on primate and early human evolution: Impetus for cooperation, in “Origins of Altruism and Cooperation. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects.” (Basingstoke, England: Springer Nature, 2011, pp. 19-40).
6. Media Psychology. 2020;23(1):52-78.
Pediatric suicide was an emerging public health crisis prior to COVID-19, and recent data indicate that pediatric suicide attempts continued to increase during the pandemic.1 In October 2021, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, and the Children’s Hospital Association declared a national state of emergency for pediatric mental health because of a surge in youth suicide attempts.2 Isolation mediated by the degradation of community and exacerbated by the pandemic, has been identified as a contributor to increasing pediatric suicidality.
It is impossible to understand this current public health crisis and to seek solutions without recognizing the ways in which the degradation of community and consequent social isolation play a central role. While the degradation of community and the isolation epidemic that preceded COVID-19 have been mediated by multiple factors, one factor associated with mental health problems in youth is electronic media use.3 During COVID-19, when physical distancing and virtual learning have been necessary to curb the spread, electronic media use has increased exponentially in the pediatric demographic. Some of this increase in screen time has been attributable to virtual schooling, but electronic devices also have become the only means by which kids can stay in contact with one another. While electronic communication has been viewed as an antidote to isolation, disturbing consequences associated with electronic media use have also been noted in our pediatric population.
In the health care system where I (P.L.L.) work as a pediatrician and a child and adolescent psychiatrist, electronic media use has been implicated in more than 90% of our inpatient admissions for suicidal ideation. Use of electronic devices has contributed to suicidal thoughts and attempts in most patients admitted to our acute crisis stabilization unit over the past year. During the pandemic, and in the absence of meaningful interpersonal interactions, many in our pediatric population have become even more dependent on electronic devices to cope with isolation. This has created an often-devastating irony, where the very devices already associated with mental health problems in youth are now being endorsed as “necessary” by mental health professionals.
So how does electronic media use relate to isolation and the continued degradation of community, and why might electronic media use be exacerbating pediatric suicide? One way we have coped with the deterioration of our communities has been the creation of the synthetic community-substitutes found on electronic devices. Unfortunately, our electronic devices create only an illusion of community, where interpersonal interaction occurs by way of inanimate objects, and by electronic text and ideograms. These become substitutes for genuine intimacy, personal contact, and reciprocity. Instead of engaging with one another, our youth are spending hours daily in isolation engaging with a piece of plastic. The mirage generated by pixels on a plastic screen creates an illusion of connectivity, but in reality, this only increases the isolation of our youth.
Human evolution and connection
Intimate social connectivity, woven together in our communities, was a fundamental mechanism for human survival. Historically, for our hunter-gatherer ancestors, the community provided access to our fundamental needs, such as safety from predators and access to substantive nutrition.4 Community allowed our ancestors to survive and procreate, and facilitated their triumph over predation and disease.5 Our distinction as the dominant species on Earth has been afforded by our social connectivity. Unfortunately, in the virtual worlds of our electronic devices the intimate social connectivity of community is absent. Our children wander in isolation, left to navigate age-old evolutionary pressures in the absence of the fundamental advantage for our survival as a species.
Unlike the living, breathing bears and wolves that threatened our ancestors, in the virtual world of the electronic device children are stalked by invisible predators seeking sexual or monetary exploitation. Children are being consumed by digital advertising and social media platforms that perpetually reinforce the requirement of perfection, and they fall prey to cyberbullies who mercilessly disparage their imperfections. In their virtual worlds, where their value is predicated upon anonymous others’ opinions, they succumb to the idea that they will never be enough.6 Their fundamental needs of competence and relatedness go unmet, and they lose their sense of purpose, belonging, and often their will to live. More importantly, absent from their children’s virtual worlds, and preoccupied within their own, parents cannot protect their children from online predators, deflect the vicious attacks of cyberbullies, or reframe their children’s imperfections as distinctive or empowering. They are unable to provide their children with the substantive interpersonal contact necessary for resilience and that bolsters their self-worth.
Human beings are inherently social creatures, who regardless of era require community to meet their fundamental needs. As the duration of daily screen time steadily increases, our youth are spending more and more of their waking hours living in isolation in an electronic world. Without the protective social connectivity of community, they are hunted by online predators, and they are consumed by the predatory culture of perfectionism that is contradictory to the reciprocal caretaking necessary to support their healthy development. Evolutionary biology informs us that, when children are isolated, they are susceptible to predation and disease. And in the socialized isolation of their electronic worlds, they are succumbing to predation and to the depressive diseases that are exacerbating the pediatric mental health crisis.
Creating and building community amid a pandemic has been challenging at best. However, now that we have better tools to fight COVID, it is important to encourage our young patients to reduce their nonacademic screen time, and to get outside and engage with others. Their mental health depends on it.
Dr. Loper is a pediatrician and child and adolescent psychiatrist at Prisma Health–Midlands in Columbia, S.C. He is an assistant professor in the department of neuropsychiatry and behavioral science at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. Dr. Loper has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaminstein is an adjunct assistant professor at the graduate school of education and affiliated faculty in the organizational dynamics program, School of Arts and Sciences, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. He is a social psychologist who has been studying groups and organizations for more than 40 years. He has no conflicts of interest.
References
1. MMWR. 2021 Jun 18;70(24):888-94.
2. Ray G. “Pediatricians, Child and Adolescent Psychiatrists and Children’s Hospitals Declare National Emergency in Children’s Mental Health.” Childrenshospitals.org. 2021 Oct 19.
3. JAMA Netw Open. 2020(8):e2011381.
4. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2018 April:165(4):777-800.
5. The influence of predation on primate and early human evolution: Impetus for cooperation, in “Origins of Altruism and Cooperation. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects.” (Basingstoke, England: Springer Nature, 2011, pp. 19-40).
6. Media Psychology. 2020;23(1):52-78.
COVID-vaccine myocarditis: Rare, mild, and usually in young men
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At-risk Americans become eligible for fourth COVID shot this week
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .