User login
Paxlovid Lowers Risk of COVID-19 Hospitalization, Study Finds
This medicine has been approved for use in the United States for people over 12 years old who are at risk of having a severe COVID-19 infection.
The study was published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Study authors examined the health records of almost 45,000 outpatients who tested positive for COVID-19 from January to August 2022. This sample period was when the Omicron strain was dominant.
The average patient age was 47. Sixty-two percent were White, 24% were Black, 6% were Hispanic, and 8% had an unknown ethnicity. A slight majority, 51%, had received two or more vaccine doses before the study period.
From the study group, 201 people were hospitalized within 28 days of their positive COVID test.
Almost 5,000 people in the study group received Paxlovid. The use of Paxlovid was the best indicator of avoiding hospitalization, with three of those people being hospitalized.
“Patients who were treated with Paxlovid were twice as likely to have received at least two doses of COVID-19 vaccine,” the University of Minnesota’s CIDRAP reported. “They were also more likely to be 70 years or older.”
People taking Paxlovid were more likely to be White and to live in middle- or upper-income areas.
“COVID-19 hospitalization risk was reduced by 84% among [Paxlovid] recipients in a large, diverse healthcare system during the Omicron wave,” the study’s authors wrote. “These results suggest that [Paxlovid] remained highly effective in a setting substantially different than the original clinical trials.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
This medicine has been approved for use in the United States for people over 12 years old who are at risk of having a severe COVID-19 infection.
The study was published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Study authors examined the health records of almost 45,000 outpatients who tested positive for COVID-19 from January to August 2022. This sample period was when the Omicron strain was dominant.
The average patient age was 47. Sixty-two percent were White, 24% were Black, 6% were Hispanic, and 8% had an unknown ethnicity. A slight majority, 51%, had received two or more vaccine doses before the study period.
From the study group, 201 people were hospitalized within 28 days of their positive COVID test.
Almost 5,000 people in the study group received Paxlovid. The use of Paxlovid was the best indicator of avoiding hospitalization, with three of those people being hospitalized.
“Patients who were treated with Paxlovid were twice as likely to have received at least two doses of COVID-19 vaccine,” the University of Minnesota’s CIDRAP reported. “They were also more likely to be 70 years or older.”
People taking Paxlovid were more likely to be White and to live in middle- or upper-income areas.
“COVID-19 hospitalization risk was reduced by 84% among [Paxlovid] recipients in a large, diverse healthcare system during the Omicron wave,” the study’s authors wrote. “These results suggest that [Paxlovid] remained highly effective in a setting substantially different than the original clinical trials.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
This medicine has been approved for use in the United States for people over 12 years old who are at risk of having a severe COVID-19 infection.
The study was published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Study authors examined the health records of almost 45,000 outpatients who tested positive for COVID-19 from January to August 2022. This sample period was when the Omicron strain was dominant.
The average patient age was 47. Sixty-two percent were White, 24% were Black, 6% were Hispanic, and 8% had an unknown ethnicity. A slight majority, 51%, had received two or more vaccine doses before the study period.
From the study group, 201 people were hospitalized within 28 days of their positive COVID test.
Almost 5,000 people in the study group received Paxlovid. The use of Paxlovid was the best indicator of avoiding hospitalization, with three of those people being hospitalized.
“Patients who were treated with Paxlovid were twice as likely to have received at least two doses of COVID-19 vaccine,” the University of Minnesota’s CIDRAP reported. “They were also more likely to be 70 years or older.”
People taking Paxlovid were more likely to be White and to live in middle- or upper-income areas.
“COVID-19 hospitalization risk was reduced by 84% among [Paxlovid] recipients in a large, diverse healthcare system during the Omicron wave,” the study’s authors wrote. “These results suggest that [Paxlovid] remained highly effective in a setting substantially different than the original clinical trials.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Dermatologic Reactions Following COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Series
Cutaneous reactions associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine have been reported worldwide since December 2020. Local injection site reactions (<1%) such as erythema, swelling, delayed local reactions (1%–10%), morbilliform rash, urticarial reactions, pityriasis rosea, Rowell syndrome, and lichen planus have been reported following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.1 Cutaneous reactions reported in association with the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine include swelling, redness, itching, discoloration, induration (1%–10%), urticaria, petechial rash, and exacerbation of psoriasis at the local injection site (<1%).2
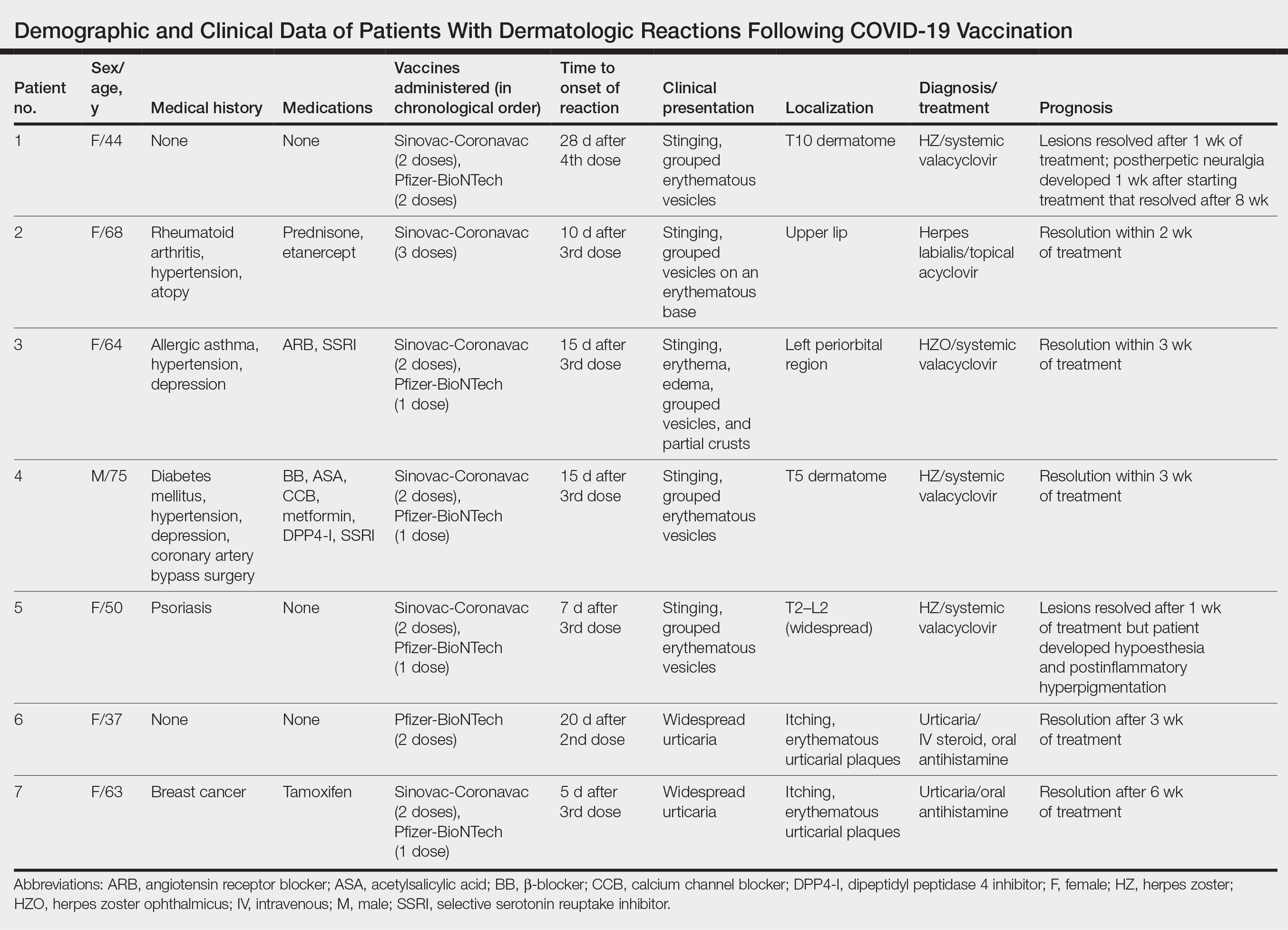
We describe 7 patients from Turkey who presented with various dermatologic problems 5 to 28 days after COVID-19 vaccination, highlighting the possibility of early and late cutaneous reactions related to the vaccine (Table).
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 44-year-old woman was admitted to the dermatology clinic with painful lesions on the trunk of 3 days’ duration. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped erythematous vesicles showing dermatomal spread in the right thoracolumbar (dermatome T10) region. The patient reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine (doses 1 and 2) and 2 doses of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (doses 3 and 4); the rash had developed 28 days after she received the 4th dose. Her medical history was unremarkable. The lesions regressed after 1 week of treatment with oral valacyclovir 1000 mg 3 times daily, but she developed postherpetic neuralgia 1 week after starting treatment, which resolved after 8 weeks.
Patient 2—A 68-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful sores on the upper lip of 1 day’s duration. She had a history of rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, and atopy and was currently taking prednisone and etanercept. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous base on the upper lip. A diagnosis of herpes labialis was made. The patient reported that she had received a third dose of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine 10 days prior to the appearance of the lesions. Her symptoms resolved completely within 2 weeks of treatment with topical acyclovir.
Patient 3—A 64-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with pain, redness, and watery sores on and around the left eyelid of 2 days’ duration. Dermatologic evaluation revealed the erythematous surface of the left eyelid and periorbital area showed partial crusts, clustered vesicles, erythema, and edema. Additionally, the conjunctiva was purulent and erythematous. The patient’s medical history was notable for allergic asthma, hypertension, anxiety, and depression. For this reason, the patient was prescribed an angiotensin receptor blocker and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. She noted that a similar rash had developed around the left eye 6 years prior that was diagnosed as herpes zoster (HZ). She also reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine followed by 1 dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, which she had received 2 weeks before the rash developed. The patient was treated at the eye clinic and was found to have ocular involvement. Ophthalmology was consulted and a diagnosis of herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) was made. Systemic valacyclovir treatment was initiated, resulting in clinical improvement within 3 weeks.
Patient 4—A 75-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with chest and back pain and widespread muscle pain of several days’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, depression, and coronary artery bypass surgery. A medication history revealed treatment with a β-blocker, acetylsalicylic acid, a calcium channel blocker, a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in dermatome T5 on the right chest and back. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The patient reported that he had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine followed by 1 dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. He was treated with valacyclovir for 1 week, and his symptoms resolved entirely within 3 weeks.
Patient 5—A 50-year-old woman presented to the hospital for evaluation of painful sores on the back, chest, groin, and abdomen of 10 days’ duration. The lesions initially had developed 7 days after receiving the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine; she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. The patient had a history of untreated psoriasis. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in the T2–L2 dermatomes on the left side of the trunk. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The lesions resolved after 1 week of treatment with systemic valacyclovir; however, she subsequently developed postherpetic neuralgia, hypoesthesia, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected regions.
Patient 6—A 37-year-old woman presented to the hospital with redness, swelling, and itching all over the body of 3 days’ duration. The patient noted that the rash would subside and reappear throughout the day. Her medical history was unremarkable, except for COVID-19 infection 6 months prior. She had received a second dose of the BioNTech vaccine 20 days prior to development of symptoms. Dermatologic examination revealed widespread erythematous urticarial plaques. A diagnosis of acute urticaria was made. The patient recovered completely after 1 week of treatment with a systemic steroid and 3 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Patient 7—A 63-year-old woman presented to the hospital with widespread itching and rash that appeared 5 days after the first dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. The patient reported that the rash resolved spontaneously within a few hours but then reappeared. Her medical history revealed that she was taking tamoxifen for breast cancer and that she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous urticarial plaques on the trunk and arms. A diagnosis of urticaria was made, and her symptoms resolved after 6 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Comment
Skin lesions associated with COVID-19 infection have been reported worldwide3,4 as well as dermatologic reactions following COVID-19 vaccination. In one case from Turkey, HZ infection was reported in a 68-year-old man 5 days after he received a second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine.5 In another case, HZ infection developed in a 78-year-old man 5 days after COVID-19 vaccination.6 Numerous cases of HZ infection developing within 1 to 26 days of COVID-19 vaccination have been reported worldwide.7-9
In a study conducted in the United States, 40 skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine were investigated; of these cases, 87.5% (35/40) were reported as varicella-zoster virus, and 12.5% (5/40) were reported as herpes simplex reactivation; 54% (19/35) and 80% (4/5) of these cases, respectively, were associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.10 The average age of patients who developed a skin reaction was 46 years, and 70% (28/40) were women. The time to onset of the reaction was 2 to 13 days after vaccination, and symptoms were reported to improve within 7 days on average.10
Another study from Spain examined 405 vaccine-related skin reactions, 40.2% of which were related to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Among them, 80.2% occurred in women; 13.8% of cases were diagnosed as varicella-zoster virus or HZ virus reactivation, and 14.6% were urticaria. Eighty reactions (21%) were classified as severe/very severe and 81% required treatment.11 One study reported 414 skin reactions from the COVID-19 vaccine from December 2020 to February 2021; of these cases, 83% occurred after the Moderna vaccine, which is not available in Turkey, and 17% occurred after the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.12A systematic review of 91 patients who developed HZ infection after COVID-19 vaccination reported that 10% (9/91) of cases were receiving immunosuppressive therapy and 13% (12/91) had an autoimmune disease.7 In our case series, it is known that at least 2 of the patients (patients 2 and 5), including 1 patient with rheumatoid arthritis (patient 2) who was on immunosuppressive treatment, had autoimmune disorders. However, reports in the literature indicate that most patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases remain stable after vaccination.13
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus is a rare form of HZ caused by involvement of the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve that manifests as vesicular lesions and retinitis, uveitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, and pain on an erythematous background. Two cases of women who developed HZO infection after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination were reported in the literature.14 Although patient 3 in our case series had a history of HZO 6 years prior, the possibility of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine triggering HZO should be taken into consideration.
Although cutaneous reactions after the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine were observed in only 1 of 7 patients in our case series, skin reactions after Sinovac-Coronavac (an inactivated viral vaccine) have been reported in the literature. In one study, after a total of 35,229 injections, the incidence of cutaneous adverse events due to Sinovac-Coronavac was reported to be 0.94% and 0.70% after the first and second doses, respectively.15 Therefore, further study results are needed to directly attribute the reactions to COVID-19 vaccination.
Conclusion
Our case series highlights that clinicians should be vigilant in diagnosing cutaneous reactions following COVID-19 vaccination early to prevent potential complications. Early recognition of reactions is crucial, and the prognosis can be improved with appropriate treatment. Despite the potential dermatologic adverse effects of the COVID-19 vaccine, the most effective way to protect against serious COVID-19 infection is to continue to be vaccinated.
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615.
- Zhang Y, Zeng G, Pan H, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:181-192.
- Tan SW, Tam YC, Oh CC. Skin manifestations of COVID-19: a worldwide review. JAAD Int. 2021;2:119-133.
- Singh H, Kaur H, Singh K, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. advances in wound care. 2021;10:51-80.
- Aksu SB, Öztürk GZ. A rare case of shingles after COVID-19 vaccine: is it a possible adverse effect? clinical and experimental vaccine research. 2021;10:198-201.
- Bostan E, Yalici-Armagan B. Herpes zoster following inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: a coexistence or coincidence? J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1566-1567.
- Katsikas Triantafyllidis K, Giannos P, Mian IT, et al. Varicella zoster virus reactivation following COVID-19 vaccination: a systematic review of case reports. Vaccines (Basel). 2021;9:1013. doi:10.3390/vaccines9091013
- Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Chicharro P, Cabrera LM, et al. Varicella-zoster virus reactivation after SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination: report of 5 cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;12:58-59. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.014
- Lee C, Cotter D, Basa J, et al. 20 Post-COVID-19 vaccine-related shingles cases seen at the Las Vegas Dermatology clinic and sent to us via social media. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1960-1964.
- Fathy RA, McMahon DE, Lee C, et al. Varicella-zoster and herpes simplex virus reactivation post-COVID-19 vaccination: a review of 40 cases in an International Dermatology Registry. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol. 2022;36:E6-E9.
- Català A, Muñoz-Santos C, Galván-Casas C, et al. Cutaneous reactions after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a cross-sectional Spanish nationwide study of 405 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:142-152.
- McMahon DE, Amerson E, Rosenbach M, et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: a registry-based study of 414 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:46-55.
- Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: a multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:1330-1338.
- Bernardini N, Skroza N, Mambrin A, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus in two women after Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine. J Med Virol. 2022;94:817-818.
- Rerknimitr P, Puaratanaarunkon T, Wongtada C, et al. Cutaneous adverse reactions from 35,229 doses of Sinovac and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccination: a prospective cohort study in healthcare workers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E158-E161.
Cutaneous reactions associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine have been reported worldwide since December 2020. Local injection site reactions (<1%) such as erythema, swelling, delayed local reactions (1%–10%), morbilliform rash, urticarial reactions, pityriasis rosea, Rowell syndrome, and lichen planus have been reported following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.1 Cutaneous reactions reported in association with the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine include swelling, redness, itching, discoloration, induration (1%–10%), urticaria, petechial rash, and exacerbation of psoriasis at the local injection site (<1%).2
We describe 7 patients from Turkey who presented with various dermatologic problems 5 to 28 days after COVID-19 vaccination, highlighting the possibility of early and late cutaneous reactions related to the vaccine (Table).

Case Reports
Patient 1—A 44-year-old woman was admitted to the dermatology clinic with painful lesions on the trunk of 3 days’ duration. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped erythematous vesicles showing dermatomal spread in the right thoracolumbar (dermatome T10) region. The patient reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine (doses 1 and 2) and 2 doses of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (doses 3 and 4); the rash had developed 28 days after she received the 4th dose. Her medical history was unremarkable. The lesions regressed after 1 week of treatment with oral valacyclovir 1000 mg 3 times daily, but she developed postherpetic neuralgia 1 week after starting treatment, which resolved after 8 weeks.
Patient 2—A 68-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful sores on the upper lip of 1 day’s duration. She had a history of rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, and atopy and was currently taking prednisone and etanercept. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous base on the upper lip. A diagnosis of herpes labialis was made. The patient reported that she had received a third dose of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine 10 days prior to the appearance of the lesions. Her symptoms resolved completely within 2 weeks of treatment with topical acyclovir.
Patient 3—A 64-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with pain, redness, and watery sores on and around the left eyelid of 2 days’ duration. Dermatologic evaluation revealed the erythematous surface of the left eyelid and periorbital area showed partial crusts, clustered vesicles, erythema, and edema. Additionally, the conjunctiva was purulent and erythematous. The patient’s medical history was notable for allergic asthma, hypertension, anxiety, and depression. For this reason, the patient was prescribed an angiotensin receptor blocker and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. She noted that a similar rash had developed around the left eye 6 years prior that was diagnosed as herpes zoster (HZ). She also reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine followed by 1 dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, which she had received 2 weeks before the rash developed. The patient was treated at the eye clinic and was found to have ocular involvement. Ophthalmology was consulted and a diagnosis of herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) was made. Systemic valacyclovir treatment was initiated, resulting in clinical improvement within 3 weeks.
Patient 4—A 75-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with chest and back pain and widespread muscle pain of several days’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, depression, and coronary artery bypass surgery. A medication history revealed treatment with a β-blocker, acetylsalicylic acid, a calcium channel blocker, a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in dermatome T5 on the right chest and back. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The patient reported that he had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine followed by 1 dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. He was treated with valacyclovir for 1 week, and his symptoms resolved entirely within 3 weeks.
Patient 5—A 50-year-old woman presented to the hospital for evaluation of painful sores on the back, chest, groin, and abdomen of 10 days’ duration. The lesions initially had developed 7 days after receiving the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine; she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. The patient had a history of untreated psoriasis. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in the T2–L2 dermatomes on the left side of the trunk. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The lesions resolved after 1 week of treatment with systemic valacyclovir; however, she subsequently developed postherpetic neuralgia, hypoesthesia, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected regions.
Patient 6—A 37-year-old woman presented to the hospital with redness, swelling, and itching all over the body of 3 days’ duration. The patient noted that the rash would subside and reappear throughout the day. Her medical history was unremarkable, except for COVID-19 infection 6 months prior. She had received a second dose of the BioNTech vaccine 20 days prior to development of symptoms. Dermatologic examination revealed widespread erythematous urticarial plaques. A diagnosis of acute urticaria was made. The patient recovered completely after 1 week of treatment with a systemic steroid and 3 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Patient 7—A 63-year-old woman presented to the hospital with widespread itching and rash that appeared 5 days after the first dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. The patient reported that the rash resolved spontaneously within a few hours but then reappeared. Her medical history revealed that she was taking tamoxifen for breast cancer and that she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous urticarial plaques on the trunk and arms. A diagnosis of urticaria was made, and her symptoms resolved after 6 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Comment
Skin lesions associated with COVID-19 infection have been reported worldwide3,4 as well as dermatologic reactions following COVID-19 vaccination. In one case from Turkey, HZ infection was reported in a 68-year-old man 5 days after he received a second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine.5 In another case, HZ infection developed in a 78-year-old man 5 days after COVID-19 vaccination.6 Numerous cases of HZ infection developing within 1 to 26 days of COVID-19 vaccination have been reported worldwide.7-9
In a study conducted in the United States, 40 skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine were investigated; of these cases, 87.5% (35/40) were reported as varicella-zoster virus, and 12.5% (5/40) were reported as herpes simplex reactivation; 54% (19/35) and 80% (4/5) of these cases, respectively, were associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.10 The average age of patients who developed a skin reaction was 46 years, and 70% (28/40) were women. The time to onset of the reaction was 2 to 13 days after vaccination, and symptoms were reported to improve within 7 days on average.10
Another study from Spain examined 405 vaccine-related skin reactions, 40.2% of which were related to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Among them, 80.2% occurred in women; 13.8% of cases were diagnosed as varicella-zoster virus or HZ virus reactivation, and 14.6% were urticaria. Eighty reactions (21%) were classified as severe/very severe and 81% required treatment.11 One study reported 414 skin reactions from the COVID-19 vaccine from December 2020 to February 2021; of these cases, 83% occurred after the Moderna vaccine, which is not available in Turkey, and 17% occurred after the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.12A systematic review of 91 patients who developed HZ infection after COVID-19 vaccination reported that 10% (9/91) of cases were receiving immunosuppressive therapy and 13% (12/91) had an autoimmune disease.7 In our case series, it is known that at least 2 of the patients (patients 2 and 5), including 1 patient with rheumatoid arthritis (patient 2) who was on immunosuppressive treatment, had autoimmune disorders. However, reports in the literature indicate that most patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases remain stable after vaccination.13
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus is a rare form of HZ caused by involvement of the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve that manifests as vesicular lesions and retinitis, uveitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, and pain on an erythematous background. Two cases of women who developed HZO infection after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination were reported in the literature.14 Although patient 3 in our case series had a history of HZO 6 years prior, the possibility of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine triggering HZO should be taken into consideration.
Although cutaneous reactions after the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine were observed in only 1 of 7 patients in our case series, skin reactions after Sinovac-Coronavac (an inactivated viral vaccine) have been reported in the literature. In one study, after a total of 35,229 injections, the incidence of cutaneous adverse events due to Sinovac-Coronavac was reported to be 0.94% and 0.70% after the first and second doses, respectively.15 Therefore, further study results are needed to directly attribute the reactions to COVID-19 vaccination.
Conclusion
Our case series highlights that clinicians should be vigilant in diagnosing cutaneous reactions following COVID-19 vaccination early to prevent potential complications. Early recognition of reactions is crucial, and the prognosis can be improved with appropriate treatment. Despite the potential dermatologic adverse effects of the COVID-19 vaccine, the most effective way to protect against serious COVID-19 infection is to continue to be vaccinated.
Cutaneous reactions associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine have been reported worldwide since December 2020. Local injection site reactions (<1%) such as erythema, swelling, delayed local reactions (1%–10%), morbilliform rash, urticarial reactions, pityriasis rosea, Rowell syndrome, and lichen planus have been reported following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.1 Cutaneous reactions reported in association with the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine include swelling, redness, itching, discoloration, induration (1%–10%), urticaria, petechial rash, and exacerbation of psoriasis at the local injection site (<1%).2
We describe 7 patients from Turkey who presented with various dermatologic problems 5 to 28 days after COVID-19 vaccination, highlighting the possibility of early and late cutaneous reactions related to the vaccine (Table).

Case Reports
Patient 1—A 44-year-old woman was admitted to the dermatology clinic with painful lesions on the trunk of 3 days’ duration. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped erythematous vesicles showing dermatomal spread in the right thoracolumbar (dermatome T10) region. The patient reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine (doses 1 and 2) and 2 doses of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (doses 3 and 4); the rash had developed 28 days after she received the 4th dose. Her medical history was unremarkable. The lesions regressed after 1 week of treatment with oral valacyclovir 1000 mg 3 times daily, but she developed postherpetic neuralgia 1 week after starting treatment, which resolved after 8 weeks.
Patient 2—A 68-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful sores on the upper lip of 1 day’s duration. She had a history of rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, and atopy and was currently taking prednisone and etanercept. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous base on the upper lip. A diagnosis of herpes labialis was made. The patient reported that she had received a third dose of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine 10 days prior to the appearance of the lesions. Her symptoms resolved completely within 2 weeks of treatment with topical acyclovir.
Patient 3—A 64-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital with pain, redness, and watery sores on and around the left eyelid of 2 days’ duration. Dermatologic evaluation revealed the erythematous surface of the left eyelid and periorbital area showed partial crusts, clustered vesicles, erythema, and edema. Additionally, the conjunctiva was purulent and erythematous. The patient’s medical history was notable for allergic asthma, hypertension, anxiety, and depression. For this reason, the patient was prescribed an angiotensin receptor blocker and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. She noted that a similar rash had developed around the left eye 6 years prior that was diagnosed as herpes zoster (HZ). She also reported that she had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac COVID-19 vaccine followed by 1 dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, which she had received 2 weeks before the rash developed. The patient was treated at the eye clinic and was found to have ocular involvement. Ophthalmology was consulted and a diagnosis of herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) was made. Systemic valacyclovir treatment was initiated, resulting in clinical improvement within 3 weeks.
Patient 4—A 75-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with chest and back pain and widespread muscle pain of several days’ duration. His medical history was remarkable for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, depression, and coronary artery bypass surgery. A medication history revealed treatment with a β-blocker, acetylsalicylic acid, a calcium channel blocker, a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in dermatome T5 on the right chest and back. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The patient reported that he had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine followed by 1 dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. He was treated with valacyclovir for 1 week, and his symptoms resolved entirely within 3 weeks.
Patient 5—A 50-year-old woman presented to the hospital for evaluation of painful sores on the back, chest, groin, and abdomen of 10 days’ duration. The lesions initially had developed 7 days after receiving the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine; she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. The patient had a history of untreated psoriasis. Dermatologic examination revealed grouped vesicles on an erythematous background in the T2–L2 dermatomes on the left side of the trunk. A diagnosis of HZ was made. The lesions resolved after 1 week of treatment with systemic valacyclovir; however, she subsequently developed postherpetic neuralgia, hypoesthesia, and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected regions.
Patient 6—A 37-year-old woman presented to the hospital with redness, swelling, and itching all over the body of 3 days’ duration. The patient noted that the rash would subside and reappear throughout the day. Her medical history was unremarkable, except for COVID-19 infection 6 months prior. She had received a second dose of the BioNTech vaccine 20 days prior to development of symptoms. Dermatologic examination revealed widespread erythematous urticarial plaques. A diagnosis of acute urticaria was made. The patient recovered completely after 1 week of treatment with a systemic steroid and 3 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Patient 7—A 63-year-old woman presented to the hospital with widespread itching and rash that appeared 5 days after the first dose of the BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. The patient reported that the rash resolved spontaneously within a few hours but then reappeared. Her medical history revealed that she was taking tamoxifen for breast cancer and that she previously had received 2 doses of the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine. Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous urticarial plaques on the trunk and arms. A diagnosis of urticaria was made, and her symptoms resolved after 6 weeks of antihistamine treatment.
Comment
Skin lesions associated with COVID-19 infection have been reported worldwide3,4 as well as dermatologic reactions following COVID-19 vaccination. In one case from Turkey, HZ infection was reported in a 68-year-old man 5 days after he received a second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine.5 In another case, HZ infection developed in a 78-year-old man 5 days after COVID-19 vaccination.6 Numerous cases of HZ infection developing within 1 to 26 days of COVID-19 vaccination have been reported worldwide.7-9
In a study conducted in the United States, 40 skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine were investigated; of these cases, 87.5% (35/40) were reported as varicella-zoster virus, and 12.5% (5/40) were reported as herpes simplex reactivation; 54% (19/35) and 80% (4/5) of these cases, respectively, were associated with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.10 The average age of patients who developed a skin reaction was 46 years, and 70% (28/40) were women. The time to onset of the reaction was 2 to 13 days after vaccination, and symptoms were reported to improve within 7 days on average.10
Another study from Spain examined 405 vaccine-related skin reactions, 40.2% of which were related to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Among them, 80.2% occurred in women; 13.8% of cases were diagnosed as varicella-zoster virus or HZ virus reactivation, and 14.6% were urticaria. Eighty reactions (21%) were classified as severe/very severe and 81% required treatment.11 One study reported 414 skin reactions from the COVID-19 vaccine from December 2020 to February 2021; of these cases, 83% occurred after the Moderna vaccine, which is not available in Turkey, and 17% occurred after the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.12A systematic review of 91 patients who developed HZ infection after COVID-19 vaccination reported that 10% (9/91) of cases were receiving immunosuppressive therapy and 13% (12/91) had an autoimmune disease.7 In our case series, it is known that at least 2 of the patients (patients 2 and 5), including 1 patient with rheumatoid arthritis (patient 2) who was on immunosuppressive treatment, had autoimmune disorders. However, reports in the literature indicate that most patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases remain stable after vaccination.13
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus is a rare form of HZ caused by involvement of the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve that manifests as vesicular lesions and retinitis, uveitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, and pain on an erythematous background. Two cases of women who developed HZO infection after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination were reported in the literature.14 Although patient 3 in our case series had a history of HZO 6 years prior, the possibility of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine triggering HZO should be taken into consideration.
Although cutaneous reactions after the Sinovac-Coronavac vaccine were observed in only 1 of 7 patients in our case series, skin reactions after Sinovac-Coronavac (an inactivated viral vaccine) have been reported in the literature. In one study, after a total of 35,229 injections, the incidence of cutaneous adverse events due to Sinovac-Coronavac was reported to be 0.94% and 0.70% after the first and second doses, respectively.15 Therefore, further study results are needed to directly attribute the reactions to COVID-19 vaccination.
Conclusion
Our case series highlights that clinicians should be vigilant in diagnosing cutaneous reactions following COVID-19 vaccination early to prevent potential complications. Early recognition of reactions is crucial, and the prognosis can be improved with appropriate treatment. Despite the potential dermatologic adverse effects of the COVID-19 vaccine, the most effective way to protect against serious COVID-19 infection is to continue to be vaccinated.
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615.
- Zhang Y, Zeng G, Pan H, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:181-192.
- Tan SW, Tam YC, Oh CC. Skin manifestations of COVID-19: a worldwide review. JAAD Int. 2021;2:119-133.
- Singh H, Kaur H, Singh K, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. advances in wound care. 2021;10:51-80.
- Aksu SB, Öztürk GZ. A rare case of shingles after COVID-19 vaccine: is it a possible adverse effect? clinical and experimental vaccine research. 2021;10:198-201.
- Bostan E, Yalici-Armagan B. Herpes zoster following inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: a coexistence or coincidence? J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1566-1567.
- Katsikas Triantafyllidis K, Giannos P, Mian IT, et al. Varicella zoster virus reactivation following COVID-19 vaccination: a systematic review of case reports. Vaccines (Basel). 2021;9:1013. doi:10.3390/vaccines9091013
- Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Chicharro P, Cabrera LM, et al. Varicella-zoster virus reactivation after SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination: report of 5 cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;12:58-59. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.014
- Lee C, Cotter D, Basa J, et al. 20 Post-COVID-19 vaccine-related shingles cases seen at the Las Vegas Dermatology clinic and sent to us via social media. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1960-1964.
- Fathy RA, McMahon DE, Lee C, et al. Varicella-zoster and herpes simplex virus reactivation post-COVID-19 vaccination: a review of 40 cases in an International Dermatology Registry. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol. 2022;36:E6-E9.
- Català A, Muñoz-Santos C, Galván-Casas C, et al. Cutaneous reactions after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a cross-sectional Spanish nationwide study of 405 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:142-152.
- McMahon DE, Amerson E, Rosenbach M, et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: a registry-based study of 414 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:46-55.
- Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: a multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:1330-1338.
- Bernardini N, Skroza N, Mambrin A, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus in two women after Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine. J Med Virol. 2022;94:817-818.
- Rerknimitr P, Puaratanaarunkon T, Wongtada C, et al. Cutaneous adverse reactions from 35,229 doses of Sinovac and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccination: a prospective cohort study in healthcare workers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E158-E161.
- Polack FP, Thomas SJ, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2603-2615.
- Zhang Y, Zeng G, Pan H, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21:181-192.
- Tan SW, Tam YC, Oh CC. Skin manifestations of COVID-19: a worldwide review. JAAD Int. 2021;2:119-133.
- Singh H, Kaur H, Singh K, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. advances in wound care. 2021;10:51-80.
- Aksu SB, Öztürk GZ. A rare case of shingles after COVID-19 vaccine: is it a possible adverse effect? clinical and experimental vaccine research. 2021;10:198-201.
- Bostan E, Yalici-Armagan B. Herpes zoster following inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: a coexistence or coincidence? J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1566-1567.
- Katsikas Triantafyllidis K, Giannos P, Mian IT, et al. Varicella zoster virus reactivation following COVID-19 vaccination: a systematic review of case reports. Vaccines (Basel). 2021;9:1013. doi:10.3390/vaccines9091013
- Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Chicharro P, Cabrera LM, et al. Varicella-zoster virus reactivation after SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination: report of 5 cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;12:58-59. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.014
- Lee C, Cotter D, Basa J, et al. 20 Post-COVID-19 vaccine-related shingles cases seen at the Las Vegas Dermatology clinic and sent to us via social media. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:1960-1964.
- Fathy RA, McMahon DE, Lee C, et al. Varicella-zoster and herpes simplex virus reactivation post-COVID-19 vaccination: a review of 40 cases in an International Dermatology Registry. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol. 2022;36:E6-E9.
- Català A, Muñoz-Santos C, Galván-Casas C, et al. Cutaneous reactions after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a cross-sectional Spanish nationwide study of 405 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2022;186:142-152.
- McMahon DE, Amerson E, Rosenbach M, et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: a registry-based study of 414 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:46-55.
- Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: a multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:1330-1338.
- Bernardini N, Skroza N, Mambrin A, et al. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus in two women after Pfizer-BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine. J Med Virol. 2022;94:817-818.
- Rerknimitr P, Puaratanaarunkon T, Wongtada C, et al. Cutaneous adverse reactions from 35,229 doses of Sinovac and AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccination: a prospective cohort study in healthcare workers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:E158-E161.
Practice Points
- Cutaneous reactions have been reported following COVID-19 vaccination.
- Herpes infections and urticarial reactions can be associated with COVID-19 vaccination, regardless of the delay in onset between the injection and symptom development.
Mixing Paxlovid With Specific Immunosuppressants Risks Serious Adverse Reactions
The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued a reminder to healthcare professionals regarding the potential serious adverse reactions associated with Paxlovid when administered in combination with specific immunosuppressants.
These immunosuppressants, encompassing calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and ciclosporin) and mTOR inhibitors (everolimus and sirolimus), possess a narrow safe dosage range. They are recognized for their role in diminishing the activity of the immune system and are typically prescribed for autoimmune conditions and organ transplant recipients.
The highlighted risk arises due to drug-drug interactions, which can compromise the body’s ability to eliminate these medicines effectively.
Paxlovid, also known as nirmatrelvir with ritonavir, is an antiviral medication used to treat COVID-19 in adults who do not require supplemental oxygen and who are at an increased risk of progressing to severe COVID-19. It should be administered as soon as possible after a diagnosis of COVID-19 has been made and within 5 days of symptom onset.
Conditional marketing authorization for Paxlovid was granted across the European Union (EU) on January 28, 2022, and subsequently transitioned to full marketing authorization on February 24, 2023.
Developed by Pfizer, Paxlovid exhibited an 89% reduction in the risk for hospitalization or death among unvaccinated individuals in a phase 2-3 clinical trial. This led the National Institutes of Health to prioritize Paxlovid over other COVID-19 treatments. Subsequent real-world studies have affirmed its effectiveness, even among the vaccinated.
When combining Paxlovid with tacrolimus, ciclosporin, everolimus, or sirolimus, healthcare professionals need to actively monitor their blood levels. This proactive approach is essential to mitigate the risk for drug-drug interactions and potential serious reactions. They should collaborate with a multidisciplinary team of specialists to navigate the complexities of administering these medications concurrently.
Further, Paxlovid must not be coadministered with medications highly reliant on CYP3A liver enzymes for elimination, such as the immunosuppressant voclosporin. When administered together, there is a risk for these drugs interfering with each other’s metabolism, potentially leading to altered blood levels, reduced effectiveness, or an increased risk for adverse reactions.
After a thorough review, PRAC has highlighted potential serious adverse reactions, including fatal cases, due to drug interactions between Paxlovid and specified immunosuppressants. Thus, it issued a direct healthcare professional communication (DHPC) to emphasize the recognized risk for these interactions, as previously outlined in Paxlovid’s product information.
The DHPC for Paxlovid will undergo further evaluation by EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use and, upon adoption, will be disseminated to healthcare professionals. The communication plan will include publication on the DHPCs page and in national registers across EU Member States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued a reminder to healthcare professionals regarding the potential serious adverse reactions associated with Paxlovid when administered in combination with specific immunosuppressants.
These immunosuppressants, encompassing calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and ciclosporin) and mTOR inhibitors (everolimus and sirolimus), possess a narrow safe dosage range. They are recognized for their role in diminishing the activity of the immune system and are typically prescribed for autoimmune conditions and organ transplant recipients.
The highlighted risk arises due to drug-drug interactions, which can compromise the body’s ability to eliminate these medicines effectively.
Paxlovid, also known as nirmatrelvir with ritonavir, is an antiviral medication used to treat COVID-19 in adults who do not require supplemental oxygen and who are at an increased risk of progressing to severe COVID-19. It should be administered as soon as possible after a diagnosis of COVID-19 has been made and within 5 days of symptom onset.
Conditional marketing authorization for Paxlovid was granted across the European Union (EU) on January 28, 2022, and subsequently transitioned to full marketing authorization on February 24, 2023.
Developed by Pfizer, Paxlovid exhibited an 89% reduction in the risk for hospitalization or death among unvaccinated individuals in a phase 2-3 clinical trial. This led the National Institutes of Health to prioritize Paxlovid over other COVID-19 treatments. Subsequent real-world studies have affirmed its effectiveness, even among the vaccinated.
When combining Paxlovid with tacrolimus, ciclosporin, everolimus, or sirolimus, healthcare professionals need to actively monitor their blood levels. This proactive approach is essential to mitigate the risk for drug-drug interactions and potential serious reactions. They should collaborate with a multidisciplinary team of specialists to navigate the complexities of administering these medications concurrently.
Further, Paxlovid must not be coadministered with medications highly reliant on CYP3A liver enzymes for elimination, such as the immunosuppressant voclosporin. When administered together, there is a risk for these drugs interfering with each other’s metabolism, potentially leading to altered blood levels, reduced effectiveness, or an increased risk for adverse reactions.
After a thorough review, PRAC has highlighted potential serious adverse reactions, including fatal cases, due to drug interactions between Paxlovid and specified immunosuppressants. Thus, it issued a direct healthcare professional communication (DHPC) to emphasize the recognized risk for these interactions, as previously outlined in Paxlovid’s product information.
The DHPC for Paxlovid will undergo further evaluation by EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use and, upon adoption, will be disseminated to healthcare professionals. The communication plan will include publication on the DHPCs page and in national registers across EU Member States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has issued a reminder to healthcare professionals regarding the potential serious adverse reactions associated with Paxlovid when administered in combination with specific immunosuppressants.
These immunosuppressants, encompassing calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and ciclosporin) and mTOR inhibitors (everolimus and sirolimus), possess a narrow safe dosage range. They are recognized for their role in diminishing the activity of the immune system and are typically prescribed for autoimmune conditions and organ transplant recipients.
The highlighted risk arises due to drug-drug interactions, which can compromise the body’s ability to eliminate these medicines effectively.
Paxlovid, also known as nirmatrelvir with ritonavir, is an antiviral medication used to treat COVID-19 in adults who do not require supplemental oxygen and who are at an increased risk of progressing to severe COVID-19. It should be administered as soon as possible after a diagnosis of COVID-19 has been made and within 5 days of symptom onset.
Conditional marketing authorization for Paxlovid was granted across the European Union (EU) on January 28, 2022, and subsequently transitioned to full marketing authorization on February 24, 2023.
Developed by Pfizer, Paxlovid exhibited an 89% reduction in the risk for hospitalization or death among unvaccinated individuals in a phase 2-3 clinical trial. This led the National Institutes of Health to prioritize Paxlovid over other COVID-19 treatments. Subsequent real-world studies have affirmed its effectiveness, even among the vaccinated.
When combining Paxlovid with tacrolimus, ciclosporin, everolimus, or sirolimus, healthcare professionals need to actively monitor their blood levels. This proactive approach is essential to mitigate the risk for drug-drug interactions and potential serious reactions. They should collaborate with a multidisciplinary team of specialists to navigate the complexities of administering these medications concurrently.
Further, Paxlovid must not be coadministered with medications highly reliant on CYP3A liver enzymes for elimination, such as the immunosuppressant voclosporin. When administered together, there is a risk for these drugs interfering with each other’s metabolism, potentially leading to altered blood levels, reduced effectiveness, or an increased risk for adverse reactions.
After a thorough review, PRAC has highlighted potential serious adverse reactions, including fatal cases, due to drug interactions between Paxlovid and specified immunosuppressants. Thus, it issued a direct healthcare professional communication (DHPC) to emphasize the recognized risk for these interactions, as previously outlined in Paxlovid’s product information.
The DHPC for Paxlovid will undergo further evaluation by EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use and, upon adoption, will be disseminated to healthcare professionals. The communication plan will include publication on the DHPCs page and in national registers across EU Member States.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID: Another Great Pretender
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Evidence Suggests Long COVID Could Be a Brain Injury
Brain fog is one of the most common, persistent complaints in patients with long COVID. It affects as many as 46% of patients who also deal with other cognitive concerns like memory loss and difficulty concentrating.
Now, researchers believe they know why. A new study has found that these symptoms may be the result of a viral-borne brain injury that may cause cognitive and mental health issues that persist for years.
The findings were based on a series of cognitive tests, self-reported symptoms, brain scans, and biomarkers.
Brain Deficits Equal to 20 Years of Brain Aging
As part of the preprint study, participants took a cognition test with their scores age-matched to those who had not suffered a serious bout of COVID-19. Then a blood sample was taken to look for specific biomarkers, showing that elevated levels of certain biomarkers were consistent with a brain injury. Using brain scans, researchers also found that certain regions of the brain associated with attention were reduced in volume.
Patients who participated in the study were “less accurate and slower” in their cognition, and suffered from at least one mental health condition, such as depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, according to researchers.
The brain deficits found in COVID-19 patients were equivalent to 20 years of brain aging and provided proof of what doctors have feared: that this virus can damage the brain and result in ongoing mental health issues.
“We found global deficits across cognition,” said lead study author Benedict Michael, PhD, director of the Infection Neuroscience Lab at the University of Liverpool in Liverpool, England. “The cognitive and memory problems that patients complained of were associated with neuroanatomical changes to the brain.”
Proof That Symptoms Aren’t ‘Figment’ of Patients’ Imaginations
Cognitive deficits were common among all patients, but the researchers said they don’t yet know whether the brain damage causes permanent cognitive decline. But the research provides patients who have been overlooked by some clinicians with proof that their conditions aren’t a figment of their imaginations, said Karla L. Thompson, PhD, lead neuropsychologist at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine’s COVID Recovery Clinic.
“Even though we’re several years into this pandemic, there are still a lot of providers who don’t believe that their patients are experiencing these residual symptoms,” said Dr. Thompson, “That’s why the use of biomarkers is important, because it provides an objective indication that the brain has been compromised in some way.”
Some patients with long COVID have said that getting their doctors to believe they have a physical ailment has been a persistent problem throughout the pandemic and especially as it relates to the sometimes-vague collection of symptoms associated with brain fog. One study found that as many as 79% of study respondents reported negative interactions with their healthcare providers when they sought treatment for their long-COVID symptoms.
How Do COVID-Related Brain Injuries Happen?
Researchers are unsure what’s causing these brain injuries, though they have identified some clues. Previous research has suggested that such injuries might be the result of a lack of oxygen to the brain, especially in patients who were hospitalized, like those in this study, and were put on ventilators.
Brain scans have previously shown atrophy to the brain›s gray matter in COVID-19 patients, likely caused by inflammation from a heightened immune response rather than the virus itself. This inflammatory response seems to affect the central nervous system. As part of the new study, researchers found some neuroprotective effects of using steroids during hospitalization to reduce brain inflammation.
The results suggest that clinicians should overcome their skepticism and consider the possibility that their patients have suffered a brain injury and should be treated appropriately, said James C. Jackson, PsyD, a neuropsychiatrist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. “The old saying is that if it walks like a duck and talks like a duck, it’s a duck,” said Dr. Jackson.
He contends that treatments used for patients who have brain injuries have also been shown to be effective in treating long COVID–related brain fog symptoms. These may include speech, cognitive, and occupational therapy as well as meeting with a neuropsychiatrist for the treatment of related mental health concerns.
A New Path Forward
Treating long-COVID brain fog like a brain injury can help patients get back to some semblance of normalcy, researchers said. “What we’re seeing in terms of brain injury biomarkers and differences in brain scans correlates to real-life problems that these patients are dealing with on a daily basis,” said Dr. Jackson. These include problems at work and in life with multitasking, remembering details, meeting deadlines, synthesizing large amounts of information, and maintaining focus on the task at hand, he said.
There’s also a fear that even with treatment, the aging of the brain caused by the virus might have long-term repercussions and that this enduring injury may cause the early onset of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in those who were already vulnerable to it. One study, from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), found that in those infected with COVID-19 who already had dementia, the virus “rapidly accelerated structural and functional brain deterioration.”
“We already know the role that neuroinflammation plays in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Thompson. “If long COVID is involved in prolonged inflammation of the brain, it goes a long way in explaining the mechanism underlying [the study’s reported] brain aging.”
Still More to Learn
In some ways, this study raises nearly as many questions as it does answers. While it provides concrete evidence around the damage the virus is doing to the brains of patients who contracted severe COVID-19, researchers don’t know about the impact on those who had less serious cases of the virus.
For Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, the concern is that some long-COVID patients may be suffering from cognitive deficits that are more subtle but still impacting their daily lives, and that they’re not getting the help they need.
What’s more, said Dr. Al-Aly, it’s unclear whether the impacts of the brain damage are permanent or how to stop them from worsening. Researchers and clinicians need a better understanding of the mechanism that allows this virus to enter the brain and do structural damage. If it’s inflammation, will anti-inflammatory or antiviral medications work at preventing it? Will steroids help to offset the damage? “It’s critical we find some answers,” he said.
“SARS-CoV-2 isn’t going anywhere. It will continue to infect the population, so if this is indeed a virus that damages the brain in the long term or permanently, we need to figure out what can be done to stop it,” said Dr. Al-Aly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Brain fog is one of the most common, persistent complaints in patients with long COVID. It affects as many as 46% of patients who also deal with other cognitive concerns like memory loss and difficulty concentrating.
Now, researchers believe they know why. A new study has found that these symptoms may be the result of a viral-borne brain injury that may cause cognitive and mental health issues that persist for years.
The findings were based on a series of cognitive tests, self-reported symptoms, brain scans, and biomarkers.
Brain Deficits Equal to 20 Years of Brain Aging
As part of the preprint study, participants took a cognition test with their scores age-matched to those who had not suffered a serious bout of COVID-19. Then a blood sample was taken to look for specific biomarkers, showing that elevated levels of certain biomarkers were consistent with a brain injury. Using brain scans, researchers also found that certain regions of the brain associated with attention were reduced in volume.
Patients who participated in the study were “less accurate and slower” in their cognition, and suffered from at least one mental health condition, such as depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, according to researchers.
The brain deficits found in COVID-19 patients were equivalent to 20 years of brain aging and provided proof of what doctors have feared: that this virus can damage the brain and result in ongoing mental health issues.
“We found global deficits across cognition,” said lead study author Benedict Michael, PhD, director of the Infection Neuroscience Lab at the University of Liverpool in Liverpool, England. “The cognitive and memory problems that patients complained of were associated with neuroanatomical changes to the brain.”
Proof That Symptoms Aren’t ‘Figment’ of Patients’ Imaginations
Cognitive deficits were common among all patients, but the researchers said they don’t yet know whether the brain damage causes permanent cognitive decline. But the research provides patients who have been overlooked by some clinicians with proof that their conditions aren’t a figment of their imaginations, said Karla L. Thompson, PhD, lead neuropsychologist at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine’s COVID Recovery Clinic.
“Even though we’re several years into this pandemic, there are still a lot of providers who don’t believe that their patients are experiencing these residual symptoms,” said Dr. Thompson, “That’s why the use of biomarkers is important, because it provides an objective indication that the brain has been compromised in some way.”
Some patients with long COVID have said that getting their doctors to believe they have a physical ailment has been a persistent problem throughout the pandemic and especially as it relates to the sometimes-vague collection of symptoms associated with brain fog. One study found that as many as 79% of study respondents reported negative interactions with their healthcare providers when they sought treatment for their long-COVID symptoms.
How Do COVID-Related Brain Injuries Happen?
Researchers are unsure what’s causing these brain injuries, though they have identified some clues. Previous research has suggested that such injuries might be the result of a lack of oxygen to the brain, especially in patients who were hospitalized, like those in this study, and were put on ventilators.
Brain scans have previously shown atrophy to the brain›s gray matter in COVID-19 patients, likely caused by inflammation from a heightened immune response rather than the virus itself. This inflammatory response seems to affect the central nervous system. As part of the new study, researchers found some neuroprotective effects of using steroids during hospitalization to reduce brain inflammation.
The results suggest that clinicians should overcome their skepticism and consider the possibility that their patients have suffered a brain injury and should be treated appropriately, said James C. Jackson, PsyD, a neuropsychiatrist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. “The old saying is that if it walks like a duck and talks like a duck, it’s a duck,” said Dr. Jackson.
He contends that treatments used for patients who have brain injuries have also been shown to be effective in treating long COVID–related brain fog symptoms. These may include speech, cognitive, and occupational therapy as well as meeting with a neuropsychiatrist for the treatment of related mental health concerns.
A New Path Forward
Treating long-COVID brain fog like a brain injury can help patients get back to some semblance of normalcy, researchers said. “What we’re seeing in terms of brain injury biomarkers and differences in brain scans correlates to real-life problems that these patients are dealing with on a daily basis,” said Dr. Jackson. These include problems at work and in life with multitasking, remembering details, meeting deadlines, synthesizing large amounts of information, and maintaining focus on the task at hand, he said.
There’s also a fear that even with treatment, the aging of the brain caused by the virus might have long-term repercussions and that this enduring injury may cause the early onset of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in those who were already vulnerable to it. One study, from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), found that in those infected with COVID-19 who already had dementia, the virus “rapidly accelerated structural and functional brain deterioration.”
“We already know the role that neuroinflammation plays in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Thompson. “If long COVID is involved in prolonged inflammation of the brain, it goes a long way in explaining the mechanism underlying [the study’s reported] brain aging.”
Still More to Learn
In some ways, this study raises nearly as many questions as it does answers. While it provides concrete evidence around the damage the virus is doing to the brains of patients who contracted severe COVID-19, researchers don’t know about the impact on those who had less serious cases of the virus.
For Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, the concern is that some long-COVID patients may be suffering from cognitive deficits that are more subtle but still impacting their daily lives, and that they’re not getting the help they need.
What’s more, said Dr. Al-Aly, it’s unclear whether the impacts of the brain damage are permanent or how to stop them from worsening. Researchers and clinicians need a better understanding of the mechanism that allows this virus to enter the brain and do structural damage. If it’s inflammation, will anti-inflammatory or antiviral medications work at preventing it? Will steroids help to offset the damage? “It’s critical we find some answers,” he said.
“SARS-CoV-2 isn’t going anywhere. It will continue to infect the population, so if this is indeed a virus that damages the brain in the long term or permanently, we need to figure out what can be done to stop it,” said Dr. Al-Aly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Brain fog is one of the most common, persistent complaints in patients with long COVID. It affects as many as 46% of patients who also deal with other cognitive concerns like memory loss and difficulty concentrating.
Now, researchers believe they know why. A new study has found that these symptoms may be the result of a viral-borne brain injury that may cause cognitive and mental health issues that persist for years.
The findings were based on a series of cognitive tests, self-reported symptoms, brain scans, and biomarkers.
Brain Deficits Equal to 20 Years of Brain Aging
As part of the preprint study, participants took a cognition test with their scores age-matched to those who had not suffered a serious bout of COVID-19. Then a blood sample was taken to look for specific biomarkers, showing that elevated levels of certain biomarkers were consistent with a brain injury. Using brain scans, researchers also found that certain regions of the brain associated with attention were reduced in volume.
Patients who participated in the study were “less accurate and slower” in their cognition, and suffered from at least one mental health condition, such as depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, according to researchers.
The brain deficits found in COVID-19 patients were equivalent to 20 years of brain aging and provided proof of what doctors have feared: that this virus can damage the brain and result in ongoing mental health issues.
“We found global deficits across cognition,” said lead study author Benedict Michael, PhD, director of the Infection Neuroscience Lab at the University of Liverpool in Liverpool, England. “The cognitive and memory problems that patients complained of were associated with neuroanatomical changes to the brain.”
Proof That Symptoms Aren’t ‘Figment’ of Patients’ Imaginations
Cognitive deficits were common among all patients, but the researchers said they don’t yet know whether the brain damage causes permanent cognitive decline. But the research provides patients who have been overlooked by some clinicians with proof that their conditions aren’t a figment of their imaginations, said Karla L. Thompson, PhD, lead neuropsychologist at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine’s COVID Recovery Clinic.
“Even though we’re several years into this pandemic, there are still a lot of providers who don’t believe that their patients are experiencing these residual symptoms,” said Dr. Thompson, “That’s why the use of biomarkers is important, because it provides an objective indication that the brain has been compromised in some way.”
Some patients with long COVID have said that getting their doctors to believe they have a physical ailment has been a persistent problem throughout the pandemic and especially as it relates to the sometimes-vague collection of symptoms associated with brain fog. One study found that as many as 79% of study respondents reported negative interactions with their healthcare providers when they sought treatment for their long-COVID symptoms.
How Do COVID-Related Brain Injuries Happen?
Researchers are unsure what’s causing these brain injuries, though they have identified some clues. Previous research has suggested that such injuries might be the result of a lack of oxygen to the brain, especially in patients who were hospitalized, like those in this study, and were put on ventilators.
Brain scans have previously shown atrophy to the brain›s gray matter in COVID-19 patients, likely caused by inflammation from a heightened immune response rather than the virus itself. This inflammatory response seems to affect the central nervous system. As part of the new study, researchers found some neuroprotective effects of using steroids during hospitalization to reduce brain inflammation.
The results suggest that clinicians should overcome their skepticism and consider the possibility that their patients have suffered a brain injury and should be treated appropriately, said James C. Jackson, PsyD, a neuropsychiatrist at Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. “The old saying is that if it walks like a duck and talks like a duck, it’s a duck,” said Dr. Jackson.
He contends that treatments used for patients who have brain injuries have also been shown to be effective in treating long COVID–related brain fog symptoms. These may include speech, cognitive, and occupational therapy as well as meeting with a neuropsychiatrist for the treatment of related mental health concerns.
A New Path Forward
Treating long-COVID brain fog like a brain injury can help patients get back to some semblance of normalcy, researchers said. “What we’re seeing in terms of brain injury biomarkers and differences in brain scans correlates to real-life problems that these patients are dealing with on a daily basis,” said Dr. Jackson. These include problems at work and in life with multitasking, remembering details, meeting deadlines, synthesizing large amounts of information, and maintaining focus on the task at hand, he said.
There’s also a fear that even with treatment, the aging of the brain caused by the virus might have long-term repercussions and that this enduring injury may cause the early onset of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in those who were already vulnerable to it. One study, from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), found that in those infected with COVID-19 who already had dementia, the virus “rapidly accelerated structural and functional brain deterioration.”
“We already know the role that neuroinflammation plays in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Thompson. “If long COVID is involved in prolonged inflammation of the brain, it goes a long way in explaining the mechanism underlying [the study’s reported] brain aging.”
Still More to Learn
In some ways, this study raises nearly as many questions as it does answers. While it provides concrete evidence around the damage the virus is doing to the brains of patients who contracted severe COVID-19, researchers don’t know about the impact on those who had less serious cases of the virus.
For Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, the concern is that some long-COVID patients may be suffering from cognitive deficits that are more subtle but still impacting their daily lives, and that they’re not getting the help they need.
What’s more, said Dr. Al-Aly, it’s unclear whether the impacts of the brain damage are permanent or how to stop them from worsening. Researchers and clinicians need a better understanding of the mechanism that allows this virus to enter the brain and do structural damage. If it’s inflammation, will anti-inflammatory or antiviral medications work at preventing it? Will steroids help to offset the damage? “It’s critical we find some answers,” he said.
“SARS-CoV-2 isn’t going anywhere. It will continue to infect the population, so if this is indeed a virus that damages the brain in the long term or permanently, we need to figure out what can be done to stop it,” said Dr. Al-Aly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
RNA Vaccines: Risk for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Clarified
Cases of menstrual disorders, particularly unusually heavy menstrual bleeding, have been reported following RNA vaccination against COVID-19.
In France, this safety signal has been confirmed and added to the product characteristics summaries and vaccine leaflets for mRNA vaccines in October 2022. However, few studies have accurately measured this risk to date.
To address this gap in research, the French scientific interest group in the epidemiology of health products, ANSM-Cnam EPI-PHARE, conducted a study to assess the risk for heavy menstrual bleeding requiring hospitalization after COVID-19 vaccination in France.
“This study provides new evidence supporting the existence of an increased risk for heavy menstrual bleeding following COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA vaccines,” wrote the authors.
Study Details
The study included all women aged 15-50 years who were diagnosed with heavy menstrual bleeding in the hospital between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022. Participants were identified in the National Health Data System, and the study population totaled 4610 women.
Each participant was randomly matched with as many as 30 women who had not been hospitalized for abnormal genital bleeding and had similar characteristics in terms of age, department of residence, social deprivation index of the commune of residence, and contraceptive method.
Women who had a recent pregnancy, hysterectomy, or coagulation disorder within the specified time frames were excluded.
At the time of the study, 71% of cases and 70% of controls had received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. Among vaccinated participants, 68% and 66%, respectively, received a vaccination dose (first or second dose). An mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) was the last vaccine for 99.8% of the population.
Increased Risk
Compared with control women, those hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding were more likely to have received their last dose of mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) in the previous 1-3 months. This association was observed for vaccination doses (odds ratio [OR], 1.20), indicating a 20% increased risk, but it was not found for booster doses (OR, 1.07).
This association was particularly notable for women residing in socially disadvantaged communities (OR, 1.28) and women not using hormonal contraception (OR, 1.28).
The risk did not appear to be increased beyond 3 months after vaccination. Researchers noted that the increased risk may have occurred earlier, considering the likely interval between initial symptoms and hospitalization.
Assuming a causal relationship, the estimated number of cases attributable to vaccination was 8 cases per million vaccinated women, totaling 103 cases among all women aged 15-50 years who were vaccinated in France between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022.
As of the study date and in the 3 years before the study, none of the authors had any conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of menstrual disorders, particularly unusually heavy menstrual bleeding, have been reported following RNA vaccination against COVID-19.
In France, this safety signal has been confirmed and added to the product characteristics summaries and vaccine leaflets for mRNA vaccines in October 2022. However, few studies have accurately measured this risk to date.
To address this gap in research, the French scientific interest group in the epidemiology of health products, ANSM-Cnam EPI-PHARE, conducted a study to assess the risk for heavy menstrual bleeding requiring hospitalization after COVID-19 vaccination in France.
“This study provides new evidence supporting the existence of an increased risk for heavy menstrual bleeding following COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA vaccines,” wrote the authors.
Study Details
The study included all women aged 15-50 years who were diagnosed with heavy menstrual bleeding in the hospital between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022. Participants were identified in the National Health Data System, and the study population totaled 4610 women.
Each participant was randomly matched with as many as 30 women who had not been hospitalized for abnormal genital bleeding and had similar characteristics in terms of age, department of residence, social deprivation index of the commune of residence, and contraceptive method.
Women who had a recent pregnancy, hysterectomy, or coagulation disorder within the specified time frames were excluded.
At the time of the study, 71% of cases and 70% of controls had received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. Among vaccinated participants, 68% and 66%, respectively, received a vaccination dose (first or second dose). An mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) was the last vaccine for 99.8% of the population.
Increased Risk
Compared with control women, those hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding were more likely to have received their last dose of mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) in the previous 1-3 months. This association was observed for vaccination doses (odds ratio [OR], 1.20), indicating a 20% increased risk, but it was not found for booster doses (OR, 1.07).
This association was particularly notable for women residing in socially disadvantaged communities (OR, 1.28) and women not using hormonal contraception (OR, 1.28).
The risk did not appear to be increased beyond 3 months after vaccination. Researchers noted that the increased risk may have occurred earlier, considering the likely interval between initial symptoms and hospitalization.
Assuming a causal relationship, the estimated number of cases attributable to vaccination was 8 cases per million vaccinated women, totaling 103 cases among all women aged 15-50 years who were vaccinated in France between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022.
As of the study date and in the 3 years before the study, none of the authors had any conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of menstrual disorders, particularly unusually heavy menstrual bleeding, have been reported following RNA vaccination against COVID-19.
In France, this safety signal has been confirmed and added to the product characteristics summaries and vaccine leaflets for mRNA vaccines in October 2022. However, few studies have accurately measured this risk to date.
To address this gap in research, the French scientific interest group in the epidemiology of health products, ANSM-Cnam EPI-PHARE, conducted a study to assess the risk for heavy menstrual bleeding requiring hospitalization after COVID-19 vaccination in France.
“This study provides new evidence supporting the existence of an increased risk for heavy menstrual bleeding following COVID-19 vaccination with mRNA vaccines,” wrote the authors.
Study Details
The study included all women aged 15-50 years who were diagnosed with heavy menstrual bleeding in the hospital between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022. Participants were identified in the National Health Data System, and the study population totaled 4610 women.
Each participant was randomly matched with as many as 30 women who had not been hospitalized for abnormal genital bleeding and had similar characteristics in terms of age, department of residence, social deprivation index of the commune of residence, and contraceptive method.
Women who had a recent pregnancy, hysterectomy, or coagulation disorder within the specified time frames were excluded.
At the time of the study, 71% of cases and 70% of controls had received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. Among vaccinated participants, 68% and 66%, respectively, received a vaccination dose (first or second dose). An mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) was the last vaccine for 99.8% of the population.
Increased Risk
Compared with control women, those hospitalized for heavy menstrual bleeding were more likely to have received their last dose of mRNA vaccine (Comirnaty or Spikevax) in the previous 1-3 months. This association was observed for vaccination doses (odds ratio [OR], 1.20), indicating a 20% increased risk, but it was not found for booster doses (OR, 1.07).
This association was particularly notable for women residing in socially disadvantaged communities (OR, 1.28) and women not using hormonal contraception (OR, 1.28).
The risk did not appear to be increased beyond 3 months after vaccination. Researchers noted that the increased risk may have occurred earlier, considering the likely interval between initial symptoms and hospitalization.
Assuming a causal relationship, the estimated number of cases attributable to vaccination was 8 cases per million vaccinated women, totaling 103 cases among all women aged 15-50 years who were vaccinated in France between May 12, 2021, and August 31, 2022.
As of the study date and in the 3 years before the study, none of the authors had any conflicts of interest with pharmaceutical companies.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bivalent COVID Vaccine Protected Children, Adolescents
Children and adolescents ages 5-17 who received a bivalent COVID-19 mRNA vaccine were less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared with those who were unvaccinated or received only the monovalent COVID-19 vaccine, according to new data published February 6 in JAMA.
“All eligible children and adolescents should remain up to date with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations,” wrote the authors, led by Leora R. Feldstein, PhD, with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta.
By the end of 2023, at least 911 youths ages 5-17 had died from COVID-related causes.
Researchers found that compared with participants who did not receive the COVID-19 vaccine or got monovalent-only doses 180 days or more before, the adjusted vaccine effectiveness of a bivalent COVID-19 vaccine dose against SARS-CoV-2 infection was 51.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 23.6%-71.9%) 7-60 days after vaccination. Relative effectiveness was 62.4% (95% CI, 38.5%-81.1%) 61-150 days after vaccination. The researchers said the confidence intervals were wide because of the small sample size.
The information can help inform public health strategies, the authors noted, especially as new variants emerge.
Bivalent Dose Recommended in Fall of 2022
Bivalent mRNA COVID vaccines were recommended in the United States for children and adolescents ages 12 years or older on Sept. 1, 2022, and for children ages 5-11 on Oct. 12, 2022, when Omicron BA.4/5 types were the predominant circulating variant.
The study included 2,959 participants who completed periodic surveys (answering questions on demographics, household details, chronic medical conditions, and COVID-19 symptoms) and submitted weekly self-collected nasal swabs (whether or not they had symptoms). Those in the study submitted additional nasal swabs if they developed any symptoms.
Median adherence to weekly upper respiratory specimen swabbing was high throughout the study period at 93.8%.
Data from Sept. 4, 2022, to Jan. 31, 2023, were combined from three prospective US cohort studies at six sites. In addition to the surveys, researchers used information from state immunization information systems and electronic medical records.
Most of the Infected Were Unvaccinated or Had Monovalent Vax
Of the 426 participants (14.4% of the combined cohorts) infected with SARS-CoV-2, 383 (89.9%) were either unvaccinated or received monovalent vaccine doses only.
Calculations were adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, health conditions, prior SARS-CoV-2 infections, geographic location, proportion of circulating variants by site, and local virus prevalence.
Participants living in Oregon, for example, had the highest uptake of bivalent COVID-19 vaccine (56.2%), whereas those in Texas had the lowest (2.4%). Participants reporting Hispanic ethnicity had lower bivalent uptake (17.1%) compared with non-Hispanic participants of all races (27.1%).
Of the 2,207 participants who did not receive a bivalent dose, 24.2% were unvaccinated and 1,672 (75.8%) received at least 1 monovalent dose.
The researchers said they saw no sign of waning effectiveness 61-150 days (the limit for this analysis) after receipt of the bivalent COVID-19 vaccine.
They wrote that continuation of the cohorts will allow study of waning patterns, which could help inform vaccine recommendations.
Among the limitations of the study are that testing methods and the COVID-19 symptoms surveyed varied among the three cohorts, so there may be some differences in defining infection or symptomatic COVID. In addition, the researchers were not able to account for the social vulnerability index and immunocompromised status, which could have affected vaccine uptake and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
This study was supported by the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Coauthor Dr. Caban-Martinez reported grants from the Florida Firefighter Cancer Initiative and the Florida Department of Health. Coauthors Dr. Chu, Dr. Englund, Dr. Martin, and Dr. Monto reported receiving personal fees or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hegmann reported being the editor of the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine practice guidelines. Coauthor Dr. Gaglani reported serving as cochair of the infectious diseases and immunization committee and the respiratory syncytial virus task force lead for the Texas Pediatric Society and the Texas Chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics. No other disclosures were reported.
Children and adolescents ages 5-17 who received a bivalent COVID-19 mRNA vaccine were less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared with those who were unvaccinated or received only the monovalent COVID-19 vaccine, according to new data published February 6 in JAMA.
“All eligible children and adolescents should remain up to date with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations,” wrote the authors, led by Leora R. Feldstein, PhD, with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta.
By the end of 2023, at least 911 youths ages 5-17 had died from COVID-related causes.
Researchers found that compared with participants who did not receive the COVID-19 vaccine or got monovalent-only doses 180 days or more before, the adjusted vaccine effectiveness of a bivalent COVID-19 vaccine dose against SARS-CoV-2 infection was 51.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 23.6%-71.9%) 7-60 days after vaccination. Relative effectiveness was 62.4% (95% CI, 38.5%-81.1%) 61-150 days after vaccination. The researchers said the confidence intervals were wide because of the small sample size.
The information can help inform public health strategies, the authors noted, especially as new variants emerge.
Bivalent Dose Recommended in Fall of 2022
Bivalent mRNA COVID vaccines were recommended in the United States for children and adolescents ages 12 years or older on Sept. 1, 2022, and for children ages 5-11 on Oct. 12, 2022, when Omicron BA.4/5 types were the predominant circulating variant.
The study included 2,959 participants who completed periodic surveys (answering questions on demographics, household details, chronic medical conditions, and COVID-19 symptoms) and submitted weekly self-collected nasal swabs (whether or not they had symptoms). Those in the study submitted additional nasal swabs if they developed any symptoms.
Median adherence to weekly upper respiratory specimen swabbing was high throughout the study period at 93.8%.
Data from Sept. 4, 2022, to Jan. 31, 2023, were combined from three prospective US cohort studies at six sites. In addition to the surveys, researchers used information from state immunization information systems and electronic medical records.
Most of the Infected Were Unvaccinated or Had Monovalent Vax
Of the 426 participants (14.4% of the combined cohorts) infected with SARS-CoV-2, 383 (89.9%) were either unvaccinated or received monovalent vaccine doses only.
Calculations were adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, health conditions, prior SARS-CoV-2 infections, geographic location, proportion of circulating variants by site, and local virus prevalence.
Participants living in Oregon, for example, had the highest uptake of bivalent COVID-19 vaccine (56.2%), whereas those in Texas had the lowest (2.4%). Participants reporting Hispanic ethnicity had lower bivalent uptake (17.1%) compared with non-Hispanic participants of all races (27.1%).
Of the 2,207 participants who did not receive a bivalent dose, 24.2% were unvaccinated and 1,672 (75.8%) received at least 1 monovalent dose.
The researchers said they saw no sign of waning effectiveness 61-150 days (the limit for this analysis) after receipt of the bivalent COVID-19 vaccine.
They wrote that continuation of the cohorts will allow study of waning patterns, which could help inform vaccine recommendations.
Among the limitations of the study are that testing methods and the COVID-19 symptoms surveyed varied among the three cohorts, so there may be some differences in defining infection or symptomatic COVID. In addition, the researchers were not able to account for the social vulnerability index and immunocompromised status, which could have affected vaccine uptake and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
This study was supported by the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Coauthor Dr. Caban-Martinez reported grants from the Florida Firefighter Cancer Initiative and the Florida Department of Health. Coauthors Dr. Chu, Dr. Englund, Dr. Martin, and Dr. Monto reported receiving personal fees or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hegmann reported being the editor of the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine practice guidelines. Coauthor Dr. Gaglani reported serving as cochair of the infectious diseases and immunization committee and the respiratory syncytial virus task force lead for the Texas Pediatric Society and the Texas Chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics. No other disclosures were reported.
Children and adolescents ages 5-17 who received a bivalent COVID-19 mRNA vaccine were less likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared with those who were unvaccinated or received only the monovalent COVID-19 vaccine, according to new data published February 6 in JAMA.
“All eligible children and adolescents should remain up to date with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations,” wrote the authors, led by Leora R. Feldstein, PhD, with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in Atlanta.
By the end of 2023, at least 911 youths ages 5-17 had died from COVID-related causes.
Researchers found that compared with participants who did not receive the COVID-19 vaccine or got monovalent-only doses 180 days or more before, the adjusted vaccine effectiveness of a bivalent COVID-19 vaccine dose against SARS-CoV-2 infection was 51.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 23.6%-71.9%) 7-60 days after vaccination. Relative effectiveness was 62.4% (95% CI, 38.5%-81.1%) 61-150 days after vaccination. The researchers said the confidence intervals were wide because of the small sample size.
The information can help inform public health strategies, the authors noted, especially as new variants emerge.
Bivalent Dose Recommended in Fall of 2022
Bivalent mRNA COVID vaccines were recommended in the United States for children and adolescents ages 12 years or older on Sept. 1, 2022, and for children ages 5-11 on Oct. 12, 2022, when Omicron BA.4/5 types were the predominant circulating variant.
The study included 2,959 participants who completed periodic surveys (answering questions on demographics, household details, chronic medical conditions, and COVID-19 symptoms) and submitted weekly self-collected nasal swabs (whether or not they had symptoms). Those in the study submitted additional nasal swabs if they developed any symptoms.
Median adherence to weekly upper respiratory specimen swabbing was high throughout the study period at 93.8%.
Data from Sept. 4, 2022, to Jan. 31, 2023, were combined from three prospective US cohort studies at six sites. In addition to the surveys, researchers used information from state immunization information systems and electronic medical records.
Most of the Infected Were Unvaccinated or Had Monovalent Vax
Of the 426 participants (14.4% of the combined cohorts) infected with SARS-CoV-2, 383 (89.9%) were either unvaccinated or received monovalent vaccine doses only.
Calculations were adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, health conditions, prior SARS-CoV-2 infections, geographic location, proportion of circulating variants by site, and local virus prevalence.
Participants living in Oregon, for example, had the highest uptake of bivalent COVID-19 vaccine (56.2%), whereas those in Texas had the lowest (2.4%). Participants reporting Hispanic ethnicity had lower bivalent uptake (17.1%) compared with non-Hispanic participants of all races (27.1%).
Of the 2,207 participants who did not receive a bivalent dose, 24.2% were unvaccinated and 1,672 (75.8%) received at least 1 monovalent dose.
The researchers said they saw no sign of waning effectiveness 61-150 days (the limit for this analysis) after receipt of the bivalent COVID-19 vaccine.
They wrote that continuation of the cohorts will allow study of waning patterns, which could help inform vaccine recommendations.
Among the limitations of the study are that testing methods and the COVID-19 symptoms surveyed varied among the three cohorts, so there may be some differences in defining infection or symptomatic COVID. In addition, the researchers were not able to account for the social vulnerability index and immunocompromised status, which could have affected vaccine uptake and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
This study was supported by the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Coauthor Dr. Caban-Martinez reported grants from the Florida Firefighter Cancer Initiative and the Florida Department of Health. Coauthors Dr. Chu, Dr. Englund, Dr. Martin, and Dr. Monto reported receiving personal fees or grants from multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Hegmann reported being the editor of the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine practice guidelines. Coauthor Dr. Gaglani reported serving as cochair of the infectious diseases and immunization committee and the respiratory syncytial virus task force lead for the Texas Pediatric Society and the Texas Chapter of the American Academy of Pediatrics. No other disclosures were reported.
FROM JAMA
Five Bold Predictions for Long COVID in 2024
With a number of large-scale clinical trials underway and researchers on the hunt for new therapies, long COVID scientists are hopeful that this is the year patients — and doctors who care for them — will finally see improvements in treating their symptoms.
Here are five bold predictions — all based on encouraging research — that could happen in 2024. At the very least, they are promising signs of progress against a debilitating and frustrating disease.
#1: We’ll gain a better understanding of each long COVID phenotype
This past year, a wide breadth of research began showing that long COVID can be defined by a number of different disease phenotypes that present a range of symptoms.
Researchers identified four clinical phenotypes: Chronic fatigue-like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; respiratory syndrome, which includes cough and difficulty breathing; chronic pain; and neurosensorial syndrome, which causes an altered sense of taste and smell.
Identifying specific diagnostic criteria for each phenotype would lead to better health outcomes for patients instead of treating them as if it were a “one-size-fits-all disease,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at UCLA Health, Los Angeles, California.
Ultimately, she hopes that this year her patients will receive treatments based on the type of long COVID they’re personally experiencing, and the symptoms they have, leading to improved health outcomes and more rapid relief.
“Many new medications are focused on different pathways of long COVID, and the challenge becomes which drug is the right drug for each treatment,” said Dr. Viswanathan.
#2: Monoclonal antibodies may change the game
We’re starting to have a better understanding that what’s been called “viral persistence” as a main cause of long COVID may potentially be treated with monoclonal antibodies. These are antibodies produced by cloning unique white blood cells to target the circulating spike proteins in the blood that hang out in viral reservoirs and cause the immune system to react as if it’s still fighting acute COVID-19.
Smaller-scale studies have already shown promising results. A January 2024 study published in The American Journal of Emergency Medicine followed three patients who completely recovered from long COVID after taking monoclonal antibodies. “Remission occurred despite dissimilar past histories, sex, age, and illness duration,” wrote the study authors.
Larger clinical trials are underway at the University of California, San Francisco, California, to test targeted monoclonal antibodies. If the results of the larger study show that monoclonal antibodies are beneficial, then it could be a game changer for a large swath of patients around the world, said David F. Putrino, PhD, who runs the long COVID clinic at Mount Sinai Health System in New York City.
“The idea is that the downstream damage caused by viral persistence will resolve itself once you wipe out the virus,” said Dr. Putrino.
#3: Paxlovid could prove effective for long COVID
The US Food and Drug Administration granted approval for Paxlovid last May for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults at a high risk for severe disease. The medication is made up of two drugs packaged together. The first, nirmatrelvir, works by blocking a key enzyme required for virus replication. The second, ritonavir, is an antiviral that’s been used in patients with HIV and helps boost levels of antivirals in the body.
In a large-scale trial headed up by Dr. Putrino and his team, the oral antiviral is being studied for use in the post-viral stage in patients who test negative for acute COVID-19 but have persisting symptoms of long COVID.
Similar to monoclonal antibodies, the idea is to quell viral persistence. If patients have long COVID because they can’t clear SAR-CoV-2 from their bodies, Paxlovid could help. But unlike monoclonal antibodies that quash the virus, Paxlovid stops the virus from replicating. It’s a different mechanism with the same end goal.
It’s been a controversial treatment because it’s life-changing for some patients and ineffective for others. In addition, it can cause a range of side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and an impaired sense of taste. The goal of the trial is to see which patients with long COVID are most likely to benefit from the treatment.
#4: Anti-inflammatories like metformin could prove useful
Many of the inflammatory markers persistent in patients with long COVID were similarly present in patients with autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, according to a July 2023 study published in JAMA.
The hope is that anti-inflammatory medications may be used to reduce inflammation causing long COVID symptoms. But drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis like abatacept and infliximabcan also have serious side effects, including increased risk for infection, flu-like symptoms, and burning of the skin.
“Powerful anti-inflammatories can change a number of pathways in the immune system,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads the long COVID RECOVER study at University Hospitals Health System in Cleveland, Ohio. Anti-inflammatories hold promise but, Dr. McComsey said, “some are more toxic with many side effects, so even if they work, there’s still a question about who should take them.”
Still, other anti-inflammatories that could work don’t have as many side effects. For example, a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that the diabetes drug metformin reduced a patient’s risk for long COVID up to 40% when the drug was taken during the acute stage.
Metformin, compared to other anti-inflammatories (also known as immune modulators), is an inexpensive and widely available drug with relatively few side effects compared with other medications.
#5: Serotonin levels — and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — may be keys to unlocking long COVID
One of the most groundbreaking studies of the year came last November. A study published in the journal Cell found lower circulating serotonin levels in patents with long COVID than in those who did not have the condition. The study also found that the SSRI fluoxetine improved cognitive function in rat models infected with the virus.
Researchers found that the reduction in serotonin levels was partially caused by the body’s inability to absorb tryptophan, an amino acid that’s a precursor to serotonin. Overactivated blood platelets may also have played a role.
Michael Peluso, MD, an assistant research professor of infectious medicine at the UCSF School of Medicine, San Francisco, California, hopes to take the finding a step further, investigating whether increased serotonin levels in patients with long COVID will lead to improvements in symptoms.
“What we need now is a good clinical trial to see whether altering levels of serotonin in people with long COVID will lead to symptom relief,” Dr. Peluso said last month in an interview with this news organization.
If patients show an improvement in symptoms, then the next step is looking into whether SSRIs boost serotonin levels in patients and, as a result, reduce their symptoms.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With a number of large-scale clinical trials underway and researchers on the hunt for new therapies, long COVID scientists are hopeful that this is the year patients — and doctors who care for them — will finally see improvements in treating their symptoms.
Here are five bold predictions — all based on encouraging research — that could happen in 2024. At the very least, they are promising signs of progress against a debilitating and frustrating disease.
#1: We’ll gain a better understanding of each long COVID phenotype
This past year, a wide breadth of research began showing that long COVID can be defined by a number of different disease phenotypes that present a range of symptoms.
Researchers identified four clinical phenotypes: Chronic fatigue-like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; respiratory syndrome, which includes cough and difficulty breathing; chronic pain; and neurosensorial syndrome, which causes an altered sense of taste and smell.
Identifying specific diagnostic criteria for each phenotype would lead to better health outcomes for patients instead of treating them as if it were a “one-size-fits-all disease,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at UCLA Health, Los Angeles, California.
Ultimately, she hopes that this year her patients will receive treatments based on the type of long COVID they’re personally experiencing, and the symptoms they have, leading to improved health outcomes and more rapid relief.
“Many new medications are focused on different pathways of long COVID, and the challenge becomes which drug is the right drug for each treatment,” said Dr. Viswanathan.
#2: Monoclonal antibodies may change the game
We’re starting to have a better understanding that what’s been called “viral persistence” as a main cause of long COVID may potentially be treated with monoclonal antibodies. These are antibodies produced by cloning unique white blood cells to target the circulating spike proteins in the blood that hang out in viral reservoirs and cause the immune system to react as if it’s still fighting acute COVID-19.
Smaller-scale studies have already shown promising results. A January 2024 study published in The American Journal of Emergency Medicine followed three patients who completely recovered from long COVID after taking monoclonal antibodies. “Remission occurred despite dissimilar past histories, sex, age, and illness duration,” wrote the study authors.
Larger clinical trials are underway at the University of California, San Francisco, California, to test targeted monoclonal antibodies. If the results of the larger study show that monoclonal antibodies are beneficial, then it could be a game changer for a large swath of patients around the world, said David F. Putrino, PhD, who runs the long COVID clinic at Mount Sinai Health System in New York City.
“The idea is that the downstream damage caused by viral persistence will resolve itself once you wipe out the virus,” said Dr. Putrino.
#3: Paxlovid could prove effective for long COVID
The US Food and Drug Administration granted approval for Paxlovid last May for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults at a high risk for severe disease. The medication is made up of two drugs packaged together. The first, nirmatrelvir, works by blocking a key enzyme required for virus replication. The second, ritonavir, is an antiviral that’s been used in patients with HIV and helps boost levels of antivirals in the body.
In a large-scale trial headed up by Dr. Putrino and his team, the oral antiviral is being studied for use in the post-viral stage in patients who test negative for acute COVID-19 but have persisting symptoms of long COVID.
Similar to monoclonal antibodies, the idea is to quell viral persistence. If patients have long COVID because they can’t clear SAR-CoV-2 from their bodies, Paxlovid could help. But unlike monoclonal antibodies that quash the virus, Paxlovid stops the virus from replicating. It’s a different mechanism with the same end goal.
It’s been a controversial treatment because it’s life-changing for some patients and ineffective for others. In addition, it can cause a range of side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and an impaired sense of taste. The goal of the trial is to see which patients with long COVID are most likely to benefit from the treatment.
#4: Anti-inflammatories like metformin could prove useful
Many of the inflammatory markers persistent in patients with long COVID were similarly present in patients with autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, according to a July 2023 study published in JAMA.
The hope is that anti-inflammatory medications may be used to reduce inflammation causing long COVID symptoms. But drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis like abatacept and infliximabcan also have serious side effects, including increased risk for infection, flu-like symptoms, and burning of the skin.
“Powerful anti-inflammatories can change a number of pathways in the immune system,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads the long COVID RECOVER study at University Hospitals Health System in Cleveland, Ohio. Anti-inflammatories hold promise but, Dr. McComsey said, “some are more toxic with many side effects, so even if they work, there’s still a question about who should take them.”
Still, other anti-inflammatories that could work don’t have as many side effects. For example, a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that the diabetes drug metformin reduced a patient’s risk for long COVID up to 40% when the drug was taken during the acute stage.
Metformin, compared to other anti-inflammatories (also known as immune modulators), is an inexpensive and widely available drug with relatively few side effects compared with other medications.
#5: Serotonin levels — and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — may be keys to unlocking long COVID
One of the most groundbreaking studies of the year came last November. A study published in the journal Cell found lower circulating serotonin levels in patents with long COVID than in those who did not have the condition. The study also found that the SSRI fluoxetine improved cognitive function in rat models infected with the virus.
Researchers found that the reduction in serotonin levels was partially caused by the body’s inability to absorb tryptophan, an amino acid that’s a precursor to serotonin. Overactivated blood platelets may also have played a role.
Michael Peluso, MD, an assistant research professor of infectious medicine at the UCSF School of Medicine, San Francisco, California, hopes to take the finding a step further, investigating whether increased serotonin levels in patients with long COVID will lead to improvements in symptoms.
“What we need now is a good clinical trial to see whether altering levels of serotonin in people with long COVID will lead to symptom relief,” Dr. Peluso said last month in an interview with this news organization.
If patients show an improvement in symptoms, then the next step is looking into whether SSRIs boost serotonin levels in patients and, as a result, reduce their symptoms.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
With a number of large-scale clinical trials underway and researchers on the hunt for new therapies, long COVID scientists are hopeful that this is the year patients — and doctors who care for them — will finally see improvements in treating their symptoms.
Here are five bold predictions — all based on encouraging research — that could happen in 2024. At the very least, they are promising signs of progress against a debilitating and frustrating disease.
#1: We’ll gain a better understanding of each long COVID phenotype
This past year, a wide breadth of research began showing that long COVID can be defined by a number of different disease phenotypes that present a range of symptoms.
Researchers identified four clinical phenotypes: Chronic fatigue-like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; respiratory syndrome, which includes cough and difficulty breathing; chronic pain; and neurosensorial syndrome, which causes an altered sense of taste and smell.
Identifying specific diagnostic criteria for each phenotype would lead to better health outcomes for patients instead of treating them as if it were a “one-size-fits-all disease,” said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at UCLA Health, Los Angeles, California.
Ultimately, she hopes that this year her patients will receive treatments based on the type of long COVID they’re personally experiencing, and the symptoms they have, leading to improved health outcomes and more rapid relief.
“Many new medications are focused on different pathways of long COVID, and the challenge becomes which drug is the right drug for each treatment,” said Dr. Viswanathan.
#2: Monoclonal antibodies may change the game
We’re starting to have a better understanding that what’s been called “viral persistence” as a main cause of long COVID may potentially be treated with monoclonal antibodies. These are antibodies produced by cloning unique white blood cells to target the circulating spike proteins in the blood that hang out in viral reservoirs and cause the immune system to react as if it’s still fighting acute COVID-19.
Smaller-scale studies have already shown promising results. A January 2024 study published in The American Journal of Emergency Medicine followed three patients who completely recovered from long COVID after taking monoclonal antibodies. “Remission occurred despite dissimilar past histories, sex, age, and illness duration,” wrote the study authors.
Larger clinical trials are underway at the University of California, San Francisco, California, to test targeted monoclonal antibodies. If the results of the larger study show that monoclonal antibodies are beneficial, then it could be a game changer for a large swath of patients around the world, said David F. Putrino, PhD, who runs the long COVID clinic at Mount Sinai Health System in New York City.
“The idea is that the downstream damage caused by viral persistence will resolve itself once you wipe out the virus,” said Dr. Putrino.
#3: Paxlovid could prove effective for long COVID
The US Food and Drug Administration granted approval for Paxlovid last May for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults at a high risk for severe disease. The medication is made up of two drugs packaged together. The first, nirmatrelvir, works by blocking a key enzyme required for virus replication. The second, ritonavir, is an antiviral that’s been used in patients with HIV and helps boost levels of antivirals in the body.
In a large-scale trial headed up by Dr. Putrino and his team, the oral antiviral is being studied for use in the post-viral stage in patients who test negative for acute COVID-19 but have persisting symptoms of long COVID.
Similar to monoclonal antibodies, the idea is to quell viral persistence. If patients have long COVID because they can’t clear SAR-CoV-2 from their bodies, Paxlovid could help. But unlike monoclonal antibodies that quash the virus, Paxlovid stops the virus from replicating. It’s a different mechanism with the same end goal.
It’s been a controversial treatment because it’s life-changing for some patients and ineffective for others. In addition, it can cause a range of side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and an impaired sense of taste. The goal of the trial is to see which patients with long COVID are most likely to benefit from the treatment.
#4: Anti-inflammatories like metformin could prove useful
Many of the inflammatory markers persistent in patients with long COVID were similarly present in patients with autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, according to a July 2023 study published in JAMA.
The hope is that anti-inflammatory medications may be used to reduce inflammation causing long COVID symptoms. But drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis like abatacept and infliximabcan also have serious side effects, including increased risk for infection, flu-like symptoms, and burning of the skin.
“Powerful anti-inflammatories can change a number of pathways in the immune system,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads the long COVID RECOVER study at University Hospitals Health System in Cleveland, Ohio. Anti-inflammatories hold promise but, Dr. McComsey said, “some are more toxic with many side effects, so even if they work, there’s still a question about who should take them.”
Still, other anti-inflammatories that could work don’t have as many side effects. For example, a study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that the diabetes drug metformin reduced a patient’s risk for long COVID up to 40% when the drug was taken during the acute stage.
Metformin, compared to other anti-inflammatories (also known as immune modulators), is an inexpensive and widely available drug with relatively few side effects compared with other medications.
#5: Serotonin levels — and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — may be keys to unlocking long COVID
One of the most groundbreaking studies of the year came last November. A study published in the journal Cell found lower circulating serotonin levels in patents with long COVID than in those who did not have the condition. The study also found that the SSRI fluoxetine improved cognitive function in rat models infected with the virus.
Researchers found that the reduction in serotonin levels was partially caused by the body’s inability to absorb tryptophan, an amino acid that’s a precursor to serotonin. Overactivated blood platelets may also have played a role.
Michael Peluso, MD, an assistant research professor of infectious medicine at the UCSF School of Medicine, San Francisco, California, hopes to take the finding a step further, investigating whether increased serotonin levels in patients with long COVID will lead to improvements in symptoms.
“What we need now is a good clinical trial to see whether altering levels of serotonin in people with long COVID will lead to symptom relief,” Dr. Peluso said last month in an interview with this news organization.
If patients show an improvement in symptoms, then the next step is looking into whether SSRIs boost serotonin levels in patients and, as a result, reduce their symptoms.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Coffee, COVID, and the Universal Antimicrobial
A recent article in Cell & Bioscience suggested that regular coffee consumption can reduce the risk of COVID infections.
The study does make some interesting points about the benefits of coffee’s different polyphenols and antioxidants and their effects on different COVID variants. Most of it is based on lab data, although one section, using serum from coffee versus water drinkers, did find that it was more effective at inhibiting the virions. Caffeinated versus decaffeinated didn’t matter.
I’m not saying coffee doesn’t impair the virus. The data are worth looking at. But the majority of adults in North America, Europe, and pretty much the entire planet drink coffee on a regular basis. A large number of them still caught COVID. Would they have had worse cases if they didn’t drink coffee? Maybe, maybe not.
The problem here is that, as always, preliminary data like this get pushed into mass media, making it sound like “COFFEE CURES COVID!!!” Never mind that that’s not what the article said, but it sure gets clicks and retweets and FaceBook “likes.”
Suddenly fringe groups are claiming the coffee cure was there all along, and hidden from them by the evil government-pharma-medical cartel. Others claim the research is flawed because of this or that. The signal gets drowned out by the noise.
Definitely, food can be a medicine. Look at all the benefits proven of the Mediterranean diet. Coffee may help, especially if we can identify and isolate the specific components that reduce COVID risk. But, as they always say at the end, the study is preliminary and further research is needed.
Once or twice a year, an adult with epilepsy comes in, waving a copy of the ketogenic diet around and upset that I never tried it on them — again proof of the evil government-pharma-medical cartel that I’m in league with. I calm them down and explain the diet in detail. Maybe 50% of them decide to go ahead with it. In 25 years of practice, my record for an otherwise normal adult sticking with it is 5 days.
You don’t have to go too far back to remember Linus Pauling, an absolutely brilliant scientist, but not the best of nutritionists. With two Nobel prizes behind him, he took a stab at medicine in the 1970s, arguing that megadoses of vitamin C worked for the common cold. While it may be good for us, and certainly most people like orange juice, but those claims about the common cold never panned out. In fact, we’re no closer to curing it now than we were then.
It might, but this doesn’t mean the “truth” is being maliciously hidden by an evil cartel. It just means we have (as always) more to learn.
I’ll still drink my single cup of coffee every weekday morning. I’m a creature of habit, and heaven knows I need the caffeine. If it also boosts my immune system, so much the better.
Besides, we still have that universal antimicrobial called chicken soup.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A recent article in Cell & Bioscience suggested that regular coffee consumption can reduce the risk of COVID infections.
The study does make some interesting points about the benefits of coffee’s different polyphenols and antioxidants and their effects on different COVID variants. Most of it is based on lab data, although one section, using serum from coffee versus water drinkers, did find that it was more effective at inhibiting the virions. Caffeinated versus decaffeinated didn’t matter.
I’m not saying coffee doesn’t impair the virus. The data are worth looking at. But the majority of adults in North America, Europe, and pretty much the entire planet drink coffee on a regular basis. A large number of them still caught COVID. Would they have had worse cases if they didn’t drink coffee? Maybe, maybe not.
The problem here is that, as always, preliminary data like this get pushed into mass media, making it sound like “COFFEE CURES COVID!!!” Never mind that that’s not what the article said, but it sure gets clicks and retweets and FaceBook “likes.”
Suddenly fringe groups are claiming the coffee cure was there all along, and hidden from them by the evil government-pharma-medical cartel. Others claim the research is flawed because of this or that. The signal gets drowned out by the noise.
Definitely, food can be a medicine. Look at all the benefits proven of the Mediterranean diet. Coffee may help, especially if we can identify and isolate the specific components that reduce COVID risk. But, as they always say at the end, the study is preliminary and further research is needed.
Once or twice a year, an adult with epilepsy comes in, waving a copy of the ketogenic diet around and upset that I never tried it on them — again proof of the evil government-pharma-medical cartel that I’m in league with. I calm them down and explain the diet in detail. Maybe 50% of them decide to go ahead with it. In 25 years of practice, my record for an otherwise normal adult sticking with it is 5 days.
You don’t have to go too far back to remember Linus Pauling, an absolutely brilliant scientist, but not the best of nutritionists. With two Nobel prizes behind him, he took a stab at medicine in the 1970s, arguing that megadoses of vitamin C worked for the common cold. While it may be good for us, and certainly most people like orange juice, but those claims about the common cold never panned out. In fact, we’re no closer to curing it now than we were then.
It might, but this doesn’t mean the “truth” is being maliciously hidden by an evil cartel. It just means we have (as always) more to learn.
I’ll still drink my single cup of coffee every weekday morning. I’m a creature of habit, and heaven knows I need the caffeine. If it also boosts my immune system, so much the better.
Besides, we still have that universal antimicrobial called chicken soup.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A recent article in Cell & Bioscience suggested that regular coffee consumption can reduce the risk of COVID infections.
The study does make some interesting points about the benefits of coffee’s different polyphenols and antioxidants and their effects on different COVID variants. Most of it is based on lab data, although one section, using serum from coffee versus water drinkers, did find that it was more effective at inhibiting the virions. Caffeinated versus decaffeinated didn’t matter.
I’m not saying coffee doesn’t impair the virus. The data are worth looking at. But the majority of adults in North America, Europe, and pretty much the entire planet drink coffee on a regular basis. A large number of them still caught COVID. Would they have had worse cases if they didn’t drink coffee? Maybe, maybe not.
The problem here is that, as always, preliminary data like this get pushed into mass media, making it sound like “COFFEE CURES COVID!!!” Never mind that that’s not what the article said, but it sure gets clicks and retweets and FaceBook “likes.”
Suddenly fringe groups are claiming the coffee cure was there all along, and hidden from them by the evil government-pharma-medical cartel. Others claim the research is flawed because of this or that. The signal gets drowned out by the noise.
Definitely, food can be a medicine. Look at all the benefits proven of the Mediterranean diet. Coffee may help, especially if we can identify and isolate the specific components that reduce COVID risk. But, as they always say at the end, the study is preliminary and further research is needed.
Once or twice a year, an adult with epilepsy comes in, waving a copy of the ketogenic diet around and upset that I never tried it on them — again proof of the evil government-pharma-medical cartel that I’m in league with. I calm them down and explain the diet in detail. Maybe 50% of them decide to go ahead with it. In 25 years of practice, my record for an otherwise normal adult sticking with it is 5 days.
You don’t have to go too far back to remember Linus Pauling, an absolutely brilliant scientist, but not the best of nutritionists. With two Nobel prizes behind him, he took a stab at medicine in the 1970s, arguing that megadoses of vitamin C worked for the common cold. While it may be good for us, and certainly most people like orange juice, but those claims about the common cold never panned out. In fact, we’re no closer to curing it now than we were then.
It might, but this doesn’t mean the “truth” is being maliciously hidden by an evil cartel. It just means we have (as always) more to learn.
I’ll still drink my single cup of coffee every weekday morning. I’m a creature of habit, and heaven knows I need the caffeine. If it also boosts my immune system, so much the better.
Besides, we still have that universal antimicrobial called chicken soup.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Analysis Finds Risk of Alopecia Areata After COVID-19 Infection
“There is a growing number of reports on new onset, exacerbation, and recurrence of AA after COVID-19,” corresponding author Jin Park, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Jeonbuk National University Medical School, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online January 10, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology. “However, evidence supporting an association between COVID-19 and AA is limited.”
To investigate the association between COVID-19 and AA, the researchers used data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency–COVID-19–National Health Insurance Service cohort to conduct a propensity score–matched, nationwide, population-based cohort study from October 8, 2020, to September 30, 2021. They used Cox proportional hazards regression to calculate the incidence, prevalence, and adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for AA.
The cohort consisted of 259,369 patients with COVID-19 and 259,369 uninfected controls. The researchers observed an increased risk of telogen effluvium in patients with COVID-19 compared with the uninfected controls (AHR, 6.40; 95% CI, 4.92-8.33), while the incidence of epidermal cysts, benign skin tumors, and other negative control outcomes did not differ between groups.
Meanwhile, the incidence of AA in patients with COVID-19 was significantly higher compared with the uninfected controls (43.19 per 10,000 person-years [PY]), regardless of clinical subtype. This translated into an AHR of 1.82 (95% CI, 1.60-2.07). In other findings, the incidence of patchy AA and alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis (AT/AU) was 35.94 and 7.24 per 10,000 PY in patients with COVID-19 compared with 19.43 and 4.18 per 10,000 PY in uninfected controls, respectively.
“These findings support the possible role of COVID-19 in AA occurrence and exacerbation, although other environmental factors, such as psychological stress, may have also contributed to AA development during the pandemic,” the authors concluded. “Plausible mechanisms of AA following COVID-19 include antigenic molecular mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 and hair follicle autoantigens, cytokine shifting, and bystander activation.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the potential for detection or misclassification bias and the fact that it did not evaluate causality between the two conditions.
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, said that strengths of the study include the large sample size, and the use of positive and negative outcome controls, and that the incidence and prevalence of AA in Korea was stable during the prepandemic period. “A weakness of the study is that all alopecia areata cases may not have necessarily been confirmed,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization.
“Based on this study, dermatologists may consider AA in the differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with hair loss with recent COVID-19 diagnosis,” she added, noting that the potential for prevention of AA flares is also a reason to recommend COVID-19 vaccination for patients with a history of AA.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to comment on the study, said that while the analysis suggests a definite epidemiologic association between COVID-19 and AA, “any causal relationship needs further study.” She added that she has no specific advice for patients who develop AA following a COVID-19 infection. “Any conversation about AA can be difficult because there is no way to prognosticate if someone will just have one small, localized area of hair loss,” or several small areas, versus loss of all hair on the head or even the body as well, Dr. Ko explained.
The study was supported with grants from the National Research Foundation of the Korean Government and the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. The authors, as well as Dr. Lipner and Dr. Ko, reported having no relevant disclosures.
“There is a growing number of reports on new onset, exacerbation, and recurrence of AA after COVID-19,” corresponding author Jin Park, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Jeonbuk National University Medical School, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online January 10, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology. “However, evidence supporting an association between COVID-19 and AA is limited.”
To investigate the association between COVID-19 and AA, the researchers used data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency–COVID-19–National Health Insurance Service cohort to conduct a propensity score–matched, nationwide, population-based cohort study from October 8, 2020, to September 30, 2021. They used Cox proportional hazards regression to calculate the incidence, prevalence, and adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for AA.
The cohort consisted of 259,369 patients with COVID-19 and 259,369 uninfected controls. The researchers observed an increased risk of telogen effluvium in patients with COVID-19 compared with the uninfected controls (AHR, 6.40; 95% CI, 4.92-8.33), while the incidence of epidermal cysts, benign skin tumors, and other negative control outcomes did not differ between groups.
Meanwhile, the incidence of AA in patients with COVID-19 was significantly higher compared with the uninfected controls (43.19 per 10,000 person-years [PY]), regardless of clinical subtype. This translated into an AHR of 1.82 (95% CI, 1.60-2.07). In other findings, the incidence of patchy AA and alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis (AT/AU) was 35.94 and 7.24 per 10,000 PY in patients with COVID-19 compared with 19.43 and 4.18 per 10,000 PY in uninfected controls, respectively.
“These findings support the possible role of COVID-19 in AA occurrence and exacerbation, although other environmental factors, such as psychological stress, may have also contributed to AA development during the pandemic,” the authors concluded. “Plausible mechanisms of AA following COVID-19 include antigenic molecular mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 and hair follicle autoantigens, cytokine shifting, and bystander activation.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the potential for detection or misclassification bias and the fact that it did not evaluate causality between the two conditions.
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, said that strengths of the study include the large sample size, and the use of positive and negative outcome controls, and that the incidence and prevalence of AA in Korea was stable during the prepandemic period. “A weakness of the study is that all alopecia areata cases may not have necessarily been confirmed,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization.
“Based on this study, dermatologists may consider AA in the differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with hair loss with recent COVID-19 diagnosis,” she added, noting that the potential for prevention of AA flares is also a reason to recommend COVID-19 vaccination for patients with a history of AA.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to comment on the study, said that while the analysis suggests a definite epidemiologic association between COVID-19 and AA, “any causal relationship needs further study.” She added that she has no specific advice for patients who develop AA following a COVID-19 infection. “Any conversation about AA can be difficult because there is no way to prognosticate if someone will just have one small, localized area of hair loss,” or several small areas, versus loss of all hair on the head or even the body as well, Dr. Ko explained.
The study was supported with grants from the National Research Foundation of the Korean Government and the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. The authors, as well as Dr. Lipner and Dr. Ko, reported having no relevant disclosures.
“There is a growing number of reports on new onset, exacerbation, and recurrence of AA after COVID-19,” corresponding author Jin Park, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Jeonbuk National University Medical School, South Korea, and colleagues wrote in a research letter published online January 10, 2024, in JAMA Dermatology. “However, evidence supporting an association between COVID-19 and AA is limited.”
To investigate the association between COVID-19 and AA, the researchers used data from the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency–COVID-19–National Health Insurance Service cohort to conduct a propensity score–matched, nationwide, population-based cohort study from October 8, 2020, to September 30, 2021. They used Cox proportional hazards regression to calculate the incidence, prevalence, and adjusted hazard ratios (AHRs) for AA.
The cohort consisted of 259,369 patients with COVID-19 and 259,369 uninfected controls. The researchers observed an increased risk of telogen effluvium in patients with COVID-19 compared with the uninfected controls (AHR, 6.40; 95% CI, 4.92-8.33), while the incidence of epidermal cysts, benign skin tumors, and other negative control outcomes did not differ between groups.
Meanwhile, the incidence of AA in patients with COVID-19 was significantly higher compared with the uninfected controls (43.19 per 10,000 person-years [PY]), regardless of clinical subtype. This translated into an AHR of 1.82 (95% CI, 1.60-2.07). In other findings, the incidence of patchy AA and alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis (AT/AU) was 35.94 and 7.24 per 10,000 PY in patients with COVID-19 compared with 19.43 and 4.18 per 10,000 PY in uninfected controls, respectively.
“These findings support the possible role of COVID-19 in AA occurrence and exacerbation, although other environmental factors, such as psychological stress, may have also contributed to AA development during the pandemic,” the authors concluded. “Plausible mechanisms of AA following COVID-19 include antigenic molecular mimicry between SARS-CoV-2 and hair follicle autoantigens, cytokine shifting, and bystander activation.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the analysis, including the potential for detection or misclassification bias and the fact that it did not evaluate causality between the two conditions.
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was asked to comment on the study, said that strengths of the study include the large sample size, and the use of positive and negative outcome controls, and that the incidence and prevalence of AA in Korea was stable during the prepandemic period. “A weakness of the study is that all alopecia areata cases may not have necessarily been confirmed,” Dr. Lipner told this news organization.
“Based on this study, dermatologists may consider AA in the differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with hair loss with recent COVID-19 diagnosis,” she added, noting that the potential for prevention of AA flares is also a reason to recommend COVID-19 vaccination for patients with a history of AA.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to comment on the study, said that while the analysis suggests a definite epidemiologic association between COVID-19 and AA, “any causal relationship needs further study.” She added that she has no specific advice for patients who develop AA following a COVID-19 infection. “Any conversation about AA can be difficult because there is no way to prognosticate if someone will just have one small, localized area of hair loss,” or several small areas, versus loss of all hair on the head or even the body as well, Dr. Ko explained.
The study was supported with grants from the National Research Foundation of the Korean Government and the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. The authors, as well as Dr. Lipner and Dr. Ko, reported having no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY

