User login
Pandemic caused treatment delay for half of patients with CTCL, study finds
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Buzzy Lancet long COVID paper under investigation for ‘data errors’
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
Covid vax prevents death in children regardless of variant
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
FROM THE BMJ
What is the genetic influence on the severity of COVID-19?
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
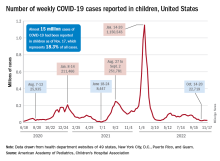
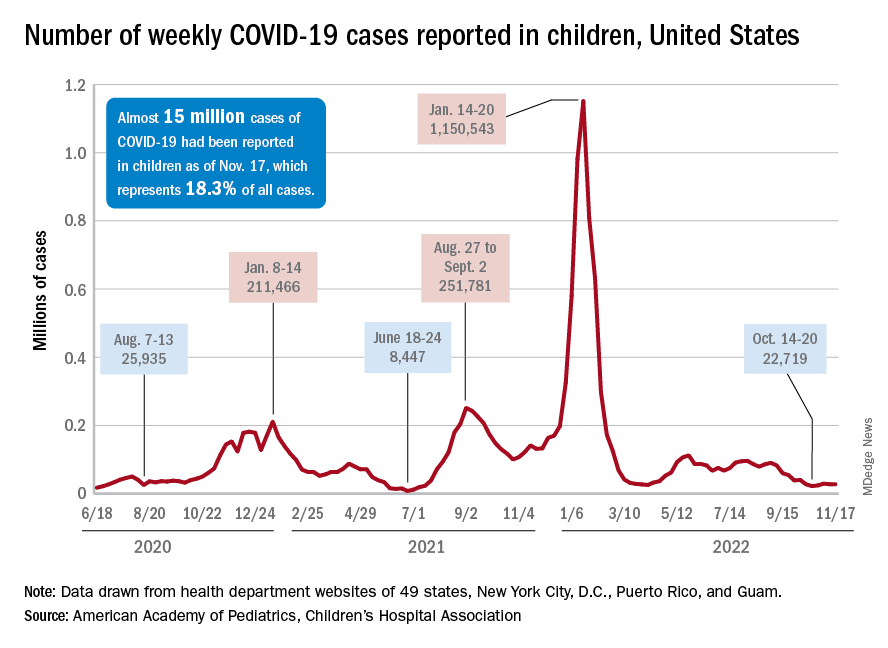
U.S. flu activity already at mid-season levels
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.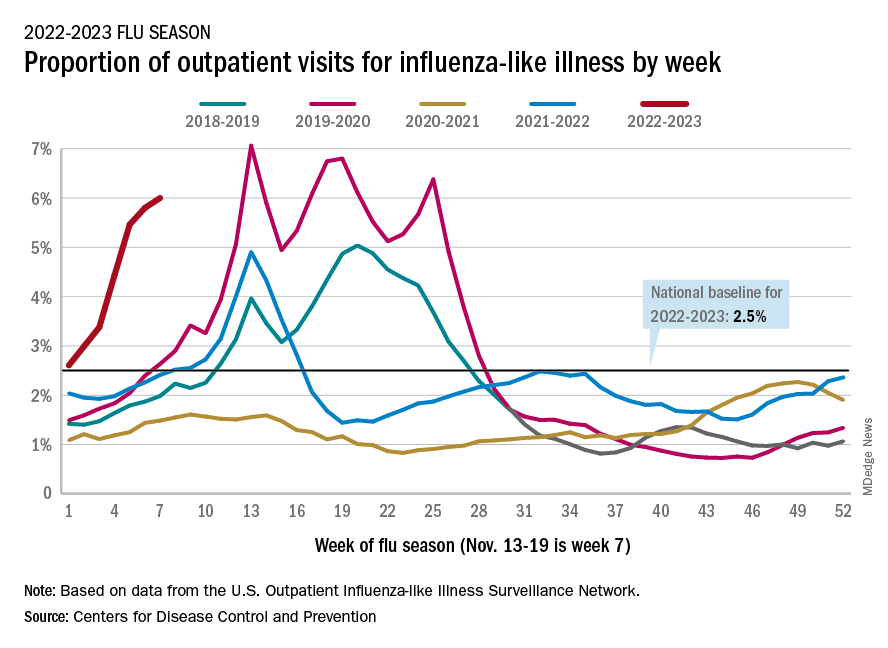
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
More vaccinated people dying of COVID as fewer get booster shots
“We can no longer say this is a pandemic of the unvaccinated,” Kaiser Family Foundation Vice President Cynthia Cox, who conducted the analysis, told The Washington Post.
People who had been vaccinated or boosted made up 58% of COVID-19 deaths in August, the analysis showed. The rate has been on the rise: 23% of coronavirus deaths were among vaccinated people in September 2021, and the vaccinated made up 42% of deaths in January and February 2022, the Post reported.
Research continues to show that people who are vaccinated or boosted have a lower risk of death. The rise in deaths among the vaccinated is the result of three factors, Ms. Cox said.
- A large majority of people in the United States have been vaccinated (267 million people, the said).
- People who are at the greatest risk of dying from COVID-19 are more likely to be vaccinated and boosted, such as the elderly.
- Vaccines lose their effectiveness over time; the virus changes to avoid vaccines; and people need to choose to get boosters to continue to be protected.
The case for the effectiveness of vaccines and boosters versus skipping the shots remains strong. People age 6 months and older who are unvaccinated are six times more likely to die of COVID-19, compared to those who got the primary series of shots, the Post reported. Survival rates were even better with additional booster shots, particularly among older people.
“I feel very confident that if people continue to get vaccinated at good numbers, if people get boosted, we can absolutely have a very safe and healthy holiday season,” Ashish Jha, White House coronavirus czar, said on Nov. 22.
The number of Americans who have gotten the most recent booster has been increasing ahead of the holidays. CDC data show that 12% of the U.S. population age 5 and older has received a booster.
A new study by a team of researchers from Harvard University and Yale University estimates that 94% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19 at least once, leaving just 1 in 20 people who have never had the virus.
“Despite these high exposure numbers, there is still substantial population susceptibility to infection with an Omicron variant,” the authors wrote.
They said that if all states achieved the vaccination levels of Vermont, where 55% of people had at least one booster and 22% got a second one, there would be “an appreciable improvement in population immunity, with greater relative impact for protection against infection versus severe disease. This additional protection results from both the recovery of immunity lost due to waning and the increased effectiveness of the bivalent booster against Omicron infections.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“We can no longer say this is a pandemic of the unvaccinated,” Kaiser Family Foundation Vice President Cynthia Cox, who conducted the analysis, told The Washington Post.
People who had been vaccinated or boosted made up 58% of COVID-19 deaths in August, the analysis showed. The rate has been on the rise: 23% of coronavirus deaths were among vaccinated people in September 2021, and the vaccinated made up 42% of deaths in January and February 2022, the Post reported.
Research continues to show that people who are vaccinated or boosted have a lower risk of death. The rise in deaths among the vaccinated is the result of three factors, Ms. Cox said.
- A large majority of people in the United States have been vaccinated (267 million people, the said).
- People who are at the greatest risk of dying from COVID-19 are more likely to be vaccinated and boosted, such as the elderly.
- Vaccines lose their effectiveness over time; the virus changes to avoid vaccines; and people need to choose to get boosters to continue to be protected.
The case for the effectiveness of vaccines and boosters versus skipping the shots remains strong. People age 6 months and older who are unvaccinated are six times more likely to die of COVID-19, compared to those who got the primary series of shots, the Post reported. Survival rates were even better with additional booster shots, particularly among older people.
“I feel very confident that if people continue to get vaccinated at good numbers, if people get boosted, we can absolutely have a very safe and healthy holiday season,” Ashish Jha, White House coronavirus czar, said on Nov. 22.
The number of Americans who have gotten the most recent booster has been increasing ahead of the holidays. CDC data show that 12% of the U.S. population age 5 and older has received a booster.
A new study by a team of researchers from Harvard University and Yale University estimates that 94% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19 at least once, leaving just 1 in 20 people who have never had the virus.
“Despite these high exposure numbers, there is still substantial population susceptibility to infection with an Omicron variant,” the authors wrote.
They said that if all states achieved the vaccination levels of Vermont, where 55% of people had at least one booster and 22% got a second one, there would be “an appreciable improvement in population immunity, with greater relative impact for protection against infection versus severe disease. This additional protection results from both the recovery of immunity lost due to waning and the increased effectiveness of the bivalent booster against Omicron infections.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“We can no longer say this is a pandemic of the unvaccinated,” Kaiser Family Foundation Vice President Cynthia Cox, who conducted the analysis, told The Washington Post.
People who had been vaccinated or boosted made up 58% of COVID-19 deaths in August, the analysis showed. The rate has been on the rise: 23% of coronavirus deaths were among vaccinated people in September 2021, and the vaccinated made up 42% of deaths in January and February 2022, the Post reported.
Research continues to show that people who are vaccinated or boosted have a lower risk of death. The rise in deaths among the vaccinated is the result of three factors, Ms. Cox said.
- A large majority of people in the United States have been vaccinated (267 million people, the said).
- People who are at the greatest risk of dying from COVID-19 are more likely to be vaccinated and boosted, such as the elderly.
- Vaccines lose their effectiveness over time; the virus changes to avoid vaccines; and people need to choose to get boosters to continue to be protected.
The case for the effectiveness of vaccines and boosters versus skipping the shots remains strong. People age 6 months and older who are unvaccinated are six times more likely to die of COVID-19, compared to those who got the primary series of shots, the Post reported. Survival rates were even better with additional booster shots, particularly among older people.
“I feel very confident that if people continue to get vaccinated at good numbers, if people get boosted, we can absolutely have a very safe and healthy holiday season,” Ashish Jha, White House coronavirus czar, said on Nov. 22.
The number of Americans who have gotten the most recent booster has been increasing ahead of the holidays. CDC data show that 12% of the U.S. population age 5 and older has received a booster.
A new study by a team of researchers from Harvard University and Yale University estimates that 94% of the U.S. population has been infected with COVID-19 at least once, leaving just 1 in 20 people who have never had the virus.
“Despite these high exposure numbers, there is still substantial population susceptibility to infection with an Omicron variant,” the authors wrote.
They said that if all states achieved the vaccination levels of Vermont, where 55% of people had at least one booster and 22% got a second one, there would be “an appreciable improvement in population immunity, with greater relative impact for protection against infection versus severe disease. This additional protection results from both the recovery of immunity lost due to waning and the increased effectiveness of the bivalent booster against Omicron infections.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Without guidelines, docs make their own long-COVID protocols
Treating the condition requires equal combinations of skill, experience, and intuition, and doctors waiting for guidelines have started cobbling together treatment plans designed to ease the worst symptoms.
Their work is urgent. In the United States alone, as many as 29 million people have long COVID, according to estimates from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
“Patients with long COVID have on average at least 14 different symptoms involving nine or more different organ systems, so a holistic approach to treatment is essential,” said Janna Friedly, MD, executive director of the Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic at the University of Washington in Seattle.
For acute COVID cases, the National Institutes of Health has treatment guidelines that are taking a lot of the guesswork out of managing patients’ complex mix of symptoms. This has made it easier for primary care providers to manage people with milder cases and for specialists to come up with effective treatment plans for those with severe illness. But no such guidelines exist for long COVID, and this is making it harder for many doctors – particularly in primary care – to determine the best treatment.
While there isn’t a single treatment that is effective for all long-COVID symptoms – and nothing is approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for this syndrome – doctors do have tools, Dr. Friedly said.
“We always start with the basics – making sure we help patients get enough restorative sleep, optimizing their nutrition, ensuring proper hydration, reducing stress, breathing exercises, and restorative exercise – because all of these are critically important to helping people’s immune system stay as healthy as possible,” she said. “In addition, we help people manage the anxiety and depression that may be exacerbating their symptoms.”
Fatigue is an obvious target. Widely available screening tools, including assessments that have been used in cancer patients and people with chronic fatigue syndrome, can pinpoint how bad symptoms are in long-COVID patients.
“Fatigue is generally the No. 1 symptom,” said Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, chair of rehabilitation medicine and director of the COVID-19 Recovery Clinic at the University of Texas Health Science Center in San Antonio. “If a patient has this, then their therapy program has to look very different, because they actually do better with pacing themselves.”
This was the first symptom tackled in a series of long-COVID treatment guidelines issued by the medical society representing many of the providers on the front lines with these patients every day – the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. These fatigue guidelines stress the importance of rest, energy conservation, and proper hydration.
For patients with only mild fatigue who can still keep up with essential activities like work and school, activity programs may begin with a gradual return to daily routines such as housework or going out with friends. As long as they have no setbacks, patients can also start with light aerobic exercise and make it more intense and frequent over time. As long as they have no setbacks in symptoms, they can ramp up exercise by about 10% every 10 days.
But with severe fatigue, this is too much, too soon. Activity plans are more apt to start with only light stretching and progress to light muscle strengthening before any aerobic exercise enters the picture.
“Traditional exercise programs may be harmful to some patients with long COVID,” said Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Many cannot tolerate graded exercise [where exertion slowly ramps up], and it actually can make them worse.”
There’s less consensus on other options for treating fatigue, like prescription medications, dietary supplements, and acupuncture. Some doctors have tried prescription drugs like the antiviral and movement disorder medication amantadine, the narcolepsy drug modafinil, and the stimulant methylphenidate, which have been studied for managing fatigue in patients with other conditions like cancer, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injuries, and Parkinson’s disease. But there isn’t yet clear evidence from clinical trials about how well these options work for long COVID.
Similarly, interventions to tackle neurological symptoms and cognitive problems borrow a page from treatments used for other conditions like stroke and dementia – but require changes to meet the needs of those with long COVID. Four in five long-COVID patients with neurological and cognitive issues have brain fog, while more than two-thirds have headaches, and more than half have numbness and tingling in their extremities, loss of taste, loss of smell, and muscle pain, one study suggests.
Patients with deficits in areas like memory, attention, executive function, and visual and spatial planning may get speech therapy or occupational therapy, for example – both approaches that are common in people with cognitive decline caused by other medical conditions.
Doctors also promote good sleep practices and treating any mood disorders – both of which can contribute to cognitive problems. But they often have to skip one of the best interventions for improving brain function – exercise – because so many long-COVID patients struggle with fatigue and exertion or have cardiovascular issues that limit their exercise.
The lack of formal guidelines is especially a problem because there aren’t nearly enough specialists to manage the surge of patients who need treatment for issues like fatigue and brain fog. And without guidelines, primary care providers lack a reliable road map to guide referrals that many patients may need.
“Given the complexity of long COVID and the wide range of symptoms and medical issues associated with long COVID, most physicians, regardless of specialty, will need to evaluate and treat long-COVID symptoms,” said Dr. Friedly. “And yet, most do not have the knowledge or experience to effectively manage long-COVID symptoms, so having guidelines that can be updated as more research is conducted is critical.”
One barrier to developing guidelines for long COVID is the lack of research into the biological causes of fatigue and autonomic dysfunction – nervous system damage that can impact critical things like blood pressure, digestion, and body temperature – that affect so many long-COVID patients, said Alba Miranda Azola, MD, codirector of the Post-Acute COVID-19 Team at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Research is also progressing much more slowly for long COVID than it did for those hospitalized with severe acute infections. The logistics of running rigorous studies to prove which treatments work best for specific symptoms – information needed to create definitive treatment guidelines – are much more complicated for people with long COVID who live at home and may be too exhausted or too preoccupied with their daily lives to take part in research.
The vast number of symptoms, surfacing in different ways for each patient, also make it hard to isolate specific ways to manage specific long-COVID symptoms. Even when two patients have fatigue and brain fog, they may still need different treatments based on the complex mix of other symptoms they have.
“All long-COVID patients are not equal, and it is critical that research focuses on establishing specific descriptions of the disease,” Dr. Azola said.
The National Institutes of Health is working on this through its long-COVID Recover Initiative. It’s unclear how long it will take for this research to yield enough definitive information to inform long-COVID treatment guidelines similar to what the agency produced for acute coronavirus infections, and it didn’t respond to questions about the timeline.
But over the next few months, the National Institutes of Health expects to begin several clinical trials focused on some of the symptoms that doctors are seeing most often in their clinics, like fatigue, brain fog, exercise intolerance, sleep disturbances, and changes in the nervous system’s ability to regulate key functions like heart rate and body temperature.
One trial starting in January will examine whether the COVID-19 drug Paxlovid can help. A recent preprint Department of Veterans Affairs study showed patients treated with Paxlovid were less likely to get long COVID in the first place.
Some professionals aren’t waiting for the agency. The LongCovid Research Consortium links researchers from Harvard and Stanford universities; the University of California, San Francisco; the J. Craig Venter Institute; Johns Hopkins University; the University of Pennsylvania; Mount Sinai; Cardiff; and Yale who are studying, for instance, whether tiny blood clots contribute to long COVID and whether drugs can reduce or eliminate them.
“Given the widespread and diverse impact the virus has on the human body, it is unlikely that there will be one cure, one treatment,” said Gary H. Gibbons, MD, director of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health. “This is why there will be multiple clinical trials over the coming months that study a range of symptoms, underlying causes, risk factors, outcomes, and potential strategies for treatment and prevention, in people of all races, ethnicities, genders, and ages.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Treating the condition requires equal combinations of skill, experience, and intuition, and doctors waiting for guidelines have started cobbling together treatment plans designed to ease the worst symptoms.
Their work is urgent. In the United States alone, as many as 29 million people have long COVID, according to estimates from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
“Patients with long COVID have on average at least 14 different symptoms involving nine or more different organ systems, so a holistic approach to treatment is essential,” said Janna Friedly, MD, executive director of the Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic at the University of Washington in Seattle.
For acute COVID cases, the National Institutes of Health has treatment guidelines that are taking a lot of the guesswork out of managing patients’ complex mix of symptoms. This has made it easier for primary care providers to manage people with milder cases and for specialists to come up with effective treatment plans for those with severe illness. But no such guidelines exist for long COVID, and this is making it harder for many doctors – particularly in primary care – to determine the best treatment.
While there isn’t a single treatment that is effective for all long-COVID symptoms – and nothing is approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for this syndrome – doctors do have tools, Dr. Friedly said.
“We always start with the basics – making sure we help patients get enough restorative sleep, optimizing their nutrition, ensuring proper hydration, reducing stress, breathing exercises, and restorative exercise – because all of these are critically important to helping people’s immune system stay as healthy as possible,” she said. “In addition, we help people manage the anxiety and depression that may be exacerbating their symptoms.”
Fatigue is an obvious target. Widely available screening tools, including assessments that have been used in cancer patients and people with chronic fatigue syndrome, can pinpoint how bad symptoms are in long-COVID patients.
“Fatigue is generally the No. 1 symptom,” said Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, chair of rehabilitation medicine and director of the COVID-19 Recovery Clinic at the University of Texas Health Science Center in San Antonio. “If a patient has this, then their therapy program has to look very different, because they actually do better with pacing themselves.”
This was the first symptom tackled in a series of long-COVID treatment guidelines issued by the medical society representing many of the providers on the front lines with these patients every day – the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. These fatigue guidelines stress the importance of rest, energy conservation, and proper hydration.
For patients with only mild fatigue who can still keep up with essential activities like work and school, activity programs may begin with a gradual return to daily routines such as housework or going out with friends. As long as they have no setbacks, patients can also start with light aerobic exercise and make it more intense and frequent over time. As long as they have no setbacks in symptoms, they can ramp up exercise by about 10% every 10 days.
But with severe fatigue, this is too much, too soon. Activity plans are more apt to start with only light stretching and progress to light muscle strengthening before any aerobic exercise enters the picture.
“Traditional exercise programs may be harmful to some patients with long COVID,” said Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Many cannot tolerate graded exercise [where exertion slowly ramps up], and it actually can make them worse.”
There’s less consensus on other options for treating fatigue, like prescription medications, dietary supplements, and acupuncture. Some doctors have tried prescription drugs like the antiviral and movement disorder medication amantadine, the narcolepsy drug modafinil, and the stimulant methylphenidate, which have been studied for managing fatigue in patients with other conditions like cancer, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injuries, and Parkinson’s disease. But there isn’t yet clear evidence from clinical trials about how well these options work for long COVID.
Similarly, interventions to tackle neurological symptoms and cognitive problems borrow a page from treatments used for other conditions like stroke and dementia – but require changes to meet the needs of those with long COVID. Four in five long-COVID patients with neurological and cognitive issues have brain fog, while more than two-thirds have headaches, and more than half have numbness and tingling in their extremities, loss of taste, loss of smell, and muscle pain, one study suggests.
Patients with deficits in areas like memory, attention, executive function, and visual and spatial planning may get speech therapy or occupational therapy, for example – both approaches that are common in people with cognitive decline caused by other medical conditions.
Doctors also promote good sleep practices and treating any mood disorders – both of which can contribute to cognitive problems. But they often have to skip one of the best interventions for improving brain function – exercise – because so many long-COVID patients struggle with fatigue and exertion or have cardiovascular issues that limit their exercise.
The lack of formal guidelines is especially a problem because there aren’t nearly enough specialists to manage the surge of patients who need treatment for issues like fatigue and brain fog. And without guidelines, primary care providers lack a reliable road map to guide referrals that many patients may need.
“Given the complexity of long COVID and the wide range of symptoms and medical issues associated with long COVID, most physicians, regardless of specialty, will need to evaluate and treat long-COVID symptoms,” said Dr. Friedly. “And yet, most do not have the knowledge or experience to effectively manage long-COVID symptoms, so having guidelines that can be updated as more research is conducted is critical.”
One barrier to developing guidelines for long COVID is the lack of research into the biological causes of fatigue and autonomic dysfunction – nervous system damage that can impact critical things like blood pressure, digestion, and body temperature – that affect so many long-COVID patients, said Alba Miranda Azola, MD, codirector of the Post-Acute COVID-19 Team at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Research is also progressing much more slowly for long COVID than it did for those hospitalized with severe acute infections. The logistics of running rigorous studies to prove which treatments work best for specific symptoms – information needed to create definitive treatment guidelines – are much more complicated for people with long COVID who live at home and may be too exhausted or too preoccupied with their daily lives to take part in research.
The vast number of symptoms, surfacing in different ways for each patient, also make it hard to isolate specific ways to manage specific long-COVID symptoms. Even when two patients have fatigue and brain fog, they may still need different treatments based on the complex mix of other symptoms they have.
“All long-COVID patients are not equal, and it is critical that research focuses on establishing specific descriptions of the disease,” Dr. Azola said.
The National Institutes of Health is working on this through its long-COVID Recover Initiative. It’s unclear how long it will take for this research to yield enough definitive information to inform long-COVID treatment guidelines similar to what the agency produced for acute coronavirus infections, and it didn’t respond to questions about the timeline.
But over the next few months, the National Institutes of Health expects to begin several clinical trials focused on some of the symptoms that doctors are seeing most often in their clinics, like fatigue, brain fog, exercise intolerance, sleep disturbances, and changes in the nervous system’s ability to regulate key functions like heart rate and body temperature.
One trial starting in January will examine whether the COVID-19 drug Paxlovid can help. A recent preprint Department of Veterans Affairs study showed patients treated with Paxlovid were less likely to get long COVID in the first place.
Some professionals aren’t waiting for the agency. The LongCovid Research Consortium links researchers from Harvard and Stanford universities; the University of California, San Francisco; the J. Craig Venter Institute; Johns Hopkins University; the University of Pennsylvania; Mount Sinai; Cardiff; and Yale who are studying, for instance, whether tiny blood clots contribute to long COVID and whether drugs can reduce or eliminate them.
“Given the widespread and diverse impact the virus has on the human body, it is unlikely that there will be one cure, one treatment,” said Gary H. Gibbons, MD, director of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health. “This is why there will be multiple clinical trials over the coming months that study a range of symptoms, underlying causes, risk factors, outcomes, and potential strategies for treatment and prevention, in people of all races, ethnicities, genders, and ages.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Treating the condition requires equal combinations of skill, experience, and intuition, and doctors waiting for guidelines have started cobbling together treatment plans designed to ease the worst symptoms.
Their work is urgent. In the United States alone, as many as 29 million people have long COVID, according to estimates from the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
“Patients with long COVID have on average at least 14 different symptoms involving nine or more different organ systems, so a holistic approach to treatment is essential,” said Janna Friedly, MD, executive director of the Post-COVID Rehabilitation and Recovery Clinic at the University of Washington in Seattle.
For acute COVID cases, the National Institutes of Health has treatment guidelines that are taking a lot of the guesswork out of managing patients’ complex mix of symptoms. This has made it easier for primary care providers to manage people with milder cases and for specialists to come up with effective treatment plans for those with severe illness. But no such guidelines exist for long COVID, and this is making it harder for many doctors – particularly in primary care – to determine the best treatment.
While there isn’t a single treatment that is effective for all long-COVID symptoms – and nothing is approved by the Food and Drug Administration specifically for this syndrome – doctors do have tools, Dr. Friedly said.
“We always start with the basics – making sure we help patients get enough restorative sleep, optimizing their nutrition, ensuring proper hydration, reducing stress, breathing exercises, and restorative exercise – because all of these are critically important to helping people’s immune system stay as healthy as possible,” she said. “In addition, we help people manage the anxiety and depression that may be exacerbating their symptoms.”
Fatigue is an obvious target. Widely available screening tools, including assessments that have been used in cancer patients and people with chronic fatigue syndrome, can pinpoint how bad symptoms are in long-COVID patients.
“Fatigue is generally the No. 1 symptom,” said Monica Verduzco-Gutierrez, MD, chair of rehabilitation medicine and director of the COVID-19 Recovery Clinic at the University of Texas Health Science Center in San Antonio. “If a patient has this, then their therapy program has to look very different, because they actually do better with pacing themselves.”
This was the first symptom tackled in a series of long-COVID treatment guidelines issued by the medical society representing many of the providers on the front lines with these patients every day – the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. These fatigue guidelines stress the importance of rest, energy conservation, and proper hydration.
For patients with only mild fatigue who can still keep up with essential activities like work and school, activity programs may begin with a gradual return to daily routines such as housework or going out with friends. As long as they have no setbacks, patients can also start with light aerobic exercise and make it more intense and frequent over time. As long as they have no setbacks in symptoms, they can ramp up exercise by about 10% every 10 days.
But with severe fatigue, this is too much, too soon. Activity plans are more apt to start with only light stretching and progress to light muscle strengthening before any aerobic exercise enters the picture.
“Traditional exercise programs may be harmful to some patients with long COVID,” said Dr. Verduzco-Gutierrez. “Many cannot tolerate graded exercise [where exertion slowly ramps up], and it actually can make them worse.”
There’s less consensus on other options for treating fatigue, like prescription medications, dietary supplements, and acupuncture. Some doctors have tried prescription drugs like the antiviral and movement disorder medication amantadine, the narcolepsy drug modafinil, and the stimulant methylphenidate, which have been studied for managing fatigue in patients with other conditions like cancer, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injuries, and Parkinson’s disease. But there isn’t yet clear evidence from clinical trials about how well these options work for long COVID.
Similarly, interventions to tackle neurological symptoms and cognitive problems borrow a page from treatments used for other conditions like stroke and dementia – but require changes to meet the needs of those with long COVID. Four in five long-COVID patients with neurological and cognitive issues have brain fog, while more than two-thirds have headaches, and more than half have numbness and tingling in their extremities, loss of taste, loss of smell, and muscle pain, one study suggests.
Patients with deficits in areas like memory, attention, executive function, and visual and spatial planning may get speech therapy or occupational therapy, for example – both approaches that are common in people with cognitive decline caused by other medical conditions.
Doctors also promote good sleep practices and treating any mood disorders – both of which can contribute to cognitive problems. But they often have to skip one of the best interventions for improving brain function – exercise – because so many long-COVID patients struggle with fatigue and exertion or have cardiovascular issues that limit their exercise.
The lack of formal guidelines is especially a problem because there aren’t nearly enough specialists to manage the surge of patients who need treatment for issues like fatigue and brain fog. And without guidelines, primary care providers lack a reliable road map to guide referrals that many patients may need.
“Given the complexity of long COVID and the wide range of symptoms and medical issues associated with long COVID, most physicians, regardless of specialty, will need to evaluate and treat long-COVID symptoms,” said Dr. Friedly. “And yet, most do not have the knowledge or experience to effectively manage long-COVID symptoms, so having guidelines that can be updated as more research is conducted is critical.”
One barrier to developing guidelines for long COVID is the lack of research into the biological causes of fatigue and autonomic dysfunction – nervous system damage that can impact critical things like blood pressure, digestion, and body temperature – that affect so many long-COVID patients, said Alba Miranda Azola, MD, codirector of the Post-Acute COVID-19 Team at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
Research is also progressing much more slowly for long COVID than it did for those hospitalized with severe acute infections. The logistics of running rigorous studies to prove which treatments work best for specific symptoms – information needed to create definitive treatment guidelines – are much more complicated for people with long COVID who live at home and may be too exhausted or too preoccupied with their daily lives to take part in research.
The vast number of symptoms, surfacing in different ways for each patient, also make it hard to isolate specific ways to manage specific long-COVID symptoms. Even when two patients have fatigue and brain fog, they may still need different treatments based on the complex mix of other symptoms they have.
“All long-COVID patients are not equal, and it is critical that research focuses on establishing specific descriptions of the disease,” Dr. Azola said.
The National Institutes of Health is working on this through its long-COVID Recover Initiative. It’s unclear how long it will take for this research to yield enough definitive information to inform long-COVID treatment guidelines similar to what the agency produced for acute coronavirus infections, and it didn’t respond to questions about the timeline.
But over the next few months, the National Institutes of Health expects to begin several clinical trials focused on some of the symptoms that doctors are seeing most often in their clinics, like fatigue, brain fog, exercise intolerance, sleep disturbances, and changes in the nervous system’s ability to regulate key functions like heart rate and body temperature.
One trial starting in January will examine whether the COVID-19 drug Paxlovid can help. A recent preprint Department of Veterans Affairs study showed patients treated with Paxlovid were less likely to get long COVID in the first place.
Some professionals aren’t waiting for the agency. The LongCovid Research Consortium links researchers from Harvard and Stanford universities; the University of California, San Francisco; the J. Craig Venter Institute; Johns Hopkins University; the University of Pennsylvania; Mount Sinai; Cardiff; and Yale who are studying, for instance, whether tiny blood clots contribute to long COVID and whether drugs can reduce or eliminate them.
“Given the widespread and diverse impact the virus has on the human body, it is unlikely that there will be one cure, one treatment,” said Gary H. Gibbons, MD, director of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health. “This is why there will be multiple clinical trials over the coming months that study a range of symptoms, underlying causes, risk factors, outcomes, and potential strategies for treatment and prevention, in people of all races, ethnicities, genders, and ages.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The right indoor relative humidity could ward off COVID
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY INTERFACE
Meet the JCOM Author with Dr. Barkoudah: Neurosurgery Operating Room Efficiency During the COVID-19 Era
Children and COVID: Weekly cases maintain a low-level plateau
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
A less-than-1% decrease in weekly COVID-19 cases in children demonstrated continued stability in the pandemic situation as the nation heads into the holiday season.
the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in the latest edition of their joint COVID report.
New cases for the week of Nov. 11-17 totaled 27,899, down by 0.9% from the previous week and just 4 weeks removed from the lowest total of the year: 22,719 for Oct. 14-20. There have been just under 15 million cases of COVID-19 in children since the pandemic began, and children represent 18.3% of cases in all ages, the AAP and CHA reported.
Conditions look favorable for that plateau to continue, despite the upcoming holidays, White House COVID-19 coordinator Ashish Jha said recently. “We are in a very different place and we will remain in a different place,” Dr. Jha said, according to STAT News. “We are now at a point where I believe if you’re up to date on your vaccines, you have access to treatments ... there really should be no restrictions on people’s activities.”
One possible spoiler, an apparent spike in COVID-related hospitalizations in children we reported last week, seems to have been a false alarm. The rate of new admissions for Nov. 11, which preliminary data suggested was 0.48 per 100,000 population, has now been revised with more solid data to 0.20 per 100,000, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“We continue to monitor the recent increases in admissions among children. Some of these may be admissions with COVID-19, not because of COVID-19. Co-infections are being noted in our surveillance systems for hospitalizations among children; as much as 10% of admissions or higher have viruses codetected (RSV, influenza, enterovirus/rhinovirus, and other respiratory viruses),” a CDC spokesperson told this news organization.
For children aged 0-17 years, the current 7-day (Nov. 13-19) average number of new admissions with confirmed COVID is 129 per day, down from 147 for the previous 7-day average. Emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, are largely holding steady. The latest 7-day averages available (Nov. 18) – 1.0% for children aged 0-11 years, 0.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds, and 0.8% in 16- to 17-year-olds – are the same or within a tenth of a percent of the rates recorded on Oct. 18, CDC data show.
New vaccinations for the week of Nov. 10-16 were down just slightly for children under age 5 years and for those aged 5-11 years, with a larger drop seen among 12- to 17-year-olds, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report. So far, 7.9% of all children under age 5 have received at least one dose of COVID vaccine, as have 39.1% of 5 to 11-year-olds and 71.5% of those aged 12-17years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.