User login
COVID dramatically increases death risk during pregnancy: Study
Women infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy are seven times more likely to die during childbirth or during the pregnancy than uninfected pregnant women, a new study shows. The new report also warns of many other severe complications linked with the virus during pregnancy, as well as risks to the baby after birth.
But the researchers said they did not find that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy impacted the risk of stillbirth or a baby’s growth rate during pregnancy.
The study, which was a meta-analysis of previous research, was published Jan. 16 in the journal BMJ Global Health. Data from 12 studies from 12 countries were combined so researchers could analyze outcomes for 13,136 pregnant women.
Babies born to mothers who were infected with COVID during pregnancy had almost double the risk of needing stays in the neonatal intensive care unit and also were more likely to be born preterm, compared with babies who were born to pregnant women who didn’t get COVID.
The researchers also found that pregnant women who got COVID were more likely to be admitted to intensive care units, need a ventilator to help them survive, develop dangerous blood clots, or develop preeclampsia, which is a high blood pressure disorder that can be fatal for the mother or baby.
One of the strengths of the study was that it included women in different trimesters during pregnancy.
“That’s something new here too is that COVID at any time during pregnancy did bring this extra risk onto mom and babies,” said lead author Emily R. Smith, ScD, MPH, assistant professor of global health at the George Washington University, in a video statement.
The report is prompting calls for improved efforts to convince pregnant women to get vaccinated for COVID-19. The rate among them remains low: About 1 in 5 pregnant women had received the most updated COVID-19 booster as of Jan. 7, according to the CDC.
“The implications here are that it’s really important that if you’re pregnant or if you’re thinking about becoming pregnant, to get vaccinated,” Dr. Smith said. “This can really reduce the risk of having some of these bad outcomes for mom or for baby.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Women infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy are seven times more likely to die during childbirth or during the pregnancy than uninfected pregnant women, a new study shows. The new report also warns of many other severe complications linked with the virus during pregnancy, as well as risks to the baby after birth.
But the researchers said they did not find that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy impacted the risk of stillbirth or a baby’s growth rate during pregnancy.
The study, which was a meta-analysis of previous research, was published Jan. 16 in the journal BMJ Global Health. Data from 12 studies from 12 countries were combined so researchers could analyze outcomes for 13,136 pregnant women.
Babies born to mothers who were infected with COVID during pregnancy had almost double the risk of needing stays in the neonatal intensive care unit and also were more likely to be born preterm, compared with babies who were born to pregnant women who didn’t get COVID.
The researchers also found that pregnant women who got COVID were more likely to be admitted to intensive care units, need a ventilator to help them survive, develop dangerous blood clots, or develop preeclampsia, which is a high blood pressure disorder that can be fatal for the mother or baby.
One of the strengths of the study was that it included women in different trimesters during pregnancy.
“That’s something new here too is that COVID at any time during pregnancy did bring this extra risk onto mom and babies,” said lead author Emily R. Smith, ScD, MPH, assistant professor of global health at the George Washington University, in a video statement.
The report is prompting calls for improved efforts to convince pregnant women to get vaccinated for COVID-19. The rate among them remains low: About 1 in 5 pregnant women had received the most updated COVID-19 booster as of Jan. 7, according to the CDC.
“The implications here are that it’s really important that if you’re pregnant or if you’re thinking about becoming pregnant, to get vaccinated,” Dr. Smith said. “This can really reduce the risk of having some of these bad outcomes for mom or for baby.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Women infected with COVID-19 during pregnancy are seven times more likely to die during childbirth or during the pregnancy than uninfected pregnant women, a new study shows. The new report also warns of many other severe complications linked with the virus during pregnancy, as well as risks to the baby after birth.
But the researchers said they did not find that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy impacted the risk of stillbirth or a baby’s growth rate during pregnancy.
The study, which was a meta-analysis of previous research, was published Jan. 16 in the journal BMJ Global Health. Data from 12 studies from 12 countries were combined so researchers could analyze outcomes for 13,136 pregnant women.
Babies born to mothers who were infected with COVID during pregnancy had almost double the risk of needing stays in the neonatal intensive care unit and also were more likely to be born preterm, compared with babies who were born to pregnant women who didn’t get COVID.
The researchers also found that pregnant women who got COVID were more likely to be admitted to intensive care units, need a ventilator to help them survive, develop dangerous blood clots, or develop preeclampsia, which is a high blood pressure disorder that can be fatal for the mother or baby.
One of the strengths of the study was that it included women in different trimesters during pregnancy.
“That’s something new here too is that COVID at any time during pregnancy did bring this extra risk onto mom and babies,” said lead author Emily R. Smith, ScD, MPH, assistant professor of global health at the George Washington University, in a video statement.
The report is prompting calls for improved efforts to convince pregnant women to get vaccinated for COVID-19. The rate among them remains low: About 1 in 5 pregnant women had received the most updated COVID-19 booster as of Jan. 7, according to the CDC.
“The implications here are that it’s really important that if you’re pregnant or if you’re thinking about becoming pregnant, to get vaccinated,” Dr. Smith said. “This can really reduce the risk of having some of these bad outcomes for mom or for baby.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Phil Robinson: Rheumatologist, colleague, huntsman spider rescuer
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helen Tanner remembers stealing glimpses of her husband, Philip (“Phil”) Robinson, MBChB, PhD, associate professor at the University of Queensland (Australia), catching and rehoming huge Huntsman spiders. Robinson made the extra effort because he didn’t want to hurt them; he wasn’t a big fan of the large spider with a potential leg span of 6 inches that’s commonly found in Australia, per the Australian Museum.
Robinson also relished taking his children, Eddie, 4, and Tommy, 7, on roller coaster rides, which they enjoyed, despite the experience typically giving him motion sickness, Tanner said.
“He would do anything to make the children happy,” she said. “His children meant the world to him.”
Robinson died Jan. 3 as a result of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma, according to his wife, who added that it was a short, 2-week-long illness.
A leader of global effort to understand COVID-19 and rheumatic disease
Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, described Robinson as “one of the hardest-working people I have ever known. ... [still] his deep love and dedication for his family and kids was always present.”
Robinson would wake up early, even on weekends, to lead international calls across multiple time zones, Yazdany said. “He was driven by a deep curiosity and an intense desire to generate scholarship that would help people with rheumatic diseases.”
Yazdany added that Robinson had a full research portfolio in gout and spondyloarthritis and a busy clinical practice.
She often caught glimpses of Robinson’s young children during Zoom calls. “He was also a talented baker and loved to bake with his kids, often posting pictures of his creations on social media,” Yazdany said.
A mutual colleague compiled some of Robinson’s baking successes. That includes “ ‘probably about to be locked down’ cookies” on July 17, 2021, and “Queensland lockdown cookies!!!” on July 2, 2021. Reuters reported on July 21, 2021, that Australia was witnessing an alarming increase in COVID-19 cases.
Robinson also worked his social media skills to rally support for the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, according to an article published by his colleagues in The Rheumatologist. Yazdany collaborated with him in this effort.
Launched on March 12, 2020, the Global Rheumatology Alliance’s mission is to “collect, analyze, and disseminate information about COVID-19 and rheumatology to patients, physicians, and other relevant groups to improve the care of patients with rheumatic disease.” Robinson served as chair of governance and policy for the collaborative effort.
Inspired by a conversation on Twitter by Leonard Calabrese, DO, a rheumatologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, about an outcomes registry created by gastroenterologists specific to patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Robinson launched a discussion about a similar effort for rheumatology on Twitter, they write.
Along with colleagues and within a single Zoom conference call, Yazdany and Robinson had a plan to organize the registry, Robinson’s colleagues write.
Two projects of the Global Rheumatology Alliance are a health care provider–entered registry for providers to enter data about rheumatology patients with COVID-19 infections, and their COVID-19 Vax Survey, which is available in 12 languages, including English.
Yazdany had never met Robinson before she started working with him on the Global Rheumatology Alliance. They started chatting on Twitter, then moved to Zoom conference calls, and subsequently had weeks when they talked by phone and “emailed constantly,” she said.
“As I reflect on our initial interactions, I am struck by how brilliantly we got along and trusted each other,” Yazdany told this news organization. “We both liked to think big, believed in inclusive collaborations, and were committed to helping people with rheumatic diseases during a scary and uncertain time.”
Still, Yazdany noted that she and Phil brought different strengths to their collaborations. She brought her skills related to the technical aspects of research databases, while “Phil worked his magic in mobilizing friends and colleagues from all over the world,” she said. “He served as a wonderful leader, one whom people believed in and would follow.”
The two colleagues, who spent much of their collaborations over Zoom calls, email, and Slack, while living more than 7,000 miles apart, finally met in person at ACR Convergence 2022, which took place in Philadelphia that year. “It felt like the best kind of reunion with a dear friend,” Yazdany remembered.
A mentor who created a platform for ‘good people to do great things’
David Liew, MBBS, PhD, consultant rheumatologist and clinical pharmacologist at Austin Health in Melbourne, marveled at Robinson’s ability to “distill things simply and cleanly, with clarity but without losing detail.” Liew, who collaborated with Robinson throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, likens the experience to “jamming with [jazz musician John] Coltrane.”
“What I think was particularly remarkable was the capacity to not only have those thoughts himself, but to facilitate others to have that springboard,” said Liew, who added that Robinson “took enormous pleasure in facilitating others’ success.”
“I think the greatest joy he drew out of the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance, apart from facing up to the challenge that needed to be faced, was creating a platform for good people to do great things,” said Liew, who recalled one situation where Robinson gently challenged him. Looking back now, Liew can “now see he very clearly was laying me up, giving me the best chance to shine.”
He describes Robinson as “a deep soul who loved his wife and two sons enormously” and “a whiskey aficionado.” “[Whiskey] suited his contemplative style,” Liew recalled. “Some of my fondest conversations with him were over a whiskey, either in person or virtually, pondering the ‘big issues.’”
A ‘friend and a colleague and so much more’
Claire Barrett, MBBS, president of the Australian Rheumatology Association, described Robinson as a “friend and a colleague and so much more. ... [He was] someone who I worked, laughed, ate, drank, danced, and had fun with,” she told this news organization. They served together as volunteers for the Australian Rheumatology Association and its Queensland branch, as well as Arthritis Queensland; they were also colleagues at Metro North Hospital and Health Service in Brisbane, Queensland.
Robinson was her “go to” for insightful comment on a variety of topics, she said. That could be advice on managing a patient with difficult gout, challenging spondyloarthritis, or the best treatment for a patient with COVID-19.
“[Phil] was a friend I could ask about anything, knowing I would not be judged,” Barrett said. “His kids and our grandkids are similar ages, so we would swap stories and photos and laugh about how cute/funny/cuddly/busy/etc. they were. My heart is broken he won’t get the chance to enjoy their future and the excitement of having Phil continuing to be such an active dad.”
Tanner, Robinson’s wife, said, “he loved everything.” That included the academic side of medicine, and working out what was wrong with his patients and helping them get better. “He was dedicated to this,” she added.
“He also loved the camaraderie of the job – all the people he met and interacted with. [Phil] loved sharing his ideas for research and also discussing complex patients with colleagues. He was driven by finding the answers to problems and doing this as part of a team of researchers/clinicians. He wasn’t interested in personal success.”
Robinson received his medical degree from Otago Medical School in Dunedin, New Zealand, according to the University of Queensland. His specialty training in general and acute care medicine and rheumatology was completed in Wellington, New Zealand, and Dunedin. Robinson also achieved a PhD in human genetics at the University of Queensland Diamantina Institute and had a postdoctoral fellowship at the Queensland Brain Institute at the University of Queensland.
Before his death, he worked at the Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital in Herston, Queensland, and at St. Andrew’s War Memorial Hospital in Spring Hill in Brisbane.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it time for yet another COVID booster? It’s complicated
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Possible bivalent vaccine link to strokes in people over 65
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: ED visits and hospitalizations start to fall again
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.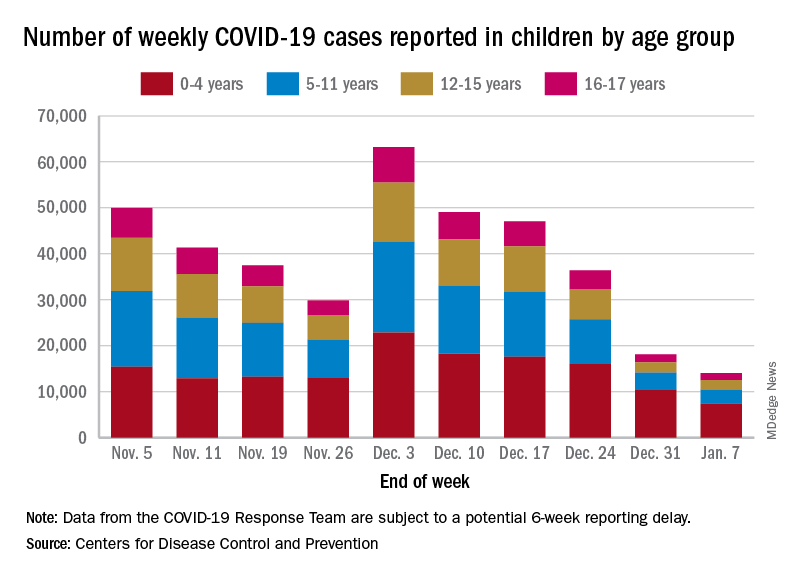
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Cardiac Adverse Events Following COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Prior Vaccine-Associated Myocarditis
Vaccinations have substantially reduced morbidity and mortality from many infectious diseases. Despite the clear value of vaccinations in public health, efforts to better understand adverse events (AEs) following immunization are important to sustain public trust and vaccine confidence. Noninfectious inflammation of the heart may manifest as myocarditis or pericarditis, or occasionally, with shared signs and symptoms of each, as myopericarditis. This is a rare AE following some immunizations. Vaccine-associated myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis (VAMP) has been most clearly associated with smallpox vaccines and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.1-6 Although extremely rare, VAMP also has been associated with other vaccines.7,8 Limited information exists to guide shared clinical decision making on COVID-19 vaccination in persons with a history of VAMP. It is unknown whether individuals with a history of VAMP are at higher risk for developing a recurrence or experiencing a more severe outcome following COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
As part of the collaborative public health mission with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for enhanced vaccine AE surveillance, the Defense Health Agency Immunization Healthcare Division (IHD) maintains a clinical database of service members and beneficiaries referred for suspected AEs following immunizations. A review of all AEs following immunization cases in this database from January 1, 2003, through February 28, 2022, identified individuals meeting the following criteria: (a) VAMP prior to receipt of COVID-19 vaccine; (b) receipt of COVID-19 vaccine in 2021; and (c) medical documentation in available electronic health records sufficient to describe health status at least 30 days following COVID-19 vaccination.9 If medical entries suggested cardiac symptoms following a COVID-19 vaccine, additional information was sought to verify VAMP based on current published criteria.10,11 Both the initial VAMP cases and the suspected COVID-19 VAMP cases were adjudicated by a team of vaccine experts and specialists in immunology, cardiology, and preventive medicine.
This retrospective review was approved and conducted in accordance with the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board protocol #20664. All individuals with recurrent VAMP consented to share their health records and clinical details.
Results
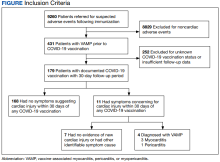
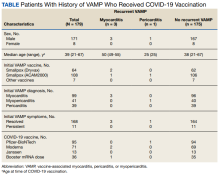
Among 9260 cases in the IHD database, 431 met the case definition for VAMP.
Among the 179 patients included in this analysis, 171 (96%) were male. Their median age was 39 years at the time of COVID-19 vaccination.
Within 1 month of receipt of any COVID-19 vaccine, 11 individuals had documented symptoms suggesting cardiac involvement, specifically, chest pain, palpitations, or dyspnea. After cardiac evaluation, 4 patients met the criteria for VAMP after COVID-19 vaccination.10,11 Seven patients either did not meet the criteria for VAMP or had alternative causes for their symptoms.
Two men aged 49 and 50 years with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following smallpox vaccination (Dryvax and ACAM2000) developed myocarditis 3 days after their second dose of the Moderna vaccine. One of these patients received a Pfizer-BioNTech booster 10 months later with no recurrence of symptoms. A 55-year-old man with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following Dryvax vaccination developed myocarditis 2 days after his Pfizer-BioNTech booster. None of the patients who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP reported residual symptoms from their initial VAMP episode, which occurred 12 to 18 years earlier. All were hospitalized briefly for observation and had complete symptom resolution within 6 weeks.
A 25-year-old man developed pericarditis 4 days after his second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination. His previous ACAM2000 vaccine-associated myocarditis occurred 3 years earlier, with no residual symptoms. Of note, he had a mild COVID-19 infection 78 days before the onset of his pericarditis. After the onset of his COVID-19 vaccine-associated pericarditis, he continued to experience transient bouts of chest pressure and exertional dyspnea that resolved within 7 months of onset.
The median interval between COVID-19 vaccine doses in those who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP was within the recommended mRNA vaccine dosing intervals of 3 to 4 weeks and was consistent with the median mRNA vaccine dosing intervals among the entire cohort.
Due to the small cohort size and other limitations of this study, the suggested rate of cardiac injury in this review (4 cases in 179 persons, or 2.2%) is an imprecise estimate of risk in a small population (95% CI, 0.1%-4.4%). While this rate may seem higher than expected within the general population after COVID-19 vaccination, it is lower than the estimated lifetime risk of recurrent myocarditis from any cause.6,12
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first report describing cardiac outcomes after COVID-19 vaccination among a cohort of individuals with prior history of VAMP. Four cases of COVID-19 VAMP were identified among 179 patients with previous VAMP. All cases had experienced VAMP after the smallpox vaccine several years earlier, with complete resolution of symptoms. Three cases presented with recurrent VAMP after their second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, and one after an mRNA booster dose. All fully recovered over the course of several months.
Myocarditis is a heterogeneous inflammatory injury with diverse, sometimes idiopathic, etiologies.13 In contrast to infection-related cardiac injury, prior reports of vaccine-associated myocarditis have suggested a hypersensitivity reaction characterized by patchy eosinophilic infiltrates, a benign clinical course, and good prognosis.2,3
There are several common features between VAMP after smallpox and COVID-19 vaccination. Cases occur predominantly in young men. The onset of symptoms after smallpox vaccine (mean, 10 days) and after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (mean, 3 days) appears to correspond to the timing of peak postvaccination pro-inflammatory cytokine elevation.14 While all VAMP cases are serious events, the majority of patients appear to have a relatively benign clinical course with rapid and full recovery.13
Patients who have experienced an inflammatory cardiac injury may be at higher risk for recurrence, but quantifying risk of this rare phenomenon is challenging. Cases of VAMP after the COVID-19 vaccine have occasionally been reported in patients with previous cardiac injury unrelated to vaccination.15-17 The cases presented here represent the first report of recurrent VAMP following prior non-COVID-19 vaccinations.
Most patients with prior VAMP in this cohort did not experience cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. Among 11 patients who developed symptoms, 3 had confirmed myocarditis and 1 had confirmed pericarditis. The clinical course for these patients with recurrent VAMP was observed to be no different in severity or duration from those who experience new-onset VAMP.4 All other patients not meeting criteria for VAMP or having alternative explanations for their symptoms also had a benign clinical course. Nonetheless, of the study cohort of 179, recurrent VAMP was diagnosed in 4 of the 11 who developed cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. The importance of cardiac evaluation should be emphasized for any patient presenting with chest pain, dyspnea, or other cardiac-suggestive symptoms following vaccination.
Strengths and Limitations
The strength of this review of VAMP recurrence associated with COVID-19 vaccination derives from our large and unique longitudinal database of VAMP among current and prior service members. Additionally, the IHD’s ongoing enhanced vaccine AEs surveillance provides the opportunity to contact patients and review their electronic health records over an extended interval of time.
When interpreting this report’s implications, limitations inherent to any retrospective case review should be considered. The cohort of cases of prior VAMP included primarily healthy, fit, young service members; this population is not representative of the general population. The cohort included prior VAMP cases that generally occurred after smallpox vaccination. Experiences after smallpox vaccine may not apply to cardiac injury from other vaccines or etiologies. By the nature of this review, the population studied at the time of COVID-19 vaccination was somewhat older than those most likely to develop an initial bout of VAMP.2 This review was limited by information available in the electronic health records of a small number of patients. Subclinical cases of VAMP and cases without adequate clinical evaluation also could not be included.
Conclusions
Noninfectious inflammation of the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis) is a rare AE following certain vaccines, especially live replicating smallpox vaccine and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. In this observational analysis, the majority of patients with previous VAMP successfully received a COVID-19 vaccine without recurrence. The 4 patients who were identified with recurrent VAMP following COVID-19 vaccination all recovered with supportive care. While the CDC endorses that individuals with a history of infectious myocarditis may receive COVID-19 vaccine after symptoms have resolved, there is currently insufficient safety data regarding COVID-19 vaccination of those with prior non-COVID-19 VAMP or following subsequent COVID-19 vaccination in those with prior VAMP related to COVID-19.10 For these individuals, COVID-19 vaccination is a precaution.10 Although insufficient to determine a precise level of risk, this report does provide data on which to base the CDC-recommended shared decision-making counseling of these patients. More research is needed to better define factors that increase risk for, or protection from, immune-mediated AEs following immunization, including VAMP. While benefits of vaccination have clearly outweighed risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, such research may optimize future vaccine recommendations.18
1. Decker MD, Garman PM, Hughes H, et al. Enhanced safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine among US military service members. Vaccine. 2021;39(39):5541-5547. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.041
2. Engler RJ, Nelson MR, Collins LC Jr, et al. A prospective study of the incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis and new onset cardiac symptoms following smallpox and influenza vaccination. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0118283. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118283
3. Faix DJ, Gordon DM, Perry LN, et al. Prospective safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine in deploying military personnel. Vaccine. 2020;38(46):7323-7330. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.09.037
4. Montgomery J, Ryan M, Engler R, et al. Myocarditis following immunization with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in members of the US military. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(10):1202-1206. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833
5. Witberg G, Barda N, Hoss S, et al. Myocarditis after Covid-19 vaccination in a large health care organization. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(23):2132-2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110737
6. Oster ME, Shay DK, Su JR, et al. Myocarditis cases reported after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in the US from December 2020 to August 2021. JAMA. 2022;327(4):331-340. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.24110
7. Su JR, McNeil MM, Welsh KJ, et al. Myopericarditis after vaccination, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), 1990-2018. Vaccine. 2021;39(5):839-845. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.12.046
8. Mei R, Raschi E, Forcesi E, Diemberger I, De Ponti F, Poluzzi E. Myocarditis and pericarditis after immunization: gaining insights through the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System. Int J Cardiol. 2018;273:183-186. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.054
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: cardiac-related events during the civilian smallpox vaccination program—United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52(21):492-496.
10. Gargano JW, Wallace M, Hadler SC, et al. Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine after reports of myocarditis among vaccine recipients: update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, June 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(27):977-982. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7027e2
11. Sexson Tejtel SK, Munoz FM, Al-Ammouri I, et al. Myocarditis and pericarditis: case definition and guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine. 2022;40(10):1499-1511. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.11.074
12. Sagar S, Liu PP, Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet. 2012;379(9817):738-747. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11) 60648-X
13. Heymans S, Cooper LT. Myocarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination: clinical observations and potential mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(2):75-77. doi:10.1038/s41569-021-00662-w
14. Cohen JI, Hohman P, Fulton R, et al. Kinetics of serum cytokines after primary or repeat vaccination with the smallpox vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2010;201(8):1183-1191. doi:10.1086/651453
15. Minocha PK, Better D, Singh RK, Hoque T. Recurrence of acute myocarditis temporally associated with receipt of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in an adolescent male. J Pediatr. 2021;238:321-323. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.035
16. Umei TC, Kishino Y, Watanabe K, et al. Recurrence of myopericarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in a male adolescent. CJC Open. 2022;4(3):350-352. doi:10.1016/j.cjco.2021.12.002
17. Pasha MA, Isaac S, Khan Z. Recurrent myocarditis following COVID-19 infection and the mRNA vaccine. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e26650. doi:10.7759/cureus.26650
18. Block JP, Boehmer TK, Forrest CB, et al. Cardiac complications after SARS-CoV-2 infection and mRNA COVID-19 vaccination—PCORnet, United States, January 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71(14):517-523. Published 2022 Apr 8. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7114e1
Vaccinations have substantially reduced morbidity and mortality from many infectious diseases. Despite the clear value of vaccinations in public health, efforts to better understand adverse events (AEs) following immunization are important to sustain public trust and vaccine confidence. Noninfectious inflammation of the heart may manifest as myocarditis or pericarditis, or occasionally, with shared signs and symptoms of each, as myopericarditis. This is a rare AE following some immunizations. Vaccine-associated myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis (VAMP) has been most clearly associated with smallpox vaccines and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.1-6 Although extremely rare, VAMP also has been associated with other vaccines.7,8 Limited information exists to guide shared clinical decision making on COVID-19 vaccination in persons with a history of VAMP. It is unknown whether individuals with a history of VAMP are at higher risk for developing a recurrence or experiencing a more severe outcome following COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
As part of the collaborative public health mission with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for enhanced vaccine AE surveillance, the Defense Health Agency Immunization Healthcare Division (IHD) maintains a clinical database of service members and beneficiaries referred for suspected AEs following immunizations. A review of all AEs following immunization cases in this database from January 1, 2003, through February 28, 2022, identified individuals meeting the following criteria: (a) VAMP prior to receipt of COVID-19 vaccine; (b) receipt of COVID-19 vaccine in 2021; and (c) medical documentation in available electronic health records sufficient to describe health status at least 30 days following COVID-19 vaccination.9 If medical entries suggested cardiac symptoms following a COVID-19 vaccine, additional information was sought to verify VAMP based on current published criteria.10,11 Both the initial VAMP cases and the suspected COVID-19 VAMP cases were adjudicated by a team of vaccine experts and specialists in immunology, cardiology, and preventive medicine.
This retrospective review was approved and conducted in accordance with the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board protocol #20664. All individuals with recurrent VAMP consented to share their health records and clinical details.
Results
Among 9260 cases in the IHD database, 431 met the case definition for VAMP.
Among the 179 patients included in this analysis, 171 (96%) were male. Their median age was 39 years at the time of COVID-19 vaccination.
Within 1 month of receipt of any COVID-19 vaccine, 11 individuals had documented symptoms suggesting cardiac involvement, specifically, chest pain, palpitations, or dyspnea. After cardiac evaluation, 4 patients met the criteria for VAMP after COVID-19 vaccination.10,11 Seven patients either did not meet the criteria for VAMP or had alternative causes for their symptoms.
Two men aged 49 and 50 years with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following smallpox vaccination (Dryvax and ACAM2000) developed myocarditis 3 days after their second dose of the Moderna vaccine. One of these patients received a Pfizer-BioNTech booster 10 months later with no recurrence of symptoms. A 55-year-old man with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following Dryvax vaccination developed myocarditis 2 days after his Pfizer-BioNTech booster. None of the patients who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP reported residual symptoms from their initial VAMP episode, which occurred 12 to 18 years earlier. All were hospitalized briefly for observation and had complete symptom resolution within 6 weeks.
A 25-year-old man developed pericarditis 4 days after his second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination. His previous ACAM2000 vaccine-associated myocarditis occurred 3 years earlier, with no residual symptoms. Of note, he had a mild COVID-19 infection 78 days before the onset of his pericarditis. After the onset of his COVID-19 vaccine-associated pericarditis, he continued to experience transient bouts of chest pressure and exertional dyspnea that resolved within 7 months of onset.
The median interval between COVID-19 vaccine doses in those who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP was within the recommended mRNA vaccine dosing intervals of 3 to 4 weeks and was consistent with the median mRNA vaccine dosing intervals among the entire cohort.
Due to the small cohort size and other limitations of this study, the suggested rate of cardiac injury in this review (4 cases in 179 persons, or 2.2%) is an imprecise estimate of risk in a small population (95% CI, 0.1%-4.4%). While this rate may seem higher than expected within the general population after COVID-19 vaccination, it is lower than the estimated lifetime risk of recurrent myocarditis from any cause.6,12
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first report describing cardiac outcomes after COVID-19 vaccination among a cohort of individuals with prior history of VAMP. Four cases of COVID-19 VAMP were identified among 179 patients with previous VAMP. All cases had experienced VAMP after the smallpox vaccine several years earlier, with complete resolution of symptoms. Three cases presented with recurrent VAMP after their second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, and one after an mRNA booster dose. All fully recovered over the course of several months.
Myocarditis is a heterogeneous inflammatory injury with diverse, sometimes idiopathic, etiologies.13 In contrast to infection-related cardiac injury, prior reports of vaccine-associated myocarditis have suggested a hypersensitivity reaction characterized by patchy eosinophilic infiltrates, a benign clinical course, and good prognosis.2,3
There are several common features between VAMP after smallpox and COVID-19 vaccination. Cases occur predominantly in young men. The onset of symptoms after smallpox vaccine (mean, 10 days) and after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (mean, 3 days) appears to correspond to the timing of peak postvaccination pro-inflammatory cytokine elevation.14 While all VAMP cases are serious events, the majority of patients appear to have a relatively benign clinical course with rapid and full recovery.13
Patients who have experienced an inflammatory cardiac injury may be at higher risk for recurrence, but quantifying risk of this rare phenomenon is challenging. Cases of VAMP after the COVID-19 vaccine have occasionally been reported in patients with previous cardiac injury unrelated to vaccination.15-17 The cases presented here represent the first report of recurrent VAMP following prior non-COVID-19 vaccinations.
Most patients with prior VAMP in this cohort did not experience cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. Among 11 patients who developed symptoms, 3 had confirmed myocarditis and 1 had confirmed pericarditis. The clinical course for these patients with recurrent VAMP was observed to be no different in severity or duration from those who experience new-onset VAMP.4 All other patients not meeting criteria for VAMP or having alternative explanations for their symptoms also had a benign clinical course. Nonetheless, of the study cohort of 179, recurrent VAMP was diagnosed in 4 of the 11 who developed cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. The importance of cardiac evaluation should be emphasized for any patient presenting with chest pain, dyspnea, or other cardiac-suggestive symptoms following vaccination.
Strengths and Limitations
The strength of this review of VAMP recurrence associated with COVID-19 vaccination derives from our large and unique longitudinal database of VAMP among current and prior service members. Additionally, the IHD’s ongoing enhanced vaccine AEs surveillance provides the opportunity to contact patients and review their electronic health records over an extended interval of time.
When interpreting this report’s implications, limitations inherent to any retrospective case review should be considered. The cohort of cases of prior VAMP included primarily healthy, fit, young service members; this population is not representative of the general population. The cohort included prior VAMP cases that generally occurred after smallpox vaccination. Experiences after smallpox vaccine may not apply to cardiac injury from other vaccines or etiologies. By the nature of this review, the population studied at the time of COVID-19 vaccination was somewhat older than those most likely to develop an initial bout of VAMP.2 This review was limited by information available in the electronic health records of a small number of patients. Subclinical cases of VAMP and cases without adequate clinical evaluation also could not be included.
Conclusions
Noninfectious inflammation of the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis) is a rare AE following certain vaccines, especially live replicating smallpox vaccine and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. In this observational analysis, the majority of patients with previous VAMP successfully received a COVID-19 vaccine without recurrence. The 4 patients who were identified with recurrent VAMP following COVID-19 vaccination all recovered with supportive care. While the CDC endorses that individuals with a history of infectious myocarditis may receive COVID-19 vaccine after symptoms have resolved, there is currently insufficient safety data regarding COVID-19 vaccination of those with prior non-COVID-19 VAMP or following subsequent COVID-19 vaccination in those with prior VAMP related to COVID-19.10 For these individuals, COVID-19 vaccination is a precaution.10 Although insufficient to determine a precise level of risk, this report does provide data on which to base the CDC-recommended shared decision-making counseling of these patients. More research is needed to better define factors that increase risk for, or protection from, immune-mediated AEs following immunization, including VAMP. While benefits of vaccination have clearly outweighed risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, such research may optimize future vaccine recommendations.18
Vaccinations have substantially reduced morbidity and mortality from many infectious diseases. Despite the clear value of vaccinations in public health, efforts to better understand adverse events (AEs) following immunization are important to sustain public trust and vaccine confidence. Noninfectious inflammation of the heart may manifest as myocarditis or pericarditis, or occasionally, with shared signs and symptoms of each, as myopericarditis. This is a rare AE following some immunizations. Vaccine-associated myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis (VAMP) has been most clearly associated with smallpox vaccines and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.1-6 Although extremely rare, VAMP also has been associated with other vaccines.7,8 Limited information exists to guide shared clinical decision making on COVID-19 vaccination in persons with a history of VAMP. It is unknown whether individuals with a history of VAMP are at higher risk for developing a recurrence or experiencing a more severe outcome following COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
As part of the collaborative public health mission with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for enhanced vaccine AE surveillance, the Defense Health Agency Immunization Healthcare Division (IHD) maintains a clinical database of service members and beneficiaries referred for suspected AEs following immunizations. A review of all AEs following immunization cases in this database from January 1, 2003, through February 28, 2022, identified individuals meeting the following criteria: (a) VAMP prior to receipt of COVID-19 vaccine; (b) receipt of COVID-19 vaccine in 2021; and (c) medical documentation in available electronic health records sufficient to describe health status at least 30 days following COVID-19 vaccination.9 If medical entries suggested cardiac symptoms following a COVID-19 vaccine, additional information was sought to verify VAMP based on current published criteria.10,11 Both the initial VAMP cases and the suspected COVID-19 VAMP cases were adjudicated by a team of vaccine experts and specialists in immunology, cardiology, and preventive medicine.
This retrospective review was approved and conducted in accordance with the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Institutional Review Board protocol #20664. All individuals with recurrent VAMP consented to share their health records and clinical details.
Results
Among 9260 cases in the IHD database, 431 met the case definition for VAMP.
Among the 179 patients included in this analysis, 171 (96%) were male. Their median age was 39 years at the time of COVID-19 vaccination.
Within 1 month of receipt of any COVID-19 vaccine, 11 individuals had documented symptoms suggesting cardiac involvement, specifically, chest pain, palpitations, or dyspnea. After cardiac evaluation, 4 patients met the criteria for VAMP after COVID-19 vaccination.10,11 Seven patients either did not meet the criteria for VAMP or had alternative causes for their symptoms.
Two men aged 49 and 50 years with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following smallpox vaccination (Dryvax and ACAM2000) developed myocarditis 3 days after their second dose of the Moderna vaccine. One of these patients received a Pfizer-BioNTech booster 10 months later with no recurrence of symptoms. A 55-year-old man with a history of vaccine-associated myocarditis following Dryvax vaccination developed myocarditis 2 days after his Pfizer-BioNTech booster. None of the patients who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP reported residual symptoms from their initial VAMP episode, which occurred 12 to 18 years earlier. All were hospitalized briefly for observation and had complete symptom resolution within 6 weeks.
A 25-year-old man developed pericarditis 4 days after his second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination. His previous ACAM2000 vaccine-associated myocarditis occurred 3 years earlier, with no residual symptoms. Of note, he had a mild COVID-19 infection 78 days before the onset of his pericarditis. After the onset of his COVID-19 vaccine-associated pericarditis, he continued to experience transient bouts of chest pressure and exertional dyspnea that resolved within 7 months of onset.
The median interval between COVID-19 vaccine doses in those who developed post-COVID-19 VAMP was within the recommended mRNA vaccine dosing intervals of 3 to 4 weeks and was consistent with the median mRNA vaccine dosing intervals among the entire cohort.
Due to the small cohort size and other limitations of this study, the suggested rate of cardiac injury in this review (4 cases in 179 persons, or 2.2%) is an imprecise estimate of risk in a small population (95% CI, 0.1%-4.4%). While this rate may seem higher than expected within the general population after COVID-19 vaccination, it is lower than the estimated lifetime risk of recurrent myocarditis from any cause.6,12
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first report describing cardiac outcomes after COVID-19 vaccination among a cohort of individuals with prior history of VAMP. Four cases of COVID-19 VAMP were identified among 179 patients with previous VAMP. All cases had experienced VAMP after the smallpox vaccine several years earlier, with complete resolution of symptoms. Three cases presented with recurrent VAMP after their second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, and one after an mRNA booster dose. All fully recovered over the course of several months.
Myocarditis is a heterogeneous inflammatory injury with diverse, sometimes idiopathic, etiologies.13 In contrast to infection-related cardiac injury, prior reports of vaccine-associated myocarditis have suggested a hypersensitivity reaction characterized by patchy eosinophilic infiltrates, a benign clinical course, and good prognosis.2,3
There are several common features between VAMP after smallpox and COVID-19 vaccination. Cases occur predominantly in young men. The onset of symptoms after smallpox vaccine (mean, 10 days) and after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (mean, 3 days) appears to correspond to the timing of peak postvaccination pro-inflammatory cytokine elevation.14 While all VAMP cases are serious events, the majority of patients appear to have a relatively benign clinical course with rapid and full recovery.13
Patients who have experienced an inflammatory cardiac injury may be at higher risk for recurrence, but quantifying risk of this rare phenomenon is challenging. Cases of VAMP after the COVID-19 vaccine have occasionally been reported in patients with previous cardiac injury unrelated to vaccination.15-17 The cases presented here represent the first report of recurrent VAMP following prior non-COVID-19 vaccinations.
Most patients with prior VAMP in this cohort did not experience cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. Among 11 patients who developed symptoms, 3 had confirmed myocarditis and 1 had confirmed pericarditis. The clinical course for these patients with recurrent VAMP was observed to be no different in severity or duration from those who experience new-onset VAMP.4 All other patients not meeting criteria for VAMP or having alternative explanations for their symptoms also had a benign clinical course. Nonetheless, of the study cohort of 179, recurrent VAMP was diagnosed in 4 of the 11 who developed cardiac-suggestive symptoms following COVID-19 vaccination. The importance of cardiac evaluation should be emphasized for any patient presenting with chest pain, dyspnea, or other cardiac-suggestive symptoms following vaccination.
Strengths and Limitations
The strength of this review of VAMP recurrence associated with COVID-19 vaccination derives from our large and unique longitudinal database of VAMP among current and prior service members. Additionally, the IHD’s ongoing enhanced vaccine AEs surveillance provides the opportunity to contact patients and review their electronic health records over an extended interval of time.
When interpreting this report’s implications, limitations inherent to any retrospective case review should be considered. The cohort of cases of prior VAMP included primarily healthy, fit, young service members; this population is not representative of the general population. The cohort included prior VAMP cases that generally occurred after smallpox vaccination. Experiences after smallpox vaccine may not apply to cardiac injury from other vaccines or etiologies. By the nature of this review, the population studied at the time of COVID-19 vaccination was somewhat older than those most likely to develop an initial bout of VAMP.2 This review was limited by information available in the electronic health records of a small number of patients. Subclinical cases of VAMP and cases without adequate clinical evaluation also could not be included.
Conclusions
Noninfectious inflammation of the heart (myocarditis, pericarditis, or myopericarditis) is a rare AE following certain vaccines, especially live replicating smallpox vaccine and mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. In this observational analysis, the majority of patients with previous VAMP successfully received a COVID-19 vaccine without recurrence. The 4 patients who were identified with recurrent VAMP following COVID-19 vaccination all recovered with supportive care. While the CDC endorses that individuals with a history of infectious myocarditis may receive COVID-19 vaccine after symptoms have resolved, there is currently insufficient safety data regarding COVID-19 vaccination of those with prior non-COVID-19 VAMP or following subsequent COVID-19 vaccination in those with prior VAMP related to COVID-19.10 For these individuals, COVID-19 vaccination is a precaution.10 Although insufficient to determine a precise level of risk, this report does provide data on which to base the CDC-recommended shared decision-making counseling of these patients. More research is needed to better define factors that increase risk for, or protection from, immune-mediated AEs following immunization, including VAMP. While benefits of vaccination have clearly outweighed risks during the COVID-19 pandemic, such research may optimize future vaccine recommendations.18
1. Decker MD, Garman PM, Hughes H, et al. Enhanced safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine among US military service members. Vaccine. 2021;39(39):5541-5547. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.041
2. Engler RJ, Nelson MR, Collins LC Jr, et al. A prospective study of the incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis and new onset cardiac symptoms following smallpox and influenza vaccination. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0118283. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118283
3. Faix DJ, Gordon DM, Perry LN, et al. Prospective safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine in deploying military personnel. Vaccine. 2020;38(46):7323-7330. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.09.037
4. Montgomery J, Ryan M, Engler R, et al. Myocarditis following immunization with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in members of the US military. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(10):1202-1206. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833
5. Witberg G, Barda N, Hoss S, et al. Myocarditis after Covid-19 vaccination in a large health care organization. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(23):2132-2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110737
6. Oster ME, Shay DK, Su JR, et al. Myocarditis cases reported after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in the US from December 2020 to August 2021. JAMA. 2022;327(4):331-340. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.24110
7. Su JR, McNeil MM, Welsh KJ, et al. Myopericarditis after vaccination, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), 1990-2018. Vaccine. 2021;39(5):839-845. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.12.046
8. Mei R, Raschi E, Forcesi E, Diemberger I, De Ponti F, Poluzzi E. Myocarditis and pericarditis after immunization: gaining insights through the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System. Int J Cardiol. 2018;273:183-186. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.054
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: cardiac-related events during the civilian smallpox vaccination program—United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52(21):492-496.
10. Gargano JW, Wallace M, Hadler SC, et al. Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine after reports of myocarditis among vaccine recipients: update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, June 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(27):977-982. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7027e2
11. Sexson Tejtel SK, Munoz FM, Al-Ammouri I, et al. Myocarditis and pericarditis: case definition and guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine. 2022;40(10):1499-1511. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.11.074
12. Sagar S, Liu PP, Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet. 2012;379(9817):738-747. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11) 60648-X
13. Heymans S, Cooper LT. Myocarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination: clinical observations and potential mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(2):75-77. doi:10.1038/s41569-021-00662-w
14. Cohen JI, Hohman P, Fulton R, et al. Kinetics of serum cytokines after primary or repeat vaccination with the smallpox vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2010;201(8):1183-1191. doi:10.1086/651453
15. Minocha PK, Better D, Singh RK, Hoque T. Recurrence of acute myocarditis temporally associated with receipt of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in an adolescent male. J Pediatr. 2021;238:321-323. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.035
16. Umei TC, Kishino Y, Watanabe K, et al. Recurrence of myopericarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in a male adolescent. CJC Open. 2022;4(3):350-352. doi:10.1016/j.cjco.2021.12.002
17. Pasha MA, Isaac S, Khan Z. Recurrent myocarditis following COVID-19 infection and the mRNA vaccine. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e26650. doi:10.7759/cureus.26650
18. Block JP, Boehmer TK, Forrest CB, et al. Cardiac complications after SARS-CoV-2 infection and mRNA COVID-19 vaccination—PCORnet, United States, January 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71(14):517-523. Published 2022 Apr 8. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7114e1
1. Decker MD, Garman PM, Hughes H, et al. Enhanced safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine among US military service members. Vaccine. 2021;39(39):5541-5547. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.041
2. Engler RJ, Nelson MR, Collins LC Jr, et al. A prospective study of the incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis and new onset cardiac symptoms following smallpox and influenza vaccination. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0118283. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118283
3. Faix DJ, Gordon DM, Perry LN, et al. Prospective safety surveillance study of ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine in deploying military personnel. Vaccine. 2020;38(46):7323-7330. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.09.037
4. Montgomery J, Ryan M, Engler R, et al. Myocarditis following immunization with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in members of the US military. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(10):1202-1206. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833
5. Witberg G, Barda N, Hoss S, et al. Myocarditis after Covid-19 vaccination in a large health care organization. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(23):2132-2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110737
6. Oster ME, Shay DK, Su JR, et al. Myocarditis cases reported after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in the US from December 2020 to August 2021. JAMA. 2022;327(4):331-340. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.24110
7. Su JR, McNeil MM, Welsh KJ, et al. Myopericarditis after vaccination, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), 1990-2018. Vaccine. 2021;39(5):839-845. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.12.046
8. Mei R, Raschi E, Forcesi E, Diemberger I, De Ponti F, Poluzzi E. Myocarditis and pericarditis after immunization: gaining insights through the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System. Int J Cardiol. 2018;273:183-186. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.09.054
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: cardiac-related events during the civilian smallpox vaccination program—United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52(21):492-496.
10. Gargano JW, Wallace M, Hadler SC, et al. Use of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine after reports of myocarditis among vaccine recipients: update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, June 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(27):977-982. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7027e2
11. Sexson Tejtel SK, Munoz FM, Al-Ammouri I, et al. Myocarditis and pericarditis: case definition and guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine. 2022;40(10):1499-1511. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.11.074
12. Sagar S, Liu PP, Cooper LT Jr. Myocarditis. Lancet. 2012;379(9817):738-747. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11) 60648-X
13. Heymans S, Cooper LT. Myocarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination: clinical observations and potential mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022;19(2):75-77. doi:10.1038/s41569-021-00662-w
14. Cohen JI, Hohman P, Fulton R, et al. Kinetics of serum cytokines after primary or repeat vaccination with the smallpox vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2010;201(8):1183-1191. doi:10.1086/651453
15. Minocha PK, Better D, Singh RK, Hoque T. Recurrence of acute myocarditis temporally associated with receipt of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in an adolescent male. J Pediatr. 2021;238:321-323. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.035
16. Umei TC, Kishino Y, Watanabe K, et al. Recurrence of myopericarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in a male adolescent. CJC Open. 2022;4(3):350-352. doi:10.1016/j.cjco.2021.12.002
17. Pasha MA, Isaac S, Khan Z. Recurrent myocarditis following COVID-19 infection and the mRNA vaccine. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e26650. doi:10.7759/cureus.26650
18. Block JP, Boehmer TK, Forrest CB, et al. Cardiac complications after SARS-CoV-2 infection and mRNA COVID-19 vaccination—PCORnet, United States, January 2021-January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71(14):517-523. Published 2022 Apr 8. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7114e1
Add this to the list of long COVID symptoms: Stigma
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
PLOS ONE
How Well Does the Third Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Work?
How effective are the COVID-19 vaccines, third time around? Researchers compared 2 large groups of veterans to find out how well a third dose protected against documented infection, symptomatic COVID-19, and COVID-19–related hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and death.
The research, published in Nature, used electronic health records of 65,196 veterans who received BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and 65,196 who received mRNA-1273 (Moderna). They chose to study the 16 weeks between October 20, 2021 and February 8, 2022, which included both Delta- and Omicron-variant waves.
During the follow-up (median, 77 days), 2994 COVID-19 infections were documented, of which 200 were detected as symptomatic, 194 required hospitalization, and 52 required ICU admission. Twenty-two patients died.
In a previous head-to-head trial comparing breakthrough COVID-19 outcomes after the first doses of the 2 vaccines (given when the Alpha and Delta variants were predominant), the researchers had found a low risk of documented infection and severe outcomes, but lower for the Moderna vaccine. They note that few head-to-head comparisons have been made of third-dose effectiveness.
As expected, in this trial, the researchers found a “nearly identical” pattern for the risk of the 2 vaccine groups. Although the risks for all of the measured outcomes over 16 weeks were low for both vaccines ≤ 4% for documented infection and < 0.03% for death in each group—those veterans who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had an excess of 45 documented infections and 11 hospitalizations per 10,000 persons, compared with the Moderna group. The Pfizer-BioNTech group also had a higher risk of documented infection over 9 weeks of follow-up, during which an Omicron-variant predominated.
Given the high effectiveness of a third dose of both vaccines, either vaccine is strongly recommended, the researchers conclude. They point to “evidence of clear and comparable benefits” for the most severe outcomes: The difference in estimated 16-week risk of death between the 2 groups was two-thousandths of 1 %.
They add that, while the differences in estimated risk for less severe outcomes between the 2 groups were small on the absolute scale, they may be meaningful when considering the population scale at which these vaccines are deployed.
How effective are the COVID-19 vaccines, third time around? Researchers compared 2 large groups of veterans to find out how well a third dose protected against documented infection, symptomatic COVID-19, and COVID-19–related hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and death.
The research, published in Nature, used electronic health records of 65,196 veterans who received BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and 65,196 who received mRNA-1273 (Moderna). They chose to study the 16 weeks between October 20, 2021 and February 8, 2022, which included both Delta- and Omicron-variant waves.
During the follow-up (median, 77 days), 2994 COVID-19 infections were documented, of which 200 were detected as symptomatic, 194 required hospitalization, and 52 required ICU admission. Twenty-two patients died.
In a previous head-to-head trial comparing breakthrough COVID-19 outcomes after the first doses of the 2 vaccines (given when the Alpha and Delta variants were predominant), the researchers had found a low risk of documented infection and severe outcomes, but lower for the Moderna vaccine. They note that few head-to-head comparisons have been made of third-dose effectiveness.
As expected, in this trial, the researchers found a “nearly identical” pattern for the risk of the 2 vaccine groups. Although the risks for all of the measured outcomes over 16 weeks were low for both vaccines ≤ 4% for documented infection and < 0.03% for death in each group—those veterans who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had an excess of 45 documented infections and 11 hospitalizations per 10,000 persons, compared with the Moderna group. The Pfizer-BioNTech group also had a higher risk of documented infection over 9 weeks of follow-up, during which an Omicron-variant predominated.
Given the high effectiveness of a third dose of both vaccines, either vaccine is strongly recommended, the researchers conclude. They point to “evidence of clear and comparable benefits” for the most severe outcomes: The difference in estimated 16-week risk of death between the 2 groups was two-thousandths of 1 %.
They add that, while the differences in estimated risk for less severe outcomes between the 2 groups were small on the absolute scale, they may be meaningful when considering the population scale at which these vaccines are deployed.
How effective are the COVID-19 vaccines, third time around? Researchers compared 2 large groups of veterans to find out how well a third dose protected against documented infection, symptomatic COVID-19, and COVID-19–related hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and death.
The research, published in Nature, used electronic health records of 65,196 veterans who received BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and 65,196 who received mRNA-1273 (Moderna). They chose to study the 16 weeks between October 20, 2021 and February 8, 2022, which included both Delta- and Omicron-variant waves.
During the follow-up (median, 77 days), 2994 COVID-19 infections were documented, of which 200 were detected as symptomatic, 194 required hospitalization, and 52 required ICU admission. Twenty-two patients died.
In a previous head-to-head trial comparing breakthrough COVID-19 outcomes after the first doses of the 2 vaccines (given when the Alpha and Delta variants were predominant), the researchers had found a low risk of documented infection and severe outcomes, but lower for the Moderna vaccine. They note that few head-to-head comparisons have been made of third-dose effectiveness.
As expected, in this trial, the researchers found a “nearly identical” pattern for the risk of the 2 vaccine groups. Although the risks for all of the measured outcomes over 16 weeks were low for both vaccines ≤ 4% for documented infection and < 0.03% for death in each group—those veterans who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had an excess of 45 documented infections and 11 hospitalizations per 10,000 persons, compared with the Moderna group. The Pfizer-BioNTech group also had a higher risk of documented infection over 9 weeks of follow-up, during which an Omicron-variant predominated.
Given the high effectiveness of a third dose of both vaccines, either vaccine is strongly recommended, the researchers conclude. They point to “evidence of clear and comparable benefits” for the most severe outcomes: The difference in estimated 16-week risk of death between the 2 groups was two-thousandths of 1 %.
They add that, while the differences in estimated risk for less severe outcomes between the 2 groups were small on the absolute scale, they may be meaningful when considering the population scale at which these vaccines are deployed.
COVID leading cause of death among law enforcement for third year
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A new report says 70 officers died of COVID-related causes after getting the virus while on the job. The number is down dramatically from 2021, when 405 officer deaths were attributed to COVID.
The annual count was published Wednesday by the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund.
In total, 226 officers died in the line of duty in 2022, which is a decrease of 61% from 2021.
The decrease “is almost entirely related to the significant reduction in COVID-19 deaths,” the report stated. The authors said the decline was likely due to “reduced infection rates and the broad availability and use of vaccinations.”
Reported deaths included federal, state, tribal, and local law enforcement officers.
Firearms-related fatalities were the second-leading cause of death among officers, with 64 in 2022. That count sustains a 21% increase seen in 2021, up from the decade-long average of 53 firearms-related deaths annually from 2010 to 2020.
Traffic-related causes ranked third for cause of death in 2022, accounting for 56 deaths.
“While overall line-of-duty deaths are trending down, the continuing trend of greater-than-average firearms-related deaths continues to be a serious concern,” Marcia Ferranto, the organization’s chief executive officer, said in a news release. “Using and reporting on this data allows us to highlight the continuing cost of maintaining our democracy, regrettably measured in the lives of the many law enforcement professionals who sacrifice everything fulfilling their promise to serve and protect.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Which treatments improve long-term outcomes of critical COVID illness?
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA