User login
Dupilumab gains off-label uses as clinicians turn to drug for more indications
.
The drug, marketed as Dupixent, is currently approved in the United States to treat atopic dermatitis, asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis in adults. Dupilumab is also approved to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in patients aged 12 years and older and atopic dermatitis and asthma in some patients as young as age 6 months.
As the roster of approved and off-label indications grows, skin specialists said, pediatricians and other primary care providers should become familiar with the drug – given the increasing likelihood that their patients may be taking the medication.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration first approved dupilumab in 2017 for eczema and has continued to add new treatment indications, the most recent being for prurigo nodularis, in 2022. Sanofi, which markets the drug with Regeneron, announced in April 2022 that some 430,000 patients worldwide were taking the drug – a figure it hoped to raise by 1.5 million by 2025.
A well-tolerated – if expensive – drug
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor alpha-antagonist biologic, blocks both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, Marlys Fassett, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Fassett said she prescribes the drug off label for chronic idiopathic urticaria, including in older patients, and finds that the side effects in older patients are similar to those in younger people. The medication costs $36,000 per year, although some patients can get it more cheaply.
“Dupixent is a super-safe drug because it doesn’t immunosuppress any other part of the immune system, so you still have good antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal immunity,” she added. “That makes perfect sense as a biological mechanism, and it’s been found safe in clinical trials.”
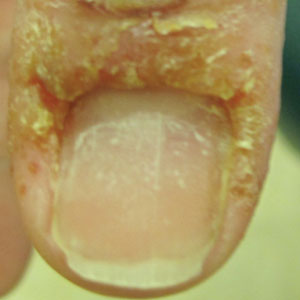
Case reports of potential adverse reactions to dupilumab have included ocular surface disease, lichen planus, and rash on the face and neck.
“We’re still learning about complications and are watching patients carefully,” said Marissa J. Perman, MD, section chief of dermatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Many people with atopic dermatitis also have other allergic conditions, such as contact dermatitis, asthma, prurigo nodularis, allergic rhinitis, and seasonal allergies. Each of these conditions has a pathway that depends on IL-4 receptors, Dr. Fassett said.
“It’s amazing how many conditions Dupixent improves. Sometimes we prescribe on-label Dupixent for atopic dermatitis, and inadvertently, the drug also improves that patient’s other, off-label conditions,” Dr. Fassett said. “I think that’s the best evidence that Dupixent works in these off-label cases.”
Lindsay C. Strowd, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said she uses off-label dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and intense pruritus of unknown etiology.
“And several times I have treated drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, a rare adverse drug reaction that causes a rash and eosinophilia,” Dr. Strowd added.
Tissa Hata, MD, professor of medicine and clinical service chief at the University of California, San Diego, mainly treats elderly patients. She uses dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and chronic pruritus. “There have been reports of using Dupixent to treat adult alopecia areata, chronic urticaria, localized scleroderma, and even keloids,” she told this news organization.
As a pediatric dermatologist, Dr. Perman treats children with atopic dermatitis as young as 3 months of age. She also uses dupilumab for alopecia areata, graft vs. host disease, and pruritus not otherwise specified.
Conjunctivitis and facial redness are two side effects Dr. Fassett sometimes sees with dupilumab. They occur similarly with all conditions and in all age groups. “We don’t know why they occur, and we don’t always know how to alleviate them,” she said. “So a small number of patients stop using Dupixent because they can’t tolerate those two side effects.
“We’re not worried about infection risk,” Dr. Fassett said. “Your patients may have heard of dupilumab as an immunosuppressant, but its immunosuppression is very focused. You can reassure them that they’re not at increased risk for viral or bacterial infections when they’re on this drug.”
“I don’t think there are any different safety signals to watch for with on-label vs. off-label Dupixent use,” Dr. Strowd added. “In general, the medicine is very safe.”
Dr. Hata said she is impressed with dupilumab’s safety in her elderly patients. All her patients older than 85 years who have taken the drug for bullous pemphigoid have tolerated it well, she said.
“Dupixent seems to be a safe alternative for elderly patients with pruritus because they often cannot tolerate sedating antihistamines due to the risk of falling,” Dr. Hata said. “And UV therapy may be difficult for elderly patients due to problems with transport.”
Although some of Dr. Hata’s elderly patients with atopic dermatitis have discontinued use of the drug after developing conjunctivitis, none taking the drug off label have discontinued it because of side effects, she noted.
“Dupixent manages the condition, but it is not a cure,” Dr. Fassett noted. “Based on the current data, we think it’s safe and effective to take long term, potentially for life.”
Making injections less bothersome
Dupilumab is injected subcutaneously from a single-dose prefilled syringe or a prefilled pen (syringe hidden in an opaque sheath), typically in the thigh, arm, abdomen, or buttocks. According to Sanofi and Regeneron, patients receive dupilumab injections every 2 to 4 weeks in doses based on their age and weight.
“The medication is somewhat viscous, so taking the syringe or pen out of the refrigerator ahead of time to warm it up can make the experience less painful,” Dr. Strowd advised. “For pediatric patients, I sometimes prescribe topical lidocaine applied 30 minutes before injection.”
Dr. Hata suggested icing the skin prior to injecting or distracting the patient by tapping a different area of the skin.
For her pediatric patients, Dr. Perman said she uses “lots of distraction, EMLA cream, and having one person hold the child while a second person injects.”
Clinic and pharmacy staff may show patients how to inject properly, Dr. Fassett added; and the product website provides injection tutorials.
Off-label dupixent can be expensive, difficult to obtain
The list price per injection, regardless of dose, is around $1,800. But according to the company’s website, most patients have health insurance or qualify for other assistance, so “very few patients pay the list price.”
Even so, “due to cost and insurance coverage hurdles, obtaining Dupixent for off-label use can be difficult,” Dr. Strowd said.
“In academic medicine, we can obtain drugs for our patients that community doctors may not get approval for,” Dr. Fassett added. “Community doctors can use information in the medical literature and in news articles to press insurance companies to spend money to provide their patients with Dupixent.”
The experts who commented have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The drug, marketed as Dupixent, is currently approved in the United States to treat atopic dermatitis, asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis in adults. Dupilumab is also approved to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in patients aged 12 years and older and atopic dermatitis and asthma in some patients as young as age 6 months.
As the roster of approved and off-label indications grows, skin specialists said, pediatricians and other primary care providers should become familiar with the drug – given the increasing likelihood that their patients may be taking the medication.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration first approved dupilumab in 2017 for eczema and has continued to add new treatment indications, the most recent being for prurigo nodularis, in 2022. Sanofi, which markets the drug with Regeneron, announced in April 2022 that some 430,000 patients worldwide were taking the drug – a figure it hoped to raise by 1.5 million by 2025.
A well-tolerated – if expensive – drug
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor alpha-antagonist biologic, blocks both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, Marlys Fassett, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Fassett said she prescribes the drug off label for chronic idiopathic urticaria, including in older patients, and finds that the side effects in older patients are similar to those in younger people. The medication costs $36,000 per year, although some patients can get it more cheaply.
“Dupixent is a super-safe drug because it doesn’t immunosuppress any other part of the immune system, so you still have good antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal immunity,” she added. “That makes perfect sense as a biological mechanism, and it’s been found safe in clinical trials.”
Case reports of potential adverse reactions to dupilumab have included ocular surface disease, lichen planus, and rash on the face and neck.
“We’re still learning about complications and are watching patients carefully,” said Marissa J. Perman, MD, section chief of dermatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Many people with atopic dermatitis also have other allergic conditions, such as contact dermatitis, asthma, prurigo nodularis, allergic rhinitis, and seasonal allergies. Each of these conditions has a pathway that depends on IL-4 receptors, Dr. Fassett said.
“It’s amazing how many conditions Dupixent improves. Sometimes we prescribe on-label Dupixent for atopic dermatitis, and inadvertently, the drug also improves that patient’s other, off-label conditions,” Dr. Fassett said. “I think that’s the best evidence that Dupixent works in these off-label cases.”
Lindsay C. Strowd, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said she uses off-label dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and intense pruritus of unknown etiology.
“And several times I have treated drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, a rare adverse drug reaction that causes a rash and eosinophilia,” Dr. Strowd added.
Tissa Hata, MD, professor of medicine and clinical service chief at the University of California, San Diego, mainly treats elderly patients. She uses dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and chronic pruritus. “There have been reports of using Dupixent to treat adult alopecia areata, chronic urticaria, localized scleroderma, and even keloids,” she told this news organization.
As a pediatric dermatologist, Dr. Perman treats children with atopic dermatitis as young as 3 months of age. She also uses dupilumab for alopecia areata, graft vs. host disease, and pruritus not otherwise specified.
Conjunctivitis and facial redness are two side effects Dr. Fassett sometimes sees with dupilumab. They occur similarly with all conditions and in all age groups. “We don’t know why they occur, and we don’t always know how to alleviate them,” she said. “So a small number of patients stop using Dupixent because they can’t tolerate those two side effects.
“We’re not worried about infection risk,” Dr. Fassett said. “Your patients may have heard of dupilumab as an immunosuppressant, but its immunosuppression is very focused. You can reassure them that they’re not at increased risk for viral or bacterial infections when they’re on this drug.”
“I don’t think there are any different safety signals to watch for with on-label vs. off-label Dupixent use,” Dr. Strowd added. “In general, the medicine is very safe.”
Dr. Hata said she is impressed with dupilumab’s safety in her elderly patients. All her patients older than 85 years who have taken the drug for bullous pemphigoid have tolerated it well, she said.
“Dupixent seems to be a safe alternative for elderly patients with pruritus because they often cannot tolerate sedating antihistamines due to the risk of falling,” Dr. Hata said. “And UV therapy may be difficult for elderly patients due to problems with transport.”
Although some of Dr. Hata’s elderly patients with atopic dermatitis have discontinued use of the drug after developing conjunctivitis, none taking the drug off label have discontinued it because of side effects, she noted.
“Dupixent manages the condition, but it is not a cure,” Dr. Fassett noted. “Based on the current data, we think it’s safe and effective to take long term, potentially for life.”
Making injections less bothersome
Dupilumab is injected subcutaneously from a single-dose prefilled syringe or a prefilled pen (syringe hidden in an opaque sheath), typically in the thigh, arm, abdomen, or buttocks. According to Sanofi and Regeneron, patients receive dupilumab injections every 2 to 4 weeks in doses based on their age and weight.
“The medication is somewhat viscous, so taking the syringe or pen out of the refrigerator ahead of time to warm it up can make the experience less painful,” Dr. Strowd advised. “For pediatric patients, I sometimes prescribe topical lidocaine applied 30 minutes before injection.”
Dr. Hata suggested icing the skin prior to injecting or distracting the patient by tapping a different area of the skin.
For her pediatric patients, Dr. Perman said she uses “lots of distraction, EMLA cream, and having one person hold the child while a second person injects.”
Clinic and pharmacy staff may show patients how to inject properly, Dr. Fassett added; and the product website provides injection tutorials.
Off-label dupixent can be expensive, difficult to obtain
The list price per injection, regardless of dose, is around $1,800. But according to the company’s website, most patients have health insurance or qualify for other assistance, so “very few patients pay the list price.”
Even so, “due to cost and insurance coverage hurdles, obtaining Dupixent for off-label use can be difficult,” Dr. Strowd said.
“In academic medicine, we can obtain drugs for our patients that community doctors may not get approval for,” Dr. Fassett added. “Community doctors can use information in the medical literature and in news articles to press insurance companies to spend money to provide their patients with Dupixent.”
The experts who commented have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
The drug, marketed as Dupixent, is currently approved in the United States to treat atopic dermatitis, asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis in adults. Dupilumab is also approved to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in patients aged 12 years and older and atopic dermatitis and asthma in some patients as young as age 6 months.
As the roster of approved and off-label indications grows, skin specialists said, pediatricians and other primary care providers should become familiar with the drug – given the increasing likelihood that their patients may be taking the medication.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration first approved dupilumab in 2017 for eczema and has continued to add new treatment indications, the most recent being for prurigo nodularis, in 2022. Sanofi, which markets the drug with Regeneron, announced in April 2022 that some 430,000 patients worldwide were taking the drug – a figure it hoped to raise by 1.5 million by 2025.
A well-tolerated – if expensive – drug
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor alpha-antagonist biologic, blocks both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, Marlys Fassett, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, told this news organization.
Dr. Fassett said she prescribes the drug off label for chronic idiopathic urticaria, including in older patients, and finds that the side effects in older patients are similar to those in younger people. The medication costs $36,000 per year, although some patients can get it more cheaply.
“Dupixent is a super-safe drug because it doesn’t immunosuppress any other part of the immune system, so you still have good antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal immunity,” she added. “That makes perfect sense as a biological mechanism, and it’s been found safe in clinical trials.”
Case reports of potential adverse reactions to dupilumab have included ocular surface disease, lichen planus, and rash on the face and neck.
“We’re still learning about complications and are watching patients carefully,” said Marissa J. Perman, MD, section chief of dermatology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Many people with atopic dermatitis also have other allergic conditions, such as contact dermatitis, asthma, prurigo nodularis, allergic rhinitis, and seasonal allergies. Each of these conditions has a pathway that depends on IL-4 receptors, Dr. Fassett said.
“It’s amazing how many conditions Dupixent improves. Sometimes we prescribe on-label Dupixent for atopic dermatitis, and inadvertently, the drug also improves that patient’s other, off-label conditions,” Dr. Fassett said. “I think that’s the best evidence that Dupixent works in these off-label cases.”
Lindsay C. Strowd, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said she uses off-label dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and intense pruritus of unknown etiology.
“And several times I have treated drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, a rare adverse drug reaction that causes a rash and eosinophilia,” Dr. Strowd added.
Tissa Hata, MD, professor of medicine and clinical service chief at the University of California, San Diego, mainly treats elderly patients. She uses dupilumab to treat bullous pemphigoid and chronic pruritus. “There have been reports of using Dupixent to treat adult alopecia areata, chronic urticaria, localized scleroderma, and even keloids,” she told this news organization.
As a pediatric dermatologist, Dr. Perman treats children with atopic dermatitis as young as 3 months of age. She also uses dupilumab for alopecia areata, graft vs. host disease, and pruritus not otherwise specified.
Conjunctivitis and facial redness are two side effects Dr. Fassett sometimes sees with dupilumab. They occur similarly with all conditions and in all age groups. “We don’t know why they occur, and we don’t always know how to alleviate them,” she said. “So a small number of patients stop using Dupixent because they can’t tolerate those two side effects.
“We’re not worried about infection risk,” Dr. Fassett said. “Your patients may have heard of dupilumab as an immunosuppressant, but its immunosuppression is very focused. You can reassure them that they’re not at increased risk for viral or bacterial infections when they’re on this drug.”
“I don’t think there are any different safety signals to watch for with on-label vs. off-label Dupixent use,” Dr. Strowd added. “In general, the medicine is very safe.”
Dr. Hata said she is impressed with dupilumab’s safety in her elderly patients. All her patients older than 85 years who have taken the drug for bullous pemphigoid have tolerated it well, she said.
“Dupixent seems to be a safe alternative for elderly patients with pruritus because they often cannot tolerate sedating antihistamines due to the risk of falling,” Dr. Hata said. “And UV therapy may be difficult for elderly patients due to problems with transport.”
Although some of Dr. Hata’s elderly patients with atopic dermatitis have discontinued use of the drug after developing conjunctivitis, none taking the drug off label have discontinued it because of side effects, she noted.
“Dupixent manages the condition, but it is not a cure,” Dr. Fassett noted. “Based on the current data, we think it’s safe and effective to take long term, potentially for life.”
Making injections less bothersome
Dupilumab is injected subcutaneously from a single-dose prefilled syringe or a prefilled pen (syringe hidden in an opaque sheath), typically in the thigh, arm, abdomen, or buttocks. According to Sanofi and Regeneron, patients receive dupilumab injections every 2 to 4 weeks in doses based on their age and weight.
“The medication is somewhat viscous, so taking the syringe or pen out of the refrigerator ahead of time to warm it up can make the experience less painful,” Dr. Strowd advised. “For pediatric patients, I sometimes prescribe topical lidocaine applied 30 minutes before injection.”
Dr. Hata suggested icing the skin prior to injecting or distracting the patient by tapping a different area of the skin.
For her pediatric patients, Dr. Perman said she uses “lots of distraction, EMLA cream, and having one person hold the child while a second person injects.”
Clinic and pharmacy staff may show patients how to inject properly, Dr. Fassett added; and the product website provides injection tutorials.
Off-label dupixent can be expensive, difficult to obtain
The list price per injection, regardless of dose, is around $1,800. But according to the company’s website, most patients have health insurance or qualify for other assistance, so “very few patients pay the list price.”
Even so, “due to cost and insurance coverage hurdles, obtaining Dupixent for off-label use can be difficult,” Dr. Strowd said.
“In academic medicine, we can obtain drugs for our patients that community doctors may not get approval for,” Dr. Fassett added. “Community doctors can use information in the medical literature and in news articles to press insurance companies to spend money to provide their patients with Dupixent.”
The experts who commented have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lanolin: The 2023 American Contact Dermatitis Society Allergen of the Year
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
Lanolin was announced as the Allergen of the Year by the American Contact Dermatitis Society in March 2023.1 However, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) to lanolin remains a matter of fierce debate among dermatologists. Herein, we discuss this important contact allergen, emphasizing the controversy behind its allergenicity and nuances to consider when patch testing.
What is Lanolin?
Lanolin is a greasy, yellow, fatlike substance derived from the sebaceous glands of sheep. It is extracted from wool using an intricate process of scouring with dilute alkali, centrifuging, and refining with hot alkali and bleach.2 It is comprised of a complex mixture of esters, alcohols, sterols, fatty acids, lactose, and hydrocarbons.3
The hydrophobic property of lanolin helps sheep shed water from their coats.3 In humans, this hydrophobicity benefits the skin by retaining moisture already present in the epidermis. Lanolin can hold as much as twice its weight in water and may reduce transepidermal water loss by 20% to 30%.4-6 In addition, lanolin maintains tissue breathability, which supports proper gas exchange, promoting wound healing and protecting against infection.3,7
Many personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, and topical medicaments contain lanolin, particularly products marketed to help restore dry cracked skin. The range of permitted concentrations of lanolin in over-the-counter products in the United States is 12.5% to 50%.3 Lanolin also may be found in industrial goods. The Table provides a comprehensive list of common items that may contain lanolin.1,3,8,9
A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing?
Despite its benefits, lanolin is a potential source of ACD. The first reported positive patch test (PPT) to lanolin worldwide was in the late 1920s.10 Subsequent cases of ACD to lanolin were described over the next 30 years, reaching a peak of recognition in the latter half of the 20th century with rates of PPT ranging from 0% to 7.4%, though the patient population and lanolin patch-test formulation used differed across studies.9 The North American Contact Dermatitis Group observed that 3.3% (1431/43,691) of patients tested from 2001 to 2018 had a PPT to either lanolin alcohol 30% in petrolatum (pet) or Amerchol L101 (10% lanolin alcohol dissolved in mineral oil) 50% pet.11 Compared to patients referred for patch testing, the prevalence of contact allergy to lanolin is lower in the general population; 0.4% of the general population in Europe (N=3119) tested positive to wool alcohols 1.0 mg/cm2 on the thin-layer rapid use Epicutaneous (TRUE) test.12
Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin is unrelated to an allergy to wool itself, which probably does not exist, though wool is well known to cause irritant contact dermatitis, particularly in atopic individuals.13

Who Is at Risk for Lanolin Allergy?
In a recent comprehensive review of lanolin allergy, Jenkins and Belsito1 summarized 4 high-risk subgroups of patients for the development of lanolin contact allergy: stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis (AD), and perianal/genital dermatitis. These chronic inflammatory skin conditions may increase the risk for ACD to lanolin via increased exposure in topical therapies and/or increased allergen penetration through an impaired epidermal barrier.14-16 Demographically, older adults and children are at-risk groups, likely secondary to the higher prevalence of stasis dermatitis/leg ulcers in the former group and AD in the latter.1
Lanolin Controversies
The allergenicity of lanolin is far from straightforward. In 1996, Wolf17 first described the “lanolin paradox,” modeled after the earlier “paraben paradox” described by Fisher.18 There are 4 clinical phenomena of the lanolin paradox17:
- Lanolin generally does not cause contact allergy when found in PCPs but may cause ACD when found in topical medicaments.
- Some patients can use lanolin-containing PCPs on healthy skin without issue but will develop ACD when a lanolin-containing topical medicament is applied to inflamed skin. This is because inflamed skin is more easily sensitized.
- False-negative patch test reactions to pure lanolin may occur. Since Wolf’s17 initial description of the paradox, free alcohols of lanolin have been found to be its principal allergen, though it also is possible that oxidation of lanolin could generate additional allergenic substances.1
- Patch testing with wool alcohol 30% can generate both false-negative and false-positive results.
At one extreme, Kligman19 also was concerned about false-positive reactions to lanolin, describing lanolin allergy as a myth attributed to overzealous patch testing and a failure to appreciate the limitations of this diagnostic modality. Indeed, just having a PPT to lanolin (ie, contact allergy) does not automatically translate to a relevant ACD,1 and determining the clinical relevance of a PPT is of utmost importance. In 2001, Wakelin et al20 reported that the majority (71% [92/130]) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% or 100% pet showed current clinical relevance. Data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group in 2009 and in 2022 were similar, with 83.4% (529/634) of positive reactions to lanolin alcohol 30% pet and 86.5% (1238/1431) of positive reactions to Amerchol L101 50% pet classified as current clinical relevance.11,21 These findings demonstrate that although lanolin may be a weak sensitizer, a PPT usually represents a highly relevant cause of dermatitis.
Considerations for Patch Testing
Considering Wolf’s17 claim that even pure lanolin is not an appropriate formulation to use for patch testing due to the risk for inaccurate results, you might now be wondering which preparation should be used. Mortensen22 popularized another compound, Amerchol L101, in 1979. In this small study of 60 patients with a PPT to lanolin and/or its derivatives, the highest proportion (37% [22/60]) were positive to Amerchol L101 but negative to wool alcohol 30%, suggesting the need to test to more than one preparation simultaneously.22 In a larger study by Miest et al,23 3.9% (11/268) of patients had a PPT to Amerchol L101 50% pet, whereas only 1.1% (3/268) had a PPT to lanolin alcohol 30% pet. This highlighted the importance of including Amerchol L101 when patch testing because it was thought to capture more positive results; however, some studies suggest that Amerchol L101 is not superior at predicting lanolin contact allergy vs lanolin alcohol 30% pet. The risk for an irritant reaction when patch testing with Amerchol L101 should be considered due to its mineral oil component.24
Although there is no universal consensus to date, some investigators suggest patch testing both lanolin alcohol 30% pet and Amerchol L101 50% pet simultaneously.1 The TRUE test utilizes 1000 µg/cm2 of wool alcohols, while the North American 80 Comprehensive Series and the American Contact Dermatitis Society Core 90 Series contain Amerchol L101 50% pet. Patch testing to the most allergenic component of lanolin—the free fatty alcohols (particularly alkane-α,β-diols and alkane-α,ω-diols)—has been suggested,1 though these formulations are not yet commercially available.
When available, the patient’s own lanolin-containing PCPs should be tested.1 Performing a repeat open application test (ROAT) to a lanolin-containing product also may be highly useful to distinguish weak-positive from irritant patch test reactions and to determine if sensitized patients can tolerate lanolin-containing products on intact skin. To complete a ROAT, a patient should apply the suspected leave-on product to a patch of unaffected skin (classically the volar forearm) twice daily for at least 10 days.25 If the application site is clear after 10 days, the patient is unlikely to have ACD to the product in question. Compared to patch testing, ROAT more accurately mimics a true use situation, which is particularly important for lanolin given its tendency to preferentially impact damaged or inflamed skin while sparing healthy skin.
Alternatives to Lanolin
Patients with confirmed ACD to lanolin may use plain petrolatum, a safe and inexpensive substitute with equivalent moisturizing efficacy. It can reduce transepidermal water loss by more than 98%,4 with essentially no risk for ACD. Humectants such as glycerin, sorbitol, and α-hydroxy acids also have moisturizing properties akin to those of lanolin. In addition, some oils may provide benefit to patients with chronic skin conditions. Sunflower seed oil and extra virgin coconut oil have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and barrier repair properties.26,27 Allergic contact dermatitis to these oils rarely, if ever, occurs.28
Final Interpretation
Lanolin is a well-known yet controversial contact allergen that is widely used in PCPs, cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial goods. Lanolin ACD preferentially impacts patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, AD, and perianal/genital dermatitis. Patch testing with more than one lanolin formulation, including lanolin alcohol 30% pet and/or Amerchol L101 50% pet, as well as testing the patient’s own products may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. In cases of ACD to lanolin, an alternative agent, such as plain petrolatum, may be used.
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
- Jenkins BA, Belsito DV. Lanolin. Dermatitis. 2023;34:4-12. doi:10.1089/derm.2022.0002
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Annotation Record for LANOLIN, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Accessed July 21, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/1817
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary lanolin. Accessed July 17, 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lanolin
- Purnamawati S, Indrastuti N, Danarti R, et al. the role of moisturizers in addressing various kinds of dermatitis: a review. Clin Med Res. 2017;15:75-87. doi:10.3121/cmr.2017.1363
- Sethi A, Kaur T, Malhotra SK, et al. Moisturizers: the slippery road. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:279-287. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.182427
- Souto EB, Yoshida CMP, Leonardi GR, et al. Lipid-polymeric films: composition, production and applications in wound healing and skin repair. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1199. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13081199
- Rüther L, Voss W. Hydrogel or ointment? comparison of five different galenics regarding tissue breathability and transepidermal water loss. Heliyon. 2021;7:E06071. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06071
- Zirwas MJ. Contact alternatives and the internet. Dermatitis. 2012;23:192-194. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e31826ea0d2
- Lee B, Warshaw E. Lanolin allergy: history, epidemiology, responsible allergens, and management. Dermatitis. 2008;19:63-72.
- Ramirez M, Eller JJ. The patch test in contact dermatitis. Allergy. 1929;1:489-493.
- Silverberg JI, Patel N, Warshaw EM, et al. Lanolin allergic reactions: North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2001 to 2018. Dermatitis. 2022;33:193-199. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000871
- Diepgen TL, Ofenloch RF, Bruze M, et al. Prevalence of contact allergy in the general population in different European regions. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:319-329. doi:10.1111/bjd.14167
- Zallmann M, Smith PK, Tang MLK, et al. Debunking the myth of wool allergy: reviewing the evidence for immune and non-immune cutaneous reactions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:906-915. doi:10.2340/00015555-2655
- Yosipovitch G, Nedorost ST, Silverberg JI, et al. Stasis dermatitis: an overview of its clinical presentation, pathogenesis, and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:275-286. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00753-5
- Johnson H, Novack DE, Adler BL, et al. Can atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis coexist? Cutis. 2022;110:139-142. doi:10.12788/cutis.0599
- Gilissen L, Schollaert I, Huygens S, et al. Iatrogenic allergic contact dermatitis in the (peri)anal and genital area. Contact Dermatitis. 2021;84:431-438. doi:10.1111/cod.13764
- Wolf R. The lanolin paradox. Dermatology. 1996;192:198-202. doi:10.1159/000246365
- Fisher AA. The paraben paradox. Cutis. 1973;12:830-832.
- Kligman AM. The myth of lanolin allergy. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:103-107. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05856.x
- Wakelin SH, Smith H, White IR, et al. A retrospective analysis of contact allergy to lanolin. Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:28-31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04277.x
- Warshaw EM, Nelsen DD, Maibach HI, et al. Positive patch test reactions to lanolin: cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis group, 1994 to 2006. Dermatitis. 2009;20:79-88.
- Mortensen T. Allergy to lanolin. Contact Dermatitis. 1979;5:137-139. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1979.tb04824.x
- Miest RY, Yiannias JA, Chang YH, et al. Diagnosis and prevalence of lanolin allergy. Dermatitis. 2013;24:119-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0b013e3182937aa4
- Knijp J, Bruynzeel DP, Rustemeyer T. Diagnosing lanolin contact allergy with lanolin alcohol and Amerchol L101. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80:298-303. doi:10.1111/cod.13210
- Amsler E, Assier H, Soria A, et al. What is the optimal duration for a ROAT? the experience of the French Dermatology and Allergology group (DAG). Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:170-175. doi:10.1111/cod.14118
- Msika P, De Belilovsky C, Piccardi N, et al. New emollient with topical corticosteroid-sparing effect in treatment of childhood atopic dermatitis: SCORAD and quality of life improvement. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:606-612. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00783.x
- Lio PA. Alternative therapies in atopic dermatitis care: part 2. Pract Dermatol. July 2011:48-50.
- Karagounis TK, Gittler JK, Rotemberg V, et al. Use of “natural” oils for moisturization: review of olive, coconut, and sunflower seed oil. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:9-15. doi:10.1111/pde.13621
Practice Points
- Lanolin is a common ingredient in personal care products (PCPs), cosmetics, topical medicaments, and industrial materials.
- Allergic contact dermatitis to lanolin appears to be most common in patients with stasis dermatitis, chronic leg ulcers, atopic dermatitis, and perianal/genital dermatitis.
- There is no single best lanolin patch test formulation. Patch testing and repeat open application testing to PCPs containing lanolin also may be of benefit.
Skin reactions common at insulin pump infusion sites
new research suggests.
Insulin pump use is increasingly common, but many patients experience infusion-site failure that in some cases leads to discontinuation. In a novel investigation, researchers at the University of Washington, Seattle, used biopsies and noninvasive imaging to compare insulin pump sites with control sites in 30 patients. Several differences were found at pump sites in comparison with control sites, including fibrosis, inflammation, eosinophils, and increased vessel density.
“These findings support allergic sensitization as a potentially common reaction at [insulin pump] sites. The leading candidates causing this include insulin preservatives, plastic materials, and adhesive glue used in device manufacturing,” wrote Andrea Kalus, MD, of the university’s dermatology division, and colleagues. The findings were published recently in Diabetes Care.
The inflammatory response, they wrote, “may result in tissue changes responsible for the infusion-site failures seen frequently in clinical practice.”
Such infusion site problems represent an “Achilles heel” of these otherwise highly beneficial devices, lead author Irl Hirsch, MD, professor of medicine in the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and nutrition, said in a statement. “It doesn’t really matter how good the technology is. We still don’t understand what is happening with the infusion sites, much less to [be able to] fix it.”
Significant differences between pump and nonpump sites
In the cross-sectional study, Dr. Kalus and colleagues used noninvasive optical coherence tomography (OCT) immediately prior to performing punch biopsies at three sites: the site currently in active use, the “recovery site” used 3-5 days prior to the procedures, and control sites never used for pump infusion. Punch biopsies were also performed at those sites.
The mean age of the patients was 48.3 years, the mean diabetes duration was 30.4 years, and the mean duration of pump use was 15.8 years. Nearly all patients (93.3%) reported itchiness at the site, and 76.7% reported skin redness.
Of the 25 patients for whom OCT imaging was successful, statistical analysis showed significant differences in vascular area density and the optical attenuation coefficient, a surrogate for skin inflammation, between the pump and control sites and between recovery sites and current pump sites. The greater vessel density is likely a result of injury and repair related to catheter insertion, the authors said.
In the biopsy samples, both current and recovery sites showed increased fibrosis, fibrin, inflammation, fat necrosis, vascularity, and eosinophils, compared with the control sites, but no significant differences were found between current and recovery sites.
Eosinophils: ‘The most surprising histologic finding’
Eosinophils were found in 73% of skin biopsy specimens from current sites and in 75% of specimens from recovery sites, compared with none from the control sites (for both, P < .01). In all study participants, eosinophils were found in at least one current and/or recovery infusion site deep in the dermis near the interface with fat. The number of eosinophils ranged from 0 to 31 per high-power field, with a median of 4.
The number of eosinophils didn’t vary by type of insulin or brand of pump, but higher counts were seen in those who had used pumps for less than 10 years, compared with more than 20 years (P = .02).
The prevalence and degree of eosinophils were “the most surprising histologic finding,” the authors wrote, adding that “eosinophils are not typically present as a component of resident inflammatory cells in the skin.”
While eosinophils may be present in normal wound healing, “the absolute number and density of eosinophil in these samples support a delayed-type hypersensitivity response, which is typically observed between 2 and 7 days after exposure to an allergen. ... Eosinophils are often correlated with symptoms of itchiness and likely explain the high percentage of participants who reported itchiness in this study,” Dr. Kalus and colleagues wrote.
Correlation found between inflammation and glycemic control
All participants used the Dexcom G6 continuous glucose monitor as part of their usual care. Inflammation scores were positively correlated with insulin dose (P = .009) and were negatively correlated with time in range (P = .01).
No other OCT or biopsy findings differed by duration of pump use, previous use of animal insulin, or type of insulin.
The reason for these findings is unclear, Dr. Hirsch said. “How much was the catheter or the insulin causing the irritation around the sites? How much was it from the preservatives, or is this because of the insulin pump itself? All these questions need to be answered in future studies. ... The real goal of all of this is to minimize skin damage and improve the experience for our patients.”
The study was funded by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. Dr. Hirsch reported grants and contracts from Insulet, Medtronic, and Dexcom outside the submitted work; consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Lifescan, and Hagar outside the submitted work; and honoraria for lectures, presentations, participation on speaker’s bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events as section editor for UpToDate outside the submitted work. Dr. Kalus has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Insulin pump use is increasingly common, but many patients experience infusion-site failure that in some cases leads to discontinuation. In a novel investigation, researchers at the University of Washington, Seattle, used biopsies and noninvasive imaging to compare insulin pump sites with control sites in 30 patients. Several differences were found at pump sites in comparison with control sites, including fibrosis, inflammation, eosinophils, and increased vessel density.
“These findings support allergic sensitization as a potentially common reaction at [insulin pump] sites. The leading candidates causing this include insulin preservatives, plastic materials, and adhesive glue used in device manufacturing,” wrote Andrea Kalus, MD, of the university’s dermatology division, and colleagues. The findings were published recently in Diabetes Care.
The inflammatory response, they wrote, “may result in tissue changes responsible for the infusion-site failures seen frequently in clinical practice.”
Such infusion site problems represent an “Achilles heel” of these otherwise highly beneficial devices, lead author Irl Hirsch, MD, professor of medicine in the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and nutrition, said in a statement. “It doesn’t really matter how good the technology is. We still don’t understand what is happening with the infusion sites, much less to [be able to] fix it.”
Significant differences between pump and nonpump sites
In the cross-sectional study, Dr. Kalus and colleagues used noninvasive optical coherence tomography (OCT) immediately prior to performing punch biopsies at three sites: the site currently in active use, the “recovery site” used 3-5 days prior to the procedures, and control sites never used for pump infusion. Punch biopsies were also performed at those sites.
The mean age of the patients was 48.3 years, the mean diabetes duration was 30.4 years, and the mean duration of pump use was 15.8 years. Nearly all patients (93.3%) reported itchiness at the site, and 76.7% reported skin redness.
Of the 25 patients for whom OCT imaging was successful, statistical analysis showed significant differences in vascular area density and the optical attenuation coefficient, a surrogate for skin inflammation, between the pump and control sites and between recovery sites and current pump sites. The greater vessel density is likely a result of injury and repair related to catheter insertion, the authors said.
In the biopsy samples, both current and recovery sites showed increased fibrosis, fibrin, inflammation, fat necrosis, vascularity, and eosinophils, compared with the control sites, but no significant differences were found between current and recovery sites.
Eosinophils: ‘The most surprising histologic finding’
Eosinophils were found in 73% of skin biopsy specimens from current sites and in 75% of specimens from recovery sites, compared with none from the control sites (for both, P < .01). In all study participants, eosinophils were found in at least one current and/or recovery infusion site deep in the dermis near the interface with fat. The number of eosinophils ranged from 0 to 31 per high-power field, with a median of 4.
The number of eosinophils didn’t vary by type of insulin or brand of pump, but higher counts were seen in those who had used pumps for less than 10 years, compared with more than 20 years (P = .02).
The prevalence and degree of eosinophils were “the most surprising histologic finding,” the authors wrote, adding that “eosinophils are not typically present as a component of resident inflammatory cells in the skin.”
While eosinophils may be present in normal wound healing, “the absolute number and density of eosinophil in these samples support a delayed-type hypersensitivity response, which is typically observed between 2 and 7 days after exposure to an allergen. ... Eosinophils are often correlated with symptoms of itchiness and likely explain the high percentage of participants who reported itchiness in this study,” Dr. Kalus and colleagues wrote.
Correlation found between inflammation and glycemic control
All participants used the Dexcom G6 continuous glucose monitor as part of their usual care. Inflammation scores were positively correlated with insulin dose (P = .009) and were negatively correlated with time in range (P = .01).
No other OCT or biopsy findings differed by duration of pump use, previous use of animal insulin, or type of insulin.
The reason for these findings is unclear, Dr. Hirsch said. “How much was the catheter or the insulin causing the irritation around the sites? How much was it from the preservatives, or is this because of the insulin pump itself? All these questions need to be answered in future studies. ... The real goal of all of this is to minimize skin damage and improve the experience for our patients.”
The study was funded by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. Dr. Hirsch reported grants and contracts from Insulet, Medtronic, and Dexcom outside the submitted work; consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Lifescan, and Hagar outside the submitted work; and honoraria for lectures, presentations, participation on speaker’s bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events as section editor for UpToDate outside the submitted work. Dr. Kalus has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Insulin pump use is increasingly common, but many patients experience infusion-site failure that in some cases leads to discontinuation. In a novel investigation, researchers at the University of Washington, Seattle, used biopsies and noninvasive imaging to compare insulin pump sites with control sites in 30 patients. Several differences were found at pump sites in comparison with control sites, including fibrosis, inflammation, eosinophils, and increased vessel density.
“These findings support allergic sensitization as a potentially common reaction at [insulin pump] sites. The leading candidates causing this include insulin preservatives, plastic materials, and adhesive glue used in device manufacturing,” wrote Andrea Kalus, MD, of the university’s dermatology division, and colleagues. The findings were published recently in Diabetes Care.
The inflammatory response, they wrote, “may result in tissue changes responsible for the infusion-site failures seen frequently in clinical practice.”
Such infusion site problems represent an “Achilles heel” of these otherwise highly beneficial devices, lead author Irl Hirsch, MD, professor of medicine in the division of metabolism, endocrinology, and nutrition, said in a statement. “It doesn’t really matter how good the technology is. We still don’t understand what is happening with the infusion sites, much less to [be able to] fix it.”
Significant differences between pump and nonpump sites
In the cross-sectional study, Dr. Kalus and colleagues used noninvasive optical coherence tomography (OCT) immediately prior to performing punch biopsies at three sites: the site currently in active use, the “recovery site” used 3-5 days prior to the procedures, and control sites never used for pump infusion. Punch biopsies were also performed at those sites.
The mean age of the patients was 48.3 years, the mean diabetes duration was 30.4 years, and the mean duration of pump use was 15.8 years. Nearly all patients (93.3%) reported itchiness at the site, and 76.7% reported skin redness.
Of the 25 patients for whom OCT imaging was successful, statistical analysis showed significant differences in vascular area density and the optical attenuation coefficient, a surrogate for skin inflammation, between the pump and control sites and between recovery sites and current pump sites. The greater vessel density is likely a result of injury and repair related to catheter insertion, the authors said.
In the biopsy samples, both current and recovery sites showed increased fibrosis, fibrin, inflammation, fat necrosis, vascularity, and eosinophils, compared with the control sites, but no significant differences were found between current and recovery sites.
Eosinophils: ‘The most surprising histologic finding’
Eosinophils were found in 73% of skin biopsy specimens from current sites and in 75% of specimens from recovery sites, compared with none from the control sites (for both, P < .01). In all study participants, eosinophils were found in at least one current and/or recovery infusion site deep in the dermis near the interface with fat. The number of eosinophils ranged from 0 to 31 per high-power field, with a median of 4.
The number of eosinophils didn’t vary by type of insulin or brand of pump, but higher counts were seen in those who had used pumps for less than 10 years, compared with more than 20 years (P = .02).
The prevalence and degree of eosinophils were “the most surprising histologic finding,” the authors wrote, adding that “eosinophils are not typically present as a component of resident inflammatory cells in the skin.”
While eosinophils may be present in normal wound healing, “the absolute number and density of eosinophil in these samples support a delayed-type hypersensitivity response, which is typically observed between 2 and 7 days after exposure to an allergen. ... Eosinophils are often correlated with symptoms of itchiness and likely explain the high percentage of participants who reported itchiness in this study,” Dr. Kalus and colleagues wrote.
Correlation found between inflammation and glycemic control
All participants used the Dexcom G6 continuous glucose monitor as part of their usual care. Inflammation scores were positively correlated with insulin dose (P = .009) and were negatively correlated with time in range (P = .01).
No other OCT or biopsy findings differed by duration of pump use, previous use of animal insulin, or type of insulin.
The reason for these findings is unclear, Dr. Hirsch said. “How much was the catheter or the insulin causing the irritation around the sites? How much was it from the preservatives, or is this because of the insulin pump itself? All these questions need to be answered in future studies. ... The real goal of all of this is to minimize skin damage and improve the experience for our patients.”
The study was funded by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. Dr. Hirsch reported grants and contracts from Insulet, Medtronic, and Dexcom outside the submitted work; consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Lifescan, and Hagar outside the submitted work; and honoraria for lectures, presentations, participation on speaker’s bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events as section editor for UpToDate outside the submitted work. Dr. Kalus has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
Dyshidroticlike Contact Dermatitis and Paronychia Resulting From a Dip Powder Manicure
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.
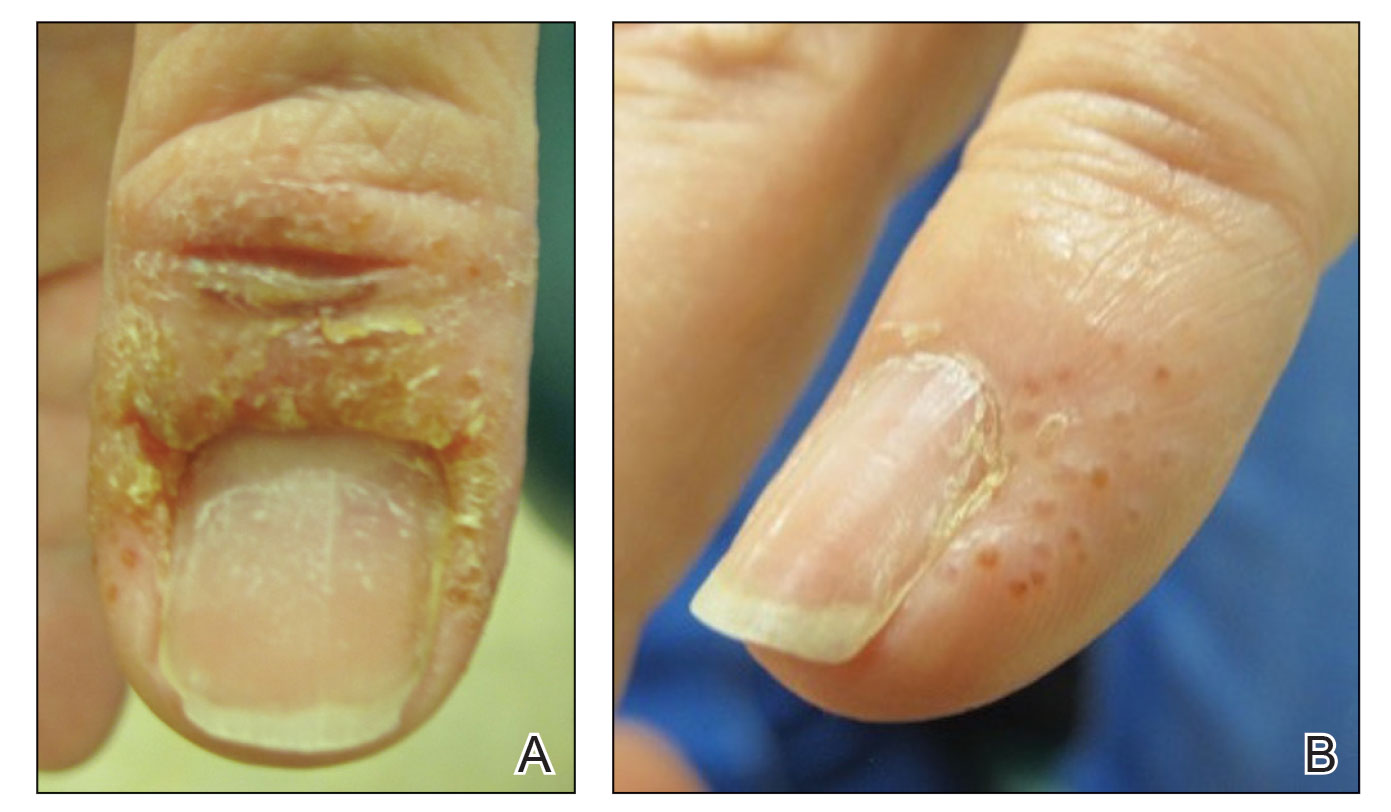
Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5
To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.

Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5

To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
To the Editor:
A 58-year-old woman presented to our dermatology clinic with a pruritic weeping eruption circumferentially on the distal digits of both hands of 5 weeks’ duration. The patient disclosed that she had been receiving dip powder manicures at a local nail salon approximately every 2 weeks over the last 3 to 6 months. She had received frequent acrylic nail extensions over the last 8 years prior to starting the dip powder manicures. Physical examination revealed well-demarcated eczematous plaques involving the lateral and proximal nail folds of the right thumb with an overlying serous crust and loss of the cuticle (Figure 1A). Erythematous plaques with firm deep-seated microvesicles also were present on the other digits, distributed distal to the distal interphalangeal joints (Figure 1B). She was diagnosed with dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia. Treatment included phenol 1.5% colorless solution and clobetasol ointment 0.05% for twice-daily application to the affected areas. The patient also was advised to stop receiving manicures. At 1-month follow-up, the paronychia had resolved and the dermatitis had nearly resolved.

Dip powder manicures use a wet adhesive base coat with acrylic powder and an activator topcoat to initiate a chemical reaction that hardens and sets the nail polish. The colored powder typically is applied by dipping the digit up to the distal interphalangeal joint into a small container of loose powder and then brushing away the excess (Figure 2). Acrylate, a chemical present in dip powders, is a known allergen and has been associated with the development of allergic contact dermatitis and onychodystrophy in patients after receiving acrylic and UV-cured gel polish manicures.1,2 Inadequate sanitation practices at nail salons also have been associated with infection transmission.3,4 Additionally, the news media has covered the potential risk of infection due to contamination from reused dip manicure powder and the use of communal powder containers.5

To increase clinical awareness of the dip manicure technique, we describe the presentation and successful treatment of dyshidroticlike contact dermatitis and paronychia that occurred in a patient after she received a dip powder manicure. Dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and frequency.
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
- Baran R. Nail cosmetics: allergies and irritations. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3:547-555.
- Chen AF, Chimento SM, Hu S, et al. Nail damage from gel polish manicure. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:27-29.
- Schmidt AN, Zic JA, Boyd AS. Pedicure-associated Mycobacterium chelonae infection in a hospitalized patient. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E248-E250.
- Sniezek PJ, Graham BS, Busch HB, et al. Rapidly growing mycobacterial infections after pedicures. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:629-634.
- Joseph T. You could be risking an infection with nail dipping. NBC Universal Media, LLC. Updated July 11, 2019. Accessed June 7, 2023. https://www.nbcmiami.com/news/local/You-Could-Be-Risking-an-Infection-with-Nail-Dipping-512550372.html
Practice Points
- Manicures performed at nail salons have been associated with the development of paronychia due to inadequate sanitation practices and contact dermatitis caused by acrylates present in nail polish.
- The dip powder manicure is a relatively new manicure technique. The distribution of dermatoses and infection limited to the distal phalanges will present in patients more frequently as dip powder manicures continue to increase in popularity and are performed more frequently.
Oval Brown Plaque on the Palm
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.
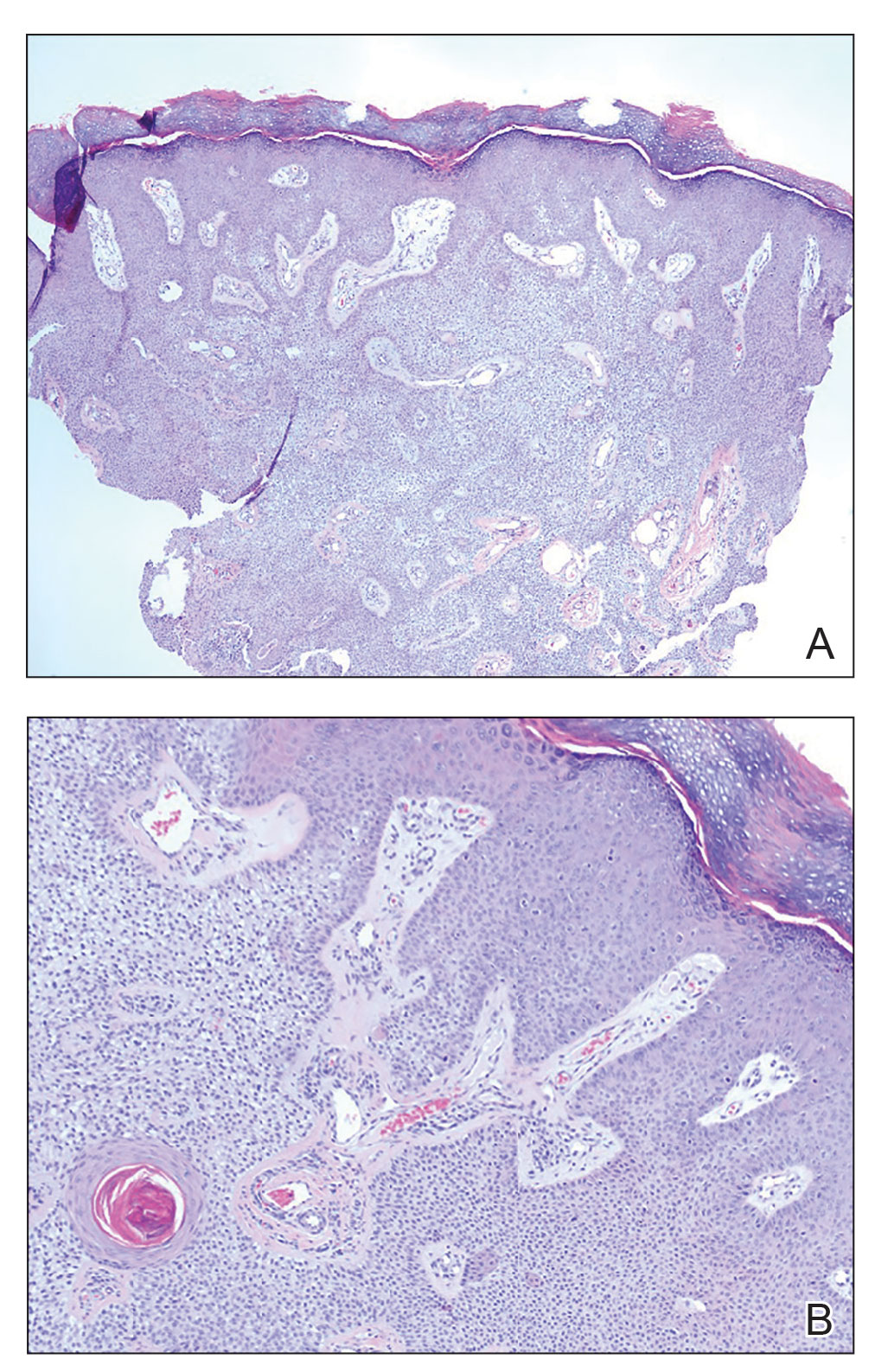
Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
A 43-year-old woman presented with a painful lesion on the palm of 30 years’ duration that had grown in size. Physical examination revealed an oval, brown, lobulated plaque with a hyperkeratotic rim on the left palm. She reported bleeding and pain. A shallow cup-shaped depression was noted within the plaque. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed.
Enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis linked to dupilumab use for atopic dermatitis
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY
Contact allergens lurk in diabetes devices
in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Advanced technologies used for the management of diabetes fall into three main categories, said Dr. Chen, of the department of dermatology, Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, which are worn on the body, collect glucose measurements. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices are attached to the body via an infusion set and are now available as tubing-free patch pumps that are attached directly to the skin via a catheter. Glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems combine the sensing and delivery features of the other two types of devices.
Once thought to be rare, reports of skin complications related to diabetes devices have been increasing in recent years, she said. Some reports suggest that at any given time, skin complications may affect as many as one quarter to one half of patients who use these devices, “so this is an important issue,” she emphasized. “Skin reactions are a major factor in device discontinuation, so we as clinicians need to be really proactive about treating these reactions.”
Risk factors for skin complications related to diabetes devices include sensitization to the adhesive used with the devices, as well as prolonged exposure to the device, Dr. Chen said. Younger age also appears to be a risk factor, as is a compromised skin barrier in the area where the device is used.
Unfortunately, obtaining details on the specific adhesives and the raw materials used in these devices, so as to customize patch testing, remains a challenge, she said. “Patch testing initially was often negative to commercially available allergens, even while patients were testing positive to pieces of device adhesive,” she noted.
Consider isobornyl acrylate
An article published in 2017 in Contact Dermatitis was “a major breakthrough” in that it identified isobornyl acrylate (IBOA) as an allergen in connection with the Freestyle Libre, a CGM device that was relatively new at the time. The finding was serendipitous, Dr. Chen said. A patient being treated for suspected allergic contact dermatitis in connection with use of a Freestyle Libre device was tested for IBOA accidentally, after the nurse administering the patch test thought that this was part of the standard acrylate series, she explained.
Subsequently, researchers identified 15 patients who had experienced reactions to the Freestyle Libre; 12 of 13 patients who were patch tested for IBOA tested positive. IBOA was found throughout the device, particularly where the top and bottom plastic components were connected, Dr. Chen said. This suggested that the IBOA was in the device housing and had diffused into the adhesive that attached the device to the skin.
An article published in 2018 in the Journal of Diabetes Science described three patients who developed severe allergic contact dermatitis from IBOA while using a CGM device, Dr. Chen said. The investigators confirmed that there were no reactions to the adhesive itself, again suggesting that IBOA had diffused into the adhesive from other parts of the device.
Although the authors were bound by a confidentiality agreement regarding the individual adhesive components, “the authors noted most of the acrylates in the adhesive were not present in commercially available acrylate series for patch testing,” she said.
IBOA, the ACDS’ Allergen of the Year in 2020, is common in sealants, glues, and adhesives, Dr. Chen said. Although IBOA had been reported infrequently as an allergen, it has now been identified as a “potential culprit” behind skin reactions in many diabetes devices, including CSII and CGM devices, she added.
In addition, N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA) is an allergen that has been identified in several diabetes devices and often occurs with IBOA in medical-grade UV-cured adhesives, Dr. Chen noted. Other allergens identified in diabetes devices include colophony, which is present in many adhesives, as well as other acrylates and epoxy resin.
Diabetes devices are constantly evolving. IBOA is no longer found in Freestyle Libre devices. It is important that clinicians stay up to date with the medical literature and advocate for partnership with device manufacturers, she emphasized.
Patch testing
When diabetes devices are suspected as the source of allergic contact dermatitis, a minimum of a baseline series that contains colophony at a concentration of 20% in petrolatum should be carried out, Dr. Chen said. Commercialized patch test trays, which include plastics, glues, acrylates, epoxy resins/isocyanates, and colophony derivatives, should be ideal. “Personal-care products should be included if they are potentially relevant,” she added.
Dr. Chen shared tables published in Contact Dermatitis in 2021 with examples of screening test series. She said to consider including screening for other allergens more recently discovered in diabetes devices, including 2,2’-methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) monoacrylate (MBPA) 1.5% pet; dipropylene glycol diacrylate (DPGDA) 0.1% pet; and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) 2% pet.
Testing for monomethyl ether of hydroquinone should also be considered; this may be included in the test preparations for IBOA and DMAA.
Management strategies
For patients who experience skin reactions to their diabetes devices, consideration may given to relocating the device to another area of skin or changing sensors more frequently, according to Dr. Chen.
For some patients, the reaction can be managed with corticosteroid cream, ointment, solution, or nasal spray. Topical antibiotics or topical antihistamines can be helpful, as can barrier dressings, solutions, or sprays, she said. The best solution is to change to a device that does not have the culprit allergen, “but that is difficult, since we don’t know what is in these devices,” she added. Good alternatives include the Eversense CGM device or devices that have been demonstrated not to contain IBOA, such as the Freestyle Libre 2 or the newer version of the Omnipod, an insulin delivery system
Looking ahead, Dr. Chen said that “mandatory labeling is needed, as devices with the same name may have different compositions, depending on the date of manufacture.” Allergens relevant to people with diabetes are constantly evolving, and many are still unidentified, so clinicians and manufacturers need to work together to identify the culprit allergens and their sources, she said.
Dr. Chen has served as principal investigator or subinvestigator for Amgen, AbbVie, and Sanofi Regeneron and as a consultant for Purity Brands.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Advanced technologies used for the management of diabetes fall into three main categories, said Dr. Chen, of the department of dermatology, Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, which are worn on the body, collect glucose measurements. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices are attached to the body via an infusion set and are now available as tubing-free patch pumps that are attached directly to the skin via a catheter. Glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems combine the sensing and delivery features of the other two types of devices.
Once thought to be rare, reports of skin complications related to diabetes devices have been increasing in recent years, she said. Some reports suggest that at any given time, skin complications may affect as many as one quarter to one half of patients who use these devices, “so this is an important issue,” she emphasized. “Skin reactions are a major factor in device discontinuation, so we as clinicians need to be really proactive about treating these reactions.”
Risk factors for skin complications related to diabetes devices include sensitization to the adhesive used with the devices, as well as prolonged exposure to the device, Dr. Chen said. Younger age also appears to be a risk factor, as is a compromised skin barrier in the area where the device is used.
Unfortunately, obtaining details on the specific adhesives and the raw materials used in these devices, so as to customize patch testing, remains a challenge, she said. “Patch testing initially was often negative to commercially available allergens, even while patients were testing positive to pieces of device adhesive,” she noted.
Consider isobornyl acrylate
An article published in 2017 in Contact Dermatitis was “a major breakthrough” in that it identified isobornyl acrylate (IBOA) as an allergen in connection with the Freestyle Libre, a CGM device that was relatively new at the time. The finding was serendipitous, Dr. Chen said. A patient being treated for suspected allergic contact dermatitis in connection with use of a Freestyle Libre device was tested for IBOA accidentally, after the nurse administering the patch test thought that this was part of the standard acrylate series, she explained.
Subsequently, researchers identified 15 patients who had experienced reactions to the Freestyle Libre; 12 of 13 patients who were patch tested for IBOA tested positive. IBOA was found throughout the device, particularly where the top and bottom plastic components were connected, Dr. Chen said. This suggested that the IBOA was in the device housing and had diffused into the adhesive that attached the device to the skin.
An article published in 2018 in the Journal of Diabetes Science described three patients who developed severe allergic contact dermatitis from IBOA while using a CGM device, Dr. Chen said. The investigators confirmed that there were no reactions to the adhesive itself, again suggesting that IBOA had diffused into the adhesive from other parts of the device.
Although the authors were bound by a confidentiality agreement regarding the individual adhesive components, “the authors noted most of the acrylates in the adhesive were not present in commercially available acrylate series for patch testing,” she said.
IBOA, the ACDS’ Allergen of the Year in 2020, is common in sealants, glues, and adhesives, Dr. Chen said. Although IBOA had been reported infrequently as an allergen, it has now been identified as a “potential culprit” behind skin reactions in many diabetes devices, including CSII and CGM devices, she added.
In addition, N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA) is an allergen that has been identified in several diabetes devices and often occurs with IBOA in medical-grade UV-cured adhesives, Dr. Chen noted. Other allergens identified in diabetes devices include colophony, which is present in many adhesives, as well as other acrylates and epoxy resin.
Diabetes devices are constantly evolving. IBOA is no longer found in Freestyle Libre devices. It is important that clinicians stay up to date with the medical literature and advocate for partnership with device manufacturers, she emphasized.
Patch testing
When diabetes devices are suspected as the source of allergic contact dermatitis, a minimum of a baseline series that contains colophony at a concentration of 20% in petrolatum should be carried out, Dr. Chen said. Commercialized patch test trays, which include plastics, glues, acrylates, epoxy resins/isocyanates, and colophony derivatives, should be ideal. “Personal-care products should be included if they are potentially relevant,” she added.
Dr. Chen shared tables published in Contact Dermatitis in 2021 with examples of screening test series. She said to consider including screening for other allergens more recently discovered in diabetes devices, including 2,2’-methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) monoacrylate (MBPA) 1.5% pet; dipropylene glycol diacrylate (DPGDA) 0.1% pet; and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) 2% pet.
Testing for monomethyl ether of hydroquinone should also be considered; this may be included in the test preparations for IBOA and DMAA.
Management strategies
For patients who experience skin reactions to their diabetes devices, consideration may given to relocating the device to another area of skin or changing sensors more frequently, according to Dr. Chen.
For some patients, the reaction can be managed with corticosteroid cream, ointment, solution, or nasal spray. Topical antibiotics or topical antihistamines can be helpful, as can barrier dressings, solutions, or sprays, she said. The best solution is to change to a device that does not have the culprit allergen, “but that is difficult, since we don’t know what is in these devices,” she added. Good alternatives include the Eversense CGM device or devices that have been demonstrated not to contain IBOA, such as the Freestyle Libre 2 or the newer version of the Omnipod, an insulin delivery system
Looking ahead, Dr. Chen said that “mandatory labeling is needed, as devices with the same name may have different compositions, depending on the date of manufacture.” Allergens relevant to people with diabetes are constantly evolving, and many are still unidentified, so clinicians and manufacturers need to work together to identify the culprit allergens and their sources, she said.
Dr. Chen has served as principal investigator or subinvestigator for Amgen, AbbVie, and Sanofi Regeneron and as a consultant for Purity Brands.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Advanced technologies used for the management of diabetes fall into three main categories, said Dr. Chen, of the department of dermatology, Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, which are worn on the body, collect glucose measurements. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices are attached to the body via an infusion set and are now available as tubing-free patch pumps that are attached directly to the skin via a catheter. Glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems combine the sensing and delivery features of the other two types of devices.
Once thought to be rare, reports of skin complications related to diabetes devices have been increasing in recent years, she said. Some reports suggest that at any given time, skin complications may affect as many as one quarter to one half of patients who use these devices, “so this is an important issue,” she emphasized. “Skin reactions are a major factor in device discontinuation, so we as clinicians need to be really proactive about treating these reactions.”
Risk factors for skin complications related to diabetes devices include sensitization to the adhesive used with the devices, as well as prolonged exposure to the device, Dr. Chen said. Younger age also appears to be a risk factor, as is a compromised skin barrier in the area where the device is used.
Unfortunately, obtaining details on the specific adhesives and the raw materials used in these devices, so as to customize patch testing, remains a challenge, she said. “Patch testing initially was often negative to commercially available allergens, even while patients were testing positive to pieces of device adhesive,” she noted.
Consider isobornyl acrylate
An article published in 2017 in Contact Dermatitis was “a major breakthrough” in that it identified isobornyl acrylate (IBOA) as an allergen in connection with the Freestyle Libre, a CGM device that was relatively new at the time. The finding was serendipitous, Dr. Chen said. A patient being treated for suspected allergic contact dermatitis in connection with use of a Freestyle Libre device was tested for IBOA accidentally, after the nurse administering the patch test thought that this was part of the standard acrylate series, she explained.
Subsequently, researchers identified 15 patients who had experienced reactions to the Freestyle Libre; 12 of 13 patients who were patch tested for IBOA tested positive. IBOA was found throughout the device, particularly where the top and bottom plastic components were connected, Dr. Chen said. This suggested that the IBOA was in the device housing and had diffused into the adhesive that attached the device to the skin.
An article published in 2018 in the Journal of Diabetes Science described three patients who developed severe allergic contact dermatitis from IBOA while using a CGM device, Dr. Chen said. The investigators confirmed that there were no reactions to the adhesive itself, again suggesting that IBOA had diffused into the adhesive from other parts of the device.
Although the authors were bound by a confidentiality agreement regarding the individual adhesive components, “the authors noted most of the acrylates in the adhesive were not present in commercially available acrylate series for patch testing,” she said.
IBOA, the ACDS’ Allergen of the Year in 2020, is common in sealants, glues, and adhesives, Dr. Chen said. Although IBOA had been reported infrequently as an allergen, it has now been identified as a “potential culprit” behind skin reactions in many diabetes devices, including CSII and CGM devices, she added.
In addition, N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA) is an allergen that has been identified in several diabetes devices and often occurs with IBOA in medical-grade UV-cured adhesives, Dr. Chen noted. Other allergens identified in diabetes devices include colophony, which is present in many adhesives, as well as other acrylates and epoxy resin.
Diabetes devices are constantly evolving. IBOA is no longer found in Freestyle Libre devices. It is important that clinicians stay up to date with the medical literature and advocate for partnership with device manufacturers, she emphasized.
Patch testing
When diabetes devices are suspected as the source of allergic contact dermatitis, a minimum of a baseline series that contains colophony at a concentration of 20% in petrolatum should be carried out, Dr. Chen said. Commercialized patch test trays, which include plastics, glues, acrylates, epoxy resins/isocyanates, and colophony derivatives, should be ideal. “Personal-care products should be included if they are potentially relevant,” she added.
Dr. Chen shared tables published in Contact Dermatitis in 2021 with examples of screening test series. She said to consider including screening for other allergens more recently discovered in diabetes devices, including 2,2’-methylenebis(6-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) monoacrylate (MBPA) 1.5% pet; dipropylene glycol diacrylate (DPGDA) 0.1% pet; and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) 2% pet.
Testing for monomethyl ether of hydroquinone should also be considered; this may be included in the test preparations for IBOA and DMAA.
Management strategies
For patients who experience skin reactions to their diabetes devices, consideration may given to relocating the device to another area of skin or changing sensors more frequently, according to Dr. Chen.
For some patients, the reaction can be managed with corticosteroid cream, ointment, solution, or nasal spray. Topical antibiotics or topical antihistamines can be helpful, as can barrier dressings, solutions, or sprays, she said. The best solution is to change to a device that does not have the culprit allergen, “but that is difficult, since we don’t know what is in these devices,” she added. Good alternatives include the Eversense CGM device or devices that have been demonstrated not to contain IBOA, such as the Freestyle Libre 2 or the newer version of the Omnipod, an insulin delivery system
Looking ahead, Dr. Chen said that “mandatory labeling is needed, as devices with the same name may have different compositions, depending on the date of manufacture.” Allergens relevant to people with diabetes are constantly evolving, and many are still unidentified, so clinicians and manufacturers need to work together to identify the culprit allergens and their sources, she said.
Dr. Chen has served as principal investigator or subinvestigator for Amgen, AbbVie, and Sanofi Regeneron and as a consultant for Purity Brands.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACDS 2023
Beware the hidden allergens in nutritional supplements
, Alison Ehrlich, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Allergens may be hidden in a range of supplement products, from colorings in vitamin C powders to some vitamins used in hair products and other products.
“In general, our patients do not tell us what supplements they are taking,” said Dr. Ehrlich, a dermatologist who practices in Washington, D.C. Antiaging, sleep, and weight loss/weight control supplements are among the most popular, she said.
Surveys have shown that many patients do not discuss supplement use with their health care providers, in part because they believe their providers would disapprove of supplement use, and patients are not educated about supplements, she said. “This is definitely an area that we should try to learn more about,” she added.
Current regulations regarding dietary supplements stem from the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, which defined dietary supplements as distinct from meals but regulated them as a category of food, not as medications. Dietary supplements can be vitamins, minerals, herbs, and extracts, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“There is not a lot of safety wrapped around how supplements come onto the market,” she explained. “It is not the manufacturer’s responsibility to test these products and make sure they are safe. When they get pulled off the market, it is because safety reports are getting back to the FDA.”
Consequently, a detailed history of supplement use is important, as it may reveal possible allergens as the cause of previously unidentified reactions, she said.
Dr. Ehrlich shared a case involving a patient who claimed to have had a reaction to a “Prevage-like” product that was labeled as a crepe repair cream. Listed among the product’s ingredients was idebenone, a synthetic version of the popular antioxidant known as Coenzyme Q.
Be wary of vitamins
Another potential source of allergy is vitamin C supplements, which became especially popular during the pandemic as people sought additional immune system support, Dr. Ehrlich noted. “What kind of vitamin C product our patients are taking is important,” she said. For example, some vitamin C powders contain coloring agents, such as carmine. Some also contain gelatin, which may cause an allergic reaction in individuals with alpha-gal syndrome, she added.
In general, water-soluble vitamins such as vitamins B1 to B9, B12, and C are more likely to cause an immediate reaction, Dr. Ehrlich said. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, are more likely to cause a delayed reaction of allergic contact dermatitis.
Dr. Ehrlich described some unusual reactions to vitamins that have been reported, including a systemic allergy associated with vitamin B1 (thiamine), burning mouth syndrome associated with vitamin B3 (nicotinate), contact urticaria associated with vitamin B5 (panthenol), systemic allergy and generalized ACD associated with vitamin E (tocopherol), and erythema multiforme–like ACD associated with vitamin K1.
Notably, vitamin B5 has been associated with ACD as an ingredient in hair products, moisturizers, and wound care products, as well as B-complex vitamins and fortified foods, Dr. Ehrlich said.
Herbs and spices can act as allergens as well. Turmeric is a spice that has become a popular supplement ingredient, she said. Turmeric and curcumin (found in turmeric) can be used as a dye for its yellow color as well as a flavoring but has been associated with allergic reactions. Another popular herbal supplement, ginkgo biloba, has been marketed as a product that improves memory and cognition. It is available in pill form and in herbal teas.
“It’s really important to think about what herbal products our patients are taking, and not just in pill form,” Dr. Ehrlich said. “We need to expand our thoughts on what the herbs are in.”
Consider food additives as allergens
Food additives, in the form of colorants, preservatives, or flavoring agents, can cause allergic reactions, Dr. Ehrlich noted.
The question of whether food-additive contact sensitivity has a role in the occurrence of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children remains unclear, she said. However, a study published in 2020 found that 62% of children with AD had positive patch test reactions to at least one food-additive allergen, compared with 20% of children without AD. The additives responsible for the most reactions were azorubine (24.4%); formic acid (15.6%); and carmine, cochineal red, and amaranth (13.3% for each).
Common colorant culprits in allergic reactions include carmine, annatto, tartrazine, and spices (such as paprika and saffron), Dr. Ehrlich said. Carmine is used in meat to prevent photo-oxidation and to preserve a red color, and it has other uses as well, she said. Carmine has been associated with ACD, AD flares, and immediate hypersensitivity. Annatto is used in foods, including processed foods, butter, and cheese, to provide a yellow color. It is also found in some lipsticks and has been associated with urticaria and angioedema, she noted.
Food preservatives that have been associated with allergic reactions include butylated hydroxyanisole and sulfites, Dr. Ehrlich said. Sulfites are used to prevent food from turning brown, and it may be present in dried fruit, fruit juice, molasses, pickled foods, vinegar, and wine.
Reports of ACD in response to sodium metabisulfite have been increasing, she noted. Other sulfite reactions may occur with exposure to other products, such as cosmetics, body washes, and swimming pool water, she said.
Awareness of allergens in supplements is important “because the number of our patients taking supplements for different reasons is increasing” and allergens in supplements could account for flares, Dr. Ehrlich said. Clinicians should encourage patients to tell them what supplements they use. Clinicians should review the ingredients in these supplements with their patients to identify potential allergens that may be causing reactions, she advised.
Dr. Ehrlich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, Alison Ehrlich, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Allergens may be hidden in a range of supplement products, from colorings in vitamin C powders to some vitamins used in hair products and other products.
“In general, our patients do not tell us what supplements they are taking,” said Dr. Ehrlich, a dermatologist who practices in Washington, D.C. Antiaging, sleep, and weight loss/weight control supplements are among the most popular, she said.
Surveys have shown that many patients do not discuss supplement use with their health care providers, in part because they believe their providers would disapprove of supplement use, and patients are not educated about supplements, she said. “This is definitely an area that we should try to learn more about,” she added.
Current regulations regarding dietary supplements stem from the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, which defined dietary supplements as distinct from meals but regulated them as a category of food, not as medications. Dietary supplements can be vitamins, minerals, herbs, and extracts, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“There is not a lot of safety wrapped around how supplements come onto the market,” she explained. “It is not the manufacturer’s responsibility to test these products and make sure they are safe. When they get pulled off the market, it is because safety reports are getting back to the FDA.”
Consequently, a detailed history of supplement use is important, as it may reveal possible allergens as the cause of previously unidentified reactions, she said.
Dr. Ehrlich shared a case involving a patient who claimed to have had a reaction to a “Prevage-like” product that was labeled as a crepe repair cream. Listed among the product’s ingredients was idebenone, a synthetic version of the popular antioxidant known as Coenzyme Q.
Be wary of vitamins
Another potential source of allergy is vitamin C supplements, which became especially popular during the pandemic as people sought additional immune system support, Dr. Ehrlich noted. “What kind of vitamin C product our patients are taking is important,” she said. For example, some vitamin C powders contain coloring agents, such as carmine. Some also contain gelatin, which may cause an allergic reaction in individuals with alpha-gal syndrome, she added.
In general, water-soluble vitamins such as vitamins B1 to B9, B12, and C are more likely to cause an immediate reaction, Dr. Ehrlich said. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, are more likely to cause a delayed reaction of allergic contact dermatitis.
Dr. Ehrlich described some unusual reactions to vitamins that have been reported, including a systemic allergy associated with vitamin B1 (thiamine), burning mouth syndrome associated with vitamin B3 (nicotinate), contact urticaria associated with vitamin B5 (panthenol), systemic allergy and generalized ACD associated with vitamin E (tocopherol), and erythema multiforme–like ACD associated with vitamin K1.
Notably, vitamin B5 has been associated with ACD as an ingredient in hair products, moisturizers, and wound care products, as well as B-complex vitamins and fortified foods, Dr. Ehrlich said.
Herbs and spices can act as allergens as well. Turmeric is a spice that has become a popular supplement ingredient, she said. Turmeric and curcumin (found in turmeric) can be used as a dye for its yellow color as well as a flavoring but has been associated with allergic reactions. Another popular herbal supplement, ginkgo biloba, has been marketed as a product that improves memory and cognition. It is available in pill form and in herbal teas.
“It’s really important to think about what herbal products our patients are taking, and not just in pill form,” Dr. Ehrlich said. “We need to expand our thoughts on what the herbs are in.”
Consider food additives as allergens
Food additives, in the form of colorants, preservatives, or flavoring agents, can cause allergic reactions, Dr. Ehrlich noted.
The question of whether food-additive contact sensitivity has a role in the occurrence of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children remains unclear, she said. However, a study published in 2020 found that 62% of children with AD had positive patch test reactions to at least one food-additive allergen, compared with 20% of children without AD. The additives responsible for the most reactions were azorubine (24.4%); formic acid (15.6%); and carmine, cochineal red, and amaranth (13.3% for each).
Common colorant culprits in allergic reactions include carmine, annatto, tartrazine, and spices (such as paprika and saffron), Dr. Ehrlich said. Carmine is used in meat to prevent photo-oxidation and to preserve a red color, and it has other uses as well, she said. Carmine has been associated with ACD, AD flares, and immediate hypersensitivity. Annatto is used in foods, including processed foods, butter, and cheese, to provide a yellow color. It is also found in some lipsticks and has been associated with urticaria and angioedema, she noted.
Food preservatives that have been associated with allergic reactions include butylated hydroxyanisole and sulfites, Dr. Ehrlich said. Sulfites are used to prevent food from turning brown, and it may be present in dried fruit, fruit juice, molasses, pickled foods, vinegar, and wine.
Reports of ACD in response to sodium metabisulfite have been increasing, she noted. Other sulfite reactions may occur with exposure to other products, such as cosmetics, body washes, and swimming pool water, she said.
Awareness of allergens in supplements is important “because the number of our patients taking supplements for different reasons is increasing” and allergens in supplements could account for flares, Dr. Ehrlich said. Clinicians should encourage patients to tell them what supplements they use. Clinicians should review the ingredients in these supplements with their patients to identify potential allergens that may be causing reactions, she advised.
Dr. Ehrlich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, Alison Ehrlich, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
Allergens may be hidden in a range of supplement products, from colorings in vitamin C powders to some vitamins used in hair products and other products.
“In general, our patients do not tell us what supplements they are taking,” said Dr. Ehrlich, a dermatologist who practices in Washington, D.C. Antiaging, sleep, and weight loss/weight control supplements are among the most popular, she said.
Surveys have shown that many patients do not discuss supplement use with their health care providers, in part because they believe their providers would disapprove of supplement use, and patients are not educated about supplements, she said. “This is definitely an area that we should try to learn more about,” she added.
Current regulations regarding dietary supplements stem from the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994, which defined dietary supplements as distinct from meals but regulated them as a category of food, not as medications. Dietary supplements can be vitamins, minerals, herbs, and extracts, Dr. Ehrlich said.
“There is not a lot of safety wrapped around how supplements come onto the market,” she explained. “It is not the manufacturer’s responsibility to test these products and make sure they are safe. When they get pulled off the market, it is because safety reports are getting back to the FDA.”
Consequently, a detailed history of supplement use is important, as it may reveal possible allergens as the cause of previously unidentified reactions, she said.
Dr. Ehrlich shared a case involving a patient who claimed to have had a reaction to a “Prevage-like” product that was labeled as a crepe repair cream. Listed among the product’s ingredients was idebenone, a synthetic version of the popular antioxidant known as Coenzyme Q.
Be wary of vitamins
Another potential source of allergy is vitamin C supplements, which became especially popular during the pandemic as people sought additional immune system support, Dr. Ehrlich noted. “What kind of vitamin C product our patients are taking is important,” she said. For example, some vitamin C powders contain coloring agents, such as carmine. Some also contain gelatin, which may cause an allergic reaction in individuals with alpha-gal syndrome, she added.
In general, water-soluble vitamins such as vitamins B1 to B9, B12, and C are more likely to cause an immediate reaction, Dr. Ehrlich said. Fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, are more likely to cause a delayed reaction of allergic contact dermatitis.
Dr. Ehrlich described some unusual reactions to vitamins that have been reported, including a systemic allergy associated with vitamin B1 (thiamine), burning mouth syndrome associated with vitamin B3 (nicotinate), contact urticaria associated with vitamin B5 (panthenol), systemic allergy and generalized ACD associated with vitamin E (tocopherol), and erythema multiforme–like ACD associated with vitamin K1.
Notably, vitamin B5 has been associated with ACD as an ingredient in hair products, moisturizers, and wound care products, as well as B-complex vitamins and fortified foods, Dr. Ehrlich said.
Herbs and spices can act as allergens as well. Turmeric is a spice that has become a popular supplement ingredient, she said. Turmeric and curcumin (found in turmeric) can be used as a dye for its yellow color as well as a flavoring but has been associated with allergic reactions. Another popular herbal supplement, ginkgo biloba, has been marketed as a product that improves memory and cognition. It is available in pill form and in herbal teas.
“It’s really important to think about what herbal products our patients are taking, and not just in pill form,” Dr. Ehrlich said. “We need to expand our thoughts on what the herbs are in.”
Consider food additives as allergens
Food additives, in the form of colorants, preservatives, or flavoring agents, can cause allergic reactions, Dr. Ehrlich noted.
The question of whether food-additive contact sensitivity has a role in the occurrence of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children remains unclear, she said. However, a study published in 2020 found that 62% of children with AD had positive patch test reactions to at least one food-additive allergen, compared with 20% of children without AD. The additives responsible for the most reactions were azorubine (24.4%); formic acid (15.6%); and carmine, cochineal red, and amaranth (13.3% for each).
Common colorant culprits in allergic reactions include carmine, annatto, tartrazine, and spices (such as paprika and saffron), Dr. Ehrlich said. Carmine is used in meat to prevent photo-oxidation and to preserve a red color, and it has other uses as well, she said. Carmine has been associated with ACD, AD flares, and immediate hypersensitivity. Annatto is used in foods, including processed foods, butter, and cheese, to provide a yellow color. It is also found in some lipsticks and has been associated with urticaria and angioedema, she noted.
Food preservatives that have been associated with allergic reactions include butylated hydroxyanisole and sulfites, Dr. Ehrlich said. Sulfites are used to prevent food from turning brown, and it may be present in dried fruit, fruit juice, molasses, pickled foods, vinegar, and wine.
Reports of ACD in response to sodium metabisulfite have been increasing, she noted. Other sulfite reactions may occur with exposure to other products, such as cosmetics, body washes, and swimming pool water, she said.
Awareness of allergens in supplements is important “because the number of our patients taking supplements for different reasons is increasing” and allergens in supplements could account for flares, Dr. Ehrlich said. Clinicians should encourage patients to tell them what supplements they use. Clinicians should review the ingredients in these supplements with their patients to identify potential allergens that may be causing reactions, she advised.
Dr. Ehrlich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACDS 2023
Botanical Briefs: Handling the Heat From Capsicum Peppers
Cutaneous Manifestations
Capsicum peppers are used worldwide in preparing spicy dishes. Their active ingredient—capsaicin—is used as a topical medicine to treat localized pain. Capsicum peppers can cause irritant contact dermatitis with symptoms of erythema, cutaneous burning, and itch.1
Irritant contact dermatitis is a common occupational skin disorder. Many cooks have experienced the sting of a chili pepper after contact with the hands or eyes. Cases of chronic exposure to Capsicum peppers with persistent burning and pain have been called Hunan hand syndrome.2 Capsicum peppers also have induced allergic contact dermatitis in a food production worker.3
Capsicum peppers also are used in pepper spray, tear gas, and animal repellents because of their stinging properties. These agents usually cause cutaneous tingling and burning that soon resolves; however, a review of 31 studies showed that crowd-control methods with Capsicum-containing tear gas and pepper spray can cause moderate to severe skin damage such as a persistent skin rash or erythema, or even first-, second-, or third-degree burns.4
Topical application of capsaicin isolate is meant to cause burning and deplete local neuropeptides, with a cutaneous reaction that ranges from mild to intolerable.5,6 Capsaicin also is found in other products. In one published case report, a 3-year-old boy broke out in facial urticaria when his mother kissed him on the cheek after she applied lip plumper containing capsaicin to her lips.7 Dermatologists should consider capsaicin an active ingredient that can irritate the skin in the garden, in the kitchen, and in topical products.
Obtaining Relief
Capsaicin-induced dermatitis can be relieved by washing the area with soap, detergent, baking soda, or oily compounds that act as solvents for the nonpolar capsaicin.8 Application of ice water or a high-potency topical steroid also may help. If the reaction is severe and persistent, a continuous stellate ganglion block may alleviate the pain of capsaicin-induced contact dermatitis.9
Identifying Features and Plant Facts
The Capsicum genus includes chili peppers, paprika, and red peppers. Capsicum peppers are native to tropical regions of the Americas (Figure). The use of Capsicum peppers in food can be traced to Indigenous peoples of Mexico as early as 7000

Capsicum belongs to the family Solanaceae, which includes tobacco, tomatoes, potatoes, and nightshade plants. There are many varieties of peppers in the Capsicum genus, with 5 domesticated species: Capsicum annuum, Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense, Capsicum frutescens, and Capsicum pubescens. These include bell, poblano, cayenne, tabasco, habanero, and ají peppers, among others. Capsicum species grow as a shrub with flowers that rotate to stellate corollas and rounded berries of different sizes and colors.12 Capsaicin and other alkaloids are concentrated in the fruit; therefore, Capsicum dermatitis is most commonly induced by contact with the flesh of peppers.
Irritant Chemicals
Capsaicin (8-methyl-6-nonanoyl vanillylamide) is a nonpolar phenol, which is why washing skin that has come in contact with capsaicin with water or vinegar alone is insufficient to solubilize it.13 Capsaicin binds to the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a calcium channel on neurons that opens in response to heat. When bound, the channel opens at a lower temperature threshold and depolarizes nerve endings, leading to vasodilation and activation of sensory nerves.14 Substance P is released and the individual experiences a painful burning sensation. When purified capsaicin is frequently applied at an appropriate dose, synthesis of substance P is diminished, resulting in reduced local pain overall.15
Capsaicin does not affect neurons without TRPV1, and administration of capsaicin is not painful if given with anesthesia. An inappropriately high dose of capsaicin destroys cells in the epidermal barrier, resulting in water loss and inducing release of vasoactive peptides and inflammatory cytokines.1 Careful handling of Capsicum peppers and capsaicin products can reduce the risk for irritation.
Medicinal Use
On-/Off-Label and Potential Uses—Capsaicin is US Food and Drug Administration approved for use in arthritis and musculoskeletal pain. It also is used to treat diabetic neuropathy,5 postherpetic neuralgia,6 psoriasis,16 and other conditions. Studies have shown that capsaicin might be useful in treating trigeminal neuralgia,17 fibromyalgia,18 migraines,14 cluster headaches,9 and HIV-associated distal sensory neuropathy.5
Delivery of Capsaicin—Capsaicin preferentially acts on C-fibers, which transmit dull, aching, chronic pain.19 The compound is available as a cream, lotion, and large bandage (for the lower back), as well as low- and high-dose patches. Capsaicin creams, lotions, and the low-dose patch are uncomfortable and must be applied for 4 to 6 weeks to take effect, which may impact patient adherence. The high-dose patch, which requires administration under local anesthesia by a health care worker, brings pain relief with a single use and improves adherence.11 Synthetic TRPV1-agonist injectables based on capsaicin have undergone clinical trials for localized pain (eg, postoperative musculoskeletal pain); many patients experience pain relief, though benefit fades over weeks to months.20,21
Use in Traditional Medicine—Capsicum peppers have been used to aid digestion and promote healing in gastrointestinal conditions, such as dyspepsia.22 The peppers are a source of important vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and E; many of the B complex vitamins; and magnesium, calcium, and iron.23
Use as Cancer Therapy—Studies of the use of capsaicin in treating cancer have produced controversial results. In cell and animal models, capsaicin induces apoptosis through downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein; upregulation of oxidative stress, tribbles-related protein 3 (TRIB3), and caspase-3; and other pathways.19,24-26 On the other hand, consumption of Capsicum peppers has been associated with cancer of the stomach and gallbladder.27 Capsaicin might have anticarcinogenic properties, but its mechanism of action varies, depending on variables not fully understood.
Final Thoughts
Capsaicin is a neuropeptide-active compound found in Capsicum peppers that has many promising applications for use. However, dermatologists should be aware of the possibility of a skin reaction to this compound from handling peppers and using topical medicines. Exposure to capsaicin can cause irritant contact dermatitis that may require clinical care.
- Otang WM, Grierson DS, Afolayan AJ. A survey of plants responsible for causing irritant contact dermatitis in the Amathole district, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157:274-284. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.002
- Weinberg RB. Hunan hand. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:1020.
- Lambrecht C, Goossens A. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by capsicum. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;72:252-253. doi:10.1111/cod.12345
- Haar RJ, Iacopino V, Ranadive N, et al. Health impacts of chemical irritants used for crowd control: a systematic review of the injuries and deaths caused by tear gas and pepper spray. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:831. doi:10.1186/s12889-017-4814-6
- Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
- Yong YL, Tan LT-H, Ming LC, et al. The effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin in postherpetic neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:538. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00538
- Firoz EF, Levin JM, Hartman RD, et al. Lip plumper contact urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:861-863. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.09.028
- Jones LA, Tandberg D, Troutman WG. Household treatment for “chile burns” of the hands. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1987;25:483-491. doi:10.3109/15563658708992651
- Saxena AK, Mandhyan R. Multimodal approach for the management of Hunan hand syndrome: a case report. Pain Pract. 2013;13:227-230. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2012.00567.x
- Cordell GA, Araujo OE. Capsaicin: identification, nomenclature, and pharmacotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;27:330-336. doi:10.1177/106002809302700316
- Baranidharan G, Das S, Bhaskar A. A review of the high-concentration capsaicin patch and experience in its use in the management of neuropathic pain. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2013;6:287-297. doi:10.1177/1756285613496862
- Carrizo García C, Barfuss MHJ, Sehr EM, et al. Phylogenetic relationships, diversification and expansion of chili peppers (Capsicum, Solanaceae). Ann Bot. 2016;118:35-51. doi:10.1093/aob/mcw079
- Basharat S, Gilani SA, Iftikhar F, et al. Capsaicin: plants of the genus Capsicum and positive effect of Oriental spice on skin health. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33:331-341. doi:10.1159/000512196
- Hopps JJ, Dunn WR, Randall MD. Vasorelaxation to capsaicin and its effects on calcium influx in arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;681:88-93. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.02.019
- Burks TF, Buck SH, Miller MS. Mechanisms of depletion of substance P by capsaicin. Fed Proc. 1985;44:2531-2534.
- Ellis CN, Berberian B, Sulica VI, et al. A double-blind evaluation of topical capsaicin in pruritic psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:438-442. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(93)70208-b
- Fusco BM, Alessandri M. Analgesic effect of capsaicin in idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Anesth Analg. 1992;74:375-377. doi:10.1213/00000539-199203000-00011
- Casanueva B, Rodero B, Quintial C, et al. Short-term efficacy of topical capsaicin therapy in severely affected fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:2665-2670. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2490-5
- Bley K, Boorman G, Mohammad B, et al. A comprehensive review of the carcinogenic and anticarcinogenic potential of capsaicin. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40:847-873. doi:10.1177/0192623312444471
- Jones IA, Togashi R, Wilson ML, et al. Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:77-90. doi:10.1038/s41584-018-0123-4
- Campbell JN, Stevens R, Hanson P, et al. Injectable capsaicin for the management of pain due to osteoarthritis. Molecules. 2021;26:778.
- Maji AK, Banerji P. Phytochemistry and gastrointestinal benefits of the medicinal spice, Capsicum annum L. (chilli): a review. J Complement Integr Med. 2016;13:97-122. doi:10.1515jcim-2015-0037
- Baenas N, Belovié M, Ilie N, et al. Industrial use of pepper (Capsicum annum L.) derived products: technological benefits and biological advantages. Food Chem. 2019;274:872-885. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.047
- Lin RJ, Wu IJ, Hong JY, et al. Capsaicin-induced TRIB3 upregulation promotes apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:4237-4248. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S162383
- Jung MY, Kang HJ, Moon A. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 hepatocarcinoma cells involves Bcl-2 downregulation and caspase-3 activation. Cancer Lett. 2001;165:139-145. doi:10.1016/s0304-3835(01)00426-8
- Ito K, Nakazato T, Yamato K, et al. Induction of apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative, capsaicin, through oxidative stress: implication of phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1071-1078. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1670
- Báez S, Tsuchiya Y, Calvo A, et al. Genetic variants involved in gallstone formation and capsaicin metabolism, and the risk of gallbladder cancer in Chilean women. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:372-378. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.372
Cutaneous Manifestations
Capsicum peppers are used worldwide in preparing spicy dishes. Their active ingredient—capsaicin—is used as a topical medicine to treat localized pain. Capsicum peppers can cause irritant contact dermatitis with symptoms of erythema, cutaneous burning, and itch.1
Irritant contact dermatitis is a common occupational skin disorder. Many cooks have experienced the sting of a chili pepper after contact with the hands or eyes. Cases of chronic exposure to Capsicum peppers with persistent burning and pain have been called Hunan hand syndrome.2 Capsicum peppers also have induced allergic contact dermatitis in a food production worker.3
Capsicum peppers also are used in pepper spray, tear gas, and animal repellents because of their stinging properties. These agents usually cause cutaneous tingling and burning that soon resolves; however, a review of 31 studies showed that crowd-control methods with Capsicum-containing tear gas and pepper spray can cause moderate to severe skin damage such as a persistent skin rash or erythema, or even first-, second-, or third-degree burns.4
Topical application of capsaicin isolate is meant to cause burning and deplete local neuropeptides, with a cutaneous reaction that ranges from mild to intolerable.5,6 Capsaicin also is found in other products. In one published case report, a 3-year-old boy broke out in facial urticaria when his mother kissed him on the cheek after she applied lip plumper containing capsaicin to her lips.7 Dermatologists should consider capsaicin an active ingredient that can irritate the skin in the garden, in the kitchen, and in topical products.
Obtaining Relief
Capsaicin-induced dermatitis can be relieved by washing the area with soap, detergent, baking soda, or oily compounds that act as solvents for the nonpolar capsaicin.8 Application of ice water or a high-potency topical steroid also may help. If the reaction is severe and persistent, a continuous stellate ganglion block may alleviate the pain of capsaicin-induced contact dermatitis.9
Identifying Features and Plant Facts
The Capsicum genus includes chili peppers, paprika, and red peppers. Capsicum peppers are native to tropical regions of the Americas (Figure). The use of Capsicum peppers in food can be traced to Indigenous peoples of Mexico as early as 7000

Capsicum belongs to the family Solanaceae, which includes tobacco, tomatoes, potatoes, and nightshade plants. There are many varieties of peppers in the Capsicum genus, with 5 domesticated species: Capsicum annuum, Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense, Capsicum frutescens, and Capsicum pubescens. These include bell, poblano, cayenne, tabasco, habanero, and ají peppers, among others. Capsicum species grow as a shrub with flowers that rotate to stellate corollas and rounded berries of different sizes and colors.12 Capsaicin and other alkaloids are concentrated in the fruit; therefore, Capsicum dermatitis is most commonly induced by contact with the flesh of peppers.
Irritant Chemicals
Capsaicin (8-methyl-6-nonanoyl vanillylamide) is a nonpolar phenol, which is why washing skin that has come in contact with capsaicin with water or vinegar alone is insufficient to solubilize it.13 Capsaicin binds to the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a calcium channel on neurons that opens in response to heat. When bound, the channel opens at a lower temperature threshold and depolarizes nerve endings, leading to vasodilation and activation of sensory nerves.14 Substance P is released and the individual experiences a painful burning sensation. When purified capsaicin is frequently applied at an appropriate dose, synthesis of substance P is diminished, resulting in reduced local pain overall.15
Capsaicin does not affect neurons without TRPV1, and administration of capsaicin is not painful if given with anesthesia. An inappropriately high dose of capsaicin destroys cells in the epidermal barrier, resulting in water loss and inducing release of vasoactive peptides and inflammatory cytokines.1 Careful handling of Capsicum peppers and capsaicin products can reduce the risk for irritation.
Medicinal Use
On-/Off-Label and Potential Uses—Capsaicin is US Food and Drug Administration approved for use in arthritis and musculoskeletal pain. It also is used to treat diabetic neuropathy,5 postherpetic neuralgia,6 psoriasis,16 and other conditions. Studies have shown that capsaicin might be useful in treating trigeminal neuralgia,17 fibromyalgia,18 migraines,14 cluster headaches,9 and HIV-associated distal sensory neuropathy.5
Delivery of Capsaicin—Capsaicin preferentially acts on C-fibers, which transmit dull, aching, chronic pain.19 The compound is available as a cream, lotion, and large bandage (for the lower back), as well as low- and high-dose patches. Capsaicin creams, lotions, and the low-dose patch are uncomfortable and must be applied for 4 to 6 weeks to take effect, which may impact patient adherence. The high-dose patch, which requires administration under local anesthesia by a health care worker, brings pain relief with a single use and improves adherence.11 Synthetic TRPV1-agonist injectables based on capsaicin have undergone clinical trials for localized pain (eg, postoperative musculoskeletal pain); many patients experience pain relief, though benefit fades over weeks to months.20,21
Use in Traditional Medicine—Capsicum peppers have been used to aid digestion and promote healing in gastrointestinal conditions, such as dyspepsia.22 The peppers are a source of important vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and E; many of the B complex vitamins; and magnesium, calcium, and iron.23
Use as Cancer Therapy—Studies of the use of capsaicin in treating cancer have produced controversial results. In cell and animal models, capsaicin induces apoptosis through downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein; upregulation of oxidative stress, tribbles-related protein 3 (TRIB3), and caspase-3; and other pathways.19,24-26 On the other hand, consumption of Capsicum peppers has been associated with cancer of the stomach and gallbladder.27 Capsaicin might have anticarcinogenic properties, but its mechanism of action varies, depending on variables not fully understood.
Final Thoughts
Capsaicin is a neuropeptide-active compound found in Capsicum peppers that has many promising applications for use. However, dermatologists should be aware of the possibility of a skin reaction to this compound from handling peppers and using topical medicines. Exposure to capsaicin can cause irritant contact dermatitis that may require clinical care.
Cutaneous Manifestations
Capsicum peppers are used worldwide in preparing spicy dishes. Their active ingredient—capsaicin—is used as a topical medicine to treat localized pain. Capsicum peppers can cause irritant contact dermatitis with symptoms of erythema, cutaneous burning, and itch.1
Irritant contact dermatitis is a common occupational skin disorder. Many cooks have experienced the sting of a chili pepper after contact with the hands or eyes. Cases of chronic exposure to Capsicum peppers with persistent burning and pain have been called Hunan hand syndrome.2 Capsicum peppers also have induced allergic contact dermatitis in a food production worker.3
Capsicum peppers also are used in pepper spray, tear gas, and animal repellents because of their stinging properties. These agents usually cause cutaneous tingling and burning that soon resolves; however, a review of 31 studies showed that crowd-control methods with Capsicum-containing tear gas and pepper spray can cause moderate to severe skin damage such as a persistent skin rash or erythema, or even first-, second-, or third-degree burns.4
Topical application of capsaicin isolate is meant to cause burning and deplete local neuropeptides, with a cutaneous reaction that ranges from mild to intolerable.5,6 Capsaicin also is found in other products. In one published case report, a 3-year-old boy broke out in facial urticaria when his mother kissed him on the cheek after she applied lip plumper containing capsaicin to her lips.7 Dermatologists should consider capsaicin an active ingredient that can irritate the skin in the garden, in the kitchen, and in topical products.
Obtaining Relief
Capsaicin-induced dermatitis can be relieved by washing the area with soap, detergent, baking soda, or oily compounds that act as solvents for the nonpolar capsaicin.8 Application of ice water or a high-potency topical steroid also may help. If the reaction is severe and persistent, a continuous stellate ganglion block may alleviate the pain of capsaicin-induced contact dermatitis.9
Identifying Features and Plant Facts
The Capsicum genus includes chili peppers, paprika, and red peppers. Capsicum peppers are native to tropical regions of the Americas (Figure). The use of Capsicum peppers in food can be traced to Indigenous peoples of Mexico as early as 7000

Capsicum belongs to the family Solanaceae, which includes tobacco, tomatoes, potatoes, and nightshade plants. There are many varieties of peppers in the Capsicum genus, with 5 domesticated species: Capsicum annuum, Capsicum baccatum, Capsicum chinense, Capsicum frutescens, and Capsicum pubescens. These include bell, poblano, cayenne, tabasco, habanero, and ají peppers, among others. Capsicum species grow as a shrub with flowers that rotate to stellate corollas and rounded berries of different sizes and colors.12 Capsaicin and other alkaloids are concentrated in the fruit; therefore, Capsicum dermatitis is most commonly induced by contact with the flesh of peppers.
Irritant Chemicals
Capsaicin (8-methyl-6-nonanoyl vanillylamide) is a nonpolar phenol, which is why washing skin that has come in contact with capsaicin with water or vinegar alone is insufficient to solubilize it.13 Capsaicin binds to the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), a calcium channel on neurons that opens in response to heat. When bound, the channel opens at a lower temperature threshold and depolarizes nerve endings, leading to vasodilation and activation of sensory nerves.14 Substance P is released and the individual experiences a painful burning sensation. When purified capsaicin is frequently applied at an appropriate dose, synthesis of substance P is diminished, resulting in reduced local pain overall.15
Capsaicin does not affect neurons without TRPV1, and administration of capsaicin is not painful if given with anesthesia. An inappropriately high dose of capsaicin destroys cells in the epidermal barrier, resulting in water loss and inducing release of vasoactive peptides and inflammatory cytokines.1 Careful handling of Capsicum peppers and capsaicin products can reduce the risk for irritation.
Medicinal Use
On-/Off-Label and Potential Uses—Capsaicin is US Food and Drug Administration approved for use in arthritis and musculoskeletal pain. It also is used to treat diabetic neuropathy,5 postherpetic neuralgia,6 psoriasis,16 and other conditions. Studies have shown that capsaicin might be useful in treating trigeminal neuralgia,17 fibromyalgia,18 migraines,14 cluster headaches,9 and HIV-associated distal sensory neuropathy.5
Delivery of Capsaicin—Capsaicin preferentially acts on C-fibers, which transmit dull, aching, chronic pain.19 The compound is available as a cream, lotion, and large bandage (for the lower back), as well as low- and high-dose patches. Capsaicin creams, lotions, and the low-dose patch are uncomfortable and must be applied for 4 to 6 weeks to take effect, which may impact patient adherence. The high-dose patch, which requires administration under local anesthesia by a health care worker, brings pain relief with a single use and improves adherence.11 Synthetic TRPV1-agonist injectables based on capsaicin have undergone clinical trials for localized pain (eg, postoperative musculoskeletal pain); many patients experience pain relief, though benefit fades over weeks to months.20,21
Use in Traditional Medicine—Capsicum peppers have been used to aid digestion and promote healing in gastrointestinal conditions, such as dyspepsia.22 The peppers are a source of important vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, and E; many of the B complex vitamins; and magnesium, calcium, and iron.23
Use as Cancer Therapy—Studies of the use of capsaicin in treating cancer have produced controversial results. In cell and animal models, capsaicin induces apoptosis through downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein; upregulation of oxidative stress, tribbles-related protein 3 (TRIB3), and caspase-3; and other pathways.19,24-26 On the other hand, consumption of Capsicum peppers has been associated with cancer of the stomach and gallbladder.27 Capsaicin might have anticarcinogenic properties, but its mechanism of action varies, depending on variables not fully understood.
Final Thoughts
Capsaicin is a neuropeptide-active compound found in Capsicum peppers that has many promising applications for use. However, dermatologists should be aware of the possibility of a skin reaction to this compound from handling peppers and using topical medicines. Exposure to capsaicin can cause irritant contact dermatitis that may require clinical care.
- Otang WM, Grierson DS, Afolayan AJ. A survey of plants responsible for causing irritant contact dermatitis in the Amathole district, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157:274-284. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.002
- Weinberg RB. Hunan hand. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:1020.
- Lambrecht C, Goossens A. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by capsicum. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;72:252-253. doi:10.1111/cod.12345
- Haar RJ, Iacopino V, Ranadive N, et al. Health impacts of chemical irritants used for crowd control: a systematic review of the injuries and deaths caused by tear gas and pepper spray. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:831. doi:10.1186/s12889-017-4814-6
- Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
- Yong YL, Tan LT-H, Ming LC, et al. The effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin in postherpetic neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:538. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00538
- Firoz EF, Levin JM, Hartman RD, et al. Lip plumper contact urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:861-863. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.09.028
- Jones LA, Tandberg D, Troutman WG. Household treatment for “chile burns” of the hands. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1987;25:483-491. doi:10.3109/15563658708992651
- Saxena AK, Mandhyan R. Multimodal approach for the management of Hunan hand syndrome: a case report. Pain Pract. 2013;13:227-230. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2012.00567.x
- Cordell GA, Araujo OE. Capsaicin: identification, nomenclature, and pharmacotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;27:330-336. doi:10.1177/106002809302700316
- Baranidharan G, Das S, Bhaskar A. A review of the high-concentration capsaicin patch and experience in its use in the management of neuropathic pain. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2013;6:287-297. doi:10.1177/1756285613496862
- Carrizo García C, Barfuss MHJ, Sehr EM, et al. Phylogenetic relationships, diversification and expansion of chili peppers (Capsicum, Solanaceae). Ann Bot. 2016;118:35-51. doi:10.1093/aob/mcw079
- Basharat S, Gilani SA, Iftikhar F, et al. Capsaicin: plants of the genus Capsicum and positive effect of Oriental spice on skin health. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33:331-341. doi:10.1159/000512196
- Hopps JJ, Dunn WR, Randall MD. Vasorelaxation to capsaicin and its effects on calcium influx in arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;681:88-93. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.02.019
- Burks TF, Buck SH, Miller MS. Mechanisms of depletion of substance P by capsaicin. Fed Proc. 1985;44:2531-2534.
- Ellis CN, Berberian B, Sulica VI, et al. A double-blind evaluation of topical capsaicin in pruritic psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:438-442. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(93)70208-b
- Fusco BM, Alessandri M. Analgesic effect of capsaicin in idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Anesth Analg. 1992;74:375-377. doi:10.1213/00000539-199203000-00011
- Casanueva B, Rodero B, Quintial C, et al. Short-term efficacy of topical capsaicin therapy in severely affected fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:2665-2670. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2490-5
- Bley K, Boorman G, Mohammad B, et al. A comprehensive review of the carcinogenic and anticarcinogenic potential of capsaicin. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40:847-873. doi:10.1177/0192623312444471
- Jones IA, Togashi R, Wilson ML, et al. Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:77-90. doi:10.1038/s41584-018-0123-4
- Campbell JN, Stevens R, Hanson P, et al. Injectable capsaicin for the management of pain due to osteoarthritis. Molecules. 2021;26:778.
- Maji AK, Banerji P. Phytochemistry and gastrointestinal benefits of the medicinal spice, Capsicum annum L. (chilli): a review. J Complement Integr Med. 2016;13:97-122. doi:10.1515jcim-2015-0037
- Baenas N, Belovié M, Ilie N, et al. Industrial use of pepper (Capsicum annum L.) derived products: technological benefits and biological advantages. Food Chem. 2019;274:872-885. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.047
- Lin RJ, Wu IJ, Hong JY, et al. Capsaicin-induced TRIB3 upregulation promotes apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:4237-4248. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S162383
- Jung MY, Kang HJ, Moon A. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 hepatocarcinoma cells involves Bcl-2 downregulation and caspase-3 activation. Cancer Lett. 2001;165:139-145. doi:10.1016/s0304-3835(01)00426-8
- Ito K, Nakazato T, Yamato K, et al. Induction of apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative, capsaicin, through oxidative stress: implication of phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1071-1078. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1670
- Báez S, Tsuchiya Y, Calvo A, et al. Genetic variants involved in gallstone formation and capsaicin metabolism, and the risk of gallbladder cancer in Chilean women. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:372-378. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.372
- Otang WM, Grierson DS, Afolayan AJ. A survey of plants responsible for causing irritant contact dermatitis in the Amathole district, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157:274-284. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.002
- Weinberg RB. Hunan hand. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:1020.
- Lambrecht C, Goossens A. Occupational allergic contact dermatitis caused by capsicum. Contact Dermatitis. 2015;72:252-253. doi:10.1111/cod.12345
- Haar RJ, Iacopino V, Ranadive N, et al. Health impacts of chemical irritants used for crowd control: a systematic review of the injuries and deaths caused by tear gas and pepper spray. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:831. doi:10.1186/s12889-017-4814-6
- Simpson DM, Robinson-Papp J, Van J, et al. Capsaicin 8% patch in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Pain. 2017;18:42-53. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.09.008
- Yong YL, Tan LT-H, Ming LC, et al. The effectiveness and safety of topical capsaicin in postherpetic neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:538. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00538
- Firoz EF, Levin JM, Hartman RD, et al. Lip plumper contact urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:861-863. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.09.028
- Jones LA, Tandberg D, Troutman WG. Household treatment for “chile burns” of the hands. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1987;25:483-491. doi:10.3109/15563658708992651
- Saxena AK, Mandhyan R. Multimodal approach for the management of Hunan hand syndrome: a case report. Pain Pract. 2013;13:227-230. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2012.00567.x
- Cordell GA, Araujo OE. Capsaicin: identification, nomenclature, and pharmacotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;27:330-336. doi:10.1177/106002809302700316
- Baranidharan G, Das S, Bhaskar A. A review of the high-concentration capsaicin patch and experience in its use in the management of neuropathic pain. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2013;6:287-297. doi:10.1177/1756285613496862
- Carrizo García C, Barfuss MHJ, Sehr EM, et al. Phylogenetic relationships, diversification and expansion of chili peppers (Capsicum, Solanaceae). Ann Bot. 2016;118:35-51. doi:10.1093/aob/mcw079
- Basharat S, Gilani SA, Iftikhar F, et al. Capsaicin: plants of the genus Capsicum and positive effect of Oriental spice on skin health. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2020;33:331-341. doi:10.1159/000512196
- Hopps JJ, Dunn WR, Randall MD. Vasorelaxation to capsaicin and its effects on calcium influx in arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;681:88-93. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.02.019
- Burks TF, Buck SH, Miller MS. Mechanisms of depletion of substance P by capsaicin. Fed Proc. 1985;44:2531-2534.
- Ellis CN, Berberian B, Sulica VI, et al. A double-blind evaluation of topical capsaicin in pruritic psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:438-442. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(93)70208-b
- Fusco BM, Alessandri M. Analgesic effect of capsaicin in idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Anesth Analg. 1992;74:375-377. doi:10.1213/00000539-199203000-00011
- Casanueva B, Rodero B, Quintial C, et al. Short-term efficacy of topical capsaicin therapy in severely affected fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:2665-2670. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2490-5
- Bley K, Boorman G, Mohammad B, et al. A comprehensive review of the carcinogenic and anticarcinogenic potential of capsaicin. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40:847-873. doi:10.1177/0192623312444471
- Jones IA, Togashi R, Wilson ML, et al. Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:77-90. doi:10.1038/s41584-018-0123-4
- Campbell JN, Stevens R, Hanson P, et al. Injectable capsaicin for the management of pain due to osteoarthritis. Molecules. 2021;26:778.
- Maji AK, Banerji P. Phytochemistry and gastrointestinal benefits of the medicinal spice, Capsicum annum L. (chilli): a review. J Complement Integr Med. 2016;13:97-122. doi:10.1515jcim-2015-0037
- Baenas N, Belovié M, Ilie N, et al. Industrial use of pepper (Capsicum annum L.) derived products: technological benefits and biological advantages. Food Chem. 2019;274:872-885. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.047
- Lin RJ, Wu IJ, Hong JY, et al. Capsaicin-induced TRIB3 upregulation promotes apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:4237-4248. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S162383
- Jung MY, Kang HJ, Moon A. Capsaicin-induced apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 hepatocarcinoma cells involves Bcl-2 downregulation and caspase-3 activation. Cancer Lett. 2001;165:139-145. doi:10.1016/s0304-3835(01)00426-8
- Ito K, Nakazato T, Yamato K, et al. Induction of apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative, capsaicin, through oxidative stress: implication of phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1071-1078. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1670
- Báez S, Tsuchiya Y, Calvo A, et al. Genetic variants involved in gallstone formation and capsaicin metabolism, and the risk of gallbladder cancer in Chilean women. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:372-378. doi:10.3748/wjg.v16.i3.372
Practice Points
- Capsicum peppers—used worldwide in food preparation, pepper spray, and cosmetic products—can cause irritant dermatitis from the active ingredient capsaicin.
- Capsaicin, which is isolated as a medication to treat musculoskeletal pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and more, can cause a mild local skin reaction.
Erythema Ab Igne: A Clinical Review
Erythema ab igne (EAI)(also known as toasted skin syndrome) was first described in the British Journal of Dermatology in the 20th century, 1 though it was known by physicians long before. Reticular netlike skin changes were seen in association with patients who spent extended time directly next to a heat source. This association led to the name of this condition, which literally means “redness by fire.” Indeed, EAI induced by chronic heat exposure has been described across the world for centuries. For example, in the cold regions of northern China, people used to sleep on beds of hot bricks called kang to stay warm at night. The people of India’s Kashmir district carried pots of hot coals called kangri next to the skin under large woven shawls to stay warm. In the past, Irish women often spent much time by a turf- or peat-burning fire. Chronic heat exposure in these cases can lead not only to EAI but also to aggressive types of cancer, often with a latency of 30 years or more. 2
More recently, the invention of home central heating led to a stark decrease in the number of cases associated with combustion-based heat, with a transition to etiologies such as use of hot water bottles, electric blankets, and electric space heaters. Over time, technological advances led to ever-increasing potential causes for EAI, such as laptops or cell phones, car heaters and heated seats, heated blankets,3,4 infrared lamps for food, and even medical devices such as ultrasound-based heating products and convective temperature management systems for hospitalized patients. As technology evolves, so do the potential causes of EAI, requiring clinicians to diagnose and deduce the cause through a thorough social and medical history as well as a workup on the present illness with considerations for the anatomical location.5-7 Herein, we describe the etiology of EAI, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Clinical Characteristics
Erythema ab igne begins as mild, transient, and erythematous macules and patches in a reticular pattern that resolve minutes to hours after removal of the heat source. With weeks to months of continued or repeated application of the heat source, the affected area eventually becomes hyperpigmented where there once was erythema (Figures 1 and 2). Sometimes papules, bullae, telangiectasia, and hyperkeratosis also form. The rash usually is asymptomatic, though pain, pruritus, and dysesthesia have been reported.7 Dermoscopy of EAI in the hyperpigmented stage can reveal diffuse superficial dark pigmentation, telangiectasia, and mild whitish scaling.8 Although the pathogenesis has remained elusive over the years, lesions do seem to be mostly associated with cumulative exposure to heat rather than length of exposure.7
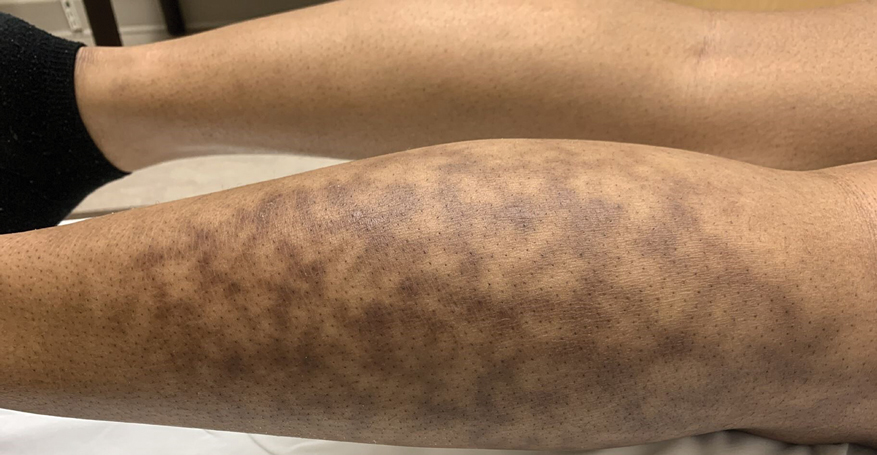
Etiology of EAI
Anatomic Location—The affected site depends on the source of heat (Table). Classic examples of this condition include a patient with EAI presenting on the anterior thighs after working in front of a hot oven or a patient with chronic back pain presenting with lower-back EAI secondary to frequent use of a hot water bottle or heating pad.7 With evolving technology over the last few decades, new etiologies have become more common—teenagers are presenting with anterior thigh EAI secondary to frequent laptop use2-29; patients are holding warm cell phones in their pant pockets, leading to unilateral geometric EAI on the anterior thigh (front pocket) or buttock (back pocket)30; plug-in radiators under computer desks are causing EAI on the lower legs31-34; and automobile seat heaters have been shown to cause EAI on the posterior legs.5,35-37 Clinicians should consider anatomic location a critical clue for etiology.
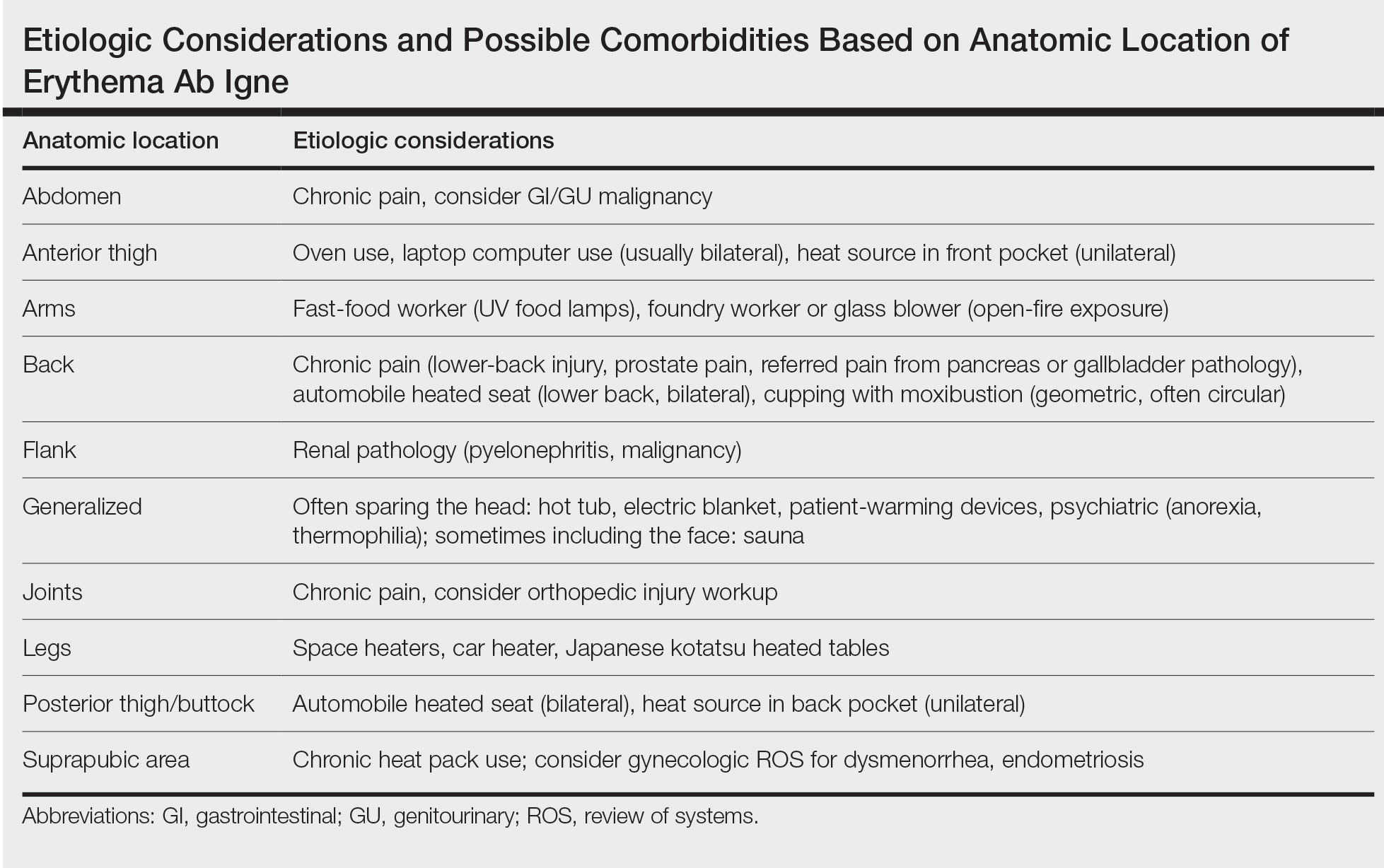
Social History—There are rarer and more highly specific causes of EAI than simple heat exposure that can be parsed from a patient’s social history. Occupational exposure has been documented, such as bakers with exposure to ovens, foundry workers with exposure to heated metals, or fast-food workers with chronic exposure to infrared food lamps.6,7 There also are cultural practices that can cause EAI. For example, the practice of cupping with moxibustion was shown to create a specific pattern in the shape of the cultural tool used.38 When footbaths with Chinese herbal remedies are performed frequently with high heat, they can lead to EAI on the feet with a linear border at the ankles. There also have been reports of kotatsu (heated tables in Japan) leading to lower-body EAI.39,40 These cultural practices also are more common in patients with darker skin types, which can lead to hyperpigmentation that is difficult to treat, making early diagnosis important.7
Medical History—Case reports have shown EAI caused by patients attempting to use heat-based methods for pain relief of an underlying serious disease such as cancer, bowel pathology (abdominal EAI), spinal disc prolapse (midline back EAI),41 sickle cell anemia, and renal pathology (posterior upper flank EAI).6,7,40-49 Patients with hypothyroidism or anorexia have been noted to have generalized EAI sparing the face secondary to repeated and extended hot baths or showers.50-53 One patient with schizophrenia was shown to have associated thermophilia due to a delusion that led the patient to soak in hot baths for long periods of time, leading to EAI.54 Finally, all physicians should be aware of iatrogenic causes of EAI, such as use of warming devices, ultrasound-based warming techniques, and laser therapy for lipolysis. Inquire about the patient’s surgical history or intensive care unit stays as well as alternative medicine or chiropractic visits. Obtaining a history of medical procedures can be enlightening when an etiology is not immediately clear.7,55,56
Diagnosis
Erythema ab igne is a clinical diagnosis based on recognizable cutaneous findings and a clear history of moderate heat exposure. However, when a clinical diagnosis of EAI is not certain (eg, when unable to obtain a clear history from the patient) or when malignant transformation is suspected, a biopsy can be performed. Pathologically, hematoxylin and eosin staining of EAI classically reveals dilated small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, hence a clinically reticular rash; interface dermatitis clinically manifesting as erythema; and pigment incontinence with melanin-laden macrophages consistent with clinical hyperpigmentation. Finally, for unclear reasons, increased numbers of elastic fibers classically are seen in biopsies of EAI.7
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for a reticular patch includes livedo reticularis (Figure 3), which usually manifests as a more generalized rash in patients with chronic disease or coagulopathy such as systemic lupus erythematosus, cryoglobulinemia, or Raynaud phenomenon. When differentiating EAI from livedo reticularis or cutis marmorata, consider that both alternative diagnoses are more vascular appearing and are associated with cold exposure rather than heat exposure. In cases that are less reticular, livedo racemosa can be considered in the differential diagnosis. Finally, poikiloderma of Civatte can be reticular, particularly on dermoscopy, but the distribution on the neck with submental sparing should help to distinguish it from EAI unless a heat source around the neck is identified while taking the patient’s history.7
In babies, a reticular generalized rash is most likely to be cutis marmorata (Figure 4), which is a physiologic response to cold exposure that resolves with rewarming of the skin. A more serious condition—cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (Figure 5)—usually is present at birth, most frequently involves a single extremity, and notably does not resolve with rewarming. This is an important differential for EAI in children because it can be associated with vascular and neurologic anomalies as well as limb asymmetry. Finally, port-wine stains can sometimes be reticular in appearance and can mimic the early erythematous stages of EAI. However, unlike the erythematous stage of EAI, the port-wine stains will be present at birth.7
Emerging in 2020, an important differential diagnosis to consider is a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19 infection. An erythematous, reticular, chilblainlike or transient livedo reticularis–like rash has been described as a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19. Although the pathophysiology is still being elucidated, it is suspected that this is caused by a major vaso-occlusive crisis secondary to COVID-19–induced thrombotic vasculopathy. Interestingly, the majority of patients with this COVID-related exanthem also displayed symptoms of COVID-19 (eg, fever, cough) at the time of presentation,57-60 but there also have been cases in patients who were asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.60
In some cases, EAI is an indication to screen for an underlying disease. For example, uncontrolled pain is an opportunity to improve interventions such as modifying the patient’s pain-control regimen, placing a palliative care pain consultation, or checking if the patient has had age-appropriate screenings for malignancy. New focal pain in a patient with a prior diagnosis of cancer may be a sign of a new metastasis. A thermophilic patient leaves opportunity to assess for underlying medical causes such as thyroid abnormalities or social/psychological issues. Geriatric patients who are diagnosed with EAI may need to be assessed for dementia or home safety issues. Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus can unknowingly develop EAI on the lower extremities, which may signal a need to assess the patient for peripheral neuropathy. Patients with gastroparesis secondary to diabetes also may develop EAI on the abdomen secondary to heating pad use for discomfort. These examples are a reminder to consider possible secondary comorbidities in all diagnoses of EAI.7
Prognosis
Although the prognosis of EAI is excellent if caught early, failure to diagnose this condition can lead to permanent discoloration of the skin and even malignancy.6 A rare sequela includes squamous cell carcinoma, most commonly seen in chronic cases of the lower leg, which is likely related to chronic inflammation of the skin.61-65 Rare cases of poorly differentiated carcinoma,66 cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma,67 and Merkel cell carcinoma68 have been reported. Patients diagnosed with EAI should receive normal periodic surveillance of the skin based on their medical history, though the physician should have an increased suspicion and plan for biopsy of any nodules or ulcerations found on the skin of the affected area.7
Treatments
Once the diagnosis of EAI is made, treatment starts with removal of the heat source causing the rash. Because the rash usually is asymptomatic, further treatment typically is not required. The discoloration can resolve over months or years, but permanent hyperpigmentation is not uncommon. If hyperpigmentation persists despite removal of the heat source and the patient desires further treatment for discoloration, there are few treatment options, none of which are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for this condition.7 There is some evidence for the use of Nd:YAG lasers to reduce hyperpigmentation in EAI.69 There have been some reports of treatment using topical hydroquinone and topical tretinoin in an attempt to lighten the skin. If associated hyperkeratosis or other epithelial atypia is present, the use of 5-fluorouracil may show some improvement.70 One case report has been published of successful treatment with systemic mesoglycan and topical bioflavonoids.71 It also is conceivable that medications used to treat postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may be helpful in this condition (eg, kojic acid, arbutin, mild topical steroids, azelaic acid). Patients with darker skin may experience permanent discoloration and may not be good candidates for alternative treatments such as laser therapy due to the risk for inducible hyperpigmentation.7
Conclusion
No matter the etiology, EAI usually is a benign skin condition that is treated by removal of the causative heat source. Once a diagnosis is made, the clinician must work with the patient to determine the etiology. Care must be taken to ensure that there are no underlying signs, such as chronic pain or psychiatric illness, that could point to associated conditions. Rarely, sequalae such as cancers have been documented in areas of chronic EAI. Once the heat source is identified and removed, any remaining hyperpigmentation usually will self-resolve over months to years, though this may take longer in patients with darker skin types. If more aggressive treatment is preferred by the patient, laser therapy, topical medications, and oral over-the-counter vitamins have been tried with minimal responses.
- Perry. Case of erythema ab igne. Br J Dermatol. 1900;xxiii:375.
- Bose S, Ortonee JP. Diseases affected by heat. In: Parish LC, Millikan LE, Amer M, et al. Global Dermatology Diagnosis and Management According to Geography, Climate, and Culture. Springer-Varlag; 1994:83-92.
- Leal-Lobato MM, Blasco-Morente G. Electric blanket induced erythema ab igne [in Spanish]. Semergen. 2015;41:456-457. doi:10.1016/j.semerg.2014.12.008
- Huynh N, Sarma D, Huerter C. Erythema ab igne: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2011;88:290-292.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20. doi:10.5070/D32011024689
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Smith ML. Environmental and sports-related skin diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1569-1594.
- Errichetti E, Stinco G. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: a practical overview. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016;6:471-507. doi:10.1007/s13555-016-0141-6
- Guarneri C, Tchernev G, Wollina U, et al. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:490-492. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.137
- Arnold AW, Itin PH. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne in a child and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2010;126:E1227-E1230. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1390
- Dickman J, Kessler S. Unilateral reticulated patch localized to the anterior thigh. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.06.007
- Boffa MJ. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne on the left breast. Cutis. 2011;87:175-176.
- Li K, Barankin B. Cutaneous manifestations of modern technology use. J Cutan Med Surg. 2011;15:347-353. doi:10.2310/7750.2011.10053
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Laptop-induced erythema ab igne: report and review of literature. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Andersen F. Laptop-thighs--laptop-induced erythema ab igne [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:635.
- Jagtman BA. Erythema ab igne due to a laptop computer. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;50:105. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2004.0295g.x
- Olechowska M, Kisiel K, Ruszkowska L, et al. Erythema ab igne (EAI) induced by a laptop computer: report of two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2014.12387
- Nayak SUK, Shenoi SD, Prabhu S. Laptop induced erythema ab igne. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:131-132. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.94284
- Salvio AG, Nunes AJ, Angarita DPR. Laptop computer induced erythema ab igne: a new presentation of an old disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:79-80. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20165139
- Schummer C, Tittelbach J, Elsner P. Right-sided laptop dermatitis [in German]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015;140:1376-1377. doi:10.1055/s-0041-103615
- Manoharan D. Erythema ab igne: usual site, unusual cause. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S74-S75. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155811
- Giraldi S, Diettrich F, Abbage KT, et al. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer in an adolescent. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:128-130. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962011000100018
- Secher LLS, Vind-Kezunovic D, Zachariae COC. Side-effects to the use of laptop computers: erythema ab igne. Dermatol Reports. 2010;31:E11. doi:10.4081/dr.2010.e11
- Botten D, Langley RGB, Webb A. Academic branding: erythema ab igne and use of laptop computers. CMAJ. 2010;182:E857. doi:10.1503/cmaj.091868
- Bilic M, Adams BB. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:973-974. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.08.007
- Fu LW, Vender R. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer gaming - a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:716-717. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05033.x
- Levinbook WS, Mallett J, Grant-Kels JM. Laptop computer-associated erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2007;80:319-320.
- Mohr MR, Scott KA, Pariser RM, et al. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne: a case report. Cutis. 2007;79:59-60.
- Cantor AS, Bartling SJ. Laptop computer-induced hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt6k37r9wm.
- Kaptanog˘lu AF, Mullaaziz D. Erythema ab igne in the palmar area induced by smart phone: case report. Turkiye Klin J Med Sci. 2015;35:284-286. doi:10.5336/medsci.2015-46976
- Redding KS, Watts AN, Lee J, et al. Space heater-induced bullous erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2017;100:E9-E10.
- Goorland J, Edens MA, Baudoin TD. An emergency department presentation of erythema ab igne caused by repeated heater exposure. J La State Med Soc. 2016;168:33-34.
- Kokturk A, Kaya TI, Baz K, et al. Bullous erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:18.
- Brzezinski P, Ismail S, Chiriac A. Radiator-induced erythema ab igne in 8-year-old girl. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2014;85:239-240. doi:10.4067/S0370-41062014000200015
- Adams BB. Heated car seat-induced erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:265-266. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.2207
- Helm TN, Spigel GT, Helm KF. Erythema ab igne caused by a car heater. Cutis. 1997;59:81-82.
- Gregory JF, Beute TC. Erythema ab igne. J Spec Oper Med. 2013;13:115-119. doi:10.55460/5AVH-NZHY
- Chua S, Chen Q, Lee HY. Erythema ab igne and dermal scarring caused by cupping and moxibustion treatment. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:337-338. doi:10.1111/ddg.12581
- Chen JF, Liu YC, Chen YF, et al. Erythema ab igne after footbath with Chinese herbal remedies. J Chinese Med Assoc. 2011;74:51-53. doi:10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.009
- Baltazar D, Brockman R, Simpson E. Kotatsu-induced erythema ab igne. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:253-254. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20198792
- Baig M, Byrne F. Erythema ab igne and its relation to spinal pathology. Cureus. 2018;10:e2914. doi:10.7759/cureus.2914
- Aria AB, Chen L, Silapunt S. Erythema ab igne from heating pad use: a report of three clinical cases and a differential diagnosis. Cureus. 2018;10:e2635. doi:10.7759/cureus.2635
- Milchak M, Smucker J, Chung CG, et al. Erythema ab igne due to heating pad use: a case report and review of clinical presentation, prevention, and complications. Case Rep Med. 2016;1862480. doi:10.1155/2016/1862480
- Gmuca S, Yu J, Weiss PF, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with chronic pain: an alarming cutaneous eruption from heat exposure. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2020;36:e236-e238. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001460
- Dizdarevic A, Karim OA, Bygum A. A reddish brown reticulated hyperpigmented erythema on the abdomen of a girl. Erythema ab igne, also known as toasted skin syndrome, caused by a heating pad onthe abdomen. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:365-367. doi:10.2340/00015555-1722
- Chatterjee S. Erythema ab igne from prolonged use of a heating pad. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1500. doi:10.4065/80.11.1500
- Waldorf DS, Rast MF, Garofalo VJ. Heating-pad erythematous dermatitis “erythema ab igne.” JAMA. 1971;218:1704. doi:10.1001/jama.1971.03190240056023
- South AM, Crispin MK, Marqueling AL, et al. A hyperpigmented reticular rash in a patient on peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2016;36:677-700. doi:10.3747/pdi.2016.00042
- Ravindran R. Erythema ab igne in an individual with diabetes and gastroparesis. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2014203856. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-203856
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A, Tzavela E, et al. Erythema ab igne in three girls with anorexia nervosa. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e149-e150. doi:10.1111/pde.12770
- Fischer J, Rein K, Erfurt-Berge C, et al. Three cases of erythema ab igne (EAI) in patients with eating disorders. Neuropsychiatr. 2010;24:141-143.
- Docx MKF, Simons A, Ramet J, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2013;46:381-383. doi:10.1002/eat.22075
- Turan E, Cimen V, Haytoglu NSK, et al. A case of bullous erythema ab igne accompanied by anemia and subclinical hypothyroidism. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:223366.
- Pavithran K. Erythema ab igne, schizophrenia and thermophilia. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1987;53:181-182.
- Dellavelle R, Gillum P. Erythema ab igne following heating/cooling blanket use in the intensive care unit. Cutis. 2000;66:136-138.
- Park SY, Kim SM, Yoon TJ. Erythema ab igne caused by weight loss heating pad. Korean J Dermatol. 2007;45:489-491.
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Gisondi P, Plaserico S, Bordin C, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: a clinical update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2499-2504. doi:10.1111/jdv.16774
- Manalo IF, Smith MK, Cheeley J, et al. A dermatologic manifestation of COVID-19: transient livedo reticularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:700. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.018
- Zhao Q, Fang X, Pang Z, et al. COVID‐19 and cutaneous manifestations: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2505-2510. doi:10.1111/jdv.16778
- Akasaka T, Kon S. Two cases of squamous cell carcinoma arising from erythema ab igne. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1989;99:735-742.
- Arrington JH 3rd, Lockman DS. Thermal keratoses and squamous cell carcinoma in situ associated with erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1226-1228.
- Wharton JB, Sheehan DJ, Lesher JL Jr. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:488-489.
- Wollina U, Helm C, Hansel G, et al. Two cases of erythema ab igne, one with a squamous cell carcinoma. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2007;142:415-418.
- Rudolph CM, Soyer HP, Wolf P, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in erythema ab igne. Hautarzt. 2000;51:260-263. doi:10.1007/s001050051115
- Sigmon JR, Cantrell J, Teague D, et al. Poorly differentiated carcinoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:676-678. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3182871648
- Wharton J, Roffwarg D, Miller J, et al. Cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:1080-1081. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.08.005
- Jones CS, Tyring SK, Lee PC, et al. Development of neuroendocrine (Merkel cell) carcinoma mixed with squamous cell carcinoma in erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:110-113.
- Kim HW, Kim EJ, Park HC, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with low fluenced 1,064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:147-148. doi:10.3109/14764172.2013.854623
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;62:77-78.
- Gianfaldoni S, Gianfaldoni R, Tchernev G, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with mesoglycan and bioflavonoids: a case-report. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:432-435. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.123
Erythema ab igne (EAI)(also known as toasted skin syndrome) was first described in the British Journal of Dermatology in the 20th century, 1 though it was known by physicians long before. Reticular netlike skin changes were seen in association with patients who spent extended time directly next to a heat source. This association led to the name of this condition, which literally means “redness by fire.” Indeed, EAI induced by chronic heat exposure has been described across the world for centuries. For example, in the cold regions of northern China, people used to sleep on beds of hot bricks called kang to stay warm at night. The people of India’s Kashmir district carried pots of hot coals called kangri next to the skin under large woven shawls to stay warm. In the past, Irish women often spent much time by a turf- or peat-burning fire. Chronic heat exposure in these cases can lead not only to EAI but also to aggressive types of cancer, often with a latency of 30 years or more. 2
More recently, the invention of home central heating led to a stark decrease in the number of cases associated with combustion-based heat, with a transition to etiologies such as use of hot water bottles, electric blankets, and electric space heaters. Over time, technological advances led to ever-increasing potential causes for EAI, such as laptops or cell phones, car heaters and heated seats, heated blankets,3,4 infrared lamps for food, and even medical devices such as ultrasound-based heating products and convective temperature management systems for hospitalized patients. As technology evolves, so do the potential causes of EAI, requiring clinicians to diagnose and deduce the cause through a thorough social and medical history as well as a workup on the present illness with considerations for the anatomical location.5-7 Herein, we describe the etiology of EAI, diagnosis, and treatment options.

Clinical Characteristics
Erythema ab igne begins as mild, transient, and erythematous macules and patches in a reticular pattern that resolve minutes to hours after removal of the heat source. With weeks to months of continued or repeated application of the heat source, the affected area eventually becomes hyperpigmented where there once was erythema (Figures 1 and 2). Sometimes papules, bullae, telangiectasia, and hyperkeratosis also form. The rash usually is asymptomatic, though pain, pruritus, and dysesthesia have been reported.7 Dermoscopy of EAI in the hyperpigmented stage can reveal diffuse superficial dark pigmentation, telangiectasia, and mild whitish scaling.8 Although the pathogenesis has remained elusive over the years, lesions do seem to be mostly associated with cumulative exposure to heat rather than length of exposure.7

Etiology of EAI
Anatomic Location—The affected site depends on the source of heat (Table). Classic examples of this condition include a patient with EAI presenting on the anterior thighs after working in front of a hot oven or a patient with chronic back pain presenting with lower-back EAI secondary to frequent use of a hot water bottle or heating pad.7 With evolving technology over the last few decades, new etiologies have become more common—teenagers are presenting with anterior thigh EAI secondary to frequent laptop use2-29; patients are holding warm cell phones in their pant pockets, leading to unilateral geometric EAI on the anterior thigh (front pocket) or buttock (back pocket)30; plug-in radiators under computer desks are causing EAI on the lower legs31-34; and automobile seat heaters have been shown to cause EAI on the posterior legs.5,35-37 Clinicians should consider anatomic location a critical clue for etiology.

Social History—There are rarer and more highly specific causes of EAI than simple heat exposure that can be parsed from a patient’s social history. Occupational exposure has been documented, such as bakers with exposure to ovens, foundry workers with exposure to heated metals, or fast-food workers with chronic exposure to infrared food lamps.6,7 There also are cultural practices that can cause EAI. For example, the practice of cupping with moxibustion was shown to create a specific pattern in the shape of the cultural tool used.38 When footbaths with Chinese herbal remedies are performed frequently with high heat, they can lead to EAI on the feet with a linear border at the ankles. There also have been reports of kotatsu (heated tables in Japan) leading to lower-body EAI.39,40 These cultural practices also are more common in patients with darker skin types, which can lead to hyperpigmentation that is difficult to treat, making early diagnosis important.7
Medical History—Case reports have shown EAI caused by patients attempting to use heat-based methods for pain relief of an underlying serious disease such as cancer, bowel pathology (abdominal EAI), spinal disc prolapse (midline back EAI),41 sickle cell anemia, and renal pathology (posterior upper flank EAI).6,7,40-49 Patients with hypothyroidism or anorexia have been noted to have generalized EAI sparing the face secondary to repeated and extended hot baths or showers.50-53 One patient with schizophrenia was shown to have associated thermophilia due to a delusion that led the patient to soak in hot baths for long periods of time, leading to EAI.54 Finally, all physicians should be aware of iatrogenic causes of EAI, such as use of warming devices, ultrasound-based warming techniques, and laser therapy for lipolysis. Inquire about the patient’s surgical history or intensive care unit stays as well as alternative medicine or chiropractic visits. Obtaining a history of medical procedures can be enlightening when an etiology is not immediately clear.7,55,56
Diagnosis
Erythema ab igne is a clinical diagnosis based on recognizable cutaneous findings and a clear history of moderate heat exposure. However, when a clinical diagnosis of EAI is not certain (eg, when unable to obtain a clear history from the patient) or when malignant transformation is suspected, a biopsy can be performed. Pathologically, hematoxylin and eosin staining of EAI classically reveals dilated small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, hence a clinically reticular rash; interface dermatitis clinically manifesting as erythema; and pigment incontinence with melanin-laden macrophages consistent with clinical hyperpigmentation. Finally, for unclear reasons, increased numbers of elastic fibers classically are seen in biopsies of EAI.7
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for a reticular patch includes livedo reticularis (Figure 3), which usually manifests as a more generalized rash in patients with chronic disease or coagulopathy such as systemic lupus erythematosus, cryoglobulinemia, or Raynaud phenomenon. When differentiating EAI from livedo reticularis or cutis marmorata, consider that both alternative diagnoses are more vascular appearing and are associated with cold exposure rather than heat exposure. In cases that are less reticular, livedo racemosa can be considered in the differential diagnosis. Finally, poikiloderma of Civatte can be reticular, particularly on dermoscopy, but the distribution on the neck with submental sparing should help to distinguish it from EAI unless a heat source around the neck is identified while taking the patient’s history.7

In babies, a reticular generalized rash is most likely to be cutis marmorata (Figure 4), which is a physiologic response to cold exposure that resolves with rewarming of the skin. A more serious condition—cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (Figure 5)—usually is present at birth, most frequently involves a single extremity, and notably does not resolve with rewarming. This is an important differential for EAI in children because it can be associated with vascular and neurologic anomalies as well as limb asymmetry. Finally, port-wine stains can sometimes be reticular in appearance and can mimic the early erythematous stages of EAI. However, unlike the erythematous stage of EAI, the port-wine stains will be present at birth.7

Emerging in 2020, an important differential diagnosis to consider is a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19 infection. An erythematous, reticular, chilblainlike or transient livedo reticularis–like rash has been described as a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19. Although the pathophysiology is still being elucidated, it is suspected that this is caused by a major vaso-occlusive crisis secondary to COVID-19–induced thrombotic vasculopathy. Interestingly, the majority of patients with this COVID-related exanthem also displayed symptoms of COVID-19 (eg, fever, cough) at the time of presentation,57-60 but there also have been cases in patients who were asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.60

In some cases, EAI is an indication to screen for an underlying disease. For example, uncontrolled pain is an opportunity to improve interventions such as modifying the patient’s pain-control regimen, placing a palliative care pain consultation, or checking if the patient has had age-appropriate screenings for malignancy. New focal pain in a patient with a prior diagnosis of cancer may be a sign of a new metastasis. A thermophilic patient leaves opportunity to assess for underlying medical causes such as thyroid abnormalities or social/psychological issues. Geriatric patients who are diagnosed with EAI may need to be assessed for dementia or home safety issues. Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus can unknowingly develop EAI on the lower extremities, which may signal a need to assess the patient for peripheral neuropathy. Patients with gastroparesis secondary to diabetes also may develop EAI on the abdomen secondary to heating pad use for discomfort. These examples are a reminder to consider possible secondary comorbidities in all diagnoses of EAI.7
Prognosis
Although the prognosis of EAI is excellent if caught early, failure to diagnose this condition can lead to permanent discoloration of the skin and even malignancy.6 A rare sequela includes squamous cell carcinoma, most commonly seen in chronic cases of the lower leg, which is likely related to chronic inflammation of the skin.61-65 Rare cases of poorly differentiated carcinoma,66 cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma,67 and Merkel cell carcinoma68 have been reported. Patients diagnosed with EAI should receive normal periodic surveillance of the skin based on their medical history, though the physician should have an increased suspicion and plan for biopsy of any nodules or ulcerations found on the skin of the affected area.7
Treatments
Once the diagnosis of EAI is made, treatment starts with removal of the heat source causing the rash. Because the rash usually is asymptomatic, further treatment typically is not required. The discoloration can resolve over months or years, but permanent hyperpigmentation is not uncommon. If hyperpigmentation persists despite removal of the heat source and the patient desires further treatment for discoloration, there are few treatment options, none of which are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for this condition.7 There is some evidence for the use of Nd:YAG lasers to reduce hyperpigmentation in EAI.69 There have been some reports of treatment using topical hydroquinone and topical tretinoin in an attempt to lighten the skin. If associated hyperkeratosis or other epithelial atypia is present, the use of 5-fluorouracil may show some improvement.70 One case report has been published of successful treatment with systemic mesoglycan and topical bioflavonoids.71 It also is conceivable that medications used to treat postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may be helpful in this condition (eg, kojic acid, arbutin, mild topical steroids, azelaic acid). Patients with darker skin may experience permanent discoloration and may not be good candidates for alternative treatments such as laser therapy due to the risk for inducible hyperpigmentation.7
Conclusion
No matter the etiology, EAI usually is a benign skin condition that is treated by removal of the causative heat source. Once a diagnosis is made, the clinician must work with the patient to determine the etiology. Care must be taken to ensure that there are no underlying signs, such as chronic pain or psychiatric illness, that could point to associated conditions. Rarely, sequalae such as cancers have been documented in areas of chronic EAI. Once the heat source is identified and removed, any remaining hyperpigmentation usually will self-resolve over months to years, though this may take longer in patients with darker skin types. If more aggressive treatment is preferred by the patient, laser therapy, topical medications, and oral over-the-counter vitamins have been tried with minimal responses.
Erythema ab igne (EAI)(also known as toasted skin syndrome) was first described in the British Journal of Dermatology in the 20th century, 1 though it was known by physicians long before. Reticular netlike skin changes were seen in association with patients who spent extended time directly next to a heat source. This association led to the name of this condition, which literally means “redness by fire.” Indeed, EAI induced by chronic heat exposure has been described across the world for centuries. For example, in the cold regions of northern China, people used to sleep on beds of hot bricks called kang to stay warm at night. The people of India’s Kashmir district carried pots of hot coals called kangri next to the skin under large woven shawls to stay warm. In the past, Irish women often spent much time by a turf- or peat-burning fire. Chronic heat exposure in these cases can lead not only to EAI but also to aggressive types of cancer, often with a latency of 30 years or more. 2
More recently, the invention of home central heating led to a stark decrease in the number of cases associated with combustion-based heat, with a transition to etiologies such as use of hot water bottles, electric blankets, and electric space heaters. Over time, technological advances led to ever-increasing potential causes for EAI, such as laptops or cell phones, car heaters and heated seats, heated blankets,3,4 infrared lamps for food, and even medical devices such as ultrasound-based heating products and convective temperature management systems for hospitalized patients. As technology evolves, so do the potential causes of EAI, requiring clinicians to diagnose and deduce the cause through a thorough social and medical history as well as a workup on the present illness with considerations for the anatomical location.5-7 Herein, we describe the etiology of EAI, diagnosis, and treatment options.

Clinical Characteristics
Erythema ab igne begins as mild, transient, and erythematous macules and patches in a reticular pattern that resolve minutes to hours after removal of the heat source. With weeks to months of continued or repeated application of the heat source, the affected area eventually becomes hyperpigmented where there once was erythema (Figures 1 and 2). Sometimes papules, bullae, telangiectasia, and hyperkeratosis also form. The rash usually is asymptomatic, though pain, pruritus, and dysesthesia have been reported.7 Dermoscopy of EAI in the hyperpigmented stage can reveal diffuse superficial dark pigmentation, telangiectasia, and mild whitish scaling.8 Although the pathogenesis has remained elusive over the years, lesions do seem to be mostly associated with cumulative exposure to heat rather than length of exposure.7

Etiology of EAI
Anatomic Location—The affected site depends on the source of heat (Table). Classic examples of this condition include a patient with EAI presenting on the anterior thighs after working in front of a hot oven or a patient with chronic back pain presenting with lower-back EAI secondary to frequent use of a hot water bottle or heating pad.7 With evolving technology over the last few decades, new etiologies have become more common—teenagers are presenting with anterior thigh EAI secondary to frequent laptop use2-29; patients are holding warm cell phones in their pant pockets, leading to unilateral geometric EAI on the anterior thigh (front pocket) or buttock (back pocket)30; plug-in radiators under computer desks are causing EAI on the lower legs31-34; and automobile seat heaters have been shown to cause EAI on the posterior legs.5,35-37 Clinicians should consider anatomic location a critical clue for etiology.

Social History—There are rarer and more highly specific causes of EAI than simple heat exposure that can be parsed from a patient’s social history. Occupational exposure has been documented, such as bakers with exposure to ovens, foundry workers with exposure to heated metals, or fast-food workers with chronic exposure to infrared food lamps.6,7 There also are cultural practices that can cause EAI. For example, the practice of cupping with moxibustion was shown to create a specific pattern in the shape of the cultural tool used.38 When footbaths with Chinese herbal remedies are performed frequently with high heat, they can lead to EAI on the feet with a linear border at the ankles. There also have been reports of kotatsu (heated tables in Japan) leading to lower-body EAI.39,40 These cultural practices also are more common in patients with darker skin types, which can lead to hyperpigmentation that is difficult to treat, making early diagnosis important.7
Medical History—Case reports have shown EAI caused by patients attempting to use heat-based methods for pain relief of an underlying serious disease such as cancer, bowel pathology (abdominal EAI), spinal disc prolapse (midline back EAI),41 sickle cell anemia, and renal pathology (posterior upper flank EAI).6,7,40-49 Patients with hypothyroidism or anorexia have been noted to have generalized EAI sparing the face secondary to repeated and extended hot baths or showers.50-53 One patient with schizophrenia was shown to have associated thermophilia due to a delusion that led the patient to soak in hot baths for long periods of time, leading to EAI.54 Finally, all physicians should be aware of iatrogenic causes of EAI, such as use of warming devices, ultrasound-based warming techniques, and laser therapy for lipolysis. Inquire about the patient’s surgical history or intensive care unit stays as well as alternative medicine or chiropractic visits. Obtaining a history of medical procedures can be enlightening when an etiology is not immediately clear.7,55,56
Diagnosis
Erythema ab igne is a clinical diagnosis based on recognizable cutaneous findings and a clear history of moderate heat exposure. However, when a clinical diagnosis of EAI is not certain (eg, when unable to obtain a clear history from the patient) or when malignant transformation is suspected, a biopsy can be performed. Pathologically, hematoxylin and eosin staining of EAI classically reveals dilated small vascular channels in the superficial dermis, hence a clinically reticular rash; interface dermatitis clinically manifesting as erythema; and pigment incontinence with melanin-laden macrophages consistent with clinical hyperpigmentation. Finally, for unclear reasons, increased numbers of elastic fibers classically are seen in biopsies of EAI.7
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for a reticular patch includes livedo reticularis (Figure 3), which usually manifests as a more generalized rash in patients with chronic disease or coagulopathy such as systemic lupus erythematosus, cryoglobulinemia, or Raynaud phenomenon. When differentiating EAI from livedo reticularis or cutis marmorata, consider that both alternative diagnoses are more vascular appearing and are associated with cold exposure rather than heat exposure. In cases that are less reticular, livedo racemosa can be considered in the differential diagnosis. Finally, poikiloderma of Civatte can be reticular, particularly on dermoscopy, but the distribution on the neck with submental sparing should help to distinguish it from EAI unless a heat source around the neck is identified while taking the patient’s history.7

In babies, a reticular generalized rash is most likely to be cutis marmorata (Figure 4), which is a physiologic response to cold exposure that resolves with rewarming of the skin. A more serious condition—cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita (Figure 5)—usually is present at birth, most frequently involves a single extremity, and notably does not resolve with rewarming. This is an important differential for EAI in children because it can be associated with vascular and neurologic anomalies as well as limb asymmetry. Finally, port-wine stains can sometimes be reticular in appearance and can mimic the early erythematous stages of EAI. However, unlike the erythematous stage of EAI, the port-wine stains will be present at birth.7

Emerging in 2020, an important differential diagnosis to consider is a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19 infection. An erythematous, reticular, chilblainlike or transient livedo reticularis–like rash has been described as a cutaneous manifestation of COVID-19. Although the pathophysiology is still being elucidated, it is suspected that this is caused by a major vaso-occlusive crisis secondary to COVID-19–induced thrombotic vasculopathy. Interestingly, the majority of patients with this COVID-related exanthem also displayed symptoms of COVID-19 (eg, fever, cough) at the time of presentation,57-60 but there also have been cases in patients who were asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic.60

In some cases, EAI is an indication to screen for an underlying disease. For example, uncontrolled pain is an opportunity to improve interventions such as modifying the patient’s pain-control regimen, placing a palliative care pain consultation, or checking if the patient has had age-appropriate screenings for malignancy. New focal pain in a patient with a prior diagnosis of cancer may be a sign of a new metastasis. A thermophilic patient leaves opportunity to assess for underlying medical causes such as thyroid abnormalities or social/psychological issues. Geriatric patients who are diagnosed with EAI may need to be assessed for dementia or home safety issues. Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus can unknowingly develop EAI on the lower extremities, which may signal a need to assess the patient for peripheral neuropathy. Patients with gastroparesis secondary to diabetes also may develop EAI on the abdomen secondary to heating pad use for discomfort. These examples are a reminder to consider possible secondary comorbidities in all diagnoses of EAI.7
Prognosis
Although the prognosis of EAI is excellent if caught early, failure to diagnose this condition can lead to permanent discoloration of the skin and even malignancy.6 A rare sequela includes squamous cell carcinoma, most commonly seen in chronic cases of the lower leg, which is likely related to chronic inflammation of the skin.61-65 Rare cases of poorly differentiated carcinoma,66 cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma,67 and Merkel cell carcinoma68 have been reported. Patients diagnosed with EAI should receive normal periodic surveillance of the skin based on their medical history, though the physician should have an increased suspicion and plan for biopsy of any nodules or ulcerations found on the skin of the affected area.7
Treatments
Once the diagnosis of EAI is made, treatment starts with removal of the heat source causing the rash. Because the rash usually is asymptomatic, further treatment typically is not required. The discoloration can resolve over months or years, but permanent hyperpigmentation is not uncommon. If hyperpigmentation persists despite removal of the heat source and the patient desires further treatment for discoloration, there are few treatment options, none of which are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for this condition.7 There is some evidence for the use of Nd:YAG lasers to reduce hyperpigmentation in EAI.69 There have been some reports of treatment using topical hydroquinone and topical tretinoin in an attempt to lighten the skin. If associated hyperkeratosis or other epithelial atypia is present, the use of 5-fluorouracil may show some improvement.70 One case report has been published of successful treatment with systemic mesoglycan and topical bioflavonoids.71 It also is conceivable that medications used to treat postinflammatory hyperpigmentation may be helpful in this condition (eg, kojic acid, arbutin, mild topical steroids, azelaic acid). Patients with darker skin may experience permanent discoloration and may not be good candidates for alternative treatments such as laser therapy due to the risk for inducible hyperpigmentation.7
Conclusion
No matter the etiology, EAI usually is a benign skin condition that is treated by removal of the causative heat source. Once a diagnosis is made, the clinician must work with the patient to determine the etiology. Care must be taken to ensure that there are no underlying signs, such as chronic pain or psychiatric illness, that could point to associated conditions. Rarely, sequalae such as cancers have been documented in areas of chronic EAI. Once the heat source is identified and removed, any remaining hyperpigmentation usually will self-resolve over months to years, though this may take longer in patients with darker skin types. If more aggressive treatment is preferred by the patient, laser therapy, topical medications, and oral over-the-counter vitamins have been tried with minimal responses.
- Perry. Case of erythema ab igne. Br J Dermatol. 1900;xxiii:375.
- Bose S, Ortonee JP. Diseases affected by heat. In: Parish LC, Millikan LE, Amer M, et al. Global Dermatology Diagnosis and Management According to Geography, Climate, and Culture. Springer-Varlag; 1994:83-92.
- Leal-Lobato MM, Blasco-Morente G. Electric blanket induced erythema ab igne [in Spanish]. Semergen. 2015;41:456-457. doi:10.1016/j.semerg.2014.12.008
- Huynh N, Sarma D, Huerter C. Erythema ab igne: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2011;88:290-292.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20. doi:10.5070/D32011024689
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Smith ML. Environmental and sports-related skin diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1569-1594.
- Errichetti E, Stinco G. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: a practical overview. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016;6:471-507. doi:10.1007/s13555-016-0141-6
- Guarneri C, Tchernev G, Wollina U, et al. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:490-492. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.137
- Arnold AW, Itin PH. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne in a child and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2010;126:E1227-E1230. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1390
- Dickman J, Kessler S. Unilateral reticulated patch localized to the anterior thigh. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.06.007
- Boffa MJ. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne on the left breast. Cutis. 2011;87:175-176.
- Li K, Barankin B. Cutaneous manifestations of modern technology use. J Cutan Med Surg. 2011;15:347-353. doi:10.2310/7750.2011.10053
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Laptop-induced erythema ab igne: report and review of literature. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Andersen F. Laptop-thighs--laptop-induced erythema ab igne [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:635.
- Jagtman BA. Erythema ab igne due to a laptop computer. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;50:105. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2004.0295g.x
- Olechowska M, Kisiel K, Ruszkowska L, et al. Erythema ab igne (EAI) induced by a laptop computer: report of two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2014.12387
- Nayak SUK, Shenoi SD, Prabhu S. Laptop induced erythema ab igne. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:131-132. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.94284
- Salvio AG, Nunes AJ, Angarita DPR. Laptop computer induced erythema ab igne: a new presentation of an old disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:79-80. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20165139
- Schummer C, Tittelbach J, Elsner P. Right-sided laptop dermatitis [in German]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015;140:1376-1377. doi:10.1055/s-0041-103615
- Manoharan D. Erythema ab igne: usual site, unusual cause. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S74-S75. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155811
- Giraldi S, Diettrich F, Abbage KT, et al. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer in an adolescent. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:128-130. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962011000100018
- Secher LLS, Vind-Kezunovic D, Zachariae COC. Side-effects to the use of laptop computers: erythema ab igne. Dermatol Reports. 2010;31:E11. doi:10.4081/dr.2010.e11
- Botten D, Langley RGB, Webb A. Academic branding: erythema ab igne and use of laptop computers. CMAJ. 2010;182:E857. doi:10.1503/cmaj.091868
- Bilic M, Adams BB. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:973-974. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.08.007
- Fu LW, Vender R. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer gaming - a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:716-717. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05033.x
- Levinbook WS, Mallett J, Grant-Kels JM. Laptop computer-associated erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2007;80:319-320.
- Mohr MR, Scott KA, Pariser RM, et al. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne: a case report. Cutis. 2007;79:59-60.
- Cantor AS, Bartling SJ. Laptop computer-induced hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt6k37r9wm.
- Kaptanog˘lu AF, Mullaaziz D. Erythema ab igne in the palmar area induced by smart phone: case report. Turkiye Klin J Med Sci. 2015;35:284-286. doi:10.5336/medsci.2015-46976
- Redding KS, Watts AN, Lee J, et al. Space heater-induced bullous erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2017;100:E9-E10.
- Goorland J, Edens MA, Baudoin TD. An emergency department presentation of erythema ab igne caused by repeated heater exposure. J La State Med Soc. 2016;168:33-34.
- Kokturk A, Kaya TI, Baz K, et al. Bullous erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:18.
- Brzezinski P, Ismail S, Chiriac A. Radiator-induced erythema ab igne in 8-year-old girl. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2014;85:239-240. doi:10.4067/S0370-41062014000200015
- Adams BB. Heated car seat-induced erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:265-266. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.2207
- Helm TN, Spigel GT, Helm KF. Erythema ab igne caused by a car heater. Cutis. 1997;59:81-82.
- Gregory JF, Beute TC. Erythema ab igne. J Spec Oper Med. 2013;13:115-119. doi:10.55460/5AVH-NZHY
- Chua S, Chen Q, Lee HY. Erythema ab igne and dermal scarring caused by cupping and moxibustion treatment. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:337-338. doi:10.1111/ddg.12581
- Chen JF, Liu YC, Chen YF, et al. Erythema ab igne after footbath with Chinese herbal remedies. J Chinese Med Assoc. 2011;74:51-53. doi:10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.009
- Baltazar D, Brockman R, Simpson E. Kotatsu-induced erythema ab igne. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:253-254. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20198792
- Baig M, Byrne F. Erythema ab igne and its relation to spinal pathology. Cureus. 2018;10:e2914. doi:10.7759/cureus.2914
- Aria AB, Chen L, Silapunt S. Erythema ab igne from heating pad use: a report of three clinical cases and a differential diagnosis. Cureus. 2018;10:e2635. doi:10.7759/cureus.2635
- Milchak M, Smucker J, Chung CG, et al. Erythema ab igne due to heating pad use: a case report and review of clinical presentation, prevention, and complications. Case Rep Med. 2016;1862480. doi:10.1155/2016/1862480
- Gmuca S, Yu J, Weiss PF, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with chronic pain: an alarming cutaneous eruption from heat exposure. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2020;36:e236-e238. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001460
- Dizdarevic A, Karim OA, Bygum A. A reddish brown reticulated hyperpigmented erythema on the abdomen of a girl. Erythema ab igne, also known as toasted skin syndrome, caused by a heating pad onthe abdomen. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:365-367. doi:10.2340/00015555-1722
- Chatterjee S. Erythema ab igne from prolonged use of a heating pad. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1500. doi:10.4065/80.11.1500
- Waldorf DS, Rast MF, Garofalo VJ. Heating-pad erythematous dermatitis “erythema ab igne.” JAMA. 1971;218:1704. doi:10.1001/jama.1971.03190240056023
- South AM, Crispin MK, Marqueling AL, et al. A hyperpigmented reticular rash in a patient on peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2016;36:677-700. doi:10.3747/pdi.2016.00042
- Ravindran R. Erythema ab igne in an individual with diabetes and gastroparesis. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2014203856. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-203856
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A, Tzavela E, et al. Erythema ab igne in three girls with anorexia nervosa. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e149-e150. doi:10.1111/pde.12770
- Fischer J, Rein K, Erfurt-Berge C, et al. Three cases of erythema ab igne (EAI) in patients with eating disorders. Neuropsychiatr. 2010;24:141-143.
- Docx MKF, Simons A, Ramet J, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2013;46:381-383. doi:10.1002/eat.22075
- Turan E, Cimen V, Haytoglu NSK, et al. A case of bullous erythema ab igne accompanied by anemia and subclinical hypothyroidism. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:223366.
- Pavithran K. Erythema ab igne, schizophrenia and thermophilia. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1987;53:181-182.
- Dellavelle R, Gillum P. Erythema ab igne following heating/cooling blanket use in the intensive care unit. Cutis. 2000;66:136-138.
- Park SY, Kim SM, Yoon TJ. Erythema ab igne caused by weight loss heating pad. Korean J Dermatol. 2007;45:489-491.
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Gisondi P, Plaserico S, Bordin C, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: a clinical update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2499-2504. doi:10.1111/jdv.16774
- Manalo IF, Smith MK, Cheeley J, et al. A dermatologic manifestation of COVID-19: transient livedo reticularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:700. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.018
- Zhao Q, Fang X, Pang Z, et al. COVID‐19 and cutaneous manifestations: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2505-2510. doi:10.1111/jdv.16778
- Akasaka T, Kon S. Two cases of squamous cell carcinoma arising from erythema ab igne. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1989;99:735-742.
- Arrington JH 3rd, Lockman DS. Thermal keratoses and squamous cell carcinoma in situ associated with erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1226-1228.
- Wharton JB, Sheehan DJ, Lesher JL Jr. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:488-489.
- Wollina U, Helm C, Hansel G, et al. Two cases of erythema ab igne, one with a squamous cell carcinoma. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2007;142:415-418.
- Rudolph CM, Soyer HP, Wolf P, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in erythema ab igne. Hautarzt. 2000;51:260-263. doi:10.1007/s001050051115
- Sigmon JR, Cantrell J, Teague D, et al. Poorly differentiated carcinoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:676-678. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3182871648
- Wharton J, Roffwarg D, Miller J, et al. Cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:1080-1081. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.08.005
- Jones CS, Tyring SK, Lee PC, et al. Development of neuroendocrine (Merkel cell) carcinoma mixed with squamous cell carcinoma in erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:110-113.
- Kim HW, Kim EJ, Park HC, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with low fluenced 1,064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:147-148. doi:10.3109/14764172.2013.854623
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;62:77-78.
- Gianfaldoni S, Gianfaldoni R, Tchernev G, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with mesoglycan and bioflavonoids: a case-report. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:432-435. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.123
- Perry. Case of erythema ab igne. Br J Dermatol. 1900;xxiii:375.
- Bose S, Ortonee JP. Diseases affected by heat. In: Parish LC, Millikan LE, Amer M, et al. Global Dermatology Diagnosis and Management According to Geography, Climate, and Culture. Springer-Varlag; 1994:83-92.
- Leal-Lobato MM, Blasco-Morente G. Electric blanket induced erythema ab igne [in Spanish]. Semergen. 2015;41:456-457. doi:10.1016/j.semerg.2014.12.008
- Huynh N, Sarma D, Huerter C. Erythema ab igne: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2011;88:290-292.
- Kesty K, Feldman SR. Erythema ab igne: evolving technology, evolving presentation. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20. doi:10.5070/D32011024689
- Miller K, Hunt R, Chu J, et al. Erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:28.
- Smith ML. Environmental and sports-related skin diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1569-1594.
- Errichetti E, Stinco G. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: a practical overview. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016;6:471-507. doi:10.1007/s13555-016-0141-6
- Guarneri C, Tchernev G, Wollina U, et al. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:490-492. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.137
- Arnold AW, Itin PH. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne in a child and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2010;126:E1227-E1230. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1390
- Dickman J, Kessler S. Unilateral reticulated patch localized to the anterior thigh. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.06.007
- Boffa MJ. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne on the left breast. Cutis. 2011;87:175-176.
- Li K, Barankin B. Cutaneous manifestations of modern technology use. J Cutan Med Surg. 2011;15:347-353. doi:10.2310/7750.2011.10053
- Riahi RR, Cohen PR. Laptop-induced erythema ab igne: report and review of literature. Dermatol Online J. 2012;18:5.
- Andersen F. Laptop-thighs--laptop-induced erythema ab igne [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:635.
- Jagtman BA. Erythema ab igne due to a laptop computer. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;50:105. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2004.0295g.x
- Olechowska M, Kisiel K, Ruszkowska L, et al. Erythema ab igne (EAI) induced by a laptop computer: report of two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2014.12387
- Nayak SUK, Shenoi SD, Prabhu S. Laptop induced erythema ab igne. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:131-132. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.94284
- Salvio AG, Nunes AJ, Angarita DPR. Laptop computer induced erythema ab igne: a new presentation of an old disease. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91:79-80. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20165139
- Schummer C, Tittelbach J, Elsner P. Right-sided laptop dermatitis [in German]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015;140:1376-1377. doi:10.1055/s-0041-103615
- Manoharan D. Erythema ab igne: usual site, unusual cause. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2015;7(suppl 1):S74-S75. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.155811
- Giraldi S, Diettrich F, Abbage KT, et al. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer in an adolescent. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:128-130. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962011000100018
- Secher LLS, Vind-Kezunovic D, Zachariae COC. Side-effects to the use of laptop computers: erythema ab igne. Dermatol Reports. 2010;31:E11. doi:10.4081/dr.2010.e11
- Botten D, Langley RGB, Webb A. Academic branding: erythema ab igne and use of laptop computers. CMAJ. 2010;182:E857. doi:10.1503/cmaj.091868
- Bilic M, Adams BB. Erythema ab igne induced by a laptop computer. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:973-974. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.08.007
- Fu LW, Vender R. Erythema ab igne caused by laptop computer gaming - a case report. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:716-717. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05033.x
- Levinbook WS, Mallett J, Grant-Kels JM. Laptop computer-associated erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2007;80:319-320.
- Mohr MR, Scott KA, Pariser RM, et al. Laptop computer-induced erythema ab igne: a case report. Cutis. 2007;79:59-60.
- Cantor AS, Bartling SJ. Laptop computer-induced hyperpigmentation. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt6k37r9wm.
- Kaptanog˘lu AF, Mullaaziz D. Erythema ab igne in the palmar area induced by smart phone: case report. Turkiye Klin J Med Sci. 2015;35:284-286. doi:10.5336/medsci.2015-46976
- Redding KS, Watts AN, Lee J, et al. Space heater-induced bullous erythema ab igne. Cutis. 2017;100:E9-E10.
- Goorland J, Edens MA, Baudoin TD. An emergency department presentation of erythema ab igne caused by repeated heater exposure. J La State Med Soc. 2016;168:33-34.
- Kokturk A, Kaya TI, Baz K, et al. Bullous erythema ab igne. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9:18.
- Brzezinski P, Ismail S, Chiriac A. Radiator-induced erythema ab igne in 8-year-old girl. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2014;85:239-240. doi:10.4067/S0370-41062014000200015
- Adams BB. Heated car seat-induced erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:265-266. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.2207
- Helm TN, Spigel GT, Helm KF. Erythema ab igne caused by a car heater. Cutis. 1997;59:81-82.
- Gregory JF, Beute TC. Erythema ab igne. J Spec Oper Med. 2013;13:115-119. doi:10.55460/5AVH-NZHY
- Chua S, Chen Q, Lee HY. Erythema ab igne and dermal scarring caused by cupping and moxibustion treatment. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2015;13:337-338. doi:10.1111/ddg.12581
- Chen JF, Liu YC, Chen YF, et al. Erythema ab igne after footbath with Chinese herbal remedies. J Chinese Med Assoc. 2011;74:51-53. doi:10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.009
- Baltazar D, Brockman R, Simpson E. Kotatsu-induced erythema ab igne. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94:253-254. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20198792
- Baig M, Byrne F. Erythema ab igne and its relation to spinal pathology. Cureus. 2018;10:e2914. doi:10.7759/cureus.2914
- Aria AB, Chen L, Silapunt S. Erythema ab igne from heating pad use: a report of three clinical cases and a differential diagnosis. Cureus. 2018;10:e2635. doi:10.7759/cureus.2635
- Milchak M, Smucker J, Chung CG, et al. Erythema ab igne due to heating pad use: a case report and review of clinical presentation, prevention, and complications. Case Rep Med. 2016;1862480. doi:10.1155/2016/1862480
- Gmuca S, Yu J, Weiss PF, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with chronic pain: an alarming cutaneous eruption from heat exposure. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2020;36:e236-e238. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001460
- Dizdarevic A, Karim OA, Bygum A. A reddish brown reticulated hyperpigmented erythema on the abdomen of a girl. Erythema ab igne, also known as toasted skin syndrome, caused by a heating pad onthe abdomen. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:365-367. doi:10.2340/00015555-1722
- Chatterjee S. Erythema ab igne from prolonged use of a heating pad. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1500. doi:10.4065/80.11.1500
- Waldorf DS, Rast MF, Garofalo VJ. Heating-pad erythematous dermatitis “erythema ab igne.” JAMA. 1971;218:1704. doi:10.1001/jama.1971.03190240056023
- South AM, Crispin MK, Marqueling AL, et al. A hyperpigmented reticular rash in a patient on peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2016;36:677-700. doi:10.3747/pdi.2016.00042
- Ravindran R. Erythema ab igne in an individual with diabetes and gastroparesis. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2014203856. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-203856
- Dessinioti C, Katsambas A, Tzavela E, et al. Erythema ab igne in three girls with anorexia nervosa. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e149-e150. doi:10.1111/pde.12770
- Fischer J, Rein K, Erfurt-Berge C, et al. Three cases of erythema ab igne (EAI) in patients with eating disorders. Neuropsychiatr. 2010;24:141-143.
- Docx MKF, Simons A, Ramet J, et al. Erythema ab igne in an adolescent with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2013;46:381-383. doi:10.1002/eat.22075
- Turan E, Cimen V, Haytoglu NSK, et al. A case of bullous erythema ab igne accompanied by anemia and subclinical hypothyroidism. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:223366.
- Pavithran K. Erythema ab igne, schizophrenia and thermophilia. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1987;53:181-182.
- Dellavelle R, Gillum P. Erythema ab igne following heating/cooling blanket use in the intensive care unit. Cutis. 2000;66:136-138.
- Park SY, Kim SM, Yoon TJ. Erythema ab igne caused by weight loss heating pad. Korean J Dermatol. 2007;45:489-491.
- Sachdeva M, Gianotti R, Shah M, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98:75-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.011
- Gisondi P, Plaserico S, Bordin C, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: a clinical update. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2499-2504. doi:10.1111/jdv.16774
- Manalo IF, Smith MK, Cheeley J, et al. A dermatologic manifestation of COVID-19: transient livedo reticularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:700. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.018
- Zhao Q, Fang X, Pang Z, et al. COVID‐19 and cutaneous manifestations: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34:2505-2510. doi:10.1111/jdv.16778
- Akasaka T, Kon S. Two cases of squamous cell carcinoma arising from erythema ab igne. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1989;99:735-742.
- Arrington JH 3rd, Lockman DS. Thermal keratoses and squamous cell carcinoma in situ associated with erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1979;115:1226-1228.
- Wharton JB, Sheehan DJ, Lesher JL Jr. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:488-489.
- Wollina U, Helm C, Hansel G, et al. Two cases of erythema ab igne, one with a squamous cell carcinoma. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2007;142:415-418.
- Rudolph CM, Soyer HP, Wolf P, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in erythema ab igne. Hautarzt. 2000;51:260-263. doi:10.1007/s001050051115
- Sigmon JR, Cantrell J, Teague D, et al. Poorly differentiated carcinoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:676-678. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3182871648
- Wharton J, Roffwarg D, Miller J, et al. Cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma arising in the setting of erythema ab igne. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:1080-1081. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.08.005
- Jones CS, Tyring SK, Lee PC, et al. Development of neuroendocrine (Merkel cell) carcinoma mixed with squamous cell carcinoma in erythema ab igne. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:110-113.
- Kim HW, Kim EJ, Park HC, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with low fluenced 1,064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16:147-148. doi:10.3109/14764172.2013.854623
- Tan S, Bertucci V. Erythema ab igne: an old condition new again. CMAJ. 2000;62:77-78.
- Gianfaldoni S, Gianfaldoni R, Tchernev G, et al. Erythema ab igne successfully treated with mesoglycan and bioflavonoids: a case-report. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5:432-435. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.123
Practice Points
- Erythema ab igne (EAI) is a skin condition caused by chronic exposure to heat; removal of the heat source often will result in self-resolution of the rash.
- Erythema ab igne can be a sign of underlying illness in patients self-treating chronic pain with application of heat.
- Recognition and discontinuation of the exposure with close observation are key components in the treatment of EAI.