User login
Opportunities missed for advance care planning for elderly ICU patients
SAN DIEGO – A nationally representative survey of the problem is more pronounced among some blacks and Hispanics and those with lower net worth. The study also found that these patients see physicians an average of 20 times in the year preceding the ICU visit, which suggests that there are plenty of opportunities to put ACP in place.
“Over two-thirds were seen by a doctor in the last 2 weeks. So they’re seeing doctors, but they’re still not doing advance care planning,” said Brian Block, MD, during a presentation of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Block is with the University of California, San Francisco.
Lack of advance planning can put major road blocks in front of patient care in the ICU, as well as complicate communication between physicians and family members. The findings underscore the need to encourage conversations about end-of-life care between physicians and their patients – before the patients wind up in intensive care.
One audience member believes these conversations are already happening. Paul Yodice, MD, chairman of medicine at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J., suggested that physicians are attempting to engage older patients and family members in ACP, but many are unready to make decisions. “In my experience, it is happening much more frequently than is captured either in the medical record or in the research that we’ve been publishing. I’ve been a part of those conversations. Those individuals who are faced with those toughest of choices choose to delay making the decision or speaking about it further because it’s just too painful to consider, and they hold out hope of being the one to beat the odds, to have one more day,” said Dr. Yodice.
He called for further research to document whether ACP conversations are happening and to identify barriers to decisions and the means to overcome them. “A next good study would be to send out a respectful survey to the families of those who have lost people they love and ask: Has someone in the past year spoken with you or offered to have a discussion about end-of-life issues? We could get a better handle on [how often] the discussion is being had, and then find a solution,” said Dr. Yodice.
ACP can also be difficult for the provider, he added. Family members and patients, desperate for another treatment option, will often ask if there’s anything else that can be done. “In medicine, the answer almost always is ‘Well, we can try something else even though I know it’s not going to work.’ And people hold on to that, including us,” said Dr. Yodice.
The study analyzed data from a Medicare cohort of 1,109 patients who died during 2000-2013 and had an ICU admission within the last 30 days of their life. Ages were fairly evenly distributed, with 29% aged 65-74 years, 39% aged 75-84, and 32% aged 85 and over. Fifty-four percent were women, 26% were nonwhite, 42% had not completed high school, and 11% were in skilled nursing facilities.
About 35% had no ACP in 2000-2001, and that percentage gradually declined, to about 20% in 2012-2013 (slope, –1.6%/year; P = .009).
Seventeen percent of white participants had no ACP, compared with 51% of blacks and 49% of Hispanics. Net worth was also strongly associated with having ACP: The top quartile had 13% lacking ACP, compared with 43% of the bottom quartile.
The study found that 94% of patients who had no ACP had visited a health care provider in the past year. The average number of visits in the past year was 20, and 83% had seen a provider within the past 30 days.
Dr. Block did not declare a source of funding or potential conflicts. Dr. Yodice had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Block B et al. CCC48, Abstract 401.
SAN DIEGO – A nationally representative survey of the problem is more pronounced among some blacks and Hispanics and those with lower net worth. The study also found that these patients see physicians an average of 20 times in the year preceding the ICU visit, which suggests that there are plenty of opportunities to put ACP in place.
“Over two-thirds were seen by a doctor in the last 2 weeks. So they’re seeing doctors, but they’re still not doing advance care planning,” said Brian Block, MD, during a presentation of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Block is with the University of California, San Francisco.
Lack of advance planning can put major road blocks in front of patient care in the ICU, as well as complicate communication between physicians and family members. The findings underscore the need to encourage conversations about end-of-life care between physicians and their patients – before the patients wind up in intensive care.
One audience member believes these conversations are already happening. Paul Yodice, MD, chairman of medicine at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J., suggested that physicians are attempting to engage older patients and family members in ACP, but many are unready to make decisions. “In my experience, it is happening much more frequently than is captured either in the medical record or in the research that we’ve been publishing. I’ve been a part of those conversations. Those individuals who are faced with those toughest of choices choose to delay making the decision or speaking about it further because it’s just too painful to consider, and they hold out hope of being the one to beat the odds, to have one more day,” said Dr. Yodice.
He called for further research to document whether ACP conversations are happening and to identify barriers to decisions and the means to overcome them. “A next good study would be to send out a respectful survey to the families of those who have lost people they love and ask: Has someone in the past year spoken with you or offered to have a discussion about end-of-life issues? We could get a better handle on [how often] the discussion is being had, and then find a solution,” said Dr. Yodice.
ACP can also be difficult for the provider, he added. Family members and patients, desperate for another treatment option, will often ask if there’s anything else that can be done. “In medicine, the answer almost always is ‘Well, we can try something else even though I know it’s not going to work.’ And people hold on to that, including us,” said Dr. Yodice.
The study analyzed data from a Medicare cohort of 1,109 patients who died during 2000-2013 and had an ICU admission within the last 30 days of their life. Ages were fairly evenly distributed, with 29% aged 65-74 years, 39% aged 75-84, and 32% aged 85 and over. Fifty-four percent were women, 26% were nonwhite, 42% had not completed high school, and 11% were in skilled nursing facilities.
About 35% had no ACP in 2000-2001, and that percentage gradually declined, to about 20% in 2012-2013 (slope, –1.6%/year; P = .009).
Seventeen percent of white participants had no ACP, compared with 51% of blacks and 49% of Hispanics. Net worth was also strongly associated with having ACP: The top quartile had 13% lacking ACP, compared with 43% of the bottom quartile.
The study found that 94% of patients who had no ACP had visited a health care provider in the past year. The average number of visits in the past year was 20, and 83% had seen a provider within the past 30 days.
Dr. Block did not declare a source of funding or potential conflicts. Dr. Yodice had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Block B et al. CCC48, Abstract 401.
SAN DIEGO – A nationally representative survey of the problem is more pronounced among some blacks and Hispanics and those with lower net worth. The study also found that these patients see physicians an average of 20 times in the year preceding the ICU visit, which suggests that there are plenty of opportunities to put ACP in place.
“Over two-thirds were seen by a doctor in the last 2 weeks. So they’re seeing doctors, but they’re still not doing advance care planning,” said Brian Block, MD, during a presentation of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Block is with the University of California, San Francisco.
Lack of advance planning can put major road blocks in front of patient care in the ICU, as well as complicate communication between physicians and family members. The findings underscore the need to encourage conversations about end-of-life care between physicians and their patients – before the patients wind up in intensive care.
One audience member believes these conversations are already happening. Paul Yodice, MD, chairman of medicine at Saint Barnabas Medical Center in Livingston, N.J., suggested that physicians are attempting to engage older patients and family members in ACP, but many are unready to make decisions. “In my experience, it is happening much more frequently than is captured either in the medical record or in the research that we’ve been publishing. I’ve been a part of those conversations. Those individuals who are faced with those toughest of choices choose to delay making the decision or speaking about it further because it’s just too painful to consider, and they hold out hope of being the one to beat the odds, to have one more day,” said Dr. Yodice.
He called for further research to document whether ACP conversations are happening and to identify barriers to decisions and the means to overcome them. “A next good study would be to send out a respectful survey to the families of those who have lost people they love and ask: Has someone in the past year spoken with you or offered to have a discussion about end-of-life issues? We could get a better handle on [how often] the discussion is being had, and then find a solution,” said Dr. Yodice.
ACP can also be difficult for the provider, he added. Family members and patients, desperate for another treatment option, will often ask if there’s anything else that can be done. “In medicine, the answer almost always is ‘Well, we can try something else even though I know it’s not going to work.’ And people hold on to that, including us,” said Dr. Yodice.
The study analyzed data from a Medicare cohort of 1,109 patients who died during 2000-2013 and had an ICU admission within the last 30 days of their life. Ages were fairly evenly distributed, with 29% aged 65-74 years, 39% aged 75-84, and 32% aged 85 and over. Fifty-four percent were women, 26% were nonwhite, 42% had not completed high school, and 11% were in skilled nursing facilities.
About 35% had no ACP in 2000-2001, and that percentage gradually declined, to about 20% in 2012-2013 (slope, –1.6%/year; P = .009).
Seventeen percent of white participants had no ACP, compared with 51% of blacks and 49% of Hispanics. Net worth was also strongly associated with having ACP: The top quartile had 13% lacking ACP, compared with 43% of the bottom quartile.
The study found that 94% of patients who had no ACP had visited a health care provider in the past year. The average number of visits in the past year was 20, and 83% had seen a provider within the past 30 days.
Dr. Block did not declare a source of funding or potential conflicts. Dr. Yodice had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Block B et al. CCC48, Abstract 401.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
U.S. measles cases up to 159 for the year
Reported measles cases are now up to 159 for the year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The most recent reporting week, which ended Feb. 21, brought another 32 cases of measles and one new outbreak of 4 cases in Illinois. The total number of outbreaks – an outbreak is defined as three or more cases – is now six, and cases have been reported in 10 states, the CDC said Feb. 25.
The majority (17) of those 32 new cases occurred in Brooklyn, one of New York state’s three outbreaks this year. The largest of the 2019 outbreaks is in Washington state, primarily in Clark County, and is up to 66 cases after 4 more were reported in the last week by the state’s department of health. The outbreaks are linked to travelers who brought the disease to the United States.
There are now two measures “advancing through the [Washington] state legislature that would bar parents from using personal or philosophical exemptions to avoid immunizing their school-age children. Both have bipartisan support despite strong antivaccination sentiment in parts of the state,” the Washington Post said on Feb. 25.
Reported measles cases are now up to 159 for the year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The most recent reporting week, which ended Feb. 21, brought another 32 cases of measles and one new outbreak of 4 cases in Illinois. The total number of outbreaks – an outbreak is defined as three or more cases – is now six, and cases have been reported in 10 states, the CDC said Feb. 25.
The majority (17) of those 32 new cases occurred in Brooklyn, one of New York state’s three outbreaks this year. The largest of the 2019 outbreaks is in Washington state, primarily in Clark County, and is up to 66 cases after 4 more were reported in the last week by the state’s department of health. The outbreaks are linked to travelers who brought the disease to the United States.
There are now two measures “advancing through the [Washington] state legislature that would bar parents from using personal or philosophical exemptions to avoid immunizing their school-age children. Both have bipartisan support despite strong antivaccination sentiment in parts of the state,” the Washington Post said on Feb. 25.
Reported measles cases are now up to 159 for the year in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The most recent reporting week, which ended Feb. 21, brought another 32 cases of measles and one new outbreak of 4 cases in Illinois. The total number of outbreaks – an outbreak is defined as three or more cases – is now six, and cases have been reported in 10 states, the CDC said Feb. 25.
The majority (17) of those 32 new cases occurred in Brooklyn, one of New York state’s three outbreaks this year. The largest of the 2019 outbreaks is in Washington state, primarily in Clark County, and is up to 66 cases after 4 more were reported in the last week by the state’s department of health. The outbreaks are linked to travelers who brought the disease to the United States.
There are now two measures “advancing through the [Washington] state legislature that would bar parents from using personal or philosophical exemptions to avoid immunizing their school-age children. Both have bipartisan support despite strong antivaccination sentiment in parts of the state,” the Washington Post said on Feb. 25.
Peripheral perfusion fails septic shock test, but optimism remains
SAN DIEGO – During resuscitation of patients but missed statistical significance.

Although the paper, published online in JAMA, concludes that normalization of capillary refill time cannot be recommended over targeting serum lactate levels, Glenn Hernández, MD, PhD, sounded more optimistic after presenting the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “I think it’s good news to develop techniques that, even though they have this integrated variability, they can provide a signal that is also very close to the [underlying] physiology,” Dr. Hernández, who is a professor of intensive medicine at Pontifical Catholic University in Santiago, Chile. The Peripheral perfusion was also associated with lower mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score at 72 hours.
The technique involves pressing a glass microscope slide to the ventral surface of the right index finger distal phalanx, increasing pressure and maintaining pressure for 10 seconds. After release, a chronometer assessed return of normal skin color, with refill times over 3 seconds considered abnormal. Clinicians applied the technique every 30 minutes during until normalization (every hour after that), compared with every 2 hours for the lactate arm of the study.
The ANDROMEDA-SHOCK randomized clinical trial was conducted at 28 hospitals in five countries (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Uruguay). The trial did not demonstrate superiority of capillary refill, and it was not designed for noninferiority. It nevertheless seems unlikely that assessment of capillary refill is inferior to lactate levels, according an accompanying editorial by JAMA-associated editor Derek Angus, MD, who also is a professor of critical care medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. The simplicity of using a capillary refill could be particularly useful in resource-limited settings, since it can be accomplished visually.
It also a natural marker for resuscitation. The body slows fluid flow to peripheral tissues until vital organs are well perfused. Normal capillary refill time “is an indirect signal of reperfusion,” said Dr. Hernández.
The researchers are not calling for this technique to replace lactate measurements, noting that in many ways the techniques can be complementary, since lactate levels are a good indicator of the patient’s overall improvement. In any case, it would take more research to prove superiority of the capillary refill, and that’s not something Dr. Hernández is planning to undertake. The current study had no external funding and required about half of his time over a 2-year period. Getting the work done at all “was sort of a miracle. We would not repeat this,” he said.
The researchers randomized 416 patients with septic shock (mean age, 63 years; 53% of whom were women) to be managed by peripheral perfusion or lactate measurement. By day 28, 43.4% in the lactate group had died, compared with 34.9% in the peripheral perfusion group (hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .06). At 72 hours, the peripheral perfusion group had less organ dysfunction as measured by SOFA (mean, 5.6 vs. 6.6; P = .045). Six other secondary outcomes revealed no between-group differences.
The peripheral perfusion group received an average of 408 fewer mL of resuscitation fluids during the first 8 hours (P = .01).
That result fits with the greater responsiveness of peripheral perfusion measurements, and it’s relevant because some septic shock patients who are unresponsive to fluids often receive fluids anyway. “The general knowledge, though not correct, is that you treat lactate or blood pressure with fluids,” said coauthor Jan Bakker, MD, PhD, who is a professor at New York-Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University, and Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
After a series of observational studies suggested that warm, well-perfused patients were doing well, the idea was tested in a small interventional trial in which physicians were forbidden from giving fluids once patients were warm and well perfused. Patients did better than did those on standard of care. “We have said, if the patient is warm and well perfused, even if they are hypotensive, don’t give fluids, it won’t benefit them anymore. Give vasopressors or whatever, but don’t give fluids,” said Dr. Bakker.
The latest research also reinforced a signal from the earlier, smaller trial. “You get less organ failure if you use [fewer] fluids,” Dr. Bakker added.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Hernández and Dr. Bakker had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Angus received consulting fees from Ferring Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer AG, and others outside the submitted work; he also has patents pending for compounds, compositions, and methods for treating sepsis and for proteomic biomarkers.
SOURCE: Hernández G et al. JAMA 2019 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0071.
SAN DIEGO – During resuscitation of patients but missed statistical significance.

Although the paper, published online in JAMA, concludes that normalization of capillary refill time cannot be recommended over targeting serum lactate levels, Glenn Hernández, MD, PhD, sounded more optimistic after presenting the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “I think it’s good news to develop techniques that, even though they have this integrated variability, they can provide a signal that is also very close to the [underlying] physiology,” Dr. Hernández, who is a professor of intensive medicine at Pontifical Catholic University in Santiago, Chile. The Peripheral perfusion was also associated with lower mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score at 72 hours.
The technique involves pressing a glass microscope slide to the ventral surface of the right index finger distal phalanx, increasing pressure and maintaining pressure for 10 seconds. After release, a chronometer assessed return of normal skin color, with refill times over 3 seconds considered abnormal. Clinicians applied the technique every 30 minutes during until normalization (every hour after that), compared with every 2 hours for the lactate arm of the study.
The ANDROMEDA-SHOCK randomized clinical trial was conducted at 28 hospitals in five countries (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Uruguay). The trial did not demonstrate superiority of capillary refill, and it was not designed for noninferiority. It nevertheless seems unlikely that assessment of capillary refill is inferior to lactate levels, according an accompanying editorial by JAMA-associated editor Derek Angus, MD, who also is a professor of critical care medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. The simplicity of using a capillary refill could be particularly useful in resource-limited settings, since it can be accomplished visually.
It also a natural marker for resuscitation. The body slows fluid flow to peripheral tissues until vital organs are well perfused. Normal capillary refill time “is an indirect signal of reperfusion,” said Dr. Hernández.
The researchers are not calling for this technique to replace lactate measurements, noting that in many ways the techniques can be complementary, since lactate levels are a good indicator of the patient’s overall improvement. In any case, it would take more research to prove superiority of the capillary refill, and that’s not something Dr. Hernández is planning to undertake. The current study had no external funding and required about half of his time over a 2-year period. Getting the work done at all “was sort of a miracle. We would not repeat this,” he said.
The researchers randomized 416 patients with septic shock (mean age, 63 years; 53% of whom were women) to be managed by peripheral perfusion or lactate measurement. By day 28, 43.4% in the lactate group had died, compared with 34.9% in the peripheral perfusion group (hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .06). At 72 hours, the peripheral perfusion group had less organ dysfunction as measured by SOFA (mean, 5.6 vs. 6.6; P = .045). Six other secondary outcomes revealed no between-group differences.
The peripheral perfusion group received an average of 408 fewer mL of resuscitation fluids during the first 8 hours (P = .01).
That result fits with the greater responsiveness of peripheral perfusion measurements, and it’s relevant because some septic shock patients who are unresponsive to fluids often receive fluids anyway. “The general knowledge, though not correct, is that you treat lactate or blood pressure with fluids,” said coauthor Jan Bakker, MD, PhD, who is a professor at New York-Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University, and Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
After a series of observational studies suggested that warm, well-perfused patients were doing well, the idea was tested in a small interventional trial in which physicians were forbidden from giving fluids once patients were warm and well perfused. Patients did better than did those on standard of care. “We have said, if the patient is warm and well perfused, even if they are hypotensive, don’t give fluids, it won’t benefit them anymore. Give vasopressors or whatever, but don’t give fluids,” said Dr. Bakker.
The latest research also reinforced a signal from the earlier, smaller trial. “You get less organ failure if you use [fewer] fluids,” Dr. Bakker added.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Hernández and Dr. Bakker had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Angus received consulting fees from Ferring Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer AG, and others outside the submitted work; he also has patents pending for compounds, compositions, and methods for treating sepsis and for proteomic biomarkers.
SOURCE: Hernández G et al. JAMA 2019 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0071.
SAN DIEGO – During resuscitation of patients but missed statistical significance.

Although the paper, published online in JAMA, concludes that normalization of capillary refill time cannot be recommended over targeting serum lactate levels, Glenn Hernández, MD, PhD, sounded more optimistic after presenting the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. “I think it’s good news to develop techniques that, even though they have this integrated variability, they can provide a signal that is also very close to the [underlying] physiology,” Dr. Hernández, who is a professor of intensive medicine at Pontifical Catholic University in Santiago, Chile. The Peripheral perfusion was also associated with lower mean Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score at 72 hours.
The technique involves pressing a glass microscope slide to the ventral surface of the right index finger distal phalanx, increasing pressure and maintaining pressure for 10 seconds. After release, a chronometer assessed return of normal skin color, with refill times over 3 seconds considered abnormal. Clinicians applied the technique every 30 minutes during until normalization (every hour after that), compared with every 2 hours for the lactate arm of the study.
The ANDROMEDA-SHOCK randomized clinical trial was conducted at 28 hospitals in five countries (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Uruguay). The trial did not demonstrate superiority of capillary refill, and it was not designed for noninferiority. It nevertheless seems unlikely that assessment of capillary refill is inferior to lactate levels, according an accompanying editorial by JAMA-associated editor Derek Angus, MD, who also is a professor of critical care medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. The simplicity of using a capillary refill could be particularly useful in resource-limited settings, since it can be accomplished visually.
It also a natural marker for resuscitation. The body slows fluid flow to peripheral tissues until vital organs are well perfused. Normal capillary refill time “is an indirect signal of reperfusion,” said Dr. Hernández.
The researchers are not calling for this technique to replace lactate measurements, noting that in many ways the techniques can be complementary, since lactate levels are a good indicator of the patient’s overall improvement. In any case, it would take more research to prove superiority of the capillary refill, and that’s not something Dr. Hernández is planning to undertake. The current study had no external funding and required about half of his time over a 2-year period. Getting the work done at all “was sort of a miracle. We would not repeat this,” he said.
The researchers randomized 416 patients with septic shock (mean age, 63 years; 53% of whom were women) to be managed by peripheral perfusion or lactate measurement. By day 28, 43.4% in the lactate group had died, compared with 34.9% in the peripheral perfusion group (hazard ratio, 0.75; P = .06). At 72 hours, the peripheral perfusion group had less organ dysfunction as measured by SOFA (mean, 5.6 vs. 6.6; P = .045). Six other secondary outcomes revealed no between-group differences.
The peripheral perfusion group received an average of 408 fewer mL of resuscitation fluids during the first 8 hours (P = .01).
That result fits with the greater responsiveness of peripheral perfusion measurements, and it’s relevant because some septic shock patients who are unresponsive to fluids often receive fluids anyway. “The general knowledge, though not correct, is that you treat lactate or blood pressure with fluids,” said coauthor Jan Bakker, MD, PhD, who is a professor at New York-Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University, and Erasmus University Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
After a series of observational studies suggested that warm, well-perfused patients were doing well, the idea was tested in a small interventional trial in which physicians were forbidden from giving fluids once patients were warm and well perfused. Patients did better than did those on standard of care. “We have said, if the patient is warm and well perfused, even if they are hypotensive, don’t give fluids, it won’t benefit them anymore. Give vasopressors or whatever, but don’t give fluids,” said Dr. Bakker.
The latest research also reinforced a signal from the earlier, smaller trial. “You get less organ failure if you use [fewer] fluids,” Dr. Bakker added.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Hernández and Dr. Bakker had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Angus received consulting fees from Ferring Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer AG, and others outside the submitted work; he also has patents pending for compounds, compositions, and methods for treating sepsis and for proteomic biomarkers.
SOURCE: Hernández G et al. JAMA 2019 Feb 17. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0071.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
Palliative care has improved for critically ill children, but challenges remain
SAN DIEGO – and is more common among older children, female children, and those with government insurance or at a high risk of mortality. The findings come from a retrospective analysis of data from 52 hospitals, which included ICU admissions (except neonatal ICU) during 2007-2018.
The good news is that palliative care consultations have increased, with consultations in less than 1% of cases at the start of the study and rising quickly to more than 7% in 2018.
“In the adult world, palliative care has expanded in recent decades, and I think now that it’s coming to the pediatric world, it’ll just continue to go up,” said Siobhan O’Keefe, MD, in an interview. Dr. O’Keefe is with Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. She presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
More work needs to be done, she said. “We are not uniformly using palliative care for critically ill children in the U.S., and it varies across institutions. That’s probably not the ideal situation,” said Dr. O’Keefe. The study did not track palliative care versus the presence of board-certified palliative care physicians or palliative care fellowships, but she suspects they would correlate.
Dr. O’Keefe called for physicians to think beyond the patient, to family members and caregivers. “We need to focus on family outcomes, how they are taking care of children with moderate disability, and incorporate that into our outcomes,” she said. Previous research has shown family members to be at risk of anxiety, depression, unemployment, and financial distress.
The researchers analyzed data from 740,890 patients with 1,024,666 hospitalizations (82% had one hospitalization). They divided subjects into three cohorts, one of which was a category of patients with criteria for palliative care based on previous research (PC-ICU). The PC-ICU cohort included patients with an expected length of stay more than 2 weeks, patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), severe brain injuries, acute respiratory failure with serious comorbidity, hematologic or oncologic disease, metabolic disease, renal failure that required continuous renal replacement therapy, hepatic failure, or serious chromosomal abnormality. A second cohort included chronic complex conditions not found in the PC-ICU cohort (additional criteria), and a third cohort had no criteria for palliative care.
Thirty percent of hospitalizations met the PC-ICU cohort criteria, 40% met the additional cohort criteria, and 30% fell in the no criteria cohort. The PC-ICU group had the highest mortality, at 8.03%, compared with 1.08% in the additional criteria group and 0.34% in the no criteria group (P less than .00001).
Palliative care consultations occurred more frequently in 5-12 year olds (odds ratio 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.13) and in those aged 13 years or older (OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.3-1.46), in females (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15), and in patients with government insurance (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.17-1.29). Compared with those in the no criteria cohort, PC-ICU patients were more likely to receive a palliative care consult (OR, 75.5; 95% CI, 60.4-94.3), as were those in the additional criteria group (OR, 19.1; 95% CI, 15.3-23.9).
Cross-institutional palliative care frequency varied widely among patients in the PC-ICU group, ranging from 0% to 44%. The frequency ranged from 0% to 12% across institutions for patients in the additional criteria group.
SOURCE: O’Keefe S et al. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 418.
SAN DIEGO – and is more common among older children, female children, and those with government insurance or at a high risk of mortality. The findings come from a retrospective analysis of data from 52 hospitals, which included ICU admissions (except neonatal ICU) during 2007-2018.
The good news is that palliative care consultations have increased, with consultations in less than 1% of cases at the start of the study and rising quickly to more than 7% in 2018.
“In the adult world, palliative care has expanded in recent decades, and I think now that it’s coming to the pediatric world, it’ll just continue to go up,” said Siobhan O’Keefe, MD, in an interview. Dr. O’Keefe is with Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. She presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
More work needs to be done, she said. “We are not uniformly using palliative care for critically ill children in the U.S., and it varies across institutions. That’s probably not the ideal situation,” said Dr. O’Keefe. The study did not track palliative care versus the presence of board-certified palliative care physicians or palliative care fellowships, but she suspects they would correlate.
Dr. O’Keefe called for physicians to think beyond the patient, to family members and caregivers. “We need to focus on family outcomes, how they are taking care of children with moderate disability, and incorporate that into our outcomes,” she said. Previous research has shown family members to be at risk of anxiety, depression, unemployment, and financial distress.
The researchers analyzed data from 740,890 patients with 1,024,666 hospitalizations (82% had one hospitalization). They divided subjects into three cohorts, one of which was a category of patients with criteria for palliative care based on previous research (PC-ICU). The PC-ICU cohort included patients with an expected length of stay more than 2 weeks, patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), severe brain injuries, acute respiratory failure with serious comorbidity, hematologic or oncologic disease, metabolic disease, renal failure that required continuous renal replacement therapy, hepatic failure, or serious chromosomal abnormality. A second cohort included chronic complex conditions not found in the PC-ICU cohort (additional criteria), and a third cohort had no criteria for palliative care.
Thirty percent of hospitalizations met the PC-ICU cohort criteria, 40% met the additional cohort criteria, and 30% fell in the no criteria cohort. The PC-ICU group had the highest mortality, at 8.03%, compared with 1.08% in the additional criteria group and 0.34% in the no criteria group (P less than .00001).
Palliative care consultations occurred more frequently in 5-12 year olds (odds ratio 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.13) and in those aged 13 years or older (OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.3-1.46), in females (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15), and in patients with government insurance (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.17-1.29). Compared with those in the no criteria cohort, PC-ICU patients were more likely to receive a palliative care consult (OR, 75.5; 95% CI, 60.4-94.3), as were those in the additional criteria group (OR, 19.1; 95% CI, 15.3-23.9).
Cross-institutional palliative care frequency varied widely among patients in the PC-ICU group, ranging from 0% to 44%. The frequency ranged from 0% to 12% across institutions for patients in the additional criteria group.
SOURCE: O’Keefe S et al. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 418.
SAN DIEGO – and is more common among older children, female children, and those with government insurance or at a high risk of mortality. The findings come from a retrospective analysis of data from 52 hospitals, which included ICU admissions (except neonatal ICU) during 2007-2018.
The good news is that palliative care consultations have increased, with consultations in less than 1% of cases at the start of the study and rising quickly to more than 7% in 2018.
“In the adult world, palliative care has expanded in recent decades, and I think now that it’s coming to the pediatric world, it’ll just continue to go up,” said Siobhan O’Keefe, MD, in an interview. Dr. O’Keefe is with Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. She presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
More work needs to be done, she said. “We are not uniformly using palliative care for critically ill children in the U.S., and it varies across institutions. That’s probably not the ideal situation,” said Dr. O’Keefe. The study did not track palliative care versus the presence of board-certified palliative care physicians or palliative care fellowships, but she suspects they would correlate.
Dr. O’Keefe called for physicians to think beyond the patient, to family members and caregivers. “We need to focus on family outcomes, how they are taking care of children with moderate disability, and incorporate that into our outcomes,” she said. Previous research has shown family members to be at risk of anxiety, depression, unemployment, and financial distress.
The researchers analyzed data from 740,890 patients with 1,024,666 hospitalizations (82% had one hospitalization). They divided subjects into three cohorts, one of which was a category of patients with criteria for palliative care based on previous research (PC-ICU). The PC-ICU cohort included patients with an expected length of stay more than 2 weeks, patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), severe brain injuries, acute respiratory failure with serious comorbidity, hematologic or oncologic disease, metabolic disease, renal failure that required continuous renal replacement therapy, hepatic failure, or serious chromosomal abnormality. A second cohort included chronic complex conditions not found in the PC-ICU cohort (additional criteria), and a third cohort had no criteria for palliative care.
Thirty percent of hospitalizations met the PC-ICU cohort criteria, 40% met the additional cohort criteria, and 30% fell in the no criteria cohort. The PC-ICU group had the highest mortality, at 8.03%, compared with 1.08% in the additional criteria group and 0.34% in the no criteria group (P less than .00001).
Palliative care consultations occurred more frequently in 5-12 year olds (odds ratio 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.13) and in those aged 13 years or older (OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.3-1.46), in females (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15), and in patients with government insurance (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.17-1.29). Compared with those in the no criteria cohort, PC-ICU patients were more likely to receive a palliative care consult (OR, 75.5; 95% CI, 60.4-94.3), as were those in the additional criteria group (OR, 19.1; 95% CI, 15.3-23.9).
Cross-institutional palliative care frequency varied widely among patients in the PC-ICU group, ranging from 0% to 44%. The frequency ranged from 0% to 12% across institutions for patients in the additional criteria group.
SOURCE: O’Keefe S et al. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 418.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
Influenza activity continues to increase
The 2018-2019 flu season is showing no signs of decline as activity measures continued to increase into mid-February, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
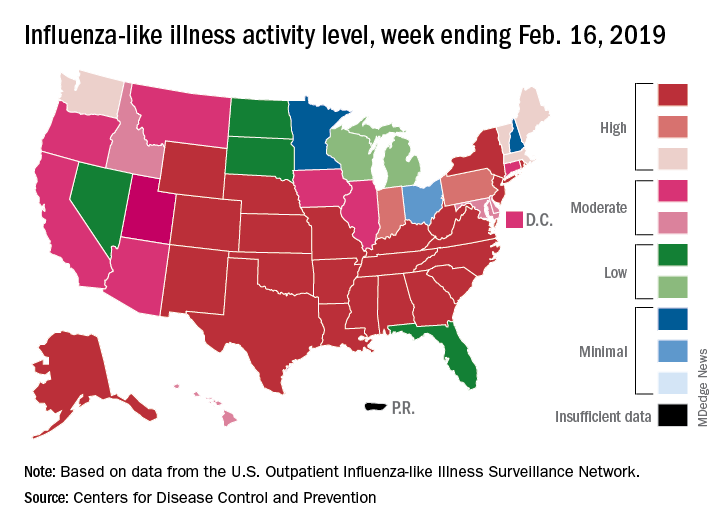
Eight of the last 10 flu seasons had already reached their peak before mid-February, but another rise brought the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) to 5.1% for the week ending Feb. 16, compared with 4.8% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 22. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
The week also brought more ILI to more states, as the number reporting an activity level of 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale rose from 21 to 24 and the number in the high range of 8-10 increased from 26 to 30. Another seven states – including California, which was at level 5 the previous week – and the District of Columbia were at level 7 for the current reporting week, the CDC said.
Two flu-related pediatric deaths occurred during the week ending Feb. 16 and another five were reported from previous weeks, which brings the total to 41 for the 2018-2019 season. Data for influenza deaths at all ages, which are reported a week later, show that 205 occurred in the week ending Feb. 9, with reporting 75% complete. There were 236 total deaths for the week ending Feb. 2 (94% reporting) and 218 deaths during the week ending Jan. 26 (99% reporting), the CDC said.
The 2018-2019 flu season is showing no signs of decline as activity measures continued to increase into mid-February, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Eight of the last 10 flu seasons had already reached their peak before mid-February, but another rise brought the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) to 5.1% for the week ending Feb. 16, compared with 4.8% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 22. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
The week also brought more ILI to more states, as the number reporting an activity level of 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale rose from 21 to 24 and the number in the high range of 8-10 increased from 26 to 30. Another seven states – including California, which was at level 5 the previous week – and the District of Columbia were at level 7 for the current reporting week, the CDC said.
Two flu-related pediatric deaths occurred during the week ending Feb. 16 and another five were reported from previous weeks, which brings the total to 41 for the 2018-2019 season. Data for influenza deaths at all ages, which are reported a week later, show that 205 occurred in the week ending Feb. 9, with reporting 75% complete. There were 236 total deaths for the week ending Feb. 2 (94% reporting) and 218 deaths during the week ending Jan. 26 (99% reporting), the CDC said.
The 2018-2019 flu season is showing no signs of decline as activity measures continued to increase into mid-February, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Eight of the last 10 flu seasons had already reached their peak before mid-February, but another rise brought the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) to 5.1% for the week ending Feb. 16, compared with 4.8% the week before, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 22. ILI is defined as fever (temperature of 100°F [37.8°C] or greater) and cough and/or sore throat.
The week also brought more ILI to more states, as the number reporting an activity level of 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale rose from 21 to 24 and the number in the high range of 8-10 increased from 26 to 30. Another seven states – including California, which was at level 5 the previous week – and the District of Columbia were at level 7 for the current reporting week, the CDC said.
Two flu-related pediatric deaths occurred during the week ending Feb. 16 and another five were reported from previous weeks, which brings the total to 41 for the 2018-2019 season. Data for influenza deaths at all ages, which are reported a week later, show that 205 occurred in the week ending Feb. 9, with reporting 75% complete. There were 236 total deaths for the week ending Feb. 2 (94% reporting) and 218 deaths during the week ending Jan. 26 (99% reporting), the CDC said.
New handoff tool can improve safety
Standardization of process reduces variation
Hospitalists know all too well that a significant source of medical errors is miscommunication during transitions: By interrupting the continuity of care, handoffs can increase the risk of adverse events.
Yet the transfer of patients from the ED to the hospitalist inpatient service has not been well studied, said Carmen Gonzalez, MD, lead author of a recent paper that examined the issue. “The scope of this study was to develop and test a handoff communication tool and a standardized process for transitioning patients from the ED to the hospitalist service at a comprehensive cancer center,” she explained.
In the study, the researchers found that the number of ICU transfers within 24 hours of admission and the number of rapid-response calls decreased after the implementation of a customized handoff tool. “The tool was named DE-PASS (DE-PASS: Decisive problem requiring admission, Evaluation time, Patient summary, Acute issues/action list, Situation unfinished/awareness, Signed out to), which was a modification of the I-PASS, and adapted to our workflow,” reported Dr. Gonzalez, who is based at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. DE-PASS stratifies patients as stable/urgent/emergent and establishes requirements for communications between providers.
Results from the 1-month pilot revealed that, within a 24-hour period, DE-PASS reduced the number of intensive care unit transfers by 58%, the number of rapid-response team calls by 39%, and time to inpatient order by 31%.
“The standardization of the language and format of the handoff process of admission from the ED to the hospitalist service reduced handoff variations, increased provider satisfaction, and improved patient safety,” she noted.
The hospitalists expressed satisfaction with the tool. “This handoff tool helps stratify newly admitted patients based on their illness acuity, hence, assists the busy admitting hospitalist in prioritizing which patient needs to be attended first,” said study coauthor Norman Brito-Dellan, MD, also of MD Anderson Cancer Center. “In this study, DE-PASS reduced admission-to-evaluation times for unstable patients. These patients tend to be evaluated earlier, improving safety.”
Reference
1. Gonzalez CE et al. Handoff tool enabling standardized transitions between the emergency department and the hospitalist inpatient service at a major cancer center. American Journal of Medical Quality. 2018 May 21. doi: 10.1177/1062860618776096.
Standardization of process reduces variation
Standardization of process reduces variation
Hospitalists know all too well that a significant source of medical errors is miscommunication during transitions: By interrupting the continuity of care, handoffs can increase the risk of adverse events.
Yet the transfer of patients from the ED to the hospitalist inpatient service has not been well studied, said Carmen Gonzalez, MD, lead author of a recent paper that examined the issue. “The scope of this study was to develop and test a handoff communication tool and a standardized process for transitioning patients from the ED to the hospitalist service at a comprehensive cancer center,” she explained.
In the study, the researchers found that the number of ICU transfers within 24 hours of admission and the number of rapid-response calls decreased after the implementation of a customized handoff tool. “The tool was named DE-PASS (DE-PASS: Decisive problem requiring admission, Evaluation time, Patient summary, Acute issues/action list, Situation unfinished/awareness, Signed out to), which was a modification of the I-PASS, and adapted to our workflow,” reported Dr. Gonzalez, who is based at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. DE-PASS stratifies patients as stable/urgent/emergent and establishes requirements for communications between providers.
Results from the 1-month pilot revealed that, within a 24-hour period, DE-PASS reduced the number of intensive care unit transfers by 58%, the number of rapid-response team calls by 39%, and time to inpatient order by 31%.
“The standardization of the language and format of the handoff process of admission from the ED to the hospitalist service reduced handoff variations, increased provider satisfaction, and improved patient safety,” she noted.
The hospitalists expressed satisfaction with the tool. “This handoff tool helps stratify newly admitted patients based on their illness acuity, hence, assists the busy admitting hospitalist in prioritizing which patient needs to be attended first,” said study coauthor Norman Brito-Dellan, MD, also of MD Anderson Cancer Center. “In this study, DE-PASS reduced admission-to-evaluation times for unstable patients. These patients tend to be evaluated earlier, improving safety.”
Reference
1. Gonzalez CE et al. Handoff tool enabling standardized transitions between the emergency department and the hospitalist inpatient service at a major cancer center. American Journal of Medical Quality. 2018 May 21. doi: 10.1177/1062860618776096.
Hospitalists know all too well that a significant source of medical errors is miscommunication during transitions: By interrupting the continuity of care, handoffs can increase the risk of adverse events.
Yet the transfer of patients from the ED to the hospitalist inpatient service has not been well studied, said Carmen Gonzalez, MD, lead author of a recent paper that examined the issue. “The scope of this study was to develop and test a handoff communication tool and a standardized process for transitioning patients from the ED to the hospitalist service at a comprehensive cancer center,” she explained.
In the study, the researchers found that the number of ICU transfers within 24 hours of admission and the number of rapid-response calls decreased after the implementation of a customized handoff tool. “The tool was named DE-PASS (DE-PASS: Decisive problem requiring admission, Evaluation time, Patient summary, Acute issues/action list, Situation unfinished/awareness, Signed out to), which was a modification of the I-PASS, and adapted to our workflow,” reported Dr. Gonzalez, who is based at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. DE-PASS stratifies patients as stable/urgent/emergent and establishes requirements for communications between providers.
Results from the 1-month pilot revealed that, within a 24-hour period, DE-PASS reduced the number of intensive care unit transfers by 58%, the number of rapid-response team calls by 39%, and time to inpatient order by 31%.
“The standardization of the language and format of the handoff process of admission from the ED to the hospitalist service reduced handoff variations, increased provider satisfaction, and improved patient safety,” she noted.
The hospitalists expressed satisfaction with the tool. “This handoff tool helps stratify newly admitted patients based on their illness acuity, hence, assists the busy admitting hospitalist in prioritizing which patient needs to be attended first,” said study coauthor Norman Brito-Dellan, MD, also of MD Anderson Cancer Center. “In this study, DE-PASS reduced admission-to-evaluation times for unstable patients. These patients tend to be evaluated earlier, improving safety.”
Reference
1. Gonzalez CE et al. Handoff tool enabling standardized transitions between the emergency department and the hospitalist inpatient service at a major cancer center. American Journal of Medical Quality. 2018 May 21. doi: 10.1177/1062860618776096.
Checklists, colleagues key when psychiatric patient overdoses
BONITA SPRINGS, FLA. — Specialized checklists and colleague support prove crucial to psychiatrists when one of their patients in treatment for substance use disorder dies from an overdose, an expert said at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Much of the knowledge about how psychiatrists are affected by overdose deaths, and what can help them handle them better, is drawn from the literature on patient suicide – both types of death are sudden and unexpected, and both involve stigma and can isolate the patients’ families and providers, said Amy Yule, MD, medical director of the Addiction Recovery Management Service at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“To our knowledge, the provider’s experience after an overdose has not been studied, and [there are] no practice guidelines to guide providers after an overdose death,” she said.
The overdose death of a patient is a particularly difficult matter because psychiatrists struggle with the emotional toll at the same time that they are dealing with fairly urgent details, including some with important legal implications, Dr. Yule said.
“Literature on the provider experience after suicide death indicates that providers are highly impacted by a patient’s suicide,” she said.
A key question is whether to contact the patient’s family. And generally, the answer should be yes.
“It’s really important to offer the option to meet with family members since these families may feel very isolated stigma as they grieve,” Dr. Yule said. What’s more, when families are not contacted by the physician, they might turn to litigation to try to seek information to help them understand their loss, she said.
In a survey of therapists whose patients died by suicide, 73% said they made contact with patient families and, in most instances, the family was not critical and expressed gratitude.
She emphasized the importance of knowing whether a patient’s family knew of the treatment. Because privacy laws extend after a patient’s death, providers cannot disclose treatment to families who did not already know, she said.
Also, she said, “communication with families should be focused on addressing the family members’ feelings and not the clinical details of the case.”
Most states have “apology statutes” that prevent expressions of sympathy – such as, “I’m sorry for your loss” – to be used as admission of liability, but providers should check the laws in their own states, she said.
If you have a colleague whose patient has overdosed or lost their lives to suicide, certain approaches are better than others, Dr. Yule said.
“It’s helpful when colleagues share their own experience with the suicide of a patient or patient who has overdosed and died,” she said. “What’s not helpful is the premature reassurance that the clinician has done nothing wrong. We may feel in these instances that we want to provide that premature reassurance, but it’s important not to do that because it doesn’t help providers resolve their grief.”
For solo providers, it’s especially important to be part of a physician network because they might otherwise not have the same support that those in larger organizations have, she said.
Beyond the grieving process, logistical details also need tending to, she said. The malpractice insurance carrier should be notified, even when there was no sign of a contentious interaction with the family. And, in her organization, the staff run down a checklist that includes not only calling the family and sending a condolence card, notifying staff promptly, and documenting the death, but also easily overlooked details like canceling future appointments in the scheduling system.
“You really don’t want a phone call going to the patient’s family with an appointment reminder after the patient is deceased,” Dr. Yule said. “These are the little details that you may not remember when you’re acutely grieving a patient’s death. And that’s why we feel it’s important to have a list.”
Dr. Yule reported no relevant disclosures.
BONITA SPRINGS, FLA. — Specialized checklists and colleague support prove crucial to psychiatrists when one of their patients in treatment for substance use disorder dies from an overdose, an expert said at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Much of the knowledge about how psychiatrists are affected by overdose deaths, and what can help them handle them better, is drawn from the literature on patient suicide – both types of death are sudden and unexpected, and both involve stigma and can isolate the patients’ families and providers, said Amy Yule, MD, medical director of the Addiction Recovery Management Service at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“To our knowledge, the provider’s experience after an overdose has not been studied, and [there are] no practice guidelines to guide providers after an overdose death,” she said.
The overdose death of a patient is a particularly difficult matter because psychiatrists struggle with the emotional toll at the same time that they are dealing with fairly urgent details, including some with important legal implications, Dr. Yule said.
“Literature on the provider experience after suicide death indicates that providers are highly impacted by a patient’s suicide,” she said.
A key question is whether to contact the patient’s family. And generally, the answer should be yes.
“It’s really important to offer the option to meet with family members since these families may feel very isolated stigma as they grieve,” Dr. Yule said. What’s more, when families are not contacted by the physician, they might turn to litigation to try to seek information to help them understand their loss, she said.
In a survey of therapists whose patients died by suicide, 73% said they made contact with patient families and, in most instances, the family was not critical and expressed gratitude.
She emphasized the importance of knowing whether a patient’s family knew of the treatment. Because privacy laws extend after a patient’s death, providers cannot disclose treatment to families who did not already know, she said.
Also, she said, “communication with families should be focused on addressing the family members’ feelings and not the clinical details of the case.”
Most states have “apology statutes” that prevent expressions of sympathy – such as, “I’m sorry for your loss” – to be used as admission of liability, but providers should check the laws in their own states, she said.
If you have a colleague whose patient has overdosed or lost their lives to suicide, certain approaches are better than others, Dr. Yule said.
“It’s helpful when colleagues share their own experience with the suicide of a patient or patient who has overdosed and died,” she said. “What’s not helpful is the premature reassurance that the clinician has done nothing wrong. We may feel in these instances that we want to provide that premature reassurance, but it’s important not to do that because it doesn’t help providers resolve their grief.”
For solo providers, it’s especially important to be part of a physician network because they might otherwise not have the same support that those in larger organizations have, she said.
Beyond the grieving process, logistical details also need tending to, she said. The malpractice insurance carrier should be notified, even when there was no sign of a contentious interaction with the family. And, in her organization, the staff run down a checklist that includes not only calling the family and sending a condolence card, notifying staff promptly, and documenting the death, but also easily overlooked details like canceling future appointments in the scheduling system.
“You really don’t want a phone call going to the patient’s family with an appointment reminder after the patient is deceased,” Dr. Yule said. “These are the little details that you may not remember when you’re acutely grieving a patient’s death. And that’s why we feel it’s important to have a list.”
Dr. Yule reported no relevant disclosures.
BONITA SPRINGS, FLA. — Specialized checklists and colleague support prove crucial to psychiatrists when one of their patients in treatment for substance use disorder dies from an overdose, an expert said at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Much of the knowledge about how psychiatrists are affected by overdose deaths, and what can help them handle them better, is drawn from the literature on patient suicide – both types of death are sudden and unexpected, and both involve stigma and can isolate the patients’ families and providers, said Amy Yule, MD, medical director of the Addiction Recovery Management Service at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
“To our knowledge, the provider’s experience after an overdose has not been studied, and [there are] no practice guidelines to guide providers after an overdose death,” she said.
The overdose death of a patient is a particularly difficult matter because psychiatrists struggle with the emotional toll at the same time that they are dealing with fairly urgent details, including some with important legal implications, Dr. Yule said.
“Literature on the provider experience after suicide death indicates that providers are highly impacted by a patient’s suicide,” she said.
A key question is whether to contact the patient’s family. And generally, the answer should be yes.
“It’s really important to offer the option to meet with family members since these families may feel very isolated stigma as they grieve,” Dr. Yule said. What’s more, when families are not contacted by the physician, they might turn to litigation to try to seek information to help them understand their loss, she said.
In a survey of therapists whose patients died by suicide, 73% said they made contact with patient families and, in most instances, the family was not critical and expressed gratitude.
She emphasized the importance of knowing whether a patient’s family knew of the treatment. Because privacy laws extend after a patient’s death, providers cannot disclose treatment to families who did not already know, she said.
Also, she said, “communication with families should be focused on addressing the family members’ feelings and not the clinical details of the case.”
Most states have “apology statutes” that prevent expressions of sympathy – such as, “I’m sorry for your loss” – to be used as admission of liability, but providers should check the laws in their own states, she said.
If you have a colleague whose patient has overdosed or lost their lives to suicide, certain approaches are better than others, Dr. Yule said.
“It’s helpful when colleagues share their own experience with the suicide of a patient or patient who has overdosed and died,” she said. “What’s not helpful is the premature reassurance that the clinician has done nothing wrong. We may feel in these instances that we want to provide that premature reassurance, but it’s important not to do that because it doesn’t help providers resolve their grief.”
For solo providers, it’s especially important to be part of a physician network because they might otherwise not have the same support that those in larger organizations have, she said.
Beyond the grieving process, logistical details also need tending to, she said. The malpractice insurance carrier should be notified, even when there was no sign of a contentious interaction with the family. And, in her organization, the staff run down a checklist that includes not only calling the family and sending a condolence card, notifying staff promptly, and documenting the death, but also easily overlooked details like canceling future appointments in the scheduling system.
“You really don’t want a phone call going to the patient’s family with an appointment reminder after the patient is deceased,” Dr. Yule said. “These are the little details that you may not remember when you’re acutely grieving a patient’s death. And that’s why we feel it’s important to have a list.”
Dr. Yule reported no relevant disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAAP 2018
Supplementary compression doesn’t improve DVT odds in critically ill
SAN DIEGO – In critically ill patients receiving pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis, (DVT), according to a new trial.
“I was surprised. My hypothesis was that it would work,” said lead author Yaseen M. Arabi, MD, chairman of the intensive care department at King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Many physicians routinely carry out the practice on the assumption that IPC should lead to better blood flow and further cut DVT risk. The procedure carries few risks, aside from patient discomfort. “The main issue is that it’s not needed. It might be useful in patients who are not receiving heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin,” said Dr. Arabi, who presented the results of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The study was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin reduces the risk of DVT by about 50%, but about 5%-20% of critically ill patients will develop DVT in spite of treatment, and mechanical thromboprophylaxis reduces DVT risk, compared with no prophylaxis. Some researchers have attempted to address whether adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression could further reduce DVT risk, but their studies were marked by a lack of controls, unoptimized pharmacologic regimens, and other limitations.
The trial included 2,003 adults from 20 sites in Saudi Arabia, Canada, Australia, and India, who were expected to have an intensive care unit stay of at least 72 hours. They were randomized to receive IPC combined with pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis (pneumatic compression group) or pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis alone (control).
The proportion of patients receiving unfractionated heparin versus low-molecular-weight heparin was similar between the two groups, with about 58% treated with unfractionated heparin.
A total of 3.9% of patients in the pneumatic compression group experienced incident proximal DVT, compared with 4.2% of controls (relative risk, 0.93; P =.74). A total of 3.4% experienced prevalent proximal DVT, compared with 2.7% of controls (RR, 1.29; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-2.12). There was no significant difference in the incidence of any lower-limb DVT (9.6% vs. 8.4%; RR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.86-1.51).
There was no difference between the two groups in a composite outcome that included pulmonary embolism or all prevalent and incident lower-limb DVT (RR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.85-1.44), and there were no between-group differences with respect to lower-limb skin injury or ischemia.
The results should change practice among those who still provide adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression, however surprising physicians may find these new results to be, according to Dr. Arabi: “People believed strongly that (adjunct IPC) should work, but you need to be evidence based, and here it showed no difference. But that’s why we do studies, right?”
The study was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology and King Abdullah International Medical Research Center. Dr. Arabi has no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Arabi Y et al. CCC48, Abstract 142. N Engl J Med Feb 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816150.
SAN DIEGO – In critically ill patients receiving pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis, (DVT), according to a new trial.
“I was surprised. My hypothesis was that it would work,” said lead author Yaseen M. Arabi, MD, chairman of the intensive care department at King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Many physicians routinely carry out the practice on the assumption that IPC should lead to better blood flow and further cut DVT risk. The procedure carries few risks, aside from patient discomfort. “The main issue is that it’s not needed. It might be useful in patients who are not receiving heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin,” said Dr. Arabi, who presented the results of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The study was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin reduces the risk of DVT by about 50%, but about 5%-20% of critically ill patients will develop DVT in spite of treatment, and mechanical thromboprophylaxis reduces DVT risk, compared with no prophylaxis. Some researchers have attempted to address whether adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression could further reduce DVT risk, but their studies were marked by a lack of controls, unoptimized pharmacologic regimens, and other limitations.
The trial included 2,003 adults from 20 sites in Saudi Arabia, Canada, Australia, and India, who were expected to have an intensive care unit stay of at least 72 hours. They were randomized to receive IPC combined with pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis (pneumatic compression group) or pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis alone (control).
The proportion of patients receiving unfractionated heparin versus low-molecular-weight heparin was similar between the two groups, with about 58% treated with unfractionated heparin.
A total of 3.9% of patients in the pneumatic compression group experienced incident proximal DVT, compared with 4.2% of controls (relative risk, 0.93; P =.74). A total of 3.4% experienced prevalent proximal DVT, compared with 2.7% of controls (RR, 1.29; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-2.12). There was no significant difference in the incidence of any lower-limb DVT (9.6% vs. 8.4%; RR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.86-1.51).
There was no difference between the two groups in a composite outcome that included pulmonary embolism or all prevalent and incident lower-limb DVT (RR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.85-1.44), and there were no between-group differences with respect to lower-limb skin injury or ischemia.
The results should change practice among those who still provide adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression, however surprising physicians may find these new results to be, according to Dr. Arabi: “People believed strongly that (adjunct IPC) should work, but you need to be evidence based, and here it showed no difference. But that’s why we do studies, right?”
The study was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology and King Abdullah International Medical Research Center. Dr. Arabi has no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Arabi Y et al. CCC48, Abstract 142. N Engl J Med Feb 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816150.
SAN DIEGO – In critically ill patients receiving pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis, (DVT), according to a new trial.
“I was surprised. My hypothesis was that it would work,” said lead author Yaseen M. Arabi, MD, chairman of the intensive care department at King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Many physicians routinely carry out the practice on the assumption that IPC should lead to better blood flow and further cut DVT risk. The procedure carries few risks, aside from patient discomfort. “The main issue is that it’s not needed. It might be useful in patients who are not receiving heparin or low-molecular-weight heparin,” said Dr. Arabi, who presented the results of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The study was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin reduces the risk of DVT by about 50%, but about 5%-20% of critically ill patients will develop DVT in spite of treatment, and mechanical thromboprophylaxis reduces DVT risk, compared with no prophylaxis. Some researchers have attempted to address whether adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression could further reduce DVT risk, but their studies were marked by a lack of controls, unoptimized pharmacologic regimens, and other limitations.
The trial included 2,003 adults from 20 sites in Saudi Arabia, Canada, Australia, and India, who were expected to have an intensive care unit stay of at least 72 hours. They were randomized to receive IPC combined with pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis (pneumatic compression group) or pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis alone (control).
The proportion of patients receiving unfractionated heparin versus low-molecular-weight heparin was similar between the two groups, with about 58% treated with unfractionated heparin.
A total of 3.9% of patients in the pneumatic compression group experienced incident proximal DVT, compared with 4.2% of controls (relative risk, 0.93; P =.74). A total of 3.4% experienced prevalent proximal DVT, compared with 2.7% of controls (RR, 1.29; 95% confidence interval, 0.78-2.12). There was no significant difference in the incidence of any lower-limb DVT (9.6% vs. 8.4%; RR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.86-1.51).
There was no difference between the two groups in a composite outcome that included pulmonary embolism or all prevalent and incident lower-limb DVT (RR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.85-1.44), and there were no between-group differences with respect to lower-limb skin injury or ischemia.
The results should change practice among those who still provide adjunct intermittent pneumatic compression, however surprising physicians may find these new results to be, according to Dr. Arabi: “People believed strongly that (adjunct IPC) should work, but you need to be evidence based, and here it showed no difference. But that’s why we do studies, right?”
The study was funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology and King Abdullah International Medical Research Center. Dr. Arabi has no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Arabi Y et al. CCC48, Abstract 142. N Engl J Med Feb 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816150.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
PERT alerts improve pulmonary embolism outcomes
SAN DIEGO – One year after implementation, a at the Christiana Medical Center in Delaware. An analysis of data collected showed reductions in ICU stays, early death, and overall hospital length of stay.
Such patients pose a challenge to clinicians because some will go on to develop more serious pulmonary embolism (PE), yet aggressive treatment options carry their own risk. Existing guidelines, such as those by the European Society of Cardiology, recommend conservative treatment of these patients, with more aggressive measures if conditions don’t quickly improve.
However, about 12% of patients on conservative therapy die, or about 100,000 per year. Those patients who go on to have bad outcomes “are obviously intermediate high risk or high risk. This is the patient population that we’re interested in [addressing through PERT]. These aren’t really sick patients. The blood pressure is normal, but they have the risk based on comorbidities or the clot burden to do poorly over the next day or two,” said Michael Benninghoff, DO, section chief of medical critical care and director of respiratory therapy at Christiana Medical Center, Wilmington, Del. Dr. Benninghoff presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The PERT concept was developed by physicians at Massachusetts General Hospital. It establishes clinical criteria that, if met, prompt a PERT alert, which in turn triggers a meeting between the initiating provider, a pulmonary intensivist, and a vascular and interventional radiology physician within 15 minutes to review the case and make rapid clinical decisions.
A PERT alert requires either a CT diagnosis of PE or a VQ scan showing a high probability of PE, combined with one of three additional criteria: elevated B-type (brain) natriuretic peptide (BNP) and troponin; echocardiographic evidence of right ventricular dysfunction; or clinical instability as indicated by heart rate over 110 beats per minute, systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, or oxygen saturation lower than 90%.
The PERT program caught Dr. Benninghoff’s attention because of institutional experience with patients deteriorating on conservative treatment, but also because the treatment of submassive PE with RV dysfunction is quite scattered. “We were seeing really conservative to really aggressive treatment. I don’t think we’ve had the data to support treating a patient whose blood pressure is normal but they have signs of right ventricular dysfunction, whether it’s echocardiographic, radiographic, or laboratory evidence of myocardial necrosis. I don’t think we have a group conscience as providers as far as how aggressive to be with those patients,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
To examine the efficacy of the PERT program after 1 year, Dr. Benninghoff’s team reviewed all PE cases from 2016 (pre-PERT, n = 717) and 2017 (post-PERT, n = 752). The mortality index declined 30%, from 1.13 to 0.79, while the percentage of early death declined 52%, from 2.51 to 1.20. The mean number of ICU days fell from 5.01 to 4.40.
When the team restricted the analysis to PE lysis patients (n = 27 in 2016; n = 33 in 2017), the mean length of ICU stay dropped from 66.1 hours to 58.8 hours, and fewer patients were transferred from a lower level of care to the ICU (6 vs. 3).
“We think we have shown that just by talking in real time, forcing physicians to communicate – it certainly doesn’t hurt, that it probably helps with ICU utilization and perhaps even mortality,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
The results are far from definitive, and much more work needs to be done to determine how best to manage patients with submassive PEs and RV dysfunction. Dr. Benninghoff doesn’t have the answers, but he’s hopeful that the PERT program can eventually provide some. “Probably the most important thing is we’re giving back to the medical community by enrolling in the consortium, putting our data in the hands of the Boston research institute, and seeing what comes of it. Hopefully in 5 years we will have a standard of care based on the work we’re doing now,” he said.
The study was funded internally. Dr. Benninghoff declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benninghoff M. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 490.
SAN DIEGO – One year after implementation, a at the Christiana Medical Center in Delaware. An analysis of data collected showed reductions in ICU stays, early death, and overall hospital length of stay.
Such patients pose a challenge to clinicians because some will go on to develop more serious pulmonary embolism (PE), yet aggressive treatment options carry their own risk. Existing guidelines, such as those by the European Society of Cardiology, recommend conservative treatment of these patients, with more aggressive measures if conditions don’t quickly improve.
However, about 12% of patients on conservative therapy die, or about 100,000 per year. Those patients who go on to have bad outcomes “are obviously intermediate high risk or high risk. This is the patient population that we’re interested in [addressing through PERT]. These aren’t really sick patients. The blood pressure is normal, but they have the risk based on comorbidities or the clot burden to do poorly over the next day or two,” said Michael Benninghoff, DO, section chief of medical critical care and director of respiratory therapy at Christiana Medical Center, Wilmington, Del. Dr. Benninghoff presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The PERT concept was developed by physicians at Massachusetts General Hospital. It establishes clinical criteria that, if met, prompt a PERT alert, which in turn triggers a meeting between the initiating provider, a pulmonary intensivist, and a vascular and interventional radiology physician within 15 minutes to review the case and make rapid clinical decisions.
A PERT alert requires either a CT diagnosis of PE or a VQ scan showing a high probability of PE, combined with one of three additional criteria: elevated B-type (brain) natriuretic peptide (BNP) and troponin; echocardiographic evidence of right ventricular dysfunction; or clinical instability as indicated by heart rate over 110 beats per minute, systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, or oxygen saturation lower than 90%.
The PERT program caught Dr. Benninghoff’s attention because of institutional experience with patients deteriorating on conservative treatment, but also because the treatment of submassive PE with RV dysfunction is quite scattered. “We were seeing really conservative to really aggressive treatment. I don’t think we’ve had the data to support treating a patient whose blood pressure is normal but they have signs of right ventricular dysfunction, whether it’s echocardiographic, radiographic, or laboratory evidence of myocardial necrosis. I don’t think we have a group conscience as providers as far as how aggressive to be with those patients,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
To examine the efficacy of the PERT program after 1 year, Dr. Benninghoff’s team reviewed all PE cases from 2016 (pre-PERT, n = 717) and 2017 (post-PERT, n = 752). The mortality index declined 30%, from 1.13 to 0.79, while the percentage of early death declined 52%, from 2.51 to 1.20. The mean number of ICU days fell from 5.01 to 4.40.
When the team restricted the analysis to PE lysis patients (n = 27 in 2016; n = 33 in 2017), the mean length of ICU stay dropped from 66.1 hours to 58.8 hours, and fewer patients were transferred from a lower level of care to the ICU (6 vs. 3).
“We think we have shown that just by talking in real time, forcing physicians to communicate – it certainly doesn’t hurt, that it probably helps with ICU utilization and perhaps even mortality,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
The results are far from definitive, and much more work needs to be done to determine how best to manage patients with submassive PEs and RV dysfunction. Dr. Benninghoff doesn’t have the answers, but he’s hopeful that the PERT program can eventually provide some. “Probably the most important thing is we’re giving back to the medical community by enrolling in the consortium, putting our data in the hands of the Boston research institute, and seeing what comes of it. Hopefully in 5 years we will have a standard of care based on the work we’re doing now,” he said.
The study was funded internally. Dr. Benninghoff declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benninghoff M. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 490.
SAN DIEGO – One year after implementation, a at the Christiana Medical Center in Delaware. An analysis of data collected showed reductions in ICU stays, early death, and overall hospital length of stay.
Such patients pose a challenge to clinicians because some will go on to develop more serious pulmonary embolism (PE), yet aggressive treatment options carry their own risk. Existing guidelines, such as those by the European Society of Cardiology, recommend conservative treatment of these patients, with more aggressive measures if conditions don’t quickly improve.
However, about 12% of patients on conservative therapy die, or about 100,000 per year. Those patients who go on to have bad outcomes “are obviously intermediate high risk or high risk. This is the patient population that we’re interested in [addressing through PERT]. These aren’t really sick patients. The blood pressure is normal, but they have the risk based on comorbidities or the clot burden to do poorly over the next day or two,” said Michael Benninghoff, DO, section chief of medical critical care and director of respiratory therapy at Christiana Medical Center, Wilmington, Del. Dr. Benninghoff presented the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The PERT concept was developed by physicians at Massachusetts General Hospital. It establishes clinical criteria that, if met, prompt a PERT alert, which in turn triggers a meeting between the initiating provider, a pulmonary intensivist, and a vascular and interventional radiology physician within 15 minutes to review the case and make rapid clinical decisions.
A PERT alert requires either a CT diagnosis of PE or a VQ scan showing a high probability of PE, combined with one of three additional criteria: elevated B-type (brain) natriuretic peptide (BNP) and troponin; echocardiographic evidence of right ventricular dysfunction; or clinical instability as indicated by heart rate over 110 beats per minute, systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, or oxygen saturation lower than 90%.
The PERT program caught Dr. Benninghoff’s attention because of institutional experience with patients deteriorating on conservative treatment, but also because the treatment of submassive PE with RV dysfunction is quite scattered. “We were seeing really conservative to really aggressive treatment. I don’t think we’ve had the data to support treating a patient whose blood pressure is normal but they have signs of right ventricular dysfunction, whether it’s echocardiographic, radiographic, or laboratory evidence of myocardial necrosis. I don’t think we have a group conscience as providers as far as how aggressive to be with those patients,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
To examine the efficacy of the PERT program after 1 year, Dr. Benninghoff’s team reviewed all PE cases from 2016 (pre-PERT, n = 717) and 2017 (post-PERT, n = 752). The mortality index declined 30%, from 1.13 to 0.79, while the percentage of early death declined 52%, from 2.51 to 1.20. The mean number of ICU days fell from 5.01 to 4.40.
When the team restricted the analysis to PE lysis patients (n = 27 in 2016; n = 33 in 2017), the mean length of ICU stay dropped from 66.1 hours to 58.8 hours, and fewer patients were transferred from a lower level of care to the ICU (6 vs. 3).
“We think we have shown that just by talking in real time, forcing physicians to communicate – it certainly doesn’t hurt, that it probably helps with ICU utilization and perhaps even mortality,” said Dr. Benninghoff.
The results are far from definitive, and much more work needs to be done to determine how best to manage patients with submassive PEs and RV dysfunction. Dr. Benninghoff doesn’t have the answers, but he’s hopeful that the PERT program can eventually provide some. “Probably the most important thing is we’re giving back to the medical community by enrolling in the consortium, putting our data in the hands of the Boston research institute, and seeing what comes of it. Hopefully in 5 years we will have a standard of care based on the work we’re doing now,” he said.
The study was funded internally. Dr. Benninghoff declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benninghoff M. Critical Care Congress 2019, Abstract 490.
REPORTING FROM CCC48
Noncardiac surgery has 7% covert stroke rate in elderly
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
HONOLULU – Covert strokes are relatively common in elderly patients who undergo noncardiac surgery, with a 7% incidence among a group of prospectively followed but generally unselected patients in a multicenter, international study.
By definition, these covert strokes were acutely asymptomatic, but showed evidence of clinical effects during the subsequent year. Twelve months after surgery, patients with acute, perioperative covert strokes found by systematic collection of postoperative MRI brain scans had a twofold increased rate of cognitive decline and a greater than twofold increased rate of delirium, compared with the patients who did not have evidence of a covert stroke, Marko Mrkobrada, MD, said at the International Stroke Conference sponsored by the American Heart Association.
The message from these findings is that, when elderly patients exhibit confusion or delirium after noncardiac surgery, their physicians should have a high index of suspicion that a covert stroke may have occurred, Dr. Mrkobrada said in a video interview. It’s possible that typical stroke symptoms do not appear in many of the covert stroke patients because they are masked in the immediate postoperative period, he added.
Right now, the only way to screen for a covert stroke is with a brain MR, a test that generally costs several hundred dollars, which is too expensive for routine screening. Dr. Mrkobrada said that his team hopes further study will identify a biomarker that can flag patients with a covert stroke at a lower cost. For example, colleagues of Dr. Mrkobrada have successfully used high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of myocardial injury, to identify patients who have myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS; JAMA. 2017 April 25;371[16]:1642-51). Study results also established that treating MINS patients with dabigatran improved their long-term clinical outcomes (Lancet. 2018 June 9;391[10137]:2325-34).
Covert stroke after noncardiac surgery “is the same concept” as MINS, said Dr. Mrkobrada, a researcher at the London Health Sciences Centre in Canada. “We find strokes that do not get picked up after noncardiac surgery just like MIs that are not picked up,” he said. It’s also possible that certain interventions may improve outcomes in patients with covert strokes, just as they have helped MINS patients, he suggested. Potentially helpful interventions could include aspirin, a statin, and improved blood pressure control. A major goal for his research group is finding a biomarker that makes diagnosing covert stroke as easy as using high sensitivity troponin T to diagnose MINS.
The NeuroVISION (Detection and Neurological Impact of Cerebrovascular Events In Noncardiac Surgery Patients: A Cohort EvaluatioN) study enrolled and tested 1,114 people aged 65 years or older scheduled for elective noncardiac surgery anticipated to keep them hospitalized for at least 2 days at any of 12 participating centers in nine countries. Patients underwent cognitive function testing before surgery and had a brain MR scan 2-9 days after surgery, and they were excluded if they developed an overt stroke prior to the scan. Patients underwent a second round of cognitive testing a year after surgery. Patients averaged 73 years old.
The screening MR scans identified covert strokes in 78 of the study subjects (7%). The 1-year cognitive tests showed measurable drops in cognitive function in 42% of those who had experience covert strokes and in 29% of everyone else. Those rates translated to a doubled odds ratio for cognitive decline after covert stroke, compared with people without covert stroke after adjustment for baseline between-group differences, a highly statistically significant between-group difference for the study’s primary endpoint. Delirium occurred 2.2-fold more often in the covert stroke patients after adjustment, and overt strokes during 1-year follow-up were 4.1-fold more common patients who’d experienced a covert stroke, compared with everyone else, after adjustment, Dr. Mrkobrada reported. NeuroVISION is the first large-scale study to assess the incidence and associations of covert strokes after noncardiac surgery, he noted.
SOURCE: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.
REPORTING FROM ISC 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Elderly patients who underwent noncardiac surgery had a 7% incidence of covert stroke.
Study details: NeuroVISION, a prospective, multicenter, observational study with 1,114 patients.
Disclosures: NeuroVISION did not receive commercial funding. Dr. Mrkobrada had no disclosures.
Source: Mrkobrada M. ISC 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract LB18.