User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
Case series suggests biologics, JAK inhibitors safe during pandemic
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
Use of biologics and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors was not associated with worse outcomes in 86 people with inflammatory diseases who contracted COVID-19, according to a case series from New York University Langone Health.
“We are not seeing worse outcomes with overall use of either. It’s reassuring” that the data support continued use during the pandemic, said rheumatologist and senior investigator Jose Scher, MD, an associate professor at New York University.
There have been concerns among rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, and dermatologists that underlying inflammatory diseases and the agents used to treat them would impact outcomes in COVID-19.
Dr. Scher and colleagues, including lead author and rheumatologist Rebecca Haberman, MD, wanted to address the issue, so they reviewed the experience in their own health system of patients with inflammatory diseases – most commonly psoriatic arthritis, RA, and Crohn’s disease – who were assessed for COVID-19 from March 3 to April 3.
Fever, cough, and shortness of breath were the most common symptoms. The infection was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction in 59 (69%) and highly suspected in 27.
A total of 62 patients (72%) were on JAK inhibitors or biologics at baseline, including 38 (44%) on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Overall, 14 patients (16%) were hospitalized with COVID-19, which is consistent the 26% hospitalization rate among the general population in New York City.
Baseline biologic and JAK inhibitor use was actually lower among hospitalized patients than among those who weren’t hospitalized (50% vs. 76%), and the hospitalization rate was only 11% among 62 subjects who had been on the agents long term, more than a year among most.
Hospitalized patients tended to be slightly older (mean, 50 vs. 46 years) with a higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. They also had a higher prevalence of RA (43% vs. 19%), methotrexate use (43% vs. 15%), and use of hydroxychloroquine (21% vs. 7%) and oral glucocorticoids (29% vs. 6%).
It’s unknown what to make of those findings for now, Dr. Scher said. The study didn’t address differences in the severity of the underlying inflammatory illness, but a new and significantly larger case series is in the works that will analyze that and other potential confounders.
Dr. Scher noted that he’s particularly interested in drilling down further on the higher prevalence of RA and methotrexate in hospitalized patients. “We want to understand those signals better. All of this needs further validation,” he said.
Of the 14 hospitalized patients, 11 (79%) were discharged after a mean of 5.6 days. One died in the ED, and two remained hospitalized as of April 3, including one in the ICU.
The investigators are contributing to COVID-19 registries for inflammatory disease patients. The registries are tending to report higher hospitalization rates, but Dr. Scher noted they might be biased towards more severe cases, among other issues.
As for the current situation in New York City, he said that the “last week in March and first 3 in April were indescribable in terms of admissions, intubations, and deaths. Over the last week or so, it has calmed down significantly.”
There was no external funding. Dr. Haberman reported ties to Janssen, and Dr. Scher reported ties to Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and other companies.
SOURCE: Haberman R et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009567.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Use of cannabinoids in dermatology here to stay
In the clinical opinion of .
“There’s no question in my mind about that. Don’t play catch-up; be at the forefront, because at a minimum your patients are going to ask you about this,” he said in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
In 2018, officials at Health Canada reviewed literature and international reviews concerning potential therapeutic uses and harmful effects of cannabis and cannabinoids and published a free downloadable guide for health care professionals. “In the book, dermatology doesn’t have its own section,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and interim chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “It falls under inflammation and makes up four paragraphs of the entire book, which is weird, given that if you survey the dispensaries in Canada, the majority of them led in with dermatologic indications, many of which are completely unsubstantiated.”
In the United States, a recent survey of 531 dermatologists led by Elizabeth S. Robinson, MD, of George Washington University, found that 55% reported at least one patient-initiated discussion about cannabinoids in the last year (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17[2]:1273-8). However, 48% were concerned about a negative stigma when proposing cannabinoid therapies to patients. While most respondents (86%) were willing to prescribe an FDA-approved cannabinoid as a topical treatment, fewer (71%) were willing to prescribe an oral form. In an unpublished study conducted 2 years later, 155 dermatologists were asked if they had ever recommended medical cannabis products for the treatment/management of a dermatologic condition. More than 80% said they had not.
“It’s important to recognize that if we have a strong fund of knowledge, we can guide these patients to use the right cannabinoids for the right indications, so long as we have some evidence supporting it,” said Dr. Friedman, residency program director and director of translational research in George Washington University’s department of dermatology.
According to existing medical literature, cannabinoids may ultimately play a role in the treatment of eczema (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.036 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03824405), psoriasis, acne, and certain collagen vascular diseases, including scleroderma, dermatomyositis, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). Most of the evidence for its use in collagen vascular diseases comes from the investigation of a synthetic cannabinoid known as anabasum, which is derived from TCH, but it has no affinity for the CB1 receptor. “Rather, it goes after the CB2 receptor, which is heavily prevalent in the immune system,” he noted.
In the summer of 2018, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to Corbus Pharmaceuticals for lenabasum, a derivative of anabasum, for the treatment of dermatomyositis. “Hopefully, we’ll see this in the next year,” said Dr. Friedman, who consults for Corbus. A more recent study showed that lenabasum could reduce the production of interleukin-31 (Br. J Dermatol 2018;179[3]:669-78), which “I think will have broader implications in dermatology beyond dermatomyositis,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also reviewed data on a topical endocannabinoid nanoparticle-based formulation his team developed and is studying for the treatment of CLE. “There is a huge unmet need as there are no topical therapies approved for CLE,” he said. “Our animal data are very promising and we plan to move forward to human studies shortly.”
Resources for clinicians to improve their understanding about the potential use of cannabinoids in dermatology include an online certificate program in cannabis medicine offered by Thomas Jefferson University, as well as their state departments of health. Other resources include the International Cannabinoid Research Society, the International Association for Cannabinoid Medicines, the University of California’s Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research, and the Canadian Consortium for the Investigation of Cannabinoids.
Dr. Friedman noted that marijuana may exacerbate appetite, sleepiness, dizziness, low blood pressure, dry mouth/eyes, decreased urination, hallucinations, paranoia, anxiety, poor balance and posture in patients with dyskinetic disorders, and impaired attention, memory, and psychomotor performance. High concentrations can cause hyperemesis syndrome and exacerbate existing psychoses. With respect to cannabidiol (CBD), “unless you go with super high concentrations, over 50 mg/kg per day, you’re probably not going to run into so much trouble,” Dr. Friedman said. “Above that, you do get some liver function test abnormalities. The problem is, a lot of CBD-based products have impurities in them.”
Different state-based requirements exist for recommending cannabinoid products to your patients “so it’s important to know those requirements,” Dr. Friedman said. “I have patients sign a cannabis contrast. There are examples of these online. My mantra is start low and go slow, and stay low as much as possible.”
The virtual meeting at George Washington University included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or adviser to numerous pharmaceutical companies, including some that produce cannabinoids. He is a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Abbvie, and Dermira, and has received grants from Pfizer and the Dermatology Foundation.
In the clinical opinion of .
“There’s no question in my mind about that. Don’t play catch-up; be at the forefront, because at a minimum your patients are going to ask you about this,” he said in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
In 2018, officials at Health Canada reviewed literature and international reviews concerning potential therapeutic uses and harmful effects of cannabis and cannabinoids and published a free downloadable guide for health care professionals. “In the book, dermatology doesn’t have its own section,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and interim chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “It falls under inflammation and makes up four paragraphs of the entire book, which is weird, given that if you survey the dispensaries in Canada, the majority of them led in with dermatologic indications, many of which are completely unsubstantiated.”
In the United States, a recent survey of 531 dermatologists led by Elizabeth S. Robinson, MD, of George Washington University, found that 55% reported at least one patient-initiated discussion about cannabinoids in the last year (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17[2]:1273-8). However, 48% were concerned about a negative stigma when proposing cannabinoid therapies to patients. While most respondents (86%) were willing to prescribe an FDA-approved cannabinoid as a topical treatment, fewer (71%) were willing to prescribe an oral form. In an unpublished study conducted 2 years later, 155 dermatologists were asked if they had ever recommended medical cannabis products for the treatment/management of a dermatologic condition. More than 80% said they had not.
“It’s important to recognize that if we have a strong fund of knowledge, we can guide these patients to use the right cannabinoids for the right indications, so long as we have some evidence supporting it,” said Dr. Friedman, residency program director and director of translational research in George Washington University’s department of dermatology.
According to existing medical literature, cannabinoids may ultimately play a role in the treatment of eczema (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.036 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03824405), psoriasis, acne, and certain collagen vascular diseases, including scleroderma, dermatomyositis, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). Most of the evidence for its use in collagen vascular diseases comes from the investigation of a synthetic cannabinoid known as anabasum, which is derived from TCH, but it has no affinity for the CB1 receptor. “Rather, it goes after the CB2 receptor, which is heavily prevalent in the immune system,” he noted.
In the summer of 2018, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to Corbus Pharmaceuticals for lenabasum, a derivative of anabasum, for the treatment of dermatomyositis. “Hopefully, we’ll see this in the next year,” said Dr. Friedman, who consults for Corbus. A more recent study showed that lenabasum could reduce the production of interleukin-31 (Br. J Dermatol 2018;179[3]:669-78), which “I think will have broader implications in dermatology beyond dermatomyositis,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also reviewed data on a topical endocannabinoid nanoparticle-based formulation his team developed and is studying for the treatment of CLE. “There is a huge unmet need as there are no topical therapies approved for CLE,” he said. “Our animal data are very promising and we plan to move forward to human studies shortly.”
Resources for clinicians to improve their understanding about the potential use of cannabinoids in dermatology include an online certificate program in cannabis medicine offered by Thomas Jefferson University, as well as their state departments of health. Other resources include the International Cannabinoid Research Society, the International Association for Cannabinoid Medicines, the University of California’s Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research, and the Canadian Consortium for the Investigation of Cannabinoids.
Dr. Friedman noted that marijuana may exacerbate appetite, sleepiness, dizziness, low blood pressure, dry mouth/eyes, decreased urination, hallucinations, paranoia, anxiety, poor balance and posture in patients with dyskinetic disorders, and impaired attention, memory, and psychomotor performance. High concentrations can cause hyperemesis syndrome and exacerbate existing psychoses. With respect to cannabidiol (CBD), “unless you go with super high concentrations, over 50 mg/kg per day, you’re probably not going to run into so much trouble,” Dr. Friedman said. “Above that, you do get some liver function test abnormalities. The problem is, a lot of CBD-based products have impurities in them.”
Different state-based requirements exist for recommending cannabinoid products to your patients “so it’s important to know those requirements,” Dr. Friedman said. “I have patients sign a cannabis contrast. There are examples of these online. My mantra is start low and go slow, and stay low as much as possible.”
The virtual meeting at George Washington University included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or adviser to numerous pharmaceutical companies, including some that produce cannabinoids. He is a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Abbvie, and Dermira, and has received grants from Pfizer and the Dermatology Foundation.
In the clinical opinion of .
“There’s no question in my mind about that. Don’t play catch-up; be at the forefront, because at a minimum your patients are going to ask you about this,” he said in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
In 2018, officials at Health Canada reviewed literature and international reviews concerning potential therapeutic uses and harmful effects of cannabis and cannabinoids and published a free downloadable guide for health care professionals. “In the book, dermatology doesn’t have its own section,” said Dr. Friedman, professor and interim chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington. “It falls under inflammation and makes up four paragraphs of the entire book, which is weird, given that if you survey the dispensaries in Canada, the majority of them led in with dermatologic indications, many of which are completely unsubstantiated.”
In the United States, a recent survey of 531 dermatologists led by Elizabeth S. Robinson, MD, of George Washington University, found that 55% reported at least one patient-initiated discussion about cannabinoids in the last year (J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17[2]:1273-8). However, 48% were concerned about a negative stigma when proposing cannabinoid therapies to patients. While most respondents (86%) were willing to prescribe an FDA-approved cannabinoid as a topical treatment, fewer (71%) were willing to prescribe an oral form. In an unpublished study conducted 2 years later, 155 dermatologists were asked if they had ever recommended medical cannabis products for the treatment/management of a dermatologic condition. More than 80% said they had not.
“It’s important to recognize that if we have a strong fund of knowledge, we can guide these patients to use the right cannabinoids for the right indications, so long as we have some evidence supporting it,” said Dr. Friedman, residency program director and director of translational research in George Washington University’s department of dermatology.
According to existing medical literature, cannabinoids may ultimately play a role in the treatment of eczema (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.036 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03824405), psoriasis, acne, and certain collagen vascular diseases, including scleroderma, dermatomyositis, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE). Most of the evidence for its use in collagen vascular diseases comes from the investigation of a synthetic cannabinoid known as anabasum, which is derived from TCH, but it has no affinity for the CB1 receptor. “Rather, it goes after the CB2 receptor, which is heavily prevalent in the immune system,” he noted.
In the summer of 2018, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to Corbus Pharmaceuticals for lenabasum, a derivative of anabasum, for the treatment of dermatomyositis. “Hopefully, we’ll see this in the next year,” said Dr. Friedman, who consults for Corbus. A more recent study showed that lenabasum could reduce the production of interleukin-31 (Br. J Dermatol 2018;179[3]:669-78), which “I think will have broader implications in dermatology beyond dermatomyositis,” he said.
Dr. Friedman also reviewed data on a topical endocannabinoid nanoparticle-based formulation his team developed and is studying for the treatment of CLE. “There is a huge unmet need as there are no topical therapies approved for CLE,” he said. “Our animal data are very promising and we plan to move forward to human studies shortly.”
Resources for clinicians to improve their understanding about the potential use of cannabinoids in dermatology include an online certificate program in cannabis medicine offered by Thomas Jefferson University, as well as their state departments of health. Other resources include the International Cannabinoid Research Society, the International Association for Cannabinoid Medicines, the University of California’s Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research, and the Canadian Consortium for the Investigation of Cannabinoids.
Dr. Friedman noted that marijuana may exacerbate appetite, sleepiness, dizziness, low blood pressure, dry mouth/eyes, decreased urination, hallucinations, paranoia, anxiety, poor balance and posture in patients with dyskinetic disorders, and impaired attention, memory, and psychomotor performance. High concentrations can cause hyperemesis syndrome and exacerbate existing psychoses. With respect to cannabidiol (CBD), “unless you go with super high concentrations, over 50 mg/kg per day, you’re probably not going to run into so much trouble,” Dr. Friedman said. “Above that, you do get some liver function test abnormalities. The problem is, a lot of CBD-based products have impurities in them.”
Different state-based requirements exist for recommending cannabinoid products to your patients “so it’s important to know those requirements,” Dr. Friedman said. “I have patients sign a cannabis contrast. There are examples of these online. My mantra is start low and go slow, and stay low as much as possible.”
The virtual meeting at George Washington University included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dr. Friedman reported that he serves as a consultant and/or adviser to numerous pharmaceutical companies, including some that produce cannabinoids. He is a speaker for Regeneron/Sanofi, Abbvie, and Dermira, and has received grants from Pfizer and the Dermatology Foundation.
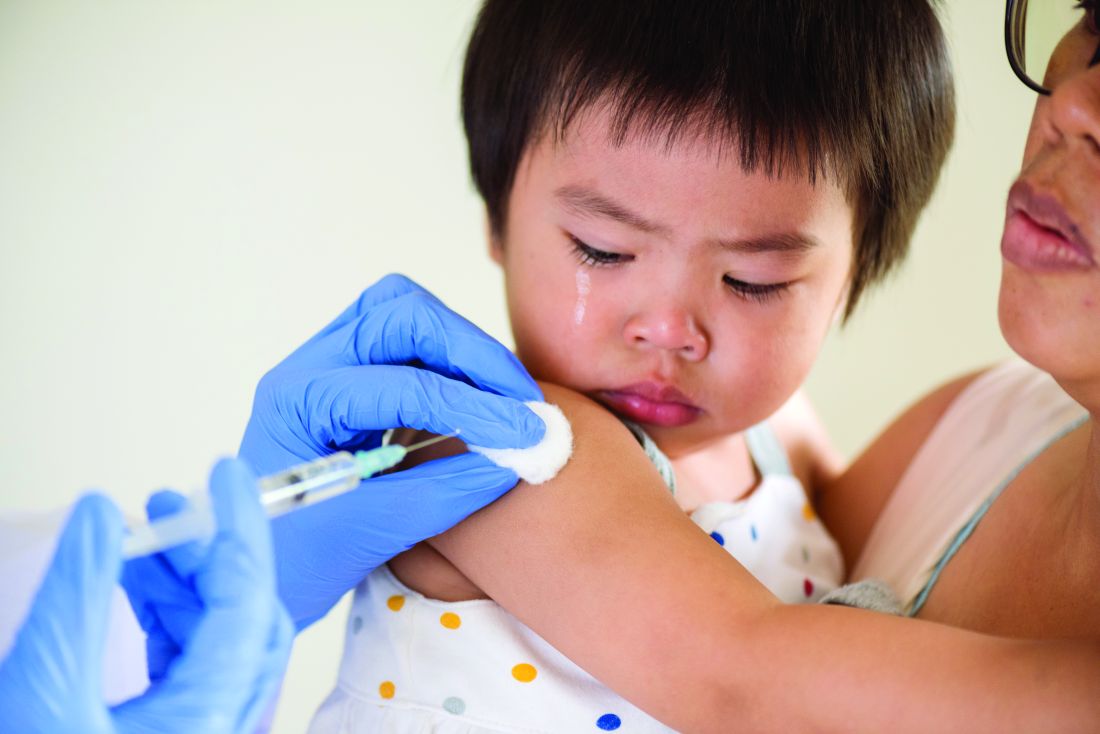
Yale’s COVID-19 inpatient protocol: Hydroxychloroquine plus/minus tocilizumab
Hydroxychloroquine is currently first-line, and tocilizumab second-line, for people hospitalized with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 in the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Health System, which operates hospitals across Connecticut, many of them hard hit by the pandemic.
Patients enter the treatment algorithm if they have an oxygen saturation at or below 93% on room air or chronic supplementation, or by being acutely ill with fever, respiratory signs, or opacities on chest x-ray, plus risk factors for severe illness such as age over 60 years, chronic heart or lung disease, immunosuppression, diabetes, hypertension, or obesity, which makes it harder to ventilate.
Physicians at Yale have seen both presentations – oxygen desaturation and frank illness – and “wanted to make sure we weren’t missing anyone,” said Nihar Desai, MD, a Yale cardiologist who is helping to coordinate the health system’s response to COVID-19.
In either case, the initial treatment is the same at Yale hospitals: hydroxychloroquine for 5 days, with tocilizumab (Actemra) considered when not contraindicated and oxygen requirements reach or pass 3 L, or 2 L with C-reactive protein levels above 70 mg/L.
Patients are put on prophylactic enoxaparin to thin the blood unless contraindicated; inflammatory, cardiac, kidney, and other markers are checked every 12 or 24 hours; and ECGs are taken daily if telemetry isn’t used. Chest x-rays are repeated if clinical signs worsen, and transthoracic echocardiograms are ordered for suspected heart problems.
ICUs are notified early if the clinical situation worsens because patients “can deteriorate very quickly; at the first sign of trouble, people are really aggressive,” said Dr. Desai, also the associate chief of clinical operations in the Section of Cardiovascular Medicine at the Yale University, New Haven.
The haze of battle
Yale has updated its algorithm several times since the virus first hit Connecticut weeks ago. A team including pulmonologists, critical care physicians, pharmacologists, infectious disease experts, and cardiologists, including Dr. Desai, are constantly monitoring the situation and making changes as new information comes in.
Much of what’s being done at Yale and elsewhere is empiric because there are simply not much data to go on. “We are trying to do the best we can” in “the haze of battle. People really came together quickly to develop this. One hopes we never have to go through anything like this again,” he said.
Hydroxychloroquine is first-line at Yale because in-vitro data show potent inhibition of the virus and possible clinical benefit, which is about as good as evidence gets at the moment. Also, “it’s cheap, it’s been used for decades, and people are relatively comfortable with it,” Dr. Desai said.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist, is second-line because it might counter the cytokine storm thought to be at least partly responsible for severe complications, and retrospective data suggest possible benefit. The antiviral remdesivir and IL-6 blocker sarulimab (Kevzara) are also potential candidates, available through clinical trials.
Dr. Desai wanted to share the algorithm with other providers because, he noted, “there are a lot of places that may not have all the resources we have.”
His home institution, Yale New Haven Hospital, is almost half full with COVID-19 patients, at more than 400.
A moving target
Yale’s approach is similar in confirmed COVID-19 cases already in respiratory failure, including those on mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: hydroxychloroquine and possibly tocilizumab, but also methylprednisolone if clinical status worsens or inflammatory markers go up. The steroid is for additional help battling the cytokine storm, Dr. Desai said.
The degree of anticoagulation in the ICU is based on d-dimer levels or suspicion or confirmation of venous thromboembolism. Telemetry is monitored closely for QTc prolongation, and point of care ultrasound is considered to check left ventricular function in the setting of markedly increased cardiac troponin levels, ECG abnormalities, or hemodynamic instability.
Previous versions of Yale’s algorithm included HIV protease inhibitors, but they were pulled after a recent trial found no benefit. Frequency of monitoring was also reduced from every 8 hours because it didn’t improve decision making and put staff collecting specimens at risk (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282).
Anticoagulation was added to newer versions after it became clear that COVID-19 is prothrombotic. “We are still seeing thrombotic events that might warrant further intensification,” Dr. Desai said.
Newer algorithms also have Yale watching QTc intervals more closely. It’s unclear if the prolongation risk is caused by the infection or hydroxychloroquine.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration reiterated it’s concern about the arrhythmia risk with hydroxychloroquine and emphasized that it should only be used for COVID-19 patients when they are hospitalized and it is not feasible for them to participate in a clinical trial.
To help keep patients safe, ECGs from confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases are now first in line to be reviewed by cardiologists across Yale hospitals to pick up prolongations and notify providers as soon as possible. Hydroxychloroquine is held if there are no other explanations.
Cardiologists are on the fontline at Yale and elsewhere, Dr. Desai said, because heart complications like myocarditis and arrhythmias emerged early as common problems in hospitalized patients.
[email protected]
This article was updated with the latest treatment algorithm on 5/6/2020.
Hydroxychloroquine is currently first-line, and tocilizumab second-line, for people hospitalized with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 in the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Health System, which operates hospitals across Connecticut, many of them hard hit by the pandemic.
Patients enter the treatment algorithm if they have an oxygen saturation at or below 93% on room air or chronic supplementation, or by being acutely ill with fever, respiratory signs, or opacities on chest x-ray, plus risk factors for severe illness such as age over 60 years, chronic heart or lung disease, immunosuppression, diabetes, hypertension, or obesity, which makes it harder to ventilate.
Physicians at Yale have seen both presentations – oxygen desaturation and frank illness – and “wanted to make sure we weren’t missing anyone,” said Nihar Desai, MD, a Yale cardiologist who is helping to coordinate the health system’s response to COVID-19.
In either case, the initial treatment is the same at Yale hospitals: hydroxychloroquine for 5 days, with tocilizumab (Actemra) considered when not contraindicated and oxygen requirements reach or pass 3 L, or 2 L with C-reactive protein levels above 70 mg/L.
Patients are put on prophylactic enoxaparin to thin the blood unless contraindicated; inflammatory, cardiac, kidney, and other markers are checked every 12 or 24 hours; and ECGs are taken daily if telemetry isn’t used. Chest x-rays are repeated if clinical signs worsen, and transthoracic echocardiograms are ordered for suspected heart problems.
ICUs are notified early if the clinical situation worsens because patients “can deteriorate very quickly; at the first sign of trouble, people are really aggressive,” said Dr. Desai, also the associate chief of clinical operations in the Section of Cardiovascular Medicine at the Yale University, New Haven.
The haze of battle
Yale has updated its algorithm several times since the virus first hit Connecticut weeks ago. A team including pulmonologists, critical care physicians, pharmacologists, infectious disease experts, and cardiologists, including Dr. Desai, are constantly monitoring the situation and making changes as new information comes in.

Much of what’s being done at Yale and elsewhere is empiric because there are simply not much data to go on. “We are trying to do the best we can” in “the haze of battle. People really came together quickly to develop this. One hopes we never have to go through anything like this again,” he said.
Hydroxychloroquine is first-line at Yale because in-vitro data show potent inhibition of the virus and possible clinical benefit, which is about as good as evidence gets at the moment. Also, “it’s cheap, it’s been used for decades, and people are relatively comfortable with it,” Dr. Desai said.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist, is second-line because it might counter the cytokine storm thought to be at least partly responsible for severe complications, and retrospective data suggest possible benefit. The antiviral remdesivir and IL-6 blocker sarulimab (Kevzara) are also potential candidates, available through clinical trials.
Dr. Desai wanted to share the algorithm with other providers because, he noted, “there are a lot of places that may not have all the resources we have.”
His home institution, Yale New Haven Hospital, is almost half full with COVID-19 patients, at more than 400.
A moving target
Yale’s approach is similar in confirmed COVID-19 cases already in respiratory failure, including those on mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: hydroxychloroquine and possibly tocilizumab, but also methylprednisolone if clinical status worsens or inflammatory markers go up. The steroid is for additional help battling the cytokine storm, Dr. Desai said.
The degree of anticoagulation in the ICU is based on d-dimer levels or suspicion or confirmation of venous thromboembolism. Telemetry is monitored closely for QTc prolongation, and point of care ultrasound is considered to check left ventricular function in the setting of markedly increased cardiac troponin levels, ECG abnormalities, or hemodynamic instability.
Previous versions of Yale’s algorithm included HIV protease inhibitors, but they were pulled after a recent trial found no benefit. Frequency of monitoring was also reduced from every 8 hours because it didn’t improve decision making and put staff collecting specimens at risk (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282).
Anticoagulation was added to newer versions after it became clear that COVID-19 is prothrombotic. “We are still seeing thrombotic events that might warrant further intensification,” Dr. Desai said.
Newer algorithms also have Yale watching QTc intervals more closely. It’s unclear if the prolongation risk is caused by the infection or hydroxychloroquine.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration reiterated it’s concern about the arrhythmia risk with hydroxychloroquine and emphasized that it should only be used for COVID-19 patients when they are hospitalized and it is not feasible for them to participate in a clinical trial.
To help keep patients safe, ECGs from confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases are now first in line to be reviewed by cardiologists across Yale hospitals to pick up prolongations and notify providers as soon as possible. Hydroxychloroquine is held if there are no other explanations.
Cardiologists are on the fontline at Yale and elsewhere, Dr. Desai said, because heart complications like myocarditis and arrhythmias emerged early as common problems in hospitalized patients.
[email protected]
This article was updated with the latest treatment algorithm on 5/6/2020.
Hydroxychloroquine is currently first-line, and tocilizumab second-line, for people hospitalized with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID-19 in the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Health System, which operates hospitals across Connecticut, many of them hard hit by the pandemic.
Patients enter the treatment algorithm if they have an oxygen saturation at or below 93% on room air or chronic supplementation, or by being acutely ill with fever, respiratory signs, or opacities on chest x-ray, plus risk factors for severe illness such as age over 60 years, chronic heart or lung disease, immunosuppression, diabetes, hypertension, or obesity, which makes it harder to ventilate.
Physicians at Yale have seen both presentations – oxygen desaturation and frank illness – and “wanted to make sure we weren’t missing anyone,” said Nihar Desai, MD, a Yale cardiologist who is helping to coordinate the health system’s response to COVID-19.
In either case, the initial treatment is the same at Yale hospitals: hydroxychloroquine for 5 days, with tocilizumab (Actemra) considered when not contraindicated and oxygen requirements reach or pass 3 L, or 2 L with C-reactive protein levels above 70 mg/L.
Patients are put on prophylactic enoxaparin to thin the blood unless contraindicated; inflammatory, cardiac, kidney, and other markers are checked every 12 or 24 hours; and ECGs are taken daily if telemetry isn’t used. Chest x-rays are repeated if clinical signs worsen, and transthoracic echocardiograms are ordered for suspected heart problems.
ICUs are notified early if the clinical situation worsens because patients “can deteriorate very quickly; at the first sign of trouble, people are really aggressive,” said Dr. Desai, also the associate chief of clinical operations in the Section of Cardiovascular Medicine at the Yale University, New Haven.
The haze of battle
Yale has updated its algorithm several times since the virus first hit Connecticut weeks ago. A team including pulmonologists, critical care physicians, pharmacologists, infectious disease experts, and cardiologists, including Dr. Desai, are constantly monitoring the situation and making changes as new information comes in.

Much of what’s being done at Yale and elsewhere is empiric because there are simply not much data to go on. “We are trying to do the best we can” in “the haze of battle. People really came together quickly to develop this. One hopes we never have to go through anything like this again,” he said.
Hydroxychloroquine is first-line at Yale because in-vitro data show potent inhibition of the virus and possible clinical benefit, which is about as good as evidence gets at the moment. Also, “it’s cheap, it’s been used for decades, and people are relatively comfortable with it,” Dr. Desai said.
Tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist, is second-line because it might counter the cytokine storm thought to be at least partly responsible for severe complications, and retrospective data suggest possible benefit. The antiviral remdesivir and IL-6 blocker sarulimab (Kevzara) are also potential candidates, available through clinical trials.
Dr. Desai wanted to share the algorithm with other providers because, he noted, “there are a lot of places that may not have all the resources we have.”
His home institution, Yale New Haven Hospital, is almost half full with COVID-19 patients, at more than 400.
A moving target
Yale’s approach is similar in confirmed COVID-19 cases already in respiratory failure, including those on mechanical ventilation and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: hydroxychloroquine and possibly tocilizumab, but also methylprednisolone if clinical status worsens or inflammatory markers go up. The steroid is for additional help battling the cytokine storm, Dr. Desai said.
The degree of anticoagulation in the ICU is based on d-dimer levels or suspicion or confirmation of venous thromboembolism. Telemetry is monitored closely for QTc prolongation, and point of care ultrasound is considered to check left ventricular function in the setting of markedly increased cardiac troponin levels, ECG abnormalities, or hemodynamic instability.
Previous versions of Yale’s algorithm included HIV protease inhibitors, but they were pulled after a recent trial found no benefit. Frequency of monitoring was also reduced from every 8 hours because it didn’t improve decision making and put staff collecting specimens at risk (N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282).
Anticoagulation was added to newer versions after it became clear that COVID-19 is prothrombotic. “We are still seeing thrombotic events that might warrant further intensification,” Dr. Desai said.
Newer algorithms also have Yale watching QTc intervals more closely. It’s unclear if the prolongation risk is caused by the infection or hydroxychloroquine.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration reiterated it’s concern about the arrhythmia risk with hydroxychloroquine and emphasized that it should only be used for COVID-19 patients when they are hospitalized and it is not feasible for them to participate in a clinical trial.
To help keep patients safe, ECGs from confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases are now first in line to be reviewed by cardiologists across Yale hospitals to pick up prolongations and notify providers as soon as possible. Hydroxychloroquine is held if there are no other explanations.
Cardiologists are on the fontline at Yale and elsewhere, Dr. Desai said, because heart complications like myocarditis and arrhythmias emerged early as common problems in hospitalized patients.
[email protected]
This article was updated with the latest treatment algorithm on 5/6/2020.
POPCoRN network mobilizes pediatric capacity during pandemic
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
Med-Peds hospitalists were an organizing force
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
As U.S. health care systems prepare for inpatient surges linked to hospitalizations of critically ill COVID-19 patients, two hospitalists with med-peds training (combined training in internal medicine and pediatrics) have launched an innovative solution to help facilities deal with the challenge.
The Pediatric Overflow Planning Contingency Response Network (POPCoRN network) has quickly linked almost 400 physicians and other health professionals, including hospitalists, attending physicians, residents, medical students, and nurses. The network wants to help provide more information about how pediatric-focused institutions can safely gear up to admit adult patients in children’s hospitals, in order to offset the predicted demand for hospital beds for patients with COVID-19.
According to the POPCoRN network website (www.popcornetwork.org), the majority of providers who have contacted the network say they have already started or are committed to planning for their pediatric facilities to be used for adult overflow. The Children’s Hospital Association has issued a guidance on this kind of community collaboration for children’s hospitals partnering with adult hospitals in their community and with policy makers.
“We are a network of folks from different institutions, many med-peds–trained hospitalists but quickly growing,” said Leah Ratner, MD, a second-year fellow in the Global Pediatrics Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and cofounder of the POPCoRN network. “We came together to think about how to increase capacity – both in the work force and for actual hospital space – by helping to train pediatric hospitalists and pediatrics-trained nurses to care for adult patients.”
A web-based platform filled with a rapidly expanding list of resources, an active Twitter account, and utilization of Zoom networking software for webinars and working group meetings have facilitated the network’s growth. “Social media has helped us,” Dr. Ratner said. But equally important are personal connections.
“It all started just a few weeks ago,” added cofounder Ashley Jenkins, MD, a med-peds hospital medicine and general academics research fellow in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I sent out some emails in mid-March, asking what other people were doing about these issues. Leah and I met as a result of these initial emails. We immediately started connecting with other health systems and it just expanded from there. Once we knew that enough other systems were thinking about it and trying to build capacity, we started pulling the people and information together.”
High-yield one-pagers
A third or more of those on the POPCoRN contact list are also participating as volunteers on its varied working groups, including health system operation groups exploring the needs of three distinct hospital models: freestanding children’s hospitals; community hospitals, which may see small numbers of children; and integrated mixed hospitals, which often means a pediatric hospital or pediatric units located within an adult hospital.
An immediate goal is to develop high-yield informational “one-pagers,” culling essential clinical facts on a variety of topics in adult inpatient medicine that may no longer be familiar to working pediatric hospitalists. These one-pagers, designed with the help of network members with graphic design skills, address topics such as syncope or chest pain or managing exacerbation of COPD in adults. They draw upon existing informational sources, encapsulating practical information tips that can be used at the bedside, including test workups, differential diagnoses, treatment approaches, and other pearls for providers. Drafts are reviewed for content by specialists, and then by pediatricians to make sure the information covers what they need.
Also under development are educational materials for nurses trained in pediatrics, a section for outpatient providers redeployed to triage or telehealth, and information for other team members including occupational, physical, and respiratory therapists. Another section offers critical care lectures for the nonintensivist. A metrics and outcomes working group is looking for ways to evaluate how the network is doing and who is being reached without having to ask frontline providers to fill out surveys.
Dr. Ratner and Dr. Jenkins have created an intentional structure for encouraging mentoring. They also call on their own mentors – Ahmet Uluer, DO, director of Weitzman Family Bridges Adult Transition Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Brian Herbst Jr., MD, medical director of the Hospital Medicine Adult Care Service at Cincinnati Children’s – for advice.
Beyond the silos
Pediatric hospitalists may have been doing similar things, working on similar projects, but not necessarily reaching out to each other across a system that tends to promote staying within administrative silos, Dr. Uluer said. “Through our personal contacts in POPCoRN, we’ve been able to reach beyond the silos. This network has worked like medical crowd sourcing, and the founders have been inspirational.”
Dr. Herbst added, “How do we expand bandwidth and safely expand services to take young patients and adults from other hospitals? What other populations do we need to expand to take? This network is a workplace of ideas. It’s amazing to see what has been built in a few weeks and how useful it can be.”
Med-peds hospitalists are an important resource for bridging the two specialties. Their experience with transitioning young adults with long-standing chronic conditions of childhood, who have received most of their care at a children’s hospital before reaching adulthood, offers a helpful model. “We’ve also tried to target junior physicians who could step up into leadership roles and to pull in medical students – who are the backbone of this network through their administrative support,” Dr. Jenkins said.
Marie Pfarr, MD, also a med-peds trained hospital medicine fellow at Cincinnati Children’s, was contacted in March by Dr. Jenkins. “She said they had this brainstorm, and they were getting feedback that it would be helpful to provide educational materials for pediatric providers. Because I have an interest in medical education, she asked if I wanted to help. I was at home struggling with what I could contribute during this crazy time, so I said yes.”
Dr. Pfarr leads POPCoRN’s educational working group, which came up with a list of 50 topics in need of one-pagers and people willing to create them, mostly still under development. The aim for the one-pagers is to offer a good starting point for pediatricians, helping them, for example, to ask the right questions during history and physical exams. “We also want to offer additional resources for those who want to do a deeper dive.”
Dr. Pfarr said she has enjoyed working closely with medical students, who really want to help. “That’s been great to see. We are all working toward the same goal, and we help to keep each other in check. I think there’s a future for this kind of mobilization through collaborations to connect pediatric to adult providers. A lot of good things will come out of the network, which is an example of how folks can talk to each other. It’s very dynamic and changing every day.”
One of those medical students is Chinma Onyewuenyi, finishing her fourth year at Baylor College of Medicine. Scheduled to start a med-peds residency at Geisinger Health on July 1, she had completed all of her rotations and was looking for ways to get involved in the pandemic response while respecting the shelter-in-place order. “I had heard about the network, which was recruiting medical students to play administrative roles for the working groups. I said, ‘If you have anything else you need help with, I have time on my hands.’”
Ms. Onyewuenyi says she fell into the role of a lead administrative volunteer, and her responsibilities grew from there, eventually taking charge of all the medical students’ recruiting, screening, and assignments, freeing up the project’s physician leaders from administrative tasks. “I wanted something active to do to contribute, and I appreciate all that I’m learning. With a master’s degree in public health, I have researched how health care is delivered,” she said.
“This experience has really opened my eyes to what’s required to deliver care, and just the level of collaboration that needs to go on with something like this. Even as a medical student, I felt glad to have an opportunity to contribute beyond the administrative tasks. At meetings, they ask for my opinion.”
Equitable access to resources
Another major focus for the network is promoting health equity – giving pediatric providers and health systems equitable access to information that meets their needs, Dr. Ratner said. “We’ve made a particular effort to reach out to hospitals that are the most vulnerable, including rural hospitals, and to those serving the most vulnerable patients,” she noted. These also include the homeless and refugees.
“We’ve been trying to be mindful of avoiding the sometimes-intimidating power structure that has been traditional in medicine,” Dr. Ratner said. The network’s equity working group is trying to provide content with structural competency and cultural humility. “We’re learning a lot about the ways the health care system is broken,” she added. “We all agree that we have a fragmented health care system, but there are ways to make it less fragmented and learn from each other.”
In the tragedy of the COVID epidemic, there are also unique opportunities to learn to work collaboratively and make the health care system stronger for those in greatest need, Dr. Ratner added. “What we hope is that our network becomes an example of that, even as it is moving so quickly.”
Audrey Uong, MD, an attending physician in the division of hospital medicine at Children’s Hospital at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, connected with POPCoRN for an educational presentation reviewing resuscitation in adult patients. She wanted to talk with peers about what’s going on, so as not to feel alone in her practice. She has also found the network’s website useful for identifying educational resources.
“As pediatricians, we have been asked to care for adult patients. One of our units has been admitting mostly patients under age 30, and we are accepting older patients in another unit on the pediatric wing.” This kind of thing is also happening in a lot of other places, Dr. Uong said. Keeping up with these changes in her own practice has been challenging.
She tries to take one day at a time. “Everyone at this institution feels the same – that we’re locked in on meeting the need. Even our child life specialists, when they’re not working with younger patients, have created this amazing support room for staff, with snacks and soothing music. There’s been a lot of attention paid to making us feel supported in this work.”
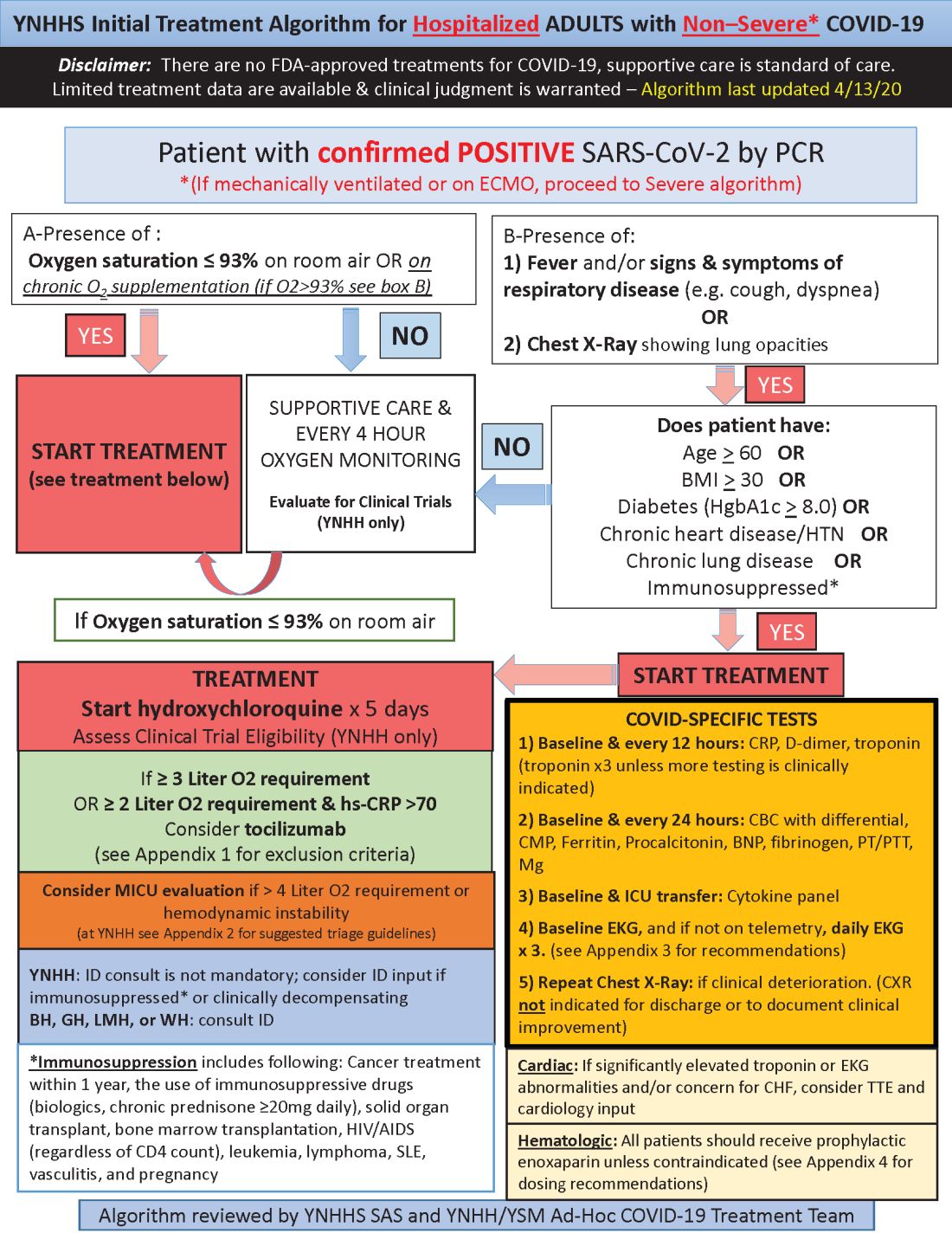
COVID-19: An opportunity, challenge for addiction treatment, NIDA boss says
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is posing significant challenges while also providing unique opportunities for patients with substance use disorders (SUD), a leading expert says.
Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said that the pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, making it easier for patients with SUD to access treatment. It has also led to the proliferation of more mental health hotlines, which is critical since the vast majority of these patients have comorbid mental illness.
In addition, COVID-19 has resulted in increased availability of “alternative” peer support mechanisms via cellphones or computers to aid individuals’ sobriety.
Dr. Volkow spoke at the virtual American Psychiatric Association Spring Highlights Meeting 2020, which is replacing the organization’s canceled annual meeting.
While methadone clinics have had to close during the pandemic, making it challenging for those on medically assisted treatment to receive methadone or buprenorphine, some of the rules and regulations have been relaxed in order to make these medications accessible without the need for in-person attendance at a clinic. In addition, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs.
Social isolation, stigma intensified
A pandemic increases anxiety in the general population, but for patients with SUD who may be also be struggling with homelessness and comorbid mental illness, the situation can further exacerbate social stigma and isolation – leading to relapse, more overdoses, and overdose deaths, Dr. Volkow said. Social interaction is “extraordinarily important” for patients and “one of the most powerful tools we have” to build resilience.
Right now, said Dr. Volkow, “we are in the dark as to how COVID infections have affected the number of overdose deaths.”
However, she noted that
“So even through this devastation, we can actually extract something that may help others in future,” she said.
Dr. Volkow noted that during the pandemic it is critical to reinforce the importance of engaging in – and remaining in – treatment to SUD patients. It’s also crucial to make patients aware of social support systems and behavioral interventions to help them cope with stress and to mitigate relapse risk.
COVID-19 and relapse
Elie G. Aoun, MD, assistant professor of psychiatry at New York University and vice chair of the APA’s Council on Addiction Psychiatry, said in an interview that Dr. Volkow’s presentation provided “exactly the kind of accessible information” clinicians need.
Dr. Aoun said he sees the impact of the COVID-19 crisis in his practice every day. Patients with SUD “are getting the short end of the stick.”
Social distancing measures prompted by the pandemic can be “very triggering” for SUD patients, he said. One of his patients told him the current isolation, loneliness, movement restrictions, and boredom remind her of the way she felt when she used drugs.
Dr. Aoun said four of his patients have relapsed since the pandemic began. Two of them had just started treatment after years of using drugs, so this was a “major setback” for them.
He and his colleagues were “not really prepared” to provide care via video link, which he believes is not as effective as in-person sessions.
In addition to disrupting patient care, said Dr. Aoun, the pandemic is forcing the medical community to face social determinants of health, such as poverty and homelessness, as they relate to addiction disorders and whether or not someone receives care.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Trials and tribulations: Neurology research during COVID-19
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
However, researchers remain determined to forge ahead – with many redesigning their studies, at least in part to optimize the safety of their participants and research staff.
Keeping people engaged while protocols are on hold; expanding normal safety considerations; and re-enlisting statisticians to keep their findings as significant as possible are just some of study survival strategies underway.
Alzheimer’s disease research on hold
The pandemic is having a significant impact on Alzheimer’s disease research, and medical research in general, says Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president, Medical & Scientific Relations at the Alzheimer’s Association.
“Many clinical trials worldwide are pausing, changing, or halting the testing of the drug or the intervention,” she told Medscape Medical News. “How the teams have adapted depends on the study,” she added. “As you can imagine, things are changing on a daily basis.”
The US Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER) trial, for example, is on hold until at least May 31. The Alzheimer’s Association is helping to implement and fund the study along with Wake Forest University Medical Center.
“We’re not randomizing participants at this point in time and the intervention — which is based on a team meeting, and there is a social aspect to that — has been paused,” Dr. Snyder said.
Another pivotal study underway is the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s study (the A4 Study). Investigators are evaluating if an anti-amyloid antibody, solanezumab (Eli Lilly), can slow memory loss among people with amyloid on imaging but no symptoms of cognitive decline at baseline.
“The A4 Study is definitely continuing. However, in an effort to minimize risk to participants, site staff and study integrity, we have implemented an optional study hiatus for both the double-blind and open-label extension phases,” lead investigator Reisa Anne Sperling, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“We wanted to prioritize the safety of our participants as well as the ability of participants to remain in the study … despite disruptions from the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Sperling, who is professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Center for Alzheimer Research and Treatment at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
The ultimate goal is for A4 participants to receive the full number of planned infusions and assessments, even if it takes longer, she added.
Many Alzheimer’s disease researchers outside the United States face similar challenges. “As you probably are well aware, Spain is now in a complete lockdown. This has affected research centers like ours, the Barcelona Brain Research Center, and the way we work,” José Luís Molinuevo Guix, MD, PhD, told Medscape Medical News.
All participants in observational studies like the ALFA+ study and initiatives, as well as those in trials including PENSA and AB1601, “are not allowed, by law, to come in, hence from a safety perspective we are on good grounds,” added Dr. Molinuevo Guix, who directs the Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders unit at the Hospital Clinic de Barcelona.
The investigators are creating protocols for communicating with participants during the pandemic and for restarting visits safely after the lockdown has ended.
Stroke studies amended or suspended
A similar situation is occurring in stroke trials. Stroke is “obviously an acute disease, as well as a disease that requires secondary prevention,” Mitchell Elkind, MD, president-elect of the American Heart Association, told Medscape Medical News.
“One could argue that patients with stroke are going to be in the hospital anyway – why not enroll them in a study? They’re not incurring any additional risk,” he said. “But the staff have to come in to see them, and we’re really trying to avoid exposure.”
One ongoing trial, the Atrial Cardiopathy and Antithrombotic Drugs In Prevention After Cryptogenic Stroke (ARCADIA), stopped randomly assigning new participants to secondary prevention with apixaban or aspirin because of COVID-19. However, Dr. Elkind and colleagues plan to provide medication to the 440 people already in the trial.
“Wherever possible, the study coordinators are shipping the drug to people and doing follow-up visits by phone or video,” said Dr. Elkind, chief of the Division of Neurology Clinical Outcomes Research and Population Sciences at Columbia University in New York City.
Protecting patients, staff, and ultimately society is a “major driving force in stopping the randomizations,” he stressed.
ARCADIA is part of the StrokeNet prevention trials network, run by the NIH’s National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Additional pivotal trials include the Carotid Revascularization Endarterectomy Versus Stenting Trial (CREST) and the Multi-arm Optimization of Stroke Thrombolysis (MOST) studies, he said.
Joseph Broderick, MD, director of the national NIH StrokeNet, agreed that safety comes first. “It was the decision of the StrokeNet leadership and the principal investigators of the trials that we needed to hold recruitment of new patients while we worked on adapting processes of enrollment to ensure the safety of both patients and researchers interacting with study patients,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Potential risks vary based on the study intervention and the need for in-person interactions. Trials that include stimulation devices or physical therapy, for example, might be most affected, added Dr. Broderick, professor and director of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio.
Nevertheless, “there are potential ways … to move as much as possible toward telemedicine and digital interactions during this time.”
Multiple challenges in multiple sclerosis
At the national level, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an “unprecedented impact on almost all the clinical trials funded by NINDS,” said Clinton Wright, MD, director of the Division of Clinical Research at NINDS. “Investigators have had to adapt quickly.”
Supplementing existing grants with money to conduct research on COVID-19 and pursuing research opportunities from different institutes are “some of the creative approaches [that] have come from the NIH [National Institutes of Health] itself,” Dr. Wright said. “Other creative approaches have come from investigators trying to keep their studies and trials going during the pandemic.”
In clinical trials, “everything from electronic consent to in-home research drug delivery is being brought to bear.”
“A few ongoing trials have been able to modify their protocols to obtain consent and carry out evaluations remotely by telephone or videoconferencing,” Dr. Wright said. “This is especially critical for trials that involve medical management of specific risk factors or conditions, where suspension of the trial could itself have adverse consequences due to reduced engagement with research participants.”
For participants already in MS studies, “each upcoming visit is assessed for whether it’s critical or could be done virtually or just skipped. If a person needs a treatment that cannot be postponed or skipped, they come in,” Jeffrey Cohen, MD, director of the Experimental Therapeutics Program at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, told Medscape Medical News.
New study enrollment is largely on hold and study visits for existing participants are limited, said Dr. Cohen, who is also president of the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Some of the major ongoing trials in MS are “looking at very fundamental questions in the field,” Dr. Cohen said. The Determining the Effectiveness of earLy Intensive Versus Escalation Approaches for RRMS (DELIVER-MS) and Traditional Versus Early Aggressive Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis (TREAT-MS) trials, for example, evaluate whether treatment should be initiated with one of the less efficacious agents with escalation as needed, or whether treatment should begin with a high-efficacy agent.
Both trials are currently on hold because of the pandemic, as is the Best Available Therapy Versus Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Multiple Sclerosis (BEAT-MS) study.
“There has been a lot of interest in hematopoietic stem cell transplants and where they fit into our overall treatment strategy, and this is intended to provide a more definitive answer,” Dr. Cohen said.
Making the most of down time
“The pandemic has been challenging” in terms of ongoing MS research, said Benjamin M. Segal, MD, chair of the Department of Neurology and director of the Neuroscience Research Institute at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
“With regard to the lab, our animal model experiments have been placed on hold. We have stopped collecting samples from clinical subjects for biomarker studies.
“However, my research team has been taking advantage of the time that has been freed up from bench work by analyzing data sets that had been placed aside, delving more deeply into the literature, and writing new grant proposals and articles,” he added.
Two of Dr. Segal’s trainees are writing review articles on the immunopathogenesis of MS and its treatment. Another postdoctoral candidate is writing a grant proposal to investigate how coinfection with a coronavirus modulates CNS pathology and the clinical course of an animal model of MS.
“I am asking my trainees to plan out experiments further in advance than they ever have before, so they are as prepared as possible to resume their research agendas once we are up and running again,” Dr. Segal said.
Confronting current challenges while planning for a future less disrupted by the pandemic is a common theme that emerges.
“The duration of this [pandemic] will dictate how we analyze the data at the end [for the US POINTER study]. There is a large group of statisticians working on this,” Dr. Snyder said.
Dr. Sperling of Harvard Medical School also remains undeterred. “This is definitely a challenging time, as we must not allow the COVID-19 to interfere with our essential mission to find a successful treatment to prevent cognitive decline in AD. We do need, however, to be as flexible as possible to protect our participants and minimize the impact to our overall study integrity,” she said.
NIH guidance
Dr. Molinuevo Guix, of the Barcelona Brain Research Center, is also determined to continue his Alzheimer’s disease research. “I am aware that after the crisis, there will be less [risk] but still a COVID-19 infection risk, so apart from trying to generate part of our visits virtually, we want to make sure we have all necessary safety measures in place. We remain very active to preserve the work we have done to keep up the fight against Alzheimer’s and dementia,” he said.
Such forward thinking also applies to major stroke trials, said Dr. Broderick of the University of Cincinnati. “As soon as we shut down enrollment in stroke trials, we immediately began to make plans about how and when we can restart our stroke trials,” he explained. “One of our trials can do every step of the trial process remotely without direct in-person interactions and will be able to restart soon.”
An individualized approach is needed, Dr. Broderick added. “For trials involving necessary in-person and hands-on assessments, we will need to consider how best to use protective equipment and expanded testing that will likely match the ongoing clinical care and requirements at a given institution.
“Even if a trial officially reopens enrollment, the decision to enroll locally will need to follow local institutional environment and guidelines. Thus, restart of trial enrollment will not likely be uniform, similar to how trials often start in the first place,” Dr. Broderick said.
The NIH published uniform standards for researchers across its institutes to help guide them during the pandemic. Future contingency plans also are underway at the NINDS.
“As the pandemic wanes and in-person research activities restart, it will be important to have in place safety measures that prevent a resurgence of the virus, such as proper personal protective equipment for staff and research participants, said Dr. Wright, the clinical research director at NINDS.
For clinical trials, NINDS is prepared to provide supplemental funds to trial investigators to help support additional activities undertaken as a result of the pandemic.
“This has been an instructive experience. The pandemic will end, and we will resume much of our old patterns of behavior,” said Ohio State’s Dr. Segal. “But some of the strategies that we have employed to get through this time will continue to influence the way we communicate information, plan experiments, and prioritize research activities in the future, to good effect.”
Drs. Snyder, Sperling, Molinuevo Guix, Elkind, Broderick, Wright, Cohen, and Segal have disclosed no relevant disclosures.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir now ‘standard of care’ for COVID-19, Fauci says
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a preliminary data analysis from a U.S.-led randomized, controlled trial.
On the basis of as yet unpublished data, remdesivir “will be the standard of care” for patients with COVID-19, Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), said during a press conference at the White House April 29.
The randomized, placebo-controlled international trial was sponsored by NIAID, which is part of the National Institutes of Health, and enrolled 1,063 patients. It began on Feb. 21.
The interim results, discussed in the press conference and in a NIAID press release, show that time to recovery (i.e., being well enough for hospital discharge or to return to normal activity level) was 31% faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo (P < .001).
The median time to recovery was 11 days for patients treated with remdesivir, compared with 15 days for those who received placebo. Results also suggested a survival benefit, with a mortality rate of 8.0% for the group receiving remdesivir and 11.6% for the patients who received placebo (P = .059).
The study, known as the Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial (ACTT), is the first clinical trial launched in the United States to evaluate an experimental treatment for COVID-19. It is being conducted at 68 sites – 47 in the United States and 21 in countries in Europe and Asia.
The data are being released after an interim review by the independent data safety monitoring board found significant benefit with the drug, Dr. Fauci said.
“The reason we are making the announcement now is something that people don’t fully appreciate: Whenever you have clear-cut evidence that a drug works, you have an ethical obligation to let the people in the placebo group know so they could have access,” he explained.
“When I was looking at the data with our team the other night, it was reminiscent of 34 years ago in 1986 when we were struggling for drugs for HIV,” said Dr. Fauci, who was a key figure in HIV/AIDS research. “We did the first randomized, placebo-controlled trial with AZT. It turned out to have an effect that was modest but that was not the endgame because, building on that, every year after, we did better and better.”
Similarly, new trials of drugs for COVID-19 will build on remdesivir, with other agents being added to block other pathways or viral enzymes, Dr. Fauci said.
The study will be submitted to a journal for peer review, he noted, but the New York Times is reporting that the Food and Drug Administration will approve remdesivir for emergency use soon.
In contrast to the positive results Dr. Fauci described from the NIAID-sponsored trial, a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of remdesivir among hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 in China was inconclusive.
The study, published online in The Lancet, showed some nonsignificant trends toward benefit but did not meet its primary endpoint.
The study was stopped early after 237 of the intended 453 patients were enrolled, owing to a lack of additional patients who met the eligibility criteria. The trial was thus underpowered.
Results showed that treatment with remdesivir did not significantly speed recovery or reduce deaths from COVID-19, but with regard to prespecified secondary outcomes, time to clinical improvement and duration of invasive mechanical ventilation were shorter among a subgroup of patients who began undergoing treatment with remdesivir within 10 days of showing symptoms, in comparison with patients who received standard care.
“To me, the studies reported here in The Lancet appear to be less promising than some statements released today from the NIH, so the situation is a bit puzzling to me,” said Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, who was not involved in the study. “I would need to look more closely at the data which NIH is looking at to understand the differences.”
Trial details
The published trial was conducted at 10 hospitals in Hubei, China. Enrollment criteria included being admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection within 12 days of symptom onset, having oxygen saturation of 94% or less, and having radiologically confirmed pneumonia.
Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive intravenous remdesivir (200 mg on day 1 followed by 100 mg on days 2–10 in single daily infusions) or placebo infusions for 10 days. Patients were permitted concomitant use of lopinavir-ritonavir, interferons, and corticosteroids.
The primary endpoint was time to clinical improvement to day 28, defined as the time (in days) from randomization to the point of a decline of two levels on a six-point ordinal scale of clinical status (on that scale, 1 indicated that the patient was discharged, and 6 indicated death) or to the patient’s being discharged alive from hospital, whichever came first.
The trial was stopped early because stringent public health measures used in Wuhan led to marked reductions in new patient presentations and because lack of available hospital beds resulted in most patients being enrolled later in the course of disease.
Between Feb. 6, 2020, and March 12, 2020, 237 patients were enrolled and were randomly assigned to receive either remdesivir (n = 158) or placebo (n = 79).
Results showed that use of remdesivir was not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement (hazard ratio [HR], 1.23; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.87-1.75).
Although not statistically significant, time to clinical improvement was numerically faster for patients who received remdesivir than for those who received placebo among patients with symptom duration of 10 days or less (median, 18 days vs. 23 days; HR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.95-2.43).
The mortality rates were similar for the two groups (14% of patients who received remdesivir died vs. 13% of those who received placebo). There was no signal that viral load decreased differentially over time between the two groups.
Adverse events were reported in 66% of remdesivir recipients, vs. 64% of those who received placebo. Remdesivir was stopped early because of adverse events in 12% of patients; it was stopped early for 5% of those who received placebo.
The authors, led by Yeming Wang, MD, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, noted that compared with a previous study of compassionate use of remdesivir, the population in the current study was less ill and was treated somewhat earlier in the disease course (median, 10 days vs. 12 days).
Because the study was terminated early, the researchers said they could not adequately assess whether earlier treatment with remdesivir might have provided clinical benefit.
“However, among patients who were treated within 10 days of symptom onset, remdesivir was not a significant factor but was associated with a numerical reduction of 5 days in median time to clinical improvement,” they stated.
They added that remdesivir was adequately tolerated and that no new safety concerns were identified.
In an accompanying comment in The Lancet, John David Norrie, MD, Edinburgh Clinical Trials Unit, United Kingdom, pointed out that this study “has not shown a statistically significant finding that confirms a remdesivir treatment benefit of at least the minimally clinically important difference, nor has it ruled such a benefit out.”
Dr. Norrie was cautious about the fact that the subgroup analysis suggested possible benefit for those treated within 10 days.
Although he said it seems biologically plausible that treating patients earlier could be more effective, he added that “as well as being vigilant against overinterpretation, we need to ensure that hypotheses generated in efficacy-based trials, even in subgroups, are confirmed or refuted in subsequent adequately powered trials or meta-analyses.”
Noting that several other trials of remdesivir are underway, he concluded: “With each individual study at heightened risk of being incomplete, pooling data across possibly several underpowered but high-quality studies looks like our best way to obtain robust insights into what works, safely, and on whom.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Standing orders for vaccines may improve pediatric vaccination rates
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
The biggest barrier to using standing orders for childhood immunizations is concern that patients will receive the wrong vaccine, according to a survey of pediatricians published in Pediatrics.
The other top reasons pediatricians give for not using standing orders for vaccines are concerns that parents may want to talk to the doctor about the vaccine before their child gets it, and a belief that the doctor should be the one who personally recommends a vaccine for their patient.
But with severe drops in vaccination rates resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, standing orders may be a valuable tool for ensuring children get their vaccines on time, suggested lead author, Jessica Cataldi, MD, of the University of Colorado and Children’s Hospital Colorado in Aurora.
“As we work to bring more families back to their pediatrician’s office for well-child checks, standing orders are one process that can streamline the visit by saving providers time and increasing vaccine delivery,” she said in an interview. “We will also need use standing orders to support different ways to get children their immunizations during times of social distancing. This could take the form of drive-through immunization clinics or telehealth well-child checks that are paired with a quick immunization-only visit.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics issued guidance April 14 that emphasizes the need to prioritize immunization of children through 2-years-old.
Paul A. Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the division of infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, agreed that it’s essential children do not fall behind on the recommended schedule during the pandemic.
“It’s important not to have greater collateral damage from this COVID-19 pandemic by putting children at increased risk from other infections that are circulating, like measles and pertussis,” he said, noting that nearly 1,300 measles cases and more than 15,000 pertussis cases occurred in the United States in 2019.
It’s important “not to delay those primary vaccines because it’s hard to catch up,” he said in an interview
Although “standing orders” may go by other names in non–inpatient settings, the researchers defined them in their survey as “a written or verbal policy that persons other than a medical provider, such as a nurse or medical assistant, may consent and vaccinate a person without speaking with the physician or advanced care provider first.” Further, the “vaccine may be given before or after a physician encounter or in the absence of a physician encounter altogether.”
Research strongly suggests that standing orders for childhood vaccines are cost-effective and increase immunization rates, the authors noted. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the federal National Vaccine Advisory Committee all recommend using standing orders to improve vaccination access and rates.
The authors sought to understand how many pediatricians use standing orders and what reasons stop them from doing so. During June-September 2017, they sent out 471 online and mail surveys to a nationally representative sample of AAP members who spent at least half their time in primary care.
The 372 pediatricians who completed the survey made up a response rate of 79%, with no differences in response based on age, sex, years in practice, practice setting, region or rural/urban location.
More than half the respondents (59%) used standing orders for childhood immunizations. Just over a third of respondents (36%) said they use standing orders for all routinely recommended vaccines, and 23% use them for some vaccines.
Among those who did not use standing orders, 68% cited the concern that patients would get the incorrect vaccine by mistake as a barrier to using them. That came as a surprise to Dr Offit, who would expect standing orders to reduce the likelihood of error.
“The standing order should make things a little more foolproof so that you’re less likely to make a mistake,” Dr Offit said.
No studies have shown that vaccine errors occur more often in clinics that use standing orders for immunizations, but the question merits continued monitoring, Dr Cataldi said.
“It is important for any clinic that is new to the use of standing orders to provide adequate education to providers and other staff about when and how to use standing orders, and to always leave room for staff to bring vaccination questions to the provider,” Dr Cataldi told this newspaper
Nearly as many physicians (62%) believed that families would want to speak to the doctor about a vaccine before getting it, and 57% of respondents who didn’t use standing orders believed they should be the one who recommends a vaccine to their patient’s parents.
All three of these reasons also ranked highest as barriers in responses from all respondents, including those who use standing orders. But those who didn’t use them were significantly more likely to cite these reasons (P less than .0001).
Since the survey occurred in 2017, however, it’s possible the pandemic and the rapid increase in telehealth as a result may influence perceptions moving forward.
“With provider concerns that standing orders remove physicians from the vaccination conversation, it may be that those conversations become less crucial as some families may start to value and accept immunizations more as a result of this pandemic,” Dr Cataldi said. “Or for families with vaccine questions, telehealth might support those conversations with a provider well.”
After adjusting for potential confounders, the only practice or physician factor significantly associated with not using standing orders for vaccines was physicians’ having a higher “physician responsibility score.” Doctors with these higher scores also were marginally more likely to make independent decisions about vaccines than counterparts working at practices where system-level decisions occur.
“Perhaps physicians who feel more personal responsibility about their role in vaccination are more likely to choose practice settings where they have more independent decision-making ability,” the authors wrote. “Alternatively, knowing the level of decision-making about vaccines in the practice may influence the amount of personal responsibility that pediatricians feel about their role in vaccine delivery.”
Again, attitudes may have shifted since the coronavirus pandemic began. The biggest risk to children in terms of immunizations is not getting them, Dr Offit said.
“The parents are scared, and the doctors are scared,” he said. “They feel that going to a doctor’s office is going to a concentrated area where they’re more likely to pick up this virus.”
He’s expressed uncertainty about whether standing orders could play a role in alleviating that anxiety. But Dr Cataldi suggests it’s possible.
“I think standing orders will be important to increasing vaccination rates during a pandemic as they can be used to support delivery of vaccines through public health departments and through vaccine-only nurse visits,” she said.
The research was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Cataldi J et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Apr;e20191855.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Two rare neurologic conditions linked to COVID-19
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old man developed Miller Fisher syndrome and a 39-year-old man developed polyneuritis cranialis. Both are variants of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), which physicians in China and Italy also linked to COVID-19 infection, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News.
In both cases, physicians made the diagnoses based on abnormal eye examinations. The two patients responded to treatment and improved over 2 weeks, with only the 50-year-old featuring residual symptoms of anosmia and ageusia.
The report was published online April 17 in Neurology.
The 50-year-old man was admitted to an emergency room with a temperature of 99.9°F (37.7°C). He reported 2 days of vertical diplopia, perioral paresthesias, and gait instability. His neurologic examination showed intact cognitive function and language.
Five days earlier he developed a cough, malaise, headache, low back pain, fever, anosmia, and ageusia.
His neuro-ophthalmologic examination showed right hypertropia in all fields of gaze, severe limitations to the adduction and downgaze movements of his right eye, and left eye nystagmus on left gaze. These findings were consistent with right internuclear ophthalmoparesis and right fascicular oculomotor palsy.
He responded to intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin therapy and was discharged home 2 weeks after admission.
The 39-year-old man was admitted to the emergency room with acute onset diplopia and ageusia. Three days earlier he had presented with diarrhea, a low-grade fever and in generally poor condition, without any headache, respiratory symptoms, or dyspnea.
He showed esotropia of 10 prism diopters at distance and 4 prism diopters at near, severe abduction deficits in both eyes, and fixation nystagmus, with the upper gaze more impaired, all consistent with bilateral abducens palsy.
The patient was discharged home and treated symptomatically with acetaminophen and telemedicine monitoring “due to a complete hospital saturation with COVID-19 patients,” wrote the researchers, led by Consuelo Gutiérrez-Ortiz, MD, PhD, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain.
Two weeks later, he had made a complete neurologic recovery with no ageusia, complete eye movements, and normal deep tendon reflexes.
“Fisher syndrome and polyneuritis cranialis in these two patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection could be simply coincidental. However, taking into account the temporal relationship, we feel that COVID-19 might have been responsible for the development of these two neurological pictures,” the authors noted.
European Regional Development Funds (FEDER) supported this research.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey: Hydroxychloroquine use fairly common in COVID-19
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.
The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.

The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”
One of five physicians in front-line treatment roles has prescribed hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19, according to a new survey from health care market research company InCrowd.

The most common treatments were acetaminophen, prescribed to 82% of patients, antibiotics (41%), and bronchodilators (40%), InCrowd said after surveying 203 primary care physicians, pediatricians, and emergency medicine or critical care physicians who are treating at least 20 patients with flulike symptoms.
On April 24, the Food and Drug Administration warned against the use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine outside of hospitals and clinical trials.
The InCrowd survey, which took place April 14-15 and is the fourth in a series investigating COVID-19’s impact on physicians, showed that access to testing was up to 82% in mid-April, compared with 67% in March and 20% in late February. The April respondents also were twice as likely (59% vs. 24% in March) to say that their facilities were prepared to treat patients, InCrowd reported.
“U.S. physicians report sluggish optimism around preparedness, safety, and institutional efforts, while many worry about the future, including a second outbreak and job security,” the company said in a separate written statement.
The average estimate for a return to normal was just over 6 months among respondents, and only 28% believed that their facility was prepared for a second outbreak later in the year, InCrowd noted.
On a personal level, 45% of the respondents were concerned about the safety of their job. An emergency/critical care physician from Tennessee said, “We’ve been cutting back on staff due to overall revenue reductions, but have increased acuity and complexity which requires more staffing. This puts even more of a burden on those of us still here.”
Support for institutional responses to slow the pandemic was strongest for state governments, which gained approval from 54% of front-line physicians, up from 33% in March. Actions taken by the federal government were supported by 21% of respondents, compared with 38% for the World Health Organization and 46% for governments outside the United States, InCrowd reported.
Suggestions for further actions by state and local authorities included this comment from an emergency/critical care physician in Florida: “Continued, broad and properly enforced stay at home and social distancing measures MUST remain in place to keep citizens and healthcare workers safe, and the latter alive and in adequate supply.”