User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
ED staff speak out about workplace violence, ask for mitigation
WASHINGTON – Speaker after speaker, veteran emergency department physicians and nurses approached the podium for a May 4 press conference on the U.S. Capitol lawn across from the East Senate steps to describe violent incidents – being bitten, punched, slapped, kicked, choked, spat on, threatened – that they have both observed and have been subject to while working in EDs.
The press conference was cosponsored by the American College of Emergency Physicians and the Emergency Nurses Association, which have partnered since 2019 on the No Silence on ED Violence campaign.
The numbers confirm their experience. A 2018 poll of 3,500 ED physicians nationwide, which was conducted by Marketing General and was reported at ACEP’s annual meeting, found that nearly half of respondents had been assaulted at work; 27% of them were injured from the assault. Nurses, who spend more time with patients, may face even higher rates.
Incidence was reported to be increasing in 2018, and that was before the social and psychological upheavals imposed by the COVID pandemic caused assaults on staff in the hospital to go up an estimated 200%-300%.
But what really grated was that more than 95% of such cases, mostly perpetrated by patients, were never prosecuted, said Jennifer Casaletto, MD, FACEP, a North Carolina emergency physician and president of the state’s ACEP chapter. “Hospital and law enforcement see violence as just part of the job in our EDs.”
It’s no secret that workplace violence is increasing, Dr. Casaletto said. Four weeks ago, she stitched up the face of a charge nurse who had been assaulted. The nurse didn’t report the incident because she didn’t believe anything would change.
“Listening to my colleagues, I know the terror they have felt in the moment – for themselves, their colleagues, their patients. I know that raw fear of being attacked, and the complex emotions that follow. I’ve been hit, bit, and punched and watched colleagues getting choked.”
Dr. Casaletto was present in the ED when an out-of-control patient clubbed a nurse with an IV pole as she tried to close the doors to other patients’ rooms. “Instinctively, I pulled my stethoscope from around my neck, hoping I wouldn’t be strangled with it.”
Tennessee emergency nurse Todd Haines, MSN, RN, AEMT, CEN, said he has stepped in to help pull patients off coworkers. “I’ve seen some staff so severely injured they could not return to the bedside. I’ve been verbally threatened. My family has been threatened by patients and their families,” he reported. “We’ve all seen it. And COVID has made some people even meaner. They just lose their minds, and ED staff take the brunt of their aggression. But then to report these incidents and hear: ‘It’s just part of your job,’ well, it’s not part of my job.”
Mr. Haines spent 10 years in law enforcement with a sheriff’s department in middle Tennessee and was on its special tactical response team before becoming an ED nurse. He said he saw many more verbal and physical assaults in 11 years in the ED than during his police career.
“I love emergency nursing at the bedside, but it got to the point where I took the first chance to leave the bedside. And I’m not alone. Other nurses are leaving in droves.” Mr. Haines now has a job directing a trauma program, and he volunteers on policy issues for the Tennessee ENA. But he worries about the toll of this violence on the ED workforce, with so many professionals already mulling over leaving the field because of job stress and burnout.
“We have to do something to keep experienced hospital emergency staff at the bedside.”
What’s the answer?
Also speaking at the press conference was Senator Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.), who pledged to introduce the Workplace Violence Prevention for Health Care and Social Services Workers Act, which passed the House in April. This bill would direct the Occupational Health and Safety Administration to issue a standard requiring employers in health care and social services to develop and implement workplace violence prevention plans. It would cover a variety of health facilities but not doctor’s offices or home-based services.
An interim final standard would be due within a year of enactment, with a final version to follow. Covered employers would have 6 months to develop and implement their own comprehensive workplace violence prevention plans, with the meaningful participation of direct care employees, tailored for and specific to the conditions and hazards of their facility, informed by past violent incidents, and subject to the size and complexity of the setting.
The plan would also name an individual responsible for its implementation, would include staff training and education, and would require facilities to track incidents and prohibit retaliation against employees who reported incidents of workplace violence.
On Wednesday, Sen. Baldwin called for unanimous consent on the Senate floor to fast-track this bill, but that was opposed by Senator Mike Braun (R-Ind.). She will soon introduce legislation similar to HR 1195, which the House passed.
“This bill will provide long overdue protections and safety standards,” she said. It will ensure that workplaces adopt proven protection techniques, such as those in OSHA’s 2015 guideline for preventing health care workplace violence. The American Hospital Association opposed the House bill on the grounds that hospitals have already implemented policies and programs specifically tailored to address workplace violence, so the OSHA standards required by the bill are not warranted.
Another speaker at the press conference, Aisha Terry, MD, MPH, FACEP, an emergency physician for George Washington University and Veterans Affairs in Washington, D.C., and current vice president of ACEP, described an incident that occurred when she was at work. A patient punched the nurse caring for him in the face, knocking her unconscious to the floor. “I’ll never forget that sound,” Dr. Terry said. “To this day, it has impacted her career. She hasn’t known what to do.”
Many people don’t realize how bad workplace violence really is, Dr. Terry added. “You assume you can serve as the safety net of this country, taking care of patients in the context of the pandemic, and feel safe – and not have to worry about your own safety. It’s past due that we put an end to this.”
Biggest win
Mr. Haines called the workplace violence bill a game changer for ED professionals, now and into the future. “We’re not going to totally eliminate violence in the emergency department. That is part of our business. But this legislation will support us and give a safer environment for us to do the work we love,” he said.
“The biggest win for this legislation is that it will create a supportive, nonretaliatory environment. It will give us as nurses a structured way to report things.” And, when these incidents do get reported, staff will get the help they need, Mr. Haines said. “The legislation will help show the importance of implementing systems and processes in emergency settings to address the risks and hazards that makes us all vulnerable to violence.”
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – Speaker after speaker, veteran emergency department physicians and nurses approached the podium for a May 4 press conference on the U.S. Capitol lawn across from the East Senate steps to describe violent incidents – being bitten, punched, slapped, kicked, choked, spat on, threatened – that they have both observed and have been subject to while working in EDs.
The press conference was cosponsored by the American College of Emergency Physicians and the Emergency Nurses Association, which have partnered since 2019 on the No Silence on ED Violence campaign.
The numbers confirm their experience. A 2018 poll of 3,500 ED physicians nationwide, which was conducted by Marketing General and was reported at ACEP’s annual meeting, found that nearly half of respondents had been assaulted at work; 27% of them were injured from the assault. Nurses, who spend more time with patients, may face even higher rates.
Incidence was reported to be increasing in 2018, and that was before the social and psychological upheavals imposed by the COVID pandemic caused assaults on staff in the hospital to go up an estimated 200%-300%.
But what really grated was that more than 95% of such cases, mostly perpetrated by patients, were never prosecuted, said Jennifer Casaletto, MD, FACEP, a North Carolina emergency physician and president of the state’s ACEP chapter. “Hospital and law enforcement see violence as just part of the job in our EDs.”
It’s no secret that workplace violence is increasing, Dr. Casaletto said. Four weeks ago, she stitched up the face of a charge nurse who had been assaulted. The nurse didn’t report the incident because she didn’t believe anything would change.
“Listening to my colleagues, I know the terror they have felt in the moment – for themselves, their colleagues, their patients. I know that raw fear of being attacked, and the complex emotions that follow. I’ve been hit, bit, and punched and watched colleagues getting choked.”
Dr. Casaletto was present in the ED when an out-of-control patient clubbed a nurse with an IV pole as she tried to close the doors to other patients’ rooms. “Instinctively, I pulled my stethoscope from around my neck, hoping I wouldn’t be strangled with it.”
Tennessee emergency nurse Todd Haines, MSN, RN, AEMT, CEN, said he has stepped in to help pull patients off coworkers. “I’ve seen some staff so severely injured they could not return to the bedside. I’ve been verbally threatened. My family has been threatened by patients and their families,” he reported. “We’ve all seen it. And COVID has made some people even meaner. They just lose their minds, and ED staff take the brunt of their aggression. But then to report these incidents and hear: ‘It’s just part of your job,’ well, it’s not part of my job.”
Mr. Haines spent 10 years in law enforcement with a sheriff’s department in middle Tennessee and was on its special tactical response team before becoming an ED nurse. He said he saw many more verbal and physical assaults in 11 years in the ED than during his police career.
“I love emergency nursing at the bedside, but it got to the point where I took the first chance to leave the bedside. And I’m not alone. Other nurses are leaving in droves.” Mr. Haines now has a job directing a trauma program, and he volunteers on policy issues for the Tennessee ENA. But he worries about the toll of this violence on the ED workforce, with so many professionals already mulling over leaving the field because of job stress and burnout.
“We have to do something to keep experienced hospital emergency staff at the bedside.”
What’s the answer?
Also speaking at the press conference was Senator Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.), who pledged to introduce the Workplace Violence Prevention for Health Care and Social Services Workers Act, which passed the House in April. This bill would direct the Occupational Health and Safety Administration to issue a standard requiring employers in health care and social services to develop and implement workplace violence prevention plans. It would cover a variety of health facilities but not doctor’s offices or home-based services.
An interim final standard would be due within a year of enactment, with a final version to follow. Covered employers would have 6 months to develop and implement their own comprehensive workplace violence prevention plans, with the meaningful participation of direct care employees, tailored for and specific to the conditions and hazards of their facility, informed by past violent incidents, and subject to the size and complexity of the setting.
The plan would also name an individual responsible for its implementation, would include staff training and education, and would require facilities to track incidents and prohibit retaliation against employees who reported incidents of workplace violence.
On Wednesday, Sen. Baldwin called for unanimous consent on the Senate floor to fast-track this bill, but that was opposed by Senator Mike Braun (R-Ind.). She will soon introduce legislation similar to HR 1195, which the House passed.
“This bill will provide long overdue protections and safety standards,” she said. It will ensure that workplaces adopt proven protection techniques, such as those in OSHA’s 2015 guideline for preventing health care workplace violence. The American Hospital Association opposed the House bill on the grounds that hospitals have already implemented policies and programs specifically tailored to address workplace violence, so the OSHA standards required by the bill are not warranted.
Another speaker at the press conference, Aisha Terry, MD, MPH, FACEP, an emergency physician for George Washington University and Veterans Affairs in Washington, D.C., and current vice president of ACEP, described an incident that occurred when she was at work. A patient punched the nurse caring for him in the face, knocking her unconscious to the floor. “I’ll never forget that sound,” Dr. Terry said. “To this day, it has impacted her career. She hasn’t known what to do.”
Many people don’t realize how bad workplace violence really is, Dr. Terry added. “You assume you can serve as the safety net of this country, taking care of patients in the context of the pandemic, and feel safe – and not have to worry about your own safety. It’s past due that we put an end to this.”
Biggest win
Mr. Haines called the workplace violence bill a game changer for ED professionals, now and into the future. “We’re not going to totally eliminate violence in the emergency department. That is part of our business. But this legislation will support us and give a safer environment for us to do the work we love,” he said.
“The biggest win for this legislation is that it will create a supportive, nonretaliatory environment. It will give us as nurses a structured way to report things.” And, when these incidents do get reported, staff will get the help they need, Mr. Haines said. “The legislation will help show the importance of implementing systems and processes in emergency settings to address the risks and hazards that makes us all vulnerable to violence.”
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – Speaker after speaker, veteran emergency department physicians and nurses approached the podium for a May 4 press conference on the U.S. Capitol lawn across from the East Senate steps to describe violent incidents – being bitten, punched, slapped, kicked, choked, spat on, threatened – that they have both observed and have been subject to while working in EDs.
The press conference was cosponsored by the American College of Emergency Physicians and the Emergency Nurses Association, which have partnered since 2019 on the No Silence on ED Violence campaign.
The numbers confirm their experience. A 2018 poll of 3,500 ED physicians nationwide, which was conducted by Marketing General and was reported at ACEP’s annual meeting, found that nearly half of respondents had been assaulted at work; 27% of them were injured from the assault. Nurses, who spend more time with patients, may face even higher rates.
Incidence was reported to be increasing in 2018, and that was before the social and psychological upheavals imposed by the COVID pandemic caused assaults on staff in the hospital to go up an estimated 200%-300%.
But what really grated was that more than 95% of such cases, mostly perpetrated by patients, were never prosecuted, said Jennifer Casaletto, MD, FACEP, a North Carolina emergency physician and president of the state’s ACEP chapter. “Hospital and law enforcement see violence as just part of the job in our EDs.”
It’s no secret that workplace violence is increasing, Dr. Casaletto said. Four weeks ago, she stitched up the face of a charge nurse who had been assaulted. The nurse didn’t report the incident because she didn’t believe anything would change.
“Listening to my colleagues, I know the terror they have felt in the moment – for themselves, their colleagues, their patients. I know that raw fear of being attacked, and the complex emotions that follow. I’ve been hit, bit, and punched and watched colleagues getting choked.”
Dr. Casaletto was present in the ED when an out-of-control patient clubbed a nurse with an IV pole as she tried to close the doors to other patients’ rooms. “Instinctively, I pulled my stethoscope from around my neck, hoping I wouldn’t be strangled with it.”
Tennessee emergency nurse Todd Haines, MSN, RN, AEMT, CEN, said he has stepped in to help pull patients off coworkers. “I’ve seen some staff so severely injured they could not return to the bedside. I’ve been verbally threatened. My family has been threatened by patients and their families,” he reported. “We’ve all seen it. And COVID has made some people even meaner. They just lose their minds, and ED staff take the brunt of their aggression. But then to report these incidents and hear: ‘It’s just part of your job,’ well, it’s not part of my job.”
Mr. Haines spent 10 years in law enforcement with a sheriff’s department in middle Tennessee and was on its special tactical response team before becoming an ED nurse. He said he saw many more verbal and physical assaults in 11 years in the ED than during his police career.
“I love emergency nursing at the bedside, but it got to the point where I took the first chance to leave the bedside. And I’m not alone. Other nurses are leaving in droves.” Mr. Haines now has a job directing a trauma program, and he volunteers on policy issues for the Tennessee ENA. But he worries about the toll of this violence on the ED workforce, with so many professionals already mulling over leaving the field because of job stress and burnout.
“We have to do something to keep experienced hospital emergency staff at the bedside.”
What’s the answer?
Also speaking at the press conference was Senator Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.), who pledged to introduce the Workplace Violence Prevention for Health Care and Social Services Workers Act, which passed the House in April. This bill would direct the Occupational Health and Safety Administration to issue a standard requiring employers in health care and social services to develop and implement workplace violence prevention plans. It would cover a variety of health facilities but not doctor’s offices or home-based services.
An interim final standard would be due within a year of enactment, with a final version to follow. Covered employers would have 6 months to develop and implement their own comprehensive workplace violence prevention plans, with the meaningful participation of direct care employees, tailored for and specific to the conditions and hazards of their facility, informed by past violent incidents, and subject to the size and complexity of the setting.
The plan would also name an individual responsible for its implementation, would include staff training and education, and would require facilities to track incidents and prohibit retaliation against employees who reported incidents of workplace violence.
On Wednesday, Sen. Baldwin called for unanimous consent on the Senate floor to fast-track this bill, but that was opposed by Senator Mike Braun (R-Ind.). She will soon introduce legislation similar to HR 1195, which the House passed.
“This bill will provide long overdue protections and safety standards,” she said. It will ensure that workplaces adopt proven protection techniques, such as those in OSHA’s 2015 guideline for preventing health care workplace violence. The American Hospital Association opposed the House bill on the grounds that hospitals have already implemented policies and programs specifically tailored to address workplace violence, so the OSHA standards required by the bill are not warranted.
Another speaker at the press conference, Aisha Terry, MD, MPH, FACEP, an emergency physician for George Washington University and Veterans Affairs in Washington, D.C., and current vice president of ACEP, described an incident that occurred when she was at work. A patient punched the nurse caring for him in the face, knocking her unconscious to the floor. “I’ll never forget that sound,” Dr. Terry said. “To this day, it has impacted her career. She hasn’t known what to do.”
Many people don’t realize how bad workplace violence really is, Dr. Terry added. “You assume you can serve as the safety net of this country, taking care of patients in the context of the pandemic, and feel safe – and not have to worry about your own safety. It’s past due that we put an end to this.”
Biggest win
Mr. Haines called the workplace violence bill a game changer for ED professionals, now and into the future. “We’re not going to totally eliminate violence in the emergency department. That is part of our business. But this legislation will support us and give a safer environment for us to do the work we love,” he said.
“The biggest win for this legislation is that it will create a supportive, nonretaliatory environment. It will give us as nurses a structured way to report things.” And, when these incidents do get reported, staff will get the help they need, Mr. Haines said. “The legislation will help show the importance of implementing systems and processes in emergency settings to address the risks and hazards that makes us all vulnerable to violence.”
No relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TikTok challenge hits Taco Bell right in its ‘Stuft Nacho’
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Recommendations for improving federal diabetes programs: How primary care clinicians can help with implementation
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Prior authorizations delay TNF inhibitors for children with JIA
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) who need a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor after failing conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment often experience insurance delays before beginning the new drug because of prior authorization denials, according to research presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA). The findings were also published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
“Prompt escalation to TNF inhibitors is recommended for children with JIA refractory to DMARDs,” author Jordan Roberts, MD, a clinical fellow of the Harvard Medical School Rheumatology Program, Boston, told CARRA attendees. TNF inhibitors are increasingly used as first-line treatment in JIA since growing evidence suggests better outcomes from early treatment with biologics. “Prior authorization requirements that delay TNF inhibitor initiation among children with JIA are common in clinical practice,” Dr. Roberts said, but little evidence exists to understand the extent of this problem and its causes.
The researchers therefore conducted a retrospective cohort study using a search of electronic health records from January 2018 to December 2019 to find all children at a single center with a new diagnosis of nonsystemic JIA. Then the authors pulled the timing of prior authorization requests, approvals, denials, and first TNF inhibitor dose from the medical notes. They also sought out any children who had been recommended a TNF inhibitor but never started one.
The total population included 54 children with an average age of 10 years, about two-thirds of whom had private insurance (63%). The group was predominantly White (63%), although 13% declined to provide race, and 7% were Hispanic. Most subtypes of disease were represented: oligoarticular persistent (28%), oligoarticular extended (2%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-negative (15%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-positive (15%), psoriatic arthritis (26%), enthesitis-related arthritis (12%), and undifferentiated arthritis (2%).
The 44 participants with private insurance had an average of two joints with active disease, while the 10 patients with public insurance had an average of four involved joints. Nearly all the patients (91%) had previously taken or were currently taking DMARDs when the prior authorization was submitted, and 61% had received NSAIDs.
All but one of the patients’ insurance plans required a prior authorization. The first prior authorization was denied for about one-third of the public insurance patients (30%) and a quarter of the private insurance patients. About 1 in 5 patients overall (22%) required a written appeal to override the denial, and 4% required peer-to-peer review. Meanwhile, 7% of patients began another medication because of the denial.
It took a median of 3 days for prior authorizations to be approved and a median of 24 days from the time the TNF inhibitor was recommended to the patient receiving the first dose. However, 22% of patients waited at least 2 weeks before the prior authorization was approved, and more than a quarter of the requests took over 30 days before the patient could begin the medication. In the public insurance group in particular, a quarter of children waited at least 19 days for approval and at least 44 days before starting the medication.
In fact, when the researchers looked at the difference in approval time between those who did and did not receive an initial denial, the difference was stark. Median approval time was 16 days when the prior authorization was denied, compared with a median of 5 days when the first prior authorization was approved. Similarly, time to initiation of the drug after recommendation was a median of 35 days for those whose prior authorization was first denied and 17 days for those with an initial approval.
The most common reason for an initial denial was the insurance company requiring a different TNF inhibitor than the one the rheumatologist wanted to prescribe. “These were all children whose rheumatologist has recommended either infliximab or etanercept that were required to use adalimumab instead,” Dr. Roberts said.
The other reasons for initial denial were similarly familiar ones:
- Required submission to another insurer
- Additional documentation required
- Lack of medical necessity
- Prescription was for an indication not approved by the Food and Drug Administration
- Age of patient
- Nonbiologic DMARD required
- NSAID required for step therapy
Only three children who were advised to begin a TNF inhibitor did not do so, including one who was lost to follow-up, one who had injection-related anxiety, and one who had safety concerns about the medication.
“Several children were required to use alternative TNF inhibitors than the one that was recommended due to restricted formularies, which may reduce shared decisionmaking between physicians and families and may not be the optimal clinical choice for an individual child,” Dr. Roberts said in her conclusion. Most children, however, were able to get approval for the TNF inhibitor originally requested, “suggesting that utilization management strategies present barriers to timely care despite appropriate specialty medication requests,” she said. “Therefore, it’s important for us to advocate for access to medications for children with JIA.”
Findings are not surprising
“I have these same experiences at my institution – often insurance will dictate clinical practice, and step therapy is the only option, causing a delay to initiation of TNFi even if we think, as the pediatric rheumatologist, that a child needs this medicine to be initiated on presentation to our clinic,” Nayimisha Balmuri, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
Dr. Balmuri, who was not involved in the study, noted that in her clinic at Johns Hopkins, it is hit or miss if an appeal to insurance companies or to the state (if it is Medicaid coverage) will be successful. “Unfortunately, [we are] mostly unsuccessful, and we have to try another DMARD for 8 to 12 weeks first before trying to get TNFi,” she said.
Dr. Balmuri called for bringing these issues to the attention of state and federal legislators. “It’s so important for us to continue to advocate for our patients at the state and national level! We are the advocates for our patients, and we are uniquely trained to know the best medications to initiate to help patients maximize their chance to reach remission of arthritis. Insurance companies need to hear our voices!”
Dr. Roberts reported grants from CARRA, the Lupus Foundation of America, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) who need a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor after failing conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment often experience insurance delays before beginning the new drug because of prior authorization denials, according to research presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA). The findings were also published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
“Prompt escalation to TNF inhibitors is recommended for children with JIA refractory to DMARDs,” author Jordan Roberts, MD, a clinical fellow of the Harvard Medical School Rheumatology Program, Boston, told CARRA attendees. TNF inhibitors are increasingly used as first-line treatment in JIA since growing evidence suggests better outcomes from early treatment with biologics. “Prior authorization requirements that delay TNF inhibitor initiation among children with JIA are common in clinical practice,” Dr. Roberts said, but little evidence exists to understand the extent of this problem and its causes.
The researchers therefore conducted a retrospective cohort study using a search of electronic health records from January 2018 to December 2019 to find all children at a single center with a new diagnosis of nonsystemic JIA. Then the authors pulled the timing of prior authorization requests, approvals, denials, and first TNF inhibitor dose from the medical notes. They also sought out any children who had been recommended a TNF inhibitor but never started one.
The total population included 54 children with an average age of 10 years, about two-thirds of whom had private insurance (63%). The group was predominantly White (63%), although 13% declined to provide race, and 7% were Hispanic. Most subtypes of disease were represented: oligoarticular persistent (28%), oligoarticular extended (2%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-negative (15%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-positive (15%), psoriatic arthritis (26%), enthesitis-related arthritis (12%), and undifferentiated arthritis (2%).
The 44 participants with private insurance had an average of two joints with active disease, while the 10 patients with public insurance had an average of four involved joints. Nearly all the patients (91%) had previously taken or were currently taking DMARDs when the prior authorization was submitted, and 61% had received NSAIDs.
All but one of the patients’ insurance plans required a prior authorization. The first prior authorization was denied for about one-third of the public insurance patients (30%) and a quarter of the private insurance patients. About 1 in 5 patients overall (22%) required a written appeal to override the denial, and 4% required peer-to-peer review. Meanwhile, 7% of patients began another medication because of the denial.
It took a median of 3 days for prior authorizations to be approved and a median of 24 days from the time the TNF inhibitor was recommended to the patient receiving the first dose. However, 22% of patients waited at least 2 weeks before the prior authorization was approved, and more than a quarter of the requests took over 30 days before the patient could begin the medication. In the public insurance group in particular, a quarter of children waited at least 19 days for approval and at least 44 days before starting the medication.
In fact, when the researchers looked at the difference in approval time between those who did and did not receive an initial denial, the difference was stark. Median approval time was 16 days when the prior authorization was denied, compared with a median of 5 days when the first prior authorization was approved. Similarly, time to initiation of the drug after recommendation was a median of 35 days for those whose prior authorization was first denied and 17 days for those with an initial approval.
The most common reason for an initial denial was the insurance company requiring a different TNF inhibitor than the one the rheumatologist wanted to prescribe. “These were all children whose rheumatologist has recommended either infliximab or etanercept that were required to use adalimumab instead,” Dr. Roberts said.
The other reasons for initial denial were similarly familiar ones:
- Required submission to another insurer
- Additional documentation required
- Lack of medical necessity
- Prescription was for an indication not approved by the Food and Drug Administration
- Age of patient
- Nonbiologic DMARD required
- NSAID required for step therapy
Only three children who were advised to begin a TNF inhibitor did not do so, including one who was lost to follow-up, one who had injection-related anxiety, and one who had safety concerns about the medication.
“Several children were required to use alternative TNF inhibitors than the one that was recommended due to restricted formularies, which may reduce shared decisionmaking between physicians and families and may not be the optimal clinical choice for an individual child,” Dr. Roberts said in her conclusion. Most children, however, were able to get approval for the TNF inhibitor originally requested, “suggesting that utilization management strategies present barriers to timely care despite appropriate specialty medication requests,” she said. “Therefore, it’s important for us to advocate for access to medications for children with JIA.”
Findings are not surprising
“I have these same experiences at my institution – often insurance will dictate clinical practice, and step therapy is the only option, causing a delay to initiation of TNFi even if we think, as the pediatric rheumatologist, that a child needs this medicine to be initiated on presentation to our clinic,” Nayimisha Balmuri, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
Dr. Balmuri, who was not involved in the study, noted that in her clinic at Johns Hopkins, it is hit or miss if an appeal to insurance companies or to the state (if it is Medicaid coverage) will be successful. “Unfortunately, [we are] mostly unsuccessful, and we have to try another DMARD for 8 to 12 weeks first before trying to get TNFi,” she said.
Dr. Balmuri called for bringing these issues to the attention of state and federal legislators. “It’s so important for us to continue to advocate for our patients at the state and national level! We are the advocates for our patients, and we are uniquely trained to know the best medications to initiate to help patients maximize their chance to reach remission of arthritis. Insurance companies need to hear our voices!”
Dr. Roberts reported grants from CARRA, the Lupus Foundation of America, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) who need a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor after failing conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment often experience insurance delays before beginning the new drug because of prior authorization denials, according to research presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA). The findings were also published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open.
“Prompt escalation to TNF inhibitors is recommended for children with JIA refractory to DMARDs,” author Jordan Roberts, MD, a clinical fellow of the Harvard Medical School Rheumatology Program, Boston, told CARRA attendees. TNF inhibitors are increasingly used as first-line treatment in JIA since growing evidence suggests better outcomes from early treatment with biologics. “Prior authorization requirements that delay TNF inhibitor initiation among children with JIA are common in clinical practice,” Dr. Roberts said, but little evidence exists to understand the extent of this problem and its causes.
The researchers therefore conducted a retrospective cohort study using a search of electronic health records from January 2018 to December 2019 to find all children at a single center with a new diagnosis of nonsystemic JIA. Then the authors pulled the timing of prior authorization requests, approvals, denials, and first TNF inhibitor dose from the medical notes. They also sought out any children who had been recommended a TNF inhibitor but never started one.
The total population included 54 children with an average age of 10 years, about two-thirds of whom had private insurance (63%). The group was predominantly White (63%), although 13% declined to provide race, and 7% were Hispanic. Most subtypes of disease were represented: oligoarticular persistent (28%), oligoarticular extended (2%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-negative (15%), polyarticular rheumatoid factor-positive (15%), psoriatic arthritis (26%), enthesitis-related arthritis (12%), and undifferentiated arthritis (2%).
The 44 participants with private insurance had an average of two joints with active disease, while the 10 patients with public insurance had an average of four involved joints. Nearly all the patients (91%) had previously taken or were currently taking DMARDs when the prior authorization was submitted, and 61% had received NSAIDs.
All but one of the patients’ insurance plans required a prior authorization. The first prior authorization was denied for about one-third of the public insurance patients (30%) and a quarter of the private insurance patients. About 1 in 5 patients overall (22%) required a written appeal to override the denial, and 4% required peer-to-peer review. Meanwhile, 7% of patients began another medication because of the denial.
It took a median of 3 days for prior authorizations to be approved and a median of 24 days from the time the TNF inhibitor was recommended to the patient receiving the first dose. However, 22% of patients waited at least 2 weeks before the prior authorization was approved, and more than a quarter of the requests took over 30 days before the patient could begin the medication. In the public insurance group in particular, a quarter of children waited at least 19 days for approval and at least 44 days before starting the medication.
In fact, when the researchers looked at the difference in approval time between those who did and did not receive an initial denial, the difference was stark. Median approval time was 16 days when the prior authorization was denied, compared with a median of 5 days when the first prior authorization was approved. Similarly, time to initiation of the drug after recommendation was a median of 35 days for those whose prior authorization was first denied and 17 days for those with an initial approval.
The most common reason for an initial denial was the insurance company requiring a different TNF inhibitor than the one the rheumatologist wanted to prescribe. “These were all children whose rheumatologist has recommended either infliximab or etanercept that were required to use adalimumab instead,” Dr. Roberts said.
The other reasons for initial denial were similarly familiar ones:
- Required submission to another insurer
- Additional documentation required
- Lack of medical necessity
- Prescription was for an indication not approved by the Food and Drug Administration
- Age of patient
- Nonbiologic DMARD required
- NSAID required for step therapy
Only three children who were advised to begin a TNF inhibitor did not do so, including one who was lost to follow-up, one who had injection-related anxiety, and one who had safety concerns about the medication.
“Several children were required to use alternative TNF inhibitors than the one that was recommended due to restricted formularies, which may reduce shared decisionmaking between physicians and families and may not be the optimal clinical choice for an individual child,” Dr. Roberts said in her conclusion. Most children, however, were able to get approval for the TNF inhibitor originally requested, “suggesting that utilization management strategies present barriers to timely care despite appropriate specialty medication requests,” she said. “Therefore, it’s important for us to advocate for access to medications for children with JIA.”
Findings are not surprising
“I have these same experiences at my institution – often insurance will dictate clinical practice, and step therapy is the only option, causing a delay to initiation of TNFi even if we think, as the pediatric rheumatologist, that a child needs this medicine to be initiated on presentation to our clinic,” Nayimisha Balmuri, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics in the division of allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, told this news organization.
Dr. Balmuri, who was not involved in the study, noted that in her clinic at Johns Hopkins, it is hit or miss if an appeal to insurance companies or to the state (if it is Medicaid coverage) will be successful. “Unfortunately, [we are] mostly unsuccessful, and we have to try another DMARD for 8 to 12 weeks first before trying to get TNFi,” she said.
Dr. Balmuri called for bringing these issues to the attention of state and federal legislators. “It’s so important for us to continue to advocate for our patients at the state and national level! We are the advocates for our patients, and we are uniquely trained to know the best medications to initiate to help patients maximize their chance to reach remission of arthritis. Insurance companies need to hear our voices!”
Dr. Roberts reported grants from CARRA, the Lupus Foundation of America, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ex–hospital porter a neglected giant of cancer research
We have a half-forgotten Indian immigrant to thank – a hospital night porter turned biochemist –for revolutionizing treatment of leukemia, the once deadly childhood scourge that is still the most common pediatric cancer.
Dr. Yellapragada SubbaRow has been called the “father of chemotherapy” for developing methotrexate, a powerful, inexpensive therapy for leukemia and other diseases, and he is celebrated for additional scientific achievements. Yet Dr. SubbaRow’s life was marked more by struggle than glory.
Born poor in southeastern India, he nearly succumbed to a tropical disease that killed two older brothers, and he didn’t focus on schoolwork until his father died. Later, prejudice dogged his years as an immigrant to the United States, and a blood clot took his life at the age of 53.
Scientifically, however, Dr. SubbaRow (pronounced sue-buh-rao) triumphed, despite mammoth challenges and a lack of recognition that persists to this day. National Cancer Research Month is a fitting time to look back on his extraordinary life and work and pay tribute to his accomplishments.
‘Yella,’ folic acid, and a paradigm shift
No one appreciates Dr. SubbaRow more than a cadre of Indian-born physicians who have kept his legacy alive in journal articles, presentations, and a Pulitzer Prize-winning book. Among them is author and oncologist Siddhartha Mukherjee, MD, who chronicled Dr. SubbaRow’s achievements in his New York Times No. 1 bestseller, “The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer.”
As Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “pioneer in many ways, a physician turned cellular physiologist, a chemist who had accidentally wandered into biology.” (Per Indian tradition, SubbaRow is the doctor’s first name, and Yellapragada is his surname, but medical literature uses SubbaRow as his cognomen, with some variations in spelling. Dr. Mukherjee wrote that his friends called him “Yella.”)
Dr. SubbaRow came to the United States in 1923, after enduring a difficult childhood and young adulthood. He’d survived bouts of religious fervor, childhood rebellion (including a bid to run away from home and become a banana trader), and a failed arranged marriage. His wife bore him a child who died in infancy. He left it all behind.
In Boston, medical officials rejected his degree. Broke, he worked for a time as a night porter at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, changing sheets and cleaning urinals. To a poor but proud high-caste Indian Brahmin, the culture shock of carrying out these tasks must have been especially jarring.
Dr. SubbaRow went on to earn a diploma from Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, and became a junior faculty member. As a foreigner, Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “reclusive, nocturnal, heavily accented vegetarian,” so different from his colleagues that advancement seemed impossible. Despite his pioneering biochemistry work, Harvard later declined to offer Dr. SubbaRow a tenured faculty position.
By the early 1940s, he took a job at an upstate New York pharmaceutical company called Lederle Labs (later purchased by Pfizer). At Lederle, Dr. SubbaRow strove to synthesize the vitamin known as folic acid. He ended up creating a kind of antivitamin, a lookalike that acted like folic acid but only succeeded in gumming up the works in receptors. But what good would it do to stop the body from absorbing folic acid? Plenty, it turned out.
Discoveries pile up, but credit and fame prove elusive
Dr. SubbaRow was no stranger to producing landmark biological work. He’d previously codiscovered phosphocreatine and ATP, which are crucial to muscular contractions. However, “in 1935, he had to disown the extent of his role in the discovery of the color test related to phosphorus, instead giving the credit to his co-author, who was being considered for promotion to a full professorship at Harvard,” wrote author Gerald Posner in his 2020 book, “Pharma: Greed, Lies and the Poisoning of America.”
Houston-area oncologist Kirtan Nautiyal, MD, who paid tribute to Dr. SubbaRow in a 2018 article, contended that “with his Indian instinct for self-effacement, he had irreparably sabotaged his own career.”
Dr. SubbaRow and his team also developed “the first effective treatment of filariasis, which causes elephantiasis of the lower limbs and genitals in millions of people, mainly in tropical countries,” Dr. Nautiyal wrote. “Later in the decade, his antibiotic program generated polymyxin, the first effective treatment against the class of bacteria called Gram negatives, and aureomycin, the first “broad-spectrum’ antibiotic.” (Aureomycin is also the first tetracycline antibiotic.)
Dr. SubbaRow’s discovery of a folic acid antagonist would again go largely unheralded. But first came the realization that folic acid made childhood leukemia worse, not better, and the prospect that this process could potentially be reversed.
Rise of methotrexate and fall of leukemia
In Boston, Sidney Farber, MD, a Boston pathologist, was desperate to help Robert Sandler, a 2-year-old leukemia patient. Dr. Farber contacted his ex-colleague Dr. SubbaRow to request a supply of aminopterin, an early version of methotrexate that Dr. SubbaRow and his team had developed. Dr. Farber injected Robert with the substance and within 3 days, the toddler’s white blood count started falling – fast. He stopped bleeding, resumed eating, and once again seemed almost identical to his twin brother, as Dr. Mukherjee wrote in his book.
Leukemia had never gone into remission before. Unfortunately, the treatment only worked temporarily. Robert, like other children treated with the drug, relapsed and died within months. But Dr. Farber “saw a door open” – a chemical, a kind of chemotherapy, that could turn back cancer. In the case of folic acid antagonists, they do so by stopping cancer cells from replicating.
Methotrexate, a related agent synthesized by Dr. SubbaRow, would become a mainstay of leukemia treatment and begin to produce long-term remission from acute lymphoblastic leukemia in 1970, when combination chemotherapy was developed.
Other cancers fell to methotrexate treatment. “Previous assumptions that cancer was nearly always fatal were revised, and the field of medical oncology (treatment of cancer with chemotherapy), which had not previously existed, was formally established in 1971,” according to the National Cancer Institute’s history of methotrexate. This account does not mention Dr. SubbaRow.
Death takes the doctor, but his legacy remains
In biographies, as well as his own words, Dr. SubbaRow comes across as a prickly, hard-driving workaholic who had little interest in intimate human connections. “It is not good to ask in every letter when I will be back,” he wrote to his wife back in India, before cutting off ties completely in the early 1930s. “I will come as early as possible. ... I do not want to write anything more.”
It seems, as his biographer S.P.K. Gupta noted, that “he was quite determined that the time allotted to him on Earth should be completely devoted to finding cures for ailments that plagued mankind.”
Still, Dr. SubbaRow’s research team was devoted to him, and he had plenty of reasons to be bitter, such as the prejudice and isolation he encountered in the United States and earlier, in British-run India. According to Mr. Posner’s book, even as a young medical student, Dr. SubbaRow heeded the call of Indian independence activist Mohandas Gandhi. He “refused the British surgical gown given him at school and instead donned a traditional and simple cotton Khadi. That act of defiance cost SubbaRow the college degree that was necessary for him to get into the State Medical College.”
During the last year of his life, Dr. SubbaRow faced yet another humiliation: In his landmark 1948 study about aminopterin as a treatment for leukemia, his colleague Dr. Farber failed to credit him, an “astonishing omission” as Yaddanapudi Ravindranath, MBBS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Wayne State University, Detroit, put it. “From everything I know, Dr. Farber spent the rest of his career apologizing and trying to make amends for it,” Dr. Ravindranath said in an interview.
A career cut short, and a lasting legacy
In 1948, at the age of 53, Dr. SubbaRow suddenly died. “Many think Dr. SubbaRow would have won [the] Nobel Prize had he lived a few years longer,” said Dr. Ravindranath.
Like Dr. SubbaRow, Dr. Ravindranath was born in Andhra Pradesh state, near the city of Chennai formerly known as Madras. “Being a compatriot, in a way I continue his legacy, and I am obviously proud of him,” said Dr. Ravindranath, who has conducted his own landmark research regarding methotrexate and leukemia.
Nearly 75 years after Dr. SubbaRow’s death, Indian-born physicians like Dr. Ravindranath continue to honor him in print, trying to ensure that he’s not forgotten. Methotrexate remains a crucial treatment for leukemia, along with a long list of other ailments, including psoriasis.
Recognition for “Yella” may have come late and infrequently, but a Lederle Laboratories research library named after him offered Dr. SubbaRow a kind of immortality. A plaque there memorialized him in stone as a scientist, teacher, philosopher, and humanitarian, featuring the quote: “Science simply prolongs life. Religion deepens it.”
By all accounts, Dr. SubbaRow was a man of science and faith who had faith in science.
We have a half-forgotten Indian immigrant to thank – a hospital night porter turned biochemist –for revolutionizing treatment of leukemia, the once deadly childhood scourge that is still the most common pediatric cancer.
Dr. Yellapragada SubbaRow has been called the “father of chemotherapy” for developing methotrexate, a powerful, inexpensive therapy for leukemia and other diseases, and he is celebrated for additional scientific achievements. Yet Dr. SubbaRow’s life was marked more by struggle than glory.
Born poor in southeastern India, he nearly succumbed to a tropical disease that killed two older brothers, and he didn’t focus on schoolwork until his father died. Later, prejudice dogged his years as an immigrant to the United States, and a blood clot took his life at the age of 53.
Scientifically, however, Dr. SubbaRow (pronounced sue-buh-rao) triumphed, despite mammoth challenges and a lack of recognition that persists to this day. National Cancer Research Month is a fitting time to look back on his extraordinary life and work and pay tribute to his accomplishments.
‘Yella,’ folic acid, and a paradigm shift
No one appreciates Dr. SubbaRow more than a cadre of Indian-born physicians who have kept his legacy alive in journal articles, presentations, and a Pulitzer Prize-winning book. Among them is author and oncologist Siddhartha Mukherjee, MD, who chronicled Dr. SubbaRow’s achievements in his New York Times No. 1 bestseller, “The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer.”
As Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “pioneer in many ways, a physician turned cellular physiologist, a chemist who had accidentally wandered into biology.” (Per Indian tradition, SubbaRow is the doctor’s first name, and Yellapragada is his surname, but medical literature uses SubbaRow as his cognomen, with some variations in spelling. Dr. Mukherjee wrote that his friends called him “Yella.”)
Dr. SubbaRow came to the United States in 1923, after enduring a difficult childhood and young adulthood. He’d survived bouts of religious fervor, childhood rebellion (including a bid to run away from home and become a banana trader), and a failed arranged marriage. His wife bore him a child who died in infancy. He left it all behind.
In Boston, medical officials rejected his degree. Broke, he worked for a time as a night porter at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, changing sheets and cleaning urinals. To a poor but proud high-caste Indian Brahmin, the culture shock of carrying out these tasks must have been especially jarring.
Dr. SubbaRow went on to earn a diploma from Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, and became a junior faculty member. As a foreigner, Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “reclusive, nocturnal, heavily accented vegetarian,” so different from his colleagues that advancement seemed impossible. Despite his pioneering biochemistry work, Harvard later declined to offer Dr. SubbaRow a tenured faculty position.
By the early 1940s, he took a job at an upstate New York pharmaceutical company called Lederle Labs (later purchased by Pfizer). At Lederle, Dr. SubbaRow strove to synthesize the vitamin known as folic acid. He ended up creating a kind of antivitamin, a lookalike that acted like folic acid but only succeeded in gumming up the works in receptors. But what good would it do to stop the body from absorbing folic acid? Plenty, it turned out.
Discoveries pile up, but credit and fame prove elusive
Dr. SubbaRow was no stranger to producing landmark biological work. He’d previously codiscovered phosphocreatine and ATP, which are crucial to muscular contractions. However, “in 1935, he had to disown the extent of his role in the discovery of the color test related to phosphorus, instead giving the credit to his co-author, who was being considered for promotion to a full professorship at Harvard,” wrote author Gerald Posner in his 2020 book, “Pharma: Greed, Lies and the Poisoning of America.”
Houston-area oncologist Kirtan Nautiyal, MD, who paid tribute to Dr. SubbaRow in a 2018 article, contended that “with his Indian instinct for self-effacement, he had irreparably sabotaged his own career.”
Dr. SubbaRow and his team also developed “the first effective treatment of filariasis, which causes elephantiasis of the lower limbs and genitals in millions of people, mainly in tropical countries,” Dr. Nautiyal wrote. “Later in the decade, his antibiotic program generated polymyxin, the first effective treatment against the class of bacteria called Gram negatives, and aureomycin, the first “broad-spectrum’ antibiotic.” (Aureomycin is also the first tetracycline antibiotic.)
Dr. SubbaRow’s discovery of a folic acid antagonist would again go largely unheralded. But first came the realization that folic acid made childhood leukemia worse, not better, and the prospect that this process could potentially be reversed.
Rise of methotrexate and fall of leukemia
In Boston, Sidney Farber, MD, a Boston pathologist, was desperate to help Robert Sandler, a 2-year-old leukemia patient. Dr. Farber contacted his ex-colleague Dr. SubbaRow to request a supply of aminopterin, an early version of methotrexate that Dr. SubbaRow and his team had developed. Dr. Farber injected Robert with the substance and within 3 days, the toddler’s white blood count started falling – fast. He stopped bleeding, resumed eating, and once again seemed almost identical to his twin brother, as Dr. Mukherjee wrote in his book.
Leukemia had never gone into remission before. Unfortunately, the treatment only worked temporarily. Robert, like other children treated with the drug, relapsed and died within months. But Dr. Farber “saw a door open” – a chemical, a kind of chemotherapy, that could turn back cancer. In the case of folic acid antagonists, they do so by stopping cancer cells from replicating.
Methotrexate, a related agent synthesized by Dr. SubbaRow, would become a mainstay of leukemia treatment and begin to produce long-term remission from acute lymphoblastic leukemia in 1970, when combination chemotherapy was developed.
Other cancers fell to methotrexate treatment. “Previous assumptions that cancer was nearly always fatal were revised, and the field of medical oncology (treatment of cancer with chemotherapy), which had not previously existed, was formally established in 1971,” according to the National Cancer Institute’s history of methotrexate. This account does not mention Dr. SubbaRow.
Death takes the doctor, but his legacy remains
In biographies, as well as his own words, Dr. SubbaRow comes across as a prickly, hard-driving workaholic who had little interest in intimate human connections. “It is not good to ask in every letter when I will be back,” he wrote to his wife back in India, before cutting off ties completely in the early 1930s. “I will come as early as possible. ... I do not want to write anything more.”
It seems, as his biographer S.P.K. Gupta noted, that “he was quite determined that the time allotted to him on Earth should be completely devoted to finding cures for ailments that plagued mankind.”
Still, Dr. SubbaRow’s research team was devoted to him, and he had plenty of reasons to be bitter, such as the prejudice and isolation he encountered in the United States and earlier, in British-run India. According to Mr. Posner’s book, even as a young medical student, Dr. SubbaRow heeded the call of Indian independence activist Mohandas Gandhi. He “refused the British surgical gown given him at school and instead donned a traditional and simple cotton Khadi. That act of defiance cost SubbaRow the college degree that was necessary for him to get into the State Medical College.”
During the last year of his life, Dr. SubbaRow faced yet another humiliation: In his landmark 1948 study about aminopterin as a treatment for leukemia, his colleague Dr. Farber failed to credit him, an “astonishing omission” as Yaddanapudi Ravindranath, MBBS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Wayne State University, Detroit, put it. “From everything I know, Dr. Farber spent the rest of his career apologizing and trying to make amends for it,” Dr. Ravindranath said in an interview.
A career cut short, and a lasting legacy
In 1948, at the age of 53, Dr. SubbaRow suddenly died. “Many think Dr. SubbaRow would have won [the] Nobel Prize had he lived a few years longer,” said Dr. Ravindranath.
Like Dr. SubbaRow, Dr. Ravindranath was born in Andhra Pradesh state, near the city of Chennai formerly known as Madras. “Being a compatriot, in a way I continue his legacy, and I am obviously proud of him,” said Dr. Ravindranath, who has conducted his own landmark research regarding methotrexate and leukemia.
Nearly 75 years after Dr. SubbaRow’s death, Indian-born physicians like Dr. Ravindranath continue to honor him in print, trying to ensure that he’s not forgotten. Methotrexate remains a crucial treatment for leukemia, along with a long list of other ailments, including psoriasis.
Recognition for “Yella” may have come late and infrequently, but a Lederle Laboratories research library named after him offered Dr. SubbaRow a kind of immortality. A plaque there memorialized him in stone as a scientist, teacher, philosopher, and humanitarian, featuring the quote: “Science simply prolongs life. Religion deepens it.”
By all accounts, Dr. SubbaRow was a man of science and faith who had faith in science.
We have a half-forgotten Indian immigrant to thank – a hospital night porter turned biochemist –for revolutionizing treatment of leukemia, the once deadly childhood scourge that is still the most common pediatric cancer.
Dr. Yellapragada SubbaRow has been called the “father of chemotherapy” for developing methotrexate, a powerful, inexpensive therapy for leukemia and other diseases, and he is celebrated for additional scientific achievements. Yet Dr. SubbaRow’s life was marked more by struggle than glory.
Born poor in southeastern India, he nearly succumbed to a tropical disease that killed two older brothers, and he didn’t focus on schoolwork until his father died. Later, prejudice dogged his years as an immigrant to the United States, and a blood clot took his life at the age of 53.
Scientifically, however, Dr. SubbaRow (pronounced sue-buh-rao) triumphed, despite mammoth challenges and a lack of recognition that persists to this day. National Cancer Research Month is a fitting time to look back on his extraordinary life and work and pay tribute to his accomplishments.
‘Yella,’ folic acid, and a paradigm shift
No one appreciates Dr. SubbaRow more than a cadre of Indian-born physicians who have kept his legacy alive in journal articles, presentations, and a Pulitzer Prize-winning book. Among them is author and oncologist Siddhartha Mukherjee, MD, who chronicled Dr. SubbaRow’s achievements in his New York Times No. 1 bestseller, “The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer.”
As Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “pioneer in many ways, a physician turned cellular physiologist, a chemist who had accidentally wandered into biology.” (Per Indian tradition, SubbaRow is the doctor’s first name, and Yellapragada is his surname, but medical literature uses SubbaRow as his cognomen, with some variations in spelling. Dr. Mukherjee wrote that his friends called him “Yella.”)
Dr. SubbaRow came to the United States in 1923, after enduring a difficult childhood and young adulthood. He’d survived bouts of religious fervor, childhood rebellion (including a bid to run away from home and become a banana trader), and a failed arranged marriage. His wife bore him a child who died in infancy. He left it all behind.
In Boston, medical officials rejected his degree. Broke, he worked for a time as a night porter at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, changing sheets and cleaning urinals. To a poor but proud high-caste Indian Brahmin, the culture shock of carrying out these tasks must have been especially jarring.
Dr. SubbaRow went on to earn a diploma from Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, and became a junior faculty member. As a foreigner, Dr. Mukherjee wrote, Dr. SubbaRow was a “reclusive, nocturnal, heavily accented vegetarian,” so different from his colleagues that advancement seemed impossible. Despite his pioneering biochemistry work, Harvard later declined to offer Dr. SubbaRow a tenured faculty position.
By the early 1940s, he took a job at an upstate New York pharmaceutical company called Lederle Labs (later purchased by Pfizer). At Lederle, Dr. SubbaRow strove to synthesize the vitamin known as folic acid. He ended up creating a kind of antivitamin, a lookalike that acted like folic acid but only succeeded in gumming up the works in receptors. But what good would it do to stop the body from absorbing folic acid? Plenty, it turned out.
Discoveries pile up, but credit and fame prove elusive
Dr. SubbaRow was no stranger to producing landmark biological work. He’d previously codiscovered phosphocreatine and ATP, which are crucial to muscular contractions. However, “in 1935, he had to disown the extent of his role in the discovery of the color test related to phosphorus, instead giving the credit to his co-author, who was being considered for promotion to a full professorship at Harvard,” wrote author Gerald Posner in his 2020 book, “Pharma: Greed, Lies and the Poisoning of America.”
Houston-area oncologist Kirtan Nautiyal, MD, who paid tribute to Dr. SubbaRow in a 2018 article, contended that “with his Indian instinct for self-effacement, he had irreparably sabotaged his own career.”
Dr. SubbaRow and his team also developed “the first effective treatment of filariasis, which causes elephantiasis of the lower limbs and genitals in millions of people, mainly in tropical countries,” Dr. Nautiyal wrote. “Later in the decade, his antibiotic program generated polymyxin, the first effective treatment against the class of bacteria called Gram negatives, and aureomycin, the first “broad-spectrum’ antibiotic.” (Aureomycin is also the first tetracycline antibiotic.)
Dr. SubbaRow’s discovery of a folic acid antagonist would again go largely unheralded. But first came the realization that folic acid made childhood leukemia worse, not better, and the prospect that this process could potentially be reversed.
Rise of methotrexate and fall of leukemia
In Boston, Sidney Farber, MD, a Boston pathologist, was desperate to help Robert Sandler, a 2-year-old leukemia patient. Dr. Farber contacted his ex-colleague Dr. SubbaRow to request a supply of aminopterin, an early version of methotrexate that Dr. SubbaRow and his team had developed. Dr. Farber injected Robert with the substance and within 3 days, the toddler’s white blood count started falling – fast. He stopped bleeding, resumed eating, and once again seemed almost identical to his twin brother, as Dr. Mukherjee wrote in his book.
Leukemia had never gone into remission before. Unfortunately, the treatment only worked temporarily. Robert, like other children treated with the drug, relapsed and died within months. But Dr. Farber “saw a door open” – a chemical, a kind of chemotherapy, that could turn back cancer. In the case of folic acid antagonists, they do so by stopping cancer cells from replicating.
Methotrexate, a related agent synthesized by Dr. SubbaRow, would become a mainstay of leukemia treatment and begin to produce long-term remission from acute lymphoblastic leukemia in 1970, when combination chemotherapy was developed.
Other cancers fell to methotrexate treatment. “Previous assumptions that cancer was nearly always fatal were revised, and the field of medical oncology (treatment of cancer with chemotherapy), which had not previously existed, was formally established in 1971,” according to the National Cancer Institute’s history of methotrexate. This account does not mention Dr. SubbaRow.
Death takes the doctor, but his legacy remains
In biographies, as well as his own words, Dr. SubbaRow comes across as a prickly, hard-driving workaholic who had little interest in intimate human connections. “It is not good to ask in every letter when I will be back,” he wrote to his wife back in India, before cutting off ties completely in the early 1930s. “I will come as early as possible. ... I do not want to write anything more.”
It seems, as his biographer S.P.K. Gupta noted, that “he was quite determined that the time allotted to him on Earth should be completely devoted to finding cures for ailments that plagued mankind.”
Still, Dr. SubbaRow’s research team was devoted to him, and he had plenty of reasons to be bitter, such as the prejudice and isolation he encountered in the United States and earlier, in British-run India. According to Mr. Posner’s book, even as a young medical student, Dr. SubbaRow heeded the call of Indian independence activist Mohandas Gandhi. He “refused the British surgical gown given him at school and instead donned a traditional and simple cotton Khadi. That act of defiance cost SubbaRow the college degree that was necessary for him to get into the State Medical College.”
During the last year of his life, Dr. SubbaRow faced yet another humiliation: In his landmark 1948 study about aminopterin as a treatment for leukemia, his colleague Dr. Farber failed to credit him, an “astonishing omission” as Yaddanapudi Ravindranath, MBBS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Wayne State University, Detroit, put it. “From everything I know, Dr. Farber spent the rest of his career apologizing and trying to make amends for it,” Dr. Ravindranath said in an interview.
A career cut short, and a lasting legacy
In 1948, at the age of 53, Dr. SubbaRow suddenly died. “Many think Dr. SubbaRow would have won [the] Nobel Prize had he lived a few years longer,” said Dr. Ravindranath.
Like Dr. SubbaRow, Dr. Ravindranath was born in Andhra Pradesh state, near the city of Chennai formerly known as Madras. “Being a compatriot, in a way I continue his legacy, and I am obviously proud of him,” said Dr. Ravindranath, who has conducted his own landmark research regarding methotrexate and leukemia.
Nearly 75 years after Dr. SubbaRow’s death, Indian-born physicians like Dr. Ravindranath continue to honor him in print, trying to ensure that he’s not forgotten. Methotrexate remains a crucial treatment for leukemia, along with a long list of other ailments, including psoriasis.
Recognition for “Yella” may have come late and infrequently, but a Lederle Laboratories research library named after him offered Dr. SubbaRow a kind of immortality. A plaque there memorialized him in stone as a scientist, teacher, philosopher, and humanitarian, featuring the quote: “Science simply prolongs life. Religion deepens it.”
By all accounts, Dr. SubbaRow was a man of science and faith who had faith in science.
Medical education programs tell how climate change affects health
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases climb slowly but steadily
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.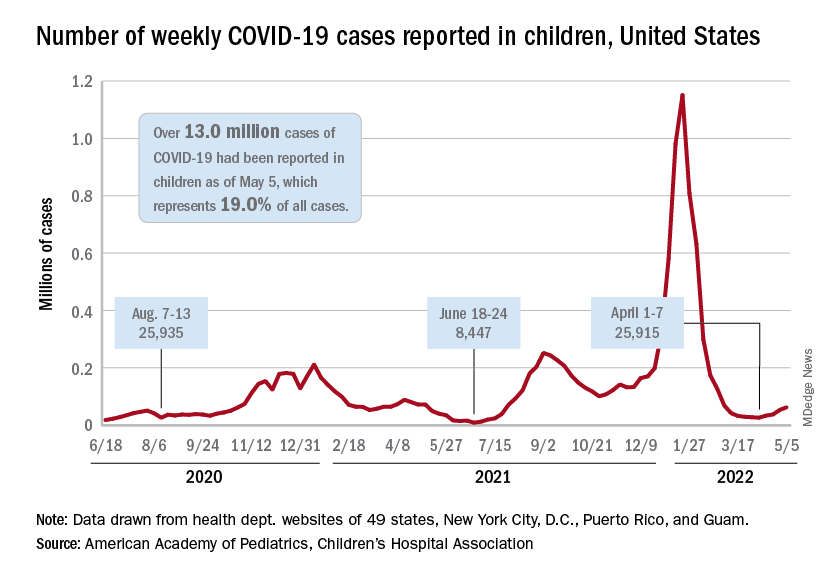
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.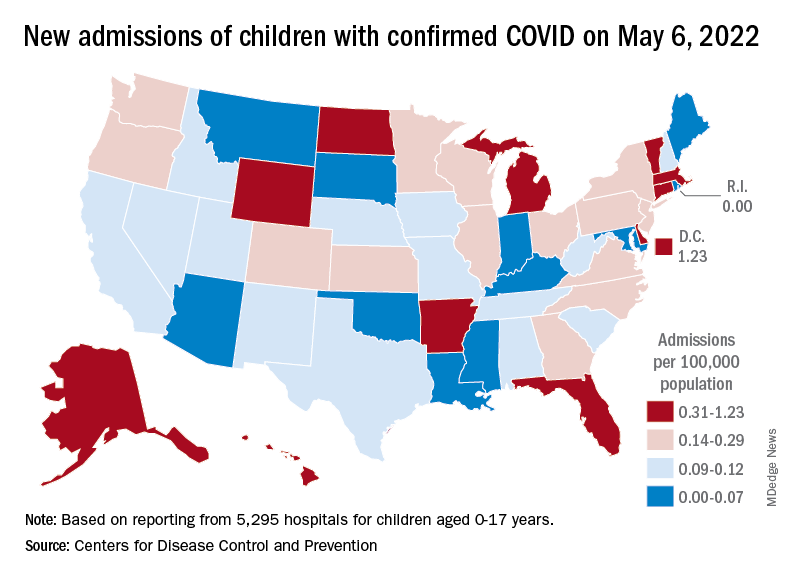
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
Anorexia nervosa in adolescent patients: What pediatricians need to know
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
Eating disorders are among the most prevalent, disabling, and potentially fatal psychiatric illnesses, and the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated their burden, with a 15.3% increase in incidence in 2020 compared with previous years.1 This increase was almost solely among adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa (AN), which is often insidious in onset and more difficult to treat as it advances. Adolescents with AN are most likely to present to their pediatricians, so awareness and early recognition of the symptoms is critical. Pediatricians are also an integral part of the treatment team in AN and can offer monitoring for serious complications, alongside valuable guidance to parents, who are central to treatment and the reestablishment of healthy eating habits in their children. Here we will review the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of anorexia, with an emphasis on what pediatricians need to know to screen and to facilitate treatment.
Epidemiology
AN is marked by a fear of gaining weight or behaviors that interfere with weight gain and a self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight and body shape. Youth with AN often deny the seriousness of their malnutrition, although that is not required for diagnosis. AN can be of a restrictive or binge-purge subtype, and amenorrhea is no longer a requirement for diagnosis. There is not a specific weight or body mass index cutoff for the diagnosis, but the severity of AN is determined by the BMI percentile normed to age and sex. The average age of onset is 18, and the prepandemic prevalence of AN was about 1% of the population. It affects about 10 times as many females as males. It is quite rare prior to puberty, affecting about 0.01% of that age group. There is a heritable component, with a fivefold relative risk in youth with a parent with AN, and twin studies suggest heritability rates as high as 75%. Youth with rigid cognitive styles appear more vulnerable, as do those who participate in activities such as ballet, gymnastics, modeling, and wrestling because of the role of appearance and weight in performance. More than half of patients with AN will have another psychiatric illness, most commonly anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder. AN becomes chronic in up to 15% of sufferers and the mortality rate is close to 10%, with approximately half dying from medical complications and half dying by suicide.
Screening
Parents and pediatricians are usually the first to notice that a child has started to lose weight or is falling off the growth curve. But weight changes usually emerge after feelings of preoccupation with weight, body shape, and body satisfaction. If parents report escalating pickiness around food, increased or compulsive exercise, persistent self-consciousness and self-criticism around weight and body shape, it is worth starting with screening questions.
If you notice preoccupation or anxiety around being weighed, even if the weight or growth curve are still normal, it is worthwhile to screen. Screening questions, such as the SCOFF questionnaire with five simple questions, can be very sensitive for both AN and bulimia nervosa.2 There are also many validated screening instruments, such as the Eating Disorder Inventory or Eating Attitudes Test (for adolescents) and the Kids Eating Disorder Survey and the Child Eating Attitudes Test (for younger children), that are short self-reports that you can have your patients fill out when you have a higher index of suspicion. Weight loss or growth failure without a preoccupation around weight or appearance needs a thorough a medical workup, and could be a function of other psychiatric problems, such as depression.
If a child screens positive for an eating disorder, your full physical examination, growth curves, and longitudinal growth charts are critical for diagnosis. Percentile BMIs must be used, given the inaccuracy of standard BMI calculations in this age group. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age and sex growth charts include methods for this calculation). Laboratory assessment, including metabolic, kidney, pancreatic, and thyroid function, and an EKG can illuminate if there are consequences of restricting or purging. Of course, you want to evaluate for significant medical symptoms, including bradycardia, orthostasis, and hypokalemia. These medical symptoms are not limited to the severely underweight and merit referral to an emergency department and possible medical admission.
Then, a referral to a clinician who is expert in the assessment and treatment of eating disorders is needed. This may be a child psychiatrist, psychologist, or a colleague pediatrician with this specialization. It is also very important to begin the conversation with the family to introduce your concerns, describe what you have noticed, and discuss the need for further assessment and possibly treatment.
Be mindful that discussing this in front of your patient may heighten the patient’s anxiety or distress. Be prepared to offer support and understanding for your patient’s anxiety, while steadfastly providing absolute clarity for the parents about the necessity of further evaluation and treatment. Many parents will be concerned and ready to do whatever is needed to get their child’s eating and growth back on track. But some parents may have more difficulty. They may have their own history with an eating disorder. They may be avoiding a sense of shame or alarm. They may be eager to avoid adding to their child’s stress. They may be tired of engaging in power struggles with the child. They may be proud of their ambitious, accomplished young athlete. Their trust in you makes you uniquely positioned to complicate their thinking. And treatment will hinge on them, so this is a critical bridge to care.
Beyond telling parents that they will need to bring more structure and supervision to mealtimes to begin addressing their child’s nutrition, you might offer guidance on other strategies. Empower parents to limit their child’s use of social media sites such as Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok, where they may be immersed in comparing themselves to idealized (and airbrushed) influencers. Empower them to make their child’s participation in beloved sports contingent on eating meals together and completely or on a stabilized weight (as will be common in treatment). Remind them that there are no bad foods, that the goal is health, and that they are not in a power struggle with their child, but instead allied with their child to treat AN. Remind them to also look for chances to have fun with their child, to help everyone remember what matters.
Treatment
Family-based therapy (FBT) is the first-line treatment of shorter-duration AN in children and adolescents. It focuses on the parents, helping them to calmly and effectively manage their child’s eating behaviors until their weight and behaviors have normalized. As a patient’s nutritional status improves, so does cognitive function, emotional flexibility, and mood. Individual therapy and psychopharmacologic treatment can be very effective for comorbid anxiety, mood, attentional, and thought disorders. Family-based work does include the child and is often done in group-based settings with clinicians from multiple disciplines. Dietitians provide education and guidance about healthy nutrition to the child and parents. Therapists may work with the child, parents, or full family to focus on behavior modification and managing distress. Most academic medical centers provide access to FBT, but there are many regions with no providers of this evidence-based treatment. One of the silver linings of the COVID-19 pandemic is that several online services have emerged offering FBT, working with families to manage mealtimes and treatment entirely at home.3 Pediatricians provide regular medical checks to measure progress and help with decisions about when it is safe to permit exercise or advance privileges and independence around eating. Some pediatricians have discovered a deep interest in this area of pediatrics and built their practices on it. Given the surge in prevalence of AN and the needs for adolescent mental health services, we hope more will do so.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Taquet M et al. Br J Psychiatry. 2022;220:262-4.
2. Morgan JF et al. West J Med. 2000 Mar;172(3):164-5.
3. Matheson BE et al. Int J Eat Disord. 2020 Jul;53(7):1142-54.
When coping skills and parenting behavioral interventions ‘don’t work’
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
You have an appointment with a 14-year-old youth you last saw for an annual camp physical. He had screened positive for depression, and you had referred him to a local therapist. He did not have an appointment until after camp, and you have only met a few times, but since you had spoken with him about his depression, he set up an appointment with you to ask about medications. When you meet him you ask about what he had been doing in therapy and he says, “I’m learning ‘coping skills,’ but they don’t work.”
From breathing exercises and sticker charts to mindfulness and grounding exercise, coping skills can be crucial for learning how to manage distress, regulate emotions, become more effective interpersonally, and function better. Similarly, parenting interventions, which change the way parents and youth interact, are a central family intervention for behavioral problems in youth.
It is very common, however, to hear that they “don’t work” or have a parent say, “We tried that, it doesn’t work.”
When kids and parents reject coping skills and behavioral interventions by saying they do not work, the consequences can be substantial. It can mean the rejection of coping skills and strategies that actually would have helped, given time and support; that kids and families bounce between services with increasing frustration; that they search for a magic bullet (which also won’t work); and, particularly concerning for physicians, a belief that the youth have not received the right medication, resulting in potentially unhelpful concoctions of medication.
One of the biggest challenges in helping youth and parents overcome their difficulties – whether these difficulties are depression and anxiety or being better parents to struggling kids – is helping them understand that despite the fact that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not seem to work, they work.
We just have to do a better job explaining what that “work” is.
There are five points you can make.
- First, the coping skill or behavioral intervention is not supposed to work if that means solving the underlying problem. Coping skills and behavioral interventions do not immediately cure anxiety, mend broken hearts, correct disruptive behaviors, disentangle power struggles, or alleviate depression. That is not what their job is. Coping skills and behavioral interventions are there to help us get better at handling complex situations and feelings. In particular, they are good at helping us manage our thoughts (“I can’t do it,” “He should behave better”) and our affect (anger, frustration, rage, anxiety, sadness), so that over time we get better at solving the problems, and break out of the patterns that perpetuate these problems.
- Second, kids and parents do not give skills credit for when they do work. That time you were spiraling out of control and told your mom you needed a break and watched some YouTube videos and then joined the family for dinner? Your coping skills worked, but nobody noticed because they worked. We need to help our young patients and families identify those times that coping skills and behavioral interventions worked.
- Third, let’s face it: Nothing works all the time. It is no wonder kids and families are disappointed by coping skills and behavioral interventions if they think they magically work once and forever. We need to manage expectations.
- Fourth, we know they are supposed to fail, and we should discuss this openly up front. This may sound surprising, but challenging behaviors often get worse when we begin to work on them. “Extinction bursts” is probably the easiest explanation, but for psychodynamically oriented youth and families we could talk about “resistance.” No matter what, things tend to get worse before they get better. We should let people know this ahead of time.
- Fifth, and this is the one that forces youth and parents to ask how hard they actually tried, these skills need to be practiced. You can’t be in the middle of a panic attack and for the first time start trying to pace your breathing with a technique a therapist told you about 3 weeks ago. This makes about as much sense as not training for a marathon. You need to practice and build up the skills, recognizing that as you become more familiar with them, they will help you manage during stressful situations. Every skill should be practiced, preferably several times or more in sessions, maybe every session, and definitely outside of sessions when not in distress.
We cannot blame children and parents for thinking that coping skills and behavioral interventions do not work. They are struggling, suffering, fighting, frightened, angry, anxious, frustrated, and often desperate for something to make everything better. Helping them recognize this desire for things to be better while managing expectations is an essential complement to supporting the use of coping skills and behavioral interventions, and a fairly easy conversation to have with youth.
So when you are talking about coping skills and parental behavioral interventions, it is important to be prepared for the “it didn’t work” conversation, and even to address these issues up front. After all, these strategies may not solve all the problems in the world, but can be lifelong ways of coping with life’s challenges.
Dr. Henderson is associate professor of clinical psychiatry at New York University and deputy director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Bellevue Hospital, New York.
Tactile stimulation for inadequate neonatal respiration at birth
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Recently, I encountered a study in Pediatrics that hoped to answer the question of whether there was any benefit to tactile stimulation in those nerve-rattling moments when a newborn didn’t seem to take much interest in breathing: “Tactile stimulation in newborn infants with inadequate respiration at birth: A systematic review.” Now there is a title that grabs the attention of every frontline pediatrician who has sweated through those minutes that seemed like hours in the delivery room when some little rascal has decided that breathing isn’t a priority.
Of course, your great grandmother and everyone else knew what needed to be done – the obstetrician hung the baby by his or her ankles and slapped it on the bottom a couple of times. But you went to medical school and learned that was barbaric. Instead, you modeled the behavior of the residents and delivery room nurses who had more refined techniques such as heel flicking and vigorous spine rubbing. You never thought to ask if there was any science behind those activities because everyone did them.
Well, the authors of the article in Pediatrics, writing on behalf of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation and Neonatal Life Support Task Force, thought the time had come to turn over a few stones and see if tactile stimulation was a benefit in resuscitation. Beginning with 2,455 possibly relevant articles, they quickly (I suspect they would quibble with the “quickly” part) winnowed these down to two observational studies, one of which was rejected because of “critical risk of bias.” The surviving study showed a reduction in tracheal intubation in infants who had received tactile stimulation. However, the authors felt that the “certainty of evidence was very low.”
So, there you have it. Aren’t you glad you didn’t invest 15 or 20 minutes discovering what you probably had guessed already? You can thank me later.
You already suspected that it may not help. However, like any good physician, what you really wanted to know is whether were you doing any harm by heel flicking and spine rubbing. And I bet you already had an opinion about the answer to that question. During your training, you may have seen delivery room personnel who were clearly too vigorous in their tactile stimulation and/or too persistent in their heel flicking and spine rubbing when the next steps in resuscitation needed to be taken. That’s the next study that needs to be done. I hope that study finds that tactile stimulation may not help but as long as it is done using specific techniques and within certain temporal parameters it does no harm.
I was never much for heel flicking. My favorite tactile stimulation was encircling the pokey infant’s chest in my hand, gently compressing and then quickly releasing a couple of times. My hope was that by mimicking the birth process the sensors in the infant’s chest wall would remind him it was time to breathe. That, and a silent plea to Mother Nature, worked most of the time.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].



















